User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Clinical pearls for administering cognitive exams during the pandemic
Patients have often been labeled as “poor historians” if they are not able to recollect their own medical history, whether through illness or difficulties in communication. But Fred Ovsiew, MD, speaking at Focus on Neuropsychiatry presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sees that label as an excuse on the part of the clinician.
“I strongly advise you to drop that phrase from your vocabulary if you do use it, because the patient is not the historian. The doctor, the clinician is the historian,” Dr. Ovsiew said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education. “It is the clinician’s job to put the story together using the account by the patient as one source, but [also] interviewing a collateral informant and/or reviewing records, which is necessary in almost every case of a neuropsychiatric illness.”
Rather, clinicians taking history at the bedside should focus on why the patients cannot give a narrative account of their illness. Patients can have narrative incapacity on a psychogenic basis, such as in patients with conversion or somatoform disorder, he explained. “I think this is a result of the narrative incapacity that develops in people who have had trauma or adverse experiences in childhood and insecure attachment. This is shown on the adult attachment interview as a disorganized account of their childhoods.”
Other patients might not be able to recount their medical history because they are amnestic, which leaves their account vague because of a lack of access to information. “It may be frozen in time in the sense that, up to a certain point in their life, they can recount the history,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “But in recent years, their account becomes vague.”
Patients with right hemisphere lesions might not know that their account has incongruity and is implausible, while patients with dorsolateral prefrontal lesions might be aspontaneous, use few words to describe their situation, and have poor insight. Those with ventromedial prefrontal lesions can be impulsive and have poor insight, not considering alternative possibilities, Dr. Ovsiew noted.
Asking open-ended questions of the patient is the first step to identifying any potential narrative incapacity, followed by a detailed medical history by the clinician. When taking a medical history, try avoiding what Dr. Ovsiew calls the “anything like that?” problem, where a clinician asks a question about a cluster of symptoms that would make sense to a doctor, but not a patient. For example, a doctor might ask whether a patient is experiencing “chest pain or leg swelling – anything like that?” because he or she knows what those symptoms have in common, but the patient might not know the relationship between those symptoms. “You can’t count on the patient to tell you all the relevant information,” he said. “You have to know what to ask about.”
“Patients with brain disease have subtle personality changes, sometimes more obvious personality changes. These need to be inquired about,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “The patient with apathy has reduced negative as well as positive emotions. The patient with depression has reduced positive emotions, but often tells you very clearly about the negative emotions of sadness, guilt. The patient with depression has diurnal variation in mood, a very telling symptom, especially when it’s disclosed spontaneously,” Dr. Ovsiew explained. “The point is, you need to know to ask about it.”
When taking a sleep history, clinicians should be aware of sleep disturbances apart from insomnia and early waking. REM sleep behavior disorder is a condition that should be inquired about. Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition that might not be immediately apparent to the patient, but a bed partner can identify whether a patient has problems breathing throughout the night.
“This is an important condition to uncover for the neuropsychiatrist because it contributes to treatment resistance and depression, and it contributes to cognitive impairment,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “These patients commonly have mild difficulties with attention and concentration.”
Always ask about head injury in every history, which can be relevant to later onset depression, PTSD, and cognitive impairment. Every head injury follows a trajectory of retrograde amnesia and altered state of consciousness (including coma), followed by a period of posttraumatic amnesia. Duration of these states can be used to assess the severity of brain injury, but the 15-point Glasgow Coma Scale is another way to assess injury severity, Dr. Ovsiew explained.
However, the two do not always overlap, he noted. “Someone may have a Glasgow Coma Scale score that is 9-12, predicting moderate brain injury, but they may have a short duration of amnesia. These don’t always follow the same path. There are many different ways of classifying how severe the brain injury is.”
Keep probes brief, straightforward
Cognitive exams of patients with suspected psychiatric disorders should be simple, easy to administer and focused on a single domain of cognition. “Probes should be brief. They should not require specialized equipment. The Purdue Pegboard Test might be a great neuropsychological instrument, but very few of us carry a pegboard around in our medical bags,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
The probe administered should also be accessible to the patient. The serial sevens clinical test, where a patient is asked to repeatedly subtract 7 from 100, is only effective at testing concentration if the patient is capable of completing the test. “There are going to be patients who can’t do the task, but it’s not because of concentration failure, it’s because of subtraction failure,” he said.
When assessing attention, effective tasks include having the patient perform the digit span test forward and backward, count backward from 20 to 1, listing the months of the year in reverse, and performing the Mental Alternation Test. However, Dr. Ovsiew explained there may be some barriers for patients in completing these tasks. “The person may be aphasic and not know the alphabet. The person may have English as a second language and not be skilled at giving the alphabet in English. In some cases, you may want to check and not assume that the patient can count and does know the alphabet.”
In assessing language, listen for aphasic abnormalities. “The patient, of course, is speaking throughout the interview, but you need to take a moment to listen for prosody, to listen to rate of speech, to listen for paraphasic errors or word-finding problems,” Dr. Ovsiew said. Any abnormalities should be probed further through confrontation naming tasks, which can be done in person and with some success through video, but not by phone. Naming to definition (“What do you call the part of a shirt that covers the arm?”) is one way of administering the test over the phone.
Visuospatial function can be assessed by clock drawing but also carries problems. Patients who do not plan their clock before beginning to draw, for example, may have an executive function problem instead of a visuospatial problem, Dr. Ovsiew noted. Patients in whom a clinician suspects hemineglect should be given a visual search task or line by section task. “I like doing clock drawing. It’s a nice screening test. It’s becoming, I think, less useful as people count on digital clocks and have trouble even imagining what an analog clock looks like.”
An approach that is better suited to in-person assessment, but also works by video, is the Poppelreuter figure visual perceptual function test, which is a prompt for the patient that involves common household items overlaying one another “in atypical positions and atypical configurations” where the patient is instructed to describe the items they see on the card. Another approach that works over video is the interlocking finger test, where the patient is asked to copy the hand positions made by the clinician.
Dr. Ovsiew admitted that visuospatial function is nearly impossible to assess over the phone. Asking topographical questions (“If you’re driving from Chicago to Los Angeles, is the Pacific Ocean in front of you, behind you, to your left, or to your right?”) may help judge visuospatial function, but this relies on the patient having the topographic knowledge to answer the questions. Some patients who are topographically disoriented can’t do them at all,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Bedside neuropsychiatry assesses encoding of a memory, its retention and its retrieval as well as verbal and visual cues. Each one of these aspects of memory can be impaired on its own and should be explored separately, Dr. Ovsiew explained. “Neuropsychiatric clinicians have a rough-and-ready, seat-of-the-pants way of approaching this that wouldn’t pass muster if you’re a psychologist, but is the best we can do at the bedside.”
To test retrieval and retention, the Three Words–Three Shapes test works well in person, with some difficulty by video, and is not possible to administer over the phone. In lieu of that test, giving the patient a simple word list and asking them to repeat the list in order. Using the word list, “these different stages of memory function can be parsed out pretty well at the bedside or chairside, and even by the phone. Figuring out where the memory failure is diagnostically important,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Executive function, which involves activation, planning, sequencing, maintaining, self-monitoring, and flexible employment of action and attention, is “complicated to evaluate because there are multiple aspects of executive function, multiple deficits that can be seen with executive dysfunction, and they don’t all correlate with each other.”
Within executive function evaluation, the Mental Alternation Test can assess working memory, motor sequencing can be assessed through the ring/fist, fist/edge/palm, alternating fist, and rampart tests. The Go/No-Go test can be used to assess response inhibition. For effortful retrieval evaluation, spontaneous word-list generation – such as thinking of all the items one can buy at a supermarket– can test category fluency, while a task to name all the words starting with a certain letter can assess letter stimulus.
Executive function “is of crucial importance in the neuropsychiatric evaluation because it’s strongly correlated with how well the person functions outside the office,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Ovsiew reported relationships with Wolters Kluwer Health in the form of consulting, receiving royalty payments, and related activities.
Patients have often been labeled as “poor historians” if they are not able to recollect their own medical history, whether through illness or difficulties in communication. But Fred Ovsiew, MD, speaking at Focus on Neuropsychiatry presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sees that label as an excuse on the part of the clinician.
“I strongly advise you to drop that phrase from your vocabulary if you do use it, because the patient is not the historian. The doctor, the clinician is the historian,” Dr. Ovsiew said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education. “It is the clinician’s job to put the story together using the account by the patient as one source, but [also] interviewing a collateral informant and/or reviewing records, which is necessary in almost every case of a neuropsychiatric illness.”
Rather, clinicians taking history at the bedside should focus on why the patients cannot give a narrative account of their illness. Patients can have narrative incapacity on a psychogenic basis, such as in patients with conversion or somatoform disorder, he explained. “I think this is a result of the narrative incapacity that develops in people who have had trauma or adverse experiences in childhood and insecure attachment. This is shown on the adult attachment interview as a disorganized account of their childhoods.”
Other patients might not be able to recount their medical history because they are amnestic, which leaves their account vague because of a lack of access to information. “It may be frozen in time in the sense that, up to a certain point in their life, they can recount the history,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “But in recent years, their account becomes vague.”
Patients with right hemisphere lesions might not know that their account has incongruity and is implausible, while patients with dorsolateral prefrontal lesions might be aspontaneous, use few words to describe their situation, and have poor insight. Those with ventromedial prefrontal lesions can be impulsive and have poor insight, not considering alternative possibilities, Dr. Ovsiew noted.
Asking open-ended questions of the patient is the first step to identifying any potential narrative incapacity, followed by a detailed medical history by the clinician. When taking a medical history, try avoiding what Dr. Ovsiew calls the “anything like that?” problem, where a clinician asks a question about a cluster of symptoms that would make sense to a doctor, but not a patient. For example, a doctor might ask whether a patient is experiencing “chest pain or leg swelling – anything like that?” because he or she knows what those symptoms have in common, but the patient might not know the relationship between those symptoms. “You can’t count on the patient to tell you all the relevant information,” he said. “You have to know what to ask about.”
“Patients with brain disease have subtle personality changes, sometimes more obvious personality changes. These need to be inquired about,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “The patient with apathy has reduced negative as well as positive emotions. The patient with depression has reduced positive emotions, but often tells you very clearly about the negative emotions of sadness, guilt. The patient with depression has diurnal variation in mood, a very telling symptom, especially when it’s disclosed spontaneously,” Dr. Ovsiew explained. “The point is, you need to know to ask about it.”
When taking a sleep history, clinicians should be aware of sleep disturbances apart from insomnia and early waking. REM sleep behavior disorder is a condition that should be inquired about. Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition that might not be immediately apparent to the patient, but a bed partner can identify whether a patient has problems breathing throughout the night.
“This is an important condition to uncover for the neuropsychiatrist because it contributes to treatment resistance and depression, and it contributes to cognitive impairment,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “These patients commonly have mild difficulties with attention and concentration.”
Always ask about head injury in every history, which can be relevant to later onset depression, PTSD, and cognitive impairment. Every head injury follows a trajectory of retrograde amnesia and altered state of consciousness (including coma), followed by a period of posttraumatic amnesia. Duration of these states can be used to assess the severity of brain injury, but the 15-point Glasgow Coma Scale is another way to assess injury severity, Dr. Ovsiew explained.
However, the two do not always overlap, he noted. “Someone may have a Glasgow Coma Scale score that is 9-12, predicting moderate brain injury, but they may have a short duration of amnesia. These don’t always follow the same path. There are many different ways of classifying how severe the brain injury is.”
Keep probes brief, straightforward
Cognitive exams of patients with suspected psychiatric disorders should be simple, easy to administer and focused on a single domain of cognition. “Probes should be brief. They should not require specialized equipment. The Purdue Pegboard Test might be a great neuropsychological instrument, but very few of us carry a pegboard around in our medical bags,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
The probe administered should also be accessible to the patient. The serial sevens clinical test, where a patient is asked to repeatedly subtract 7 from 100, is only effective at testing concentration if the patient is capable of completing the test. “There are going to be patients who can’t do the task, but it’s not because of concentration failure, it’s because of subtraction failure,” he said.
When assessing attention, effective tasks include having the patient perform the digit span test forward and backward, count backward from 20 to 1, listing the months of the year in reverse, and performing the Mental Alternation Test. However, Dr. Ovsiew explained there may be some barriers for patients in completing these tasks. “The person may be aphasic and not know the alphabet. The person may have English as a second language and not be skilled at giving the alphabet in English. In some cases, you may want to check and not assume that the patient can count and does know the alphabet.”
In assessing language, listen for aphasic abnormalities. “The patient, of course, is speaking throughout the interview, but you need to take a moment to listen for prosody, to listen to rate of speech, to listen for paraphasic errors or word-finding problems,” Dr. Ovsiew said. Any abnormalities should be probed further through confrontation naming tasks, which can be done in person and with some success through video, but not by phone. Naming to definition (“What do you call the part of a shirt that covers the arm?”) is one way of administering the test over the phone.
Visuospatial function can be assessed by clock drawing but also carries problems. Patients who do not plan their clock before beginning to draw, for example, may have an executive function problem instead of a visuospatial problem, Dr. Ovsiew noted. Patients in whom a clinician suspects hemineglect should be given a visual search task or line by section task. “I like doing clock drawing. It’s a nice screening test. It’s becoming, I think, less useful as people count on digital clocks and have trouble even imagining what an analog clock looks like.”
An approach that is better suited to in-person assessment, but also works by video, is the Poppelreuter figure visual perceptual function test, which is a prompt for the patient that involves common household items overlaying one another “in atypical positions and atypical configurations” where the patient is instructed to describe the items they see on the card. Another approach that works over video is the interlocking finger test, where the patient is asked to copy the hand positions made by the clinician.
Dr. Ovsiew admitted that visuospatial function is nearly impossible to assess over the phone. Asking topographical questions (“If you’re driving from Chicago to Los Angeles, is the Pacific Ocean in front of you, behind you, to your left, or to your right?”) may help judge visuospatial function, but this relies on the patient having the topographic knowledge to answer the questions. Some patients who are topographically disoriented can’t do them at all,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Bedside neuropsychiatry assesses encoding of a memory, its retention and its retrieval as well as verbal and visual cues. Each one of these aspects of memory can be impaired on its own and should be explored separately, Dr. Ovsiew explained. “Neuropsychiatric clinicians have a rough-and-ready, seat-of-the-pants way of approaching this that wouldn’t pass muster if you’re a psychologist, but is the best we can do at the bedside.”
To test retrieval and retention, the Three Words–Three Shapes test works well in person, with some difficulty by video, and is not possible to administer over the phone. In lieu of that test, giving the patient a simple word list and asking them to repeat the list in order. Using the word list, “these different stages of memory function can be parsed out pretty well at the bedside or chairside, and even by the phone. Figuring out where the memory failure is diagnostically important,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Executive function, which involves activation, planning, sequencing, maintaining, self-monitoring, and flexible employment of action and attention, is “complicated to evaluate because there are multiple aspects of executive function, multiple deficits that can be seen with executive dysfunction, and they don’t all correlate with each other.”
Within executive function evaluation, the Mental Alternation Test can assess working memory, motor sequencing can be assessed through the ring/fist, fist/edge/palm, alternating fist, and rampart tests. The Go/No-Go test can be used to assess response inhibition. For effortful retrieval evaluation, spontaneous word-list generation – such as thinking of all the items one can buy at a supermarket– can test category fluency, while a task to name all the words starting with a certain letter can assess letter stimulus.
Executive function “is of crucial importance in the neuropsychiatric evaluation because it’s strongly correlated with how well the person functions outside the office,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Ovsiew reported relationships with Wolters Kluwer Health in the form of consulting, receiving royalty payments, and related activities.
Patients have often been labeled as “poor historians” if they are not able to recollect their own medical history, whether through illness or difficulties in communication. But Fred Ovsiew, MD, speaking at Focus on Neuropsychiatry presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, sees that label as an excuse on the part of the clinician.
“I strongly advise you to drop that phrase from your vocabulary if you do use it, because the patient is not the historian. The doctor, the clinician is the historian,” Dr. Ovsiew said at the meeting, presented by Global Academy for Medical Education. “It is the clinician’s job to put the story together using the account by the patient as one source, but [also] interviewing a collateral informant and/or reviewing records, which is necessary in almost every case of a neuropsychiatric illness.”
Rather, clinicians taking history at the bedside should focus on why the patients cannot give a narrative account of their illness. Patients can have narrative incapacity on a psychogenic basis, such as in patients with conversion or somatoform disorder, he explained. “I think this is a result of the narrative incapacity that develops in people who have had trauma or adverse experiences in childhood and insecure attachment. This is shown on the adult attachment interview as a disorganized account of their childhoods.”
Other patients might not be able to recount their medical history because they are amnestic, which leaves their account vague because of a lack of access to information. “It may be frozen in time in the sense that, up to a certain point in their life, they can recount the history,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “But in recent years, their account becomes vague.”
Patients with right hemisphere lesions might not know that their account has incongruity and is implausible, while patients with dorsolateral prefrontal lesions might be aspontaneous, use few words to describe their situation, and have poor insight. Those with ventromedial prefrontal lesions can be impulsive and have poor insight, not considering alternative possibilities, Dr. Ovsiew noted.
Asking open-ended questions of the patient is the first step to identifying any potential narrative incapacity, followed by a detailed medical history by the clinician. When taking a medical history, try avoiding what Dr. Ovsiew calls the “anything like that?” problem, where a clinician asks a question about a cluster of symptoms that would make sense to a doctor, but not a patient. For example, a doctor might ask whether a patient is experiencing “chest pain or leg swelling – anything like that?” because he or she knows what those symptoms have in common, but the patient might not know the relationship between those symptoms. “You can’t count on the patient to tell you all the relevant information,” he said. “You have to know what to ask about.”
“Patients with brain disease have subtle personality changes, sometimes more obvious personality changes. These need to be inquired about,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “The patient with apathy has reduced negative as well as positive emotions. The patient with depression has reduced positive emotions, but often tells you very clearly about the negative emotions of sadness, guilt. The patient with depression has diurnal variation in mood, a very telling symptom, especially when it’s disclosed spontaneously,” Dr. Ovsiew explained. “The point is, you need to know to ask about it.”
When taking a sleep history, clinicians should be aware of sleep disturbances apart from insomnia and early waking. REM sleep behavior disorder is a condition that should be inquired about. Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition that might not be immediately apparent to the patient, but a bed partner can identify whether a patient has problems breathing throughout the night.
“This is an important condition to uncover for the neuropsychiatrist because it contributes to treatment resistance and depression, and it contributes to cognitive impairment,” Dr. Ovsiew said. “These patients commonly have mild difficulties with attention and concentration.”
Always ask about head injury in every history, which can be relevant to later onset depression, PTSD, and cognitive impairment. Every head injury follows a trajectory of retrograde amnesia and altered state of consciousness (including coma), followed by a period of posttraumatic amnesia. Duration of these states can be used to assess the severity of brain injury, but the 15-point Glasgow Coma Scale is another way to assess injury severity, Dr. Ovsiew explained.
However, the two do not always overlap, he noted. “Someone may have a Glasgow Coma Scale score that is 9-12, predicting moderate brain injury, but they may have a short duration of amnesia. These don’t always follow the same path. There are many different ways of classifying how severe the brain injury is.”
Keep probes brief, straightforward
Cognitive exams of patients with suspected psychiatric disorders should be simple, easy to administer and focused on a single domain of cognition. “Probes should be brief. They should not require specialized equipment. The Purdue Pegboard Test might be a great neuropsychological instrument, but very few of us carry a pegboard around in our medical bags,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
The probe administered should also be accessible to the patient. The serial sevens clinical test, where a patient is asked to repeatedly subtract 7 from 100, is only effective at testing concentration if the patient is capable of completing the test. “There are going to be patients who can’t do the task, but it’s not because of concentration failure, it’s because of subtraction failure,” he said.
When assessing attention, effective tasks include having the patient perform the digit span test forward and backward, count backward from 20 to 1, listing the months of the year in reverse, and performing the Mental Alternation Test. However, Dr. Ovsiew explained there may be some barriers for patients in completing these tasks. “The person may be aphasic and not know the alphabet. The person may have English as a second language and not be skilled at giving the alphabet in English. In some cases, you may want to check and not assume that the patient can count and does know the alphabet.”
In assessing language, listen for aphasic abnormalities. “The patient, of course, is speaking throughout the interview, but you need to take a moment to listen for prosody, to listen to rate of speech, to listen for paraphasic errors or word-finding problems,” Dr. Ovsiew said. Any abnormalities should be probed further through confrontation naming tasks, which can be done in person and with some success through video, but not by phone. Naming to definition (“What do you call the part of a shirt that covers the arm?”) is one way of administering the test over the phone.
Visuospatial function can be assessed by clock drawing but also carries problems. Patients who do not plan their clock before beginning to draw, for example, may have an executive function problem instead of a visuospatial problem, Dr. Ovsiew noted. Patients in whom a clinician suspects hemineglect should be given a visual search task or line by section task. “I like doing clock drawing. It’s a nice screening test. It’s becoming, I think, less useful as people count on digital clocks and have trouble even imagining what an analog clock looks like.”
An approach that is better suited to in-person assessment, but also works by video, is the Poppelreuter figure visual perceptual function test, which is a prompt for the patient that involves common household items overlaying one another “in atypical positions and atypical configurations” where the patient is instructed to describe the items they see on the card. Another approach that works over video is the interlocking finger test, where the patient is asked to copy the hand positions made by the clinician.
Dr. Ovsiew admitted that visuospatial function is nearly impossible to assess over the phone. Asking topographical questions (“If you’re driving from Chicago to Los Angeles, is the Pacific Ocean in front of you, behind you, to your left, or to your right?”) may help judge visuospatial function, but this relies on the patient having the topographic knowledge to answer the questions. Some patients who are topographically disoriented can’t do them at all,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Bedside neuropsychiatry assesses encoding of a memory, its retention and its retrieval as well as verbal and visual cues. Each one of these aspects of memory can be impaired on its own and should be explored separately, Dr. Ovsiew explained. “Neuropsychiatric clinicians have a rough-and-ready, seat-of-the-pants way of approaching this that wouldn’t pass muster if you’re a psychologist, but is the best we can do at the bedside.”
To test retrieval and retention, the Three Words–Three Shapes test works well in person, with some difficulty by video, and is not possible to administer over the phone. In lieu of that test, giving the patient a simple word list and asking them to repeat the list in order. Using the word list, “these different stages of memory function can be parsed out pretty well at the bedside or chairside, and even by the phone. Figuring out where the memory failure is diagnostically important,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Executive function, which involves activation, planning, sequencing, maintaining, self-monitoring, and flexible employment of action and attention, is “complicated to evaluate because there are multiple aspects of executive function, multiple deficits that can be seen with executive dysfunction, and they don’t all correlate with each other.”
Within executive function evaluation, the Mental Alternation Test can assess working memory, motor sequencing can be assessed through the ring/fist, fist/edge/palm, alternating fist, and rampart tests. The Go/No-Go test can be used to assess response inhibition. For effortful retrieval evaluation, spontaneous word-list generation – such as thinking of all the items one can buy at a supermarket– can test category fluency, while a task to name all the words starting with a certain letter can assess letter stimulus.
Executive function “is of crucial importance in the neuropsychiatric evaluation because it’s strongly correlated with how well the person functions outside the office,” Dr. Ovsiew said.
Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same parent company. Dr. Ovsiew reported relationships with Wolters Kluwer Health in the form of consulting, receiving royalty payments, and related activities.
FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2020
‘The pandemic within the pandemic’
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.
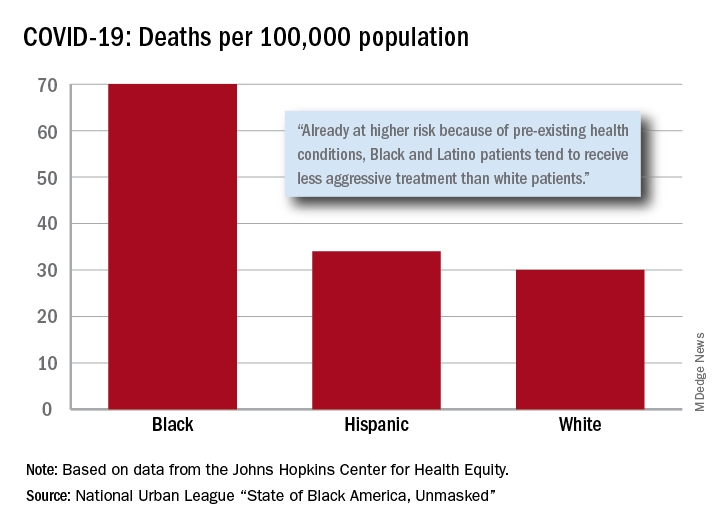
“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.

“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
The coronavirus has infected millions of Americans and killed over 174,000. But could it be worse? Maybe.

“Racism is the pandemic within the pandemic,” Marc H. Morial, president and CEO of the National Urban League, said in the 2020 “State of Black America, Unmasked” report.
“Black people with COVID-19 symptoms in February and March were less likely to get tested or treated than white patients,” he wrote.
After less testing and less treatment, the next step seems inevitable. The death rate from COVID-19 is 70 per 100,000 population among Black Americans, compared with 30 per 100,000 for Whites and 34 per 100,000 for Hispanics, the league said based on data from the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Equity.
Black and Hispanic patients with COVID-19 are more likely to have preexisting health conditions, but they “tend to receive less aggressive treatment than white patients,” the report noted. The lower death rate among Hispanics may be explained by the Black population’s greater age, although Hispanic Americans have a higher infection rate (73 per 10,000) than Blacks (62 per 10,000) or Whites (23 per 10,000).
Another possible explanation for the differences in infection rates: Blacks and Hispanics are less able to work at home because they “are overrepresented in low-wage jobs that offer the least flexibility and increase their risk of exposure to the coronavirus,” the league said.
Hispanics and Blacks also are more likely to be uninsured than Whites – 19.5% and 11.5%, respectively, vs. 7.5% – so “they tend to delay seeking treatment and are sicker than white patients when they finally do,” the league said. That may account for their much higher COVID-19 hospitalization rates: 213 per 100,000 for Blacks, 205 for Hispanics, and 46 for Whites.
“The silver lining during these dark times is that this pandemic has revealed our shared vulnerability and our interconnectedness. Many people are beginning to see that when others don’t have the opportunity to be healthy, it puts all of us at risk,” Lisa Cooper, MD, James F. Fries Professor of Medicine and Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Health Equity at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an essay accompanying the report.
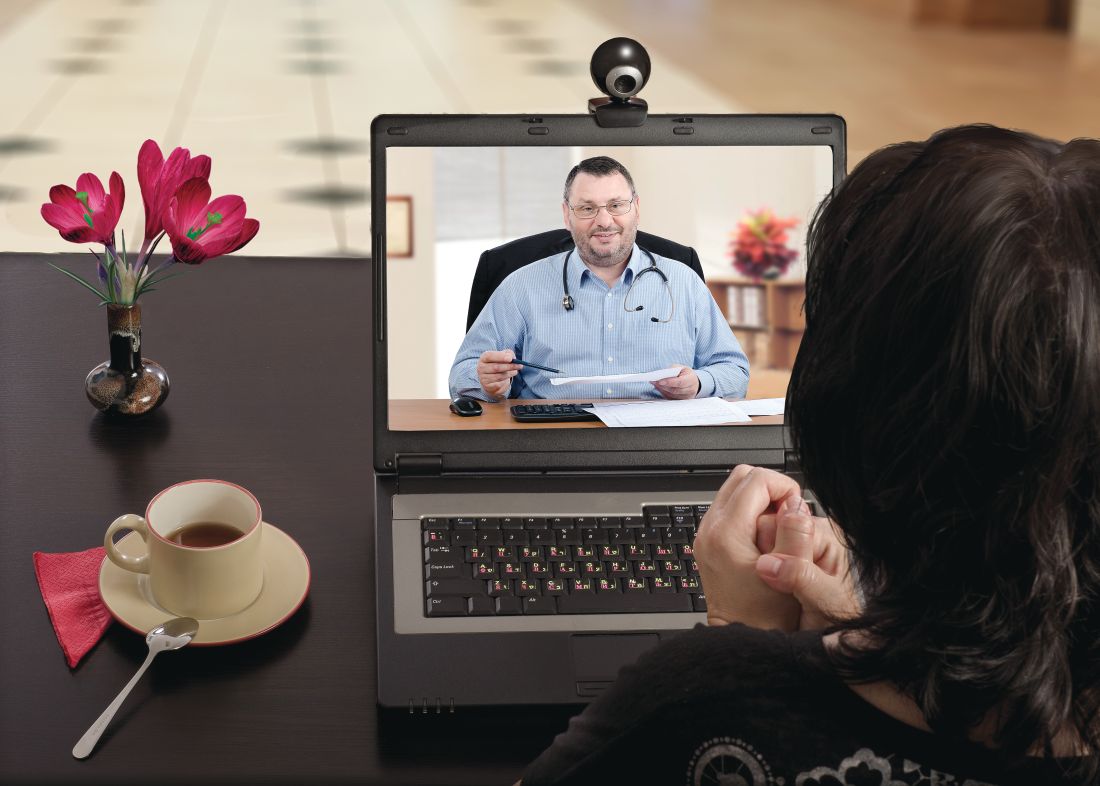
Patient visits post COVID-19
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Has telemedicine found its footing?
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Swab, spit, stay home? College coronavirus testing plans are all over the map
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
Yousuf El-Jayyousi, a junior engineering student at the University of Missouri, wanted guidance and reassurance that it would be safe to go back to school for the fall semester. He tuned into a pair of online town halls organized by the university hoping to find that.
He did not.

What he got instead from those town halls last month was encouragement to return to class at the institution affectionately known as Mizzou. The university, in Columbia, would be testing only people with symptoms, and at that point, the university said people who test positive off campus were under no obligation to inform the school.
“It feels like the university doesn’t really care whether we get sick or not,” said El-Jayyousi, who is scheduled for two in-person classes, and lives at home with his parents and 90-year-old grandmother.
He’s seen the studies from researchers at Yale and Harvard that suggest testing needs to be much more widespread. He asked his instructors if he could join lectures remotely once classes begin Monday. One was considering it; the other rejected it.
“It was kind of very dismissive, like ‘so what?’ ” El-Jayyousi said.
But it’s an enormous “so what?” packed with fear and unknowns for Jayyousi and some 20 million other students enrolled in some level of postsecondary education in America, if they are not already online only.
Policies for reentry onto campuses that were abruptly shut in March are all over the map.
Hundreds Undecided
According to the College Crisis Initiative, or C2i, a project of Davidson College that monitors how higher ed is responding to the pandemic, there is nothing resembling a common approach. Of 2,958 institutions it follows, 151 were planning to open fully online, 729 were mostly online and 433 were taking a hybrid approach. Just 75 schools were insisting on students attending fully in person, and 614 were aiming to be primarily in-person. Some 800 others were still deciding, just weeks before instruction was to start.
The decisions often have little correlation with the public health advisories in the region. Mizzou, which is in an area with recent COVID spikes, is holding some in-person instruction and has nearly 7,000 students signed up to live in dorms and other university-owned housing. Harvard, in a region with extremely low rates of viral spread, has opted to go all online and allowed students to defer a year.
The specific circumstances colleges and universities face are as much determined by local fiscal and political dictates as by medicine and epidemiology. It is often unclear who is making the call. So it’s every student for herself to chart these unknown waters, even as students (or their families) have written tuition checks for tens of thousands of dollars and signed leases for campus and off-campus housing.
And the risks – health, educational and financial – boomerang back on individual students: Two weeks after University of North Carolina students, as instructed, returned to the flagship campus in Chapel Hill with the promise of at least some in-person learning, all classes went online. Early outbreaks surged from a few students to more than 130 in a matter of days. Most undergrads have about a week to clear out of their dorms.
“It’s really tough,” said neuroscience major Luke Lawless, 20. “Chapel Hill is an amazing place, and as a senior it’s tough to know that my time’s running out – and the virus only adds to that.”
Location, location, location
C2i’s creator, Davidson education Assistant Professor Chris Marsicano, said the extreme diversity of approaches comes from the sheer diversity of schools, the penchant of many to follow the leads of more prestigious peers, and local politics.
“Some states have very strong and stringent mask requirements. Some have stronger stay-at-home orders. Others are sort of leaving it up to localities. So the confluence of politics, institutional isomorphism – that imitation – and different needs that the institutions have are driving the differences,” Marsicano said.
Location matters a lot, too, Marsicano said, pointing to schools like George Washington University and Boston University in urban settings where the environment is beyond the control of the school, versus a place like the University of the South in remote, rural Sewanee, Tennessee, where 90% of students will return to campus.
“It’s a lot easier to control an outbreak if you are a fairly isolated college campus than if you are in the middle of a city,” Marsicano said.
Student behavior is another wild card, Marsicano said, since even the best plans will fail if college kids “do something stupid, like have a massive frat party without masks.”
“You’ve got student affairs professionals across the country who are screaming at the top of their lungs, ‘We can’t control student behavior when they go off campus’” Marsicano said.
Another factor is a vacuum at the federal level. Although the Department of Education says Secretary Betsy DeVos has held dozens of calls with governors and state education superintendents, there’s no sign of an attempt to offer unified guidance to colleges beyond a webpage that links to relaxed regulatory requirements and anodyne fact sheets from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on preventing viral spread.
Even the money that the department notes it has dispensed – $30 billion from Congress’ CARES Act – is weighted toward K-12 schools, with about $13 billion for higher education, including student aid.
The U.S. Senate adjourned last week until Sept. 8, having never taken up a House-passed relief package that included some $30 billion for higher education. A trio of Democratic senators, including Sen. Elizabeth Warren, is calling for national reporting standards on college campuses.
No benchmarks
Campus communities with very different levels of contagion are making opposite calls about in-person learning. Mizzou’s Boone County has seen more than 1,400 confirmed COVID cases after a spike in mid-July. According to the Harvard Global Health Institute’s COVID risk map, Boone has accelerated spread, with 14 infections per day per 100,000 people. The institute advises stay-at-home orders or rigorous testing and tracing at such rates of infection. Two neighboring counties were in the red zone recently, with more than 25 cases per day per 100,000 people. Mizzou has left it up to deans whether classes will meet in person, making a strong argument for face-to-face instruction.
Meanwhile, Columbia University in New York City opted for all online instruction, even though the rate of infection there is a comparatively low 3.8 cases per day per 100,000 people.
Administrators at Mizzou considered and rejected mandatory testing. “All that does is provide one a snapshot of the situation,” University of Missouri system President Mun Choi said in one of the town halls.
Mizzou has an in-house team that will carry out case investigation and contact tracing with the local health department. This week, following questions from the press and pressure from the public, the university announced students will be required to report any positive COVID test to the school.
Who do you test? When?
CDC guidance for higher education suggests there’s not enough data to know whether testing everyone is effective, but some influential researchers, such as those at Harvard and Yale, disagree.
“This virus is subject to silent spreading and asymptomatic spreading, and it’s very hard to play catch-up,” said Yale professor David Paltiel, who studies public health policy. “And so thinking that you can keep your campus safe by simply waiting until students develop symptoms before acting, I think, is a very dangerous game.”
Simulation models conducted by Paltiel and his colleagues show that, of all the factors university administrators can control – including the sensitivity and specificity of COVID-19 tests – the frequency of testing is most important.
He’s “painfully aware” that testing everyone on campus every few days sets a very high bar – logistically, financially, behaviorally – that may be beyond what most schools can reach. But he says the consequences of reopening campuses without those measures are severe, not just for students, but for vulnerable populations among school workers and in the surrounding community.
“You really have to ask yourself whether you have any business reopening if you’re not going to commit to an aggressive program of high-frequency testing,” he said.
The fighting – and testing – Illini
Some institutions that desperately want students to return to campus are backing the goal with a maximal approach to safety and testing.
About a 4-hour drive east along the interstates from Mizzou is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, whose sports teams are known as the Fighting Illini.
Weeks ago, large white tents with signs reading “Walk-Up COVID-19 Testing” have popped up across campus; there students take a simple saliva test.
“This seems to be a lot easier than sticking a cotton swab up your nose,” graduate student Kristen Muñoz said after collecting a bit of her saliva in a plastic tube and sealing it in a bag labeled “Biohazard.”
In just a few hours, she got back her result: negative.
The school plans to offer free tests to the 50,000 students expected to return this month, as well as some 11,000 faculty and staff members.
“The exciting thing is, because we can test up to 10,000 per day, it allows the scientist to do what’s really the best for trying to protect the community as opposed to having to cut corners, because of the limitations of the testing,” said University of Illinois chemist Martin Burke, who helped develop the campus’s saliva test, which received emergency use authorization from the federal Food and Drug Administration this week.
The test is similar to one designed by Yale and funded by the NBA that cleared the FDA hurdle just before the Illinois test. Both Yale and Illinois hope aggressive testing will allow most undergraduate students to live on campus, even though most classes will be online.
University of Illinois epidemiologist Becky Smith said they are following data that suggest campuses need to test everyone every few days because the virus is not detectable in infected people for 3 or 4 days.
“But about two days after that, your infectiousness peaks,” she said. “So, we have a very small window of time in which to catch people before they have done most of the infection that they’re going to be doing.”
Campus officials accepted Smith’s recommendation that all faculty, staffers and students participating in any on-campus activities be required to get tested twice a week.
Illinois can do that because its test is convenient and not invasive, which spares the campus from using as much personal protective equipment as the more invasive tests require, Burke said. And on-site analysis avoids backlogs at public health and commercial labs.
Muddled in the middle
Most other colleges fall somewhere between the approaches of Mizzou and the University of Illinois, and many of their students still are uncertain how their fall semester will go.
At the University of Southern California, a private campus of about 48,500 students in Los Angeles, officials had hoped to have about 20% of classes in person – but the county government scaled that back, insisting on tougher rules for reopening than the statewide standards.
If students eventually are allowed back, they will have to show a recent coronavirus test result that they obtained on their own, said Dr. Sarah Van Orman, chief health officer of USC Student Health.
They will be asked to do daily health assessments, such as fever checks, and those who have been exposed to the virus or show symptoms will receive a rapid test, with about a 24-hour turnaround through the university medical center’s lab. “We believe it is really important to have very rapid access to those results,” Van Orman said.
At California State University – the nation’s largest 4-year system, with 23 campuses and nearly a half-million students – officials decided back in May to move nearly all its fall courses online.
“The first priority was really the health and safety of all of the campus community,” said Mike Uhlenkamp, spokesperson for the CSU Chancellor’s Office. About 10% of CSU students are expected to attend some in-person classes, such as nursing lab courses, fine art and dance classes, and some graduate classes.
Uhlenkamp said testing protocols are being left up to each campus, though all are required to follow local safety guidelines. And without a medical campus in the system, CSU campuses do not have the same capacity to take charge of their own testing, as the University of Illinois is doing.
For students who know they won’t be on campus this fall, there is regret at lost social experiences, networking and hands-on learning so important to college.
But the certainty also brings relief.
“I don’t think I would want to be indoors with a group of, you know, even just a handful of people, even if we have masks on,” said Haley Gray, a 28-year-old graduate student at the University of California-Berkeley starting the second year of her journalism program.
She knows she won’t have access to Berkeley’s advanced media labs or the collaborative sessions students experience there. And she said she realized the other day she probably won’t just sit around the student lounge and strike up unexpected friendships.
“That’s a pretty big bummer but, you know, I think overall we’re all just doing our best, and given the circumstances, I feel pretty OK about it,” she said.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente. This story is part of a partnership that includes KBIA, Illinois Public Media, Side Effects Public Media, NPR and Kaiser Health News.
COVID-19 linked to development of myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Myasthenia gravis should be added to the growing list of potential neurological sequelae associated with COVID-19, new research suggests. Clinicians from Italy have described what they believe are
“I think it is possible that there could be many more cases,” said lead author Domenico Restivo, MD, of the Garibaldi Hospital, Catania, Italy. “In fact, myasthenia gravis could be underestimated especially in the course of COVID-19 infection in which a specific muscular weakness is frequently present. For this reason, this association is easy to miss if not top of mind,” Dr. Restivo said.
None of the three patients had previous neurologic or autoimmune disorders. In all three cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis appeared within 5-7 days after onset of fever caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. The time from presumed SARS-CoV-2 infection to myasthenia gravis symptoms “is consistent with the time from infection to symptoms in other neurologic disorders triggered by infections,” the investigators reported.
The findings were published online August 10 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
First patients
The first patient described in the report was a 64-year-old man who had a fever as high as 39° C (102.2° F) for 4 days. Five days after fever onset, he developed diplopia and muscle fatigue. The patient’s neurologic examination was “unremarkable.” Computed tomography (CT) of the thorax excluded thymoma, and findings on chest radiograph were normal. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
The patient’s symptoms led the investigators to suspect myasthenia gravis. Repetitive stimulation of the patient’s facial nerve showed a 57% decrement, confirming involvement of the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. The concentration of AChR antibodies in serum was also elevated (22.8 pmol/L; reference range, <0.4 pmol/L). The patient was treated with pyridostigmine bromide and prednisone and had a response “typical for someone with myasthenia gravis,” the researchers wrote.
The second patient was a 68-year-old man who had a fever as high as 38.8° C (101.8° F) for 7 days. On day 7, he developed muscle fatigue, diplopia, and dysphagia. Findings of a chest CT and neurologic exam were normal. Nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR testing for COVID-19 were positive. As with the first patient, myasthenia gravis was suspected because of the patient’s symptoms. Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the facial (52%) and ulnar (21%) nerves. His serum AChR antibody level was elevated (27.6 pmol/L). The patient improved after one cycle of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment.
Possible mechanisms
The third patient was a 71-year-old woman with cough and a fever up to 38.6° C (101.5° F) for 6 days. She initially tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 on nasopharyngeal swab and RT-PCR. Five days after her symptoms began, she developed bilateral ocular ptosis, diplopia, and hypophonia. CT of the thorax excluded thymoma but showed bilateral interstitial pneumonia. On day 6, she developed dysphagia and respiratory failure, and was transferred to the ICU where she received mechanical ventilation.
Repetitive nerve stimulation revealed a postsynaptic deficit of neuromuscular transmission of the ulnar nerve (56%), and her serum AChR antibody level was elevated (35.6 pmol/L). Five days later, a second nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 was positive. The patient improved following plasmapheresis treatment and was successfully extubated.
The investigators noted that this patient received hydroxychloroquine the day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, but the drug was withdrawn a day later, so they do not believe that it caused the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
The observations in these three patients are “consistent with reports of other infections that induce autoimmune disorders, as well as with the growing evidence of other neurologic disorders with presumed autoimmune mechanisms after COVID-19 onset,” the researchers wrote.
They offered several possible explanations for the link between COVID-19 and myasthenia gravis. “Antibodies that are directed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins may cross-react with AChR subunits, because the virus has epitopes that are similar to components of the neuromuscular junction; this is known to occur in other neurologic autoimmune disorders after infection. Alternatively, COVID-19 infection may break immunologic self-tolerance,” the investigators wrote.
“The main message for clinicians is that myasthenia gravis, as well as other neurological disorders associated with autoimmunity, could occur in the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection,” Dr. Restivo said. Prompt recognition of the disease “could lead to a drug treatment that limits its evolution as quickly as possible,” he added.
An “unmasking”
Commenting on the findings, Anthony Geraci, MD, director of neuromuscular medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, N.Y., said these case reports of myasthenia gravis after SARS-CoV-2 infection are “not unique or novel as there has been a long understanding that seropositive [AChR antibody-positive] myasthenia gravis can and is frequently ‘unmasked’ in the setting” of several viral and bacterial infections.
“Antibodies in myasthenia gravis are of a type that take several weeks to develop to measurable levels as in the reported cases by Restivo et al., giving strong support to the notion that subclinical myasthenia gravis can be immunologically upregulated in the setting of viral infection and this is a far more likely explanation of the observed association reported,” added Dr. Geraci, who was not involved with the research.
He noted that, at his institution, “we have also observed ocular myasthenia gravis emerge in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, with similar double vision and lid droop, as we have seen similarly in patients with Zika, West Nile, and other viral infections, as well as a multiplicity of bacterial infections.”
“Most of our observed patients have responded to treatment much the same as reported by the three cases from Restivo and colleagues,” Dr.Geraci reported.
The authors of the study disclosed no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ADHD and dyslexia may affect evaluation of concussion
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study shows.
“Our results suggest kids with certain learning disorders may respond differently to concussion tests, and this needs to be taken into account when advising on recovery times and when they can return to sport,” said lead author Mathew Stokes, MD. Dr. Stokes is assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology/neurotherapeutics at the University of Texas–Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Neurology Sports Concussion Virtual Conference, held online July 31 to Aug. 1.
Learning disorders affected scores
The researchers analyzed data from participants aged 10-18 years who were enrolled in the North Texas Concussion Registry (ConTex). Participants had been diagnosed with a concussion that was sustained within 30 days of enrollment. The researchers investigated whether there were differences between patients who had no history of learning disorders and those with a history of dyslexia and/or ADD/ADHD with regard to results of clinical testing following concussion.
Of the 1,298 individuals in the study, 58 had been diagnosed with dyslexia, 158 had been diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, and 35 had been diagnosed with both conditions. There was no difference in age, time since injury, or history of concussion between those with learning disorders and those without, but there were more male patients in the ADD/ADHD group.
Results showed that in the dyslexia group, mean time was slower (P = .011), and there was an increase in error scores on the King-Devick (KD) test (P = .028). That test assesses eye movements and involves the rapid naming of numbers that are spaced differently. In addition, those with ADD/ADHD had significantly higher impulse control scores (P = .007) on the ImPACT series of tests, which are commonly used in the evaluation of concussion. Participants with both dyslexia and ADHD demonstrated slower KD times (P = .009) and had higher depression scores and anxiety scores.
Dr. Stokes noted that a limiting factor of the study was that baseline scores were not available. “It is possible that kids with ADD have less impulse control even at baseline, and this would need to be taken into account,” he said. “You may perhaps also expect someone with dyslexia to have a worse score on the KD tests, so we need more data on how these scores are affected from baseline in these individuals. But our results show that when evaluating kids pre- or post concussion, it is important to know about learning disorders, as this will affect how we interpret the data.”
At 3-month follow-up, there were no longer significant differences in anxiety and depression scores for those with and those without learning disorders. “This suggests anxiety and depression may well be worse temporarily after concussion for those with ADD/ADHD but gets better with time,” Dr. Stokes said.
Follow-up data were not available for the other cognitive tests.
Are recovery times longer?
Asked whether young people with these learning disorders needed a longer time to recover after concussion, Dr. Stokes said: “That is a million-dollar question. Studies so far on this have shown conflicting results. Our results add to a growing body of literature on this.” He stressed that it is important to include anxiety and depression scores on both baseline and postconcussion tests. “People don’t tend to think of these symptoms as being associated with concussion, but they are actually very prominent in this situation,” he noted. “Our results suggest that individuals with ADHD may be more prone to anxiety and depression, and a blow to the head may tip them more into these symptoms.”
Discussing the study at a virtual press conference as part of the AAN Sports Concussion meeting, the codirector of the meeting, David Dodick, MD, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz., said: “This is a very interesting and important study which suggests there are differences between adolescents with a history of dyslexia/ADHD and those without these conditions in performance in concussion tests. Understanding the differences in these groups will help health care providers in evaluating these athletes and assisting in counseling them and their families with regard to their risk of injury.
“It is important to recognize that athletes with ADHD, whether or not they are on medication, may take longer to recover from a concussion,” Dr. Dodick added. They also exhibit greater reductions in cognitive skills and visual motor speed regarding hand-eye coordination, he said. There is an increase in the severity of symptoms. “Symptoms that exist in both groups tend to more severe in those individuals with ADHD,” he noted.
“Ascertaining the presence or absence of ADHD or dyslexia in those who are participating in sport is important, especially when trying to interpret the results of baseline testing, the results of postinjury testing, decisions on when to return to play, and assessing for individuals and their families the risk of long-term repeat concussions and adverse outcomes,” he concluded.
The other codirector of the AAN meeting, Brian Hainline, MD, chief medical officer of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, added: “It appears that athletes with ADHD may suffer more with concussion and have a longer recovery time. This can inform our decision making and help these individuals to understand that they are at higher risk.”
Dr. Hainline said this raises another important point: “Concussion is not a homogeneous entity. It is a brain injury that can manifest in multiple parts of the brain, and the way the brain is from a premorbid or comorbid point of view can influence the manifestation of concussion as well,” he said. “All these things need to be taken into account.”
Attentional deficit may itself make an individual more susceptible to sustaining an injury in the first place, he said. “All of this is an evolving body of research which is helping clinicians to make better-informed decisions for athletes who may manifest differently.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAN Sports Concussion Conference
More evidence links gum disease and dementia risk
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
especially in those with severe gum inflammation and edentulism, new research suggests.
Over a 20-year period, investigators prospectively followed more than 8,000 individuals aged around 63 years who did not have cognitive impairment or dementia at baseline, grouping them based on the extent and severity of their periodontal disease and number of lost teeth.
Results showed that 14% of participants with healthy gums and all their teeth at baseline developed dementia, compared with 18% of those with mild periodontal disease and 22% who had severe periodontal disease. The highest percentage (23%) of participants who developed dementia was found in those who were edentulous.
After accounting for comorbidities that might affect dementia risk, edentulous participants had a 20% higher risk for developing MCI or dementia, compared with the healthy group.
Because the study was observational, “we don’t have knowledge of causality so we cannot state that if you treat periodontal disease you can prevent or treat dementia,” said lead author Ryan T. Demmer, PhD, MPH, associate professor, division of epidemiology and community health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. However, “the take-home message from this paper is that it further supports the possibility that oral infections could be a risk factor for dementia.”
The study was published online July 29 in Neurology.
The ARIC trial
Prior studies have “described the interrelation of tooth loss or periodontal disease and cognitive outcomes, although many reports were cross-sectional or case-control … and often lacked robust confounder adjustment,” the investigators noted. Additionally, lack of longitudinal data impedes the “potential for baseline periodontal status to predict incident MCI.”
To explore the associations between periodontal status and incident MCI and dementia, the researchers studied participants in the ARIC study, a community-based longitudinal cohort consisting of 15,792 predominantly Black and White participants aged 45-64 years. The current analysis included 8,275 individuals (55% women; 21% black; mean age, 63 years) who at baseline did not meet criteria for dementia or MCI.
A full-mouth periodontal examination was conducted at baseline and participants were categorized according to the severity and extent of gingival inflammation and tooth attachment loss based on the Periodontal Profile Class (PPC) seven-category model. Potential confounding variables included age, race, education level, physical activity, smoking status, oral hygiene and access to care, plasma lipid levels, APOE genotype, body mass index, blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure.
Based on PPC categorization, 22% of the patients had healthy gums, 12% had mild periodontal disease, 8% had a high gingival inflammation index, and 12% had posterior disease (with 6% having severe disease). In addition, 9% had tooth loss, 11% had severe tooth loss, and 20% were edentulous.
Infection hypothesis
Results showed that participants with worse periodontal status were more likely to have risk factors for vascular disease and dementia, such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease. During median follow-up of 18.4 years, 19% of participants overall (n = 1,569) developed dementia, translating into 11.8 cases per 1,000 person-years. There were notable differences between the PPC categories in rates of incident dementia, with edentulous participants at twice the risk for developing dementia, compared with those who had healthy gums.
For participants with severe PPC, including severe tooth loss and severe disease, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for incident dementia was 1.22 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.47) versus those who were periodontally healthy. For participants with edentulism, the HR was 1.21 (95% CI, 0.99-1.48). The adjusted risk ratios for the combined dementia/MCI outcome among participants with mild to intermediate PPC, severe PPC, or edentulism versus the periodontal healthy group were 1.22 (95% CI, 1.00-1.48), 1.15 (95% CI, 0.88-1.51), and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.40-2.58), respectively.
These findings were most pronounced among younger (median age at dental exam, younger than 62) versus older (62 years and older) participants (P = .02). Severe disease or total tooth loss were associated with an approximately 20% greater dementia incidence during the follow-up period, compared with healthy gums.
The investigators noted that the findings were “generally consistent” when considering the combined outcome of MCI and dementia. However, they noted that the association between edentulism and MCI was “markedly stronger,” with an approximate 100% increase in MCI or MCI plus dementia.
The association between periodontal disease and MCI or dementia “is rooted in the infection hypothesis, meaning adverse microbial exposures in the mucosal surfaces of the mouth, especially the subgingival space,” Dr. Demmer said. “One notion is that there could somehow be a direct infection of the brain with oral organisms, which posits that the oral organism could travel to the brain, colonize there, and cause damage that impairs cognition.”
Another possible mechanism is that chronic systemic inflammation in response to oral infections can eventually lead to vascular disease which, in turn, is a known risk factor for future dementia, he noted.
“Brush and floss”
Commenting on the research findings, James M. Noble, MD, associate professor of neurology, Taub Institute for Research on Alzheimer’s and the Aging Brain, Columbia University, New York, called the study “well characterized both by whole-mouth assessments and cognitive assessments performed in a standardized manner.” Moreover, “the study was sufficiently sized to allow for exploration of age and suggests that oral health may be a more important factor earlier in the course of aging, in late adulthood,” said Dr. Noble, who was not involved with the research.
The study also “makes an important contribution to this field through a rigorously followed cohort and robust design for both periodontal predictor and cognitive outcome assessments,” he said, noting that, “as always, the take-home message is ‘brush and floss.’
“Although we don’t know if treating periodontal disease can help treat dementia, this study suggests that we have to pay attention to good oral hygiene and make referrals to dentists when appropriate,” Dr. Demmer added.
The ARIC trial is carried out as a collaborative study supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Demmer, the study coauthors, and Dr. Noble have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
NBA star Mason Plumlee on COVID and life inside the Orlando ‘bubble’
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the August 20 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast has been edited for clarity. Click this link to listen to the full episode.
David Henry, MD: Welcome to this Blood & Cancer podcast. I’m your host, Dr. David Henry. This podcast airs on Thursday morning each week. This interview and others are archived with show notes from our residents at Pennsylvania Hospital at this link.
Each week we interview key opinion leaders involved in various aspects of blood and cancer. Mason was a first round pick in the NBA, a gold medalist for the U.S. men’s national team, and NBA All-Rookie first team honoree. He’s one of the top playmaking forwards in the country, if not the world, in my opinion. In his four-year college career at Duke University, he helped lead the Blue Devils to a National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) championship and twice earned All-America first team academic honors at Duke. So he’s not just a basketball star, but an academic star as well. Mason, thanks so much for taking some time out from the bubble in Florida to talk with us today.
Mason Plumlee: Thanks for having me on. I’m happy to be here.
Henry: Beginning in March, the NBA didn’t know what to do about the COVID pandemic but finally decided to put you professional players in a ‘bubble.’ What did you have to go through to get there? You, your teammates, coaches, trainers, etc. And what’s the ongoing plan to be sure you continue to be safe?
Plumlee: Back to when the season shut down in March, the NBA shut down the practice facilities at the same time. Most people went home. I went back to Indiana. And then, as the idea of this bubble came up and the NBA formalized a plan to start the season again, players started to go back to market. I went back to Denver and was working out there.
About two weeks before we were scheduled to arrive in Orlando, they started testing us every other day. They used the deep nasal swab as well as the throat swab. But they were also taking two to three blood tests in that time period. You needed a certain number of consecutive negative tests before they would allow you to fly on the team plane down to Orlando. So there was an incredible amount of testing in the market. Once you got to Orlando, you went into a 48-hour quarantine. You had to have two negative tests with 48 hours between them before you could leave your hotel room.
Since then, it’s been quite strict down here. And although it’s annoying in a lot of ways, I think it’s one of the reasons our league has been able to pull this off. We’ve had no positive tests within the bubble and we are tested every day. A company called BioReference Laboratories has a setup in one of the meeting rooms here, and it’s like clockwork—we go in, we get our tests. One of my teammates missed a test and they made him stay in his room until he could get another test and get the results, so he missed a game because of that.
Henry: During this bubble time, no one has tested positive—players, coaches, staff?
Plumlee: Correct.
Henry: That’s incredible, and it’s allowed those of us who want to watch the NBA and those of you who are in it professionally to continue the sport. It must be a real nuisance for you and your family and friends, because no one can visit you, right?
Plumlee: Right. There’s no visitation. We had one false positive. It was our media relations person and the actions they took when that positive test came in -- they quarantined him in his room and interviewed everybody he had talked to; they tested anyone who had any interaction with him and those people had to go into quarantine. They’re on top of things down here. In addition to the testing, we each have a pulse oximeter and a thermometer, and we use these to check in everyday on an app. So, they’re getting all the insight they need. After the first round of the playoffs, they’re going to open the bubble to friends and family, but those friends and family will be subject to all the same protocols that we were coming in and once they’re here as well.
Henry: I’m sure you’ve heard about the Broadway star [Nick Cordero] who was healthy and suddenly got sick, lost a leg, and then lost his life. There have been some heart attacks that surprised us. Have your colleagues—players, coaches, etc.—been worried? Or are they thinking, what’s the big deal? Has the sense of how serious this is permeated through this sport?
Plumlee: The NBA is one of the groups that has heightened the understanding and awareness of this by shutting down. I think a lot of people were moving forward as is, and then, when the NBA decided to cancel the season, it let the world know, look, this is to be taken seriously.
Henry: A couple of players did test positive early on.
Plumlee: Exactly. A couple of people tested positive. I think at the outset, the unknown is always scarier. As we’ve learned more about the virus, the guys have become more comfortable. You know, I tested positive back in March. At the time, a loss of taste and smell was not a reported symptom.
Henry: And you had that?
Plumlee: I did have that, but I didn’t know what to think. More research has come out and we have a better understanding of that. I think most of the players are comfortable with the virus. We’re at a time in our lives where we’re healthy, we’re active, and we should be able to fight it off. We know the numbers for our age group. Even still, I think nobody wants to get it. Nobody wants to have to go through it. So why chance it?
Henry: Hats off to you and your sport. Other sports such as Major League Baseball haven’t been quite so successful. Of course, they’re wrestling with the players testing positive, and this has stopped games this season.
I was looking over your background prior to the interview and learned that your mother and father have been involved in the medical arena. Can you tell us about that and how it’s rubbed off on you?
Plumlee: Definitely. My mom is a pharmacist, so I spent a lot of time as a kid going to see her at work. And my dad is general counsel for an orthopedic company. My hometown is Warsaw, Ind. Some people refer to it as the “Orthopedic Capital of the World.” Zimmer Biomet is headquartered there. DePuy Synthes is there. Medtronic has offices there, as well as a lot of cottage businesses that support the orthopedic industry. In my hometown, the rock star was Dane Miller, who founded Biomet. I have no formal education in medicine or health care, but I’ve seen the impact of it. From my parents and some cousins, uncles who are doctors and surgeons, it’s been interesting to see their work and learn about what’s the latest and greatest in health care.
Henry: What’s so nice about you in particular is, with that background of interests from your family and your celebrity and accomplishments in professional basketball, you have used that to explore and promote ways to make progress in health care and help others who are less fortunate. For example, you’re involved in a telehealth platform for all-in-one practice management; affordable telehealth for pediatrics; health benefits for small businesses; prior authorization—if you can help with prior authorization, we will be in the stands for you at every game because it’s the bane of our existence; radiotherapy; and probably from mom’s background, pharmacy benefit management. Pick any of those you’d like to talk about, and tell us about your involvement and how it’s going.
Plumlee: My ticket into the arena is investment. Nobody’s calling me, asking for my expertise. But a lot of these visionary founders need financial support, and that’s where I get involved. Then also, with the celebrity angle from being an athlete, sometimes you can open doors for a start-up founder that they may not be able to open themselves.
I’m happy to speak about any of those companies. I am excited about the relaxed regulation that’s come from the pandemic; not that it’s like the Wild West out here, but I think it has allowed companies to implement solutions or think about problems in a way that they couldn’t before the pandemic. Take the prior authorization play, for example, and a company called Banjo Health, with one of my favorite founders, a guy named Saar Mahna. Medicare mandates that you turn around prior authorizations within three days. This company has an artificial intelligence and machine-learning play on prior authorizations that can deliver on that.
So efficiencies, things that increase access or affordability, better outcomes, those are the things that attract me. I lean on other people for the due diligence. The pediatric play that you referenced is a company called Blueberry Pediatrics. You have a monthly subscription for $15 that can be reimbursed by Medicaid. They send two devices to your home—an otoscope and an oximeter. The company is live in Florida right now, and it’s diverting a ton of emergency room (ER) visits. From home, for $15 a month, a mom has an otoscope and an oximeter, and she can chat or video conference with a pediatrician. There’s no additional fee. So that’s saving everyone time and saving the system money. Those are the kinds of things I’m attracted to.
Henry: You’ve touched on a couple of hot button issues for us. In oncology, unfortunately, most of our patients have pain. I am mystified every time I try to get a narcotic or a strong painkiller for a patient on a Friday night and I’m told it requires prior authorization and they’ll open up again on Monday. Well, that’s insane. These patients need something right away. So if you have a special interest in helping all of us with prior authorization, the artificial intelligence is a no brainer. If this kind of computer algorithm could happen overnight, that would be wonderful.
You mentioned the ER. Many people go to the ER as a default. They don’t know what else to do. In the COVID era, we’re trying to dial that down because we want to be able to see the sickest and have the non-sick get care elsewhere. If this particular person or people don’t know what to do, they go to the ER, it costs money, takes a lot of time, and others who may be sick are diverted from care. Families worry terribly about their children, so a device for mom and access to a pediatrician for $15 a month is another wonderful idea. These are both very interesting. Another company is in the pharmacy benefit management (PBM) space. Anything you could say about how that works?
Plumlee: I can give an overview of how I look at this as an investor in the PBM space. Three companies control about 75% of a multibillion dollar market. Several initiatives have been pursued politically to provide transparent pricing between these PBMs and pharmaceutical companies, and a lot of people are pointing fingers, but ultimately, drug prices just keep going up. Everybody knows it.
A couple of start-up founders are really set on bringing a competitive marketplace back to the pharmacy benefit manager. As an investor, when you see three people controlling a market, and you have small or medium PBMs that depend on aggregators to get competitive pricing with those big three, you get interested. It’s an interesting industry. My feeling is that somebody is going to disrupt it and bring competition back to that space. Ultimately, drug prices will come down because it’s not sustainable. The insurance companies just accommodate whatever the drug pricing is. If the drug prices go up, your premiums go up. I think these new companies will be level-setting.
Henry: In my world of oncology, we’re just a little more than halfway through 2020 and we’ve had five, six, seven new drugs approved. They all will be very expensive. One of the nicer things that’s happening and may help to tamp this down involves biosimilars. When you go to CVS or Rite Aid, you go down the aspirin aisle and see the generics, and they’re identical to the brand name aspirin. Well, these very complex molecules we used to treat cancer are antibodies or proteins, and they’re made in nature’s factories called cells. They’re not identical to the brand name drugs, but they’re called biosimilars. They work exactly the same as the branded drugs with exactly the same safety–our U.S. FDA has done a nice job of vetting that, to be sure. X, Y, Z Company has copied the brand drug after the patent expires. They were hoping for about a 30% discount in price but we’re seeing more like 15%. Nothing’s ever easy. So you make a very good point. This is not sustainable and the competition will be wonderful to tamp down these prices.
Plumlee: My hope is that those biosimilars and generics get placement in these formularies because the formularies are what’s valuable to the drug manufacturers. But they have to accommodate what the Big Three want in the PBM space. To me, making things affordable and accessible is what a lot of these startups are trying to do. And hopefully they will win.
Henry: What have you been going through, in terms of COVID? Have you recovered fully? Have your taste and smell returned, and you’re back to normal?
Plumlee: I’m all good. It caught me off guard but the symptoms weren’t too intense. For me, it was less than a flu, but more than a cold. And I’m all good today.
Henry: We’re so glad and wish you the best of luck.
Dr. Henry is a clinical professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and vice chairman of the department of medicine at Pennsylvania Hospital in Philadelphia and the host of the Blood & Cancer podcast. He has no relevant financial conflicts.
Mr. Plumlee is a board advisor to both Formsense and the Prysm Institute and a board observer with Voiceitt.
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the August 20 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast has been edited for clarity. Click this link to listen to the full episode.
David Henry, MD: Welcome to this Blood & Cancer podcast. I’m your host, Dr. David Henry. This podcast airs on Thursday morning each week. This interview and others are archived with show notes from our residents at Pennsylvania Hospital at this link.
Each week we interview key opinion leaders involved in various aspects of blood and cancer. Mason was a first round pick in the NBA, a gold medalist for the U.S. men’s national team, and NBA All-Rookie first team honoree. He’s one of the top playmaking forwards in the country, if not the world, in my opinion. In his four-year college career at Duke University, he helped lead the Blue Devils to a National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) championship and twice earned All-America first team academic honors at Duke. So he’s not just a basketball star, but an academic star as well. Mason, thanks so much for taking some time out from the bubble in Florida to talk with us today.
Mason Plumlee: Thanks for having me on. I’m happy to be here.
Henry: Beginning in March, the NBA didn’t know what to do about the COVID pandemic but finally decided to put you professional players in a ‘bubble.’ What did you have to go through to get there? You, your teammates, coaches, trainers, etc. And what’s the ongoing plan to be sure you continue to be safe?
Plumlee: Back to when the season shut down in March, the NBA shut down the practice facilities at the same time. Most people went home. I went back to Indiana. And then, as the idea of this bubble came up and the NBA formalized a plan to start the season again, players started to go back to market. I went back to Denver and was working out there.
About two weeks before we were scheduled to arrive in Orlando, they started testing us every other day. They used the deep nasal swab as well as the throat swab. But they were also taking two to three blood tests in that time period. You needed a certain number of consecutive negative tests before they would allow you to fly on the team plane down to Orlando. So there was an incredible amount of testing in the market. Once you got to Orlando, you went into a 48-hour quarantine. You had to have two negative tests with 48 hours between them before you could leave your hotel room.
Since then, it’s been quite strict down here. And although it’s annoying in a lot of ways, I think it’s one of the reasons our league has been able to pull this off. We’ve had no positive tests within the bubble and we are tested every day. A company called BioReference Laboratories has a setup in one of the meeting rooms here, and it’s like clockwork—we go in, we get our tests. One of my teammates missed a test and they made him stay in his room until he could get another test and get the results, so he missed a game because of that.
Henry: During this bubble time, no one has tested positive—players, coaches, staff?
Plumlee: Correct.
Henry: That’s incredible, and it’s allowed those of us who want to watch the NBA and those of you who are in it professionally to continue the sport. It must be a real nuisance for you and your family and friends, because no one can visit you, right?
Plumlee: Right. There’s no visitation. We had one false positive. It was our media relations person and the actions they took when that positive test came in -- they quarantined him in his room and interviewed everybody he had talked to; they tested anyone who had any interaction with him and those people had to go into quarantine. They’re on top of things down here. In addition to the testing, we each have a pulse oximeter and a thermometer, and we use these to check in everyday on an app. So, they’re getting all the insight they need. After the first round of the playoffs, they’re going to open the bubble to friends and family, but those friends and family will be subject to all the same protocols that we were coming in and once they’re here as well.
Henry: I’m sure you’ve heard about the Broadway star [Nick Cordero] who was healthy and suddenly got sick, lost a leg, and then lost his life. There have been some heart attacks that surprised us. Have your colleagues—players, coaches, etc.—been worried? Or are they thinking, what’s the big deal? Has the sense of how serious this is permeated through this sport?
Plumlee: The NBA is one of the groups that has heightened the understanding and awareness of this by shutting down. I think a lot of people were moving forward as is, and then, when the NBA decided to cancel the season, it let the world know, look, this is to be taken seriously.
Henry: A couple of players did test positive early on.
Plumlee: Exactly. A couple of people tested positive. I think at the outset, the unknown is always scarier. As we’ve learned more about the virus, the guys have become more comfortable. You know, I tested positive back in March. At the time, a loss of taste and smell was not a reported symptom.
Henry: And you had that?
Plumlee: I did have that, but I didn’t know what to think. More research has come out and we have a better understanding of that. I think most of the players are comfortable with the virus. We’re at a time in our lives where we’re healthy, we’re active, and we should be able to fight it off. We know the numbers for our age group. Even still, I think nobody wants to get it. Nobody wants to have to go through it. So why chance it?
Henry: Hats off to you and your sport. Other sports such as Major League Baseball haven’t been quite so successful. Of course, they’re wrestling with the players testing positive, and this has stopped games this season.
I was looking over your background prior to the interview and learned that your mother and father have been involved in the medical arena. Can you tell us about that and how it’s rubbed off on you?
Plumlee: Definitely. My mom is a pharmacist, so I spent a lot of time as a kid going to see her at work. And my dad is general counsel for an orthopedic company. My hometown is Warsaw, Ind. Some people refer to it as the “Orthopedic Capital of the World.” Zimmer Biomet is headquartered there. DePuy Synthes is there. Medtronic has offices there, as well as a lot of cottage businesses that support the orthopedic industry. In my hometown, the rock star was Dane Miller, who founded Biomet. I have no formal education in medicine or health care, but I’ve seen the impact of it. From my parents and some cousins, uncles who are doctors and surgeons, it’s been interesting to see their work and learn about what’s the latest and greatest in health care.
Henry: What’s so nice about you in particular is, with that background of interests from your family and your celebrity and accomplishments in professional basketball, you have used that to explore and promote ways to make progress in health care and help others who are less fortunate. For example, you’re involved in a telehealth platform for all-in-one practice management; affordable telehealth for pediatrics; health benefits for small businesses; prior authorization—if you can help with prior authorization, we will be in the stands for you at every game because it’s the bane of our existence; radiotherapy; and probably from mom’s background, pharmacy benefit management. Pick any of those you’d like to talk about, and tell us about your involvement and how it’s going.
Plumlee: My ticket into the arena is investment. Nobody’s calling me, asking for my expertise. But a lot of these visionary founders need financial support, and that’s where I get involved. Then also, with the celebrity angle from being an athlete, sometimes you can open doors for a start-up founder that they may not be able to open themselves.
I’m happy to speak about any of those companies. I am excited about the relaxed regulation that’s come from the pandemic; not that it’s like the Wild West out here, but I think it has allowed companies to implement solutions or think about problems in a way that they couldn’t before the pandemic. Take the prior authorization play, for example, and a company called Banjo Health, with one of my favorite founders, a guy named Saar Mahna. Medicare mandates that you turn around prior authorizations within three days. This company has an artificial intelligence and machine-learning play on prior authorizations that can deliver on that.
So efficiencies, things that increase access or affordability, better outcomes, those are the things that attract me. I lean on other people for the due diligence. The pediatric play that you referenced is a company called Blueberry Pediatrics. You have a monthly subscription for $15 that can be reimbursed by Medicaid. They send two devices to your home—an otoscope and an oximeter. The company is live in Florida right now, and it’s diverting a ton of emergency room (ER) visits. From home, for $15 a month, a mom has an otoscope and an oximeter, and she can chat or video conference with a pediatrician. There’s no additional fee. So that’s saving everyone time and saving the system money. Those are the kinds of things I’m attracted to.
Henry: You’ve touched on a couple of hot button issues for us. In oncology, unfortunately, most of our patients have pain. I am mystified every time I try to get a narcotic or a strong painkiller for a patient on a Friday night and I’m told it requires prior authorization and they’ll open up again on Monday. Well, that’s insane. These patients need something right away. So if you have a special interest in helping all of us with prior authorization, the artificial intelligence is a no brainer. If this kind of computer algorithm could happen overnight, that would be wonderful.
You mentioned the ER. Many people go to the ER as a default. They don’t know what else to do. In the COVID era, we’re trying to dial that down because we want to be able to see the sickest and have the non-sick get care elsewhere. If this particular person or people don’t know what to do, they go to the ER, it costs money, takes a lot of time, and others who may be sick are diverted from care. Families worry terribly about their children, so a device for mom and access to a pediatrician for $15 a month is another wonderful idea. These are both very interesting. Another company is in the pharmacy benefit management (PBM) space. Anything you could say about how that works?
Plumlee: I can give an overview of how I look at this as an investor in the PBM space. Three companies control about 75% of a multibillion dollar market. Several initiatives have been pursued politically to provide transparent pricing between these PBMs and pharmaceutical companies, and a lot of people are pointing fingers, but ultimately, drug prices just keep going up. Everybody knows it.
A couple of start-up founders are really set on bringing a competitive marketplace back to the pharmacy benefit manager. As an investor, when you see three people controlling a market, and you have small or medium PBMs that depend on aggregators to get competitive pricing with those big three, you get interested. It’s an interesting industry. My feeling is that somebody is going to disrupt it and bring competition back to that space. Ultimately, drug prices will come down because it’s not sustainable. The insurance companies just accommodate whatever the drug pricing is. If the drug prices go up, your premiums go up. I think these new companies will be level-setting.
Henry: In my world of oncology, we’re just a little more than halfway through 2020 and we’ve had five, six, seven new drugs approved. They all will be very expensive. One of the nicer things that’s happening and may help to tamp this down involves biosimilars. When you go to CVS or Rite Aid, you go down the aspirin aisle and see the generics, and they’re identical to the brand name aspirin. Well, these very complex molecules we used to treat cancer are antibodies or proteins, and they’re made in nature’s factories called cells. They’re not identical to the brand name drugs, but they’re called biosimilars. They work exactly the same as the branded drugs with exactly the same safety–our U.S. FDA has done a nice job of vetting that, to be sure. X, Y, Z Company has copied the brand drug after the patent expires. They were hoping for about a 30% discount in price but we’re seeing more like 15%. Nothing’s ever easy. So you make a very good point. This is not sustainable and the competition will be wonderful to tamp down these prices.
Plumlee: My hope is that those biosimilars and generics get placement in these formularies because the formularies are what’s valuable to the drug manufacturers. But they have to accommodate what the Big Three want in the PBM space. To me, making things affordable and accessible is what a lot of these startups are trying to do. And hopefully they will win.
Henry: What have you been going through, in terms of COVID? Have you recovered fully? Have your taste and smell returned, and you’re back to normal?
Plumlee: I’m all good. It caught me off guard but the symptoms weren’t too intense. For me, it was less than a flu, but more than a cold. And I’m all good today.
Henry: We’re so glad and wish you the best of luck.
Dr. Henry is a clinical professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and vice chairman of the department of medicine at Pennsylvania Hospital in Philadelphia and the host of the Blood & Cancer podcast. He has no relevant financial conflicts.
Mr. Plumlee is a board advisor to both Formsense and the Prysm Institute and a board observer with Voiceitt.
Editor’s Note: This transcript from the August 20 episode of the Blood & Cancer podcast has been edited for clarity. Click this link to listen to the full episode.
David Henry, MD: Welcome to this Blood & Cancer podcast. I’m your host, Dr. David Henry. This podcast airs on Thursday morning each week. This interview and others are archived with show notes from our residents at Pennsylvania Hospital at this link.
Each week we interview key opinion leaders involved in various aspects of blood and cancer. Mason was a first round pick in the NBA, a gold medalist for the U.S. men’s national team, and NBA All-Rookie first team honoree. He’s one of the top playmaking forwards in the country, if not the world, in my opinion. In his four-year college career at Duke University, he helped lead the Blue Devils to a National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) championship and twice earned All-America first team academic honors at Duke. So he’s not just a basketball star, but an academic star as well. Mason, thanks so much for taking some time out from the bubble in Florida to talk with us today.
Mason Plumlee: Thanks for having me on. I’m happy to be here.
Henry: Beginning in March, the NBA didn’t know what to do about the COVID pandemic but finally decided to put you professional players in a ‘bubble.’ What did you have to go through to get there? You, your teammates, coaches, trainers, etc. And what’s the ongoing plan to be sure you continue to be safe?
Plumlee: Back to when the season shut down in March, the NBA shut down the practice facilities at the same time. Most people went home. I went back to Indiana. And then, as the idea of this bubble came up and the NBA formalized a plan to start the season again, players started to go back to market. I went back to Denver and was working out there.
About two weeks before we were scheduled to arrive in Orlando, they started testing us every other day. They used the deep nasal swab as well as the throat swab. But they were also taking two to three blood tests in that time period. You needed a certain number of consecutive negative tests before they would allow you to fly on the team plane down to Orlando. So there was an incredible amount of testing in the market. Once you got to Orlando, you went into a 48-hour quarantine. You had to have two negative tests with 48 hours between them before you could leave your hotel room.
Since then, it’s been quite strict down here. And although it’s annoying in a lot of ways, I think it’s one of the reasons our league has been able to pull this off. We’ve had no positive tests within the bubble and we are tested every day. A company called BioReference Laboratories has a setup in one of the meeting rooms here, and it’s like clockwork—we go in, we get our tests. One of my teammates missed a test and they made him stay in his room until he could get another test and get the results, so he missed a game because of that.
Henry: During this bubble time, no one has tested positive—players, coaches, staff?
Plumlee: Correct.
Henry: That’s incredible, and it’s allowed those of us who want to watch the NBA and those of you who are in it professionally to continue the sport. It must be a real nuisance for you and your family and friends, because no one can visit you, right?
Plumlee: Right. There’s no visitation. We had one false positive. It was our media relations person and the actions they took when that positive test came in -- they quarantined him in his room and interviewed everybody he had talked to; they tested anyone who had any interaction with him and those people had to go into quarantine. They’re on top of things down here. In addition to the testing, we each have a pulse oximeter and a thermometer, and we use these to check in everyday on an app. So, they’re getting all the insight they need. After the first round of the playoffs, they’re going to open the bubble to friends and family, but those friends and family will be subject to all the same protocols that we were coming in and once they’re here as well.
Henry: I’m sure you’ve heard about the Broadway star [Nick Cordero] who was healthy and suddenly got sick, lost a leg, and then lost his life. There have been some heart attacks that surprised us. Have your colleagues—players, coaches, etc.—been worried? Or are they thinking, what’s the big deal? Has the sense of how serious this is permeated through this sport?
Plumlee: The NBA is one of the groups that has heightened the understanding and awareness of this by shutting down. I think a lot of people were moving forward as is, and then, when the NBA decided to cancel the season, it let the world know, look, this is to be taken seriously.
Henry: A couple of players did test positive early on.
Plumlee: Exactly. A couple of people tested positive. I think at the outset, the unknown is always scarier. As we’ve learned more about the virus, the guys have become more comfortable. You know, I tested positive back in March. At the time, a loss of taste and smell was not a reported symptom.
Henry: And you had that?
Plumlee: I did have that, but I didn’t know what to think. More research has come out and we have a better understanding of that. I think most of the players are comfortable with the virus. We’re at a time in our lives where we’re healthy, we’re active, and we should be able to fight it off. We know the numbers for our age group. Even still, I think nobody wants to get it. Nobody wants to have to go through it. So why chance it?
Henry: Hats off to you and your sport. Other sports such as Major League Baseball haven’t been quite so successful. Of course, they’re wrestling with the players testing positive, and this has stopped games this season.
I was looking over your background prior to the interview and learned that your mother and father have been involved in the medical arena. Can you tell us about that and how it’s rubbed off on you?
Plumlee: Definitely. My mom is a pharmacist, so I spent a lot of time as a kid going to see her at work. And my dad is general counsel for an orthopedic company. My hometown is Warsaw, Ind. Some people refer to it as the “Orthopedic Capital of the World.” Zimmer Biomet is headquartered there. DePuy Synthes is there. Medtronic has offices there, as well as a lot of cottage businesses that support the orthopedic industry. In my hometown, the rock star was Dane Miller, who founded Biomet. I have no formal education in medicine or health care, but I’ve seen the impact of it. From my parents and some cousins, uncles who are doctors and surgeons, it’s been interesting to see their work and learn about what’s the latest and greatest in health care.
Henry: What’s so nice about you in particular is, with that background of interests from your family and your celebrity and accomplishments in professional basketball, you have used that to explore and promote ways to make progress in health care and help others who are less fortunate. For example, you’re involved in a telehealth platform for all-in-one practice management; affordable telehealth for pediatrics; health benefits for small businesses; prior authorization—if you can help with prior authorization, we will be in the stands for you at every game because it’s the bane of our existence; radiotherapy; and probably from mom’s background, pharmacy benefit management. Pick any of those you’d like to talk about, and tell us about your involvement and how it’s going.
Plumlee: My ticket into the arena is investment. Nobody’s calling me, asking for my expertise. But a lot of these visionary founders need financial support, and that’s where I get involved. Then also, with the celebrity angle from being an athlete, sometimes you can open doors for a start-up founder that they may not be able to open themselves.
I’m happy to speak about any of those companies. I am excited about the relaxed regulation that’s come from the pandemic; not that it’s like the Wild West out here, but I think it has allowed companies to implement solutions or think about problems in a way that they couldn’t before the pandemic. Take the prior authorization play, for example, and a company called Banjo Health, with one of my favorite founders, a guy named Saar Mahna. Medicare mandates that you turn around prior authorizations within three days. This company has an artificial intelligence and machine-learning play on prior authorizations that can deliver on that.
So efficiencies, things that increase access or affordability, better outcomes, those are the things that attract me. I lean on other people for the due diligence. The pediatric play that you referenced is a company called Blueberry Pediatrics. You have a monthly subscription for $15 that can be reimbursed by Medicaid. They send two devices to your home—an otoscope and an oximeter. The company is live in Florida right now, and it’s diverting a ton of emergency room (ER) visits. From home, for $15 a month, a mom has an otoscope and an oximeter, and she can chat or video conference with a pediatrician. There’s no additional fee. So that’s saving everyone time and saving the system money. Those are the kinds of things I’m attracted to.
Henry: You’ve touched on a couple of hot button issues for us. In oncology, unfortunately, most of our patients have pain. I am mystified every time I try to get a narcotic or a strong painkiller for a patient on a Friday night and I’m told it requires prior authorization and they’ll open up again on Monday. Well, that’s insane. These patients need something right away. So if you have a special interest in helping all of us with prior authorization, the artificial intelligence is a no brainer. If this kind of computer algorithm could happen overnight, that would be wonderful.
You mentioned the ER. Many people go to the ER as a default. They don’t know what else to do. In the COVID era, we’re trying to dial that down because we want to be able to see the sickest and have the non-sick get care elsewhere. If this particular person or people don’t know what to do, they go to the ER, it costs money, takes a lot of time, and others who may be sick are diverted from care. Families worry terribly about their children, so a device for mom and access to a pediatrician for $15 a month is another wonderful idea. These are both very interesting. Another company is in the pharmacy benefit management (PBM) space. Anything you could say about how that works?
Plumlee: I can give an overview of how I look at this as an investor in the PBM space. Three companies control about 75% of a multibillion dollar market. Several initiatives have been pursued politically to provide transparent pricing between these PBMs and pharmaceutical companies, and a lot of people are pointing fingers, but ultimately, drug prices just keep going up. Everybody knows it.
A couple of start-up founders are really set on bringing a competitive marketplace back to the pharmacy benefit manager. As an investor, when you see three people controlling a market, and you have small or medium PBMs that depend on aggregators to get competitive pricing with those big three, you get interested. It’s an interesting industry. My feeling is that somebody is going to disrupt it and bring competition back to that space. Ultimately, drug prices will come down because it’s not sustainable. The insurance companies just accommodate whatever the drug pricing is. If the drug prices go up, your premiums go up. I think these new companies will be level-setting.
Henry: In my world of oncology, we’re just a little more than halfway through 2020 and we’ve had five, six, seven new drugs approved. They all will be very expensive. One of the nicer things that’s happening and may help to tamp this down involves biosimilars. When you go to CVS or Rite Aid, you go down the aspirin aisle and see the generics, and they’re identical to the brand name aspirin. Well, these very complex molecules we used to treat cancer are antibodies or proteins, and they’re made in nature’s factories called cells. They’re not identical to the brand name drugs, but they’re called biosimilars. They work exactly the same as the branded drugs with exactly the same safety–our U.S. FDA has done a nice job of vetting that, to be sure. X, Y, Z Company has copied the brand drug after the patent expires. They were hoping for about a 30% discount in price but we’re seeing more like 15%. Nothing’s ever easy. So you make a very good point. This is not sustainable and the competition will be wonderful to tamp down these prices.
Plumlee: My hope is that those biosimilars and generics get placement in these formularies because the formularies are what’s valuable to the drug manufacturers. But they have to accommodate what the Big Three want in the PBM space. To me, making things affordable and accessible is what a lot of these startups are trying to do. And hopefully they will win.
Henry: What have you been going through, in terms of COVID? Have you recovered fully? Have your taste and smell returned, and you’re back to normal?
Plumlee: I’m all good. It caught me off guard but the symptoms weren’t too intense. For me, it was less than a flu, but more than a cold. And I’m all good today.
Henry: We’re so glad and wish you the best of luck.
Dr. Henry is a clinical professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and vice chairman of the department of medicine at Pennsylvania Hospital in Philadelphia and the host of the Blood & Cancer podcast. He has no relevant financial conflicts.
Mr. Plumlee is a board advisor to both Formsense and the Prysm Institute and a board observer with Voiceitt.
COVID-19 plans put to test as firefighters crowd camps for peak wildfire season
Jon Paul was leery entering his first wildfire camp of the year late last month to fight three lightning-caused fires scorching parts of a Northern California forest that hadn’t burned in 40 years.

The 54-year-old engine captain from southern Oregon knew from experience that these crowded, grimy camps can be breeding grounds for norovirus and a respiratory illness that firefighters call the “camp crud” in a normal year. He wondered what the coronavirus would do in the tent cities where hundreds of men and women eat, sleep, wash, and spend their downtime between shifts.
Mr. Paul thought about his immunocompromised wife and his 84-year-old mother back home. Then he joined the approximately 1,300 people spread across the Modoc National Forest who would provide a major test for the COVID-prevention measures that had been developed for wildland firefighters.
“We’re still first responders and we have that responsibility to go and deal with these emergencies,” he said in a recent interview. “I don’t scare easy, but I’m very wary and concerned about my surroundings. I’m still going to work and do my job.”
Mr. Paul is one of thousands of firefighters from across the United States battling dozens of wildfires burning throughout the West. It’s an inherently dangerous job that now carries the additional risk of COVID-19 transmission. Any outbreak that ripples through a camp could easily sideline crews and spread the virus across multiple fires – and back to communities across the country – as personnel transfer in and out of “hot zones” and return home.
Though most firefighters are young and fit, some will inevitably fall ill in these remote makeshift communities of shared showers and portable toilets, where medical care can be limited. The pollutants in the smoke they breathe daily also make them more susceptible to COVID-19 and can worsen the effects of the disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Also, one suspected or positive case in a camp will mean many other firefighters will need to be quarantined, unable to work. The worst-case scenario is that multiple outbreaks could hamstring the nation’s ability to respond as wildfire season peaks in August, the hottest and driest month of the year in the western United States.
The number of acres burned so far this year is below the 10-year average, but the fire outlook for August is above average in nine states, according to the National Interagency Fire Center. Twenty-two large fires were ignited on Monday alone after lightning storms passed through the Northwest.
A study published this month by researchers at Colorado State University and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station concluded that COVID outbreaks “could be a serious threat to the firefighting mission” and urged vigilant social distancing and screening measures in the camps.
“If simultaneous fires incurred outbreaks, the entire wildland response system could be stressed substantially, with a large portion of the workforce quarantined,” the study’s authors wrote.
This spring, the National Wildfire Coordinating Group’s Fire Management Board wrote – and has since been updating – protocols to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in fire camps, based on CDC guidelines. Though they can be adapted by managers at different fires and even by individual team, they center on some key recommendations, including the following:
- Firefighters should be screened for fever and other COVID symptoms when they arrive at camp.
- Every crew should insulate itself as a “module of one” for the fire season and limit interactions with other crews.
- Firefighters should maintain social distancing and wear face coverings when social distancing isn’t possible. Smaller satellite camps, known as spike camps, can be built to ensure enough space.
- Shared areas should be regularly cleaned and disinfected, and sharing tools and radios should be minimized.
The guidance does not include routine testing of newly arrived firefighters – a practice used for athletes at training camps and students returning to college campuses.
The Fire Management Board’s Wildland Fire Medical and Public Health Advisory Team wrote in a July 2 memo that it “does not recommend utilizing universal COVID-19 laboratory testing as a standalone risk mitigation or screening measure among wildland firefighters.” Rather, the group recommends testing an individual and directly exposed coworkers, saying that approach is in line with CDC guidance.
The lack of testing capacity and long turnaround times are factors, according to Forest Service spokesperson Dan Hottle.
The exception is Alaska, where firefighters are tested upon arrival at the airport and are quarantined in a hotel while awaiting results, which come within 24 hours, Mr. Hottle said.
Fire crews responding to early-season fires in the spring had some problems adjusting to the new protocols, according to assessments written by fire leaders and compiled by the Wildland Fire Lessons Learned Center.
Shawn Faiella, superintendent of the interagency “hotshot crew” – so named because they work the most challenging or “hottest” parts of wildfires – based at Montana’s Lolo National Forest, questioned the need to wear masks inside vehicles and the safety of bringing extra vehicles to space out firefighters traveling to a blaze. Parking extra vehicles at the scene of a fire is difficult in tight dirt roads – and would be dangerous if evacuations are necessary, he wrote.
“It’s damn tough to take these practices to the fire line,” Mr. Faiella wrote after his team responded to a 40-acre Montana fire in April.
One recommendation that fire managers say has been particularly effective is the “module of one” concept requiring crews to eat and sleep together in isolation for the entire fire season.
“Whoever came up with it, it is working,” said Mike Goicoechea, the Montana-based incident commander for the Forest Service’s Northern Region Type 1 team, which manages the nation’s largest and most complex wildfires and natural disasters. “Somebody may test positive, and you end up having to take that module out of service for 14 days. But the nice part is you’re not taking out a whole camp. ... It’s just that module.”
The total number of positive COVID cases among wildland firefighters among the various federal, state, local, and tribal agencies is not being tracked. Each fire agency has its own system for tracking and reporting COVID-19, said Jessica Gardetto, a spokesperson for the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the National Interagency Fire Center in Idaho.
The largest wildland firefighting agency is the Department of Agriculture’s Forest Service, with 10,000 firefighters. Another major agency is the Department of the Interior, which BLM is part of and which had more than 3,500 full-time fire employees last year. As of the first week of August, 111 Forest Service firefighters and 40 BLM firefighters (who work underneath the broader Interior Department agency) had tested positive for COVID-19, according to officials for the respective agencies.
“Considering we’ve now been experiencing fire activity for several months, this number is surprisingly low if you think about the thousands of fire personnel who’ve been suppressing wildfires this summer,” Ms. Gardetto said.
Mr. Goicoechea and his Montana team traveled north of Tucson, Arizona, on June 22 to manage a rapidly spreading fire in the Santa Catalina Mountains that required 1,200 responders at its peak. Within 2 days of the team’s arrival, his managers were overwhelmed by calls from firefighters worried or with questions about preventing the spread of COVID-19 or carrying the virus home to their families.
In an unusual move, Mr. Goicoechea called upon Montana physician – and former National Park Service ranger with wildfire experience – Harry Sibold, MD, to join the team. Physicians are rarely, if ever, part of a wildfire camp’s medical team, Mr. Goicoechea said.
Dr. Sibold gave regular coronavirus updates during morning briefings, consulted with local health officials, soothed firefighters worried about bringing the virus home to their families, and advised fire managers on how to handle scenarios that might come up.
But Dr. Sibold said he wasn’t optimistic at the beginning about keeping the coronavirus in check in a large camp in Pima County, which has the second-highest number of confirmed cases in Arizona, at the time a national COVID-19 hot spot. “I quite firmly expected that we might have two or three outbreaks,” he said.
There were no positive cases during the team’s 2-week deployment, just three or four cases in which a firefighter showed symptoms but tested negative for the virus. After the Montana team returned home, nine firefighters at the Arizona fire from other units tested positive, Mr. Goicoechea said. Contact tracers notified the Montana team, some of whom were tested. All tests returned negative.
“I can’t say enough about having that doctor to help,” Mr. Goicoechea said, suggesting other teams might consider doing the same. “We’re not the experts in a pandemic. We’re the experts with fire.”
That early success will be tested as the number of fires increases across the West, along with the number of firefighters responding to them. There were more than 15,000 firefighters and support personnel assigned to fires across the nation as of mid-August, and the success of those COVID-19 prevention protocols depend largely on them.
Mr. Paul, the Oregon firefighter, said that the guidelines were followed closely in camp, but less so out on the fire line. It also appeared to him that younger firefighters were less likely to follow the masking and social-distancing rules than the veterans like him. That worried him as he realized it wouldn’t take much to spark an outbreak that could sideline crews and cripple the ability to respond to a fire.
“We’re outside, so it definitely helps with mitigation and makes it simpler to social distance,” Mr. Paul said. “But I think if there’s a mistake made, it could happen.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Jon Paul was leery entering his first wildfire camp of the year late last month to fight three lightning-caused fires scorching parts of a Northern California forest that hadn’t burned in 40 years.

The 54-year-old engine captain from southern Oregon knew from experience that these crowded, grimy camps can be breeding grounds for norovirus and a respiratory illness that firefighters call the “camp crud” in a normal year. He wondered what the coronavirus would do in the tent cities where hundreds of men and women eat, sleep, wash, and spend their downtime between shifts.
Mr. Paul thought about his immunocompromised wife and his 84-year-old mother back home. Then he joined the approximately 1,300 people spread across the Modoc National Forest who would provide a major test for the COVID-prevention measures that had been developed for wildland firefighters.
“We’re still first responders and we have that responsibility to go and deal with these emergencies,” he said in a recent interview. “I don’t scare easy, but I’m very wary and concerned about my surroundings. I’m still going to work and do my job.”
Mr. Paul is one of thousands of firefighters from across the United States battling dozens of wildfires burning throughout the West. It’s an inherently dangerous job that now carries the additional risk of COVID-19 transmission. Any outbreak that ripples through a camp could easily sideline crews and spread the virus across multiple fires – and back to communities across the country – as personnel transfer in and out of “hot zones” and return home.
Though most firefighters are young and fit, some will inevitably fall ill in these remote makeshift communities of shared showers and portable toilets, where medical care can be limited. The pollutants in the smoke they breathe daily also make them more susceptible to COVID-19 and can worsen the effects of the disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Also, one suspected or positive case in a camp will mean many other firefighters will need to be quarantined, unable to work. The worst-case scenario is that multiple outbreaks could hamstring the nation’s ability to respond as wildfire season peaks in August, the hottest and driest month of the year in the western United States.
The number of acres burned so far this year is below the 10-year average, but the fire outlook for August is above average in nine states, according to the National Interagency Fire Center. Twenty-two large fires were ignited on Monday alone after lightning storms passed through the Northwest.
A study published this month by researchers at Colorado State University and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station concluded that COVID outbreaks “could be a serious threat to the firefighting mission” and urged vigilant social distancing and screening measures in the camps.
“If simultaneous fires incurred outbreaks, the entire wildland response system could be stressed substantially, with a large portion of the workforce quarantined,” the study’s authors wrote.
This spring, the National Wildfire Coordinating Group’s Fire Management Board wrote – and has since been updating – protocols to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in fire camps, based on CDC guidelines. Though they can be adapted by managers at different fires and even by individual team, they center on some key recommendations, including the following:
- Firefighters should be screened for fever and other COVID symptoms when they arrive at camp.
- Every crew should insulate itself as a “module of one” for the fire season and limit interactions with other crews.
- Firefighters should maintain social distancing and wear face coverings when social distancing isn’t possible. Smaller satellite camps, known as spike camps, can be built to ensure enough space.
- Shared areas should be regularly cleaned and disinfected, and sharing tools and radios should be minimized.
The guidance does not include routine testing of newly arrived firefighters – a practice used for athletes at training camps and students returning to college campuses.
The Fire Management Board’s Wildland Fire Medical and Public Health Advisory Team wrote in a July 2 memo that it “does not recommend utilizing universal COVID-19 laboratory testing as a standalone risk mitigation or screening measure among wildland firefighters.” Rather, the group recommends testing an individual and directly exposed coworkers, saying that approach is in line with CDC guidance.
The lack of testing capacity and long turnaround times are factors, according to Forest Service spokesperson Dan Hottle.
The exception is Alaska, where firefighters are tested upon arrival at the airport and are quarantined in a hotel while awaiting results, which come within 24 hours, Mr. Hottle said.
Fire crews responding to early-season fires in the spring had some problems adjusting to the new protocols, according to assessments written by fire leaders and compiled by the Wildland Fire Lessons Learned Center.
Shawn Faiella, superintendent of the interagency “hotshot crew” – so named because they work the most challenging or “hottest” parts of wildfires – based at Montana’s Lolo National Forest, questioned the need to wear masks inside vehicles and the safety of bringing extra vehicles to space out firefighters traveling to a blaze. Parking extra vehicles at the scene of a fire is difficult in tight dirt roads – and would be dangerous if evacuations are necessary, he wrote.
“It’s damn tough to take these practices to the fire line,” Mr. Faiella wrote after his team responded to a 40-acre Montana fire in April.
One recommendation that fire managers say has been particularly effective is the “module of one” concept requiring crews to eat and sleep together in isolation for the entire fire season.
“Whoever came up with it, it is working,” said Mike Goicoechea, the Montana-based incident commander for the Forest Service’s Northern Region Type 1 team, which manages the nation’s largest and most complex wildfires and natural disasters. “Somebody may test positive, and you end up having to take that module out of service for 14 days. But the nice part is you’re not taking out a whole camp. ... It’s just that module.”
The total number of positive COVID cases among wildland firefighters among the various federal, state, local, and tribal agencies is not being tracked. Each fire agency has its own system for tracking and reporting COVID-19, said Jessica Gardetto, a spokesperson for the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the National Interagency Fire Center in Idaho.
The largest wildland firefighting agency is the Department of Agriculture’s Forest Service, with 10,000 firefighters. Another major agency is the Department of the Interior, which BLM is part of and which had more than 3,500 full-time fire employees last year. As of the first week of August, 111 Forest Service firefighters and 40 BLM firefighters (who work underneath the broader Interior Department agency) had tested positive for COVID-19, according to officials for the respective agencies.
“Considering we’ve now been experiencing fire activity for several months, this number is surprisingly low if you think about the thousands of fire personnel who’ve been suppressing wildfires this summer,” Ms. Gardetto said.
Mr. Goicoechea and his Montana team traveled north of Tucson, Arizona, on June 22 to manage a rapidly spreading fire in the Santa Catalina Mountains that required 1,200 responders at its peak. Within 2 days of the team’s arrival, his managers were overwhelmed by calls from firefighters worried or with questions about preventing the spread of COVID-19 or carrying the virus home to their families.
In an unusual move, Mr. Goicoechea called upon Montana physician – and former National Park Service ranger with wildfire experience – Harry Sibold, MD, to join the team. Physicians are rarely, if ever, part of a wildfire camp’s medical team, Mr. Goicoechea said.
Dr. Sibold gave regular coronavirus updates during morning briefings, consulted with local health officials, soothed firefighters worried about bringing the virus home to their families, and advised fire managers on how to handle scenarios that might come up.
But Dr. Sibold said he wasn’t optimistic at the beginning about keeping the coronavirus in check in a large camp in Pima County, which has the second-highest number of confirmed cases in Arizona, at the time a national COVID-19 hot spot. “I quite firmly expected that we might have two or three outbreaks,” he said.
There were no positive cases during the team’s 2-week deployment, just three or four cases in which a firefighter showed symptoms but tested negative for the virus. After the Montana team returned home, nine firefighters at the Arizona fire from other units tested positive, Mr. Goicoechea said. Contact tracers notified the Montana team, some of whom were tested. All tests returned negative.
“I can’t say enough about having that doctor to help,” Mr. Goicoechea said, suggesting other teams might consider doing the same. “We’re not the experts in a pandemic. We’re the experts with fire.”
That early success will be tested as the number of fires increases across the West, along with the number of firefighters responding to them. There were more than 15,000 firefighters and support personnel assigned to fires across the nation as of mid-August, and the success of those COVID-19 prevention protocols depend largely on them.
Mr. Paul, the Oregon firefighter, said that the guidelines were followed closely in camp, but less so out on the fire line. It also appeared to him that younger firefighters were less likely to follow the masking and social-distancing rules than the veterans like him. That worried him as he realized it wouldn’t take much to spark an outbreak that could sideline crews and cripple the ability to respond to a fire.
“We’re outside, so it definitely helps with mitigation and makes it simpler to social distance,” Mr. Paul said. “But I think if there’s a mistake made, it could happen.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Jon Paul was leery entering his first wildfire camp of the year late last month to fight three lightning-caused fires scorching parts of a Northern California forest that hadn’t burned in 40 years.

The 54-year-old engine captain from southern Oregon knew from experience that these crowded, grimy camps can be breeding grounds for norovirus and a respiratory illness that firefighters call the “camp crud” in a normal year. He wondered what the coronavirus would do in the tent cities where hundreds of men and women eat, sleep, wash, and spend their downtime between shifts.
Mr. Paul thought about his immunocompromised wife and his 84-year-old mother back home. Then he joined the approximately 1,300 people spread across the Modoc National Forest who would provide a major test for the COVID-prevention measures that had been developed for wildland firefighters.
“We’re still first responders and we have that responsibility to go and deal with these emergencies,” he said in a recent interview. “I don’t scare easy, but I’m very wary and concerned about my surroundings. I’m still going to work and do my job.”
Mr. Paul is one of thousands of firefighters from across the United States battling dozens of wildfires burning throughout the West. It’s an inherently dangerous job that now carries the additional risk of COVID-19 transmission. Any outbreak that ripples through a camp could easily sideline crews and spread the virus across multiple fires – and back to communities across the country – as personnel transfer in and out of “hot zones” and return home.
Though most firefighters are young and fit, some will inevitably fall ill in these remote makeshift communities of shared showers and portable toilets, where medical care can be limited. The pollutants in the smoke they breathe daily also make them more susceptible to COVID-19 and can worsen the effects of the disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Also, one suspected or positive case in a camp will mean many other firefighters will need to be quarantined, unable to work. The worst-case scenario is that multiple outbreaks could hamstring the nation’s ability to respond as wildfire season peaks in August, the hottest and driest month of the year in the western United States.
The number of acres burned so far this year is below the 10-year average, but the fire outlook for August is above average in nine states, according to the National Interagency Fire Center. Twenty-two large fires were ignited on Monday alone after lightning storms passed through the Northwest.
A study published this month by researchers at Colorado State University and the U.S. Forest Service’s Rocky Mountain Research Station concluded that COVID outbreaks “could be a serious threat to the firefighting mission” and urged vigilant social distancing and screening measures in the camps.
“If simultaneous fires incurred outbreaks, the entire wildland response system could be stressed substantially, with a large portion of the workforce quarantined,” the study’s authors wrote.
This spring, the National Wildfire Coordinating Group’s Fire Management Board wrote – and has since been updating – protocols to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in fire camps, based on CDC guidelines. Though they can be adapted by managers at different fires and even by individual team, they center on some key recommendations, including the following:
- Firefighters should be screened for fever and other COVID symptoms when they arrive at camp.
- Every crew should insulate itself as a “module of one” for the fire season and limit interactions with other crews.
- Firefighters should maintain social distancing and wear face coverings when social distancing isn’t possible. Smaller satellite camps, known as spike camps, can be built to ensure enough space.
- Shared areas should be regularly cleaned and disinfected, and sharing tools and radios should be minimized.
The guidance does not include routine testing of newly arrived firefighters – a practice used for athletes at training camps and students returning to college campuses.
The Fire Management Board’s Wildland Fire Medical and Public Health Advisory Team wrote in a July 2 memo that it “does not recommend utilizing universal COVID-19 laboratory testing as a standalone risk mitigation or screening measure among wildland firefighters.” Rather, the group recommends testing an individual and directly exposed coworkers, saying that approach is in line with CDC guidance.
The lack of testing capacity and long turnaround times are factors, according to Forest Service spokesperson Dan Hottle.
The exception is Alaska, where firefighters are tested upon arrival at the airport and are quarantined in a hotel while awaiting results, which come within 24 hours, Mr. Hottle said.
Fire crews responding to early-season fires in the spring had some problems adjusting to the new protocols, according to assessments written by fire leaders and compiled by the Wildland Fire Lessons Learned Center.
Shawn Faiella, superintendent of the interagency “hotshot crew” – so named because they work the most challenging or “hottest” parts of wildfires – based at Montana’s Lolo National Forest, questioned the need to wear masks inside vehicles and the safety of bringing extra vehicles to space out firefighters traveling to a blaze. Parking extra vehicles at the scene of a fire is difficult in tight dirt roads – and would be dangerous if evacuations are necessary, he wrote.
“It’s damn tough to take these practices to the fire line,” Mr. Faiella wrote after his team responded to a 40-acre Montana fire in April.
One recommendation that fire managers say has been particularly effective is the “module of one” concept requiring crews to eat and sleep together in isolation for the entire fire season.
“Whoever came up with it, it is working,” said Mike Goicoechea, the Montana-based incident commander for the Forest Service’s Northern Region Type 1 team, which manages the nation’s largest and most complex wildfires and natural disasters. “Somebody may test positive, and you end up having to take that module out of service for 14 days. But the nice part is you’re not taking out a whole camp. ... It’s just that module.”
The total number of positive COVID cases among wildland firefighters among the various federal, state, local, and tribal agencies is not being tracked. Each fire agency has its own system for tracking and reporting COVID-19, said Jessica Gardetto, a spokesperson for the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the National Interagency Fire Center in Idaho.
The largest wildland firefighting agency is the Department of Agriculture’s Forest Service, with 10,000 firefighters. Another major agency is the Department of the Interior, which BLM is part of and which had more than 3,500 full-time fire employees last year. As of the first week of August, 111 Forest Service firefighters and 40 BLM firefighters (who work underneath the broader Interior Department agency) had tested positive for COVID-19, according to officials for the respective agencies.
“Considering we’ve now been experiencing fire activity for several months, this number is surprisingly low if you think about the thousands of fire personnel who’ve been suppressing wildfires this summer,” Ms. Gardetto said.
Mr. Goicoechea and his Montana team traveled north of Tucson, Arizona, on June 22 to manage a rapidly spreading fire in the Santa Catalina Mountains that required 1,200 responders at its peak. Within 2 days of the team’s arrival, his managers were overwhelmed by calls from firefighters worried or with questions about preventing the spread of COVID-19 or carrying the virus home to their families.
In an unusual move, Mr. Goicoechea called upon Montana physician – and former National Park Service ranger with wildfire experience – Harry Sibold, MD, to join the team. Physicians are rarely, if ever, part of a wildfire camp’s medical team, Mr. Goicoechea said.
Dr. Sibold gave regular coronavirus updates during morning briefings, consulted with local health officials, soothed firefighters worried about bringing the virus home to their families, and advised fire managers on how to handle scenarios that might come up.
But Dr. Sibold said he wasn’t optimistic at the beginning about keeping the coronavirus in check in a large camp in Pima County, which has the second-highest number of confirmed cases in Arizona, at the time a national COVID-19 hot spot. “I quite firmly expected that we might have two or three outbreaks,” he said.
There were no positive cases during the team’s 2-week deployment, just three or four cases in which a firefighter showed symptoms but tested negative for the virus. After the Montana team returned home, nine firefighters at the Arizona fire from other units tested positive, Mr. Goicoechea said. Contact tracers notified the Montana team, some of whom were tested. All tests returned negative.
“I can’t say enough about having that doctor to help,” Mr. Goicoechea said, suggesting other teams might consider doing the same. “We’re not the experts in a pandemic. We’re the experts with fire.”
That early success will be tested as the number of fires increases across the West, along with the number of firefighters responding to them. There were more than 15,000 firefighters and support personnel assigned to fires across the nation as of mid-August, and the success of those COVID-19 prevention protocols depend largely on them.
Mr. Paul, the Oregon firefighter, said that the guidelines were followed closely in camp, but less so out on the fire line. It also appeared to him that younger firefighters were less likely to follow the masking and social-distancing rules than the veterans like him. That worried him as he realized it wouldn’t take much to spark an outbreak that could sideline crews and cripple the ability to respond to a fire.
“We’re outside, so it definitely helps with mitigation and makes it simpler to social distance,” Mr. Paul said. “But I think if there’s a mistake made, it could happen.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
COVID-19: Optimizing therapeutic strategies for children, adolescents with ADHD
Recently, the Yakima Health District (YHD), in collaboration with the Washington State Department of Health, issued dramatic revisions to its educational curriculum, opting for exclusively remote learning as an important next step in COVID-19 containment measures.
The newly implemented “enhanced” distance-learning paradigm has garnered considerable national attention. Even more noteworthy is how YHD addressed those with language barriers and learning differences such as ADHD as a “priority group”; these individuals are exempt from the newly implemented measures, and small instructional groups of no more than five “at-risk” students will be directly supervised by specialized educators.1,2 To overcome these new unprecedented challenges from the coronavirus pandemic, especially from the perspective of distance education and mental health for susceptible groups such as those with ADHD, it is of utmost importance to explore various programs of interest, as well as the targeted therapies being considered during this crisis.
From a therapeutic standpoint, individuals with learning differences are more likely to play catch-up with their age-matched peers. This puts them at significant risk for developmental delays with symptoms manifesting as disruptive behavioral issues. This is why ongoing parental guidance, coupled with a paradoxically stimulating environment, is critical for children and adolescents with ADHD.3 Accumulating evidence, based on a myriad of studies, demonstrates that childhood treatment with ADHD stimulants reduces the incidence of future substance use, as well as that of other negative outcomes.4,5
Therapeutic strategies that work
“The new normal” has forced unique challenges on clinicians for mitigating distress by novel means of health care delivery. Given the paucity of research exploring the interactions of individuals with ADHD within the context of COVID-19, Take for example, the suggested guidelines from the European ADHD Guidelines Group (EAGG) – such as the following:
- Telecommunications in general, and telepsychiatry in particular, should function as the primary mode of health care delivery to fulfill societal standards of physical distancing.
- Children and adolescents with ADHD should be designated as a “priority group” with respect to monitoring initiatives by educators in a school setting, be it virtual or otherwise.
- Implementation of behavioral strategies by parent or guardian to address psychological well-being and reduce the presence of comorbid behavioral conditions (such as oppositional defiant disorder).
In addition to the aforementioned guidance, EAGG maintains that individuals with ADHD may be initiated on medications after the completion of a baseline examination; if the patients in question are already on a treatment regimen, they should proceed with it as indicated. Interruptions to therapy are not ideal because patients are then subjected to health-related stressors of COVID-19. Reasonable regulations concerning access to medications, without unnecessary delays, undoubtedly will facilitate patient needs, allowing for a smooth transition in day-to-day activities. The family, as a cohesive unit, may benefit from reeducation because it contributes toward the therapeutic process. Neurofeedback, coping skills, and cognitive restructuring training are potential modalities that can augment medications.
Although it may seem counterintuitive, parents or caregivers should resist the urge to increase the medication dose during an outbreak with the intended goal of diminishing the psychosocial burden of ADHD symptomatology. Likewise, unless indicated by a specialist, antipsychotics and/or hypnotics should not be introduced for addressing behavioral dysregulation (such as agitation) during the confinement period.
Historically, numerous clinicians have suggested that patients undergo a routine cardiovascular examination and EKG before being prescribed psychostimulants (the rationale for this recommendation is that sympathomimetics unduly affect blood pressure and heart rate).6,7 However, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Heart Association (AHA) eventually amended their previous stance by releasing a joint statement in which they deemed a baseline EKG necessary only in ADHD patients with preexisting cardiac risk. For all other patients, the use of EKGs was entirely contingent on physician discretion. However, given the nature of safety precautions for COVID-19, it is prudent to discourage or delay in-person cardiovascular examination/monitoring protocols altogether, especially in those patients without known heart conditions.
Another area of concern is sleep dysfunction, which might exist as an untoward effect of ADHD medication intake or because of the presence of COVID-19 psychosocial stressors. However, clinicians advise that unnecessary psychopharmacology (such as hypnotics or melatonin) be avoided. Instead, conservative lifestyle measures should be enacted, emphasizing the role of proper sleep hygiene in maintaining optimal behavioral health. Despite setbacks to in-person appointments, patients are expected to continue their pharmacotherapy with “parent-focused” ADHD interventions taking a primary role in facilitating compliance through remote monitoring.
ADMiRE, a tertiary-level, dedicated ADHD intervention program from South Dublin, Ireland, has identified several roadblocks with respect to streamlining health care for individuals with ADHD during the confinement period. The proposed resolution to these issues, some of which are derived from EAGG guidelines, might have universal applications elsewhere, thereby facilitating the development of therapeutic services of interest. ADMiRE has noted a correspondence between the guidelines established by EAGG and that of the Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance (CADDRA), including minimal in-person interactions (in favor of virtual teleconferencing) and a cardiovascular screen can be performed in lieu of baseline cardiac auscultation. Moreover, in the event that the patient is a low cardiac risk candidate for ADHD treatment, monitoring protocols may be continued from a home setting. However, if a physical examination is indicated, CADDRA recommends the use of precautionary PPE before commencing ADHD pharmacotherapy.
One of the most significant hurdles is that of school closures because teacher feedback for baseline behavior was traditionally instrumental in dictating patient medical management (for example, for titration schedule). It is expected that, for the time being, this role will be supplanted by parental reports. As well as disclosing information on behavioral dysregulation, family members should be trained to relay critical information about the development of stimulant-induced cardiovascular symptoms – namely, dyspnea, chest pain, and/or palpitations. Furthermore, as primary caregivers, parents should harbor a certain degree of emotional sensitivity because their mood state may influence the child’s overall behavioral course in terms of symptom exacerbation.8
Toward adopting an integrated model for care
Developing an effective assessment plan for patients with ADHD often proves to be a challenging task for clinicians, perhaps even more so in environments that enforce social distancing and limited physical contact by default. As a neurodevelopmental disorder from childhood, the symptoms (including inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity) of ADHD do not arise in a vacuum – comorbid conditions include mood and anxiety disorders, which are complicated further by a background risk for substance use and self-medicating tendencies.9 Unfortunately, the pandemic has limited the breadth of non-COVID doctors visits, which hinders the overall diagnostic and monitoring process for identifiable comorbid conditions, such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, oppositional defiant and conduct disorders, and so on.10 Since ADHD symptoms cannot be treated by pharmacotherapy or behavioral interventions alone, our team advocates that families provide additional emotional support and continuous encouragement during these uncertain times.
ADHD and the self-medication hypothesis
The Khantzian self-medication hypothesis posits that a drug seeker may subconsciously gravitate toward a particular agent only to discover a sense of relief concerning inner turmoil or restlessness after use. Observations support the notion that individuals with undiagnosed ADHD have sought cocaine or even recreational designer drugs (such as methylenedioxypyrovalerone, or “bath salts”).11 Given the similar mechanism of action between cocaine, methylenedioxypyrovalerone, and prescribed psychostimulants such as methylphenidate, the results are hardly surprising because these agents all work on the brain’s “reward center” (for example, the nucleus accumbens) by invoking dopamine release. Aside from the aforementioned self-medication hypothesis, “downers” such as Xanax recently have experienced a prescription spike during the outbreak. While there isn’t an immediate cause for concern of Xanax abuse in ADHD individuals, the potential for addiction is certainly real, especially when taking into account comorbid anxiety disorder or sleep dysfunction.
Because of limited resources and precautionary guidelines, clinicians are at a considerable disadvantage in terms of formulating a comprehensive diagnostic and treatment plan for children and adolescents with ADHD. This situation is further compounded by the recent closure of schools and the lack of feedback with respect to baseline behavior from teachers and specialized educators. This is why it is imperative for primary caregivers to closely monitor children with ADHD for developing changes in behavioral patterns (for example, mood or anxiety issues and drug-seeking or disruptive behavior) and work with health care professionals.
References
1. “Distance learning strongly recommended for all Yakima county schools.” NBC Right Now. 2020 Aug 5.
2. Retka J. “Enhanced” remote learning in Yakima county schools? What that means for students this fall. Yakima Herald-Republic. 2020 Aug 8.
3. Armstrong T. “To empower! Not Control! A holistic approach to ADHD.” American Institute for Learning and Development. 1998.
4. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2014 Aug;55(8):878-85.
5. Ir J Psychol Med. 2020 May 21:1-22.
6. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020 Jun;4(6):412-4.
7. O’Keefe L. AAP News. 2008 Jun;29(6):1.
8. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020 Jun;51:102077.
9. Current Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;14(12):e3-4.
10. Encephale. 2020 Jun 7;46(3S):S85-92.
11. Current Psychiatry. 2014 Dec; 3(12): e3-4.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF), Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Zaid Ulhaq Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clini-cal research at the IMCHF and is Mr. Choudhry’s father. He has no disclosures.
Recently, the Yakima Health District (YHD), in collaboration with the Washington State Department of Health, issued dramatic revisions to its educational curriculum, opting for exclusively remote learning as an important next step in COVID-19 containment measures.
The newly implemented “enhanced” distance-learning paradigm has garnered considerable national attention. Even more noteworthy is how YHD addressed those with language barriers and learning differences such as ADHD as a “priority group”; these individuals are exempt from the newly implemented measures, and small instructional groups of no more than five “at-risk” students will be directly supervised by specialized educators.1,2 To overcome these new unprecedented challenges from the coronavirus pandemic, especially from the perspective of distance education and mental health for susceptible groups such as those with ADHD, it is of utmost importance to explore various programs of interest, as well as the targeted therapies being considered during this crisis.
From a therapeutic standpoint, individuals with learning differences are more likely to play catch-up with their age-matched peers. This puts them at significant risk for developmental delays with symptoms manifesting as disruptive behavioral issues. This is why ongoing parental guidance, coupled with a paradoxically stimulating environment, is critical for children and adolescents with ADHD.3 Accumulating evidence, based on a myriad of studies, demonstrates that childhood treatment with ADHD stimulants reduces the incidence of future substance use, as well as that of other negative outcomes.4,5
Therapeutic strategies that work
“The new normal” has forced unique challenges on clinicians for mitigating distress by novel means of health care delivery. Given the paucity of research exploring the interactions of individuals with ADHD within the context of COVID-19, Take for example, the suggested guidelines from the European ADHD Guidelines Group (EAGG) – such as the following:
- Telecommunications in general, and telepsychiatry in particular, should function as the primary mode of health care delivery to fulfill societal standards of physical distancing.
- Children and adolescents with ADHD should be designated as a “priority group” with respect to monitoring initiatives by educators in a school setting, be it virtual or otherwise.
- Implementation of behavioral strategies by parent or guardian to address psychological well-being and reduce the presence of comorbid behavioral conditions (such as oppositional defiant disorder).
In addition to the aforementioned guidance, EAGG maintains that individuals with ADHD may be initiated on medications after the completion of a baseline examination; if the patients in question are already on a treatment regimen, they should proceed with it as indicated. Interruptions to therapy are not ideal because patients are then subjected to health-related stressors of COVID-19. Reasonable regulations concerning access to medications, without unnecessary delays, undoubtedly will facilitate patient needs, allowing for a smooth transition in day-to-day activities. The family, as a cohesive unit, may benefit from reeducation because it contributes toward the therapeutic process. Neurofeedback, coping skills, and cognitive restructuring training are potential modalities that can augment medications.
Although it may seem counterintuitive, parents or caregivers should resist the urge to increase the medication dose during an outbreak with the intended goal of diminishing the psychosocial burden of ADHD symptomatology. Likewise, unless indicated by a specialist, antipsychotics and/or hypnotics should not be introduced for addressing behavioral dysregulation (such as agitation) during the confinement period.
Historically, numerous clinicians have suggested that patients undergo a routine cardiovascular examination and EKG before being prescribed psychostimulants (the rationale for this recommendation is that sympathomimetics unduly affect blood pressure and heart rate).6,7 However, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Heart Association (AHA) eventually amended their previous stance by releasing a joint statement in which they deemed a baseline EKG necessary only in ADHD patients with preexisting cardiac risk. For all other patients, the use of EKGs was entirely contingent on physician discretion. However, given the nature of safety precautions for COVID-19, it is prudent to discourage or delay in-person cardiovascular examination/monitoring protocols altogether, especially in those patients without known heart conditions.
Another area of concern is sleep dysfunction, which might exist as an untoward effect of ADHD medication intake or because of the presence of COVID-19 psychosocial stressors. However, clinicians advise that unnecessary psychopharmacology (such as hypnotics or melatonin) be avoided. Instead, conservative lifestyle measures should be enacted, emphasizing the role of proper sleep hygiene in maintaining optimal behavioral health. Despite setbacks to in-person appointments, patients are expected to continue their pharmacotherapy with “parent-focused” ADHD interventions taking a primary role in facilitating compliance through remote monitoring.
ADMiRE, a tertiary-level, dedicated ADHD intervention program from South Dublin, Ireland, has identified several roadblocks with respect to streamlining health care for individuals with ADHD during the confinement period. The proposed resolution to these issues, some of which are derived from EAGG guidelines, might have universal applications elsewhere, thereby facilitating the development of therapeutic services of interest. ADMiRE has noted a correspondence between the guidelines established by EAGG and that of the Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance (CADDRA), including minimal in-person interactions (in favor of virtual teleconferencing) and a cardiovascular screen can be performed in lieu of baseline cardiac auscultation. Moreover, in the event that the patient is a low cardiac risk candidate for ADHD treatment, monitoring protocols may be continued from a home setting. However, if a physical examination is indicated, CADDRA recommends the use of precautionary PPE before commencing ADHD pharmacotherapy.
One of the most significant hurdles is that of school closures because teacher feedback for baseline behavior was traditionally instrumental in dictating patient medical management (for example, for titration schedule). It is expected that, for the time being, this role will be supplanted by parental reports. As well as disclosing information on behavioral dysregulation, family members should be trained to relay critical information about the development of stimulant-induced cardiovascular symptoms – namely, dyspnea, chest pain, and/or palpitations. Furthermore, as primary caregivers, parents should harbor a certain degree of emotional sensitivity because their mood state may influence the child’s overall behavioral course in terms of symptom exacerbation.8
Toward adopting an integrated model for care
Developing an effective assessment plan for patients with ADHD often proves to be a challenging task for clinicians, perhaps even more so in environments that enforce social distancing and limited physical contact by default. As a neurodevelopmental disorder from childhood, the symptoms (including inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity) of ADHD do not arise in a vacuum – comorbid conditions include mood and anxiety disorders, which are complicated further by a background risk for substance use and self-medicating tendencies.9 Unfortunately, the pandemic has limited the breadth of non-COVID doctors visits, which hinders the overall diagnostic and monitoring process for identifiable comorbid conditions, such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, oppositional defiant and conduct disorders, and so on.10 Since ADHD symptoms cannot be treated by pharmacotherapy or behavioral interventions alone, our team advocates that families provide additional emotional support and continuous encouragement during these uncertain times.
ADHD and the self-medication hypothesis
The Khantzian self-medication hypothesis posits that a drug seeker may subconsciously gravitate toward a particular agent only to discover a sense of relief concerning inner turmoil or restlessness after use. Observations support the notion that individuals with undiagnosed ADHD have sought cocaine or even recreational designer drugs (such as methylenedioxypyrovalerone, or “bath salts”).11 Given the similar mechanism of action between cocaine, methylenedioxypyrovalerone, and prescribed psychostimulants such as methylphenidate, the results are hardly surprising because these agents all work on the brain’s “reward center” (for example, the nucleus accumbens) by invoking dopamine release. Aside from the aforementioned self-medication hypothesis, “downers” such as Xanax recently have experienced a prescription spike during the outbreak. While there isn’t an immediate cause for concern of Xanax abuse in ADHD individuals, the potential for addiction is certainly real, especially when taking into account comorbid anxiety disorder or sleep dysfunction.
Because of limited resources and precautionary guidelines, clinicians are at a considerable disadvantage in terms of formulating a comprehensive diagnostic and treatment plan for children and adolescents with ADHD. This situation is further compounded by the recent closure of schools and the lack of feedback with respect to baseline behavior from teachers and specialized educators. This is why it is imperative for primary caregivers to closely monitor children with ADHD for developing changes in behavioral patterns (for example, mood or anxiety issues and drug-seeking or disruptive behavior) and work with health care professionals.
References
1. “Distance learning strongly recommended for all Yakima county schools.” NBC Right Now. 2020 Aug 5.
2. Retka J. “Enhanced” remote learning in Yakima county schools? What that means for students this fall. Yakima Herald-Republic. 2020 Aug 8.
3. Armstrong T. “To empower! Not Control! A holistic approach to ADHD.” American Institute for Learning and Development. 1998.
4. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2014 Aug;55(8):878-85.
5. Ir J Psychol Med. 2020 May 21:1-22.
6. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020 Jun;4(6):412-4.
7. O’Keefe L. AAP News. 2008 Jun;29(6):1.
8. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020 Jun;51:102077.
9. Current Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;14(12):e3-4.
10. Encephale. 2020 Jun 7;46(3S):S85-92.
11. Current Psychiatry. 2014 Dec; 3(12): e3-4.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF), Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Zaid Ulhaq Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clini-cal research at the IMCHF and is Mr. Choudhry’s father. He has no disclosures.
Recently, the Yakima Health District (YHD), in collaboration with the Washington State Department of Health, issued dramatic revisions to its educational curriculum, opting for exclusively remote learning as an important next step in COVID-19 containment measures.
The newly implemented “enhanced” distance-learning paradigm has garnered considerable national attention. Even more noteworthy is how YHD addressed those with language barriers and learning differences such as ADHD as a “priority group”; these individuals are exempt from the newly implemented measures, and small instructional groups of no more than five “at-risk” students will be directly supervised by specialized educators.1,2 To overcome these new unprecedented challenges from the coronavirus pandemic, especially from the perspective of distance education and mental health for susceptible groups such as those with ADHD, it is of utmost importance to explore various programs of interest, as well as the targeted therapies being considered during this crisis.
From a therapeutic standpoint, individuals with learning differences are more likely to play catch-up with their age-matched peers. This puts them at significant risk for developmental delays with symptoms manifesting as disruptive behavioral issues. This is why ongoing parental guidance, coupled with a paradoxically stimulating environment, is critical for children and adolescents with ADHD.3 Accumulating evidence, based on a myriad of studies, demonstrates that childhood treatment with ADHD stimulants reduces the incidence of future substance use, as well as that of other negative outcomes.4,5
Therapeutic strategies that work
“The new normal” has forced unique challenges on clinicians for mitigating distress by novel means of health care delivery. Given the paucity of research exploring the interactions of individuals with ADHD within the context of COVID-19, Take for example, the suggested guidelines from the European ADHD Guidelines Group (EAGG) – such as the following:
- Telecommunications in general, and telepsychiatry in particular, should function as the primary mode of health care delivery to fulfill societal standards of physical distancing.
- Children and adolescents with ADHD should be designated as a “priority group” with respect to monitoring initiatives by educators in a school setting, be it virtual or otherwise.
- Implementation of behavioral strategies by parent or guardian to address psychological well-being and reduce the presence of comorbid behavioral conditions (such as oppositional defiant disorder).
In addition to the aforementioned guidance, EAGG maintains that individuals with ADHD may be initiated on medications after the completion of a baseline examination; if the patients in question are already on a treatment regimen, they should proceed with it as indicated. Interruptions to therapy are not ideal because patients are then subjected to health-related stressors of COVID-19. Reasonable regulations concerning access to medications, without unnecessary delays, undoubtedly will facilitate patient needs, allowing for a smooth transition in day-to-day activities. The family, as a cohesive unit, may benefit from reeducation because it contributes toward the therapeutic process. Neurofeedback, coping skills, and cognitive restructuring training are potential modalities that can augment medications.
Although it may seem counterintuitive, parents or caregivers should resist the urge to increase the medication dose during an outbreak with the intended goal of diminishing the psychosocial burden of ADHD symptomatology. Likewise, unless indicated by a specialist, antipsychotics and/or hypnotics should not be introduced for addressing behavioral dysregulation (such as agitation) during the confinement period.
Historically, numerous clinicians have suggested that patients undergo a routine cardiovascular examination and EKG before being prescribed psychostimulants (the rationale for this recommendation is that sympathomimetics unduly affect blood pressure and heart rate).6,7 However, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Heart Association (AHA) eventually amended their previous stance by releasing a joint statement in which they deemed a baseline EKG necessary only in ADHD patients with preexisting cardiac risk. For all other patients, the use of EKGs was entirely contingent on physician discretion. However, given the nature of safety precautions for COVID-19, it is prudent to discourage or delay in-person cardiovascular examination/monitoring protocols altogether, especially in those patients without known heart conditions.
Another area of concern is sleep dysfunction, which might exist as an untoward effect of ADHD medication intake or because of the presence of COVID-19 psychosocial stressors. However, clinicians advise that unnecessary psychopharmacology (such as hypnotics or melatonin) be avoided. Instead, conservative lifestyle measures should be enacted, emphasizing the role of proper sleep hygiene in maintaining optimal behavioral health. Despite setbacks to in-person appointments, patients are expected to continue their pharmacotherapy with “parent-focused” ADHD interventions taking a primary role in facilitating compliance through remote monitoring.
ADMiRE, a tertiary-level, dedicated ADHD intervention program from South Dublin, Ireland, has identified several roadblocks with respect to streamlining health care for individuals with ADHD during the confinement period. The proposed resolution to these issues, some of which are derived from EAGG guidelines, might have universal applications elsewhere, thereby facilitating the development of therapeutic services of interest. ADMiRE has noted a correspondence between the guidelines established by EAGG and that of the Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance (CADDRA), including minimal in-person interactions (in favor of virtual teleconferencing) and a cardiovascular screen can be performed in lieu of baseline cardiac auscultation. Moreover, in the event that the patient is a low cardiac risk candidate for ADHD treatment, monitoring protocols may be continued from a home setting. However, if a physical examination is indicated, CADDRA recommends the use of precautionary PPE before commencing ADHD pharmacotherapy.
One of the most significant hurdles is that of school closures because teacher feedback for baseline behavior was traditionally instrumental in dictating patient medical management (for example, for titration schedule). It is expected that, for the time being, this role will be supplanted by parental reports. As well as disclosing information on behavioral dysregulation, family members should be trained to relay critical information about the development of stimulant-induced cardiovascular symptoms – namely, dyspnea, chest pain, and/or palpitations. Furthermore, as primary caregivers, parents should harbor a certain degree of emotional sensitivity because their mood state may influence the child’s overall behavioral course in terms of symptom exacerbation.8
Toward adopting an integrated model for care
Developing an effective assessment plan for patients with ADHD often proves to be a challenging task for clinicians, perhaps even more so in environments that enforce social distancing and limited physical contact by default. As a neurodevelopmental disorder from childhood, the symptoms (including inattention, hyperactivity, and/or impulsivity) of ADHD do not arise in a vacuum – comorbid conditions include mood and anxiety disorders, which are complicated further by a background risk for substance use and self-medicating tendencies.9 Unfortunately, the pandemic has limited the breadth of non-COVID doctors visits, which hinders the overall diagnostic and monitoring process for identifiable comorbid conditions, such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, oppositional defiant and conduct disorders, and so on.10 Since ADHD symptoms cannot be treated by pharmacotherapy or behavioral interventions alone, our team advocates that families provide additional emotional support and continuous encouragement during these uncertain times.
ADHD and the self-medication hypothesis
The Khantzian self-medication hypothesis posits that a drug seeker may subconsciously gravitate toward a particular agent only to discover a sense of relief concerning inner turmoil or restlessness after use. Observations support the notion that individuals with undiagnosed ADHD have sought cocaine or even recreational designer drugs (such as methylenedioxypyrovalerone, or “bath salts”).11 Given the similar mechanism of action between cocaine, methylenedioxypyrovalerone, and prescribed psychostimulants such as methylphenidate, the results are hardly surprising because these agents all work on the brain’s “reward center” (for example, the nucleus accumbens) by invoking dopamine release. Aside from the aforementioned self-medication hypothesis, “downers” such as Xanax recently have experienced a prescription spike during the outbreak. While there isn’t an immediate cause for concern of Xanax abuse in ADHD individuals, the potential for addiction is certainly real, especially when taking into account comorbid anxiety disorder or sleep dysfunction.
Because of limited resources and precautionary guidelines, clinicians are at a considerable disadvantage in terms of formulating a comprehensive diagnostic and treatment plan for children and adolescents with ADHD. This situation is further compounded by the recent closure of schools and the lack of feedback with respect to baseline behavior from teachers and specialized educators. This is why it is imperative for primary caregivers to closely monitor children with ADHD for developing changes in behavioral patterns (for example, mood or anxiety issues and drug-seeking or disruptive behavior) and work with health care professionals.
References
1. “Distance learning strongly recommended for all Yakima county schools.” NBC Right Now. 2020 Aug 5.
2. Retka J. “Enhanced” remote learning in Yakima county schools? What that means for students this fall. Yakima Herald-Republic. 2020 Aug 8.
3. Armstrong T. “To empower! Not Control! A holistic approach to ADHD.” American Institute for Learning and Development. 1998.
4. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2014 Aug;55(8):878-85.
5. Ir J Psychol Med. 2020 May 21:1-22.
6. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020 Jun;4(6):412-4.
7. O’Keefe L. AAP News. 2008 Jun;29(6):1.
8. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020 Jun;51:102077.
9. Current Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;14(12):e3-4.
10. Encephale. 2020 Jun 7;46(3S):S85-92.
11. Current Psychiatry. 2014 Dec; 3(12): e3-4.
Dr. Islam is a medical adviser for the International Maternal and Child Health Foundation (IMCHF), Montreal, and is based in New York. He also is a postdoctoral fellow, psychopharmacologist, and a board-certified medical affairs specialist. Dr. Islam disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Zaid Ulhaq Choudhry is a research assistant at the IMCHF. He has no disclosures. Dr. Zia Choudhry is the chief scientific officer and head of the department of mental health and clini-cal research at the IMCHF and is Mr. Choudhry’s father. He has no disclosures.