User login
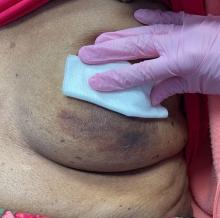
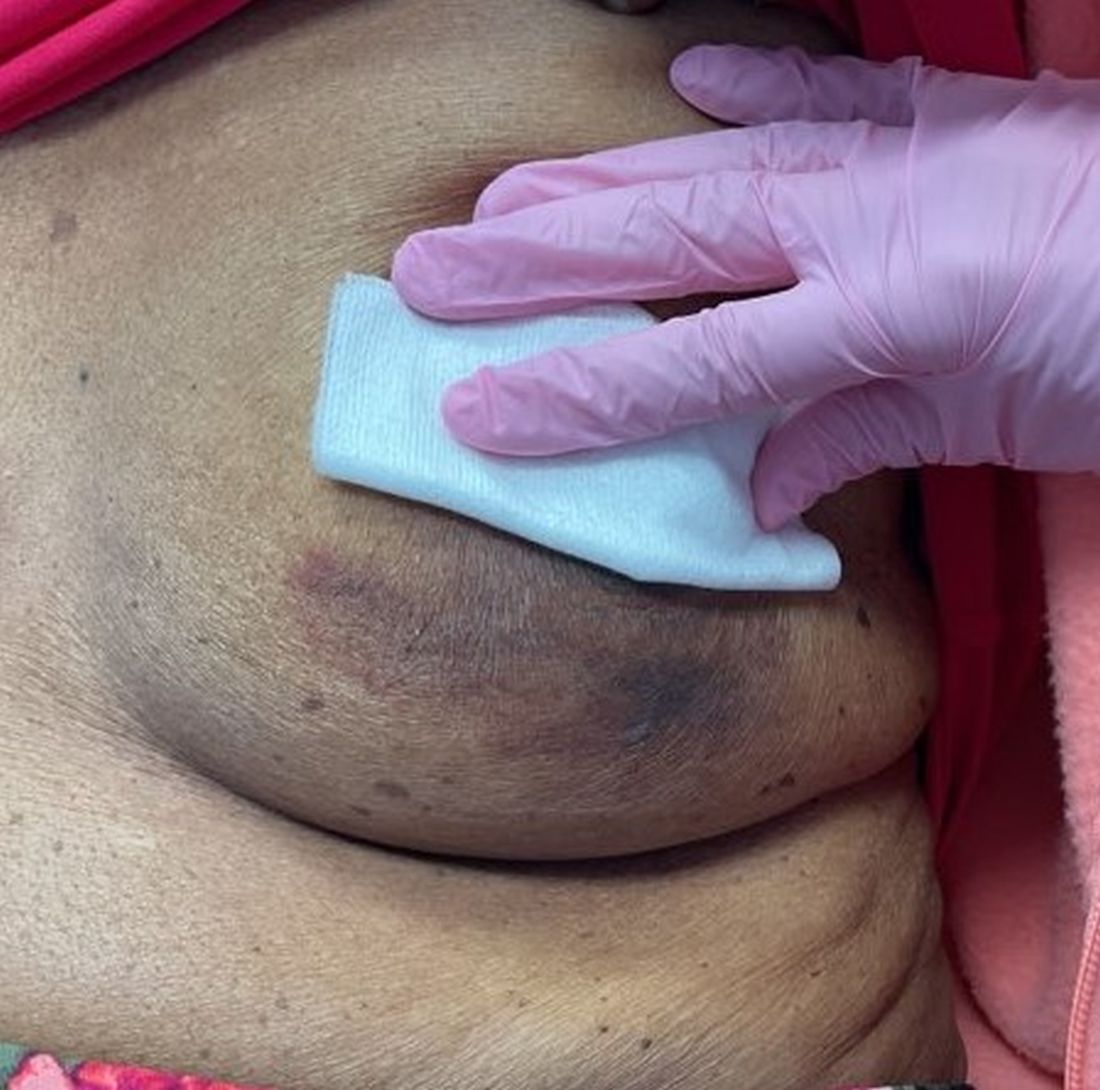
An 88-year-old Black woman presented with 3 months duration of asymptomatic, violaceous patches on the left breast
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
Angiosarcomas are uncommon, high-grade malignant tumors of endothelial cell origin that can arise via the lymphatics or vasculature. They typically occur spontaneously; however, there have been cases reported of benign vascular transformation. These tumors are more commonly found in elderly men on the head and neck in sun-damaged skin. . This is a late complication, typically occurring about 5-10 years after radiation. Stewart-Treves syndrome, chronic lymphedema occurring after breast cancer treatment with axillary node dissection, increases the risk of angiosarcoma. As a vascular tumor, angiosarcoma spreads hematogenously and carries a poor prognosis if not caught early. Differential diagnoses include other vascular tumors such as retiform hemangioendothelioma. In this specific patient, the differential diagnosis includes Paget’s disease, chronic radiation skin changes, and eczema.
Histopathologically, angiosarcomas exhibit abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. As the tumor progresses, the cell architecture becomes more distorted and cells form layers with papillary projections into the vascular lumen. Malignant cells may stain positive for CD31, CD34, the oncogene ERG and the proto-oncogene FLI-1. Histology in this patient revealed radiation changes in the dermis, as well as few vascular channels lined by large endothelial cells with marked nuclear atypia, in the form of large nucleoli and variably coarse chromatin. The cells were positive for MYC.
Treatment of angiosarcoma involves a multidisciplinary approach. Resection with wide margins is generally the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is relatively common, which may be a result of microsatellite deposits of the tumor. Perioperative radiation is recommended, and adjuvant chemotherapy often is recommended for metastatic disease. Specifically, paclitaxel has been found to promote survival in some cases of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Metastatic disease may be treated with cytotoxic drugs such as anthracyclines and taxanes. Additionally, targeted therapy including anti-VEGF drugs and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tested.
The case and photo were submitted by Mr. Shapiro of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Dr. Bilu Martin. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Cohen-Hallaleh RB et al. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2017 Aug 7:7:15.
Cozzi S et al. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Sep 30;26(5):827-32.
Spiker AM, Mangla A, Ramsey ML. Angiosarcoma. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441983/
Review estimates acne risk with JAK inhibitor therapy
TOPLINE:
, according to an analysis of 25 JAK inhibitor studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Acne has been reported to be an adverse effect of JAK inhibitors, but not much is known about how common acne is overall and how incidence differs between different JAK inhibitors and the disease being treated.
- For the systematic review and meta-analysis, researchers identified 25 phase 2 or 3 randomized, controlled trials that reported acne as an adverse event associated with the use of JAK inhibitors.
- The study population included 10,839 participants (54% male, 46% female).
- The primary outcome was the incidence of acne following a period of JAK inhibitor use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, the risk of acne was significantly higher among those treated with JAK inhibitors in comparison with patients given placebo in a pooled analysis (odds ratio [OR], 3.83).
- The risk of acne was highest with abrocitinib (OR, 13.47), followed by baricitinib (OR, 4.96), upadacitinib (OR, 4.79), deuruxolitinib (OR, 3.30), and deucravacitinib (OR, 2.64). By JAK inhibitor class, results were as follows: JAK1-specific inhibitors (OR, 4.69), combined JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitors (OR, 3.43), and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors (OR, 2.64).
- In a subgroup analysis, risk of acne was higher among patients using JAK inhibitors for dermatologic conditions in comparison with those using JAK inhibitors for nondermatologic conditions (OR, 4.67 vs 1.18).
- Age and gender had no apparent impact on the effect of JAK inhibitor use on acne risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“The occurrence of acne following treatment with certain classes of JAK inhibitors is of potential concern, as this adverse effect may jeopardize treatment adherence among some patients,” the researchers wrote. More studies are needed “to characterize the underlying mechanism of acne with JAK inhibitor use and to identify best practices for treatment,” they added.
SOURCE:
The lead author was Jeremy Martinez, MPH, of Harvard Medical School, Boston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The review was limited by the variable classification and reporting of acne across studies, the potential exclusion of relevant studies, and the small number of studies for certain drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies were mainly funded by the pharmaceutical industry. Mr. Martinez disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have ties with Dexcel Pharma Technologies, AbbVie, Concert, Pfizer, 3Derm Systems, Incyte, Aclaris, Eli Lilly, Concert, Equillium, ASLAN, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to an analysis of 25 JAK inhibitor studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Acne has been reported to be an adverse effect of JAK inhibitors, but not much is known about how common acne is overall and how incidence differs between different JAK inhibitors and the disease being treated.
- For the systematic review and meta-analysis, researchers identified 25 phase 2 or 3 randomized, controlled trials that reported acne as an adverse event associated with the use of JAK inhibitors.
- The study population included 10,839 participants (54% male, 46% female).
- The primary outcome was the incidence of acne following a period of JAK inhibitor use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, the risk of acne was significantly higher among those treated with JAK inhibitors in comparison with patients given placebo in a pooled analysis (odds ratio [OR], 3.83).
- The risk of acne was highest with abrocitinib (OR, 13.47), followed by baricitinib (OR, 4.96), upadacitinib (OR, 4.79), deuruxolitinib (OR, 3.30), and deucravacitinib (OR, 2.64). By JAK inhibitor class, results were as follows: JAK1-specific inhibitors (OR, 4.69), combined JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitors (OR, 3.43), and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors (OR, 2.64).
- In a subgroup analysis, risk of acne was higher among patients using JAK inhibitors for dermatologic conditions in comparison with those using JAK inhibitors for nondermatologic conditions (OR, 4.67 vs 1.18).
- Age and gender had no apparent impact on the effect of JAK inhibitor use on acne risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“The occurrence of acne following treatment with certain classes of JAK inhibitors is of potential concern, as this adverse effect may jeopardize treatment adherence among some patients,” the researchers wrote. More studies are needed “to characterize the underlying mechanism of acne with JAK inhibitor use and to identify best practices for treatment,” they added.
SOURCE:
The lead author was Jeremy Martinez, MPH, of Harvard Medical School, Boston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The review was limited by the variable classification and reporting of acne across studies, the potential exclusion of relevant studies, and the small number of studies for certain drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies were mainly funded by the pharmaceutical industry. Mr. Martinez disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have ties with Dexcel Pharma Technologies, AbbVie, Concert, Pfizer, 3Derm Systems, Incyte, Aclaris, Eli Lilly, Concert, Equillium, ASLAN, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to an analysis of 25 JAK inhibitor studies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Acne has been reported to be an adverse effect of JAK inhibitors, but not much is known about how common acne is overall and how incidence differs between different JAK inhibitors and the disease being treated.
- For the systematic review and meta-analysis, researchers identified 25 phase 2 or 3 randomized, controlled trials that reported acne as an adverse event associated with the use of JAK inhibitors.
- The study population included 10,839 participants (54% male, 46% female).
- The primary outcome was the incidence of acne following a period of JAK inhibitor use.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, the risk of acne was significantly higher among those treated with JAK inhibitors in comparison with patients given placebo in a pooled analysis (odds ratio [OR], 3.83).
- The risk of acne was highest with abrocitinib (OR, 13.47), followed by baricitinib (OR, 4.96), upadacitinib (OR, 4.79), deuruxolitinib (OR, 3.30), and deucravacitinib (OR, 2.64). By JAK inhibitor class, results were as follows: JAK1-specific inhibitors (OR, 4.69), combined JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitors (OR, 3.43), and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors (OR, 2.64).
- In a subgroup analysis, risk of acne was higher among patients using JAK inhibitors for dermatologic conditions in comparison with those using JAK inhibitors for nondermatologic conditions (OR, 4.67 vs 1.18).
- Age and gender had no apparent impact on the effect of JAK inhibitor use on acne risk.
IN PRACTICE:
“The occurrence of acne following treatment with certain classes of JAK inhibitors is of potential concern, as this adverse effect may jeopardize treatment adherence among some patients,” the researchers wrote. More studies are needed “to characterize the underlying mechanism of acne with JAK inhibitor use and to identify best practices for treatment,” they added.
SOURCE:
The lead author was Jeremy Martinez, MPH, of Harvard Medical School, Boston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The review was limited by the variable classification and reporting of acne across studies, the potential exclusion of relevant studies, and the small number of studies for certain drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
The studies were mainly funded by the pharmaceutical industry. Mr. Martinez disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have ties with Dexcel Pharma Technologies, AbbVie, Concert, Pfizer, 3Derm Systems, Incyte, Aclaris, Eli Lilly, Concert, Equillium, ASLAN, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical ivermectin study sheds light on dysbiosis in rosacea
, according to a report presented at the recent European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2023 Congress.
“This is the first hint that the host’s cutaneous microbiome plays a secondary role in the immunopathogenesis of rosacea,” said Bernard Homey, MD, director of the department of dermatology at University Hospital Düsseldorf in Germany.
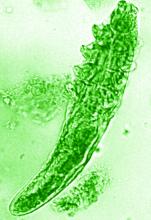
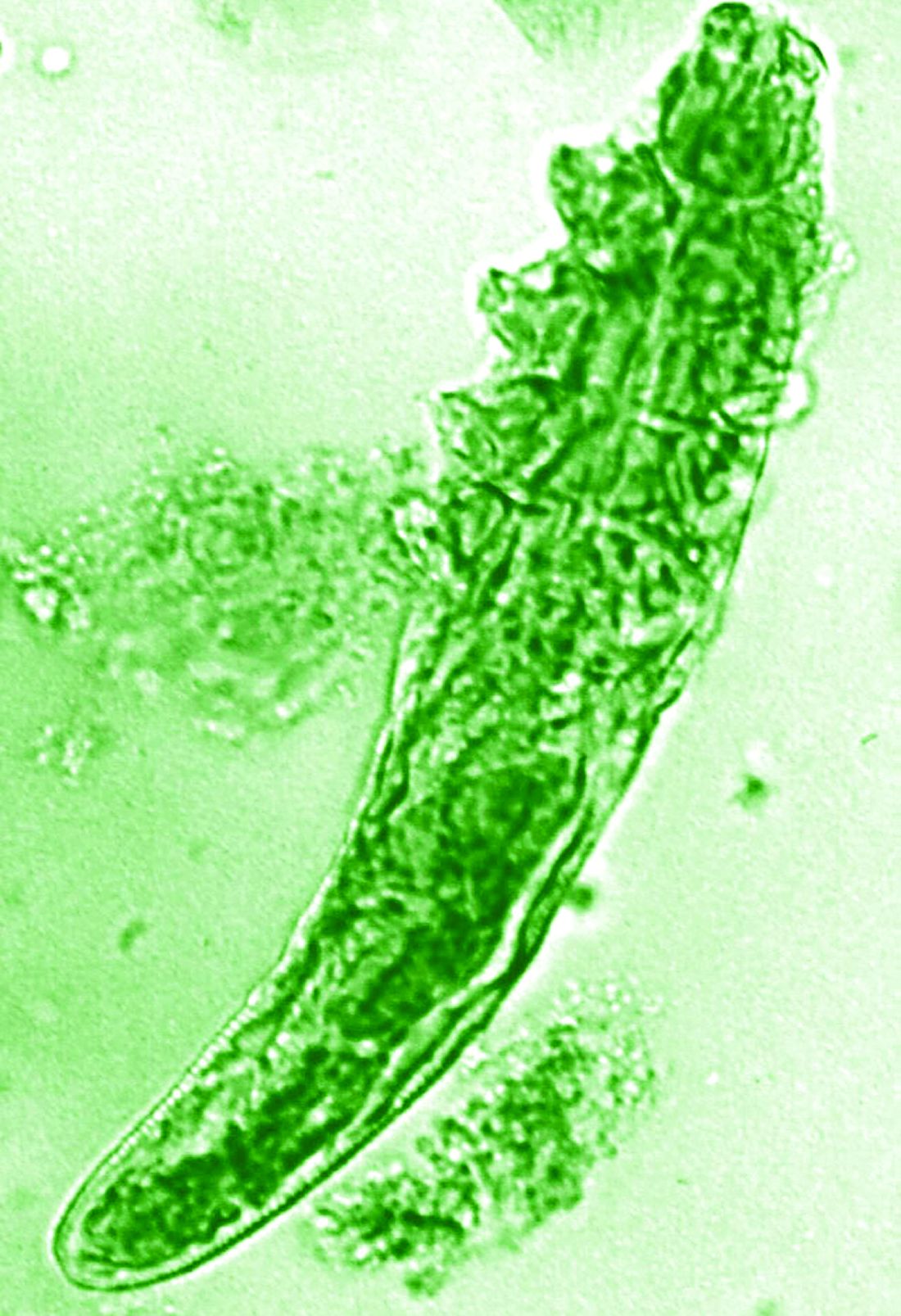
“In rosacea, we are well aware of trigger factors such as stress, UV light, heat, cold, food, and alcohol,” he said. “We are also well aware that there is an increase in Demodex mites in the pilosebaceous unit.”
Research over the past decade has also started to look at the potential role of the skin microbiome in the disease process, but answers have remained “largely elusive,” Dr. Homey said.
Ivermectin helps, but how?
Ivermectin 1% cream (Soolantra) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration since 2014 for the treatment of the inflammatory lesions that are characteristic of rosacea, but its mechanism of action is not clear.
Dr. Homey presented the results of a study of 61 patients designed to look at how ivermectin might be working in the treatment of people with rosacea and investigate if there was any relation to the skin microbiome and transcriptome of patients.
The trial included 41 individuals with papulopustular rosacea and 20 individuals who did not have rosacea. For all patients, surface skin biopsies were performed twice 30 days apart using cyanoacrylate glue; patients with rosacea were treated with topical ivermectin 1% between biopsies. Skin samples obtained at day 0 and day 30 were examined under the microscope, and Demodex counts (mites/cm2) of skin and RNA sequencing of the cutaneous microbiome were undertaken.
The mean age of the patients with rosacea was 54.9 years, and the mean Demodex counts before and after treatment were a respective 7.2 cm2 and 0.9 cm2.
Using the Investigator’s General Assessment to assess the severity of rosacea, Homey reported that 43.9% of patients with rosacea had a decrease in scores at day 30, indicating improvement.
In addition, topical ivermectin resulted in a marked or total decrease in Demodex mite density for 87.5% of patients (n = 24) who were identified as having the mites.
Skin microbiome changes seen
As a form of quality control, skin microbiome changes among the patients were compared with control patients using 16S rRNA sequencing.
“The taxa we find within the cutaneous niche of inflammatory lesions of rosacea patients are significantly different from healthy volunteers,” Dr. Homey said.
Cutibacterium species are predominant in healthy control persons but are not present when there is inflammation in patients with rosacea. Instead, staphylococcus species “take over the niche, similar to atopic dermatitis,” he noted.
Looking at how treatment with ivermectin influences the organisms, the decrease in C. acnes seen in patients with rosacea persisted despite treatment, and the abundance of Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. hominis, and S. capitis increased further. This suggests a possible protective or homeostatic role of C. acnes but a pathogenic role for staphylococci, explained Dr. Homey.
“Surprisingly, although inflammatory lesions decrease, patients get better, the cutaneous microbiome does not revert to homeostatic conditions during topical ivermectin treatment,” he observed.
There is, of course, variability among individuals.
Dr. Homey also reported that Snodgrassella alvi – a microorganism believed to reside in the gut of Demodex folliculorum mites – was found in the skin microbiome of patients with rosacea before but not after ivermectin treatment. This may mean that this microorganism could be partially triggering inflammation in rosacea patients.
Looking at the transcriptome of patients, Dr. Homey said that there was downregulation of distinct genes that might make for more favorable conditions for Demodex mites.
Moreover, insufficient upregulation of interleukin-17 pathways might be working together with barrier defects in the skin and metabolic changes to “pave the way” for colonization by S. epidermidis.
Pulling it together
Dr. Homey and associates conclude in their abstract that the findings “support that rosacea lesions are associated with dysbiosis.”
Although treatment with ivermectin did not normalize the skin’s microbiome, it was associated with a decrease in Demodex mite density and the reduction of microbes associated with Demodex.
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra in Portugal, who cochaired the late-breaking news session where the data were presented, asked whether healthy and affected skin in patients with rosacea had been compared, rather than comparing the skin of rosacea lesions with healthy control samples.
“No, we did not this, as this is methodologically a little bit more difficult,” Dr. Homey responded.
Also cochairing the session was Michel Gilliet, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at the University Hospital CHUV in Lausanne, Switzerland. He commented that these “data suggest that there’s an intimate link between Demodex and the skin microbiota and dysbiosis in in rosacea.”
Dr. Gilliet added: “You have a whole dysbiosis going on in rosacea, which is probably only dependent on these bacteria.”
It would be “very interesting,” as a “proof-of-concept” study, to look at whether depleting Demodex would also delete S. alvi, he suggested.
The study was funded by Galderma. Dr. Homey has acted as a consultant, speaker or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies including Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a report presented at the recent European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2023 Congress.
“This is the first hint that the host’s cutaneous microbiome plays a secondary role in the immunopathogenesis of rosacea,” said Bernard Homey, MD, director of the department of dermatology at University Hospital Düsseldorf in Germany.
“In rosacea, we are well aware of trigger factors such as stress, UV light, heat, cold, food, and alcohol,” he said. “We are also well aware that there is an increase in Demodex mites in the pilosebaceous unit.”
Research over the past decade has also started to look at the potential role of the skin microbiome in the disease process, but answers have remained “largely elusive,” Dr. Homey said.
Ivermectin helps, but how?
Ivermectin 1% cream (Soolantra) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration since 2014 for the treatment of the inflammatory lesions that are characteristic of rosacea, but its mechanism of action is not clear.
Dr. Homey presented the results of a study of 61 patients designed to look at how ivermectin might be working in the treatment of people with rosacea and investigate if there was any relation to the skin microbiome and transcriptome of patients.
The trial included 41 individuals with papulopustular rosacea and 20 individuals who did not have rosacea. For all patients, surface skin biopsies were performed twice 30 days apart using cyanoacrylate glue; patients with rosacea were treated with topical ivermectin 1% between biopsies. Skin samples obtained at day 0 and day 30 were examined under the microscope, and Demodex counts (mites/cm2) of skin and RNA sequencing of the cutaneous microbiome were undertaken.
The mean age of the patients with rosacea was 54.9 years, and the mean Demodex counts before and after treatment were a respective 7.2 cm2 and 0.9 cm2.
Using the Investigator’s General Assessment to assess the severity of rosacea, Homey reported that 43.9% of patients with rosacea had a decrease in scores at day 30, indicating improvement.
In addition, topical ivermectin resulted in a marked or total decrease in Demodex mite density for 87.5% of patients (n = 24) who were identified as having the mites.
Skin microbiome changes seen
As a form of quality control, skin microbiome changes among the patients were compared with control patients using 16S rRNA sequencing.
“The taxa we find within the cutaneous niche of inflammatory lesions of rosacea patients are significantly different from healthy volunteers,” Dr. Homey said.
Cutibacterium species are predominant in healthy control persons but are not present when there is inflammation in patients with rosacea. Instead, staphylococcus species “take over the niche, similar to atopic dermatitis,” he noted.
Looking at how treatment with ivermectin influences the organisms, the decrease in C. acnes seen in patients with rosacea persisted despite treatment, and the abundance of Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. hominis, and S. capitis increased further. This suggests a possible protective or homeostatic role of C. acnes but a pathogenic role for staphylococci, explained Dr. Homey.
“Surprisingly, although inflammatory lesions decrease, patients get better, the cutaneous microbiome does not revert to homeostatic conditions during topical ivermectin treatment,” he observed.
There is, of course, variability among individuals.
Dr. Homey also reported that Snodgrassella alvi – a microorganism believed to reside in the gut of Demodex folliculorum mites – was found in the skin microbiome of patients with rosacea before but not after ivermectin treatment. This may mean that this microorganism could be partially triggering inflammation in rosacea patients.
Looking at the transcriptome of patients, Dr. Homey said that there was downregulation of distinct genes that might make for more favorable conditions for Demodex mites.
Moreover, insufficient upregulation of interleukin-17 pathways might be working together with barrier defects in the skin and metabolic changes to “pave the way” for colonization by S. epidermidis.
Pulling it together
Dr. Homey and associates conclude in their abstract that the findings “support that rosacea lesions are associated with dysbiosis.”
Although treatment with ivermectin did not normalize the skin’s microbiome, it was associated with a decrease in Demodex mite density and the reduction of microbes associated with Demodex.
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra in Portugal, who cochaired the late-breaking news session where the data were presented, asked whether healthy and affected skin in patients with rosacea had been compared, rather than comparing the skin of rosacea lesions with healthy control samples.
“No, we did not this, as this is methodologically a little bit more difficult,” Dr. Homey responded.
Also cochairing the session was Michel Gilliet, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at the University Hospital CHUV in Lausanne, Switzerland. He commented that these “data suggest that there’s an intimate link between Demodex and the skin microbiota and dysbiosis in in rosacea.”
Dr. Gilliet added: “You have a whole dysbiosis going on in rosacea, which is probably only dependent on these bacteria.”
It would be “very interesting,” as a “proof-of-concept” study, to look at whether depleting Demodex would also delete S. alvi, he suggested.
The study was funded by Galderma. Dr. Homey has acted as a consultant, speaker or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies including Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a report presented at the recent European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2023 Congress.
“This is the first hint that the host’s cutaneous microbiome plays a secondary role in the immunopathogenesis of rosacea,” said Bernard Homey, MD, director of the department of dermatology at University Hospital Düsseldorf in Germany.
“In rosacea, we are well aware of trigger factors such as stress, UV light, heat, cold, food, and alcohol,” he said. “We are also well aware that there is an increase in Demodex mites in the pilosebaceous unit.”
Research over the past decade has also started to look at the potential role of the skin microbiome in the disease process, but answers have remained “largely elusive,” Dr. Homey said.
Ivermectin helps, but how?
Ivermectin 1% cream (Soolantra) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration since 2014 for the treatment of the inflammatory lesions that are characteristic of rosacea, but its mechanism of action is not clear.
Dr. Homey presented the results of a study of 61 patients designed to look at how ivermectin might be working in the treatment of people with rosacea and investigate if there was any relation to the skin microbiome and transcriptome of patients.
The trial included 41 individuals with papulopustular rosacea and 20 individuals who did not have rosacea. For all patients, surface skin biopsies were performed twice 30 days apart using cyanoacrylate glue; patients with rosacea were treated with topical ivermectin 1% between biopsies. Skin samples obtained at day 0 and day 30 were examined under the microscope, and Demodex counts (mites/cm2) of skin and RNA sequencing of the cutaneous microbiome were undertaken.
The mean age of the patients with rosacea was 54.9 years, and the mean Demodex counts before and after treatment were a respective 7.2 cm2 and 0.9 cm2.
Using the Investigator’s General Assessment to assess the severity of rosacea, Homey reported that 43.9% of patients with rosacea had a decrease in scores at day 30, indicating improvement.
In addition, topical ivermectin resulted in a marked or total decrease in Demodex mite density for 87.5% of patients (n = 24) who were identified as having the mites.
Skin microbiome changes seen
As a form of quality control, skin microbiome changes among the patients were compared with control patients using 16S rRNA sequencing.
“The taxa we find within the cutaneous niche of inflammatory lesions of rosacea patients are significantly different from healthy volunteers,” Dr. Homey said.
Cutibacterium species are predominant in healthy control persons but are not present when there is inflammation in patients with rosacea. Instead, staphylococcus species “take over the niche, similar to atopic dermatitis,” he noted.
Looking at how treatment with ivermectin influences the organisms, the decrease in C. acnes seen in patients with rosacea persisted despite treatment, and the abundance of Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. hominis, and S. capitis increased further. This suggests a possible protective or homeostatic role of C. acnes but a pathogenic role for staphylococci, explained Dr. Homey.
“Surprisingly, although inflammatory lesions decrease, patients get better, the cutaneous microbiome does not revert to homeostatic conditions during topical ivermectin treatment,” he observed.
There is, of course, variability among individuals.
Dr. Homey also reported that Snodgrassella alvi – a microorganism believed to reside in the gut of Demodex folliculorum mites – was found in the skin microbiome of patients with rosacea before but not after ivermectin treatment. This may mean that this microorganism could be partially triggering inflammation in rosacea patients.
Looking at the transcriptome of patients, Dr. Homey said that there was downregulation of distinct genes that might make for more favorable conditions for Demodex mites.
Moreover, insufficient upregulation of interleukin-17 pathways might be working together with barrier defects in the skin and metabolic changes to “pave the way” for colonization by S. epidermidis.
Pulling it together
Dr. Homey and associates conclude in their abstract that the findings “support that rosacea lesions are associated with dysbiosis.”
Although treatment with ivermectin did not normalize the skin’s microbiome, it was associated with a decrease in Demodex mite density and the reduction of microbes associated with Demodex.
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra in Portugal, who cochaired the late-breaking news session where the data were presented, asked whether healthy and affected skin in patients with rosacea had been compared, rather than comparing the skin of rosacea lesions with healthy control samples.
“No, we did not this, as this is methodologically a little bit more difficult,” Dr. Homey responded.
Also cochairing the session was Michel Gilliet, MD, chair of the department of dermatology at the University Hospital CHUV in Lausanne, Switzerland. He commented that these “data suggest that there’s an intimate link between Demodex and the skin microbiota and dysbiosis in in rosacea.”
Dr. Gilliet added: “You have a whole dysbiosis going on in rosacea, which is probably only dependent on these bacteria.”
It would be “very interesting,” as a “proof-of-concept” study, to look at whether depleting Demodex would also delete S. alvi, he suggested.
The study was funded by Galderma. Dr. Homey has acted as a consultant, speaker or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies including Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2023
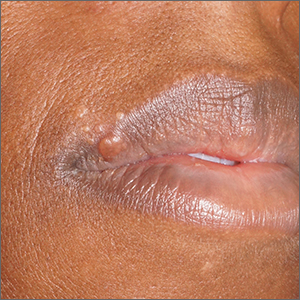
Papules on lip
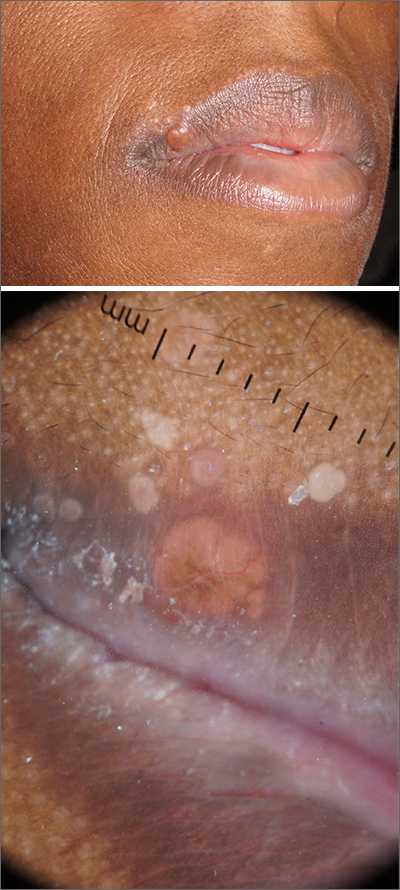
Pathology showed noncaseating granulomas consistent with cutaneous sarcoidosis. Based on these biopsy findings, a chest x-ray was ordered, and it confirmed a pulmonary sarcoid. A multidisciplinary work-up (including cardiac evaluation, continued rheumatologic care, and evaluation by Hematology) addressed this new finding.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by the development of granulomas that can arise in any organ, but frequently involve the skin and lungs. Patients with cutaneous disease develop smooth skin lesions, including flesh-colored to pink or brown papules on the face. Genetic and environmental factors are both thought to contribute to the disease.
Race is a significant factor in the development of disease. Hispanic and Asian patients are significantly less likely to develop the disease compared to White or Black patients. In the Black Women’s Health Study, incidence in Black women was 71 per 100,000.1 Women are more likely to be affected than men.1
Many patients with sarcoidosis have a mild course, but for others the disease may progress on the skin or include pulmonary, renal, neurologic, or cardiac disease. Sometimes sarcoidosis is fatal. Recurrence can occur at any point later in life. Race influences disease severity as well as incidence, with hospitalization being 9 times as likely in Black patients compared with White patients.2 One recent study puts sarcoidosis mortality rates for Black women at 10 per million compared with 3 per million in Black men, and 1 per million in White women or men.3
Patients with disease limited to the skin may be treated with topical steroids such as clobetasol 0.05% cream or ointment or intralesional triamcinolone 10 mg/mL injected into affected lesions every 2 to 4 weeks. With pulmonary or other systemic disease, treatment may include various disease-modifying agents including prednisone, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and TNF-alpha inhibitors. Because of the long-term adverse effects of systemic steroids, these agents are reserved for instances when pulmonary function is significantly impacted.
This patient had a reassuring cardiac and hematology work-up. Her pulmonary function was impacted sufficiently enough that her pulmonologist added a course of prednisone 10 mg daily tapered over 6 weeks. She had been on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily prior to the diagnosis of sarcoidosis for presumed mixed connective tissue disease and was continued on it for sarcoidosis after completing the prednisone taper. With these treatments, her facial lesions cleared and her breathing symptoms and fatigue improved. She remains under surveillance with a multidisciplinary team.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Cozier Y, Berman J, Palmer J, et al. Sarcoidosis in black women in the United States: data from the Black Women's Health Study. Chest. 2011;139:144-150. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0413
2. Foreman MG, Mannino DM, Kamugisha L, et al. Hospitalization for patients with sarcoidosis: 1979-2000. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2006;23:124-129.
3. Mirsaeidi M, Machado R, Schraufnagel D, et al. Racial difference in sarcoidosis mortality in the United States. Chest. 2015; 147: 438-449. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1120

Pathology showed noncaseating granulomas consistent with cutaneous sarcoidosis. Based on these biopsy findings, a chest x-ray was ordered, and it confirmed a pulmonary sarcoid. A multidisciplinary work-up (including cardiac evaluation, continued rheumatologic care, and evaluation by Hematology) addressed this new finding.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by the development of granulomas that can arise in any organ, but frequently involve the skin and lungs. Patients with cutaneous disease develop smooth skin lesions, including flesh-colored to pink or brown papules on the face. Genetic and environmental factors are both thought to contribute to the disease.
Race is a significant factor in the development of disease. Hispanic and Asian patients are significantly less likely to develop the disease compared to White or Black patients. In the Black Women’s Health Study, incidence in Black women was 71 per 100,000.1 Women are more likely to be affected than men.1
Many patients with sarcoidosis have a mild course, but for others the disease may progress on the skin or include pulmonary, renal, neurologic, or cardiac disease. Sometimes sarcoidosis is fatal. Recurrence can occur at any point later in life. Race influences disease severity as well as incidence, with hospitalization being 9 times as likely in Black patients compared with White patients.2 One recent study puts sarcoidosis mortality rates for Black women at 10 per million compared with 3 per million in Black men, and 1 per million in White women or men.3
Patients with disease limited to the skin may be treated with topical steroids such as clobetasol 0.05% cream or ointment or intralesional triamcinolone 10 mg/mL injected into affected lesions every 2 to 4 weeks. With pulmonary or other systemic disease, treatment may include various disease-modifying agents including prednisone, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and TNF-alpha inhibitors. Because of the long-term adverse effects of systemic steroids, these agents are reserved for instances when pulmonary function is significantly impacted.
This patient had a reassuring cardiac and hematology work-up. Her pulmonary function was impacted sufficiently enough that her pulmonologist added a course of prednisone 10 mg daily tapered over 6 weeks. She had been on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily prior to the diagnosis of sarcoidosis for presumed mixed connective tissue disease and was continued on it for sarcoidosis after completing the prednisone taper. With these treatments, her facial lesions cleared and her breathing symptoms and fatigue improved. She remains under surveillance with a multidisciplinary team.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

Pathology showed noncaseating granulomas consistent with cutaneous sarcoidosis. Based on these biopsy findings, a chest x-ray was ordered, and it confirmed a pulmonary sarcoid. A multidisciplinary work-up (including cardiac evaluation, continued rheumatologic care, and evaluation by Hematology) addressed this new finding.
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by the development of granulomas that can arise in any organ, but frequently involve the skin and lungs. Patients with cutaneous disease develop smooth skin lesions, including flesh-colored to pink or brown papules on the face. Genetic and environmental factors are both thought to contribute to the disease.
Race is a significant factor in the development of disease. Hispanic and Asian patients are significantly less likely to develop the disease compared to White or Black patients. In the Black Women’s Health Study, incidence in Black women was 71 per 100,000.1 Women are more likely to be affected than men.1
Many patients with sarcoidosis have a mild course, but for others the disease may progress on the skin or include pulmonary, renal, neurologic, or cardiac disease. Sometimes sarcoidosis is fatal. Recurrence can occur at any point later in life. Race influences disease severity as well as incidence, with hospitalization being 9 times as likely in Black patients compared with White patients.2 One recent study puts sarcoidosis mortality rates for Black women at 10 per million compared with 3 per million in Black men, and 1 per million in White women or men.3
Patients with disease limited to the skin may be treated with topical steroids such as clobetasol 0.05% cream or ointment or intralesional triamcinolone 10 mg/mL injected into affected lesions every 2 to 4 weeks. With pulmonary or other systemic disease, treatment may include various disease-modifying agents including prednisone, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and TNF-alpha inhibitors. Because of the long-term adverse effects of systemic steroids, these agents are reserved for instances when pulmonary function is significantly impacted.
This patient had a reassuring cardiac and hematology work-up. Her pulmonary function was impacted sufficiently enough that her pulmonologist added a course of prednisone 10 mg daily tapered over 6 weeks. She had been on hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily prior to the diagnosis of sarcoidosis for presumed mixed connective tissue disease and was continued on it for sarcoidosis after completing the prednisone taper. With these treatments, her facial lesions cleared and her breathing symptoms and fatigue improved. She remains under surveillance with a multidisciplinary team.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Cozier Y, Berman J, Palmer J, et al. Sarcoidosis in black women in the United States: data from the Black Women's Health Study. Chest. 2011;139:144-150. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0413
2. Foreman MG, Mannino DM, Kamugisha L, et al. Hospitalization for patients with sarcoidosis: 1979-2000. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2006;23:124-129.
3. Mirsaeidi M, Machado R, Schraufnagel D, et al. Racial difference in sarcoidosis mortality in the United States. Chest. 2015; 147: 438-449. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1120
1. Cozier Y, Berman J, Palmer J, et al. Sarcoidosis in black women in the United States: data from the Black Women's Health Study. Chest. 2011;139:144-150. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0413
2. Foreman MG, Mannino DM, Kamugisha L, et al. Hospitalization for patients with sarcoidosis: 1979-2000. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2006;23:124-129.
3. Mirsaeidi M, Machado R, Schraufnagel D, et al. Racial difference in sarcoidosis mortality in the United States. Chest. 2015; 147: 438-449. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1120
Researchers tease apart multiple biologic failure in psoriasis, PsA
WASHINGTON – Multiple biologic failure in a minority of patients with psoriasis may have several causes, from genetic endotypes and immunologic factors to lower serum drug levels, the presence of anti-drug antibody levels, female sex, and certain comorbidities, Wilson Liao, MD, said at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“Tough-to-treat psoriasis remains a challenge despite newer therapies ... Why do we still have this sub-population of patients who seem to be refractory?” said Dr. Liao, professor and associate vice chair of research in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who coauthored a 2015-2022 prospective cohort analysis that documented about 6% of patients failing two or more biologic agents of different mechanistic classes.
“These patients are really suffering,” he said. “We need to have better guidelines and treatment algorithms for these patients.”
A significant number of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), meanwhile, are inadequate responders to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy/immunology and rheumatology and the Center of Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said during another session at the meeting.
The long-term “persistence,” or usage, of first-line biologics in patients with PsA – and of second-line biologics in patients who failed one TNF-inhibitor – is low, but the literature offers little information on the reasons for TNF-inhibitor discontinuation, said Dr. Ritchlin, who coauthored a perspective piece in Arthritis & Rheumatology on managing the patient with PsA who fails one TNF inhibitor.
Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors were asked to provide evidence-informed advice and algorithms, but the task was difficult. “It’s hard to know what to recommend for the next step if we don’t know why patients failed the first,” he said. “The point is, we need more data. [Clinical trials] are not recording the kind of information we need.”
Anti-drug antibodies, genetics, other factors in psoriasis
Research shows that in large cohorts, “all the biologics do seem to lose efficacy over time,” said Dr. Liao, who directs the UCSF Psoriasis and Skin Treatment Center. “Some are better than others, but we do see a loss of effectiveness over time.”
A cohort study published in 2022 in JAMA Dermatology, for instance, documented declining “drug survival” associated with ineffectiveness during 2 years of treatment for each of five biologics studied (adalimumab [Humira], ustekinumab [Stelara], secukinumab [Cosentyx], guselkumab [Tremfya], and ixekizumab [Taltz]).
“There have been a number of theories put forward” as to why that’s the case, including lower serum drug levels, “which of course can be related to anti-drug antibody production,” he said.
He pointed to two studies of ustekinumab: One prospective observational cohort study that reported an association of lower early drug levels of the IL-12/23 receptor antagonist with lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores, and another observational study that documented an association between anti-drug antibody positivity with lower ustekinumab levels and impaired clinical response.
“We also now know ... that there are genetic endotypes in psoriasis, and that patients who are [HLA-C*06:02]-positive tend to respond a little better to drugs like ustekinumab, and those who are [HLA-C*06:02]-negative tend to do a little better with the TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Liao said. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele HLA-C*06:02 is associated with susceptibility to psoriasis.
In a study using a national psoriasis registry, HLA-C*06:02-negative patients were 3 times more likely to achieve PASI90 status in response to adalimumab, a TNF-alpha inhibitor, than with ustekinumab treatment. And in a meta-analysis covering eight studies with more than 1,000 patients with psoriasis, the median PASI75 response rate after 6 months of ustekinumab therapy was 92% in the HLA-C*06:02-positive group and 67% in HLA-C*06:02-negative patients.
The recently published cohort study showing a 6% rate of multiple biologic failure evaluated patients in the multicenter CorEvitas Psoriasis Registry who initiated their first biologic between 2015 and 2020 and were followed for 2 or more years. Investigators looked for sociodemographic and clinical differences between the patients who continued use of their first biologic for at least 2 years (“good response”), and those who discontinued two or more biologics of different classes, each used for at least 90 days, because of inadequate efficacy.
Of 1,039 evaluated patients, 490 (47.2%) had good clinical response to their first biologic and 65 (6.3%) had multiple biologic failure. All biologic classes were represented among those who failed multiple biologics. The first and second biologic classes used were attempted for a mean duration of 10 months – “an adequate trial” of each, Dr. Liao said.
In multivariable regression analysis, six variables were significantly associated with multiple biologic failure: female sex at birth, shorter disease duration, earlier year of biologic initiation, prior nonbiologic systemic therapy, having Medicaid insurance, and a history of hyperlipidemia. The latter is “interesting because other studies have shown that metabolic syndrome, of which hyperlipidemia is a component, can also relate to poor response to biologics,” Dr. Liao said.
The most common sequences of first-to-second biologics among those with multiple biologic failure were TNF inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (30.8%); IL-12/23 inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (21.5%); TNF inhibitor to IL-12/23 inhibitor (12.3%); and IL-17 inhibitor to IL-23 inhibitor (10.8%).
The vast majority of patients failed more than two biologics, however, and “more than 20% had five or more biologics tried over a relatively short period,” Dr. Liao said.
Comorbidities and biologic failure in psoriasis, PsA
In practice, it was said during a discussion period, biologic failures in psoriasis can be of two types: a primary inadequate response or initial failure, or a secondary failure with initial improvement followed by declining or no response. “I agree 100% that these probably represent two different endotypes,” Dr. Liao said. “There’s research emerging that psoriasis isn’t necessarily a clean phenotype.”
The option of focusing on comorbidities in the face of biologic failure was another point of discussion. “Maybe the next biologic is not the answer,” a meeting participant said. “Maybe we should focus on metabolic syndrome.”
“I agree,” Dr. Liao said. “In clinic, there are people who may not respond to therapies but have other comorbidities and factors that make it difficult to manage [their psoriasis] ... that may be causative for psoriasis. Maybe if we treat the comorbidities, it will make it easier to treat the psoriasis.”
Addressing comorbidities and “extra-articular traits” such as poorly controlled diabetes, centralized pain, anxiety and depression, and obesity is something Dr. Ritchlin advocates for PsA. “Centralized pain, I believe, is a major driver of nonresponse,” he said at the meeting. “We have to be careful about blaming nonresponse and lack of efficacy of biologics when it could be a wholly different mechanism the biologic won’t treat ... for example, centralized pain.”
As with psoriasis, the emergence of antidrug antibodies may be one reason for the secondary failure of biologic agents for PsA, Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors wrote in their paper on management of PsA after failure of one TNF inhibitor. Other areas to consider in evaluating failure, they wrote, are compliance and time of dosing, and financial barriers.
Low long-term persistence of second-line biologics for patients with PsA was demonstrated in a national cohort study utilizing the French health insurance database, Dr. Ritchlin noted at the research meeting.
The French study covered almost 3,000 patients who started a second biologic after discontinuing a TNF inhibitor during 2015-2020. Overall, 1-year and 3-year persistence rates were 42% and 17%, respectively.
Dr. Liao disclosed research grant funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Leo, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Trex Bio. Dr. Ritchlin reported no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Multiple biologic failure in a minority of patients with psoriasis may have several causes, from genetic endotypes and immunologic factors to lower serum drug levels, the presence of anti-drug antibody levels, female sex, and certain comorbidities, Wilson Liao, MD, said at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“Tough-to-treat psoriasis remains a challenge despite newer therapies ... Why do we still have this sub-population of patients who seem to be refractory?” said Dr. Liao, professor and associate vice chair of research in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who coauthored a 2015-2022 prospective cohort analysis that documented about 6% of patients failing two or more biologic agents of different mechanistic classes.
“These patients are really suffering,” he said. “We need to have better guidelines and treatment algorithms for these patients.”
A significant number of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), meanwhile, are inadequate responders to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy/immunology and rheumatology and the Center of Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said during another session at the meeting.
The long-term “persistence,” or usage, of first-line biologics in patients with PsA – and of second-line biologics in patients who failed one TNF-inhibitor – is low, but the literature offers little information on the reasons for TNF-inhibitor discontinuation, said Dr. Ritchlin, who coauthored a perspective piece in Arthritis & Rheumatology on managing the patient with PsA who fails one TNF inhibitor.
Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors were asked to provide evidence-informed advice and algorithms, but the task was difficult. “It’s hard to know what to recommend for the next step if we don’t know why patients failed the first,” he said. “The point is, we need more data. [Clinical trials] are not recording the kind of information we need.”
Anti-drug antibodies, genetics, other factors in psoriasis
Research shows that in large cohorts, “all the biologics do seem to lose efficacy over time,” said Dr. Liao, who directs the UCSF Psoriasis and Skin Treatment Center. “Some are better than others, but we do see a loss of effectiveness over time.”
A cohort study published in 2022 in JAMA Dermatology, for instance, documented declining “drug survival” associated with ineffectiveness during 2 years of treatment for each of five biologics studied (adalimumab [Humira], ustekinumab [Stelara], secukinumab [Cosentyx], guselkumab [Tremfya], and ixekizumab [Taltz]).
“There have been a number of theories put forward” as to why that’s the case, including lower serum drug levels, “which of course can be related to anti-drug antibody production,” he said.
He pointed to two studies of ustekinumab: One prospective observational cohort study that reported an association of lower early drug levels of the IL-12/23 receptor antagonist with lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores, and another observational study that documented an association between anti-drug antibody positivity with lower ustekinumab levels and impaired clinical response.
“We also now know ... that there are genetic endotypes in psoriasis, and that patients who are [HLA-C*06:02]-positive tend to respond a little better to drugs like ustekinumab, and those who are [HLA-C*06:02]-negative tend to do a little better with the TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Liao said. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele HLA-C*06:02 is associated with susceptibility to psoriasis.
In a study using a national psoriasis registry, HLA-C*06:02-negative patients were 3 times more likely to achieve PASI90 status in response to adalimumab, a TNF-alpha inhibitor, than with ustekinumab treatment. And in a meta-analysis covering eight studies with more than 1,000 patients with psoriasis, the median PASI75 response rate after 6 months of ustekinumab therapy was 92% in the HLA-C*06:02-positive group and 67% in HLA-C*06:02-negative patients.
The recently published cohort study showing a 6% rate of multiple biologic failure evaluated patients in the multicenter CorEvitas Psoriasis Registry who initiated their first biologic between 2015 and 2020 and were followed for 2 or more years. Investigators looked for sociodemographic and clinical differences between the patients who continued use of their first biologic for at least 2 years (“good response”), and those who discontinued two or more biologics of different classes, each used for at least 90 days, because of inadequate efficacy.
Of 1,039 evaluated patients, 490 (47.2%) had good clinical response to their first biologic and 65 (6.3%) had multiple biologic failure. All biologic classes were represented among those who failed multiple biologics. The first and second biologic classes used were attempted for a mean duration of 10 months – “an adequate trial” of each, Dr. Liao said.
In multivariable regression analysis, six variables were significantly associated with multiple biologic failure: female sex at birth, shorter disease duration, earlier year of biologic initiation, prior nonbiologic systemic therapy, having Medicaid insurance, and a history of hyperlipidemia. The latter is “interesting because other studies have shown that metabolic syndrome, of which hyperlipidemia is a component, can also relate to poor response to biologics,” Dr. Liao said.
The most common sequences of first-to-second biologics among those with multiple biologic failure were TNF inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (30.8%); IL-12/23 inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (21.5%); TNF inhibitor to IL-12/23 inhibitor (12.3%); and IL-17 inhibitor to IL-23 inhibitor (10.8%).
The vast majority of patients failed more than two biologics, however, and “more than 20% had five or more biologics tried over a relatively short period,” Dr. Liao said.
Comorbidities and biologic failure in psoriasis, PsA
In practice, it was said during a discussion period, biologic failures in psoriasis can be of two types: a primary inadequate response or initial failure, or a secondary failure with initial improvement followed by declining or no response. “I agree 100% that these probably represent two different endotypes,” Dr. Liao said. “There’s research emerging that psoriasis isn’t necessarily a clean phenotype.”
The option of focusing on comorbidities in the face of biologic failure was another point of discussion. “Maybe the next biologic is not the answer,” a meeting participant said. “Maybe we should focus on metabolic syndrome.”
“I agree,” Dr. Liao said. “In clinic, there are people who may not respond to therapies but have other comorbidities and factors that make it difficult to manage [their psoriasis] ... that may be causative for psoriasis. Maybe if we treat the comorbidities, it will make it easier to treat the psoriasis.”
Addressing comorbidities and “extra-articular traits” such as poorly controlled diabetes, centralized pain, anxiety and depression, and obesity is something Dr. Ritchlin advocates for PsA. “Centralized pain, I believe, is a major driver of nonresponse,” he said at the meeting. “We have to be careful about blaming nonresponse and lack of efficacy of biologics when it could be a wholly different mechanism the biologic won’t treat ... for example, centralized pain.”
As with psoriasis, the emergence of antidrug antibodies may be one reason for the secondary failure of biologic agents for PsA, Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors wrote in their paper on management of PsA after failure of one TNF inhibitor. Other areas to consider in evaluating failure, they wrote, are compliance and time of dosing, and financial barriers.
Low long-term persistence of second-line biologics for patients with PsA was demonstrated in a national cohort study utilizing the French health insurance database, Dr. Ritchlin noted at the research meeting.
The French study covered almost 3,000 patients who started a second biologic after discontinuing a TNF inhibitor during 2015-2020. Overall, 1-year and 3-year persistence rates were 42% and 17%, respectively.
Dr. Liao disclosed research grant funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Leo, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Trex Bio. Dr. Ritchlin reported no disclosures.
WASHINGTON – Multiple biologic failure in a minority of patients with psoriasis may have several causes, from genetic endotypes and immunologic factors to lower serum drug levels, the presence of anti-drug antibody levels, female sex, and certain comorbidities, Wilson Liao, MD, said at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“Tough-to-treat psoriasis remains a challenge despite newer therapies ... Why do we still have this sub-population of patients who seem to be refractory?” said Dr. Liao, professor and associate vice chair of research in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco, who coauthored a 2015-2022 prospective cohort analysis that documented about 6% of patients failing two or more biologic agents of different mechanistic classes.
“These patients are really suffering,” he said. “We need to have better guidelines and treatment algorithms for these patients.”
A significant number of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), meanwhile, are inadequate responders to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, Christopher T. Ritchlin, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in the division of allergy/immunology and rheumatology and the Center of Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), said during another session at the meeting.
The long-term “persistence,” or usage, of first-line biologics in patients with PsA – and of second-line biologics in patients who failed one TNF-inhibitor – is low, but the literature offers little information on the reasons for TNF-inhibitor discontinuation, said Dr. Ritchlin, who coauthored a perspective piece in Arthritis & Rheumatology on managing the patient with PsA who fails one TNF inhibitor.
Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors were asked to provide evidence-informed advice and algorithms, but the task was difficult. “It’s hard to know what to recommend for the next step if we don’t know why patients failed the first,” he said. “The point is, we need more data. [Clinical trials] are not recording the kind of information we need.”
Anti-drug antibodies, genetics, other factors in psoriasis
Research shows that in large cohorts, “all the biologics do seem to lose efficacy over time,” said Dr. Liao, who directs the UCSF Psoriasis and Skin Treatment Center. “Some are better than others, but we do see a loss of effectiveness over time.”
A cohort study published in 2022 in JAMA Dermatology, for instance, documented declining “drug survival” associated with ineffectiveness during 2 years of treatment for each of five biologics studied (adalimumab [Humira], ustekinumab [Stelara], secukinumab [Cosentyx], guselkumab [Tremfya], and ixekizumab [Taltz]).
“There have been a number of theories put forward” as to why that’s the case, including lower serum drug levels, “which of course can be related to anti-drug antibody production,” he said.
He pointed to two studies of ustekinumab: One prospective observational cohort study that reported an association of lower early drug levels of the IL-12/23 receptor antagonist with lower Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores, and another observational study that documented an association between anti-drug antibody positivity with lower ustekinumab levels and impaired clinical response.
“We also now know ... that there are genetic endotypes in psoriasis, and that patients who are [HLA-C*06:02]-positive tend to respond a little better to drugs like ustekinumab, and those who are [HLA-C*06:02]-negative tend to do a little better with the TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Liao said. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele HLA-C*06:02 is associated with susceptibility to psoriasis.
In a study using a national psoriasis registry, HLA-C*06:02-negative patients were 3 times more likely to achieve PASI90 status in response to adalimumab, a TNF-alpha inhibitor, than with ustekinumab treatment. And in a meta-analysis covering eight studies with more than 1,000 patients with psoriasis, the median PASI75 response rate after 6 months of ustekinumab therapy was 92% in the HLA-C*06:02-positive group and 67% in HLA-C*06:02-negative patients.
The recently published cohort study showing a 6% rate of multiple biologic failure evaluated patients in the multicenter CorEvitas Psoriasis Registry who initiated their first biologic between 2015 and 2020 and were followed for 2 or more years. Investigators looked for sociodemographic and clinical differences between the patients who continued use of their first biologic for at least 2 years (“good response”), and those who discontinued two or more biologics of different classes, each used for at least 90 days, because of inadequate efficacy.
Of 1,039 evaluated patients, 490 (47.2%) had good clinical response to their first biologic and 65 (6.3%) had multiple biologic failure. All biologic classes were represented among those who failed multiple biologics. The first and second biologic classes used were attempted for a mean duration of 10 months – “an adequate trial” of each, Dr. Liao said.
In multivariable regression analysis, six variables were significantly associated with multiple biologic failure: female sex at birth, shorter disease duration, earlier year of biologic initiation, prior nonbiologic systemic therapy, having Medicaid insurance, and a history of hyperlipidemia. The latter is “interesting because other studies have shown that metabolic syndrome, of which hyperlipidemia is a component, can also relate to poor response to biologics,” Dr. Liao said.
The most common sequences of first-to-second biologics among those with multiple biologic failure were TNF inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (30.8%); IL-12/23 inhibitor to IL-17 inhibitor (21.5%); TNF inhibitor to IL-12/23 inhibitor (12.3%); and IL-17 inhibitor to IL-23 inhibitor (10.8%).
The vast majority of patients failed more than two biologics, however, and “more than 20% had five or more biologics tried over a relatively short period,” Dr. Liao said.
Comorbidities and biologic failure in psoriasis, PsA
In practice, it was said during a discussion period, biologic failures in psoriasis can be of two types: a primary inadequate response or initial failure, or a secondary failure with initial improvement followed by declining or no response. “I agree 100% that these probably represent two different endotypes,” Dr. Liao said. “There’s research emerging that psoriasis isn’t necessarily a clean phenotype.”
The option of focusing on comorbidities in the face of biologic failure was another point of discussion. “Maybe the next biologic is not the answer,” a meeting participant said. “Maybe we should focus on metabolic syndrome.”
“I agree,” Dr. Liao said. “In clinic, there are people who may not respond to therapies but have other comorbidities and factors that make it difficult to manage [their psoriasis] ... that may be causative for psoriasis. Maybe if we treat the comorbidities, it will make it easier to treat the psoriasis.”
Addressing comorbidities and “extra-articular traits” such as poorly controlled diabetes, centralized pain, anxiety and depression, and obesity is something Dr. Ritchlin advocates for PsA. “Centralized pain, I believe, is a major driver of nonresponse,” he said at the meeting. “We have to be careful about blaming nonresponse and lack of efficacy of biologics when it could be a wholly different mechanism the biologic won’t treat ... for example, centralized pain.”
As with psoriasis, the emergence of antidrug antibodies may be one reason for the secondary failure of biologic agents for PsA, Dr. Ritchlin and his coauthors wrote in their paper on management of PsA after failure of one TNF inhibitor. Other areas to consider in evaluating failure, they wrote, are compliance and time of dosing, and financial barriers.
Low long-term persistence of second-line biologics for patients with PsA was demonstrated in a national cohort study utilizing the French health insurance database, Dr. Ritchlin noted at the research meeting.
The French study covered almost 3,000 patients who started a second biologic after discontinuing a TNF inhibitor during 2015-2020. Overall, 1-year and 3-year persistence rates were 42% and 17%, respectively.
Dr. Liao disclosed research grant funding from AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Leo, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Trex Bio. Dr. Ritchlin reported no disclosures.
AT THE NPF RESEARCH SYMPOSIUM 2023
Body dysmorphic disorder diagnosis guidelines completed in Europe
BERLIN – were outlined in a late-breaker presentation at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The development of guidelines for BDD, a disorder familiar to many clinical dermatologists, is intended as a practical tool, according to Maria-Angeliki Gkini, MD, who has appointments at both Bart’s Health NHS Trust in London and the 401 General Army Hospital in Athens.
“BDD is a relatively common disorder in which the patients are preoccupied with a perceived defect or defects,” Dr. Gkini explained. “This affects them so intensely that it affects their mental health and their quality of life.”
In the DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, BDD is specifically defined as a preoccupation with “one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others.” But Dr. Gkini said that BDD can also develop as a comorbidity of dermatological disorders that are visible.
These patients are challenging because they are difficult to please, added Dr. Gkini, who said they commonly become involved in doctor shopping, leaving negative reviews on social media for the clinicians they have cycled through. The problem is that the defects they seek to resolve typically stem from distorted perceptions.
BDD is related to obsessive-compulsive disorder by the frequency with which patients pursue repetitive behaviors related to their preoccupation, such as intensive grooming, frequent trips to the mirror, or difficulty in focusing on topics other than their own appearance.
The process to develop the soon-to-be-published guidelines began with a literature search. Of the approximately 3,200 articles identified on BDD, only 10 involved randomized controlled trials. Moreover, even the quality of these trials was considered “low to very low” by the experts who reviewed them, Dr. Gkini said.
One explanation is that psychodermatology has only recently started to attract more research interest, and better studies are now underway, she noted.
However, because of the dearth of high quality evidence now available, the guideline development relied on a Delphi method to reach consensus based on expert opinion in discussion of the available data.
Consensus reached by 17 experts
Specifically, 17 experts, all of whom were members of the European Society for Dermatology and Psychiatry proceeded to systematically address a series of clinical questions and recommendations. Consensus was defined as at least 75% of the participants strongly agreeing or agreeing. Several rounds of discussion were often required.
Among the conclusions, the guidelines support uniform screening for BDD in all patients prior to cosmetic procedures. In identifying depression, anxiety, and distorted perceptions, simple tools, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire might be adequate for an initial evaluation, but Dr. Gkini also recommended routinely inquiring about suicidal ideation, which has been reported in up to 80% of individuals with BDD.
Other instruments for screening that can be considered include DSM-5 criteria for BDD and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology Version, which might be particularly useful and appropriate for dermatologists.
One of the reasons to screen for BDD is that these patients often convince themselves that some specific procedure is needed to resolve the source of their obsession. The goal of screening is to verify that it is the dermatologic concern, not an underlying psychiatric disorder that is driving their search for relief. The risk of dermatologic interventions is not only that expectations are not met, but the patient’s perception of a failed intervention “sometimes makes these worse,” Dr. Gkini explained.
Collaboration with psychiatrists recommended
The guidelines include suggestions for treatment of BDD. Of these, SSRIs are recommended at high relative doses, according to Dr. Gkini. Consistent with the consensus recommendation of collaborating with mental health specialists, she said that the recommendations acknowledge evidence of greater benefits when SSRIs are combined with psychotherapy.
Katharine A. Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has been conducting BDD research for several years and has written numerous books and articles about this topic, including a review in the journal Focus. She cautioned that, because of a normal concern for appearance, BDD is easily missed by dermatologists.
“For BDD to be diagnosed, the preoccupation with a nonexistent or slight defect in appearance must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning,” she said in an interview. “This is necessary to differentiate BDD from more normal and common appearance concerns that do not qualify for the diagnosis”
She specified that patients should be considered for cognitive-behavioral therapy rather than psychotherapy, a generic term that covers many forms of treatment. She said that most other types of psychotherapy “are probably not effective” for BDD.
Dr. Phillips highly endorsed the development of BDD guidelines for dermatologists because of the frequency with which physicians in this specialty encounter BDD – and believes that more attention to this diagnosis is needed.
“I recommend that dermatologists who have a patient with BDD collaborate with a psychiatrist in delivering care with an SSRI,” she said. “High doses of these medications are often needed to effectively treat BDD.”
Dr. Gkini reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO, Novartis, Sanofi, and Regenlab. Dr. Phillips reported no relevant financial relationships.
BERLIN – were outlined in a late-breaker presentation at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The development of guidelines for BDD, a disorder familiar to many clinical dermatologists, is intended as a practical tool, according to Maria-Angeliki Gkini, MD, who has appointments at both Bart’s Health NHS Trust in London and the 401 General Army Hospital in Athens.
“BDD is a relatively common disorder in which the patients are preoccupied with a perceived defect or defects,” Dr. Gkini explained. “This affects them so intensely that it affects their mental health and their quality of life.”
In the DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, BDD is specifically defined as a preoccupation with “one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others.” But Dr. Gkini said that BDD can also develop as a comorbidity of dermatological disorders that are visible.
These patients are challenging because they are difficult to please, added Dr. Gkini, who said they commonly become involved in doctor shopping, leaving negative reviews on social media for the clinicians they have cycled through. The problem is that the defects they seek to resolve typically stem from distorted perceptions.
BDD is related to obsessive-compulsive disorder by the frequency with which patients pursue repetitive behaviors related to their preoccupation, such as intensive grooming, frequent trips to the mirror, or difficulty in focusing on topics other than their own appearance.
The process to develop the soon-to-be-published guidelines began with a literature search. Of the approximately 3,200 articles identified on BDD, only 10 involved randomized controlled trials. Moreover, even the quality of these trials was considered “low to very low” by the experts who reviewed them, Dr. Gkini said.
One explanation is that psychodermatology has only recently started to attract more research interest, and better studies are now underway, she noted.
However, because of the dearth of high quality evidence now available, the guideline development relied on a Delphi method to reach consensus based on expert opinion in discussion of the available data.
Consensus reached by 17 experts
Specifically, 17 experts, all of whom were members of the European Society for Dermatology and Psychiatry proceeded to systematically address a series of clinical questions and recommendations. Consensus was defined as at least 75% of the participants strongly agreeing or agreeing. Several rounds of discussion were often required.
Among the conclusions, the guidelines support uniform screening for BDD in all patients prior to cosmetic procedures. In identifying depression, anxiety, and distorted perceptions, simple tools, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire might be adequate for an initial evaluation, but Dr. Gkini also recommended routinely inquiring about suicidal ideation, which has been reported in up to 80% of individuals with BDD.
Other instruments for screening that can be considered include DSM-5 criteria for BDD and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology Version, which might be particularly useful and appropriate for dermatologists.
One of the reasons to screen for BDD is that these patients often convince themselves that some specific procedure is needed to resolve the source of their obsession. The goal of screening is to verify that it is the dermatologic concern, not an underlying psychiatric disorder that is driving their search for relief. The risk of dermatologic interventions is not only that expectations are not met, but the patient’s perception of a failed intervention “sometimes makes these worse,” Dr. Gkini explained.
Collaboration with psychiatrists recommended
The guidelines include suggestions for treatment of BDD. Of these, SSRIs are recommended at high relative doses, according to Dr. Gkini. Consistent with the consensus recommendation of collaborating with mental health specialists, she said that the recommendations acknowledge evidence of greater benefits when SSRIs are combined with psychotherapy.
Katharine A. Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has been conducting BDD research for several years and has written numerous books and articles about this topic, including a review in the journal Focus. She cautioned that, because of a normal concern for appearance, BDD is easily missed by dermatologists.
“For BDD to be diagnosed, the preoccupation with a nonexistent or slight defect in appearance must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning,” she said in an interview. “This is necessary to differentiate BDD from more normal and common appearance concerns that do not qualify for the diagnosis”
She specified that patients should be considered for cognitive-behavioral therapy rather than psychotherapy, a generic term that covers many forms of treatment. She said that most other types of psychotherapy “are probably not effective” for BDD.
Dr. Phillips highly endorsed the development of BDD guidelines for dermatologists because of the frequency with which physicians in this specialty encounter BDD – and believes that more attention to this diagnosis is needed.
“I recommend that dermatologists who have a patient with BDD collaborate with a psychiatrist in delivering care with an SSRI,” she said. “High doses of these medications are often needed to effectively treat BDD.”
Dr. Gkini reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO, Novartis, Sanofi, and Regenlab. Dr. Phillips reported no relevant financial relationships.
BERLIN – were outlined in a late-breaker presentation at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The development of guidelines for BDD, a disorder familiar to many clinical dermatologists, is intended as a practical tool, according to Maria-Angeliki Gkini, MD, who has appointments at both Bart’s Health NHS Trust in London and the 401 General Army Hospital in Athens.
“BDD is a relatively common disorder in which the patients are preoccupied with a perceived defect or defects,” Dr. Gkini explained. “This affects them so intensely that it affects their mental health and their quality of life.”
In the DSM-5, published by the American Psychiatric Association, BDD is specifically defined as a preoccupation with “one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others.” But Dr. Gkini said that BDD can also develop as a comorbidity of dermatological disorders that are visible.
These patients are challenging because they are difficult to please, added Dr. Gkini, who said they commonly become involved in doctor shopping, leaving negative reviews on social media for the clinicians they have cycled through. The problem is that the defects they seek to resolve typically stem from distorted perceptions.
BDD is related to obsessive-compulsive disorder by the frequency with which patients pursue repetitive behaviors related to their preoccupation, such as intensive grooming, frequent trips to the mirror, or difficulty in focusing on topics other than their own appearance.
The process to develop the soon-to-be-published guidelines began with a literature search. Of the approximately 3,200 articles identified on BDD, only 10 involved randomized controlled trials. Moreover, even the quality of these trials was considered “low to very low” by the experts who reviewed them, Dr. Gkini said.
One explanation is that psychodermatology has only recently started to attract more research interest, and better studies are now underway, she noted.
However, because of the dearth of high quality evidence now available, the guideline development relied on a Delphi method to reach consensus based on expert opinion in discussion of the available data.
Consensus reached by 17 experts
Specifically, 17 experts, all of whom were members of the European Society for Dermatology and Psychiatry proceeded to systematically address a series of clinical questions and recommendations. Consensus was defined as at least 75% of the participants strongly agreeing or agreeing. Several rounds of discussion were often required.
Among the conclusions, the guidelines support uniform screening for BDD in all patients prior to cosmetic procedures. In identifying depression, anxiety, and distorted perceptions, simple tools, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire might be adequate for an initial evaluation, but Dr. Gkini also recommended routinely inquiring about suicidal ideation, which has been reported in up to 80% of individuals with BDD.
Other instruments for screening that can be considered include DSM-5 criteria for BDD and the Body Dysmorphic Disorder Questionnaire–Dermatology Version, which might be particularly useful and appropriate for dermatologists.
One of the reasons to screen for BDD is that these patients often convince themselves that some specific procedure is needed to resolve the source of their obsession. The goal of screening is to verify that it is the dermatologic concern, not an underlying psychiatric disorder that is driving their search for relief. The risk of dermatologic interventions is not only that expectations are not met, but the patient’s perception of a failed intervention “sometimes makes these worse,” Dr. Gkini explained.
Collaboration with psychiatrists recommended
The guidelines include suggestions for treatment of BDD. Of these, SSRIs are recommended at high relative doses, according to Dr. Gkini. Consistent with the consensus recommendation of collaborating with mental health specialists, she said that the recommendations acknowledge evidence of greater benefits when SSRIs are combined with psychotherapy.
Katharine A. Phillips, MD, professor of psychiatry at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has been conducting BDD research for several years and has written numerous books and articles about this topic, including a review in the journal Focus. She cautioned that, because of a normal concern for appearance, BDD is easily missed by dermatologists.
“For BDD to be diagnosed, the preoccupation with a nonexistent or slight defect in appearance must cause clinically significant distress or impairment in functioning,” she said in an interview. “This is necessary to differentiate BDD from more normal and common appearance concerns that do not qualify for the diagnosis”
She specified that patients should be considered for cognitive-behavioral therapy rather than psychotherapy, a generic term that covers many forms of treatment. She said that most other types of psychotherapy “are probably not effective” for BDD.
Dr. Phillips highly endorsed the development of BDD guidelines for dermatologists because of the frequency with which physicians in this specialty encounter BDD – and believes that more attention to this diagnosis is needed.
“I recommend that dermatologists who have a patient with BDD collaborate with a psychiatrist in delivering care with an SSRI,” she said. “High doses of these medications are often needed to effectively treat BDD.”
Dr. Gkini reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, LEO, Novartis, Sanofi, and Regenlab. Dr. Phillips reported no relevant financial relationships.
AT THE EADV CONGRESS
Most patients with psoriasis not engaged in highly shared decision-making
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers drew from the 2014-2017 and 2019 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to identify 3,715,027 patients with psoriasis, to evaluate the association between SDM (a patient-centered approach to selecting treatment on the basis of a discussion between the clinician and patient) and satisfaction with care.
- SDM was determined by patient responses on a 4-point Likert scale to seven MEPS variables, including the question, “How often did doctors or other health providers listen carefully to you?”
- Patient satisfaction with care was measured with a MEPS variable that asked respondents to rate their health care providers on a scale of 1-10.
- Researchers used multiple logistic regression to assess the association between SDM and demographic and clinical characteristics in patients with psoriasis, and multiple linear regression analysis to assess the association between SDM and patient satisfaction with care.
TAKEAWAY:
- The average SDM score was 3.6 out of 4, and the average satisfaction with care score was 8.6 out of 10.
- However, only about 42% of the cohort reported a high SDM, defined as a score of 3.9 or greater.
- After adjusting for covariates, the researchers found that patients who had high SDM had, on average, 85% higher satisfaction with care (P < .001).
- Compared with men, women had about 27% higher satisfaction with care (P = .023), whereas non-Hispanic patients had lower satisfaction with care compared with Hispanic patients (P = .037).
IN PRACTICE:
“It is important to construct a framework for carrying out SDM with patients with psoriasis to enhance clinician-patient communication and improve patient outcomes,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The ability to measure SDM in patients with psoriasis was limited by the seven items from MEPS. The diagnosis of psoriasis was based on self-report.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she has served as a research investigator and/or scientific adviser to AbbVie, Almirall, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, EPI, Incyte, Leo, UCB, Janssen, Lilly, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Sun, Dermavant, Dermira, Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and Modmed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers drew from the 2014-2017 and 2019 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to identify 3,715,027 patients with psoriasis, to evaluate the association between SDM (a patient-centered approach to selecting treatment on the basis of a discussion between the clinician and patient) and satisfaction with care.
- SDM was determined by patient responses on a 4-point Likert scale to seven MEPS variables, including the question, “How often did doctors or other health providers listen carefully to you?”
- Patient satisfaction with care was measured with a MEPS variable that asked respondents to rate their health care providers on a scale of 1-10.
- Researchers used multiple logistic regression to assess the association between SDM and demographic and clinical characteristics in patients with psoriasis, and multiple linear regression analysis to assess the association between SDM and patient satisfaction with care.
TAKEAWAY:
- The average SDM score was 3.6 out of 4, and the average satisfaction with care score was 8.6 out of 10.
- However, only about 42% of the cohort reported a high SDM, defined as a score of 3.9 or greater.
- After adjusting for covariates, the researchers found that patients who had high SDM had, on average, 85% higher satisfaction with care (P < .001).
- Compared with men, women had about 27% higher satisfaction with care (P = .023), whereas non-Hispanic patients had lower satisfaction with care compared with Hispanic patients (P = .037).
IN PRACTICE:
“It is important to construct a framework for carrying out SDM with patients with psoriasis to enhance clinician-patient communication and improve patient outcomes,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The ability to measure SDM in patients with psoriasis was limited by the seven items from MEPS. The diagnosis of psoriasis was based on self-report.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she has served as a research investigator and/or scientific adviser to AbbVie, Almirall, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, EPI, Incyte, Leo, UCB, Janssen, Lilly, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Sun, Dermavant, Dermira, Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and Modmed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers drew from the 2014-2017 and 2019 Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) to identify 3,715,027 patients with psoriasis, to evaluate the association between SDM (a patient-centered approach to selecting treatment on the basis of a discussion between the clinician and patient) and satisfaction with care.
- SDM was determined by patient responses on a 4-point Likert scale to seven MEPS variables, including the question, “How often did doctors or other health providers listen carefully to you?”
- Patient satisfaction with care was measured with a MEPS variable that asked respondents to rate their health care providers on a scale of 1-10.
- Researchers used multiple logistic regression to assess the association between SDM and demographic and clinical characteristics in patients with psoriasis, and multiple linear regression analysis to assess the association between SDM and patient satisfaction with care.
TAKEAWAY:
- The average SDM score was 3.6 out of 4, and the average satisfaction with care score was 8.6 out of 10.
- However, only about 42% of the cohort reported a high SDM, defined as a score of 3.9 or greater.
- After adjusting for covariates, the researchers found that patients who had high SDM had, on average, 85% higher satisfaction with care (P < .001).
- Compared with men, women had about 27% higher satisfaction with care (P = .023), whereas non-Hispanic patients had lower satisfaction with care compared with Hispanic patients (P = .037).
IN PRACTICE:
“It is important to construct a framework for carrying out SDM with patients with psoriasis to enhance clinician-patient communication and improve patient outcomes,” the authors concluded.
SOURCE:
April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, chief of dermatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, led the research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The ability to measure SDM in patients with psoriasis was limited by the seven items from MEPS. The diagnosis of psoriasis was based on self-report.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Dr. Armstrong disclosed that she has served as a research investigator and/or scientific adviser to AbbVie, Almirall, Arcutis, ASLAN, Beiersdorf, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, EPI, Incyte, Leo, UCB, Janssen, Lilly, Nimbus, Novartis, Ortho Dermatologics, Sun, Dermavant, Dermira, Sanofi, Regeneron, Pfizer, and Modmed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dupilumab-associated lymphoid reactions require caution
, according to a study published in JAMA Dermatology
The potential for such reactions requires diagnosing AD carefully, monitoring patients on dupilumab for new and unusual symptoms, and thoroughly working up suspicious LRs, according to an accompanying editorial and experts interviewed for this article.
“Dupilumab has become such an important first-line systemic medication for our patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. It’s important for us to understand everything we can about its use in the real world – both good and bad,”Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. He was uninvolved with either publication.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, added that, although the affected patient group was small, studying lymphoid reactions associated with dupilumab is important because of the risk for diagnostic misadventure that these reactions carry. He is a professor of pediatrics and division head of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital and the University of Washington, Seattle.
“AD and MF are easily confused for one another at baseline,” explained Dr. Sidbury, who was not involved with the study or editorial. “Dupilumab is known to make AD better and theoretically could help MF via its effect on interleukin (IL)–13, yet case reports of exacerbation and/or unmasking of MF are out there.”
For the study, researchers retrospectively examined records of 530 patients with AD treated with dupilumab at the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands). Reviewing pretreatment biopsies revealed that among 14 (2.6%) patients who developed clinical suspicion of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) while on treatment, three actually had preexisting MF.
All 14 patients with LR initially responded to dupilumab then developed worsening symptoms at a median of 4 months. Patients reported that the worsening lesions looked and felt different than did previous lesions, with symptoms including burning/pain and an appearance of generalized erythematous maculopapular plaques, sometimes with severe lichenification, on the lower trunk and upper thighs.
The 14 patients’ posttreatment biopsies showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with lichenoid or perivascular distribution and intraepithelial T-cell lymphocytes. Whereas patients with MF had hyperconvoluted cerebriform lymphocytes aligned in the epidermal basal layer at the dermoepidermal junction, the 11 with LR had similar-looking lesions dispersed throughout the upper epidermis.
Immunohistochemically, both groups had a dysregulated (mostly increased) CD4:CD8 ratio. CD30 overexpression, usually absent in early-stage MF, affected only patients with LR and one patient with advanced MF. In addition, patients with LR maintained pan–T-cell antigens (CD2, CD3, and CD5), whereas those with MF did not. The 11 patients with LR experienced biopsy-confirmed resolution once they discontinued dupilumab.
It is reassuring that the LRs resolved after dupilumab discontinuation, writes the author of the accompanying editorial, Joan Guitart, MD, chief of dermatopathology at Northwestern University. Nevertheless, he added, such patients deserve “a comprehensive workup including skin biopsy with T-cell receptor clonality assay, blood cell counts with flow cytometry analysis, serum lactate dehydrogenase, and documentation of possible adenopathy, followed with imaging studies and/or local biopsies in cases with abnormal results.”
The possibility that these LRs may represent a first step toward lymphoma requires dermatologists to remain vigilant in ruling out MF, Dr. Guitart wrote, particularly in atypical presentations such as adult-onset AD, cases lacking a history of AD, and cases involving erythrodermic and other uncharacteristic presentations such as plaques, nodules, or spared flexural sites.
For dermatopathologists, Dr. Guitart recommended a cautious approach that resists overdiagnosing MF and acknowledging that insufficient evidence exists to report such reactions as benign. The fact that one study patient had both MF and LR raises concerns that the LR may not always be reversible, Dr. Guitart added.
Clinicians and patients must consider the possibility of dupilumab-induced LR as part of the shared decision-making process and risk-benefit calculus, Dr. Sidbury said. In cases involving unexpected responses or atypical presentations, he added, clinicians must have a low threshold for stopping dupilumab.
For patients who must discontinue dupilumab because of LR, the list of treatment options is growing. “While more investigation is required to understand the role of newer IL-13–blocking biologics and JAK inhibitors among patients experiencing lymphoid reactions,” said Dr. Chovatiya, “traditional atopic dermatitis therapies like narrowband UVB phototherapy and the oral immunosuppressant methotrexate may be reassuring in this population.” Conversely, cyclosporine has been associated with progression of MF.
Also reassuring, said Dr. Sidbury and Dr. Chovatiya, is the rarity of LR overall. Dr. Sidbury said, “The numbers of patients in whom LR or onset/exacerbation of MF occurs is extraordinarily low when compared to those helped immeasurably by dupilumab.”
Dr. Sidbury added that the study and accompanying editorial also will alert clinicians to the potential for newer AD biologics that target solely IL-13 and not IL-4/13, as dupilumab does. “If the deregulated response leading to LR and potentially MF in the affected few is driven by IL-4 inhibition,” he said, “drugs such as tralokinumab (Adbry), lebrikizumab (once approved), and perhaps other newer options might calm AD without causing LRs.”
(Lebrikizumab is not yet approved. In an Oct. 2 press release, Eli Lilly and Company, developer of lebrikizumab, said that it would address issues the U.S. Food and Drug Administration had raised about a third-party manufacturing facility that arose during evaluation of the lebrikizumab biologic license application.)
Study limitations include the fact that most patients who experienced LR had already undergone skin biopsies before dupilumab treatment, which suggests that they had a more atypical AD presentation from the start. The authors add that their having treated all study patients in a tertiary referral hospital indicates a hard-to-treat AD subpopulation.
Study authors reported relationships with several biologic drug manufacturers including Sanofi and Regeneron (dupilumab), LEO Pharma (tralokinumab), and Eli Lilly (lebrikizumab). However, none of these companies provided support for the study.
Dr. Sidbury has been an investigator for Regeneron, Pfizer, and Galderma and a consultant for LEO Pharma and Eli Lilly. Dr. Chovatiya has served as an advisor, consultant, speaker, and investigator for Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Guitart reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a study published in JAMA Dermatology
The potential for such reactions requires diagnosing AD carefully, monitoring patients on dupilumab for new and unusual symptoms, and thoroughly working up suspicious LRs, according to an accompanying editorial and experts interviewed for this article.
“Dupilumab has become such an important first-line systemic medication for our patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. It’s important for us to understand everything we can about its use in the real world – both good and bad,”Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. He was uninvolved with either publication.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, added that, although the affected patient group was small, studying lymphoid reactions associated with dupilumab is important because of the risk for diagnostic misadventure that these reactions carry. He is a professor of pediatrics and division head of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital and the University of Washington, Seattle.
“AD and MF are easily confused for one another at baseline,” explained Dr. Sidbury, who was not involved with the study or editorial. “Dupilumab is known to make AD better and theoretically could help MF via its effect on interleukin (IL)–13, yet case reports of exacerbation and/or unmasking of MF are out there.”
For the study, researchers retrospectively examined records of 530 patients with AD treated with dupilumab at the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands). Reviewing pretreatment biopsies revealed that among 14 (2.6%) patients who developed clinical suspicion of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) while on treatment, three actually had preexisting MF.
All 14 patients with LR initially responded to dupilumab then developed worsening symptoms at a median of 4 months. Patients reported that the worsening lesions looked and felt different than did previous lesions, with symptoms including burning/pain and an appearance of generalized erythematous maculopapular plaques, sometimes with severe lichenification, on the lower trunk and upper thighs.
The 14 patients’ posttreatment biopsies showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with lichenoid or perivascular distribution and intraepithelial T-cell lymphocytes. Whereas patients with MF had hyperconvoluted cerebriform lymphocytes aligned in the epidermal basal layer at the dermoepidermal junction, the 11 with LR had similar-looking lesions dispersed throughout the upper epidermis.
Immunohistochemically, both groups had a dysregulated (mostly increased) CD4:CD8 ratio. CD30 overexpression, usually absent in early-stage MF, affected only patients with LR and one patient with advanced MF. In addition, patients with LR maintained pan–T-cell antigens (CD2, CD3, and CD5), whereas those with MF did not. The 11 patients with LR experienced biopsy-confirmed resolution once they discontinued dupilumab.
It is reassuring that the LRs resolved after dupilumab discontinuation, writes the author of the accompanying editorial, Joan Guitart, MD, chief of dermatopathology at Northwestern University. Nevertheless, he added, such patients deserve “a comprehensive workup including skin biopsy with T-cell receptor clonality assay, blood cell counts with flow cytometry analysis, serum lactate dehydrogenase, and documentation of possible adenopathy, followed with imaging studies and/or local biopsies in cases with abnormal results.”
The possibility that these LRs may represent a first step toward lymphoma requires dermatologists to remain vigilant in ruling out MF, Dr. Guitart wrote, particularly in atypical presentations such as adult-onset AD, cases lacking a history of AD, and cases involving erythrodermic and other uncharacteristic presentations such as plaques, nodules, or spared flexural sites.
For dermatopathologists, Dr. Guitart recommended a cautious approach that resists overdiagnosing MF and acknowledging that insufficient evidence exists to report such reactions as benign. The fact that one study patient had both MF and LR raises concerns that the LR may not always be reversible, Dr. Guitart added.
Clinicians and patients must consider the possibility of dupilumab-induced LR as part of the shared decision-making process and risk-benefit calculus, Dr. Sidbury said. In cases involving unexpected responses or atypical presentations, he added, clinicians must have a low threshold for stopping dupilumab.
For patients who must discontinue dupilumab because of LR, the list of treatment options is growing. “While more investigation is required to understand the role of newer IL-13–blocking biologics and JAK inhibitors among patients experiencing lymphoid reactions,” said Dr. Chovatiya, “traditional atopic dermatitis therapies like narrowband UVB phototherapy and the oral immunosuppressant methotrexate may be reassuring in this population.” Conversely, cyclosporine has been associated with progression of MF.
Also reassuring, said Dr. Sidbury and Dr. Chovatiya, is the rarity of LR overall. Dr. Sidbury said, “The numbers of patients in whom LR or onset/exacerbation of MF occurs is extraordinarily low when compared to those helped immeasurably by dupilumab.”
Dr. Sidbury added that the study and accompanying editorial also will alert clinicians to the potential for newer AD biologics that target solely IL-13 and not IL-4/13, as dupilumab does. “If the deregulated response leading to LR and potentially MF in the affected few is driven by IL-4 inhibition,” he said, “drugs such as tralokinumab (Adbry), lebrikizumab (once approved), and perhaps other newer options might calm AD without causing LRs.”
(Lebrikizumab is not yet approved. In an Oct. 2 press release, Eli Lilly and Company, developer of lebrikizumab, said that it would address issues the U.S. Food and Drug Administration had raised about a third-party manufacturing facility that arose during evaluation of the lebrikizumab biologic license application.)
Study limitations include the fact that most patients who experienced LR had already undergone skin biopsies before dupilumab treatment, which suggests that they had a more atypical AD presentation from the start. The authors add that their having treated all study patients in a tertiary referral hospital indicates a hard-to-treat AD subpopulation.
Study authors reported relationships with several biologic drug manufacturers including Sanofi and Regeneron (dupilumab), LEO Pharma (tralokinumab), and Eli Lilly (lebrikizumab). However, none of these companies provided support for the study.
Dr. Sidbury has been an investigator for Regeneron, Pfizer, and Galderma and a consultant for LEO Pharma and Eli Lilly. Dr. Chovatiya has served as an advisor, consultant, speaker, and investigator for Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Guitart reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a study published in JAMA Dermatology
The potential for such reactions requires diagnosing AD carefully, monitoring patients on dupilumab for new and unusual symptoms, and thoroughly working up suspicious LRs, according to an accompanying editorial and experts interviewed for this article.
“Dupilumab has become such an important first-line systemic medication for our patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. It’s important for us to understand everything we can about its use in the real world – both good and bad,”Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. He was uninvolved with either publication.
Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, added that, although the affected patient group was small, studying lymphoid reactions associated with dupilumab is important because of the risk for diagnostic misadventure that these reactions carry. He is a professor of pediatrics and division head of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital and the University of Washington, Seattle.
“AD and MF are easily confused for one another at baseline,” explained Dr. Sidbury, who was not involved with the study or editorial. “Dupilumab is known to make AD better and theoretically could help MF via its effect on interleukin (IL)–13, yet case reports of exacerbation and/or unmasking of MF are out there.”
For the study, researchers retrospectively examined records of 530 patients with AD treated with dupilumab at the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands). Reviewing pretreatment biopsies revealed that among 14 (2.6%) patients who developed clinical suspicion of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) while on treatment, three actually had preexisting MF.
All 14 patients with LR initially responded to dupilumab then developed worsening symptoms at a median of 4 months. Patients reported that the worsening lesions looked and felt different than did previous lesions, with symptoms including burning/pain and an appearance of generalized erythematous maculopapular plaques, sometimes with severe lichenification, on the lower trunk and upper thighs.
The 14 patients’ posttreatment biopsies showed an atypical lymphoid infiltrate with lichenoid or perivascular distribution and intraepithelial T-cell lymphocytes. Whereas patients with MF had hyperconvoluted cerebriform lymphocytes aligned in the epidermal basal layer at the dermoepidermal junction, the 11 with LR had similar-looking lesions dispersed throughout the upper epidermis.
Immunohistochemically, both groups had a dysregulated (mostly increased) CD4:CD8 ratio. CD30 overexpression, usually absent in early-stage MF, affected only patients with LR and one patient with advanced MF. In addition, patients with LR maintained pan–T-cell antigens (CD2, CD3, and CD5), whereas those with MF did not. The 11 patients with LR experienced biopsy-confirmed resolution once they discontinued dupilumab.
It is reassuring that the LRs resolved after dupilumab discontinuation, writes the author of the accompanying editorial, Joan Guitart, MD, chief of dermatopathology at Northwestern University. Nevertheless, he added, such patients deserve “a comprehensive workup including skin biopsy with T-cell receptor clonality assay, blood cell counts with flow cytometry analysis, serum lactate dehydrogenase, and documentation of possible adenopathy, followed with imaging studies and/or local biopsies in cases with abnormal results.”
The possibility that these LRs may represent a first step toward lymphoma requires dermatologists to remain vigilant in ruling out MF, Dr. Guitart wrote, particularly in atypical presentations such as adult-onset AD, cases lacking a history of AD, and cases involving erythrodermic and other uncharacteristic presentations such as plaques, nodules, or spared flexural sites.
For dermatopathologists, Dr. Guitart recommended a cautious approach that resists overdiagnosing MF and acknowledging that insufficient evidence exists to report such reactions as benign. The fact that one study patient had both MF and LR raises concerns that the LR may not always be reversible, Dr. Guitart added.
Clinicians and patients must consider the possibility of dupilumab-induced LR as part of the shared decision-making process and risk-benefit calculus, Dr. Sidbury said. In cases involving unexpected responses or atypical presentations, he added, clinicians must have a low threshold for stopping dupilumab.
For patients who must discontinue dupilumab because of LR, the list of treatment options is growing. “While more investigation is required to understand the role of newer IL-13–blocking biologics and JAK inhibitors among patients experiencing lymphoid reactions,” said Dr. Chovatiya, “traditional atopic dermatitis therapies like narrowband UVB phototherapy and the oral immunosuppressant methotrexate may be reassuring in this population.” Conversely, cyclosporine has been associated with progression of MF.
Also reassuring, said Dr. Sidbury and Dr. Chovatiya, is the rarity of LR overall. Dr. Sidbury said, “The numbers of patients in whom LR or onset/exacerbation of MF occurs is extraordinarily low when compared to those helped immeasurably by dupilumab.”
Dr. Sidbury added that the study and accompanying editorial also will alert clinicians to the potential for newer AD biologics that target solely IL-13 and not IL-4/13, as dupilumab does. “If the deregulated response leading to LR and potentially MF in the affected few is driven by IL-4 inhibition,” he said, “drugs such as tralokinumab (Adbry), lebrikizumab (once approved), and perhaps other newer options might calm AD without causing LRs.”
(Lebrikizumab is not yet approved. In an Oct. 2 press release, Eli Lilly and Company, developer of lebrikizumab, said that it would address issues the U.S. Food and Drug Administration had raised about a third-party manufacturing facility that arose during evaluation of the lebrikizumab biologic license application.)
Study limitations include the fact that most patients who experienced LR had already undergone skin biopsies before dupilumab treatment, which suggests that they had a more atypical AD presentation from the start. The authors add that their having treated all study patients in a tertiary referral hospital indicates a hard-to-treat AD subpopulation.
Study authors reported relationships with several biologic drug manufacturers including Sanofi and Regeneron (dupilumab), LEO Pharma (tralokinumab), and Eli Lilly (lebrikizumab). However, none of these companies provided support for the study.
Dr. Sidbury has been an investigator for Regeneron, Pfizer, and Galderma and a consultant for LEO Pharma and Eli Lilly. Dr. Chovatiya has served as an advisor, consultant, speaker, and investigator for Sanofi and Regeneron. Dr. Guitart reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
More phase 3 data support use of nemolizumab for prurigo nodularis
reported at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
In the OLYMPIA 1 study, clinically significant improvements in both itch and skin lesions were seen after 16 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab compared with placebo (P < .0001).
Indeed, among the 286 patients who participated in the trial (190 on nemolizumab and 96 on placebo), 58.4% of those treated with nemolizumab and 16.7% of those who received placebo had an improvement of 4 points or more in the weekly average peak pruritus numeric rating scale (PP-NRS) at week 16 (P < .0001).
Skin lesions were assessed using an investigators general assessment (IGA) score, where IGA success was defined as a score of 0/1 indicating clear or almost clear skin or where there had been at least a 2-point change from baseline values. Over a quarter (26.3%) of nemolizumab-treated patients met these criteria versus 7.3% for those on placebo (P = .0001).
“These results confirm the results of the OLYMPIA 2 study, the other phase 3 study, and now I hope you understand why we are so excited,” lead investigator Sonja Ständer, MD, of the Center for Chronic Pruritus at University Hospital Münster, Germany, said at the meeting, where she presented the data.
The OLYMPIA 2 study included 274 patients and the results showed a weekly average PP-NRS score improvement of 56.3% vs. 20.9% for placebo and IGA success in 37.7% and 11% of patients, respectively, at 16 weeks.
First-in-class therapy
“We know how difficult it is to treat patients; they are refractory to treatment, frustrated, and this really impacts them regarding their quality of life,” said Dr. Ständer. New options are needed to help patients, and nemolizumab, a first-in-class interleukin-31 (IL-31) receptor alpha antagonist, is one treatment that may answer this call.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic neuroimmune skin condition characterized by severe itch and multiple nodular skin lesions, Dr. Ständer explained. She added that there is evidence that IL-31 has a key role to play in the development of itch, and in differentiation of keratinocytes, type 2 and type 17 immune responses, and fibrosis associated with the condition.
The OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials are part of a large developmental program that includes two ongoing trials. One is assessing the durability of response over 24 weeks in 40 patients and the other is a long-term extension trial involving 450 patients from the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials.
Inclusion criteria and additional results
For inclusion in the study, adults with prurigo nodularis for at least 6 months had to have 20 or more nodules on the body with a bilateral distribution, an IGA score of 3 or more, and an average PP-NRS of 7 or higher. The latter “was really a high bar for them to qualify for the trial,” said Dr. Ständer.
After an initial 4-week screening period, patients were randomly assigned to 24 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab or placebo given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. An 8-week “off-treatment” period followed.
The nemolizumab dose was based on the patient’s body weight, with patients weighing less than 90 kg (198 pounds) getting a loading dose of 60 mg followed by further doses of 30 mg; while patients weighing 90 kg or more receiving 50 mg of nemolizumab.
Dr. Ständer reported that nemolizumab met all of the trials’ secondary endpoints; this included at least a 4-point improvement in sleep disturbance. She noted that changes in itch and subsequent sleep disturbance occurred early, at 4 weeks of treatment – after just one injection of nemolizumab.
The response rates seen in the moderate to severe prurigo nodularis population studies are quite unique when compared with conventional therapies, Dr. Ständer maintained. “We’ve never seen something like this before.”
No safety concerns
No significant difference in tolerability was seen between the nemolizumab and placebo groups, Dr. Ständer observed. Any adverse event occurred in 71.7% and 65.3% of patients, respectively, and serious adverse events in 8.6% and 10.5%.
There was a similar rate of adverse events leading to discontinuation, respectively (4.8% vs. 4.2%).
Headache was seen more frequently among those on nemolizumab than those on placebo (7.0% vs. 2.1%), and there was a higher number of eczema cases among those on nemolizumab (5.3% vs. 1.1%). The latter is somewhat paradoxical because nemolizumab is also being studied as a treatment for atopic dermatitis, with good results seen in phase 3 trials. Asked about this finding after her presentation, Dr. Ständer said “we are following up on that to know exactly what is going on; this is a side effect of nemolizumab that is seen also with other biologics.”
JAK inhibitor trial for PN, CPUO
Nemolizumab is not the only promising new approach to treating prurigo nodularis. During a separate late-breaking news session at the meeting, Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center in Baltimore, presented “dramatic” data from a “proof-of-concept” phase 2 study with the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor abrocitinib (Cibinqo), which is approved for atopic dermatitis in the United States and Europe.
The investigator-initiated trial took a different approach from most other trials, Dr. Kwatra said. The starting point was to look at studying multiple rather than single dermatologic diseases that were perhaps being left a little by the wayside but may share some common ground. Those two diseases were prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus of unknown origin (CPUO).
“They’re actually very analogous conditions in the way we treat, so I thought those would be a good pair,” Dr. Kwatra said, noting that there were several studies that made him think that JAK inhibition “would be an interesting concept to try.”
On that basis, 10 women with prurigo nodularis (mean age, 58 years) and two women and eight men with CPUO (mean age, 70 years) were recruited and all were treated with abrocitinib at a once-daily oral dose of 200 mg for 12 weeks.
“They all had really intense itch,” before treatment, Dr. Kwatra said. The mean baseline PP-NRS was 9.2 and 8.2 in the prurigo nodularis and CPUO groups, respectively. By the end of treatment, however, “the improvement in itch was pretty dramatic,” especially for prurigo nodularis, he said.
At 12 weeks, the PP-NRS score had fallen to 2.0 in the prurigo nodularis group, equating to a significant 78% change from baseline (P < .001). And, in the CPUO group, the 12-week PP-NRS score was 3.8, nearly a 54% drop from baseline (P = .01).
Sleep disturbance was improved for both conditions, and in the patients with prurigo nodularis, there were improvements in skin lesions. Looking at the patients who responded to treatment, Dr. Kwatra noted that “if you responded, you respond fast, and you respond almost entirely.”
Additional findings from cutaneous transcriptome analysis showed that JAK inhibition with abrocitinib was modulating Th1-, Th2-, Th17-, and Th22-mediated pathways in both groups of patients.
The overall frequency of adverse events was low, and no serious adverse events occurred.
Commenting on the potential use of abrocitinib in managing patients with PN and CPUO, Tiago dos Reis Matos, MD, PhD, MSc, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization that JAK1 inhibitors “are showing promising results in treating several diseases.”
Dr. Matos, who was not involved in the study, added that JAK inhibition was “of special interest in prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus, since these are some of the most difficult diseases to treat with limited therapeutic options.”
Dr. Kwatra observed: “Obviously, we need further development. But we also have clues here about how to design phase 3 trials.”
Galderma funded the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 studies. Dr. Ständer was an investigator for the trial and reported serving as a consultant, speaker, or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma.
Johns Hopkins University supported the abrocitinib study with funding from Pfizer. Dr. Kwatra is an advisory board member or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies and is an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
reported at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
In the OLYMPIA 1 study, clinically significant improvements in both itch and skin lesions were seen after 16 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab compared with placebo (P < .0001).
Indeed, among the 286 patients who participated in the trial (190 on nemolizumab and 96 on placebo), 58.4% of those treated with nemolizumab and 16.7% of those who received placebo had an improvement of 4 points or more in the weekly average peak pruritus numeric rating scale (PP-NRS) at week 16 (P < .0001).
Skin lesions were assessed using an investigators general assessment (IGA) score, where IGA success was defined as a score of 0/1 indicating clear or almost clear skin or where there had been at least a 2-point change from baseline values. Over a quarter (26.3%) of nemolizumab-treated patients met these criteria versus 7.3% for those on placebo (P = .0001).
“These results confirm the results of the OLYMPIA 2 study, the other phase 3 study, and now I hope you understand why we are so excited,” lead investigator Sonja Ständer, MD, of the Center for Chronic Pruritus at University Hospital Münster, Germany, said at the meeting, where she presented the data.
The OLYMPIA 2 study included 274 patients and the results showed a weekly average PP-NRS score improvement of 56.3% vs. 20.9% for placebo and IGA success in 37.7% and 11% of patients, respectively, at 16 weeks.
First-in-class therapy
“We know how difficult it is to treat patients; they are refractory to treatment, frustrated, and this really impacts them regarding their quality of life,” said Dr. Ständer. New options are needed to help patients, and nemolizumab, a first-in-class interleukin-31 (IL-31) receptor alpha antagonist, is one treatment that may answer this call.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic neuroimmune skin condition characterized by severe itch and multiple nodular skin lesions, Dr. Ständer explained. She added that there is evidence that IL-31 has a key role to play in the development of itch, and in differentiation of keratinocytes, type 2 and type 17 immune responses, and fibrosis associated with the condition.
The OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials are part of a large developmental program that includes two ongoing trials. One is assessing the durability of response over 24 weeks in 40 patients and the other is a long-term extension trial involving 450 patients from the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials.
Inclusion criteria and additional results
For inclusion in the study, adults with prurigo nodularis for at least 6 months had to have 20 or more nodules on the body with a bilateral distribution, an IGA score of 3 or more, and an average PP-NRS of 7 or higher. The latter “was really a high bar for them to qualify for the trial,” said Dr. Ständer.
After an initial 4-week screening period, patients were randomly assigned to 24 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab or placebo given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. An 8-week “off-treatment” period followed.
The nemolizumab dose was based on the patient’s body weight, with patients weighing less than 90 kg (198 pounds) getting a loading dose of 60 mg followed by further doses of 30 mg; while patients weighing 90 kg or more receiving 50 mg of nemolizumab.
Dr. Ständer reported that nemolizumab met all of the trials’ secondary endpoints; this included at least a 4-point improvement in sleep disturbance. She noted that changes in itch and subsequent sleep disturbance occurred early, at 4 weeks of treatment – after just one injection of nemolizumab.
The response rates seen in the moderate to severe prurigo nodularis population studies are quite unique when compared with conventional therapies, Dr. Ständer maintained. “We’ve never seen something like this before.”
No safety concerns
No significant difference in tolerability was seen between the nemolizumab and placebo groups, Dr. Ständer observed. Any adverse event occurred in 71.7% and 65.3% of patients, respectively, and serious adverse events in 8.6% and 10.5%.
There was a similar rate of adverse events leading to discontinuation, respectively (4.8% vs. 4.2%).
Headache was seen more frequently among those on nemolizumab than those on placebo (7.0% vs. 2.1%), and there was a higher number of eczema cases among those on nemolizumab (5.3% vs. 1.1%). The latter is somewhat paradoxical because nemolizumab is also being studied as a treatment for atopic dermatitis, with good results seen in phase 3 trials. Asked about this finding after her presentation, Dr. Ständer said “we are following up on that to know exactly what is going on; this is a side effect of nemolizumab that is seen also with other biologics.”
JAK inhibitor trial for PN, CPUO
Nemolizumab is not the only promising new approach to treating prurigo nodularis. During a separate late-breaking news session at the meeting, Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center in Baltimore, presented “dramatic” data from a “proof-of-concept” phase 2 study with the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor abrocitinib (Cibinqo), which is approved for atopic dermatitis in the United States and Europe.
The investigator-initiated trial took a different approach from most other trials, Dr. Kwatra said. The starting point was to look at studying multiple rather than single dermatologic diseases that were perhaps being left a little by the wayside but may share some common ground. Those two diseases were prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus of unknown origin (CPUO).
“They’re actually very analogous conditions in the way we treat, so I thought those would be a good pair,” Dr. Kwatra said, noting that there were several studies that made him think that JAK inhibition “would be an interesting concept to try.”
On that basis, 10 women with prurigo nodularis (mean age, 58 years) and two women and eight men with CPUO (mean age, 70 years) were recruited and all were treated with abrocitinib at a once-daily oral dose of 200 mg for 12 weeks.
“They all had really intense itch,” before treatment, Dr. Kwatra said. The mean baseline PP-NRS was 9.2 and 8.2 in the prurigo nodularis and CPUO groups, respectively. By the end of treatment, however, “the improvement in itch was pretty dramatic,” especially for prurigo nodularis, he said.
At 12 weeks, the PP-NRS score had fallen to 2.0 in the prurigo nodularis group, equating to a significant 78% change from baseline (P < .001). And, in the CPUO group, the 12-week PP-NRS score was 3.8, nearly a 54% drop from baseline (P = .01).
Sleep disturbance was improved for both conditions, and in the patients with prurigo nodularis, there were improvements in skin lesions. Looking at the patients who responded to treatment, Dr. Kwatra noted that “if you responded, you respond fast, and you respond almost entirely.”
Additional findings from cutaneous transcriptome analysis showed that JAK inhibition with abrocitinib was modulating Th1-, Th2-, Th17-, and Th22-mediated pathways in both groups of patients.
The overall frequency of adverse events was low, and no serious adverse events occurred.
Commenting on the potential use of abrocitinib in managing patients with PN and CPUO, Tiago dos Reis Matos, MD, PhD, MSc, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization that JAK1 inhibitors “are showing promising results in treating several diseases.”
Dr. Matos, who was not involved in the study, added that JAK inhibition was “of special interest in prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus, since these are some of the most difficult diseases to treat with limited therapeutic options.”
Dr. Kwatra observed: “Obviously, we need further development. But we also have clues here about how to design phase 3 trials.”
Galderma funded the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 studies. Dr. Ständer was an investigator for the trial and reported serving as a consultant, speaker, or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma.
Johns Hopkins University supported the abrocitinib study with funding from Pfizer. Dr. Kwatra is an advisory board member or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies and is an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
reported at the annual Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
In the OLYMPIA 1 study, clinically significant improvements in both itch and skin lesions were seen after 16 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab compared with placebo (P < .0001).
Indeed, among the 286 patients who participated in the trial (190 on nemolizumab and 96 on placebo), 58.4% of those treated with nemolizumab and 16.7% of those who received placebo had an improvement of 4 points or more in the weekly average peak pruritus numeric rating scale (PP-NRS) at week 16 (P < .0001).
Skin lesions were assessed using an investigators general assessment (IGA) score, where IGA success was defined as a score of 0/1 indicating clear or almost clear skin or where there had been at least a 2-point change from baseline values. Over a quarter (26.3%) of nemolizumab-treated patients met these criteria versus 7.3% for those on placebo (P = .0001).
“These results confirm the results of the OLYMPIA 2 study, the other phase 3 study, and now I hope you understand why we are so excited,” lead investigator Sonja Ständer, MD, of the Center for Chronic Pruritus at University Hospital Münster, Germany, said at the meeting, where she presented the data.
The OLYMPIA 2 study included 274 patients and the results showed a weekly average PP-NRS score improvement of 56.3% vs. 20.9% for placebo and IGA success in 37.7% and 11% of patients, respectively, at 16 weeks.
First-in-class therapy
“We know how difficult it is to treat patients; they are refractory to treatment, frustrated, and this really impacts them regarding their quality of life,” said Dr. Ständer. New options are needed to help patients, and nemolizumab, a first-in-class interleukin-31 (IL-31) receptor alpha antagonist, is one treatment that may answer this call.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic neuroimmune skin condition characterized by severe itch and multiple nodular skin lesions, Dr. Ständer explained. She added that there is evidence that IL-31 has a key role to play in the development of itch, and in differentiation of keratinocytes, type 2 and type 17 immune responses, and fibrosis associated with the condition.
The OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials are part of a large developmental program that includes two ongoing trials. One is assessing the durability of response over 24 weeks in 40 patients and the other is a long-term extension trial involving 450 patients from the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 trials.
Inclusion criteria and additional results
For inclusion in the study, adults with prurigo nodularis for at least 6 months had to have 20 or more nodules on the body with a bilateral distribution, an IGA score of 3 or more, and an average PP-NRS of 7 or higher. The latter “was really a high bar for them to qualify for the trial,” said Dr. Ständer.
After an initial 4-week screening period, patients were randomly assigned to 24 weeks of treatment with nemolizumab or placebo given as a subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. An 8-week “off-treatment” period followed.
The nemolizumab dose was based on the patient’s body weight, with patients weighing less than 90 kg (198 pounds) getting a loading dose of 60 mg followed by further doses of 30 mg; while patients weighing 90 kg or more receiving 50 mg of nemolizumab.
Dr. Ständer reported that nemolizumab met all of the trials’ secondary endpoints; this included at least a 4-point improvement in sleep disturbance. She noted that changes in itch and subsequent sleep disturbance occurred early, at 4 weeks of treatment – after just one injection of nemolizumab.
The response rates seen in the moderate to severe prurigo nodularis population studies are quite unique when compared with conventional therapies, Dr. Ständer maintained. “We’ve never seen something like this before.”
No safety concerns
No significant difference in tolerability was seen between the nemolizumab and placebo groups, Dr. Ständer observed. Any adverse event occurred in 71.7% and 65.3% of patients, respectively, and serious adverse events in 8.6% and 10.5%.
There was a similar rate of adverse events leading to discontinuation, respectively (4.8% vs. 4.2%).
Headache was seen more frequently among those on nemolizumab than those on placebo (7.0% vs. 2.1%), and there was a higher number of eczema cases among those on nemolizumab (5.3% vs. 1.1%). The latter is somewhat paradoxical because nemolizumab is also being studied as a treatment for atopic dermatitis, with good results seen in phase 3 trials. Asked about this finding after her presentation, Dr. Ständer said “we are following up on that to know exactly what is going on; this is a side effect of nemolizumab that is seen also with other biologics.”
JAK inhibitor trial for PN, CPUO
Nemolizumab is not the only promising new approach to treating prurigo nodularis. During a separate late-breaking news session at the meeting, Shawn Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center in Baltimore, presented “dramatic” data from a “proof-of-concept” phase 2 study with the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor abrocitinib (Cibinqo), which is approved for atopic dermatitis in the United States and Europe.
The investigator-initiated trial took a different approach from most other trials, Dr. Kwatra said. The starting point was to look at studying multiple rather than single dermatologic diseases that were perhaps being left a little by the wayside but may share some common ground. Those two diseases were prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus of unknown origin (CPUO).
“They’re actually very analogous conditions in the way we treat, so I thought those would be a good pair,” Dr. Kwatra said, noting that there were several studies that made him think that JAK inhibition “would be an interesting concept to try.”
On that basis, 10 women with prurigo nodularis (mean age, 58 years) and two women and eight men with CPUO (mean age, 70 years) were recruited and all were treated with abrocitinib at a once-daily oral dose of 200 mg for 12 weeks.
“They all had really intense itch,” before treatment, Dr. Kwatra said. The mean baseline PP-NRS was 9.2 and 8.2 in the prurigo nodularis and CPUO groups, respectively. By the end of treatment, however, “the improvement in itch was pretty dramatic,” especially for prurigo nodularis, he said.
At 12 weeks, the PP-NRS score had fallen to 2.0 in the prurigo nodularis group, equating to a significant 78% change from baseline (P < .001). And, in the CPUO group, the 12-week PP-NRS score was 3.8, nearly a 54% drop from baseline (P = .01).
Sleep disturbance was improved for both conditions, and in the patients with prurigo nodularis, there were improvements in skin lesions. Looking at the patients who responded to treatment, Dr. Kwatra noted that “if you responded, you respond fast, and you respond almost entirely.”
Additional findings from cutaneous transcriptome analysis showed that JAK inhibition with abrocitinib was modulating Th1-, Th2-, Th17-, and Th22-mediated pathways in both groups of patients.
The overall frequency of adverse events was low, and no serious adverse events occurred.
Commenting on the potential use of abrocitinib in managing patients with PN and CPUO, Tiago dos Reis Matos, MD, PhD, MSc, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization that JAK1 inhibitors “are showing promising results in treating several diseases.”
Dr. Matos, who was not involved in the study, added that JAK inhibition was “of special interest in prurigo nodularis and chronic pruritus, since these are some of the most difficult diseases to treat with limited therapeutic options.”
Dr. Kwatra observed: “Obviously, we need further development. But we also have clues here about how to design phase 3 trials.”
Galderma funded the OLYMPIA 1 and 2 studies. Dr. Ständer was an investigator for the trial and reported serving as a consultant, speaker, or investigator for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including Galderma.
Johns Hopkins University supported the abrocitinib study with funding from Pfizer. Dr. Kwatra is an advisory board member or consultant to several pharmaceutical companies and is an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Birch bark–derived treatment reduces daily dressings in patients with epidermolysis bullosa
Additional when compared with a control gel.
In a final, post hoc analysis to come from the trial, 15 of 45 (33%) patients treated with Oleogel-S10 versus 5 of 48 (10.4%) treated with the control gel were reported as no longer needing daily dressing changes at 45 days of follow-up.
Moreover, the effect was sustained, with similar percentages of patients no longer requiring daily dressing changes at 60 days (34% vs. 13%, respectively) and 90 days (36% vs. 11%) of follow-up.
The mean reduction in daily dressing changes was 1.36 for Oleogel-S10 and 0.41 for the control gel (P = .005).
“Patients who, in the beginning, had daily dressing changes had almost three fewer dressing changes every 2 weeks if they were treated with Oleogel-S10,” Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Freiburg (Germany), reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. By comparison, patients in the control group had just one fewer daily dressing change in 2 weeks.
“You might say okay, but what does this mean in terms of time?” added Dr. Kiritsi. Using historical data on the time required for whole body care (Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1279-y), it was estimated that treatment with Oleogel-S10 was associated with an overall time-saving per week of 11 hours (6.6 hours for the patient and 4.4 hours for the caregiver) and use of the control gel was associated with an overall time-saving of 4 hours (2.4 hours for the patient and 1.6 hours for the caregiver).
“This is, for our patients, important,” said Dr. Kiritsi, as “it is time that they can spend doing something nice with the family” instead, avoiding the pain and distress associated with frequent dressing changes.
Approved in Europe, not in the United States
Oleogel-S10, classified as an herbal product, contains triterpenes derived from birch bark extract, which have been formulated with sunflower oil to form a gel.
Despite being approved for use in Europe, Oleogel-S10 has not yet been approved to treat EB in the United States. The FDA did not approve Amryt Pharma’s new drug application in February 2022. The application had included data from the EASE trial.
EASE included 223 patients with dystrophic or junctional EB, including 156 children, at 58 sites in 28 countries. As such, this makes it the largest treatment study in this rare genetic disease to date.
The trial had consisted of an initial 90-day, double-blind treatment period, during which time 109 patients had used Oleogel-S10 and 114 had used a control gel. This was followed by a 24-month open-label phase, during which time all remaining patients (n = 205) had used Oleogel-S10 on top of their standard of care.
Dr. Kiritsi summarized the main results of the EASE trial as follows.
- Complete healing of target wounds (primary endpoint) in 41.3% of patients treated with Oleogel-S10 and 28.9% of patients treated with the control gel (P = .013).
- Improved total body wound burden measured by both Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index and Body Surface Area Percentage scores.
- Reduced frequency of dressing changes (1 less per 2 weeks for Oleogel-S10 versus 0 less per 2 weeks for control gel).
- Improved pain among participants aged 4 years and older while their dressings were being changed.
- Reduced rates of wound infection (0.9% Oleogel-S10 vs. 4.4% control gel).
- Similar rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (24.8% vs. 22.8%, respectively), which were mostly deemed to be mild or moderate.
The EASE study – an important trial for EB
EASE is an important trial for EB, the study’s principal investigator Dédée Murrell, MD, DSc, University of New South Wales, Sydney, has pointed out previously.
“This was the first EB study to meet its primary endpoint and demonstrated a statistically significant acceleration of target wound healing by day 45,” Dr. Murrell said in a press release issued by Amryt Pharma to coincide with the online publication of the trial results.
“In addition, the favorable trends we see with key secondary endpoints such as reduced wound burden, pain, and frequency of dressing changes are considered as being very meaningful for patients,” Dr. Murrell said.
The EASE study was funded by Amryt Research Limited. Dr. Kiritsi reported receiving honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt, RHEACELL GmbH, and Fibrx Derm. She also acknowledged grant or research support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz-Thyssen Foundation, German Research Foundation, and RHEACELL. Dr. Murrell has ties to Amryt and Amicus and is a co-owner of the patent for topical sirolimus for EB simplex.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional when compared with a control gel.
In a final, post hoc analysis to come from the trial, 15 of 45 (33%) patients treated with Oleogel-S10 versus 5 of 48 (10.4%) treated with the control gel were reported as no longer needing daily dressing changes at 45 days of follow-up.
Moreover, the effect was sustained, with similar percentages of patients no longer requiring daily dressing changes at 60 days (34% vs. 13%, respectively) and 90 days (36% vs. 11%) of follow-up.
The mean reduction in daily dressing changes was 1.36 for Oleogel-S10 and 0.41 for the control gel (P = .005).
“Patients who, in the beginning, had daily dressing changes had almost three fewer dressing changes every 2 weeks if they were treated with Oleogel-S10,” Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Freiburg (Germany), reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. By comparison, patients in the control group had just one fewer daily dressing change in 2 weeks.
“You might say okay, but what does this mean in terms of time?” added Dr. Kiritsi. Using historical data on the time required for whole body care (Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1279-y), it was estimated that treatment with Oleogel-S10 was associated with an overall time-saving per week of 11 hours (6.6 hours for the patient and 4.4 hours for the caregiver) and use of the control gel was associated with an overall time-saving of 4 hours (2.4 hours for the patient and 1.6 hours for the caregiver).
“This is, for our patients, important,” said Dr. Kiritsi, as “it is time that they can spend doing something nice with the family” instead, avoiding the pain and distress associated with frequent dressing changes.
Approved in Europe, not in the United States
Oleogel-S10, classified as an herbal product, contains triterpenes derived from birch bark extract, which have been formulated with sunflower oil to form a gel.
Despite being approved for use in Europe, Oleogel-S10 has not yet been approved to treat EB in the United States. The FDA did not approve Amryt Pharma’s new drug application in February 2022. The application had included data from the EASE trial.
EASE included 223 patients with dystrophic or junctional EB, including 156 children, at 58 sites in 28 countries. As such, this makes it the largest treatment study in this rare genetic disease to date.
The trial had consisted of an initial 90-day, double-blind treatment period, during which time 109 patients had used Oleogel-S10 and 114 had used a control gel. This was followed by a 24-month open-label phase, during which time all remaining patients (n = 205) had used Oleogel-S10 on top of their standard of care.
Dr. Kiritsi summarized the main results of the EASE trial as follows.
- Complete healing of target wounds (primary endpoint) in 41.3% of patients treated with Oleogel-S10 and 28.9% of patients treated with the control gel (P = .013).
- Improved total body wound burden measured by both Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index and Body Surface Area Percentage scores.
- Reduced frequency of dressing changes (1 less per 2 weeks for Oleogel-S10 versus 0 less per 2 weeks for control gel).
- Improved pain among participants aged 4 years and older while their dressings were being changed.
- Reduced rates of wound infection (0.9% Oleogel-S10 vs. 4.4% control gel).
- Similar rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (24.8% vs. 22.8%, respectively), which were mostly deemed to be mild or moderate.
The EASE study – an important trial for EB
EASE is an important trial for EB, the study’s principal investigator Dédée Murrell, MD, DSc, University of New South Wales, Sydney, has pointed out previously.
“This was the first EB study to meet its primary endpoint and demonstrated a statistically significant acceleration of target wound healing by day 45,” Dr. Murrell said in a press release issued by Amryt Pharma to coincide with the online publication of the trial results.
“In addition, the favorable trends we see with key secondary endpoints such as reduced wound burden, pain, and frequency of dressing changes are considered as being very meaningful for patients,” Dr. Murrell said.
The EASE study was funded by Amryt Research Limited. Dr. Kiritsi reported receiving honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt, RHEACELL GmbH, and Fibrx Derm. She also acknowledged grant or research support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz-Thyssen Foundation, German Research Foundation, and RHEACELL. Dr. Murrell has ties to Amryt and Amicus and is a co-owner of the patent for topical sirolimus for EB simplex.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional when compared with a control gel.
In a final, post hoc analysis to come from the trial, 15 of 45 (33%) patients treated with Oleogel-S10 versus 5 of 48 (10.4%) treated with the control gel were reported as no longer needing daily dressing changes at 45 days of follow-up.
Moreover, the effect was sustained, with similar percentages of patients no longer requiring daily dressing changes at 60 days (34% vs. 13%, respectively) and 90 days (36% vs. 11%) of follow-up.
The mean reduction in daily dressing changes was 1.36 for Oleogel-S10 and 0.41 for the control gel (P = .005).
“Patients who, in the beginning, had daily dressing changes had almost three fewer dressing changes every 2 weeks if they were treated with Oleogel-S10,” Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Freiburg (Germany), reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. By comparison, patients in the control group had just one fewer daily dressing change in 2 weeks.
“You might say okay, but what does this mean in terms of time?” added Dr. Kiritsi. Using historical data on the time required for whole body care (Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Jan 3. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1279-y), it was estimated that treatment with Oleogel-S10 was associated with an overall time-saving per week of 11 hours (6.6 hours for the patient and 4.4 hours for the caregiver) and use of the control gel was associated with an overall time-saving of 4 hours (2.4 hours for the patient and 1.6 hours for the caregiver).
“This is, for our patients, important,” said Dr. Kiritsi, as “it is time that they can spend doing something nice with the family” instead, avoiding the pain and distress associated with frequent dressing changes.
Approved in Europe, not in the United States
Oleogel-S10, classified as an herbal product, contains triterpenes derived from birch bark extract, which have been formulated with sunflower oil to form a gel.
Despite being approved for use in Europe, Oleogel-S10 has not yet been approved to treat EB in the United States. The FDA did not approve Amryt Pharma’s new drug application in February 2022. The application had included data from the EASE trial.
EASE included 223 patients with dystrophic or junctional EB, including 156 children, at 58 sites in 28 countries. As such, this makes it the largest treatment study in this rare genetic disease to date.
The trial had consisted of an initial 90-day, double-blind treatment period, during which time 109 patients had used Oleogel-S10 and 114 had used a control gel. This was followed by a 24-month open-label phase, during which time all remaining patients (n = 205) had used Oleogel-S10 on top of their standard of care.
Dr. Kiritsi summarized the main results of the EASE trial as follows.
- Complete healing of target wounds (primary endpoint) in 41.3% of patients treated with Oleogel-S10 and 28.9% of patients treated with the control gel (P = .013).
- Improved total body wound burden measured by both Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index and Body Surface Area Percentage scores.
- Reduced frequency of dressing changes (1 less per 2 weeks for Oleogel-S10 versus 0 less per 2 weeks for control gel).
- Improved pain among participants aged 4 years and older while their dressings were being changed.
- Reduced rates of wound infection (0.9% Oleogel-S10 vs. 4.4% control gel).
- Similar rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (24.8% vs. 22.8%, respectively), which were mostly deemed to be mild or moderate.
The EASE study – an important trial for EB
EASE is an important trial for EB, the study’s principal investigator Dédée Murrell, MD, DSc, University of New South Wales, Sydney, has pointed out previously.
“This was the first EB study to meet its primary endpoint and demonstrated a statistically significant acceleration of target wound healing by day 45,” Dr. Murrell said in a press release issued by Amryt Pharma to coincide with the online publication of the trial results.
“In addition, the favorable trends we see with key secondary endpoints such as reduced wound burden, pain, and frequency of dressing changes are considered as being very meaningful for patients,” Dr. Murrell said.
The EASE study was funded by Amryt Research Limited. Dr. Kiritsi reported receiving honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt, RHEACELL GmbH, and Fibrx Derm. She also acknowledged grant or research support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz-Thyssen Foundation, German Research Foundation, and RHEACELL. Dr. Murrell has ties to Amryt and Amicus and is a co-owner of the patent for topical sirolimus for EB simplex.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS