User login
Diagnosing patients with sarcoidosis
A 40-year-old women is evaluated for liver abnormalities. She had elevated transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. A liver ultrasound showed multiple lesions. She underwent liver biopsy, which showed granulomas. What test results, if abnormal, would be most suggestive of sarcoidosis?
A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
B. C-reactive protein
C. Lymphocyte count
D. Antinuclear antibodies
The correct answer here is lymphocyte count. Sarcoidosis is in just about every differential diagnosis, as it can involve every organ system. I will share with you a few pearls I have learned over 30 years of taking care of patients with sarcoidosis. Lymphocyte counts drop with active sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis should always be part of the differential when you see lymphopenia. El Jammal et al. studied 90 patients referred for possible granulomatous hepatitis.1 Seventy-three patients had a final diagnosis of granulomatous hepatitis, and 38 of those patients had sarcoidosis. Lymphopenia had a high specificity (85.7%) for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis, with a specificity of 100% in the patients under 50 years old.
Morell and colleagues looked at whether low lymphocyte counts and low lymphocyte percentage were markers of active sarcoidosis.2 Forty patients with biopsy-proven sarcoidosis were prospectively evaluated every 6 months. A low lymphocyte count and a low lymphocyte percentage (< 20%) were detected more frequently in patients with active sarcoidosis than in the patients with asymptomatic sarcoidosis (P < .02 and P < .0001).
Jones et al. looked at lymphopenia as a marker of sarcoidosis in patients presenting with uveitis.3 The study was a retrospective case-control study (112 patients with sarcoidosis-associated uveitis and 398 controls with other forms of uveitis). The mean lymphocyte count for patients with sarcoidosis was 1.43 vs. 2.04 for other causes of uveitis (P ≤ .0001).
Patients with sarcoidosis are at risk of hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and kidney stones. These are common in patients with sarcoidosis, with up to 50% of such patients having hypercalciuria. This is because in sarcoidosis patients 25(OH) vitamin D is converted in granulomas by activated macrophages to 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D, which is the active form of vitamin D.
Several studies have looked at the diagnostic utility of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels in patients with suspected sarcoidosis. Rohmer and colleagues looked at whether 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels could help with the diagnosis of sarcoidosis as the cause of uveitis.4 They found that the level of 25(OH) vitamin D in sarcoidosis patients with uveitis was lower than in patients with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 34 vs. 43 nmol/mL (P < .02), whereas the 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level was higher in patients with sarcoidosis than in those with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 132 vs. 108 pmol/L (P = .02). They looked at the 1,25(OH)2D/25(OH)D ratio; a ratio > 3.5 was strongly associated with an abnormal chest CT-scan (OR = 5.7, P = .003) and granulomas on bronchial biopsy (OR = 14.7, P = .007).
Kavathia et al. looked at whether elevated 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels predicted chronicity of sarcoidosis.5 A total of 59 sarcoidosis patients were recruited for the study. Higher serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels were associated with patients requiring repeated systemic immunosuppressive therapy or > 1 year of therapy. Increasing quartiles of serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level were associated with increased odds of patients having chronic sarcoidosis (OR = 1.82; 95% CI, 1.11-2.99, P = .019).
Because of the higher activated vitamin D levels in sarcoidosis patients, they are at risk for problems with vitamin D supplementation. I have seen two patients develop large numbers of kidney stones after receiving high-dose vitamin D. Sodhi and Aldrich reported on a cohort of 196 sarcoidosis patients who had received vitamin D and compared them with 196 control patients with sarcoidosis who were not receiving vitamin D.6 Hypercalcemia was more frequent in the group that received vitamin D (42.3%) than in the group that did not (18.3%, P < .0001). In this study, only a minority (23%) of patients receiving vitamin D had their 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level checked.
Pearl: Lymphocyte count and 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels can be helpful tests in assessing sarcoidosis activity. Patients with sarcoidosis who receive vitamin D should have their 1.25(OH)2 vitamin D levels monitored.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. El Jammal et al. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023 Sep 13;40(3):e2023031.
2. Morell F et al. Chest. 2002 Apr;121(4):1239-44.
3. Jones NP et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;100(10):1393-6.
4. Rohmer J et al. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Apr 2;28(3):341-7.
5. Kavathia D et al. Respir Med. 2010 Apr;104(4):564–70.
6. Sodhi A and Aldrich T. Am J Med Sci. 2016 Sep;352(3):252-7.
A 40-year-old women is evaluated for liver abnormalities. She had elevated transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. A liver ultrasound showed multiple lesions. She underwent liver biopsy, which showed granulomas. What test results, if abnormal, would be most suggestive of sarcoidosis?
A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
B. C-reactive protein
C. Lymphocyte count
D. Antinuclear antibodies
The correct answer here is lymphocyte count. Sarcoidosis is in just about every differential diagnosis, as it can involve every organ system. I will share with you a few pearls I have learned over 30 years of taking care of patients with sarcoidosis. Lymphocyte counts drop with active sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis should always be part of the differential when you see lymphopenia. El Jammal et al. studied 90 patients referred for possible granulomatous hepatitis.1 Seventy-three patients had a final diagnosis of granulomatous hepatitis, and 38 of those patients had sarcoidosis. Lymphopenia had a high specificity (85.7%) for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis, with a specificity of 100% in the patients under 50 years old.
Morell and colleagues looked at whether low lymphocyte counts and low lymphocyte percentage were markers of active sarcoidosis.2 Forty patients with biopsy-proven sarcoidosis were prospectively evaluated every 6 months. A low lymphocyte count and a low lymphocyte percentage (< 20%) were detected more frequently in patients with active sarcoidosis than in the patients with asymptomatic sarcoidosis (P < .02 and P < .0001).
Jones et al. looked at lymphopenia as a marker of sarcoidosis in patients presenting with uveitis.3 The study was a retrospective case-control study (112 patients with sarcoidosis-associated uveitis and 398 controls with other forms of uveitis). The mean lymphocyte count for patients with sarcoidosis was 1.43 vs. 2.04 for other causes of uveitis (P ≤ .0001).
Patients with sarcoidosis are at risk of hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and kidney stones. These are common in patients with sarcoidosis, with up to 50% of such patients having hypercalciuria. This is because in sarcoidosis patients 25(OH) vitamin D is converted in granulomas by activated macrophages to 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D, which is the active form of vitamin D.
Several studies have looked at the diagnostic utility of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels in patients with suspected sarcoidosis. Rohmer and colleagues looked at whether 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels could help with the diagnosis of sarcoidosis as the cause of uveitis.4 They found that the level of 25(OH) vitamin D in sarcoidosis patients with uveitis was lower than in patients with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 34 vs. 43 nmol/mL (P < .02), whereas the 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level was higher in patients with sarcoidosis than in those with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 132 vs. 108 pmol/L (P = .02). They looked at the 1,25(OH)2D/25(OH)D ratio; a ratio > 3.5 was strongly associated with an abnormal chest CT-scan (OR = 5.7, P = .003) and granulomas on bronchial biopsy (OR = 14.7, P = .007).
Kavathia et al. looked at whether elevated 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels predicted chronicity of sarcoidosis.5 A total of 59 sarcoidosis patients were recruited for the study. Higher serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels were associated with patients requiring repeated systemic immunosuppressive therapy or > 1 year of therapy. Increasing quartiles of serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level were associated with increased odds of patients having chronic sarcoidosis (OR = 1.82; 95% CI, 1.11-2.99, P = .019).
Because of the higher activated vitamin D levels in sarcoidosis patients, they are at risk for problems with vitamin D supplementation. I have seen two patients develop large numbers of kidney stones after receiving high-dose vitamin D. Sodhi and Aldrich reported on a cohort of 196 sarcoidosis patients who had received vitamin D and compared them with 196 control patients with sarcoidosis who were not receiving vitamin D.6 Hypercalcemia was more frequent in the group that received vitamin D (42.3%) than in the group that did not (18.3%, P < .0001). In this study, only a minority (23%) of patients receiving vitamin D had their 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level checked.
Pearl: Lymphocyte count and 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels can be helpful tests in assessing sarcoidosis activity. Patients with sarcoidosis who receive vitamin D should have their 1.25(OH)2 vitamin D levels monitored.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. El Jammal et al. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023 Sep 13;40(3):e2023031.
2. Morell F et al. Chest. 2002 Apr;121(4):1239-44.
3. Jones NP et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;100(10):1393-6.
4. Rohmer J et al. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Apr 2;28(3):341-7.
5. Kavathia D et al. Respir Med. 2010 Apr;104(4):564–70.
6. Sodhi A and Aldrich T. Am J Med Sci. 2016 Sep;352(3):252-7.
A 40-year-old women is evaluated for liver abnormalities. She had elevated transaminases and alkaline phosphatase. A liver ultrasound showed multiple lesions. She underwent liver biopsy, which showed granulomas. What test results, if abnormal, would be most suggestive of sarcoidosis?
A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
B. C-reactive protein
C. Lymphocyte count
D. Antinuclear antibodies
The correct answer here is lymphocyte count. Sarcoidosis is in just about every differential diagnosis, as it can involve every organ system. I will share with you a few pearls I have learned over 30 years of taking care of patients with sarcoidosis. Lymphocyte counts drop with active sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis should always be part of the differential when you see lymphopenia. El Jammal et al. studied 90 patients referred for possible granulomatous hepatitis.1 Seventy-three patients had a final diagnosis of granulomatous hepatitis, and 38 of those patients had sarcoidosis. Lymphopenia had a high specificity (85.7%) for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis, with a specificity of 100% in the patients under 50 years old.
Morell and colleagues looked at whether low lymphocyte counts and low lymphocyte percentage were markers of active sarcoidosis.2 Forty patients with biopsy-proven sarcoidosis were prospectively evaluated every 6 months. A low lymphocyte count and a low lymphocyte percentage (< 20%) were detected more frequently in patients with active sarcoidosis than in the patients with asymptomatic sarcoidosis (P < .02 and P < .0001).
Jones et al. looked at lymphopenia as a marker of sarcoidosis in patients presenting with uveitis.3 The study was a retrospective case-control study (112 patients with sarcoidosis-associated uveitis and 398 controls with other forms of uveitis). The mean lymphocyte count for patients with sarcoidosis was 1.43 vs. 2.04 for other causes of uveitis (P ≤ .0001).
Patients with sarcoidosis are at risk of hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, and kidney stones. These are common in patients with sarcoidosis, with up to 50% of such patients having hypercalciuria. This is because in sarcoidosis patients 25(OH) vitamin D is converted in granulomas by activated macrophages to 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D, which is the active form of vitamin D.
Several studies have looked at the diagnostic utility of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels in patients with suspected sarcoidosis. Rohmer and colleagues looked at whether 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels could help with the diagnosis of sarcoidosis as the cause of uveitis.4 They found that the level of 25(OH) vitamin D in sarcoidosis patients with uveitis was lower than in patients with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 34 vs. 43 nmol/mL (P < .02), whereas the 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level was higher in patients with sarcoidosis than in those with uveitis without sarcoidosis, 132 vs. 108 pmol/L (P = .02). They looked at the 1,25(OH)2D/25(OH)D ratio; a ratio > 3.5 was strongly associated with an abnormal chest CT-scan (OR = 5.7, P = .003) and granulomas on bronchial biopsy (OR = 14.7, P = .007).
Kavathia et al. looked at whether elevated 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels predicted chronicity of sarcoidosis.5 A total of 59 sarcoidosis patients were recruited for the study. Higher serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels were associated with patients requiring repeated systemic immunosuppressive therapy or > 1 year of therapy. Increasing quartiles of serum 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level were associated with increased odds of patients having chronic sarcoidosis (OR = 1.82; 95% CI, 1.11-2.99, P = .019).
Because of the higher activated vitamin D levels in sarcoidosis patients, they are at risk for problems with vitamin D supplementation. I have seen two patients develop large numbers of kidney stones after receiving high-dose vitamin D. Sodhi and Aldrich reported on a cohort of 196 sarcoidosis patients who had received vitamin D and compared them with 196 control patients with sarcoidosis who were not receiving vitamin D.6 Hypercalcemia was more frequent in the group that received vitamin D (42.3%) than in the group that did not (18.3%, P < .0001). In this study, only a minority (23%) of patients receiving vitamin D had their 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D level checked.
Pearl: Lymphocyte count and 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels can be helpful tests in assessing sarcoidosis activity. Patients with sarcoidosis who receive vitamin D should have their 1.25(OH)2 vitamin D levels monitored.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. El Jammal et al. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023 Sep 13;40(3):e2023031.
2. Morell F et al. Chest. 2002 Apr;121(4):1239-44.
3. Jones NP et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;100(10):1393-6.
4. Rohmer J et al. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2020 Apr 2;28(3):341-7.
5. Kavathia D et al. Respir Med. 2010 Apr;104(4):564–70.
6. Sodhi A and Aldrich T. Am J Med Sci. 2016 Sep;352(3):252-7.
Lower-extremity lymphedema associated with more skin cancer risk
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TNF blockers not associated with poorer pregnancy outcomes
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Continuing a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) during pregnancy does not increase risk of worse fetal or obstetric outcomes, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Patients who continued a TNFi also had fewer severe infections requiring hospitalization, compared with those who stopped taking the medication during their pregnancy.
“The main message is that patients continuing were not doing worse than the patients stopping. It’s an important clinical message for rheumatologists who are not really confident in dealing with these drugs during pregnancy,” said Anna Moltó, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist at Cochin Hospital, Paris, who led the research. “It adds to the data that it seems to be safe,” she added in an interview.
Previous research, largely from pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease, suggests that taking a TNFi during pregnancy is safe, and 2020 ACR guidelines conditionally recommend continuing therapy prior to and during pregnancy; however, many people still stop taking the drugs during pregnancy for fear of potentially harming the fetus.
To better understand how TNFi use affected pregnancy outcomes, Dr. Moltó and colleagues analyzed data from a French nationwide health insurance database to identify adult women with chronic rheumatic inflammatory disease. All women included in the cohort had a singleton pregnancy between 2008 and 2017 and were taking a TNFi upon pregnancy diagnosis.
Patients who restarted TNFi after initially pausing because of pregnancy were included in the continuation group.
Researchers identified more than 2,000 pregnancies, including 1,503 in individuals with spondyloarthritis and 579 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Patients were, on average, 31 years old and were diagnosed with a rheumatic disease 4 years prior to their pregnancy.
About 72% (n = 1,497) discontinued TNFi after learning they were pregnant, and 584 individuals continued treatment. Dr. Moltó noted that data from more recent years might have captured lower discontinuation rates among pregnant individuals, but those data were not available for the study.
There was no difference in unfavorable obstetrical or infant outcomes, including spontaneous abortion, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, major congenital malformation, and severe infection of the infant requiring hospitalization. Somewhat surprisingly, the data showed that women who discontinued a TNFi were more likely to be hospitalized for infection either during their pregnancy or up to 6 weeks after delivery, compared with those who continued therapy (1.3% vs. 0.2%, respectively).
Dr. Moltó is currently looking into what could be behind this counterintuitive result, but she hypothesizes that patients who had stopped TNFi may have been taking more glucocorticoids.
“At our institution, there is generally a comfort level with continuing TNF inhibitors during pregnancy, at least until about 36 weeks,” said Sara K. Tedeschi, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. Sometimes, there is concern for risk of infection to the infant, depending on the type of TNFi being used, she added during a press conference.
“I think that these are really informative and supportive data to let women know that they probably have a really good chance of doing very well during the pregnancy if they continue” their TNFi, said Dr. Tedeschi, who was not involved with the study.
TNF discontinuation on the decline
In a related study, researchers at McGill University, Montreal, found that TNFi discontinuation prior to pregnancy had decreased over time in individuals with chronic inflammatory diseases.
Using a database of U.S. insurance claims, they identified 3,372 women with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and/or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who previously used a TNFi and gave birth between 2011 and 2019. A patient was considered to have used a TNFi if she had filled a prescription or had an infusion procedure insurance claim within 12 weeks before the gestational period or anytime during pregnancy. Researchers did not have time-specific data to account for women who stopped treatment at pregnancy diagnosis.
Nearly half (47%) of all identified pregnancies were in individuals with IBD, and the rest included patients with RA (24%), psoriasis or PsA (16%), AS (3%), or more than one diagnosis (10%).
In total, 14% of women discontinued TNFi use in the 12 weeks before becoming pregnant and did not restart. From 2011 to 2013, 19% of patients stopped their TNFi, but this proportion decreased overtime, with 10% of patients stopping therapy from 2017 to 2019 (P < .0001).
This decline “possibly reflects the increase in real-world evidence about the safety of TNFi in pregnancy. That research, in turn, led to new guidelines recommending the continuation of TNFi during pregnancy,” first author Leah Flatman, a PhD candidate in epidemiology at McGill, said in an interview. “I think we can see this potentially as good news.”
More patients with RA, psoriasis/PsA, and AS discontinued TNFi therapy prior to conception (23%-25%), compared with those with IBD (5%).
Ms. Flatman noted that her study and Moltó’s study complement each other by providing data on individuals stopping TNFi prior to conception versus those stopping treatment after pregnancy diagnosis.
“These findings demonstrate that continuing TNFi during pregnancy appears not to be associated with an increase in adverse obstetrical or infant outcomes,” Ms. Flatman said of Dr. Moltó’s study. “As guidelines currently recommend continuing TNFi, studies like this help demonstrate that the guideline changes do not appear to be associated with an increase in adverse events.”
Dr. Moltó and Ms. Flatman disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tedeschi has worked as a consultant for Novartis.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2023
Actinic keratoses may predict skin cancers in older adults
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Incipient ulceration may affect prognosis in primary melanoma
TOPLINE:
Incipient ulceration in primary cutaneous melanoma may represent a more biologically aggressive disease population than truly nonulcerated tumors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The final cohort included 40 cases of incipient ulceration that were matched 1:2 with 80 nonulcerated controls and 80 ulcerated controls.
- The prognostic significance of incipient ulceration in cutaneous melanoma is unclear.
- Current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) guidelines classify incipient ulceration as nonulcerated.
- In a retrospective case-control study, researchers drew from the Melanoma Institute Australia database to identify resected primary cutaneous melanomas diagnosed between 2005 and 2015 that had slides available at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney and a Breslow thickness greater than 0 mm.
- Clinical outcomes compared between cases and controls were recurrence-free survival (RFS), melanoma-specific survival (MSS), and overall survival (OS).
TAKEAWAY:
- The median Breslow depth was 2.8 mm for incipient cases, compared with 1.0 mm for nonulcerated melanomas and 5.3 mm for ulcerated melanomas, while the median tumor mitotic rate was 5.0 per mm2 for incipient cases, compared with 1 per mm2 in nonulcerated controls and 9 per mm2 in ulcerated controls.
- On univariable analyses, compared with patients with incipiently ulcerated cases, patients with nonulcerated tumors had significantly better OS (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49) and RFS (HR, 0.37), while patients with ulcerated tumors showed worse RFS (HR, 1.67).
- On multivariable analyses, no differences in survival outcomes were observed, perhaps due to the moderate number of incipient ulceration cases included in the study, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future editions of the AJCC staging system should consider acknowledging this interpretive challenge and provide guidance on how primary melanomas with incipient ulceration should be classified,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Richard A. Scolyer, MD, a pathologist at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Camperdown, Australia, is the senior author on the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and the relatively small number of cases that met criteria for inclusion.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Scolyer disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and personal fees from MetaOptima, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Evaxion, Provectus, QBiotics, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, NeraCare, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Myriad Genetics, and GlaxoSmithKline, all outside the submitted work. Four coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Incipient ulceration in primary cutaneous melanoma may represent a more biologically aggressive disease population than truly nonulcerated tumors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The final cohort included 40 cases of incipient ulceration that were matched 1:2 with 80 nonulcerated controls and 80 ulcerated controls.
- The prognostic significance of incipient ulceration in cutaneous melanoma is unclear.
- Current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) guidelines classify incipient ulceration as nonulcerated.
- In a retrospective case-control study, researchers drew from the Melanoma Institute Australia database to identify resected primary cutaneous melanomas diagnosed between 2005 and 2015 that had slides available at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney and a Breslow thickness greater than 0 mm.
- Clinical outcomes compared between cases and controls were recurrence-free survival (RFS), melanoma-specific survival (MSS), and overall survival (OS).
TAKEAWAY:
- The median Breslow depth was 2.8 mm for incipient cases, compared with 1.0 mm for nonulcerated melanomas and 5.3 mm for ulcerated melanomas, while the median tumor mitotic rate was 5.0 per mm2 for incipient cases, compared with 1 per mm2 in nonulcerated controls and 9 per mm2 in ulcerated controls.
- On univariable analyses, compared with patients with incipiently ulcerated cases, patients with nonulcerated tumors had significantly better OS (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49) and RFS (HR, 0.37), while patients with ulcerated tumors showed worse RFS (HR, 1.67).
- On multivariable analyses, no differences in survival outcomes were observed, perhaps due to the moderate number of incipient ulceration cases included in the study, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future editions of the AJCC staging system should consider acknowledging this interpretive challenge and provide guidance on how primary melanomas with incipient ulceration should be classified,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Richard A. Scolyer, MD, a pathologist at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Camperdown, Australia, is the senior author on the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and the relatively small number of cases that met criteria for inclusion.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Scolyer disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and personal fees from MetaOptima, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Evaxion, Provectus, QBiotics, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, NeraCare, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Myriad Genetics, and GlaxoSmithKline, all outside the submitted work. Four coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Incipient ulceration in primary cutaneous melanoma may represent a more biologically aggressive disease population than truly nonulcerated tumors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The final cohort included 40 cases of incipient ulceration that were matched 1:2 with 80 nonulcerated controls and 80 ulcerated controls.
- The prognostic significance of incipient ulceration in cutaneous melanoma is unclear.
- Current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) guidelines classify incipient ulceration as nonulcerated.
- In a retrospective case-control study, researchers drew from the Melanoma Institute Australia database to identify resected primary cutaneous melanomas diagnosed between 2005 and 2015 that had slides available at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney and a Breslow thickness greater than 0 mm.
- Clinical outcomes compared between cases and controls were recurrence-free survival (RFS), melanoma-specific survival (MSS), and overall survival (OS).
TAKEAWAY:
- The median Breslow depth was 2.8 mm for incipient cases, compared with 1.0 mm for nonulcerated melanomas and 5.3 mm for ulcerated melanomas, while the median tumor mitotic rate was 5.0 per mm2 for incipient cases, compared with 1 per mm2 in nonulcerated controls and 9 per mm2 in ulcerated controls.
- On univariable analyses, compared with patients with incipiently ulcerated cases, patients with nonulcerated tumors had significantly better OS (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49) and RFS (HR, 0.37), while patients with ulcerated tumors showed worse RFS (HR, 1.67).
- On multivariable analyses, no differences in survival outcomes were observed, perhaps due to the moderate number of incipient ulceration cases included in the study, the authors wrote.
IN PRACTICE:
“Future editions of the AJCC staging system should consider acknowledging this interpretive challenge and provide guidance on how primary melanomas with incipient ulceration should be classified,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
Richard A. Scolyer, MD, a pathologist at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Camperdown, Australia, is the senior author on the study, which was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the study include its retrospective design and the relatively small number of cases that met criteria for inclusion.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Scolyer disclosed that he has received grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and personal fees from MetaOptima, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Evaxion, Provectus, QBiotics, Novartis, Merck Sharp & Dohme, NeraCare, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Myriad Genetics, and GlaxoSmithKline, all outside the submitted work. Four coauthors reported having received financial support outside of the submitted work.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Multiple basal cell carcinomas
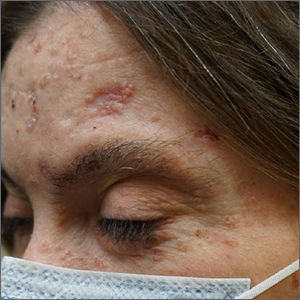
These skin findings were the latest manifestation of a condition that the patient had been diagnosed with at age 32: basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS), also called Gorlin syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by multiple biopsy-proven BCCs, palmar pitting, frontal bossing, scoliosis, and gum cysts. This patient had had gum cysts since she was 8 years old; her sister and mother had similar gum cysts and her mother had at least 1 BCC. BCNS is caused by an inheritable defect in the Patched 1 (PTCH1) gene, leading to various findings—including numerous BCCs at a young age.1
The Oncology team started the patient on the oral small-molecule chemotherapy agent vismodegib, 150 mg/d. The patient was also referred to Medical Genetics and Wound Care. Although her diagnosis had been made clinically years earlier, genetic testing was performed and confirmed a defect in the PTCH1 gene. This helped with surveillance plans. A computed tomography scan of the head revealed a nasal dermoid cyst of the ethmoid sinus that the Ear, Nose, & Throat and Neurology teams felt safe to observe.
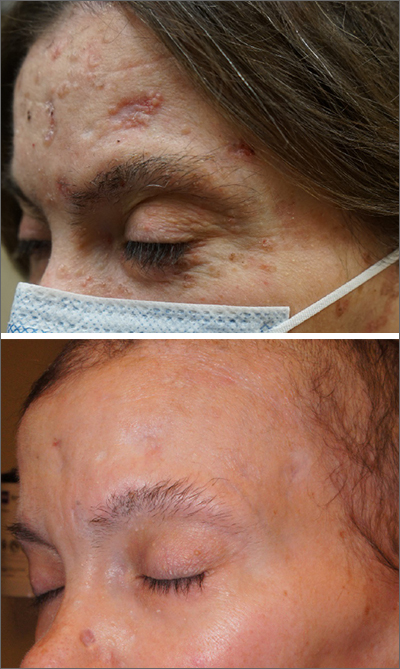
After 3 months of therapy with vismodegib, the patient had significant improvement of facial lesions and significant re-epithelialization of the crown.
Patients on vismodegib often deal with adverse effects, but adjusted dosing regimens have proved to improve tolerability. This patient had substantial adverse effects including fatigue, hair loss, loss of taste, and weight loss (26 lbs). Because of these adverse effects, her regimen was adjusted to 1 month of every other day active treatment and 2 months off treatment, cycled continuously. With this regimen, her weight returned to normal and her sense of taste returned for most days in the treatment cycle.
She has been tolerating this regimen for 3 years with continued control of BCCs.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Yang X, Dinehart SM. Intermittent vismodegib therapy in basal cell nevus syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:223-224. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.3210

These skin findings were the latest manifestation of a condition that the patient had been diagnosed with at age 32: basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS), also called Gorlin syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by multiple biopsy-proven BCCs, palmar pitting, frontal bossing, scoliosis, and gum cysts. This patient had had gum cysts since she was 8 years old; her sister and mother had similar gum cysts and her mother had at least 1 BCC. BCNS is caused by an inheritable defect in the Patched 1 (PTCH1) gene, leading to various findings—including numerous BCCs at a young age.1
The Oncology team started the patient on the oral small-molecule chemotherapy agent vismodegib, 150 mg/d. The patient was also referred to Medical Genetics and Wound Care. Although her diagnosis had been made clinically years earlier, genetic testing was performed and confirmed a defect in the PTCH1 gene. This helped with surveillance plans. A computed tomography scan of the head revealed a nasal dermoid cyst of the ethmoid sinus that the Ear, Nose, & Throat and Neurology teams felt safe to observe.
After 3 months of therapy with vismodegib, the patient had significant improvement of facial lesions and significant re-epithelialization of the crown.
Patients on vismodegib often deal with adverse effects, but adjusted dosing regimens have proved to improve tolerability. This patient had substantial adverse effects including fatigue, hair loss, loss of taste, and weight loss (26 lbs). Because of these adverse effects, her regimen was adjusted to 1 month of every other day active treatment and 2 months off treatment, cycled continuously. With this regimen, her weight returned to normal and her sense of taste returned for most days in the treatment cycle.
She has been tolerating this regimen for 3 years with continued control of BCCs.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

These skin findings were the latest manifestation of a condition that the patient had been diagnosed with at age 32: basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS), also called Gorlin syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by multiple biopsy-proven BCCs, palmar pitting, frontal bossing, scoliosis, and gum cysts. This patient had had gum cysts since she was 8 years old; her sister and mother had similar gum cysts and her mother had at least 1 BCC. BCNS is caused by an inheritable defect in the Patched 1 (PTCH1) gene, leading to various findings—including numerous BCCs at a young age.1
The Oncology team started the patient on the oral small-molecule chemotherapy agent vismodegib, 150 mg/d. The patient was also referred to Medical Genetics and Wound Care. Although her diagnosis had been made clinically years earlier, genetic testing was performed and confirmed a defect in the PTCH1 gene. This helped with surveillance plans. A computed tomography scan of the head revealed a nasal dermoid cyst of the ethmoid sinus that the Ear, Nose, & Throat and Neurology teams felt safe to observe.
After 3 months of therapy with vismodegib, the patient had significant improvement of facial lesions and significant re-epithelialization of the crown.
Patients on vismodegib often deal with adverse effects, but adjusted dosing regimens have proved to improve tolerability. This patient had substantial adverse effects including fatigue, hair loss, loss of taste, and weight loss (26 lbs). Because of these adverse effects, her regimen was adjusted to 1 month of every other day active treatment and 2 months off treatment, cycled continuously. With this regimen, her weight returned to normal and her sense of taste returned for most days in the treatment cycle.
She has been tolerating this regimen for 3 years with continued control of BCCs.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. Yang X, Dinehart SM. Intermittent vismodegib therapy in basal cell nevus syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:223-224. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.3210
1. Yang X, Dinehart SM. Intermittent vismodegib therapy in basal cell nevus syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:223-224. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.3210
AAD updates guidelines for managing AD with phototherapy and systemic therapies
.
The guidelines cover approved and off-label uses of systemic therapies and phototherapy, including new treatments that have become available since the last guidelines were published almost a decade ago. These include biologics and oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as older oral or injectable immunomodulators and antimetabolites, oral antibiotics, antihistamines, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. The guidelines rate the existing evidence as “strong” for dupilumab, tralokinumab, abrocitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. They also conditionally recommend phototherapy, as well as cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate, but recommend against the use of systemic corticosteroids.
The guidelines update the AAD’s 2014 recommendations for managing AD in adults with phototherapy and systemic therapies. “At that time, prednisone – universally agreed to be the least appropriate chronic therapy for AD – was the only Food and Drug Administration–approved agent,” Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, who cochaired a 14-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization. “This was the driver.”
The latest guidelines were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Broad evidence review
Dr. Sidbury, chief of the division of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, guidelines cochair Dawn M. R. Davis, MD, a dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues conducted a systematic evidence review of phototherapy such as narrowband and broadband UVB and systemic therapies, including biologics such as dupilumab and tralokinumab, JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, and immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine.
Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
Recommendations, future studies
Of the 11 evidence-based recommendations of therapies for adults with AD refractory to topical medications, the work group ranks 5 as “strong” based on the evidence and the rest as “conditional.” “Strong” implies the benefits clearly outweigh risks and burdens, they apply to most patients in most circumstances, and they fall under good clinical practice. “Conditional” means the benefits and risks are closely balanced for most patients, “but the appropriate action may different depending on the patient or other stakeholder values,” the authors wrote.
In their remarks about phototherapy, the work group noted that most published literature on the topic “reports on the efficacy and safety of narrow band UVB. Wherever possible, use a light source that minimizes the potential for harm under the supervision of a qualified clinician.”
In their remarks about cyclosporine, they noted that evidence suggests an initial dose of 3 mg/kg per day to 5 mg/kg per day is effective, but that the Food and Drug Administration has not approved cyclosporine for use in AD. “The FDA has approved limited-term use (up to 1 year) in psoriasis,” they wrote. “Comorbidities or drug interactions that may exacerbate toxicity make this intervention inappropriate for select patients.” The work group noted that significant research gaps remain in phototherapy, especially trials that compare different phototherapy modalities and those that compare phototherapy with other AD treatment strategies.
“Larger clinical trials would also be helpful for cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate to improve the certainty of evidence for those medications,” they added. “Furthermore, formal cost-effectiveness analyses comparing older to newer treatments are needed.”
They recommended the inclusion of active comparator arms in randomized, controlled trials as new systemic therapies continue to be developed and tested.
The work group ranked the level of evidence they reviewed for the therapies from very low to moderate. No therapy was judged to have high evidence. They also cited the short duration of most randomized controlled trials of phototherapy.
Using the guidelines in clinical care
According to Dr. Davis, the topic of which agent if any should be considered “first line” generated robust discussion among the work group members.
“When there are not robust head-to-head trials – and there are not – it is often opinion that governs this decision, and opinion should not, when possible, govern a guideline,” Dr. Davis said. “Accordingly, we determined based upon the evidence agents – plural – that deserve to be considered ‘first line’ but not a single agent.”
In her opinion, the top three considerations regarding use of systemic therapy for AD relate to patient selection and shared decision making. One, standard therapy has failed. Two, diagnosis is assured. And three, “steroid phobia should be considered,” and patients should be “fully informed of risks and benefits of both treating and not treating,” she said.
Dr. Sidbury reported that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma USA, and a consultant for Galderma Global and Micreos. Dr. Davis reported having no relevant disclosures. Other work group members reported having financial disclosures with many pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by internal funds from the American Academy of Dermatology.
.
The guidelines cover approved and off-label uses of systemic therapies and phototherapy, including new treatments that have become available since the last guidelines were published almost a decade ago. These include biologics and oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as older oral or injectable immunomodulators and antimetabolites, oral antibiotics, antihistamines, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. The guidelines rate the existing evidence as “strong” for dupilumab, tralokinumab, abrocitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. They also conditionally recommend phototherapy, as well as cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate, but recommend against the use of systemic corticosteroids.
The guidelines update the AAD’s 2014 recommendations for managing AD in adults with phototherapy and systemic therapies. “At that time, prednisone – universally agreed to be the least appropriate chronic therapy for AD – was the only Food and Drug Administration–approved agent,” Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, who cochaired a 14-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization. “This was the driver.”
The latest guidelines were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Broad evidence review
Dr. Sidbury, chief of the division of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, guidelines cochair Dawn M. R. Davis, MD, a dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues conducted a systematic evidence review of phototherapy such as narrowband and broadband UVB and systemic therapies, including biologics such as dupilumab and tralokinumab, JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, and immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine.
Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
Recommendations, future studies
Of the 11 evidence-based recommendations of therapies for adults with AD refractory to topical medications, the work group ranks 5 as “strong” based on the evidence and the rest as “conditional.” “Strong” implies the benefits clearly outweigh risks and burdens, they apply to most patients in most circumstances, and they fall under good clinical practice. “Conditional” means the benefits and risks are closely balanced for most patients, “but the appropriate action may different depending on the patient or other stakeholder values,” the authors wrote.
In their remarks about phototherapy, the work group noted that most published literature on the topic “reports on the efficacy and safety of narrow band UVB. Wherever possible, use a light source that minimizes the potential for harm under the supervision of a qualified clinician.”
In their remarks about cyclosporine, they noted that evidence suggests an initial dose of 3 mg/kg per day to 5 mg/kg per day is effective, but that the Food and Drug Administration has not approved cyclosporine for use in AD. “The FDA has approved limited-term use (up to 1 year) in psoriasis,” they wrote. “Comorbidities or drug interactions that may exacerbate toxicity make this intervention inappropriate for select patients.” The work group noted that significant research gaps remain in phototherapy, especially trials that compare different phototherapy modalities and those that compare phototherapy with other AD treatment strategies.
“Larger clinical trials would also be helpful for cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate to improve the certainty of evidence for those medications,” they added. “Furthermore, formal cost-effectiveness analyses comparing older to newer treatments are needed.”
They recommended the inclusion of active comparator arms in randomized, controlled trials as new systemic therapies continue to be developed and tested.
The work group ranked the level of evidence they reviewed for the therapies from very low to moderate. No therapy was judged to have high evidence. They also cited the short duration of most randomized controlled trials of phototherapy.
Using the guidelines in clinical care
According to Dr. Davis, the topic of which agent if any should be considered “first line” generated robust discussion among the work group members.
“When there are not robust head-to-head trials – and there are not – it is often opinion that governs this decision, and opinion should not, when possible, govern a guideline,” Dr. Davis said. “Accordingly, we determined based upon the evidence agents – plural – that deserve to be considered ‘first line’ but not a single agent.”
In her opinion, the top three considerations regarding use of systemic therapy for AD relate to patient selection and shared decision making. One, standard therapy has failed. Two, diagnosis is assured. And three, “steroid phobia should be considered,” and patients should be “fully informed of risks and benefits of both treating and not treating,” she said.
Dr. Sidbury reported that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma USA, and a consultant for Galderma Global and Micreos. Dr. Davis reported having no relevant disclosures. Other work group members reported having financial disclosures with many pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by internal funds from the American Academy of Dermatology.
.
The guidelines cover approved and off-label uses of systemic therapies and phototherapy, including new treatments that have become available since the last guidelines were published almost a decade ago. These include biologics and oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, as well as older oral or injectable immunomodulators and antimetabolites, oral antibiotics, antihistamines, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors. The guidelines rate the existing evidence as “strong” for dupilumab, tralokinumab, abrocitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib. They also conditionally recommend phototherapy, as well as cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate, but recommend against the use of systemic corticosteroids.
The guidelines update the AAD’s 2014 recommendations for managing AD in adults with phototherapy and systemic therapies. “At that time, prednisone – universally agreed to be the least appropriate chronic therapy for AD – was the only Food and Drug Administration–approved agent,” Robert Sidbury, MD, MPH, who cochaired a 14-member multidisciplinary work group that assembled the guidelines, told this news organization. “This was the driver.”
The latest guidelines were published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Broad evidence review
Dr. Sidbury, chief of the division of dermatology at Seattle Children’s Hospital, guidelines cochair Dawn M. R. Davis, MD, a dermatologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues conducted a systematic evidence review of phototherapy such as narrowband and broadband UVB and systemic therapies, including biologics such as dupilumab and tralokinumab, JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib and abrocitinib, and immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine.
Next, the work group applied the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach for assessing the certainty of the evidence and formulating and grading clinical recommendations based on relevant randomized trials in the medical literature.
Recommendations, future studies
Of the 11 evidence-based recommendations of therapies for adults with AD refractory to topical medications, the work group ranks 5 as “strong” based on the evidence and the rest as “conditional.” “Strong” implies the benefits clearly outweigh risks and burdens, they apply to most patients in most circumstances, and they fall under good clinical practice. “Conditional” means the benefits and risks are closely balanced for most patients, “but the appropriate action may different depending on the patient or other stakeholder values,” the authors wrote.
In their remarks about phototherapy, the work group noted that most published literature on the topic “reports on the efficacy and safety of narrow band UVB. Wherever possible, use a light source that minimizes the potential for harm under the supervision of a qualified clinician.”
In their remarks about cyclosporine, they noted that evidence suggests an initial dose of 3 mg/kg per day to 5 mg/kg per day is effective, but that the Food and Drug Administration has not approved cyclosporine for use in AD. “The FDA has approved limited-term use (up to 1 year) in psoriasis,” they wrote. “Comorbidities or drug interactions that may exacerbate toxicity make this intervention inappropriate for select patients.” The work group noted that significant research gaps remain in phototherapy, especially trials that compare different phototherapy modalities and those that compare phototherapy with other AD treatment strategies.
“Larger clinical trials would also be helpful for cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine, and mycophenolate to improve the certainty of evidence for those medications,” they added. “Furthermore, formal cost-effectiveness analyses comparing older to newer treatments are needed.”
They recommended the inclusion of active comparator arms in randomized, controlled trials as new systemic therapies continue to be developed and tested.
The work group ranked the level of evidence they reviewed for the therapies from very low to moderate. No therapy was judged to have high evidence. They also cited the short duration of most randomized controlled trials of phototherapy.
Using the guidelines in clinical care
According to Dr. Davis, the topic of which agent if any should be considered “first line” generated robust discussion among the work group members.
“When there are not robust head-to-head trials – and there are not – it is often opinion that governs this decision, and opinion should not, when possible, govern a guideline,” Dr. Davis said. “Accordingly, we determined based upon the evidence agents – plural – that deserve to be considered ‘first line’ but not a single agent.”
In her opinion, the top three considerations regarding use of systemic therapy for AD relate to patient selection and shared decision making. One, standard therapy has failed. Two, diagnosis is assured. And three, “steroid phobia should be considered,” and patients should be “fully informed of risks and benefits of both treating and not treating,” she said.
Dr. Sidbury reported that he serves as an advisory board member for Pfizer, a principal investigator for Regeneron, an investigator for Brickell Biotech and Galderma USA, and a consultant for Galderma Global and Micreos. Dr. Davis reported having no relevant disclosures. Other work group members reported having financial disclosures with many pharmaceutical companies. The study was supported by internal funds from the American Academy of Dermatology.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Specialty-trained pathologists more likely to make higher-grade diagnoses for melanocytic lesions
, results from an exploratory study showed.
The findings “could in part play a role in the rising incidence of early-stage melanoma with low risk of progression or patient morbidity, thereby contributing to increasing rates of overdiagnosis,” researchers led by co–senior authors Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and Raymond L. Barnhill, MD, MBA, of the Institut Curie, Paris, wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
To investigate the characteristics associated with rendering higher-grade diagnoses, including invasive melanoma, the researchers drew from two national data sets: the Melanoma Pathology (M-Path) study, conducted from July 2013 to May 2016, and the Reducing Errors in Melanocytic Interpretations (REMI) study, conducted from August 2018 to March 2021. In both studies, pathologists who interpreted melanocytic lesions in their clinical practices interpreted study cases in glass slide format. For the current study, researchers used logistic regression to examine the association of pathologist characteristics with diagnosis of a study case as higher grade (including severely dysplastic and melanoma in situ) vs. lower grade (including mild to moderately dysplastic nevi) and diagnosis of invasive melanoma vs. any less severe diagnosis.
A total of 338 pathologists were included in the analysis. Of these, 113 were general pathologists and 225 were dermatopathologists (those who were board certified and/or fellowship trained in dermatopathology).
The researchers found that, compared with general pathologists, dermatopathologists were 2.63 times more likely to render higher-grade diagnoses and 1.95 times more likely to diagnose invasive melanoma (P < .001 for both associations). Diagnoses of stage pT1a melanomas with no mitotic activity completely accounted for the difference between dermatopathologists and general pathologists in diagnosing invasive melanoma.
For the analysis limited to the 225 dermatopathologists, those with a higher practice caseload of melanocytic lesions were more likely to assign higher-grade diagnoses (odds ratio for trend, 1.27; P = .02), while those affiliated with an academic center had lower odds of diagnosing invasive melanoma (OR, 0.61; P = .049).
The researchers acknowledged limitations of their analysis, including the lack of data on patient outcomes, “so we could not make conclusions about the clinical outcome of any particular diagnosis by a study participant,” they wrote. “While our analyses revealed pathologist characteristics associated with assigning more vs. less severe diagnoses of melanocytic lesions, we could not conclude that any particular diagnosis by a study participant was overcalling or undercalling. However, the epidemiologic evidence that melanoma is overdiagnosed suggests that overcalling by some pathologists may be contributing to increasing rates of low-risk melanoma diagnoses.”
In an accompanying editorial, authors Klaus J. Busam, MD, of the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, Pedram Gerami, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and Richard A. Scolyer, MD, of the Melanoma Institute, Wollstonecraft, Australia, wrote that the study findings “raise the question of whether subspecialization in dermatopathology may be a factor contributing to the epidemiologic phenomenon of overdiagnosis – that is, the discordance in the rise of melanoma incidence and relatively constant annual mortality rates over many decades. The findings also invite a discussion about strategies to minimize harm from overdiagnosis for both patients and the health care system.”
To minimize misdiagnoses, they continued, efforts to facilitate diagnostic accuracy should be encouraged. “Excisional (rather than partial) biopsies and provision of relevant clinical information would facilitate rendering of the correct histopathologic diagnosis,” they wrote. “When the diagnosis is uncertain, this is best acknowledged. If felt necessary, a reexcision of a lesion with an uncertain diagnosis can be recommended without upgrading the diagnosis.”
In addition, “improvements in prognosis are needed beyond American Joint Committee on Cancer staging,” they noted. “This will likely require a multimodal approach with novel methods, including artificial intelligence and biomarkers that help distinguish low-risk melanomas, for which a conservative approach may be appropriate, from those that require surgical intervention.”
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and by the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, and another disclosed serving as editor in chief of Primary Care topics at UpToDate; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Busam reported receiving nonfinancial support from the American Society of Dermatopathology. Dr. Gerami reported receiving consulting fees from Castle Biosciences. Dr. Scolyer reported receiving an investigator grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia during the conduct of the study and personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
, results from an exploratory study showed.
The findings “could in part play a role in the rising incidence of early-stage melanoma with low risk of progression or patient morbidity, thereby contributing to increasing rates of overdiagnosis,” researchers led by co–senior authors Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and Raymond L. Barnhill, MD, MBA, of the Institut Curie, Paris, wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
To investigate the characteristics associated with rendering higher-grade diagnoses, including invasive melanoma, the researchers drew from two national data sets: the Melanoma Pathology (M-Path) study, conducted from July 2013 to May 2016, and the Reducing Errors in Melanocytic Interpretations (REMI) study, conducted from August 2018 to March 2021. In both studies, pathologists who interpreted melanocytic lesions in their clinical practices interpreted study cases in glass slide format. For the current study, researchers used logistic regression to examine the association of pathologist characteristics with diagnosis of a study case as higher grade (including severely dysplastic and melanoma in situ) vs. lower grade (including mild to moderately dysplastic nevi) and diagnosis of invasive melanoma vs. any less severe diagnosis.
A total of 338 pathologists were included in the analysis. Of these, 113 were general pathologists and 225 were dermatopathologists (those who were board certified and/or fellowship trained in dermatopathology).
The researchers found that, compared with general pathologists, dermatopathologists were 2.63 times more likely to render higher-grade diagnoses and 1.95 times more likely to diagnose invasive melanoma (P < .001 for both associations). Diagnoses of stage pT1a melanomas with no mitotic activity completely accounted for the difference between dermatopathologists and general pathologists in diagnosing invasive melanoma.
For the analysis limited to the 225 dermatopathologists, those with a higher practice caseload of melanocytic lesions were more likely to assign higher-grade diagnoses (odds ratio for trend, 1.27; P = .02), while those affiliated with an academic center had lower odds of diagnosing invasive melanoma (OR, 0.61; P = .049).
The researchers acknowledged limitations of their analysis, including the lack of data on patient outcomes, “so we could not make conclusions about the clinical outcome of any particular diagnosis by a study participant,” they wrote. “While our analyses revealed pathologist characteristics associated with assigning more vs. less severe diagnoses of melanocytic lesions, we could not conclude that any particular diagnosis by a study participant was overcalling or undercalling. However, the epidemiologic evidence that melanoma is overdiagnosed suggests that overcalling by some pathologists may be contributing to increasing rates of low-risk melanoma diagnoses.”
In an accompanying editorial, authors Klaus J. Busam, MD, of the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, Pedram Gerami, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and Richard A. Scolyer, MD, of the Melanoma Institute, Wollstonecraft, Australia, wrote that the study findings “raise the question of whether subspecialization in dermatopathology may be a factor contributing to the epidemiologic phenomenon of overdiagnosis – that is, the discordance in the rise of melanoma incidence and relatively constant annual mortality rates over many decades. The findings also invite a discussion about strategies to minimize harm from overdiagnosis for both patients and the health care system.”
To minimize misdiagnoses, they continued, efforts to facilitate diagnostic accuracy should be encouraged. “Excisional (rather than partial) biopsies and provision of relevant clinical information would facilitate rendering of the correct histopathologic diagnosis,” they wrote. “When the diagnosis is uncertain, this is best acknowledged. If felt necessary, a reexcision of a lesion with an uncertain diagnosis can be recommended without upgrading the diagnosis.”
In addition, “improvements in prognosis are needed beyond American Joint Committee on Cancer staging,” they noted. “This will likely require a multimodal approach with novel methods, including artificial intelligence and biomarkers that help distinguish low-risk melanomas, for which a conservative approach may be appropriate, from those that require surgical intervention.”
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and by the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, and another disclosed serving as editor in chief of Primary Care topics at UpToDate; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Busam reported receiving nonfinancial support from the American Society of Dermatopathology. Dr. Gerami reported receiving consulting fees from Castle Biosciences. Dr. Scolyer reported receiving an investigator grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia during the conduct of the study and personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
, results from an exploratory study showed.
The findings “could in part play a role in the rising incidence of early-stage melanoma with low risk of progression or patient morbidity, thereby contributing to increasing rates of overdiagnosis,” researchers led by co–senior authors Joann G. Elmore, MD, MPH, of the University of California, Los Angeles, and Raymond L. Barnhill, MD, MBA, of the Institut Curie, Paris, wrote in their study, published online in JAMA Dermatology.
To investigate the characteristics associated with rendering higher-grade diagnoses, including invasive melanoma, the researchers drew from two national data sets: the Melanoma Pathology (M-Path) study, conducted from July 2013 to May 2016, and the Reducing Errors in Melanocytic Interpretations (REMI) study, conducted from August 2018 to March 2021. In both studies, pathologists who interpreted melanocytic lesions in their clinical practices interpreted study cases in glass slide format. For the current study, researchers used logistic regression to examine the association of pathologist characteristics with diagnosis of a study case as higher grade (including severely dysplastic and melanoma in situ) vs. lower grade (including mild to moderately dysplastic nevi) and diagnosis of invasive melanoma vs. any less severe diagnosis.
A total of 338 pathologists were included in the analysis. Of these, 113 were general pathologists and 225 were dermatopathologists (those who were board certified and/or fellowship trained in dermatopathology).
The researchers found that, compared with general pathologists, dermatopathologists were 2.63 times more likely to render higher-grade diagnoses and 1.95 times more likely to diagnose invasive melanoma (P < .001 for both associations). Diagnoses of stage pT1a melanomas with no mitotic activity completely accounted for the difference between dermatopathologists and general pathologists in diagnosing invasive melanoma.
For the analysis limited to the 225 dermatopathologists, those with a higher practice caseload of melanocytic lesions were more likely to assign higher-grade diagnoses (odds ratio for trend, 1.27; P = .02), while those affiliated with an academic center had lower odds of diagnosing invasive melanoma (OR, 0.61; P = .049).
The researchers acknowledged limitations of their analysis, including the lack of data on patient outcomes, “so we could not make conclusions about the clinical outcome of any particular diagnosis by a study participant,” they wrote. “While our analyses revealed pathologist characteristics associated with assigning more vs. less severe diagnoses of melanocytic lesions, we could not conclude that any particular diagnosis by a study participant was overcalling or undercalling. However, the epidemiologic evidence that melanoma is overdiagnosed suggests that overcalling by some pathologists may be contributing to increasing rates of low-risk melanoma diagnoses.”
In an accompanying editorial, authors Klaus J. Busam, MD, of the department of pathology and laboratory medicine at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, Pedram Gerami, MD, of the department of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, and Richard A. Scolyer, MD, of the Melanoma Institute, Wollstonecraft, Australia, wrote that the study findings “raise the question of whether subspecialization in dermatopathology may be a factor contributing to the epidemiologic phenomenon of overdiagnosis – that is, the discordance in the rise of melanoma incidence and relatively constant annual mortality rates over many decades. The findings also invite a discussion about strategies to minimize harm from overdiagnosis for both patients and the health care system.”
To minimize misdiagnoses, they continued, efforts to facilitate diagnostic accuracy should be encouraged. “Excisional (rather than partial) biopsies and provision of relevant clinical information would facilitate rendering of the correct histopathologic diagnosis,” they wrote. “When the diagnosis is uncertain, this is best acknowledged. If felt necessary, a reexcision of a lesion with an uncertain diagnosis can be recommended without upgrading the diagnosis.”
In addition, “improvements in prognosis are needed beyond American Joint Committee on Cancer staging,” they noted. “This will likely require a multimodal approach with novel methods, including artificial intelligence and biomarkers that help distinguish low-risk melanomas, for which a conservative approach may be appropriate, from those that require surgical intervention.”
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and by the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study, and another disclosed serving as editor in chief of Primary Care topics at UpToDate; other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Busam reported receiving nonfinancial support from the American Society of Dermatopathology. Dr. Gerami reported receiving consulting fees from Castle Biosciences. Dr. Scolyer reported receiving an investigator grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia during the conduct of the study and personal fees from several pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Prurigo nodularis diagnosis delay in skin of color gains added significance
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
NEW YORK – according to an expert evaluating current approaches at the Skin of Color Update 2023.
“As dermatologists, prurigo nodularis is one of the most severe diseases we treat, said Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, director of the Johns Hopkins Itch Center, Baltimore. Now with one approved therapy and more coming, “it offers one of the most important opportunities we have to dramatically improve someone’s entire life.”
Prior to the September 2022 approval of dupilumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis (the first treatment approved for this indication), Dr. Kwatra said that the limited options for control of pruritus made him anxious. Prurigo nodularis is characterized by highly itchy nodules that can produce symptoms patients describe as unbearable.
Itch typically severe
On a scale for which 10 represents the worst itch imaginable, scores of 8 or greater are not unusual, according to Dr. Kwatra. Nodules on the trunk and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are characteristic, but the persistent itch is the immediate target of treatment once the diagnosis is made. For that reason, he urged clinicians to be familiar with the presentation in patients with darker skin types to reduce time to treatment.
In addition to the difficulty of seeing the characteristic red that is typical of erythema in lighter skin, patients with darker skin types tend to have larger nodules that might vary in shape relative to lighter skin types, Dr. Kwatra said. Given that the presentation of prurigo nodularis is highly heterogeneous even among the same skin types, the nuances in patients with darker skin can be that much more confusing for those without prior experience.
Among Blacks in particular, the nodules in some cases “can be huge,” he added. “They can almost look like keloids due to their thickened and fibrotic appearance.”
Phenotypes appear to be racially linked
In Black patients, the appearance can vary enough relative to lighter skin individuals, that “there seems to be something a little bit different going on,” he said, and this is, in fact, supported by a cluster analysis of circulating biomarkers reported by Dr. Kwatra and colleagues in 2022, in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
In that study, the biomarker profile distinguished two distinct groups. Whites were more common in a cluster with relatively low expression of inflammatory markers (cluster 1), while Blacks were more common in a cluster with an inflammatory plasma profile (cluster 2), with higher relative expression of multiple cytokines, C-reactive protein, eosinophils, and other markers of up-regulated inflammation.
In addition to a lower rate of myelopathy in cluster 2 than cluster 1 (18% vs. 67%; P = .028), patients in cluster 2 had a significantly worse itch than those in cluster 1 on the Numeric Rating Scale for itch and a significantly lower quality of life based on the Dermatology Life Quality Index score.
Other work at Dr. Kwatra’s center that is based on genetic sequencing has provided evidence that Blacks – and Asians to a lesser extent – are predisposed genetically to develop nodules, perhaps explaining why the nodules tend to be larger than those seen in Whites.
The significance of the evidence that prurigo nodularis is associated with a more up-regulated inflammatory profile in Blacks than in Whites is that they might be particularly likely to respond to dupilumab or other targeted immunomodulating therapies that are in development, according to Dr. Kwatra. Although he did not provide data on response by race, he did provide several case examples of complete itch control following dupilumab therapy in Black patients.
In his experience, high levels of blood eosinophils and other inflammatory markers are predictors of response to dupilumab regardless of skin type, but he expressed concern that time to diagnosis is sometimes longer in Black patients if the nuances of disease expression are not appreciated.
For treating prurigo nodularis in Blacks as well as Whites, Dr. Kwatra suggested that clinicians stay current with what he predicted will be a growing array of treatment options. He did not discuss nemolizumab, an interleukin-31 receptor alpha antagonist. Soon after the meeting, results of a phase 3 trial of nemolizumab in patients with moderate to severe prurigo nodularis were published in the New England Journal of Medicine. (Dr. Kwatra is the lead author of the study but did not specifically discuss this treatment at the meeting.)
In the international placebo-controlled trial, called OLYMPIA 2, treatment was associated with a significant reduction in the signs and symptoms of prurigo nodularis, including reductions in itch, at 16 weeks, although only 4% of patients in the study were Black.
Given the expanding array of therapies, the message of considering prurigo nodularis in Black patients in order to accelerate the time to diagnosis is timely, Andrew F. Alexis, MD, MPH, professor of clinical dermatology and vice-chair for diversity and inclusion for the department of dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“Current studies suggest a higher prevalence and greater severity of prurigo nodularis among Black patients compared to White patients,” said Dr. Alexis, agreeing with Dr. Kwatra. Referring to evidence that Blacks might mount a greater inflammatory response to prurigo nodularis than Whites, Dr. Alexis called for “a better understanding of the pathomechanisms” of this disease in order “to address unmet needs and reduce disparities for our diverse population of patients who suffer from prurigo nodularis.’
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Arcutis, ASLAN, Cara, Castle Biosciences, Celldex, Galderma, Incyte, Johnson & Johnson, LEO pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
AT SOC 2023
The challenges of palmoplantar pustulosis and other acral psoriatic disease
WASHINGTON – The approval last year of the interleukin (IL)-36 receptor antagonist spesolimab for treating generalized pustular psoriasis flares brightened the treatment landscape for this rare condition, and a recently published phase 2 study suggests a potential role of spesolimab for flare prevention. , according to speakers at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“The IL-36 receptor antagonists don’t seem to be quite the answer for [palmoplantar pustulosis] that they are for generalized pustular psoriasis [GPP],” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the meeting.
Psoriasis affecting the hands and feet – both pustular and nonpustular – has a higher impact on quality of life and higher functional disability than does non-acral psoriasis, is less responsive to treatment, and has a “very confusing nomenclature” that complicates research and thus management, said Jason Ezra Hawkes, MD, a dermatologist in Rocklin, Calif., and former faculty member of several departments of dermatology. Both he and Dr. Noe spoke during a tough-to-treat session at the NPF meeting.
IL-17 and IL-23 blockade, as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, are effective overall for palmoplantar psoriasis (nonpustular), but in general, responses are lower than for plaque psoriasis. Apremilast (Otezla), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has some efficacy for pustular variants, but for hyperkeratotic variants it “does not perform as well as more selective inhibition of IL-17 and IL-23 blockade,” he said.
In general, ”what’s happening in the acral sites is different from an immune perspective than what’s happening in the non-acral sites,” and more research utilizing a clearer, descriptive nomenclature is needed to tease out differing immunophenotypes, explained Dr. Hawkes, who has led multiple clinical trials of treatments for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Palmoplantar pustulosis, and a word on generalized disease
Dermatologists are using a variety of treatments for palmoplantar pustulosis, with no clear first-line choices, Dr. Noe said. In a case series of almost 200 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis across 20 dermatology practices, published in JAMA Dermatology, 35% of patients received a systemic therapy prescription at their initial encounter – most commonly acitretin, followed by methotrexate and phototherapy. “Biologics were used, but use was varied and not as often as with oral agents,” said Dr. Noe, a coauthor of the study.
TNF blockers led to improvements ranging from 57% to 84%, depending on the agent, in a 2020 retrospective study of patients with palmoplantar pustulosis or acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau, Dr. Noe noted. However, rates of complete clearance were only 20%-29%.
Apremilast showed modest efficacy after 5 months of treatment, with 62% of patients achieving at least a 50% improvement in the Palmoplantar Pustulosis Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PPPASI) in a 2021 open-label, phase 2 study involving 21 patients. “This may represent a potential treatment option,” Dr. Noe said. “It’s something, but not what we’re used to seeing in our plaque psoriasis patients.”
A 2021 phase 2a, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of spesolimab in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis, meanwhile, failed to meet its primary endpoint, with only 32% of patients achieving a 50% improvement at 16 weeks, compared with 24% of patients in the placebo arm. And a recently published network meta-analysis found that none of the five drugs studied in seven randomized controlled trials – biologic or oral – was more effective than placebo for clearance or improvement of palmoplantar pustulosis.
The spesolimab (Spevigo) results have been disappointing considering the biologic’s newfound efficacy and role as the first Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy for generalized pustular disease, according to Dr. Noe. The ability of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of the IL-36 receptor antagonist to completely clear pustules at 1 week in 54% of patients with generalized disease, compared with 6% of the placebo group, was “groundbreaking,” she said, referring to results of the pivotal trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
And given that “preventing GPP flares is ultimately what we want,” she said, more good news was reported this year in The Lancet: The finding from an international, randomized, placebo-controlled study that high-dose subcutaneous spesolimab significantly reduced the risk of a flare over 48 weeks. “There are lots of ongoing studies right now to understand the best way to dose spesolimab,” she said.
Moreover, another IL-36 receptor antagonist, imsidolimab, is being investigated in a phase 3 trial for generalized pustular disease, she noted. A phase 2, open-label study of patients with GPP found that “more than half of patients were very much improved at 4 weeks, and some patients started showing improvement at day 3,” Dr. Noe said.
An area of research she is interested in is the potential for Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors as a treatment for palmoplantar pustulosis. For pustulosis on the hands and feet, recent case reports describing the efficacy of JAK inhibitors have caught her eye. “Right now, all we have is this case report data, mostly with tofacitinib, but I think it’s exciting,” she said, noting a recently published report in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Pustular psoriatic disease can be localized to the hand and/or feet only, or can co-occur with generalized pustular disease, just as palmoplantar psoriasis can be localized to the hands and/or feet or, more commonly, can co-occur with widespread plaque psoriasis. Research has shown, Dr. Hawkes said, that with both types of acral disease, many patients have or have had plaque psoriasis outside of acral sites.
The nomenclature and acronyms for palmoplantar psoriatic disease have complicated patient education, communication, and research, Dr. Hawkes said. Does PPP refer to palmoplantar psoriasis, or palmoplantar pustulosis, for instance? What is the difference between palmoplantar pustulosis (coined PPP) and palmoplantar pustular psoriasis (referred to as PPPP)?
What if disease is only on the hands, only on the feet, or only on the backs of the hands? And at what point is disease not classified as palmoplantar psoriasis, but plaque psoriasis with involvement of the hands and feet? Inconsistencies and lack of clarification lead to “confusing” literature, he said.
Heterogeneity in populations across trials resulting from “inconsistent categorization and phenotype inclusion” may partly account for the recalcitrance to treatment reported in the literature, he said. Misdiagnosis as psoriasis in cases of localized disease (confusion with eczema, for instance), and the fact that hands and feet are subject to increased trauma and injury, compared with non-acral sites, are also at play.
Trials may also allow insufficient time for improvement, compared with non-acral sites. “What we’ve learned about the hands and feet is that it takes a much longer time for disease to improve,” Dr. Hawkes said, so primary endpoints must take this into account.
There is unique immunologic signaling in palmoplantar disease that differs from the predominant signaling in traditional plaque psoriasis, he emphasized, and “mixed immunophenotypes” that need to be unraveled.
Dr. Hawkes disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and UCB. Dr. Noe disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and Boehringer Ingelheim.
WASHINGTON – The approval last year of the interleukin (IL)-36 receptor antagonist spesolimab for treating generalized pustular psoriasis flares brightened the treatment landscape for this rare condition, and a recently published phase 2 study suggests a potential role of spesolimab for flare prevention. , according to speakers at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“The IL-36 receptor antagonists don’t seem to be quite the answer for [palmoplantar pustulosis] that they are for generalized pustular psoriasis [GPP],” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the meeting.
Psoriasis affecting the hands and feet – both pustular and nonpustular – has a higher impact on quality of life and higher functional disability than does non-acral psoriasis, is less responsive to treatment, and has a “very confusing nomenclature” that complicates research and thus management, said Jason Ezra Hawkes, MD, a dermatologist in Rocklin, Calif., and former faculty member of several departments of dermatology. Both he and Dr. Noe spoke during a tough-to-treat session at the NPF meeting.
IL-17 and IL-23 blockade, as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, are effective overall for palmoplantar psoriasis (nonpustular), but in general, responses are lower than for plaque psoriasis. Apremilast (Otezla), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has some efficacy for pustular variants, but for hyperkeratotic variants it “does not perform as well as more selective inhibition of IL-17 and IL-23 blockade,” he said.
In general, ”what’s happening in the acral sites is different from an immune perspective than what’s happening in the non-acral sites,” and more research utilizing a clearer, descriptive nomenclature is needed to tease out differing immunophenotypes, explained Dr. Hawkes, who has led multiple clinical trials of treatments for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Palmoplantar pustulosis, and a word on generalized disease
Dermatologists are using a variety of treatments for palmoplantar pustulosis, with no clear first-line choices, Dr. Noe said. In a case series of almost 200 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis across 20 dermatology practices, published in JAMA Dermatology, 35% of patients received a systemic therapy prescription at their initial encounter – most commonly acitretin, followed by methotrexate and phototherapy. “Biologics were used, but use was varied and not as often as with oral agents,” said Dr. Noe, a coauthor of the study.
TNF blockers led to improvements ranging from 57% to 84%, depending on the agent, in a 2020 retrospective study of patients with palmoplantar pustulosis or acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau, Dr. Noe noted. However, rates of complete clearance were only 20%-29%.
Apremilast showed modest efficacy after 5 months of treatment, with 62% of patients achieving at least a 50% improvement in the Palmoplantar Pustulosis Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PPPASI) in a 2021 open-label, phase 2 study involving 21 patients. “This may represent a potential treatment option,” Dr. Noe said. “It’s something, but not what we’re used to seeing in our plaque psoriasis patients.”
A 2021 phase 2a, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of spesolimab in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis, meanwhile, failed to meet its primary endpoint, with only 32% of patients achieving a 50% improvement at 16 weeks, compared with 24% of patients in the placebo arm. And a recently published network meta-analysis found that none of the five drugs studied in seven randomized controlled trials – biologic or oral – was more effective than placebo for clearance or improvement of palmoplantar pustulosis.
The spesolimab (Spevigo) results have been disappointing considering the biologic’s newfound efficacy and role as the first Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy for generalized pustular disease, according to Dr. Noe. The ability of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of the IL-36 receptor antagonist to completely clear pustules at 1 week in 54% of patients with generalized disease, compared with 6% of the placebo group, was “groundbreaking,” she said, referring to results of the pivotal trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
And given that “preventing GPP flares is ultimately what we want,” she said, more good news was reported this year in The Lancet: The finding from an international, randomized, placebo-controlled study that high-dose subcutaneous spesolimab significantly reduced the risk of a flare over 48 weeks. “There are lots of ongoing studies right now to understand the best way to dose spesolimab,” she said.
Moreover, another IL-36 receptor antagonist, imsidolimab, is being investigated in a phase 3 trial for generalized pustular disease, she noted. A phase 2, open-label study of patients with GPP found that “more than half of patients were very much improved at 4 weeks, and some patients started showing improvement at day 3,” Dr. Noe said.
An area of research she is interested in is the potential for Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors as a treatment for palmoplantar pustulosis. For pustulosis on the hands and feet, recent case reports describing the efficacy of JAK inhibitors have caught her eye. “Right now, all we have is this case report data, mostly with tofacitinib, but I think it’s exciting,” she said, noting a recently published report in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Pustular psoriatic disease can be localized to the hand and/or feet only, or can co-occur with generalized pustular disease, just as palmoplantar psoriasis can be localized to the hands and/or feet or, more commonly, can co-occur with widespread plaque psoriasis. Research has shown, Dr. Hawkes said, that with both types of acral disease, many patients have or have had plaque psoriasis outside of acral sites.
The nomenclature and acronyms for palmoplantar psoriatic disease have complicated patient education, communication, and research, Dr. Hawkes said. Does PPP refer to palmoplantar psoriasis, or palmoplantar pustulosis, for instance? What is the difference between palmoplantar pustulosis (coined PPP) and palmoplantar pustular psoriasis (referred to as PPPP)?
What if disease is only on the hands, only on the feet, or only on the backs of the hands? And at what point is disease not classified as palmoplantar psoriasis, but plaque psoriasis with involvement of the hands and feet? Inconsistencies and lack of clarification lead to “confusing” literature, he said.
Heterogeneity in populations across trials resulting from “inconsistent categorization and phenotype inclusion” may partly account for the recalcitrance to treatment reported in the literature, he said. Misdiagnosis as psoriasis in cases of localized disease (confusion with eczema, for instance), and the fact that hands and feet are subject to increased trauma and injury, compared with non-acral sites, are also at play.
Trials may also allow insufficient time for improvement, compared with non-acral sites. “What we’ve learned about the hands and feet is that it takes a much longer time for disease to improve,” Dr. Hawkes said, so primary endpoints must take this into account.
There is unique immunologic signaling in palmoplantar disease that differs from the predominant signaling in traditional plaque psoriasis, he emphasized, and “mixed immunophenotypes” that need to be unraveled.
Dr. Hawkes disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and UCB. Dr. Noe disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and Boehringer Ingelheim.
WASHINGTON – The approval last year of the interleukin (IL)-36 receptor antagonist spesolimab for treating generalized pustular psoriasis flares brightened the treatment landscape for this rare condition, and a recently published phase 2 study suggests a potential role of spesolimab for flare prevention. , according to speakers at the annual research symposium of the National Psoriasis Foundation.
“The IL-36 receptor antagonists don’t seem to be quite the answer for [palmoplantar pustulosis] that they are for generalized pustular psoriasis [GPP],” Megan H. Noe, MD, MPH, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and a dermatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the meeting.
Psoriasis affecting the hands and feet – both pustular and nonpustular – has a higher impact on quality of life and higher functional disability than does non-acral psoriasis, is less responsive to treatment, and has a “very confusing nomenclature” that complicates research and thus management, said Jason Ezra Hawkes, MD, a dermatologist in Rocklin, Calif., and former faculty member of several departments of dermatology. Both he and Dr. Noe spoke during a tough-to-treat session at the NPF meeting.
IL-17 and IL-23 blockade, as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibition, are effective overall for palmoplantar psoriasis (nonpustular), but in general, responses are lower than for plaque psoriasis. Apremilast (Otezla), a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, has some efficacy for pustular variants, but for hyperkeratotic variants it “does not perform as well as more selective inhibition of IL-17 and IL-23 blockade,” he said.
In general, ”what’s happening in the acral sites is different from an immune perspective than what’s happening in the non-acral sites,” and more research utilizing a clearer, descriptive nomenclature is needed to tease out differing immunophenotypes, explained Dr. Hawkes, who has led multiple clinical trials of treatments for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions.
Palmoplantar pustulosis, and a word on generalized disease
Dermatologists are using a variety of treatments for palmoplantar pustulosis, with no clear first-line choices, Dr. Noe said. In a case series of almost 200 patients with palmoplantar pustulosis across 20 dermatology practices, published in JAMA Dermatology, 35% of patients received a systemic therapy prescription at their initial encounter – most commonly acitretin, followed by methotrexate and phototherapy. “Biologics were used, but use was varied and not as often as with oral agents,” said Dr. Noe, a coauthor of the study.
TNF blockers led to improvements ranging from 57% to 84%, depending on the agent, in a 2020 retrospective study of patients with palmoplantar pustulosis or acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau, Dr. Noe noted. However, rates of complete clearance were only 20%-29%.
Apremilast showed modest efficacy after 5 months of treatment, with 62% of patients achieving at least a 50% improvement in the Palmoplantar Pustulosis Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PPPASI) in a 2021 open-label, phase 2 study involving 21 patients. “This may represent a potential treatment option,” Dr. Noe said. “It’s something, but not what we’re used to seeing in our plaque psoriasis patients.”
A 2021 phase 2a, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of spesolimab in patients with palmoplantar pustulosis, meanwhile, failed to meet its primary endpoint, with only 32% of patients achieving a 50% improvement at 16 weeks, compared with 24% of patients in the placebo arm. And a recently published network meta-analysis found that none of the five drugs studied in seven randomized controlled trials – biologic or oral – was more effective than placebo for clearance or improvement of palmoplantar pustulosis.
The spesolimab (Spevigo) results have been disappointing considering the biologic’s newfound efficacy and role as the first Food and Drug Administration–approved therapy for generalized pustular disease, according to Dr. Noe. The ability of a single 900-mg intravenous dose of the IL-36 receptor antagonist to completely clear pustules at 1 week in 54% of patients with generalized disease, compared with 6% of the placebo group, was “groundbreaking,” she said, referring to results of the pivotal trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
And given that “preventing GPP flares is ultimately what we want,” she said, more good news was reported this year in The Lancet: The finding from an international, randomized, placebo-controlled study that high-dose subcutaneous spesolimab significantly reduced the risk of a flare over 48 weeks. “There are lots of ongoing studies right now to understand the best way to dose spesolimab,” she said.
Moreover, another IL-36 receptor antagonist, imsidolimab, is being investigated in a phase 3 trial for generalized pustular disease, she noted. A phase 2, open-label study of patients with GPP found that “more than half of patients were very much improved at 4 weeks, and some patients started showing improvement at day 3,” Dr. Noe said.
An area of research she is interested in is the potential for Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors as a treatment for palmoplantar pustulosis. For pustulosis on the hands and feet, recent case reports describing the efficacy of JAK inhibitors have caught her eye. “Right now, all we have is this case report data, mostly with tofacitinib, but I think it’s exciting,” she said, noting a recently published report in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Palmoplantar psoriasis
Pustular psoriatic disease can be localized to the hand and/or feet only, or can co-occur with generalized pustular disease, just as palmoplantar psoriasis can be localized to the hands and/or feet or, more commonly, can co-occur with widespread plaque psoriasis. Research has shown, Dr. Hawkes said, that with both types of acral disease, many patients have or have had plaque psoriasis outside of acral sites.
The nomenclature and acronyms for palmoplantar psoriatic disease have complicated patient education, communication, and research, Dr. Hawkes said. Does PPP refer to palmoplantar psoriasis, or palmoplantar pustulosis, for instance? What is the difference between palmoplantar pustulosis (coined PPP) and palmoplantar pustular psoriasis (referred to as PPPP)?
What if disease is only on the hands, only on the feet, or only on the backs of the hands? And at what point is disease not classified as palmoplantar psoriasis, but plaque psoriasis with involvement of the hands and feet? Inconsistencies and lack of clarification lead to “confusing” literature, he said.
Heterogeneity in populations across trials resulting from “inconsistent categorization and phenotype inclusion” may partly account for the recalcitrance to treatment reported in the literature, he said. Misdiagnosis as psoriasis in cases of localized disease (confusion with eczema, for instance), and the fact that hands and feet are subject to increased trauma and injury, compared with non-acral sites, are also at play.
Trials may also allow insufficient time for improvement, compared with non-acral sites. “What we’ve learned about the hands and feet is that it takes a much longer time for disease to improve,” Dr. Hawkes said, so primary endpoints must take this into account.
There is unique immunologic signaling in palmoplantar disease that differs from the predominant signaling in traditional plaque psoriasis, he emphasized, and “mixed immunophenotypes” that need to be unraveled.
Dr. Hawkes disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, and UCB. Dr. Noe disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb and Boehringer Ingelheim.
AT THE NPF RESEARCH SYMPOSIUM 2023