User login
Getting COVID shots in same arm may be more effective, study says
Scientists in Germany looked at health data for 303 people who got the mRNA vaccine and then a booster shot. Their antibody levels were measured two weeks after the second shot. None of the people had had COVID before the vaccinations.
Scientists found that the number of protective “killer T cells” was higher in the 147 study participants who got both shots in the same arm, said the study published in EBioMedicine.
The killer cells were found in 67% of cases in which both shots went into the same arm, compared with 43% of cases with different arms.
“That may suggest that that ipsilateral vaccination (in the same arm) is more likely to provide better protection should the vaccinated person become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Laura Ziegler, a doctoral student at Saarland University, Germany, said in a news release.
William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CBS News that same-arm vaccinations may work better because the cells that provide the immune response are in local lymph nodes.
There’s greater immunological response if the immune cells in the lymph nodes are restimulated in the same place, said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the German study.
The scientists from Saarland University said more research is needed before they can be certain that having vaccinations in the same arm is actually more effective for COVID shots and sequential vaccinations against diseases such as the flu.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists in Germany looked at health data for 303 people who got the mRNA vaccine and then a booster shot. Their antibody levels were measured two weeks after the second shot. None of the people had had COVID before the vaccinations.
Scientists found that the number of protective “killer T cells” was higher in the 147 study participants who got both shots in the same arm, said the study published in EBioMedicine.
The killer cells were found in 67% of cases in which both shots went into the same arm, compared with 43% of cases with different arms.
“That may suggest that that ipsilateral vaccination (in the same arm) is more likely to provide better protection should the vaccinated person become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Laura Ziegler, a doctoral student at Saarland University, Germany, said in a news release.
William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CBS News that same-arm vaccinations may work better because the cells that provide the immune response are in local lymph nodes.
There’s greater immunological response if the immune cells in the lymph nodes are restimulated in the same place, said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the German study.
The scientists from Saarland University said more research is needed before they can be certain that having vaccinations in the same arm is actually more effective for COVID shots and sequential vaccinations against diseases such as the flu.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists in Germany looked at health data for 303 people who got the mRNA vaccine and then a booster shot. Their antibody levels were measured two weeks after the second shot. None of the people had had COVID before the vaccinations.
Scientists found that the number of protective “killer T cells” was higher in the 147 study participants who got both shots in the same arm, said the study published in EBioMedicine.
The killer cells were found in 67% of cases in which both shots went into the same arm, compared with 43% of cases with different arms.
“That may suggest that that ipsilateral vaccination (in the same arm) is more likely to provide better protection should the vaccinated person become infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus,” Laura Ziegler, a doctoral student at Saarland University, Germany, said in a news release.
William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CBS News that same-arm vaccinations may work better because the cells that provide the immune response are in local lymph nodes.
There’s greater immunological response if the immune cells in the lymph nodes are restimulated in the same place, said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the German study.
The scientists from Saarland University said more research is needed before they can be certain that having vaccinations in the same arm is actually more effective for COVID shots and sequential vaccinations against diseases such as the flu.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EBIOMEDICINE
FDA approves first RSV vaccine for pregnancy
The vaccine, known as Abrysvo, can be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy and is designed to protect infants from the virus from birth to 6 months of age.
Administered as a single-dose, intramuscular injection, the FDA approved Abrysvo at the end of May for the prevention of lower respiratory tract illness caused by RSV in people aged 60 years and older.
However, “RSV is a common cause of illness in children, and infants are among those at highest risk for severe disease, which can lead to hospitalization,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, pointed out in a news release. “This approval provides an option for health care providers and pregnant individuals to protect infants from this potentially life-threatening disease.”
Most children are infected with the contagious virus at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, and in clinical trials, the new vaccine reduced that risk by up to 82%.
Before the vaccine became available, up to 3% of infants infected with RSV needed to be hospitalized, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the hospital, treatment typically includes oxygen, intravenous fluids, and mechanical ventilation.
RSV often causes common cold symptoms, but the virus poses the risk of severe complications that can lead to death among young children and older people. The CDC estimates 100-300 deaths of children younger than 5 years and 6,000-10,000 deaths of people aged 65 years and older are linked to RSV annually.
This is also the first year that an antibody shot is available to be given after birth to prevent severe RSV in infants younger than 1 year.
In its approval announcement, the FDA pointed out that preeclampsia occurred in 1.8% of pregnancies after Abrysvo, compared with 1.4% of those who received placebo. The FDA also reported that, in infants, low birth weight and jaundice occurred at a higher rate among the pregnant Abrysvo recipients, compared with the placebo group.
Studies have also shown that pregnant vaccine recipients experienced preterm birth at a rate of 5.7%, compared with a rate of 4.7% among those who received placebo. The FDA called the difference “a numerical imbalance” but said in the approval announcement that a “causal relationship” could not be established.
The FDA also noted that people already at high risk of preterm birth were excluded from clinical trials and that Pfizer must conduct ongoing studies to monitor the risk of preeclampsia as well as preterm birth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vaccine, known as Abrysvo, can be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy and is designed to protect infants from the virus from birth to 6 months of age.
Administered as a single-dose, intramuscular injection, the FDA approved Abrysvo at the end of May for the prevention of lower respiratory tract illness caused by RSV in people aged 60 years and older.
However, “RSV is a common cause of illness in children, and infants are among those at highest risk for severe disease, which can lead to hospitalization,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, pointed out in a news release. “This approval provides an option for health care providers and pregnant individuals to protect infants from this potentially life-threatening disease.”
Most children are infected with the contagious virus at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, and in clinical trials, the new vaccine reduced that risk by up to 82%.
Before the vaccine became available, up to 3% of infants infected with RSV needed to be hospitalized, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the hospital, treatment typically includes oxygen, intravenous fluids, and mechanical ventilation.
RSV often causes common cold symptoms, but the virus poses the risk of severe complications that can lead to death among young children and older people. The CDC estimates 100-300 deaths of children younger than 5 years and 6,000-10,000 deaths of people aged 65 years and older are linked to RSV annually.
This is also the first year that an antibody shot is available to be given after birth to prevent severe RSV in infants younger than 1 year.
In its approval announcement, the FDA pointed out that preeclampsia occurred in 1.8% of pregnancies after Abrysvo, compared with 1.4% of those who received placebo. The FDA also reported that, in infants, low birth weight and jaundice occurred at a higher rate among the pregnant Abrysvo recipients, compared with the placebo group.
Studies have also shown that pregnant vaccine recipients experienced preterm birth at a rate of 5.7%, compared with a rate of 4.7% among those who received placebo. The FDA called the difference “a numerical imbalance” but said in the approval announcement that a “causal relationship” could not be established.
The FDA also noted that people already at high risk of preterm birth were excluded from clinical trials and that Pfizer must conduct ongoing studies to monitor the risk of preeclampsia as well as preterm birth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The vaccine, known as Abrysvo, can be given between weeks 32 and 36 of pregnancy and is designed to protect infants from the virus from birth to 6 months of age.
Administered as a single-dose, intramuscular injection, the FDA approved Abrysvo at the end of May for the prevention of lower respiratory tract illness caused by RSV in people aged 60 years and older.
However, “RSV is a common cause of illness in children, and infants are among those at highest risk for severe disease, which can lead to hospitalization,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, pointed out in a news release. “This approval provides an option for health care providers and pregnant individuals to protect infants from this potentially life-threatening disease.”
Most children are infected with the contagious virus at least once by the time they reach age 2 years. Very young children are at particular risk of severe complications, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, and in clinical trials, the new vaccine reduced that risk by up to 82%.
Before the vaccine became available, up to 3% of infants infected with RSV needed to be hospitalized, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In the hospital, treatment typically includes oxygen, intravenous fluids, and mechanical ventilation.
RSV often causes common cold symptoms, but the virus poses the risk of severe complications that can lead to death among young children and older people. The CDC estimates 100-300 deaths of children younger than 5 years and 6,000-10,000 deaths of people aged 65 years and older are linked to RSV annually.
This is also the first year that an antibody shot is available to be given after birth to prevent severe RSV in infants younger than 1 year.
In its approval announcement, the FDA pointed out that preeclampsia occurred in 1.8% of pregnancies after Abrysvo, compared with 1.4% of those who received placebo. The FDA also reported that, in infants, low birth weight and jaundice occurred at a higher rate among the pregnant Abrysvo recipients, compared with the placebo group.
Studies have also shown that pregnant vaccine recipients experienced preterm birth at a rate of 5.7%, compared with a rate of 4.7% among those who received placebo. The FDA called the difference “a numerical imbalance” but said in the approval announcement that a “causal relationship” could not be established.
The FDA also noted that people already at high risk of preterm birth were excluded from clinical trials and that Pfizer must conduct ongoing studies to monitor the risk of preeclampsia as well as preterm birth.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evaluating Pharmacists’ Time Collecting Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Data
The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients on intensive insulin regimens self-monitor blood glucose (SMBG) to assist in therapy optimization.1 To be useful, SMBG data must be captured by patients, shared with care teams, and used and interpreted by patients and practitioners.2,3 Communication of SMBG data from the patient to practitioner can be challenging. Although technology can help in this process, limitations exist, such as manual data entry into systems, patient and/or practitioner technological challenges (eg, accessing interface), and compatibility and integration between SMBG devices and electronic health record (EHR) systems.4
The Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center (BVAMC) in Idaho serves more than 100,000 veterans. It includes a main site, community-based outpatient clinics, and a clinical resource hub that provides telehealth services to veterans residing in rural neighboring states. The BVAMC pharmacy department provides both inpatient and outpatient services. At the BVAMC, clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) are independent practitioners who support their care teams in comprehensive medication management and have the ability to initiate, modify, and discontinue drug therapy for referred patients.5 A prominent role of CPPs in primary care teams is to manage patients with uncontrolled diabetes and intensive insulin regimens, in which SMBG data are vital to therapy optimization. As collecting SMBG data from patients is seen anecdotally as time intensive, we determined the mean time spent by CPPs collecting patient SMBG data and its potential implications.
Methods
Pharmacists at BVAMC were asked to estimate and record the following: SMBG data collection method, time spent collecting data, extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings, total patient visit time, and visit type. Time was collected in minutes. Extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings included any additional time formatting or entering data in the clinical note after talking to the patient; if this was done while multitasking and talking to the patient, it was not considered extra time. For total patient visit time, pharmacists were asked to estimate only time spent discussing diabetes care and collecting SMBG data. Visit types were categorized as in-person/face-to-face, telephone, and telehealth using clinical video telehealth (CVT)/VA Video Connect (VVC). Data were collected using a standardized spreadsheet. The spreadsheet was pilot tested by a CPP before distribution to all pharmacists.
CPPs were educated about the project in March 2021 and were asked to record data for a 1-week period between April 5, 2021, and April 30, 2021. One CPP also provided delayed data collected from May 17 to 21, 2021, and these data were included in our analysis.
Descriptive statistics were used to determine the mean time spent by CPPs collecting SMBG data. Unpaired t tests were used to compare time spent collecting SMBG data by different collection methods and patient visit types. A P value of ≤ .05 was considered statistically significant. Data were organized in Microsoft Excel, and statistics were completed with JMP Pro v15.
Results
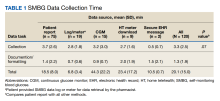
Eight CPPs provided data from 120 patient encounters. For all pa
When compared by the SMBG collection method, the longest time spent collecting SMBG data was with patient report (3.7 minutes), and the longest time spent documenting/formatting time was with meter download/home telehealth (2 minutes). There was no statistically significant difference in the time to collect SMBG data between patient report and other methods (3.7 minutes vs 2.8 minutes; P = .07).
When compared by visit type, there was not a statistically significant difference between time spent collecting SMBG data (3.8 minutes vs 3.2 minutes; P = .39) (Table 2).
Discussion
We found that the mean amount of time spent collecting and documenting/formatting SMBG data was only 4.6 minutes; however, this still represented a substantial portion of visit time. For telephone and CVT/VVC appointments, this represented > 25% of total visit time. While CPPs make important contributions to interprofessional team management of patients with diabetes, their cost is not trivial.6-8 It is worth exploring the most effective and efficient ways to use CPPs. Our results indicate that streamlining SMBG data collection may be beneficial.
Pharmacy technicians, licensed practical nurses/clinical associates, registered nurses/nurse care managers, or other team members could help improve SMBG data collection. Using other team members is also an opportunity for comanagement, for team collaboration, and for more patients to be seen. For example, if a CPP currently has 12 patient encounters that last 20 minutes each, this results in about 240 minutes of direct patient care. If patient encounters were 16 minutes, CPPS could have 15 patient encounters in 240 minutes. Saved time could be used for other clinical tasks involved in disease management or clinical reminder reviews. While there are benefits to CPPs collecting SMBG data, such as further inquiry about patient-reported values, other team members could also be trained to ask appropriate follow-up questions for abnormal blood glucose readings. In addition, leveraging current team members and optimizing their roles could prevent the need to acquire additional full-time equivalent employees.
Another opportunity to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection is with SMBG devices and EHR integration.4,9 However, integration can be difficult with different types of SMBG devices and EHR platforms. Education for patients and practitioners could help to ensure accurate and reliable data uploads; patient internet availability; data protection, privacy, and sharing; workflow management; and clear patient-practitioner expectations.10 For example, if patient SMBG data are automatically uploaded to practitioners, patients’ expectations for practitioner review of data and follow-up need to be determined.
We found a subset of patient encounters (n = 23) where data collection and documenting/formatting represented more than half of the total visit time. In this subset, 13 SMBG reports were pulled from a log or meter, 8 were patient reported, and 3 were meter download or home telehealth.
Limitations
A potential reason for the lack of statistically significant differences in SMBG collection method or visit type in this study includes the small sample size. Participation in this work was voluntary, and all participating CPPs had ≥ 3 years of practice in their current setting, which includes a heavy workload of diabetes management. These pharmacists noted self-established procedures/systems for SMBG data collection, including the use of Excel spreadsheets with pregenerated formulas. For less experienced CPPs, SMBG data collection time may be even longer. Pharmacists also noted that they may limit time spent collecting SMBG data depending on the patient encounter and whether they have gathered sufficient data to guide clinical care. Other limitations of this work include data collection from a single institution and that the time documented represented estimates; there was no external monitor.
Conclusions
In this analysis, we found that CPPs spend about 3 minutes collecting SMBG data from patients, and about an additional 1 minute documenting and formatting data. While 4 to 5 minutes may not represent a substantial amount of time for one patient, it can be when multiplied by several patient encounters. The time spent collecting SMBG data did not significantly differ by collection method or visit type. Opportunities to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection, such as the use of nonpharmacist team members are worth exploring.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the pharmacists at the Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center for their time and support of this work: Danielle Ahlstrom, Paul Black, Robyn Cruz, Sarah Naidoo, Anthony Nelson, Laura Spoutz, Eileen Twomey, Donovan Victorine, and Michelle Wilkin.
1. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(suppl 1):S85-S99. doi:10.2337/dc21-S007
2. Austin MM. The two skill sets of self-monitoring of blood glucose education: the operational and the interpretive. Diabetes Spectr. 2013;26(2):83-90. doi:10.2337/diaspect.26.2.83
3. Gallichan M. Self monitoring of glucose by people with diabetes: evidence based practice. BMJ. 1997;314(7085):964-967. doi:10.1136/bmj.314.7085.964
4. Lewinski AA, Drake C, Shaw RJ, et al. Bridging the integration gap between patient-generated blood glucose data and electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(7):667-672. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz039
5. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Jorgenson T, et al. Role of the US Veterans Health Administration clinical pharmacy specialist provider: shaping the future of comprehensive medication management. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2020;73(2):152-158. doi:10.4212/cjhp.v73i2.2982
6. Schmidt K, Caudill J. Hamilton T. Impact of clinical pharmacy specialists on glycemic control in veterans with type 2 diabetes. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(suppl 1):S9-S14. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy015
7. Sullivan J, Jett BP, Cradick M, Zuber J. Effect of clinical pharmacist intervention on hemoglobin A1c reduction in veteran patients with type 2 diabetes in a rural setting. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(12):1023-1027. doi:10.1177/1060028016663564
8. Bloom CI, Ku M, Williams M. Clinical pharmacy specialists’ impact in patient aligned care teams for type 2 diabetes management. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(5):717-721. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.05.002
9. Kumar RB, Goren ND, Stark DE, Wall DP, Longhurst CA. Automated integration of continuous glucose monitor data in the electronic health record using consumer technology. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2016;23(3):532-537. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocv206
10. Reading MJ, Merrill JA. Converging and diverging needs between patients and providers who are collecting and using patient-generated health data: an integrative review. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018;25(6):759-771. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy006
The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients on intensive insulin regimens self-monitor blood glucose (SMBG) to assist in therapy optimization.1 To be useful, SMBG data must be captured by patients, shared with care teams, and used and interpreted by patients and practitioners.2,3 Communication of SMBG data from the patient to practitioner can be challenging. Although technology can help in this process, limitations exist, such as manual data entry into systems, patient and/or practitioner technological challenges (eg, accessing interface), and compatibility and integration between SMBG devices and electronic health record (EHR) systems.4
The Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center (BVAMC) in Idaho serves more than 100,000 veterans. It includes a main site, community-based outpatient clinics, and a clinical resource hub that provides telehealth services to veterans residing in rural neighboring states. The BVAMC pharmacy department provides both inpatient and outpatient services. At the BVAMC, clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) are independent practitioners who support their care teams in comprehensive medication management and have the ability to initiate, modify, and discontinue drug therapy for referred patients.5 A prominent role of CPPs in primary care teams is to manage patients with uncontrolled diabetes and intensive insulin regimens, in which SMBG data are vital to therapy optimization. As collecting SMBG data from patients is seen anecdotally as time intensive, we determined the mean time spent by CPPs collecting patient SMBG data and its potential implications.
Methods
Pharmacists at BVAMC were asked to estimate and record the following: SMBG data collection method, time spent collecting data, extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings, total patient visit time, and visit type. Time was collected in minutes. Extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings included any additional time formatting or entering data in the clinical note after talking to the patient; if this was done while multitasking and talking to the patient, it was not considered extra time. For total patient visit time, pharmacists were asked to estimate only time spent discussing diabetes care and collecting SMBG data. Visit types were categorized as in-person/face-to-face, telephone, and telehealth using clinical video telehealth (CVT)/VA Video Connect (VVC). Data were collected using a standardized spreadsheet. The spreadsheet was pilot tested by a CPP before distribution to all pharmacists.
CPPs were educated about the project in March 2021 and were asked to record data for a 1-week period between April 5, 2021, and April 30, 2021. One CPP also provided delayed data collected from May 17 to 21, 2021, and these data were included in our analysis.
Descriptive statistics were used to determine the mean time spent by CPPs collecting SMBG data. Unpaired t tests were used to compare time spent collecting SMBG data by different collection methods and patient visit types. A P value of ≤ .05 was considered statistically significant. Data were organized in Microsoft Excel, and statistics were completed with JMP Pro v15.
Results
Eight CPPs provided data from 120 patient encounters. For all pa
When compared by the SMBG collection method, the longest time spent collecting SMBG data was with patient report (3.7 minutes), and the longest time spent documenting/formatting time was with meter download/home telehealth (2 minutes). There was no statistically significant difference in the time to collect SMBG data between patient report and other methods (3.7 minutes vs 2.8 minutes; P = .07).
When compared by visit type, there was not a statistically significant difference between time spent collecting SMBG data (3.8 minutes vs 3.2 minutes; P = .39) (Table 2).
Discussion
We found that the mean amount of time spent collecting and documenting/formatting SMBG data was only 4.6 minutes; however, this still represented a substantial portion of visit time. For telephone and CVT/VVC appointments, this represented > 25% of total visit time. While CPPs make important contributions to interprofessional team management of patients with diabetes, their cost is not trivial.6-8 It is worth exploring the most effective and efficient ways to use CPPs. Our results indicate that streamlining SMBG data collection may be beneficial.
Pharmacy technicians, licensed practical nurses/clinical associates, registered nurses/nurse care managers, or other team members could help improve SMBG data collection. Using other team members is also an opportunity for comanagement, for team collaboration, and for more patients to be seen. For example, if a CPP currently has 12 patient encounters that last 20 minutes each, this results in about 240 minutes of direct patient care. If patient encounters were 16 minutes, CPPS could have 15 patient encounters in 240 minutes. Saved time could be used for other clinical tasks involved in disease management or clinical reminder reviews. While there are benefits to CPPs collecting SMBG data, such as further inquiry about patient-reported values, other team members could also be trained to ask appropriate follow-up questions for abnormal blood glucose readings. In addition, leveraging current team members and optimizing their roles could prevent the need to acquire additional full-time equivalent employees.
Another opportunity to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection is with SMBG devices and EHR integration.4,9 However, integration can be difficult with different types of SMBG devices and EHR platforms. Education for patients and practitioners could help to ensure accurate and reliable data uploads; patient internet availability; data protection, privacy, and sharing; workflow management; and clear patient-practitioner expectations.10 For example, if patient SMBG data are automatically uploaded to practitioners, patients’ expectations for practitioner review of data and follow-up need to be determined.
We found a subset of patient encounters (n = 23) where data collection and documenting/formatting represented more than half of the total visit time. In this subset, 13 SMBG reports were pulled from a log or meter, 8 were patient reported, and 3 were meter download or home telehealth.
Limitations
A potential reason for the lack of statistically significant differences in SMBG collection method or visit type in this study includes the small sample size. Participation in this work was voluntary, and all participating CPPs had ≥ 3 years of practice in their current setting, which includes a heavy workload of diabetes management. These pharmacists noted self-established procedures/systems for SMBG data collection, including the use of Excel spreadsheets with pregenerated formulas. For less experienced CPPs, SMBG data collection time may be even longer. Pharmacists also noted that they may limit time spent collecting SMBG data depending on the patient encounter and whether they have gathered sufficient data to guide clinical care. Other limitations of this work include data collection from a single institution and that the time documented represented estimates; there was no external monitor.
Conclusions
In this analysis, we found that CPPs spend about 3 minutes collecting SMBG data from patients, and about an additional 1 minute documenting and formatting data. While 4 to 5 minutes may not represent a substantial amount of time for one patient, it can be when multiplied by several patient encounters. The time spent collecting SMBG data did not significantly differ by collection method or visit type. Opportunities to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection, such as the use of nonpharmacist team members are worth exploring.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the pharmacists at the Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center for their time and support of this work: Danielle Ahlstrom, Paul Black, Robyn Cruz, Sarah Naidoo, Anthony Nelson, Laura Spoutz, Eileen Twomey, Donovan Victorine, and Michelle Wilkin.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that patients on intensive insulin regimens self-monitor blood glucose (SMBG) to assist in therapy optimization.1 To be useful, SMBG data must be captured by patients, shared with care teams, and used and interpreted by patients and practitioners.2,3 Communication of SMBG data from the patient to practitioner can be challenging. Although technology can help in this process, limitations exist, such as manual data entry into systems, patient and/or practitioner technological challenges (eg, accessing interface), and compatibility and integration between SMBG devices and electronic health record (EHR) systems.4
The Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center (BVAMC) in Idaho serves more than 100,000 veterans. It includes a main site, community-based outpatient clinics, and a clinical resource hub that provides telehealth services to veterans residing in rural neighboring states. The BVAMC pharmacy department provides both inpatient and outpatient services. At the BVAMC, clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) are independent practitioners who support their care teams in comprehensive medication management and have the ability to initiate, modify, and discontinue drug therapy for referred patients.5 A prominent role of CPPs in primary care teams is to manage patients with uncontrolled diabetes and intensive insulin regimens, in which SMBG data are vital to therapy optimization. As collecting SMBG data from patients is seen anecdotally as time intensive, we determined the mean time spent by CPPs collecting patient SMBG data and its potential implications.
Methods
Pharmacists at BVAMC were asked to estimate and record the following: SMBG data collection method, time spent collecting data, extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings, total patient visit time, and visit type. Time was collected in minutes. Extra time spent documenting or formatting SMBG readings included any additional time formatting or entering data in the clinical note after talking to the patient; if this was done while multitasking and talking to the patient, it was not considered extra time. For total patient visit time, pharmacists were asked to estimate only time spent discussing diabetes care and collecting SMBG data. Visit types were categorized as in-person/face-to-face, telephone, and telehealth using clinical video telehealth (CVT)/VA Video Connect (VVC). Data were collected using a standardized spreadsheet. The spreadsheet was pilot tested by a CPP before distribution to all pharmacists.
CPPs were educated about the project in March 2021 and were asked to record data for a 1-week period between April 5, 2021, and April 30, 2021. One CPP also provided delayed data collected from May 17 to 21, 2021, and these data were included in our analysis.
Descriptive statistics were used to determine the mean time spent by CPPs collecting SMBG data. Unpaired t tests were used to compare time spent collecting SMBG data by different collection methods and patient visit types. A P value of ≤ .05 was considered statistically significant. Data were organized in Microsoft Excel, and statistics were completed with JMP Pro v15.
Results
Eight CPPs provided data from 120 patient encounters. For all pa
When compared by the SMBG collection method, the longest time spent collecting SMBG data was with patient report (3.7 minutes), and the longest time spent documenting/formatting time was with meter download/home telehealth (2 minutes). There was no statistically significant difference in the time to collect SMBG data between patient report and other methods (3.7 minutes vs 2.8 minutes; P = .07).
When compared by visit type, there was not a statistically significant difference between time spent collecting SMBG data (3.8 minutes vs 3.2 minutes; P = .39) (Table 2).
Discussion
We found that the mean amount of time spent collecting and documenting/formatting SMBG data was only 4.6 minutes; however, this still represented a substantial portion of visit time. For telephone and CVT/VVC appointments, this represented > 25% of total visit time. While CPPs make important contributions to interprofessional team management of patients with diabetes, their cost is not trivial.6-8 It is worth exploring the most effective and efficient ways to use CPPs. Our results indicate that streamlining SMBG data collection may be beneficial.
Pharmacy technicians, licensed practical nurses/clinical associates, registered nurses/nurse care managers, or other team members could help improve SMBG data collection. Using other team members is also an opportunity for comanagement, for team collaboration, and for more patients to be seen. For example, if a CPP currently has 12 patient encounters that last 20 minutes each, this results in about 240 minutes of direct patient care. If patient encounters were 16 minutes, CPPS could have 15 patient encounters in 240 minutes. Saved time could be used for other clinical tasks involved in disease management or clinical reminder reviews. While there are benefits to CPPs collecting SMBG data, such as further inquiry about patient-reported values, other team members could also be trained to ask appropriate follow-up questions for abnormal blood glucose readings. In addition, leveraging current team members and optimizing their roles could prevent the need to acquire additional full-time equivalent employees.
Another opportunity to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection is with SMBG devices and EHR integration.4,9 However, integration can be difficult with different types of SMBG devices and EHR platforms. Education for patients and practitioners could help to ensure accurate and reliable data uploads; patient internet availability; data protection, privacy, and sharing; workflow management; and clear patient-practitioner expectations.10 For example, if patient SMBG data are automatically uploaded to practitioners, patients’ expectations for practitioner review of data and follow-up need to be determined.
We found a subset of patient encounters (n = 23) where data collection and documenting/formatting represented more than half of the total visit time. In this subset, 13 SMBG reports were pulled from a log or meter, 8 were patient reported, and 3 were meter download or home telehealth.
Limitations
A potential reason for the lack of statistically significant differences in SMBG collection method or visit type in this study includes the small sample size. Participation in this work was voluntary, and all participating CPPs had ≥ 3 years of practice in their current setting, which includes a heavy workload of diabetes management. These pharmacists noted self-established procedures/systems for SMBG data collection, including the use of Excel spreadsheets with pregenerated formulas. For less experienced CPPs, SMBG data collection time may be even longer. Pharmacists also noted that they may limit time spent collecting SMBG data depending on the patient encounter and whether they have gathered sufficient data to guide clinical care. Other limitations of this work include data collection from a single institution and that the time documented represented estimates; there was no external monitor.
Conclusions
In this analysis, we found that CPPs spend about 3 minutes collecting SMBG data from patients, and about an additional 1 minute documenting and formatting data. While 4 to 5 minutes may not represent a substantial amount of time for one patient, it can be when multiplied by several patient encounters. The time spent collecting SMBG data did not significantly differ by collection method or visit type. Opportunities to increase efficiency in SMBG data collection, such as the use of nonpharmacist team members are worth exploring.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the pharmacists at the Boise Veterans Affairs Medical Center for their time and support of this work: Danielle Ahlstrom, Paul Black, Robyn Cruz, Sarah Naidoo, Anthony Nelson, Laura Spoutz, Eileen Twomey, Donovan Victorine, and Michelle Wilkin.
1. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(suppl 1):S85-S99. doi:10.2337/dc21-S007
2. Austin MM. The two skill sets of self-monitoring of blood glucose education: the operational and the interpretive. Diabetes Spectr. 2013;26(2):83-90. doi:10.2337/diaspect.26.2.83
3. Gallichan M. Self monitoring of glucose by people with diabetes: evidence based practice. BMJ. 1997;314(7085):964-967. doi:10.1136/bmj.314.7085.964
4. Lewinski AA, Drake C, Shaw RJ, et al. Bridging the integration gap between patient-generated blood glucose data and electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(7):667-672. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz039
5. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Jorgenson T, et al. Role of the US Veterans Health Administration clinical pharmacy specialist provider: shaping the future of comprehensive medication management. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2020;73(2):152-158. doi:10.4212/cjhp.v73i2.2982
6. Schmidt K, Caudill J. Hamilton T. Impact of clinical pharmacy specialists on glycemic control in veterans with type 2 diabetes. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(suppl 1):S9-S14. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy015
7. Sullivan J, Jett BP, Cradick M, Zuber J. Effect of clinical pharmacist intervention on hemoglobin A1c reduction in veteran patients with type 2 diabetes in a rural setting. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(12):1023-1027. doi:10.1177/1060028016663564
8. Bloom CI, Ku M, Williams M. Clinical pharmacy specialists’ impact in patient aligned care teams for type 2 diabetes management. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(5):717-721. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.05.002
9. Kumar RB, Goren ND, Stark DE, Wall DP, Longhurst CA. Automated integration of continuous glucose monitor data in the electronic health record using consumer technology. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2016;23(3):532-537. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocv206
10. Reading MJ, Merrill JA. Converging and diverging needs between patients and providers who are collecting and using patient-generated health data: an integrative review. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018;25(6):759-771. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy006
1. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44(suppl 1):S85-S99. doi:10.2337/dc21-S007
2. Austin MM. The two skill sets of self-monitoring of blood glucose education: the operational and the interpretive. Diabetes Spectr. 2013;26(2):83-90. doi:10.2337/diaspect.26.2.83
3. Gallichan M. Self monitoring of glucose by people with diabetes: evidence based practice. BMJ. 1997;314(7085):964-967. doi:10.1136/bmj.314.7085.964
4. Lewinski AA, Drake C, Shaw RJ, et al. Bridging the integration gap between patient-generated blood glucose data and electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019;26(7):667-672. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocz039
5. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Jorgenson T, et al. Role of the US Veterans Health Administration clinical pharmacy specialist provider: shaping the future of comprehensive medication management. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2020;73(2):152-158. doi:10.4212/cjhp.v73i2.2982
6. Schmidt K, Caudill J. Hamilton T. Impact of clinical pharmacy specialists on glycemic control in veterans with type 2 diabetes. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(suppl 1):S9-S14. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy015
7. Sullivan J, Jett BP, Cradick M, Zuber J. Effect of clinical pharmacist intervention on hemoglobin A1c reduction in veteran patients with type 2 diabetes in a rural setting. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(12):1023-1027. doi:10.1177/1060028016663564
8. Bloom CI, Ku M, Williams M. Clinical pharmacy specialists’ impact in patient aligned care teams for type 2 diabetes management. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(5):717-721. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2019.05.002
9. Kumar RB, Goren ND, Stark DE, Wall DP, Longhurst CA. Automated integration of continuous glucose monitor data in the electronic health record using consumer technology. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2016;23(3):532-537. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocv206
10. Reading MJ, Merrill JA. Converging and diverging needs between patients and providers who are collecting and using patient-generated health data: an integrative review. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018;25(6):759-771. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocy006
Dementia diagnosis a good time to reduce polypharmacy
Physicians may be missing opportunities to reduce harmful polypharmacy in elderly patients with newly diagnosed dementia, investigators for a large study of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
They found that those with an incident dementia diagnosis were somewhat more likely to initiate central nervous system–active medications and slightly more likely to discontinue cardiometabolic and anticholinergic medications, compared with controls.
According to the authors, time of diagnosis can be a potential inflexion point for deprescribing long-term medications with high safety risks, limited likelihood of benefit, or possible association with impaired cognition.
“Understanding the chronology of medication changes following a first dementia diagnosis may identify targets for deprescribing interventions to reduce preventable medication-related harms, said Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, of the division of general medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our results provide a baseline to inform efforts to rethink the clinical approach to medication use at the time of a new dementia diagnosis.”
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are diagnosed annually with Alzheimer’s and related dementias, the authors pointed out, and the majority have multiple other chronic conditions. Worsening cognitive impairment may alter the risk-benefit balance of medications taken for these conditions.
Matched cohort study
The sample consisted of adults 67 years or older enrolled in traditional Medicare and Medicare Part D. Patients with an initial incident dementia diagnosis between January 2012 and December 2018 were matched with controls (as of last doctor’s office visit) based on demographics, geographic location, and baseline medication count. Data were analyzed from 2021 to June 2023.
The study included 266,675 adults with incident dementia and 266,675 controls. In both groups, 65.1% were 80 years or older (mean age, 82.2) and 67.8% were female. At baseline, patients with incident dementia were more likely than controls to use CNS-active medications (54.32% vs. 48.39%) and anticholinergic medications (17.79% vs. 15.96%) and less likely to use most cardiometabolic medications (for example, antidiabetics, 31.19% vs. 36.45%).
Immediately following the index diagnosis, the dementia cohort had greater increases in the mean number of medications used: 0.41 vs. –0.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.27-0.66) and in the proportion using CNS-active medications (absolute change, 3.44% vs. 0.79%; 95% CI, 0.85%-4.45%). The rise was because of an increased use of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics.
The affected cohort showed a modestly greater decline in anticholinergic medications: quarterly change in use: −0.53% vs. −0.21% (95% CI, −0.55% to −0.08%); and in most cardiometabolic medications: for example, quarterly change in antihypertensive use: –0.84% vs. –0.40% (95% CI, –0.64% to –0.25%). Still, a year post diagnosis, 75.2% of dementia patients were using five or more medications, for a 2.8% increase.
The drug classes with the steepest rate of discontinuation – such as lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications – had low risks for adverse drug events, while higher-risk classes – such as insulins and antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents – had smaller or no reductions in use.
While the findings point to opportunities to reduce polypharmacy by deprescribing long-term medications of dubious benefit, interventions to reduce polypharmacy and inappropriate medications have been modestly successful for patients without dementia, the authors said. But the recent OPTIMIZE trial, an educational effort aimed at primary care clinicians and patients with cognitive impairment, reduced neither polypharmacy nor potentially inappropriate medications.
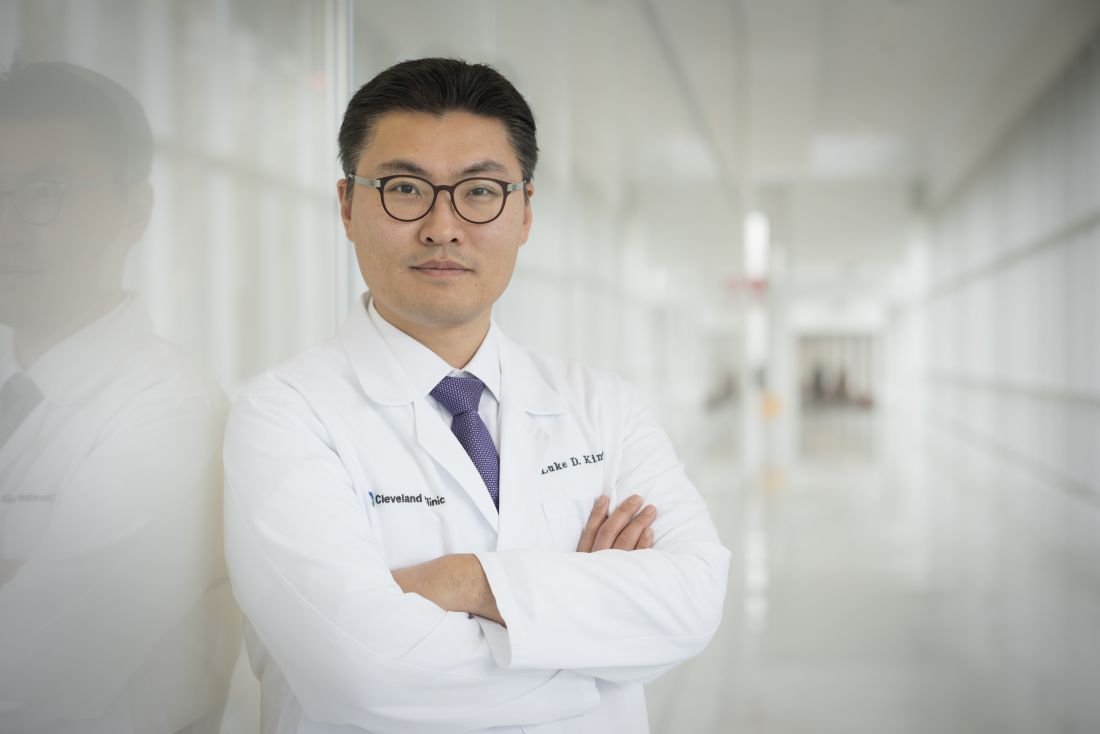
Luke D. Kim, MD, a geriatrician at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, agreed that seniors with dementia can benefit from reassessment of their pharmacologic therapies. “Older adults in general are more prone to have side effects from medications as their renal and hepatic clearance and metabolism are different and lower than those of younger individuals. But they tend to take multiple medications owing to more comorbidities,” said Dr. Kim, who was not involved in the study. “While all older adults need to be more careful about medication management, those with dementia need an even more careful approach as they have diminished cognitive reserve and risk more potential harm from medications.”
The authors noted that since decision-making models aligned with patient priorities for older adults without dementia led to reductions in overall medication use, that may be a path forward in populations with dementia.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health. The authors had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Kim disclosed no competing interests relevant to his comments.
Physicians may be missing opportunities to reduce harmful polypharmacy in elderly patients with newly diagnosed dementia, investigators for a large study of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
They found that those with an incident dementia diagnosis were somewhat more likely to initiate central nervous system–active medications and slightly more likely to discontinue cardiometabolic and anticholinergic medications, compared with controls.
According to the authors, time of diagnosis can be a potential inflexion point for deprescribing long-term medications with high safety risks, limited likelihood of benefit, or possible association with impaired cognition.
“Understanding the chronology of medication changes following a first dementia diagnosis may identify targets for deprescribing interventions to reduce preventable medication-related harms, said Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, of the division of general medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our results provide a baseline to inform efforts to rethink the clinical approach to medication use at the time of a new dementia diagnosis.”
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are diagnosed annually with Alzheimer’s and related dementias, the authors pointed out, and the majority have multiple other chronic conditions. Worsening cognitive impairment may alter the risk-benefit balance of medications taken for these conditions.
Matched cohort study
The sample consisted of adults 67 years or older enrolled in traditional Medicare and Medicare Part D. Patients with an initial incident dementia diagnosis between January 2012 and December 2018 were matched with controls (as of last doctor’s office visit) based on demographics, geographic location, and baseline medication count. Data were analyzed from 2021 to June 2023.
The study included 266,675 adults with incident dementia and 266,675 controls. In both groups, 65.1% were 80 years or older (mean age, 82.2) and 67.8% were female. At baseline, patients with incident dementia were more likely than controls to use CNS-active medications (54.32% vs. 48.39%) and anticholinergic medications (17.79% vs. 15.96%) and less likely to use most cardiometabolic medications (for example, antidiabetics, 31.19% vs. 36.45%).
Immediately following the index diagnosis, the dementia cohort had greater increases in the mean number of medications used: 0.41 vs. –0.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.27-0.66) and in the proportion using CNS-active medications (absolute change, 3.44% vs. 0.79%; 95% CI, 0.85%-4.45%). The rise was because of an increased use of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics.
The affected cohort showed a modestly greater decline in anticholinergic medications: quarterly change in use: −0.53% vs. −0.21% (95% CI, −0.55% to −0.08%); and in most cardiometabolic medications: for example, quarterly change in antihypertensive use: –0.84% vs. –0.40% (95% CI, –0.64% to –0.25%). Still, a year post diagnosis, 75.2% of dementia patients were using five or more medications, for a 2.8% increase.
The drug classes with the steepest rate of discontinuation – such as lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications – had low risks for adverse drug events, while higher-risk classes – such as insulins and antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents – had smaller or no reductions in use.
While the findings point to opportunities to reduce polypharmacy by deprescribing long-term medications of dubious benefit, interventions to reduce polypharmacy and inappropriate medications have been modestly successful for patients without dementia, the authors said. But the recent OPTIMIZE trial, an educational effort aimed at primary care clinicians and patients with cognitive impairment, reduced neither polypharmacy nor potentially inappropriate medications.
Luke D. Kim, MD, a geriatrician at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, agreed that seniors with dementia can benefit from reassessment of their pharmacologic therapies. “Older adults in general are more prone to have side effects from medications as their renal and hepatic clearance and metabolism are different and lower than those of younger individuals. But they tend to take multiple medications owing to more comorbidities,” said Dr. Kim, who was not involved in the study. “While all older adults need to be more careful about medication management, those with dementia need an even more careful approach as they have diminished cognitive reserve and risk more potential harm from medications.”
The authors noted that since decision-making models aligned with patient priorities for older adults without dementia led to reductions in overall medication use, that may be a path forward in populations with dementia.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health. The authors had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Kim disclosed no competing interests relevant to his comments.
Physicians may be missing opportunities to reduce harmful polypharmacy in elderly patients with newly diagnosed dementia, investigators for a large study of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
They found that those with an incident dementia diagnosis were somewhat more likely to initiate central nervous system–active medications and slightly more likely to discontinue cardiometabolic and anticholinergic medications, compared with controls.
According to the authors, time of diagnosis can be a potential inflexion point for deprescribing long-term medications with high safety risks, limited likelihood of benefit, or possible association with impaired cognition.
“Understanding the chronology of medication changes following a first dementia diagnosis may identify targets for deprescribing interventions to reduce preventable medication-related harms, said Timothy S. Anderson, MD, MAS, of the division of general medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and colleagues in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Our results provide a baseline to inform efforts to rethink the clinical approach to medication use at the time of a new dementia diagnosis.”
Hundreds of thousands of Americans are diagnosed annually with Alzheimer’s and related dementias, the authors pointed out, and the majority have multiple other chronic conditions. Worsening cognitive impairment may alter the risk-benefit balance of medications taken for these conditions.
Matched cohort study
The sample consisted of adults 67 years or older enrolled in traditional Medicare and Medicare Part D. Patients with an initial incident dementia diagnosis between January 2012 and December 2018 were matched with controls (as of last doctor’s office visit) based on demographics, geographic location, and baseline medication count. Data were analyzed from 2021 to June 2023.
The study included 266,675 adults with incident dementia and 266,675 controls. In both groups, 65.1% were 80 years or older (mean age, 82.2) and 67.8% were female. At baseline, patients with incident dementia were more likely than controls to use CNS-active medications (54.32% vs. 48.39%) and anticholinergic medications (17.79% vs. 15.96%) and less likely to use most cardiometabolic medications (for example, antidiabetics, 31.19% vs. 36.45%).
Immediately following the index diagnosis, the dementia cohort had greater increases in the mean number of medications used: 0.41 vs. –0.06 (95% confidence interval, 0.27-0.66) and in the proportion using CNS-active medications (absolute change, 3.44% vs. 0.79%; 95% CI, 0.85%-4.45%). The rise was because of an increased use of antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antiepileptics.
The affected cohort showed a modestly greater decline in anticholinergic medications: quarterly change in use: −0.53% vs. −0.21% (95% CI, −0.55% to −0.08%); and in most cardiometabolic medications: for example, quarterly change in antihypertensive use: –0.84% vs. –0.40% (95% CI, –0.64% to –0.25%). Still, a year post diagnosis, 75.2% of dementia patients were using five or more medications, for a 2.8% increase.
The drug classes with the steepest rate of discontinuation – such as lipid-lowering and antihypertensive medications – had low risks for adverse drug events, while higher-risk classes – such as insulins and antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents – had smaller or no reductions in use.
While the findings point to opportunities to reduce polypharmacy by deprescribing long-term medications of dubious benefit, interventions to reduce polypharmacy and inappropriate medications have been modestly successful for patients without dementia, the authors said. But the recent OPTIMIZE trial, an educational effort aimed at primary care clinicians and patients with cognitive impairment, reduced neither polypharmacy nor potentially inappropriate medications.
Luke D. Kim, MD, a geriatrician at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, agreed that seniors with dementia can benefit from reassessment of their pharmacologic therapies. “Older adults in general are more prone to have side effects from medications as their renal and hepatic clearance and metabolism are different and lower than those of younger individuals. But they tend to take multiple medications owing to more comorbidities,” said Dr. Kim, who was not involved in the study. “While all older adults need to be more careful about medication management, those with dementia need an even more careful approach as they have diminished cognitive reserve and risk more potential harm from medications.”
The authors noted that since decision-making models aligned with patient priorities for older adults without dementia led to reductions in overall medication use, that may be a path forward in populations with dementia.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health. The authors had no competing interests to disclose. Dr. Kim disclosed no competing interests relevant to his comments.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Low-dose oral minoxidil for female pattern hair loss: Benefits, impact on BP, heart rate evaluated
results from a small retrospective analysis showed.
“Additionally, few patients experienced hair loss progression while slightly over a third experienced hair regrowth,” the study’s first author, Reese Imhof, MD, a third-year resident in the department of dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. The results were published online in JAAD International.
At low doses, oral minoxidil, approved as an antihypertensive over 40 years ago, has become an increasingly popular treatment for hair loss, particularly since an article about its use for hair loss was published in the New York Times in August 2022. (Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating alopecia, and is used off label for this purpose.)
To evaluate the effects of LDOM in female patients with female pattern hair loss, Dr. Imhof, along with colleagues Beija Villalpando, MD, of the department of medicine and Rochelle R. Torgerson, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, reviewed the records of 25 adult women who were evaluated for female pattern hair loss at the Mayo Clinic over a 5-year period that ended on Nov. 27, 2022. Previous studies have looked at the cardiovascular effects of treatment with oral minoxidil and impact on BP in men, but “few studies have reported on female patients receiving LDOM as monotherapy for female pattern hair loss,” the authors noted.
The mean age of the women in their study was 61 years, and they took LDOM for a mean of 6.2 months. Slightly more than half (52%) took a dose of 1.25 mg daily, while 40% took 2.5 mg daily and 8% took 0.625 mg daily.
Of the 25 patients, 10 (40%) had previously tried topical minoxidil but had discontinued it because of local side effects or challenges with adherence. Also, three patients (12%) had previously tried finasteride and spironolactone but discontinued those medications because of adverse side effects.
The researchers noted disease improvement and hair regrowth was observed in nine patients who were treated with LDOM (36%), while three patients (12%) had “unaltered disease progression.” Adverse side effects observed in the cohort included four patients with facial hypertrichosis (16%) and one patient with fluid retention/lower limb edema (4%).
The patients who developed hypertrichosis did not discontinue LDOM, but the patient who developed edema did stop treatment.
At baseline, systolic BP (SBP) ranged from 107-161 mm Hg, diastolic BP (DBP) ranged from 58-88 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 54-114 beats per minute. Post treatment, SBP ranged from 102-152 mm Hg, DBP ranged from 63-90 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 56 to 105 bpm. “It was surprising how little ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate changed after an average of 6 months of treatment,” Dr. Imhof said in an interview. “On average, SBP decreased by 2.8 mm HG while DBP decreased by 1.4 mm Hg. Heart rate increased an average of 4.4 beats per minute.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and lack of inclusion of patients who were being treated for hypertension with concomitant antihypertensive medications. “Some unique aspects of our study are that we focused on women, and we had a slightly older cohort than prior studies (61 years old on average) as well as exposure to higher doses of LDOM, with most patients on either 1.25 mg daily or 2.5 mg daily,” Dr. Imhof said.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures, and there was no funding source for the study.
results from a small retrospective analysis showed.
“Additionally, few patients experienced hair loss progression while slightly over a third experienced hair regrowth,” the study’s first author, Reese Imhof, MD, a third-year resident in the department of dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. The results were published online in JAAD International.
At low doses, oral minoxidil, approved as an antihypertensive over 40 years ago, has become an increasingly popular treatment for hair loss, particularly since an article about its use for hair loss was published in the New York Times in August 2022. (Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating alopecia, and is used off label for this purpose.)
To evaluate the effects of LDOM in female patients with female pattern hair loss, Dr. Imhof, along with colleagues Beija Villalpando, MD, of the department of medicine and Rochelle R. Torgerson, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, reviewed the records of 25 adult women who were evaluated for female pattern hair loss at the Mayo Clinic over a 5-year period that ended on Nov. 27, 2022. Previous studies have looked at the cardiovascular effects of treatment with oral minoxidil and impact on BP in men, but “few studies have reported on female patients receiving LDOM as monotherapy for female pattern hair loss,” the authors noted.
The mean age of the women in their study was 61 years, and they took LDOM for a mean of 6.2 months. Slightly more than half (52%) took a dose of 1.25 mg daily, while 40% took 2.5 mg daily and 8% took 0.625 mg daily.
Of the 25 patients, 10 (40%) had previously tried topical minoxidil but had discontinued it because of local side effects or challenges with adherence. Also, three patients (12%) had previously tried finasteride and spironolactone but discontinued those medications because of adverse side effects.
The researchers noted disease improvement and hair regrowth was observed in nine patients who were treated with LDOM (36%), while three patients (12%) had “unaltered disease progression.” Adverse side effects observed in the cohort included four patients with facial hypertrichosis (16%) and one patient with fluid retention/lower limb edema (4%).
The patients who developed hypertrichosis did not discontinue LDOM, but the patient who developed edema did stop treatment.
At baseline, systolic BP (SBP) ranged from 107-161 mm Hg, diastolic BP (DBP) ranged from 58-88 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 54-114 beats per minute. Post treatment, SBP ranged from 102-152 mm Hg, DBP ranged from 63-90 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 56 to 105 bpm. “It was surprising how little ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate changed after an average of 6 months of treatment,” Dr. Imhof said in an interview. “On average, SBP decreased by 2.8 mm HG while DBP decreased by 1.4 mm Hg. Heart rate increased an average of 4.4 beats per minute.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and lack of inclusion of patients who were being treated for hypertension with concomitant antihypertensive medications. “Some unique aspects of our study are that we focused on women, and we had a slightly older cohort than prior studies (61 years old on average) as well as exposure to higher doses of LDOM, with most patients on either 1.25 mg daily or 2.5 mg daily,” Dr. Imhof said.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures, and there was no funding source for the study.
results from a small retrospective analysis showed.
“Additionally, few patients experienced hair loss progression while slightly over a third experienced hair regrowth,” the study’s first author, Reese Imhof, MD, a third-year resident in the department of dermatology at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said in an interview. The results were published online in JAAD International.
At low doses, oral minoxidil, approved as an antihypertensive over 40 years ago, has become an increasingly popular treatment for hair loss, particularly since an article about its use for hair loss was published in the New York Times in August 2022. (Oral minoxidil is not approved for treating alopecia, and is used off label for this purpose.)
To evaluate the effects of LDOM in female patients with female pattern hair loss, Dr. Imhof, along with colleagues Beija Villalpando, MD, of the department of medicine and Rochelle R. Torgerson, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, reviewed the records of 25 adult women who were evaluated for female pattern hair loss at the Mayo Clinic over a 5-year period that ended on Nov. 27, 2022. Previous studies have looked at the cardiovascular effects of treatment with oral minoxidil and impact on BP in men, but “few studies have reported on female patients receiving LDOM as monotherapy for female pattern hair loss,” the authors noted.
The mean age of the women in their study was 61 years, and they took LDOM for a mean of 6.2 months. Slightly more than half (52%) took a dose of 1.25 mg daily, while 40% took 2.5 mg daily and 8% took 0.625 mg daily.
Of the 25 patients, 10 (40%) had previously tried topical minoxidil but had discontinued it because of local side effects or challenges with adherence. Also, three patients (12%) had previously tried finasteride and spironolactone but discontinued those medications because of adverse side effects.
The researchers noted disease improvement and hair regrowth was observed in nine patients who were treated with LDOM (36%), while three patients (12%) had “unaltered disease progression.” Adverse side effects observed in the cohort included four patients with facial hypertrichosis (16%) and one patient with fluid retention/lower limb edema (4%).
The patients who developed hypertrichosis did not discontinue LDOM, but the patient who developed edema did stop treatment.
At baseline, systolic BP (SBP) ranged from 107-161 mm Hg, diastolic BP (DBP) ranged from 58-88 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 54-114 beats per minute. Post treatment, SBP ranged from 102-152 mm Hg, DBP ranged from 63-90 mm Hg, and heart rate ranged from 56 to 105 bpm. “It was surprising how little ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate changed after an average of 6 months of treatment,” Dr. Imhof said in an interview. “On average, SBP decreased by 2.8 mm HG while DBP decreased by 1.4 mm Hg. Heart rate increased an average of 4.4 beats per minute.”
He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its small sample size and lack of inclusion of patients who were being treated for hypertension with concomitant antihypertensive medications. “Some unique aspects of our study are that we focused on women, and we had a slightly older cohort than prior studies (61 years old on average) as well as exposure to higher doses of LDOM, with most patients on either 1.25 mg daily or 2.5 mg daily,” Dr. Imhof said.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures, and there was no funding source for the study.
FROM JAAD INTERNATIONAL
Can this common herb help grow hair?
If you’re looking to grow hair, you might just have a solution in your kitchen cabinet – if TikTok and some dermatologists are correct.
The herb might also protect hair from the sun, pollution, and other environmental elements, according to an article in Insider.
The study published in Skinmed found that rosemary oil was similar to the effectiveness of minoxidil for regrowing hair in men with androgenetic alopecia. The scalp was also less itchy after 3-6 months of use.
The study included only men.
Still, dermatologist Shilpi Khetarpal, MD, told the Cleveland Clinic that it seems to work.
“The study really prompted people to look at rosemary oil for hair growth,” she said. “It became much more common in over-the-counter products after that, too.”
The Cleveland Clinic also reports that rosemary oil might help against dandruff and premature graying.
Dr. Khetarpal suggested massaging rosemary oil into the scalp, letting it soak overnight, and then washing it out. This should be done two or three times a week.
She also noted that only a few drops of rosemary oil are needed, and that the focus should be on the scalp rather than the hair, which rosemary oil makes look greasy.
It may take 6 months for “meaningful improvement,” Dr. Khetarpal said.
Meanwhile, TikTok users love hyping the oil’s hair care qualities. On the social media platform, videos with the hashtag #rosemaryoil have been viewed more than 2 billion times.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
If you’re looking to grow hair, you might just have a solution in your kitchen cabinet – if TikTok and some dermatologists are correct.
The herb might also protect hair from the sun, pollution, and other environmental elements, according to an article in Insider.
The study published in Skinmed found that rosemary oil was similar to the effectiveness of minoxidil for regrowing hair in men with androgenetic alopecia. The scalp was also less itchy after 3-6 months of use.
The study included only men.
Still, dermatologist Shilpi Khetarpal, MD, told the Cleveland Clinic that it seems to work.
“The study really prompted people to look at rosemary oil for hair growth,” she said. “It became much more common in over-the-counter products after that, too.”
The Cleveland Clinic also reports that rosemary oil might help against dandruff and premature graying.
Dr. Khetarpal suggested massaging rosemary oil into the scalp, letting it soak overnight, and then washing it out. This should be done two or three times a week.
She also noted that only a few drops of rosemary oil are needed, and that the focus should be on the scalp rather than the hair, which rosemary oil makes look greasy.
It may take 6 months for “meaningful improvement,” Dr. Khetarpal said.
Meanwhile, TikTok users love hyping the oil’s hair care qualities. On the social media platform, videos with the hashtag #rosemaryoil have been viewed more than 2 billion times.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
If you’re looking to grow hair, you might just have a solution in your kitchen cabinet – if TikTok and some dermatologists are correct.
The herb might also protect hair from the sun, pollution, and other environmental elements, according to an article in Insider.
The study published in Skinmed found that rosemary oil was similar to the effectiveness of minoxidil for regrowing hair in men with androgenetic alopecia. The scalp was also less itchy after 3-6 months of use.
The study included only men.
Still, dermatologist Shilpi Khetarpal, MD, told the Cleveland Clinic that it seems to work.
“The study really prompted people to look at rosemary oil for hair growth,” she said. “It became much more common in over-the-counter products after that, too.”
The Cleveland Clinic also reports that rosemary oil might help against dandruff and premature graying.
Dr. Khetarpal suggested massaging rosemary oil into the scalp, letting it soak overnight, and then washing it out. This should be done two or three times a week.
She also noted that only a few drops of rosemary oil are needed, and that the focus should be on the scalp rather than the hair, which rosemary oil makes look greasy.
It may take 6 months for “meaningful improvement,” Dr. Khetarpal said.
Meanwhile, TikTok users love hyping the oil’s hair care qualities. On the social media platform, videos with the hashtag #rosemaryoil have been viewed more than 2 billion times.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Piroxicam boosts success of levonorgestrel for emergency contraception
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE LANCET
ADHD meds cut hospitalization risk in borderline personality disorder patients
Although most patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD) receive psychopharmacological treatment, clinical guidance and outcomes data for specific medication use in these patients are lacking, wrote Johannes Lieslehto, MD, PhD, of the University of Eastern Finland, Niuvankuja, and colleagues.
In a study published in Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica , the researchers – using national databases in Sweden – identified 17,532 adults with BPD who were treated with medications between 2006 and 2018.
Medications included benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, as well as medications often used for ADHD: clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate. The mean age of the study population was 29.8 years and 2,649 were men.
The primary outcomes were psychiatric hospitalization (which served as an indication of treatment failure), all-cause hospitalization, or death.
Overall, treatment with benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants was associated with increased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 1.38, 1.19, and 1.18, respectively, and with increased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR 1.37, HR 1.21, HR 1.17, respectively).
By contrast, treatment with ADHD medication was associated with decreased risk of psychiatric hospitalization (HR = 0.88), as well as a decreased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR = 0.86).
Specifically, clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate were associated with decreased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 0.54, 0.79, 0.84, and 0.90, respectively.
Treatment with mood stabilizers had no significant impact on outcomes.
BPD patients treated with ADHD medications also may exhibit ADHD symptoms, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, “Although BPD and ADHD partially overlap in symptoms such as impulsivity and emotion dysregulation, previous efforts to investigate the efficacy of ADHD medication treatment in BPD are scarce,” and randomized, controlled trials are needed to determine whether these medications should be given to BPD patients without comorbid ADHD symptoms, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinical parameters on symptom severity, quality of life, and level of function, and premature prescribing of medication (protopathic bias) may have affected the results, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the large sample size and long follow-up, which increases the generalizability to real-world patients, and suggest that many pharmacological treatments for BPD may not improve outcomes, the researchers said. However, “even in the presence of possible protopathic bias, treatment with lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, methylphenidate, and clozapine was associated with improved outcomes, encouraging further research on these treatments,” they said.
The study was supported by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health and the Academy of Finland. Dr. Lieslehto had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Although most patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD) receive psychopharmacological treatment, clinical guidance and outcomes data for specific medication use in these patients are lacking, wrote Johannes Lieslehto, MD, PhD, of the University of Eastern Finland, Niuvankuja, and colleagues.
In a study published in Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica , the researchers – using national databases in Sweden – identified 17,532 adults with BPD who were treated with medications between 2006 and 2018.
Medications included benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, as well as medications often used for ADHD: clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate. The mean age of the study population was 29.8 years and 2,649 were men.
The primary outcomes were psychiatric hospitalization (which served as an indication of treatment failure), all-cause hospitalization, or death.
Overall, treatment with benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants was associated with increased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 1.38, 1.19, and 1.18, respectively, and with increased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR 1.37, HR 1.21, HR 1.17, respectively).
By contrast, treatment with ADHD medication was associated with decreased risk of psychiatric hospitalization (HR = 0.88), as well as a decreased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR = 0.86).
Specifically, clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate were associated with decreased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 0.54, 0.79, 0.84, and 0.90, respectively.
Treatment with mood stabilizers had no significant impact on outcomes.
BPD patients treated with ADHD medications also may exhibit ADHD symptoms, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, “Although BPD and ADHD partially overlap in symptoms such as impulsivity and emotion dysregulation, previous efforts to investigate the efficacy of ADHD medication treatment in BPD are scarce,” and randomized, controlled trials are needed to determine whether these medications should be given to BPD patients without comorbid ADHD symptoms, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinical parameters on symptom severity, quality of life, and level of function, and premature prescribing of medication (protopathic bias) may have affected the results, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the large sample size and long follow-up, which increases the generalizability to real-world patients, and suggest that many pharmacological treatments for BPD may not improve outcomes, the researchers said. However, “even in the presence of possible protopathic bias, treatment with lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, methylphenidate, and clozapine was associated with improved outcomes, encouraging further research on these treatments,” they said.
The study was supported by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health and the Academy of Finland. Dr. Lieslehto had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Although most patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD) receive psychopharmacological treatment, clinical guidance and outcomes data for specific medication use in these patients are lacking, wrote Johannes Lieslehto, MD, PhD, of the University of Eastern Finland, Niuvankuja, and colleagues.
In a study published in Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica , the researchers – using national databases in Sweden – identified 17,532 adults with BPD who were treated with medications between 2006 and 2018.
Medications included benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, as well as medications often used for ADHD: clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate. The mean age of the study population was 29.8 years and 2,649 were men.
The primary outcomes were psychiatric hospitalization (which served as an indication of treatment failure), all-cause hospitalization, or death.
Overall, treatment with benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, and antidepressants was associated with increased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 1.38, 1.19, and 1.18, respectively, and with increased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR 1.37, HR 1.21, HR 1.17, respectively).
By contrast, treatment with ADHD medication was associated with decreased risk of psychiatric hospitalization (HR = 0.88), as well as a decreased risk of all-cause hospitalization or death (HR = 0.86).
Specifically, clozapine, lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, and methylphenidate were associated with decreased risk of psychiatric rehospitalization, with hazard ratios of 0.54, 0.79, 0.84, and 0.90, respectively.
Treatment with mood stabilizers had no significant impact on outcomes.
BPD patients treated with ADHD medications also may exhibit ADHD symptoms, the researchers wrote in their discussion. However, “Although BPD and ADHD partially overlap in symptoms such as impulsivity and emotion dysregulation, previous efforts to investigate the efficacy of ADHD medication treatment in BPD are scarce,” and randomized, controlled trials are needed to determine whether these medications should be given to BPD patients without comorbid ADHD symptoms, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of clinical parameters on symptom severity, quality of life, and level of function, and premature prescribing of medication (protopathic bias) may have affected the results, the researchers noted.
The results were strengthened by the large sample size and long follow-up, which increases the generalizability to real-world patients, and suggest that many pharmacological treatments for BPD may not improve outcomes, the researchers said. However, “even in the presence of possible protopathic bias, treatment with lisdexamphetamine, bupropion, methylphenidate, and clozapine was associated with improved outcomes, encouraging further research on these treatments,” they said.
The study was supported by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health and the Academy of Finland. Dr. Lieslehto had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ACTA PSYCHIATRICA SCANDINAVICA
Could colchicine replace aspirin after PCI for ACS?
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) consisting of aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor has been the standard of care to prevent thrombotic events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
in these patients, while mitigating the increased bleeding risk associated with aspirin.
Investigators conducted a pilot trial in ACS patients treated with drug-eluting stents (DES) who received low-dose colchicine the day after PCI, together with P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) maintenance therapy. Aspirin use was discontinued.
At 3 months, only 1% of the patients experienced stent thrombosis, and only 1 patient showed high platelet reactivity. Moreover, at 1 month, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and platelet reactivity both decreased, pointing to reduced inflammation.
“In ACS patients undergoing PCI, it is feasible to discontinue aspirin therapy and administer low-dose colchicine on the day after PCI in addition to ticagrelor or prasugrel P2Y12 inhibitors,” write Seung-Yul Lee, MD, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, South Korea, and colleagues. “This approach is associated with favorable platelet function and inflammatory profiles.”
The study was published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Safety without compromised efficacy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently approved colchicine 0.5-mg tablets (Lodoco, Agepha Pharma) as the first anti-inflammatory drug shown to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with either established atherosclerotic disease or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease. It targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of cardiovascular events.
Patients after PCI are generally treated using DAPT, but given the risk for increased bleeding associated with aspirin – especially when used long-term – there is a “need to identify strategies associated with a more favorable safety profile without compromising efficacy,” the authors write.
Previous research has yielded mixed results in terms of the discontinuation of aspirin therapy after 1-3 months and maintenance on P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy. But one trial found colchicine to be effective in reducing recurrent ischemia, and its benefits may be more beneficial with early initiation in the hospital.
In this new study, researchers tested a “strategy that substitutes aspirin with colchicine during the acute phase to maximize the treatment effect of reducing recurrent ischemia and bleeding,” they write. The Mono Antiplatelet and Colchicine Therapy (MACT) single-arm, open-label proof-of-concept study was designed to investigate this approach.
The researchers studied 200 patients with non–ST-segment elevation ACS and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent PCI with DES (mean [SD] age, 61.4 [10.7] years; 90% male; 100% of Asian ethnicity), who were receiving either ticagrelor or prasugrel plus a loading dose of aspirin.
On the day after PCI, aspirin was discontinued, and low-dose colchicine (0.6 mg once daily) was administered in addition to the P2Y12 inhibitor. In the case of staged PCI, it was performed under the maintenance of colchicine and ticagrelor or prasugrel.
No other antiplatelet or anticoagulant agents were permitted.
Patients underwent platelet function testing using the VerifyNow P2Y12 assay before discharge. Levels of hs-CRP were measured at admission, at 24 and 48 hours after PCI, and at 1-month follow-up. Clinical follow-up was performed at 1 and at 3 months.
The primary outcome was stent thrombosis within 3 months of follow-up. Secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, MI, revascularization, major bleeding, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel MI, or target lesion revascularization, P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), and change in hs-CRP levels between 24 hours post-PCI and 1-month follow-up.
The role of inflammation
Of the original 200 patients, 190 completed the full protocol and were available for follow-up.
The primary outcome occurred in only two patients. It turned out that one of the patients had not been adherent with antiplatelet medications.
“Although bleeding occurred in 36 patients, major bleeding occurred in only 1 patient,” the authors report.
The level of platelet reactivity at discharge was 27 ± 42 PRUs. Most patients (91%) met the criteria for low platelet reactivity, while only 0.5% met the criteria for high platelet reactivity. Platelet reactivity was similar, regardless of which P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) the patients were taking.
In all patients, the level of inflammation was “reduced considerably” over time: After 1 month, the hs-CRP level decreased from 6.1 mg/L (interquartile range [IQR], 2.6-15.9 mg/L) at 24 hours after PCI to 0.6 mg/L (IQR, 0.4-1.2 mg/L; P < .001).
The prevalence of high-inflammation criteria, defined as hs-CRP ≥ 2 mg/L, decreased significantly, from 81.8% at 24 hours after PCI to 11.8% at 1 month (P < .001).
Major bleeding was rare, they report, with a 3-month incidence of 0.5%.
“Inflammation plays a fundamental role in the development and progression of the atherothrombotic process,” the authors explain. A series of factors also trigger “an intense inflammatory response” in the acute phase of MI, which may lead to adverse myocardial remodeling. In the present study, inflammatory levels were rapidly reduced.
They noted several limitations. For example, all enrolled patients were Asian and were at relatively low bleeding and ischemic risk. “Although ticagrelor or prasugrel is effective regardless of ethnicity, clinical data supporting this de-escalation strategy are limited,” they state. Additionally, there was no control group for comparison.
The findings warrant further investigation, they conclude.
Promising but preliminary
Commenting for this news organization, Francesco Costa, MD, PhD, interventional cardiologist and assistant professor, University of Messina, Sicily, Italy, said he thinks it’s “too early for extensive clinical translation of these findings.”
Rather, larger and more extensive randomized trials are “on their way to give more precise estimates regarding the risks and benefits of early aspirin withdrawal in ACS.”
However, added Dr. Costa, who was not involved with the current research, “in this setting, adding colchicine early looks very promising to mitigate potential thrombotic risk without increasing bleeding risk.”
In the meantime, the study “provides novel insights on early aspirin withdrawal and P2Y12 monotherapy in an unselected population, including [those with] STEMI,” said Dr. Costa, also the coauthor of an accompanying editorial. The findings “could be of particular interest for those patients at extremely high bleeding risk or who are truly intolerant to aspirin, a scenario in which options are limited.”
This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Research Center, Seoul, South Korea. Dr. Lee reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Costa has served on an advisory board for AstraZeneca and has received speaker fees from Chiesi Farmaceutici. His coauthor reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) consisting of aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor has been the standard of care to prevent thrombotic events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
in these patients, while mitigating the increased bleeding risk associated with aspirin.
Investigators conducted a pilot trial in ACS patients treated with drug-eluting stents (DES) who received low-dose colchicine the day after PCI, together with P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) maintenance therapy. Aspirin use was discontinued.
At 3 months, only 1% of the patients experienced stent thrombosis, and only 1 patient showed high platelet reactivity. Moreover, at 1 month, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and platelet reactivity both decreased, pointing to reduced inflammation.
“In ACS patients undergoing PCI, it is feasible to discontinue aspirin therapy and administer low-dose colchicine on the day after PCI in addition to ticagrelor or prasugrel P2Y12 inhibitors,” write Seung-Yul Lee, MD, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, South Korea, and colleagues. “This approach is associated with favorable platelet function and inflammatory profiles.”
The study was published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Safety without compromised efficacy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently approved colchicine 0.5-mg tablets (Lodoco, Agepha Pharma) as the first anti-inflammatory drug shown to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with either established atherosclerotic disease or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease. It targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of cardiovascular events.
Patients after PCI are generally treated using DAPT, but given the risk for increased bleeding associated with aspirin – especially when used long-term – there is a “need to identify strategies associated with a more favorable safety profile without compromising efficacy,” the authors write.
Previous research has yielded mixed results in terms of the discontinuation of aspirin therapy after 1-3 months and maintenance on P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy. But one trial found colchicine to be effective in reducing recurrent ischemia, and its benefits may be more beneficial with early initiation in the hospital.
In this new study, researchers tested a “strategy that substitutes aspirin with colchicine during the acute phase to maximize the treatment effect of reducing recurrent ischemia and bleeding,” they write. The Mono Antiplatelet and Colchicine Therapy (MACT) single-arm, open-label proof-of-concept study was designed to investigate this approach.
The researchers studied 200 patients with non–ST-segment elevation ACS and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent PCI with DES (mean [SD] age, 61.4 [10.7] years; 90% male; 100% of Asian ethnicity), who were receiving either ticagrelor or prasugrel plus a loading dose of aspirin.
On the day after PCI, aspirin was discontinued, and low-dose colchicine (0.6 mg once daily) was administered in addition to the P2Y12 inhibitor. In the case of staged PCI, it was performed under the maintenance of colchicine and ticagrelor or prasugrel.
No other antiplatelet or anticoagulant agents were permitted.
Patients underwent platelet function testing using the VerifyNow P2Y12 assay before discharge. Levels of hs-CRP were measured at admission, at 24 and 48 hours after PCI, and at 1-month follow-up. Clinical follow-up was performed at 1 and at 3 months.
The primary outcome was stent thrombosis within 3 months of follow-up. Secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, MI, revascularization, major bleeding, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel MI, or target lesion revascularization, P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), and change in hs-CRP levels between 24 hours post-PCI and 1-month follow-up.
The role of inflammation
Of the original 200 patients, 190 completed the full protocol and were available for follow-up.
The primary outcome occurred in only two patients. It turned out that one of the patients had not been adherent with antiplatelet medications.
“Although bleeding occurred in 36 patients, major bleeding occurred in only 1 patient,” the authors report.
The level of platelet reactivity at discharge was 27 ± 42 PRUs. Most patients (91%) met the criteria for low platelet reactivity, while only 0.5% met the criteria for high platelet reactivity. Platelet reactivity was similar, regardless of which P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) the patients were taking.
In all patients, the level of inflammation was “reduced considerably” over time: After 1 month, the hs-CRP level decreased from 6.1 mg/L (interquartile range [IQR], 2.6-15.9 mg/L) at 24 hours after PCI to 0.6 mg/L (IQR, 0.4-1.2 mg/L; P < .001).
The prevalence of high-inflammation criteria, defined as hs-CRP ≥ 2 mg/L, decreased significantly, from 81.8% at 24 hours after PCI to 11.8% at 1 month (P < .001).
Major bleeding was rare, they report, with a 3-month incidence of 0.5%.
“Inflammation plays a fundamental role in the development and progression of the atherothrombotic process,” the authors explain. A series of factors also trigger “an intense inflammatory response” in the acute phase of MI, which may lead to adverse myocardial remodeling. In the present study, inflammatory levels were rapidly reduced.
They noted several limitations. For example, all enrolled patients were Asian and were at relatively low bleeding and ischemic risk. “Although ticagrelor or prasugrel is effective regardless of ethnicity, clinical data supporting this de-escalation strategy are limited,” they state. Additionally, there was no control group for comparison.
The findings warrant further investigation, they conclude.
Promising but preliminary
Commenting for this news organization, Francesco Costa, MD, PhD, interventional cardiologist and assistant professor, University of Messina, Sicily, Italy, said he thinks it’s “too early for extensive clinical translation of these findings.”
Rather, larger and more extensive randomized trials are “on their way to give more precise estimates regarding the risks and benefits of early aspirin withdrawal in ACS.”
However, added Dr. Costa, who was not involved with the current research, “in this setting, adding colchicine early looks very promising to mitigate potential thrombotic risk without increasing bleeding risk.”
In the meantime, the study “provides novel insights on early aspirin withdrawal and P2Y12 monotherapy in an unselected population, including [those with] STEMI,” said Dr. Costa, also the coauthor of an accompanying editorial. The findings “could be of particular interest for those patients at extremely high bleeding risk or who are truly intolerant to aspirin, a scenario in which options are limited.”
This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Research Center, Seoul, South Korea. Dr. Lee reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Costa has served on an advisory board for AstraZeneca and has received speaker fees from Chiesi Farmaceutici. His coauthor reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) consisting of aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor has been the standard of care to prevent thrombotic events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
in these patients, while mitigating the increased bleeding risk associated with aspirin.
Investigators conducted a pilot trial in ACS patients treated with drug-eluting stents (DES) who received low-dose colchicine the day after PCI, together with P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) maintenance therapy. Aspirin use was discontinued.
At 3 months, only 1% of the patients experienced stent thrombosis, and only 1 patient showed high platelet reactivity. Moreover, at 1 month, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and platelet reactivity both decreased, pointing to reduced inflammation.
“In ACS patients undergoing PCI, it is feasible to discontinue aspirin therapy and administer low-dose colchicine on the day after PCI in addition to ticagrelor or prasugrel P2Y12 inhibitors,” write Seung-Yul Lee, MD, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, South Korea, and colleagues. “This approach is associated with favorable platelet function and inflammatory profiles.”
The study was published online in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Safety without compromised efficacy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently approved colchicine 0.5-mg tablets (Lodoco, Agepha Pharma) as the first anti-inflammatory drug shown to reduce the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization, and cardiovascular death in adult patients with either established atherosclerotic disease or multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease. It targets residual inflammation as an underlying cause of cardiovascular events.
Patients after PCI are generally treated using DAPT, but given the risk for increased bleeding associated with aspirin – especially when used long-term – there is a “need to identify strategies associated with a more favorable safety profile without compromising efficacy,” the authors write.
Previous research has yielded mixed results in terms of the discontinuation of aspirin therapy after 1-3 months and maintenance on P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy. But one trial found colchicine to be effective in reducing recurrent ischemia, and its benefits may be more beneficial with early initiation in the hospital.
In this new study, researchers tested a “strategy that substitutes aspirin with colchicine during the acute phase to maximize the treatment effect of reducing recurrent ischemia and bleeding,” they write. The Mono Antiplatelet and Colchicine Therapy (MACT) single-arm, open-label proof-of-concept study was designed to investigate this approach.
The researchers studied 200 patients with non–ST-segment elevation ACS and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent PCI with DES (mean [SD] age, 61.4 [10.7] years; 90% male; 100% of Asian ethnicity), who were receiving either ticagrelor or prasugrel plus a loading dose of aspirin.
On the day after PCI, aspirin was discontinued, and low-dose colchicine (0.6 mg once daily) was administered in addition to the P2Y12 inhibitor. In the case of staged PCI, it was performed under the maintenance of colchicine and ticagrelor or prasugrel.
No other antiplatelet or anticoagulant agents were permitted.
Patients underwent platelet function testing using the VerifyNow P2Y12 assay before discharge. Levels of hs-CRP were measured at admission, at 24 and 48 hours after PCI, and at 1-month follow-up. Clinical follow-up was performed at 1 and at 3 months.
The primary outcome was stent thrombosis within 3 months of follow-up. Secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, MI, revascularization, major bleeding, a composite of cardiac death, target vessel MI, or target lesion revascularization, P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), and change in hs-CRP levels between 24 hours post-PCI and 1-month follow-up.
The role of inflammation
Of the original 200 patients, 190 completed the full protocol and were available for follow-up.
The primary outcome occurred in only two patients. It turned out that one of the patients had not been adherent with antiplatelet medications.
“Although bleeding occurred in 36 patients, major bleeding occurred in only 1 patient,” the authors report.
The level of platelet reactivity at discharge was 27 ± 42 PRUs. Most patients (91%) met the criteria for low platelet reactivity, while only 0.5% met the criteria for high platelet reactivity. Platelet reactivity was similar, regardless of which P2Y12 inhibitor (ticagrelor or prasugrel) the patients were taking.
In all patients, the level of inflammation was “reduced considerably” over time: After 1 month, the hs-CRP level decreased from 6.1 mg/L (interquartile range [IQR], 2.6-15.9 mg/L) at 24 hours after PCI to 0.6 mg/L (IQR, 0.4-1.2 mg/L; P < .001).
The prevalence of high-inflammation criteria, defined as hs-CRP ≥ 2 mg/L, decreased significantly, from 81.8% at 24 hours after PCI to 11.8% at 1 month (P < .001).
Major bleeding was rare, they report, with a 3-month incidence of 0.5%.
“Inflammation plays a fundamental role in the development and progression of the atherothrombotic process,” the authors explain. A series of factors also trigger “an intense inflammatory response” in the acute phase of MI, which may lead to adverse myocardial remodeling. In the present study, inflammatory levels were rapidly reduced.
They noted several limitations. For example, all enrolled patients were Asian and were at relatively low bleeding and ischemic risk. “Although ticagrelor or prasugrel is effective regardless of ethnicity, clinical data supporting this de-escalation strategy are limited,” they state. Additionally, there was no control group for comparison.
The findings warrant further investigation, they conclude.
Promising but preliminary
Commenting for this news organization, Francesco Costa, MD, PhD, interventional cardiologist and assistant professor, University of Messina, Sicily, Italy, said he thinks it’s “too early for extensive clinical translation of these findings.”
Rather, larger and more extensive randomized trials are “on their way to give more precise estimates regarding the risks and benefits of early aspirin withdrawal in ACS.”
However, added Dr. Costa, who was not involved with the current research, “in this setting, adding colchicine early looks very promising to mitigate potential thrombotic risk without increasing bleeding risk.”
In the meantime, the study “provides novel insights on early aspirin withdrawal and P2Y12 monotherapy in an unselected population, including [those with] STEMI,” said Dr. Costa, also the coauthor of an accompanying editorial. The findings “could be of particular interest for those patients at extremely high bleeding risk or who are truly intolerant to aspirin, a scenario in which options are limited.”
This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Research Center, Seoul, South Korea. Dr. Lee reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Costa has served on an advisory board for AstraZeneca and has received speaker fees from Chiesi Farmaceutici. His coauthor reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: CARIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS
FDA okays first-ever new drug for rare bone disorder
Affecting roughly 400 people in the United States and 900 worldwide, FOP is an autosomal dominant condition in which bone develops in soft connective tissue areas of the body where it isn’t normally present (heterotopic ossification), such as the ligaments, tendons, and skeletal muscles. This leads to severe restriction in mobility and function, to the point that people lose the ability to feed or care for themselves. Most are completely disabled by age 30 years and median life expectancy is 56 years, with death often caused by bone formation around the rib cage restricting respiration.
“As a clinician caring for patients with FOP, I personally see the daily challenges and stresses that our patients and their families must contend with ... since the accumulation of heterotopic ossification in FOP is progressive, irreversible, and life altering. This medication is an important treatment option for our FOP community,” said endocrinologist Edward Hsiao, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in a statement from Ipsen.
Taken orally, palovarotene selectively targets the gamma subtype of retinoic acid receptors that regulate skeletal development and ectopic bone in the retinoid signaling pathway. The drug mediates interactions between these receptors, growth factors, and proteins within that pathway to reduce new abnormal bone formation.
It is now FDA approved for the treatment of FOP in female patients aged 8 years or older and male patients aged 10 years or older. The recommended dosing is 5 mg daily or weight-based equivalent for pediatric patients under 14 years of age, which can be modified or increased for flare-up symptoms. It is contraindicated during pregnancy.
The FDA approval was based on 18-month data from the phase 3, multicenter, open-label MOVE trial that included 107 adult and pediatric patients, over 10% of the world’s population with FOP. All received oral palovarotene and were compared with untreated individuals from a prior natural history study of the condition. The drug reduced annualized heterotopic ossification volume by 54%.
Side effects were typical of those seen with other systemic retinoid drugs, including mucocutaneous events such as dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, alopecia, drug eruption, rash, and pruritus, and musculoskeletal events, such as arthralgia and premature growth plate closure in growing children.
According to Dr. Hsiao, who was a MOVE investigator, the study “showed that Sohonos can decrease new heterotopic ossification, and that palovarotene can be tolerated by many patients with FOP. Sohonos is not for everyone. As with all medicines there are risks in this case especially for young children who may develop early growth plate closure. In addition, Sohonos has the same side effects as other retinoids.”
The FDA approval of palovarotene follows its rejection for marketing authorization in the European Union in July 2023.
Reached for comment, an Ipsen spokesperson said in an interview: “We reached the end of the regulatory process in the European Union for Sohonos and are disappointed the European Commission decided not to approved palovarotene for people with FOP in Europe.”
The company is developing another drug, fidrisertib, for treating FOP. A pivotal phase 2 trial for that drug is now recruiting patients. Asked where Ipsen might try to market fidrisertib, the spokesperson replied:“At this point, our focus is on the completion of the pivotal trial.”
Meanwhile, in the United States, the FOP community is celebrating the palovarotene approval. In a statement, Michelle Davis, executive director of the International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association, said: “FOP is life altering to the individuals diagnosed and their families. There’s not a day that goes by where those impacted don’t worry about the debilitating physical pain of muscle that is replaced by bone, another joint locking, or the relentless emotional toll of losing the ability to do an activity they love, or hold a loved one close. ... The first treatment for FOP has been proven to reduce the volume of new abnormal bone growth, which may result in better health outcomes for people living with FOP.”
Ipsen is offering a patient support program to assist with education, coverage, and reimbursement (1-866-435-5677).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Affecting roughly 400 people in the United States and 900 worldwide, FOP is an autosomal dominant condition in which bone develops in soft connective tissue areas of the body where it isn’t normally present (heterotopic ossification), such as the ligaments, tendons, and skeletal muscles. This leads to severe restriction in mobility and function, to the point that people lose the ability to feed or care for themselves. Most are completely disabled by age 30 years and median life expectancy is 56 years, with death often caused by bone formation around the rib cage restricting respiration.
“As a clinician caring for patients with FOP, I personally see the daily challenges and stresses that our patients and their families must contend with ... since the accumulation of heterotopic ossification in FOP is progressive, irreversible, and life altering. This medication is an important treatment option for our FOP community,” said endocrinologist Edward Hsiao, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in a statement from Ipsen.
Taken orally, palovarotene selectively targets the gamma subtype of retinoic acid receptors that regulate skeletal development and ectopic bone in the retinoid signaling pathway. The drug mediates interactions between these receptors, growth factors, and proteins within that pathway to reduce new abnormal bone formation.
It is now FDA approved for the treatment of FOP in female patients aged 8 years or older and male patients aged 10 years or older. The recommended dosing is 5 mg daily or weight-based equivalent for pediatric patients under 14 years of age, which can be modified or increased for flare-up symptoms. It is contraindicated during pregnancy.
The FDA approval was based on 18-month data from the phase 3, multicenter, open-label MOVE trial that included 107 adult and pediatric patients, over 10% of the world’s population with FOP. All received oral palovarotene and were compared with untreated individuals from a prior natural history study of the condition. The drug reduced annualized heterotopic ossification volume by 54%.
Side effects were typical of those seen with other systemic retinoid drugs, including mucocutaneous events such as dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, alopecia, drug eruption, rash, and pruritus, and musculoskeletal events, such as arthralgia and premature growth plate closure in growing children.
According to Dr. Hsiao, who was a MOVE investigator, the study “showed that Sohonos can decrease new heterotopic ossification, and that palovarotene can be tolerated by many patients with FOP. Sohonos is not for everyone. As with all medicines there are risks in this case especially for young children who may develop early growth plate closure. In addition, Sohonos has the same side effects as other retinoids.”
The FDA approval of palovarotene follows its rejection for marketing authorization in the European Union in July 2023.
Reached for comment, an Ipsen spokesperson said in an interview: “We reached the end of the regulatory process in the European Union for Sohonos and are disappointed the European Commission decided not to approved palovarotene for people with FOP in Europe.”
The company is developing another drug, fidrisertib, for treating FOP. A pivotal phase 2 trial for that drug is now recruiting patients. Asked where Ipsen might try to market fidrisertib, the spokesperson replied:“At this point, our focus is on the completion of the pivotal trial.”
Meanwhile, in the United States, the FOP community is celebrating the palovarotene approval. In a statement, Michelle Davis, executive director of the International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association, said: “FOP is life altering to the individuals diagnosed and their families. There’s not a day that goes by where those impacted don’t worry about the debilitating physical pain of muscle that is replaced by bone, another joint locking, or the relentless emotional toll of losing the ability to do an activity they love, or hold a loved one close. ... The first treatment for FOP has been proven to reduce the volume of new abnormal bone growth, which may result in better health outcomes for people living with FOP.”
Ipsen is offering a patient support program to assist with education, coverage, and reimbursement (1-866-435-5677).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Affecting roughly 400 people in the United States and 900 worldwide, FOP is an autosomal dominant condition in which bone develops in soft connective tissue areas of the body where it isn’t normally present (heterotopic ossification), such as the ligaments, tendons, and skeletal muscles. This leads to severe restriction in mobility and function, to the point that people lose the ability to feed or care for themselves. Most are completely disabled by age 30 years and median life expectancy is 56 years, with death often caused by bone formation around the rib cage restricting respiration.
“As a clinician caring for patients with FOP, I personally see the daily challenges and stresses that our patients and their families must contend with ... since the accumulation of heterotopic ossification in FOP is progressive, irreversible, and life altering. This medication is an important treatment option for our FOP community,” said endocrinologist Edward Hsiao, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, in a statement from Ipsen.
Taken orally, palovarotene selectively targets the gamma subtype of retinoic acid receptors that regulate skeletal development and ectopic bone in the retinoid signaling pathway. The drug mediates interactions between these receptors, growth factors, and proteins within that pathway to reduce new abnormal bone formation.
It is now FDA approved for the treatment of FOP in female patients aged 8 years or older and male patients aged 10 years or older. The recommended dosing is 5 mg daily or weight-based equivalent for pediatric patients under 14 years of age, which can be modified or increased for flare-up symptoms. It is contraindicated during pregnancy.
The FDA approval was based on 18-month data from the phase 3, multicenter, open-label MOVE trial that included 107 adult and pediatric patients, over 10% of the world’s population with FOP. All received oral palovarotene and were compared with untreated individuals from a prior natural history study of the condition. The drug reduced annualized heterotopic ossification volume by 54%.
Side effects were typical of those seen with other systemic retinoid drugs, including mucocutaneous events such as dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, alopecia, drug eruption, rash, and pruritus, and musculoskeletal events, such as arthralgia and premature growth plate closure in growing children.
According to Dr. Hsiao, who was a MOVE investigator, the study “showed that Sohonos can decrease new heterotopic ossification, and that palovarotene can be tolerated by many patients with FOP. Sohonos is not for everyone. As with all medicines there are risks in this case especially for young children who may develop early growth plate closure. In addition, Sohonos has the same side effects as other retinoids.”
The FDA approval of palovarotene follows its rejection for marketing authorization in the European Union in July 2023.
Reached for comment, an Ipsen spokesperson said in an interview: “We reached the end of the regulatory process in the European Union for Sohonos and are disappointed the European Commission decided not to approved palovarotene for people with FOP in Europe.”
The company is developing another drug, fidrisertib, for treating FOP. A pivotal phase 2 trial for that drug is now recruiting patients. Asked where Ipsen might try to market fidrisertib, the spokesperson replied:“At this point, our focus is on the completion of the pivotal trial.”
Meanwhile, in the United States, the FOP community is celebrating the palovarotene approval. In a statement, Michelle Davis, executive director of the International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association, said: “FOP is life altering to the individuals diagnosed and their families. There’s not a day that goes by where those impacted don’t worry about the debilitating physical pain of muscle that is replaced by bone, another joint locking, or the relentless emotional toll of losing the ability to do an activity they love, or hold a loved one close. ... The first treatment for FOP has been proven to reduce the volume of new abnormal bone growth, which may result in better health outcomes for people living with FOP.”
Ipsen is offering a patient support program to assist with education, coverage, and reimbursement (1-866-435-5677).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.