User login
Screening Options for Rare Malignancies
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
Obesity: A Social Vulnerability
Sometime in the last year or 2 I wrote that, despite my considerable reservations, I had finally come to the conclusion that the American Medical Association’s decision to designate obesity as a disease was appropriate. My rationalization was that the disease label would open more opportunities for funding obesity treatments. However, the explosive growth and popularity of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists over the last year has had me rethinking my decision to suppress my long-held reservations about the disease designation.
So, if it’s not a disease, then what should we call it? How do we explain its surge in high-income countries that began in the 1980s? While there are still some folks who see obesity as a character flaw, I think you and I as healthcare providers have difficulty explaining the increase prevalence of obesity as either global breakdown of willpower or a widespread genetic shift as the result of burst of radiation from solar flares.
However, if we want to continue our search and finger-pointing we need to have a better definition of exactly what obesity is. If we’re going to continue calling it a disease we have done a pretty sloppy job of creating diagnostic criteria. To be honest, we aren’t doing such a hot job with “long COVID” either.
A recent article in the New York Times makes it clear that I’m not the only physician who is feeling uncomfortable with this lack of diagnostic specificity.
We know that using body mass index (BMI) as a criteria is imprecise. There are healthy individuals with elevated BMIs and there are others who are carrying an unhealthy amount of fat who have normal BMIs. And, there are individuals who have what might appear to be an excess amount of fat who are fit and healthy by other criteria.
Some investigators feel that a set of measurements that includes a waist and/or hip measurement may be a more accurate way of determining visceral adipose tissue. However, this body roundness index (BRI) currently relies on a tape measurement. Until the technique can be preformed by an inexpensive and readily available scanner, the BRI cannot be considered a practical tool for determining obesity.
Dr. Francisco Rubino, the chair of metabolic and bariatric surgery at Kings College in London, England, has been quoted as saying that, “if one defines a disease inaccurately, everything that stems from that – from diagnosis to treatment to policies – will be distorted and biased.”
Denmark has been forced to relabel obesity as a risk factor because the disease designation was stressing the financial viability of their healthcare system as more and more patients were being prescribe GLP-1 agonists, sometimes off label. A rationing strategy was resulting in suboptimal treatment of a significant portion of the obese population.
Spearheaded by Dr. Rubino, a Lancet Commission composed of physicians has tasked itself to define an “evidence-based diagnosis for obesity. Instead of relying on a single metric such as the BMI or BRI, diagnosing “clinical obesity” would involve a broad array of observations including a history, physical examination, standard laboratory and additional testing, “naming signs and symptoms, organ by organ, tissue by tissue, with plausible mechanisms for each one.” In other words, treating each patient as an individual using evidence-based criteria to make a diagnosis. While likely to be time consuming, this strategy feels like a more scientific approach. I suspect once clinical obesity is more rigorously defined it could be divided into several subtypes. For example, there would be a few conditions that were genetic; Prader-Willi syndrome being the best known.
However, I think the Lancet Commission’s strategy will find that the majority of individuals who make up this half-century global surge have become clinically obese because they have been unable to adapt to the obeseogenic forces in our society, which include diet, autocentricity, and attractive sedentary forms of entertainment, to name just three.
In some cases these unfortunate individuals are more vulnerable because there were born into an economically disadvantaged situation. In other scenarios a lack of foresight and/or political will may have left individuals with no other choice but to rely on automobiles to get around. Still others may find themselves living in a nutritional desert because all of the grocery stores have closed.
I recently encountered a descriptor in a story about the Federal Emergency Management Agency which could easily be adapted to describe this large and growing subtype of individuals with clinical obesity. “Social vulnerability” is measure of how well a community can withstand external stressors that impact human health. For example, the emergency management folks are thinking in terms of natural disaster such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes and are asking how well a given community can meet the challenges one would create.
But, the term social vulnerability can easily be applied to individuals living in a society in which unhealthy food is abundant, an infrastructure that discourages or outright prevents non-motorized travel, and the temptation of sedentary entertainment options is unavoidable. Fortunately, not every citizen living in an obesogenic society becomes obese. What factors have protected the non-obese individuals from these obeseogenic stressors? What are the characteristics of the unfortunate “vulnerables” living in the same society who end up being obese?
It is time to shift our focus away from a poorly defined disease model to one in which we begin looking at our society to find out why we have so many socially vulnerable individuals. The toll of obesity as it is currently defined is many order of magnitudes greater than any natural disaster. We have become communities that can no longer withstand the its obesogenic stressors many of which we have created and/or allowed to accumulate over the last century.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Sometime in the last year or 2 I wrote that, despite my considerable reservations, I had finally come to the conclusion that the American Medical Association’s decision to designate obesity as a disease was appropriate. My rationalization was that the disease label would open more opportunities for funding obesity treatments. However, the explosive growth and popularity of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists over the last year has had me rethinking my decision to suppress my long-held reservations about the disease designation.
So, if it’s not a disease, then what should we call it? How do we explain its surge in high-income countries that began in the 1980s? While there are still some folks who see obesity as a character flaw, I think you and I as healthcare providers have difficulty explaining the increase prevalence of obesity as either global breakdown of willpower or a widespread genetic shift as the result of burst of radiation from solar flares.
However, if we want to continue our search and finger-pointing we need to have a better definition of exactly what obesity is. If we’re going to continue calling it a disease we have done a pretty sloppy job of creating diagnostic criteria. To be honest, we aren’t doing such a hot job with “long COVID” either.
A recent article in the New York Times makes it clear that I’m not the only physician who is feeling uncomfortable with this lack of diagnostic specificity.
We know that using body mass index (BMI) as a criteria is imprecise. There are healthy individuals with elevated BMIs and there are others who are carrying an unhealthy amount of fat who have normal BMIs. And, there are individuals who have what might appear to be an excess amount of fat who are fit and healthy by other criteria.
Some investigators feel that a set of measurements that includes a waist and/or hip measurement may be a more accurate way of determining visceral adipose tissue. However, this body roundness index (BRI) currently relies on a tape measurement. Until the technique can be preformed by an inexpensive and readily available scanner, the BRI cannot be considered a practical tool for determining obesity.
Dr. Francisco Rubino, the chair of metabolic and bariatric surgery at Kings College in London, England, has been quoted as saying that, “if one defines a disease inaccurately, everything that stems from that – from diagnosis to treatment to policies – will be distorted and biased.”
Denmark has been forced to relabel obesity as a risk factor because the disease designation was stressing the financial viability of their healthcare system as more and more patients were being prescribe GLP-1 agonists, sometimes off label. A rationing strategy was resulting in suboptimal treatment of a significant portion of the obese population.
Spearheaded by Dr. Rubino, a Lancet Commission composed of physicians has tasked itself to define an “evidence-based diagnosis for obesity. Instead of relying on a single metric such as the BMI or BRI, diagnosing “clinical obesity” would involve a broad array of observations including a history, physical examination, standard laboratory and additional testing, “naming signs and symptoms, organ by organ, tissue by tissue, with plausible mechanisms for each one.” In other words, treating each patient as an individual using evidence-based criteria to make a diagnosis. While likely to be time consuming, this strategy feels like a more scientific approach. I suspect once clinical obesity is more rigorously defined it could be divided into several subtypes. For example, there would be a few conditions that were genetic; Prader-Willi syndrome being the best known.
However, I think the Lancet Commission’s strategy will find that the majority of individuals who make up this half-century global surge have become clinically obese because they have been unable to adapt to the obeseogenic forces in our society, which include diet, autocentricity, and attractive sedentary forms of entertainment, to name just three.
In some cases these unfortunate individuals are more vulnerable because there were born into an economically disadvantaged situation. In other scenarios a lack of foresight and/or political will may have left individuals with no other choice but to rely on automobiles to get around. Still others may find themselves living in a nutritional desert because all of the grocery stores have closed.
I recently encountered a descriptor in a story about the Federal Emergency Management Agency which could easily be adapted to describe this large and growing subtype of individuals with clinical obesity. “Social vulnerability” is measure of how well a community can withstand external stressors that impact human health. For example, the emergency management folks are thinking in terms of natural disaster such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes and are asking how well a given community can meet the challenges one would create.
But, the term social vulnerability can easily be applied to individuals living in a society in which unhealthy food is abundant, an infrastructure that discourages or outright prevents non-motorized travel, and the temptation of sedentary entertainment options is unavoidable. Fortunately, not every citizen living in an obesogenic society becomes obese. What factors have protected the non-obese individuals from these obeseogenic stressors? What are the characteristics of the unfortunate “vulnerables” living in the same society who end up being obese?
It is time to shift our focus away from a poorly defined disease model to one in which we begin looking at our society to find out why we have so many socially vulnerable individuals. The toll of obesity as it is currently defined is many order of magnitudes greater than any natural disaster. We have become communities that can no longer withstand the its obesogenic stressors many of which we have created and/or allowed to accumulate over the last century.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Sometime in the last year or 2 I wrote that, despite my considerable reservations, I had finally come to the conclusion that the American Medical Association’s decision to designate obesity as a disease was appropriate. My rationalization was that the disease label would open more opportunities for funding obesity treatments. However, the explosive growth and popularity of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists over the last year has had me rethinking my decision to suppress my long-held reservations about the disease designation.
So, if it’s not a disease, then what should we call it? How do we explain its surge in high-income countries that began in the 1980s? While there are still some folks who see obesity as a character flaw, I think you and I as healthcare providers have difficulty explaining the increase prevalence of obesity as either global breakdown of willpower or a widespread genetic shift as the result of burst of radiation from solar flares.
However, if we want to continue our search and finger-pointing we need to have a better definition of exactly what obesity is. If we’re going to continue calling it a disease we have done a pretty sloppy job of creating diagnostic criteria. To be honest, we aren’t doing such a hot job with “long COVID” either.
A recent article in the New York Times makes it clear that I’m not the only physician who is feeling uncomfortable with this lack of diagnostic specificity.
We know that using body mass index (BMI) as a criteria is imprecise. There are healthy individuals with elevated BMIs and there are others who are carrying an unhealthy amount of fat who have normal BMIs. And, there are individuals who have what might appear to be an excess amount of fat who are fit and healthy by other criteria.
Some investigators feel that a set of measurements that includes a waist and/or hip measurement may be a more accurate way of determining visceral adipose tissue. However, this body roundness index (BRI) currently relies on a tape measurement. Until the technique can be preformed by an inexpensive and readily available scanner, the BRI cannot be considered a practical tool for determining obesity.
Dr. Francisco Rubino, the chair of metabolic and bariatric surgery at Kings College in London, England, has been quoted as saying that, “if one defines a disease inaccurately, everything that stems from that – from diagnosis to treatment to policies – will be distorted and biased.”
Denmark has been forced to relabel obesity as a risk factor because the disease designation was stressing the financial viability of their healthcare system as more and more patients were being prescribe GLP-1 agonists, sometimes off label. A rationing strategy was resulting in suboptimal treatment of a significant portion of the obese population.
Spearheaded by Dr. Rubino, a Lancet Commission composed of physicians has tasked itself to define an “evidence-based diagnosis for obesity. Instead of relying on a single metric such as the BMI or BRI, diagnosing “clinical obesity” would involve a broad array of observations including a history, physical examination, standard laboratory and additional testing, “naming signs and symptoms, organ by organ, tissue by tissue, with plausible mechanisms for each one.” In other words, treating each patient as an individual using evidence-based criteria to make a diagnosis. While likely to be time consuming, this strategy feels like a more scientific approach. I suspect once clinical obesity is more rigorously defined it could be divided into several subtypes. For example, there would be a few conditions that were genetic; Prader-Willi syndrome being the best known.
However, I think the Lancet Commission’s strategy will find that the majority of individuals who make up this half-century global surge have become clinically obese because they have been unable to adapt to the obeseogenic forces in our society, which include diet, autocentricity, and attractive sedentary forms of entertainment, to name just three.
In some cases these unfortunate individuals are more vulnerable because there were born into an economically disadvantaged situation. In other scenarios a lack of foresight and/or political will may have left individuals with no other choice but to rely on automobiles to get around. Still others may find themselves living in a nutritional desert because all of the grocery stores have closed.
I recently encountered a descriptor in a story about the Federal Emergency Management Agency which could easily be adapted to describe this large and growing subtype of individuals with clinical obesity. “Social vulnerability” is measure of how well a community can withstand external stressors that impact human health. For example, the emergency management folks are thinking in terms of natural disaster such as hurricanes, floods, and tornadoes and are asking how well a given community can meet the challenges one would create.
But, the term social vulnerability can easily be applied to individuals living in a society in which unhealthy food is abundant, an infrastructure that discourages or outright prevents non-motorized travel, and the temptation of sedentary entertainment options is unavoidable. Fortunately, not every citizen living in an obesogenic society becomes obese. What factors have protected the non-obese individuals from these obeseogenic stressors? What are the characteristics of the unfortunate “vulnerables” living in the same society who end up being obese?
It is time to shift our focus away from a poorly defined disease model to one in which we begin looking at our society to find out why we have so many socially vulnerable individuals. The toll of obesity as it is currently defined is many order of magnitudes greater than any natural disaster. We have become communities that can no longer withstand the its obesogenic stressors many of which we have created and/or allowed to accumulate over the last century.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Preventing Pediatric Migraine
I suspect you all have some experience with childhood migraine. It can mean a painful several hours for the patient, arriving often without warning, with recurrences spaced months or sometimes even years apart. It may be accompanied by vomiting, which in some cases overshadows the severity of the headache. It can result in lost days from school and ruin family activities. It can occur so infrequently that the family can’t recall accurately when the last episode happened. In some ways it is a different animal than the adult version.
Most of the pediatric patients with migraine I have seen have experienced attacks that were occurring so infrequently that the families and I seldom discussed medication as an option. Back then imipramine was the only choice. However, currently there are more than a half dozen medications and combinations that have been tried. Recently a review of 45 clinical trials of these medications was published in JAMA Network Open.
I will let you review for yourself the details of these Iranian investigators’ network meta-analysis, but the bottom line is that some medications were associated with a reduction in migraine frequency. Others were associated with headache intensity. “However, no treatments were associated with significant improvements in quality of life or reduction of the duration of migraine attacks.”
Obviously, this paper illustrates clearly that we have not yet discovered the medicinal magic bullet for pediatric migraine prophylaxis. This doesn’t surprise me. After listening to scores of families tell their migraine stories, it became apparent to me that there was often a pattern in which the child’s headache had arrived after a period of acute sleep deprivation. For example, a trip to an amusement park in which travel or excitement may have resulted in the child going to bed later and/or getting up earlier. By afternoon the child’s reserves of something (currently unknown) were depleted to a point that the headache and/or vomiting struck.
Because these episodes were often so infrequent, separated by months, that taking a history demonstrating a recurring pattern could take considerable patience on the part of the family and the provider, even for a physician like myself who believes that better sleep is the answer for everything. However, once I could convince a family of the connection between the sleep deprivation and the headaches, they could often recall other episodes in the past that substantiated my explanation.
In some cases there was no obvious history of acute sleep deprivation, or at least it was so subtle that even a history taker with a sleep obsession couldn’t detect it. However, in these cases I could usually elicit a history of chronic sleep deprivation. For example, falling asleep instantly on automobile rides, difficulty with waking in the morning, or unhealthy bedtime routines. With this underlying vulnerability of chronic sleep deprivation, a slightly more exciting or vigorous day was all that was necessary to trigger the headache.
For those of you who don’t share my contention that childhood migraine is usually the result of sleep deprivation, consider the similarity between an epileptic seizure, which can be triggered by fatigue. Both events are usually followed by a deep sleep from which the child wakes refreshed and symptom free.
I think it is interesting that this recent meta-analysis could find no benefit in the quality of life for any of the medications. The explanation may be that the child with migraine already had a somewhat diminished quality of life as a result of the sleep deprivation, either acute or chronic.
When speaking with parents of migraine sufferers, I would tell them that once the headache had started there was little I had to offer to forestall the inevitable pain and vomiting. Certainly not in the form of an oral medication. While many adults will have an aura that warns them of the headache onset, I have found that most children don’t describe an aura. It may be they simply lack the ability to express it. Occasionally an observant parent may detect pallor or a behavior change that indicates a migraine is beginning. On rare occasions a parent may be able to abort the attack by quickly getting the child to a quiet, dark, and calm environment.
Although this recent meta-analysis review of treatment options is discouraging, it may be providing a clue to effective prophylaxis. Some of the medications that decrease the frequency of the attacks may be doing so because they improve the patient’s sleep patterns. Those that decrease the intensity of the pain are probably working on pain pathway that is not specific to migraine.
Continuing a search for a prophylactic medication is a worthy goal, particularly for those patients in which their migraines are debilitating. However, based on my experience, enhanced by my bias, the safest and most effective prophylaxis results from increasing the family’s awareness of the role that sleep deprivation plays in the illness. Even when the family buys into the message and attempts to avoid situations that will tax their vulnerable children, parents will need to accept that sometimes stuff happens even though siblings and peers may be able to tolerate the situation. Spontaneous activities can converge on a day when for whatever reason the migraine-prone child is overtired and the headache and vomiting will erupt.
A lifestyle change is always preferable to a pharmacological intervention. However, that doesn’t mean it is always easy to achieve.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect you all have some experience with childhood migraine. It can mean a painful several hours for the patient, arriving often without warning, with recurrences spaced months or sometimes even years apart. It may be accompanied by vomiting, which in some cases overshadows the severity of the headache. It can result in lost days from school and ruin family activities. It can occur so infrequently that the family can’t recall accurately when the last episode happened. In some ways it is a different animal than the adult version.
Most of the pediatric patients with migraine I have seen have experienced attacks that were occurring so infrequently that the families and I seldom discussed medication as an option. Back then imipramine was the only choice. However, currently there are more than a half dozen medications and combinations that have been tried. Recently a review of 45 clinical trials of these medications was published in JAMA Network Open.
I will let you review for yourself the details of these Iranian investigators’ network meta-analysis, but the bottom line is that some medications were associated with a reduction in migraine frequency. Others were associated with headache intensity. “However, no treatments were associated with significant improvements in quality of life or reduction of the duration of migraine attacks.”
Obviously, this paper illustrates clearly that we have not yet discovered the medicinal magic bullet for pediatric migraine prophylaxis. This doesn’t surprise me. After listening to scores of families tell their migraine stories, it became apparent to me that there was often a pattern in which the child’s headache had arrived after a period of acute sleep deprivation. For example, a trip to an amusement park in which travel or excitement may have resulted in the child going to bed later and/or getting up earlier. By afternoon the child’s reserves of something (currently unknown) were depleted to a point that the headache and/or vomiting struck.
Because these episodes were often so infrequent, separated by months, that taking a history demonstrating a recurring pattern could take considerable patience on the part of the family and the provider, even for a physician like myself who believes that better sleep is the answer for everything. However, once I could convince a family of the connection between the sleep deprivation and the headaches, they could often recall other episodes in the past that substantiated my explanation.
In some cases there was no obvious history of acute sleep deprivation, or at least it was so subtle that even a history taker with a sleep obsession couldn’t detect it. However, in these cases I could usually elicit a history of chronic sleep deprivation. For example, falling asleep instantly on automobile rides, difficulty with waking in the morning, or unhealthy bedtime routines. With this underlying vulnerability of chronic sleep deprivation, a slightly more exciting or vigorous day was all that was necessary to trigger the headache.
For those of you who don’t share my contention that childhood migraine is usually the result of sleep deprivation, consider the similarity between an epileptic seizure, which can be triggered by fatigue. Both events are usually followed by a deep sleep from which the child wakes refreshed and symptom free.
I think it is interesting that this recent meta-analysis could find no benefit in the quality of life for any of the medications. The explanation may be that the child with migraine already had a somewhat diminished quality of life as a result of the sleep deprivation, either acute or chronic.
When speaking with parents of migraine sufferers, I would tell them that once the headache had started there was little I had to offer to forestall the inevitable pain and vomiting. Certainly not in the form of an oral medication. While many adults will have an aura that warns them of the headache onset, I have found that most children don’t describe an aura. It may be they simply lack the ability to express it. Occasionally an observant parent may detect pallor or a behavior change that indicates a migraine is beginning. On rare occasions a parent may be able to abort the attack by quickly getting the child to a quiet, dark, and calm environment.
Although this recent meta-analysis review of treatment options is discouraging, it may be providing a clue to effective prophylaxis. Some of the medications that decrease the frequency of the attacks may be doing so because they improve the patient’s sleep patterns. Those that decrease the intensity of the pain are probably working on pain pathway that is not specific to migraine.
Continuing a search for a prophylactic medication is a worthy goal, particularly for those patients in which their migraines are debilitating. However, based on my experience, enhanced by my bias, the safest and most effective prophylaxis results from increasing the family’s awareness of the role that sleep deprivation plays in the illness. Even when the family buys into the message and attempts to avoid situations that will tax their vulnerable children, parents will need to accept that sometimes stuff happens even though siblings and peers may be able to tolerate the situation. Spontaneous activities can converge on a day when for whatever reason the migraine-prone child is overtired and the headache and vomiting will erupt.
A lifestyle change is always preferable to a pharmacological intervention. However, that doesn’t mean it is always easy to achieve.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect you all have some experience with childhood migraine. It can mean a painful several hours for the patient, arriving often without warning, with recurrences spaced months or sometimes even years apart. It may be accompanied by vomiting, which in some cases overshadows the severity of the headache. It can result in lost days from school and ruin family activities. It can occur so infrequently that the family can’t recall accurately when the last episode happened. In some ways it is a different animal than the adult version.
Most of the pediatric patients with migraine I have seen have experienced attacks that were occurring so infrequently that the families and I seldom discussed medication as an option. Back then imipramine was the only choice. However, currently there are more than a half dozen medications and combinations that have been tried. Recently a review of 45 clinical trials of these medications was published in JAMA Network Open.
I will let you review for yourself the details of these Iranian investigators’ network meta-analysis, but the bottom line is that some medications were associated with a reduction in migraine frequency. Others were associated with headache intensity. “However, no treatments were associated with significant improvements in quality of life or reduction of the duration of migraine attacks.”
Obviously, this paper illustrates clearly that we have not yet discovered the medicinal magic bullet for pediatric migraine prophylaxis. This doesn’t surprise me. After listening to scores of families tell their migraine stories, it became apparent to me that there was often a pattern in which the child’s headache had arrived after a period of acute sleep deprivation. For example, a trip to an amusement park in which travel or excitement may have resulted in the child going to bed later and/or getting up earlier. By afternoon the child’s reserves of something (currently unknown) were depleted to a point that the headache and/or vomiting struck.
Because these episodes were often so infrequent, separated by months, that taking a history demonstrating a recurring pattern could take considerable patience on the part of the family and the provider, even for a physician like myself who believes that better sleep is the answer for everything. However, once I could convince a family of the connection between the sleep deprivation and the headaches, they could often recall other episodes in the past that substantiated my explanation.
In some cases there was no obvious history of acute sleep deprivation, or at least it was so subtle that even a history taker with a sleep obsession couldn’t detect it. However, in these cases I could usually elicit a history of chronic sleep deprivation. For example, falling asleep instantly on automobile rides, difficulty with waking in the morning, or unhealthy bedtime routines. With this underlying vulnerability of chronic sleep deprivation, a slightly more exciting or vigorous day was all that was necessary to trigger the headache.
For those of you who don’t share my contention that childhood migraine is usually the result of sleep deprivation, consider the similarity between an epileptic seizure, which can be triggered by fatigue. Both events are usually followed by a deep sleep from which the child wakes refreshed and symptom free.
I think it is interesting that this recent meta-analysis could find no benefit in the quality of life for any of the medications. The explanation may be that the child with migraine already had a somewhat diminished quality of life as a result of the sleep deprivation, either acute or chronic.
When speaking with parents of migraine sufferers, I would tell them that once the headache had started there was little I had to offer to forestall the inevitable pain and vomiting. Certainly not in the form of an oral medication. While many adults will have an aura that warns them of the headache onset, I have found that most children don’t describe an aura. It may be they simply lack the ability to express it. Occasionally an observant parent may detect pallor or a behavior change that indicates a migraine is beginning. On rare occasions a parent may be able to abort the attack by quickly getting the child to a quiet, dark, and calm environment.
Although this recent meta-analysis review of treatment options is discouraging, it may be providing a clue to effective prophylaxis. Some of the medications that decrease the frequency of the attacks may be doing so because they improve the patient’s sleep patterns. Those that decrease the intensity of the pain are probably working on pain pathway that is not specific to migraine.
Continuing a search for a prophylactic medication is a worthy goal, particularly for those patients in which their migraines are debilitating. However, based on my experience, enhanced by my bias, the safest and most effective prophylaxis results from increasing the family’s awareness of the role that sleep deprivation plays in the illness. Even when the family buys into the message and attempts to avoid situations that will tax their vulnerable children, parents will need to accept that sometimes stuff happens even though siblings and peers may be able to tolerate the situation. Spontaneous activities can converge on a day when for whatever reason the migraine-prone child is overtired and the headache and vomiting will erupt.
A lifestyle change is always preferable to a pharmacological intervention. However, that doesn’t mean it is always easy to achieve.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Just Call It ‘Chronic Rhinitis’ and Reach for These Treatments
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular Disease 2050: No, GLP-1s Won’t Save the Day
This transcript has been edited for clarity .
Robert A. Harrington, MD: I’m here in London at the European Society of Cardiology meetings, at theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology booth, using the meetings as an opportunity to meet with colleagues to talk about recent things that they’ve been writing about.
Today I’m joined by a good friend and colleague, Dr. Dhruv Kazi from Beth Israel Deaconess in Boston. Thanks for joining us.
Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, MS: Thank you for having me.
Harrington: Dr. Kazi is an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He’s also the associate director of the Smith Center, which is an outcomes research center at the Beth Israel Deaconess. Thanks for joining us.
Kazi: Excited to be here.
Harrington: The topic I think you know that I want to discuss is a really important paper. There are two papers. They’re part of the American Heart Association’s 100th anniversary celebration, if you will. Many of the papers looked back at where science taken us.
With your coauthor, Karen Joynt Maddox, your papers are looking forward. They’re about the burden of cardiovascular disease in 2050. One paper really focused on what I would call the clinical and public health issues. Yours is focused on the economics. Is that a good description?
Kazi: Perfect.
Harrington: Tell us what you, Karen, and the other writers set out to do. What were you asked to do?
Kazi: As you know, the American Heart Association is entering its second century. Part of this was an exercise to say, where will the country be in 2050, which is a long enough time horizon for us to start planning for the future.
We looked back and said, if prior trends remain the same, where will we be in 2050, accounting for changes in demographics, changes in the composition of the population, and knowing that some of the cardiovascular risk factors are getting worse?
Harrington: For me, what was really striking is that, when I first saw the title and read “2050,” I thought, Oh, that’s a long way away. Then as I started reading it, I realized that this is not so far away.
Kazi: Absolutely.
Harrington: If we’re going to make a difference, it might take us 25 years.
Kazi: Especially if we set ourselves ambitious goals, we›re going to have to dig deep. Business-as-usual is not going to get us there.
Harrington: No. What I think has happened is we›ve spent so much time taking care of acute illness. Case fatality rates are fantastic. I was actually making the comment yesterday to a colleague that when I was an intern, the 30-day death rate from acute myocardial infarction was about 20%.
Kazi: Oh, wow.
Harrington: Now it’s 5%. That’s a big difference in a career.
Trends in the Wrong Direction
Kazi: There are fundamental trends. The decline in case fatalities is a really positive development, and I would hope that, going forward, that would continue. Those are risk-adjusted death rates and what is happening is that risk is going up. This is a function of the fact that the US population is aging; 2030 will be the first year that all the baby boomers will be over the age of 65.
By the mid-2030s, we’ll have more adults over the age of 65 than kids. That aging of the population is going to increase risk. The second is — and this is a positive development — we are a more diverse population, but the populations that are minoritized have higher cardiovascular risk, for a variety of reasons.
As the population of Asian Americans increases and doubles, in fact, as the population of Hispanic Americans doubles, we’re going to see an increase in risk related to cardiovascular disease. The third is that, over the past decade, there are some risk factors that are going in the wrong direction.
Harrington: Let’s talk about that because that’s humbling. I’m involved, as you know, with the American Heart Association, as are you. Despite all the work on Life’s Simple 7 and now Life’s Essential 8, we still have some issues.
Kazi: The big ones that come to mind are hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, all of which are trending in the wrong direction. Hypertension, we were gaining traction; and then over the past decade, we’ve slipped again. As you know, national blood pressure control rates have declined in many populations.
Harrington: Rather substantially.
Kazi: Substantially so, which has implications, in particular, for stroke rates in the future and stroke rates in young adults in the future. Obesity is a problem that we have very little control over. We’re already at 40% on average, which means that some populations are already in the 60% range.
Harrington: We also have obesity in kids — the burden, I’ll call it, of obesity. It’s not that you become obese in your thirties or your forties; you›re becoming obese as a teenager or even younger.
Kazi: Exactly. Since the 1990s, obesity in US adults has doubled, but obesity in US children has quadrupled. It’s starting from a lower base, but it’s very much an escalating problem.
Harrington: Diabetes is tightly linked to it but not totally explained.
Kazi: Exactly. The increase in diabetes is largely driven by obesity, but it›s probably also driven by changes in diet and lifestyle that don›t go through obesity.
Harrington: Yeah, it’s interesting. I think I have this figure correctly. It used to be rare that you saw a child with type 2 diabetes or what we call type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Now, the vast majority of kids with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: In the adolescents/young adults age group, most of it is type 2.
Harrington: Diabetes going up, obesity up, hypertension not well controlled, smoking combustible cigarettes way down.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Cholesterol levels. I was surprised. Cholesterol looked better. You said — because I was at a meeting where somebody asked you — that’s not explained by treatment.
Kazi: No, it’s not, at least going back to the ‘70s, but likely even sooner. I think that can only be attributed to substantial dietary changes. We are consuming less fat and less trans-fat. It’s possible that those collectively are improving our cholesterol levels, possibly at the expense of our glucose levels, because we basically substituted fats in our diet with more carbs at a population level.
Cigarettes and Vaping
Harrington: Some things certainly trend in the right direction but others in a really difficult direction. It’s going to lead to pretty large changes in risk for coronary disease, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure.
Kazi: I want to go back to the tobacco point. There are definitely marked declines in tobacco, still tightly related to income in the country. You see much higher prevalence of tobacco use in lower-income populations, but it’s unclear to me where it’s going in kids. We know that combustible tobacco use is going down but e-cigarettes went up. What that leads to over the next 30 years is unclear to me.
Harrington: That is a really important comment that’s worth sidebarring. The vaping use has been a terrible epidemic among our high schoolers. What is that going to lead to? Is it going to lead to the use of combustible cigarettes and we’re going to see that go back up? It remains to be seen.
Kazi: Yes, it remains to be seen. Going back to your point about this change in risk factors and this change in demographics, both aging and becoming a more diverse population means that we have large increases in some healthcare conditions.
Coronary heart disease goes up some, there›s a big jump in stroke — nearly a doubling in stroke — which is related to hypertension, obesity, an aging population, and a more diverse population. There are changes in stroke in the young, and atrial fibrillation related to, again, hypertension. We’re seeing these projections, and with them come these pretty large projections in changes in healthcare spending.
Healthcare Spending Not Sustainable
Harrington: Big. I mean, it’s not sustainable. Give the audience the number — it’s pretty frightening.
Kazi: We’re talking about a quadrupling of healthcare costs related to cardiovascular disease over 25 years. We’ve gotten used to the narrative that healthcare in the US is expensive and drugs are expensive, but this is an enormous problem — an unsustainable problem, like you called it.
It’s a doubling as a proportion of the economy. I was looking this up this morning. If the US healthcare economy were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest economy in the world.
Harrington: Healthcare as it is today, is it 21% of our economy?
Kazi: It’s 17% now. If it were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest in the world. We are spending more on healthcare than all but two other countries’ total economies. It’s kind of crazy.
Harrington: We’re talking about a quadrupling.
Kazi: Within that, the cardiovascular piece is a big piece, and we›re talking about a quadrupling.
Harrington: That’s both direct and indirect costs.
Kazi: The quadrupling of costs is just the direct costs. Indirect costs, for the listeners, refer to costs unrelated to healthcare but changes in productivity, either because people are disabled and unable to participate fully in the workforce or they die early.
The productivity costs are also increased substantially as a result. If you look at both healthcare and productivity, that goes up threefold. These are very large changes.
Harrington: Let’s now get to what we can do about it. I made the comment to you when I first read the papers that I was very depressed. Then, after I went through my Kübler-Ross stages of depression, death, and dying, I came to acceptance.
What are we going to do about it? This is a focus on policy, but also a focus on how we deliver healthcare, how we think about healthcare, and how we develop drugs and devices.
The drug question is going to be the one the audience is thinking about. They say, well, what about GLP-1 agonists? Aren’t those going to save the day?
Kazi: Yes and no. I’ll say that, early in my career, I used to be very attracted to simple solutions to complex problems. I’ve come to realize that simple solutions are elegant, attractive, and wrong. We›re dealing with a very complex issue and I think we’re going to need a multipronged approach.
The way I think about it is that there was a group of people who are at very high risk today. How do we help those individuals? Then how do we help the future generation so that they’re not dealing with the projections that we’re talking about.
My colleague, Karen Joynt Maddox, who led one of the papers, as you mentioned, has an elegant line in the paper where she says projections are not destiny. These are things we can change.
Harrington: If nothing changes, this is what it’s going to look like.
Kazi: This is where we’re headed.
Harrington: We can change. We’ve got some time to change, but we don’t have forever.
Kazi: Yes, exactly. We picked the 25-year timeline instead of a “let’s plan for the next century” timeline because we want something concrete and actionable. It’s close enough to be meaningful but far enough to give us the runway we need to act.
Harrington: Give me two things from the policy perspective, because it’s mostly policy.
Kazi: There are policy and clinical interventions. From the policy perspective, if I had to list two things, one is expansion of access to care. As we talk about this big increase in the burden of disease and risk factors, if you have a large proportion of your population that has hypertension or diabetes, you’re going to have to expand access to care to ensure that people get treated so they can get access to this care before they develop the complications that we worry about, like stroke and heart disease, that are very expensive to treat downstream.
The second, more broadly related to access to care, is the access to medications that are effective. You bring up GLP-1s. I think we need a real strategy for how we can give people access to GLP-1s at a price that is affordable to individuals but also affordable to the health system, and to help them stay on the drugs.
GLP-1s are transformative in what they do for weight loss and for diabetes, but more than 50% of people who start one are off it at 12 months. There’s something fundamentally wrong about how we’re delivering GLP-1s today. It’s not just about the cost of the drugs but the support system people need to stay on.
Harrington: I’ve made the comment, in many forms now, that we know the drugs work. We have to figure out how to use them.
Kazi: Exactly, yes.
Harrington: Using them includes chronicity. This is a chronic condition. Some people can come off the drugs, but many can’t. We’re going to have to figure this out, and maybe the newer generations of drugs will help us address what people call the off-ramping. How are we going to do that? I think you’re spot-on. Those are critically important questions.
Kazi: As we looked at this modeling, I’ll tell you — I had a come-to-Jesus moment where I was like, there is no way to fix cardiovascular disease in the US without going through obesity and diabetes. We have to address obesity in the US. We can’t just treat our way out of it. Obesity is fundamentally a food problem and we’ve got to engage again with food policy in a meaningful way.
Harrington: As you know, with the American Heart Association, we›re doing a large amount of work now on food as medicine and food is medicine. We are trying to figure out what the levers are that we can pull to actually help people eat healthier diets.
Kazi: Yes. Rather than framing it as an individual choice that people are eating poorly, it’s, how do we make healthy diets the default in the environment?
Harrington: This is where you get to the children as well.
Kazi: Exactly.
Harrington: I could talk about this all day. I’ve had the benefit of reading the papers now a few times and talking to you on several occasions. Thank you for joining us.
Kazi: Thank you.
Dr. Harrington, Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Dean, Weill Cornell Medicine; Provost for Medical Affairs, Cornell University, New York, NY, disclosed ties with Baim Institute (DSMB); CSL (RCT Executive Committee); Janssen (RCT Char), NHLBI (RCT Executive Committee, DSMB Chair); PCORI (RCT Co-Chair); DCRI, Atropos Health; Bitterroot Bio; Bristol Myers Squibb; BridgeBio; Element Science; Edwards Lifesciences; Foresite Labs; Medscape/WebMD Board of Directors for: American Heart Association; College of the Holy Cross; and Cytokinetics. Dr. Kazi, Associate Director, Smith Center for Outcomes Research, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Harvard Medical School, Director, Department of Cardiac Critical Care Unit, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed receiving a research grant from Boston Scientific (grant to examine the economics of stroke prevention).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity .
Robert A. Harrington, MD: I’m here in London at the European Society of Cardiology meetings, at theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology booth, using the meetings as an opportunity to meet with colleagues to talk about recent things that they’ve been writing about.
Today I’m joined by a good friend and colleague, Dr. Dhruv Kazi from Beth Israel Deaconess in Boston. Thanks for joining us.
Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, MS: Thank you for having me.
Harrington: Dr. Kazi is an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He’s also the associate director of the Smith Center, which is an outcomes research center at the Beth Israel Deaconess. Thanks for joining us.
Kazi: Excited to be here.
Harrington: The topic I think you know that I want to discuss is a really important paper. There are two papers. They’re part of the American Heart Association’s 100th anniversary celebration, if you will. Many of the papers looked back at where science taken us.
With your coauthor, Karen Joynt Maddox, your papers are looking forward. They’re about the burden of cardiovascular disease in 2050. One paper really focused on what I would call the clinical and public health issues. Yours is focused on the economics. Is that a good description?
Kazi: Perfect.
Harrington: Tell us what you, Karen, and the other writers set out to do. What were you asked to do?
Kazi: As you know, the American Heart Association is entering its second century. Part of this was an exercise to say, where will the country be in 2050, which is a long enough time horizon for us to start planning for the future.
We looked back and said, if prior trends remain the same, where will we be in 2050, accounting for changes in demographics, changes in the composition of the population, and knowing that some of the cardiovascular risk factors are getting worse?
Harrington: For me, what was really striking is that, when I first saw the title and read “2050,” I thought, Oh, that’s a long way away. Then as I started reading it, I realized that this is not so far away.
Kazi: Absolutely.
Harrington: If we’re going to make a difference, it might take us 25 years.
Kazi: Especially if we set ourselves ambitious goals, we›re going to have to dig deep. Business-as-usual is not going to get us there.
Harrington: No. What I think has happened is we›ve spent so much time taking care of acute illness. Case fatality rates are fantastic. I was actually making the comment yesterday to a colleague that when I was an intern, the 30-day death rate from acute myocardial infarction was about 20%.
Kazi: Oh, wow.
Harrington: Now it’s 5%. That’s a big difference in a career.
Trends in the Wrong Direction
Kazi: There are fundamental trends. The decline in case fatalities is a really positive development, and I would hope that, going forward, that would continue. Those are risk-adjusted death rates and what is happening is that risk is going up. This is a function of the fact that the US population is aging; 2030 will be the first year that all the baby boomers will be over the age of 65.
By the mid-2030s, we’ll have more adults over the age of 65 than kids. That aging of the population is going to increase risk. The second is — and this is a positive development — we are a more diverse population, but the populations that are minoritized have higher cardiovascular risk, for a variety of reasons.
As the population of Asian Americans increases and doubles, in fact, as the population of Hispanic Americans doubles, we’re going to see an increase in risk related to cardiovascular disease. The third is that, over the past decade, there are some risk factors that are going in the wrong direction.
Harrington: Let’s talk about that because that’s humbling. I’m involved, as you know, with the American Heart Association, as are you. Despite all the work on Life’s Simple 7 and now Life’s Essential 8, we still have some issues.
Kazi: The big ones that come to mind are hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, all of which are trending in the wrong direction. Hypertension, we were gaining traction; and then over the past decade, we’ve slipped again. As you know, national blood pressure control rates have declined in many populations.
Harrington: Rather substantially.
Kazi: Substantially so, which has implications, in particular, for stroke rates in the future and stroke rates in young adults in the future. Obesity is a problem that we have very little control over. We’re already at 40% on average, which means that some populations are already in the 60% range.
Harrington: We also have obesity in kids — the burden, I’ll call it, of obesity. It’s not that you become obese in your thirties or your forties; you›re becoming obese as a teenager or even younger.
Kazi: Exactly. Since the 1990s, obesity in US adults has doubled, but obesity in US children has quadrupled. It’s starting from a lower base, but it’s very much an escalating problem.
Harrington: Diabetes is tightly linked to it but not totally explained.
Kazi: Exactly. The increase in diabetes is largely driven by obesity, but it›s probably also driven by changes in diet and lifestyle that don›t go through obesity.
Harrington: Yeah, it’s interesting. I think I have this figure correctly. It used to be rare that you saw a child with type 2 diabetes or what we call type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Now, the vast majority of kids with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: In the adolescents/young adults age group, most of it is type 2.
Harrington: Diabetes going up, obesity up, hypertension not well controlled, smoking combustible cigarettes way down.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Cholesterol levels. I was surprised. Cholesterol looked better. You said — because I was at a meeting where somebody asked you — that’s not explained by treatment.
Kazi: No, it’s not, at least going back to the ‘70s, but likely even sooner. I think that can only be attributed to substantial dietary changes. We are consuming less fat and less trans-fat. It’s possible that those collectively are improving our cholesterol levels, possibly at the expense of our glucose levels, because we basically substituted fats in our diet with more carbs at a population level.
Cigarettes and Vaping
Harrington: Some things certainly trend in the right direction but others in a really difficult direction. It’s going to lead to pretty large changes in risk for coronary disease, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure.
Kazi: I want to go back to the tobacco point. There are definitely marked declines in tobacco, still tightly related to income in the country. You see much higher prevalence of tobacco use in lower-income populations, but it’s unclear to me where it’s going in kids. We know that combustible tobacco use is going down but e-cigarettes went up. What that leads to over the next 30 years is unclear to me.
Harrington: That is a really important comment that’s worth sidebarring. The vaping use has been a terrible epidemic among our high schoolers. What is that going to lead to? Is it going to lead to the use of combustible cigarettes and we’re going to see that go back up? It remains to be seen.
Kazi: Yes, it remains to be seen. Going back to your point about this change in risk factors and this change in demographics, both aging and becoming a more diverse population means that we have large increases in some healthcare conditions.
Coronary heart disease goes up some, there›s a big jump in stroke — nearly a doubling in stroke — which is related to hypertension, obesity, an aging population, and a more diverse population. There are changes in stroke in the young, and atrial fibrillation related to, again, hypertension. We’re seeing these projections, and with them come these pretty large projections in changes in healthcare spending.
Healthcare Spending Not Sustainable
Harrington: Big. I mean, it’s not sustainable. Give the audience the number — it’s pretty frightening.
Kazi: We’re talking about a quadrupling of healthcare costs related to cardiovascular disease over 25 years. We’ve gotten used to the narrative that healthcare in the US is expensive and drugs are expensive, but this is an enormous problem — an unsustainable problem, like you called it.
It’s a doubling as a proportion of the economy. I was looking this up this morning. If the US healthcare economy were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest economy in the world.
Harrington: Healthcare as it is today, is it 21% of our economy?
Kazi: It’s 17% now. If it were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest in the world. We are spending more on healthcare than all but two other countries’ total economies. It’s kind of crazy.
Harrington: We’re talking about a quadrupling.
Kazi: Within that, the cardiovascular piece is a big piece, and we›re talking about a quadrupling.
Harrington: That’s both direct and indirect costs.
Kazi: The quadrupling of costs is just the direct costs. Indirect costs, for the listeners, refer to costs unrelated to healthcare but changes in productivity, either because people are disabled and unable to participate fully in the workforce or they die early.
The productivity costs are also increased substantially as a result. If you look at both healthcare and productivity, that goes up threefold. These are very large changes.
Harrington: Let’s now get to what we can do about it. I made the comment to you when I first read the papers that I was very depressed. Then, after I went through my Kübler-Ross stages of depression, death, and dying, I came to acceptance.
What are we going to do about it? This is a focus on policy, but also a focus on how we deliver healthcare, how we think about healthcare, and how we develop drugs and devices.
The drug question is going to be the one the audience is thinking about. They say, well, what about GLP-1 agonists? Aren’t those going to save the day?
Kazi: Yes and no. I’ll say that, early in my career, I used to be very attracted to simple solutions to complex problems. I’ve come to realize that simple solutions are elegant, attractive, and wrong. We›re dealing with a very complex issue and I think we’re going to need a multipronged approach.
The way I think about it is that there was a group of people who are at very high risk today. How do we help those individuals? Then how do we help the future generation so that they’re not dealing with the projections that we’re talking about.
My colleague, Karen Joynt Maddox, who led one of the papers, as you mentioned, has an elegant line in the paper where she says projections are not destiny. These are things we can change.
Harrington: If nothing changes, this is what it’s going to look like.
Kazi: This is where we’re headed.
Harrington: We can change. We’ve got some time to change, but we don’t have forever.
Kazi: Yes, exactly. We picked the 25-year timeline instead of a “let’s plan for the next century” timeline because we want something concrete and actionable. It’s close enough to be meaningful but far enough to give us the runway we need to act.
Harrington: Give me two things from the policy perspective, because it’s mostly policy.
Kazi: There are policy and clinical interventions. From the policy perspective, if I had to list two things, one is expansion of access to care. As we talk about this big increase in the burden of disease and risk factors, if you have a large proportion of your population that has hypertension or diabetes, you’re going to have to expand access to care to ensure that people get treated so they can get access to this care before they develop the complications that we worry about, like stroke and heart disease, that are very expensive to treat downstream.
The second, more broadly related to access to care, is the access to medications that are effective. You bring up GLP-1s. I think we need a real strategy for how we can give people access to GLP-1s at a price that is affordable to individuals but also affordable to the health system, and to help them stay on the drugs.
GLP-1s are transformative in what they do for weight loss and for diabetes, but more than 50% of people who start one are off it at 12 months. There’s something fundamentally wrong about how we’re delivering GLP-1s today. It’s not just about the cost of the drugs but the support system people need to stay on.
Harrington: I’ve made the comment, in many forms now, that we know the drugs work. We have to figure out how to use them.
Kazi: Exactly, yes.
Harrington: Using them includes chronicity. This is a chronic condition. Some people can come off the drugs, but many can’t. We’re going to have to figure this out, and maybe the newer generations of drugs will help us address what people call the off-ramping. How are we going to do that? I think you’re spot-on. Those are critically important questions.
Kazi: As we looked at this modeling, I’ll tell you — I had a come-to-Jesus moment where I was like, there is no way to fix cardiovascular disease in the US without going through obesity and diabetes. We have to address obesity in the US. We can’t just treat our way out of it. Obesity is fundamentally a food problem and we’ve got to engage again with food policy in a meaningful way.
Harrington: As you know, with the American Heart Association, we›re doing a large amount of work now on food as medicine and food is medicine. We are trying to figure out what the levers are that we can pull to actually help people eat healthier diets.
Kazi: Yes. Rather than framing it as an individual choice that people are eating poorly, it’s, how do we make healthy diets the default in the environment?
Harrington: This is where you get to the children as well.
Kazi: Exactly.
Harrington: I could talk about this all day. I’ve had the benefit of reading the papers now a few times and talking to you on several occasions. Thank you for joining us.
Kazi: Thank you.
Dr. Harrington, Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Dean, Weill Cornell Medicine; Provost for Medical Affairs, Cornell University, New York, NY, disclosed ties with Baim Institute (DSMB); CSL (RCT Executive Committee); Janssen (RCT Char), NHLBI (RCT Executive Committee, DSMB Chair); PCORI (RCT Co-Chair); DCRI, Atropos Health; Bitterroot Bio; Bristol Myers Squibb; BridgeBio; Element Science; Edwards Lifesciences; Foresite Labs; Medscape/WebMD Board of Directors for: American Heart Association; College of the Holy Cross; and Cytokinetics. Dr. Kazi, Associate Director, Smith Center for Outcomes Research, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Harvard Medical School, Director, Department of Cardiac Critical Care Unit, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed receiving a research grant from Boston Scientific (grant to examine the economics of stroke prevention).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity .
Robert A. Harrington, MD: I’m here in London at the European Society of Cardiology meetings, at theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology booth, using the meetings as an opportunity to meet with colleagues to talk about recent things that they’ve been writing about.
Today I’m joined by a good friend and colleague, Dr. Dhruv Kazi from Beth Israel Deaconess in Boston. Thanks for joining us.
Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, MS: Thank you for having me.
Harrington: Dr. Kazi is an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School. He’s also the associate director of the Smith Center, which is an outcomes research center at the Beth Israel Deaconess. Thanks for joining us.
Kazi: Excited to be here.
Harrington: The topic I think you know that I want to discuss is a really important paper. There are two papers. They’re part of the American Heart Association’s 100th anniversary celebration, if you will. Many of the papers looked back at where science taken us.
With your coauthor, Karen Joynt Maddox, your papers are looking forward. They’re about the burden of cardiovascular disease in 2050. One paper really focused on what I would call the clinical and public health issues. Yours is focused on the economics. Is that a good description?
Kazi: Perfect.
Harrington: Tell us what you, Karen, and the other writers set out to do. What were you asked to do?
Kazi: As you know, the American Heart Association is entering its second century. Part of this was an exercise to say, where will the country be in 2050, which is a long enough time horizon for us to start planning for the future.
We looked back and said, if prior trends remain the same, where will we be in 2050, accounting for changes in demographics, changes in the composition of the population, and knowing that some of the cardiovascular risk factors are getting worse?
Harrington: For me, what was really striking is that, when I first saw the title and read “2050,” I thought, Oh, that’s a long way away. Then as I started reading it, I realized that this is not so far away.
Kazi: Absolutely.
Harrington: If we’re going to make a difference, it might take us 25 years.
Kazi: Especially if we set ourselves ambitious goals, we›re going to have to dig deep. Business-as-usual is not going to get us there.
Harrington: No. What I think has happened is we›ve spent so much time taking care of acute illness. Case fatality rates are fantastic. I was actually making the comment yesterday to a colleague that when I was an intern, the 30-day death rate from acute myocardial infarction was about 20%.
Kazi: Oh, wow.
Harrington: Now it’s 5%. That’s a big difference in a career.
Trends in the Wrong Direction
Kazi: There are fundamental trends. The decline in case fatalities is a really positive development, and I would hope that, going forward, that would continue. Those are risk-adjusted death rates and what is happening is that risk is going up. This is a function of the fact that the US population is aging; 2030 will be the first year that all the baby boomers will be over the age of 65.
By the mid-2030s, we’ll have more adults over the age of 65 than kids. That aging of the population is going to increase risk. The second is — and this is a positive development — we are a more diverse population, but the populations that are minoritized have higher cardiovascular risk, for a variety of reasons.
As the population of Asian Americans increases and doubles, in fact, as the population of Hispanic Americans doubles, we’re going to see an increase in risk related to cardiovascular disease. The third is that, over the past decade, there are some risk factors that are going in the wrong direction.
Harrington: Let’s talk about that because that’s humbling. I’m involved, as you know, with the American Heart Association, as are you. Despite all the work on Life’s Simple 7 and now Life’s Essential 8, we still have some issues.
Kazi: The big ones that come to mind are hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, all of which are trending in the wrong direction. Hypertension, we were gaining traction; and then over the past decade, we’ve slipped again. As you know, national blood pressure control rates have declined in many populations.
Harrington: Rather substantially.
Kazi: Substantially so, which has implications, in particular, for stroke rates in the future and stroke rates in young adults in the future. Obesity is a problem that we have very little control over. We’re already at 40% on average, which means that some populations are already in the 60% range.
Harrington: We also have obesity in kids — the burden, I’ll call it, of obesity. It’s not that you become obese in your thirties or your forties; you›re becoming obese as a teenager or even younger.
Kazi: Exactly. Since the 1990s, obesity in US adults has doubled, but obesity in US children has quadrupled. It’s starting from a lower base, but it’s very much an escalating problem.
Harrington: Diabetes is tightly linked to it but not totally explained.
Kazi: Exactly. The increase in diabetes is largely driven by obesity, but it›s probably also driven by changes in diet and lifestyle that don›t go through obesity.
Harrington: Yeah, it’s interesting. I think I have this figure correctly. It used to be rare that you saw a child with type 2 diabetes or what we call type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Now, the vast majority of kids with diabetes have type 2 diabetes.
Kazi: In the adolescents/young adults age group, most of it is type 2.
Harrington: Diabetes going up, obesity up, hypertension not well controlled, smoking combustible cigarettes way down.
Kazi: Yeah.
Harrington: Cholesterol levels. I was surprised. Cholesterol looked better. You said — because I was at a meeting where somebody asked you — that’s not explained by treatment.
Kazi: No, it’s not, at least going back to the ‘70s, but likely even sooner. I think that can only be attributed to substantial dietary changes. We are consuming less fat and less trans-fat. It’s possible that those collectively are improving our cholesterol levels, possibly at the expense of our glucose levels, because we basically substituted fats in our diet with more carbs at a population level.
Cigarettes and Vaping
Harrington: Some things certainly trend in the right direction but others in a really difficult direction. It’s going to lead to pretty large changes in risk for coronary disease, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure.
Kazi: I want to go back to the tobacco point. There are definitely marked declines in tobacco, still tightly related to income in the country. You see much higher prevalence of tobacco use in lower-income populations, but it’s unclear to me where it’s going in kids. We know that combustible tobacco use is going down but e-cigarettes went up. What that leads to over the next 30 years is unclear to me.
Harrington: That is a really important comment that’s worth sidebarring. The vaping use has been a terrible epidemic among our high schoolers. What is that going to lead to? Is it going to lead to the use of combustible cigarettes and we’re going to see that go back up? It remains to be seen.
Kazi: Yes, it remains to be seen. Going back to your point about this change in risk factors and this change in demographics, both aging and becoming a more diverse population means that we have large increases in some healthcare conditions.
Coronary heart disease goes up some, there›s a big jump in stroke — nearly a doubling in stroke — which is related to hypertension, obesity, an aging population, and a more diverse population. There are changes in stroke in the young, and atrial fibrillation related to, again, hypertension. We’re seeing these projections, and with them come these pretty large projections in changes in healthcare spending.
Healthcare Spending Not Sustainable
Harrington: Big. I mean, it’s not sustainable. Give the audience the number — it’s pretty frightening.
Kazi: We’re talking about a quadrupling of healthcare costs related to cardiovascular disease over 25 years. We’ve gotten used to the narrative that healthcare in the US is expensive and drugs are expensive, but this is an enormous problem — an unsustainable problem, like you called it.
It’s a doubling as a proportion of the economy. I was looking this up this morning. If the US healthcare economy were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest economy in the world.
Harrington: Healthcare as it is today, is it 21% of our economy?
Kazi: It’s 17% now. If it were its own economy, it would be the fourth largest in the world. We are spending more on healthcare than all but two other countries’ total economies. It’s kind of crazy.
Harrington: We’re talking about a quadrupling.
Kazi: Within that, the cardiovascular piece is a big piece, and we›re talking about a quadrupling.
Harrington: That’s both direct and indirect costs.
Kazi: The quadrupling of costs is just the direct costs. Indirect costs, for the listeners, refer to costs unrelated to healthcare but changes in productivity, either because people are disabled and unable to participate fully in the workforce or they die early.
The productivity costs are also increased substantially as a result. If you look at both healthcare and productivity, that goes up threefold. These are very large changes.
Harrington: Let’s now get to what we can do about it. I made the comment to you when I first read the papers that I was very depressed. Then, after I went through my Kübler-Ross stages of depression, death, and dying, I came to acceptance.
What are we going to do about it? This is a focus on policy, but also a focus on how we deliver healthcare, how we think about healthcare, and how we develop drugs and devices.
The drug question is going to be the one the audience is thinking about. They say, well, what about GLP-1 agonists? Aren’t those going to save the day?
Kazi: Yes and no. I’ll say that, early in my career, I used to be very attracted to simple solutions to complex problems. I’ve come to realize that simple solutions are elegant, attractive, and wrong. We›re dealing with a very complex issue and I think we’re going to need a multipronged approach.
The way I think about it is that there was a group of people who are at very high risk today. How do we help those individuals? Then how do we help the future generation so that they’re not dealing with the projections that we’re talking about.
My colleague, Karen Joynt Maddox, who led one of the papers, as you mentioned, has an elegant line in the paper where she says projections are not destiny. These are things we can change.
Harrington: If nothing changes, this is what it’s going to look like.
Kazi: This is where we’re headed.
Harrington: We can change. We’ve got some time to change, but we don’t have forever.
Kazi: Yes, exactly. We picked the 25-year timeline instead of a “let’s plan for the next century” timeline because we want something concrete and actionable. It’s close enough to be meaningful but far enough to give us the runway we need to act.
Harrington: Give me two things from the policy perspective, because it’s mostly policy.
Kazi: There are policy and clinical interventions. From the policy perspective, if I had to list two things, one is expansion of access to care. As we talk about this big increase in the burden of disease and risk factors, if you have a large proportion of your population that has hypertension or diabetes, you’re going to have to expand access to care to ensure that people get treated so they can get access to this care before they develop the complications that we worry about, like stroke and heart disease, that are very expensive to treat downstream.
The second, more broadly related to access to care, is the access to medications that are effective. You bring up GLP-1s. I think we need a real strategy for how we can give people access to GLP-1s at a price that is affordable to individuals but also affordable to the health system, and to help them stay on the drugs.
GLP-1s are transformative in what they do for weight loss and for diabetes, but more than 50% of people who start one are off it at 12 months. There’s something fundamentally wrong about how we’re delivering GLP-1s today. It’s not just about the cost of the drugs but the support system people need to stay on.
Harrington: I’ve made the comment, in many forms now, that we know the drugs work. We have to figure out how to use them.
Kazi: Exactly, yes.
Harrington: Using them includes chronicity. This is a chronic condition. Some people can come off the drugs, but many can’t. We’re going to have to figure this out, and maybe the newer generations of drugs will help us address what people call the off-ramping. How are we going to do that? I think you’re spot-on. Those are critically important questions.
Kazi: As we looked at this modeling, I’ll tell you — I had a come-to-Jesus moment where I was like, there is no way to fix cardiovascular disease in the US without going through obesity and diabetes. We have to address obesity in the US. We can’t just treat our way out of it. Obesity is fundamentally a food problem and we’ve got to engage again with food policy in a meaningful way.
Harrington: As you know, with the American Heart Association, we›re doing a large amount of work now on food as medicine and food is medicine. We are trying to figure out what the levers are that we can pull to actually help people eat healthier diets.
Kazi: Yes. Rather than framing it as an individual choice that people are eating poorly, it’s, how do we make healthy diets the default in the environment?
Harrington: This is where you get to the children as well.
Kazi: Exactly.
Harrington: I could talk about this all day. I’ve had the benefit of reading the papers now a few times and talking to you on several occasions. Thank you for joining us.
Kazi: Thank you.
Dr. Harrington, Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Dean, Weill Cornell Medicine; Provost for Medical Affairs, Cornell University, New York, NY, disclosed ties with Baim Institute (DSMB); CSL (RCT Executive Committee); Janssen (RCT Char), NHLBI (RCT Executive Committee, DSMB Chair); PCORI (RCT Co-Chair); DCRI, Atropos Health; Bitterroot Bio; Bristol Myers Squibb; BridgeBio; Element Science; Edwards Lifesciences; Foresite Labs; Medscape/WebMD Board of Directors for: American Heart Association; College of the Holy Cross; and Cytokinetics. Dr. Kazi, Associate Director, Smith Center for Outcomes Research, Associate Professor, Department of Medicine (Cardiology), Harvard Medical School, Director, Department of Cardiac Critical Care Unit, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed receiving a research grant from Boston Scientific (grant to examine the economics of stroke prevention).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Old Are You? Stand on One Leg and I’ll Tell You
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
So I was lying in bed the other night, trying to read my phone, and started complaining to my wife about how my vision keeps getting worse, and then how stiff I feel when I wake up in the morning, and how a recent injury is taking too long to heal, and she said, “Well, yeah. You’re 44. That’s when things start to head downhill.”
And I was like, “Forty-four? That seems very specific. I thought 50 was what people complain about.” And she said, “No, it’s a thing — 44 years old and 60 years old. There’s a drop-off there.”
And you know what? She was right.
A study, “Nonlinear dynamics of multi-omics profiles during human aging,” published in Nature Aging in August 2024, analyzed a ton of proteins and metabolites in people of various ages and found, when you put it all together, that I should know better than to doubt my brilliant spouse.
But deep down, I believe the cliché that age is just a number. I don’t particularly care about being 44, or turning 50 or 60. I care about how my body and brain are aging. If I can be a happy, healthy, 80-year-old in full command of my faculties, I would consider that a major win no matter what the calendar says.
So I’m always interested in ways to quantify how my body is aging, independent of how many birthdays I have passed. And, according to a new study, there’s actually a really easy way to do this: Just stand on one leg.
The surprising results come from “Age-related changes in gait, balance, and strength parameters: A cross-sectional study,” appearing in PLOS One, which analyzed 40 individuals — half under age 65 and half over age 65 — across a variety of domains of strength, balance, and gait. The conceit of the study? We all know that things like strength and balance worsen over time, but what worsens fastest? What might be the best metric to tell us how our bodies are aging?
To that end, you have a variety of correlations between various metrics and calendar age.
As age increases, grip strength goes down. Men (inexplicably in pink) have higher grip strength overall, and women (confusingly in blue) lower. Somewhat less strong correlations were seen for knee strength.
What about balance?
To assess this, the researchers had the participants stand on a pressure plate. In one scenario, they did this with eyes open, and the next with eyes closed. They then measured how much the pressure varied around the center of the individual on the plate — basically, how much the person swayed while they were standing there.
Sway increased as age increased. Sway increased a bit more with eyes closed than with eyes open.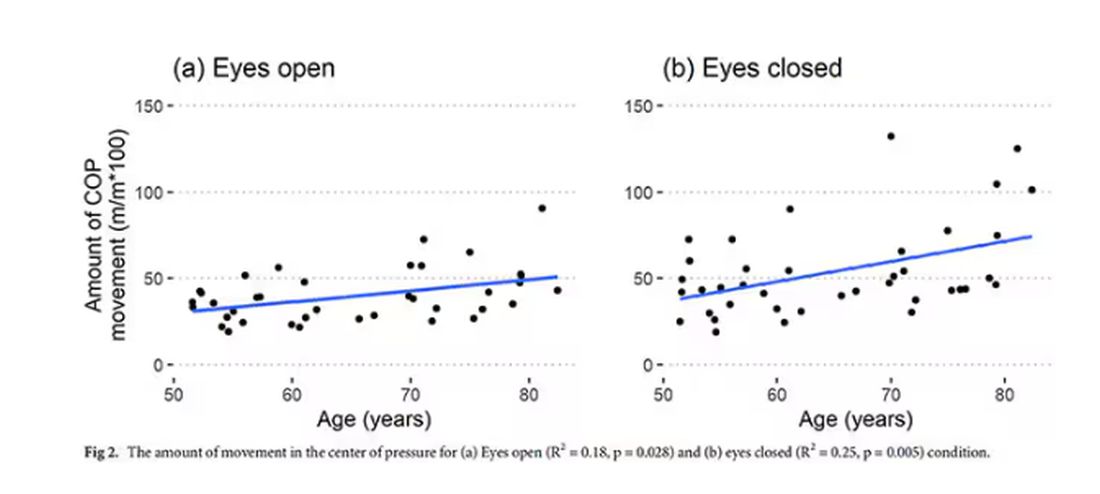
But the strongest correlation between any of these metrics and age was a simple one: How long can you stand on one leg?
Particularly for the nondominant leg, what you see here is a pretty dramatic drop-off in balance time around age 65, with younger people able to do 10 seconds with ease and some older people barely being able to make it to 2.
Of course, I had to try this for myself. And as I was standing around on one leg, it became clear to me exactly why this might be a good metric. It really integrates balance and strength in a way that the other tests don’t: balance, clearly, since you have to stay vertical over a relatively small base; but strength as well, because, well, one leg is holding up all the rest of you. You do feel it after a while.
So this metric passes the smell test to me, at least as a potential proxy for age-related physical decline.
But I should be careful to note that this was a cross-sectional study; the researchers looked at various people who were all different ages, not the same people over time to watch how these things change as they aged.
Also, the use of the correlation coefficient in graphs like this implies a certain linear relationship between age and standing-on-one-foot time. The raw data — the points on this graph — don’t appear that linear to me. As I mentioned above, it seems like there might be a bit of a sharp drop-off somewhere in the mid-60s. That means that we may not be able to use this as a sensitive test for aging that slowly changes as your body gets older. It might be that you’re able to essentially stand on one leg as long as you want until, one day, you can’t. That gives us less warning and less to act on.
And finally, we don’t know that changing this metric will change your health for the better. I’m sure a good physiatrist or physical therapist could design some exercises to increase any of our standing-on-one leg times. And no doubt, with practice, you could get your numbers way up. But that doesn’t necessarily mean you’re healthier. It’s like “teaching to the test”; you might score better on the standardized exam but you didn’t really learn the material.
So I am not adding one-leg standing to my daily exercise routine. But I won’t lie and tell you that, from time to time, and certainly on my 60th birthday, you may find me standing like a flamingo with a stopwatch in my hand.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
So I was lying in bed the other night, trying to read my phone, and started complaining to my wife about how my vision keeps getting worse, and then how stiff I feel when I wake up in the morning, and how a recent injury is taking too long to heal, and she said, “Well, yeah. You’re 44. That’s when things start to head downhill.”
And I was like, “Forty-four? That seems very specific. I thought 50 was what people complain about.” And she said, “No, it’s a thing — 44 years old and 60 years old. There’s a drop-off there.”
And you know what? She was right.
A study, “Nonlinear dynamics of multi-omics profiles during human aging,” published in Nature Aging in August 2024, analyzed a ton of proteins and metabolites in people of various ages and found, when you put it all together, that I should know better than to doubt my brilliant spouse.
But deep down, I believe the cliché that age is just a number. I don’t particularly care about being 44, or turning 50 or 60. I care about how my body and brain are aging. If I can be a happy, healthy, 80-year-old in full command of my faculties, I would consider that a major win no matter what the calendar says.
So I’m always interested in ways to quantify how my body is aging, independent of how many birthdays I have passed. And, according to a new study, there’s actually a really easy way to do this: Just stand on one leg.
The surprising results come from “Age-related changes in gait, balance, and strength parameters: A cross-sectional study,” appearing in PLOS One, which analyzed 40 individuals — half under age 65 and half over age 65 — across a variety of domains of strength, balance, and gait. The conceit of the study? We all know that things like strength and balance worsen over time, but what worsens fastest? What might be the best metric to tell us how our bodies are aging?
To that end, you have a variety of correlations between various metrics and calendar age.
As age increases, grip strength goes down. Men (inexplicably in pink) have higher grip strength overall, and women (confusingly in blue) lower. Somewhat less strong correlations were seen for knee strength.
What about balance?
To assess this, the researchers had the participants stand on a pressure plate. In one scenario, they did this with eyes open, and the next with eyes closed. They then measured how much the pressure varied around the center of the individual on the plate — basically, how much the person swayed while they were standing there.
Sway increased as age increased. Sway increased a bit more with eyes closed than with eyes open.
But the strongest correlation between any of these metrics and age was a simple one: How long can you stand on one leg?
Particularly for the nondominant leg, what you see here is a pretty dramatic drop-off in balance time around age 65, with younger people able to do 10 seconds with ease and some older people barely being able to make it to 2.
Of course, I had to try this for myself. And as I was standing around on one leg, it became clear to me exactly why this might be a good metric. It really integrates balance and strength in a way that the other tests don’t: balance, clearly, since you have to stay vertical over a relatively small base; but strength as well, because, well, one leg is holding up all the rest of you. You do feel it after a while.
So this metric passes the smell test to me, at least as a potential proxy for age-related physical decline.
But I should be careful to note that this was a cross-sectional study; the researchers looked at various people who were all different ages, not the same people over time to watch how these things change as they aged.
Also, the use of the correlation coefficient in graphs like this implies a certain linear relationship between age and standing-on-one-foot time. The raw data — the points on this graph — don’t appear that linear to me. As I mentioned above, it seems like there might be a bit of a sharp drop-off somewhere in the mid-60s. That means that we may not be able to use this as a sensitive test for aging that slowly changes as your body gets older. It might be that you’re able to essentially stand on one leg as long as you want until, one day, you can’t. That gives us less warning and less to act on.
And finally, we don’t know that changing this metric will change your health for the better. I’m sure a good physiatrist or physical therapist could design some exercises to increase any of our standing-on-one leg times. And no doubt, with practice, you could get your numbers way up. But that doesn’t necessarily mean you’re healthier. It’s like “teaching to the test”; you might score better on the standardized exam but you didn’t really learn the material.
So I am not adding one-leg standing to my daily exercise routine. But I won’t lie and tell you that, from time to time, and certainly on my 60th birthday, you may find me standing like a flamingo with a stopwatch in my hand.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
So I was lying in bed the other night, trying to read my phone, and started complaining to my wife about how my vision keeps getting worse, and then how stiff I feel when I wake up in the morning, and how a recent injury is taking too long to heal, and she said, “Well, yeah. You’re 44. That’s when things start to head downhill.”
And I was like, “Forty-four? That seems very specific. I thought 50 was what people complain about.” And she said, “No, it’s a thing — 44 years old and 60 years old. There’s a drop-off there.”
And you know what? She was right.
A study, “Nonlinear dynamics of multi-omics profiles during human aging,” published in Nature Aging in August 2024, analyzed a ton of proteins and metabolites in people of various ages and found, when you put it all together, that I should know better than to doubt my brilliant spouse.
But deep down, I believe the cliché that age is just a number. I don’t particularly care about being 44, or turning 50 or 60. I care about how my body and brain are aging. If I can be a happy, healthy, 80-year-old in full command of my faculties, I would consider that a major win no matter what the calendar says.
So I’m always interested in ways to quantify how my body is aging, independent of how many birthdays I have passed. And, according to a new study, there’s actually a really easy way to do this: Just stand on one leg.
The surprising results come from “Age-related changes in gait, balance, and strength parameters: A cross-sectional study,” appearing in PLOS One, which analyzed 40 individuals — half under age 65 and half over age 65 — across a variety of domains of strength, balance, and gait. The conceit of the study? We all know that things like strength and balance worsen over time, but what worsens fastest? What might be the best metric to tell us how our bodies are aging?
To that end, you have a variety of correlations between various metrics and calendar age.
As age increases, grip strength goes down. Men (inexplicably in pink) have higher grip strength overall, and women (confusingly in blue) lower. Somewhat less strong correlations were seen for knee strength.
What about balance?
To assess this, the researchers had the participants stand on a pressure plate. In one scenario, they did this with eyes open, and the next with eyes closed. They then measured how much the pressure varied around the center of the individual on the plate — basically, how much the person swayed while they were standing there.
Sway increased as age increased. Sway increased a bit more with eyes closed than with eyes open.
But the strongest correlation between any of these metrics and age was a simple one: How long can you stand on one leg?
Particularly for the nondominant leg, what you see here is a pretty dramatic drop-off in balance time around age 65, with younger people able to do 10 seconds with ease and some older people barely being able to make it to 2.
Of course, I had to try this for myself. And as I was standing around on one leg, it became clear to me exactly why this might be a good metric. It really integrates balance and strength in a way that the other tests don’t: balance, clearly, since you have to stay vertical over a relatively small base; but strength as well, because, well, one leg is holding up all the rest of you. You do feel it after a while.
So this metric passes the smell test to me, at least as a potential proxy for age-related physical decline.
But I should be careful to note that this was a cross-sectional study; the researchers looked at various people who were all different ages, not the same people over time to watch how these things change as they aged.
Also, the use of the correlation coefficient in graphs like this implies a certain linear relationship between age and standing-on-one-foot time. The raw data — the points on this graph — don’t appear that linear to me. As I mentioned above, it seems like there might be a bit of a sharp drop-off somewhere in the mid-60s. That means that we may not be able to use this as a sensitive test for aging that slowly changes as your body gets older. It might be that you’re able to essentially stand on one leg as long as you want until, one day, you can’t. That gives us less warning and less to act on.
And finally, we don’t know that changing this metric will change your health for the better. I’m sure a good physiatrist or physical therapist could design some exercises to increase any of our standing-on-one leg times. And no doubt, with practice, you could get your numbers way up. But that doesn’t necessarily mean you’re healthier. It’s like “teaching to the test”; you might score better on the standardized exam but you didn’t really learn the material.
So I am not adding one-leg standing to my daily exercise routine. But I won’t lie and tell you that, from time to time, and certainly on my 60th birthday, you may find me standing like a flamingo with a stopwatch in my hand.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
H pylori: ACG Guideline Advises New Approaches to Treatment
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Helicobacter pylori is one of the most common human bacterial chronic infections globally. Its prevalence has actually decreased in North America in recent years, although its current range of approximately 30%-40% remains substantial given the potential clinical implications of infection.
Standards have changed considerably regarding the testing, treatment, and follow-up of H pylori. This is made clear by the just-published clinical practice guideline from the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), which provides several new recommendations based on recent scientific evidence that should change your clinical approach to managing this common infection.
This discussion aims to synthesize and highlight key concepts from the ACG’s comprehensive publication.
Who Should Be Tested and Treated?
The cardinal diseases caused by H pylori have traditionally included peptic ulcer disease, marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, gastric adenocarcinoma, and dyspepsia.
Additional associations have been made with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and otherwise unexplained iron deficiency.
New evidence suggests that patients taking long-term nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including low-dose aspirin, are relatively more susceptible to infection.
The ACG’s guideline also recommends testing persons at an increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma (eg, those with autoimmune gastritis, current or history of premalignant conditions, or first-degree relative with gastric cancer), as well as household members of patients with a positive nonserologic test for H pylori.
The authors note that those with an indication for testing should be offered treatment if determined to have an infection. These patients should also undergo a posttreatment test-of-cure, which should occur at least 4 weeks afterwards using a urea breath test, fecal antigen test, or gastric biopsy.
Caveats to Treatment
Patients with H pylori infections are advised to undergo treatment for a duration of 14 days. Some of the commercial prepackaged H pylori treatment options (eg, Pylera, which contains bismuth subcitrate/metronidazole/tetracycline) are dispensed in regimens lasting only 10 days and currently are viewed as inadequate.
In the United States, the patterns of antibiotic resistance for the previously used standard drugs in the treatment of H pylori have increased considerably. They range from 32% for clarithromycin, 38% for levofloxacin, and 42% for metronidazole, in contrast to 3% for amoxicillin, 1% for tetracycline, and 0% for rifabutin.
Clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-containing treatments should be avoided in treatment-naive patients unless specifically directed following the results of susceptibility tests with either a phenotypic method (culture-based) or a molecular method (polymerase chain reaction or next-generation sequencing). Notably, the mutations responsible for both clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance may be detectable by stool-based testing.
Maintenance of intragastric acid suppression is key to H pylori eradication, as elevated intragastric pH promotes active replication of H pylori and makes it more susceptible to bactericidal antibiotics.
Therefore, the use of histamine-2 receptors is not recommended, as they are inadequate for achieving acid suppression. Instead, a dual-based therapy of either the potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) vonoprazan (20 mg) or a high-dose proton pump inhibitor (PPI) and amoxicillin, administered twice daily, is effective, although this finding is based on limited evidence.
Treatment-Naive Patients
In treatment-naive patients without penicillin allergy and for whom antibiotic susceptibility testing has not been obtained, the guideline offers its strongest recommendation for bismuth quadruple therapy. This therapy typically consists of a PPI, bismuth subcitrate or subsalicylate, tetracycline, and metronidazole.
Among those with a penicillin allergy, bismuth quadruple therapy is also the primary treatment choice. The authors suggest that patients with a suspected allergy are referred to an allergist for possible penicillin desensitization, given that less than 1% of the population is thought to present with a “true” allergy.
The guideline also presented conditional recommendations, based on low- to moderate-quality evidence, for using a rifabutin-based triple regimen of omeprazole, amoxicillin, and rifabutin (Talicia); a PCAB-based dual regimen of vonoprazan and amoxicillin (Voquezna Dual Pak); and a PCAB-based triple regimen of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak). In patients with unknown clarithromycin susceptibility, the PCAB-based triple therapy is preferred over PPI-clarithromycin triple therapy.
Although probiotics have been suggested to possibly lead to increased effectiveness or tolerability for H pylori eradication, this was based on studies with significant heterogeneity in their designs. At present, no high-quality data support probiotic therapy.
Clinicians may substitute doxycycline for tetracycline due to availability or cost, and also may prescribe metronidazole at a lower dose than recommended (1.5-2 g/d) to limit side effects. Both modifications have been associated with lower rates of H pylori eradication and are not recommended.
Treatment-Experienced Patients
Quadruple bismuth therapy is the optimal approach among treatment-experienced patients with persistent H pylori infection who have not previously received this therapy. However, this recommendation was rated as conditional, given that it was based on a low quality of evidence.
The guideline offered other recommendations for treatment-experienced patients with persistent infection who had received bismuth quadruple therapy — also conditionally based on a low quality of evidence.
In such patients, it is recommended to consider the use of a rifabutin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard to double dose, amoxicillin, and rifabutin) and a levofloxacin-based triple therapy (ie, a PPI standard dose, levofloxacin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole).
Although significant evidence gaps prevented the authors from providing formal recommendations, they included a PCAB-based triple therapy of vonoprazan, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin (Voquezna Triple Pak) and a high-dose dual therapy of either vonoprazan (20 mg) or PPI (double dose) and amoxicillin among their suggested salvage regimens for these patients.
A New Standard
We must recognize, however, that there are still substantial evidence gaps, particularly around the use of a PCAB-based regimen and its relative advantages over a standard or high-dose PPI-based regimen. This may be of particular importance based on the variable prevalence of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphisms in the specific patient populations, as PCABs are not metabolized by CYP2C19.
Reviewing the entirety of the ACG’s clinical guideline is encouraged for additional details about the management of H pylori beyond what is highlighted herein.
Dr. Johnson, Professor of Medicine, Chief of Gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, Virginia, disclosed ties with ISOTHRIVE and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Help Your Patients Reap the Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
Research pooled from nearly 100 studies has indicated that people who adhere to a vegan diet (ie, completely devoid of animal products) or a vegetarian diet (ie, devoid of meat, but may include dairy and eggs) are able to ward off some chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, optimize glycemic control, and decrease their risk for cancer compared with those who consume omnivorous diets.
Vegan and vegetarian diets, or flexitarian diets — which are less reliant on animal protein than the standard US diet but do not completely exclude meat, fish, eggs, or dairy — may promote homeostasis and decrease inflammation by providing more fiber, antioxidants, and unsaturated fatty acids than the typical Western diet.
Inflammation and Obesity
Adipose tissue is a major producer of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin (IL)-6, whose presence then triggers a rush of acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein (CRP) by the liver. This process develops into chronic low-grade inflammation that can increase a person’s chances of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and related complications.
Adopting a plant-based diet can improve markers of chronic low-grade inflammation that can lead to chronic disease and worsen existent chronic disease. A meta-analysis of 29 studies encompassing nearly 2700 participants found that initiation of a plant-based diet showed significant improvement in CRP, IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1.
If we want to prevent these inflammatory disease states and their complications, the obvious response is to counsel patients to avoid excessive weight gain or to lose weight if obesity is their baseline. This can be tough for some patients, but it is nonetheless an important step in chronic disease prevention and management.
Plant-Based Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
According to a review of nine studies of patients living with type 2 diabetes who adhered to a plant-based diet, all but one found that this approach led to significantly lower A1c values than those seen in control groups. Six of the included studies reported that participants were able to decrease or discontinue medications for the management of diabetes. Researchers across all included studies also noted a decrease in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, as well as increased weight loss in participants in each intervention group.
Such improvements are probably the result of the increase in fiber intake that occurs with a plant-based diet. A high-fiber diet is known to promote improved glucose and lipid metabolism as well as weight loss.
It is also worth noting that participants in the intervention groups also experienced improvements in depression and less chronic pain than did those in the control groups.
Plant-Based Diet for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Although the use of a plant-based diet in the prevention of CKD is well documented, adopting such diets for the treatment of CKD may intimidate both patients and practitioners owing to the high potassium and phosphorus content of many fruits and vegetables.
However, research indicates that the bioavailability of both potassium and phosphorus is lower in plant-based, whole foods than in preservatives and the highly processed food items that incorporate them. This makes a plant-based diet more viable than previously thought.
Diets rich in vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes have been shown to decrease dietary acid load, both preventing and treating metabolic acidosis. Such diets have also been shown to decrease blood pressure and the risk for a decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate. This type of diet would also prioritize the unsaturated fatty acids and fiber-rich proteins such as avocados, beans, and nuts shown to improve dyslipidemia, which may occur alongside CKD.
Realistic Options for Patients on Medical Diets
There is one question that I always seem to get from when recommending a plant-based diet: “These patients already have so many restrictions. Why would you add more?” And my answer is also always the same: I don’t.
I rarely, if ever, recommend completely cutting out any food item or food group. Instead, I ask the patient to increase their intake of plant-based foods and only limit highly processed foods and fatty meats. By shifting a patient’s focus to beans; nuts; and low-carbohydrate, high-fiber fruits and vegetables, I am often opening up a whole new world of possibilities.
Instead of a sandwich with low-sodium turkey and cheese on white bread with a side of unsalted pretzels, I recommend a caprese salad with blueberries and almonds or a Southwest salad with black beans, corn, and avocado. I don’t encourage my patients to skip the foods that they love, but instead to only think about all the delicious plant-based options that will provide them with more than just calories.
Meat, dairy, seafood, and eggs can certainly be a part of a healthy diet, but what if our chronically ill patients, especially those with diabetes, had more options than just grilled chicken and green beans for every meal? What if we focus on decreasing dietary restrictions, incorporating a variety of nourishing foods, and educating our patients, instead of on portion control and moderation?
This is how I choose to incorporate plant-based diets into my practice to treat and prevent these chronic inflammatory conditions and promote sustainable, realistic change in my clients’ health.
Brandy Winfree Root, a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Research pooled from nearly 100 studies has indicated that people who adhere to a vegan diet (ie, completely devoid of animal products) or a vegetarian diet (ie, devoid of meat, but may include dairy and eggs) are able to ward off some chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, optimize glycemic control, and decrease their risk for cancer compared with those who consume omnivorous diets.
Vegan and vegetarian diets, or flexitarian diets — which are less reliant on animal protein than the standard US diet but do not completely exclude meat, fish, eggs, or dairy — may promote homeostasis and decrease inflammation by providing more fiber, antioxidants, and unsaturated fatty acids than the typical Western diet.
Inflammation and Obesity
Adipose tissue is a major producer of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin (IL)-6, whose presence then triggers a rush of acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein (CRP) by the liver. This process develops into chronic low-grade inflammation that can increase a person’s chances of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and related complications.
Adopting a plant-based diet can improve markers of chronic low-grade inflammation that can lead to chronic disease and worsen existent chronic disease. A meta-analysis of 29 studies encompassing nearly 2700 participants found that initiation of a plant-based diet showed significant improvement in CRP, IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1.
If we want to prevent these inflammatory disease states and their complications, the obvious response is to counsel patients to avoid excessive weight gain or to lose weight if obesity is their baseline. This can be tough for some patients, but it is nonetheless an important step in chronic disease prevention and management.
Plant-Based Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
According to a review of nine studies of patients living with type 2 diabetes who adhered to a plant-based diet, all but one found that this approach led to significantly lower A1c values than those seen in control groups. Six of the included studies reported that participants were able to decrease or discontinue medications for the management of diabetes. Researchers across all included studies also noted a decrease in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, as well as increased weight loss in participants in each intervention group.
Such improvements are probably the result of the increase in fiber intake that occurs with a plant-based diet. A high-fiber diet is known to promote improved glucose and lipid metabolism as well as weight loss.
It is also worth noting that participants in the intervention groups also experienced improvements in depression and less chronic pain than did those in the control groups.
Plant-Based Diet for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Although the use of a plant-based diet in the prevention of CKD is well documented, adopting such diets for the treatment of CKD may intimidate both patients and practitioners owing to the high potassium and phosphorus content of many fruits and vegetables.
However, research indicates that the bioavailability of both potassium and phosphorus is lower in plant-based, whole foods than in preservatives and the highly processed food items that incorporate them. This makes a plant-based diet more viable than previously thought.
Diets rich in vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes have been shown to decrease dietary acid load, both preventing and treating metabolic acidosis. Such diets have also been shown to decrease blood pressure and the risk for a decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate. This type of diet would also prioritize the unsaturated fatty acids and fiber-rich proteins such as avocados, beans, and nuts shown to improve dyslipidemia, which may occur alongside CKD.
Realistic Options for Patients on Medical Diets
There is one question that I always seem to get from when recommending a plant-based diet: “These patients already have so many restrictions. Why would you add more?” And my answer is also always the same: I don’t.
I rarely, if ever, recommend completely cutting out any food item or food group. Instead, I ask the patient to increase their intake of plant-based foods and only limit highly processed foods and fatty meats. By shifting a patient’s focus to beans; nuts; and low-carbohydrate, high-fiber fruits and vegetables, I am often opening up a whole new world of possibilities.
Instead of a sandwich with low-sodium turkey and cheese on white bread with a side of unsalted pretzels, I recommend a caprese salad with blueberries and almonds or a Southwest salad with black beans, corn, and avocado. I don’t encourage my patients to skip the foods that they love, but instead to only think about all the delicious plant-based options that will provide them with more than just calories.
Meat, dairy, seafood, and eggs can certainly be a part of a healthy diet, but what if our chronically ill patients, especially those with diabetes, had more options than just grilled chicken and green beans for every meal? What if we focus on decreasing dietary restrictions, incorporating a variety of nourishing foods, and educating our patients, instead of on portion control and moderation?
This is how I choose to incorporate plant-based diets into my practice to treat and prevent these chronic inflammatory conditions and promote sustainable, realistic change in my clients’ health.
Brandy Winfree Root, a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Research pooled from nearly 100 studies has indicated that people who adhere to a vegan diet (ie, completely devoid of animal products) or a vegetarian diet (ie, devoid of meat, but may include dairy and eggs) are able to ward off some chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, optimize glycemic control, and decrease their risk for cancer compared with those who consume omnivorous diets.
Vegan and vegetarian diets, or flexitarian diets — which are less reliant on animal protein than the standard US diet but do not completely exclude meat, fish, eggs, or dairy — may promote homeostasis and decrease inflammation by providing more fiber, antioxidants, and unsaturated fatty acids than the typical Western diet.
Inflammation and Obesity
Adipose tissue is a major producer of pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin (IL)-6, whose presence then triggers a rush of acute-phase reactants such as C-reactive protein (CRP) by the liver. This process develops into chronic low-grade inflammation that can increase a person’s chances of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, metabolic syndrome, and related complications.
Adopting a plant-based diet can improve markers of chronic low-grade inflammation that can lead to chronic disease and worsen existent chronic disease. A meta-analysis of 29 studies encompassing nearly 2700 participants found that initiation of a plant-based diet showed significant improvement in CRP, IL-6, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1.
If we want to prevent these inflammatory disease states and their complications, the obvious response is to counsel patients to avoid excessive weight gain or to lose weight if obesity is their baseline. This can be tough for some patients, but it is nonetheless an important step in chronic disease prevention and management.
Plant-Based Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
According to a review of nine studies of patients living with type 2 diabetes who adhered to a plant-based diet, all but one found that this approach led to significantly lower A1c values than those seen in control groups. Six of the included studies reported that participants were able to decrease or discontinue medications for the management of diabetes. Researchers across all included studies also noted a decrease in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, as well as increased weight loss in participants in each intervention group.
Such improvements are probably the result of the increase in fiber intake that occurs with a plant-based diet. A high-fiber diet is known to promote improved glucose and lipid metabolism as well as weight loss.
It is also worth noting that participants in the intervention groups also experienced improvements in depression and less chronic pain than did those in the control groups.
Plant-Based Diet for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Although the use of a plant-based diet in the prevention of CKD is well documented, adopting such diets for the treatment of CKD may intimidate both patients and practitioners owing to the high potassium and phosphorus content of many fruits and vegetables.
However, research indicates that the bioavailability of both potassium and phosphorus is lower in plant-based, whole foods than in preservatives and the highly processed food items that incorporate them. This makes a plant-based diet more viable than previously thought.
Diets rich in vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes have been shown to decrease dietary acid load, both preventing and treating metabolic acidosis. Such diets have also been shown to decrease blood pressure and the risk for a decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate. This type of diet would also prioritize the unsaturated fatty acids and fiber-rich proteins such as avocados, beans, and nuts shown to improve dyslipidemia, which may occur alongside CKD.
Realistic Options for Patients on Medical Diets
There is one question that I always seem to get from when recommending a plant-based diet: “These patients already have so many restrictions. Why would you add more?” And my answer is also always the same: I don’t.
I rarely, if ever, recommend completely cutting out any food item or food group. Instead, I ask the patient to increase their intake of plant-based foods and only limit highly processed foods and fatty meats. By shifting a patient’s focus to beans; nuts; and low-carbohydrate, high-fiber fruits and vegetables, I am often opening up a whole new world of possibilities.
Instead of a sandwich with low-sodium turkey and cheese on white bread with a side of unsalted pretzels, I recommend a caprese salad with blueberries and almonds or a Southwest salad with black beans, corn, and avocado. I don’t encourage my patients to skip the foods that they love, but instead to only think about all the delicious plant-based options that will provide them with more than just calories.
Meat, dairy, seafood, and eggs can certainly be a part of a healthy diet, but what if our chronically ill patients, especially those with diabetes, had more options than just grilled chicken and green beans for every meal? What if we focus on decreasing dietary restrictions, incorporating a variety of nourishing foods, and educating our patients, instead of on portion control and moderation?
This is how I choose to incorporate plant-based diets into my practice to treat and prevent these chronic inflammatory conditions and promote sustainable, realistic change in my clients’ health.
Brandy Winfree Root, a renal dietitian in private practice in Mary Esther, Florida, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is CGM the New CBT?
Lauren is a 45-year-old corporate lawyer who managed to excel in every aspect of her life, including parenting her three children while working full-time as a corporate lawyer. A math major at Harvard, she loves data.
Suffice it to say, given that I was treating her for a thyroid condition rather than diabetes, I was a little surprised when she requested I prescribe her a FreeStyle Libre (Abbott) monitor. She explained she was struggling to lose 10 pounds, and she thought continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) would help her determine which foods were impeding her weight loss journey.
While I didn’t see much downside to acquiescing, I felt she had probably been spending too much time on Reddit. What information could CGM give someone without diabetes that couldn’t be gleaned from a food label? Nevertheless, Lauren filled the prescription and began her foray into this relatively uncharted world. When she returned for a follow-up visit several months later, I was shocked to see that she had lost her intended weight. With my tail between my legs, I decided to review the theories and science behind the use of CGM in patients without insulin resistance.
Although it’s not rocket science, CGM can help patients through a “carrot and stick” approach to dieting. Lean proteins, nonstarchy vegetables, and monounsaturated fats such as nuts and avocado all support weight loss and tend to keep blood glucose levels stable. In contrast, foods known to cause weight gain (eg, sugary foods, refined starches, and processed foods) cause sugar spikes in real time. Similarly, large portion sizes are more likely to result in sugar spikes, and pairing proteins with carbohydrates minimizes blood glucose excursions.
Though all of this is basic common sense, . And because blood glucose is influenced by myriad factors including stress, genetics and metabolism, CGM can also potentially help create personal guidance for food choices.
In addition, CGM can reveal the effect of poor sleep and stress on blood glucose levels, thereby encouraging healthier lifestyle choices. The data collected also may provide information on how different modalities of physical activity affect blood glucose levels. A recent study compared the effect of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and continuous moderate-intensity exercise on postmeal blood glucose in overweight individuals without diabetes. CGM revealed that HIIT is more advantageous for preventing postmeal spikes.
Although CGM appears to be a sophisticated form of cognitive-behavioral therapy, I do worry that the incessant stream of information can lead to worsening anxiety, obsessive compulsive behaviors, or restrictive eating tendencies. Still, thanks to Lauren, I now believe that real-time CGM may lead to behavior modification in food selection and physical activity.
Dr. Messer, Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine; Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lauren is a 45-year-old corporate lawyer who managed to excel in every aspect of her life, including parenting her three children while working full-time as a corporate lawyer. A math major at Harvard, she loves data.
Suffice it to say, given that I was treating her for a thyroid condition rather than diabetes, I was a little surprised when she requested I prescribe her a FreeStyle Libre (Abbott) monitor. She explained she was struggling to lose 10 pounds, and she thought continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) would help her determine which foods were impeding her weight loss journey.
While I didn’t see much downside to acquiescing, I felt she had probably been spending too much time on Reddit. What information could CGM give someone without diabetes that couldn’t be gleaned from a food label? Nevertheless, Lauren filled the prescription and began her foray into this relatively uncharted world. When she returned for a follow-up visit several months later, I was shocked to see that she had lost her intended weight. With my tail between my legs, I decided to review the theories and science behind the use of CGM in patients without insulin resistance.
Although it’s not rocket science, CGM can help patients through a “carrot and stick” approach to dieting. Lean proteins, nonstarchy vegetables, and monounsaturated fats such as nuts and avocado all support weight loss and tend to keep blood glucose levels stable. In contrast, foods known to cause weight gain (eg, sugary foods, refined starches, and processed foods) cause sugar spikes in real time. Similarly, large portion sizes are more likely to result in sugar spikes, and pairing proteins with carbohydrates minimizes blood glucose excursions.
Though all of this is basic common sense, . And because blood glucose is influenced by myriad factors including stress, genetics and metabolism, CGM can also potentially help create personal guidance for food choices.
In addition, CGM can reveal the effect of poor sleep and stress on blood glucose levels, thereby encouraging healthier lifestyle choices. The data collected also may provide information on how different modalities of physical activity affect blood glucose levels. A recent study compared the effect of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and continuous moderate-intensity exercise on postmeal blood glucose in overweight individuals without diabetes. CGM revealed that HIIT is more advantageous for preventing postmeal spikes.
Although CGM appears to be a sophisticated form of cognitive-behavioral therapy, I do worry that the incessant stream of information can lead to worsening anxiety, obsessive compulsive behaviors, or restrictive eating tendencies. Still, thanks to Lauren, I now believe that real-time CGM may lead to behavior modification in food selection and physical activity.
Dr. Messer, Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine; Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Lauren is a 45-year-old corporate lawyer who managed to excel in every aspect of her life, including parenting her three children while working full-time as a corporate lawyer. A math major at Harvard, she loves data.
Suffice it to say, given that I was treating her for a thyroid condition rather than diabetes, I was a little surprised when she requested I prescribe her a FreeStyle Libre (Abbott) monitor. She explained she was struggling to lose 10 pounds, and she thought continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) would help her determine which foods were impeding her weight loss journey.
While I didn’t see much downside to acquiescing, I felt she had probably been spending too much time on Reddit. What information could CGM give someone without diabetes that couldn’t be gleaned from a food label? Nevertheless, Lauren filled the prescription and began her foray into this relatively uncharted world. When she returned for a follow-up visit several months later, I was shocked to see that she had lost her intended weight. With my tail between my legs, I decided to review the theories and science behind the use of CGM in patients without insulin resistance.
Although it’s not rocket science, CGM can help patients through a “carrot and stick” approach to dieting. Lean proteins, nonstarchy vegetables, and monounsaturated fats such as nuts and avocado all support weight loss and tend to keep blood glucose levels stable. In contrast, foods known to cause weight gain (eg, sugary foods, refined starches, and processed foods) cause sugar spikes in real time. Similarly, large portion sizes are more likely to result in sugar spikes, and pairing proteins with carbohydrates minimizes blood glucose excursions.
Though all of this is basic common sense, . And because blood glucose is influenced by myriad factors including stress, genetics and metabolism, CGM can also potentially help create personal guidance for food choices.
In addition, CGM can reveal the effect of poor sleep and stress on blood glucose levels, thereby encouraging healthier lifestyle choices. The data collected also may provide information on how different modalities of physical activity affect blood glucose levels. A recent study compared the effect of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and continuous moderate-intensity exercise on postmeal blood glucose in overweight individuals without diabetes. CGM revealed that HIIT is more advantageous for preventing postmeal spikes.
Although CGM appears to be a sophisticated form of cognitive-behavioral therapy, I do worry that the incessant stream of information can lead to worsening anxiety, obsessive compulsive behaviors, or restrictive eating tendencies. Still, thanks to Lauren, I now believe that real-time CGM may lead to behavior modification in food selection and physical activity.
Dr. Messer, Clinical Assistant Professor, Mount Sinai School of Medicine; Associate Professor, Hofstra School of Medicine, New York, NY, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A Brief Glimpse Into 80,000 Years of Human History
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Like millions of other modern humans, my daughter and I stood in the backyard recently and watched comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan–ATLAS) with binoculars. It took a few minutes to locate, but once you see it is unmistakable.
It’s got a long (at least in human terms) orbit, roughly 80,000 years. So what was going on here, on our pale blue dot, the last time it graced our skies?
Well, here in Phoenix, the people were ... not here. Nor were they in Arizona, or North America, or pretty much the entire Western Hemisphere.
In fact, Homo sapiens were confined to Africa. The hardier Neanderthals had successfully moved into Eurasia, but our lineage was just starting to migrate there. There’s some evidence that we numbered maybe 10,000-15,000 at that point. Far more people saw the comet that night in the United States than our entire population count last time it swung by.
But we were moving up in the world. Our ancestors at the time had developed the first forms of jewelry, using seashells. There’s evidence that we’d learned to trade with other, distant, communities. We were using spears to put dinner on the table with less risk to ourselves than clubs posed.
And, in what’s now Kenya, in the same time frame, a pair of grieving parents carefully buried their 3-year-old child, wrapped in a covering and gently placed on a pillow.
Sadly, this isn’t a scene we’re unfamiliar with. Possibly the most famous painting of a physician is “The Doctor” (1891) by Luke Fildes, showing a physician trying to treat a seriously ill child while the parents look on helplessly.

What did the Kenyan child die from? We’ll probably never know. Did they try to treat it? Most likely.
Humans, by nature, form societies. The size varies, but everyone has a role. There was probably some ancestor of Fildes’ doctor in the group who tried to help. Perhaps with prayers in an unknown tongue, or a preparation of certain leaves, or placing the child near a fire. When whatever they tried failed, the same person likely consoled the parents. Maybe they were involved in the burial, too.
The child would be found in 2017, giving us the first clear evidence of a ritual human burial in Africa. Just like today, we let go of our lost ones with ceremony. Perhaps the parents noticed the comet and thought it was their child’s spirit departing.
Now the comet is back. The planet hasn’t changed dramatically in 80,000 years (which isn’t much in geological time), but we have.
Would today’s doctors have been able to save the child? No idea, though we probably have a better chance than our professional ancestor did.
But our job hasn’t changed. Like us, the ancient practitioner probably tried to figure out why the child was sick and what could be done about it. When it was over they, and others, grieved with the parents.
The comet will be back in 80,000 years. On our scale, that’s a long time. The entire recorded history of our species is only 5,000 to 8,000 years. We’ve come a long way, but where we’re going in 80,000 years is anyone’s guess.
Will doctors in the year 82024 even know what we do now to care for people? Will they still be practicing on the third rock from the sun, or spread out across the galaxy? Will there even be doctors? (Probably, in one form or another.)
But We do our best to care, heal, and hope now, as we did then, and as our descendants will.
And, like my daughter and I did, no matter where we are, we will still look up at the sky with wonder.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.