User login
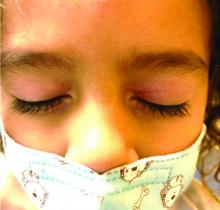
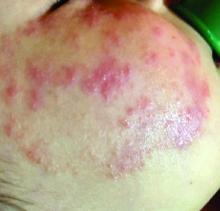
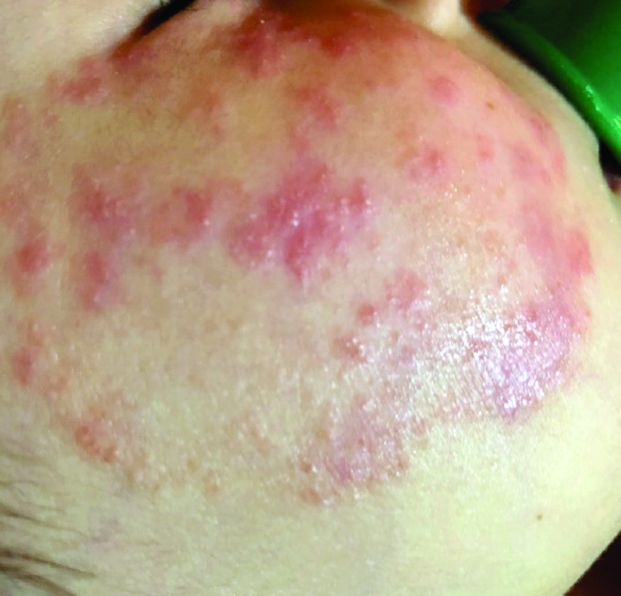
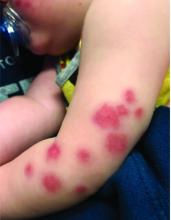
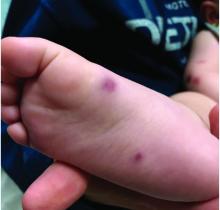
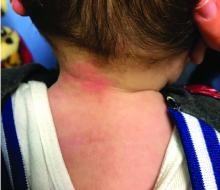
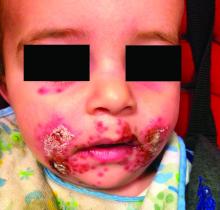
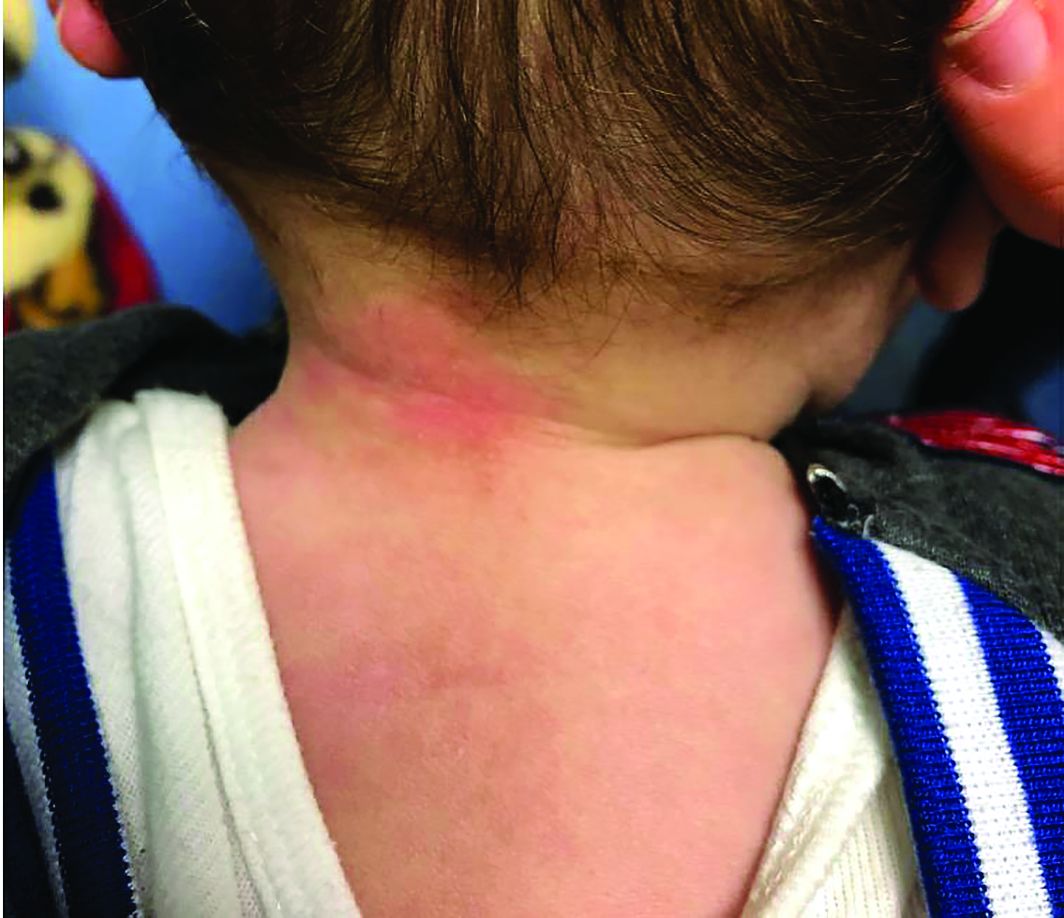
Four-year-old boy presents with itchy rash on face, extremities
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
A 4-year-old healthy male with no significant prior medical history presents for evaluation of "itchy bumps" on the face and extremities of 2 weeks' duration.
The child was well until around 2 and a half weeks ago when he presented for evaluation of two lesions on the lower eyelids, diagnosed as hordeolum (a stye). He was prescribed ofloxacin ophthalmic solution.
One week later he developed bilateral itchy red eyes with red, thickened areas on the upper lids, followed several days later by pruritic papules on the ears, wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles. His mother used Vaseline for the eyelids for 1 week with no improvement. Physical exam at the dermatologist's office showed mild erythema, induration, and lichenification of the upper eyelids, and bilateral periocular eczematous patches with overlying scale. Subtle papules were evident on the elbows and feet.
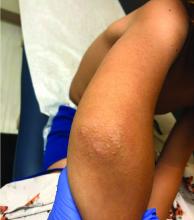
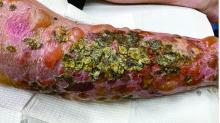
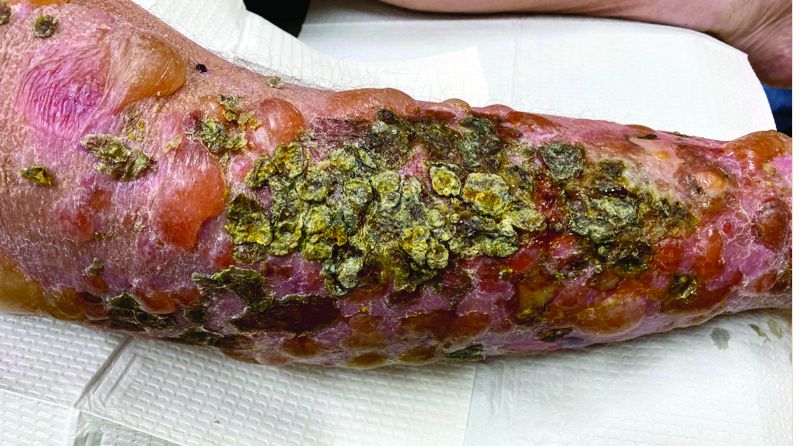
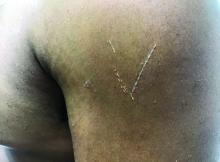
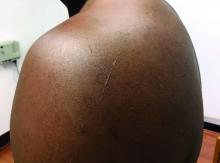
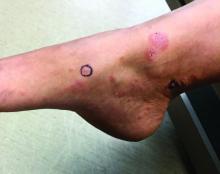
A 72-year-old with an acute, pruritic, bullous eruption involving his right pretibial extremity
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
Localized bullous pemphigoid
with a predilection in the elderly population.1
Localized variants of bullous pemphigoid (BP) are rare and have been reported to arise at sites of mechanical trauma, prior radiation, lymphedema, surgical scars, burns, fistulas, and ostomies.1-3 Although the mechanism remains unclear, the Koebner phenomenon is thought to induce dysregulation of immunologic and vascular factors in sites of mechanical shear and trauma in susceptible individuals.3
Localized BP is an important entity for the dermatologist to be familiar with, as the diagnosis is often delayed. The localized, well-defined skin lesions frequently mimic contact dermatitis. In fact, previous reports have shown the most likely misdiagnosis of localized BP is acute allergic contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, and eczematous dermatitis.4,5
In this patient, histopathologic examination of a biopsy revealed a subepidermal blister with numerous eosinophils. Direct immunofluorescence study of perilesional skin showed strong linear IgG and C3 deposits at the basal membrane level. Serum level of autoantibody to BP180 antigen was elevated. Bacterial culture was positive for Staphylococcus aureus. These findings were suggestive of unilateral, localized BP with superimposed bacterial infection. Initial treatment with an extended course of doxycycline 200 mg twice daily, topical triamcinolone 0.1% ointment twice daily with compression therapy, and leg elevation led to clinical improvement with healing of previous lesions on the leg. At follow-up 3 weeks later, the patient had continued to develop new bullous lesions on the trunk and upper thighs. He was subsequently started on systemic immunosuppressive therapy for generalized bullous pemphigoid.
Importantly, localized BP generally follows a more benign disease course, although long-term follow-up is recommended for monitoring given the potential risk of developing the generalized form of BP of approximately 15%.3 Topical corticosteroids and oral antibiotics are recommended as the first-line therapy in these patients, with an escalated systemic therapy if needed for disease progression.3,5
Our case represents an important differential diagnosis to consider when evaluating an acute localized bullous eruption in an elderly patient.
Dr. Cusick and Dr. Dolohanty are with the department of dermatology, University of Rochester (N.Y.), and provided the case and photo. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Kohroh K et al. J Dermatol. 2007 Jul;34(7):482-5.
2. Nguyen T et al. Dermatology 2014;229(2):88-96.
3. Sen BB et al. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79(4):554.
4. Salomon RJ et al. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Mar;123(3):389-92.
5. Tran JT, Mutasim DF. Int J Dermatol. 2005 Nov;44(11):942-5.
What presents as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque?
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
Scrapings of the child’s rash were analyzed with potassium hydroxide (KOH) under microscopy which revealed multiple septate hyphae.
She was diagnosed with Majocchi’s granuloma. The fungal culture was positive for Trichophyton rubrum.
Majocchi’s granuloma (MG) is cutaneous mycosis in which the fungal infection goes deeper into the hair follicle causing granulomatous folliculitis and perifolliculitis.1 It was first described by Domenico Majocchi in 1883, and he named the condition “granuloma tricofitico.”2
It is commonly caused by T. rubrum but also can be caused by T. mentagrophytes, T. tonsurans, T. verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Epidermophyton floccosum.2,3 Patients at risk for developing this infection include those previously treated with topical corticosteroids, immunosuppressed patients, patients with areas under occlusion, and those with areas traumatized by shaving. This infection is most commonly seen in the lower extremities, but can happen anywhere in the body. The lesions present as deep erythematous papules, pustules, and may form an annular or circular plaque as seen on our patient.
A KOH test of skin scrapings and hair extractions often can reveal fungal hyphae. Identification of the pathogen can be performed with culture or polymerase chain reaction of skin samples. If the diagnosis is uncertain or the KOH is negative, a skin biopsy can be performed. Histopathologic examination reveals perifollicular granulomas with associated dermal abscesses. Giant cells may be observed. MG is associated with chronic inflammation with lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells, and scattered multinucleated giant cells.2,3
The differential diagnosis for these lesions in children includes other granulomatous conditions such as granulomatous rosacea, sarcoidosis, and granuloma faciale, as well as bacterial or atypical mycobacterial infections, cutaneous leishmaniasis, and eosinophilic pustular folliculitis.
Treatment of MG requires systemic treatment with griseofulvin, itraconazole, or terbinafine for at least 4-8 weeks or until all the lesions have resolved. Our patient was treated with 6 weeks of high-dose griseofulvin with resolution of her lesions.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Dec 15;24(12):13030/qt89k4t6wj.
2. Med Mycol. 2012 Jul;50(5):449-57.
3. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011 Apr;24(2):247-80.
A 3-year-old girl with a known history of eczema presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a persistent rash for about a year on the right cheek.
The mother reported she was treating the lesions with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% as instructed previously for her eczema. Initially the rash got partially better but then started getting worse again. The area was itchy.
The child was later seen in the emergency department, where she was recommended to treat the area with a combination cream of terbinafine 1% and betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%. The mother applied this cream as instructed for 3 weeks with some improvement of the lesions on the cheek.
A few weeks later, pimples started coming back. The mother tried the medication again but this time it was not helpful and the rash continued to expand.
The mother reported having a rash on her hand months back, which she successfully treated with the combination cream provided at the emergency department. They have no pets at home.
The child has a little sister who also has mild eczema.
She goes to day care and dances ballet.
Flat-topped papules on the neck, arms, and trunk
that typically occur on the trunk, extremities, or genitalia of children and young adults. However, it can affect people of all ages and all areas of skin. Lichen nitidus lesions may emerge in areas of trauma, often in a linear arrangement, called the Koebner phenomenon. It is not thought to be associated with any systemic disease. Nail involvement may be present. Oral lesions are not commonly seen. The diagnosis of LN is often a clinical one.
Histopathology for this patient showed a focally dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells in the papillary dermis, associated with overlying epidermal atrophy and adjacent elongated rete ridges surrounding the infiltrate in a characteristic “ball and claw” pattern. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
The differential diagnosis includes lichen planus (LP). In LP, lesions tend to be larger and more violaceous. They tend to favor wrists, lower extremities, and genitalia. Oral and nail involvement are common. Histologically, a band-like lichenoid infiltrate in the dermis is present. Granulomatous inflammation and giant cells are absent. Direct immunofluorescence is positive for globular deposits of IgG, IgA, IgM and/or complement at the dermal-epidermal junction.
A hepatitis panel was drawn for this patient and was negative. Treatment for lichen nitidus is only needed if symptomatic because lesions will generally resolve spontaneously. Lesions may take months or years to resolve. For significant pruritus, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be used. Topical emollients are recommended. Topical tacrolimus has been reported to improve lesions. Oral steroids and light therapy have been reported to improve generalized lichen nitidus not responding to topical treatments.
The case and these photos were submitted byMs. Swartz of Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla.; Dr. Chen and Dr. Walder of Bay Harbor Islands, Fla.; and Dr. Winslow of Pompano Beach, Fla. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, editor of this column, is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
that typically occur on the trunk, extremities, or genitalia of children and young adults. However, it can affect people of all ages and all areas of skin. Lichen nitidus lesions may emerge in areas of trauma, often in a linear arrangement, called the Koebner phenomenon. It is not thought to be associated with any systemic disease. Nail involvement may be present. Oral lesions are not commonly seen. The diagnosis of LN is often a clinical one.
Histopathology for this patient showed a focally dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells in the papillary dermis, associated with overlying epidermal atrophy and adjacent elongated rete ridges surrounding the infiltrate in a characteristic “ball and claw” pattern. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
The differential diagnosis includes lichen planus (LP). In LP, lesions tend to be larger and more violaceous. They tend to favor wrists, lower extremities, and genitalia. Oral and nail involvement are common. Histologically, a band-like lichenoid infiltrate in the dermis is present. Granulomatous inflammation and giant cells are absent. Direct immunofluorescence is positive for globular deposits of IgG, IgA, IgM and/or complement at the dermal-epidermal junction.
A hepatitis panel was drawn for this patient and was negative. Treatment for lichen nitidus is only needed if symptomatic because lesions will generally resolve spontaneously. Lesions may take months or years to resolve. For significant pruritus, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be used. Topical emollients are recommended. Topical tacrolimus has been reported to improve lesions. Oral steroids and light therapy have been reported to improve generalized lichen nitidus not responding to topical treatments.
The case and these photos were submitted byMs. Swartz of Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla.; Dr. Chen and Dr. Walder of Bay Harbor Islands, Fla.; and Dr. Winslow of Pompano Beach, Fla. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, editor of this column, is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
that typically occur on the trunk, extremities, or genitalia of children and young adults. However, it can affect people of all ages and all areas of skin. Lichen nitidus lesions may emerge in areas of trauma, often in a linear arrangement, called the Koebner phenomenon. It is not thought to be associated with any systemic disease. Nail involvement may be present. Oral lesions are not commonly seen. The diagnosis of LN is often a clinical one.
Histopathology for this patient showed a focally dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with multinucleate giant cells in the papillary dermis, associated with overlying epidermal atrophy and adjacent elongated rete ridges surrounding the infiltrate in a characteristic “ball and claw” pattern. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of lichen nitidus.
The differential diagnosis includes lichen planus (LP). In LP, lesions tend to be larger and more violaceous. They tend to favor wrists, lower extremities, and genitalia. Oral and nail involvement are common. Histologically, a band-like lichenoid infiltrate in the dermis is present. Granulomatous inflammation and giant cells are absent. Direct immunofluorescence is positive for globular deposits of IgG, IgA, IgM and/or complement at the dermal-epidermal junction.
A hepatitis panel was drawn for this patient and was negative. Treatment for lichen nitidus is only needed if symptomatic because lesions will generally resolve spontaneously. Lesions may take months or years to resolve. For significant pruritus, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be used. Topical emollients are recommended. Topical tacrolimus has been reported to improve lesions. Oral steroids and light therapy have been reported to improve generalized lichen nitidus not responding to topical treatments.
The case and these photos were submitted byMs. Swartz of Nova Southeastern University, Ft. Lauderdale, Fla.; Dr. Chen and Dr. Walder of Bay Harbor Islands, Fla.; and Dr. Winslow of Pompano Beach, Fla. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, editor of this column, is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
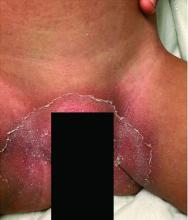
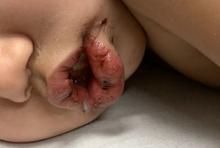
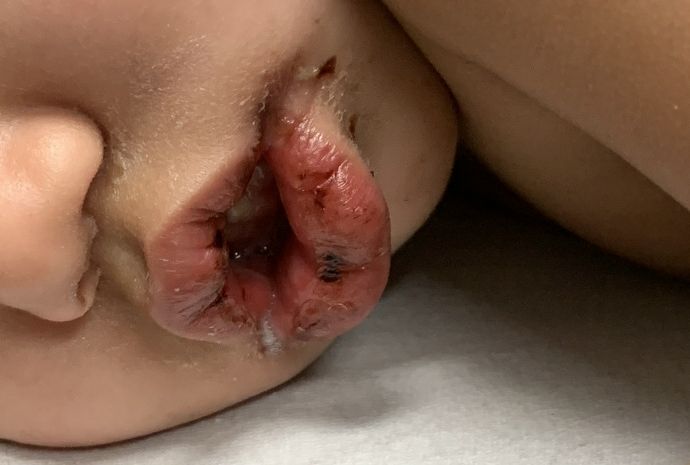
A toddler with a fever and desquamating perineal rash
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
Kawasaki disease
Given (KD). An echocardiogram revealed diffuse dilation of the left anterior descending artery without evidence of an aneurysm. The patient was promptly started on 2 g/kg IVIG and high-dose aspirin. She was later transitioned to low-dose aspirin. Long-term follow-up thus far has revealed no cardiac sequelae.
KD, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is a multisystem vasculitis with predilection for the coronary arteries that most commonly affects children between 6 months and 5 years of age.1 While the etiology remains unclear, the pathogenesis is thought to be the result of an immune response to an infection in the setting of genetic susceptibility.1 Approximately 90% of patients have mucocutaneous manifestations, highlighting the important role dermatologists play in the diagnosis and early intervention to prevent cardiovascular morbidity.
The diagnostic criteria include fever for at least 5 days accompanied by at least four of the following:
- Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate that is classically limbal sparing.
- Oral mucosal changes with cracked fissured lips, “strawberry tongue,” or erythema of the lips and mucosa.
- Changes in the extremities: erythema, swelling, or periungual peeling.
- Polymorphous exanthem.
- Cervical lymphadenopathy, often unilateral (greater than 1.5 cm).
Although nonspecific for diagnosis, laboratory abnormalities are common, including anemia, thrombocytosis, leukocytosis, elevated inflammatory markers, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), hypoalbuminemia, and sterile pyuria on urine analysis.1
Notably, a classic finding of KD is perineal dermatitis with desquamation occurring in the acute phase of disease in 80%-90% of patients.2-5 In a retrospective review, up to 67% of patients with KD developed a perineal rash in the first week, most often beginning in the diaper area.2 The perineal rash classically desquamates early during the acute phase of the disease.1
While most individuals with KD follow a benign disease course, it is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in the United States.1 Treatment is aimed at decreasing the risk of developing coronary abnormalities through the prompt administration of IVIG and high-dose aspirin initiated early in the acute phase.6 A second dose of IVIG may be given to patients who remain febrile within 24-48 hours after treatment.6 Infliximab has been used safely and effectively in patients with refractory KD.7 Long-term cardiac follow-up of KD patients is recommended.
Recently, there has been an emerging association between COVID-19 and pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome, which shares features with KD. Patients with pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome who meet clinical criteria for KD should be promptly treated with IVIG and aspirin to avoid long-term cardiac sequelae.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Elizabeth H. Cusick and Dr. Molly E. Plovanich, both with the department of dermatology at the University of Rochester (N.Y.). Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the case.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
1. Bayers S et al. (2013). J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Oct;69(4):501.e1-11.
2. Friter BS and Lucky AW. Arch Dermatol. 1988 Dec;124(12):1805-10.
3. Urbach AH et al. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Nov;142(11):1174-6.
4. Fink CW. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr; 2(2):140-1.
5. Aballi A J and Bisken LC. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;3(2):187.
6. McCrindle BW et al. Circulation. 2017 Apr 25;135(17):e927-e99.
7.Sauvaget E et al. J Pediatr. 2012 May; 160(5),875-6.
An otherwise healthy 18-month-old female presented to the emergency department with 5 days of fever, erythema, fissuring of the lips, conjunctival injection, and a desquamating perineal rash. In addition, she had nasal congestion and cough for which she was started on amoxicillin 2 days prior to presentation given concern for pneumonia.
On exam, she was also noted to have several palpable cervical lymph nodes and edematous hands with overlying erythema. Laboratory evaluation was notable for respiratory syncytial virus positivity by polymerase chain reaction assay, leukocytosis, and elevated inflammatory markers (erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein).
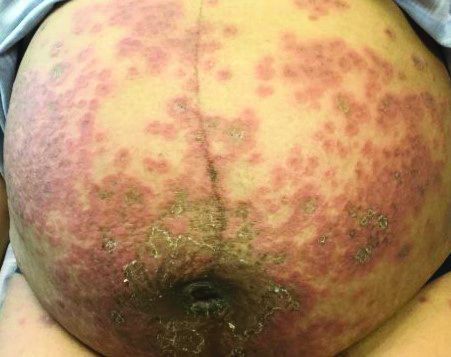
Itchy, vesicular rash
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
What's your diagnosis?
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
A punch biopsy of one of the lesions showed a superficial and deep mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, including neutrophils and eosinophils. There was also vasculitis, karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells. The findings are those of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, suggestive of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Direct immunofluorescence was positive for IgM, C3, and fibrinogen, but negative for IgA.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), also known as Finkelstein disease, is form of leukocytoclastic vasculitis that occurs in infants and toddlers aged between4 months and 3 years.
The lesions start as petechiae or edematous, erythematous to violaceous nodules that later coalesce and form “cockade”-like plaques with a central clearing on the face and extremities. Gastrointestinal, renal, and joint involvement are rare.1 AHEI follows a benign course with resolution of the lesions and symptoms within days to weeks. The etiology of this condition is not known but infection triggers have been reported including coronavirus infections, coxsackie virus infections, Escherichia coli urinary tract infections, herpes simplex virus stomatitis, and pneumococcal bacteremia.2,3 Our patient had a prior history of pneumococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. MMR vaccine also has been reported as a possible trigger, as well as some medications.
Laboratory results are usually normal, but some patients may have elevated inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate), as noted in our patient, and leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and eosinophilia. Microscopic analysis demonstrates leukocytoclastic vasculitis of small vessels with associated karyorrhexis and extravasated red blood cells.
The differential diagnosis includes other vasculitic conditions, primarily Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP). Patients with HSP tend to be older in age and the lesions described as palpable purpura commonly affect the lower extremities and buttocks. These patients can present with abdominal pain and arthritis; renal compromise also can occur. Direct immunofluorescence can commonly be positive for IgA, which was negative in our patient.
AHEI and HSP are considered different entities, but both present with leukocytoclastic vasculitis.1 Another condition to consider in patients with fever, rash, and edema is Kawasaki disease, also a form of vasculitis, that affects small- and medium-size muscular vessels with predilection for the coronary arteries. Patients with Kawasaki disease present with fever (usually longer than 5 days), facial and extremity edema (similar to AHEI), skin lesions (which may have multiple presentations, the most common being macular, papular and erythematous, and urticarial eruptions), but also lymphadenopathy and conjunctivitis. These patients appear sicker than children with AHEI. Their laboratory results show leukocytosis, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, elevated inflammatory markers, and sterile pyuria.4
Patients with erythema nodosum present with tender erythematous nodules, which can look like early AHEI lesions. The most common location is the lower extremities, but in children erythema nodosum can occur on the face, trunk, and arms. The lesions can occur secondary to infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis, as well as to malignancy or medications. These patients do not appear sick, are not febrile, and are rarely seen under 2 years of age.5
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis – Sweets’ syndrome – also should be considered in a patient with tender nodules, fever, and leukocytosis. The skin lesions in Sweets’ syndrome, compared with those in AHEI, are painful and can present as papules, nodules, and bullae on the face and extremities. A prior history of an upper respiratory infection is commonly described in children with Sweets’ syndrome. These patients present with fever, which may start days to weeks prior to the lesions starting. Children with Sweets’ syndrome also can have conjunctivitis, myalgias, polyarthritis, and in severe cases septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction. Sweets’ syndrome can be seen in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, and malignancy; it also may be induced by certain medications.6
As mentioned above, the course of AHEI is benign, and the condition resolves within days to weeks. Treatment is supportive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Matiz at [email protected].
References
1. F1000Res. 2019;8:1771.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2006 Jul-Aug;23(4):361-4.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;32(6):e309-11.
4. Clin Dermatol. 2017 Nov-Dec;35(6):530-40.
5. Yonsei Med J. 2019 Mar;60(3):312-4.
6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):437-46.
At 3 a.m., you receive a call from the ED for a baby with a new rash on the arms, legs, and face. Some of the lesions appear to be tender. He has a mild fever of 38.4° C (101.1° F) and is not in acute distress. He is drinking, but not eating much.
The parents also have noted some swelling on the hands and the feet. He has no upper respiratory or gastrointestinal symptoms. He is not walking yet.
He was admitted to the hospital 3 weeks prior for streptococcal pneumonia and metapneumovirus infection. He was treated with ceftriaxone, supportive respiratory care, and an albuterol inhaler. Influenza and respiratory syncytial virus tests were negative.
On physical exam, the child is tired and sleeping in his mom's arms. He has red and some purpuric papules on the face. On the arms and legs, he has purpuric papules and nodules. There is some edema on the face, hands, and feet. His conjunctiva is normal, and he has no oral lesions. He has no lymphadenopathy or hepatosplenomegaly.
Blood work shows normal complete blood count, coagulation tests, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis, but he has an elevated C-reactive protein of 114 mg/L and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 71 mm/hour.
April 2020
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis
that resemble whiplash marks. The lesions may be extremely pruritic, and petechiae may be present in the streaks. The trunk is most commonly affected, although lesions can occur on the limbs. Mucosa is not affected. Sun exposure may exacerbate the condition. The dermatitis has been described in all ages and races, and males seem to be more affected than females.
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis typically occurs following the ingestion of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes). The mushrooms contain a polysaccharide called lentinan. Ingestion of lentinan activates interleukin-1 (IL-1), resulting in vasodilation and the subsequent dermatitis that can occur within a few hours and up to 5 days post ingestion. Associated gastrointestinal symptoms, fever, and localized swelling have been reported. The rash will resolve spontaneously over a few days to weeks.
Flagellate erythema has been described with bleomycin treatment. Other reported associations include peplomycin (a bleomycin derivative) and docetaxel. The rash may appear following administration of bleomycin by any route and has been shown to be dose independent. Onset occurs anywhere from 1 day to several months after exposure. Over time, the erythema will develop into postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Dermatomyositis may present with flagellate erythema. Other symptoms include muscle weakness and an inflammatory myopathy. A heliotrope rash on the eyelids, Gottron’s papules on the hands, ragged cuticles with prominent vessels on nail folds may be seen. Blood work may reveal elevated antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti–Mi-2 and anti–Jo-1. Adult-onset Still disease is characterized by fever, arthritis, and salmon-colored patches.
Our patient’s dermatitis resolved spontaneously without treatment.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis
that resemble whiplash marks. The lesions may be extremely pruritic, and petechiae may be present in the streaks. The trunk is most commonly affected, although lesions can occur on the limbs. Mucosa is not affected. Sun exposure may exacerbate the condition. The dermatitis has been described in all ages and races, and males seem to be more affected than females.
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis typically occurs following the ingestion of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes). The mushrooms contain a polysaccharide called lentinan. Ingestion of lentinan activates interleukin-1 (IL-1), resulting in vasodilation and the subsequent dermatitis that can occur within a few hours and up to 5 days post ingestion. Associated gastrointestinal symptoms, fever, and localized swelling have been reported. The rash will resolve spontaneously over a few days to weeks.
Flagellate erythema has been described with bleomycin treatment. Other reported associations include peplomycin (a bleomycin derivative) and docetaxel. The rash may appear following administration of bleomycin by any route and has been shown to be dose independent. Onset occurs anywhere from 1 day to several months after exposure. Over time, the erythema will develop into postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Dermatomyositis may present with flagellate erythema. Other symptoms include muscle weakness and an inflammatory myopathy. A heliotrope rash on the eyelids, Gottron’s papules on the hands, ragged cuticles with prominent vessels on nail folds may be seen. Blood work may reveal elevated antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti–Mi-2 and anti–Jo-1. Adult-onset Still disease is characterized by fever, arthritis, and salmon-colored patches.
Our patient’s dermatitis resolved spontaneously without treatment.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis
that resemble whiplash marks. The lesions may be extremely pruritic, and petechiae may be present in the streaks. The trunk is most commonly affected, although lesions can occur on the limbs. Mucosa is not affected. Sun exposure may exacerbate the condition. The dermatitis has been described in all ages and races, and males seem to be more affected than females.
Shiitake mushroom flagellate dermatitis typically occurs following the ingestion of raw or undercooked shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes). The mushrooms contain a polysaccharide called lentinan. Ingestion of lentinan activates interleukin-1 (IL-1), resulting in vasodilation and the subsequent dermatitis that can occur within a few hours and up to 5 days post ingestion. Associated gastrointestinal symptoms, fever, and localized swelling have been reported. The rash will resolve spontaneously over a few days to weeks.
Flagellate erythema has been described with bleomycin treatment. Other reported associations include peplomycin (a bleomycin derivative) and docetaxel. The rash may appear following administration of bleomycin by any route and has been shown to be dose independent. Onset occurs anywhere from 1 day to several months after exposure. Over time, the erythema will develop into postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Dermatomyositis may present with flagellate erythema. Other symptoms include muscle weakness and an inflammatory myopathy. A heliotrope rash on the eyelids, Gottron’s papules on the hands, ragged cuticles with prominent vessels on nail folds may be seen. Blood work may reveal elevated antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti–Mi-2 and anti–Jo-1. Adult-onset Still disease is characterized by fever, arthritis, and salmon-colored patches.
Our patient’s dermatitis resolved spontaneously without treatment.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
A 7-month-old male presents with perioral rash and fever
Patients with atopic dermatitis are at risk for developing the herpes simplex virus (HSV)–related skin complication “eczema herpeticum,” also known as Kaposi’s varicelliform eruption. Eczema herpeticum is characterized by cutaneous pain and vesicular skin lesions, most commonly secondary to infection with HSV-1. The condition may affect individuals with atopic dermatitis or other inflammatory skin disorders. Eczema herpeticum develops when the virus infects large areas of skin, rather than being confined to a small area as in the common cold sore. Eczema herpeticum often appears on the face and neck, although it can appear anywhere on the body. In some cases, the rash may be difficult to distinguish from a patient’s baseline eczema if the latter is poorly controlled. Skin symptoms of eczema herpeticum include clusters of small blisters that are itchy and painful; vesicles that appear red, purple, or black; purulent blisters; or crusting. Classically, the morphology of vesicles or crusted lesions shows a “cluster of grapes” appearance. Eczema herpeticum may present with a high fever, chills, and swollen lymph glands.
While a clinical diagnosis based on the history, physical findings, and morphologic appearance of the rash is reasonable, testing may confirm the diagnosis. The most sensitive and specific tests are polymerase chain reaction sequencing for HSV, direct fluorescent antibody stain, and/or viral culture, while Tzanck smear may show characteristic histologic changes. Treatment is with oral antiviral therapy and treatment of the eczema.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness usually affecting infants and children. The infection often involves the hands, feet, mouth, and sometimes, the genitals and buttocks. The viral exanthem is most commonly caused by the coxsackievirus, of the enterovirus family. Coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus A71 are the serotypes that are most commonly implicated as the causative agents. HFMD initially presents with a low-grade fever, reduced appetite, and general malaise. About 1-2 days later, the child may develop painful mouth sores with an exanthem that involves the dorsum of the hands, soles of the feet, buttocks, legs, and arms. The exanthem consists of vesicles surrounded by a thin halo of erythema, eventually rupturing and forming superficial ulcers with a gray-yellow base and erythematous rim. The exanthem is itchy, and can be macular, papular, or vesicular. The lesions are nonpruritic, and typically not painful. The diagnosis of HFMD usually is made clinically, although a physician can swab the mouth or get a stool sample for polymerase chain reaction, which will show the virus; treatment is supportive. In children with atopic dermatitis, lesions also can tend to concentrate in areas previously or currently affected by the dermatitis, similar to eczema herpeticum, and the terms eczema coxsackium or atypical HFMD are applicable. In young adults, the disease may present with erythematous papulovesicular lesions on the face, oral mucosa, extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities, and palms and soles; confluent, hemorrhagic, and crusted lesions also can be seen on the extremities. Systemic symptoms usually subside in a few days; the skin lesions resolve without scarring in days to weeks.
Secondary bacterial infection is not uncommon in eczema herpeticum patients, reflecting common Staphylococcus aureus infection in atopic dermatitis patients. Streptococcus also may be seen as a concurrent infection. Treatment of secondary bacterial infection may be considered based on clinic context and culture.
Impetiginized eczema also is in the differential diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. S. aureus and Streptococci are the most important causative organisms. Lesions can manifest as a single red papule or macule that quickly becomes vesicular or eroded. Subsequently, the content dries, forming honey-colored crusts. Impetigo may resolve spontaneously, although in the context of infected eczema both topical anti-inflammatory agents (e.g. topical corticosteroids) along with systemic antibiotics may be a reasonable treatment option. Although our patient had honey-colored crusting, the wound culture showed normal bacterial flora.
Primary varicella infection causes acute fever and rash, with an initial exanthem of disseminated pruritic erythematous macules that progress beyond the papular stage, forming clear, fluid-filled vesicles (like dewdrops on a rose petal). In children, the rash presents on the stomach, back, and face, and then spreads to other parts of the body. Blisters also can arise inside the mouth.
In this patient, perioral HSV PCR 1 was positive, and wound culture showed normal oral flora with no organisms or white blood cells seen. The patient responded well to oral acyclovir, and treatment of his underlying atopic dermatitis with low-potency topical corticosteroids.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither of the physicians had relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
Sources
Can Fam Physician. 2012 Dec;58(12):1358-61.
William L Weston, MD., William Howe, MD. UpToDate. Treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Christine Johnson, MD, Anna Wald, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Atypical exanthems in children.
National Eczema Association. Eczema herpeticum.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptoms and diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD).
Patients with atopic dermatitis are at risk for developing the herpes simplex virus (HSV)–related skin complication “eczema herpeticum,” also known as Kaposi’s varicelliform eruption. Eczema herpeticum is characterized by cutaneous pain and vesicular skin lesions, most commonly secondary to infection with HSV-1. The condition may affect individuals with atopic dermatitis or other inflammatory skin disorders. Eczema herpeticum develops when the virus infects large areas of skin, rather than being confined to a small area as in the common cold sore. Eczema herpeticum often appears on the face and neck, although it can appear anywhere on the body. In some cases, the rash may be difficult to distinguish from a patient’s baseline eczema if the latter is poorly controlled. Skin symptoms of eczema herpeticum include clusters of small blisters that are itchy and painful; vesicles that appear red, purple, or black; purulent blisters; or crusting. Classically, the morphology of vesicles or crusted lesions shows a “cluster of grapes” appearance. Eczema herpeticum may present with a high fever, chills, and swollen lymph glands.
While a clinical diagnosis based on the history, physical findings, and morphologic appearance of the rash is reasonable, testing may confirm the diagnosis. The most sensitive and specific tests are polymerase chain reaction sequencing for HSV, direct fluorescent antibody stain, and/or viral culture, while Tzanck smear may show characteristic histologic changes. Treatment is with oral antiviral therapy and treatment of the eczema.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness usually affecting infants and children. The infection often involves the hands, feet, mouth, and sometimes, the genitals and buttocks. The viral exanthem is most commonly caused by the coxsackievirus, of the enterovirus family. Coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus A71 are the serotypes that are most commonly implicated as the causative agents. HFMD initially presents with a low-grade fever, reduced appetite, and general malaise. About 1-2 days later, the child may develop painful mouth sores with an exanthem that involves the dorsum of the hands, soles of the feet, buttocks, legs, and arms. The exanthem consists of vesicles surrounded by a thin halo of erythema, eventually rupturing and forming superficial ulcers with a gray-yellow base and erythematous rim. The exanthem is itchy, and can be macular, papular, or vesicular. The lesions are nonpruritic, and typically not painful. The diagnosis of HFMD usually is made clinically, although a physician can swab the mouth or get a stool sample for polymerase chain reaction, which will show the virus; treatment is supportive. In children with atopic dermatitis, lesions also can tend to concentrate in areas previously or currently affected by the dermatitis, similar to eczema herpeticum, and the terms eczema coxsackium or atypical HFMD are applicable. In young adults, the disease may present with erythematous papulovesicular lesions on the face, oral mucosa, extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities, and palms and soles; confluent, hemorrhagic, and crusted lesions also can be seen on the extremities. Systemic symptoms usually subside in a few days; the skin lesions resolve without scarring in days to weeks.
Secondary bacterial infection is not uncommon in eczema herpeticum patients, reflecting common Staphylococcus aureus infection in atopic dermatitis patients. Streptococcus also may be seen as a concurrent infection. Treatment of secondary bacterial infection may be considered based on clinic context and culture.
Impetiginized eczema also is in the differential diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. S. aureus and Streptococci are the most important causative organisms. Lesions can manifest as a single red papule or macule that quickly becomes vesicular or eroded. Subsequently, the content dries, forming honey-colored crusts. Impetigo may resolve spontaneously, although in the context of infected eczema both topical anti-inflammatory agents (e.g. topical corticosteroids) along with systemic antibiotics may be a reasonable treatment option. Although our patient had honey-colored crusting, the wound culture showed normal bacterial flora.
Primary varicella infection causes acute fever and rash, with an initial exanthem of disseminated pruritic erythematous macules that progress beyond the papular stage, forming clear, fluid-filled vesicles (like dewdrops on a rose petal). In children, the rash presents on the stomach, back, and face, and then spreads to other parts of the body. Blisters also can arise inside the mouth.
In this patient, perioral HSV PCR 1 was positive, and wound culture showed normal oral flora with no organisms or white blood cells seen. The patient responded well to oral acyclovir, and treatment of his underlying atopic dermatitis with low-potency topical corticosteroids.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither of the physicians had relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
Sources
Can Fam Physician. 2012 Dec;58(12):1358-61.
William L Weston, MD., William Howe, MD. UpToDate. Treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Christine Johnson, MD, Anna Wald, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Atypical exanthems in children.
National Eczema Association. Eczema herpeticum.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptoms and diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD).
Patients with atopic dermatitis are at risk for developing the herpes simplex virus (HSV)–related skin complication “eczema herpeticum,” also known as Kaposi’s varicelliform eruption. Eczema herpeticum is characterized by cutaneous pain and vesicular skin lesions, most commonly secondary to infection with HSV-1. The condition may affect individuals with atopic dermatitis or other inflammatory skin disorders. Eczema herpeticum develops when the virus infects large areas of skin, rather than being confined to a small area as in the common cold sore. Eczema herpeticum often appears on the face and neck, although it can appear anywhere on the body. In some cases, the rash may be difficult to distinguish from a patient’s baseline eczema if the latter is poorly controlled. Skin symptoms of eczema herpeticum include clusters of small blisters that are itchy and painful; vesicles that appear red, purple, or black; purulent blisters; or crusting. Classically, the morphology of vesicles or crusted lesions shows a “cluster of grapes” appearance. Eczema herpeticum may present with a high fever, chills, and swollen lymph glands.
While a clinical diagnosis based on the history, physical findings, and morphologic appearance of the rash is reasonable, testing may confirm the diagnosis. The most sensitive and specific tests are polymerase chain reaction sequencing for HSV, direct fluorescent antibody stain, and/or viral culture, while Tzanck smear may show characteristic histologic changes. Treatment is with oral antiviral therapy and treatment of the eczema.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness usually affecting infants and children. The infection often involves the hands, feet, mouth, and sometimes, the genitals and buttocks. The viral exanthem is most commonly caused by the coxsackievirus, of the enterovirus family. Coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus A71 are the serotypes that are most commonly implicated as the causative agents. HFMD initially presents with a low-grade fever, reduced appetite, and general malaise. About 1-2 days later, the child may develop painful mouth sores with an exanthem that involves the dorsum of the hands, soles of the feet, buttocks, legs, and arms. The exanthem consists of vesicles surrounded by a thin halo of erythema, eventually rupturing and forming superficial ulcers with a gray-yellow base and erythematous rim. The exanthem is itchy, and can be macular, papular, or vesicular. The lesions are nonpruritic, and typically not painful. The diagnosis of HFMD usually is made clinically, although a physician can swab the mouth or get a stool sample for polymerase chain reaction, which will show the virus; treatment is supportive. In children with atopic dermatitis, lesions also can tend to concentrate in areas previously or currently affected by the dermatitis, similar to eczema herpeticum, and the terms eczema coxsackium or atypical HFMD are applicable. In young adults, the disease may present with erythematous papulovesicular lesions on the face, oral mucosa, extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities, and palms and soles; confluent, hemorrhagic, and crusted lesions also can be seen on the extremities. Systemic symptoms usually subside in a few days; the skin lesions resolve without scarring in days to weeks.
Secondary bacterial infection is not uncommon in eczema herpeticum patients, reflecting common Staphylococcus aureus infection in atopic dermatitis patients. Streptococcus also may be seen as a concurrent infection. Treatment of secondary bacterial infection may be considered based on clinic context and culture.
Impetiginized eczema also is in the differential diagnosis of eczema herpeticum. S. aureus and Streptococci are the most important causative organisms. Lesions can manifest as a single red papule or macule that quickly becomes vesicular or eroded. Subsequently, the content dries, forming honey-colored crusts. Impetigo may resolve spontaneously, although in the context of infected eczema both topical anti-inflammatory agents (e.g. topical corticosteroids) along with systemic antibiotics may be a reasonable treatment option. Although our patient had honey-colored crusting, the wound culture showed normal bacterial flora.
Primary varicella infection causes acute fever and rash, with an initial exanthem of disseminated pruritic erythematous macules that progress beyond the papular stage, forming clear, fluid-filled vesicles (like dewdrops on a rose petal). In children, the rash presents on the stomach, back, and face, and then spreads to other parts of the body. Blisters also can arise inside the mouth.
In this patient, perioral HSV PCR 1 was positive, and wound culture showed normal oral flora with no organisms or white blood cells seen. The patient responded well to oral acyclovir, and treatment of his underlying atopic dermatitis with low-potency topical corticosteroids.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Neither of the physicians had relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
Sources
Can Fam Physician. 2012 Dec;58(12):1358-61.
William L Weston, MD., William Howe, MD. UpToDate. Treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Christine Johnson, MD, Anna Wald, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH. UpToDate. Atypical exanthems in children.
National Eczema Association. Eczema herpeticum.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptoms and diagnosis of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD).
Nail dystrophy and nail plate thinning
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
At a follow-up visit, a biopsy of the skin on the fingertips was performed, which showed lichenoid lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate with associated hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, and acanthosis.
No fungal elements were seen. The findings were consistent with lichen planus.
The patient was started on hydroxychloroquine. It was recommended she start a 6-week course of oral prednisone, but the mother was opposed to systemic treatment because of potential side effects.
She continued topical betamethasone without much change. Topical tacrolimus later was recommended to use on off days of betamethasone, which led to no improvement. Narrow-band UVB also was started with minimal improvement. Unfortunately,
Nail lichen planus (NLP) in children is not a common condition.1 In a recent series from Chiheb et al., NLP was reported in 90 patients, of which 40% were children; a quarter of the patients reported having extracutaneous involvement as well.2 In another childhood LP series,14 % of the children presented with nail disease.3 It can be a severe disease that, if not treated aggressively, may lead to destruction of the nail bed. This condition seems to be more prevalent in boys than girls and more prevalent in African American children.3 Unfortunately, in this patient’s case, the mother was hesitant to use systemic therapy and aggressive treatment was delayed.
Possible but not clear associations with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, autoimmune thyroiditis, myasthenia gravis, alopecia areata, thymoma, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, atopic dermatitis, and lichen nitidus have been described in children with LP.
The clinical characteristics of NLP include nail plate thinning with longitudinal ridging and fissuring, with or without pterygium; trachyonychia; and erythema of the lunula when the nail matrix is involved. When the nail bed is affected, the patient can present with onycholysis with or without subungual hyperkeratosis and violaceous hue of the nail bed.4 NLP can have three different clinical presentations described by Tosti et al., which include typical NLP, 20‐nail dystrophy (trachyonychia), and idiopathic nail atrophy. Idiopathic nail atrophy is described solely in children as an acute and rapid progression that leads to destruction of the nail within months, which appears to be the clinical presentation in our patient.
The differential diagnosis of nail dystrophy in children includes infectious processes such as onychomycosis, especially when children present with onycholysis and subungual hyperkeratosis. Because of this, it is recommended to perform a nail culture or submit a sample of nail clippings for microscopic evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis prior to starting systemic therapy in children. Fingernail involvement without toenail involvement is an unusual presentation of onychomycosis.
Twenty-nail dystrophy – also known as trachyonychia – can be caused by several inflammatory skin conditions such as lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, pemphigus vulgaris, and alopecia areata. Clinically, there is uniformly monomorphic thinning of the nail plate with longitudinal ridging without splitting or pterygium.1 This is a benign condition and should not cause scarring. About 10% of the cases of 20-nail dystrophy are caused by lichen planus.
Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail pitting, oil spots on the nail plate, leukonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis, and onycholysis, as well as nail crumbling, which were not seen in our patient. Although her initial presentation was of 20-nail dystrophy, which also can be a presentation of nail psoriasis, its rapid evolution with associated nail atrophy and pterygium make it unlikely to be psoriasis in this particular patient.
Patients with pachyonychia congenita – which is a genetic disorder or keratinization caused by mutations on several genes encoding keratin such as K6a, K16, K17, K6b, and possibly K6c – present with nail thickening (pachyonychia) and discoloration of the nails, as well as pincer nails. These patients also present with oral leukokeratosis and focal palmoplantar keratoderma.
The main treatment of lichen planus is potent topical corticosteroids.
For nail disease, topical treatment may not be effective and systemic treatment may be necessary. Systemic corticosteroids have been used in several pediatric series varying from a short course given at a dose of 1- 2 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to a longer 3-month course followed by tapering.3 There are several protocols of intramuscular triamcinolone at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg in children in once a month injections for about 3 months that have been reported successful with minimal side effects.1 Other medications reported useful in patients with NLP include dapsone and acitretin. Other treatment options include narrow-band UVB and PUVA.3
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Aug;137(8):1027-32.
2. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Jan;142(1):21-5.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;31(1):59-67.
4. Dermatological diseases, in “Nails: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Surgery,” 3rd ed. (Oxford: Elsevier Saunders, 2005, p. 105).
An 8-year-old female child comes to our pediatric dermatology clinic for evaluation of onychomycosis on her fingernails. The mother stated the child started developing funny-looking nails 1 year prior to the visit. It started with only two fingernails affected and now has spread to all her fingernails. Her toenails are not involved.
She denied any pain or itching. She initially was treated with topical antifungal medications as well as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, and a 6-week course of oral griseofulvin without any improvement. Her nails progressively have gotten much worse. She has no history of atopic dermatitis or any other skin conditions. She denied any joint pain, sun sensitivity, hair loss, or any other symptoms. The mother denied any family history of nail fungus, ringworm, psoriasis, or eczema.
She likes to play basketball and enjoys arts and crafts. She has a cat and a dog; neither of them have any skin problems.
On physical examination, there is nail dystrophy with nail plate thinning and longitudinal fissuring of all fingernails but not of the toenails. She also has hyperpigmented violaceous plaques on the surrounding periungual skin. There are no other skin lesions, and there are no oral or genital lesions. There is no scalp involvement or hair loss. At follow-up several months later, she had complete destruction of the nail plate with scar formation.
A fungal culture was performed, as well as microscopic analysis of the nail with periodic acid fast and giemsa stains, which showed no fungal organisms.
She initially was treated with topical betamethasone twice a day for 6 weeks and then 2 weeks on and 2 weeks off without much change.