User login
Immune dysregulation may drive long-term postpartum depression
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Postpartum depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder that persist 2-3 years after birth are associated with a dysregulated immune system that is characterized by increased inflammatory signaling, according to investigators.
These findings suggest that mental health screening for women who have given birth should continue beyond the first year post partum, reported lead author Jennifer M. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
“Delayed postpartum depression, also known as late-onset postpartum depression, can affect women up to 18 months after delivery,” the investigators wrote in the American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. “It can appear even later in some women, depending on the hormonal changes that occur after having a baby (for example, timing of weaning). However, the majority of research on maternal mental health focuses on the first year post birth, leaving a gap in research beyond 12 months post partum.”
To address this gap, the investigators enrolled 33 women who were 2-3 years post partum. Participants completed self-guided questionnaires on PTSD, depression, and anxiety, and provided blood samples for gene expression analysis.
Sixteen of the 33 women had clinically significant mood disturbances. and significantly reduced activation of genes associated with viral response.
“The results provide preliminary evidence of a mechanism (e.g., immune dysregulation) that might be contributing to mood disorders and bring us closer to the goal of identifying targetable biomarkers for mood disorders,” Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara said in a written comment. “This work highlights the need for standardized and continual depression and anxiety screening in ob.gyn. and primary care settings that extends beyond the 6-week maternal visit and possibly beyond the first postpartum year.”
Findings draw skepticism
“The authors argue that mothers need to be screened for depression/anxiety longer than the first year post partum, and this is true, but it has nothing to do with their findings,” said Jennifer L. Payne, MD, an expert in reproductive psychiatry at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
In a written comment, she explained that the cross-sectional design makes it impossible to know whether the mood disturbances were linked with delivery at all.
“It is unclear if the depression/anxiety symptoms began after delivery or not,” Dr. Payne said. “In addition, it is unclear if the findings are causative or a result of depression/anxiety symptoms (the authors admit this in the limitations section). It is likely that the findings are not specific or even related to having delivered a child, but rather reflect a more general process related to depression/anxiety outside of the postpartum time period.”
Only prospective studies can answer these questions, she said.
Dr. Nicoloro-SantaBarbara agreed that further research is needed.
“Our findings are exciting, but still need to be replicated in larger samples with diverse women in order to make sure they generalize,” she said. “More work is needed to understand why inflammation plays a role in postpartum mental illness for some women and not others.”
The study was supported by a Cedars-Sinai Precision Health Grant, the Cousins Center for Psychoneuroimmunology, University of California, Los Angeles, and the National Institute of Mental Health. The investigators and Dr. Payne disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF REPRODUCTIVE IMMUNOLOGY
Digital treatment may help relieve PTSD, panic disorder
The 28-day home-based treatment, known as the capnometry guided respiratory intervention (CGRI), uses an app-based feedback protocol to normalize respiration and increase patients’ ability to cope with symptoms of stress, anxiety, and panic by providing real time breath-to-breath feedback of respiratory rate and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels via a nasal cannula.
Results from the large real-world study showed that over 65% of patients with PD and over 72% of those with PTSD responded to the treatment. In addition, almost 75% of participants adhered to the study protocol, with low dropout rates.
“The brief duration of treatment, high adherence rates, and clinical benefit suggests that CGRI provides an important addition to treatment options for PD and PTSD,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Digital Health.
‘New kid on the block’
The “respiratory dysregulation hypothesis” links CO2 sensitivity to panic attacks and PD, and similar reactivity has been identified in PTSD, but a “common limitation of psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic approaches to PD and PTSD is that neither address the role of respiratory physiology and breathing style,” the investigators note.
The most widely studied treatment for PTSD is trauma-focused psychotherapy, in which the patient reviews and revisits the trauma, but it has a high dropout rate, study investigator Michael Telch, PhD, director of the Laboratory for the Study of Anxiety Disorders, University of Texas, Austin, told this news organization.
He described CGRI for PTSD as a “relatively new kid on the block, so to speak.” The intervention was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of PD and PTSD in 2013 and 2018, respectively, and is currently available through the Veterans Administration for veterans with PTSD. It is also covered by some commercial insurance plans.
“The underlying assumption [of CGRI] is that a person can learn to develop skills for controlling some of their physiological reactions that are triggered as a result of trauma,” said Dr. Telch.
The device uses a biofeedback approach to give patients “greater control over their physiological reactions, such as hyperventilation and increased respiration rate, and the focus is on providing a sense of mastery,” he said.
Participants with PTSD were assigned to a health coach. The device was delivered to the patient’s home, and patients met with the trained coach weekly and could check in between visits via text or e-mail. Twice-daily sessions were recommended.
“The coach gets feedback about what’s happening with the patient’s respiration and end-tidal CO2 levels [etCO2] and instructs participants how to keep their respiration rate and etCO2 at a more normal level,” said Dr. Telch.
The CGRI “teaches a specific breathing style via a system providing real-time feedback of respiratory rate (RR) and exhaled carbon dioxide levels facilitated by data capture,” the authors note.
Sense of mastery
Of the 1,569 participants, 1,395 had PD and 174 had PTSD (mean age, 39.2 [standard deviation, 13.9] years and 40.9 [SD, 14.9] years, respectively; 76% and 73% female, respectively). Those with PD completed the Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS) and those with PTSD completed the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), before and after the intervention.
The treatment response rate for PD was defined as a 40% or greater reduction in PDSS total scores, whereas treatment response rate for PTSD was defined as a 10-point or greater reduction in PCL-5 scores.
At baseline, patients were classified either as normocapnic or hypocapnic (etCO2 ≥ 37 or < 37, respectively), with 65% classified as normocapnic and 35% classified as hypocapnic.
Among patients with PD, there was a 50.2% mean pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PDSS scores (P < .001; d = 1.31), with a treatment response rate of 65.3% of patients.
Among patients with PTSD, there was a 41.1% pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PCL-5 scores (P < .001; d = 1.16), with a treatment response rate of 72.4%.
When investigators analyzed the response at the individual level, they found that 55.7% of patients with PD and 53.5% of those with PTSD were classified as treatment responders. This determination was based on a two-pronged approach that first calculated the Reliable Change Index (RCI) for each participant, and, in participants showing statistically reliable improvement, whether the posttreatment score was closer to the distribution of scores for patients without or with the given disorder.
“Patients with both normal and below-normal baseline exhaled CO2 levels experienced comparable benefit,” the authors report.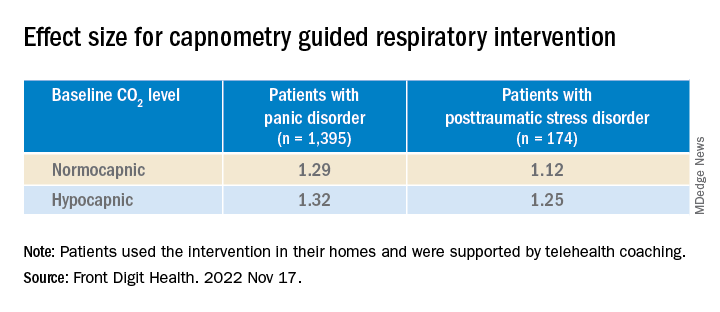
There were high levels of adherence across the full treatment period in both the PD and the PTSD groups (74.8% and 74.9%, respectively), with low dropout rates (10% and 11%, respectively).
“Not every single patient who undergoes any treatment has a perfect response, but the response rates to this treatment have, surprisingly, been quite positive and there have been no negative side effects,” Dr. Telch remarked.
He noted that one of the effects of PTSD is that the “patient has negative beliefs about their ability to control the world. ‘I can’t control my reactions. At any time, I could have a flashback.’ Helping the patient to develop any sense of mastery over some of their reactions can spill over and give them a greater sense of mastery and control, which can have a positive effect in reducing PTSD symptoms.”
‘A viable alternative’
Commenting on the research, Charles Marmar, MD, chair and Peter H. Schub Professor of Psychiatry, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that the study has some limitations, probably the most significant of which is that most participants had normal baseline CO2 levels.
“The treatment is fundamentally designed for people who hyperventilate and blow off too much CO2 so they can breathe in a more calm, relaxed way, but most people in the trial had normal CO2 to begin with,” said Dr. Marmar, who was not involved with the study.
“It’s likely that the major benefits were the relaxation from doing the breathing exercises rather than the change in CO2 levels,” he speculated.
The treatment is “probably a good thing for those patients who actually have abnormal CO2 levels. This treatment could be used in precision medicine, where you tailor treatments to those who actually need them rather than giving the same treatment to everyone,” he said.
“For patients who don’t respond to trauma-focused therapy or it’s too aversive for them to undergo, this new intervention provides a viable alternative,” Dr. Telch added.
The study was internally funded by Freespira. Dr. Telch is a scientific advisor at Freespira and receives compensation by way of stock options. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Marmar has declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 28-day home-based treatment, known as the capnometry guided respiratory intervention (CGRI), uses an app-based feedback protocol to normalize respiration and increase patients’ ability to cope with symptoms of stress, anxiety, and panic by providing real time breath-to-breath feedback of respiratory rate and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels via a nasal cannula.
Results from the large real-world study showed that over 65% of patients with PD and over 72% of those with PTSD responded to the treatment. In addition, almost 75% of participants adhered to the study protocol, with low dropout rates.
“The brief duration of treatment, high adherence rates, and clinical benefit suggests that CGRI provides an important addition to treatment options for PD and PTSD,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Digital Health.
‘New kid on the block’
The “respiratory dysregulation hypothesis” links CO2 sensitivity to panic attacks and PD, and similar reactivity has been identified in PTSD, but a “common limitation of psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic approaches to PD and PTSD is that neither address the role of respiratory physiology and breathing style,” the investigators note.
The most widely studied treatment for PTSD is trauma-focused psychotherapy, in which the patient reviews and revisits the trauma, but it has a high dropout rate, study investigator Michael Telch, PhD, director of the Laboratory for the Study of Anxiety Disorders, University of Texas, Austin, told this news organization.
He described CGRI for PTSD as a “relatively new kid on the block, so to speak.” The intervention was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of PD and PTSD in 2013 and 2018, respectively, and is currently available through the Veterans Administration for veterans with PTSD. It is also covered by some commercial insurance plans.
“The underlying assumption [of CGRI] is that a person can learn to develop skills for controlling some of their physiological reactions that are triggered as a result of trauma,” said Dr. Telch.
The device uses a biofeedback approach to give patients “greater control over their physiological reactions, such as hyperventilation and increased respiration rate, and the focus is on providing a sense of mastery,” he said.
Participants with PTSD were assigned to a health coach. The device was delivered to the patient’s home, and patients met with the trained coach weekly and could check in between visits via text or e-mail. Twice-daily sessions were recommended.
“The coach gets feedback about what’s happening with the patient’s respiration and end-tidal CO2 levels [etCO2] and instructs participants how to keep their respiration rate and etCO2 at a more normal level,” said Dr. Telch.
The CGRI “teaches a specific breathing style via a system providing real-time feedback of respiratory rate (RR) and exhaled carbon dioxide levels facilitated by data capture,” the authors note.
Sense of mastery
Of the 1,569 participants, 1,395 had PD and 174 had PTSD (mean age, 39.2 [standard deviation, 13.9] years and 40.9 [SD, 14.9] years, respectively; 76% and 73% female, respectively). Those with PD completed the Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS) and those with PTSD completed the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), before and after the intervention.
The treatment response rate for PD was defined as a 40% or greater reduction in PDSS total scores, whereas treatment response rate for PTSD was defined as a 10-point or greater reduction in PCL-5 scores.
At baseline, patients were classified either as normocapnic or hypocapnic (etCO2 ≥ 37 or < 37, respectively), with 65% classified as normocapnic and 35% classified as hypocapnic.
Among patients with PD, there was a 50.2% mean pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PDSS scores (P < .001; d = 1.31), with a treatment response rate of 65.3% of patients.
Among patients with PTSD, there was a 41.1% pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PCL-5 scores (P < .001; d = 1.16), with a treatment response rate of 72.4%.
When investigators analyzed the response at the individual level, they found that 55.7% of patients with PD and 53.5% of those with PTSD were classified as treatment responders. This determination was based on a two-pronged approach that first calculated the Reliable Change Index (RCI) for each participant, and, in participants showing statistically reliable improvement, whether the posttreatment score was closer to the distribution of scores for patients without or with the given disorder.
“Patients with both normal and below-normal baseline exhaled CO2 levels experienced comparable benefit,” the authors report.
There were high levels of adherence across the full treatment period in both the PD and the PTSD groups (74.8% and 74.9%, respectively), with low dropout rates (10% and 11%, respectively).
“Not every single patient who undergoes any treatment has a perfect response, but the response rates to this treatment have, surprisingly, been quite positive and there have been no negative side effects,” Dr. Telch remarked.
He noted that one of the effects of PTSD is that the “patient has negative beliefs about their ability to control the world. ‘I can’t control my reactions. At any time, I could have a flashback.’ Helping the patient to develop any sense of mastery over some of their reactions can spill over and give them a greater sense of mastery and control, which can have a positive effect in reducing PTSD symptoms.”
‘A viable alternative’
Commenting on the research, Charles Marmar, MD, chair and Peter H. Schub Professor of Psychiatry, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that the study has some limitations, probably the most significant of which is that most participants had normal baseline CO2 levels.
“The treatment is fundamentally designed for people who hyperventilate and blow off too much CO2 so they can breathe in a more calm, relaxed way, but most people in the trial had normal CO2 to begin with,” said Dr. Marmar, who was not involved with the study.
“It’s likely that the major benefits were the relaxation from doing the breathing exercises rather than the change in CO2 levels,” he speculated.
The treatment is “probably a good thing for those patients who actually have abnormal CO2 levels. This treatment could be used in precision medicine, where you tailor treatments to those who actually need them rather than giving the same treatment to everyone,” he said.
“For patients who don’t respond to trauma-focused therapy or it’s too aversive for them to undergo, this new intervention provides a viable alternative,” Dr. Telch added.
The study was internally funded by Freespira. Dr. Telch is a scientific advisor at Freespira and receives compensation by way of stock options. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Marmar has declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 28-day home-based treatment, known as the capnometry guided respiratory intervention (CGRI), uses an app-based feedback protocol to normalize respiration and increase patients’ ability to cope with symptoms of stress, anxiety, and panic by providing real time breath-to-breath feedback of respiratory rate and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels via a nasal cannula.
Results from the large real-world study showed that over 65% of patients with PD and over 72% of those with PTSD responded to the treatment. In addition, almost 75% of participants adhered to the study protocol, with low dropout rates.
“The brief duration of treatment, high adherence rates, and clinical benefit suggests that CGRI provides an important addition to treatment options for PD and PTSD,” the investigators write.
The study was published online in Frontiers in Digital Health.
‘New kid on the block’
The “respiratory dysregulation hypothesis” links CO2 sensitivity to panic attacks and PD, and similar reactivity has been identified in PTSD, but a “common limitation of psychotherapeutic and pharmacologic approaches to PD and PTSD is that neither address the role of respiratory physiology and breathing style,” the investigators note.
The most widely studied treatment for PTSD is trauma-focused psychotherapy, in which the patient reviews and revisits the trauma, but it has a high dropout rate, study investigator Michael Telch, PhD, director of the Laboratory for the Study of Anxiety Disorders, University of Texas, Austin, told this news organization.
He described CGRI for PTSD as a “relatively new kid on the block, so to speak.” The intervention was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of PD and PTSD in 2013 and 2018, respectively, and is currently available through the Veterans Administration for veterans with PTSD. It is also covered by some commercial insurance plans.
“The underlying assumption [of CGRI] is that a person can learn to develop skills for controlling some of their physiological reactions that are triggered as a result of trauma,” said Dr. Telch.
The device uses a biofeedback approach to give patients “greater control over their physiological reactions, such as hyperventilation and increased respiration rate, and the focus is on providing a sense of mastery,” he said.
Participants with PTSD were assigned to a health coach. The device was delivered to the patient’s home, and patients met with the trained coach weekly and could check in between visits via text or e-mail. Twice-daily sessions were recommended.
“The coach gets feedback about what’s happening with the patient’s respiration and end-tidal CO2 levels [etCO2] and instructs participants how to keep their respiration rate and etCO2 at a more normal level,” said Dr. Telch.
The CGRI “teaches a specific breathing style via a system providing real-time feedback of respiratory rate (RR) and exhaled carbon dioxide levels facilitated by data capture,” the authors note.
Sense of mastery
Of the 1,569 participants, 1,395 had PD and 174 had PTSD (mean age, 39.2 [standard deviation, 13.9] years and 40.9 [SD, 14.9] years, respectively; 76% and 73% female, respectively). Those with PD completed the Panic Disorder Severity Scale (PDSS) and those with PTSD completed the Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), before and after the intervention.
The treatment response rate for PD was defined as a 40% or greater reduction in PDSS total scores, whereas treatment response rate for PTSD was defined as a 10-point or greater reduction in PCL-5 scores.
At baseline, patients were classified either as normocapnic or hypocapnic (etCO2 ≥ 37 or < 37, respectively), with 65% classified as normocapnic and 35% classified as hypocapnic.
Among patients with PD, there was a 50.2% mean pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PDSS scores (P < .001; d = 1.31), with a treatment response rate of 65.3% of patients.
Among patients with PTSD, there was a 41.1% pre- to posttreatment reduction in total PCL-5 scores (P < .001; d = 1.16), with a treatment response rate of 72.4%.
When investigators analyzed the response at the individual level, they found that 55.7% of patients with PD and 53.5% of those with PTSD were classified as treatment responders. This determination was based on a two-pronged approach that first calculated the Reliable Change Index (RCI) for each participant, and, in participants showing statistically reliable improvement, whether the posttreatment score was closer to the distribution of scores for patients without or with the given disorder.
“Patients with both normal and below-normal baseline exhaled CO2 levels experienced comparable benefit,” the authors report.
There were high levels of adherence across the full treatment period in both the PD and the PTSD groups (74.8% and 74.9%, respectively), with low dropout rates (10% and 11%, respectively).
“Not every single patient who undergoes any treatment has a perfect response, but the response rates to this treatment have, surprisingly, been quite positive and there have been no negative side effects,” Dr. Telch remarked.
He noted that one of the effects of PTSD is that the “patient has negative beliefs about their ability to control the world. ‘I can’t control my reactions. At any time, I could have a flashback.’ Helping the patient to develop any sense of mastery over some of their reactions can spill over and give them a greater sense of mastery and control, which can have a positive effect in reducing PTSD symptoms.”
‘A viable alternative’
Commenting on the research, Charles Marmar, MD, chair and Peter H. Schub Professor of Psychiatry, department of psychiatry, New York University, said that the study has some limitations, probably the most significant of which is that most participants had normal baseline CO2 levels.
“The treatment is fundamentally designed for people who hyperventilate and blow off too much CO2 so they can breathe in a more calm, relaxed way, but most people in the trial had normal CO2 to begin with,” said Dr. Marmar, who was not involved with the study.
“It’s likely that the major benefits were the relaxation from doing the breathing exercises rather than the change in CO2 levels,” he speculated.
The treatment is “probably a good thing for those patients who actually have abnormal CO2 levels. This treatment could be used in precision medicine, where you tailor treatments to those who actually need them rather than giving the same treatment to everyone,” he said.
“For patients who don’t respond to trauma-focused therapy or it’s too aversive for them to undergo, this new intervention provides a viable alternative,” Dr. Telch added.
The study was internally funded by Freespira. Dr. Telch is a scientific advisor at Freespira and receives compensation by way of stock options. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Marmar has declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FRONTIERS IN DIGITAL HEALTH
Visualization can improve sports performance
Over the past 30 years, Dr. Richard W. Cohen has used visualization techniques to help world class tennis players and recreational tennis players become the best they could be.
Visualization should be used in two ways to help players improve. First, to improve technique, after every practice session I have the player think about one shot they did not do well technically, and I have them, in vivo, shadow the shot on the court correctly before they leave the court. That night I tell the player to put themselves in a quiet, relaxed place and, in vitro, visualize themselves hitting the shot the correct way.
Almost always, the next day the players tell me they are hitting that one shot better and are motivated to again think about the one shot that was not technically correct and repeat the in vivo technique with similar great results.
The second way I use visualization for tennis players is to decrease their anxiety before matches. It is important to have some preparatory anxiety to perform optimally but having excessive anxiety will decrease performance. To alleviate excessive anxiety before matches, I have players watch their opponents hit the day before the match for at least 5 minutes to see their strengths and weaknesses. Then, the night before the match, I have them visualize how they will play a big point utilizing their strength into their opponent’s weakness. This rehearsal using imagery the night before a big match will decrease a player’s excessive anxiety and allow them to achieve their best effort in the match.
An example of this is if their opponent has a weak backhand that they can only slice. They visualize hitting wide to their forehand to get into their weak backhand and see themselves going forward and putting away a volley. Visualization used in these two ways helps improve stroke mechanics and match results in players of all levels. These visualization techniques can also be extended to other sports and to help improve life habits.
For example, Dr. Susan A. Cohen has seen that many patients have a decline in their dental health because of fear of going to the dentist to receive the treatment they need. Visualization techniques decrease the patient’s anxiety by rehearsing the possible traumatic events of the dental visit – e.g., the injection of anesthesia before the dental procedure. Visualization of calmness with systematic desensitization has helped decrease anxiety in patients.
In 20 years of clinical experience as a dentist, Dr. Cohen has seen how these techniques have increased compliance in her dental patients. She has also noted that visualizing the results of having a healthy mouth with improved appearance and function leads to an overall willingness to visit the dentist regularly and enjoy the dental experience. These examples demonstrate how visualization can enhance sports performance, quality of life, and overall health.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for over 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. He has won 18 USTA national tennis championships. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
Over the past 30 years, Dr. Richard W. Cohen has used visualization techniques to help world class tennis players and recreational tennis players become the best they could be.
Visualization should be used in two ways to help players improve. First, to improve technique, after every practice session I have the player think about one shot they did not do well technically, and I have them, in vivo, shadow the shot on the court correctly before they leave the court. That night I tell the player to put themselves in a quiet, relaxed place and, in vitro, visualize themselves hitting the shot the correct way.
Almost always, the next day the players tell me they are hitting that one shot better and are motivated to again think about the one shot that was not technically correct and repeat the in vivo technique with similar great results.
The second way I use visualization for tennis players is to decrease their anxiety before matches. It is important to have some preparatory anxiety to perform optimally but having excessive anxiety will decrease performance. To alleviate excessive anxiety before matches, I have players watch their opponents hit the day before the match for at least 5 minutes to see their strengths and weaknesses. Then, the night before the match, I have them visualize how they will play a big point utilizing their strength into their opponent’s weakness. This rehearsal using imagery the night before a big match will decrease a player’s excessive anxiety and allow them to achieve their best effort in the match.
An example of this is if their opponent has a weak backhand that they can only slice. They visualize hitting wide to their forehand to get into their weak backhand and see themselves going forward and putting away a volley. Visualization used in these two ways helps improve stroke mechanics and match results in players of all levels. These visualization techniques can also be extended to other sports and to help improve life habits.
For example, Dr. Susan A. Cohen has seen that many patients have a decline in their dental health because of fear of going to the dentist to receive the treatment they need. Visualization techniques decrease the patient’s anxiety by rehearsing the possible traumatic events of the dental visit – e.g., the injection of anesthesia before the dental procedure. Visualization of calmness with systematic desensitization has helped decrease anxiety in patients.
In 20 years of clinical experience as a dentist, Dr. Cohen has seen how these techniques have increased compliance in her dental patients. She has also noted that visualizing the results of having a healthy mouth with improved appearance and function leads to an overall willingness to visit the dentist regularly and enjoy the dental experience. These examples demonstrate how visualization can enhance sports performance, quality of life, and overall health.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for over 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. He has won 18 USTA national tennis championships. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
Over the past 30 years, Dr. Richard W. Cohen has used visualization techniques to help world class tennis players and recreational tennis players become the best they could be.
Visualization should be used in two ways to help players improve. First, to improve technique, after every practice session I have the player think about one shot they did not do well technically, and I have them, in vivo, shadow the shot on the court correctly before they leave the court. That night I tell the player to put themselves in a quiet, relaxed place and, in vitro, visualize themselves hitting the shot the correct way.
Almost always, the next day the players tell me they are hitting that one shot better and are motivated to again think about the one shot that was not technically correct and repeat the in vivo technique with similar great results.
The second way I use visualization for tennis players is to decrease their anxiety before matches. It is important to have some preparatory anxiety to perform optimally but having excessive anxiety will decrease performance. To alleviate excessive anxiety before matches, I have players watch their opponents hit the day before the match for at least 5 minutes to see their strengths and weaknesses. Then, the night before the match, I have them visualize how they will play a big point utilizing their strength into their opponent’s weakness. This rehearsal using imagery the night before a big match will decrease a player’s excessive anxiety and allow them to achieve their best effort in the match.
An example of this is if their opponent has a weak backhand that they can only slice. They visualize hitting wide to their forehand to get into their weak backhand and see themselves going forward and putting away a volley. Visualization used in these two ways helps improve stroke mechanics and match results in players of all levels. These visualization techniques can also be extended to other sports and to help improve life habits.
For example, Dr. Susan A. Cohen has seen that many patients have a decline in their dental health because of fear of going to the dentist to receive the treatment they need. Visualization techniques decrease the patient’s anxiety by rehearsing the possible traumatic events of the dental visit – e.g., the injection of anesthesia before the dental procedure. Visualization of calmness with systematic desensitization has helped decrease anxiety in patients.
In 20 years of clinical experience as a dentist, Dr. Cohen has seen how these techniques have increased compliance in her dental patients. She has also noted that visualizing the results of having a healthy mouth with improved appearance and function leads to an overall willingness to visit the dentist regularly and enjoy the dental experience. These examples demonstrate how visualization can enhance sports performance, quality of life, and overall health.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for over 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. He has won 18 USTA national tennis championships. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
What are the risk factors for Mohs surgery–related anxiety?
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
confirmed by a health care provider (HCP), results from a single-center survey demonstrated.
“Higher patient-reported anxiety in hospital settings is significantly linked to lower patient satisfaction with the quality of care and higher patient-reported postoperative pain,” corresponding author Ally-Khan Somani, MD, PhD, and colleagues wrote in the study, which was published online in Dermatologic Surgery. “Identifying factors associated with perioperative patient anxiety could improve outcomes and patient satisfaction.”
Dr. Somani, director of dermatologic surgery and cutaneous oncology in the department of dermatology at the University of Indiana, Indianapolis, and coauthors surveyed 145 patients who underwent Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) at the university from February 2018 to March 2020. They collected patient self-reported demographics, medical history, and administered a 10-point visual analog scale assessment of anxiety at multiple stages. They also sought HCP-perceived assessments of anxiety and used a stepwise regression mode to explore factors that potentially contributed to anxiety outcomes. The mean age of the 145 patients was 63 years, 60% were female, and 77% had no self-reported anxiety confirmed by a prior HCP’s diagnosis.
Two-thirds of patients (66%) received a pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon, 59% had a history of skin cancer removal surgery, and 86% had 1-2 layers removed during the current MMS.
Prior to MMS, the researchers found that significant risk factors for increased anxiety included younger age, female sex, and self-reported history of anxiety confirmed by an HCP (P < .05), while intraoperatively, HCP-perceived patient anxiety increased with younger patient age and more layers removed. Following MMS, patient anxiety increased significantly with more layers removed and higher self-reported preoperative anxiety levels. “Although existing research is divided regarding the efficacy of pre-MMS consultation for anxiety reduction, these findings suggest that patient-reported and HCP-perceived anxiety were not significantly affected by in-person pre-MMS consultation with the surgeon,” Dr. Somani and colleagues wrote. “Thus, routinely recommending consultations may not be the best approach for improving anxiety outcomes.”
They acknowledged certain limitations of their analysis, including its single-center design, enrollment of demographically similar patients, and the fact that no objective measurements of anxiety such as heart rate or blood pressure were taken.
“One of the main benefits of Mohs surgery is that we are able to operate under local anesthesia, but this also means that our patients are acutely aware of everything going on around them,” said Patricia M. Richey, MD, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and was asked to comment on the study.
“I think it is so important that this study is primarily focusing on the patient experience,” she said. “While this study did not find that a pre-op consult impacted patient anxiety levels, I do think we can infer that it is critical to connect with your patients on some level prior to surgery, as it helps you tailor your process to make the day more tolerable for them [such as] playing music, determining the need for an oral anxiolytic, etc.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Richey reported having financial disclosures.
FROM DERMATOLOGIC SURGERY
New guidelines say pediatricians should screen for anxiety: Now what?
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Recently the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force issued a formal recommendation that adolescents and children as young as 8 should be screened for anxiety.1 The advice was based on a review of the research that concluded that anxiety disorders were common in youth (prevalence around 8%), screening was not overly burdensome or dangerous, and treatments were available and effective.
While pediatricians fully appreciate how common clinically significant anxiety is and its impact on the lives of youth, the reception for the recommendations have been mixed. Some are concerned that it could lead to the overprescribing of medications. Arguably, the biggest pushback, however, relates to the question of what to do when a child screens positive in a time when finding an available child and adolescent psychiatrist or other type of pediatric mental health professional can feel next to impossible. The hope of this article is to fill in some of those gaps.
Screening for anxiety disorders
The recommendations suggest using a rating scale as part of the screen but doesn’t dictate which one. A common instrument that has been employed is the Screen for Child Anxiety and Related Disorders, which is a freely available 41-item instrument that has versions for youth self-report and parent-report. A shorter 7-item rating scale, the General Anxiety Disorder–7, and the even shorter GAD-2 (the first two questions of the GAD-7), are also popular but focus, as the name applies, on general anxiety disorder and not related conditions such as social or separation anxiety that can have some different symptoms. These instruments can be given to patients and families in the waiting room or administered with the help of a nurse, physician, or embedded mental health professional. The recommendations do not include specific guidance on how often the screening should be done but repeated screenings are likely important at some interval.
Confirming the diagnosis
Of course, a screening isn’t a formal diagnosis. The American Academy of Pediatrics has expressed the view that the initial diagnosis and treatment for anxiety disorders is well within a pediatrician’s scope of practice, which means further steps are likely required beyond a referral. Fortunately, going from a positive screen to an initial diagnosis does not have to overly laborious and can focus on reviewing the DSM-5 criteria for key anxiety disorders while also ensuring that there isn’t a nonpsychiatric cause driving the symptoms, such as the often cited but rarely seen pheochromocytoma. More common rule-outs include medication-induced anxiety or substance use, excessive caffeine intake, and cardiac arrhythmias. Assessing for current and past trauma or specific causes of the anxiety such as bullying are also important.
It is important to note that it is the rule rather than the exception that youth with clinical levels of anxiety will frequently endorse a number of criteria that span multiple diagnoses including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and separation anxiety disorder.2 Spending a lot of effort to narrow things down to a single anxiety diagnosis often is unnecessary, as both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatments don’t change all that much between individual diagnoses.
Explaining the diagnosis
In general, I’m a strong proponent of trying to explain any behavioral diagnoses that you make to kids in a way that is accurate but nonstigmatizing. When it comes to anxiety, one parallel I often draw is to our immune system, which most youth understand at least in basic terms. Both our immune system and our anxiety networks are natural and important; as a species, we wouldn’t have lasted long without them. Both are built to assess and respond to threats. Problems can arise, however, if the response is too strong relative to the threat or the response is activated when it doesn’t need to be. Treatment is directed not at ridding ourselves of anxiety but at helping regulate it so it works for us and not against us. Spending a few minutes going through a discussion like this can be very helpful, and perhaps more so than some dry summary of DSM-5 criteria.
Starting treatment
It is important to note that best practice recommendations when it comes to the treatment of anxiety disorder in youth do not suggest medications as the only type of treatment and often urge clinicians to try nonpharmacological interventions first.3 A specific type of psychotherapy called cognitive-behavioral therapy has the strongest scientific support as an effective treatment for anxiety but other modalities, including parenting guidance, can be helpful as well. Consequently, a referral to a good psychotherapist is paramount. For many kids, the key to overcoming anxiety is exposure: which means confronting anxiety slowly, with support, and with specific skills.
If there is a traumatic source of the anxiety, addressing that as much as possible is obviously critical and could involve working with the family or school. For some kids, this may involve frightening things they are seeing online or through other media. Finally, some health promotion activities such as exercise or mindfulness can also be quite useful.
Despite the fact that SSRIs are referred to as antidepressants, there is increasing appreciation that these medications are useful for anxiety, perhaps even more so than for mood. While only one medication, duloxetine, has Food and Drug Administration approval to treat anxiety in children as young as 7, there is good evidence to support the use of many of the most common SSRIs in treating clinical anxiety. Buspirone, beta-blockers, and antihistamine medications like hydroxyzine also can have their place in treatment, while benzodiazepines and antipsychotic medications are generally best avoided for anxious youth, especially in the primary care setting. A short but helpful medication guide with regard to pediatric anxiety has been published by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.4
Conclusions
Clinical levels of anxiety in children and adolescents are both common and quite treatable, which has prompted new recommendations that primary care clinicians screen for them starting at age 8. While this recommendation may at first seem like yet one more task to fit in, following the guidance can be accomplished with the help of short screening tools and a managed multimodal approach to treatment.
Dr. Rettew is a child and adolescent psychiatrist with Lane County Behavioral Health in Eugene, Ore., and Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. You can follow him on Twitter and Facebook @PediPsych.
References
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;328(14):1438-44.
2. Strawn JR. Curr Psychiatry. 2012;11(9):16-21.
3. Walter HJ et al. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(10):1107-24.
4. Anxiety Disorders: Parents’ Medication Guide Workgroup. “Anxiety disorders: Parents’ medication guide.” Washington D.C.: American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 2020.
Scurvy in psychiatric patients: An easy-to-miss diagnosis
Two years ago, I cared for Ms. L, a woman in her late 40s who had a history of generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. Unable to work and highly distressed throughout the day, Ms. L was admitted to our psychiatric unit due to her functional decompensation and symptom severity.
Ms. L was extremely focused on physical symptoms. She had rigid rules regarding which beauty products she could and could not use (she insisted most soaps gave her a rash, though she did not have any clear documentation of this) as well as the types of food she could and could not eat due to fear of an allergic reaction (skin testing was negative for the foods she claimed were problematic, though this did not change her selective eating habits). By the time she was admitted to our unit, in addition to outpatient mental health, she was being treated by internal medicine, allergy and immunology, and dermatology, with largely equivocal objective findings.
During her psychiatric admission intake, Ms. L mentioned that due to her fear of anaphylaxis, she hadn’t eaten any fruits or vegetables for at least 2 years. As a result, I ordered testing of her vitamin C level.
Three days following admission, Ms. L requested to be discharged because she said she needed to care for her pet. She reported feeling less anxious, and because the treatment team felt she did not meet the criteria for an involuntary hold, she was discharged. A week later, the results of her vitamin C level came back, indicating a severe deficiency (<0.1 mg/dL; reference range: 0.3 to 2.7 mg/dL). I contacted her outpatient team, and vitamin C supplementation was started immediately.
Notes from Ms. L’s subsequent outpatient mental health visits indicated improvement in her somatic symptoms (less perseveration), although over the next year her scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 scales were largely unchanged (fluctuating within the range of 11 to 17 and 12 to 17, respectively). One year later, Ms. L stopped taking vitamin C supplements because she was afraid she was becoming allergic to them, though there was no objective evidence to support this belief. Her vitamin C levels were within the normal range at the time and have not been rechecked since then.
Ms. L’s obsession with “healthy eating” led to numerous red herrings for clinicians, as she was anxious about every food. Countertransference and feelings of frustration may have also led clinicians in multiple specialties to miss the diagnosis of scurvy. Vitamin C supplementation did not result in remission of Ms. L’s symptoms, which reflects the complexity and severity of her comorbid psychiatric illnesses. However, a decrease in her perseveration on somatic symptoms afforded increased opportunities to address her other psychiatric diagnoses. Ms. L eventually enrolled in an eating disorders program, which was beneficial to her.
Keep scurvy in the differential Dx
Symptoms of scurvy include malaise; lethargy; anemia; myalgia; bone pain; easy bruising; petechiae and perifollicular hemorrhages (due to capillary fragility); gum disease; mood changes; and depression.1 In later stages, the presentation can progress to edema; jaundice; hemolysis and spontaneous bleeding; neuropathy; fever; convulsions; and death.
1. Léger D. Scurvy: reemergence of nutritional deficiencies. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(10):1403-1406.
2. Velandia B, Centor RM, McConnell V, et al. Scurvy is still present in developed countries. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(8):1281-1284.
3. Meisel K, Daggubati S, Josephson SA. Scurvy in the 21st century? Vitamin C deficiency presenting to the neurologist. Neurol Clin Pract. 2015;5(6):491-493.
Two years ago, I cared for Ms. L, a woman in her late 40s who had a history of generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. Unable to work and highly distressed throughout the day, Ms. L was admitted to our psychiatric unit due to her functional decompensation and symptom severity.
Ms. L was extremely focused on physical symptoms. She had rigid rules regarding which beauty products she could and could not use (she insisted most soaps gave her a rash, though she did not have any clear documentation of this) as well as the types of food she could and could not eat due to fear of an allergic reaction (skin testing was negative for the foods she claimed were problematic, though this did not change her selective eating habits). By the time she was admitted to our unit, in addition to outpatient mental health, she was being treated by internal medicine, allergy and immunology, and dermatology, with largely equivocal objective findings.
During her psychiatric admission intake, Ms. L mentioned that due to her fear of anaphylaxis, she hadn’t eaten any fruits or vegetables for at least 2 years. As a result, I ordered testing of her vitamin C level.
Three days following admission, Ms. L requested to be discharged because she said she needed to care for her pet. She reported feeling less anxious, and because the treatment team felt she did not meet the criteria for an involuntary hold, she was discharged. A week later, the results of her vitamin C level came back, indicating a severe deficiency (<0.1 mg/dL; reference range: 0.3 to 2.7 mg/dL). I contacted her outpatient team, and vitamin C supplementation was started immediately.
Notes from Ms. L’s subsequent outpatient mental health visits indicated improvement in her somatic symptoms (less perseveration), although over the next year her scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 scales were largely unchanged (fluctuating within the range of 11 to 17 and 12 to 17, respectively). One year later, Ms. L stopped taking vitamin C supplements because she was afraid she was becoming allergic to them, though there was no objective evidence to support this belief. Her vitamin C levels were within the normal range at the time and have not been rechecked since then.
Ms. L’s obsession with “healthy eating” led to numerous red herrings for clinicians, as she was anxious about every food. Countertransference and feelings of frustration may have also led clinicians in multiple specialties to miss the diagnosis of scurvy. Vitamin C supplementation did not result in remission of Ms. L’s symptoms, which reflects the complexity and severity of her comorbid psychiatric illnesses. However, a decrease in her perseveration on somatic symptoms afforded increased opportunities to address her other psychiatric diagnoses. Ms. L eventually enrolled in an eating disorders program, which was beneficial to her.
Keep scurvy in the differential Dx
Symptoms of scurvy include malaise; lethargy; anemia; myalgia; bone pain; easy bruising; petechiae and perifollicular hemorrhages (due to capillary fragility); gum disease; mood changes; and depression.1 In later stages, the presentation can progress to edema; jaundice; hemolysis and spontaneous bleeding; neuropathy; fever; convulsions; and death.
Two years ago, I cared for Ms. L, a woman in her late 40s who had a history of generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. Unable to work and highly distressed throughout the day, Ms. L was admitted to our psychiatric unit due to her functional decompensation and symptom severity.
Ms. L was extremely focused on physical symptoms. She had rigid rules regarding which beauty products she could and could not use (she insisted most soaps gave her a rash, though she did not have any clear documentation of this) as well as the types of food she could and could not eat due to fear of an allergic reaction (skin testing was negative for the foods she claimed were problematic, though this did not change her selective eating habits). By the time she was admitted to our unit, in addition to outpatient mental health, she was being treated by internal medicine, allergy and immunology, and dermatology, with largely equivocal objective findings.
During her psychiatric admission intake, Ms. L mentioned that due to her fear of anaphylaxis, she hadn’t eaten any fruits or vegetables for at least 2 years. As a result, I ordered testing of her vitamin C level.
Three days following admission, Ms. L requested to be discharged because she said she needed to care for her pet. She reported feeling less anxious, and because the treatment team felt she did not meet the criteria for an involuntary hold, she was discharged. A week later, the results of her vitamin C level came back, indicating a severe deficiency (<0.1 mg/dL; reference range: 0.3 to 2.7 mg/dL). I contacted her outpatient team, and vitamin C supplementation was started immediately.
Notes from Ms. L’s subsequent outpatient mental health visits indicated improvement in her somatic symptoms (less perseveration), although over the next year her scores on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 scales were largely unchanged (fluctuating within the range of 11 to 17 and 12 to 17, respectively). One year later, Ms. L stopped taking vitamin C supplements because she was afraid she was becoming allergic to them, though there was no objective evidence to support this belief. Her vitamin C levels were within the normal range at the time and have not been rechecked since then.
Ms. L’s obsession with “healthy eating” led to numerous red herrings for clinicians, as she was anxious about every food. Countertransference and feelings of frustration may have also led clinicians in multiple specialties to miss the diagnosis of scurvy. Vitamin C supplementation did not result in remission of Ms. L’s symptoms, which reflects the complexity and severity of her comorbid psychiatric illnesses. However, a decrease in her perseveration on somatic symptoms afforded increased opportunities to address her other psychiatric diagnoses. Ms. L eventually enrolled in an eating disorders program, which was beneficial to her.
Keep scurvy in the differential Dx
Symptoms of scurvy include malaise; lethargy; anemia; myalgia; bone pain; easy bruising; petechiae and perifollicular hemorrhages (due to capillary fragility); gum disease; mood changes; and depression.1 In later stages, the presentation can progress to edema; jaundice; hemolysis and spontaneous bleeding; neuropathy; fever; convulsions; and death.
1. Léger D. Scurvy: reemergence of nutritional deficiencies. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(10):1403-1406.
2. Velandia B, Centor RM, McConnell V, et al. Scurvy is still present in developed countries. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(8):1281-1284.
3. Meisel K, Daggubati S, Josephson SA. Scurvy in the 21st century? Vitamin C deficiency presenting to the neurologist. Neurol Clin Pract. 2015;5(6):491-493.
1. Léger D. Scurvy: reemergence of nutritional deficiencies. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54(10):1403-1406.
2. Velandia B, Centor RM, McConnell V, et al. Scurvy is still present in developed countries. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(8):1281-1284.
3. Meisel K, Daggubati S, Josephson SA. Scurvy in the 21st century? Vitamin C deficiency presenting to the neurologist. Neurol Clin Pract. 2015;5(6):491-493.
The importance of connection and community
You only are free when you realize you belong no place – you belong every place – no place at all. The price is high. The reward is great. ~ Maya Angelou
At 8 o’clock, every weekday morning, for years and years now, two friends appear in my kitchen for coffee, and so one identity I carry includes being part of the “coffee ladies.” While this is one of the smaller and more intimate groups to which I belong, I am also a member (“distinguished,” no less) of a slightly larger group: the American Psychiatric Association, and being part of both groups is meaningful to me in more ways than I can describe.
When I think back over the years, I – like most people – have belonged to many people and places, either officially or unofficially. It is these connections that define us, fill our time, give us meaning and purpose, and anchor us. We belong to our families and friends, but we also belong to our professional and community groups, our institutions – whether they are hospitals, schools, religious centers, country clubs, or charitable organizations – as well as interest and advocacy groups. And finally, we belong to our coworkers and to our patients, and they to us, especially if we see the same people over time. Being a psychiatrist can be a solitary career, and it can take a little effort to be a part of larger worlds, especially for those who find solace in more individual activities.
As I’ve gotten older, I’ve noticed that I belong to fewer of these groups. I’m no longer a little league or field hockey mom, nor a member of the neighborhood babysitting co-op, and I’ve exhausted the gamut of council and leadership positions in my APA district branch. I’ve joined organizations only to pay the membership fee, and then never gone to their meetings or events. The pandemic has accounted for some of this: I still belong to my book club, but I often read the book and don’t go to the Zoom meetings as I miss the real-life aspect of getting together. Being boxed on a screen is not the same as the one-on-one conversations before the formal book discussion. And while I still carry a host of identities, I imagine it is not unusual to belong to fewer organizations as time passes. It’s not all bad, there is something good to be said for living life at a less frenetic pace as fewer entities lay claim to my time.
In psychiatry, our patients span the range of human experience: Some are very engaged with their worlds, while others struggle to make even the most basic of connections. Their lives may seem disconnected – empty, even – and I find myself encouraging people to reach out, to find activities that will ease their loneliness and integrate a feeling of belonging in a way that adds meaning and purpose. For some people, this may be as simple as asking a friend to have lunch, but even that can be an overwhelming obstacle for someone who is depressed, or for someone who has no friends.
Patients may counter my suggestions with a host of reasons as to why they can’t connect. Perhaps their friend is too busy with work or his family, the lunch would cost too much, there’s no transportation, or no restaurant that could meet their dietary needs. Or perhaps they are just too fearful of being rejected.
Psychiatric disorders, by their nature, can be very isolating. Depressed and anxious people often find it a struggle just to get through their days, adding new people and activities is not something that brings joy. For people suffering with psychosis, their internal realities are often all-consuming and there may be no room for accommodating others. And finally, what I hear over and over, is that people are afraid of what others might think of them, and this fear is paralyzing. I try to suggest that we never really know or control what others think of us, but obviously, this does not reassure most patients as they are also bewildered by their irrational fear. To go to an event unaccompanied, or even to a party to which they have been invited, is a hurdle they won’t (or can’t) attempt.
The pandemic, with its initial months of shutdown, and then with years of fear of illness, has created new ways of connecting. Our “Zoom” world can be very convenient – in many ways it has opened up aspects of learning and connection for people who are short on time,or struggle with transportation. In the comfort of our living rooms, in pajamas and slippers, we can take classes, join clubs, attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings, go to conferences or religious services, and be part of any number of organizations without flying or searching for parking. I love that, with 1 hour and a single click, I can now attend my department’s weekly Grand Rounds. But for many who struggle with using technology, or who don’t feel the same benefits from online encounters, the pandemic has been an isolating and lonely time.
It should not be assumed that isolation has been a negative experience for everyone. For many who struggle with interpersonal relationships, for children who are bullied or teased at school or who feel self-conscious sitting alone at lunch, there may not be the presumed “fear of missing out.” As one adult patient told me: “You know, I do ‘alone’ well.” For some, it has been a relief to be relieved of the pressure to socialize, attend parties, or pursue online dating – a process I think of as “people-shopping” which looks so different from the old days of organic interactions that led to romantic interactions over time. Many have found relief without the pressures of social interactions.
Community, connection, and belonging are not inconsequential things, however. They are part of what adds to life’s richness, and they are associated with good health and longevity. The Harvard Study of Adult Development, begun in 1938, has been tracking two groups of Boston teenagers – and now their wives and children – for 84 years. Tracking one group of Harvard students and another group of teens from poorer areas in Boston, the project is now on its 4th director.
George Vaillant, MD, author of “Aging Well: Surprising Guideposts to a Happier Life from the Landmark Harvard Study of Adult Development” (New York: Little, Brown Spark, 2002) was the program’s director from 1972 to 2004. “When the study began, nobody cared about empathy or attachment. But the key to healthy aging is relationships, relationships, relationships,” Dr. Vaillant said in an interview in the Harvard Gazette.
Susan Pinker is a social psychologist and author of “The Village Effect: How Face-to-Face Contact Can Make Us Healthier and Happier” (Toronto: Random House Canada, 2014). In her 2017 TED talk, she notes that in all developed countries, women live 6-8 years longer than men, and are half as likely to die at any age. She is underwhelmed by digital relationships, and says that real life relationships affect our physiological states differently and in more beneficial ways. “Building your village and sustaining it is a matter of life and death,” she states at the end of her TED talk.
I spoke with Ms. Pinker about her thoughts on how our personal villages change over time. She was quick to tell me that she is not against digital communities. “I’m not a Luddite. As a writer, I probably spend as much time facing a screen as anyone else. But it’s important to remember that digital communities can amplify existing relationships, and don’t replace in-person social contact. A lot of people have drunk the Kool-Aid about virtual experiences, even though they are not the same as real life interactions.
“Loneliness takes on a U-shaped function across adulthood,” she explained with regard to how age impacts our social connections. “People are lonely when they first leave home or when they finish college and go out into the world. Then they settle into new situations; they can make friends at work, through their children, in their neighborhood, or by belonging to organizations. As people settle into their adult lives, there are increased opportunities to connect in person. But loneliness increases again in late middle age.” She explained that everyone loses people as their children move away, friends move, and couples may divorce or a spouse dies.
“Attrition of our social face-to-face networks is an ugly feature of aging,” Ms. Pinker said. “Some people are good at replacing the vacant spots; they sense that it is important to invest in different relationships as you age. It’s like a garden that you need to tend by replacing the perennials that die off in the winter.” The United States, she pointed out, has a culture that is particularly difficult for people in their later years.
My world is a little quieter than it once was, but collecting and holding on to people is important to me. The organizations and affiliations change over time, as does the brand of coffee. So I try to inspire some of my more isolated patients to prioritize their relationships, to let go of their grudges, to tolerate the discomfort of moving from their places of comfort to the temporary discomfort of reaching out in the service of achieving a less solitary, more purposeful, and healthier life. When it doesn’t come naturally, it can be hard work.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
You only are free when you realize you belong no place – you belong every place – no place at all. The price is high. The reward is great. ~ Maya Angelou
At 8 o’clock, every weekday morning, for years and years now, two friends appear in my kitchen for coffee, and so one identity I carry includes being part of the “coffee ladies.” While this is one of the smaller and more intimate groups to which I belong, I am also a member (“distinguished,” no less) of a slightly larger group: the American Psychiatric Association, and being part of both groups is meaningful to me in more ways than I can describe.
When I think back over the years, I – like most people – have belonged to many people and places, either officially or unofficially. It is these connections that define us, fill our time, give us meaning and purpose, and anchor us. We belong to our families and friends, but we also belong to our professional and community groups, our institutions – whether they are hospitals, schools, religious centers, country clubs, or charitable organizations – as well as interest and advocacy groups. And finally, we belong to our coworkers and to our patients, and they to us, especially if we see the same people over time. Being a psychiatrist can be a solitary career, and it can take a little effort to be a part of larger worlds, especially for those who find solace in more individual activities.
As I’ve gotten older, I’ve noticed that I belong to fewer of these groups. I’m no longer a little league or field hockey mom, nor a member of the neighborhood babysitting co-op, and I’ve exhausted the gamut of council and leadership positions in my APA district branch. I’ve joined organizations only to pay the membership fee, and then never gone to their meetings or events. The pandemic has accounted for some of this: I still belong to my book club, but I often read the book and don’t go to the Zoom meetings as I miss the real-life aspect of getting together. Being boxed on a screen is not the same as the one-on-one conversations before the formal book discussion. And while I still carry a host of identities, I imagine it is not unusual to belong to fewer organizations as time passes. It’s not all bad, there is something good to be said for living life at a less frenetic pace as fewer entities lay claim to my time.
In psychiatry, our patients span the range of human experience: Some are very engaged with their worlds, while others struggle to make even the most basic of connections. Their lives may seem disconnected – empty, even – and I find myself encouraging people to reach out, to find activities that will ease their loneliness and integrate a feeling of belonging in a way that adds meaning and purpose. For some people, this may be as simple as asking a friend to have lunch, but even that can be an overwhelming obstacle for someone who is depressed, or for someone who has no friends.
Patients may counter my suggestions with a host of reasons as to why they can’t connect. Perhaps their friend is too busy with work or his family, the lunch would cost too much, there’s no transportation, or no restaurant that could meet their dietary needs. Or perhaps they are just too fearful of being rejected.
Psychiatric disorders, by their nature, can be very isolating. Depressed and anxious people often find it a struggle just to get through their days, adding new people and activities is not something that brings joy. For people suffering with psychosis, their internal realities are often all-consuming and there may be no room for accommodating others. And finally, what I hear over and over, is that people are afraid of what others might think of them, and this fear is paralyzing. I try to suggest that we never really know or control what others think of us, but obviously, this does not reassure most patients as they are also bewildered by their irrational fear. To go to an event unaccompanied, or even to a party to which they have been invited, is a hurdle they won’t (or can’t) attempt.
The pandemic, with its initial months of shutdown, and then with years of fear of illness, has created new ways of connecting. Our “Zoom” world can be very convenient – in many ways it has opened up aspects of learning and connection for people who are short on time,or struggle with transportation. In the comfort of our living rooms, in pajamas and slippers, we can take classes, join clubs, attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings, go to conferences or religious services, and be part of any number of organizations without flying or searching for parking. I love that, with 1 hour and a single click, I can now attend my department’s weekly Grand Rounds. But for many who struggle with using technology, or who don’t feel the same benefits from online encounters, the pandemic has been an isolating and lonely time.
It should not be assumed that isolation has been a negative experience for everyone. For many who struggle with interpersonal relationships, for children who are bullied or teased at school or who feel self-conscious sitting alone at lunch, there may not be the presumed “fear of missing out.” As one adult patient told me: “You know, I do ‘alone’ well.” For some, it has been a relief to be relieved of the pressure to socialize, attend parties, or pursue online dating – a process I think of as “people-shopping” which looks so different from the old days of organic interactions that led to romantic interactions over time. Many have found relief without the pressures of social interactions.
Community, connection, and belonging are not inconsequential things, however. They are part of what adds to life’s richness, and they are associated with good health and longevity. The Harvard Study of Adult Development, begun in 1938, has been tracking two groups of Boston teenagers – and now their wives and children – for 84 years. Tracking one group of Harvard students and another group of teens from poorer areas in Boston, the project is now on its 4th director.
George Vaillant, MD, author of “Aging Well: Surprising Guideposts to a Happier Life from the Landmark Harvard Study of Adult Development” (New York: Little, Brown Spark, 2002) was the program’s director from 1972 to 2004. “When the study began, nobody cared about empathy or attachment. But the key to healthy aging is relationships, relationships, relationships,” Dr. Vaillant said in an interview in the Harvard Gazette.
Susan Pinker is a social psychologist and author of “The Village Effect: How Face-to-Face Contact Can Make Us Healthier and Happier” (Toronto: Random House Canada, 2014). In her 2017 TED talk, she notes that in all developed countries, women live 6-8 years longer than men, and are half as likely to die at any age. She is underwhelmed by digital relationships, and says that real life relationships affect our physiological states differently and in more beneficial ways. “Building your village and sustaining it is a matter of life and death,” she states at the end of her TED talk.
I spoke with Ms. Pinker about her thoughts on how our personal villages change over time. She was quick to tell me that she is not against digital communities. “I’m not a Luddite. As a writer, I probably spend as much time facing a screen as anyone else. But it’s important to remember that digital communities can amplify existing relationships, and don’t replace in-person social contact. A lot of people have drunk the Kool-Aid about virtual experiences, even though they are not the same as real life interactions.
“Loneliness takes on a U-shaped function across adulthood,” she explained with regard to how age impacts our social connections. “People are lonely when they first leave home or when they finish college and go out into the world. Then they settle into new situations; they can make friends at work, through their children, in their neighborhood, or by belonging to organizations. As people settle into their adult lives, there are increased opportunities to connect in person. But loneliness increases again in late middle age.” She explained that everyone loses people as their children move away, friends move, and couples may divorce or a spouse dies.
“Attrition of our social face-to-face networks is an ugly feature of aging,” Ms. Pinker said. “Some people are good at replacing the vacant spots; they sense that it is important to invest in different relationships as you age. It’s like a garden that you need to tend by replacing the perennials that die off in the winter.” The United States, she pointed out, has a culture that is particularly difficult for people in their later years.
My world is a little quieter than it once was, but collecting and holding on to people is important to me. The organizations and affiliations change over time, as does the brand of coffee. So I try to inspire some of my more isolated patients to prioritize their relationships, to let go of their grudges, to tolerate the discomfort of moving from their places of comfort to the temporary discomfort of reaching out in the service of achieving a less solitary, more purposeful, and healthier life. When it doesn’t come naturally, it can be hard work.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
You only are free when you realize you belong no place – you belong every place – no place at all. The price is high. The reward is great. ~ Maya Angelou
At 8 o’clock, every weekday morning, for years and years now, two friends appear in my kitchen for coffee, and so one identity I carry includes being part of the “coffee ladies.” While this is one of the smaller and more intimate groups to which I belong, I am also a member (“distinguished,” no less) of a slightly larger group: the American Psychiatric Association, and being part of both groups is meaningful to me in more ways than I can describe.
When I think back over the years, I – like most people – have belonged to many people and places, either officially or unofficially. It is these connections that define us, fill our time, give us meaning and purpose, and anchor us. We belong to our families and friends, but we also belong to our professional and community groups, our institutions – whether they are hospitals, schools, religious centers, country clubs, or charitable organizations – as well as interest and advocacy groups. And finally, we belong to our coworkers and to our patients, and they to us, especially if we see the same people over time. Being a psychiatrist can be a solitary career, and it can take a little effort to be a part of larger worlds, especially for those who find solace in more individual activities.
As I’ve gotten older, I’ve noticed that I belong to fewer of these groups. I’m no longer a little league or field hockey mom, nor a member of the neighborhood babysitting co-op, and I’ve exhausted the gamut of council and leadership positions in my APA district branch. I’ve joined organizations only to pay the membership fee, and then never gone to their meetings or events. The pandemic has accounted for some of this: I still belong to my book club, but I often read the book and don’t go to the Zoom meetings as I miss the real-life aspect of getting together. Being boxed on a screen is not the same as the one-on-one conversations before the formal book discussion. And while I still carry a host of identities, I imagine it is not unusual to belong to fewer organizations as time passes. It’s not all bad, there is something good to be said for living life at a less frenetic pace as fewer entities lay claim to my time.
In psychiatry, our patients span the range of human experience: Some are very engaged with their worlds, while others struggle to make even the most basic of connections. Their lives may seem disconnected – empty, even – and I find myself encouraging people to reach out, to find activities that will ease their loneliness and integrate a feeling of belonging in a way that adds meaning and purpose. For some people, this may be as simple as asking a friend to have lunch, but even that can be an overwhelming obstacle for someone who is depressed, or for someone who has no friends.
Patients may counter my suggestions with a host of reasons as to why they can’t connect. Perhaps their friend is too busy with work or his family, the lunch would cost too much, there’s no transportation, or no restaurant that could meet their dietary needs. Or perhaps they are just too fearful of being rejected.
Psychiatric disorders, by their nature, can be very isolating. Depressed and anxious people often find it a struggle just to get through their days, adding new people and activities is not something that brings joy. For people suffering with psychosis, their internal realities are often all-consuming and there may be no room for accommodating others. And finally, what I hear over and over, is that people are afraid of what others might think of them, and this fear is paralyzing. I try to suggest that we never really know or control what others think of us, but obviously, this does not reassure most patients as they are also bewildered by their irrational fear. To go to an event unaccompanied, or even to a party to which they have been invited, is a hurdle they won’t (or can’t) attempt.
The pandemic, with its initial months of shutdown, and then with years of fear of illness, has created new ways of connecting. Our “Zoom” world can be very convenient – in many ways it has opened up aspects of learning and connection for people who are short on time,or struggle with transportation. In the comfort of our living rooms, in pajamas and slippers, we can take classes, join clubs, attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings, go to conferences or religious services, and be part of any number of organizations without flying or searching for parking. I love that, with 1 hour and a single click, I can now attend my department’s weekly Grand Rounds. But for many who struggle with using technology, or who don’t feel the same benefits from online encounters, the pandemic has been an isolating and lonely time.
It should not be assumed that isolation has been a negative experience for everyone. For many who struggle with interpersonal relationships, for children who are bullied or teased at school or who feel self-conscious sitting alone at lunch, there may not be the presumed “fear of missing out.” As one adult patient told me: “You know, I do ‘alone’ well.” For some, it has been a relief to be relieved of the pressure to socialize, attend parties, or pursue online dating – a process I think of as “people-shopping” which looks so different from the old days of organic interactions that led to romantic interactions over time. Many have found relief without the pressures of social interactions.
Community, connection, and belonging are not inconsequential things, however. They are part of what adds to life’s richness, and they are associated with good health and longevity. The Harvard Study of Adult Development, begun in 1938, has been tracking two groups of Boston teenagers – and now their wives and children – for 84 years. Tracking one group of Harvard students and another group of teens from poorer areas in Boston, the project is now on its 4th director.
George Vaillant, MD, author of “Aging Well: Surprising Guideposts to a Happier Life from the Landmark Harvard Study of Adult Development” (New York: Little, Brown Spark, 2002) was the program’s director from 1972 to 2004. “When the study began, nobody cared about empathy or attachment. But the key to healthy aging is relationships, relationships, relationships,” Dr. Vaillant said in an interview in the Harvard Gazette.
Susan Pinker is a social psychologist and author of “The Village Effect: How Face-to-Face Contact Can Make Us Healthier and Happier” (Toronto: Random House Canada, 2014). In her 2017 TED talk, she notes that in all developed countries, women live 6-8 years longer than men, and are half as likely to die at any age. She is underwhelmed by digital relationships, and says that real life relationships affect our physiological states differently and in more beneficial ways. “Building your village and sustaining it is a matter of life and death,” she states at the end of her TED talk.
I spoke with Ms. Pinker about her thoughts on how our personal villages change over time. She was quick to tell me that she is not against digital communities. “I’m not a Luddite. As a writer, I probably spend as much time facing a screen as anyone else. But it’s important to remember that digital communities can amplify existing relationships, and don’t replace in-person social contact. A lot of people have drunk the Kool-Aid about virtual experiences, even though they are not the same as real life interactions.
“Loneliness takes on a U-shaped function across adulthood,” she explained with regard to how age impacts our social connections. “People are lonely when they first leave home or when they finish college and go out into the world. Then they settle into new situations; they can make friends at work, through their children, in their neighborhood, or by belonging to organizations. As people settle into their adult lives, there are increased opportunities to connect in person. But loneliness increases again in late middle age.” She explained that everyone loses people as their children move away, friends move, and couples may divorce or a spouse dies.
“Attrition of our social face-to-face networks is an ugly feature of aging,” Ms. Pinker said. “Some people are good at replacing the vacant spots; they sense that it is important to invest in different relationships as you age. It’s like a garden that you need to tend by replacing the perennials that die off in the winter.” The United States, she pointed out, has a culture that is particularly difficult for people in their later years.
My world is a little quieter than it once was, but collecting and holding on to people is important to me. The organizations and affiliations change over time, as does the brand of coffee. So I try to inspire some of my more isolated patients to prioritize their relationships, to let go of their grudges, to tolerate the discomfort of moving from their places of comfort to the temporary discomfort of reaching out in the service of achieving a less solitary, more purposeful, and healthier life. When it doesn’t come naturally, it can be hard work.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Meditation equal to first-line medication for anxiety
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“I would encourage clinicians to list meditation training as one possible treatment option for patients who are diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Doctors should feel comfortable recommending in-person, group-based meditation classes,” study investigator Elizabeth A. Hoge, MD, director, Anxiety Disorders Research Program, Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Screening recommended
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, panic disorder, and agoraphobia, are the most common type of mental disorder, affecting an estimated 301 million people worldwide. Owing to their high prevalence, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening for anxiety disorders.
Effective treatments for anxiety disorders include medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy. However, not all patients have access to these interventions, respond to them, or are comfortable seeking care in a psychiatric setting.
Mindfulness meditation, which has risen in popularity in recent years, may help people experiencing intrusive, anxious thoughts. “By practicing mindfulness meditation, people learn not to be overwhelmed by those thoughts,” said Dr. Hoge.
The study included 276 adult patients with an anxiety disorder, mostly generalized anxiety or social anxiety. The mean age of the study population was 33 years; 75% were women, 59% were White, 15% were Black, and 20% were Asian.
Researchers randomly assigned 136 patients to receive MBSR and 140 to receive the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor escitalopram, a first-line medication for treating anxiety disorders.
The MBSR intervention included a weekly 2.5-hour class and a day-long weekend class. Participants also completed daily 45-minute guided meditation sessions at home. They learned mindfulness meditation exercises, including breath awareness, body scanning, and mindful movement.
Those in the escitalopram group initially received 10 mg of the oral drug daily. The dose was increased to 20 mg daily at week 2 if well tolerated.
The primary outcome was the score on the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale for anxiety, assessed by clinicians blinded to treatment allocation. This instrument measures overall symptom severity on a scale from 1 (not at all ill) to 7 (most extremely ill) and can be used to assess different types of anxiety disorders, said Dr. Hoge.
Among the 208 participants who completed the study, the baseline mean CGI-S score was 4.44 for MBSR and 4.51 for escitalopram. At week 8, on the CGI-S scale, the MBSR group’s score improved by a mean of 1.35 points, and the escitalopram group’s score improved by 1.43 points (difference of –0.07; 95% CI, –0.38 to 0.23; P = .65).
The lower end of the confidence interval (–0.38) was smaller than the prespecified noninferiority margin of –0.495, indicating noninferiority of MBSR, compared with escitalopram.
Remarkable results
“What was remarkable was that the medication worked great, like it always does, but the meditation also worked great; we saw about a 30% drop in symptoms for both groups,” said Dr. Hoge. “That helps us know that meditation, and in particular mindfulness meditation, could be useful as a first-line treatment for patients with anxiety disorders.”
The patient-reported outcome of the Overall Anxiety Severity and Impairment Scale also showed no significant group differences. “It’s important to have the self-reports, because that gives us two ways to look at the information,” said Dr. Hoge.
Anecdotally, participants noted that the meditation helped with their personal relationships and with being “kinder to themselves,” said Dr. Hoge. “In meditation, there’s an implicit teaching to be accepting and nonjudgmental towards your own thoughts, and that teaches people to be more self-compassionate.”
Just over 78% of patients in the escitalopram group had at least one treatment-related adverse event (AE), which included sleep disturbances, nausea, fatigue, and headache, compared with 15.4% in the MBSR group.
The most common AE in the meditation group was anxiety, which is “counterintuitive” but represents “a momentary anxiety,” said Dr. Hoge. “People who are meditating have feelings come up that maybe they didn’t pay attention to before. This gives them an opportunity to process through those emotions.”
Fatigue was the next most common AE for meditators, which “makes sense,” since they’re putting away their phones and not being stimulated, said Dr. Hoge.
MBSR was delivered in person, which limits extrapolation to mindfulness apps or programs delivered over the internet. Dr. Hoge believes apps would likely be less effective because they don’t have the face-to-face component, instructors available for consultation, or fellow participants contributing group support.
But online classes might work if “the exact same class,” including all its components, is moved online, she said.
MBSR is available in all major U.S. cities, doesn’t require finding a therapist, and is available outside a mental health environment – for example, at yoga centers and some places of employment. Anyone can learn MBSR, although it takes time and commitment, said Dr. Hoge.
A time-tested intervention
Commenting on the study, psychiatrist Gregory Scott Brown, MD, affiliate faculty, University of Texas Dell Medical School, and author of “The Self-Healing Mind: An Essential Five-Step Practice for Overcoming Anxiety and Depression and Revitalizing Your Life,” said the results aren’t surprising inasmuch as mindfulness, including spirituality, breath work, and meditation, is a “time-tested and evidence-based” intervention.
“I’m encouraged by the fact studies like this are now being conducted and there’s more evidence that supports these mindfulness-based interventions, so they can start to make their way into standard-of-care treatments.” he said.
He noted that mindfulness can produce “long-term, sustainable improvements” and that the 45-minute daily home exercise included in the study “is not a huge time commitment when you talk about benefits you can potentially glean from incorporating that time.”
Because most study participants were women and “men are anxious too,” Dr. Brown said he would like to see the study replicated “with a more diverse pool of participants.”
The study was supported by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Hoge and Dr. Brown have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
With a little help from your friends
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
New statement guides the diagnosis of pediatric anxiety
The Canadian Paediatric Society (CPS) has issued a position statement on the diagnosis of anxiety disorders in children and youth. The organization aims to “offer evidence-informed guidance to support pediatric health care providers making decisions around the care of children and adolescents with these conditions.”
“It’s been a long time coming,” lead author Benjamin Klein, MD, assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., told this news organization. The target audience for the documents includes community pediatricians, subspecialists, family doctors, and nurse practitioners. “There was a great demand from that audience for a position statement, for guidance, obviously in the backdrop of rising child and adolescent mental health incidence over the years and of course COVID,” said Dr. Klein.
The statement was published on the CPS website.
‘A comprehensive approach’
Although many other guidelines on this topic are available, it was important to have a Canadian document, said Dr. Klein. “Obviously, there’s going to be a great deal of overlap with European or American guidelines, but it’s just kind of assumed that people want specifically Canadian content. ... Physicians want to know that they’re practicing within a standard of care in Canada.” Dr. Klein is medical director of the Lansdowne Children’s Centre, Brantford, Ont., which provides help for children with communication, developmental, and physical special needs across Ontario.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental disorders among children and adolescents in Canada, according to the position statement. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) groups these disorders into separation anxiety disorder, selective mutism, specific phobia, social anxiety disorder (social phobia), panic disorder, agoraphobia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Distinguishing normal, age-appropriate anxiety from anxiety disorder, while also recognizing other comorbidities, is complicated, said Dr. Klein. “Anxiety is one possible diagnosis or feature, and children with mental health and developmental problems often present with a number of problems. Anxiety may be one of them, but if it’s one of them, it may not be the main driver. So, a comprehensive approach is needed ... combining the medical model with biopsychosocial thinking to give a better picture of anxiety in the context of anything else that may be contributing to a presentation.”
The statement outlines recommendations for anxiety assessment, starting with a screening questionnaire such as the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED), which is completed by parents and children, to assess symptom severity. Standardized measures for medical, mental health, and developmental histories are available on the CPS website.
The document next recommends an interview about presenting concerns (such as sleep problems or school difficulties), inciting events, and parent-child interactions. The process includes confidential, nonjudgmental interviews with adolescents using a history-taking tool such as HEEADSSS (Home, Education/Employment, Eating, Activities, Drugs, Sexuality, Suicide/Mental Health, and Safety).
“The diagnosis and treatment of anxiety disorders kind of sounds simple if you just read about it as an isolated thing, but the reality is ... there’s no MRI. It’s detective work,” said Dr. Klein. Clinicians must distinguish between normal anxiety, situational anxiety, and specific anxiety disorder, he added. He usually allows 90 minutes for an anxiety assessment, partly to gain the patient’s trust. “These are sensitive issues. It’s common that people don’t trust a diagnosis if you haven’t spent enough time with them. That relational care piece just needs to be there, or people aren’t going to buy in.”
The CPS position statement was reviewed and endorsed by the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Methodology unclear
Joanna Henderson, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and director of the Margaret and Wallace McCain Centre for Child, Youth, and Family Mental Health at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, said that the guidelines have been released at an important time. “Conversations about mental health have become more common, and many children, youth, and families are reaching out for support. It is essential that health care professionals be equipped with accessible information about practices to provide appropriate care. These guidelines support that vision.”
It would be helpful to know more about the methods used to arrive at the recommendations, however, said Dr. Henderson. “It is critical that health care providers be guided by evidence-based guidelines that adhere to criteria for establishing high-quality guidelines. Because the authors did not provide information about their methods, I am not able to provide a comment about the quality of their guidelines. There are established approaches for evaluating quality, and I would encourage the authors to publish as a supplement to this article their methods, including in reference to the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE II) checklist.”
In the absence of readily available information about methods, she said, “clinicians are encouraged to use guidelines from sources that provide information about the guideline development process and include quality appraisal,” such as the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, which is “generally recognized as a reputable source for high-quality practice guidelines.”
Responding to this concern, Dr. Klein said, “There is no specific evidence base for diagnosis. That robust science doesn’t exist. No one has done randomized controlled trials of different methods of diagnosing kids with anxiety. We looked at other position statements, we looked at textbooks, and obviously we drew from our own clinical experience, so it comes from clinical judgment and expert opinion.”
Dr. Henderson also noted that in the future “it will be important to contextualize the recommendations by highlighting the importance of cultural competence in conducting assessments and providing treatment.” Moreover, current evidence can be expanded through the incorporation of diverse cultural and racial perspectives, experiences, and data, she added.
Health service providers should reflect on their own potential biases, which can influence clinician-patient interactions, Dr. Henderson continued. It also is important to consider biases in the evidence, which influence practice. Clinicians should also consider how their recommendations fit with patients’ “cultural and race-based experiences, beliefs, and practices.”
No source of funding for the position statement was reported. Dr. Klein and Dr. Henderson had disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Canadian Paediatric Society (CPS) has issued a position statement on the diagnosis of anxiety disorders in children and youth. The organization aims to “offer evidence-informed guidance to support pediatric health care providers making decisions around the care of children and adolescents with these conditions.”
“It’s been a long time coming,” lead author Benjamin Klein, MD, assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., told this news organization. The target audience for the documents includes community pediatricians, subspecialists, family doctors, and nurse practitioners. “There was a great demand from that audience for a position statement, for guidance, obviously in the backdrop of rising child and adolescent mental health incidence over the years and of course COVID,” said Dr. Klein.
The statement was published on the CPS website.
‘A comprehensive approach’
Although many other guidelines on this topic are available, it was important to have a Canadian document, said Dr. Klein. “Obviously, there’s going to be a great deal of overlap with European or American guidelines, but it’s just kind of assumed that people want specifically Canadian content. ... Physicians want to know that they’re practicing within a standard of care in Canada.” Dr. Klein is medical director of the Lansdowne Children’s Centre, Brantford, Ont., which provides help for children with communication, developmental, and physical special needs across Ontario.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental disorders among children and adolescents in Canada, according to the position statement. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) groups these disorders into separation anxiety disorder, selective mutism, specific phobia, social anxiety disorder (social phobia), panic disorder, agoraphobia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Distinguishing normal, age-appropriate anxiety from anxiety disorder, while also recognizing other comorbidities, is complicated, said Dr. Klein. “Anxiety is one possible diagnosis or feature, and children with mental health and developmental problems often present with a number of problems. Anxiety may be one of them, but if it’s one of them, it may not be the main driver. So, a comprehensive approach is needed ... combining the medical model with biopsychosocial thinking to give a better picture of anxiety in the context of anything else that may be contributing to a presentation.”
The statement outlines recommendations for anxiety assessment, starting with a screening questionnaire such as the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED), which is completed by parents and children, to assess symptom severity. Standardized measures for medical, mental health, and developmental histories are available on the CPS website.
The document next recommends an interview about presenting concerns (such as sleep problems or school difficulties), inciting events, and parent-child interactions. The process includes confidential, nonjudgmental interviews with adolescents using a history-taking tool such as HEEADSSS (Home, Education/Employment, Eating, Activities, Drugs, Sexuality, Suicide/Mental Health, and Safety).
“The diagnosis and treatment of anxiety disorders kind of sounds simple if you just read about it as an isolated thing, but the reality is ... there’s no MRI. It’s detective work,” said Dr. Klein. Clinicians must distinguish between normal anxiety, situational anxiety, and specific anxiety disorder, he added. He usually allows 90 minutes for an anxiety assessment, partly to gain the patient’s trust. “These are sensitive issues. It’s common that people don’t trust a diagnosis if you haven’t spent enough time with them. That relational care piece just needs to be there, or people aren’t going to buy in.”
The CPS position statement was reviewed and endorsed by the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Methodology unclear
Joanna Henderson, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and director of the Margaret and Wallace McCain Centre for Child, Youth, and Family Mental Health at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, said that the guidelines have been released at an important time. “Conversations about mental health have become more common, and many children, youth, and families are reaching out for support. It is essential that health care professionals be equipped with accessible information about practices to provide appropriate care. These guidelines support that vision.”
It would be helpful to know more about the methods used to arrive at the recommendations, however, said Dr. Henderson. “It is critical that health care providers be guided by evidence-based guidelines that adhere to criteria for establishing high-quality guidelines. Because the authors did not provide information about their methods, I am not able to provide a comment about the quality of their guidelines. There are established approaches for evaluating quality, and I would encourage the authors to publish as a supplement to this article their methods, including in reference to the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE II) checklist.”
In the absence of readily available information about methods, she said, “clinicians are encouraged to use guidelines from sources that provide information about the guideline development process and include quality appraisal,” such as the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, which is “generally recognized as a reputable source for high-quality practice guidelines.”
Responding to this concern, Dr. Klein said, “There is no specific evidence base for diagnosis. That robust science doesn’t exist. No one has done randomized controlled trials of different methods of diagnosing kids with anxiety. We looked at other position statements, we looked at textbooks, and obviously we drew from our own clinical experience, so it comes from clinical judgment and expert opinion.”
Dr. Henderson also noted that in the future “it will be important to contextualize the recommendations by highlighting the importance of cultural competence in conducting assessments and providing treatment.” Moreover, current evidence can be expanded through the incorporation of diverse cultural and racial perspectives, experiences, and data, she added.
Health service providers should reflect on their own potential biases, which can influence clinician-patient interactions, Dr. Henderson continued. It also is important to consider biases in the evidence, which influence practice. Clinicians should also consider how their recommendations fit with patients’ “cultural and race-based experiences, beliefs, and practices.”
No source of funding for the position statement was reported. Dr. Klein and Dr. Henderson had disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Canadian Paediatric Society (CPS) has issued a position statement on the diagnosis of anxiety disorders in children and youth. The organization aims to “offer evidence-informed guidance to support pediatric health care providers making decisions around the care of children and adolescents with these conditions.”
“It’s been a long time coming,” lead author Benjamin Klein, MD, assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., told this news organization. The target audience for the documents includes community pediatricians, subspecialists, family doctors, and nurse practitioners. “There was a great demand from that audience for a position statement, for guidance, obviously in the backdrop of rising child and adolescent mental health incidence over the years and of course COVID,” said Dr. Klein.
The statement was published on the CPS website.
‘A comprehensive approach’
Although many other guidelines on this topic are available, it was important to have a Canadian document, said Dr. Klein. “Obviously, there’s going to be a great deal of overlap with European or American guidelines, but it’s just kind of assumed that people want specifically Canadian content. ... Physicians want to know that they’re practicing within a standard of care in Canada.” Dr. Klein is medical director of the Lansdowne Children’s Centre, Brantford, Ont., which provides help for children with communication, developmental, and physical special needs across Ontario.
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental disorders among children and adolescents in Canada, according to the position statement. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) groups these disorders into separation anxiety disorder, selective mutism, specific phobia, social anxiety disorder (social phobia), panic disorder, agoraphobia, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Distinguishing normal, age-appropriate anxiety from anxiety disorder, while also recognizing other comorbidities, is complicated, said Dr. Klein. “Anxiety is one possible diagnosis or feature, and children with mental health and developmental problems often present with a number of problems. Anxiety may be one of them, but if it’s one of them, it may not be the main driver. So, a comprehensive approach is needed ... combining the medical model with biopsychosocial thinking to give a better picture of anxiety in the context of anything else that may be contributing to a presentation.”
The statement outlines recommendations for anxiety assessment, starting with a screening questionnaire such as the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED), which is completed by parents and children, to assess symptom severity. Standardized measures for medical, mental health, and developmental histories are available on the CPS website.
The document next recommends an interview about presenting concerns (such as sleep problems or school difficulties), inciting events, and parent-child interactions. The process includes confidential, nonjudgmental interviews with adolescents using a history-taking tool such as HEEADSSS (Home, Education/Employment, Eating, Activities, Drugs, Sexuality, Suicide/Mental Health, and Safety).
“The diagnosis and treatment of anxiety disorders kind of sounds simple if you just read about it as an isolated thing, but the reality is ... there’s no MRI. It’s detective work,” said Dr. Klein. Clinicians must distinguish between normal anxiety, situational anxiety, and specific anxiety disorder, he added. He usually allows 90 minutes for an anxiety assessment, partly to gain the patient’s trust. “These are sensitive issues. It’s common that people don’t trust a diagnosis if you haven’t spent enough time with them. That relational care piece just needs to be there, or people aren’t going to buy in.”
The CPS position statement was reviewed and endorsed by the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
Methodology unclear
Joanna Henderson, MD, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and director of the Margaret and Wallace McCain Centre for Child, Youth, and Family Mental Health at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, said that the guidelines have been released at an important time. “Conversations about mental health have become more common, and many children, youth, and families are reaching out for support. It is essential that health care professionals be equipped with accessible information about practices to provide appropriate care. These guidelines support that vision.”
It would be helpful to know more about the methods used to arrive at the recommendations, however, said Dr. Henderson. “It is critical that health care providers be guided by evidence-based guidelines that adhere to criteria for establishing high-quality guidelines. Because the authors did not provide information about their methods, I am not able to provide a comment about the quality of their guidelines. There are established approaches for evaluating quality, and I would encourage the authors to publish as a supplement to this article their methods, including in reference to the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE II) checklist.”
In the absence of readily available information about methods, she said, “clinicians are encouraged to use guidelines from sources that provide information about the guideline development process and include quality appraisal,” such as the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, which is “generally recognized as a reputable source for high-quality practice guidelines.”
Responding to this concern, Dr. Klein said, “There is no specific evidence base for diagnosis. That robust science doesn’t exist. No one has done randomized controlled trials of different methods of diagnosing kids with anxiety. We looked at other position statements, we looked at textbooks, and obviously we drew from our own clinical experience, so it comes from clinical judgment and expert opinion.”
Dr. Henderson also noted that in the future “it will be important to contextualize the recommendations by highlighting the importance of cultural competence in conducting assessments and providing treatment.” Moreover, current evidence can be expanded through the incorporation of diverse cultural and racial perspectives, experiences, and data, she added.
Health service providers should reflect on their own potential biases, which can influence clinician-patient interactions, Dr. Henderson continued. It also is important to consider biases in the evidence, which influence practice. Clinicians should also consider how their recommendations fit with patients’ “cultural and race-based experiences, beliefs, and practices.”
No source of funding for the position statement was reported. Dr. Klein and Dr. Henderson had disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
















