User login
‘It’s Time’ to Empower Care for Patients With Obesity
A few weeks ago, I made a patient who lost 100 pounds following a sleeve gastrectomy 9 months prior feel bad because I told her she lost too much weight. As I spoke to her, I realized that she found it hard to make life changes and that the surgery was a huge aide in changing her life and her lifestyle. I ended up apologizing for initially saying she lost too much weight.
For the first time in her life, she was successful in losing weight and keeping it off. The surgery allowed her body to defend a lower body weight by altering the secretion of gut hormones that lead to satiety in the brain. It’s not her fault that her body responded so well!
I asked her to be on my next orientation virtual meeting with prospective weight management patients to urge those with a body mass index (BMI) > 40 to consider bariatric surgery as the most effective durable and safe treatment for their degree of obesity.
Metabolic bariatric surgery, primarily sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass , alters the gut hormone milieu such that the body defends a lower mass of adipose tissue and a lower weight. We have learned what it takes to alter body weight defense to a healthy lower weight by studying why metabolic bariatric surgery works so well. It turns out that there are several hormones secreted by the gut that allow the brain to register fullness.
One of these gut hormones, glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1, has been researched as an analog to help reduce body weight by 16% and has also been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in the SELECT trial, as published in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
It’s the first weight loss medication to be shown in a cardiovascular outcomes trial to be superior to placebo in reduction of major cardiovascular events, including cardiovascular deaths, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke. The results presented at the 2023 American Heart Association meetings in Philadelphia ended in wholehearted applause by a “standing only” audience even before the presentation’s conclusion.
As we pave the way for nutrient-stimulated hormone (NuSH) therapies to be prescribed to all Americans with a BMI > 30 to improve health, we need to remember what these medications actually do. We used to think that metabolic bariatric surgery worked by restricting the stomach contents and malabsorbing nutrients. We now know that the surgeries work by altering NuSH secretion, allowing for less secretion of the hunger hormone ghrelin and more secretion of GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), peptide YY (PYY), cholecystokinin (CCK), oxyntomodulin (OXM), and other satiety hormones with less food ingestion.
They have pleiotropic effects on many organ systems in the body, including the brain, heart, adipose tissue, and liver. They decrease inflammation and also increase satiety and delay gastric emptying. None of these effects automatically produce weight loss, but they certainly aid in the adoption of a healthier body weight and better health. The weight loss occurs because these medications steer the body toward behavioral changes that promote weight loss.
As we delve into the SELECT trial results, a 20% reduction in major cardiovascular events was accompanied by an average weight loss of 9.6%, without a behavioral component added to either the placebo or intervention arms, as is usual in antiobesity agent trials.
Does this mean that primary care providers (PCPs) don’t have to educate patients on behavior change, diet, and exercise therapy? Well, if we consider obesity a disease as we do type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia or hypertension, then no — PCPs don’t have to, just like they don’t in treating these other diseases.
However, we should rethink this practice. The recently published SURMOUNT-3 trial looked at another NuSH, tirzepatide, with intensive behavioral therapy; it resulted in a 26.6% weight loss, which is comparable to results with bariatric surgery. The SURMOUNT-1 trial of tirzepatide with nonintensive behavioral therapy resulted in a 20.9% weight loss, which is still substantial, but SURMOUNT-3 showed how much more is achievable with robust behavior-change therapy.
In other words, it’s time that PCPs provide education on behavior change to maximize the power of the medications prescribed in practice for the most common diseases suffered in the United States: obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension. These are all chronic, relapsing diseases. Medication alone will improve numbers (weight, blood glucose, A1c, and blood pressure), but a relapsing disease continues relentlessly as patients age to overcome the medications prescribed.
Today I made another patient feel bad because she lost over 100 pounds on semaglutide (Wegovy) 2.4 mg over 1 year, reducing her BMI from 57 to 36. She wanted to keep losing, so I recommended sleeve gastrectomy to lose more weight. I told her she could always restart the Wegovy after the procedure if needed.
We really don’t have an answer to this issue of NuSH therapy not getting to goal and bariatric surgery following medication therapy. The reality is that bariatric surgery should be considered a safe, effective treatment for extreme obesity somewhere along the trajectory of treatments starting with behavior (diet, exercise) and medications. It is still considered a last resort, and for some, just too aggressive.
We have learned much about the incretin hormones and what they can accomplish for obesity from studying bariatric — now called metabolic — surgery. Surgery should be seen as we see stent placement for angina, only more effective for longevity. The COURAGE trial, published in 2007 in NEJM, showed that when compared with medication treatment alone for angina, stent placement plus medications resulted in no difference in mortality after a 7-year follow-up period. Compare this to bariatric surgery, which in many retrospective analyses shows a 20% reduction in cardiovascular mortality after 20-year follow-up (Swedish Obesity Study). In the United States, there are 2 million stent procedures performed per year vs 250,000 bariatric surgical procedures. There are millions of Americans with a BMI > 40 and, yes, millions of Americans with angina. I think I make my point that we need to do more bariatric surgeries to effectively treat extreme obesity.
The solution to this negligent medical practice in obesity treatment is to empower PCPs to treat obesity (at least uncomplicated obesity) and refer to obesity medicine practices for complicated obesity with multiple complications, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and to refer to obesity medicine practices with a surgical component for BMIs > 40 or > 35 with type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and/or cardiovascular disease or other serious conditions.
How do we empower PCPs? Insurance coverage of NuSH therapies due to life-saving properties — as evidenced by the SELECT trial — without prior authorizations; and education on how and why metabolic surgery works, as well as education on behavioral approaches, such as healthy diet and exercise, as a core therapy for all BMI categories.
It’s time.
Caroline Apovian, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Altimmune; Cowen and Company; Currax Pharmaceuticals; EPG Communication Holdings; Gelesis, Srl; L-Nutra; and NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals. Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and GI Dynamics. Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Altimmune; Cowen and Company; NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals; and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A few weeks ago, I made a patient who lost 100 pounds following a sleeve gastrectomy 9 months prior feel bad because I told her she lost too much weight. As I spoke to her, I realized that she found it hard to make life changes and that the surgery was a huge aide in changing her life and her lifestyle. I ended up apologizing for initially saying she lost too much weight.
For the first time in her life, she was successful in losing weight and keeping it off. The surgery allowed her body to defend a lower body weight by altering the secretion of gut hormones that lead to satiety in the brain. It’s not her fault that her body responded so well!
I asked her to be on my next orientation virtual meeting with prospective weight management patients to urge those with a body mass index (BMI) > 40 to consider bariatric surgery as the most effective durable and safe treatment for their degree of obesity.
Metabolic bariatric surgery, primarily sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass , alters the gut hormone milieu such that the body defends a lower mass of adipose tissue and a lower weight. We have learned what it takes to alter body weight defense to a healthy lower weight by studying why metabolic bariatric surgery works so well. It turns out that there are several hormones secreted by the gut that allow the brain to register fullness.
One of these gut hormones, glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1, has been researched as an analog to help reduce body weight by 16% and has also been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in the SELECT trial, as published in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
It’s the first weight loss medication to be shown in a cardiovascular outcomes trial to be superior to placebo in reduction of major cardiovascular events, including cardiovascular deaths, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke. The results presented at the 2023 American Heart Association meetings in Philadelphia ended in wholehearted applause by a “standing only” audience even before the presentation’s conclusion.
As we pave the way for nutrient-stimulated hormone (NuSH) therapies to be prescribed to all Americans with a BMI > 30 to improve health, we need to remember what these medications actually do. We used to think that metabolic bariatric surgery worked by restricting the stomach contents and malabsorbing nutrients. We now know that the surgeries work by altering NuSH secretion, allowing for less secretion of the hunger hormone ghrelin and more secretion of GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), peptide YY (PYY), cholecystokinin (CCK), oxyntomodulin (OXM), and other satiety hormones with less food ingestion.
They have pleiotropic effects on many organ systems in the body, including the brain, heart, adipose tissue, and liver. They decrease inflammation and also increase satiety and delay gastric emptying. None of these effects automatically produce weight loss, but they certainly aid in the adoption of a healthier body weight and better health. The weight loss occurs because these medications steer the body toward behavioral changes that promote weight loss.
As we delve into the SELECT trial results, a 20% reduction in major cardiovascular events was accompanied by an average weight loss of 9.6%, without a behavioral component added to either the placebo or intervention arms, as is usual in antiobesity agent trials.
Does this mean that primary care providers (PCPs) don’t have to educate patients on behavior change, diet, and exercise therapy? Well, if we consider obesity a disease as we do type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia or hypertension, then no — PCPs don’t have to, just like they don’t in treating these other diseases.
However, we should rethink this practice. The recently published SURMOUNT-3 trial looked at another NuSH, tirzepatide, with intensive behavioral therapy; it resulted in a 26.6% weight loss, which is comparable to results with bariatric surgery. The SURMOUNT-1 trial of tirzepatide with nonintensive behavioral therapy resulted in a 20.9% weight loss, which is still substantial, but SURMOUNT-3 showed how much more is achievable with robust behavior-change therapy.
In other words, it’s time that PCPs provide education on behavior change to maximize the power of the medications prescribed in practice for the most common diseases suffered in the United States: obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension. These are all chronic, relapsing diseases. Medication alone will improve numbers (weight, blood glucose, A1c, and blood pressure), but a relapsing disease continues relentlessly as patients age to overcome the medications prescribed.
Today I made another patient feel bad because she lost over 100 pounds on semaglutide (Wegovy) 2.4 mg over 1 year, reducing her BMI from 57 to 36. She wanted to keep losing, so I recommended sleeve gastrectomy to lose more weight. I told her she could always restart the Wegovy after the procedure if needed.
We really don’t have an answer to this issue of NuSH therapy not getting to goal and bariatric surgery following medication therapy. The reality is that bariatric surgery should be considered a safe, effective treatment for extreme obesity somewhere along the trajectory of treatments starting with behavior (diet, exercise) and medications. It is still considered a last resort, and for some, just too aggressive.
We have learned much about the incretin hormones and what they can accomplish for obesity from studying bariatric — now called metabolic — surgery. Surgery should be seen as we see stent placement for angina, only more effective for longevity. The COURAGE trial, published in 2007 in NEJM, showed that when compared with medication treatment alone for angina, stent placement plus medications resulted in no difference in mortality after a 7-year follow-up period. Compare this to bariatric surgery, which in many retrospective analyses shows a 20% reduction in cardiovascular mortality after 20-year follow-up (Swedish Obesity Study). In the United States, there are 2 million stent procedures performed per year vs 250,000 bariatric surgical procedures. There are millions of Americans with a BMI > 40 and, yes, millions of Americans with angina. I think I make my point that we need to do more bariatric surgeries to effectively treat extreme obesity.
The solution to this negligent medical practice in obesity treatment is to empower PCPs to treat obesity (at least uncomplicated obesity) and refer to obesity medicine practices for complicated obesity with multiple complications, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and to refer to obesity medicine practices with a surgical component for BMIs > 40 or > 35 with type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and/or cardiovascular disease or other serious conditions.
How do we empower PCPs? Insurance coverage of NuSH therapies due to life-saving properties — as evidenced by the SELECT trial — without prior authorizations; and education on how and why metabolic surgery works, as well as education on behavioral approaches, such as healthy diet and exercise, as a core therapy for all BMI categories.
It’s time.
Caroline Apovian, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Altimmune; Cowen and Company; Currax Pharmaceuticals; EPG Communication Holdings; Gelesis, Srl; L-Nutra; and NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals. Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and GI Dynamics. Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Altimmune; Cowen and Company; NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals; and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A few weeks ago, I made a patient who lost 100 pounds following a sleeve gastrectomy 9 months prior feel bad because I told her she lost too much weight. As I spoke to her, I realized that she found it hard to make life changes and that the surgery was a huge aide in changing her life and her lifestyle. I ended up apologizing for initially saying she lost too much weight.
For the first time in her life, she was successful in losing weight and keeping it off. The surgery allowed her body to defend a lower body weight by altering the secretion of gut hormones that lead to satiety in the brain. It’s not her fault that her body responded so well!
I asked her to be on my next orientation virtual meeting with prospective weight management patients to urge those with a body mass index (BMI) > 40 to consider bariatric surgery as the most effective durable and safe treatment for their degree of obesity.
Metabolic bariatric surgery, primarily sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass , alters the gut hormone milieu such that the body defends a lower mass of adipose tissue and a lower weight. We have learned what it takes to alter body weight defense to a healthy lower weight by studying why metabolic bariatric surgery works so well. It turns out that there are several hormones secreted by the gut that allow the brain to register fullness.
One of these gut hormones, glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1, has been researched as an analog to help reduce body weight by 16% and has also been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in the SELECT trial, as published in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
It’s the first weight loss medication to be shown in a cardiovascular outcomes trial to be superior to placebo in reduction of major cardiovascular events, including cardiovascular deaths, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke. The results presented at the 2023 American Heart Association meetings in Philadelphia ended in wholehearted applause by a “standing only” audience even before the presentation’s conclusion.
As we pave the way for nutrient-stimulated hormone (NuSH) therapies to be prescribed to all Americans with a BMI > 30 to improve health, we need to remember what these medications actually do. We used to think that metabolic bariatric surgery worked by restricting the stomach contents and malabsorbing nutrients. We now know that the surgeries work by altering NuSH secretion, allowing for less secretion of the hunger hormone ghrelin and more secretion of GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), peptide YY (PYY), cholecystokinin (CCK), oxyntomodulin (OXM), and other satiety hormones with less food ingestion.
They have pleiotropic effects on many organ systems in the body, including the brain, heart, adipose tissue, and liver. They decrease inflammation and also increase satiety and delay gastric emptying. None of these effects automatically produce weight loss, but they certainly aid in the adoption of a healthier body weight and better health. The weight loss occurs because these medications steer the body toward behavioral changes that promote weight loss.
As we delve into the SELECT trial results, a 20% reduction in major cardiovascular events was accompanied by an average weight loss of 9.6%, without a behavioral component added to either the placebo or intervention arms, as is usual in antiobesity agent trials.
Does this mean that primary care providers (PCPs) don’t have to educate patients on behavior change, diet, and exercise therapy? Well, if we consider obesity a disease as we do type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia or hypertension, then no — PCPs don’t have to, just like they don’t in treating these other diseases.
However, we should rethink this practice. The recently published SURMOUNT-3 trial looked at another NuSH, tirzepatide, with intensive behavioral therapy; it resulted in a 26.6% weight loss, which is comparable to results with bariatric surgery. The SURMOUNT-1 trial of tirzepatide with nonintensive behavioral therapy resulted in a 20.9% weight loss, which is still substantial, but SURMOUNT-3 showed how much more is achievable with robust behavior-change therapy.
In other words, it’s time that PCPs provide education on behavior change to maximize the power of the medications prescribed in practice for the most common diseases suffered in the United States: obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension. These are all chronic, relapsing diseases. Medication alone will improve numbers (weight, blood glucose, A1c, and blood pressure), but a relapsing disease continues relentlessly as patients age to overcome the medications prescribed.
Today I made another patient feel bad because she lost over 100 pounds on semaglutide (Wegovy) 2.4 mg over 1 year, reducing her BMI from 57 to 36. She wanted to keep losing, so I recommended sleeve gastrectomy to lose more weight. I told her she could always restart the Wegovy after the procedure if needed.
We really don’t have an answer to this issue of NuSH therapy not getting to goal and bariatric surgery following medication therapy. The reality is that bariatric surgery should be considered a safe, effective treatment for extreme obesity somewhere along the trajectory of treatments starting with behavior (diet, exercise) and medications. It is still considered a last resort, and for some, just too aggressive.
We have learned much about the incretin hormones and what they can accomplish for obesity from studying bariatric — now called metabolic — surgery. Surgery should be seen as we see stent placement for angina, only more effective for longevity. The COURAGE trial, published in 2007 in NEJM, showed that when compared with medication treatment alone for angina, stent placement plus medications resulted in no difference in mortality after a 7-year follow-up period. Compare this to bariatric surgery, which in many retrospective analyses shows a 20% reduction in cardiovascular mortality after 20-year follow-up (Swedish Obesity Study). In the United States, there are 2 million stent procedures performed per year vs 250,000 bariatric surgical procedures. There are millions of Americans with a BMI > 40 and, yes, millions of Americans with angina. I think I make my point that we need to do more bariatric surgeries to effectively treat extreme obesity.
The solution to this negligent medical practice in obesity treatment is to empower PCPs to treat obesity (at least uncomplicated obesity) and refer to obesity medicine practices for complicated obesity with multiple complications, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and to refer to obesity medicine practices with a surgical component for BMIs > 40 or > 35 with type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and/or cardiovascular disease or other serious conditions.
How do we empower PCPs? Insurance coverage of NuSH therapies due to life-saving properties — as evidenced by the SELECT trial — without prior authorizations; and education on how and why metabolic surgery works, as well as education on behavioral approaches, such as healthy diet and exercise, as a core therapy for all BMI categories.
It’s time.
Caroline Apovian, MD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for Altimmune; Cowen and Company; Currax Pharmaceuticals; EPG Communication Holdings; Gelesis, Srl; L-Nutra; and NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals. Received research grant from: National Institutes of Health; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and GI Dynamics. Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Altimmune; Cowen and Company; NeuroBo Pharmaceuticals; and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
First Impressions and Lessons Learned
“He was one of those fresh Jewish types you want to kill at sight ... she on the other hand looked Italian, a goaty slant to her eyes ... She looked dirty. So did he ... And she smelled, the usual smell of sweat and dirt you find among people who habitually do not wash or bathe ... People like that belong in clinics ... Just dumb oxen. Why the hell do they let them into the country? Half idiots at best.”
Who wrote that? Some hate-mongering pundit on a cable channel? A Twitter troll?
Nope. It was William Carlos Williams, MD, the patron saint of physician-writers.
You’re thinking “No! Not him!” We all read “The Use of Force” and “Red Wheelbarrow” in high school or college. But this blatant anti-Semitism and xenophobia?
The short story is “A Face of Stone” from his collection “The Doctor Stories” (highly recommended). When Williams was asked to remove those parts before publication, he refused because they’re a key part of the story. And I agree with him.
The point, as in so much of life, is the big picture. Despite his vivid disgust, he examines their infant, reassuring the mother that everything is okay, and later helping her with her leg pain and walking difficulties. At the end of the short story he realizes that his impressions were wrong and that people he started out hating are, well, just people who need help. And, as doctors, isn’t helping what we’re here to do?
It’s not just Williams, it’s all of us. First impressions aren’t always correct, but we rely on them — a lot. We’re programmed to. Our ancestors in the caves didn’t have much time to decided friend or foe when they encountered others.
So we initially judge people on their faces, expressions, hair, clothes, religious symbols (if present), jewelry ... The things that are registered by the brain in a split-second before the first words are exchanged.
All of us are constantly “scanning” others we encounter. In the office, store, restaurant, whatever. Usually those impressions are fleeting as we forget that person within a minute or two since we don’t see them again. But as doctors we do get to know them as patients, and so are constantly “updating” our mental files as new information comes in.
As Williams tells the story, he realizes that the “face of stone” isn’t that of the young mother he mentally derided — it’s his own face, turned that way by his first dismissive impression of the family, and then melted as he realizes he was wrong and learns from the experience to be a better doctor.
In vivid terms he reminds us that, although doctors, we are still susceptible to the same foibles, errors, and incorrect snap-judgments that all people are, but what matters is that we can, and have to, overcome them.
As a wall plaque in St. Mary’s General Hospital in Passaic, New Jersey, reminds us: “We walk the wards that Williams walked.”
We all do. Everyday. Everywhere.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“He was one of those fresh Jewish types you want to kill at sight ... she on the other hand looked Italian, a goaty slant to her eyes ... She looked dirty. So did he ... And she smelled, the usual smell of sweat and dirt you find among people who habitually do not wash or bathe ... People like that belong in clinics ... Just dumb oxen. Why the hell do they let them into the country? Half idiots at best.”
Who wrote that? Some hate-mongering pundit on a cable channel? A Twitter troll?
Nope. It was William Carlos Williams, MD, the patron saint of physician-writers.
You’re thinking “No! Not him!” We all read “The Use of Force” and “Red Wheelbarrow” in high school or college. But this blatant anti-Semitism and xenophobia?
The short story is “A Face of Stone” from his collection “The Doctor Stories” (highly recommended). When Williams was asked to remove those parts before publication, he refused because they’re a key part of the story. And I agree with him.
The point, as in so much of life, is the big picture. Despite his vivid disgust, he examines their infant, reassuring the mother that everything is okay, and later helping her with her leg pain and walking difficulties. At the end of the short story he realizes that his impressions were wrong and that people he started out hating are, well, just people who need help. And, as doctors, isn’t helping what we’re here to do?
It’s not just Williams, it’s all of us. First impressions aren’t always correct, but we rely on them — a lot. We’re programmed to. Our ancestors in the caves didn’t have much time to decided friend or foe when they encountered others.
So we initially judge people on their faces, expressions, hair, clothes, religious symbols (if present), jewelry ... The things that are registered by the brain in a split-second before the first words are exchanged.
All of us are constantly “scanning” others we encounter. In the office, store, restaurant, whatever. Usually those impressions are fleeting as we forget that person within a minute or two since we don’t see them again. But as doctors we do get to know them as patients, and so are constantly “updating” our mental files as new information comes in.
As Williams tells the story, he realizes that the “face of stone” isn’t that of the young mother he mentally derided — it’s his own face, turned that way by his first dismissive impression of the family, and then melted as he realizes he was wrong and learns from the experience to be a better doctor.
In vivid terms he reminds us that, although doctors, we are still susceptible to the same foibles, errors, and incorrect snap-judgments that all people are, but what matters is that we can, and have to, overcome them.
As a wall plaque in St. Mary’s General Hospital in Passaic, New Jersey, reminds us: “We walk the wards that Williams walked.”
We all do. Everyday. Everywhere.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“He was one of those fresh Jewish types you want to kill at sight ... she on the other hand looked Italian, a goaty slant to her eyes ... She looked dirty. So did he ... And she smelled, the usual smell of sweat and dirt you find among people who habitually do not wash or bathe ... People like that belong in clinics ... Just dumb oxen. Why the hell do they let them into the country? Half idiots at best.”
Who wrote that? Some hate-mongering pundit on a cable channel? A Twitter troll?
Nope. It was William Carlos Williams, MD, the patron saint of physician-writers.
You’re thinking “No! Not him!” We all read “The Use of Force” and “Red Wheelbarrow” in high school or college. But this blatant anti-Semitism and xenophobia?
The short story is “A Face of Stone” from his collection “The Doctor Stories” (highly recommended). When Williams was asked to remove those parts before publication, he refused because they’re a key part of the story. And I agree with him.
The point, as in so much of life, is the big picture. Despite his vivid disgust, he examines their infant, reassuring the mother that everything is okay, and later helping her with her leg pain and walking difficulties. At the end of the short story he realizes that his impressions were wrong and that people he started out hating are, well, just people who need help. And, as doctors, isn’t helping what we’re here to do?
It’s not just Williams, it’s all of us. First impressions aren’t always correct, but we rely on them — a lot. We’re programmed to. Our ancestors in the caves didn’t have much time to decided friend or foe when they encountered others.
So we initially judge people on their faces, expressions, hair, clothes, religious symbols (if present), jewelry ... The things that are registered by the brain in a split-second before the first words are exchanged.
All of us are constantly “scanning” others we encounter. In the office, store, restaurant, whatever. Usually those impressions are fleeting as we forget that person within a minute or two since we don’t see them again. But as doctors we do get to know them as patients, and so are constantly “updating” our mental files as new information comes in.
As Williams tells the story, he realizes that the “face of stone” isn’t that of the young mother he mentally derided — it’s his own face, turned that way by his first dismissive impression of the family, and then melted as he realizes he was wrong and learns from the experience to be a better doctor.
In vivid terms he reminds us that, although doctors, we are still susceptible to the same foibles, errors, and incorrect snap-judgments that all people are, but what matters is that we can, and have to, overcome them.
As a wall plaque in St. Mary’s General Hospital in Passaic, New Jersey, reminds us: “We walk the wards that Williams walked.”
We all do. Everyday. Everywhere.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Physicians as First Responders I
When I was an intern and junior resident there was a fellow house officer who seemed to be a magnet for out-of-hospital emergencies. There were a couple of car accidents, a baby to be delivered, an elderly neighbor with alarming chest pain, and a little old lady with syncope, plus a few playground incidents that required more than a little on-site tending and triage. It got to the point where he felt he needed to raid the hospital supply closets to build himself a proper emergency kit.
Envious of his excitement I, of course, followed suit. However, my well-appointed plastic tackle box remained unopened on the floor behind the driver’s seat in my car. Sure, there were Band-Aids to be dispensed from time to time but mostly I was the on-site reassurer and triage consultant at the playground. I almost never suggested a trip to the emergency room. No little old ladies crumpled to the floor in front of me in the checkout line at the grocery store. No distracted teenage drivers plowed into telephone poles anywhere within earshot.
When I began my practice here on the midcoast of Maine, my protective aura traveled with me. I went looking for excitement by signing on as the team physician for the local high school football team. But, other than a few minor concussions, which in those days we “treated” with a “sit on the bench for awhile and I’ll ask you a few questions,” my first responder experiences continued to be boringly undramatic. Not even any obvious dislocations or angulated fractures on the playground or athletic fields I frequented.
My professional adventures were confined to the hospital, where every physician regardless of specialty training was required to take a shift covering the emergency room. Talk about a situation looking for trouble. The concept of physicians with specialty training in emergency room medicine had not yet occurred to anyone in rural Maine. Although there were anxiety-provoking nights waiting for the disasters to arrive, somehow the shit never hit the fan while I was on duty.
Finally, after several more years of this bad (or good) fortune I was on a bike ride out in the country alone on a back road and came upon a fresh single-vehicle-single-occupant accident. Steam and smoke coming out of the engine compartment, the young driver slumped over the steering wheel. I was able to pry the door open but couldn’t find a pulse. I thumped him three times on the chest and eventually could detect a pulse and he began to stir. When the ambulance arrived I dragged my bike into the back of the ambulance with me and monitored him on the way to the hospital. He did fine, only to die in another accident a few years later.
A recent article in one of our local newspapers described a fledgling program in which three emergency room physicians are being equipped with supplies and communication links that will allow them to respond to emergent situations in the field. The program is currently seeking to extend its funding for another year. Its advocates argue that the need is twofold. There is currently a regional shortage of fully trained first responder EMTs. And having an extra pair of hands in the field could ease the burden of the already overutilized emergency rooms.
I am sure the physicians who have signed on to become first responders are passionate about the need and probably enjoy the excitement of in-the-field professional experiences, much as my fellow house officer did. However, were I sitting on the committee that controls the funding of programs like this I would want to take a step back and consider whether using primary care physicians, who are already in short supply, as first responders made sense. Some of the scenarios may be dramatic and the physician’s contribution may be life saving. But I suspect in the long run these headline-making stories will be few and far between.
The argument that putting physicians in the field will make a significant dent in the emergency room overutilization crisis we have in this country doesn’t hold water. Extending outpatient office hours, education, and improved phone triage to name just a few would have a bigger impact. I suspect there are other countries and even some counties in this country that may already use physicians as first responders. It just doesn’t seem to be a model that will work well given the realities in most semirural and suburban locales.
The real question that must wait for another Letters From Maine column is how well prepared should all of us who have graduated from medical school be to function as first responders. There are thousands of us out there who initially had the training and could, with some updating, become a valuable source of first-responders. Where do issues like continuing education requirements and Good Samaritan protection fit into the equation? The answers in a future Letter.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
When I was an intern and junior resident there was a fellow house officer who seemed to be a magnet for out-of-hospital emergencies. There were a couple of car accidents, a baby to be delivered, an elderly neighbor with alarming chest pain, and a little old lady with syncope, plus a few playground incidents that required more than a little on-site tending and triage. It got to the point where he felt he needed to raid the hospital supply closets to build himself a proper emergency kit.
Envious of his excitement I, of course, followed suit. However, my well-appointed plastic tackle box remained unopened on the floor behind the driver’s seat in my car. Sure, there were Band-Aids to be dispensed from time to time but mostly I was the on-site reassurer and triage consultant at the playground. I almost never suggested a trip to the emergency room. No little old ladies crumpled to the floor in front of me in the checkout line at the grocery store. No distracted teenage drivers plowed into telephone poles anywhere within earshot.
When I began my practice here on the midcoast of Maine, my protective aura traveled with me. I went looking for excitement by signing on as the team physician for the local high school football team. But, other than a few minor concussions, which in those days we “treated” with a “sit on the bench for awhile and I’ll ask you a few questions,” my first responder experiences continued to be boringly undramatic. Not even any obvious dislocations or angulated fractures on the playground or athletic fields I frequented.
My professional adventures were confined to the hospital, where every physician regardless of specialty training was required to take a shift covering the emergency room. Talk about a situation looking for trouble. The concept of physicians with specialty training in emergency room medicine had not yet occurred to anyone in rural Maine. Although there were anxiety-provoking nights waiting for the disasters to arrive, somehow the shit never hit the fan while I was on duty.
Finally, after several more years of this bad (or good) fortune I was on a bike ride out in the country alone on a back road and came upon a fresh single-vehicle-single-occupant accident. Steam and smoke coming out of the engine compartment, the young driver slumped over the steering wheel. I was able to pry the door open but couldn’t find a pulse. I thumped him three times on the chest and eventually could detect a pulse and he began to stir. When the ambulance arrived I dragged my bike into the back of the ambulance with me and monitored him on the way to the hospital. He did fine, only to die in another accident a few years later.
A recent article in one of our local newspapers described a fledgling program in which three emergency room physicians are being equipped with supplies and communication links that will allow them to respond to emergent situations in the field. The program is currently seeking to extend its funding for another year. Its advocates argue that the need is twofold. There is currently a regional shortage of fully trained first responder EMTs. And having an extra pair of hands in the field could ease the burden of the already overutilized emergency rooms.
I am sure the physicians who have signed on to become first responders are passionate about the need and probably enjoy the excitement of in-the-field professional experiences, much as my fellow house officer did. However, were I sitting on the committee that controls the funding of programs like this I would want to take a step back and consider whether using primary care physicians, who are already in short supply, as first responders made sense. Some of the scenarios may be dramatic and the physician’s contribution may be life saving. But I suspect in the long run these headline-making stories will be few and far between.
The argument that putting physicians in the field will make a significant dent in the emergency room overutilization crisis we have in this country doesn’t hold water. Extending outpatient office hours, education, and improved phone triage to name just a few would have a bigger impact. I suspect there are other countries and even some counties in this country that may already use physicians as first responders. It just doesn’t seem to be a model that will work well given the realities in most semirural and suburban locales.
The real question that must wait for another Letters From Maine column is how well prepared should all of us who have graduated from medical school be to function as first responders. There are thousands of us out there who initially had the training and could, with some updating, become a valuable source of first-responders. Where do issues like continuing education requirements and Good Samaritan protection fit into the equation? The answers in a future Letter.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
When I was an intern and junior resident there was a fellow house officer who seemed to be a magnet for out-of-hospital emergencies. There were a couple of car accidents, a baby to be delivered, an elderly neighbor with alarming chest pain, and a little old lady with syncope, plus a few playground incidents that required more than a little on-site tending and triage. It got to the point where he felt he needed to raid the hospital supply closets to build himself a proper emergency kit.
Envious of his excitement I, of course, followed suit. However, my well-appointed plastic tackle box remained unopened on the floor behind the driver’s seat in my car. Sure, there were Band-Aids to be dispensed from time to time but mostly I was the on-site reassurer and triage consultant at the playground. I almost never suggested a trip to the emergency room. No little old ladies crumpled to the floor in front of me in the checkout line at the grocery store. No distracted teenage drivers plowed into telephone poles anywhere within earshot.
When I began my practice here on the midcoast of Maine, my protective aura traveled with me. I went looking for excitement by signing on as the team physician for the local high school football team. But, other than a few minor concussions, which in those days we “treated” with a “sit on the bench for awhile and I’ll ask you a few questions,” my first responder experiences continued to be boringly undramatic. Not even any obvious dislocations or angulated fractures on the playground or athletic fields I frequented.
My professional adventures were confined to the hospital, where every physician regardless of specialty training was required to take a shift covering the emergency room. Talk about a situation looking for trouble. The concept of physicians with specialty training in emergency room medicine had not yet occurred to anyone in rural Maine. Although there were anxiety-provoking nights waiting for the disasters to arrive, somehow the shit never hit the fan while I was on duty.
Finally, after several more years of this bad (or good) fortune I was on a bike ride out in the country alone on a back road and came upon a fresh single-vehicle-single-occupant accident. Steam and smoke coming out of the engine compartment, the young driver slumped over the steering wheel. I was able to pry the door open but couldn’t find a pulse. I thumped him three times on the chest and eventually could detect a pulse and he began to stir. When the ambulance arrived I dragged my bike into the back of the ambulance with me and monitored him on the way to the hospital. He did fine, only to die in another accident a few years later.
A recent article in one of our local newspapers described a fledgling program in which three emergency room physicians are being equipped with supplies and communication links that will allow them to respond to emergent situations in the field. The program is currently seeking to extend its funding for another year. Its advocates argue that the need is twofold. There is currently a regional shortage of fully trained first responder EMTs. And having an extra pair of hands in the field could ease the burden of the already overutilized emergency rooms.
I am sure the physicians who have signed on to become first responders are passionate about the need and probably enjoy the excitement of in-the-field professional experiences, much as my fellow house officer did. However, were I sitting on the committee that controls the funding of programs like this I would want to take a step back and consider whether using primary care physicians, who are already in short supply, as first responders made sense. Some of the scenarios may be dramatic and the physician’s contribution may be life saving. But I suspect in the long run these headline-making stories will be few and far between.
The argument that putting physicians in the field will make a significant dent in the emergency room overutilization crisis we have in this country doesn’t hold water. Extending outpatient office hours, education, and improved phone triage to name just a few would have a bigger impact. I suspect there are other countries and even some counties in this country that may already use physicians as first responders. It just doesn’t seem to be a model that will work well given the realities in most semirural and suburban locales.
The real question that must wait for another Letters From Maine column is how well prepared should all of us who have graduated from medical school be to function as first responders. There are thousands of us out there who initially had the training and could, with some updating, become a valuable source of first-responders. Where do issues like continuing education requirements and Good Samaritan protection fit into the equation? The answers in a future Letter.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Iron Overload in Non-HFE Liver Disease: Not all Iron is Ready to Strike
Pathological iron overload with end-organ damage in hemochromatosis occurs in individuals who are homozygous for the major mutation C282Y. Phenotypic hemochromatosis occurs much less frequently in compound heterozygotes with one C282Y mutation and one H63D mutation. Iron overload can be confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging, which shows a loss of signal intensity in affected tissues and avoids the need for liver biopsy.
The serum ferritin level, an acute phase reactant, may be elevated for reasons other than iron overload, including infection and malignancy; in such cases, the iron saturation is usually normal. In patients with liver disease, iron overload is not restricted to patients with genetic hemochromatosis. In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), up to one-third of patients have an elevated iron saturation (> 45%) and an elevated serum ferritin level. Iron accumulation in NAFLD can occur in hepatocytes, the reticuloendothelial system, or both. Deposition of iron in the reticuloendothelial system has been implicated in more severe liver disease (steatohepatitis and fibrosis) in NAFLD. Hepatic iron accumulation is also frequent in alcohol-associated liver disease. In chronic hepatitis B and C, accumulation of hepatic iron is also recognized.
Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Massachusetts, and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. The authors disclosed no conflicts. Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.10.004.
Pathological iron overload with end-organ damage in hemochromatosis occurs in individuals who are homozygous for the major mutation C282Y. Phenotypic hemochromatosis occurs much less frequently in compound heterozygotes with one C282Y mutation and one H63D mutation. Iron overload can be confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging, which shows a loss of signal intensity in affected tissues and avoids the need for liver biopsy.
The serum ferritin level, an acute phase reactant, may be elevated for reasons other than iron overload, including infection and malignancy; in such cases, the iron saturation is usually normal. In patients with liver disease, iron overload is not restricted to patients with genetic hemochromatosis. In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), up to one-third of patients have an elevated iron saturation (> 45%) and an elevated serum ferritin level. Iron accumulation in NAFLD can occur in hepatocytes, the reticuloendothelial system, or both. Deposition of iron in the reticuloendothelial system has been implicated in more severe liver disease (steatohepatitis and fibrosis) in NAFLD. Hepatic iron accumulation is also frequent in alcohol-associated liver disease. In chronic hepatitis B and C, accumulation of hepatic iron is also recognized.
Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Massachusetts, and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. The authors disclosed no conflicts. Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.10.004.
Pathological iron overload with end-organ damage in hemochromatosis occurs in individuals who are homozygous for the major mutation C282Y. Phenotypic hemochromatosis occurs much less frequently in compound heterozygotes with one C282Y mutation and one H63D mutation. Iron overload can be confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging, which shows a loss of signal intensity in affected tissues and avoids the need for liver biopsy.
The serum ferritin level, an acute phase reactant, may be elevated for reasons other than iron overload, including infection and malignancy; in such cases, the iron saturation is usually normal. In patients with liver disease, iron overload is not restricted to patients with genetic hemochromatosis. In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), up to one-third of patients have an elevated iron saturation (> 45%) and an elevated serum ferritin level. Iron accumulation in NAFLD can occur in hepatocytes, the reticuloendothelial system, or both. Deposition of iron in the reticuloendothelial system has been implicated in more severe liver disease (steatohepatitis and fibrosis) in NAFLD. Hepatic iron accumulation is also frequent in alcohol-associated liver disease. In chronic hepatitis B and C, accumulation of hepatic iron is also recognized.
Dr. Martin is chief of the division of digestive health and liver diseases at the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, where he is the Mandel Chair of Gastroenterology. Dr. Friedman is the Anton R. Fried, MD, Chair of the department of medicine at Newton-Wellesley Hospital in Newton, Massachusetts, and assistant chief of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and Tufts University School of Medicine, all in Boston. The authors disclosed no conflicts. Previously published in Gastro Hep Advances. 2023 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.10.004.
Guidelines Aren’t For Everybody
An 88-year-old man comes for clinic follow up. He has a medical history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and chronic kidney disease. He recently had laboratory tests done: BUN, 32 mg/dL; creatinine, 2.3 mg/dL; potassium, 4.5 mmol/L; bicarbonate, 22 Eq/L; and A1c, 8.2%.
He checks his blood glucose daily (alternating between fasting blood glucose and before dinner) and his fasting blood glucose levels are around 130 mg/dL. His highest glucose reading was 240 mg/dL. He does not have polyuria or visual changes. Current medications: atorvastatin, irbesartan, empagliflozin, and amlodipine. On physical exam his blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80, and his BMI 20.
What medication adjustments would you recommend?
A. Begin insulin glargine at bedtime
B. Begin mealtime insulin aspart
C. Begin semaglutide
D. Begin metformin
E. No changes
I think the correct approach here would be no changes. Most physicians know guideline recommendations for A1c of less than 7% are used for patients with diabetes with few comorbid conditions, normal cognition, and functional status. Many of our elderly patients do not meet these criteria and the goal of intense medical treatment of diabetes is different in those patients. The American Diabetes Association has issued a thoughtful paper on treatment of diabetes in elderly people, stressing that patients should have very individualized goals, and that there is no one-size-fits all A1c goal.1
In this patient I would avoid adding insulin, given hypoglycemia risk. A GLP-1 agonist might appear attractive given his multiple cardiovascular risk factors, but his low BMI is a major concern for frailty that may well be worsened with reduced nutrient intake. Diabetes is the chronic condition that probably has the most guidance for management in elderly patients.
I recently saw a 92-year-old man with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and atrial fibrillation who had been losing weight and becoming weaker. He had suffered several falls in the previous 2 weeks. His medication list included amiodarone, apixaban, sacubitril/valsartan, carvedilol, empagliflozin, spironolactone, and furosemide. He was extremely frail and had stopped eating. He was receiving all guideline-directed therapies, yet he was miserable and dying. Falls in this population are potentially as fatal as decompensated heart disease.
I stopped his amiodarone, furosemide, and spironolactone, and reduced his doses of sacubitril/valsartan and carvedilol. His appetite returned and his will to live returned. Heart failure guidelines do not include robust studies of very elderly patients because few studies exist in this population. Frailty assessment is crucial in decision making in your elderly patients.2,3 and frequent check-ins to make sure that they are not suffering from the effects of polypharmacy are crucial. Our goal in our very elderly patients is quality life-years. Polypharmacy has the potential to decrease the quality of life, as well as potentially shorten life.
The very elderly are at risk of the negative consequences of polypharmacy, especially if they have several diseases like diabetes, congestive heart failure, and hypertension that may require multiple medications. Gutierrez-Valencia and colleagues performed a systematic review of 25 articles on frailty and polypharmacy.4 Their findings demonstrated a significant association between an increased number of medications and frailty. They postulated that polypharmacy could actually be a contributor to frailty. There just isn’t enough evidence for the benefit of guidelines in the very aged and the risks of polypharmacy are real. We should use the lowest possible doses of medications in this population, frequently reassess goals, and monitor closely for side effects.
Pearl: Always consider the risks of polypharmacy when considering therapies for your elderly patients.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S168–S179.
2. Gaur A et al. Cardiogeriatrics: The current state of the art. Heart. 2024 Jan 11:heartjnl-2022-322117.
3. Denfeld QE et al. Assessing and managing frailty in advanced heart failure: An International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation consensus statement. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2023 Nov 29:S1053-2498(23)02028-4.
4. Gutiérrez-Valencia M et al. The relationship between frailty and polypharmacy in older people: A systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1432-44.
An 88-year-old man comes for clinic follow up. He has a medical history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and chronic kidney disease. He recently had laboratory tests done: BUN, 32 mg/dL; creatinine, 2.3 mg/dL; potassium, 4.5 mmol/L; bicarbonate, 22 Eq/L; and A1c, 8.2%.
He checks his blood glucose daily (alternating between fasting blood glucose and before dinner) and his fasting blood glucose levels are around 130 mg/dL. His highest glucose reading was 240 mg/dL. He does not have polyuria or visual changes. Current medications: atorvastatin, irbesartan, empagliflozin, and amlodipine. On physical exam his blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80, and his BMI 20.
What medication adjustments would you recommend?
A. Begin insulin glargine at bedtime
B. Begin mealtime insulin aspart
C. Begin semaglutide
D. Begin metformin
E. No changes
I think the correct approach here would be no changes. Most physicians know guideline recommendations for A1c of less than 7% are used for patients with diabetes with few comorbid conditions, normal cognition, and functional status. Many of our elderly patients do not meet these criteria and the goal of intense medical treatment of diabetes is different in those patients. The American Diabetes Association has issued a thoughtful paper on treatment of diabetes in elderly people, stressing that patients should have very individualized goals, and that there is no one-size-fits all A1c goal.1
In this patient I would avoid adding insulin, given hypoglycemia risk. A GLP-1 agonist might appear attractive given his multiple cardiovascular risk factors, but his low BMI is a major concern for frailty that may well be worsened with reduced nutrient intake. Diabetes is the chronic condition that probably has the most guidance for management in elderly patients.
I recently saw a 92-year-old man with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and atrial fibrillation who had been losing weight and becoming weaker. He had suffered several falls in the previous 2 weeks. His medication list included amiodarone, apixaban, sacubitril/valsartan, carvedilol, empagliflozin, spironolactone, and furosemide. He was extremely frail and had stopped eating. He was receiving all guideline-directed therapies, yet he was miserable and dying. Falls in this population are potentially as fatal as decompensated heart disease.
I stopped his amiodarone, furosemide, and spironolactone, and reduced his doses of sacubitril/valsartan and carvedilol. His appetite returned and his will to live returned. Heart failure guidelines do not include robust studies of very elderly patients because few studies exist in this population. Frailty assessment is crucial in decision making in your elderly patients.2,3 and frequent check-ins to make sure that they are not suffering from the effects of polypharmacy are crucial. Our goal in our very elderly patients is quality life-years. Polypharmacy has the potential to decrease the quality of life, as well as potentially shorten life.
The very elderly are at risk of the negative consequences of polypharmacy, especially if they have several diseases like diabetes, congestive heart failure, and hypertension that may require multiple medications. Gutierrez-Valencia and colleagues performed a systematic review of 25 articles on frailty and polypharmacy.4 Their findings demonstrated a significant association between an increased number of medications and frailty. They postulated that polypharmacy could actually be a contributor to frailty. There just isn’t enough evidence for the benefit of guidelines in the very aged and the risks of polypharmacy are real. We should use the lowest possible doses of medications in this population, frequently reassess goals, and monitor closely for side effects.
Pearl: Always consider the risks of polypharmacy when considering therapies for your elderly patients.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S168–S179.
2. Gaur A et al. Cardiogeriatrics: The current state of the art. Heart. 2024 Jan 11:heartjnl-2022-322117.
3. Denfeld QE et al. Assessing and managing frailty in advanced heart failure: An International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation consensus statement. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2023 Nov 29:S1053-2498(23)02028-4.
4. Gutiérrez-Valencia M et al. The relationship between frailty and polypharmacy in older people: A systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1432-44.
An 88-year-old man comes for clinic follow up. He has a medical history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and chronic kidney disease. He recently had laboratory tests done: BUN, 32 mg/dL; creatinine, 2.3 mg/dL; potassium, 4.5 mmol/L; bicarbonate, 22 Eq/L; and A1c, 8.2%.
He checks his blood glucose daily (alternating between fasting blood glucose and before dinner) and his fasting blood glucose levels are around 130 mg/dL. His highest glucose reading was 240 mg/dL. He does not have polyuria or visual changes. Current medications: atorvastatin, irbesartan, empagliflozin, and amlodipine. On physical exam his blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80, and his BMI 20.
What medication adjustments would you recommend?
A. Begin insulin glargine at bedtime
B. Begin mealtime insulin aspart
C. Begin semaglutide
D. Begin metformin
E. No changes
I think the correct approach here would be no changes. Most physicians know guideline recommendations for A1c of less than 7% are used for patients with diabetes with few comorbid conditions, normal cognition, and functional status. Many of our elderly patients do not meet these criteria and the goal of intense medical treatment of diabetes is different in those patients. The American Diabetes Association has issued a thoughtful paper on treatment of diabetes in elderly people, stressing that patients should have very individualized goals, and that there is no one-size-fits all A1c goal.1
In this patient I would avoid adding insulin, given hypoglycemia risk. A GLP-1 agonist might appear attractive given his multiple cardiovascular risk factors, but his low BMI is a major concern for frailty that may well be worsened with reduced nutrient intake. Diabetes is the chronic condition that probably has the most guidance for management in elderly patients.
I recently saw a 92-year-old man with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and atrial fibrillation who had been losing weight and becoming weaker. He had suffered several falls in the previous 2 weeks. His medication list included amiodarone, apixaban, sacubitril/valsartan, carvedilol, empagliflozin, spironolactone, and furosemide. He was extremely frail and had stopped eating. He was receiving all guideline-directed therapies, yet he was miserable and dying. Falls in this population are potentially as fatal as decompensated heart disease.
I stopped his amiodarone, furosemide, and spironolactone, and reduced his doses of sacubitril/valsartan and carvedilol. His appetite returned and his will to live returned. Heart failure guidelines do not include robust studies of very elderly patients because few studies exist in this population. Frailty assessment is crucial in decision making in your elderly patients.2,3 and frequent check-ins to make sure that they are not suffering from the effects of polypharmacy are crucial. Our goal in our very elderly patients is quality life-years. Polypharmacy has the potential to decrease the quality of life, as well as potentially shorten life.
The very elderly are at risk of the negative consequences of polypharmacy, especially if they have several diseases like diabetes, congestive heart failure, and hypertension that may require multiple medications. Gutierrez-Valencia and colleagues performed a systematic review of 25 articles on frailty and polypharmacy.4 Their findings demonstrated a significant association between an increased number of medications and frailty. They postulated that polypharmacy could actually be a contributor to frailty. There just isn’t enough evidence for the benefit of guidelines in the very aged and the risks of polypharmacy are real. We should use the lowest possible doses of medications in this population, frequently reassess goals, and monitor closely for side effects.
Pearl: Always consider the risks of polypharmacy when considering therapies for your elderly patients.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — 2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S168–S179.
2. Gaur A et al. Cardiogeriatrics: The current state of the art. Heart. 2024 Jan 11:heartjnl-2022-322117.
3. Denfeld QE et al. Assessing and managing frailty in advanced heart failure: An International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation consensus statement. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2023 Nov 29:S1053-2498(23)02028-4.
4. Gutiérrez-Valencia M et al. The relationship between frailty and polypharmacy in older people: A systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1432-44.
Offsetting Side Effects of New Antiobesity Medications
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s 2 a.m. and my phone wakes me up with a start. My patient, Christine Z*, is vomiting uncontrollably, and Dr Google has diagnosed her with acute pancreatitis from semaglutide (Wegovy). Ten hours, several imaging studies, one blood draw, and many bags of fluids later, the verdict is in: Christine is alarmingly constipated. In fact, her entire large intestine is packed to the brim with stool. In residency, we called this diagnosis FOS, and I’ll leave it to your imagination to figure out what it stands for.
In retrospect, Christine mentions that upon raising her Wegovy dose, her bowel movements had become increasingly smaller and infrequent. This begs the question:
Proper nutrition always starts with drinking copious amounts of water. In general, I recommend a minimum of 64 ounces of water daily in patients taking incretins such as semaglutide (Wegovy for weight loss, Ozempic and Rybelsus for type 2 diabetes) or tirzepatide (Zepbound for weight loss, Mounjaro for type 2 diabetes). While these medications don’t directly dehydrate patients, they can increase the risk for dehydration due to severe nausea. Drinking copious amounts of water can prevent dehydration, preserve kidney function, and minimize fatigue and dizziness. In addition, fluids help soften bowel movements, making them easier to pass.
Occasionally incretins make it so easy for patients to drop pounds that their eating patterns become sloppier — more sweets and simple carbohydrates. I recommend a realistic and low glycemic index meal plan. While no foods are strictly contraindicated, processed, high-sugar, and fatty foods are likely to worsen side effects like nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Similarly, alcohol not only worsens nausea, but it’s also likely to exacerbate reflux by relaxing the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus.
The next most important dietary advice is consuming sufficient fiber. In the majority of patients, increasing fiber intake relieves constipation. There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. In practical terms, most fiber-rich foods contain a mixture of these two types. The general recommendation is 38 g/d for men and 25 g/d for women. The caveat to this advice is that a minority of patients, such as those with irritable bowel syndrome, may develop worsening constipation with increasing fiber.
To minimize side effects, some patients find it useful to eat five small meals throughout the day rather than three larger meals. In addition, I recommend eating slowly and stopping before the point of satiety. Finally, because weight loss of any kind is inevitably associated with muscle loss, I stress the importance of adequate protein. In general, I advise 25-30 g of protein per meal.
Christine eventually restarted her Wegovy after recovering from her grueling night in the emergency room. As this was her second go-around on Wegovy, she dug out my “guide to preventing side effects of incretins” and followed it to a T. So far, she’s feeling great.
*The patient’s name has been changed.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Unlikely Breakthrough of the Year: Chemo for Lung Cancer
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’ve been spending time recently reflecting on the biggest developments from last year. I have to say that the breakthrough of the year, based on the amount of data presented and the importance of the data, is chemotherapy. I never thought I would say that. Many folks have tried to relegate chemotherapy to the museum, but last year it came to the forefront.
Let’s start with neoadjuvant therapy. We now have multiple drug approvals for giving a checkpoint inhibitor and neoadjuvant therapy in what I would say is a new standard of care for patients with locally advanced lung cancers who are candidates for surgery. In all those trials, there was a clear improvement in progression-free survival by adding a checkpoint inhibitor to chemotherapy. The cornerstone of this regimen is chemotherapy.
What about adjuvant therapy? I think one of the most astounding pieces of data last year was in the adjuvant realm. In the trial comparing adjuvant osimertinib with placebo in patients with EGFR-mutant disease, patients who received chemotherapy in addition to osimertinib had a 7% improvement in 5-year survival. Patients who had placebo, who got chemotherapy vs didn’t, had a 9% improvement in 5-year survival. Those are huge numbers for that kind of metric, and it happened with chemotherapy.
What about targeted therapies? Again, I think people were astounded that, by adding chemotherapy to osimertinib compared with osimertinib alone, there was a 9-month improvement overall in progression-free survival. I think in the presentation of the data that has been made, the most remarkable piece of data is that, in patients with brain metastases, chemotherapy on top of osimertinib improved progression-free survival. Not only did it improve progression-free survival, but it did it with brain metastases, where people think it just doesn’t help at all.
What about other, newer agents with chemotherapy? Amivantamab, I would say, has hitched itself to chemotherapy. A trial in EGFR exon 20 compared chemo to amivantamab plus chemotherapy. There again, chemo is the common denominator. Amivantamab added approximately 5 months of improved progression-free survival. Again, chemo was used. In adjuvant, neoadjuvant, and targeted therapies, chemotherapy adds.
What about the second line? I think everybody was very disappointed when second-line sotorasib gave a very tiny amount of progression-free survival improvement over docetaxel. I think we all want more for our patients than we can deliver with docetaxel. The roughly 5-week improvement seen with sotorasib was one that raised a question about the place of sotorasib in this setting.
Clearly, we’ve all seen patients have an excellent result with sotorasib as an additional option for treating patients with long progression-free survival, high rates of response, and good tolerability even at the 960 mg dose. But in the randomized trial, it wasn’t better than docetaxel. Again, I think we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine in that it could not beat docetaxel either. I think the idea here is that chemo still has a huge place and still remains the treatment that we have to beat.
We’re all very excited about the antibody-drug conjugates and I think everybody sees them as another advance. Many folks have said that they are just a more precise way of delivering chemotherapy, and when you look at the side effects, it supports that — they’re largely side effects of chemotherapy with these drugs across the board. Also, when you look at the patterns of resistance, the resistance really isn’t a resistance to the targeted therapy; it’s a resistance to chemotherapy more than anything else.
So we’re happy that the antibody-drug conjugates are available and we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine because we thought that it could beat docetaxel. But in truth, it didn’t, and unfortunately, that pivotal trial led to the end of the entire development program for that agent, as stated in a press release.
The molecule or treatment of the year is chemotherapy — added to targeted therapies, used with immunotherapy, and now attached to antibodies as part of antibody-drug conjugates. I think it remains, more than any one treatment, a very effective treatment for patients and deserves to be used.
There are a lot of choices here. I think you have to be very careful to choose wisely, and you also have to be careful because chemotherapy has side effects. The nice thing is that many of those side effects can be ameliorated. We have to make sure that we use all the supportive medications we can.
Who would have thought that chemotherapy would be the treatment of the year in 2023 for lung cancers?
Dr. Kris is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc, and PUMA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’ve been spending time recently reflecting on the biggest developments from last year. I have to say that the breakthrough of the year, based on the amount of data presented and the importance of the data, is chemotherapy. I never thought I would say that. Many folks have tried to relegate chemotherapy to the museum, but last year it came to the forefront.
Let’s start with neoadjuvant therapy. We now have multiple drug approvals for giving a checkpoint inhibitor and neoadjuvant therapy in what I would say is a new standard of care for patients with locally advanced lung cancers who are candidates for surgery. In all those trials, there was a clear improvement in progression-free survival by adding a checkpoint inhibitor to chemotherapy. The cornerstone of this regimen is chemotherapy.
What about adjuvant therapy? I think one of the most astounding pieces of data last year was in the adjuvant realm. In the trial comparing adjuvant osimertinib with placebo in patients with EGFR-mutant disease, patients who received chemotherapy in addition to osimertinib had a 7% improvement in 5-year survival. Patients who had placebo, who got chemotherapy vs didn’t, had a 9% improvement in 5-year survival. Those are huge numbers for that kind of metric, and it happened with chemotherapy.
What about targeted therapies? Again, I think people were astounded that, by adding chemotherapy to osimertinib compared with osimertinib alone, there was a 9-month improvement overall in progression-free survival. I think in the presentation of the data that has been made, the most remarkable piece of data is that, in patients with brain metastases, chemotherapy on top of osimertinib improved progression-free survival. Not only did it improve progression-free survival, but it did it with brain metastases, where people think it just doesn’t help at all.
What about other, newer agents with chemotherapy? Amivantamab, I would say, has hitched itself to chemotherapy. A trial in EGFR exon 20 compared chemo to amivantamab plus chemotherapy. There again, chemo is the common denominator. Amivantamab added approximately 5 months of improved progression-free survival. Again, chemo was used. In adjuvant, neoadjuvant, and targeted therapies, chemotherapy adds.
What about the second line? I think everybody was very disappointed when second-line sotorasib gave a very tiny amount of progression-free survival improvement over docetaxel. I think we all want more for our patients than we can deliver with docetaxel. The roughly 5-week improvement seen with sotorasib was one that raised a question about the place of sotorasib in this setting.
Clearly, we’ve all seen patients have an excellent result with sotorasib as an additional option for treating patients with long progression-free survival, high rates of response, and good tolerability even at the 960 mg dose. But in the randomized trial, it wasn’t better than docetaxel. Again, I think we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine in that it could not beat docetaxel either. I think the idea here is that chemo still has a huge place and still remains the treatment that we have to beat.
We’re all very excited about the antibody-drug conjugates and I think everybody sees them as another advance. Many folks have said that they are just a more precise way of delivering chemotherapy, and when you look at the side effects, it supports that — they’re largely side effects of chemotherapy with these drugs across the board. Also, when you look at the patterns of resistance, the resistance really isn’t a resistance to the targeted therapy; it’s a resistance to chemotherapy more than anything else.
So we’re happy that the antibody-drug conjugates are available and we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine because we thought that it could beat docetaxel. But in truth, it didn’t, and unfortunately, that pivotal trial led to the end of the entire development program for that agent, as stated in a press release.
The molecule or treatment of the year is chemotherapy — added to targeted therapies, used with immunotherapy, and now attached to antibodies as part of antibody-drug conjugates. I think it remains, more than any one treatment, a very effective treatment for patients and deserves to be used.
There are a lot of choices here. I think you have to be very careful to choose wisely, and you also have to be careful because chemotherapy has side effects. The nice thing is that many of those side effects can be ameliorated. We have to make sure that we use all the supportive medications we can.
Who would have thought that chemotherapy would be the treatment of the year in 2023 for lung cancers?
Dr. Kris is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc, and PUMA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’ve been spending time recently reflecting on the biggest developments from last year. I have to say that the breakthrough of the year, based on the amount of data presented and the importance of the data, is chemotherapy. I never thought I would say that. Many folks have tried to relegate chemotherapy to the museum, but last year it came to the forefront.
Let’s start with neoadjuvant therapy. We now have multiple drug approvals for giving a checkpoint inhibitor and neoadjuvant therapy in what I would say is a new standard of care for patients with locally advanced lung cancers who are candidates for surgery. In all those trials, there was a clear improvement in progression-free survival by adding a checkpoint inhibitor to chemotherapy. The cornerstone of this regimen is chemotherapy.
What about adjuvant therapy? I think one of the most astounding pieces of data last year was in the adjuvant realm. In the trial comparing adjuvant osimertinib with placebo in patients with EGFR-mutant disease, patients who received chemotherapy in addition to osimertinib had a 7% improvement in 5-year survival. Patients who had placebo, who got chemotherapy vs didn’t, had a 9% improvement in 5-year survival. Those are huge numbers for that kind of metric, and it happened with chemotherapy.
What about targeted therapies? Again, I think people were astounded that, by adding chemotherapy to osimertinib compared with osimertinib alone, there was a 9-month improvement overall in progression-free survival. I think in the presentation of the data that has been made, the most remarkable piece of data is that, in patients with brain metastases, chemotherapy on top of osimertinib improved progression-free survival. Not only did it improve progression-free survival, but it did it with brain metastases, where people think it just doesn’t help at all.
What about other, newer agents with chemotherapy? Amivantamab, I would say, has hitched itself to chemotherapy. A trial in EGFR exon 20 compared chemo to amivantamab plus chemotherapy. There again, chemo is the common denominator. Amivantamab added approximately 5 months of improved progression-free survival. Again, chemo was used. In adjuvant, neoadjuvant, and targeted therapies, chemotherapy adds.
What about the second line? I think everybody was very disappointed when second-line sotorasib gave a very tiny amount of progression-free survival improvement over docetaxel. I think we all want more for our patients than we can deliver with docetaxel. The roughly 5-week improvement seen with sotorasib was one that raised a question about the place of sotorasib in this setting.
Clearly, we’ve all seen patients have an excellent result with sotorasib as an additional option for treating patients with long progression-free survival, high rates of response, and good tolerability even at the 960 mg dose. But in the randomized trial, it wasn’t better than docetaxel. Again, I think we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine in that it could not beat docetaxel either. I think the idea here is that chemo still has a huge place and still remains the treatment that we have to beat.
We’re all very excited about the antibody-drug conjugates and I think everybody sees them as another advance. Many folks have said that they are just a more precise way of delivering chemotherapy, and when you look at the side effects, it supports that — they’re largely side effects of chemotherapy with these drugs across the board. Also, when you look at the patterns of resistance, the resistance really isn’t a resistance to the targeted therapy; it’s a resistance to chemotherapy more than anything else.
So we’re happy that the antibody-drug conjugates are available and we were disappointed with tusamitamab ravtansine because we thought that it could beat docetaxel. But in truth, it didn’t, and unfortunately, that pivotal trial led to the end of the entire development program for that agent, as stated in a press release.
The molecule or treatment of the year is chemotherapy — added to targeted therapies, used with immunotherapy, and now attached to antibodies as part of antibody-drug conjugates. I think it remains, more than any one treatment, a very effective treatment for patients and deserves to be used.
There are a lot of choices here. I think you have to be very careful to choose wisely, and you also have to be careful because chemotherapy has side effects. The nice thing is that many of those side effects can be ameliorated. We have to make sure that we use all the supportive medications we can.
Who would have thought that chemotherapy would be the treatment of the year in 2023 for lung cancers?
Dr. Kris is chief of the thoracic oncology service and the William and Joy Ruane Chair in Thoracic Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. He disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc, and PUMA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Implementing Trustworthy AI in VA High Reliability Health Care Organizations
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has lagged in health care but has considerable potential to improve quality, safety, clinician experience, and access to care. It is being tested in areas like billing, hospital operations, and preventing adverse events (eg, sepsis mortality) with some early success. However, there are still many barriers preventing the widespread use of AI, such as data problems, mismatched rewards, and workplace obstacles. Innovative projects, partnerships, better rewards, and more investment could remove barriers. Implemented reliably and safely, AI can add to what clinicians know, help them work faster, cut costs, and, most importantly, improve patient care.1
AI can potentially bring several clinical benefits, such as reducing the administrative strain on clinicians and granting them more time for direct patient care. It can also improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing patient data and diagnostic images, providing differential diagnoses, and increasing access to care by providing medical information and essential online services to patients.2
High Reliability Organizations
High reliability health care organizations have considerable experience safely launching new programs. For example, the Patient Safety Adoption Framework gives practical tips for smoothly rolling out safety initiatives (Table 1). Developed with experts and diverse views, this framework has 5 key areas: leadership, culture and context, process, measurement, and person-centeredness. These address adoption problems, guide leaders step-by-step, and focus on leadership buy-in, safety culture, cooperation, and local customization. Checklists and tools make it systematic to go from ideas to action on patient safety.3
Leadership involves establishing organizational commitment behind new safety programs. This visible commitment signals importance and priorities to others. Leaders model desired behaviors and language around safety, allocate resources, remove obstacles, and keep initiatives energized over time through consistent messaging.4 Culture and context recognizes that safety culture differs across units and facilities. Local input tailors programs to fit and examines strengths to build on, like psychological safety. Surveys gauge the existing culture and its need for change. Process details how to plan, design, test, implement, and improve new safety practices and provides a phased roadmap from idea to results. Measurement collects data to drive improvement and show impact. Metrics track progress and allow benchmarking. Person-centeredness puts patients first in safety efforts through participation, education, and transparency.
The Veterans Health Administration piloted a comprehensive high reliability hospital (HRH) model. Over 3 years, the Veterans Health Administration focused on leadership, culture, and process improvement at a hospital. After initiating the model, the pilot hospital improved its safety culture, reported more minor safety issues, and reduced deaths and complications better than other hospitals. The high-reliability approach successfully instilled principles and improved culture and outcomes. The HRH model is set to be expanded to 18 more US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites for further evaluation across diverse settings.5
Trustworthy AI Framework
AI systems are growing more powerful and widespread, including in health care. Unfortunately, irresponsible AI can introduce new harm. ChatGPT and other large language models, for example, sometimes are known to provide erroneous information in a compelling way. Clinicians and patients who use such programs can act on such information, which would lead to unforeseen negative consequences. Several frameworks on ethical AI have come from governmental groups.6-9 In 2023, the VA National AI Institute suggested a Trustworthy AI Framework based on core principles tailored for federal health care. The framework has 6 key principles: purposeful, effective and safe, secure and private, fair and equitable, transparent and explainable, and accountable and monitored (Table 2).10
First, AI must clearly help veterans while minimizing risks. To ensure purpose, the VA will assess patient and clinician needs and design AI that targets meaningful problems to avoid scope creep or feature bloat. For example, adding new features to the AI software after release can clutter and complicate the interface, making it difficult to use. Rigorous testing will confirm that AI meets intent prior to deployment. Second, AI is designed and checked for effectiveness, safety, and reliability. The VA pledges to monitor AI’s impact to ensure it performs as expected without unintended consequences. Algorithms will be stress tested across representative datasets and approval processes will screen for safety issues. Third, AI models are secured from vulnerabilities and misuse. Technical controls will prevent unauthorized access or changes to AI systems. Audits will check for appropriate internal usage per policies. Continual patches and upgrades will maintain security. Fourth, the VA manages AI for fairness, avoiding bias. They will proactively assess datasets and algorithms for potential biases based on protected attributes like race, gender, or age. Biased outputs will be addressed through techniques such as data augmentation, reweighting, and algorithm tweaks. Fifth, transparency explains AI’s role in care. Documentation will detail an AI system’s data sources, methodology, testing, limitations, and integration with clinical workflows. Clinicians and patients will receive education on interpreting AI outputs. Finally, the VA pledges to closely monitor AI systems to sustain trust. The VA will establish oversight processes to quickly identify any declines in reliability or unfair impacts on subgroups. AI models will be retrained as needed based on incoming data patterns.
Each Trustworthy AI Framework principle connects to others in existing frameworks. The purpose principle aligns with human-centric AI focused on benefits. Effectiveness and safety link to technical robustness and risk management principles. Security maps to privacy protection principles. Fairness connects to principles of avoiding bias and discrimination. Transparency corresponds with accountable and explainable AI. Monitoring and accountability tie back to governance principles. Overall, the VA framework aims to guide ethical AI based on context. It offers a model for managing risks and building trust in health care AI.
Combining VA principles with high-reliability safety principles can ensure that AI benefits veterans. The leadership and culture aspects will drive commitment to trustworthy AI practices. Leaders will communicate the importance of responsible AI through words and actions. Culture surveys can assess baseline awareness of AI ethics issues to target education. AI security and fairness will be emphasized as safety critical. The process aspect will institute policies and procedures to uphold AI principles through the project lifecycle. For example, structured testing processes will validate safety. Measurement will collect data on principles like transparency and fairness. Dashboards can track metrics like explainability and biases. A patient-centered approach will incorporate veteran perspectives on AI through participatory design and advisory councils. They can give input on AI explainability and potential biases based on their diverse backgrounds.
Conclusions
Joint principles will lead to successful AI that improves care while proactively managing risks. Involve leaders to stress the necessity of eliminating biases. Build security into the AI development process. Co-design AI transparency features with end users. Closely monitor the impact of AI across safety, fairness, and other principles. Adhering to both Trustworthy AI and high reliability organizations principles will earn veterans’ confidence. Health care organizations like the VA can integrate ethical AI safely via established frameworks. With responsible design and implementation, AI’s potential to enhance care quality, safety, and access can be realized.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Joshua Mueller, Theo Tiffney, John Zachary, and Gil Alterovitz for their excellent work creating the VA Trustworthy Principles. This material is the result of work supported by resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital.
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
1. Sahni NR, Carrus B. Artificial intelligence in U.S. health care delivery. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(4):348-358. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2204673
2. Borkowski AA, Jakey CE, Mastorides SM, et al. Applications of ChatGPT and large language models in medicine and health care: benefits and pitfalls. Fed Pract. 2023;40(6):170-173. doi:10.12788/fp.0386
3. Moyal-Smith R, Margo J, Maloney FL, et al. The patient safety adoption framework: a practical framework to bridge the know-do gap. J Patient Saf. 2023;19(4):243-248. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000001118
4. Isaacks DB, Anderson TM, Moore SC, Patterson W, Govindan S. High reliability organization principles improve VA workplace burnout: the Truman THRIVE2 model. Am J Med Qual. 2021;36(6):422-428. doi:10.1097/01.JMQ.0000735516.35323.97
5. Sculli GL, Pendley-Louis R, Neily J, et al. A high-reliability organization framework for health care: a multiyear implementation strategy and associated outcomes. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):64-70. doi:10.1097/PTS.0000000000000788
6. National Institute of Standards and Technology. AI risk management framework. Accessed January 2, 2024. https://www.nist.gov/itl/ai-risk-management-framework
7. Executive Office of the President, Office of Science and Technology Policy. Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/ostp/ai-bill-of-rights
8. Executive Office of the President. Executive Order 13960: promoting the use of trustworthy artificial intelligence in the federal government. Fed Regist. 2020;89(236):78939-78943.
9. Biden JR. Executive Order on the safe, secure, and trustworthy development and use of artificial intelligence. Published October 30, 2023. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/presidential-actions/2023/10/30/executive-order-on-the-safe-secure-and-trustworthy-development-and-use-of-artificial-intelligence/
10. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Trustworthy AI. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://department.va.gov/ai/trustworthy/
Top 5 Medications That Can Increase Blood Glucose Levels
It’s that time of the year, when social media is rife with many top 5 and top 10 lists. Let’s revisit some of the most commonly used medications known to increase glucose levels and look at some practical tips on overcoming these.
1. Glucocorticoids
Without a doubt, corticosteroids are at the top of the list when it comes to the potential for increasing blood glucose levels. High-dose glucocorticoid therapy is known to lead to new-onset diabetes (steroid-induced diabetes). Similarly, people with preexisting diabetes may notice significant worsening of glycemic control when they start on glucocorticoid therapy. The extent of glucose elevation depends on their glycemic status prior to initiation on steroids, the dose and duration of glucocorticoid therapy, and comorbid conditions, among other factors.
Management tip: For those with previously well-controlled diabetes or borderline diabetes, glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia may be managed by metformin with or without sulfonylurea therapy, especially if corticosteroid treatment is low-dose and for a shorter duration. However, for many individuals with preexisting poorly controlled diabetes or those initiated on high-dose corticosteroids, insulin therapy would perhaps be the treatment of choice. Glucocorticoid therapy generally leads to more pronounced postprandial hyperglycemia compared with fasting hyperglycemia; hence, the use of short-acting insulin therapy or perhaps NPH insulin in the morning might be a better option for many individuals. Dietary modification plays an important role in limiting the extent of postprandial hyperglycemia. Use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices may also be very helpful for understanding glycemic excursions and how to adjust insulin. In individuals for whom glucocorticoid therapy is tapered down, it is important to adjust the dose of medications with potential to cause hypoglycemia, such as insulin/sulfonylurea therapy, as the degree of hyperglycemia may decrease with decreased dose of the glucocorticoid therapy.
2. Antipsychotic Therapy
Antipsychotic medications can be obesogenic; between 15% and 72% of people who take second-generation antipsychotics experience weight gain of 7% or more. Increases in weight are not the only factor contributing to an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Antipsychotics are thought to cause downregulation of intracellular insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance. At the same time, there seems to be a direct effect on the pancreatic beta cells. Antagonism of the dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT2C, and muscarinic M3 receptors impairs beta-cell response to changes in blood glucose. In addition to the pharmacologic effects, cell culture experiments have shown that antipsychotics increase apoptosis of beta cells. Increased weight and concomitant development of type 2 diabetes is seen particularly in agents that exhibit high muscarinic M3 and histamine H1 receptor blockade. The effect on glucose metabolism is seen the most with agents such as clozapine, olanzapine, and haloperidol and the least with agents such as ziprasidone.
Management tip: Given the ongoing change in the understanding of increases in weight and their association with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a metabolically safer approach involves starting with medications that have a lower propensity for weight gain, and the partial agonists/third-generation antipsychotics as a family presently have the best overall data.
3. Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics are commonly used for the management of hypertension and are associated with metabolic complications including hypokalemia; higher cholesterol, triglycerides, and other circulating lipids; and elevated glucose. It’s thought that the reduced potassium level occurring as a result of these medications might contribute to new-onset diabetes. The hypokalemia occurring from these medications is thought to lead to a decrease in insulin secretion and sensitivity, which is dose dependent. Studies show that the number needed to harm for chlorthalidone-induced diabetes is 29 over 1 year. There is believed to be no additional risk beyond 1 year.
Management tip: It’s important to monitor potassium levels for those initiated on thiazide diuretics. If hypokalemia occurs, it would be pertinent to correct the hypokalemia with potassium supplements to mitigate the risk for new-onset diabetes.
4. Statin Therapy
Statin therapy is thought to be associated with decreased insulin sensitivity and impairment in insulin secretion. The overall incidence of diabetes is pegged to be between 9% and 12% on statin therapy on the basis of meta-analysis studies, and higher on the basis of population-based studies. Overall, the estimated number needed to harm is: 1 out of every 255 patients on statin therapy for 4 years may develop new-onset diabetes. Compare this with the extremely strong evidence for number needed to treat being 39 for 5 years with statin therapy in patients with preexisting heart disease to prevent one occurrence of a nonfatal myocardial infarction.
Management tip: Although statins are associated with a small incident increase in the risk of developing diabetes, the potential benefits of using statin therapy for both primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease significantly outweigh any of the potential risks associated with hyperglycemia. This is an important discussion to have with patients who are reluctant to use statin therapy because of the potential risk for new-onset diabetes as a side effect.
5. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are another commonly used group of medications for managing hypertension, heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmia. Nonvasodilating beta-blockers such as metoprolol and atenolol are more likely to be associated with increases in A1c, mean plasma glucose, body weight, and triglycerides compared with vasodilating beta-blockers such as carvedilol, nebivolol, and labetalol (Bakris GL et al; Giugliano D et al). Similarly, studies have also shown that atenolol and metoprolol are associated with increased odds of hypoglycemia compared with carvedilol. People on beta-blockers may have masking of some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as tremor, irritability, and palpitations, while other symptoms such as diaphoresis may remain unaffected on beta-blockers.
Management tip: Education on recognizing and managing hypoglycemia would be important when starting patients on beta-blockers if they are on preexisting insulin/sulfonylurea therapy. Use of CGM devices may be helpful if there is a high risk for hypoglycemia, especially as symptoms of hypoglycemia are often masked.
Honorable Mention
Several other medications — including antiretroviral therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, immunosuppressants, and interferon alpha — are associated with worsening glycemic control and new-onset diabetes. Consider these agents’ effects on blood glucose, especially in people with an elevated risk of developing diabetes or those with preexisting diabetes, when prescribing.
A special mention should also be made of androgen deprivation therapy. These include treatment options like goserelin and leuprolide, which are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapies and are commonly used for prostate cancer management. Depending on the patient, these agents may be used for prolonged duration. Androgen deprivation therapy, by definition, decreases testosterone levels in men, thereby leading to worsening insulin resistance. Increase in fat mass and concomitant muscle wasting have been associated with the use of these medications; these, in turn, lead to peripheral insulin resistance. Nearly 1 out of every 5 men treated with long-term androgen deprivation therapy may be prone to developing worsening of A1c by 1% or more.
Management tip: Men on androgen deprivation therapy should be encouraged to participate in regular physical activity to reduce the burden of insulin resistance and to promote cardiovascular health.
Drug-induced diabetes is potentially reversible in many cases. Similarly, worsening of glycemic control due to medications in people with preexisting diabetes may also attenuate once the effect of the drug wears off. Blood glucose should be monitored on an ongoing basis so that diabetes medications can be adjusted. For some individuals, however, the worsening of glycemic status may be more chronic and may require long-term use of antihyperglycemic agents, especially if the benefits of continuation of the medication leading to hyperglycemia far exceed any potential risks.
Dr. Jain is Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, Fraser River Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. He disclosed ties with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s that time of the year, when social media is rife with many top 5 and top 10 lists. Let’s revisit some of the most commonly used medications known to increase glucose levels and look at some practical tips on overcoming these.
1. Glucocorticoids
Without a doubt, corticosteroids are at the top of the list when it comes to the potential for increasing blood glucose levels. High-dose glucocorticoid therapy is known to lead to new-onset diabetes (steroid-induced diabetes). Similarly, people with preexisting diabetes may notice significant worsening of glycemic control when they start on glucocorticoid therapy. The extent of glucose elevation depends on their glycemic status prior to initiation on steroids, the dose and duration of glucocorticoid therapy, and comorbid conditions, among other factors.
Management tip: For those with previously well-controlled diabetes or borderline diabetes, glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia may be managed by metformin with or without sulfonylurea therapy, especially if corticosteroid treatment is low-dose and for a shorter duration. However, for many individuals with preexisting poorly controlled diabetes or those initiated on high-dose corticosteroids, insulin therapy would perhaps be the treatment of choice. Glucocorticoid therapy generally leads to more pronounced postprandial hyperglycemia compared with fasting hyperglycemia; hence, the use of short-acting insulin therapy or perhaps NPH insulin in the morning might be a better option for many individuals. Dietary modification plays an important role in limiting the extent of postprandial hyperglycemia. Use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices may also be very helpful for understanding glycemic excursions and how to adjust insulin. In individuals for whom glucocorticoid therapy is tapered down, it is important to adjust the dose of medications with potential to cause hypoglycemia, such as insulin/sulfonylurea therapy, as the degree of hyperglycemia may decrease with decreased dose of the glucocorticoid therapy.
2. Antipsychotic Therapy
Antipsychotic medications can be obesogenic; between 15% and 72% of people who take second-generation antipsychotics experience weight gain of 7% or more. Increases in weight are not the only factor contributing to an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Antipsychotics are thought to cause downregulation of intracellular insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance. At the same time, there seems to be a direct effect on the pancreatic beta cells. Antagonism of the dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT2C, and muscarinic M3 receptors impairs beta-cell response to changes in blood glucose. In addition to the pharmacologic effects, cell culture experiments have shown that antipsychotics increase apoptosis of beta cells. Increased weight and concomitant development of type 2 diabetes is seen particularly in agents that exhibit high muscarinic M3 and histamine H1 receptor blockade. The effect on glucose metabolism is seen the most with agents such as clozapine, olanzapine, and haloperidol and the least with agents such as ziprasidone.
Management tip: Given the ongoing change in the understanding of increases in weight and their association with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a metabolically safer approach involves starting with medications that have a lower propensity for weight gain, and the partial agonists/third-generation antipsychotics as a family presently have the best overall data.
3. Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics are commonly used for the management of hypertension and are associated with metabolic complications including hypokalemia; higher cholesterol, triglycerides, and other circulating lipids; and elevated glucose. It’s thought that the reduced potassium level occurring as a result of these medications might contribute to new-onset diabetes. The hypokalemia occurring from these medications is thought to lead to a decrease in insulin secretion and sensitivity, which is dose dependent. Studies show that the number needed to harm for chlorthalidone-induced diabetes is 29 over 1 year. There is believed to be no additional risk beyond 1 year.
Management tip: It’s important to monitor potassium levels for those initiated on thiazide diuretics. If hypokalemia occurs, it would be pertinent to correct the hypokalemia with potassium supplements to mitigate the risk for new-onset diabetes.
4. Statin Therapy
Statin therapy is thought to be associated with decreased insulin sensitivity and impairment in insulin secretion. The overall incidence of diabetes is pegged to be between 9% and 12% on statin therapy on the basis of meta-analysis studies, and higher on the basis of population-based studies. Overall, the estimated number needed to harm is: 1 out of every 255 patients on statin therapy for 4 years may develop new-onset diabetes. Compare this with the extremely strong evidence for number needed to treat being 39 for 5 years with statin therapy in patients with preexisting heart disease to prevent one occurrence of a nonfatal myocardial infarction.
Management tip: Although statins are associated with a small incident increase in the risk of developing diabetes, the potential benefits of using statin therapy for both primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease significantly outweigh any of the potential risks associated with hyperglycemia. This is an important discussion to have with patients who are reluctant to use statin therapy because of the potential risk for new-onset diabetes as a side effect.
5. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are another commonly used group of medications for managing hypertension, heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmia. Nonvasodilating beta-blockers such as metoprolol and atenolol are more likely to be associated with increases in A1c, mean plasma glucose, body weight, and triglycerides compared with vasodilating beta-blockers such as carvedilol, nebivolol, and labetalol (Bakris GL et al; Giugliano D et al). Similarly, studies have also shown that atenolol and metoprolol are associated with increased odds of hypoglycemia compared with carvedilol. People on beta-blockers may have masking of some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as tremor, irritability, and palpitations, while other symptoms such as diaphoresis may remain unaffected on beta-blockers.
Management tip: Education on recognizing and managing hypoglycemia would be important when starting patients on beta-blockers if they are on preexisting insulin/sulfonylurea therapy. Use of CGM devices may be helpful if there is a high risk for hypoglycemia, especially as symptoms of hypoglycemia are often masked.
Honorable Mention
Several other medications — including antiretroviral therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, immunosuppressants, and interferon alpha — are associated with worsening glycemic control and new-onset diabetes. Consider these agents’ effects on blood glucose, especially in people with an elevated risk of developing diabetes or those with preexisting diabetes, when prescribing.
A special mention should also be made of androgen deprivation therapy. These include treatment options like goserelin and leuprolide, which are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapies and are commonly used for prostate cancer management. Depending on the patient, these agents may be used for prolonged duration. Androgen deprivation therapy, by definition, decreases testosterone levels in men, thereby leading to worsening insulin resistance. Increase in fat mass and concomitant muscle wasting have been associated with the use of these medications; these, in turn, lead to peripheral insulin resistance. Nearly 1 out of every 5 men treated with long-term androgen deprivation therapy may be prone to developing worsening of A1c by 1% or more.
Management tip: Men on androgen deprivation therapy should be encouraged to participate in regular physical activity to reduce the burden of insulin resistance and to promote cardiovascular health.
Drug-induced diabetes is potentially reversible in many cases. Similarly, worsening of glycemic control due to medications in people with preexisting diabetes may also attenuate once the effect of the drug wears off. Blood glucose should be monitored on an ongoing basis so that diabetes medications can be adjusted. For some individuals, however, the worsening of glycemic status may be more chronic and may require long-term use of antihyperglycemic agents, especially if the benefits of continuation of the medication leading to hyperglycemia far exceed any potential risks.
Dr. Jain is Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, Fraser River Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. He disclosed ties with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s that time of the year, when social media is rife with many top 5 and top 10 lists. Let’s revisit some of the most commonly used medications known to increase glucose levels and look at some practical tips on overcoming these.
1. Glucocorticoids
Without a doubt, corticosteroids are at the top of the list when it comes to the potential for increasing blood glucose levels. High-dose glucocorticoid therapy is known to lead to new-onset diabetes (steroid-induced diabetes). Similarly, people with preexisting diabetes may notice significant worsening of glycemic control when they start on glucocorticoid therapy. The extent of glucose elevation depends on their glycemic status prior to initiation on steroids, the dose and duration of glucocorticoid therapy, and comorbid conditions, among other factors.
Management tip: For those with previously well-controlled diabetes or borderline diabetes, glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia may be managed by metformin with or without sulfonylurea therapy, especially if corticosteroid treatment is low-dose and for a shorter duration. However, for many individuals with preexisting poorly controlled diabetes or those initiated on high-dose corticosteroids, insulin therapy would perhaps be the treatment of choice. Glucocorticoid therapy generally leads to more pronounced postprandial hyperglycemia compared with fasting hyperglycemia; hence, the use of short-acting insulin therapy or perhaps NPH insulin in the morning might be a better option for many individuals. Dietary modification plays an important role in limiting the extent of postprandial hyperglycemia. Use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices may also be very helpful for understanding glycemic excursions and how to adjust insulin. In individuals for whom glucocorticoid therapy is tapered down, it is important to adjust the dose of medications with potential to cause hypoglycemia, such as insulin/sulfonylurea therapy, as the degree of hyperglycemia may decrease with decreased dose of the glucocorticoid therapy.
2. Antipsychotic Therapy
Antipsychotic medications can be obesogenic; between 15% and 72% of people who take second-generation antipsychotics experience weight gain of 7% or more. Increases in weight are not the only factor contributing to an elevated risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Antipsychotics are thought to cause downregulation of intracellular insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance. At the same time, there seems to be a direct effect on the pancreatic beta cells. Antagonism of the dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT2C, and muscarinic M3 receptors impairs beta-cell response to changes in blood glucose. In addition to the pharmacologic effects, cell culture experiments have shown that antipsychotics increase apoptosis of beta cells. Increased weight and concomitant development of type 2 diabetes is seen particularly in agents that exhibit high muscarinic M3 and histamine H1 receptor blockade. The effect on glucose metabolism is seen the most with agents such as clozapine, olanzapine, and haloperidol and the least with agents such as ziprasidone.
Management tip: Given the ongoing change in the understanding of increases in weight and their association with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a metabolically safer approach involves starting with medications that have a lower propensity for weight gain, and the partial agonists/third-generation antipsychotics as a family presently have the best overall data.
3. Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics are commonly used for the management of hypertension and are associated with metabolic complications including hypokalemia; higher cholesterol, triglycerides, and other circulating lipids; and elevated glucose. It’s thought that the reduced potassium level occurring as a result of these medications might contribute to new-onset diabetes. The hypokalemia occurring from these medications is thought to lead to a decrease in insulin secretion and sensitivity, which is dose dependent. Studies show that the number needed to harm for chlorthalidone-induced diabetes is 29 over 1 year. There is believed to be no additional risk beyond 1 year.
Management tip: It’s important to monitor potassium levels for those initiated on thiazide diuretics. If hypokalemia occurs, it would be pertinent to correct the hypokalemia with potassium supplements to mitigate the risk for new-onset diabetes.
4. Statin Therapy
Statin therapy is thought to be associated with decreased insulin sensitivity and impairment in insulin secretion. The overall incidence of diabetes is pegged to be between 9% and 12% on statin therapy on the basis of meta-analysis studies, and higher on the basis of population-based studies. Overall, the estimated number needed to harm is: 1 out of every 255 patients on statin therapy for 4 years may develop new-onset diabetes. Compare this with the extremely strong evidence for number needed to treat being 39 for 5 years with statin therapy in patients with preexisting heart disease to prevent one occurrence of a nonfatal myocardial infarction.
Management tip: Although statins are associated with a small incident increase in the risk of developing diabetes, the potential benefits of using statin therapy for both primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease significantly outweigh any of the potential risks associated with hyperglycemia. This is an important discussion to have with patients who are reluctant to use statin therapy because of the potential risk for new-onset diabetes as a side effect.
5. Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are another commonly used group of medications for managing hypertension, heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmia. Nonvasodilating beta-blockers such as metoprolol and atenolol are more likely to be associated with increases in A1c, mean plasma glucose, body weight, and triglycerides compared with vasodilating beta-blockers such as carvedilol, nebivolol, and labetalol (Bakris GL et al; Giugliano D et al). Similarly, studies have also shown that atenolol and metoprolol are associated with increased odds of hypoglycemia compared with carvedilol. People on beta-blockers may have masking of some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as tremor, irritability, and palpitations, while other symptoms such as diaphoresis may remain unaffected on beta-blockers.
Management tip: Education on recognizing and managing hypoglycemia would be important when starting patients on beta-blockers if they are on preexisting insulin/sulfonylurea therapy. Use of CGM devices may be helpful if there is a high risk for hypoglycemia, especially as symptoms of hypoglycemia are often masked.
Honorable Mention
Several other medications — including antiretroviral therapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, immunosuppressants, and interferon alpha — are associated with worsening glycemic control and new-onset diabetes. Consider these agents’ effects on blood glucose, especially in people with an elevated risk of developing diabetes or those with preexisting diabetes, when prescribing.
A special mention should also be made of androgen deprivation therapy. These include treatment options like goserelin and leuprolide, which are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist therapies and are commonly used for prostate cancer management. Depending on the patient, these agents may be used for prolonged duration. Androgen deprivation therapy, by definition, decreases testosterone levels in men, thereby leading to worsening insulin resistance. Increase in fat mass and concomitant muscle wasting have been associated with the use of these medications; these, in turn, lead to peripheral insulin resistance. Nearly 1 out of every 5 men treated with long-term androgen deprivation therapy may be prone to developing worsening of A1c by 1% or more.
Management tip: Men on androgen deprivation therapy should be encouraged to participate in regular physical activity to reduce the burden of insulin resistance and to promote cardiovascular health.
Drug-induced diabetes is potentially reversible in many cases. Similarly, worsening of glycemic control due to medications in people with preexisting diabetes may also attenuate once the effect of the drug wears off. Blood glucose should be monitored on an ongoing basis so that diabetes medications can be adjusted. For some individuals, however, the worsening of glycemic status may be more chronic and may require long-term use of antihyperglycemic agents, especially if the benefits of continuation of the medication leading to hyperglycemia far exceed any potential risks.
Dr. Jain is Clinical Instructor, Department of Endocrinology, University of British Columbia; Endocrinologist, Fraser River Endocrinology, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. He disclosed ties with Abbott, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sodium vs Potassium for Lowering Blood Pressure?
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.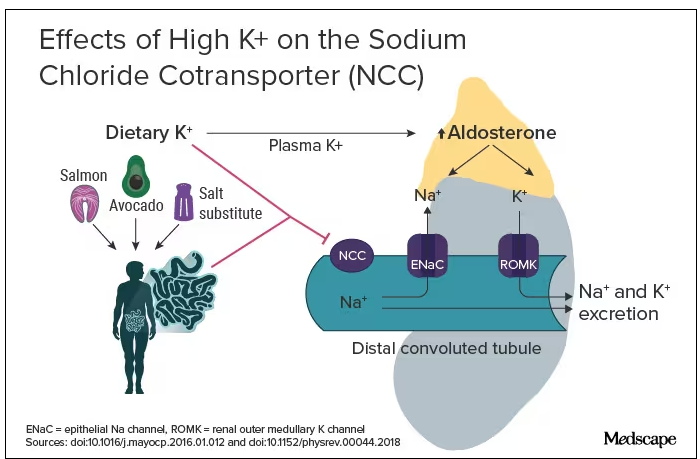
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A pair of dueling editorials in the journal Hypertension debate whether our focus should be on sodium or its often neglected partner, potassium.
A meta-analysis of 85 trials showed a consistent and linear. It may also depend on where you live and whether your concern is treating individuals or implementing effective food policy.
The Case for Sodium Restriction
Stephen Juraschek, MD, PhD, of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, co-author of one editorial, told me in a zoom interview that he believes his side of the debate clearly has the stronger argument. Of the two cations in question, there has been infinitely more ink spilled about sodium.
Studies such as INTERSALT, the DASH diet, and TOHP may be the most well-known, but there are many, many intervention studies of sodium restriction’s effect on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of 85 trials of showed a consistent and linear relationship between sodium reduction and blood pressure. In contrast, the evidence base for potassium is more limited and less consistent. There are half as many trials with potassium, and its ability to lower blood pressure may depend on how much sodium is present in the diet.
An outlier in the sodium restriction evidence base is the PURE study, which suggested that extreme sodium restriction could increase cardiovascular mortality, but the trial suffered from two potential issues. First, it used a single spot urine specimen to measure sodium rather than the generally accepted more accurate 24-hour urine collection. A reanalysis of the TOHP study using a spot urine rather than a 24-hour urine collection changed the relationship between sodium intake and mortality and possibly explained the U-shaped association observed in PURE. Second, PURE was an observational cohort and was prone to confounding, or in this case, reverse causation. Why did people who consumed very little salt have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease? It is very possible that people with a high risk for cardiovascular disease were told to consume less salt to begin with. Hence B led to A rather than A leading to B.
The debate on sodium restriction has been bitter at times. Opposing camps formed, and people took sides in the “salt wars.” A group of researchers, termed the Jackson 6, met and decided to end the controversy by running a randomized trial in US prisons (having discounted the options of long-term care homes and military bases). They detailed their plan in an editorial in Hypertension. The study never came to fruition for two reasons: the obvious ethical problems of experimenting on prisoners and the revelation of undisclosed salt industry funding.
More recent studies have mercifully been more conventional. The SSaSS study, a randomized controlled trial of a salt substitute, provided the cardiovascular outcomes data that many were waiting for. And CARDIA-SSBP, a cross-over randomized trial recently presented at the American Heart Association meeting, showed that reducing dietary sodium was on par with medication when it came to lowering blood pressure.
For Dr. Juraschek, the evidence is clear: “If you were going to choose one, I would say the weight of the evidence is still really heavily on the sodium side.”
The Case for Potassium Supplementation
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”
No Salt War Here
Despite their different editorial takes, Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek largely agree on the broad strokes of the problem. This isn’t X (or Twitter) after all. Potassium supplementation may be useful in some parts of the world but may not address the underlying problem in countries where processed foods are the source of most dietary sodium.
The CARDIA-SSBP trial showed that a very low–sodium diet had the same blood pressure–lowering effect as a first-line antihypertensive, but most people will not be able to limit themselves to 500 mg of dietary sodium per day. In CARDIA-SSBP, just as in DASH, participants were provided with meals from study kitchens. They were not just told to eat less salt, which would almost certainly have failed.
“We should aim for stuff that is practical and doable rather than aim for stuff that cannot be done,” according to Dr. Hiremath. Whether that should be salt substitutes or policy change may depend on which part of the planet you live on.
One recent positive change may herald the beginning of a policy change, at least in the United States. In March 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration proposed a rule change to allow salt substitutes to be labeled as salt. This would make it easier for food manufacturers to swap out sodium chloride for a low-sodium alternative and reduce the amount of sodium in the US diet without having a large impact on taste and consumer uptake. Both Dr. Hiremath and Dr. Juraschek agree that it may not be enough on its own but that it’s a start.
Christopher Labos is a cardiologist with a degree in epidemiology. He spends most of his time doing things that he doesn’t get paid for, like research, teaching, and podcasting. Occasionally, he finds time to practice cardiology to pay the rent. He realizes that half of his research findings will be disproved in 5 years; he just doesn’t know which half. He is a regular contributor to the Montreal Gazette, CJAD radio, and CTV television in Montreal, and is host of the award-winning podcast The Body of Evidence.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.