User login
Breast cancer chemoprophylaxis in high-risk women: How persistent is the impact of an aromatase inhibitor after 5 years of use?
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
A manufacturer-sponsored trial initiated in 2003, IBIS-II (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study II) included 3,864 menopausal women (mean age at baseline, 59.4 years) at elevated risk for breast cancer. The women were randomly assigned to 5-year treatment with either placebo (N = 1,944) or the aromatase inhibitor anastrozole 1 mg daily (N = 1,920).1
Reporting on the long-term follow-up results of the trial, Cuzick and colleagues found that anastrozole use substantially reduced the incidence of all breast cancer, including invasive breast cancer and ductal carcinoma in situ. Key adverse events associated with anastrozole were fractures, arthralgias, and menopausal symptoms (vasomotor symptoms and vaginal dryness).
To determine whether anastrozole had any persistent impact, the investigators continued to follow participants for all breast cancers and other outcomes.2
Details of the study
This randomized controlled trial that included 3,864 postmenopausal women had a median overall follow-up of 131 months; the primary outcome was all breast cancer. Random assignment to anastrozole use (1,920 women) was associated with a 49% reduction in all breast cancer (85 cases vs 165 cases in the placebo group [N = 1,944]; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.39–0.66; P<.0001).
In the first 5 years, risk reduction was 61% with anastrozole (P<.0001 for overall and the first 5 years of follow-up). Subsequently, the magnitude of the risk reduction attenuated to 37% (P = .014). With 12 years of follow-up, the estimated risk of being diagnosed with breast cancer was 8.8% and 5.3% in the placebo and anastrozole groups, respectively. The number needed to treat for 5 years to prevent 1 breast cancer was 29.
With anastrozole, prevention of estrogen–receptor positive tumors was substantially more robust at 54% (HR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.33–0.65; P<.0001) than for estrogen–receptor negative tumors at 27% (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.41–1.44; P = .41).
Over the course of the long-term study, the incidence of fractures and cardiovascular events was similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups. Arthralgias and menopausal symptoms were not assessed after the trial’s initial 5 years. Overall, the number of deaths (all cause as well as breast cancer related) were similar in the placebo and anastrozole groups.
Continue to: Study strengths and limitations...
Study strengths and limitations
The authors noted that this updated analysis of the IBIS-II trial data offers further support for the use of anastrozole in breast cancer prevention for high-risk postmenopausal women. The extended posttreatment follow-up showed a significant continuing reduction in breast cancer, and there was no evidence of new late adverse effects. A limitation of the analysis, however, is that very few deaths from breast cancer occurred during the study timeframe. Thus, additional follow-up would be needed to assess anastrozole’s effect on breast cancer mortality.
The breast cancer chemoprophylactic efficacy of anastrozole compares favorably with that of tamoxifen. Furthermore, in women with an intact uterus, the increased risks of gynecologic problems, including endometrial cancer, associated with tamoxifen do not occur with aromatase inhibitors. However, the lack of any obvious mortality benefit means the ultimate value of estrogen deprivation breast cancer chemoprophylaxis continues to be uncertain, especially given other risks, including bone loss. In view of these new data, it will be important for high-risk women considering aromatase inhibitor prophylaxis to understand that these medications have not been associated with a mortality benefit.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, NCMP
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Anastrozole for prevention of breast cancer in high-risk postmenopausal women (IBIS-II): an international, double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;383:1041-1048.
- Cuzick J, Sestak I, Forbes JF, et al; IBIS-II Investigators. Use of anastrozole for breast cancer prevention (IBIS-II): long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395;117-122.
New tools could help predict complication risks in lung and breast cancer
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight the potential role of new models for predicting risks of common, clinically important situations in general oncology practice: severe neutropenia in lung cancer patients and locoregional recurrence of breast cancer.
Predicting neutropenia
Accurate, lung cancer–specific prediction models would be useful to estimate risk of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN), especially febrile neutropenia (FN), since that particular toxicity is linked to infection, dose delays and dose reductions that can compromise treatment efficacy, and poor health-related quality of life. Lung cancer patients are often older adults, with advanced disease and comorbid conditions, so they are a particularly vulnerable population for CIN.
Xiaowen Cao of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and coinvestigators published a model for predicting risk of severe CIN in advanced lung cancer patients, based on 10 pretreatment variables (Lung Cancer. 2020 Jan 5. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.004). They developed their model to overcome limitations of the previously published work of Gary H. Lyman, MD, and colleagues that is not specific to lung cancer and incorporated relative dose intensity as a predictor (Cancer. 2011;117:1917-27). Relative dose intensity is not determined until after a treatment course is completed.
The new prediction model was based on a lung cancer data set encompassing 11,352 patients from 67 phase 2-3 cooperative group studies conducted between 1991 and 2010. In this data set, the Lyman model had an area under the curve of 0.8772 in patients with small cell lung cancer, but an area under the curve of just 0.6787 in non–small cell lung cancer.
The derivation model was derived from about two-thirds of the patients, randomly selected. The validation set was conducted using the remaining third. The variables included were readily clinically available: age, gender, weight, body mass index, insurance status, disease stage, number of metastatic sites, chemotherapy agents used, number of chemotherapy agents, planned growth factor use, duration of planned therapy, pleural effusion, presence of symptoms, and performance status. Their model had an area under the curve of 0.8348 in the training set and 0.8234 in the testing set.
How these results influence practice
The risk of an initial episode of FN is highest during a patient’s initial cycle of chemotherapy, when most patients are receiving full-dose treatment, often without prophylactic measures. Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network suggest the use of prophylactic growth factors in patients with more than a 20% risk of FN, and considering using prophylaxis in patients with 10%-20% risk of FN. Underestimating those risks and failure to take adequate precautions may be particularly important for patients with lung cancer who are generally older adults, with comorbid conditions.
The comprehensive risk model for neutropenic complications that was developed by Dr. Lyman and colleagues was based on a large, prospective cohort including nearly 3,800 patients. The model had a 90% sensitivity and 96% predictive value, but was not lung cancer specific and, in this latest study, did not perform as well in the 85% of lung cancer patients with non–small cell lung cancer. The Lyman data, however, was obtained in cancer patients treated with investigator-choice chemotherapy in community practices. It remains the National Comprehensive Cancer Network standard for evaluating FN risk in patients embarking on chemotherapy for advanced malignancies. That should remain the case, pending the additional validation testing of the new lung cancer–specific model at independent institutions, treating heterogeneous patients in real-world settings.
Locoregional recurrence
A retrospective cohort analysis of SWOG 8814, a phase 3 study of tamoxifen alone versus chemotherapy plus by tamoxifen in postmenopausal, node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer patients suggests that the 21-gene assay recurrence score (RS) can aid decisions about radiotherapy (RT).
Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, and colleagues, analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery as their local therapy (JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559). They found that patients with an intermediate or high RS – according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX – had more locoregional recurrences (LRR; breast, chest wall, axilla, internal mammary, supraclavicular or infraclavicular nodes).
There were 367 patients in SWOG 8814 who received tamoxifen alone or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen. LRR was observed in 5.8% of patients with a low RS (less than 18) and in 13.8% of patients with an intermediate or high RS (more than 18). The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
In the subset of patients with one to three positive nodes who had mastectomy without radiotherapy, the LRR was 1.5% for those with low RS and 11.1% for those with intermediate or high RS (P = .051). No difference by RS was found in the 10-year rates of LRR among patients with four or more involved nodes who received a mastectomy without RT (25.9% vs. 27.0%; P = .27).
In multivariate analysis, incorporating RS, type of surgery, and number of involved nodes, intermediate or high RS was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). The investigators suggested that RS, when available, should be one of the factors considered in selecting patients for postmastectomy RT.
How these results influence practice
Selecting the node-positive, hormone receptor–positive, breast cancer patients who should receive postmastectomy RT is difficult and controversial. This is particularly true for those postmenopausal patients with fewer than four involved nodes, no lymphatic or vascular invasion, and no extracapsular spread of disease into the axillary fat. Limited information exists on the ability of genomic assays to identify LRR risk.
Eleftherios P. Mamounas, MD, and colleagues examined the results of NSABP B-28, a trial of chemotherapy plus tamoxifen (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109[4]. doi:10.1093/jnci/djw259). Postmastectomy RT was not permitted. They found high RS correlated with greater LRR and low RS with decreased LRR among patients with one to three positive nodes. At first blush, the prospectively treated cohort of SWOG 8814 represents a uniformly treated cohort with long-term follow-up (median, 8.5 years) and extends in an independent analysis the findings of NSABP B-28.
However, as Dr. Woodward and colleagues point out, the current study has limitations. The use of RT was extracted retrospectively and may be underreported. More modern chemotherapy and RT may lower LRR from the risks observed in SWOG 8814. Finally, the modest numbers of LRR events precluded secondary analysis of RS as a continuous variable. This is important because the risk group cutoffs suggested by the authors are not aligned with those in the recently published TailorRx study or the ongoing RxPonder trial.
The TailorRT (Regional Radiotherapy in Biomarker Low Risk Node Positive Breast Cancer) study examines the safety of omitting RT among patients with low RS and one to three positive nodes. Until the TailorRT results are reported, the controversy regarding the role of postmastectomy RT in this group will continue for patients with low nodal tumor burden and less aggressive tumor features, including low RS.
An observed LRR risk of 11.1% in SWOG 8814 among patients with N1 disease and an RS above 18 suggest that genomic risk could be one of the factors that may justify postmastectomy RT in postmenopausal patients with node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer until additional data emerge from the contemporary trials.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight the potential role of new models for predicting risks of common, clinically important situations in general oncology practice: severe neutropenia in lung cancer patients and locoregional recurrence of breast cancer.
Predicting neutropenia
Accurate, lung cancer–specific prediction models would be useful to estimate risk of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN), especially febrile neutropenia (FN), since that particular toxicity is linked to infection, dose delays and dose reductions that can compromise treatment efficacy, and poor health-related quality of life. Lung cancer patients are often older adults, with advanced disease and comorbid conditions, so they are a particularly vulnerable population for CIN.
Xiaowen Cao of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and coinvestigators published a model for predicting risk of severe CIN in advanced lung cancer patients, based on 10 pretreatment variables (Lung Cancer. 2020 Jan 5. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.004). They developed their model to overcome limitations of the previously published work of Gary H. Lyman, MD, and colleagues that is not specific to lung cancer and incorporated relative dose intensity as a predictor (Cancer. 2011;117:1917-27). Relative dose intensity is not determined until after a treatment course is completed.
The new prediction model was based on a lung cancer data set encompassing 11,352 patients from 67 phase 2-3 cooperative group studies conducted between 1991 and 2010. In this data set, the Lyman model had an area under the curve of 0.8772 in patients with small cell lung cancer, but an area under the curve of just 0.6787 in non–small cell lung cancer.
The derivation model was derived from about two-thirds of the patients, randomly selected. The validation set was conducted using the remaining third. The variables included were readily clinically available: age, gender, weight, body mass index, insurance status, disease stage, number of metastatic sites, chemotherapy agents used, number of chemotherapy agents, planned growth factor use, duration of planned therapy, pleural effusion, presence of symptoms, and performance status. Their model had an area under the curve of 0.8348 in the training set and 0.8234 in the testing set.
How these results influence practice
The risk of an initial episode of FN is highest during a patient’s initial cycle of chemotherapy, when most patients are receiving full-dose treatment, often without prophylactic measures. Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network suggest the use of prophylactic growth factors in patients with more than a 20% risk of FN, and considering using prophylaxis in patients with 10%-20% risk of FN. Underestimating those risks and failure to take adequate precautions may be particularly important for patients with lung cancer who are generally older adults, with comorbid conditions.
The comprehensive risk model for neutropenic complications that was developed by Dr. Lyman and colleagues was based on a large, prospective cohort including nearly 3,800 patients. The model had a 90% sensitivity and 96% predictive value, but was not lung cancer specific and, in this latest study, did not perform as well in the 85% of lung cancer patients with non–small cell lung cancer. The Lyman data, however, was obtained in cancer patients treated with investigator-choice chemotherapy in community practices. It remains the National Comprehensive Cancer Network standard for evaluating FN risk in patients embarking on chemotherapy for advanced malignancies. That should remain the case, pending the additional validation testing of the new lung cancer–specific model at independent institutions, treating heterogeneous patients in real-world settings.
Locoregional recurrence
A retrospective cohort analysis of SWOG 8814, a phase 3 study of tamoxifen alone versus chemotherapy plus by tamoxifen in postmenopausal, node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer patients suggests that the 21-gene assay recurrence score (RS) can aid decisions about radiotherapy (RT).
Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, and colleagues, analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery as their local therapy (JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559). They found that patients with an intermediate or high RS – according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX – had more locoregional recurrences (LRR; breast, chest wall, axilla, internal mammary, supraclavicular or infraclavicular nodes).
There were 367 patients in SWOG 8814 who received tamoxifen alone or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen. LRR was observed in 5.8% of patients with a low RS (less than 18) and in 13.8% of patients with an intermediate or high RS (more than 18). The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
In the subset of patients with one to three positive nodes who had mastectomy without radiotherapy, the LRR was 1.5% for those with low RS and 11.1% for those with intermediate or high RS (P = .051). No difference by RS was found in the 10-year rates of LRR among patients with four or more involved nodes who received a mastectomy without RT (25.9% vs. 27.0%; P = .27).
In multivariate analysis, incorporating RS, type of surgery, and number of involved nodes, intermediate or high RS was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). The investigators suggested that RS, when available, should be one of the factors considered in selecting patients for postmastectomy RT.
How these results influence practice
Selecting the node-positive, hormone receptor–positive, breast cancer patients who should receive postmastectomy RT is difficult and controversial. This is particularly true for those postmenopausal patients with fewer than four involved nodes, no lymphatic or vascular invasion, and no extracapsular spread of disease into the axillary fat. Limited information exists on the ability of genomic assays to identify LRR risk.
Eleftherios P. Mamounas, MD, and colleagues examined the results of NSABP B-28, a trial of chemotherapy plus tamoxifen (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109[4]. doi:10.1093/jnci/djw259). Postmastectomy RT was not permitted. They found high RS correlated with greater LRR and low RS with decreased LRR among patients with one to three positive nodes. At first blush, the prospectively treated cohort of SWOG 8814 represents a uniformly treated cohort with long-term follow-up (median, 8.5 years) and extends in an independent analysis the findings of NSABP B-28.
However, as Dr. Woodward and colleagues point out, the current study has limitations. The use of RT was extracted retrospectively and may be underreported. More modern chemotherapy and RT may lower LRR from the risks observed in SWOG 8814. Finally, the modest numbers of LRR events precluded secondary analysis of RS as a continuous variable. This is important because the risk group cutoffs suggested by the authors are not aligned with those in the recently published TailorRx study or the ongoing RxPonder trial.
The TailorRT (Regional Radiotherapy in Biomarker Low Risk Node Positive Breast Cancer) study examines the safety of omitting RT among patients with low RS and one to three positive nodes. Until the TailorRT results are reported, the controversy regarding the role of postmastectomy RT in this group will continue for patients with low nodal tumor burden and less aggressive tumor features, including low RS.
An observed LRR risk of 11.1% in SWOG 8814 among patients with N1 disease and an RS above 18 suggest that genomic risk could be one of the factors that may justify postmastectomy RT in postmenopausal patients with node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer until additional data emerge from the contemporary trials.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight the potential role of new models for predicting risks of common, clinically important situations in general oncology practice: severe neutropenia in lung cancer patients and locoregional recurrence of breast cancer.
Predicting neutropenia
Accurate, lung cancer–specific prediction models would be useful to estimate risk of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN), especially febrile neutropenia (FN), since that particular toxicity is linked to infection, dose delays and dose reductions that can compromise treatment efficacy, and poor health-related quality of life. Lung cancer patients are often older adults, with advanced disease and comorbid conditions, so they are a particularly vulnerable population for CIN.
Xiaowen Cao of Duke University, Durham, N.C., and coinvestigators published a model for predicting risk of severe CIN in advanced lung cancer patients, based on 10 pretreatment variables (Lung Cancer. 2020 Jan 5. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.004). They developed their model to overcome limitations of the previously published work of Gary H. Lyman, MD, and colleagues that is not specific to lung cancer and incorporated relative dose intensity as a predictor (Cancer. 2011;117:1917-27). Relative dose intensity is not determined until after a treatment course is completed.
The new prediction model was based on a lung cancer data set encompassing 11,352 patients from 67 phase 2-3 cooperative group studies conducted between 1991 and 2010. In this data set, the Lyman model had an area under the curve of 0.8772 in patients with small cell lung cancer, but an area under the curve of just 0.6787 in non–small cell lung cancer.
The derivation model was derived from about two-thirds of the patients, randomly selected. The validation set was conducted using the remaining third. The variables included were readily clinically available: age, gender, weight, body mass index, insurance status, disease stage, number of metastatic sites, chemotherapy agents used, number of chemotherapy agents, planned growth factor use, duration of planned therapy, pleural effusion, presence of symptoms, and performance status. Their model had an area under the curve of 0.8348 in the training set and 0.8234 in the testing set.
How these results influence practice
The risk of an initial episode of FN is highest during a patient’s initial cycle of chemotherapy, when most patients are receiving full-dose treatment, often without prophylactic measures. Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network suggest the use of prophylactic growth factors in patients with more than a 20% risk of FN, and considering using prophylaxis in patients with 10%-20% risk of FN. Underestimating those risks and failure to take adequate precautions may be particularly important for patients with lung cancer who are generally older adults, with comorbid conditions.
The comprehensive risk model for neutropenic complications that was developed by Dr. Lyman and colleagues was based on a large, prospective cohort including nearly 3,800 patients. The model had a 90% sensitivity and 96% predictive value, but was not lung cancer specific and, in this latest study, did not perform as well in the 85% of lung cancer patients with non–small cell lung cancer. The Lyman data, however, was obtained in cancer patients treated with investigator-choice chemotherapy in community practices. It remains the National Comprehensive Cancer Network standard for evaluating FN risk in patients embarking on chemotherapy for advanced malignancies. That should remain the case, pending the additional validation testing of the new lung cancer–specific model at independent institutions, treating heterogeneous patients in real-world settings.
Locoregional recurrence
A retrospective cohort analysis of SWOG 8814, a phase 3 study of tamoxifen alone versus chemotherapy plus by tamoxifen in postmenopausal, node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer patients suggests that the 21-gene assay recurrence score (RS) can aid decisions about radiotherapy (RT).
Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, and colleagues, analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery as their local therapy (JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559). They found that patients with an intermediate or high RS – according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX – had more locoregional recurrences (LRR; breast, chest wall, axilla, internal mammary, supraclavicular or infraclavicular nodes).
There were 367 patients in SWOG 8814 who received tamoxifen alone or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen. LRR was observed in 5.8% of patients with a low RS (less than 18) and in 13.8% of patients with an intermediate or high RS (more than 18). The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
In the subset of patients with one to three positive nodes who had mastectomy without radiotherapy, the LRR was 1.5% for those with low RS and 11.1% for those with intermediate or high RS (P = .051). No difference by RS was found in the 10-year rates of LRR among patients with four or more involved nodes who received a mastectomy without RT (25.9% vs. 27.0%; P = .27).
In multivariate analysis, incorporating RS, type of surgery, and number of involved nodes, intermediate or high RS was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). The investigators suggested that RS, when available, should be one of the factors considered in selecting patients for postmastectomy RT.
How these results influence practice
Selecting the node-positive, hormone receptor–positive, breast cancer patients who should receive postmastectomy RT is difficult and controversial. This is particularly true for those postmenopausal patients with fewer than four involved nodes, no lymphatic or vascular invasion, and no extracapsular spread of disease into the axillary fat. Limited information exists on the ability of genomic assays to identify LRR risk.
Eleftherios P. Mamounas, MD, and colleagues examined the results of NSABP B-28, a trial of chemotherapy plus tamoxifen (J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109[4]. doi:10.1093/jnci/djw259). Postmastectomy RT was not permitted. They found high RS correlated with greater LRR and low RS with decreased LRR among patients with one to three positive nodes. At first blush, the prospectively treated cohort of SWOG 8814 represents a uniformly treated cohort with long-term follow-up (median, 8.5 years) and extends in an independent analysis the findings of NSABP B-28.
However, as Dr. Woodward and colleagues point out, the current study has limitations. The use of RT was extracted retrospectively and may be underreported. More modern chemotherapy and RT may lower LRR from the risks observed in SWOG 8814. Finally, the modest numbers of LRR events precluded secondary analysis of RS as a continuous variable. This is important because the risk group cutoffs suggested by the authors are not aligned with those in the recently published TailorRx study or the ongoing RxPonder trial.
The TailorRT (Regional Radiotherapy in Biomarker Low Risk Node Positive Breast Cancer) study examines the safety of omitting RT among patients with low RS and one to three positive nodes. Until the TailorRT results are reported, the controversy regarding the role of postmastectomy RT in this group will continue for patients with low nodal tumor burden and less aggressive tumor features, including low RS.
An observed LRR risk of 11.1% in SWOG 8814 among patients with N1 disease and an RS above 18 suggest that genomic risk could be one of the factors that may justify postmastectomy RT in postmenopausal patients with node-positive, hormone receptor–positive breast cancer until additional data emerge from the contemporary trials.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
Should supplemental MRI be used in otherwise average-risk women with extremely dense breasts?
While the frequency of dense breasts decreases with age, approximately 10% of women in the United States have extremely dense breasts (Breast Imaging, Reporting, and Data System [BI-RADS] category D), and another 40% have heterogeneously dense breasts (BI-RADS category C).1 Women with dense breasts have both an increased risk for developing breast cancer and reduced mammographic sensitivity for breast cancer detection compared with women who have nondense breasts.2
These 2 observations have led the majority of states to pass legislation requiring that women with dense breasts be informed of their breast density, and most require that providers discuss these results with their patients. Thoughtful clinicians who review the available literature, however, will find sparse evidence on which to counsel patients as to next steps.
Now, a recent trial adds to our knowledge about supplemental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) breast screening in women with extremely dense breasts.
DENSE trial offers high-quality data
Bakker and colleagues studied women aged 50 to 74 who were participating in a Netherlands population-based biennial mammography screening program.3 They enrolled average-risk women with extremely dense breasts who had a negative screening digital mammogram into the Dense Tissue and Early Breast Neoplasm Screening (DENSE) multicenter trial. The women were randomly assigned to receive either continued biennial digital mammography or supplemental breast MRI.
The primary outcome was the between-group difference in the development of interval breast cancers—that is, breast cancers detected by women or their providers between rounds of screening mammography. Interval breast cancers were chosen as the primary outcome for 2 reasons:
- interval cancers appear to be more aggressive tumors than those cancers detected by screening mammography
- interval cancers can be identified over a shorter time interval, making them easier to study than outcomes such as breast cancer mortality, which typically require more than a decade to identify.
The DENSE trial’s secondary outcomes included recall rates from MRI, cancer detection rates on MRI, positive predictive value of MRIs requiring biopsy, and breast cancer characteristics (size, stage) diagnosed in the different groups.
Between-group difference in incidence of interval cancers
A total of 40,373 women with extremely dense breasts were screened; 8,061 of these were randomly assigned to receive breast MRI and 32,312 to continued mammography only (1:4 cluster randomization) across 12 mammography centers in the Netherlands. Among the women assigned to the MRI group, 59% actually underwent MRI (4,783 of the 8,061).
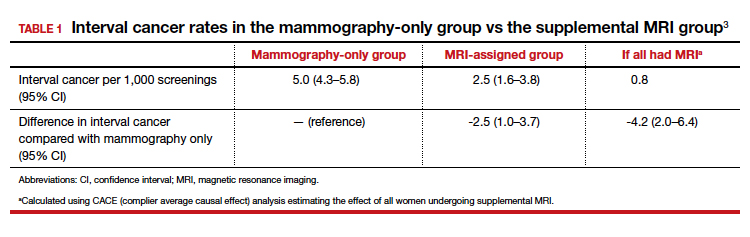
The interval cancer rate in the mammography-only group was 5.0 per 1,000 screenings (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.3–5.8), while the interval cancer rate in the MRI-assigned group was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (95% CI, 1.6–3.8) (TABLE 1).3
Key secondary outcomes
Of the women who underwent supplemental MRI, 9.49% were recalled for additional imaging, follow-up, or biopsy. Of the 4,783 women who had an MRI, 300 (6.3%) underwent a breast biopsy, and 79 breast cancers (1.65%) were detected. Sixty-four of these cancers were invasive, and 15 were ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Among women who underwent a biopsy for an MRI-detected abnormality, the positive predictive value was 26.3%.
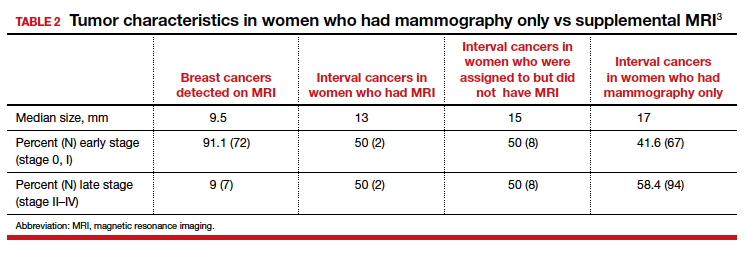
Tumor characteristics. For women who developed breast cancer during the study, both tumor size at diagnosis and tumor stage (early vs late) were described. TABLE 2 shows these results in the women who had their breast cancer detected on MRI, those in the MRI-assigned group who developed interval cancer, and those in the mammography-only group who had interval cancers.3 Overall, tumor size was smaller in the interval group who underwent MRI compared with those who underwent mammography only.
Continue to: Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes...
Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes
The trial by Bakker and colleagues employed a solid study design as women were randomly assigned to supplemental MRI screening or ongoing biennial mammography, and nearly all cancers were identified in the short-term of follow-up. In addition, very few women were lost to follow-up, and secondary outcomes, including false-positive rates, were collected to help providers and patients better understand some of the potential downsides of supplemental screening.
The substantial reduction in interval cancers (50% in the intent-to-screen analysis and 84% in the women who actually underwent supplemental MRI) was highly statistically significant (P<.001). While there were substantially fewer interval cancers in the MRI-assigned group, the interval cancers that did occur were of similar stage as those in the women assigned to the mammography-only group (TABLE 2).
Data demonstrate that interval cancers appear to be more aggressive than screen-detected cancers.4 While reducing interval cancers should be a good thing overall, it remains unproven that using supplemental MRI in all women with dense breasts would reduce breast cancer specific mortality, all-cause mortality, or the risk of more invasive treatments (for example, the need for chemotherapy or requirement for mastectomy).
On the other hand, using routine supplemental breast MRI in women with extremely dense breasts would result in very substantial use of resources, including cost, radiologist time, provider time, and machine time. In the United States, approximately 49 million women are aged 50 to 74.5 Breast MRI charges commonly range from $1,000 to $4,000. If the 4.9 million women with extremely dense breasts underwent supplemental MRI this year, the approximate cost would be somewhere between $4.9 and $19.5 billion for imaging alone. This does not include callbacks, biopsies, or provider time for ordering, interpreting, and arranging for follow-up.
While the reduction in interval cancers seen in this study is promising, more assurance of improvement in important outcomes—such as reduced mortality or reduced need for more invasive breast cancer treatments—should precede any routine change in practice.
Unanswered questions
This study did not address a number of other important questions, including:
Should MRI be done with every round of breast cancer screening given the possibility of prevalence bias? Prevalence bias can be defined as more cancers detected in the first round of MRI screening with possible reduced benefit in future rounds of screening. The study authors indicated that they will continue to analyze the study results to see what occurs in the next round of screening.
Is there a similar impact on decreased interval cancers in women undergoing annual mammography or in women screened between ages 40 and 49? This study was conducted in women aged 50 to 74 undergoing mammography every 2 years. In the United States, annual mammography in women aged 40 to 49 is frequently recommended.
What effect does supplemental MRI screening have in women with heterogeneously dense breasts, which represents 40% of the population? The US Food and Drug Administration recommends that all women with dense breasts be counseled regarding options for management.6
Do these results translate to the more racially and ethnically diverse populations of the United States? In the Netherlands, where this study was conducted, 85% to 90% of women are either Dutch or of western European origin. Women of different racial and ancestral backgrounds have biologically different breast cancers and cancer risk (for example, higher rates of triple-negative breast cancers in African American women; 10-fold higher rates of BRCA pathogenic variants in Ashkenazi Jewish women).
Continue to: Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively...
Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively
Women aged 50 to 74 with extremely dense breasts have reduced interval cancers following a normal biennial mammogram if supplemental MRI is offered, but the long-term benefit of identifying these cancers earlier is unclear. Until more data are available on important long-term outcomes (such as breast cancer mortality and need for more invasive treatments), providers should consider breast density in the context of a more comprehensive assessment of breast cancer risk using a validated breast cancer risk assessment tool.
I prefer the modified version of the International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) tool, which is readily available online (https://ibis.ikonopedia.com/).7 This tool incorporates several breast cancer risk factors, including reproductive risk factors, body mass index, BRCA gene status, breast density, and family history. The tool takes 1 to 2 minutes to complete and provides an estimate of a woman’s 10-year risk and lifetime risk of breast cancer.
If the lifetime risk exceeds 20%, I offer the patient supplemental MRI screening, consistent with current recommendations of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Cancer Society.8,9 I generally recommend starting breast imaging screening 7 to 10 years prior to the youngest breast cancer occurrence in the family, with mammography starting no earlier than age 30 and MRI no earlier than age 25. Other validated tools also can be used.10-13
Incorporating breast density and other important risk factors allows a more comprehensive analysis upon which to counsel women about the value (benefits and harms) of breast imaging.8
- Sprague BL, Gagnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jcni/dju255.
- Boyd NF, Guo H, Martin LJ, et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:227-236.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al; for the DENSE Trial Study Group. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102.
- Drukker CA, Schmidt MK, Rutgers EJT, et al. Mammographic screening detects low-risk tumor biology breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;144:103-111.
- Statista website. Resident population of the United States by sex and age as of July 1, 2018. https://www.statista.com/statistics/241488/population-of-the-us-by-sex-and-age. Accessed January 6, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Mammography: what you need to know. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/mammography-what-you-need-know. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- IBIS (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study) website. Online Tyrer-Cuzick Model Breast Cancer Risk Evaluation Tool. ibis.ikonopedia.com. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- Bevers TB, Anderson BO, Bonaccio E, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis: NCCN practice guidelines in oncology. JNCCN. 2009;7:1060-1096.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- Antoniou AC, Cunningham AP, Peto J, et al. The BOADICEA model of genetic susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancers: updates and extensions. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1457-1466.
- Claus EB, Risch N, Thompson WD. Autosomal dominant inheritance of early-onset breast cancer: implications for risk prediction. Cancer. 1994;73:643-651.
- Parmigiani G, Berry D, Aguilar O. Determining carrier probabilities for breast cancer-susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:145-158.
- Tyrer J, Duffy SW, Cuzick J. A breast cancer prediction model incorporating familial and personal risk factors. Stat Med. 2004;23:1111-1130.
While the frequency of dense breasts decreases with age, approximately 10% of women in the United States have extremely dense breasts (Breast Imaging, Reporting, and Data System [BI-RADS] category D), and another 40% have heterogeneously dense breasts (BI-RADS category C).1 Women with dense breasts have both an increased risk for developing breast cancer and reduced mammographic sensitivity for breast cancer detection compared with women who have nondense breasts.2
These 2 observations have led the majority of states to pass legislation requiring that women with dense breasts be informed of their breast density, and most require that providers discuss these results with their patients. Thoughtful clinicians who review the available literature, however, will find sparse evidence on which to counsel patients as to next steps.
Now, a recent trial adds to our knowledge about supplemental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) breast screening in women with extremely dense breasts.
DENSE trial offers high-quality data
Bakker and colleagues studied women aged 50 to 74 who were participating in a Netherlands population-based biennial mammography screening program.3 They enrolled average-risk women with extremely dense breasts who had a negative screening digital mammogram into the Dense Tissue and Early Breast Neoplasm Screening (DENSE) multicenter trial. The women were randomly assigned to receive either continued biennial digital mammography or supplemental breast MRI.
The primary outcome was the between-group difference in the development of interval breast cancers—that is, breast cancers detected by women or their providers between rounds of screening mammography. Interval breast cancers were chosen as the primary outcome for 2 reasons:
- interval cancers appear to be more aggressive tumors than those cancers detected by screening mammography
- interval cancers can be identified over a shorter time interval, making them easier to study than outcomes such as breast cancer mortality, which typically require more than a decade to identify.
The DENSE trial’s secondary outcomes included recall rates from MRI, cancer detection rates on MRI, positive predictive value of MRIs requiring biopsy, and breast cancer characteristics (size, stage) diagnosed in the different groups.
Between-group difference in incidence of interval cancers
A total of 40,373 women with extremely dense breasts were screened; 8,061 of these were randomly assigned to receive breast MRI and 32,312 to continued mammography only (1:4 cluster randomization) across 12 mammography centers in the Netherlands. Among the women assigned to the MRI group, 59% actually underwent MRI (4,783 of the 8,061).
The interval cancer rate in the mammography-only group was 5.0 per 1,000 screenings (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.3–5.8), while the interval cancer rate in the MRI-assigned group was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (95% CI, 1.6–3.8) (TABLE 1).3

Key secondary outcomes
Of the women who underwent supplemental MRI, 9.49% were recalled for additional imaging, follow-up, or biopsy. Of the 4,783 women who had an MRI, 300 (6.3%) underwent a breast biopsy, and 79 breast cancers (1.65%) were detected. Sixty-four of these cancers were invasive, and 15 were ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Among women who underwent a biopsy for an MRI-detected abnormality, the positive predictive value was 26.3%.
Tumor characteristics. For women who developed breast cancer during the study, both tumor size at diagnosis and tumor stage (early vs late) were described. TABLE 2 shows these results in the women who had their breast cancer detected on MRI, those in the MRI-assigned group who developed interval cancer, and those in the mammography-only group who had interval cancers.3 Overall, tumor size was smaller in the interval group who underwent MRI compared with those who underwent mammography only.

Continue to: Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes...
Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes
The trial by Bakker and colleagues employed a solid study design as women were randomly assigned to supplemental MRI screening or ongoing biennial mammography, and nearly all cancers were identified in the short-term of follow-up. In addition, very few women were lost to follow-up, and secondary outcomes, including false-positive rates, were collected to help providers and patients better understand some of the potential downsides of supplemental screening.
The substantial reduction in interval cancers (50% in the intent-to-screen analysis and 84% in the women who actually underwent supplemental MRI) was highly statistically significant (P<.001). While there were substantially fewer interval cancers in the MRI-assigned group, the interval cancers that did occur were of similar stage as those in the women assigned to the mammography-only group (TABLE 2).
Data demonstrate that interval cancers appear to be more aggressive than screen-detected cancers.4 While reducing interval cancers should be a good thing overall, it remains unproven that using supplemental MRI in all women with dense breasts would reduce breast cancer specific mortality, all-cause mortality, or the risk of more invasive treatments (for example, the need for chemotherapy or requirement for mastectomy).
On the other hand, using routine supplemental breast MRI in women with extremely dense breasts would result in very substantial use of resources, including cost, radiologist time, provider time, and machine time. In the United States, approximately 49 million women are aged 50 to 74.5 Breast MRI charges commonly range from $1,000 to $4,000. If the 4.9 million women with extremely dense breasts underwent supplemental MRI this year, the approximate cost would be somewhere between $4.9 and $19.5 billion for imaging alone. This does not include callbacks, biopsies, or provider time for ordering, interpreting, and arranging for follow-up.
While the reduction in interval cancers seen in this study is promising, more assurance of improvement in important outcomes—such as reduced mortality or reduced need for more invasive breast cancer treatments—should precede any routine change in practice.
Unanswered questions
This study did not address a number of other important questions, including:
Should MRI be done with every round of breast cancer screening given the possibility of prevalence bias? Prevalence bias can be defined as more cancers detected in the first round of MRI screening with possible reduced benefit in future rounds of screening. The study authors indicated that they will continue to analyze the study results to see what occurs in the next round of screening.
Is there a similar impact on decreased interval cancers in women undergoing annual mammography or in women screened between ages 40 and 49? This study was conducted in women aged 50 to 74 undergoing mammography every 2 years. In the United States, annual mammography in women aged 40 to 49 is frequently recommended.
What effect does supplemental MRI screening have in women with heterogeneously dense breasts, which represents 40% of the population? The US Food and Drug Administration recommends that all women with dense breasts be counseled regarding options for management.6
Do these results translate to the more racially and ethnically diverse populations of the United States? In the Netherlands, where this study was conducted, 85% to 90% of women are either Dutch or of western European origin. Women of different racial and ancestral backgrounds have biologically different breast cancers and cancer risk (for example, higher rates of triple-negative breast cancers in African American women; 10-fold higher rates of BRCA pathogenic variants in Ashkenazi Jewish women).
Continue to: Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively...
Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively
Women aged 50 to 74 with extremely dense breasts have reduced interval cancers following a normal biennial mammogram if supplemental MRI is offered, but the long-term benefit of identifying these cancers earlier is unclear. Until more data are available on important long-term outcomes (such as breast cancer mortality and need for more invasive treatments), providers should consider breast density in the context of a more comprehensive assessment of breast cancer risk using a validated breast cancer risk assessment tool.
I prefer the modified version of the International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) tool, which is readily available online (https://ibis.ikonopedia.com/).7 This tool incorporates several breast cancer risk factors, including reproductive risk factors, body mass index, BRCA gene status, breast density, and family history. The tool takes 1 to 2 minutes to complete and provides an estimate of a woman’s 10-year risk and lifetime risk of breast cancer.
If the lifetime risk exceeds 20%, I offer the patient supplemental MRI screening, consistent with current recommendations of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Cancer Society.8,9 I generally recommend starting breast imaging screening 7 to 10 years prior to the youngest breast cancer occurrence in the family, with mammography starting no earlier than age 30 and MRI no earlier than age 25. Other validated tools also can be used.10-13
Incorporating breast density and other important risk factors allows a more comprehensive analysis upon which to counsel women about the value (benefits and harms) of breast imaging.8
While the frequency of dense breasts decreases with age, approximately 10% of women in the United States have extremely dense breasts (Breast Imaging, Reporting, and Data System [BI-RADS] category D), and another 40% have heterogeneously dense breasts (BI-RADS category C).1 Women with dense breasts have both an increased risk for developing breast cancer and reduced mammographic sensitivity for breast cancer detection compared with women who have nondense breasts.2
These 2 observations have led the majority of states to pass legislation requiring that women with dense breasts be informed of their breast density, and most require that providers discuss these results with their patients. Thoughtful clinicians who review the available literature, however, will find sparse evidence on which to counsel patients as to next steps.
Now, a recent trial adds to our knowledge about supplemental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) breast screening in women with extremely dense breasts.
DENSE trial offers high-quality data
Bakker and colleagues studied women aged 50 to 74 who were participating in a Netherlands population-based biennial mammography screening program.3 They enrolled average-risk women with extremely dense breasts who had a negative screening digital mammogram into the Dense Tissue and Early Breast Neoplasm Screening (DENSE) multicenter trial. The women were randomly assigned to receive either continued biennial digital mammography or supplemental breast MRI.
The primary outcome was the between-group difference in the development of interval breast cancers—that is, breast cancers detected by women or their providers between rounds of screening mammography. Interval breast cancers were chosen as the primary outcome for 2 reasons:
- interval cancers appear to be more aggressive tumors than those cancers detected by screening mammography
- interval cancers can be identified over a shorter time interval, making them easier to study than outcomes such as breast cancer mortality, which typically require more than a decade to identify.
The DENSE trial’s secondary outcomes included recall rates from MRI, cancer detection rates on MRI, positive predictive value of MRIs requiring biopsy, and breast cancer characteristics (size, stage) diagnosed in the different groups.
Between-group difference in incidence of interval cancers
A total of 40,373 women with extremely dense breasts were screened; 8,061 of these were randomly assigned to receive breast MRI and 32,312 to continued mammography only (1:4 cluster randomization) across 12 mammography centers in the Netherlands. Among the women assigned to the MRI group, 59% actually underwent MRI (4,783 of the 8,061).
The interval cancer rate in the mammography-only group was 5.0 per 1,000 screenings (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.3–5.8), while the interval cancer rate in the MRI-assigned group was 2.5 per 1,000 screenings (95% CI, 1.6–3.8) (TABLE 1).3

Key secondary outcomes
Of the women who underwent supplemental MRI, 9.49% were recalled for additional imaging, follow-up, or biopsy. Of the 4,783 women who had an MRI, 300 (6.3%) underwent a breast biopsy, and 79 breast cancers (1.65%) were detected. Sixty-four of these cancers were invasive, and 15 were ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Among women who underwent a biopsy for an MRI-detected abnormality, the positive predictive value was 26.3%.
Tumor characteristics. For women who developed breast cancer during the study, both tumor size at diagnosis and tumor stage (early vs late) were described. TABLE 2 shows these results in the women who had their breast cancer detected on MRI, those in the MRI-assigned group who developed interval cancer, and those in the mammography-only group who had interval cancers.3 Overall, tumor size was smaller in the interval group who underwent MRI compared with those who underwent mammography only.

Continue to: Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes...
Study contributes valuable data, but we need more on long-term outcomes
The trial by Bakker and colleagues employed a solid study design as women were randomly assigned to supplemental MRI screening or ongoing biennial mammography, and nearly all cancers were identified in the short-term of follow-up. In addition, very few women were lost to follow-up, and secondary outcomes, including false-positive rates, were collected to help providers and patients better understand some of the potential downsides of supplemental screening.
The substantial reduction in interval cancers (50% in the intent-to-screen analysis and 84% in the women who actually underwent supplemental MRI) was highly statistically significant (P<.001). While there were substantially fewer interval cancers in the MRI-assigned group, the interval cancers that did occur were of similar stage as those in the women assigned to the mammography-only group (TABLE 2).
Data demonstrate that interval cancers appear to be more aggressive than screen-detected cancers.4 While reducing interval cancers should be a good thing overall, it remains unproven that using supplemental MRI in all women with dense breasts would reduce breast cancer specific mortality, all-cause mortality, or the risk of more invasive treatments (for example, the need for chemotherapy or requirement for mastectomy).
On the other hand, using routine supplemental breast MRI in women with extremely dense breasts would result in very substantial use of resources, including cost, radiologist time, provider time, and machine time. In the United States, approximately 49 million women are aged 50 to 74.5 Breast MRI charges commonly range from $1,000 to $4,000. If the 4.9 million women with extremely dense breasts underwent supplemental MRI this year, the approximate cost would be somewhere between $4.9 and $19.5 billion for imaging alone. This does not include callbacks, biopsies, or provider time for ordering, interpreting, and arranging for follow-up.
While the reduction in interval cancers seen in this study is promising, more assurance of improvement in important outcomes—such as reduced mortality or reduced need for more invasive breast cancer treatments—should precede any routine change in practice.
Unanswered questions
This study did not address a number of other important questions, including:
Should MRI be done with every round of breast cancer screening given the possibility of prevalence bias? Prevalence bias can be defined as more cancers detected in the first round of MRI screening with possible reduced benefit in future rounds of screening. The study authors indicated that they will continue to analyze the study results to see what occurs in the next round of screening.
Is there a similar impact on decreased interval cancers in women undergoing annual mammography or in women screened between ages 40 and 49? This study was conducted in women aged 50 to 74 undergoing mammography every 2 years. In the United States, annual mammography in women aged 40 to 49 is frequently recommended.
What effect does supplemental MRI screening have in women with heterogeneously dense breasts, which represents 40% of the population? The US Food and Drug Administration recommends that all women with dense breasts be counseled regarding options for management.6
Do these results translate to the more racially and ethnically diverse populations of the United States? In the Netherlands, where this study was conducted, 85% to 90% of women are either Dutch or of western European origin. Women of different racial and ancestral backgrounds have biologically different breast cancers and cancer risk (for example, higher rates of triple-negative breast cancers in African American women; 10-fold higher rates of BRCA pathogenic variants in Ashkenazi Jewish women).
Continue to: Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively...
Use validated tools to assess risk comprehensively
Women aged 50 to 74 with extremely dense breasts have reduced interval cancers following a normal biennial mammogram if supplemental MRI is offered, but the long-term benefit of identifying these cancers earlier is unclear. Until more data are available on important long-term outcomes (such as breast cancer mortality and need for more invasive treatments), providers should consider breast density in the context of a more comprehensive assessment of breast cancer risk using a validated breast cancer risk assessment tool.
I prefer the modified version of the International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) tool, which is readily available online (https://ibis.ikonopedia.com/).7 This tool incorporates several breast cancer risk factors, including reproductive risk factors, body mass index, BRCA gene status, breast density, and family history. The tool takes 1 to 2 minutes to complete and provides an estimate of a woman’s 10-year risk and lifetime risk of breast cancer.
If the lifetime risk exceeds 20%, I offer the patient supplemental MRI screening, consistent with current recommendations of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Cancer Society.8,9 I generally recommend starting breast imaging screening 7 to 10 years prior to the youngest breast cancer occurrence in the family, with mammography starting no earlier than age 30 and MRI no earlier than age 25. Other validated tools also can be used.10-13
Incorporating breast density and other important risk factors allows a more comprehensive analysis upon which to counsel women about the value (benefits and harms) of breast imaging.8
- Sprague BL, Gagnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jcni/dju255.
- Boyd NF, Guo H, Martin LJ, et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:227-236.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al; for the DENSE Trial Study Group. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102.
- Drukker CA, Schmidt MK, Rutgers EJT, et al. Mammographic screening detects low-risk tumor biology breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;144:103-111.
- Statista website. Resident population of the United States by sex and age as of July 1, 2018. https://www.statista.com/statistics/241488/population-of-the-us-by-sex-and-age. Accessed January 6, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Mammography: what you need to know. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/mammography-what-you-need-know. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- IBIS (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study) website. Online Tyrer-Cuzick Model Breast Cancer Risk Evaluation Tool. ibis.ikonopedia.com. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- Bevers TB, Anderson BO, Bonaccio E, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis: NCCN practice guidelines in oncology. JNCCN. 2009;7:1060-1096.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- Antoniou AC, Cunningham AP, Peto J, et al. The BOADICEA model of genetic susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancers: updates and extensions. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1457-1466.
- Claus EB, Risch N, Thompson WD. Autosomal dominant inheritance of early-onset breast cancer: implications for risk prediction. Cancer. 1994;73:643-651.
- Parmigiani G, Berry D, Aguilar O. Determining carrier probabilities for breast cancer-susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:145-158.
- Tyrer J, Duffy SW, Cuzick J. A breast cancer prediction model incorporating familial and personal risk factors. Stat Med. 2004;23:1111-1130.
- Sprague BL, Gagnon RE, Burt V, et al. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:dju255. doi: 10.1093/jcni/dju255.
- Boyd NF, Guo H, Martin LJ, et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:227-236.
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al; for the DENSE Trial Study Group. Supplemental MRI screening for women with extremely dense breast tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2091-2102.
- Drukker CA, Schmidt MK, Rutgers EJT, et al. Mammographic screening detects low-risk tumor biology breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;144:103-111.
- Statista website. Resident population of the United States by sex and age as of July 1, 2018. https://www.statista.com/statistics/241488/population-of-the-us-by-sex-and-age. Accessed January 6, 2020.
- US Food and Drug Administration website. Mammography: what you need to know. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/mammography-what-you-need-know. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- IBIS (International Breast Cancer Intervention Study) website. Online Tyrer-Cuzick Model Breast Cancer Risk Evaluation Tool. ibis.ikonopedia.com. Accessed January 13, 2020.
- Bevers TB, Anderson BO, Bonaccio E, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis: NCCN practice guidelines in oncology. JNCCN. 2009;7:1060-1096.
- Saslow D, Boetes C, Burke W, et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:75-89.
- Antoniou AC, Cunningham AP, Peto J, et al. The BOADICEA model of genetic susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancers: updates and extensions. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1457-1466.
- Claus EB, Risch N, Thompson WD. Autosomal dominant inheritance of early-onset breast cancer: implications for risk prediction. Cancer. 1994;73:643-651.
- Parmigiani G, Berry D, Aguilar O. Determining carrier probabilities for breast cancer-susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:145-158.
- Tyrer J, Duffy SW, Cuzick J. A breast cancer prediction model incorporating familial and personal risk factors. Stat Med. 2004;23:1111-1130.
Global project reveals cancer’s genomic playbook
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
A massive collaborative project spanning four continents and 744 research centers has revealed driver mutations in both protein-coding and noncoding regions of 38 cancer types.
The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) is an integrative analysis of the whole-genome sequences from 2,658 donors across 38 common tumor types. The findings are expected to add exponentially to what’s currently known about the complex genetics of cancer, and they point to possible strategies for improving cancer prevention, diagnosis, and care.
Six articles summarizing the findings are presented in a series of papers in Nature, and 16 more appear in affiliated publications.
“It’s humbling that it was only 14 years ago that the genomics community sequenced its very first cancer exome, and it was able to identify mutations within the roughly 20,000 protein-coding genes in the human cell,” investigator Lincoln Stein, MD, PhD, of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research in Toronto, said in a telephone briefing.
Exome sequencing, however, covers only protein-coding genomic regions, which constitute only about 1% of the entire genome, “so assembling an accurate portrait of the cancer genome using just the exome data is like trying to put together a 100,000-piece jigsaw puzzle when you’re missing 99% of the pieces and there’s no puzzle box with a completed picture to guide you,” Dr. Stein said.
Members of the PCAWG from centers in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia screened 2,658 whole-cancer genomes and matched samples of noncancerous tissues from the same individuals, along with 1,188 transcriptomes cataloging the sequences and expression of RNA transcripts in a given tumor. The 6-year project netted more than 800 terabytes of genomic data, roughly equivalent to the digital holdings of the U.S. Library of Congress multiplied by 11.
The findings are summarized in papers focusing on cancer drivers, noncoding changes, mutational signatures, structural variants, cancer evolution over time, and RNA alterations.
Driver mutations
Investigators found that the average cancer genome contains four or five driver mutations located in both coding and noncoding regions. They also found, however, that in approximately 5% of cases no driver mutations could be identified.
A substantial proportion of tumors displayed “hallmarks of genomic catastrophes.” About 22% of tumors exhibited chromothripsis, a mutational process marked by hundreds or even thousands of clustered chromosomal rearrangements. About 18% showed chromoplexy, which is characterized by scattering and rearrangement of multiple strands of DNA from one or more chromosomes.
Analyzing driver point mutations and structural variants in noncoding regions, the investigators found the usual suspects – previously reported culprits – as well as novel candidates.
For example, they identified point mutations in the five prime region of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 and the three prime untranslated regions of NFKBIZ (a nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor) and TOB1 (an antiproliferative protein), focal deletion in BRD4 (a transcriptional and epigenetic regulator), and rearrangements in chromosomal loci in members of the AKR1C family of enzymes thought to play a role in disease progression.
In addition, investigators identified mutations in noncoding regions of TERT, a telomerase gene. These mutations result in ramped-up expression of telomerase, which in turn promotes uncontrollable division of tumor cells.
Mutational signatures
In a related line of research, PCAWG investigators identified new DNA mutational signatures ranging from single nucleotide polymorphisms to insertions and deletions, as well as to structural variants – rearrangements of large sections of the genome.
“The substantial size of our dataset, compared with previous analyses, enabled the discovery of new signatures, the separation of overlapping signatures, and the decomposition of signatures into components that may represent associated – but distinct – DNA damage, repair, and/or replication mechanisms. By estimating the contribution of each signature to the mutational catalogs of individual cancer genomes, we revealed associations of signatures to exogenous or endogenous exposures, as well as to defective DNA maintenance processes,” the investigators wrote.
They also acknowledged, however, that “many signatures are of unknown cause.”
Cancer evolution
One of the six main studies focused on the evolution of cancer over time. Instead of providing a “snapshot” of the genome as captured by sequencing tissue from a single biopsy, consortium investigators created full-length features of the “life history and evolution of mutational processes and driver mutation sequences.”
They found that early cancer development was marked by relatively few mutations in driver genes and by identifiable copy-number gains, including trisomy 7 in glioblastoma, and an abnormal mirroring of the arms (isochromosome) of chromosome 17 in medulloblastoma.
In 40% of the samples, however, there were significant changes in the mutational spectrum as the cancers grew, leading to a near quadrupling of driver genes and increased genomic instability in later-stage tumors.
“Copy-number alterations often occur in mitotic crises and lead to simultaneous gains of chromosomal segments,” the investigators wrote. “Timing analyses suggest that driver mutations often precede diagnosis by many years, if not decades. Together, these results determine the evolutionary trajectories of cancer and highlight opportunities for early cancer detection.”
Implications for cancer care
“When I used to treat patients with cancer, I was always completely amazed and puzzled by how two patients could have what looked like the same tumor. It would look the same under the microscope, have the same size, and the two patients would receive exactly the same treatment, but the two patients would have completely opposite outcomes; one would survive, and one would die. What this analysis … has done is really laid bare the reasons for that unpredictability in clinical outcomes,” Peter Campbell, MD, PhD, of the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Hinxton, England, said during the telebriefing.
“The most striking finding out of all of the suite of papers is just how different one person’s cancer genome is from another person’s. We see thousands of different combinations of mutations that can cause the cancer, and more than 80 different underlying processes generating the mutations in a cancer, and that leads to very different shapes and patterns in the genome that result,” he added.
On a positive note, the research shows that one or more driver mutations can be identified in about 95% of all cancer patients, and it elucidates the sequence of events leading to oncogenesis and tumor evolution, providing opportunities for earlier identification and potential interventions to prevent cancer, Dr. Campbell said.
The PCAWG was a collaborative multinational effort with multiple funding sources and many investigators.
SOURCE: Nature. 2020 Feb 5. https://www.nature.com/collections/pcawg/
FROM NATURE
High-dose chemo offers survival benefit only for highest-risk breast cancer
High-dose chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting offers a long-term survival advantage for women with very-high-risk stage III breast cancer, but does not improve survival odds for women with lower-risk cancers, an analysis of 20 years of follow-up data shows.
Among 885 women younger than 56 years at the time of treatment who had 4 or more involved axilliary lymph nodes, there was no overall survival difference over 2 decades between the total population of women randomized to receive adjuvant high-dose chemotherapy (HDCT) and those assigned to receive conventional-dose chemotherapy (CDCT).
However, women with 10 or more involved axilliary nodes and those with triple-negative breast cancer had an approximately 15% absolute improvement in 20-year overall survival with high-dose chemotherapy, although the difference for triple-negative disease fell just short of statistical significance, reported Tessa G. Steenbruggen, MD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam and colleagues.
“Our analysis confirms earlier results that HDCT has no significant overall survival benefit compared with CDCT for unselected patients with stage III [breast cancer]. However, we found a 14.6%improvement in 20-year OS estimates with HDCT in the predefined subgroup of patients with 10 or more involved [axilliary lymph nodes],” they wrote in JAMA Oncology.
And although other studies of chemotherapy regimens containing high doses of alkylating agents have shown increases in risk of late second malignancies and major cardiovascular events, there were no significant increases of either adverse event with HDCT in this study, the authors noted.
They reported 20-year follow-up results for 885 women who were enrolled in a 10-center randomized clinical trial conducted in the Netherlands from August 1, 1993, through July 31, 1999.
The participants were younger than age 56 years with breast cancer involving at least 4 axillary lymph nodes. All patients underwent surgery with complete axillary clearance and were then randomized to receive either conventional chemotherapy, which consisted of five cycles of fluorouracil 500mg/m2, epirubicin 90 mg/m2, and cyclophosphamide 500mg/m2 (FEC), or high-dose chemotherapy, with the first 4 cycles identical to conventional-dose chemotherapy but the fifth cycle consisting of cyclophosphamide 6000 mg/m2, thiotepa 480 mg/m2, and carboplatin 1600 mg/m2, supported with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
In addition, all patients received radiotherapy according to the local standard and 2 years of adjuvant tamoxifen.
After a median follow-up of 20.4 years, the 20-year overall survival (OS) rates were 45.3% for patients who had received high-dose chemotherapy and 41.5% for those who had received the conventional dose. This translated into a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.89.
However, for patients with 10 or more involved axillary nodes, the 20-year OS rates were 44.5% with HDCT and 29.9% with CDCT, translating into an absolute OS advantage for high-dose chemotherapy of 14.6% and an HR of 0.72 (P = .02).
Respective 20-year OS rates for women with triple-negative breast cancer were 52.9% and 37.5%, an absolute difference of 15.4% and a HR of 0.67, which fell just short of statistical significance, possibly because of the small number of patients with triple-negative breast cancer (140).
“In our 20-year follow-up analysis, there was no increase in cumulative risk for a second malignant neoplasm or for incidence of major cardiovascular events after HDCT,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that women randomized to high-dose chemotherapy had more frequent dysrhythmias, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, adding that the latter two adverse events may be partly attributable to a higher incidence of menopause induction among women who received HDCT.
The study was sponsored by University Medical Center Groningen and the The Netherlands Cancer Institute. Dr Steenbruggen reported receiving grants from the Dutch Health Insurance Council during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Steenbruggen TG et al. JAMA Oncology. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6276.
High-dose chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting offers a long-term survival advantage for women with very-high-risk stage III breast cancer, but does not improve survival odds for women with lower-risk cancers, an analysis of 20 years of follow-up data shows.
Among 885 women younger than 56 years at the time of treatment who had 4 or more involved axilliary lymph nodes, there was no overall survival difference over 2 decades between the total population of women randomized to receive adjuvant high-dose chemotherapy (HDCT) and those assigned to receive conventional-dose chemotherapy (CDCT).
However, women with 10 or more involved axilliary nodes and those with triple-negative breast cancer had an approximately 15% absolute improvement in 20-year overall survival with high-dose chemotherapy, although the difference for triple-negative disease fell just short of statistical significance, reported Tessa G. Steenbruggen, MD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam and colleagues.
“Our analysis confirms earlier results that HDCT has no significant overall survival benefit compared with CDCT for unselected patients with stage III [breast cancer]. However, we found a 14.6%improvement in 20-year OS estimates with HDCT in the predefined subgroup of patients with 10 or more involved [axilliary lymph nodes],” they wrote in JAMA Oncology.
And although other studies of chemotherapy regimens containing high doses of alkylating agents have shown increases in risk of late second malignancies and major cardiovascular events, there were no significant increases of either adverse event with HDCT in this study, the authors noted.
They reported 20-year follow-up results for 885 women who were enrolled in a 10-center randomized clinical trial conducted in the Netherlands from August 1, 1993, through July 31, 1999.
The participants were younger than age 56 years with breast cancer involving at least 4 axillary lymph nodes. All patients underwent surgery with complete axillary clearance and were then randomized to receive either conventional chemotherapy, which consisted of five cycles of fluorouracil 500mg/m2, epirubicin 90 mg/m2, and cyclophosphamide 500mg/m2 (FEC), or high-dose chemotherapy, with the first 4 cycles identical to conventional-dose chemotherapy but the fifth cycle consisting of cyclophosphamide 6000 mg/m2, thiotepa 480 mg/m2, and carboplatin 1600 mg/m2, supported with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
In addition, all patients received radiotherapy according to the local standard and 2 years of adjuvant tamoxifen.
After a median follow-up of 20.4 years, the 20-year overall survival (OS) rates were 45.3% for patients who had received high-dose chemotherapy and 41.5% for those who had received the conventional dose. This translated into a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.89.
However, for patients with 10 or more involved axillary nodes, the 20-year OS rates were 44.5% with HDCT and 29.9% with CDCT, translating into an absolute OS advantage for high-dose chemotherapy of 14.6% and an HR of 0.72 (P = .02).
Respective 20-year OS rates for women with triple-negative breast cancer were 52.9% and 37.5%, an absolute difference of 15.4% and a HR of 0.67, which fell just short of statistical significance, possibly because of the small number of patients with triple-negative breast cancer (140).
“In our 20-year follow-up analysis, there was no increase in cumulative risk for a second malignant neoplasm or for incidence of major cardiovascular events after HDCT,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that women randomized to high-dose chemotherapy had more frequent dysrhythmias, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, adding that the latter two adverse events may be partly attributable to a higher incidence of menopause induction among women who received HDCT.
The study was sponsored by University Medical Center Groningen and the The Netherlands Cancer Institute. Dr Steenbruggen reported receiving grants from the Dutch Health Insurance Council during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Steenbruggen TG et al. JAMA Oncology. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6276.
High-dose chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting offers a long-term survival advantage for women with very-high-risk stage III breast cancer, but does not improve survival odds for women with lower-risk cancers, an analysis of 20 years of follow-up data shows.
Among 885 women younger than 56 years at the time of treatment who had 4 or more involved axilliary lymph nodes, there was no overall survival difference over 2 decades between the total population of women randomized to receive adjuvant high-dose chemotherapy (HDCT) and those assigned to receive conventional-dose chemotherapy (CDCT).
However, women with 10 or more involved axilliary nodes and those with triple-negative breast cancer had an approximately 15% absolute improvement in 20-year overall survival with high-dose chemotherapy, although the difference for triple-negative disease fell just short of statistical significance, reported Tessa G. Steenbruggen, MD, from the Netherlands Cancer Institute in Amsterdam and colleagues.
“Our analysis confirms earlier results that HDCT has no significant overall survival benefit compared with CDCT for unselected patients with stage III [breast cancer]. However, we found a 14.6%improvement in 20-year OS estimates with HDCT in the predefined subgroup of patients with 10 or more involved [axilliary lymph nodes],” they wrote in JAMA Oncology.
And although other studies of chemotherapy regimens containing high doses of alkylating agents have shown increases in risk of late second malignancies and major cardiovascular events, there were no significant increases of either adverse event with HDCT in this study, the authors noted.
They reported 20-year follow-up results for 885 women who were enrolled in a 10-center randomized clinical trial conducted in the Netherlands from August 1, 1993, through July 31, 1999.
The participants were younger than age 56 years with breast cancer involving at least 4 axillary lymph nodes. All patients underwent surgery with complete axillary clearance and were then randomized to receive either conventional chemotherapy, which consisted of five cycles of fluorouracil 500mg/m2, epirubicin 90 mg/m2, and cyclophosphamide 500mg/m2 (FEC), or high-dose chemotherapy, with the first 4 cycles identical to conventional-dose chemotherapy but the fifth cycle consisting of cyclophosphamide 6000 mg/m2, thiotepa 480 mg/m2, and carboplatin 1600 mg/m2, supported with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
In addition, all patients received radiotherapy according to the local standard and 2 years of adjuvant tamoxifen.
After a median follow-up of 20.4 years, the 20-year overall survival (OS) rates were 45.3% for patients who had received high-dose chemotherapy and 41.5% for those who had received the conventional dose. This translated into a nonsignificant hazard ratio of 0.89.
However, for patients with 10 or more involved axillary nodes, the 20-year OS rates were 44.5% with HDCT and 29.9% with CDCT, translating into an absolute OS advantage for high-dose chemotherapy of 14.6% and an HR of 0.72 (P = .02).
Respective 20-year OS rates for women with triple-negative breast cancer were 52.9% and 37.5%, an absolute difference of 15.4% and a HR of 0.67, which fell just short of statistical significance, possibly because of the small number of patients with triple-negative breast cancer (140).
“In our 20-year follow-up analysis, there was no increase in cumulative risk for a second malignant neoplasm or for incidence of major cardiovascular events after HDCT,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that women randomized to high-dose chemotherapy had more frequent dysrhythmias, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, adding that the latter two adverse events may be partly attributable to a higher incidence of menopause induction among women who received HDCT.
The study was sponsored by University Medical Center Groningen and the The Netherlands Cancer Institute. Dr Steenbruggen reported receiving grants from the Dutch Health Insurance Council during the conduct of the study.
SOURCE: Steenbruggen TG et al. JAMA Oncology. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6276.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: High-dose chemotherapy offers a long-term breast cancer survival advantage only for women with very-high-risk disease.
Major finding: The absolute 20-year overall survival benefit for women with 10 or more involved lymph nodes was 14.6%.
Study details: Long-term, follow-up study of 885 women under age 56 years with stage III breast cancer treated with adjuvant high- or conventional-dose chemotherapy.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by University Medical Center Groningen and the The Netherlands Cancer Institute. Dr. Steenbruggen reported receiving grants from the Dutch Health Insurance Council during the conduct of the study.
Source: Steenbruggen TG et al. JAMA Oncology. 2020 Jan 30. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.6276.
Researchers win funding for breast cancer studies
Five breast cancer researchers have won 3 years of funding from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network’s Oncology Research Program and Pfizer Global Medical Grants. The researchers will receive up to $1.4 million.
Allison Lipitz-Snyderman, PhD, and Erin Gillespie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, have won funding for a project entitled, “Leveraging an academic-community partnership model to improve the quality of radiation treatment for metastatic breast cancer patients.”
Dr. Gillespie and Dr. Lipitz-Snyderman plan to use an existing partnership between Memorial Sloan Kettering and three community-based institutions to test a system for implementing best practices in radiation treatment. The system includes a web-based platform that disseminates expert recommendations as well as weekly conferences during which community radiation oncologists can consult with specialists on complex cases.
Aki Morikawa, MD, PhD, of the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center in Ann Arbor, won funding for a project entitled, “Personalized multi-care: A tailored approach to multidisciplinary care coordination delivery for metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases.”
The goals of Dr. Morikawa’s project are to educate patients and providers on managing central nervous system metastases in the breast cancer setting, tailor care coordination and planning to patient and provider needs, and increase patient participation in studies.
Karen Lisa Smith, MD, of the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore, won funding for a project entitled, “The Johns Hopkins Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program: Collaborating to improve metastatic breast cancer care.”
The goal of the Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program is for Johns Hopkins and mid-Atlantic regional practices to fight metastatic breast cancer together. To that end, Dr. Smith plans to create a multidisciplinary clinic that offers supportive care and treatment recommendations, a database for patient tracking and trial screening, educational resources, and new opportunities for provider collaboration.
Laura Spring, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, won funding for a project entitled, “Expanding precision medicine for patients with metastatic breast cancer in the community: Leveraging academic strength and community partnership.”
The goal of Dr. Spring’s project is to extend academic resources to affiliated network sites. This will involve increasing access to tissue-based and blood-based tumor genotyping for patients with metastatic breast cancer, creating a virtual molecular and precision medicine clinic that provides interpretation of genomic data and treatment recommendations, and offering clinical trial matching to metastatic breast cancer patients treated at network sites.
Five breast cancer researchers have won 3 years of funding from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network’s Oncology Research Program and Pfizer Global Medical Grants. The researchers will receive up to $1.4 million.
Allison Lipitz-Snyderman, PhD, and Erin Gillespie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, have won funding for a project entitled, “Leveraging an academic-community partnership model to improve the quality of radiation treatment for metastatic breast cancer patients.”
Dr. Gillespie and Dr. Lipitz-Snyderman plan to use an existing partnership between Memorial Sloan Kettering and three community-based institutions to test a system for implementing best practices in radiation treatment. The system includes a web-based platform that disseminates expert recommendations as well as weekly conferences during which community radiation oncologists can consult with specialists on complex cases.
Aki Morikawa, MD, PhD, of the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center in Ann Arbor, won funding for a project entitled, “Personalized multi-care: A tailored approach to multidisciplinary care coordination delivery for metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases.”
The goals of Dr. Morikawa’s project are to educate patients and providers on managing central nervous system metastases in the breast cancer setting, tailor care coordination and planning to patient and provider needs, and increase patient participation in studies.
Karen Lisa Smith, MD, of the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore, won funding for a project entitled, “The Johns Hopkins Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program: Collaborating to improve metastatic breast cancer care.”
The goal of the Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program is for Johns Hopkins and mid-Atlantic regional practices to fight metastatic breast cancer together. To that end, Dr. Smith plans to create a multidisciplinary clinic that offers supportive care and treatment recommendations, a database for patient tracking and trial screening, educational resources, and new opportunities for provider collaboration.
Laura Spring, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, won funding for a project entitled, “Expanding precision medicine for patients with metastatic breast cancer in the community: Leveraging academic strength and community partnership.”
The goal of Dr. Spring’s project is to extend academic resources to affiliated network sites. This will involve increasing access to tissue-based and blood-based tumor genotyping for patients with metastatic breast cancer, creating a virtual molecular and precision medicine clinic that provides interpretation of genomic data and treatment recommendations, and offering clinical trial matching to metastatic breast cancer patients treated at network sites.
Five breast cancer researchers have won 3 years of funding from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network’s Oncology Research Program and Pfizer Global Medical Grants. The researchers will receive up to $1.4 million.
Allison Lipitz-Snyderman, PhD, and Erin Gillespie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, have won funding for a project entitled, “Leveraging an academic-community partnership model to improve the quality of radiation treatment for metastatic breast cancer patients.”
Dr. Gillespie and Dr. Lipitz-Snyderman plan to use an existing partnership between Memorial Sloan Kettering and three community-based institutions to test a system for implementing best practices in radiation treatment. The system includes a web-based platform that disseminates expert recommendations as well as weekly conferences during which community radiation oncologists can consult with specialists on complex cases.
Aki Morikawa, MD, PhD, of the University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center in Ann Arbor, won funding for a project entitled, “Personalized multi-care: A tailored approach to multidisciplinary care coordination delivery for metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases.”
The goals of Dr. Morikawa’s project are to educate patients and providers on managing central nervous system metastases in the breast cancer setting, tailor care coordination and planning to patient and provider needs, and increase patient participation in studies.
Karen Lisa Smith, MD, of the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore, won funding for a project entitled, “The Johns Hopkins Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program: Collaborating to improve metastatic breast cancer care.”
The goal of the Metastatic Breast Cancer Partners Program is for Johns Hopkins and mid-Atlantic regional practices to fight metastatic breast cancer together. To that end, Dr. Smith plans to create a multidisciplinary clinic that offers supportive care and treatment recommendations, a database for patient tracking and trial screening, educational resources, and new opportunities for provider collaboration.
Laura Spring, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, won funding for a project entitled, “Expanding precision medicine for patients with metastatic breast cancer in the community: Leveraging academic strength and community partnership.”
The goal of Dr. Spring’s project is to extend academic resources to affiliated network sites. This will involve increasing access to tissue-based and blood-based tumor genotyping for patients with metastatic breast cancer, creating a virtual molecular and precision medicine clinic that provides interpretation of genomic data and treatment recommendations, and offering clinical trial matching to metastatic breast cancer patients treated at network sites.
Score predicts locoregional recurrence of breast cancer
The 21-gene assay recurrence score can aid decisions about radiotherapy for postmenopausal patients with node-positive breast cancer, according to researchers.
The researchers analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery (excision and radiation) and received chemotherapy plus tamoxifen or tamoxifen alone. Results showed that patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score, according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX, were more likely to have locoregional recurrence (LRR).
“We believe that the recurrence score adds independent prognostic information that could be used with standard clinical factors for identifying LRR risk and making radiotherapy decisions,” Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Dr. Woodward and colleagues analyzed data from a phase 3 trial (NCT00929591) of postmenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor–positive, node-positive breast cancer. There were 367 patients who received tamoxifen alone (n = 148) or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen (n = 219).
Of the 367 patients, 316 were included in the primary analysis. This includes 252 patients who underwent mastectomy without radiotherapy and 64 patients who underwent breast-conserving surgery with radiotherapy.
The researchers defined LRR as a recurrence in the breast; chest wall; or axillary, infraclavicular, supraclavicular, or internal mammary lymph nodes.
The LRR incidence was 5.8% (7/121) among patients with a low recurrence score and 13.8% (27/195) among patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score. The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
The researchers conducted a multivariable analysis for LRR, which included the recurrence score, randomized treatment (combination regimen vs. tamoxifen alone), number of positive nodes (three or fewer vs. four or more), and type of surgery (mastectomy vs. excision and radiation).
Having intermediate or high recurrence scores was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). Having four or more involved nodes was a significant predictor of LRR as well (hazard ratio, 3.37; P = .001). Randomized treatment and surgery were not significantly associated with LRR.
The researchers also conducted an exploratory analysis and found that a recurrence score of 18 was the optimal cutoff for the association of recurrence score and LRR.
“This study found that higher recurrence scores were associated with increased LRR after adjustment for treatment, type of surgical procedure, and number of positive nodes,” Dr. Woodward and colleagues wrote. “This finding suggests that the recurrence score may be used, along with accepted clinical variables, to assess the risk of LRR during radiotherapy decision making. We recommend considering the recurrence score, when available, as one of the factors in selecting patients for postmastectomy radiotherapy.”
This research was funded by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Canadian Cancer Society, and Genomic Health, which markets the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX. Dr. Woodward disclosed receiving personal fees from Genomic Health outside this research as well as an advisory fee from Merck.
SOURCE: Woodward WA et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559.
The 21-gene assay recurrence score can aid decisions about radiotherapy for postmenopausal patients with node-positive breast cancer, according to researchers.
The researchers analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery (excision and radiation) and received chemotherapy plus tamoxifen or tamoxifen alone. Results showed that patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score, according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX, were more likely to have locoregional recurrence (LRR).
“We believe that the recurrence score adds independent prognostic information that could be used with standard clinical factors for identifying LRR risk and making radiotherapy decisions,” Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Dr. Woodward and colleagues analyzed data from a phase 3 trial (NCT00929591) of postmenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor–positive, node-positive breast cancer. There were 367 patients who received tamoxifen alone (n = 148) or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen (n = 219).
Of the 367 patients, 316 were included in the primary analysis. This includes 252 patients who underwent mastectomy without radiotherapy and 64 patients who underwent breast-conserving surgery with radiotherapy.
The researchers defined LRR as a recurrence in the breast; chest wall; or axillary, infraclavicular, supraclavicular, or internal mammary lymph nodes.
The LRR incidence was 5.8% (7/121) among patients with a low recurrence score and 13.8% (27/195) among patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score. The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
The researchers conducted a multivariable analysis for LRR, which included the recurrence score, randomized treatment (combination regimen vs. tamoxifen alone), number of positive nodes (three or fewer vs. four or more), and type of surgery (mastectomy vs. excision and radiation).
Having intermediate or high recurrence scores was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). Having four or more involved nodes was a significant predictor of LRR as well (hazard ratio, 3.37; P = .001). Randomized treatment and surgery were not significantly associated with LRR.
The researchers also conducted an exploratory analysis and found that a recurrence score of 18 was the optimal cutoff for the association of recurrence score and LRR.
“This study found that higher recurrence scores were associated with increased LRR after adjustment for treatment, type of surgical procedure, and number of positive nodes,” Dr. Woodward and colleagues wrote. “This finding suggests that the recurrence score may be used, along with accepted clinical variables, to assess the risk of LRR during radiotherapy decision making. We recommend considering the recurrence score, when available, as one of the factors in selecting patients for postmastectomy radiotherapy.”
This research was funded by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Canadian Cancer Society, and Genomic Health, which markets the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX. Dr. Woodward disclosed receiving personal fees from Genomic Health outside this research as well as an advisory fee from Merck.
SOURCE: Woodward WA et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559.
The 21-gene assay recurrence score can aid decisions about radiotherapy for postmenopausal patients with node-positive breast cancer, according to researchers.
The researchers analyzed patients who underwent mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery (excision and radiation) and received chemotherapy plus tamoxifen or tamoxifen alone. Results showed that patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score, according to the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX, were more likely to have locoregional recurrence (LRR).
“We believe that the recurrence score adds independent prognostic information that could be used with standard clinical factors for identifying LRR risk and making radiotherapy decisions,” Wendy A. Woodward, MD, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and coauthors wrote in JAMA Oncology.
Dr. Woodward and colleagues analyzed data from a phase 3 trial (NCT00929591) of postmenopausal women with estrogen or progesterone receptor–positive, node-positive breast cancer. There were 367 patients who received tamoxifen alone (n = 148) or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and fluorouracil followed by tamoxifen (n = 219).
Of the 367 patients, 316 were included in the primary analysis. This includes 252 patients who underwent mastectomy without radiotherapy and 64 patients who underwent breast-conserving surgery with radiotherapy.
The researchers defined LRR as a recurrence in the breast; chest wall; or axillary, infraclavicular, supraclavicular, or internal mammary lymph nodes.
The LRR incidence was 5.8% (7/121) among patients with a low recurrence score and 13.8% (27/195) among patients with an intermediate or high recurrence score. The estimated 10-year cumulative LRR incidence rates were 9.7% and 16.5%, respectively (P = .02).
The researchers conducted a multivariable analysis for LRR, which included the recurrence score, randomized treatment (combination regimen vs. tamoxifen alone), number of positive nodes (three or fewer vs. four or more), and type of surgery (mastectomy vs. excision and radiation).
Having intermediate or high recurrence scores was a significant predictor of LRR, with a hazard ratio of 2.36 (P = .04). Having four or more involved nodes was a significant predictor of LRR as well (hazard ratio, 3.37; P = .001). Randomized treatment and surgery were not significantly associated with LRR.
The researchers also conducted an exploratory analysis and found that a recurrence score of 18 was the optimal cutoff for the association of recurrence score and LRR.
“This study found that higher recurrence scores were associated with increased LRR after adjustment for treatment, type of surgical procedure, and number of positive nodes,” Dr. Woodward and colleagues wrote. “This finding suggests that the recurrence score may be used, along with accepted clinical variables, to assess the risk of LRR during radiotherapy decision making. We recommend considering the recurrence score, when available, as one of the factors in selecting patients for postmastectomy radiotherapy.”
This research was funded by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Canadian Cancer Society, and Genomic Health, which markets the 21-gene assay OncotypeDX. Dr. Woodward disclosed receiving personal fees from Genomic Health outside this research as well as an advisory fee from Merck.
SOURCE: Woodward WA et al. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5559.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Insurance coverage mediates racial disparities in breast cancer
according to new study.
Insurance coverage “mediates nearly half of the increased risk for later-stage breast cancer diagnosis seen among racial/ethnic minorities,” Naomi Ko, MD, of Boston University and colleagues wrote in a research report published in JAMA Oncology.
With Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program data, the researchers looked at patient records on 177,075 women (148,124 insured and 28,951 uninsured or on Medicaid) aged 40-64 years who received a breast cancer diagnosis between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 31, 2016. They found that a higher proportion of women (20%) uninsured or on Medicaid received a diagnosis of a higher-stage breast cancer (stage III), compared with women who had health insurance (11%).
More non-Hispanic black women (17%), American Indian or Alaskan native (15%), and Hispanic women (16%) received a stage III breast cancer diagnosis, compared with non-Hispanic white women (12%). Non-Hispanic white women were more likely to have insurance coverage at the time of diagnosis (89%), compared with non-Hispanic black women (75%), American Indian or Alaskan native (58%), and Hispanic women (67%).
“Without insurance coverage, the lack of prevention, screening, and access to care, as well as delays in diagnosis, lead to later stage of disease at diagnosis and thus worse survival,” Dr. Ko and colleagues wrote, adding that patients with a diagnosis of later-stage cancer require more intensive treatment and are at higher risk for treatment-associated morbidity and poorer overall quality of life.
Another consequence of the later-stage diagnosis is increased financial costs related to treatment for these patients, according to the investigator. They cite research that shows stage III cancer was 58% more costly to treat than was stage I or II breast cancer.
“Overall, earlier stage at diagnosis of breast cancer is not only beneficial for individual patients and families but also on society as a whole to decrease costs and equity among all populations,” Dr. Ko and colleagues added.
The researchers noted some of the limitations of the study, which include the source of data (the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, which covers 18 regions and might not be generalizable to all populations), as well as the age range of the studied population.
That being said, the authors also acknowledged that the findings “do not suggest that insurance alone will eliminate racial/ethnic disparities in breast cancer,” but “the ability to quantify the association that insurance has with breast cancer stage is relevant to potential policy changes regarding insurance and a prioritization of solutions for the increased burden of cancer mortality and morbidity disproportionately placed on racial/ethnic minority populations.”
Funding sources include the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Cancer Institute, and National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The authors reported no conflicts of interest related to this study.
SOURCE: Ko N et al. JAMA Onc. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5672.
according to new study.
Insurance coverage “mediates nearly half of the increased risk for later-stage breast cancer diagnosis seen among racial/ethnic minorities,” Naomi Ko, MD, of Boston University and colleagues wrote in a research report published in JAMA Oncology.
With Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program data, the researchers looked at patient records on 177,075 women (148,124 insured and 28,951 uninsured or on Medicaid) aged 40-64 years who received a breast cancer diagnosis between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 31, 2016. They found that a higher proportion of women (20%) uninsured or on Medicaid received a diagnosis of a higher-stage breast cancer (stage III), compared with women who had health insurance (11%).
More non-Hispanic black women (17%), American Indian or Alaskan native (15%), and Hispanic women (16%) received a stage III breast cancer diagnosis, compared with non-Hispanic white women (12%). Non-Hispanic white women were more likely to have insurance coverage at the time of diagnosis (89%), compared with non-Hispanic black women (75%), American Indian or Alaskan native (58%), and Hispanic women (67%).
“Without insurance coverage, the lack of prevention, screening, and access to care, as well as delays in diagnosis, lead to later stage of disease at diagnosis and thus worse survival,” Dr. Ko and colleagues wrote, adding that patients with a diagnosis of later-stage cancer require more intensive treatment and are at higher risk for treatment-associated morbidity and poorer overall quality of life.
Another consequence of the later-stage diagnosis is increased financial costs related to treatment for these patients, according to the investigator. They cite research that shows stage III cancer was 58% more costly to treat than was stage I or II breast cancer.
“Overall, earlier stage at diagnosis of breast cancer is not only beneficial for individual patients and families but also on society as a whole to decrease costs and equity among all populations,” Dr. Ko and colleagues added.
The researchers noted some of the limitations of the study, which include the source of data (the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, which covers 18 regions and might not be generalizable to all populations), as well as the age range of the studied population.
That being said, the authors also acknowledged that the findings “do not suggest that insurance alone will eliminate racial/ethnic disparities in breast cancer,” but “the ability to quantify the association that insurance has with breast cancer stage is relevant to potential policy changes regarding insurance and a prioritization of solutions for the increased burden of cancer mortality and morbidity disproportionately placed on racial/ethnic minority populations.”
Funding sources include the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Cancer Institute, and National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The authors reported no conflicts of interest related to this study.
SOURCE: Ko N et al. JAMA Onc. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5672.
according to new study.
Insurance coverage “mediates nearly half of the increased risk for later-stage breast cancer diagnosis seen among racial/ethnic minorities,” Naomi Ko, MD, of Boston University and colleagues wrote in a research report published in JAMA Oncology.
With Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program data, the researchers looked at patient records on 177,075 women (148,124 insured and 28,951 uninsured or on Medicaid) aged 40-64 years who received a breast cancer diagnosis between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 31, 2016. They found that a higher proportion of women (20%) uninsured or on Medicaid received a diagnosis of a higher-stage breast cancer (stage III), compared with women who had health insurance (11%).
More non-Hispanic black women (17%), American Indian or Alaskan native (15%), and Hispanic women (16%) received a stage III breast cancer diagnosis, compared with non-Hispanic white women (12%). Non-Hispanic white women were more likely to have insurance coverage at the time of diagnosis (89%), compared with non-Hispanic black women (75%), American Indian or Alaskan native (58%), and Hispanic women (67%).
“Without insurance coverage, the lack of prevention, screening, and access to care, as well as delays in diagnosis, lead to later stage of disease at diagnosis and thus worse survival,” Dr. Ko and colleagues wrote, adding that patients with a diagnosis of later-stage cancer require more intensive treatment and are at higher risk for treatment-associated morbidity and poorer overall quality of life.
Another consequence of the later-stage diagnosis is increased financial costs related to treatment for these patients, according to the investigator. They cite research that shows stage III cancer was 58% more costly to treat than was stage I or II breast cancer.
“Overall, earlier stage at diagnosis of breast cancer is not only beneficial for individual patients and families but also on society as a whole to decrease costs and equity among all populations,” Dr. Ko and colleagues added.
The researchers noted some of the limitations of the study, which include the source of data (the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, which covers 18 regions and might not be generalizable to all populations), as well as the age range of the studied population.
That being said, the authors also acknowledged that the findings “do not suggest that insurance alone will eliminate racial/ethnic disparities in breast cancer,” but “the ability to quantify the association that insurance has with breast cancer stage is relevant to potential policy changes regarding insurance and a prioritization of solutions for the increased burden of cancer mortality and morbidity disproportionately placed on racial/ethnic minority populations.”
Funding sources include the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Cancer Institute, and National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The authors reported no conflicts of interest related to this study.
SOURCE: Ko N et al. JAMA Onc. 2020 Jan 9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5672.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
SABCS research changes practice
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two presentations from the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) that will likely change practice for some breast cancer patients – even before the ball drops in Times Square on New Year’s Eve.
Residual cancer burden
Researchers reported a multi-institutional analysis of individual patient-level data on 5,160 patients who had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for localized breast cancer at 11 different centers. They found that residual cancer burden (RCB) was significantly associated with event-free (EFS) and distant recurrence-free survival. The value of calculating RCB was seen across all breast cancer tumor phenotypes (SABCS 2019, Abstract GS5-01).
RCB is calculated by analyzing the residual disease after NAC for the primary tumor bed, the number of positive axillary nodes, and the size of largest node metastasis. It is graded from RCB-0 (pCR) to RCB-III (extensive residual disease).
Both EFS and distant recurrence-free survival were strongly associated with RCB for the overall population and for each breast cancer subtype. For hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative disease there was a slight hiccup in that RCB-0 was associated with a 10-year EFS of 81%, but EFS was 86% for RCB-I. Fortunately, the prognostic reliability of RCB was clear for RCB-II (69%) and RCB-III (52%). The presenter, W. Fraser Symmans, MD, commented that RCB is most prognostic when higher levels of residual disease are present. RCB remained prognostic in multivariate models adjusting for age, grade, and clinical T and N stage at diagnosis.
How these results influence practice
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with localized breast cancer, we struggle when patients ask: “So, doctor, how am I likely to do?” We piece together a complicated – and inconsistent – answer, based on breast cancer subtype, original stage of disease, whether pCR was attained, and other factors.
For patients with triple-negative breast cancer, we have the option of adding capecitabine and/or participation in ongoing clinical trials, for patients with residual disease after NAC. Among the HER2-positive patients, we have data from the KATHERINE, ExtaNET, and APHINITY trials that provide options for additional treatment in those patients, as well. For patients with potentially hormonally responsive, HER2-negative disease, we can emphasize the importance of postoperative adjuvant endocrine therapy, the mandate for continued adherence to oral therapy, and the lower likelihood of (and prognostic value of) pCR in that breast cancer subtype.
Where we previously had a complicated, nuanced discussion, we now have data from a multi-institutional, meticulous analysis to guide further treatment, candidacy for clinical trials, and our expectations of what would be meaningful results from additional therapy. This meets my definition of “practice-changing” research.
APHINITY follow-up
APHINITY was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that previously demonstrated that pertuzumab added to standard chemotherapy plus 1 year of trastuzumab in operable HER2-positive breast cancer was associated with modest, but statistically significant, improvement in invasive disease–free survival (IDFS), compared with placebo and chemotherapy plus trastuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.81; P = .04). When the initial results – with a median follow-up of 45.4 months – were published, the authors promised an update at 6 years. Martine Piccart, MD, PhD, provided that update at the 2019 SABCS (Abstract GS1-04).
In the updated analysis, overall survival was 94.8% among patients on the pertuzumab arm and 93.9% among patients taking placebo (HR, 0.85). IDFS rates were 90.6% versus 87.8% in the intent-to-treat population. The investigator commented that this difference was caused mainly by a reduction in distant and loco-regional recurrences.
Central nervous system metastases, contralateral invasive breast cancers, and death without a prior event were no different between the two treatment groups.
Improvement in IDFS (the primary endpoint) from pertuzumab was most impressive in the node-positive cohort, 87.9% versus 83.4% for placebo (HR, 0.72). There was no benefit in the node-negative population (95.0% vs. 94.9%; HR, 1.02).
In contrast to the 3-year analysis, the benefits in IDFS were seen regardless of hormone receptor status. Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged. The rate of severe cardiac events was below 1% in both groups.
How these results influence practice
“Patience is a virtue” appeared for the first time in the English language around 1360, in William Langland’s poem “Piers Plowman.” They are true words, indeed.
When the initial results of APHINITY were published in 2017, they led to the approval of pertuzumab as an addition to chemotherapy plus trastuzumab for high-risk, early, HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Still, the difference in IDFS curves was visually unimpressive (absolute difference 1.7% in the intent-to-treat and 3.2% in the node-positive patients) and pertuzumab was associated with more grade 3 toxicities (primarily diarrhea) and treatment discontinuations.
An optimist would have observed that the IDFS curves in 2017 did not start to diverge until 24 months and would have noted that the divergence increased with time. That virtuously patient person would have expected that the second interim analysis would show larger absolute benefits, and that the hormone receptor–positive patients (64% of the total) would not yet have relapsed by the first interim analysis and that pertuzumab’s benefit in that group would emerge late.
That appears to be what is happening. It provides hope that an overall survival benefit will become more evident with time. If the target P value for an overall survival difference (.0012) is met by the time of the third interim analysis, our patience (and the FDA’s decision to grant approval for pertuzumab for this indication) will have been amply rewarded. For selected HER2-posiitve patients with high RCB, especially those who tolerated neoadjuvant trastuzumab plus pertuzumab regimens, postoperative adjuvant pertuzumab may be an appealing option.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two presentations from the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) that will likely change practice for some breast cancer patients – even before the ball drops in Times Square on New Year’s Eve.
Residual cancer burden
Researchers reported a multi-institutional analysis of individual patient-level data on 5,160 patients who had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for localized breast cancer at 11 different centers. They found that residual cancer burden (RCB) was significantly associated with event-free (EFS) and distant recurrence-free survival. The value of calculating RCB was seen across all breast cancer tumor phenotypes (SABCS 2019, Abstract GS5-01).
RCB is calculated by analyzing the residual disease after NAC for the primary tumor bed, the number of positive axillary nodes, and the size of largest node metastasis. It is graded from RCB-0 (pCR) to RCB-III (extensive residual disease).
Both EFS and distant recurrence-free survival were strongly associated with RCB for the overall population and for each breast cancer subtype. For hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative disease there was a slight hiccup in that RCB-0 was associated with a 10-year EFS of 81%, but EFS was 86% for RCB-I. Fortunately, the prognostic reliability of RCB was clear for RCB-II (69%) and RCB-III (52%). The presenter, W. Fraser Symmans, MD, commented that RCB is most prognostic when higher levels of residual disease are present. RCB remained prognostic in multivariate models adjusting for age, grade, and clinical T and N stage at diagnosis.
How these results influence practice
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with localized breast cancer, we struggle when patients ask: “So, doctor, how am I likely to do?” We piece together a complicated – and inconsistent – answer, based on breast cancer subtype, original stage of disease, whether pCR was attained, and other factors.
For patients with triple-negative breast cancer, we have the option of adding capecitabine and/or participation in ongoing clinical trials, for patients with residual disease after NAC. Among the HER2-positive patients, we have data from the KATHERINE, ExtaNET, and APHINITY trials that provide options for additional treatment in those patients, as well. For patients with potentially hormonally responsive, HER2-negative disease, we can emphasize the importance of postoperative adjuvant endocrine therapy, the mandate for continued adherence to oral therapy, and the lower likelihood of (and prognostic value of) pCR in that breast cancer subtype.
Where we previously had a complicated, nuanced discussion, we now have data from a multi-institutional, meticulous analysis to guide further treatment, candidacy for clinical trials, and our expectations of what would be meaningful results from additional therapy. This meets my definition of “practice-changing” research.
APHINITY follow-up
APHINITY was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that previously demonstrated that pertuzumab added to standard chemotherapy plus 1 year of trastuzumab in operable HER2-positive breast cancer was associated with modest, but statistically significant, improvement in invasive disease–free survival (IDFS), compared with placebo and chemotherapy plus trastuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.81; P = .04). When the initial results – with a median follow-up of 45.4 months – were published, the authors promised an update at 6 years. Martine Piccart, MD, PhD, provided that update at the 2019 SABCS (Abstract GS1-04).
In the updated analysis, overall survival was 94.8% among patients on the pertuzumab arm and 93.9% among patients taking placebo (HR, 0.85). IDFS rates were 90.6% versus 87.8% in the intent-to-treat population. The investigator commented that this difference was caused mainly by a reduction in distant and loco-regional recurrences.
Central nervous system metastases, contralateral invasive breast cancers, and death without a prior event were no different between the two treatment groups.
Improvement in IDFS (the primary endpoint) from pertuzumab was most impressive in the node-positive cohort, 87.9% versus 83.4% for placebo (HR, 0.72). There was no benefit in the node-negative population (95.0% vs. 94.9%; HR, 1.02).
In contrast to the 3-year analysis, the benefits in IDFS were seen regardless of hormone receptor status. Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged. The rate of severe cardiac events was below 1% in both groups.
How these results influence practice
“Patience is a virtue” appeared for the first time in the English language around 1360, in William Langland’s poem “Piers Plowman.” They are true words, indeed.
When the initial results of APHINITY were published in 2017, they led to the approval of pertuzumab as an addition to chemotherapy plus trastuzumab for high-risk, early, HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Still, the difference in IDFS curves was visually unimpressive (absolute difference 1.7% in the intent-to-treat and 3.2% in the node-positive patients) and pertuzumab was associated with more grade 3 toxicities (primarily diarrhea) and treatment discontinuations.
An optimist would have observed that the IDFS curves in 2017 did not start to diverge until 24 months and would have noted that the divergence increased with time. That virtuously patient person would have expected that the second interim analysis would show larger absolute benefits, and that the hormone receptor–positive patients (64% of the total) would not yet have relapsed by the first interim analysis and that pertuzumab’s benefit in that group would emerge late.
That appears to be what is happening. It provides hope that an overall survival benefit will become more evident with time. If the target P value for an overall survival difference (.0012) is met by the time of the third interim analysis, our patience (and the FDA’s decision to grant approval for pertuzumab for this indication) will have been amply rewarded. For selected HER2-posiitve patients with high RCB, especially those who tolerated neoadjuvant trastuzumab plus pertuzumab regimens, postoperative adjuvant pertuzumab may be an appealing option.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two presentations from the recent San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) that will likely change practice for some breast cancer patients – even before the ball drops in Times Square on New Year’s Eve.
Residual cancer burden
Researchers reported a multi-institutional analysis of individual patient-level data on 5,160 patients who had received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for localized breast cancer at 11 different centers. They found that residual cancer burden (RCB) was significantly associated with event-free (EFS) and distant recurrence-free survival. The value of calculating RCB was seen across all breast cancer tumor phenotypes (SABCS 2019, Abstract GS5-01).
RCB is calculated by analyzing the residual disease after NAC for the primary tumor bed, the number of positive axillary nodes, and the size of largest node metastasis. It is graded from RCB-0 (pCR) to RCB-III (extensive residual disease).
Both EFS and distant recurrence-free survival were strongly associated with RCB for the overall population and for each breast cancer subtype. For hormone receptor–positive/HER2-negative disease there was a slight hiccup in that RCB-0 was associated with a 10-year EFS of 81%, but EFS was 86% for RCB-I. Fortunately, the prognostic reliability of RCB was clear for RCB-II (69%) and RCB-III (52%). The presenter, W. Fraser Symmans, MD, commented that RCB is most prognostic when higher levels of residual disease are present. RCB remained prognostic in multivariate models adjusting for age, grade, and clinical T and N stage at diagnosis.
How these results influence practice
After neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with localized breast cancer, we struggle when patients ask: “So, doctor, how am I likely to do?” We piece together a complicated – and inconsistent – answer, based on breast cancer subtype, original stage of disease, whether pCR was attained, and other factors.
For patients with triple-negative breast cancer, we have the option of adding capecitabine and/or participation in ongoing clinical trials, for patients with residual disease after NAC. Among the HER2-positive patients, we have data from the KATHERINE, ExtaNET, and APHINITY trials that provide options for additional treatment in those patients, as well. For patients with potentially hormonally responsive, HER2-negative disease, we can emphasize the importance of postoperative adjuvant endocrine therapy, the mandate for continued adherence to oral therapy, and the lower likelihood of (and prognostic value of) pCR in that breast cancer subtype.
Where we previously had a complicated, nuanced discussion, we now have data from a multi-institutional, meticulous analysis to guide further treatment, candidacy for clinical trials, and our expectations of what would be meaningful results from additional therapy. This meets my definition of “practice-changing” research.
APHINITY follow-up
APHINITY was a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that previously demonstrated that pertuzumab added to standard chemotherapy plus 1 year of trastuzumab in operable HER2-positive breast cancer was associated with modest, but statistically significant, improvement in invasive disease–free survival (IDFS), compared with placebo and chemotherapy plus trastuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.81; P = .04). When the initial results – with a median follow-up of 45.4 months – were published, the authors promised an update at 6 years. Martine Piccart, MD, PhD, provided that update at the 2019 SABCS (Abstract GS1-04).
In the updated analysis, overall survival was 94.8% among patients on the pertuzumab arm and 93.9% among patients taking placebo (HR, 0.85). IDFS rates were 90.6% versus 87.8% in the intent-to-treat population. The investigator commented that this difference was caused mainly by a reduction in distant and loco-regional recurrences.
Central nervous system metastases, contralateral invasive breast cancers, and death without a prior event were no different between the two treatment groups.
Improvement in IDFS (the primary endpoint) from pertuzumab was most impressive in the node-positive cohort, 87.9% versus 83.4% for placebo (HR, 0.72). There was no benefit in the node-negative population (95.0% vs. 94.9%; HR, 1.02).
In contrast to the 3-year analysis, the benefits in IDFS were seen regardless of hormone receptor status. Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged. The rate of severe cardiac events was below 1% in both groups.
How these results influence practice
“Patience is a virtue” appeared for the first time in the English language around 1360, in William Langland’s poem “Piers Plowman.” They are true words, indeed.
When the initial results of APHINITY were published in 2017, they led to the approval of pertuzumab as an addition to chemotherapy plus trastuzumab for high-risk, early, HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Still, the difference in IDFS curves was visually unimpressive (absolute difference 1.7% in the intent-to-treat and 3.2% in the node-positive patients) and pertuzumab was associated with more grade 3 toxicities (primarily diarrhea) and treatment discontinuations.
An optimist would have observed that the IDFS curves in 2017 did not start to diverge until 24 months and would have noted that the divergence increased with time. That virtuously patient person would have expected that the second interim analysis would show larger absolute benefits, and that the hormone receptor–positive patients (64% of the total) would not yet have relapsed by the first interim analysis and that pertuzumab’s benefit in that group would emerge late.
That appears to be what is happening. It provides hope that an overall survival benefit will become more evident with time. If the target P value for an overall survival difference (.0012) is met by the time of the third interim analysis, our patience (and the FDA’s decision to grant approval for pertuzumab for this indication) will have been amply rewarded. For selected HER2-posiitve patients with high RCB, especially those who tolerated neoadjuvant trastuzumab plus pertuzumab regimens, postoperative adjuvant pertuzumab may be an appealing option.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
ctDNA shows clinical value in advanced breast cancer
SAN ANTONIO – The high accuracy and efficiency of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) testing allows for routine clinical use in advanced breast cancer, according to investigators.
The plasmaMATCH trial showed that gene level agreement between ctDNA results measured by digital PCR versus sequencing was as high as 99.4%, reported lead author Nicholas Turner, MA, MRCP, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London.
Dr. Turner, who presented findings at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, said that ctDNA testing can detect rare mutations and link patients with targeted therapies that have clinically relevant response rates.
“Multiple somatic mutations are potentially targetable in the treatment of advanced breast cancer,” Dr. Turner said. “In addition, mutations may be acquired [during treatment].”
The diverse and dynamic landscape of mutations in breast cancer creates a need to genotype tumors without repeating biopsies, Dr. Turner said. He noted that ctDNA is one possible means of fulfilling this need, although more prospective research is required to determine clinical utility.
To this end, the investigators conducted the phase II plasmaMATCH trial, a multiple parallel cohort, multicenter study involving 1,044 patients with advanced breast cancer. All patients had ctDNA testing performed prospectively with digital droplet PCR (ddPCR); in addition, ctDNA testing was performed with error-corrected sequencing using Guardant360, either prospectively or retrospectively. If actionable mutations were identified, and consent was provided, then patients entered the treatment cohort, which was composed of 142 participants.
Patients were divided into four parallel treatment cohorts based on ctDNA mutation results and accompanying treatments, as follows:
- (A) ESR1 mutation; extended-dose fulvestrant.
- (B) HER2 mutation; neratinib with or without fulvestrant.
- (C) AKT1 in estrogen receptor–positive disease; capivasertib plus fulvestrant.
- (D) “AKT basket” – AKT1 in estrogen receptor–negative disease or PTEN inactivating mutation; capivasertib.
The primary objective was response rate. For cohort A, at least 13 out of 78 evaluable patients (17%) needed to have a response to infer sufficient efficacy of the matched therapy. For the remaining cohorts, sufficient efficacy was defined by responses in at least 3 out of 16 evaluable patients (19%).
Secondary objectives included frequency of targetable mutations, accuracy of ctDNA testing (to be reported later), and others.
Results showed that ESR1 mutations were most common within the original population (27.7%), followed by AKT1 mutations (4.2%) and HER2 mutations (2.7%). In the treatment cohort, more than half of the patients had a HER2 mutation (58%) and/or an AKT1 mutation (54%), whereas a smaller proportion had an ESR1 mutation (38%). Approximately two-thirds of patients (64%) had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer; 17% had triple-negative breast cancer; 6% had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-positive disease; 3% had hormone receptor–negative, HER2-positive disease; and 9% had other/unknown phenotypes. Approximately two-thirds of patients (65%) had received at least two lines of prior therapy for advanced disease.
For patients with an ESR1 mutation treated with extended-dose fulvestrant (cohort A) only 8.1% achieved a response, which was below the threshold for inferred efficacy. For patients with a HER2 mutation treated with neratinib with or without fulvestrant (cohort B), 25.0% had a response, thereby demonstrating inferred efficacy. Efficacy was also inferred in patients with an AKT1 mutation treated with capivasertib plus fulvestrant (cohort C), as 22.2% of these patients had a response. In the AKT basket (cohort D), 10.5% of patients had a response, which fell below the efficacy threshold; however, an exploratory analysis of this cohort showed that patients with an AKT1 mutation had a response rate of 33.3% (two out of six patients), which did meet efficacy criteria.
Adverse events were consistent with previous reports. The investigators noted that extended-dose fulvestrant was well tolerated.
“In conclusion, we show that circulating tumor DNA testing offers a simple, efficient and relatively fast method of tumor genotyping,” Dr. Turner said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Puma Biotechnology, AstraZeneca, Guardant Health, and Bio-Rad.
SOURCE: Turner et al. SABCS. 2019 Dec 12. Abstract GS3-06.
SAN ANTONIO – The high accuracy and efficiency of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) testing allows for routine clinical use in advanced breast cancer, according to investigators.
The plasmaMATCH trial showed that gene level agreement between ctDNA results measured by digital PCR versus sequencing was as high as 99.4%, reported lead author Nicholas Turner, MA, MRCP, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London.
Dr. Turner, who presented findings at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, said that ctDNA testing can detect rare mutations and link patients with targeted therapies that have clinically relevant response rates.
“Multiple somatic mutations are potentially targetable in the treatment of advanced breast cancer,” Dr. Turner said. “In addition, mutations may be acquired [during treatment].”
The diverse and dynamic landscape of mutations in breast cancer creates a need to genotype tumors without repeating biopsies, Dr. Turner said. He noted that ctDNA is one possible means of fulfilling this need, although more prospective research is required to determine clinical utility.
To this end, the investigators conducted the phase II plasmaMATCH trial, a multiple parallel cohort, multicenter study involving 1,044 patients with advanced breast cancer. All patients had ctDNA testing performed prospectively with digital droplet PCR (ddPCR); in addition, ctDNA testing was performed with error-corrected sequencing using Guardant360, either prospectively or retrospectively. If actionable mutations were identified, and consent was provided, then patients entered the treatment cohort, which was composed of 142 participants.
Patients were divided into four parallel treatment cohorts based on ctDNA mutation results and accompanying treatments, as follows:
- (A) ESR1 mutation; extended-dose fulvestrant.
- (B) HER2 mutation; neratinib with or without fulvestrant.
- (C) AKT1 in estrogen receptor–positive disease; capivasertib plus fulvestrant.
- (D) “AKT basket” – AKT1 in estrogen receptor–negative disease or PTEN inactivating mutation; capivasertib.
The primary objective was response rate. For cohort A, at least 13 out of 78 evaluable patients (17%) needed to have a response to infer sufficient efficacy of the matched therapy. For the remaining cohorts, sufficient efficacy was defined by responses in at least 3 out of 16 evaluable patients (19%).
Secondary objectives included frequency of targetable mutations, accuracy of ctDNA testing (to be reported later), and others.
Results showed that ESR1 mutations were most common within the original population (27.7%), followed by AKT1 mutations (4.2%) and HER2 mutations (2.7%). In the treatment cohort, more than half of the patients had a HER2 mutation (58%) and/or an AKT1 mutation (54%), whereas a smaller proportion had an ESR1 mutation (38%). Approximately two-thirds of patients (64%) had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer; 17% had triple-negative breast cancer; 6% had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-positive disease; 3% had hormone receptor–negative, HER2-positive disease; and 9% had other/unknown phenotypes. Approximately two-thirds of patients (65%) had received at least two lines of prior therapy for advanced disease.
For patients with an ESR1 mutation treated with extended-dose fulvestrant (cohort A) only 8.1% achieved a response, which was below the threshold for inferred efficacy. For patients with a HER2 mutation treated with neratinib with or without fulvestrant (cohort B), 25.0% had a response, thereby demonstrating inferred efficacy. Efficacy was also inferred in patients with an AKT1 mutation treated with capivasertib plus fulvestrant (cohort C), as 22.2% of these patients had a response. In the AKT basket (cohort D), 10.5% of patients had a response, which fell below the efficacy threshold; however, an exploratory analysis of this cohort showed that patients with an AKT1 mutation had a response rate of 33.3% (two out of six patients), which did meet efficacy criteria.
Adverse events were consistent with previous reports. The investigators noted that extended-dose fulvestrant was well tolerated.
“In conclusion, we show that circulating tumor DNA testing offers a simple, efficient and relatively fast method of tumor genotyping,” Dr. Turner said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Puma Biotechnology, AstraZeneca, Guardant Health, and Bio-Rad.
SOURCE: Turner et al. SABCS. 2019 Dec 12. Abstract GS3-06.
SAN ANTONIO – The high accuracy and efficiency of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) testing allows for routine clinical use in advanced breast cancer, according to investigators.
The plasmaMATCH trial showed that gene level agreement between ctDNA results measured by digital PCR versus sequencing was as high as 99.4%, reported lead author Nicholas Turner, MA, MRCP, PhD, of The Institute of Cancer Research and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust, London.
Dr. Turner, who presented findings at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, said that ctDNA testing can detect rare mutations and link patients with targeted therapies that have clinically relevant response rates.
“Multiple somatic mutations are potentially targetable in the treatment of advanced breast cancer,” Dr. Turner said. “In addition, mutations may be acquired [during treatment].”
The diverse and dynamic landscape of mutations in breast cancer creates a need to genotype tumors without repeating biopsies, Dr. Turner said. He noted that ctDNA is one possible means of fulfilling this need, although more prospective research is required to determine clinical utility.
To this end, the investigators conducted the phase II plasmaMATCH trial, a multiple parallel cohort, multicenter study involving 1,044 patients with advanced breast cancer. All patients had ctDNA testing performed prospectively with digital droplet PCR (ddPCR); in addition, ctDNA testing was performed with error-corrected sequencing using Guardant360, either prospectively or retrospectively. If actionable mutations were identified, and consent was provided, then patients entered the treatment cohort, which was composed of 142 participants.
Patients were divided into four parallel treatment cohorts based on ctDNA mutation results and accompanying treatments, as follows:
- (A) ESR1 mutation; extended-dose fulvestrant.
- (B) HER2 mutation; neratinib with or without fulvestrant.
- (C) AKT1 in estrogen receptor–positive disease; capivasertib plus fulvestrant.
- (D) “AKT basket” – AKT1 in estrogen receptor–negative disease or PTEN inactivating mutation; capivasertib.
The primary objective was response rate. For cohort A, at least 13 out of 78 evaluable patients (17%) needed to have a response to infer sufficient efficacy of the matched therapy. For the remaining cohorts, sufficient efficacy was defined by responses in at least 3 out of 16 evaluable patients (19%).
Secondary objectives included frequency of targetable mutations, accuracy of ctDNA testing (to be reported later), and others.
Results showed that ESR1 mutations were most common within the original population (27.7%), followed by AKT1 mutations (4.2%) and HER2 mutations (2.7%). In the treatment cohort, more than half of the patients had a HER2 mutation (58%) and/or an AKT1 mutation (54%), whereas a smaller proportion had an ESR1 mutation (38%). Approximately two-thirds of patients (64%) had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer; 17% had triple-negative breast cancer; 6% had hormone receptor–positive, HER2-positive disease; 3% had hormone receptor–negative, HER2-positive disease; and 9% had other/unknown phenotypes. Approximately two-thirds of patients (65%) had received at least two lines of prior therapy for advanced disease.
For patients with an ESR1 mutation treated with extended-dose fulvestrant (cohort A) only 8.1% achieved a response, which was below the threshold for inferred efficacy. For patients with a HER2 mutation treated with neratinib with or without fulvestrant (cohort B), 25.0% had a response, thereby demonstrating inferred efficacy. Efficacy was also inferred in patients with an AKT1 mutation treated with capivasertib plus fulvestrant (cohort C), as 22.2% of these patients had a response. In the AKT basket (cohort D), 10.5% of patients had a response, which fell below the efficacy threshold; however, an exploratory analysis of this cohort showed that patients with an AKT1 mutation had a response rate of 33.3% (two out of six patients), which did meet efficacy criteria.
Adverse events were consistent with previous reports. The investigators noted that extended-dose fulvestrant was well tolerated.
“In conclusion, we show that circulating tumor DNA testing offers a simple, efficient and relatively fast method of tumor genotyping,” Dr. Turner said.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Puma Biotechnology, AstraZeneca, Guardant Health, and Bio-Rad.
SOURCE: Turner et al. SABCS. 2019 Dec 12. Abstract GS3-06.
REPORTING FROM SABCS 2019