User login
Vaccine rollout on track, expect 300 million doses through March: Feds
If the initial success of the Pfizer-BioNTech rollout continues, and emergency use authorization (EAU) is granted to Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines in development, Operation Warp Speed officials expect to have 300 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines to distribute across the United States between now and March 31.
The initial rollout remains on track, said Alex Azar, US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) secretary, during a media briefing today. “We continue to have good news to report. As of today, shipments of vaccine will have been delivered to every delivery site identified by public health jurisdictions for our first wave of shipments.”
Anomalies in shipments to California and Alabama arose when temperature monitors showed the Pfizer vaccine dropped lower than the recommended -80 ºC (-112 °F). These vaccine trays remained on delivery trucks and were returned to Pfizer for prompt replacement, said Operation Warp Speed Chief Operating Officer Gen. Gustave F. Perna.
Azar estimated another 2 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine will be available next week. “And if the Moderna vaccine is authorized by the FDA in the coming days, we have allocated nearly 5.9 million doses of that product.”
The Moderna vaccine data released this week look promising, said Moncef Slaoui, PhD, Operation Warp Speed chief scientific adviser. “In the short term, I expect the protection to be quite significant.”
The findings in the first 2 weeks after the first dose show up to 65% protection, he said, and predicted the second-dose efficacy data will be coming in the next few weeks.
Enrollment in the phase 3 Johnson & Johnson trial with nearly 44,000 participants is expected to end December 17. Initial efficacy results are anticipated by early January, with more complete efficacy numbers by late January, Slaoui said.
The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine trial also is underway with enrollment continuing. “We expect accruement to end in late December or early next year, with first results expected probably in February,” Slaoui said.
Antibody treatments underutilized
The media briefing also addressed COVID-19 therapeutics. Azar reported low uptake of available antibody therapies. “I want to remind Americans that there are two authorized antibody treatments that Operation Warp Speed has supported. They can help prevent hospitalization in those patients with the highest risk for severe disease.”
The higher-risk group includes those who are 65 and older and people with comorbid conditions that put them at increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization.
The federal government allocated more than 330,000 doses of these treatments and many states have product available, Azar said.
Slaoui agreed, saying there is a “disappointing level of usage of monoclonal antibody therapy in hospitals. We look forward to that improving.”
Up to 3 billion vaccine doses possible
“We now have more than 900 million doses of the vaccine we have contracted delivery for,” Azar said. The government has options to increase that to a total of 3 billion doses.
In addition to the 100 million Pfizer vaccine doses and 100 million Moderna doses already ordered, the government just took an option for another 100 million Moderna doses for the second quarter of 2021. Operation Warp Speed officials are negotiating with Pfizer for additional product as well.
Azar added that there are 100 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in active production and expects AstraZeneca can provide 300 million doses of their product.
With the possibility of three or more vaccine products and with 330 million Americans, minus the 70 million or so children under age 16, “we believe we will actually have surplus supplies,” Azar said. Plans are to take the US surplus vaccine and surplus manufacturing capacity “and use that for the benefit of the world community.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If the initial success of the Pfizer-BioNTech rollout continues, and emergency use authorization (EAU) is granted to Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines in development, Operation Warp Speed officials expect to have 300 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines to distribute across the United States between now and March 31.
The initial rollout remains on track, said Alex Azar, US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) secretary, during a media briefing today. “We continue to have good news to report. As of today, shipments of vaccine will have been delivered to every delivery site identified by public health jurisdictions for our first wave of shipments.”
Anomalies in shipments to California and Alabama arose when temperature monitors showed the Pfizer vaccine dropped lower than the recommended -80 ºC (-112 °F). These vaccine trays remained on delivery trucks and were returned to Pfizer for prompt replacement, said Operation Warp Speed Chief Operating Officer Gen. Gustave F. Perna.
Azar estimated another 2 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine will be available next week. “And if the Moderna vaccine is authorized by the FDA in the coming days, we have allocated nearly 5.9 million doses of that product.”
The Moderna vaccine data released this week look promising, said Moncef Slaoui, PhD, Operation Warp Speed chief scientific adviser. “In the short term, I expect the protection to be quite significant.”
The findings in the first 2 weeks after the first dose show up to 65% protection, he said, and predicted the second-dose efficacy data will be coming in the next few weeks.
Enrollment in the phase 3 Johnson & Johnson trial with nearly 44,000 participants is expected to end December 17. Initial efficacy results are anticipated by early January, with more complete efficacy numbers by late January, Slaoui said.
The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine trial also is underway with enrollment continuing. “We expect accruement to end in late December or early next year, with first results expected probably in February,” Slaoui said.
Antibody treatments underutilized
The media briefing also addressed COVID-19 therapeutics. Azar reported low uptake of available antibody therapies. “I want to remind Americans that there are two authorized antibody treatments that Operation Warp Speed has supported. They can help prevent hospitalization in those patients with the highest risk for severe disease.”
The higher-risk group includes those who are 65 and older and people with comorbid conditions that put them at increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization.
The federal government allocated more than 330,000 doses of these treatments and many states have product available, Azar said.
Slaoui agreed, saying there is a “disappointing level of usage of monoclonal antibody therapy in hospitals. We look forward to that improving.”
Up to 3 billion vaccine doses possible
“We now have more than 900 million doses of the vaccine we have contracted delivery for,” Azar said. The government has options to increase that to a total of 3 billion doses.
In addition to the 100 million Pfizer vaccine doses and 100 million Moderna doses already ordered, the government just took an option for another 100 million Moderna doses for the second quarter of 2021. Operation Warp Speed officials are negotiating with Pfizer for additional product as well.
Azar added that there are 100 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in active production and expects AstraZeneca can provide 300 million doses of their product.
With the possibility of three or more vaccine products and with 330 million Americans, minus the 70 million or so children under age 16, “we believe we will actually have surplus supplies,” Azar said. Plans are to take the US surplus vaccine and surplus manufacturing capacity “and use that for the benefit of the world community.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
If the initial success of the Pfizer-BioNTech rollout continues, and emergency use authorization (EAU) is granted to Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines in development, Operation Warp Speed officials expect to have 300 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines to distribute across the United States between now and March 31.
The initial rollout remains on track, said Alex Azar, US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) secretary, during a media briefing today. “We continue to have good news to report. As of today, shipments of vaccine will have been delivered to every delivery site identified by public health jurisdictions for our first wave of shipments.”
Anomalies in shipments to California and Alabama arose when temperature monitors showed the Pfizer vaccine dropped lower than the recommended -80 ºC (-112 °F). These vaccine trays remained on delivery trucks and were returned to Pfizer for prompt replacement, said Operation Warp Speed Chief Operating Officer Gen. Gustave F. Perna.
Azar estimated another 2 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine will be available next week. “And if the Moderna vaccine is authorized by the FDA in the coming days, we have allocated nearly 5.9 million doses of that product.”
The Moderna vaccine data released this week look promising, said Moncef Slaoui, PhD, Operation Warp Speed chief scientific adviser. “In the short term, I expect the protection to be quite significant.”
The findings in the first 2 weeks after the first dose show up to 65% protection, he said, and predicted the second-dose efficacy data will be coming in the next few weeks.
Enrollment in the phase 3 Johnson & Johnson trial with nearly 44,000 participants is expected to end December 17. Initial efficacy results are anticipated by early January, with more complete efficacy numbers by late January, Slaoui said.
The AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine trial also is underway with enrollment continuing. “We expect accruement to end in late December or early next year, with first results expected probably in February,” Slaoui said.
Antibody treatments underutilized
The media briefing also addressed COVID-19 therapeutics. Azar reported low uptake of available antibody therapies. “I want to remind Americans that there are two authorized antibody treatments that Operation Warp Speed has supported. They can help prevent hospitalization in those patients with the highest risk for severe disease.”
The higher-risk group includes those who are 65 and older and people with comorbid conditions that put them at increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization.
The federal government allocated more than 330,000 doses of these treatments and many states have product available, Azar said.
Slaoui agreed, saying there is a “disappointing level of usage of monoclonal antibody therapy in hospitals. We look forward to that improving.”
Up to 3 billion vaccine doses possible
“We now have more than 900 million doses of the vaccine we have contracted delivery for,” Azar said. The government has options to increase that to a total of 3 billion doses.
In addition to the 100 million Pfizer vaccine doses and 100 million Moderna doses already ordered, the government just took an option for another 100 million Moderna doses for the second quarter of 2021. Operation Warp Speed officials are negotiating with Pfizer for additional product as well.
Azar added that there are 100 million doses of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine in active production and expects AstraZeneca can provide 300 million doses of their product.
With the possibility of three or more vaccine products and with 330 million Americans, minus the 70 million or so children under age 16, “we believe we will actually have surplus supplies,” Azar said. Plans are to take the US surplus vaccine and surplus manufacturing capacity “and use that for the benefit of the world community.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Urgent recall for Penumbra JET 7 Xtra Flex reperfusion catheters
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“All users should stop using this device, and facilities should remove these devices from inventory,” the recall notice, posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website, advises.
The recall covers the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, which was cleared for use in June 2019, and the JET 7MAX configuration (which includes the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter and MAX delivery device), which was cleared in February of this year.
The recall does not apply to the Penumbra JET 7 reperfusion catheter with standard tip.
The FDA says it has received over 200 medical device reports (MDRs) associated with the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter, including reports of deaths, serious injuries, and malfunctions.
Twenty of these MDRs describe 14 unique patient deaths. Other MDRs describe serious patient injury, such as vessel damage, hemorrhage, and cerebral infarction.
Device malfunctions described in the reports include ballooning, expansion, rupture, breakage or complete separation, and exposure of internal support coils near the distal tip region of the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter.
According to the FDA, bench testing by the manufacturer, in which the catheter distal tip is plugged and pressurized to failure, indicates that the JET 7 Xtra Flex catheter is not able to withstand the same burst pressures to failure as the manufacturer’s other large-bore aspiration catheters used to remove thrombus for patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Penumbra’s urgent medical device recall letter advises health care providers and facilities to remove and quarantine all unused devices covered by this recall, to complete the product identification and return form, and to return all products to Penumbra in accordance with instructions provided.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Penumbra customer service by phone at 888-272-4606 or by email at [email protected].
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Parents favored virtual learning over in-person school attendance
Parents of school-aged children were generally more comfortable with full-time virtual learning in schools in the fall of 2020, compared with full-capacity in-person attendance, according to a survey conducted in July.
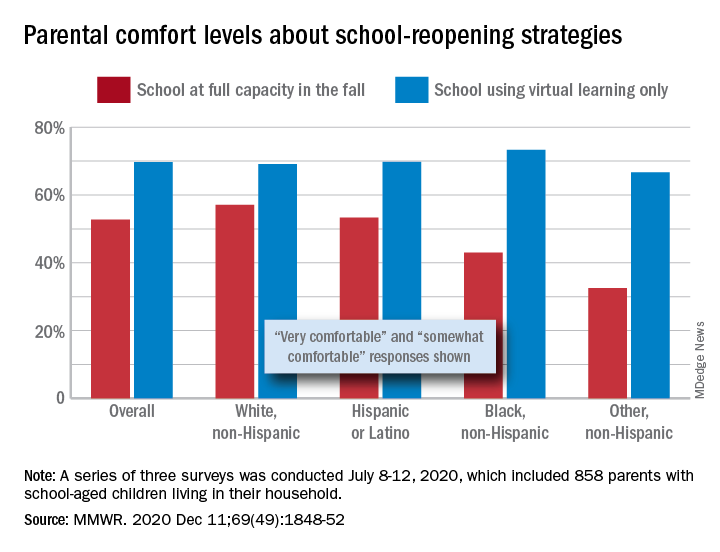
Those of racial/ethnic minorities, however, “were less likely to feel that schools should reopen for all students and were more concerned about” several aspects of in-person instruction than were White parents, Leah K. Gilbert, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Team said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A slim majority, just under 53% of the 858 parents surveyed, said that they were very or somewhat comfortable with their children returning to schools that were reopening at full capacity, while almost 70% said they were very/somewhat comfortable with schools going exclusively with virtual learning, the investigators reported.
The question about full-capacity attendance in particular showed considerable variation by race and ethnicity, with 57% of White parents saying they were very/somewhat comfortable, versus 53% of Hispanic or Latino parents, 43% of Black parents, and 32.5% of parents of other races/ethnicities (American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, or multiracial).
Comfort levels were closer regarding virtual learning: Parents of other races/ethnicities were lowest at 67% and Black parents were highest at 73%. When asked about schools reopening at 50% capacity and 50% virtual learning, Black parents were again lowest at 58% with strong or moderate comfort and White parents were highest at 68%, Dr. Gilbert and associates said.
“Although the majority of parent respondents had concerns about both school reopening for in-person instruction and virtual learning, the perceived risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor health outcomes might account for the differences in parental attitudes and concerns by race and ethnicity,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Gilbert LK et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec 11;69(49):1848-52.
Parents of school-aged children were generally more comfortable with full-time virtual learning in schools in the fall of 2020, compared with full-capacity in-person attendance, according to a survey conducted in July.

Those of racial/ethnic minorities, however, “were less likely to feel that schools should reopen for all students and were more concerned about” several aspects of in-person instruction than were White parents, Leah K. Gilbert, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Team said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A slim majority, just under 53% of the 858 parents surveyed, said that they were very or somewhat comfortable with their children returning to schools that were reopening at full capacity, while almost 70% said they were very/somewhat comfortable with schools going exclusively with virtual learning, the investigators reported.
The question about full-capacity attendance in particular showed considerable variation by race and ethnicity, with 57% of White parents saying they were very/somewhat comfortable, versus 53% of Hispanic or Latino parents, 43% of Black parents, and 32.5% of parents of other races/ethnicities (American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, or multiracial).
Comfort levels were closer regarding virtual learning: Parents of other races/ethnicities were lowest at 67% and Black parents were highest at 73%. When asked about schools reopening at 50% capacity and 50% virtual learning, Black parents were again lowest at 58% with strong or moderate comfort and White parents were highest at 68%, Dr. Gilbert and associates said.
“Although the majority of parent respondents had concerns about both school reopening for in-person instruction and virtual learning, the perceived risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor health outcomes might account for the differences in parental attitudes and concerns by race and ethnicity,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Gilbert LK et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec 11;69(49):1848-52.
Parents of school-aged children were generally more comfortable with full-time virtual learning in schools in the fall of 2020, compared with full-capacity in-person attendance, according to a survey conducted in July.

Those of racial/ethnic minorities, however, “were less likely to feel that schools should reopen for all students and were more concerned about” several aspects of in-person instruction than were White parents, Leah K. Gilbert, MD, and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s COVID-19 Response Team said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
A slim majority, just under 53% of the 858 parents surveyed, said that they were very or somewhat comfortable with their children returning to schools that were reopening at full capacity, while almost 70% said they were very/somewhat comfortable with schools going exclusively with virtual learning, the investigators reported.
The question about full-capacity attendance in particular showed considerable variation by race and ethnicity, with 57% of White parents saying they were very/somewhat comfortable, versus 53% of Hispanic or Latino parents, 43% of Black parents, and 32.5% of parents of other races/ethnicities (American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, or multiracial).
Comfort levels were closer regarding virtual learning: Parents of other races/ethnicities were lowest at 67% and Black parents were highest at 73%. When asked about schools reopening at 50% capacity and 50% virtual learning, Black parents were again lowest at 58% with strong or moderate comfort and White parents were highest at 68%, Dr. Gilbert and associates said.
“Although the majority of parent respondents had concerns about both school reopening for in-person instruction and virtual learning, the perceived risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor health outcomes might account for the differences in parental attitudes and concerns by race and ethnicity,” they wrote.
SOURCE: Gilbert LK et al. MMWR. 2020 Dec 11;69(49):1848-52.
FROM MMWR
FDA safety alert: Face masks with metal can burn during MRI
After a patient’s face was burned in the outline of a mask worn during a 3-Tesla MRI neck scan, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cautioned that face masks containing metal can heat to unsafe temperatures during scanning.
Clinicians have known for years to ask patients to remove all metal jewelry and other objects prior to an MRI. The widespread wearing of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic, however, adds one more consideration to the list.
The FDA’s December 7 safety communication applies to surgical and nonsurgical face masks and respirators.
The injury risk relates to rapid heating of metal components. Many face masks contain a nose wire or metal clip that helps the product conform to the face. Some masks contain metal nanoparticles, while others feature antimicrobial coatings with silver or copper. Each of these products should be avoided during MRI scanning. Also watch out for staples on headbands, the FDA warned.
If the metal content of a face mask is unknown, the FDA suggests providing the patient with a facial covering that is known not to contain any metal.
Robert E. Watson Jr, MD, PhD, chair of the American College of Radiology (ACR) Committee on MR Safety, agreed. He recommended that facilities “provide patients with masks known to be MRI-safe and not permit patient-owned masks in the MRI.”
Watson suggested this strategy at a time when face masks are required.
“COVID-19 safety protocols require that patients wear masks when being scanned, to decrease infection risk to MRI staff, decrease risk of contaminating the MRI scanner, and to protect themselves from infection,” he told Medscape Medical News. “Any conducting metal that enters the MRI machine is at risk of heating due to the radiofrequency fields inherent to image generation.”
Adverse events related to the metal components of a face mask should be reported to the FDA using the MedWatch voluntary reporting form. In addition, healthcare providers subject to the FDA user facility reporting requirements should follow procedures at their facilities to report such events.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After a patient’s face was burned in the outline of a mask worn during a 3-Tesla MRI neck scan, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cautioned that face masks containing metal can heat to unsafe temperatures during scanning.
Clinicians have known for years to ask patients to remove all metal jewelry and other objects prior to an MRI. The widespread wearing of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic, however, adds one more consideration to the list.
The FDA’s December 7 safety communication applies to surgical and nonsurgical face masks and respirators.
The injury risk relates to rapid heating of metal components. Many face masks contain a nose wire or metal clip that helps the product conform to the face. Some masks contain metal nanoparticles, while others feature antimicrobial coatings with silver or copper. Each of these products should be avoided during MRI scanning. Also watch out for staples on headbands, the FDA warned.
If the metal content of a face mask is unknown, the FDA suggests providing the patient with a facial covering that is known not to contain any metal.
Robert E. Watson Jr, MD, PhD, chair of the American College of Radiology (ACR) Committee on MR Safety, agreed. He recommended that facilities “provide patients with masks known to be MRI-safe and not permit patient-owned masks in the MRI.”
Watson suggested this strategy at a time when face masks are required.
“COVID-19 safety protocols require that patients wear masks when being scanned, to decrease infection risk to MRI staff, decrease risk of contaminating the MRI scanner, and to protect themselves from infection,” he told Medscape Medical News. “Any conducting metal that enters the MRI machine is at risk of heating due to the radiofrequency fields inherent to image generation.”
Adverse events related to the metal components of a face mask should be reported to the FDA using the MedWatch voluntary reporting form. In addition, healthcare providers subject to the FDA user facility reporting requirements should follow procedures at their facilities to report such events.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After a patient’s face was burned in the outline of a mask worn during a 3-Tesla MRI neck scan, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cautioned that face masks containing metal can heat to unsafe temperatures during scanning.
Clinicians have known for years to ask patients to remove all metal jewelry and other objects prior to an MRI. The widespread wearing of face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic, however, adds one more consideration to the list.
The FDA’s December 7 safety communication applies to surgical and nonsurgical face masks and respirators.
The injury risk relates to rapid heating of metal components. Many face masks contain a nose wire or metal clip that helps the product conform to the face. Some masks contain metal nanoparticles, while others feature antimicrobial coatings with silver or copper. Each of these products should be avoided during MRI scanning. Also watch out for staples on headbands, the FDA warned.
If the metal content of a face mask is unknown, the FDA suggests providing the patient with a facial covering that is known not to contain any metal.
Robert E. Watson Jr, MD, PhD, chair of the American College of Radiology (ACR) Committee on MR Safety, agreed. He recommended that facilities “provide patients with masks known to be MRI-safe and not permit patient-owned masks in the MRI.”
Watson suggested this strategy at a time when face masks are required.
“COVID-19 safety protocols require that patients wear masks when being scanned, to decrease infection risk to MRI staff, decrease risk of contaminating the MRI scanner, and to protect themselves from infection,” he told Medscape Medical News. “Any conducting metal that enters the MRI machine is at risk of heating due to the radiofrequency fields inherent to image generation.”
Adverse events related to the metal components of a face mask should be reported to the FDA using the MedWatch voluntary reporting form. In addition, healthcare providers subject to the FDA user facility reporting requirements should follow procedures at their facilities to report such events.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves first agent for PSMA-PET imaging in prostate cancer
A radioactive diagnostic agent has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with prostate cancer, but only for those treated at two institutions in California.
The product, Gallium 68 PSMA-11 (Ga 68 PSMA-11), is the first agent approved specifically for use in positron-emission tomography (PET) imaging of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions in men with prostate cancer, the FDA noted.
This imaging approach can “detect whether or not the cancer has spread to other parts of the body,” commented Alex Gorovets, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Specialty Medicine in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Ga 68 PSMA-11 is indicated for use in patients with suspected prostate cancer metastasis whose conditions are potentially curable by surgery or radiotherapy and in patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence, as determined on the basis of elevated serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Institutional use only
Ga 68 PSMA-11 has been approved for institutional use at the University of California, Los Angeles and the University of California, San Francisco under an academic new drug application (NDA).
The FDA approval was based partly on a clinical trial conducted by the UCSF and UCLA research teams on the effectiveness of PSMA-PET.
“It is rare for academic institutions to obtain FDA approval of a drug, and this unique collaboration has led to what is one of the first coapprovals of a drug at two institutions,” said Thomas Hope, MD, an associate professor at UCSF. “We hope that this first step will lead to a more widespread availability of this imaging test to men with prostate cancer throughout the country.”
Ga 68 PSMA-11 was developed outside the United States at the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
A commercial NDA from Telix Pharmaceuticals for TL591-CDx, a radiopharmaceutical cold kit for the preparation of Ga 68 PSMA-11 injection, is under consideration by the FDA.
The agency noted that two other PET diagnostic agents – fluciclovine F18 and choline C11 – are approved for prostate cancer imaging. However, they are only approved for use in patients with suspected cancer recurrence.
Trial results with PSMA-PET/CT
“PSMA-PET/CT is a novel molecular and functional imaging modality specific for prostate cancer cells that has good sensitivity and outstanding specificity in detecting metastasis,” commented T. Martin Ma, MD, PhD, of UCLA.
Dr. Ma presented a U.S. study on the technique at the recent annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology. That study showed that PSMA-PET/CT led to nodal upstaging in 19.7% of patients and metastasis upstaging in 9.4%.
He said these results were similar to those from the Australian proPSMA trial, which was published in The Lancet earlier this year. That trial found PSMA-PET/CT to be superior to conventional imaging with CT and bone scanning for primary staging of high-risk prostate cancer.
“These findings carry significant clinical implications and can affect treatment decision-making,” Dr. Ma commented.
“PSMA-PET has been a real game changer in high-risk prostate cancer and has implications in the various stages of prostate cancer management from diagnosis and staging to theranostics,” said Renu Eapen, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, who was not involved in either study.
“PSMA-PET/CT has challenged conventional imaging in staging before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy,” Dr. Eapen added.
The accuracy of PSMA-PET/CT was 27% higher than that of conventional imaging in the proPSMA trial, she noted in an interview last month. This superior accuracy can ultimately affect management. The imaging has additional benefits of lower radiation dose as well as reproducibility with high reporter agreement, potentially making it a “one-stop-shop” scan.
Trial results with Ga 68 PSMA-11
The safety and efficacy of Ga 68 PSMA-11 were evaluated in two prospective clinical trials with a total of 960 men with prostate cancer, each of whom received one injection of the product.
The first trial involved 325 patients with biopsy-proven prostate cancer who underwent PET/CT or PET/MRI scans performed with Ga 68 PSMA-11.
“These patients were candidates for surgical removal of the prostate gland and pelvic lymph nodes and were considered at higher risk for metastasis. Among the patients who proceeded to surgery, those with positive readings in the pelvic lymph nodes on Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET had a clinically important rate of metastatic cancer confirmed by surgical pathology,” the FDA noted.
“The availability of this information prior to treatment is expected to have important implications for patient care,” the FDA commented. “For example, it may spare certain patients from undergoing unnecessary surgery.”
The second trial enrolled 635 patients with rising serum PSA levels after initial prostate surgery or radiotherapy. All patients received a single Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET/CT scan or PET/MRI scan.
About three-quarters of patients (74%) had at least one positive lesion detected by Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET in at least one region – bone, prostate bed, pelvic lymph node, or extra-pelvic soft tissue.
“In patients with positive Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET readings who had correlative tissue pathology from biopsies, results from baseline or follow-up imaging by conventional methods, and serial PSA levels available for comparison, local recurrence or metastasis of prostate cancer was confirmed in an estimated 91% of cases,” the FDA noted.
“Thus, the second trial demonstrated that Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET can detect sites of disease in patients with biochemical evidence of recurrent prostate cancer, thereby providing important information that may impact the approach to therapy,” the agency added.
The FDA also noted that no serious adverse reactions were attributed to Ga 68 PSMA-11. The most common adverse reactions were nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness.
The FDA said there is a risk for misdiagnosis because Ga 68 PSMA-11 binding may occur in other types of cancer, and certain nonmalignant processes may lead to errors in interpreting images. In addition, there are radiation risks because Ga 68 PSMA-11 contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure, which is associated with an increased risk for cancer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A radioactive diagnostic agent has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with prostate cancer, but only for those treated at two institutions in California.
The product, Gallium 68 PSMA-11 (Ga 68 PSMA-11), is the first agent approved specifically for use in positron-emission tomography (PET) imaging of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions in men with prostate cancer, the FDA noted.
This imaging approach can “detect whether or not the cancer has spread to other parts of the body,” commented Alex Gorovets, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Specialty Medicine in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Ga 68 PSMA-11 is indicated for use in patients with suspected prostate cancer metastasis whose conditions are potentially curable by surgery or radiotherapy and in patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence, as determined on the basis of elevated serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Institutional use only
Ga 68 PSMA-11 has been approved for institutional use at the University of California, Los Angeles and the University of California, San Francisco under an academic new drug application (NDA).
The FDA approval was based partly on a clinical trial conducted by the UCSF and UCLA research teams on the effectiveness of PSMA-PET.
“It is rare for academic institutions to obtain FDA approval of a drug, and this unique collaboration has led to what is one of the first coapprovals of a drug at two institutions,” said Thomas Hope, MD, an associate professor at UCSF. “We hope that this first step will lead to a more widespread availability of this imaging test to men with prostate cancer throughout the country.”
Ga 68 PSMA-11 was developed outside the United States at the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
A commercial NDA from Telix Pharmaceuticals for TL591-CDx, a radiopharmaceutical cold kit for the preparation of Ga 68 PSMA-11 injection, is under consideration by the FDA.
The agency noted that two other PET diagnostic agents – fluciclovine F18 and choline C11 – are approved for prostate cancer imaging. However, they are only approved for use in patients with suspected cancer recurrence.
Trial results with PSMA-PET/CT
“PSMA-PET/CT is a novel molecular and functional imaging modality specific for prostate cancer cells that has good sensitivity and outstanding specificity in detecting metastasis,” commented T. Martin Ma, MD, PhD, of UCLA.
Dr. Ma presented a U.S. study on the technique at the recent annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology. That study showed that PSMA-PET/CT led to nodal upstaging in 19.7% of patients and metastasis upstaging in 9.4%.
He said these results were similar to those from the Australian proPSMA trial, which was published in The Lancet earlier this year. That trial found PSMA-PET/CT to be superior to conventional imaging with CT and bone scanning for primary staging of high-risk prostate cancer.
“These findings carry significant clinical implications and can affect treatment decision-making,” Dr. Ma commented.
“PSMA-PET has been a real game changer in high-risk prostate cancer and has implications in the various stages of prostate cancer management from diagnosis and staging to theranostics,” said Renu Eapen, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, who was not involved in either study.
“PSMA-PET/CT has challenged conventional imaging in staging before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy,” Dr. Eapen added.
The accuracy of PSMA-PET/CT was 27% higher than that of conventional imaging in the proPSMA trial, she noted in an interview last month. This superior accuracy can ultimately affect management. The imaging has additional benefits of lower radiation dose as well as reproducibility with high reporter agreement, potentially making it a “one-stop-shop” scan.
Trial results with Ga 68 PSMA-11
The safety and efficacy of Ga 68 PSMA-11 were evaluated in two prospective clinical trials with a total of 960 men with prostate cancer, each of whom received one injection of the product.
The first trial involved 325 patients with biopsy-proven prostate cancer who underwent PET/CT or PET/MRI scans performed with Ga 68 PSMA-11.
“These patients were candidates for surgical removal of the prostate gland and pelvic lymph nodes and were considered at higher risk for metastasis. Among the patients who proceeded to surgery, those with positive readings in the pelvic lymph nodes on Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET had a clinically important rate of metastatic cancer confirmed by surgical pathology,” the FDA noted.
“The availability of this information prior to treatment is expected to have important implications for patient care,” the FDA commented. “For example, it may spare certain patients from undergoing unnecessary surgery.”
The second trial enrolled 635 patients with rising serum PSA levels after initial prostate surgery or radiotherapy. All patients received a single Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET/CT scan or PET/MRI scan.
About three-quarters of patients (74%) had at least one positive lesion detected by Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET in at least one region – bone, prostate bed, pelvic lymph node, or extra-pelvic soft tissue.
“In patients with positive Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET readings who had correlative tissue pathology from biopsies, results from baseline or follow-up imaging by conventional methods, and serial PSA levels available for comparison, local recurrence or metastasis of prostate cancer was confirmed in an estimated 91% of cases,” the FDA noted.
“Thus, the second trial demonstrated that Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET can detect sites of disease in patients with biochemical evidence of recurrent prostate cancer, thereby providing important information that may impact the approach to therapy,” the agency added.
The FDA also noted that no serious adverse reactions were attributed to Ga 68 PSMA-11. The most common adverse reactions were nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness.
The FDA said there is a risk for misdiagnosis because Ga 68 PSMA-11 binding may occur in other types of cancer, and certain nonmalignant processes may lead to errors in interpreting images. In addition, there are radiation risks because Ga 68 PSMA-11 contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure, which is associated with an increased risk for cancer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A radioactive diagnostic agent has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with prostate cancer, but only for those treated at two institutions in California.
The product, Gallium 68 PSMA-11 (Ga 68 PSMA-11), is the first agent approved specifically for use in positron-emission tomography (PET) imaging of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–positive lesions in men with prostate cancer, the FDA noted.
This imaging approach can “detect whether or not the cancer has spread to other parts of the body,” commented Alex Gorovets, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Specialty Medicine in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Ga 68 PSMA-11 is indicated for use in patients with suspected prostate cancer metastasis whose conditions are potentially curable by surgery or radiotherapy and in patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence, as determined on the basis of elevated serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Institutional use only
Ga 68 PSMA-11 has been approved for institutional use at the University of California, Los Angeles and the University of California, San Francisco under an academic new drug application (NDA).
The FDA approval was based partly on a clinical trial conducted by the UCSF and UCLA research teams on the effectiveness of PSMA-PET.
“It is rare for academic institutions to obtain FDA approval of a drug, and this unique collaboration has led to what is one of the first coapprovals of a drug at two institutions,” said Thomas Hope, MD, an associate professor at UCSF. “We hope that this first step will lead to a more widespread availability of this imaging test to men with prostate cancer throughout the country.”
Ga 68 PSMA-11 was developed outside the United States at the University of Heidelberg (Germany).
A commercial NDA from Telix Pharmaceuticals for TL591-CDx, a radiopharmaceutical cold kit for the preparation of Ga 68 PSMA-11 injection, is under consideration by the FDA.
The agency noted that two other PET diagnostic agents – fluciclovine F18 and choline C11 – are approved for prostate cancer imaging. However, they are only approved for use in patients with suspected cancer recurrence.
Trial results with PSMA-PET/CT
“PSMA-PET/CT is a novel molecular and functional imaging modality specific for prostate cancer cells that has good sensitivity and outstanding specificity in detecting metastasis,” commented T. Martin Ma, MD, PhD, of UCLA.
Dr. Ma presented a U.S. study on the technique at the recent annual meeting of the American Society for Radiation Oncology. That study showed that PSMA-PET/CT led to nodal upstaging in 19.7% of patients and metastasis upstaging in 9.4%.
He said these results were similar to those from the Australian proPSMA trial, which was published in The Lancet earlier this year. That trial found PSMA-PET/CT to be superior to conventional imaging with CT and bone scanning for primary staging of high-risk prostate cancer.
“These findings carry significant clinical implications and can affect treatment decision-making,” Dr. Ma commented.
“PSMA-PET has been a real game changer in high-risk prostate cancer and has implications in the various stages of prostate cancer management from diagnosis and staging to theranostics,” said Renu Eapen, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, who was not involved in either study.
“PSMA-PET/CT has challenged conventional imaging in staging before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy,” Dr. Eapen added.
The accuracy of PSMA-PET/CT was 27% higher than that of conventional imaging in the proPSMA trial, she noted in an interview last month. This superior accuracy can ultimately affect management. The imaging has additional benefits of lower radiation dose as well as reproducibility with high reporter agreement, potentially making it a “one-stop-shop” scan.
Trial results with Ga 68 PSMA-11
The safety and efficacy of Ga 68 PSMA-11 were evaluated in two prospective clinical trials with a total of 960 men with prostate cancer, each of whom received one injection of the product.
The first trial involved 325 patients with biopsy-proven prostate cancer who underwent PET/CT or PET/MRI scans performed with Ga 68 PSMA-11.
“These patients were candidates for surgical removal of the prostate gland and pelvic lymph nodes and were considered at higher risk for metastasis. Among the patients who proceeded to surgery, those with positive readings in the pelvic lymph nodes on Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET had a clinically important rate of metastatic cancer confirmed by surgical pathology,” the FDA noted.
“The availability of this information prior to treatment is expected to have important implications for patient care,” the FDA commented. “For example, it may spare certain patients from undergoing unnecessary surgery.”
The second trial enrolled 635 patients with rising serum PSA levels after initial prostate surgery or radiotherapy. All patients received a single Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET/CT scan or PET/MRI scan.
About three-quarters of patients (74%) had at least one positive lesion detected by Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET in at least one region – bone, prostate bed, pelvic lymph node, or extra-pelvic soft tissue.
“In patients with positive Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET readings who had correlative tissue pathology from biopsies, results from baseline or follow-up imaging by conventional methods, and serial PSA levels available for comparison, local recurrence or metastasis of prostate cancer was confirmed in an estimated 91% of cases,” the FDA noted.
“Thus, the second trial demonstrated that Ga 68 PSMA-11 PET can detect sites of disease in patients with biochemical evidence of recurrent prostate cancer, thereby providing important information that may impact the approach to therapy,” the agency added.
The FDA also noted that no serious adverse reactions were attributed to Ga 68 PSMA-11. The most common adverse reactions were nausea, diarrhea, and dizziness.
The FDA said there is a risk for misdiagnosis because Ga 68 PSMA-11 binding may occur in other types of cancer, and certain nonmalignant processes may lead to errors in interpreting images. In addition, there are radiation risks because Ga 68 PSMA-11 contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure, which is associated with an increased risk for cancer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New drug approved for relapsed/refractory neuroblastoma
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval for naxitamab (Danyelza) to treat certain patients with neuroblastoma, based on response rates in two small trials.
Naxitamab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets GD2, a disialoganglioside highly expressed on neuroblastomas.
The FDA approved naxitamab for use in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in adults and children aged 1 year and older who have relapsed or refractory, high-risk neuroblastoma in the bone or bone marrow that demonstrated a partial response, minor response, or stable disease to prior therapy.
Naxitamab was originally developed at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and licensed exclusively to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. As a result of the licensing arrangement, MSKCC has institutional financial interests in the product, the company noted.
Study results
The accelerated approval of naxitamab was based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response in two single-arm, open-label trials: Study 201 (NCT03363373) in 22 patients and Study 12-230 (NCT01757626) in 38 patients.
In both studies, patients received naxitamab at 3 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion on days 1, 3, and 5 of each 4-week cycle in combination with GM-CSF subcutaneously at 250 mcg/m2/day on days -4 to 0 and at 500 mcg/m2/day on days 1-5.
Some patients also received radiotherapy. At the investigator’s discretion, patients were permitted to receive preplanned radiation to the primary disease site in Study 201 and radiation to nontarget bony lesions or soft tissue disease in Study 12-230.
The ORR was 45% in Study 201 and 34% in Study 12-230. Responses were observed in the bone and/or bone marrow, the FDA noted.
Less than a third of patients had a duration of response that lasted 6 months or more – 30% of responders in Study 201 and 23% of responders in Study 12-230.
The FDA noted that continued approval of naxitamab may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The agency also noted that naxitamab was granted priority review, breakthrough therapy, and orphan drug designation. In addition, a priority review voucher was issued for the rare pediatric disease product application.
Boxed warning and adverse events
Naxitamab has a boxed warning about serious infusion-related reactions and neurotoxicity.
The product information notes that, in clinical studies, naxitamab has been shown to cause serious infusion reactions, including anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, bronchospasm, stridor, and hypotension. Infusion reactions generally occurred within 24 hours of completing an infusion, most often within 30 minutes of initiation. Infusion reactions were most frequent during the first infusion in each cycle.
To mitigate these risks, Y-mAbs Therapeutics recommends premedication with an antihistamine, acetaminophen, an H2 antagonist, and corticosteroid, as well as close monitoring of patients during and for at least 2 hours after each infusion in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available.
Based on its mechanism of action, naxitamab can cause severe pain, according to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. The company recommends premedication with gabapentin and, for example, oral oxycodone, and recommends treating break-through pain with intravenous hydromorphone or an equivalent intervention.
In addition, naxitamab may cause severe hypertension. The onset of hypertension may be delayed, so blood pressure should be monitored both during and after infusion.
The product insert also notes that one case of transverse myelitis (grade 3) and two cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome have been reported.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 25% in either trial) were infusion-related reactions, pain, tachycardia, vomiting, cough, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, hypertension, fatigue, erythema multiforme, peripheral neuropathy, urticaria, pyrexia, headache, injection site reaction, edema, anxiety, localized edema, and irritability.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 5% in either trial) were decreased lymphocytes, decreased neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, decreased platelet count, decreased potassium, increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased glucose, decreased calcium, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, and decreased phosphate.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval for naxitamab (Danyelza) to treat certain patients with neuroblastoma, based on response rates in two small trials.
Naxitamab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets GD2, a disialoganglioside highly expressed on neuroblastomas.
The FDA approved naxitamab for use in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in adults and children aged 1 year and older who have relapsed or refractory, high-risk neuroblastoma in the bone or bone marrow that demonstrated a partial response, minor response, or stable disease to prior therapy.
Naxitamab was originally developed at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and licensed exclusively to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. As a result of the licensing arrangement, MSKCC has institutional financial interests in the product, the company noted.
Study results
The accelerated approval of naxitamab was based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response in two single-arm, open-label trials: Study 201 (NCT03363373) in 22 patients and Study 12-230 (NCT01757626) in 38 patients.
In both studies, patients received naxitamab at 3 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion on days 1, 3, and 5 of each 4-week cycle in combination with GM-CSF subcutaneously at 250 mcg/m2/day on days -4 to 0 and at 500 mcg/m2/day on days 1-5.
Some patients also received radiotherapy. At the investigator’s discretion, patients were permitted to receive preplanned radiation to the primary disease site in Study 201 and radiation to nontarget bony lesions or soft tissue disease in Study 12-230.
The ORR was 45% in Study 201 and 34% in Study 12-230. Responses were observed in the bone and/or bone marrow, the FDA noted.
Less than a third of patients had a duration of response that lasted 6 months or more – 30% of responders in Study 201 and 23% of responders in Study 12-230.
The FDA noted that continued approval of naxitamab may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The agency also noted that naxitamab was granted priority review, breakthrough therapy, and orphan drug designation. In addition, a priority review voucher was issued for the rare pediatric disease product application.
Boxed warning and adverse events
Naxitamab has a boxed warning about serious infusion-related reactions and neurotoxicity.
The product information notes that, in clinical studies, naxitamab has been shown to cause serious infusion reactions, including anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, bronchospasm, stridor, and hypotension. Infusion reactions generally occurred within 24 hours of completing an infusion, most often within 30 minutes of initiation. Infusion reactions were most frequent during the first infusion in each cycle.
To mitigate these risks, Y-mAbs Therapeutics recommends premedication with an antihistamine, acetaminophen, an H2 antagonist, and corticosteroid, as well as close monitoring of patients during and for at least 2 hours after each infusion in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available.
Based on its mechanism of action, naxitamab can cause severe pain, according to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. The company recommends premedication with gabapentin and, for example, oral oxycodone, and recommends treating break-through pain with intravenous hydromorphone or an equivalent intervention.
In addition, naxitamab may cause severe hypertension. The onset of hypertension may be delayed, so blood pressure should be monitored both during and after infusion.
The product insert also notes that one case of transverse myelitis (grade 3) and two cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome have been reported.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 25% in either trial) were infusion-related reactions, pain, tachycardia, vomiting, cough, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, hypertension, fatigue, erythema multiforme, peripheral neuropathy, urticaria, pyrexia, headache, injection site reaction, edema, anxiety, localized edema, and irritability.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 5% in either trial) were decreased lymphocytes, decreased neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, decreased platelet count, decreased potassium, increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased glucose, decreased calcium, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, and decreased phosphate.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval for naxitamab (Danyelza) to treat certain patients with neuroblastoma, based on response rates in two small trials.
Naxitamab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets GD2, a disialoganglioside highly expressed on neuroblastomas.
The FDA approved naxitamab for use in combination with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in adults and children aged 1 year and older who have relapsed or refractory, high-risk neuroblastoma in the bone or bone marrow that demonstrated a partial response, minor response, or stable disease to prior therapy.
Naxitamab was originally developed at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and licensed exclusively to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. As a result of the licensing arrangement, MSKCC has institutional financial interests in the product, the company noted.
Study results
The accelerated approval of naxitamab was based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response in two single-arm, open-label trials: Study 201 (NCT03363373) in 22 patients and Study 12-230 (NCT01757626) in 38 patients.
In both studies, patients received naxitamab at 3 mg/kg administered as an intravenous infusion on days 1, 3, and 5 of each 4-week cycle in combination with GM-CSF subcutaneously at 250 mcg/m2/day on days -4 to 0 and at 500 mcg/m2/day on days 1-5.
Some patients also received radiotherapy. At the investigator’s discretion, patients were permitted to receive preplanned radiation to the primary disease site in Study 201 and radiation to nontarget bony lesions or soft tissue disease in Study 12-230.
The ORR was 45% in Study 201 and 34% in Study 12-230. Responses were observed in the bone and/or bone marrow, the FDA noted.
Less than a third of patients had a duration of response that lasted 6 months or more – 30% of responders in Study 201 and 23% of responders in Study 12-230.
The FDA noted that continued approval of naxitamab may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.
The agency also noted that naxitamab was granted priority review, breakthrough therapy, and orphan drug designation. In addition, a priority review voucher was issued for the rare pediatric disease product application.
Boxed warning and adverse events
Naxitamab has a boxed warning about serious infusion-related reactions and neurotoxicity.
The product information notes that, in clinical studies, naxitamab has been shown to cause serious infusion reactions, including anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, bronchospasm, stridor, and hypotension. Infusion reactions generally occurred within 24 hours of completing an infusion, most often within 30 minutes of initiation. Infusion reactions were most frequent during the first infusion in each cycle.
To mitigate these risks, Y-mAbs Therapeutics recommends premedication with an antihistamine, acetaminophen, an H2 antagonist, and corticosteroid, as well as close monitoring of patients during and for at least 2 hours after each infusion in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available.
Based on its mechanism of action, naxitamab can cause severe pain, according to Y-mAbs Therapeutics. The company recommends premedication with gabapentin and, for example, oral oxycodone, and recommends treating break-through pain with intravenous hydromorphone or an equivalent intervention.
In addition, naxitamab may cause severe hypertension. The onset of hypertension may be delayed, so blood pressure should be monitored both during and after infusion.
The product insert also notes that one case of transverse myelitis (grade 3) and two cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome have been reported.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 25% in either trial) were infusion-related reactions, pain, tachycardia, vomiting, cough, nausea, diarrhea, decreased appetite, hypertension, fatigue, erythema multiforme, peripheral neuropathy, urticaria, pyrexia, headache, injection site reaction, edema, anxiety, localized edema, and irritability.
The most common grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥ 5% in either trial) were decreased lymphocytes, decreased neutrophils, decreased hemoglobin, decreased platelet count, decreased potassium, increased alanine aminotransferase, decreased glucose, decreased calcium, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, and decreased phosphate.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel delves into priorities for COVID vaccine distribution
On Monday, members of an influential federal panel delved into the challenges ahead in deciding who will get the first doses of COVID-19 vaccines, including questions about which healthcare workers need those initial vaccinations the most.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) did not take any votes or seek to establish formal positions. Instead, the meeting served as a forum for experts to discuss the thorny issues ahead. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) could make a decision next month regarding clearance for the first COVID-19 vaccine.
An FDA advisory committee will meet December 10 to review the request for emergency use authorization (EUA) of a COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, in partnership with BioNTech. Moderna Inc said on November 16 that it expects to soon ask the FDA for an EUA of its rival COVID vaccine.
ACIP will face a two-part task after the FDA clears COVID-19 vaccines, said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. ACIP will need to first decide whether to recommend use of the vaccine and then address the “complicated and difficult” question of which groups should get the initial limited quantities.
“There aren’t any perfect decisions,” she told the ACIP members. “I know this is something that most of you didn’t anticipate doing, making these kinds of huge decisions in the midst of a pandemic.”
There has been considerable public discussion of prioritization of COVID-19 vaccines, including a set of recommendations offered by a special committee created by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. In addition, CDC staff and members of ACIP outlined what they termed the “four ethical principles” meant to guide these decisions in a November 23 report in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. These four principles are to maximize benefits and minimize harms; promote justice; mitigate health inequities; and promote transparency.
But as the issuing of the first EUA nears, it falls to ACIP to move beyond endorsing broad goals. The panel will need to make decisions as to which groups will have to wait for COVID-19 vaccines.
ACIP members on Monday delved into these kinds of more detailed questions, using a proposed three-stage model as a discussion point.
In phase 1a of this model, healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities would be the first people to be vaccinated. Phase 1b would include those deemed essential workers, including police officers, firefighters, and those in education, transportation, food, and agriculture sectors. Phase 1c would include adults with high-risk medical conditions and those aged 65 years and older.
ACIP member Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, questioned whether healthcare workers who are not seeing patients in person should wait to get the vaccines. There has been a marked rise in the use of telehealth during the pandemic, which has spared some clinicians from in-person COVID-19 patient visits in their practices.
“Close partnership with our public health colleagues will be critically important to make sure that we are not trying to vaccinate 100% of our healthcare workforce, if some proportion of our workforce can work from home,” Lee said.
ACIP member Pablo Sánchez, MD, of the Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, concurred. Some clinicians, he noted, may have better access to personal protective equipment than others, he said.
“Unfortunately, not all healthcare workers are equal in terms of risk,” Sánchez said. “Within institutions, we’re going to have to prioritize which ones will get” the vaccine.
Clinicians may also make judgments about their own risk and need for early access to COVID-19 vaccinations, Sánchez said.
“I’m 66, and I’d rather give it to somebody much older and sicker than me,” he said.
Broader access
Fairly large populations will essentially be competing for limited doses of the first vaccines to reach the market.
The overlap is significant in the four priority groups put forward by CDC. The CDC staff estimated that about 21 million people would fall into the healthcare personnel category, which includes hospital staff, pharmacists, and those working in long-term care facilities. There are about 87 million people in the essential workers groups. More than 100 million adults in the United States, such as those with diabetes and cancers, fall into the high-risk medical conditions group. Another 53 million people are aged 65 and older.
Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar on November 18 said the federal government expects to have about 40 million doses of these two vaccines by the end of December, which is enough to provide the two-dose regimen for about 20 million. If all goes as expected, Pfizer and Moderna will ramp up production.
Moderna has said that it expects by the end of this year to have approximately 20 million doses of its vaccine ready to ship in the United States and that it is on track to manufacture 500 million to 1 billion doses globally in 2021. Pfizer and BioNTech have said they expect to produce globally up to 50 million doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses by the end of 2021.
At the Monday meeting, several ACIP panelists stressed the need to ensure that essential workers get early doses of vaccines.
In many cases, these workers serve in jobs with significant public interaction and live in poor communities. They put themselves and their families at risk. Many of them lack the resources to take precautions available to those better able to isolate, said ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington.
“These essential workers are out there putting themselves at risk to allow the rest of us to socially distance,” she said. “Recognizing that not all of them may want to be vaccinated at this stage, we need to provide them with the opportunity early on in the process.”
In Bell’s view, the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines will send an important message about sharing this resource.
“If we’re serious about valuing equity, we need to have that baked in early on in the vaccination program,” she said.
Bell also said she was in favor of including people living in nursing homes in the initial wave of vaccinations. Concerns were raised about the frailty of this population.
“Given the mortality impact on the healthcare system from the number of nursing home residents that have been dying, I think on balance it makes sense to include them in phase 1a,” Bell said.
Other ACIP panelists said missteps with early vaccination of people in nursing homes could undermine faith in the treatments. Because of the ages and medical conditions of people in nursing homes, many of them may die after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine. Such deaths would not be associated with vaccine, but the medical community would not yet have evidence to disprove a connection.
There could be a backlash, with people falsely linking the death of a grandparent to the vaccine.
Fellow ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, was among those who had raised concerns about including people living in long-term care facilities in phase 1a. He said there are not yet enough data to judge the balance of benefits and harms of vaccination for this population.
The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are “reactagenic,” meaning people may not feel well in the days after receiving the shots. The symptoms could lead to additional health evaluations of older people in nursing homes as clinicians try to figure out whether the patient’s reactions to the vaccine are caused by some condition or infection, Atmar said.
“Those of us who see these patients in the hospital recognize that there are often medical interventions that are done in the pursuit of a diagnosis, of a change in clinical status, that in and of themselves can lead to harm,” Atmar said.
Clinicians likely will have to encourage their patients of all ages to receive second doses of COVID-19 vaccines, despite the malaise they may provoke.
“We really need to make patients aware that this is not going to be a walk in the park. I mean, they’re going to know they had a vaccine, they’re probably not going to feel wonderful, but they’ve got to come back for that second dose,” said Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, who represented the American Medical Association.
ACIP is expected to meet again to offer specific recommendations on the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. ACIP’s recommendations trigger reimbursement processes, Azar said at a Tuesday press conference. ACIP’s work will inform decisions made by the federal government and governors about deploying shipments of COVID-19 vaccines, he said.
“At the end of the day, that is a decision, though, of the US government to make, which is where to recommend the prioritization,” Azar said. “It will be our nation’s governors in implementing the distribution plans to tell us” where to ship the vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Monday, members of an influential federal panel delved into the challenges ahead in deciding who will get the first doses of COVID-19 vaccines, including questions about which healthcare workers need those initial vaccinations the most.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) did not take any votes or seek to establish formal positions. Instead, the meeting served as a forum for experts to discuss the thorny issues ahead. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) could make a decision next month regarding clearance for the first COVID-19 vaccine.
An FDA advisory committee will meet December 10 to review the request for emergency use authorization (EUA) of a COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, in partnership with BioNTech. Moderna Inc said on November 16 that it expects to soon ask the FDA for an EUA of its rival COVID vaccine.
ACIP will face a two-part task after the FDA clears COVID-19 vaccines, said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. ACIP will need to first decide whether to recommend use of the vaccine and then address the “complicated and difficult” question of which groups should get the initial limited quantities.
“There aren’t any perfect decisions,” she told the ACIP members. “I know this is something that most of you didn’t anticipate doing, making these kinds of huge decisions in the midst of a pandemic.”
There has been considerable public discussion of prioritization of COVID-19 vaccines, including a set of recommendations offered by a special committee created by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. In addition, CDC staff and members of ACIP outlined what they termed the “four ethical principles” meant to guide these decisions in a November 23 report in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. These four principles are to maximize benefits and minimize harms; promote justice; mitigate health inequities; and promote transparency.
But as the issuing of the first EUA nears, it falls to ACIP to move beyond endorsing broad goals. The panel will need to make decisions as to which groups will have to wait for COVID-19 vaccines.
ACIP members on Monday delved into these kinds of more detailed questions, using a proposed three-stage model as a discussion point.
In phase 1a of this model, healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities would be the first people to be vaccinated. Phase 1b would include those deemed essential workers, including police officers, firefighters, and those in education, transportation, food, and agriculture sectors. Phase 1c would include adults with high-risk medical conditions and those aged 65 years and older.
ACIP member Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, questioned whether healthcare workers who are not seeing patients in person should wait to get the vaccines. There has been a marked rise in the use of telehealth during the pandemic, which has spared some clinicians from in-person COVID-19 patient visits in their practices.
“Close partnership with our public health colleagues will be critically important to make sure that we are not trying to vaccinate 100% of our healthcare workforce, if some proportion of our workforce can work from home,” Lee said.
ACIP member Pablo Sánchez, MD, of the Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, concurred. Some clinicians, he noted, may have better access to personal protective equipment than others, he said.
“Unfortunately, not all healthcare workers are equal in terms of risk,” Sánchez said. “Within institutions, we’re going to have to prioritize which ones will get” the vaccine.
Clinicians may also make judgments about their own risk and need for early access to COVID-19 vaccinations, Sánchez said.
“I’m 66, and I’d rather give it to somebody much older and sicker than me,” he said.
Broader access
Fairly large populations will essentially be competing for limited doses of the first vaccines to reach the market.
The overlap is significant in the four priority groups put forward by CDC. The CDC staff estimated that about 21 million people would fall into the healthcare personnel category, which includes hospital staff, pharmacists, and those working in long-term care facilities. There are about 87 million people in the essential workers groups. More than 100 million adults in the United States, such as those with diabetes and cancers, fall into the high-risk medical conditions group. Another 53 million people are aged 65 and older.
Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar on November 18 said the federal government expects to have about 40 million doses of these two vaccines by the end of December, which is enough to provide the two-dose regimen for about 20 million. If all goes as expected, Pfizer and Moderna will ramp up production.
Moderna has said that it expects by the end of this year to have approximately 20 million doses of its vaccine ready to ship in the United States and that it is on track to manufacture 500 million to 1 billion doses globally in 2021. Pfizer and BioNTech have said they expect to produce globally up to 50 million doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses by the end of 2021.
At the Monday meeting, several ACIP panelists stressed the need to ensure that essential workers get early doses of vaccines.
In many cases, these workers serve in jobs with significant public interaction and live in poor communities. They put themselves and their families at risk. Many of them lack the resources to take precautions available to those better able to isolate, said ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington.
“These essential workers are out there putting themselves at risk to allow the rest of us to socially distance,” she said. “Recognizing that not all of them may want to be vaccinated at this stage, we need to provide them with the opportunity early on in the process.”
In Bell’s view, the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines will send an important message about sharing this resource.
“If we’re serious about valuing equity, we need to have that baked in early on in the vaccination program,” she said.
Bell also said she was in favor of including people living in nursing homes in the initial wave of vaccinations. Concerns were raised about the frailty of this population.
“Given the mortality impact on the healthcare system from the number of nursing home residents that have been dying, I think on balance it makes sense to include them in phase 1a,” Bell said.
Other ACIP panelists said missteps with early vaccination of people in nursing homes could undermine faith in the treatments. Because of the ages and medical conditions of people in nursing homes, many of them may die after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine. Such deaths would not be associated with vaccine, but the medical community would not yet have evidence to disprove a connection.
There could be a backlash, with people falsely linking the death of a grandparent to the vaccine.
Fellow ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, was among those who had raised concerns about including people living in long-term care facilities in phase 1a. He said there are not yet enough data to judge the balance of benefits and harms of vaccination for this population.
The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are “reactagenic,” meaning people may not feel well in the days after receiving the shots. The symptoms could lead to additional health evaluations of older people in nursing homes as clinicians try to figure out whether the patient’s reactions to the vaccine are caused by some condition or infection, Atmar said.
“Those of us who see these patients in the hospital recognize that there are often medical interventions that are done in the pursuit of a diagnosis, of a change in clinical status, that in and of themselves can lead to harm,” Atmar said.
Clinicians likely will have to encourage their patients of all ages to receive second doses of COVID-19 vaccines, despite the malaise they may provoke.
“We really need to make patients aware that this is not going to be a walk in the park. I mean, they’re going to know they had a vaccine, they’re probably not going to feel wonderful, but they’ve got to come back for that second dose,” said Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, who represented the American Medical Association.
ACIP is expected to meet again to offer specific recommendations on the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. ACIP’s recommendations trigger reimbursement processes, Azar said at a Tuesday press conference. ACIP’s work will inform decisions made by the federal government and governors about deploying shipments of COVID-19 vaccines, he said.
“At the end of the day, that is a decision, though, of the US government to make, which is where to recommend the prioritization,” Azar said. “It will be our nation’s governors in implementing the distribution plans to tell us” where to ship the vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On Monday, members of an influential federal panel delved into the challenges ahead in deciding who will get the first doses of COVID-19 vaccines, including questions about which healthcare workers need those initial vaccinations the most.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) did not take any votes or seek to establish formal positions. Instead, the meeting served as a forum for experts to discuss the thorny issues ahead. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) could make a decision next month regarding clearance for the first COVID-19 vaccine.
An FDA advisory committee will meet December 10 to review the request for emergency use authorization (EUA) of a COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, in partnership with BioNTech. Moderna Inc said on November 16 that it expects to soon ask the FDA for an EUA of its rival COVID vaccine.
ACIP will face a two-part task after the FDA clears COVID-19 vaccines, said Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. ACIP will need to first decide whether to recommend use of the vaccine and then address the “complicated and difficult” question of which groups should get the initial limited quantities.
“There aren’t any perfect decisions,” she told the ACIP members. “I know this is something that most of you didn’t anticipate doing, making these kinds of huge decisions in the midst of a pandemic.”
There has been considerable public discussion of prioritization of COVID-19 vaccines, including a set of recommendations offered by a special committee created by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. In addition, CDC staff and members of ACIP outlined what they termed the “four ethical principles” meant to guide these decisions in a November 23 report in the agency’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. These four principles are to maximize benefits and minimize harms; promote justice; mitigate health inequities; and promote transparency.
But as the issuing of the first EUA nears, it falls to ACIP to move beyond endorsing broad goals. The panel will need to make decisions as to which groups will have to wait for COVID-19 vaccines.
ACIP members on Monday delved into these kinds of more detailed questions, using a proposed three-stage model as a discussion point.
In phase 1a of this model, healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities would be the first people to be vaccinated. Phase 1b would include those deemed essential workers, including police officers, firefighters, and those in education, transportation, food, and agriculture sectors. Phase 1c would include adults with high-risk medical conditions and those aged 65 years and older.
ACIP member Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, of Stanford University, Stanford, California, questioned whether healthcare workers who are not seeing patients in person should wait to get the vaccines. There has been a marked rise in the use of telehealth during the pandemic, which has spared some clinicians from in-person COVID-19 patient visits in their practices.
“Close partnership with our public health colleagues will be critically important to make sure that we are not trying to vaccinate 100% of our healthcare workforce, if some proportion of our workforce can work from home,” Lee said.
ACIP member Pablo Sánchez, MD, of the Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, concurred. Some clinicians, he noted, may have better access to personal protective equipment than others, he said.
“Unfortunately, not all healthcare workers are equal in terms of risk,” Sánchez said. “Within institutions, we’re going to have to prioritize which ones will get” the vaccine.
Clinicians may also make judgments about their own risk and need for early access to COVID-19 vaccinations, Sánchez said.
“I’m 66, and I’d rather give it to somebody much older and sicker than me,” he said.
Broader access
Fairly large populations will essentially be competing for limited doses of the first vaccines to reach the market.
The overlap is significant in the four priority groups put forward by CDC. The CDC staff estimated that about 21 million people would fall into the healthcare personnel category, which includes hospital staff, pharmacists, and those working in long-term care facilities. There are about 87 million people in the essential workers groups. More than 100 million adults in the United States, such as those with diabetes and cancers, fall into the high-risk medical conditions group. Another 53 million people are aged 65 and older.
Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar on November 18 said the federal government expects to have about 40 million doses of these two vaccines by the end of December, which is enough to provide the two-dose regimen for about 20 million. If all goes as expected, Pfizer and Moderna will ramp up production.
Moderna has said that it expects by the end of this year to have approximately 20 million doses of its vaccine ready to ship in the United States and that it is on track to manufacture 500 million to 1 billion doses globally in 2021. Pfizer and BioNTech have said they expect to produce globally up to 50 million doses in 2020 and up to 1.3 billion doses by the end of 2021.
At the Monday meeting, several ACIP panelists stressed the need to ensure that essential workers get early doses of vaccines.
In many cases, these workers serve in jobs with significant public interaction and live in poor communities. They put themselves and their families at risk. Many of them lack the resources to take precautions available to those better able to isolate, said ACIP member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, of the University of Washington, Seattle, Washington.
“These essential workers are out there putting themselves at risk to allow the rest of us to socially distance,” she said. “Recognizing that not all of them may want to be vaccinated at this stage, we need to provide them with the opportunity early on in the process.”
In Bell’s view, the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines will send an important message about sharing this resource.
“If we’re serious about valuing equity, we need to have that baked in early on in the vaccination program,” she said.
Bell also said she was in favor of including people living in nursing homes in the initial wave of vaccinations. Concerns were raised about the frailty of this population.
“Given the mortality impact on the healthcare system from the number of nursing home residents that have been dying, I think on balance it makes sense to include them in phase 1a,” Bell said.
Other ACIP panelists said missteps with early vaccination of people in nursing homes could undermine faith in the treatments. Because of the ages and medical conditions of people in nursing homes, many of them may die after receiving the COVID-19 vaccine. Such deaths would not be associated with vaccine, but the medical community would not yet have evidence to disprove a connection.
There could be a backlash, with people falsely linking the death of a grandparent to the vaccine.
Fellow ACIP member Robert L. Atmar, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, was among those who had raised concerns about including people living in long-term care facilities in phase 1a. He said there are not yet enough data to judge the balance of benefits and harms of vaccination for this population.
The Pfizer and Moderna vaccines are “reactagenic,” meaning people may not feel well in the days after receiving the shots. The symptoms could lead to additional health evaluations of older people in nursing homes as clinicians try to figure out whether the patient’s reactions to the vaccine are caused by some condition or infection, Atmar said.
“Those of us who see these patients in the hospital recognize that there are often medical interventions that are done in the pursuit of a diagnosis, of a change in clinical status, that in and of themselves can lead to harm,” Atmar said.
Clinicians likely will have to encourage their patients of all ages to receive second doses of COVID-19 vaccines, despite the malaise they may provoke.
“We really need to make patients aware that this is not going to be a walk in the park. I mean, they’re going to know they had a vaccine, they’re probably not going to feel wonderful, but they’ve got to come back for that second dose,” said Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, MD, who represented the American Medical Association.
ACIP is expected to meet again to offer specific recommendations on the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. ACIP’s recommendations trigger reimbursement processes, Azar said at a Tuesday press conference. ACIP’s work will inform decisions made by the federal government and governors about deploying shipments of COVID-19 vaccines, he said.
“At the end of the day, that is a decision, though, of the US government to make, which is where to recommend the prioritization,” Azar said. “It will be our nation’s governors in implementing the distribution plans to tell us” where to ship the vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA expands Xofluza indication to include postexposure flu prophylaxis
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the indication for the antiviral baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza) to include postexposure prophylaxis of uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years and older.
“This expanded indication for Xofluza will provide an important option to help prevent influenza just in time for a flu season that is anticipated to be unlike any other because it will coincide with the coronavirus pandemic,” Debra Birnkrant, MD, director, Division of Antiviral Products, FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
In addition, Xofluza, which was previously available only in tablet form, is also now available as granules for mixing in water, the FDA said.
The agency first approved baloxavir marboxil in 2018 for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years or older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours.
A year later, the FDA expanded the indication to include people at high risk of developing influenza-related complications, such as those with asthma, chronic lung disease, diabetes, heart disease, or morbid obesity, as well as adults aged 65 years or older.
The safety and efficacy of Xofluza for influenza postexposure prophylaxis is supported by a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial involving 607 people aged 12 years and older. After exposure to a person with influenza in their household, they received a single dose of Xofluza or placebo.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of individuals who became infected with influenza and presented with fever and at least one respiratory symptom from day 1 to day 10.
Of the 303 people who received Xofluza, 1% of individuals met these criteria, compared with 13% of those who received placebo.
The most common adverse effects of Xofluza include diarrhea, bronchitis, nausea, sinusitis, and headache.
Hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients taking Xofluza. The antiviral is contraindicated in people with a known hypersensitivity reaction to Xofluza.
Xofluza should not be coadministered with dairy products, calcium-fortified beverages, laxatives, antacids, or oral supplements containing calcium, iron, magnesium, selenium, aluminium, or zinc.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the indication for the antiviral baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza) to include postexposure prophylaxis of uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years and older.
“This expanded indication for Xofluza will provide an important option to help prevent influenza just in time for a flu season that is anticipated to be unlike any other because it will coincide with the coronavirus pandemic,” Debra Birnkrant, MD, director, Division of Antiviral Products, FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
In addition, Xofluza, which was previously available only in tablet form, is also now available as granules for mixing in water, the FDA said.
The agency first approved baloxavir marboxil in 2018 for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years or older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours.
A year later, the FDA expanded the indication to include people at high risk of developing influenza-related complications, such as those with asthma, chronic lung disease, diabetes, heart disease, or morbid obesity, as well as adults aged 65 years or older.
The safety and efficacy of Xofluza for influenza postexposure prophylaxis is supported by a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial involving 607 people aged 12 years and older. After exposure to a person with influenza in their household, they received a single dose of Xofluza or placebo.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of individuals who became infected with influenza and presented with fever and at least one respiratory symptom from day 1 to day 10.
Of the 303 people who received Xofluza, 1% of individuals met these criteria, compared with 13% of those who received placebo.
The most common adverse effects of Xofluza include diarrhea, bronchitis, nausea, sinusitis, and headache.
Hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients taking Xofluza. The antiviral is contraindicated in people with a known hypersensitivity reaction to Xofluza.
Xofluza should not be coadministered with dairy products, calcium-fortified beverages, laxatives, antacids, or oral supplements containing calcium, iron, magnesium, selenium, aluminium, or zinc.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has expanded the indication for the antiviral baloxavir marboxil (Xofluza) to include postexposure prophylaxis of uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years and older.
“This expanded indication for Xofluza will provide an important option to help prevent influenza just in time for a flu season that is anticipated to be unlike any other because it will coincide with the coronavirus pandemic,” Debra Birnkrant, MD, director, Division of Antiviral Products, FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
In addition, Xofluza, which was previously available only in tablet form, is also now available as granules for mixing in water, the FDA said.
The agency first approved baloxavir marboxil in 2018 for the treatment of acute uncomplicated influenza in people aged 12 years or older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours.
A year later, the FDA expanded the indication to include people at high risk of developing influenza-related complications, such as those with asthma, chronic lung disease, diabetes, heart disease, or morbid obesity, as well as adults aged 65 years or older.
The safety and efficacy of Xofluza for influenza postexposure prophylaxis is supported by a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial involving 607 people aged 12 years and older. After exposure to a person with influenza in their household, they received a single dose of Xofluza or placebo.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of individuals who became infected with influenza and presented with fever and at least one respiratory symptom from day 1 to day 10.
Of the 303 people who received Xofluza, 1% of individuals met these criteria, compared with 13% of those who received placebo.
The most common adverse effects of Xofluza include diarrhea, bronchitis, nausea, sinusitis, and headache.
Hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients taking Xofluza. The antiviral is contraindicated in people with a known hypersensitivity reaction to Xofluza.
Xofluza should not be coadministered with dairy products, calcium-fortified beverages, laxatives, antacids, or oral supplements containing calcium, iron, magnesium, selenium, aluminium, or zinc.
Full prescribing information is available online.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
50.6 million tobacco users are not a homogeneous group
Cigarettes are still the product of choice among U.S. adults who use tobacco, but the youngest adults are more likely to use e-cigarettes than any other product, according to data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey.
with cigarette use reported by the largest share of respondents (14.0%) and e-cigarettes next at 4.5%, Monica E. Cornelius, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among adults aged 18-24 years, however, e-cigarettes were used by 9.3% of respondents in 2019, compared with 8.0% who used cigarettes every day or some days. Current e-cigarette use was 6.4% in 25- to 44-year-olds and continued to diminish with increasing age, said Dr. Cornelius and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
Men were more likely than women to use e-cigarettes (5.5% vs. 3.5%), and to use any tobacco product (26.2% vs. 15.7%). Use of other products, including cigarettes (15.3% for men vs. 12.7% for women), followed the same pattern to varying degrees, the national survey data show.
“Differences in prevalence of tobacco use also were also seen across population groups, with higher prevalence among those with a [high school equivalency degree], American Indian/Alaska Natives, uninsured adults and adults with Medicaid, and [lesbian, gay, or bisexual] adults,” the investigators said.
Among those groups, overall tobacco use and cigarette use were highest in those with an equivalency degree (43.8%, 37.1%), while lesbian/gay/bisexual individuals had the highest prevalence of e-cigarette use at 11.5%, they reported.
“As part of a comprehensive approach” to reduce tobacco-related disease and death, Dr. Cornelius and associates suggested, “targeted interventions are also warranted to reach subpopulations with the highest prevalence of use, which might vary by tobacco product type.”
SOURCE: Cornelius ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Nov 20;69(46);1736-42.
Cigarettes are still the product of choice among U.S. adults who use tobacco, but the youngest adults are more likely to use e-cigarettes than any other product, according to data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey.

with cigarette use reported by the largest share of respondents (14.0%) and e-cigarettes next at 4.5%, Monica E. Cornelius, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among adults aged 18-24 years, however, e-cigarettes were used by 9.3% of respondents in 2019, compared with 8.0% who used cigarettes every day or some days. Current e-cigarette use was 6.4% in 25- to 44-year-olds and continued to diminish with increasing age, said Dr. Cornelius and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
Men were more likely than women to use e-cigarettes (5.5% vs. 3.5%), and to use any tobacco product (26.2% vs. 15.7%). Use of other products, including cigarettes (15.3% for men vs. 12.7% for women), followed the same pattern to varying degrees, the national survey data show.
“Differences in prevalence of tobacco use also were also seen across population groups, with higher prevalence among those with a [high school equivalency degree], American Indian/Alaska Natives, uninsured adults and adults with Medicaid, and [lesbian, gay, or bisexual] adults,” the investigators said.
Among those groups, overall tobacco use and cigarette use were highest in those with an equivalency degree (43.8%, 37.1%), while lesbian/gay/bisexual individuals had the highest prevalence of e-cigarette use at 11.5%, they reported.
“As part of a comprehensive approach” to reduce tobacco-related disease and death, Dr. Cornelius and associates suggested, “targeted interventions are also warranted to reach subpopulations with the highest prevalence of use, which might vary by tobacco product type.”
SOURCE: Cornelius ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Nov 20;69(46);1736-42.
Cigarettes are still the product of choice among U.S. adults who use tobacco, but the youngest adults are more likely to use e-cigarettes than any other product, according to data from the 2019 National Health Interview Survey.

with cigarette use reported by the largest share of respondents (14.0%) and e-cigarettes next at 4.5%, Monica E. Cornelius, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among adults aged 18-24 years, however, e-cigarettes were used by 9.3% of respondents in 2019, compared with 8.0% who used cigarettes every day or some days. Current e-cigarette use was 6.4% in 25- to 44-year-olds and continued to diminish with increasing age, said Dr. Cornelius and associates at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
Men were more likely than women to use e-cigarettes (5.5% vs. 3.5%), and to use any tobacco product (26.2% vs. 15.7%). Use of other products, including cigarettes (15.3% for men vs. 12.7% for women), followed the same pattern to varying degrees, the national survey data show.
“Differences in prevalence of tobacco use also were also seen across population groups, with higher prevalence among those with a [high school equivalency degree], American Indian/Alaska Natives, uninsured adults and adults with Medicaid, and [lesbian, gay, or bisexual] adults,” the investigators said.
Among those groups, overall tobacco use and cigarette use were highest in those with an equivalency degree (43.8%, 37.1%), while lesbian/gay/bisexual individuals had the highest prevalence of e-cigarette use at 11.5%, they reported.
“As part of a comprehensive approach” to reduce tobacco-related disease and death, Dr. Cornelius and associates suggested, “targeted interventions are also warranted to reach subpopulations with the highest prevalence of use, which might vary by tobacco product type.”
SOURCE: Cornelius ME et al. MMWR. 2020 Nov 20;69(46);1736-42.
FROM MMWR
FDA authorizes baricitinib combo for COVID-19
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Nov. 19 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly) in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead) for treating hospitalized adults and children at least 2 years old with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination treatment is meant for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Baricitinib/remdesivir was shown in a clinical trial to reduce time to recovery within 29 days of starting the treatment compared with a control group who received placebo/remdesivir, according to the FDA press release.
The median time to recovery from COVID-19 was 7 days for the combination group vs. 8 days for those in the placebo/remdesivir group. Recovery was defined as either discharge from the hospital or “being hospitalized but not requiring supplemental oxygen and no longer requiring ongoing medical care,” the agency explained in the press release.
The odds of a patient dying or being ventilated at day 29 was lower in the combination group compared with those taking placebo/remdesivir, the press release said without providing specific data. “For all of these endpoints, the effects were statistically significant,” the agency stated.
The safety and efficacy continues to be evaluated. Baricitinib alone is not approved as a treatment for COVID-19.
“The FDA’s emergency authorization of this combination therapy represents an incremental step forward in the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, and FDA’s first authorization of a drug that acts on the inflammation pathway,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
“Despite advances in the management of COVID-19 infection since the onset of the pandemic, we need more therapies to accelerate recovery and additional clinical research will be essential to identifying therapies that slow disease progression and lower mortality in the sicker patients,” she said.
As a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib interferes with a pathway that leads to inflammation. Baricitinib is already prescribed as an oral medication and is FDA-approved for treating moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis.
The data supporting the EUA for the combination treatment are based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (ACTT-2), conducted by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
The trial followed patients for 29 days and included 1,033 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19; 515 patients received baricitinib/remdesivir, and 518 patients received placebo/remdesivir.
The FDA emphasizes that an EUA is not a full FDA approval.
In reviewing the combination, the FDA “determined that it is reasonable to believe that baricitinib, in combination with remdesivir, may be effective in treating COVID-19 for the authorized population” and the known benefits outweigh the known and potential risks. Additionally, there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives for the treatment population.
“Today’s action demonstrates the FDA’s steadfast efforts to make potential COVID-19 treatments available in a timely manner, where appropriate, while continuing to support research to further evaluate whether they are safe and effective,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD. “As part of our Coronavirus Treatment Acceleration Program, the FDA continues to use every possible avenue to facilitate new treatments for patients as quickly as possible to combat COVID-19.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.