User login
Factors Influencing Outcomes of a Telehealth-Based Physical Activity Program in Older Veterans Postdischarge
Factors Influencing Outcomes of a Telehealth-Based Physical Activity Program in Older Veterans Postdischarge
Deconditioning among hospitalized older adults contributes to significant decline in posthospitalization functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity.1-10 Previous hospital-to-home interventions have targeted improving function and physical activity, including recent programs leveraging home telehealth as a feasible and potentially effective mode of delivering in-home exercise and rehabilitation.11-14 However, pilot interventions have shown mixed effectiveness.11,12,14 This study expands on a previously published intervention describing a pilot home telehealth program for veterans posthospital discharge that demonstrated significant 6-month improvement in physical activity as well as trends in physical function improvement, including among those with cognitive impairment.15 Factors that contribute to improved outcomes are the focus of the present study.
Key factors underlying the complexity of hospital-to-home transitions include hospitalization elements (ie, reason for admission and length of stay), associated posthospital syndromes (ie, postdischarge falls, medication changes, cognitive impairment, and pain), and postdischarge health care application (ie, physical therapy and hospital readmission).16-18 These factors may be associated with postdischarge functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity, but their direct influence on intervention outcomes is unclear (Figure 1).5,7,9,16-20 The objective of this study was to examine the influence of hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors on outcomes of a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Video Connect (VVC) intervention to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge.
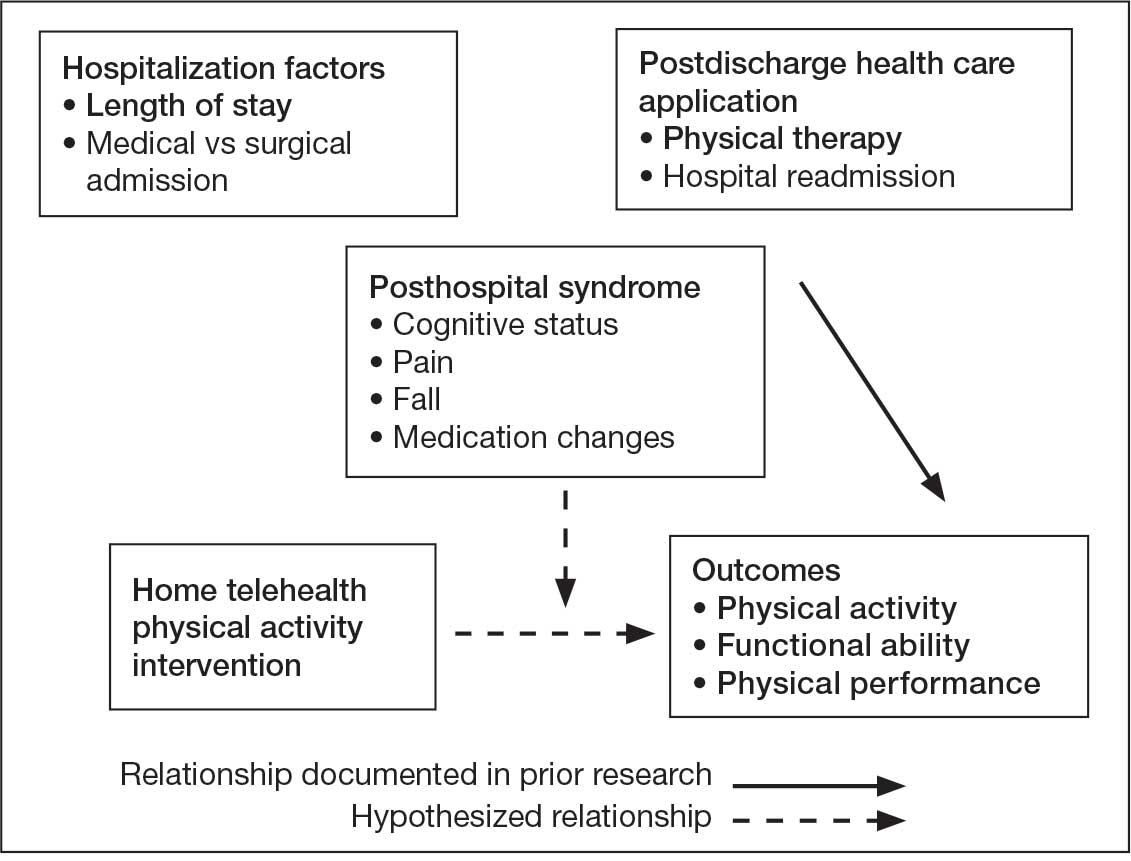
health care application factors on physical activity, functional ability, and
physical performance intervention outcomes.
Methods
The previous analysis reported on patient characteristics, program feasibility, and preliminary outcomes.13,15 The current study reports on relationships between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors and change in key outcomes, namely postdischarge self-reported functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity from baseline to endpoint.
Participants provided written informed consent. The protocol and consent forms were approved by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) Research and Development Committee, and the project was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04045054).
Intervention
The pilot program targeted older adults following recent hospital discharge from VAAAHS. Participants were eligible if they were aged ≥ 50 years, had been discharged following an inpatient stay in the past 1 to 2 weeks, evaluated by physical therapy during hospitalization with stated rehabilitation goals on discharge, and followed by a VAAAHS primary care physician. Participants were either recruited during hospital admission or shortly after discharge.13
An experienced physical activity trainer (PAT) supported the progression of participants’ rehabilitation goals via a home exercise program and coached the patient and caregiver to optimize functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity. The PAT was a nonlicensed research assistant with extensive experience in applying standard physical activity enhancement protocols (eg, increased walking) to older adults with comorbidities. Participation in the program lasted about 6 months. Initiation of the PAT program was delayed if the patient was already receiving postdischarge home-based or outpatient physical therapy. The PAT contacted the patient weekly via VVC for the first 6 weeks, then monthly for a total of 6 months. Each contact included information on optimal walking form, injury prevention, program progression, and ways to incorporate sit-to-stand transitions, nonsitting behavior, and walking into daily routines. The initial VVC contact lasted about 60 minutes and subsequent sessions lasted about 30 minutes.13
Demographic characteristics were self-reported by participants and included age, sex, race, years of education, and marital status. Clinical characteristics were obtained from each participant’s electronic health record (EHR), including copay status, index hospitalization length of stay, admission diagnosis, and postsurgery status (postsurgery vs nonpostsurgery). Intervention adherence was tracked as the number of PAT sessions attended.
Posthospital Syndrome Factors
Participant falls (categorized as those who reported a fall vs those who did not) and medication changes (number of changes reported, including new medication, discontinued medication, dose changes, medication changes, or changes in medication schedule) were reported by participants or caregivers during each VVC contact. Participants completed the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) at baseline, and were dichotomized into 2 groups: no cognitive impairment (MoCA score ≥ 26) and mild to moderate cognitive impairment (MoCA score 10-25).13,21
Participants rated how much pain interfered with their normal daily activities since the previous VVC session on a 5-point Likert scale (1, not at all; to 5, extremely).22 Similar to prior research, participants were placed into 2 groups based on their mean pain interference score (individuals with scores from 1.0 to 2.0 in 1 group, and individuals with > 2.0 in another).23-25 Participants were separated into a no or mild pain interference group and a moderate to severe pain interference group. Hospital readmissions (VA and non-VA) and postdischarge physical therapy outcomes were obtained from the participant’s EHR, including primary care visits.
Outcomes
Outcomes were collected at baseline (posthospital discharge) and 6 months postenrollment.
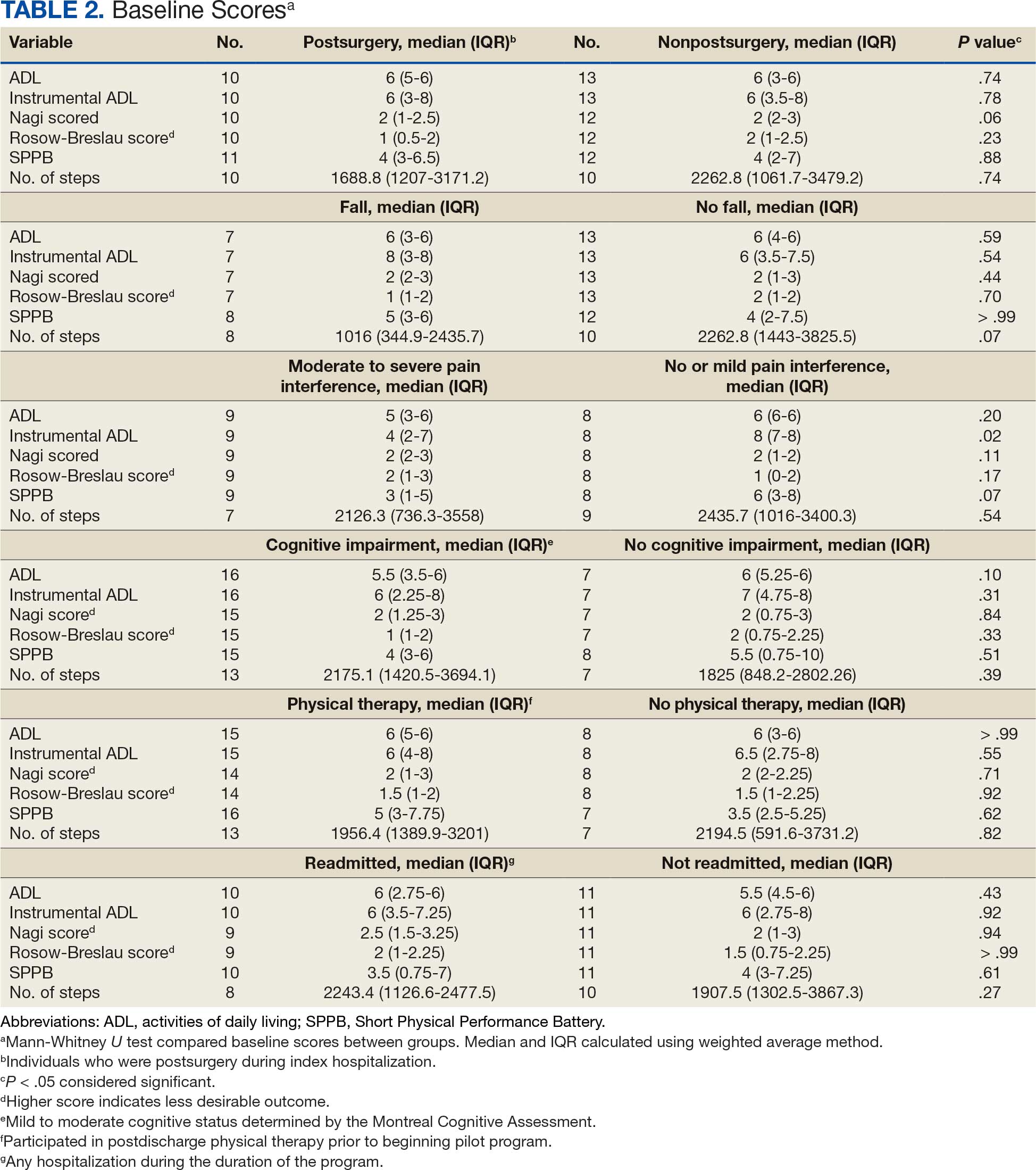
Self-Reported Functional Ability. This measure is provided by participants or caregivers and measured by the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living (ADL), Lawton and Brody Instrumental ADL Scale (IADL), Nagi Disability Model, and Rosow-Breslau Scale. The Katz ADL assesses the ability to complete 6 self-care activities and awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-6).26 The Lawton and Brody IADL measures an individual’s independence in 8 instrumental ADLs; it awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-8).27 The Nagi Disability Model evaluates an individual’s difficulty performing 5 tasks (total score range, 0-5) and tallies the number of items with a response other than “no difficulty at all” (higher total score indicates greater difficulty). 28 The Rosow-Breslau Scale is a 3-item measure of mobility disability; individual responses are 0 (no help) and 1 (requires help or unable); higher total score (range, 0-3) indicates greater disability.29
Physical Performance. Measured using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which evaluates standing balance, sit to stand, and walking performance. Scores range from 0 to 4 on the balance, gait speed, and chair stand tests, for a total composite score between 0 and 12 (higher score indicates better performance).30
Physical Activity. Measured using actigraphy, namely a physical activity monitor adherent to the thigh (activ-PAL3TM, PAL Technologies Ltd., Glasgow, UK).31 Participants were instructed to wear the activPal for ≥ 1 week. Participants with a minimum of 5 days of wear were included in this analysis.
Data Analyses
Analyses were performed using SPSS software version 29.0.32 Continuous variables were summarized using mean (SD) or median and IQR using the weighted average method; categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages. Baseline scores on outcome variables were compared by categorical hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factor variables using Mann-Whitney U tests. The differences between outcome variables from baseline to endpoint were then calculated to produce change scores. Relationships between the number of PAT sessions attended and baseline outcomes and outcome change scores were estimated using Spearman correlations. Relationships between categorical factors (hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application) and outcome variable change scores (which were normally distributed) were examined using Mann-Whitney U tests. Relationships with continuous hospitalization (length of stay) and posthospital syndrome factors (medication changes) were estimated using Spearman correlations. Effect sizes (ES) were estimated with Cohen d; small (d = 0.2), medium (d = 0.5), or large (d ≥ 0.8). Missing data were handled using pairwise deletion.33 Therefore, sample sizes were reported for each analysis. For all statistical tests, P < .05 was considered significant.
Results
Twenty-four individuals completed the pilot intervention.15 Mean (SD) age was 73.6 (8.1) years (range, 64-93 years) and participants were predominantly White males (Table 1). Eight participants had a high school education only and 13 had more than a high school education. Diagnoses at admission included 9 patients with orthopedic/musculoskeletal conditions (6 were for joint replacement), 6 patients with vascular/pulmonary conditions, and 4 with gastrointestinal/renal/urological conditions. Of the 11 postsurgery participants, 7 were orthopedic, 4 were gastrointestinal, and 1 was peripheral vascular.
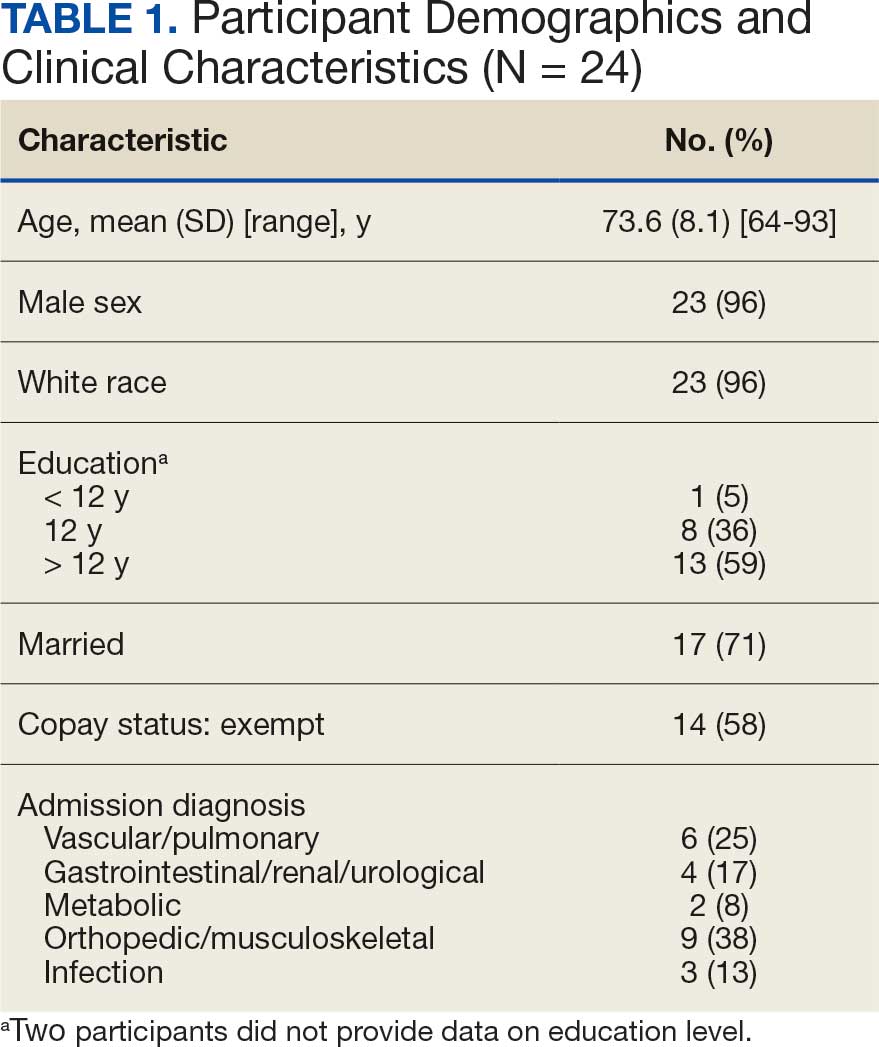
Baseline outcome scores did not differ significantly between groups, except individuals with moderate to severe pain interference reported a significantly lower IADL score (median [IQR] 4 [2-7]) than individuals with mild or moderate pain interference (median [IQR] 8 [7-8]; P = .02) (Table 2). The mean (SD) number of PAT sessions attended was 9.3 (3.7) (range, 3-19). There were no significant relationships between number of sessions attended and any baseline outcome variables or outcome change scores.
Hospitalization Factors
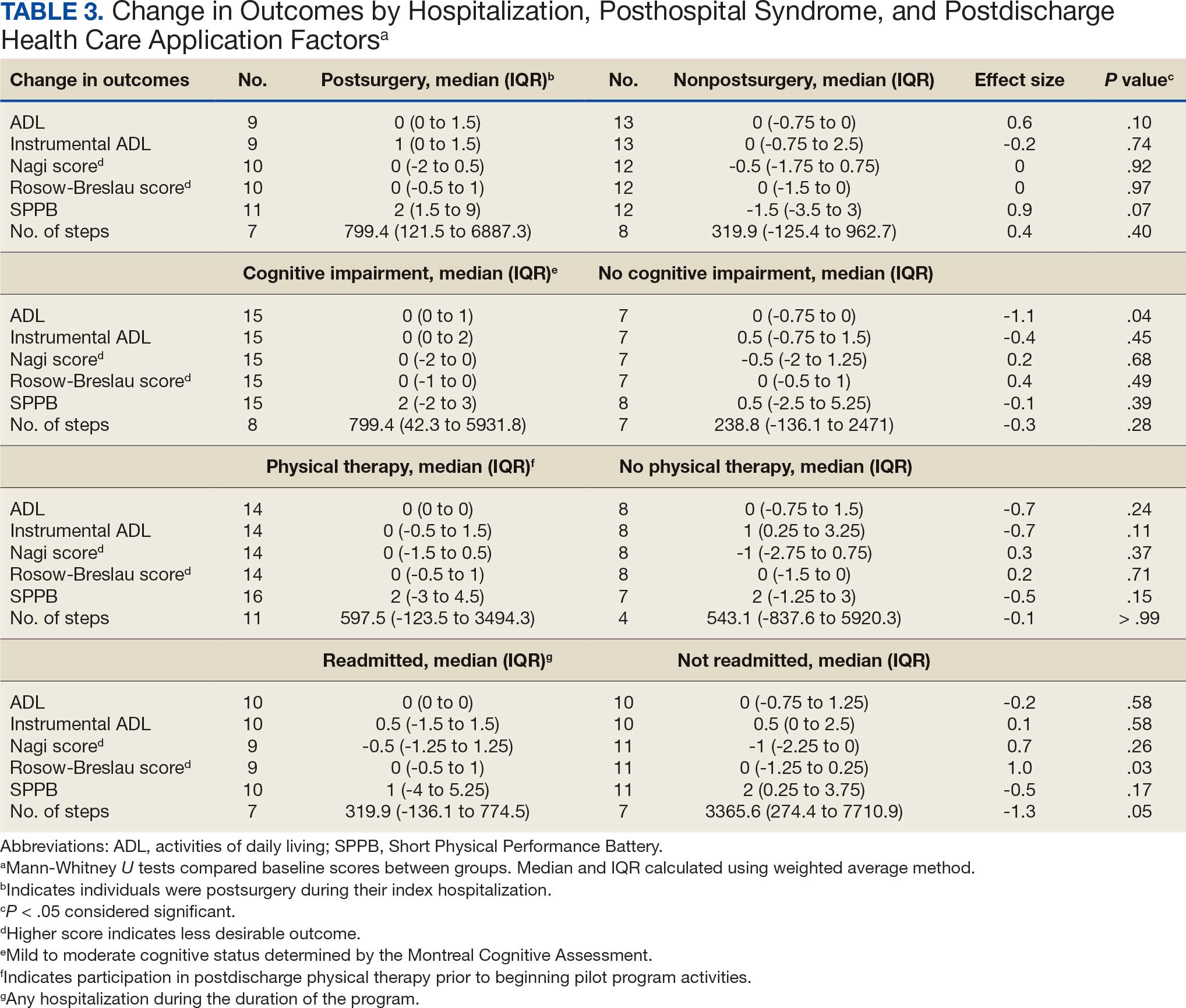
Participants who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvement than individuals who were nonpostsurgery in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1.5]; ES, 0.6; P = .10) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [1.5-9]; ES, 0.9; P = .07), but the improvements were not statistically significant (Table 3). Mean (SD) length of stay of the index hospitalization was 6.7 (6.1) days. Longer length of stay was significantly correlated with an increase in Nagi score (ρ, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.01-0.75). There were no other significant or trending relationships between length of stay and outcome variables.
Posthospital Syndrome Factors
The 16 participants with mild to moderate cognitive impairment had less improvement in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1]) than the 8 participants with no impairment (median [IQR] 0 [-0.75 to 0]; ES, -1.1; P = .04). Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint did not significantly differ between the 8 patients who reported a fall compared with the 13 who did not, nor were any trends observed. Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint also did not significantly differ between the 8 participants who reported no or mild pain interference compared with the 10 patients with moderate to severe pain interference, nor were any trends observed. Mean (SD) number of medication changes was 2.5 (1.6). Higher number of medication changes was significantly correlated with a decrease in Rosow-Breslau score (ρ, -0.47; 95% CI, -0.76 to -0.02). There were no other significant or trending relationships between number of medication changes and outcome variables.
Postdischarge Health Care Application Factors
The 16 participants who attended posthospital physical therapy trended towards less improvement in IADLs (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.5]; ES, -0.7; P = .11) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [-3.0 to 4.5]; ES, -0.5; P = .15) than the 8 patients with no postdischarge physical therapy. Eleven participants were readmitted, while 13 had no readmissions in their medical records between baseline and endpoint. Participants with ≥ 1 readmission experienced a greater increase in Rosow-Breslau score (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.0]) than those not readmitted (median [IQR] 0 [-1.25 to 0.25]; ES, 1.0; P = .03). Borderline greater improvement in number of steps was found in those not readmitted (median [IQR] 3365.6 [274.4-7710.9]) compared with those readmitted (median [IQR] 319.9 [-136.1 to 774.5]; ES, -1.3; P = .05). Patients who were readmitted also tended to have lower and not statistically significant improvements in SPPB (median [IQR] 1 [-4.0 to 5.3]) compared with those not readmitted (median [IQR] 2 [0.3-3.8]; ES, -0.5; P = .17) (Table 3).
Discussion
This study examined the association between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care use in patients undergoing a VVC-based intervention following hospital discharge. Participants who had no or mild cognitive impairment, no readmissions, higher medication changes, and a shorter hospital length of stay tended to experience lower disability, including in mobility and ADLs. This suggests individuals who are less clinically complex may be more likely to benefit from this type of virtual rehabilitation program. These findings are consistent with clinical experiences; home-based programs to improve physical activity posthospital discharge can be challenging for those who were medically ill (and did not undergo a specific surgical procedure), cognitively impaired, and become acutely ill and trigger hospital readmission. 15 For example, the sample in this study had higher rates of falls, pain, and readmissions compared to previous research.2,3,34-39
The importance of posthospital syndrome in the context of recovery of function and health at home following hospitalization is well documented.16-18 The potential impact of posthospital syndrome on physical activity-focused interventions is less understood. In our analysis, participants with mild or moderate cognitive impairment tended to become more dependent in their ADLs, while those with no cognitive impairment tended to become more independent in their ADLs. This functional decline over time is perhaps expected in persons with cognitive impairment, but the significant difference with a large ES warrants further consideration on how to tailor interventions to better promote functional recovery in these individuals.40,41 While some cognitive decline may not be preventable, this finding supports the need to promote healthy cognitive aging, identify declines in cognition, and work to mitigate additional decline. Programs specifically designed to promote function and physical activity in older adults with cognitive impairment are needed, especially during care transitions.41-43
While participants reported that falls and pain interference did not have a significant impact on change in outcomes between baseline and endpoint, these areas need further investigation. Falls and pain have been associated with function and physical activity in older adults.42-46 Pain is common, yet underappreciated during older adult hospital-to-home transitions.11,12,45,46 There is a need for more comprehensive assessment of pain (including pain intensity) and qualitative research.
Hospitalization and postdischarge health care application factors may have a significant impact on home-telehealth physical activity intervention success. Individuals who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvements in ADLs and physical performance. Most postsurgery participants had joint replacement surgery. Postsurgery status may not be modifiable, but it is important to note expected differences in recovery between medical and surgical admissions and the need to tailor care based on admission diagnosis. Those with a longer length of hospital stay may be considered at higher risk of suboptimal outcomes postdischarge, which indicates an opportunity for targeting resources and support, in addition to efforts of reducing length of stay where possible.47
Readmissions were significantly related to a change in Rosow-Breslau mobility disability score. This may indicate the detrimental impact a readmission can have on increasing mobility and physical activity postdischarge, or the potential of this pilot program to impact readmissions by increasing mobility and physical activity, contrary to prior physical exercise interventions.5,7,9,48 With 5% to 79% of readmissions considered preventable, continued efforts and program dissemination and implementation to address preventable readmissions are warranted.49 Individuals with postdischarge physical therapy (prior to beginning the pilot program) tended to demonstrate less improvement in disability and physical performance. This relationship needs further investigation; the 2 groups did not appear to have significant differences at baseline, albeit with a small sample size. It is possible they experienced initial improvements with postdischarge physical therapy and plateaued or had little further reserve to improve upon entering the VVC program.
Strengths and Limitations
This pilot program provided evaluative data on the use of VVC to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge. It included individual (eg, fall, pain, cognitive impairment) and health service (eg, readmission, physical therapy) level factors as predictors of function and physical activity posthospitalization.5,7,9,15-19
The results of this pilot project stem from a small sample lacking diversity in terms of race, ethnicity, and sex. There was some variation in baseline and endpoints between participants, and when hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors were collected. The majority of participants were recruited within a month postdischarge, and the program lasted about 6 months. Data collection was attempted at regular PAT contacts, but there was some variation in when visits occurred based on participant availability and preference. Some participants had missing data, which was handled using pairwise deletion.33 Larger studies are needed to confirm the findings of this study, particularly the trends that did not reach statistical significance. Home health services other than physical therapy (eg, nursing, occupational therapy) were not fully accounted for and should be considered in future research.
Conclusions
In patients undergoing a 6-month pilot VVC-based physical activity intervention posthospital discharge, improvements in mobility and disability were most likely in those who had no cognitive impairment and were not readmitted. Larger sample and qualitative investigations are necessary to optimize outcomes for patients who meet these clinical profiles.
- Liebzeit D, Bratzke L, Boltz M, Purvis S, King B. Getting back to normal: a grounded theory study of function in post-hospitalized older adults. Gerontologist. 2020;60:704-714. doi:10.1093/geront/gnz057
- Ponzetto M, Zanocchi M, Maero B, et al. Post-hospitalization mortality in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2003;36:83-91. doi:10.1016/s0167-4943(02)00061-4
- Buurman BM, Hoogerduijn JG, de Haan RJ, et al. Geriatric conditions in acutely hospitalized older patients: prevalence and one-year survival and functional decline. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026951
- Ponzetto M, Maero B, Maina P, et al. Risk factors for early and late mortality in hospitalized older patients: the continuing importance of functional status. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58:1049-1054. doi:10.1093/gerona/58.11.m1049
- Huang HT, Chang CM, Liu LF, Lin HS, Chen CH. Trajectories and predictors of functional decline of hospitalised older patients. J Clin Nurs. 2013;22:1322-1331. doi:10.1111/jocn.12055
- Boyd CM, Landefeld CS, Counsell SR, et al. Recovery of activities of daily living in older adults after hospitalization for acute medical illness. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:2171- 2179. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02023.x
- Helvik AS, Selbæk G, Engedal K. Functional decline in older adults one year after hospitalization. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57:305-310. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2013.05.008
- Zaslavsky O, Zisberg A, Shadmi E. Impact of functional change before and during hospitalization on functional recovery 1 month following hospitalization. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70:381-386. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu168
- Chen CC, Wang C, Huang GH. Functional trajectory 6 months posthospitalization: a cohort study of older hospitalized patients in Taiwan. Nurs Res. 2008;57:93-100. doi:10.1097/01.NNR.0000313485.18670.e2
- Kleinpell RM, Fletcher K, Jennings BM. Reducing functional decline in hospitalized elderly. In: Hughes RG, ed. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008. Accessed September 3, 2025. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2629/
- Liebzeit D, Rutkowski R, Arbaje AI, Fields B, Werner NE. A scoping review of interventions for older adults transitioning from hospital to home. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69:2950-2962. doi:10.1111/jgs.17323
- Hladkowicz E, Dumitrascu F, Auais M, et al. Evaluations of postoperative transitions in care for older adults: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:329. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02989-6
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA Video Connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21:502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Dawson R, Oliveira JS, Kwok WS, et al. Exercise interventions delivered through telehealth to improve physical functioning for older adults with frailty, cognitive, or mobility disability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30:940-950. doi:10.1089/tmj.2023.0177
- Liebzeit D, Phillips KK, Hogikyan RV, Cigolle CT, Alexander NB. A pilot home-telehealth program to enhance functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity in older adult veterans post-hospital discharge. Res Gerontol Nurs. 2024;17:271-279. doi:10.3928/19404921-20241105-01
- Krumholz HM. Post-hospital syndrome—an acquired, transient condition of generalized risk. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:100-102. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1212324
- Caraballo C, Dharmarajan K, Krumholz HM. Post hospital syndrome: is the stress of hospitalization causing harm? Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2019;72:896-898. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2019.04.010
- Rawal S, Kwan JL, Razak F, et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:38- 45. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.5100
- Dutzi I, Schwenk M, Kirchner M, Jooss E, Bauer JM, Hauer K. Influence of cognitive impairment on rehabilitation received and its mediating effect on functional recovery. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;84:745-756. doi:10.3233/JAD-210620
- Uriz-Otano F, Uriz-Otano JI, Malafarina V. Factors associated with short-term functional recovery in elderly people with a hip fracture. Influence ofcognitiveimpairment. JAmMedDirAssoc. 2015;16:215-220. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.09.009
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
- White RS, Jiang J, Hall CB, et al. Higher perceived stress scale scores are associated with higher pain intensity and pain interference levels in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:2350-2356. doi:10.1111/jgs.13135
- Blyth FM, March LM, Brnabic AJ, et al. Chronic pain in Australia: a prevalence study. Pain. 2001;89:127-134. doi:10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00355-9
- Thomas E, Peat G, Harris L, Wilkie R, Croft PR. The prevalence of pain and pain interference in a general population of older adults: cross-sectional findings from the North Staffordshire Osteoarthritis Project (NorStOP). Pain. 2004;110:361-368. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.04.017
- Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA. 1963;185:914-919. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120024016
- Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179-186.
- Alexander NB, Guire KE, Thelen DG, et al. Self-reported walking ability predicts functional mobility performance in frail older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000;48:1408-1413. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb02630.x
- Rosow I, Breslau N. A Guttman health scale for the aged. J Gerontol. 1966;21:556-559. doi:10.1093/geronj/21.4.556
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49:M85-M94. doi:10.1093/geronj/49.2.m85
- Chan CS, Slaughter SE, Jones CA, Ickert C, Wagg AS. Measuring activity performance of older adults using the activPAL: a rapid review. Healthcare (Basel). 2017;5:94. doi:10.3390/healthcare5040094
- IBM SPSS software. IBM Corp; 2019. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.ibm.com/spss
- Kang H. The prevention and handling of the missing data. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013;64:402-406. doi:10.4097/kjae.2013.64.5.402
- Epstein AM, Jha AK, Orav EJ. The relationship between hospital admission rates and rehospitalizations. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2287-2295. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1101942
- Bogaisky M, Dezieck L. Early hospital readmission of nursing home residents and community-dwelling elderly adults discharged from the geriatrics service of an urban teaching hospital: patterns and risk factors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:548-552. doi:10.1111/jgs.13317
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1418-1428. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0803563
- Hoyer EH, Needham DM, Atanelov L, Knox B, Friedman M, Brotman DJ. Association of impaired functional status at hospital discharge and subsequent rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2014;9:277-282. doi:10.1002/jhm.2152
- Mahoney J, Sager M, Dunham NC, Johnson J. Risk of falls after hospital discharge. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42:269- 274. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1994.tb01750.x
- Hoffman GJ, Liu H, Alexander NB, Tinetti M, Braun TM, Min LC. Posthospital fall injuries and 30-day readmissions in adults 65 years and older. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e194276. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4276
- Gill DP, Hubbard RA, Koepsell TD, et al. Differences in rate of functional decline across three dementia types. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:S63-S71. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.10.010
- Auyeung TW, Kwok T, Lee J, Leung PC, Leung J, Woo J. Functional decline in cognitive impairment–the relationship between physical and cognitive function. Neuroepidemiology. 2008;31:167-173. doi:10.1159/000154929
- Patti A, Zangla D, Sahin FN, et al. Physical exercise and prevention of falls. Effects of a Pilates training method compared with a general physical activity program. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e25289. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025289
- Nagarkar A, Kulkarni S. Association between daily activities and fall in older adults: an analysis of longitudinal ageing study in India (2017-18). BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:203. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02879-x
- Ek S, Rizzuto D, Xu W, Calderón-Larrañaga A, Welmer AK. Predictors for functional decline after an injurious fall: a population-based cohort study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33:2183-2190. doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01747-1
- Dagnino APA, Campos MM. Chronic pain in the elderly: mechanisms and perspectives. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:736688. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2022.736688
- Ritchie CS, Patel K, Boscardin J, et al. Impact of persistent pain on function, cognition, and well-being of older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71:26-35. doi:10.1111/jgs.18125
- Han TS, Murray P, Robin J, et al. Evaluation of the association of length of stay in hospital and outcomes. Int J Qual Health Care. 2022;34:mzab160. doi:10.1093/intqhc/ mzab160
- Lærum-Onsager E, Molin M, Olsen CF, et al. Effect of nutritional and physical exercise intervention on hospital readmission for patients aged 65 or older: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021;18:62. doi:10.1186/s12966-021-01123-w
- Van Walraven C, Bennett C, Jennings A, Austin PC, Forster AJ. Proportion of hospital readmissions deemed avoidable: a systematic review. CMAJ. 2011;183:E391-E402. doi:10.1503/cmaj.101860
Deconditioning among hospitalized older adults contributes to significant decline in posthospitalization functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity.1-10 Previous hospital-to-home interventions have targeted improving function and physical activity, including recent programs leveraging home telehealth as a feasible and potentially effective mode of delivering in-home exercise and rehabilitation.11-14 However, pilot interventions have shown mixed effectiveness.11,12,14 This study expands on a previously published intervention describing a pilot home telehealth program for veterans posthospital discharge that demonstrated significant 6-month improvement in physical activity as well as trends in physical function improvement, including among those with cognitive impairment.15 Factors that contribute to improved outcomes are the focus of the present study.
Key factors underlying the complexity of hospital-to-home transitions include hospitalization elements (ie, reason for admission and length of stay), associated posthospital syndromes (ie, postdischarge falls, medication changes, cognitive impairment, and pain), and postdischarge health care application (ie, physical therapy and hospital readmission).16-18 These factors may be associated with postdischarge functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity, but their direct influence on intervention outcomes is unclear (Figure 1).5,7,9,16-20 The objective of this study was to examine the influence of hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors on outcomes of a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Video Connect (VVC) intervention to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge.

health care application factors on physical activity, functional ability, and
physical performance intervention outcomes.
Methods
The previous analysis reported on patient characteristics, program feasibility, and preliminary outcomes.13,15 The current study reports on relationships between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors and change in key outcomes, namely postdischarge self-reported functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity from baseline to endpoint.
Participants provided written informed consent. The protocol and consent forms were approved by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) Research and Development Committee, and the project was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04045054).
Intervention
The pilot program targeted older adults following recent hospital discharge from VAAAHS. Participants were eligible if they were aged ≥ 50 years, had been discharged following an inpatient stay in the past 1 to 2 weeks, evaluated by physical therapy during hospitalization with stated rehabilitation goals on discharge, and followed by a VAAAHS primary care physician. Participants were either recruited during hospital admission or shortly after discharge.13
An experienced physical activity trainer (PAT) supported the progression of participants’ rehabilitation goals via a home exercise program and coached the patient and caregiver to optimize functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity. The PAT was a nonlicensed research assistant with extensive experience in applying standard physical activity enhancement protocols (eg, increased walking) to older adults with comorbidities. Participation in the program lasted about 6 months. Initiation of the PAT program was delayed if the patient was already receiving postdischarge home-based or outpatient physical therapy. The PAT contacted the patient weekly via VVC for the first 6 weeks, then monthly for a total of 6 months. Each contact included information on optimal walking form, injury prevention, program progression, and ways to incorporate sit-to-stand transitions, nonsitting behavior, and walking into daily routines. The initial VVC contact lasted about 60 minutes and subsequent sessions lasted about 30 minutes.13
Demographic characteristics were self-reported by participants and included age, sex, race, years of education, and marital status. Clinical characteristics were obtained from each participant’s electronic health record (EHR), including copay status, index hospitalization length of stay, admission diagnosis, and postsurgery status (postsurgery vs nonpostsurgery). Intervention adherence was tracked as the number of PAT sessions attended.
Posthospital Syndrome Factors
Participant falls (categorized as those who reported a fall vs those who did not) and medication changes (number of changes reported, including new medication, discontinued medication, dose changes, medication changes, or changes in medication schedule) were reported by participants or caregivers during each VVC contact. Participants completed the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) at baseline, and were dichotomized into 2 groups: no cognitive impairment (MoCA score ≥ 26) and mild to moderate cognitive impairment (MoCA score 10-25).13,21
Participants rated how much pain interfered with their normal daily activities since the previous VVC session on a 5-point Likert scale (1, not at all; to 5, extremely).22 Similar to prior research, participants were placed into 2 groups based on their mean pain interference score (individuals with scores from 1.0 to 2.0 in 1 group, and individuals with > 2.0 in another).23-25 Participants were separated into a no or mild pain interference group and a moderate to severe pain interference group. Hospital readmissions (VA and non-VA) and postdischarge physical therapy outcomes were obtained from the participant’s EHR, including primary care visits.
Outcomes
Outcomes were collected at baseline (posthospital discharge) and 6 months postenrollment.
Self-Reported Functional Ability. This measure is provided by participants or caregivers and measured by the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living (ADL), Lawton and Brody Instrumental ADL Scale (IADL), Nagi Disability Model, and Rosow-Breslau Scale. The Katz ADL assesses the ability to complete 6 self-care activities and awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-6).26 The Lawton and Brody IADL measures an individual’s independence in 8 instrumental ADLs; it awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-8).27 The Nagi Disability Model evaluates an individual’s difficulty performing 5 tasks (total score range, 0-5) and tallies the number of items with a response other than “no difficulty at all” (higher total score indicates greater difficulty). 28 The Rosow-Breslau Scale is a 3-item measure of mobility disability; individual responses are 0 (no help) and 1 (requires help or unable); higher total score (range, 0-3) indicates greater disability.29
Physical Performance. Measured using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which evaluates standing balance, sit to stand, and walking performance. Scores range from 0 to 4 on the balance, gait speed, and chair stand tests, for a total composite score between 0 and 12 (higher score indicates better performance).30
Physical Activity. Measured using actigraphy, namely a physical activity monitor adherent to the thigh (activ-PAL3TM, PAL Technologies Ltd., Glasgow, UK).31 Participants were instructed to wear the activPal for ≥ 1 week. Participants with a minimum of 5 days of wear were included in this analysis.
Data Analyses
Analyses were performed using SPSS software version 29.0.32 Continuous variables were summarized using mean (SD) or median and IQR using the weighted average method; categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages. Baseline scores on outcome variables were compared by categorical hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factor variables using Mann-Whitney U tests. The differences between outcome variables from baseline to endpoint were then calculated to produce change scores. Relationships between the number of PAT sessions attended and baseline outcomes and outcome change scores were estimated using Spearman correlations. Relationships between categorical factors (hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application) and outcome variable change scores (which were normally distributed) were examined using Mann-Whitney U tests. Relationships with continuous hospitalization (length of stay) and posthospital syndrome factors (medication changes) were estimated using Spearman correlations. Effect sizes (ES) were estimated with Cohen d; small (d = 0.2), medium (d = 0.5), or large (d ≥ 0.8). Missing data were handled using pairwise deletion.33 Therefore, sample sizes were reported for each analysis. For all statistical tests, P < .05 was considered significant.
Results
Twenty-four individuals completed the pilot intervention.15 Mean (SD) age was 73.6 (8.1) years (range, 64-93 years) and participants were predominantly White males (Table 1). Eight participants had a high school education only and 13 had more than a high school education. Diagnoses at admission included 9 patients with orthopedic/musculoskeletal conditions (6 were for joint replacement), 6 patients with vascular/pulmonary conditions, and 4 with gastrointestinal/renal/urological conditions. Of the 11 postsurgery participants, 7 were orthopedic, 4 were gastrointestinal, and 1 was peripheral vascular.

Baseline outcome scores did not differ significantly between groups, except individuals with moderate to severe pain interference reported a significantly lower IADL score (median [IQR] 4 [2-7]) than individuals with mild or moderate pain interference (median [IQR] 8 [7-8]; P = .02) (Table 2). The mean (SD) number of PAT sessions attended was 9.3 (3.7) (range, 3-19). There were no significant relationships between number of sessions attended and any baseline outcome variables or outcome change scores.

Hospitalization Factors
Participants who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvement than individuals who were nonpostsurgery in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1.5]; ES, 0.6; P = .10) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [1.5-9]; ES, 0.9; P = .07), but the improvements were not statistically significant (Table 3). Mean (SD) length of stay of the index hospitalization was 6.7 (6.1) days. Longer length of stay was significantly correlated with an increase in Nagi score (ρ, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.01-0.75). There were no other significant or trending relationships between length of stay and outcome variables.

Posthospital Syndrome Factors
The 16 participants with mild to moderate cognitive impairment had less improvement in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1]) than the 8 participants with no impairment (median [IQR] 0 [-0.75 to 0]; ES, -1.1; P = .04). Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint did not significantly differ between the 8 patients who reported a fall compared with the 13 who did not, nor were any trends observed. Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint also did not significantly differ between the 8 participants who reported no or mild pain interference compared with the 10 patients with moderate to severe pain interference, nor were any trends observed. Mean (SD) number of medication changes was 2.5 (1.6). Higher number of medication changes was significantly correlated with a decrease in Rosow-Breslau score (ρ, -0.47; 95% CI, -0.76 to -0.02). There were no other significant or trending relationships between number of medication changes and outcome variables.
Postdischarge Health Care Application Factors
The 16 participants who attended posthospital physical therapy trended towards less improvement in IADLs (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.5]; ES, -0.7; P = .11) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [-3.0 to 4.5]; ES, -0.5; P = .15) than the 8 patients with no postdischarge physical therapy. Eleven participants were readmitted, while 13 had no readmissions in their medical records between baseline and endpoint. Participants with ≥ 1 readmission experienced a greater increase in Rosow-Breslau score (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.0]) than those not readmitted (median [IQR] 0 [-1.25 to 0.25]; ES, 1.0; P = .03). Borderline greater improvement in number of steps was found in those not readmitted (median [IQR] 3365.6 [274.4-7710.9]) compared with those readmitted (median [IQR] 319.9 [-136.1 to 774.5]; ES, -1.3; P = .05). Patients who were readmitted also tended to have lower and not statistically significant improvements in SPPB (median [IQR] 1 [-4.0 to 5.3]) compared with those not readmitted (median [IQR] 2 [0.3-3.8]; ES, -0.5; P = .17) (Table 3).
Discussion
This study examined the association between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care use in patients undergoing a VVC-based intervention following hospital discharge. Participants who had no or mild cognitive impairment, no readmissions, higher medication changes, and a shorter hospital length of stay tended to experience lower disability, including in mobility and ADLs. This suggests individuals who are less clinically complex may be more likely to benefit from this type of virtual rehabilitation program. These findings are consistent with clinical experiences; home-based programs to improve physical activity posthospital discharge can be challenging for those who were medically ill (and did not undergo a specific surgical procedure), cognitively impaired, and become acutely ill and trigger hospital readmission. 15 For example, the sample in this study had higher rates of falls, pain, and readmissions compared to previous research.2,3,34-39
The importance of posthospital syndrome in the context of recovery of function and health at home following hospitalization is well documented.16-18 The potential impact of posthospital syndrome on physical activity-focused interventions is less understood. In our analysis, participants with mild or moderate cognitive impairment tended to become more dependent in their ADLs, while those with no cognitive impairment tended to become more independent in their ADLs. This functional decline over time is perhaps expected in persons with cognitive impairment, but the significant difference with a large ES warrants further consideration on how to tailor interventions to better promote functional recovery in these individuals.40,41 While some cognitive decline may not be preventable, this finding supports the need to promote healthy cognitive aging, identify declines in cognition, and work to mitigate additional decline. Programs specifically designed to promote function and physical activity in older adults with cognitive impairment are needed, especially during care transitions.41-43
While participants reported that falls and pain interference did not have a significant impact on change in outcomes between baseline and endpoint, these areas need further investigation. Falls and pain have been associated with function and physical activity in older adults.42-46 Pain is common, yet underappreciated during older adult hospital-to-home transitions.11,12,45,46 There is a need for more comprehensive assessment of pain (including pain intensity) and qualitative research.
Hospitalization and postdischarge health care application factors may have a significant impact on home-telehealth physical activity intervention success. Individuals who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvements in ADLs and physical performance. Most postsurgery participants had joint replacement surgery. Postsurgery status may not be modifiable, but it is important to note expected differences in recovery between medical and surgical admissions and the need to tailor care based on admission diagnosis. Those with a longer length of hospital stay may be considered at higher risk of suboptimal outcomes postdischarge, which indicates an opportunity for targeting resources and support, in addition to efforts of reducing length of stay where possible.47
Readmissions were significantly related to a change in Rosow-Breslau mobility disability score. This may indicate the detrimental impact a readmission can have on increasing mobility and physical activity postdischarge, or the potential of this pilot program to impact readmissions by increasing mobility and physical activity, contrary to prior physical exercise interventions.5,7,9,48 With 5% to 79% of readmissions considered preventable, continued efforts and program dissemination and implementation to address preventable readmissions are warranted.49 Individuals with postdischarge physical therapy (prior to beginning the pilot program) tended to demonstrate less improvement in disability and physical performance. This relationship needs further investigation; the 2 groups did not appear to have significant differences at baseline, albeit with a small sample size. It is possible they experienced initial improvements with postdischarge physical therapy and plateaued or had little further reserve to improve upon entering the VVC program.
Strengths and Limitations
This pilot program provided evaluative data on the use of VVC to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge. It included individual (eg, fall, pain, cognitive impairment) and health service (eg, readmission, physical therapy) level factors as predictors of function and physical activity posthospitalization.5,7,9,15-19
The results of this pilot project stem from a small sample lacking diversity in terms of race, ethnicity, and sex. There was some variation in baseline and endpoints between participants, and when hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors were collected. The majority of participants were recruited within a month postdischarge, and the program lasted about 6 months. Data collection was attempted at regular PAT contacts, but there was some variation in when visits occurred based on participant availability and preference. Some participants had missing data, which was handled using pairwise deletion.33 Larger studies are needed to confirm the findings of this study, particularly the trends that did not reach statistical significance. Home health services other than physical therapy (eg, nursing, occupational therapy) were not fully accounted for and should be considered in future research.
Conclusions
In patients undergoing a 6-month pilot VVC-based physical activity intervention posthospital discharge, improvements in mobility and disability were most likely in those who had no cognitive impairment and were not readmitted. Larger sample and qualitative investigations are necessary to optimize outcomes for patients who meet these clinical profiles.
Deconditioning among hospitalized older adults contributes to significant decline in posthospitalization functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity.1-10 Previous hospital-to-home interventions have targeted improving function and physical activity, including recent programs leveraging home telehealth as a feasible and potentially effective mode of delivering in-home exercise and rehabilitation.11-14 However, pilot interventions have shown mixed effectiveness.11,12,14 This study expands on a previously published intervention describing a pilot home telehealth program for veterans posthospital discharge that demonstrated significant 6-month improvement in physical activity as well as trends in physical function improvement, including among those with cognitive impairment.15 Factors that contribute to improved outcomes are the focus of the present study.
Key factors underlying the complexity of hospital-to-home transitions include hospitalization elements (ie, reason for admission and length of stay), associated posthospital syndromes (ie, postdischarge falls, medication changes, cognitive impairment, and pain), and postdischarge health care application (ie, physical therapy and hospital readmission).16-18 These factors may be associated with postdischarge functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity, but their direct influence on intervention outcomes is unclear (Figure 1).5,7,9,16-20 The objective of this study was to examine the influence of hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors on outcomes of a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Video Connect (VVC) intervention to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge.

health care application factors on physical activity, functional ability, and
physical performance intervention outcomes.
Methods
The previous analysis reported on patient characteristics, program feasibility, and preliminary outcomes.13,15 The current study reports on relationships between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors and change in key outcomes, namely postdischarge self-reported functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity from baseline to endpoint.
Participants provided written informed consent. The protocol and consent forms were approved by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) Research and Development Committee, and the project was registered on clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04045054).
Intervention
The pilot program targeted older adults following recent hospital discharge from VAAAHS. Participants were eligible if they were aged ≥ 50 years, had been discharged following an inpatient stay in the past 1 to 2 weeks, evaluated by physical therapy during hospitalization with stated rehabilitation goals on discharge, and followed by a VAAAHS primary care physician. Participants were either recruited during hospital admission or shortly after discharge.13
An experienced physical activity trainer (PAT) supported the progression of participants’ rehabilitation goals via a home exercise program and coached the patient and caregiver to optimize functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity. The PAT was a nonlicensed research assistant with extensive experience in applying standard physical activity enhancement protocols (eg, increased walking) to older adults with comorbidities. Participation in the program lasted about 6 months. Initiation of the PAT program was delayed if the patient was already receiving postdischarge home-based or outpatient physical therapy. The PAT contacted the patient weekly via VVC for the first 6 weeks, then monthly for a total of 6 months. Each contact included information on optimal walking form, injury prevention, program progression, and ways to incorporate sit-to-stand transitions, nonsitting behavior, and walking into daily routines. The initial VVC contact lasted about 60 minutes and subsequent sessions lasted about 30 minutes.13
Demographic characteristics were self-reported by participants and included age, sex, race, years of education, and marital status. Clinical characteristics were obtained from each participant’s electronic health record (EHR), including copay status, index hospitalization length of stay, admission diagnosis, and postsurgery status (postsurgery vs nonpostsurgery). Intervention adherence was tracked as the number of PAT sessions attended.
Posthospital Syndrome Factors
Participant falls (categorized as those who reported a fall vs those who did not) and medication changes (number of changes reported, including new medication, discontinued medication, dose changes, medication changes, or changes in medication schedule) were reported by participants or caregivers during each VVC contact. Participants completed the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) at baseline, and were dichotomized into 2 groups: no cognitive impairment (MoCA score ≥ 26) and mild to moderate cognitive impairment (MoCA score 10-25).13,21
Participants rated how much pain interfered with their normal daily activities since the previous VVC session on a 5-point Likert scale (1, not at all; to 5, extremely).22 Similar to prior research, participants were placed into 2 groups based on their mean pain interference score (individuals with scores from 1.0 to 2.0 in 1 group, and individuals with > 2.0 in another).23-25 Participants were separated into a no or mild pain interference group and a moderate to severe pain interference group. Hospital readmissions (VA and non-VA) and postdischarge physical therapy outcomes were obtained from the participant’s EHR, including primary care visits.
Outcomes
Outcomes were collected at baseline (posthospital discharge) and 6 months postenrollment.
Self-Reported Functional Ability. This measure is provided by participants or caregivers and measured by the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living (ADL), Lawton and Brody Instrumental ADL Scale (IADL), Nagi Disability Model, and Rosow-Breslau Scale. The Katz ADL assesses the ability to complete 6 self-care activities and awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-6).26 The Lawton and Brody IADL measures an individual’s independence in 8 instrumental ADLs; it awards 1 point for independence and 0 if the individual is dependent (total score range, 0-8).27 The Nagi Disability Model evaluates an individual’s difficulty performing 5 tasks (total score range, 0-5) and tallies the number of items with a response other than “no difficulty at all” (higher total score indicates greater difficulty). 28 The Rosow-Breslau Scale is a 3-item measure of mobility disability; individual responses are 0 (no help) and 1 (requires help or unable); higher total score (range, 0-3) indicates greater disability.29
Physical Performance. Measured using the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), which evaluates standing balance, sit to stand, and walking performance. Scores range from 0 to 4 on the balance, gait speed, and chair stand tests, for a total composite score between 0 and 12 (higher score indicates better performance).30
Physical Activity. Measured using actigraphy, namely a physical activity monitor adherent to the thigh (activ-PAL3TM, PAL Technologies Ltd., Glasgow, UK).31 Participants were instructed to wear the activPal for ≥ 1 week. Participants with a minimum of 5 days of wear were included in this analysis.
Data Analyses
Analyses were performed using SPSS software version 29.0.32 Continuous variables were summarized using mean (SD) or median and IQR using the weighted average method; categorical variables were summarized using frequencies and percentages. Baseline scores on outcome variables were compared by categorical hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factor variables using Mann-Whitney U tests. The differences between outcome variables from baseline to endpoint were then calculated to produce change scores. Relationships between the number of PAT sessions attended and baseline outcomes and outcome change scores were estimated using Spearman correlations. Relationships between categorical factors (hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application) and outcome variable change scores (which were normally distributed) were examined using Mann-Whitney U tests. Relationships with continuous hospitalization (length of stay) and posthospital syndrome factors (medication changes) were estimated using Spearman correlations. Effect sizes (ES) were estimated with Cohen d; small (d = 0.2), medium (d = 0.5), or large (d ≥ 0.8). Missing data were handled using pairwise deletion.33 Therefore, sample sizes were reported for each analysis. For all statistical tests, P < .05 was considered significant.
Results
Twenty-four individuals completed the pilot intervention.15 Mean (SD) age was 73.6 (8.1) years (range, 64-93 years) and participants were predominantly White males (Table 1). Eight participants had a high school education only and 13 had more than a high school education. Diagnoses at admission included 9 patients with orthopedic/musculoskeletal conditions (6 were for joint replacement), 6 patients with vascular/pulmonary conditions, and 4 with gastrointestinal/renal/urological conditions. Of the 11 postsurgery participants, 7 were orthopedic, 4 were gastrointestinal, and 1 was peripheral vascular.

Baseline outcome scores did not differ significantly between groups, except individuals with moderate to severe pain interference reported a significantly lower IADL score (median [IQR] 4 [2-7]) than individuals with mild or moderate pain interference (median [IQR] 8 [7-8]; P = .02) (Table 2). The mean (SD) number of PAT sessions attended was 9.3 (3.7) (range, 3-19). There were no significant relationships between number of sessions attended and any baseline outcome variables or outcome change scores.

Hospitalization Factors
Participants who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvement than individuals who were nonpostsurgery in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1.5]; ES, 0.6; P = .10) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [1.5-9]; ES, 0.9; P = .07), but the improvements were not statistically significant (Table 3). Mean (SD) length of stay of the index hospitalization was 6.7 (6.1) days. Longer length of stay was significantly correlated with an increase in Nagi score (ρ, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.01-0.75). There were no other significant or trending relationships between length of stay and outcome variables.

Posthospital Syndrome Factors
The 16 participants with mild to moderate cognitive impairment had less improvement in ADLs (median [IQR] 0 [0-1]) than the 8 participants with no impairment (median [IQR] 0 [-0.75 to 0]; ES, -1.1; P = .04). Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint did not significantly differ between the 8 patients who reported a fall compared with the 13 who did not, nor were any trends observed. Change in outcome variables from baseline to endpoint also did not significantly differ between the 8 participants who reported no or mild pain interference compared with the 10 patients with moderate to severe pain interference, nor were any trends observed. Mean (SD) number of medication changes was 2.5 (1.6). Higher number of medication changes was significantly correlated with a decrease in Rosow-Breslau score (ρ, -0.47; 95% CI, -0.76 to -0.02). There were no other significant or trending relationships between number of medication changes and outcome variables.
Postdischarge Health Care Application Factors
The 16 participants who attended posthospital physical therapy trended towards less improvement in IADLs (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.5]; ES, -0.7; P = .11) and SPPB (median [IQR] 2 [-3.0 to 4.5]; ES, -0.5; P = .15) than the 8 patients with no postdischarge physical therapy. Eleven participants were readmitted, while 13 had no readmissions in their medical records between baseline and endpoint. Participants with ≥ 1 readmission experienced a greater increase in Rosow-Breslau score (median [IQR] 0 [-0.5 to 1.0]) than those not readmitted (median [IQR] 0 [-1.25 to 0.25]; ES, 1.0; P = .03). Borderline greater improvement in number of steps was found in those not readmitted (median [IQR] 3365.6 [274.4-7710.9]) compared with those readmitted (median [IQR] 319.9 [-136.1 to 774.5]; ES, -1.3; P = .05). Patients who were readmitted also tended to have lower and not statistically significant improvements in SPPB (median [IQR] 1 [-4.0 to 5.3]) compared with those not readmitted (median [IQR] 2 [0.3-3.8]; ES, -0.5; P = .17) (Table 3).
Discussion
This study examined the association between hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care use in patients undergoing a VVC-based intervention following hospital discharge. Participants who had no or mild cognitive impairment, no readmissions, higher medication changes, and a shorter hospital length of stay tended to experience lower disability, including in mobility and ADLs. This suggests individuals who are less clinically complex may be more likely to benefit from this type of virtual rehabilitation program. These findings are consistent with clinical experiences; home-based programs to improve physical activity posthospital discharge can be challenging for those who were medically ill (and did not undergo a specific surgical procedure), cognitively impaired, and become acutely ill and trigger hospital readmission. 15 For example, the sample in this study had higher rates of falls, pain, and readmissions compared to previous research.2,3,34-39
The importance of posthospital syndrome in the context of recovery of function and health at home following hospitalization is well documented.16-18 The potential impact of posthospital syndrome on physical activity-focused interventions is less understood. In our analysis, participants with mild or moderate cognitive impairment tended to become more dependent in their ADLs, while those with no cognitive impairment tended to become more independent in their ADLs. This functional decline over time is perhaps expected in persons with cognitive impairment, but the significant difference with a large ES warrants further consideration on how to tailor interventions to better promote functional recovery in these individuals.40,41 While some cognitive decline may not be preventable, this finding supports the need to promote healthy cognitive aging, identify declines in cognition, and work to mitigate additional decline. Programs specifically designed to promote function and physical activity in older adults with cognitive impairment are needed, especially during care transitions.41-43
While participants reported that falls and pain interference did not have a significant impact on change in outcomes between baseline and endpoint, these areas need further investigation. Falls and pain have been associated with function and physical activity in older adults.42-46 Pain is common, yet underappreciated during older adult hospital-to-home transitions.11,12,45,46 There is a need for more comprehensive assessment of pain (including pain intensity) and qualitative research.
Hospitalization and postdischarge health care application factors may have a significant impact on home-telehealth physical activity intervention success. Individuals who were postsurgery tended to have greater improvements in ADLs and physical performance. Most postsurgery participants had joint replacement surgery. Postsurgery status may not be modifiable, but it is important to note expected differences in recovery between medical and surgical admissions and the need to tailor care based on admission diagnosis. Those with a longer length of hospital stay may be considered at higher risk of suboptimal outcomes postdischarge, which indicates an opportunity for targeting resources and support, in addition to efforts of reducing length of stay where possible.47
Readmissions were significantly related to a change in Rosow-Breslau mobility disability score. This may indicate the detrimental impact a readmission can have on increasing mobility and physical activity postdischarge, or the potential of this pilot program to impact readmissions by increasing mobility and physical activity, contrary to prior physical exercise interventions.5,7,9,48 With 5% to 79% of readmissions considered preventable, continued efforts and program dissemination and implementation to address preventable readmissions are warranted.49 Individuals with postdischarge physical therapy (prior to beginning the pilot program) tended to demonstrate less improvement in disability and physical performance. This relationship needs further investigation; the 2 groups did not appear to have significant differences at baseline, albeit with a small sample size. It is possible they experienced initial improvements with postdischarge physical therapy and plateaued or had little further reserve to improve upon entering the VVC program.
Strengths and Limitations
This pilot program provided evaluative data on the use of VVC to enhance function and physical activity in older adults posthospital discharge. It included individual (eg, fall, pain, cognitive impairment) and health service (eg, readmission, physical therapy) level factors as predictors of function and physical activity posthospitalization.5,7,9,15-19
The results of this pilot project stem from a small sample lacking diversity in terms of race, ethnicity, and sex. There was some variation in baseline and endpoints between participants, and when hospitalization, posthospital syndrome, and postdischarge health care application factors were collected. The majority of participants were recruited within a month postdischarge, and the program lasted about 6 months. Data collection was attempted at regular PAT contacts, but there was some variation in when visits occurred based on participant availability and preference. Some participants had missing data, which was handled using pairwise deletion.33 Larger studies are needed to confirm the findings of this study, particularly the trends that did not reach statistical significance. Home health services other than physical therapy (eg, nursing, occupational therapy) were not fully accounted for and should be considered in future research.
Conclusions
In patients undergoing a 6-month pilot VVC-based physical activity intervention posthospital discharge, improvements in mobility and disability were most likely in those who had no cognitive impairment and were not readmitted. Larger sample and qualitative investigations are necessary to optimize outcomes for patients who meet these clinical profiles.
- Liebzeit D, Bratzke L, Boltz M, Purvis S, King B. Getting back to normal: a grounded theory study of function in post-hospitalized older adults. Gerontologist. 2020;60:704-714. doi:10.1093/geront/gnz057
- Ponzetto M, Zanocchi M, Maero B, et al. Post-hospitalization mortality in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2003;36:83-91. doi:10.1016/s0167-4943(02)00061-4
- Buurman BM, Hoogerduijn JG, de Haan RJ, et al. Geriatric conditions in acutely hospitalized older patients: prevalence and one-year survival and functional decline. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026951
- Ponzetto M, Maero B, Maina P, et al. Risk factors for early and late mortality in hospitalized older patients: the continuing importance of functional status. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58:1049-1054. doi:10.1093/gerona/58.11.m1049
- Huang HT, Chang CM, Liu LF, Lin HS, Chen CH. Trajectories and predictors of functional decline of hospitalised older patients. J Clin Nurs. 2013;22:1322-1331. doi:10.1111/jocn.12055
- Boyd CM, Landefeld CS, Counsell SR, et al. Recovery of activities of daily living in older adults after hospitalization for acute medical illness. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:2171- 2179. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02023.x
- Helvik AS, Selbæk G, Engedal K. Functional decline in older adults one year after hospitalization. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57:305-310. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2013.05.008
- Zaslavsky O, Zisberg A, Shadmi E. Impact of functional change before and during hospitalization on functional recovery 1 month following hospitalization. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70:381-386. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu168
- Chen CC, Wang C, Huang GH. Functional trajectory 6 months posthospitalization: a cohort study of older hospitalized patients in Taiwan. Nurs Res. 2008;57:93-100. doi:10.1097/01.NNR.0000313485.18670.e2
- Kleinpell RM, Fletcher K, Jennings BM. Reducing functional decline in hospitalized elderly. In: Hughes RG, ed. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008. Accessed September 3, 2025. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2629/
- Liebzeit D, Rutkowski R, Arbaje AI, Fields B, Werner NE. A scoping review of interventions for older adults transitioning from hospital to home. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69:2950-2962. doi:10.1111/jgs.17323
- Hladkowicz E, Dumitrascu F, Auais M, et al. Evaluations of postoperative transitions in care for older adults: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:329. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02989-6
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA Video Connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21:502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Dawson R, Oliveira JS, Kwok WS, et al. Exercise interventions delivered through telehealth to improve physical functioning for older adults with frailty, cognitive, or mobility disability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30:940-950. doi:10.1089/tmj.2023.0177
- Liebzeit D, Phillips KK, Hogikyan RV, Cigolle CT, Alexander NB. A pilot home-telehealth program to enhance functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity in older adult veterans post-hospital discharge. Res Gerontol Nurs. 2024;17:271-279. doi:10.3928/19404921-20241105-01
- Krumholz HM. Post-hospital syndrome—an acquired, transient condition of generalized risk. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:100-102. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1212324
- Caraballo C, Dharmarajan K, Krumholz HM. Post hospital syndrome: is the stress of hospitalization causing harm? Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2019;72:896-898. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2019.04.010
- Rawal S, Kwan JL, Razak F, et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:38- 45. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.5100
- Dutzi I, Schwenk M, Kirchner M, Jooss E, Bauer JM, Hauer K. Influence of cognitive impairment on rehabilitation received and its mediating effect on functional recovery. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;84:745-756. doi:10.3233/JAD-210620
- Uriz-Otano F, Uriz-Otano JI, Malafarina V. Factors associated with short-term functional recovery in elderly people with a hip fracture. Influence ofcognitiveimpairment. JAmMedDirAssoc. 2015;16:215-220. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.09.009
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
- White RS, Jiang J, Hall CB, et al. Higher perceived stress scale scores are associated with higher pain intensity and pain interference levels in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:2350-2356. doi:10.1111/jgs.13135
- Blyth FM, March LM, Brnabic AJ, et al. Chronic pain in Australia: a prevalence study. Pain. 2001;89:127-134. doi:10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00355-9
- Thomas E, Peat G, Harris L, Wilkie R, Croft PR. The prevalence of pain and pain interference in a general population of older adults: cross-sectional findings from the North Staffordshire Osteoarthritis Project (NorStOP). Pain. 2004;110:361-368. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.04.017
- Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA. 1963;185:914-919. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120024016
- Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179-186.
- Alexander NB, Guire KE, Thelen DG, et al. Self-reported walking ability predicts functional mobility performance in frail older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000;48:1408-1413. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb02630.x
- Rosow I, Breslau N. A Guttman health scale for the aged. J Gerontol. 1966;21:556-559. doi:10.1093/geronj/21.4.556
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49:M85-M94. doi:10.1093/geronj/49.2.m85
- Chan CS, Slaughter SE, Jones CA, Ickert C, Wagg AS. Measuring activity performance of older adults using the activPAL: a rapid review. Healthcare (Basel). 2017;5:94. doi:10.3390/healthcare5040094
- IBM SPSS software. IBM Corp; 2019. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.ibm.com/spss
- Kang H. The prevention and handling of the missing data. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013;64:402-406. doi:10.4097/kjae.2013.64.5.402
- Epstein AM, Jha AK, Orav EJ. The relationship between hospital admission rates and rehospitalizations. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2287-2295. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1101942
- Bogaisky M, Dezieck L. Early hospital readmission of nursing home residents and community-dwelling elderly adults discharged from the geriatrics service of an urban teaching hospital: patterns and risk factors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:548-552. doi:10.1111/jgs.13317
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1418-1428. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0803563
- Hoyer EH, Needham DM, Atanelov L, Knox B, Friedman M, Brotman DJ. Association of impaired functional status at hospital discharge and subsequent rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2014;9:277-282. doi:10.1002/jhm.2152
- Mahoney J, Sager M, Dunham NC, Johnson J. Risk of falls after hospital discharge. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42:269- 274. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1994.tb01750.x
- Hoffman GJ, Liu H, Alexander NB, Tinetti M, Braun TM, Min LC. Posthospital fall injuries and 30-day readmissions in adults 65 years and older. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e194276. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4276
- Gill DP, Hubbard RA, Koepsell TD, et al. Differences in rate of functional decline across three dementia types. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:S63-S71. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.10.010
- Auyeung TW, Kwok T, Lee J, Leung PC, Leung J, Woo J. Functional decline in cognitive impairment–the relationship between physical and cognitive function. Neuroepidemiology. 2008;31:167-173. doi:10.1159/000154929
- Patti A, Zangla D, Sahin FN, et al. Physical exercise and prevention of falls. Effects of a Pilates training method compared with a general physical activity program. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e25289. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025289
- Nagarkar A, Kulkarni S. Association between daily activities and fall in older adults: an analysis of longitudinal ageing study in India (2017-18). BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:203. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02879-x
- Ek S, Rizzuto D, Xu W, Calderón-Larrañaga A, Welmer AK. Predictors for functional decline after an injurious fall: a population-based cohort study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33:2183-2190. doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01747-1
- Dagnino APA, Campos MM. Chronic pain in the elderly: mechanisms and perspectives. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:736688. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2022.736688
- Ritchie CS, Patel K, Boscardin J, et al. Impact of persistent pain on function, cognition, and well-being of older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71:26-35. doi:10.1111/jgs.18125
- Han TS, Murray P, Robin J, et al. Evaluation of the association of length of stay in hospital and outcomes. Int J Qual Health Care. 2022;34:mzab160. doi:10.1093/intqhc/ mzab160
- Lærum-Onsager E, Molin M, Olsen CF, et al. Effect of nutritional and physical exercise intervention on hospital readmission for patients aged 65 or older: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021;18:62. doi:10.1186/s12966-021-01123-w
- Van Walraven C, Bennett C, Jennings A, Austin PC, Forster AJ. Proportion of hospital readmissions deemed avoidable: a systematic review. CMAJ. 2011;183:E391-E402. doi:10.1503/cmaj.101860
- Liebzeit D, Bratzke L, Boltz M, Purvis S, King B. Getting back to normal: a grounded theory study of function in post-hospitalized older adults. Gerontologist. 2020;60:704-714. doi:10.1093/geront/gnz057
- Ponzetto M, Zanocchi M, Maero B, et al. Post-hospitalization mortality in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2003;36:83-91. doi:10.1016/s0167-4943(02)00061-4
- Buurman BM, Hoogerduijn JG, de Haan RJ, et al. Geriatric conditions in acutely hospitalized older patients: prevalence and one-year survival and functional decline. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026951
- Ponzetto M, Maero B, Maina P, et al. Risk factors for early and late mortality in hospitalized older patients: the continuing importance of functional status. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003;58:1049-1054. doi:10.1093/gerona/58.11.m1049
- Huang HT, Chang CM, Liu LF, Lin HS, Chen CH. Trajectories and predictors of functional decline of hospitalised older patients. J Clin Nurs. 2013;22:1322-1331. doi:10.1111/jocn.12055
- Boyd CM, Landefeld CS, Counsell SR, et al. Recovery of activities of daily living in older adults after hospitalization for acute medical illness. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:2171- 2179. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.02023.x
- Helvik AS, Selbæk G, Engedal K. Functional decline in older adults one year after hospitalization. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;57:305-310. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2013.05.008
- Zaslavsky O, Zisberg A, Shadmi E. Impact of functional change before and during hospitalization on functional recovery 1 month following hospitalization. J Gerontol Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70:381-386. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu168
- Chen CC, Wang C, Huang GH. Functional trajectory 6 months posthospitalization: a cohort study of older hospitalized patients in Taiwan. Nurs Res. 2008;57:93-100. doi:10.1097/01.NNR.0000313485.18670.e2
- Kleinpell RM, Fletcher K, Jennings BM. Reducing functional decline in hospitalized elderly. In: Hughes RG, ed. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008. Accessed September 3, 2025. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2629/
- Liebzeit D, Rutkowski R, Arbaje AI, Fields B, Werner NE. A scoping review of interventions for older adults transitioning from hospital to home. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69:2950-2962. doi:10.1111/jgs.17323
- Hladkowicz E, Dumitrascu F, Auais M, et al. Evaluations of postoperative transitions in care for older adults: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:329. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02989-6
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA Video Connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21:502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Dawson R, Oliveira JS, Kwok WS, et al. Exercise interventions delivered through telehealth to improve physical functioning for older adults with frailty, cognitive, or mobility disability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Telemed J E Health. 2024;30:940-950. doi:10.1089/tmj.2023.0177
- Liebzeit D, Phillips KK, Hogikyan RV, Cigolle CT, Alexander NB. A pilot home-telehealth program to enhance functional ability, physical performance, and physical activity in older adult veterans post-hospital discharge. Res Gerontol Nurs. 2024;17:271-279. doi:10.3928/19404921-20241105-01
- Krumholz HM. Post-hospital syndrome—an acquired, transient condition of generalized risk. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:100-102. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1212324
- Caraballo C, Dharmarajan K, Krumholz HM. Post hospital syndrome: is the stress of hospitalization causing harm? Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2019;72:896-898. doi:10.1016/j.rec.2019.04.010
- Rawal S, Kwan JL, Razak F, et al. Association of the trauma of hospitalization with 30-day readmission or emergency department visit. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179:38- 45. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.5100
- Dutzi I, Schwenk M, Kirchner M, Jooss E, Bauer JM, Hauer K. Influence of cognitive impairment on rehabilitation received and its mediating effect on functional recovery. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;84:745-756. doi:10.3233/JAD-210620
- Uriz-Otano F, Uriz-Otano JI, Malafarina V. Factors associated with short-term functional recovery in elderly people with a hip fracture. Influence ofcognitiveimpairment. JAmMedDirAssoc. 2015;16:215-220. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.09.009
- Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53:695-699. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30:473-483.
- White RS, Jiang J, Hall CB, et al. Higher perceived stress scale scores are associated with higher pain intensity and pain interference levels in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:2350-2356. doi:10.1111/jgs.13135
- Blyth FM, March LM, Brnabic AJ, et al. Chronic pain in Australia: a prevalence study. Pain. 2001;89:127-134. doi:10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00355-9
- Thomas E, Peat G, Harris L, Wilkie R, Croft PR. The prevalence of pain and pain interference in a general population of older adults: cross-sectional findings from the North Staffordshire Osteoarthritis Project (NorStOP). Pain. 2004;110:361-368. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.04.017
- Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA. 1963;185:914-919. doi:10.1001/jama.1963.03060120024016
- Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179-186.
- Alexander NB, Guire KE, Thelen DG, et al. Self-reported walking ability predicts functional mobility performance in frail older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2000;48:1408-1413. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2000.tb02630.x
- Rosow I, Breslau N. A Guttman health scale for the aged. J Gerontol. 1966;21:556-559. doi:10.1093/geronj/21.4.556
- Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49:M85-M94. doi:10.1093/geronj/49.2.m85
- Chan CS, Slaughter SE, Jones CA, Ickert C, Wagg AS. Measuring activity performance of older adults using the activPAL: a rapid review. Healthcare (Basel). 2017;5:94. doi:10.3390/healthcare5040094
- IBM SPSS software. IBM Corp; 2019. Accessed September 3, 2025. https://www.ibm.com/spss
- Kang H. The prevention and handling of the missing data. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013;64:402-406. doi:10.4097/kjae.2013.64.5.402
- Epstein AM, Jha AK, Orav EJ. The relationship between hospital admission rates and rehospitalizations. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2287-2295. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa1101942
- Bogaisky M, Dezieck L. Early hospital readmission of nursing home residents and community-dwelling elderly adults discharged from the geriatrics service of an urban teaching hospital: patterns and risk factors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015;63:548-552. doi:10.1111/jgs.13317
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1418-1428. doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0803563
- Hoyer EH, Needham DM, Atanelov L, Knox B, Friedman M, Brotman DJ. Association of impaired functional status at hospital discharge and subsequent rehospitalization. J Hosp Med. 2014;9:277-282. doi:10.1002/jhm.2152
- Mahoney J, Sager M, Dunham NC, Johnson J. Risk of falls after hospital discharge. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994;42:269- 274. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1994.tb01750.x
- Hoffman GJ, Liu H, Alexander NB, Tinetti M, Braun TM, Min LC. Posthospital fall injuries and 30-day readmissions in adults 65 years and older. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e194276. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4276
- Gill DP, Hubbard RA, Koepsell TD, et al. Differences in rate of functional decline across three dementia types. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:S63-S71. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.10.010
- Auyeung TW, Kwok T, Lee J, Leung PC, Leung J, Woo J. Functional decline in cognitive impairment–the relationship between physical and cognitive function. Neuroepidemiology. 2008;31:167-173. doi:10.1159/000154929
- Patti A, Zangla D, Sahin FN, et al. Physical exercise and prevention of falls. Effects of a Pilates training method compared with a general physical activity program. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e25289. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000025289
- Nagarkar A, Kulkarni S. Association between daily activities and fall in older adults: an analysis of longitudinal ageing study in India (2017-18). BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:203. doi:10.1186/s12877-022-02879-x
- Ek S, Rizzuto D, Xu W, Calderón-Larrañaga A, Welmer AK. Predictors for functional decline after an injurious fall: a population-based cohort study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33:2183-2190. doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01747-1
- Dagnino APA, Campos MM. Chronic pain in the elderly: mechanisms and perspectives. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:736688. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2022.736688
- Ritchie CS, Patel K, Boscardin J, et al. Impact of persistent pain on function, cognition, and well-being of older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71:26-35. doi:10.1111/jgs.18125
- Han TS, Murray P, Robin J, et al. Evaluation of the association of length of stay in hospital and outcomes. Int J Qual Health Care. 2022;34:mzab160. doi:10.1093/intqhc/ mzab160
- Lærum-Onsager E, Molin M, Olsen CF, et al. Effect of nutritional and physical exercise intervention on hospital readmission for patients aged 65 or older: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021;18:62. doi:10.1186/s12966-021-01123-w
- Van Walraven C, Bennett C, Jennings A, Austin PC, Forster AJ. Proportion of hospital readmissions deemed avoidable: a systematic review. CMAJ. 2011;183:E391-E402. doi:10.1503/cmaj.101860
Factors Influencing Outcomes of a Telehealth-Based Physical Activity Program in Older Veterans Postdischarge
Factors Influencing Outcomes of a Telehealth-Based Physical Activity Program in Older Veterans Postdischarge
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provide care for patients with higher rates of many diseases—diabetes, heart disease, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and stroke—compared to the nonveteran population. 1 Due to the medical complexities of these diseases, they are often misdiagnosed or not diagnosed at all.
COPD is hiding in plain sight, impacting quality of life and burdening US health care systems.2 Research has yielded new treatments and evidence-based guidelines; however, COPD remains underdiagnosed. Only 13 million of the estimated 79 million US adults with COPD aged 20 to 79 years have been formally diagnosed.3 By the time patients are diagnosed, the disease is often advanced, and therapies are less effective. In 2 large studies of patients with COPD symptoms, later diagnosis was associated with worse outcomes.4,5
Veterans have a higher prevalence of COPD (8%-19%) than nonveterans (6%), likely due to higher rates of smoking and service-related exposures, especially among veterans of post-9/11 conflicts.6,7 Veterans do not always report symptoms and PCPs may not ask about symptoms, leading to underdiagnosis.8 The combination of high likelihood and underdetection of COPD presents a challenge and a target for VA quality improvement (QI).
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against screening asymptomatic patients for COPD. However, both the USPSTF and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Report advocate for active case finding in primary care clinics to determine whether high-risk patients, such as smokers, experience COPD symptoms and warrant spirometry. 9,10 To make early COPD diagnoses, clinicians may use questionnaires alone or in combination with handheld peak expiratory flow rate measurements.11,12 Formal spirometry, considered the gold standard for COPD diagnosis, is ordered for patients who report COPD symptoms (ie, shortness of breath with exertion) or who have both COPD symptoms and reduced peak flow rates.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found that while the combination of questionnaires and peak flows was the more effective strategy overall, questionnaires alone were also valuable for identifying patients with possible COPD.13 Implementation of either screening method in primary care practices would be challenging. In a simulation study that applied chronic disease and preventive care guidelines to hypothetical patient panels, the time required for PCPs to provide guideline-recommended chronic and preventive care in addition to acute care far exceeded 8 hours per day, even in team-based settings.14 Overburdened PCPs are therefore unlikely to accept additional tasks like COPD case finding.
Why don’t patients report their pulmonary symptoms? Patients may not recognize the symptoms as evidence of COPD. Others may be afraid of a COPD diagnosis or the stigma that is associated with it.15 Perhaps they believe COPD treatment is ineffective because of lung damage from smoking. Some patients may not want to know if they have COPD, while others reduce activity levels to avoid symptoms.16
QUALITY IMPROVEMENT PROJECT
Given the high prevalence of COPD among veterans and the potential for underdiagnosis, VA Northeast Ohio Healthcare System (VANEOHS) internal medicine residents and faculty assessed the state of COPD diagnosis in its primary care clinic with a QI project in 2022. Patients in the clinic between August 1, 2015, and November 30, 2022, with an International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) COPD diagnosis code (J44) in the electronic health record were included. Of 157 included patients, 105 patients who had prior spirometry testing were excluded. Of the 52 patients with diagnosed COPD and no spirometry testing, 30 patients had computed tomography (CT) findings consistent with COPD (ie, airway thickening, emphysema, air trapping) that was performed for CT lung cancer screening (LCS).17 Twenty-three of these 30 patients were contacted by phone. All 23 were ever smokers and 13 reported COPD symptoms. The PCPs of the symptomatic patients were then contacted. Spirometry was ordered for all 13 patients and completed by 7. Three spirometry tests confirmed the COPD diagnosis. One PCP initiated inhaler therapy for a patient with newly diagnosed COPD.
All 11 PCPs of symptomatic patients were interviewed (many had > 1 symptomatic patient). They reported being unaware of patients’ COPD symptoms because the patients did not mention them, noting that screening for COPD was not a priority.
Role of Lung Cancer Screening
VA PCPs use electronic health record clinical reminders to track tests, consults, chronic disease education, cancer screenings, and routine health maintenance. A clinical reminder already exists (based on USPSTF recommendations) for LCS for patients aged 50 to 80 years who have a smoking history of 20 pack years. Patients who meet these criteria would also be considered high risk for COPD.
The VANEOHS QI project suggests that previously undiagnosed patients with findings of COPD on LCS may also have symptoms of COPD. Therefore, we wondered whether the LCS clinical reminder could serve a second purpose by prompting PCPs to ask veterans who meet LCS criteria about their COPD symptoms.
In 2022, about 13 million patients were eligible for LCS.18 Patients who qualify for LCS are at high risk for other cardiopulmonary disorders, such as COPD and coronary artery disease. Lung cancer is detected in only 1% of patients screened with CT at baseline. However, more often LCS yields evidence of additional cardiopulmonary disorders, such as emphysema or coronary artery calcifications. The International Early Lung Cancer Program (I-ELCAP) and the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial (NLST), which included > 79,000 patients, found evidence of emphysema on CT imaging in 24% and 31% of cases, respectively.19,20 In both cohorts, > 80% of patients with emphysema on CT imaging had no prior history of COPD.
In a 2022 article summarizing the potential impact of CT LCS on COPD diagnosis, Mulshine et al suggest that detection of emphysema on CT LCS provides “earlier recognition for PCPs to identify patients who would benefit from detailed symptom screening to prompt spirometry for COPD detection” and additional motivation for tobacco cessation.21 The VANEOHS QI project was developed and implemented prior to I-ELCAP or NLST reporting results but reinforces the value of CT LCS for COPD diagnosis.
Early diagnosis of COPD remains challenging because PCPs do not ask, patients do not tell, and symptoms can easily be dismissed. However, earlier diagnosis of COPD in symptomatic patients improves outcomes.3,4 To bridge this gap, VA PCPs and primary care patient aligned care teams (PACTs) need to commit to probing high-risk patients for COPD symptoms and ordering spirometry for those who are symptomatic. To accomplish this task, primary care teams need help.
The VANEOHS QI project confirmed that some patients with evidence of COPD on CT have symptoms of COPD that they did not share with their PCPs and suggests that LCS can be used as a dual action case finding method to screen both for lung cancer and COPD. We propose that patients who are eligible for LCS should also be probed for COPD symptoms at their clinic visits; for symptomatic patients, spirometry should be ordered, and COPD evidence-based management should be initiated when spirometry results are consistent with COPD. Annual probing for COPD symptoms could be considered in asymptomatic patients with ongoing tobacco use or emphysema on CT, since they may develop symptoms in the future. This new case-finding method bypasses the need for time-prohibitive questionnaires or peak flow measurements.
Future Opportunities
VA PCPs juggle many priorities and despite the simplicity of this new case finding COPD method, it may be unintentionally overlooked. PCPs often run out of time or may forget to ask patients about COPD symptoms when ordering LCS.
Future innovations to increase COPD diagnosis could include the creation of a yearly VA clinical reminder linked to the tobacco use reminder that has check boxes asking about symptoms of COPD in current and prior smokers. If patients have COPD symptoms, the reminder can prompt the ordering of spirometry. Similar reminders could be implemented to identify veterans with exposures to burn pits or other military environmental exposures who may have COPD symptoms. Another possible way to increase COPD diagnosis would be a partnership between primary care and the VA LCS program where patients receiving screening are asked about COPD symptoms during their LCS interviews and PACTs are alerted to order spirometry for symptomatic patients.
Elusive no longer! We can pull the veil back on COPD diagnosis and identify patients with possible COPD earlier in their course using their eligibility for LCS as a yearly reminder to probe them for symptoms. While not all patients who undergo LCS—even those with evidence of COPD on CT—will have COPD symptoms, symptoms may develop over time. LCS provides the possibility of 2 diagnoses from 1 test. This is an opportunity we cannot afford to miss.
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
- Betancourt JA, Granados PS, Pacheco GJ, et al. Exploring health outcomes for U.S. veterans compared to non-veterans from 2003 to 2019. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(5):604. doi:10.3390/healthcare90506064
- Bamonti PM, Fischer I, Moye J, Poghosyan H, Pietrzak RH. Obstructive respiratory disease in U.S. veterans: prevalence, characteristics, and health burden. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;176:140-147. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.05.053
- Criner RN, Han MK. COPD care in the 21st century: a public health priority. Respir Care. 2018;63(5):591-600. doi:10.4187/respcare.06276
- Larsson K, Janson C, Ställberg B, et al. Impact of COPD diagnosis timing on clinical and economic outcomes: the ARCTIC observational cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:995-1008. doi:10.2147/COPD.S195382
- Kostikas K, Price D, Gutzwiller FS, et al. Clinical impact and healthcare resource utilization associated with early versus late COPD diagnosis in patients from UK CPRD Database. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1729- 1738. doi:10.2147/COPD.S255414
- Bamonti PM, Robinson SA, Wan ES, Moy ML. Improving physiological, physical, and psychological health outcomes: a narrative review in US veterans with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:1269-1283. doi:10.2147/COPD.S339323
- Savitz DA, Woskie SR, Bello A, et al. Deployment to military bases with open burn pits and respiratory and cardiovascular disease. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247629. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7629
- Murphy DE, Chaudhry Z, Almoosa KF, Panos RJ. High prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among veterans in the urban midwest. Mil Med. 2011;176(5):552-560. doi:10.7205/milmed-d-10-00377
- Guirguis-Blake JM, Senger CA, Webber EM, Mularski RA, Whitlock EP. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1378-1393. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.2654
- Capriotti T, Tomy R, Morales M. COPD updates: 2023 GOLD Report for primary care providers. Clinical Advisor. May 9, 2023. Accessed May 14, 2025. https://www.clinicaladvisor.com/features/copd-updates-2023-gold-report-primary-care/
- Leidy NK, Martinez FJ, Malley KG, et al. Can CAPTURE be used to identify undiagnosed patients with mild- to- moderate COPD likely to benefit from treatment? Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1901-1912. doi:10.2147/COPD.S152226
- Jithoo A, Enright PL, Burney P, et al. Case-finding options for COPD: results from the burden of obstructive lung disease study. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):548-555. doi:10.1183/09031936.00132011
- Haroon SM, Jordan RE, O’Beirne-Elliman J, Adab P. Effectiveness of case finding strategies for COPD in primary care: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2015;25:15056. doi:10.1038/npjpcrm.2015.56
- Porter J, Boyd C, Skandari MR, Laiteerapong N. Revisiting the time needed to provide adult primary care. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(1)147-155. doi:10.1007/s11606-022-07707-x
- Woo S, Zhou W, Larson JL. Stigma experiences in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative review. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:1647- 1659. doi:10.2147/COPD.S306874
- Aaron SD, Montes de Oca M, Celli B, et al. Early diagnosis and treatment of COPD: the costs and benefits of case finding. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(8):928-937. doi:10.1164/rccm.202311-2120PP
- Kwon A, Lee C, Arafah A, Klein M, Namboodiri S, Lee C. Increasing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) diagnosis with pulmonary function testing for patients with chest imaging evidence of COPD. Poster presented at: Society of General Internal Medicine Midwest Regional Meeting; October 19-20, 2023; Chicago, IL.
- Henderson LM, Su I, Rivera MP, et al. Prevalence of lung cancer screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(3):e243190. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3190
- Steiger D, Siddiqi MF, Yip R, Yankelevitz DF, Henschke CI; I-ELCAP investigators. The importance of low-dose CT screening to identify emphysema in asymptomatic participants with and without a prior diagnosis of COPD. Clin Imaging. 2021;78:136-141. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.012
- Pinsky PF, Lynch DA, Gierada DS. Incidental findings on low-dose CT scan lung cancer screenings and deaths from respiratory diseases. Chest. 2022;161(4):1092-1100. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.11.015
- Mulshine JL, Aldigé CR, Ambrose LF, et al. Emphysema detection in the course of lung cancer screening: optimizing a rare opportunity to impact population health. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(4):499- 503. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202207-631PS
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
The Use of Lung Cancer Screening to Increase Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis in Veterans Affairs Primary Care
Utilization and Cost of Veterans Health Administration Referrals to Community Care-Based Physical Therapy
Utilization and Cost of Veterans Health Administration Referrals to Community Care-Based Physical Therapy
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest US integrated health system, providing care to veterans through VHA and non-VHA practitioners and facilities.1,2 Providing high-quality, timely, and veteran-centric care remains a priority for the VHA. Legislative efforts have expanded opportunities for eligible veterans to receive care in the community purchased by VHA, known as community care (CC).1 The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 came in response to reports of long wait times and drive times for patients.3-5 The MISSION Act of 2018 expanded access to CC by streamlining it and broadening eligibility criteria, especially for veterans in rural communities who often experience more barriers in accessing care than veterans living in urban communities.1,6-10 Since the implementation of the Choice and MISSION Acts, > 2.7 million veterans have received care through community practitioners within the VHA CC network.11
Background
Increased access to CC could benefit veterans living in rural communities by increasing care options and circumventing challenges to accessing VHA care (ie, geographic, transportation, and distance barriers, practitioner and specialist shortages, and hospital closures). 5,9,10,12,13 However, health care system deficits in rural areas could also limit CC effectiveness for veterans living in those communities. 3 Other challenges posed by using CC include care coordination, information sharing, care continuity, delayed payments to CC practitioners, and mixed findings regarding CC quality.5,8,13,14 VHA practitioners are specifically trained to meet the multifaceted needs unique to veterans’ health and subculture, training CC practitioners may not receive.5,15
CC offers services for primary care and a broad range of specialties, including rehabilitation services such as physical therapy (PT).6 PT is used for the effective treatment of various conditions veterans experience and promote wellbeing and independence.16 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) databases reveal a high prevalence of veterans receiving PT services through CC; PT is one of the most frequently used CC outpatient specialty services by veterans living in rural communities.14,17
Telerehabitltation Enterprisewide Initiative
VHA has greatly invested in delivering care virtually, especially for veterans living in rural communities.18 In 2017, the VHA Office of Rural Health funded the Telerehabilitation Enterprise-Wide Initiative (TR-EWI) in partnership with the Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Services national program office to increase access to specialized rehabilitation services for veterans living in rural communities by leveraging telehealth technologies.18-21 This alternative mode of health care delivery allows clinicians to overcome access barriers by delivering rehabilitation therapies directly to veterans' homes or nearby community-based outpatient clinics. TR-EWI was conceived as a hub-and-spoke model, where rehabilitation expertise at the hub was virtually delivered to spoke sites that did not have in-house expertise. In subsequent years, the TR-EWI also evolved to provide targeted telerehabilitation programs within rural-serving community-based outpatient clinics, including PT as a predominant service.19,20
As TR-EWI progressed—and in conjunction with the uptake of telehealth across VHA during the COVID-19 pandemic—there has been increased focus on PT telerehabilitation, especially for the 4.6 million veterans in rural communities.18,22,23 Because health care delivery system deficits in rural areas could limit the effective use of CC, many TR-EWI sites hope to reduce their CC referrals by providing telehealth PT services to veterans who might otherwise need to be referred to CC. This strategy aligns with VHA goals of providing high-quality and timely care. To better understand opportunities for programs like TR-EWI to provide rehabilitation services for veterans and reduce care sent to the community, research that examines CC referral trends for PT over time is warranted.
This study examines CC from a rehabilitation perspective with a focus on CC referral trends for PT, specifically for Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) where TREWI sites are located. The study’s objectives were to describe rehabilitation PT services being referred to CC and examine associated CC costs for PT services. Two research questions guided the study. First, what are the utilization trends for CC PT referrals from fiscal year (FY) 2019 to FY 2022? Secondly, what is the cost breakdown of CC for PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022?
Methods
This study was conducted by a multidisciplinary team comprised of public health, disability, rehabilitation counseling, and PT professionals. It was deemed a quality improvement project under VA guidance and followed the SQUIRE guidelines for quality improvement reporting.24,25 The study used the VA Common Operating Platform (Palantir) to obtain individual-level CC referral data from the HealthShare Referral Manager (HSRM) database and consult data from the Computerized Patient Record System. Palantir is used to store and integrate VA data derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and VHA Support Service Center. Referrals are authorizations for care to be delivered by a CC practitioner.
TR-EWI is comprised of 7 sites: VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 8, VISN 12, VISN 15, VISN 19, and VISN 22. Each site provides telerehabilitation services with an emphasis on reaching veterans living in rural communities. We joined the referrals and consults cubes in Palantir to extract PT referrals for FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs with TR-EWI sites and obtain referral-specific information and demographic characteristics. 26 Data were extracted in October 2022.
The VHA Community Care Referral Dashboard (CC Dashboard) provided nonindividual level CC cost data.27 The CC Dashboard provides insights into the costs of CC services for VHA enrollees by category of care, standardized episode of care, and eligibility. Data are based on nationallevel HSRM referrals that are not suspended or linked to a canceled or discontinued consult. Data were aggregated by VISN. The dashboard only includes referrals dating back to FY 2020; therefore, PT data from FY 2020 through FY 2022 for VISNs with TR-EWI sites were collected. Data were extracted in December 2022.
This study examined CC referrals, station name, eligibility types, clinical diagnoses (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes), and demographic information in the Palantir dataset. Six eligibility criteria can qualify a veteran to receive CC.28 Within clinical diagnoses, the variable of interest was the provisional diagnosis. Patient demographics included age, gender, and rurality of residence, as determined by the Rural-Urban Commuting Area system.29,30 Rural and highly rural categories were combined for analysis. For the CC cost dataset, this study examined CC referrals, referral cost, and eligibility type.
Analysis
For the first research question, we examined referral data from FY 2019 to FY 2022 using the Palantir dataset, performed descriptive statistical analysis for all variables, and analyzed data to identify trends. Descriptive statistics were completed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows Version 29.0.0.0.
A qualitative analysis of provisional diagnosis data revealed what is being referred to CC for PT. A preliminary overview of provisional diagnosis data was conducted to familiarize coders with the data. We developed a coding framework to categorize diagnoses based on anatomical location, body structure, and clinical areas of interest. Data were reviewed individually and grouped into categories within the coding framework before meeting as a team to achieve group consensus on categorization. We then totaled the frequency of occurrence for provisional diagnoses within each category. Qualitative analyses were completed using Microsoft Excel.
For the second research question, the study used the CC cost dataset to examine the cost breakdown of CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. We calculated the number and cost of PT referrals across eligibility groups for each FY and VISN. Data were analyzed using SPSS to identify cost trends.
Results
There were 344,406 referrals to CC for PT from FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs analyzed (Table 1). Of these, 22.5% were from FY 2019, 19.1% from FY 2020, 28.2% from FY 2021, and 30.3% from FY 2022. VISN 8 and VISN 22 reported the most overall PT referrals, with VISN 8 comprising 22.2% and VISN 22 comprising 18.1% of all referrals. VISN 2 reported the least overall referrals (3.7%). VISN 4 and VISN 12 had decreases in referrals over time. VISN 2 and VISN 15 had decreases in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2021 and slight increases from FY 2021 to FY 2022. VISN 19 and VISN 22 both saw slight increases from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and substantial increases from FY 2020 to FY 2022, with FY 2022 accounting for 40.0% and 42.3% of all referrals for VISN 19 and VISN 20, respectively (Figure 1).
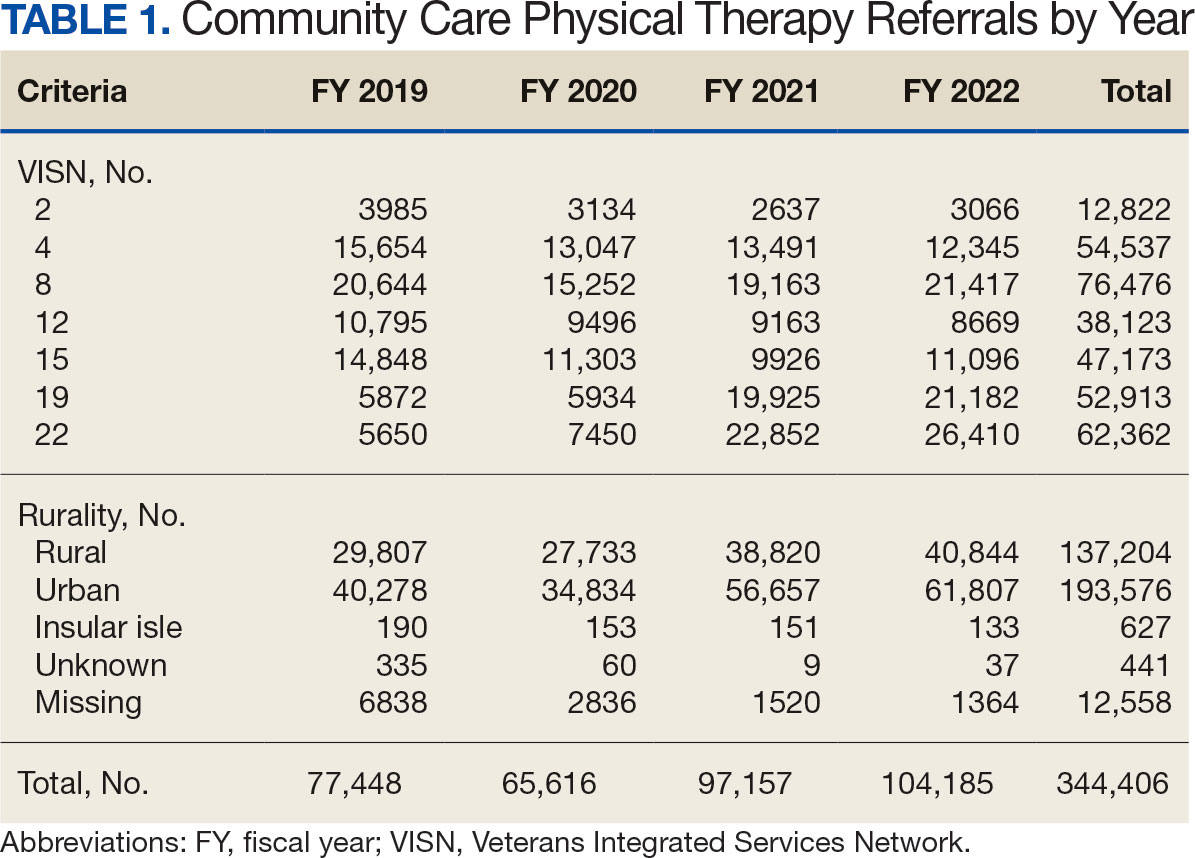
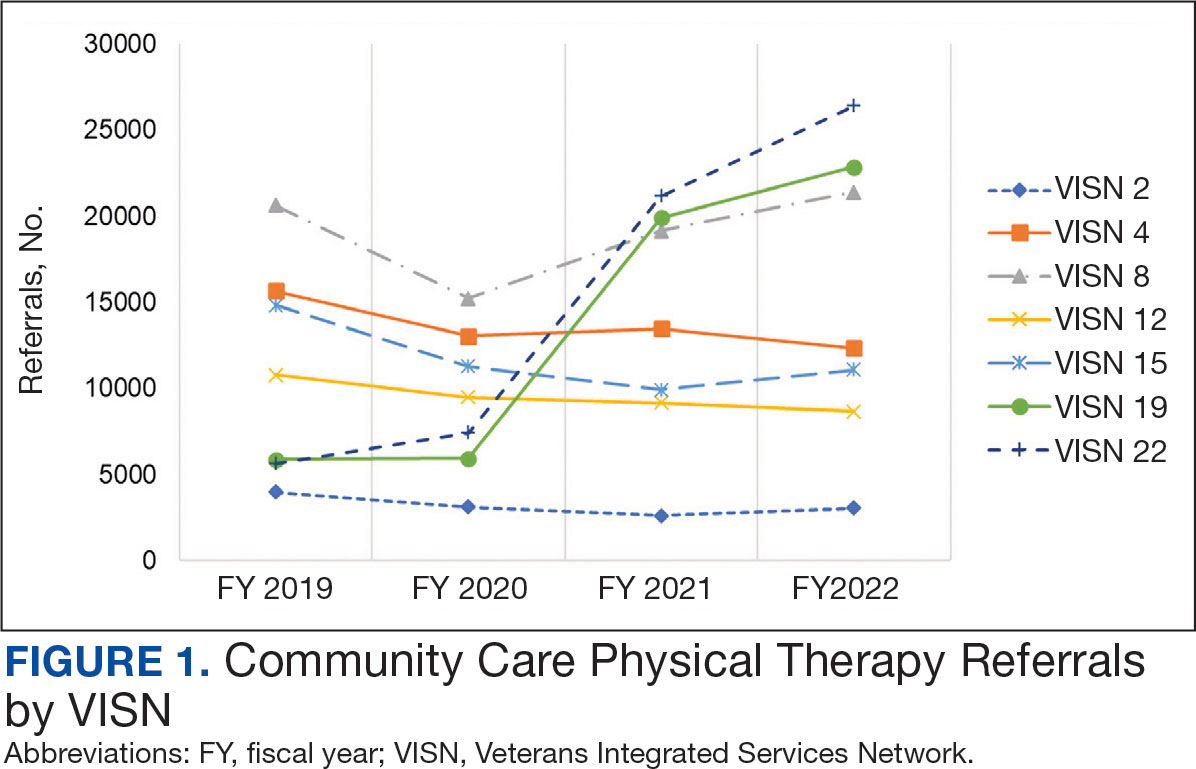
For FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 8 had the highest percentage of referrals (26.7% and 23.2%, respectively), whereas VISN 22 was among the lowest (7.3% and 11.4%, respectively). However, for FY 2021 and FY 2022, VISN 22 reported the highest percentage of referrals (23.5% and 25.3%, respectively) compared to all other VISNs. VISN 2 consistently reported the lowest percentage of referrals across all years.
There were 56 stations analyzed across the 7 VISNs (Appendix 1). Nine stations each accounted for ≥ 3.0% of the total PT referrals and only 2 stations accounted for > 5.0% of referrals. Orlando, Florida (6.0%), Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (5.2%), Tampa, Florida (4.9%), Aurora, Colorado (4.9%), and Gainesville, Florida (4.4%) reported the top 5 highest referrals, with 3 being from VISN 8 (Orlando, Tampa, Gainesville). Stations with the lowest reported referrals were all in VISN 2 in New York: The Bronx, (0%), New York Harbor (0%), Hudson Valley (0.1%) and Finger Lakes (0.2%).
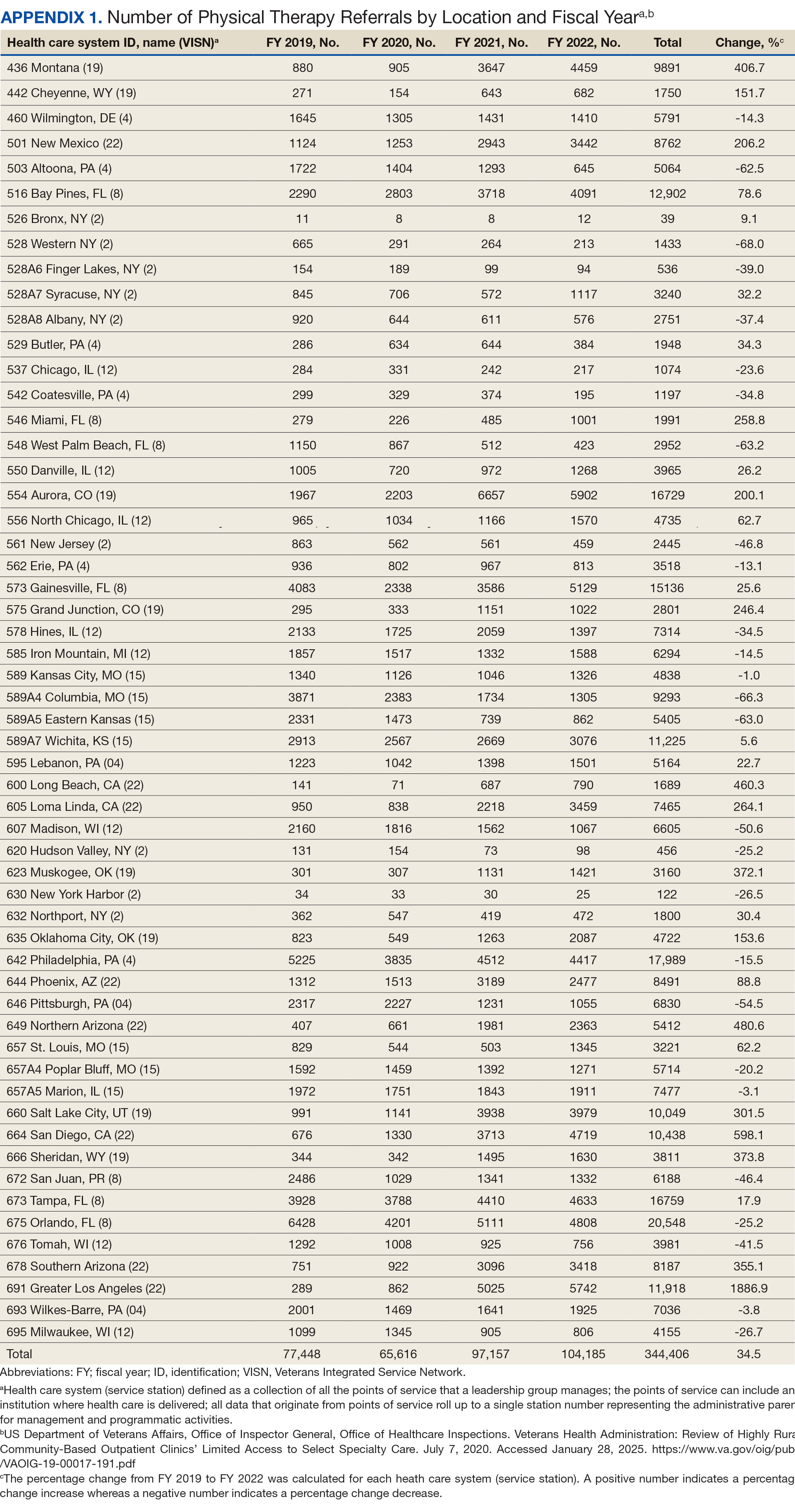
Rurality
Urban stations comprised 56.2% and rural stations comprised 39.8% of PT CC referrals, while 0.2% of referrals were from insular isle US territories: Guam, American Samoa, Northern Marianas, and the Virgin Islands. The sample had missing or unknown data for 3.8% of referrals. FY 2022 had the largest difference in rural and urban referrals. Additionally, there was an overall trend of more referrals over time for rural and urban, with a large increase in rural (+40.0%) and urban (+62.7%) referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2021 and a modest increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 (+5.2% for rural and +9.1% for urban). There was a decrease in rural (-7.0%) and urban (-3.5%) referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 (Figure 2).
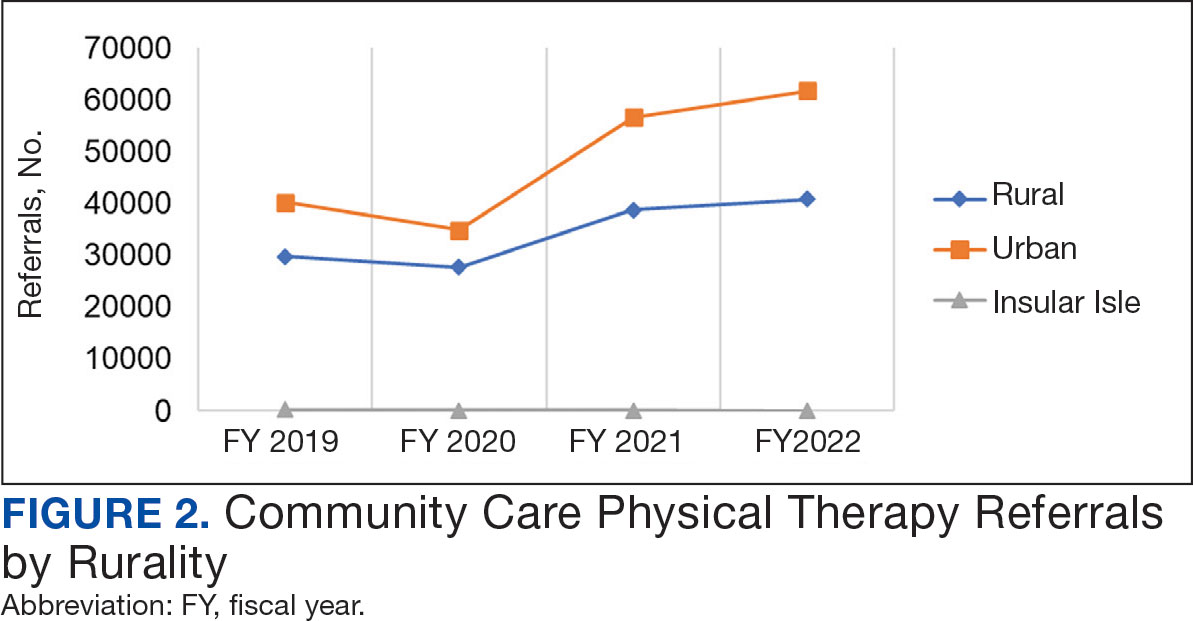
There were differences in referrals by rurality and VISN (Table 2). VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals, whereas VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 reported more urban than rural referrals. VISN 2 reported similar numbers for both, with slightly more urban than rural referrals. When reviewing trends over time for each FY, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 had more urban than rural referrals. In FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 2 reported slightly more urban than rural referrals but almost the same number of referrals in FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Appendix 2).
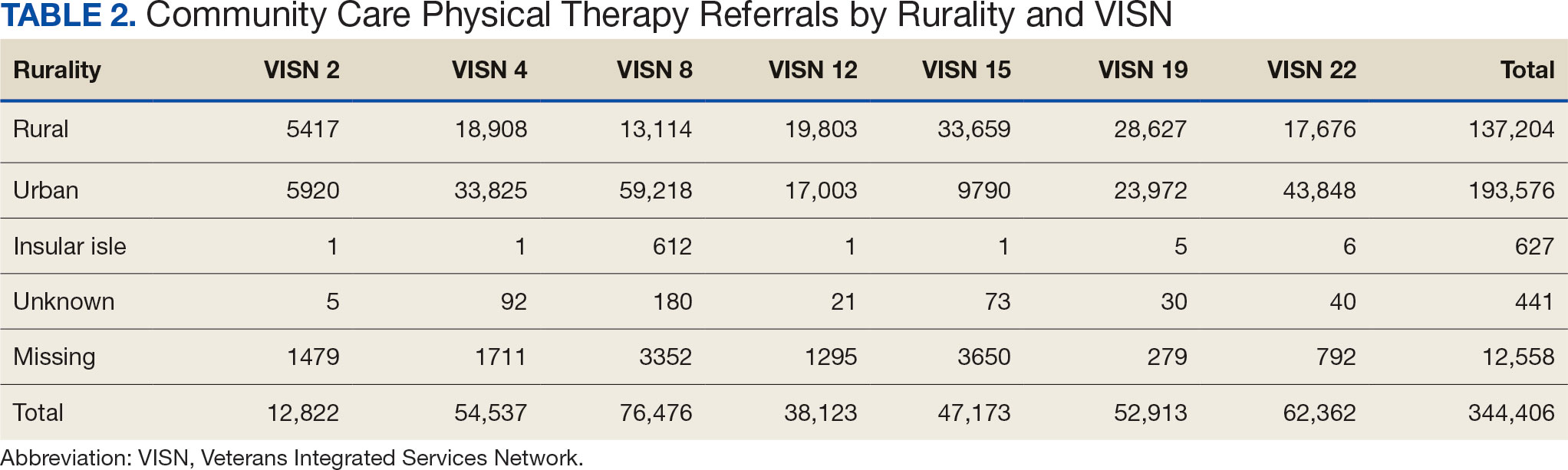
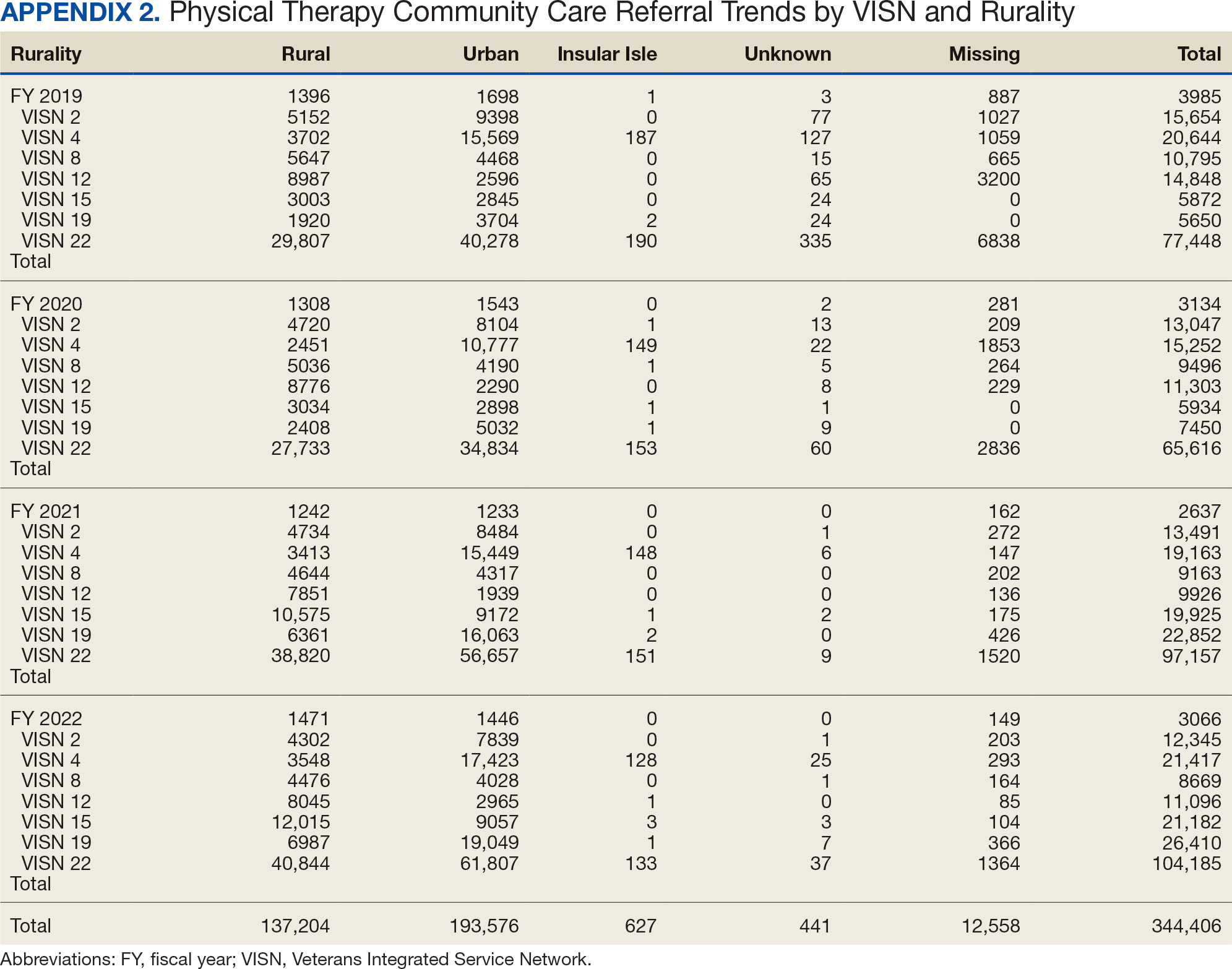
Demographics
The mean (SD) age was 61.2 (15.8) years (range, 20-105). Most PT CC referrals were for veterans aged 70 to 79 years (26.9%), followed by 60 to 69 years (20.7%), and 50 to 59 years (16.4%) (Appendix 3). Trends were consistent across VISNs. There was less of a difference between rural and urban referral percentages as the population aged. Veterans aged < 49 years residing in more urban areas accounted for more referrals to CC compared to their rural counterparts. This difference was less apparent in the 70 to 79 years and 80 to 89 years age brackets.
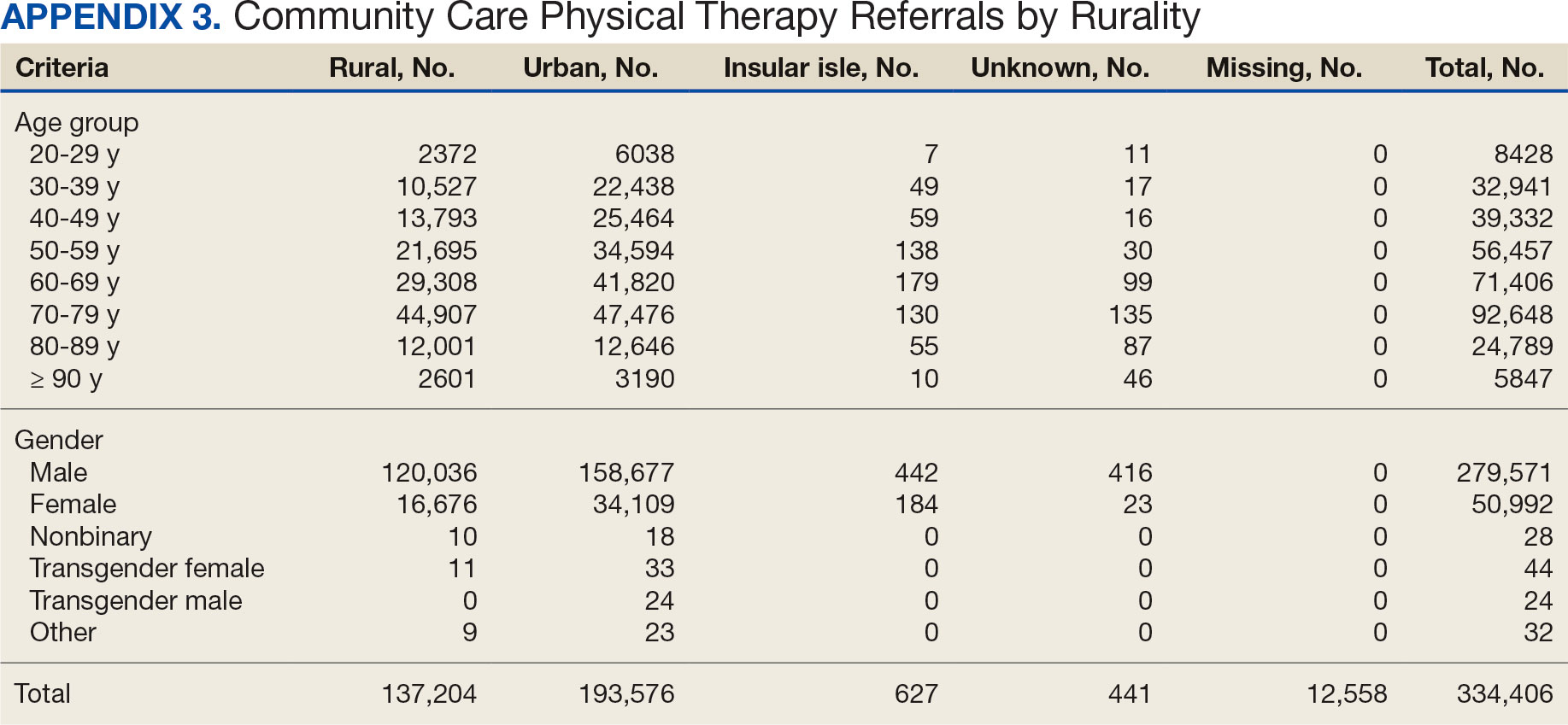
Most PT CC referrals (81.2%) were male and 14.8% were female. About 3.6% of referral data were missing sex information, and there was a smaller difference between male veterans living in rural communities and male veterans living in urban communities compared with female veterans. A total of 42.9% of male veterans resided in rural areas compared to 56.8% in urban areas; 32.7% of female veterans resided in rural areas compared to 66.9% in urban areas (Appendix 3).
Other Criteria
Of the 334,406 referrals, 114,983 (34.4%) had eligibility data, mostly from FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Table 3). Available eligibility data were likely affected by the MISSION Act and new regulations for reporting CC eligibility. Distance (33.4%) was the most common eligibility criteria, followed by timeliness of care (28.8%), and best medical interest (19.8%); 40.4% were rural and 59.5% were urban. Distance (55.4%) was most common for rural veterans, while timeliness of care (39.7%) was most common for urban veterans. For both groups, the second most common eligibility reason was best medical interest (Appendix 4).
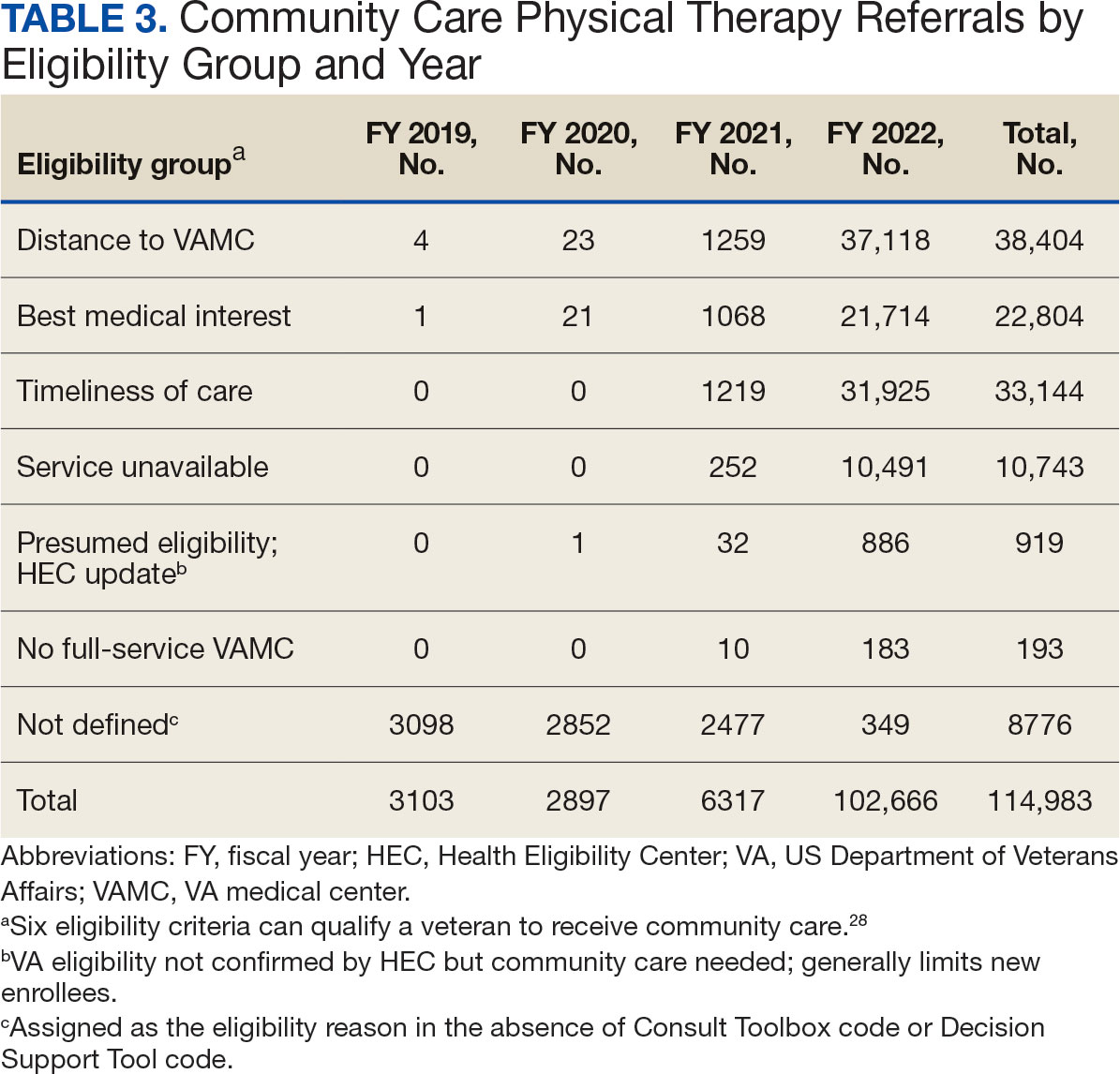
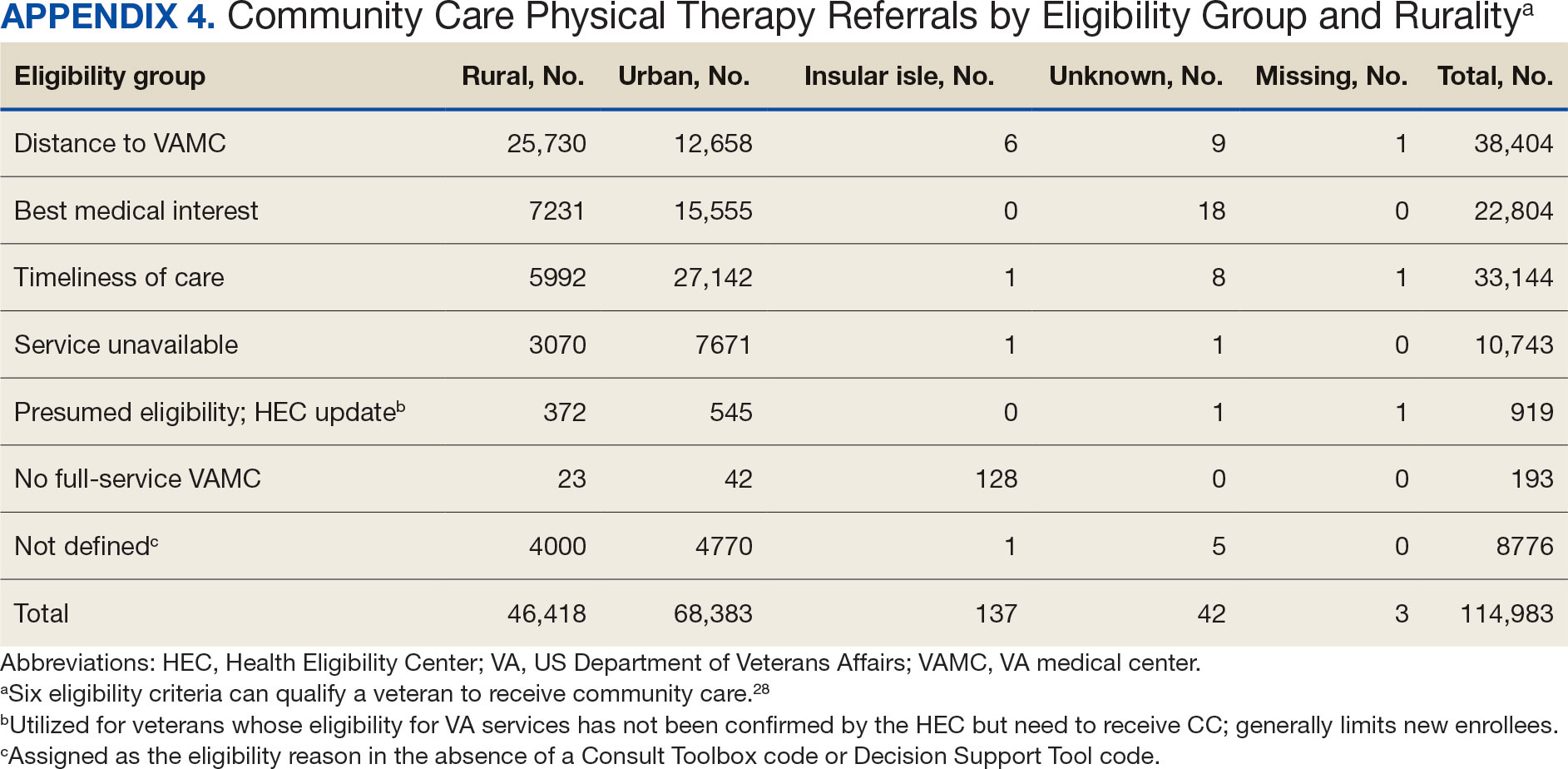
Bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders were common diagnoses, with 25.2% located in the lower back, 14.7% in the shoulder, and 12.8% in the knee (Appendix 5). Amputations of the upper and lower limbs, fractures, cancer-related diagnoses, integumentary system disorders, thoracic and abdominal injuries and disorders, and other medical and mental health conditions each accounted for < 1% of the total diagnoses.
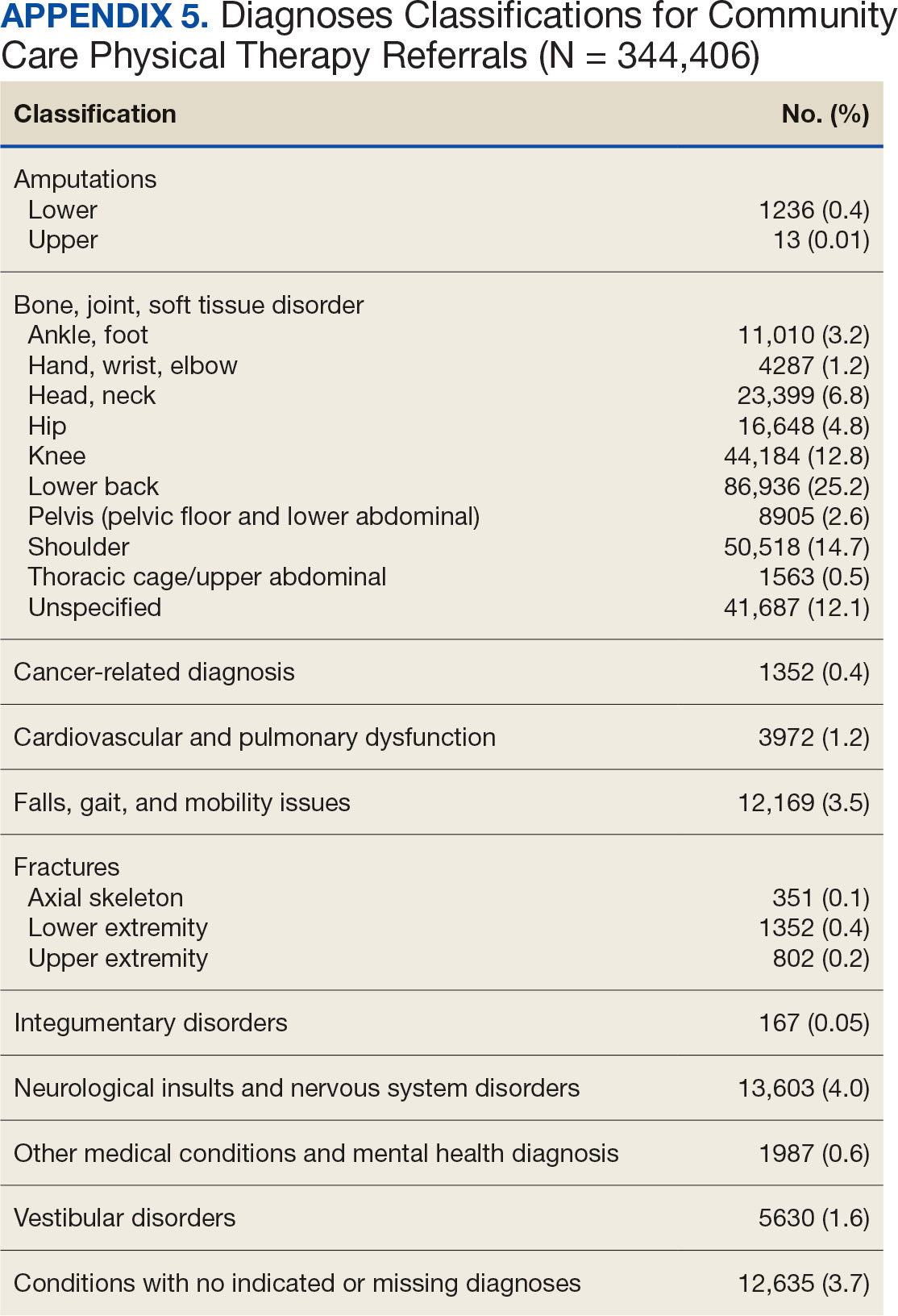
Costs
At time of analysis, the CC Dashboard had cost data available for 200,204 CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. The difference in referral numbers for the 2 datasets is likely attributed to several factors: CC cost data is exclusively from the HSRM, whereas Palantir includes other data sources; how VA cleans data pulled into Palantir; how the CC Dashboard algorithm populates data; and variances based on timing of reporting and/or if referrals are eventually canceled.
The total cost of PT CC referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 in selected VISNs was about $220,615,399 (Appendix 6). Appendix 7 details the methodology for determining the average standardized episode- of-care cost by VISN and how referral costs are calculated. Data show a continuous increase in total estimated cost from $46.8 million in FY 2020 to $92.1 million in FY 2022. From FY 2020 to FY 2022, aggregate costs ranged from $6,758,053 in VISN 2 to $47,209,162 in VISN 8 (Figure 3). The total referral cost for PT was highest at VISN 4 in FY 2020 ($10,447,140) and highest at VISN 22 in FY 2021 ($18,835,657) and FY 2022 ($22,962,438) (Figure 4). For referral costs from FY 2020 to FY 2022, distance accounted for $75,561,948 (34.3%), timeliness of care accounted for $60,413,496 (27.3%), and best medical interest accounted for $46,291,390 (21.0%) (Table 4).
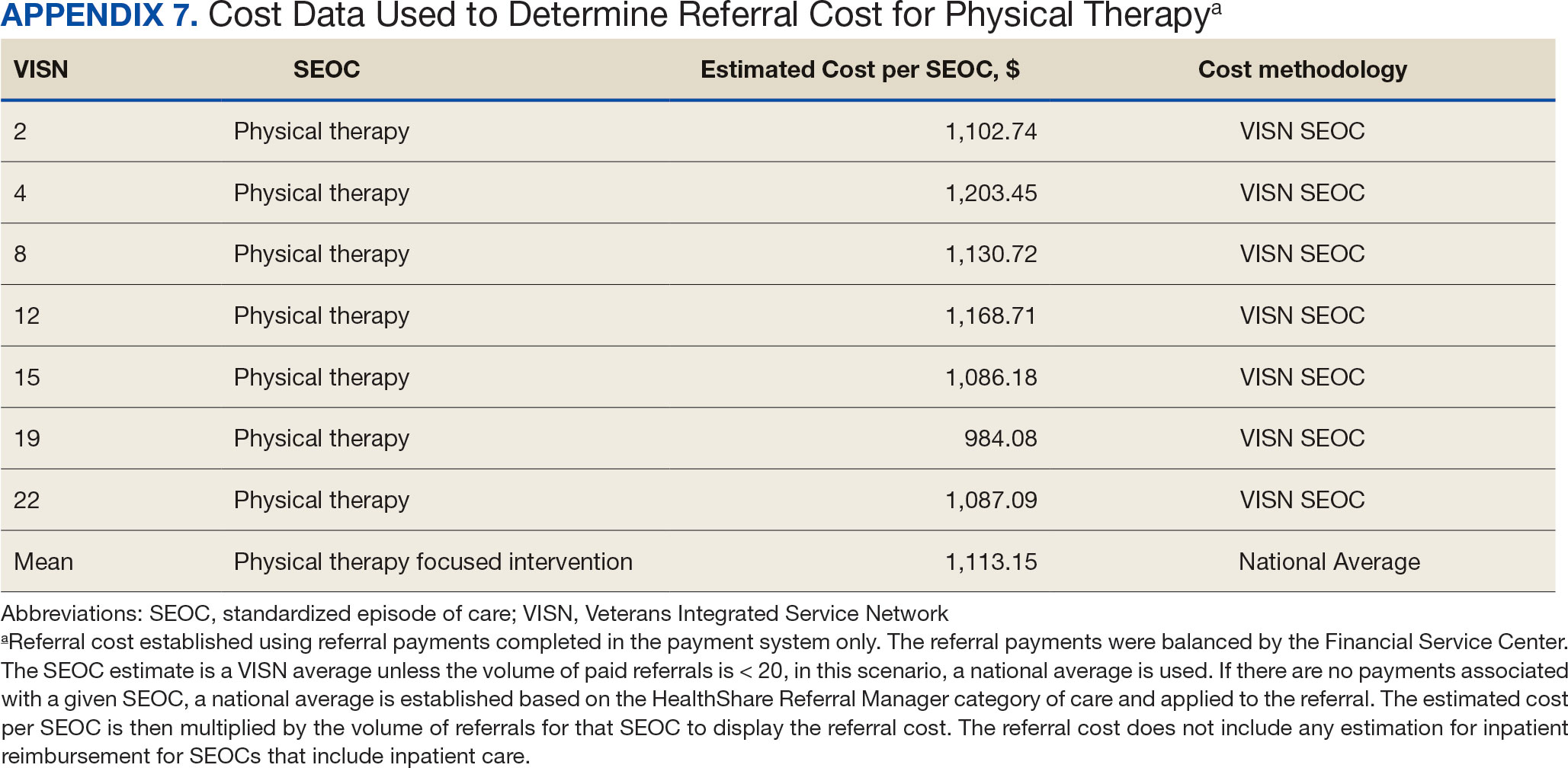
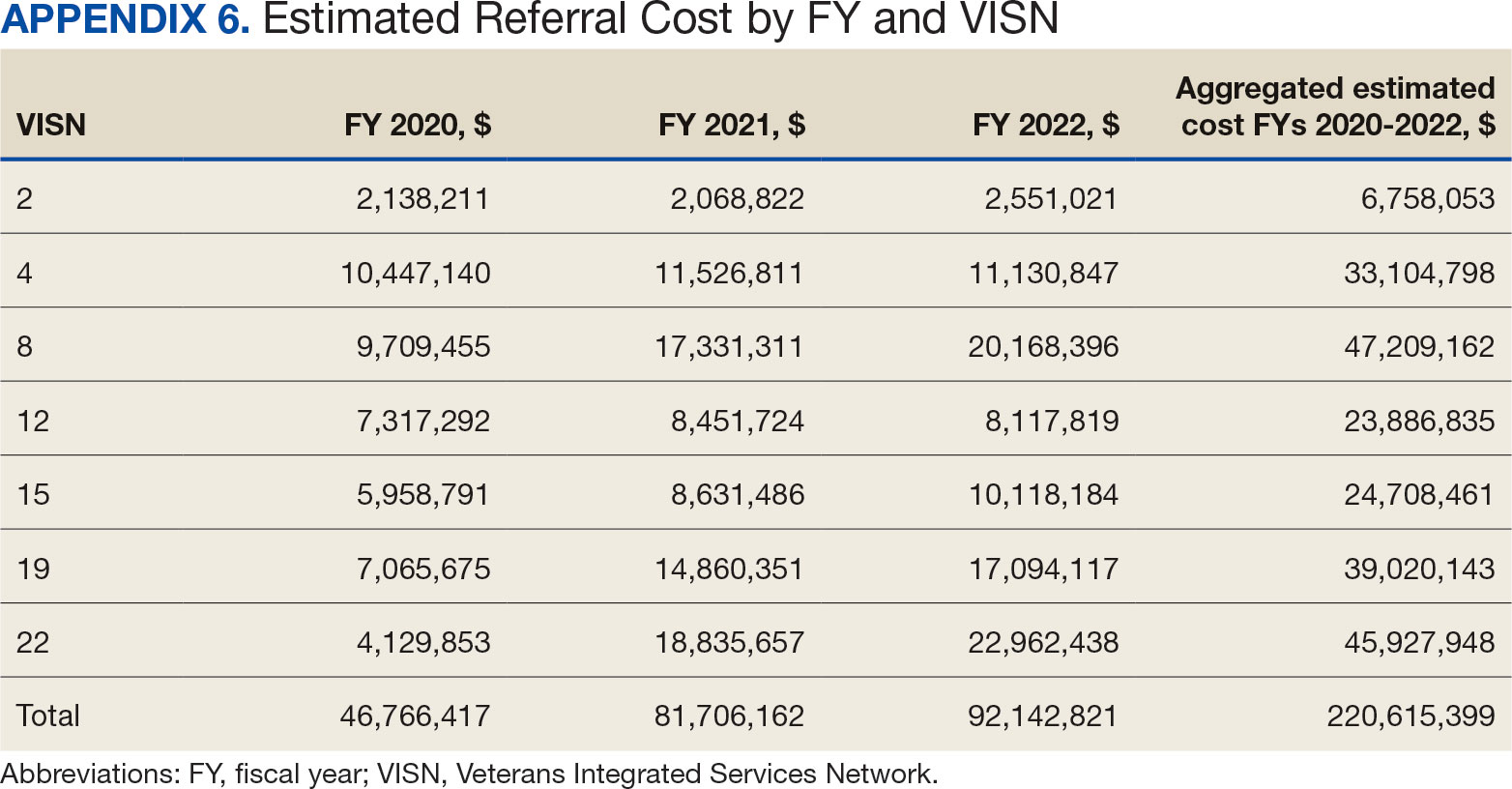
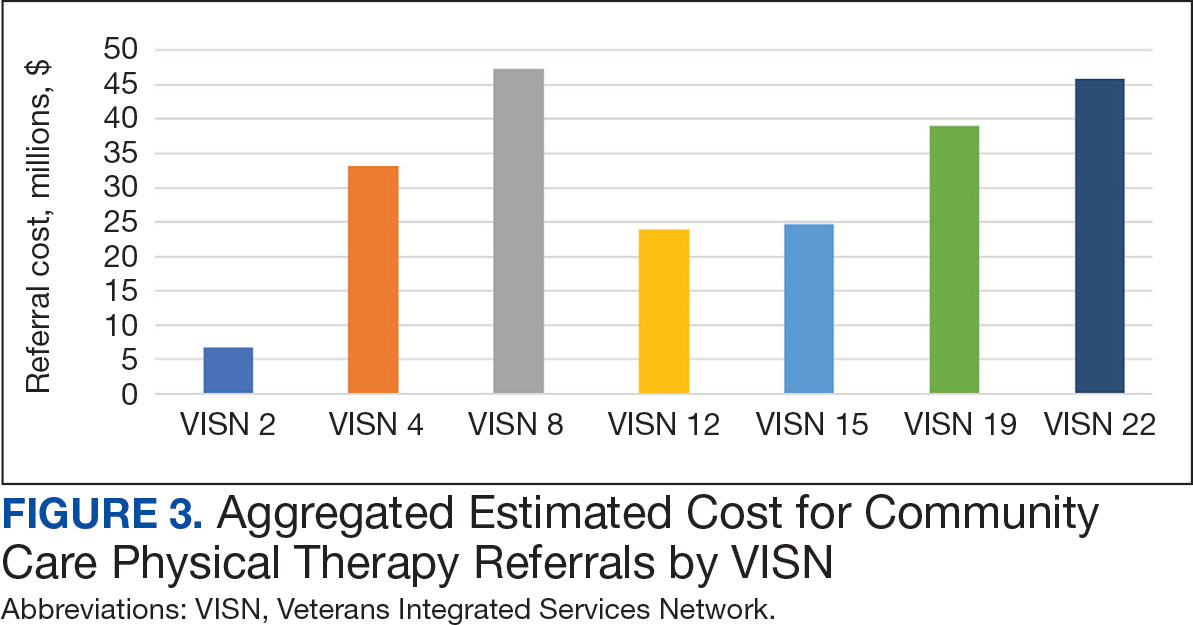
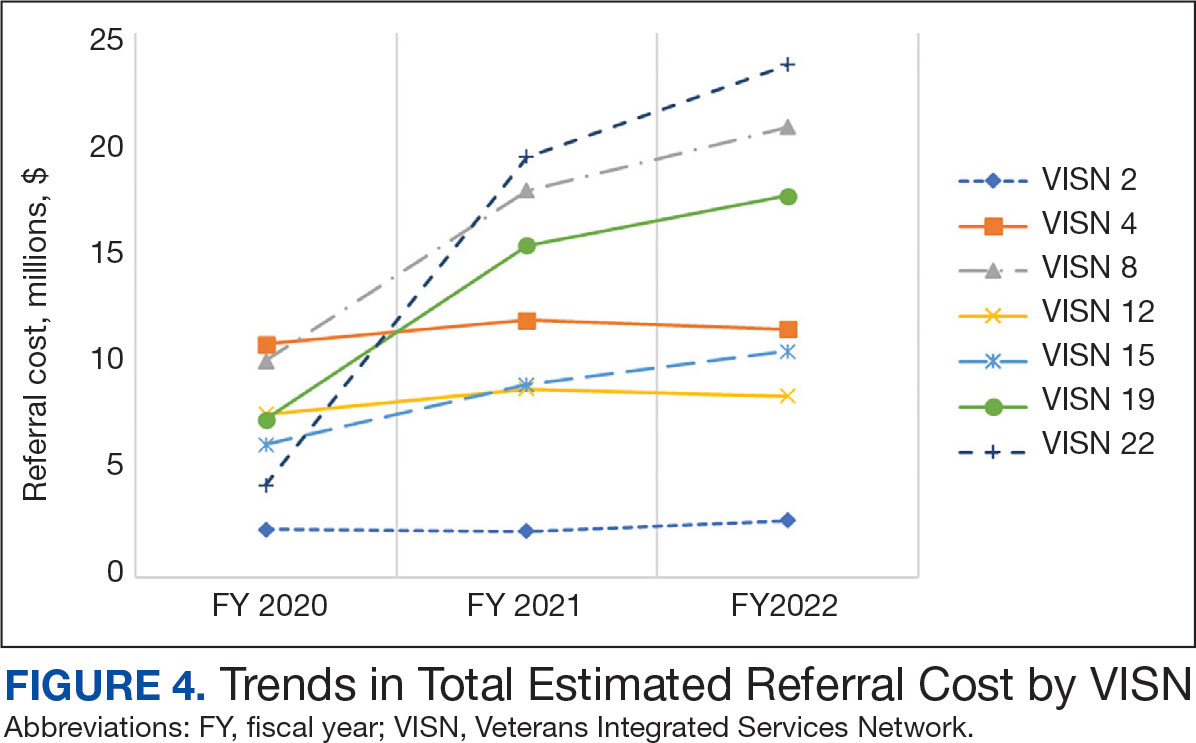
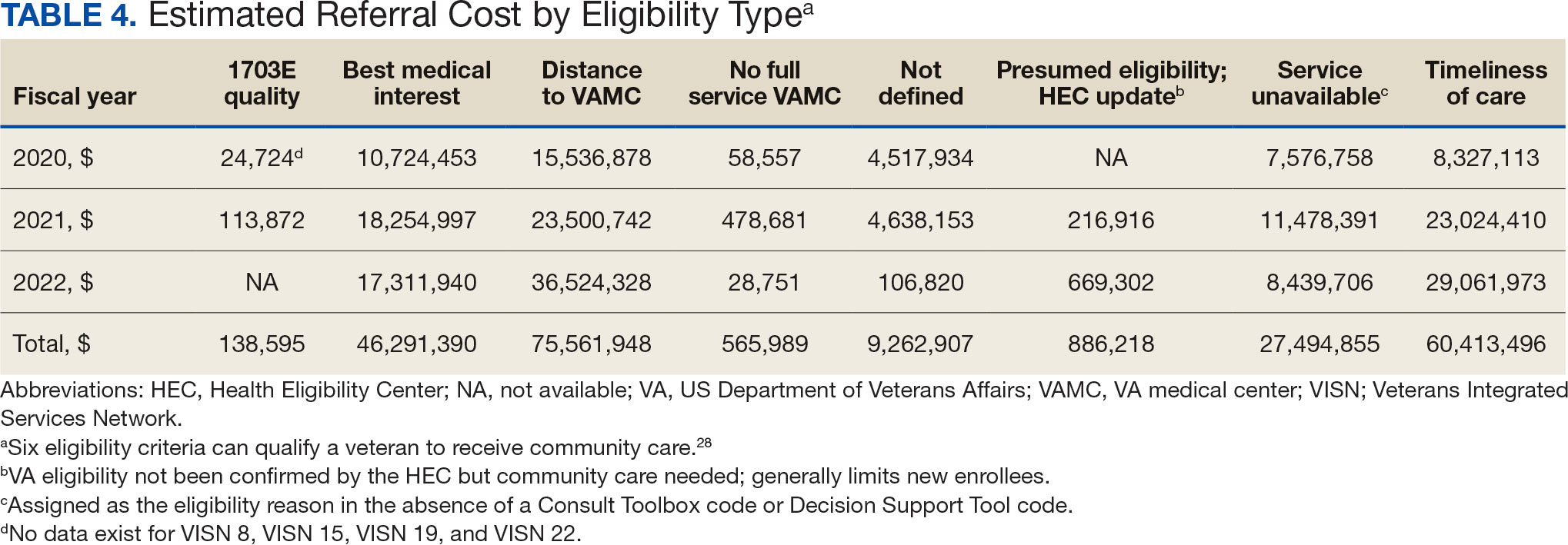
Overall costs were primarily driven by specific VISNs within each eligibility type (Appendix 8; Figure 5). VISN 19, VISN 22, and VISN 15 accounted for the highest referral costs for distance; VISN 22, VISN 8, and VISN 19 accounted for the secondhighest referral cost, timeliness of care; and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 12 accounted for the third-highest referral cost, best medical interest (Figure 5). VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 22 had service unavailable as an eligibility type with 1 of the top 3 associated referral costs, which was higher in cost than timeliness of care for VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, and VISN 15.
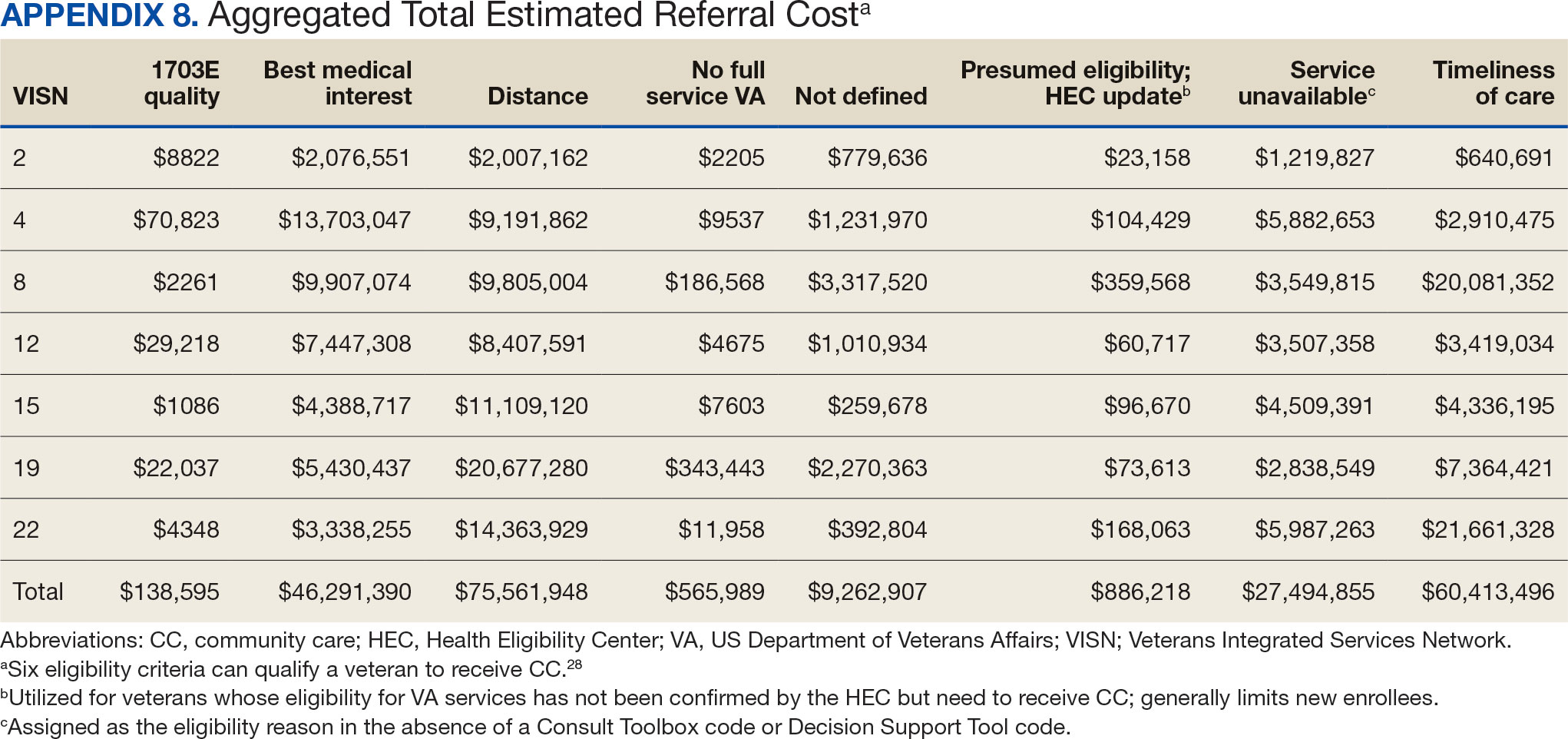
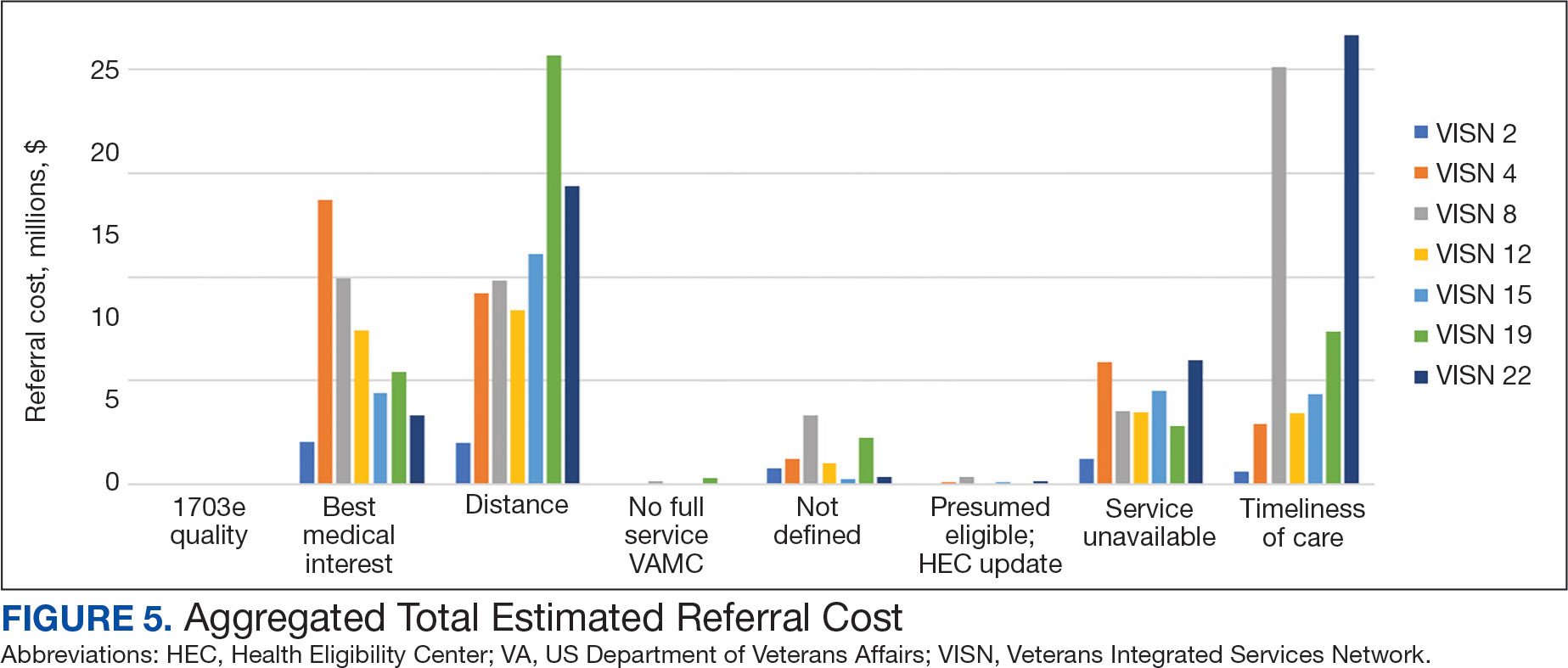
Discussion
This study examines the referral of rehabilitation PT services to CC, evaluates CC costs for PT services, and analyzes utilization and cost trends among veterans within the VHA. Utilization data demonstrated a decrease in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and increases in referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 for most variables of interest, with cost data exhibiting similar trends. Results highlight the need for further investigation to address variations in PT referrals and costs across VISNs and eligibility reasons for CC referral.
Results demonstrated a noteworthy increase in PT CC referrals over time. The largest increase occurred from FY 2020 to FY 2021, with a smaller increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022. During this period, total enrollee numbers decreased by 3.0% across the 7 VISNs included in this analysis and by 1.6% across all VISNs, a trend that illustrates an overall decrease in enrollees as CC use increased. Results align with the implementation of the MISSION Act of 2018, which further expanded veterans’ options to use CC.1,6,7 Results also align with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted care access for many veterans, placed a larger emphasis on the use of telehealth, and increased opportunities to stay within the VA for care by rapidly shifting to telehealth and leveraging telerehabilitation investments and initiatives (such as TR-EWI).20,31
VISN 8, VISN 19, and VISN 22, accounted for more than half of PT referrals. These VISNs had higher enrollee counts compared to the other VISNs.32 VISN 8 consistently had high levels of referrals, whereas VISN 19 and VISN 22 saw dramatic increases in FY 2021 and FY 2022. In contrast, VISN 4 and VISN 12 gradually decreased referrals during the study. VISN 2 had the lowest referral numbers during the study period, and all stations with the lowest individual referral numbers were located within VISN 2. Of the VISNs included in this study, VISN 2 had the second lowest number of enrollees (324,042).32 Reasons for increases and decreases over time could not be determined based on data collected in this study.
There were more urban than rural PT CC referrals; however, both exhibited an increase in referrals over time. This is consistent with population trends showing that most VHA patients (62.6%) and veterans (75.9%) reside in urban areas, which could explain some of the trends in this study.33 Some VISNs have larger urban catchment areas (eg, VISN 8 and VISN 22), and some have larger rural catchment areas (eg, VISN 15 and VISN 19), which could partially explain the rural-urban differences by VISN.32 Rural-urban referral trends might also reflect existing health care delivery system deficits in rural areas and known challenges associated with accessing health care for veterans living in rural communities.8,9
This study found larger differences in rural and urban PT CC referrals for younger age groups, with more than twice as many urban referrals in veterans aged 20 to 29 years and aged 30 to 39 years, and roughly 1.8 times as many urban referrals in veterans aged 40 to 49 years. However, there were similar numbers of rural and urban referrals in those aged 70 to 79 years and aged 80 to 89 years. These trends are consistent with data showing veterans residing in rural communities are older than their urban counterparts.23,34 Data suggest that older veteran populations might seek PT at higher rates than younger veteran populations. Moreover, data suggest there could be differences in PT-seeking rates for younger veteran populations who reside in rural vs urban areas. Additional research is needed to understand these trends.
Distance and timeliness of care were the predominant reasons for referral among eligibility groups, which is consistent with the MISSION Act goals.1,6,7 The most common eligibility reason for rural referrals was distance; timeliness of care was most common for urban referrals. This finding is expected, as veterans living in rural communities are farther away from VHA facilities and have longer drive times, whereas veterans living in urban communities might live closer, yet experience longer wait times due to services and/or appointment availability. Best medical interest accounted for almost 20% of referrals, which does not provide detailed insights into why those veterans were referred to CC.
The top PT diagnoses referred to CC were related to bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders of the lower back, shoulder, and knee. This suggests that musculoskeletal-related issues are prevalent among veterans seeking PT care, which is consistent with research that found > 50% of veterans receiving VHA care have musculoskeletal disorders.35 The probability of experiencing musculoskeletal problems increases with age, as does the need for PT services. Amputations and fractures accounted for < 1% of CC referrals, which is consistent with the historic provision of VHA clinical specialized care to conditions prevalent among veterans. It may also represent VHA efforts to internally provide care for complex conditions requiring more extensive interdisciplinary coordination.
The total cost of referrals over time was about $221 million. VISN 8 accounted for the highest overall cost; VISN 2 had the lowest, mirroring referral utilization trends and aligning with VISN enrollee numbers. VISN 19 and VISN 22 reported large cost increases from FY 2020 to FY 2021. Total referral costs increased by $34.9 million from FY 2020 to FY 2021, which may be due to health care inflation (2.9% during FY 2019 to FY 2022), increased awareness of CC services, or increased VHA wait times.36 Additionally, there were limitations in care provided across health care systems during the COVID-19 pandemic, including the VA.5 The increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021 may reflect a rebound from restrictions in appointments across VA, CC, and the private sector.
While the increase in total referral cost may be partly attributed to inflation, the cost effectiveness and efficiency of referring veterans to CC vs keeping veterans within VHA care is an ongoing debate.5 Examining and addressing cost drivers within the top eligibility types and their respective VISNs is necessary to determine resource allocation and improve quality of care. This study found that best medical interest and unavailable services accounted for 33.4% of the total cost of CC referrals, highlighting the need for policies that strengthen in-house competencies and recruit personnel to provide PT services currently unavailable within the VA.
Future Directions
The VHA should explore opportunities for in-house care, especially for services appropriate for telehealth.18,20,37 Data indicated a smaller cost increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 compared to the relatively large increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021. The increased telehealth usage across VHA by TR-EWI and non—TR-EWI sites within selected VISNs may have contributed to limiting the increase in CC costs. Future studies should investigate contextual factors of increased telehealth usage, which would offer guidance for implementation to optimize the integration of telehealth with PT rehabilitation provided in-house. Additionally, future studies can examine potential limitations experienced during PT telehealth visits, such as the inability to conduct hands-on assessments, challenges in viewing the quality of patient movement, ensuring patient safety in the remote environment, and the lack of PT equipment in homes for telehealth visits, and how these challenges are being addressed.38,39 Research is also needed to understand tradeoffs of CC vs VHA care and the potential and cost benefits of keeping veterans within VHA using programs like TR-EWI.5 Veterans living in rural communities may especially benefit from this as expanding telehealth options can provide access to PT care that may not be readily available, enabling them to stay connected and engaged in their care.18,40
Future studies could examine contributory factors to rising costs, such as demographic shifts, changes in PT service utilization, and policy. Researchers might also consider qualitative studies with clinicians and veterans within each VISN, which may provide insights into how local factors impact PT referral to the community.
Limitations
Due to its descriptive nature, this study can only speculate about factors influencing trends. Limitations include the inability to link the Palantir and CC Dashboard datasets for cost comparisons and potential data change over time on Palantir due to platform updates. The focus on VISNs with TREWI sites limited generalizability and this study did not compare CC PT vs VHA PT. Finally, there may have been cost drivers not identified in this study.
Conclusions
This descriptive study provides insights into the utilization and cost of PT CC referrals for selected VISNs. Cost trends underscore the financial commitment to providing PT services to veterans. Understanding what factors are driving this cost is necessary for VHA to optimally provide and manage the rehabilitation resources needed to serve veterans through traditional in-person care, telehealth, and CC options while ensuring timely, highquality care.
- Congressional Budget Office. The Veterans Community Care Program: Background and Early Effects. October 26, 2021. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.cbo.gov/publication/57257
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Providing Health Care for Veterans. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/
- Davila H, Rosen AK, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Chatelain LJ, Gurewich D. Rural veterans’ experiences with outpatient care in the Veterans Health Administration versus community care. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S286-S291. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001552
- Vanneman ME, Wagner TH, Shwartz M, et al. Veterans’ experiences with outpatient care: comparing the Veterans Affairs system with community-based care. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1368-1376. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01375
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10(3):9.
- Feyman Y, Legler A, Griffith KN. Appointment wait time data for primary & specialty care in veterans health administration facilities vs. community medical centers. Data Brief. 2021;36:107134. doi:10.1016/j.dib.2021.107134
- Kelley AT, Greenstone CL, Kirsh SR. Defining access and the role of community care in the Veterans Health Administration. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(5):1584-1585. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05358-z
- Garvin LA, Pugatch M, Gurewich D, Pendergast JN, Miller CJ. Interorganizational care coordination of rural veterans by Veterans Affairs and community care programs: a systematic review. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S259-S269. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001542
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans: Rural Veteran Health Care Challenges. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https:// www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- Ohl ME, Carrell M, Thurman A, et al. “Availability of healthcare providers for rural veterans eligible for purchased care under the veterans choice act.” BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):315. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3108-8
- Mattocks KM, Cunningham KJ, Greenstone C, Atkins D, Rosen AK, Upton M. Innovations in community care programs, policies, and research. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S229-S231. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001550
- Doyle JM, Streeter RA. Veterans’ location in health professional shortage areas: implications for access to care and workforce supply. Health Serv Res. 2017;52 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):459-480. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.12633
- Patzel M, Barnes C, Ramalingam N, et al. Jumping through hoops: community care clinician and staff experiences providing primary care to rural veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(Suppl 3):821-828. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08126-2
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Olenick M, Flowers M, Diaz VJ. US veterans and their unique issues: enhancing health care professional awareness. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2015;6:635-639. doi:10.2147/AMEP.S89479
- Campbell P, Pope R, Simas V, Canetti E, Schram B, Orr R. The effects of early physiotherapy treatment on musculoskeletal injury outcomes in military personnel: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(20):13416. doi:10.3390/ijerph192013416
- Gurewich D, Shwartz M, Beilstein-Wedel E, Davila H, Rosen AK. Did access to care improve since passage of the veterans choice act? Differences between rural and urban veterans. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S270-S278. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001490
- Myers US, Birks A, Grubaugh AL, Axon RN. Flattening the curve by getting ahead of it: how the VA healthcare system is leveraging telehealth to provide continued access to care for rural veterans. J Rural Health. 2021;37(1):194-196. doi:10.1111/jrh.12449
- Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for rural veterans: a qualitative assessment of barriers and facilitators to implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
- Kreider CM, Hale-Gallardo J, Kramer JC, et al. Providers’ shift to telerehabilitation at the U.S. Veterans Health Administration during COVID-19: practical applications. Front Public Health. 2022;10:831762. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.831762
- Cowper-Ripley DC, Jia H, Wang X, et al. Trends in VA telerehabilitation patients and encounters over time and by rurality. Fed Pract. 2019;36(3):122-128.
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. VHA Office of Rural Health. Updated August 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/index.asp
- National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Rural Veterans: 2021-2023. April 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.datahub.va.gov/stories/s/Rural-Veterans-FY2021-2023/kkh2-eymp/
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Program Guide: 1200.21, VHA Operations Activities That May Constitute Research. January 9, 2019. https://www.research.va.gov/resources/policies/ProgramGuide-1200-21-VHA-Operations-Activities.pdf
- Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. J Nurs Care Qual. 2016;31(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000153
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Updated January 29, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- Stomberg C, Frost A, Becker C, Stang H, Windschitl M, Carrier E. Community Care referral dashboard [Data dashboard]. https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/reports/090d22a7-0e1f-4cc5-bea8-0a1b87aa0bd9/ReportSectionacfd03cdebd76ffca9ec [Source not verified]
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for community care outside VA. Updated May 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/programs/veterans/General_Care.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. How to define rurality fact sheet. Updated December 2023. Accessed January 28, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/docs/ORH_RuralityFactSheet_508.pdf
- Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes.aspx
- Gurewich D, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Davila H, Rosen AK. Disparities in wait times for care among US veterans by race and ethnici t y. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2252061. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.52061
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Office of Rural Health, Veterans Rural Health Resource Center-Gainesville, GeoSpatial Outcomes Division. VA and Community Healthcare, and VHA Rurality web map application. Published 2023. https://portal.vhagis.inv.vaec.va.gov/arcgis/apps/webappbuilder/index.html [source not verified]
- Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans: National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; November 2020. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/research/findings/nhqrdr/chartbooks/veterans/index.html
- Lum HD, Nearing K, Pimentel CB, Levy CR, Hung WW. Anywhere to anywhere: use of telehealth to increase health care access for older, rural veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):12-18. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz030
- Goulet JL, Kerns RD, Bair M, et al. The musculoskeletal diagnosis cohort: examining pain and pain care among veterans. Pain. 2016;157(8):1696-1703. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000567
- US Inflation Calculator. Health Care Inflation in the United States (1948-2024). Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.usinflationcalculator.com/inflation/health-care-inflation-in-the-united-states/
- Cottrell MA, Galea OA, O’Leary SP, Hill AJ, Russell TG. Real-time telerehabilitation for the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions is effective and comparable to standard practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2017;31(5):625-638. doi:10.1177/0269215516645148
- Elor A, Conde S, Powel l M, Robbins A, Chen NN, Kurniawan S. Physical therapist impressions of telehealth and virtual reality needs amidst a pandemic. Front Virtual Real. 2022;3. doi:10.3389/frvir.2022.915332
- Lee AC, Harada N. Telehealth as a means of health care delivery for physical therapist practice. Phys Ther. 2012;92(3):463-468. doi:10.2522/ptj.20110100
- Hynes DM, Edwards S, Hickok A, et al. Veterans’ use of Veterans Health Administration primary care in an era of expanding choice. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S292- S300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001554
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest US integrated health system, providing care to veterans through VHA and non-VHA practitioners and facilities.1,2 Providing high-quality, timely, and veteran-centric care remains a priority for the VHA. Legislative efforts have expanded opportunities for eligible veterans to receive care in the community purchased by VHA, known as community care (CC).1 The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 came in response to reports of long wait times and drive times for patients.3-5 The MISSION Act of 2018 expanded access to CC by streamlining it and broadening eligibility criteria, especially for veterans in rural communities who often experience more barriers in accessing care than veterans living in urban communities.1,6-10 Since the implementation of the Choice and MISSION Acts, > 2.7 million veterans have received care through community practitioners within the VHA CC network.11
Background
Increased access to CC could benefit veterans living in rural communities by increasing care options and circumventing challenges to accessing VHA care (ie, geographic, transportation, and distance barriers, practitioner and specialist shortages, and hospital closures). 5,9,10,12,13 However, health care system deficits in rural areas could also limit CC effectiveness for veterans living in those communities. 3 Other challenges posed by using CC include care coordination, information sharing, care continuity, delayed payments to CC practitioners, and mixed findings regarding CC quality.5,8,13,14 VHA practitioners are specifically trained to meet the multifaceted needs unique to veterans’ health and subculture, training CC practitioners may not receive.5,15
CC offers services for primary care and a broad range of specialties, including rehabilitation services such as physical therapy (PT).6 PT is used for the effective treatment of various conditions veterans experience and promote wellbeing and independence.16 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) databases reveal a high prevalence of veterans receiving PT services through CC; PT is one of the most frequently used CC outpatient specialty services by veterans living in rural communities.14,17
Telerehabitltation Enterprisewide Initiative
VHA has greatly invested in delivering care virtually, especially for veterans living in rural communities.18 In 2017, the VHA Office of Rural Health funded the Telerehabilitation Enterprise-Wide Initiative (TR-EWI) in partnership with the Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Services national program office to increase access to specialized rehabilitation services for veterans living in rural communities by leveraging telehealth technologies.18-21 This alternative mode of health care delivery allows clinicians to overcome access barriers by delivering rehabilitation therapies directly to veterans' homes or nearby community-based outpatient clinics. TR-EWI was conceived as a hub-and-spoke model, where rehabilitation expertise at the hub was virtually delivered to spoke sites that did not have in-house expertise. In subsequent years, the TR-EWI also evolved to provide targeted telerehabilitation programs within rural-serving community-based outpatient clinics, including PT as a predominant service.19,20
As TR-EWI progressed—and in conjunction with the uptake of telehealth across VHA during the COVID-19 pandemic—there has been increased focus on PT telerehabilitation, especially for the 4.6 million veterans in rural communities.18,22,23 Because health care delivery system deficits in rural areas could limit the effective use of CC, many TR-EWI sites hope to reduce their CC referrals by providing telehealth PT services to veterans who might otherwise need to be referred to CC. This strategy aligns with VHA goals of providing high-quality and timely care. To better understand opportunities for programs like TR-EWI to provide rehabilitation services for veterans and reduce care sent to the community, research that examines CC referral trends for PT over time is warranted.
This study examines CC from a rehabilitation perspective with a focus on CC referral trends for PT, specifically for Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) where TREWI sites are located. The study’s objectives were to describe rehabilitation PT services being referred to CC and examine associated CC costs for PT services. Two research questions guided the study. First, what are the utilization trends for CC PT referrals from fiscal year (FY) 2019 to FY 2022? Secondly, what is the cost breakdown of CC for PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022?
Methods
This study was conducted by a multidisciplinary team comprised of public health, disability, rehabilitation counseling, and PT professionals. It was deemed a quality improvement project under VA guidance and followed the SQUIRE guidelines for quality improvement reporting.24,25 The study used the VA Common Operating Platform (Palantir) to obtain individual-level CC referral data from the HealthShare Referral Manager (HSRM) database and consult data from the Computerized Patient Record System. Palantir is used to store and integrate VA data derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and VHA Support Service Center. Referrals are authorizations for care to be delivered by a CC practitioner.
TR-EWI is comprised of 7 sites: VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 8, VISN 12, VISN 15, VISN 19, and VISN 22. Each site provides telerehabilitation services with an emphasis on reaching veterans living in rural communities. We joined the referrals and consults cubes in Palantir to extract PT referrals for FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs with TR-EWI sites and obtain referral-specific information and demographic characteristics. 26 Data were extracted in October 2022.
The VHA Community Care Referral Dashboard (CC Dashboard) provided nonindividual level CC cost data.27 The CC Dashboard provides insights into the costs of CC services for VHA enrollees by category of care, standardized episode of care, and eligibility. Data are based on nationallevel HSRM referrals that are not suspended or linked to a canceled or discontinued consult. Data were aggregated by VISN. The dashboard only includes referrals dating back to FY 2020; therefore, PT data from FY 2020 through FY 2022 for VISNs with TR-EWI sites were collected. Data were extracted in December 2022.
This study examined CC referrals, station name, eligibility types, clinical diagnoses (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes), and demographic information in the Palantir dataset. Six eligibility criteria can qualify a veteran to receive CC.28 Within clinical diagnoses, the variable of interest was the provisional diagnosis. Patient demographics included age, gender, and rurality of residence, as determined by the Rural-Urban Commuting Area system.29,30 Rural and highly rural categories were combined for analysis. For the CC cost dataset, this study examined CC referrals, referral cost, and eligibility type.
Analysis
For the first research question, we examined referral data from FY 2019 to FY 2022 using the Palantir dataset, performed descriptive statistical analysis for all variables, and analyzed data to identify trends. Descriptive statistics were completed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows Version 29.0.0.0.
A qualitative analysis of provisional diagnosis data revealed what is being referred to CC for PT. A preliminary overview of provisional diagnosis data was conducted to familiarize coders with the data. We developed a coding framework to categorize diagnoses based on anatomical location, body structure, and clinical areas of interest. Data were reviewed individually and grouped into categories within the coding framework before meeting as a team to achieve group consensus on categorization. We then totaled the frequency of occurrence for provisional diagnoses within each category. Qualitative analyses were completed using Microsoft Excel.
For the second research question, the study used the CC cost dataset to examine the cost breakdown of CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. We calculated the number and cost of PT referrals across eligibility groups for each FY and VISN. Data were analyzed using SPSS to identify cost trends.
Results
There were 344,406 referrals to CC for PT from FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs analyzed (Table 1). Of these, 22.5% were from FY 2019, 19.1% from FY 2020, 28.2% from FY 2021, and 30.3% from FY 2022. VISN 8 and VISN 22 reported the most overall PT referrals, with VISN 8 comprising 22.2% and VISN 22 comprising 18.1% of all referrals. VISN 2 reported the least overall referrals (3.7%). VISN 4 and VISN 12 had decreases in referrals over time. VISN 2 and VISN 15 had decreases in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2021 and slight increases from FY 2021 to FY 2022. VISN 19 and VISN 22 both saw slight increases from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and substantial increases from FY 2020 to FY 2022, with FY 2022 accounting for 40.0% and 42.3% of all referrals for VISN 19 and VISN 20, respectively (Figure 1).


For FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 8 had the highest percentage of referrals (26.7% and 23.2%, respectively), whereas VISN 22 was among the lowest (7.3% and 11.4%, respectively). However, for FY 2021 and FY 2022, VISN 22 reported the highest percentage of referrals (23.5% and 25.3%, respectively) compared to all other VISNs. VISN 2 consistently reported the lowest percentage of referrals across all years.
There were 56 stations analyzed across the 7 VISNs (Appendix 1). Nine stations each accounted for ≥ 3.0% of the total PT referrals and only 2 stations accounted for > 5.0% of referrals. Orlando, Florida (6.0%), Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (5.2%), Tampa, Florida (4.9%), Aurora, Colorado (4.9%), and Gainesville, Florida (4.4%) reported the top 5 highest referrals, with 3 being from VISN 8 (Orlando, Tampa, Gainesville). Stations with the lowest reported referrals were all in VISN 2 in New York: The Bronx, (0%), New York Harbor (0%), Hudson Valley (0.1%) and Finger Lakes (0.2%).

Rurality
Urban stations comprised 56.2% and rural stations comprised 39.8% of PT CC referrals, while 0.2% of referrals were from insular isle US territories: Guam, American Samoa, Northern Marianas, and the Virgin Islands. The sample had missing or unknown data for 3.8% of referrals. FY 2022 had the largest difference in rural and urban referrals. Additionally, there was an overall trend of more referrals over time for rural and urban, with a large increase in rural (+40.0%) and urban (+62.7%) referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2021 and a modest increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 (+5.2% for rural and +9.1% for urban). There was a decrease in rural (-7.0%) and urban (-3.5%) referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 (Figure 2).

There were differences in referrals by rurality and VISN (Table 2). VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals, whereas VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 reported more urban than rural referrals. VISN 2 reported similar numbers for both, with slightly more urban than rural referrals. When reviewing trends over time for each FY, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 had more urban than rural referrals. In FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 2 reported slightly more urban than rural referrals but almost the same number of referrals in FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Appendix 2).


Demographics
The mean (SD) age was 61.2 (15.8) years (range, 20-105). Most PT CC referrals were for veterans aged 70 to 79 years (26.9%), followed by 60 to 69 years (20.7%), and 50 to 59 years (16.4%) (Appendix 3). Trends were consistent across VISNs. There was less of a difference between rural and urban referral percentages as the population aged. Veterans aged < 49 years residing in more urban areas accounted for more referrals to CC compared to their rural counterparts. This difference was less apparent in the 70 to 79 years and 80 to 89 years age brackets.

Most PT CC referrals (81.2%) were male and 14.8% were female. About 3.6% of referral data were missing sex information, and there was a smaller difference between male veterans living in rural communities and male veterans living in urban communities compared with female veterans. A total of 42.9% of male veterans resided in rural areas compared to 56.8% in urban areas; 32.7% of female veterans resided in rural areas compared to 66.9% in urban areas (Appendix 3).
Other Criteria
Of the 334,406 referrals, 114,983 (34.4%) had eligibility data, mostly from FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Table 3). Available eligibility data were likely affected by the MISSION Act and new regulations for reporting CC eligibility. Distance (33.4%) was the most common eligibility criteria, followed by timeliness of care (28.8%), and best medical interest (19.8%); 40.4% were rural and 59.5% were urban. Distance (55.4%) was most common for rural veterans, while timeliness of care (39.7%) was most common for urban veterans. For both groups, the second most common eligibility reason was best medical interest (Appendix 4).


Bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders were common diagnoses, with 25.2% located in the lower back, 14.7% in the shoulder, and 12.8% in the knee (Appendix 5). Amputations of the upper and lower limbs, fractures, cancer-related diagnoses, integumentary system disorders, thoracic and abdominal injuries and disorders, and other medical and mental health conditions each accounted for < 1% of the total diagnoses.

Costs
At time of analysis, the CC Dashboard had cost data available for 200,204 CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. The difference in referral numbers for the 2 datasets is likely attributed to several factors: CC cost data is exclusively from the HSRM, whereas Palantir includes other data sources; how VA cleans data pulled into Palantir; how the CC Dashboard algorithm populates data; and variances based on timing of reporting and/or if referrals are eventually canceled.
The total cost of PT CC referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 in selected VISNs was about $220,615,399 (Appendix 6). Appendix 7 details the methodology for determining the average standardized episode- of-care cost by VISN and how referral costs are calculated. Data show a continuous increase in total estimated cost from $46.8 million in FY 2020 to $92.1 million in FY 2022. From FY 2020 to FY 2022, aggregate costs ranged from $6,758,053 in VISN 2 to $47,209,162 in VISN 8 (Figure 3). The total referral cost for PT was highest at VISN 4 in FY 2020 ($10,447,140) and highest at VISN 22 in FY 2021 ($18,835,657) and FY 2022 ($22,962,438) (Figure 4). For referral costs from FY 2020 to FY 2022, distance accounted for $75,561,948 (34.3%), timeliness of care accounted for $60,413,496 (27.3%), and best medical interest accounted for $46,291,390 (21.0%) (Table 4).





Overall costs were primarily driven by specific VISNs within each eligibility type (Appendix 8; Figure 5). VISN 19, VISN 22, and VISN 15 accounted for the highest referral costs for distance; VISN 22, VISN 8, and VISN 19 accounted for the secondhighest referral cost, timeliness of care; and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 12 accounted for the third-highest referral cost, best medical interest (Figure 5). VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 22 had service unavailable as an eligibility type with 1 of the top 3 associated referral costs, which was higher in cost than timeliness of care for VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, and VISN 15.


Discussion
This study examines the referral of rehabilitation PT services to CC, evaluates CC costs for PT services, and analyzes utilization and cost trends among veterans within the VHA. Utilization data demonstrated a decrease in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and increases in referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 for most variables of interest, with cost data exhibiting similar trends. Results highlight the need for further investigation to address variations in PT referrals and costs across VISNs and eligibility reasons for CC referral.
Results demonstrated a noteworthy increase in PT CC referrals over time. The largest increase occurred from FY 2020 to FY 2021, with a smaller increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022. During this period, total enrollee numbers decreased by 3.0% across the 7 VISNs included in this analysis and by 1.6% across all VISNs, a trend that illustrates an overall decrease in enrollees as CC use increased. Results align with the implementation of the MISSION Act of 2018, which further expanded veterans’ options to use CC.1,6,7 Results also align with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted care access for many veterans, placed a larger emphasis on the use of telehealth, and increased opportunities to stay within the VA for care by rapidly shifting to telehealth and leveraging telerehabilitation investments and initiatives (such as TR-EWI).20,31
VISN 8, VISN 19, and VISN 22, accounted for more than half of PT referrals. These VISNs had higher enrollee counts compared to the other VISNs.32 VISN 8 consistently had high levels of referrals, whereas VISN 19 and VISN 22 saw dramatic increases in FY 2021 and FY 2022. In contrast, VISN 4 and VISN 12 gradually decreased referrals during the study. VISN 2 had the lowest referral numbers during the study period, and all stations with the lowest individual referral numbers were located within VISN 2. Of the VISNs included in this study, VISN 2 had the second lowest number of enrollees (324,042).32 Reasons for increases and decreases over time could not be determined based on data collected in this study.
There were more urban than rural PT CC referrals; however, both exhibited an increase in referrals over time. This is consistent with population trends showing that most VHA patients (62.6%) and veterans (75.9%) reside in urban areas, which could explain some of the trends in this study.33 Some VISNs have larger urban catchment areas (eg, VISN 8 and VISN 22), and some have larger rural catchment areas (eg, VISN 15 and VISN 19), which could partially explain the rural-urban differences by VISN.32 Rural-urban referral trends might also reflect existing health care delivery system deficits in rural areas and known challenges associated with accessing health care for veterans living in rural communities.8,9
This study found larger differences in rural and urban PT CC referrals for younger age groups, with more than twice as many urban referrals in veterans aged 20 to 29 years and aged 30 to 39 years, and roughly 1.8 times as many urban referrals in veterans aged 40 to 49 years. However, there were similar numbers of rural and urban referrals in those aged 70 to 79 years and aged 80 to 89 years. These trends are consistent with data showing veterans residing in rural communities are older than their urban counterparts.23,34 Data suggest that older veteran populations might seek PT at higher rates than younger veteran populations. Moreover, data suggest there could be differences in PT-seeking rates for younger veteran populations who reside in rural vs urban areas. Additional research is needed to understand these trends.
Distance and timeliness of care were the predominant reasons for referral among eligibility groups, which is consistent with the MISSION Act goals.1,6,7 The most common eligibility reason for rural referrals was distance; timeliness of care was most common for urban referrals. This finding is expected, as veterans living in rural communities are farther away from VHA facilities and have longer drive times, whereas veterans living in urban communities might live closer, yet experience longer wait times due to services and/or appointment availability. Best medical interest accounted for almost 20% of referrals, which does not provide detailed insights into why those veterans were referred to CC.
The top PT diagnoses referred to CC were related to bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders of the lower back, shoulder, and knee. This suggests that musculoskeletal-related issues are prevalent among veterans seeking PT care, which is consistent with research that found > 50% of veterans receiving VHA care have musculoskeletal disorders.35 The probability of experiencing musculoskeletal problems increases with age, as does the need for PT services. Amputations and fractures accounted for < 1% of CC referrals, which is consistent with the historic provision of VHA clinical specialized care to conditions prevalent among veterans. It may also represent VHA efforts to internally provide care for complex conditions requiring more extensive interdisciplinary coordination.
The total cost of referrals over time was about $221 million. VISN 8 accounted for the highest overall cost; VISN 2 had the lowest, mirroring referral utilization trends and aligning with VISN enrollee numbers. VISN 19 and VISN 22 reported large cost increases from FY 2020 to FY 2021. Total referral costs increased by $34.9 million from FY 2020 to FY 2021, which may be due to health care inflation (2.9% during FY 2019 to FY 2022), increased awareness of CC services, or increased VHA wait times.36 Additionally, there were limitations in care provided across health care systems during the COVID-19 pandemic, including the VA.5 The increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021 may reflect a rebound from restrictions in appointments across VA, CC, and the private sector.
While the increase in total referral cost may be partly attributed to inflation, the cost effectiveness and efficiency of referring veterans to CC vs keeping veterans within VHA care is an ongoing debate.5 Examining and addressing cost drivers within the top eligibility types and their respective VISNs is necessary to determine resource allocation and improve quality of care. This study found that best medical interest and unavailable services accounted for 33.4% of the total cost of CC referrals, highlighting the need for policies that strengthen in-house competencies and recruit personnel to provide PT services currently unavailable within the VA.
Future Directions
The VHA should explore opportunities for in-house care, especially for services appropriate for telehealth.18,20,37 Data indicated a smaller cost increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 compared to the relatively large increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021. The increased telehealth usage across VHA by TR-EWI and non—TR-EWI sites within selected VISNs may have contributed to limiting the increase in CC costs. Future studies should investigate contextual factors of increased telehealth usage, which would offer guidance for implementation to optimize the integration of telehealth with PT rehabilitation provided in-house. Additionally, future studies can examine potential limitations experienced during PT telehealth visits, such as the inability to conduct hands-on assessments, challenges in viewing the quality of patient movement, ensuring patient safety in the remote environment, and the lack of PT equipment in homes for telehealth visits, and how these challenges are being addressed.38,39 Research is also needed to understand tradeoffs of CC vs VHA care and the potential and cost benefits of keeping veterans within VHA using programs like TR-EWI.5 Veterans living in rural communities may especially benefit from this as expanding telehealth options can provide access to PT care that may not be readily available, enabling them to stay connected and engaged in their care.18,40
Future studies could examine contributory factors to rising costs, such as demographic shifts, changes in PT service utilization, and policy. Researchers might also consider qualitative studies with clinicians and veterans within each VISN, which may provide insights into how local factors impact PT referral to the community.
Limitations
Due to its descriptive nature, this study can only speculate about factors influencing trends. Limitations include the inability to link the Palantir and CC Dashboard datasets for cost comparisons and potential data change over time on Palantir due to platform updates. The focus on VISNs with TREWI sites limited generalizability and this study did not compare CC PT vs VHA PT. Finally, there may have been cost drivers not identified in this study.
Conclusions
This descriptive study provides insights into the utilization and cost of PT CC referrals for selected VISNs. Cost trends underscore the financial commitment to providing PT services to veterans. Understanding what factors are driving this cost is necessary for VHA to optimally provide and manage the rehabilitation resources needed to serve veterans through traditional in-person care, telehealth, and CC options while ensuring timely, highquality care.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the largest US integrated health system, providing care to veterans through VHA and non-VHA practitioners and facilities.1,2 Providing high-quality, timely, and veteran-centric care remains a priority for the VHA. Legislative efforts have expanded opportunities for eligible veterans to receive care in the community purchased by VHA, known as community care (CC).1 The Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014 came in response to reports of long wait times and drive times for patients.3-5 The MISSION Act of 2018 expanded access to CC by streamlining it and broadening eligibility criteria, especially for veterans in rural communities who often experience more barriers in accessing care than veterans living in urban communities.1,6-10 Since the implementation of the Choice and MISSION Acts, > 2.7 million veterans have received care through community practitioners within the VHA CC network.11
Background
Increased access to CC could benefit veterans living in rural communities by increasing care options and circumventing challenges to accessing VHA care (ie, geographic, transportation, and distance barriers, practitioner and specialist shortages, and hospital closures). 5,9,10,12,13 However, health care system deficits in rural areas could also limit CC effectiveness for veterans living in those communities. 3 Other challenges posed by using CC include care coordination, information sharing, care continuity, delayed payments to CC practitioners, and mixed findings regarding CC quality.5,8,13,14 VHA practitioners are specifically trained to meet the multifaceted needs unique to veterans’ health and subculture, training CC practitioners may not receive.5,15
CC offers services for primary care and a broad range of specialties, including rehabilitation services such as physical therapy (PT).6 PT is used for the effective treatment of various conditions veterans experience and promote wellbeing and independence.16 US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) databases reveal a high prevalence of veterans receiving PT services through CC; PT is one of the most frequently used CC outpatient specialty services by veterans living in rural communities.14,17
Telerehabitltation Enterprisewide Initiative
VHA has greatly invested in delivering care virtually, especially for veterans living in rural communities.18 In 2017, the VHA Office of Rural Health funded the Telerehabilitation Enterprise-Wide Initiative (TR-EWI) in partnership with the Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Services national program office to increase access to specialized rehabilitation services for veterans living in rural communities by leveraging telehealth technologies.18-21 This alternative mode of health care delivery allows clinicians to overcome access barriers by delivering rehabilitation therapies directly to veterans' homes or nearby community-based outpatient clinics. TR-EWI was conceived as a hub-and-spoke model, where rehabilitation expertise at the hub was virtually delivered to spoke sites that did not have in-house expertise. In subsequent years, the TR-EWI also evolved to provide targeted telerehabilitation programs within rural-serving community-based outpatient clinics, including PT as a predominant service.19,20
As TR-EWI progressed—and in conjunction with the uptake of telehealth across VHA during the COVID-19 pandemic—there has been increased focus on PT telerehabilitation, especially for the 4.6 million veterans in rural communities.18,22,23 Because health care delivery system deficits in rural areas could limit the effective use of CC, many TR-EWI sites hope to reduce their CC referrals by providing telehealth PT services to veterans who might otherwise need to be referred to CC. This strategy aligns with VHA goals of providing high-quality and timely care. To better understand opportunities for programs like TR-EWI to provide rehabilitation services for veterans and reduce care sent to the community, research that examines CC referral trends for PT over time is warranted.
This study examines CC from a rehabilitation perspective with a focus on CC referral trends for PT, specifically for Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs) where TREWI sites are located. The study’s objectives were to describe rehabilitation PT services being referred to CC and examine associated CC costs for PT services. Two research questions guided the study. First, what are the utilization trends for CC PT referrals from fiscal year (FY) 2019 to FY 2022? Secondly, what is the cost breakdown of CC for PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022?
Methods
This study was conducted by a multidisciplinary team comprised of public health, disability, rehabilitation counseling, and PT professionals. It was deemed a quality improvement project under VA guidance and followed the SQUIRE guidelines for quality improvement reporting.24,25 The study used the VA Common Operating Platform (Palantir) to obtain individual-level CC referral data from the HealthShare Referral Manager (HSRM) database and consult data from the Computerized Patient Record System. Palantir is used to store and integrate VA data derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse and VHA Support Service Center. Referrals are authorizations for care to be delivered by a CC practitioner.
TR-EWI is comprised of 7 sites: VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 8, VISN 12, VISN 15, VISN 19, and VISN 22. Each site provides telerehabilitation services with an emphasis on reaching veterans living in rural communities. We joined the referrals and consults cubes in Palantir to extract PT referrals for FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs with TR-EWI sites and obtain referral-specific information and demographic characteristics. 26 Data were extracted in October 2022.
The VHA Community Care Referral Dashboard (CC Dashboard) provided nonindividual level CC cost data.27 The CC Dashboard provides insights into the costs of CC services for VHA enrollees by category of care, standardized episode of care, and eligibility. Data are based on nationallevel HSRM referrals that are not suspended or linked to a canceled or discontinued consult. Data were aggregated by VISN. The dashboard only includes referrals dating back to FY 2020; therefore, PT data from FY 2020 through FY 2022 for VISNs with TR-EWI sites were collected. Data were extracted in December 2022.
This study examined CC referrals, station name, eligibility types, clinical diagnoses (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision codes), and demographic information in the Palantir dataset. Six eligibility criteria can qualify a veteran to receive CC.28 Within clinical diagnoses, the variable of interest was the provisional diagnosis. Patient demographics included age, gender, and rurality of residence, as determined by the Rural-Urban Commuting Area system.29,30 Rural and highly rural categories were combined for analysis. For the CC cost dataset, this study examined CC referrals, referral cost, and eligibility type.
Analysis
For the first research question, we examined referral data from FY 2019 to FY 2022 using the Palantir dataset, performed descriptive statistical analysis for all variables, and analyzed data to identify trends. Descriptive statistics were completed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows Version 29.0.0.0.
A qualitative analysis of provisional diagnosis data revealed what is being referred to CC for PT. A preliminary overview of provisional diagnosis data was conducted to familiarize coders with the data. We developed a coding framework to categorize diagnoses based on anatomical location, body structure, and clinical areas of interest. Data were reviewed individually and grouped into categories within the coding framework before meeting as a team to achieve group consensus on categorization. We then totaled the frequency of occurrence for provisional diagnoses within each category. Qualitative analyses were completed using Microsoft Excel.
For the second research question, the study used the CC cost dataset to examine the cost breakdown of CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. We calculated the number and cost of PT referrals across eligibility groups for each FY and VISN. Data were analyzed using SPSS to identify cost trends.
Results
There were 344,406 referrals to CC for PT from FY 2019 to FY 2022 for the 7 VISNs analyzed (Table 1). Of these, 22.5% were from FY 2019, 19.1% from FY 2020, 28.2% from FY 2021, and 30.3% from FY 2022. VISN 8 and VISN 22 reported the most overall PT referrals, with VISN 8 comprising 22.2% and VISN 22 comprising 18.1% of all referrals. VISN 2 reported the least overall referrals (3.7%). VISN 4 and VISN 12 had decreases in referrals over time. VISN 2 and VISN 15 had decreases in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2021 and slight increases from FY 2021 to FY 2022. VISN 19 and VISN 22 both saw slight increases from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and substantial increases from FY 2020 to FY 2022, with FY 2022 accounting for 40.0% and 42.3% of all referrals for VISN 19 and VISN 20, respectively (Figure 1).


For FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 8 had the highest percentage of referrals (26.7% and 23.2%, respectively), whereas VISN 22 was among the lowest (7.3% and 11.4%, respectively). However, for FY 2021 and FY 2022, VISN 22 reported the highest percentage of referrals (23.5% and 25.3%, respectively) compared to all other VISNs. VISN 2 consistently reported the lowest percentage of referrals across all years.
There were 56 stations analyzed across the 7 VISNs (Appendix 1). Nine stations each accounted for ≥ 3.0% of the total PT referrals and only 2 stations accounted for > 5.0% of referrals. Orlando, Florida (6.0%), Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (5.2%), Tampa, Florida (4.9%), Aurora, Colorado (4.9%), and Gainesville, Florida (4.4%) reported the top 5 highest referrals, with 3 being from VISN 8 (Orlando, Tampa, Gainesville). Stations with the lowest reported referrals were all in VISN 2 in New York: The Bronx, (0%), New York Harbor (0%), Hudson Valley (0.1%) and Finger Lakes (0.2%).

Rurality
Urban stations comprised 56.2% and rural stations comprised 39.8% of PT CC referrals, while 0.2% of referrals were from insular isle US territories: Guam, American Samoa, Northern Marianas, and the Virgin Islands. The sample had missing or unknown data for 3.8% of referrals. FY 2022 had the largest difference in rural and urban referrals. Additionally, there was an overall trend of more referrals over time for rural and urban, with a large increase in rural (+40.0%) and urban (+62.7%) referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2021 and a modest increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 (+5.2% for rural and +9.1% for urban). There was a decrease in rural (-7.0%) and urban (-3.5%) referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 (Figure 2).

There were differences in referrals by rurality and VISN (Table 2). VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals, whereas VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 reported more urban than rural referrals. VISN 2 reported similar numbers for both, with slightly more urban than rural referrals. When reviewing trends over time for each FY, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 19 reported more rural than urban referrals and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 22 had more urban than rural referrals. In FY 2019 and FY 2020, VISN 2 reported slightly more urban than rural referrals but almost the same number of referrals in FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Appendix 2).


Demographics
The mean (SD) age was 61.2 (15.8) years (range, 20-105). Most PT CC referrals were for veterans aged 70 to 79 years (26.9%), followed by 60 to 69 years (20.7%), and 50 to 59 years (16.4%) (Appendix 3). Trends were consistent across VISNs. There was less of a difference between rural and urban referral percentages as the population aged. Veterans aged < 49 years residing in more urban areas accounted for more referrals to CC compared to their rural counterparts. This difference was less apparent in the 70 to 79 years and 80 to 89 years age brackets.

Most PT CC referrals (81.2%) were male and 14.8% were female. About 3.6% of referral data were missing sex information, and there was a smaller difference between male veterans living in rural communities and male veterans living in urban communities compared with female veterans. A total of 42.9% of male veterans resided in rural areas compared to 56.8% in urban areas; 32.7% of female veterans resided in rural areas compared to 66.9% in urban areas (Appendix 3).
Other Criteria
Of the 334,406 referrals, 114,983 (34.4%) had eligibility data, mostly from FY 2021 and FY 2022 (Table 3). Available eligibility data were likely affected by the MISSION Act and new regulations for reporting CC eligibility. Distance (33.4%) was the most common eligibility criteria, followed by timeliness of care (28.8%), and best medical interest (19.8%); 40.4% were rural and 59.5% were urban. Distance (55.4%) was most common for rural veterans, while timeliness of care (39.7%) was most common for urban veterans. For both groups, the second most common eligibility reason was best medical interest (Appendix 4).


Bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders were common diagnoses, with 25.2% located in the lower back, 14.7% in the shoulder, and 12.8% in the knee (Appendix 5). Amputations of the upper and lower limbs, fractures, cancer-related diagnoses, integumentary system disorders, thoracic and abdominal injuries and disorders, and other medical and mental health conditions each accounted for < 1% of the total diagnoses.

Costs
At time of analysis, the CC Dashboard had cost data available for 200,204 CC PT referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022. The difference in referral numbers for the 2 datasets is likely attributed to several factors: CC cost data is exclusively from the HSRM, whereas Palantir includes other data sources; how VA cleans data pulled into Palantir; how the CC Dashboard algorithm populates data; and variances based on timing of reporting and/or if referrals are eventually canceled.
The total cost of PT CC referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 in selected VISNs was about $220,615,399 (Appendix 6). Appendix 7 details the methodology for determining the average standardized episode- of-care cost by VISN and how referral costs are calculated. Data show a continuous increase in total estimated cost from $46.8 million in FY 2020 to $92.1 million in FY 2022. From FY 2020 to FY 2022, aggregate costs ranged from $6,758,053 in VISN 2 to $47,209,162 in VISN 8 (Figure 3). The total referral cost for PT was highest at VISN 4 in FY 2020 ($10,447,140) and highest at VISN 22 in FY 2021 ($18,835,657) and FY 2022 ($22,962,438) (Figure 4). For referral costs from FY 2020 to FY 2022, distance accounted for $75,561,948 (34.3%), timeliness of care accounted for $60,413,496 (27.3%), and best medical interest accounted for $46,291,390 (21.0%) (Table 4).





Overall costs were primarily driven by specific VISNs within each eligibility type (Appendix 8; Figure 5). VISN 19, VISN 22, and VISN 15 accounted for the highest referral costs for distance; VISN 22, VISN 8, and VISN 19 accounted for the secondhighest referral cost, timeliness of care; and VISN 4, VISN 8, and VISN 12 accounted for the third-highest referral cost, best medical interest (Figure 5). VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, VISN 15, and VISN 22 had service unavailable as an eligibility type with 1 of the top 3 associated referral costs, which was higher in cost than timeliness of care for VISN 2, VISN 4, VISN 12, and VISN 15.


Discussion
This study examines the referral of rehabilitation PT services to CC, evaluates CC costs for PT services, and analyzes utilization and cost trends among veterans within the VHA. Utilization data demonstrated a decrease in referrals from FY 2019 to FY 2020 and increases in referrals from FY 2020 to FY 2022 for most variables of interest, with cost data exhibiting similar trends. Results highlight the need for further investigation to address variations in PT referrals and costs across VISNs and eligibility reasons for CC referral.
Results demonstrated a noteworthy increase in PT CC referrals over time. The largest increase occurred from FY 2020 to FY 2021, with a smaller increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022. During this period, total enrollee numbers decreased by 3.0% across the 7 VISNs included in this analysis and by 1.6% across all VISNs, a trend that illustrates an overall decrease in enrollees as CC use increased. Results align with the implementation of the MISSION Act of 2018, which further expanded veterans’ options to use CC.1,6,7 Results also align with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted care access for many veterans, placed a larger emphasis on the use of telehealth, and increased opportunities to stay within the VA for care by rapidly shifting to telehealth and leveraging telerehabilitation investments and initiatives (such as TR-EWI).20,31
VISN 8, VISN 19, and VISN 22, accounted for more than half of PT referrals. These VISNs had higher enrollee counts compared to the other VISNs.32 VISN 8 consistently had high levels of referrals, whereas VISN 19 and VISN 22 saw dramatic increases in FY 2021 and FY 2022. In contrast, VISN 4 and VISN 12 gradually decreased referrals during the study. VISN 2 had the lowest referral numbers during the study period, and all stations with the lowest individual referral numbers were located within VISN 2. Of the VISNs included in this study, VISN 2 had the second lowest number of enrollees (324,042).32 Reasons for increases and decreases over time could not be determined based on data collected in this study.
There were more urban than rural PT CC referrals; however, both exhibited an increase in referrals over time. This is consistent with population trends showing that most VHA patients (62.6%) and veterans (75.9%) reside in urban areas, which could explain some of the trends in this study.33 Some VISNs have larger urban catchment areas (eg, VISN 8 and VISN 22), and some have larger rural catchment areas (eg, VISN 15 and VISN 19), which could partially explain the rural-urban differences by VISN.32 Rural-urban referral trends might also reflect existing health care delivery system deficits in rural areas and known challenges associated with accessing health care for veterans living in rural communities.8,9
This study found larger differences in rural and urban PT CC referrals for younger age groups, with more than twice as many urban referrals in veterans aged 20 to 29 years and aged 30 to 39 years, and roughly 1.8 times as many urban referrals in veterans aged 40 to 49 years. However, there were similar numbers of rural and urban referrals in those aged 70 to 79 years and aged 80 to 89 years. These trends are consistent with data showing veterans residing in rural communities are older than their urban counterparts.23,34 Data suggest that older veteran populations might seek PT at higher rates than younger veteran populations. Moreover, data suggest there could be differences in PT-seeking rates for younger veteran populations who reside in rural vs urban areas. Additional research is needed to understand these trends.
Distance and timeliness of care were the predominant reasons for referral among eligibility groups, which is consistent with the MISSION Act goals.1,6,7 The most common eligibility reason for rural referrals was distance; timeliness of care was most common for urban referrals. This finding is expected, as veterans living in rural communities are farther away from VHA facilities and have longer drive times, whereas veterans living in urban communities might live closer, yet experience longer wait times due to services and/or appointment availability. Best medical interest accounted for almost 20% of referrals, which does not provide detailed insights into why those veterans were referred to CC.
The top PT diagnoses referred to CC were related to bone, joint, or soft tissue disorders of the lower back, shoulder, and knee. This suggests that musculoskeletal-related issues are prevalent among veterans seeking PT care, which is consistent with research that found > 50% of veterans receiving VHA care have musculoskeletal disorders.35 The probability of experiencing musculoskeletal problems increases with age, as does the need for PT services. Amputations and fractures accounted for < 1% of CC referrals, which is consistent with the historic provision of VHA clinical specialized care to conditions prevalent among veterans. It may also represent VHA efforts to internally provide care for complex conditions requiring more extensive interdisciplinary coordination.
The total cost of referrals over time was about $221 million. VISN 8 accounted for the highest overall cost; VISN 2 had the lowest, mirroring referral utilization trends and aligning with VISN enrollee numbers. VISN 19 and VISN 22 reported large cost increases from FY 2020 to FY 2021. Total referral costs increased by $34.9 million from FY 2020 to FY 2021, which may be due to health care inflation (2.9% during FY 2019 to FY 2022), increased awareness of CC services, or increased VHA wait times.36 Additionally, there were limitations in care provided across health care systems during the COVID-19 pandemic, including the VA.5 The increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021 may reflect a rebound from restrictions in appointments across VA, CC, and the private sector.
While the increase in total referral cost may be partly attributed to inflation, the cost effectiveness and efficiency of referring veterans to CC vs keeping veterans within VHA care is an ongoing debate.5 Examining and addressing cost drivers within the top eligibility types and their respective VISNs is necessary to determine resource allocation and improve quality of care. This study found that best medical interest and unavailable services accounted for 33.4% of the total cost of CC referrals, highlighting the need for policies that strengthen in-house competencies and recruit personnel to provide PT services currently unavailable within the VA.
Future Directions
The VHA should explore opportunities for in-house care, especially for services appropriate for telehealth.18,20,37 Data indicated a smaller cost increase from FY 2021 to FY 2022 compared to the relatively large increase from FY 2020 to FY 2021. The increased telehealth usage across VHA by TR-EWI and non—TR-EWI sites within selected VISNs may have contributed to limiting the increase in CC costs. Future studies should investigate contextual factors of increased telehealth usage, which would offer guidance for implementation to optimize the integration of telehealth with PT rehabilitation provided in-house. Additionally, future studies can examine potential limitations experienced during PT telehealth visits, such as the inability to conduct hands-on assessments, challenges in viewing the quality of patient movement, ensuring patient safety in the remote environment, and the lack of PT equipment in homes for telehealth visits, and how these challenges are being addressed.38,39 Research is also needed to understand tradeoffs of CC vs VHA care and the potential and cost benefits of keeping veterans within VHA using programs like TR-EWI.5 Veterans living in rural communities may especially benefit from this as expanding telehealth options can provide access to PT care that may not be readily available, enabling them to stay connected and engaged in their care.18,40
Future studies could examine contributory factors to rising costs, such as demographic shifts, changes in PT service utilization, and policy. Researchers might also consider qualitative studies with clinicians and veterans within each VISN, which may provide insights into how local factors impact PT referral to the community.
Limitations
Due to its descriptive nature, this study can only speculate about factors influencing trends. Limitations include the inability to link the Palantir and CC Dashboard datasets for cost comparisons and potential data change over time on Palantir due to platform updates. The focus on VISNs with TREWI sites limited generalizability and this study did not compare CC PT vs VHA PT. Finally, there may have been cost drivers not identified in this study.
Conclusions
This descriptive study provides insights into the utilization and cost of PT CC referrals for selected VISNs. Cost trends underscore the financial commitment to providing PT services to veterans. Understanding what factors are driving this cost is necessary for VHA to optimally provide and manage the rehabilitation resources needed to serve veterans through traditional in-person care, telehealth, and CC options while ensuring timely, highquality care.
- Congressional Budget Office. The Veterans Community Care Program: Background and Early Effects. October 26, 2021. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.cbo.gov/publication/57257
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Providing Health Care for Veterans. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/
- Davila H, Rosen AK, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Chatelain LJ, Gurewich D. Rural veterans’ experiences with outpatient care in the Veterans Health Administration versus community care. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S286-S291. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001552
- Vanneman ME, Wagner TH, Shwartz M, et al. Veterans’ experiences with outpatient care: comparing the Veterans Affairs system with community-based care. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1368-1376. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01375
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10(3):9.
- Feyman Y, Legler A, Griffith KN. Appointment wait time data for primary & specialty care in veterans health administration facilities vs. community medical centers. Data Brief. 2021;36:107134. doi:10.1016/j.dib.2021.107134
- Kelley AT, Greenstone CL, Kirsh SR. Defining access and the role of community care in the Veterans Health Administration. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(5):1584-1585. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05358-z
- Garvin LA, Pugatch M, Gurewich D, Pendergast JN, Miller CJ. Interorganizational care coordination of rural veterans by Veterans Affairs and community care programs: a systematic review. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S259-S269. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001542
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans: Rural Veteran Health Care Challenges. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https:// www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- Ohl ME, Carrell M, Thurman A, et al. “Availability of healthcare providers for rural veterans eligible for purchased care under the veterans choice act.” BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):315. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3108-8
- Mattocks KM, Cunningham KJ, Greenstone C, Atkins D, Rosen AK, Upton M. Innovations in community care programs, policies, and research. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S229-S231. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001550
- Doyle JM, Streeter RA. Veterans’ location in health professional shortage areas: implications for access to care and workforce supply. Health Serv Res. 2017;52 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):459-480. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.12633
- Patzel M, Barnes C, Ramalingam N, et al. Jumping through hoops: community care clinician and staff experiences providing primary care to rural veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(Suppl 3):821-828. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08126-2
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Olenick M, Flowers M, Diaz VJ. US veterans and their unique issues: enhancing health care professional awareness. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2015;6:635-639. doi:10.2147/AMEP.S89479
- Campbell P, Pope R, Simas V, Canetti E, Schram B, Orr R. The effects of early physiotherapy treatment on musculoskeletal injury outcomes in military personnel: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(20):13416. doi:10.3390/ijerph192013416
- Gurewich D, Shwartz M, Beilstein-Wedel E, Davila H, Rosen AK. Did access to care improve since passage of the veterans choice act? Differences between rural and urban veterans. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S270-S278. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001490
- Myers US, Birks A, Grubaugh AL, Axon RN. Flattening the curve by getting ahead of it: how the VA healthcare system is leveraging telehealth to provide continued access to care for rural veterans. J Rural Health. 2021;37(1):194-196. doi:10.1111/jrh.12449
- Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for rural veterans: a qualitative assessment of barriers and facilitators to implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
- Kreider CM, Hale-Gallardo J, Kramer JC, et al. Providers’ shift to telerehabilitation at the U.S. Veterans Health Administration during COVID-19: practical applications. Front Public Health. 2022;10:831762. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.831762
- Cowper-Ripley DC, Jia H, Wang X, et al. Trends in VA telerehabilitation patients and encounters over time and by rurality. Fed Pract. 2019;36(3):122-128.
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. VHA Office of Rural Health. Updated August 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/index.asp
- National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Rural Veterans: 2021-2023. April 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.datahub.va.gov/stories/s/Rural-Veterans-FY2021-2023/kkh2-eymp/
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Program Guide: 1200.21, VHA Operations Activities That May Constitute Research. January 9, 2019. https://www.research.va.gov/resources/policies/ProgramGuide-1200-21-VHA-Operations-Activities.pdf
- Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. J Nurs Care Qual. 2016;31(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000153
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Updated January 29, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- Stomberg C, Frost A, Becker C, Stang H, Windschitl M, Carrier E. Community Care referral dashboard [Data dashboard]. https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/reports/090d22a7-0e1f-4cc5-bea8-0a1b87aa0bd9/ReportSectionacfd03cdebd76ffca9ec [Source not verified]
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for community care outside VA. Updated May 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/programs/veterans/General_Care.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. How to define rurality fact sheet. Updated December 2023. Accessed January 28, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/docs/ORH_RuralityFactSheet_508.pdf
- Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes.aspx
- Gurewich D, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Davila H, Rosen AK. Disparities in wait times for care among US veterans by race and ethnici t y. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2252061. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.52061
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Office of Rural Health, Veterans Rural Health Resource Center-Gainesville, GeoSpatial Outcomes Division. VA and Community Healthcare, and VHA Rurality web map application. Published 2023. https://portal.vhagis.inv.vaec.va.gov/arcgis/apps/webappbuilder/index.html [source not verified]
- Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans: National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; November 2020. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/research/findings/nhqrdr/chartbooks/veterans/index.html
- Lum HD, Nearing K, Pimentel CB, Levy CR, Hung WW. Anywhere to anywhere: use of telehealth to increase health care access for older, rural veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):12-18. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz030
- Goulet JL, Kerns RD, Bair M, et al. The musculoskeletal diagnosis cohort: examining pain and pain care among veterans. Pain. 2016;157(8):1696-1703. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000567
- US Inflation Calculator. Health Care Inflation in the United States (1948-2024). Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.usinflationcalculator.com/inflation/health-care-inflation-in-the-united-states/
- Cottrell MA, Galea OA, O’Leary SP, Hill AJ, Russell TG. Real-time telerehabilitation for the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions is effective and comparable to standard practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2017;31(5):625-638. doi:10.1177/0269215516645148
- Elor A, Conde S, Powel l M, Robbins A, Chen NN, Kurniawan S. Physical therapist impressions of telehealth and virtual reality needs amidst a pandemic. Front Virtual Real. 2022;3. doi:10.3389/frvir.2022.915332
- Lee AC, Harada N. Telehealth as a means of health care delivery for physical therapist practice. Phys Ther. 2012;92(3):463-468. doi:10.2522/ptj.20110100
- Hynes DM, Edwards S, Hickok A, et al. Veterans’ use of Veterans Health Administration primary care in an era of expanding choice. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S292- S300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001554
- Congressional Budget Office. The Veterans Community Care Program: Background and Early Effects. October 26, 2021. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.cbo.gov/publication/57257
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Providing Health Care for Veterans. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/
- Davila H, Rosen AK, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Chatelain LJ, Gurewich D. Rural veterans’ experiences with outpatient care in the Veterans Health Administration versus community care. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S286-S291. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001552
- Vanneman ME, Wagner TH, Shwartz M, et al. Veterans’ experiences with outpatient care: comparing the Veterans Affairs system with community-based care. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1368-1376. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.01375
- Rasmussen P, Farmer CM. The promise and challenges of VA community care: veterans’ issues in focus. Rand Health Q. 2023;10(3):9.
- Feyman Y, Legler A, Griffith KN. Appointment wait time data for primary & specialty care in veterans health administration facilities vs. community medical centers. Data Brief. 2021;36:107134. doi:10.1016/j.dib.2021.107134
- Kelley AT, Greenstone CL, Kirsh SR. Defining access and the role of community care in the Veterans Health Administration. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(5):1584-1585. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05358-z
- Garvin LA, Pugatch M, Gurewich D, Pendergast JN, Miller CJ. Interorganizational care coordination of rural veterans by Veterans Affairs and community care programs: a systematic review. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S259-S269. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001542
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural Veterans: Rural Veteran Health Care Challenges. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https:// www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- Ohl ME, Carrell M, Thurman A, et al. “Availability of healthcare providers for rural veterans eligible for purchased care under the veterans choice act.” BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):315. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3108-8
- Mattocks KM, Cunningham KJ, Greenstone C, Atkins D, Rosen AK, Upton M. Innovations in community care programs, policies, and research. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S229-S231. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001550
- Doyle JM, Streeter RA. Veterans’ location in health professional shortage areas: implications for access to care and workforce supply. Health Serv Res. 2017;52 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):459-480. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.12633
- Patzel M, Barnes C, Ramalingam N, et al. Jumping through hoops: community care clinician and staff experiences providing primary care to rural veterans. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(Suppl 3):821-828. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08126-2
- Mattocks KM, Kroll-Desrosiers A, Kinney R, Elwy AR, Cunningham KJ, Mengeling MA. Understanding VA’s use of and relationships with community care providers under the MISSION Act. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S252-S258. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001545
- Olenick M, Flowers M, Diaz VJ. US veterans and their unique issues: enhancing health care professional awareness. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2015;6:635-639. doi:10.2147/AMEP.S89479
- Campbell P, Pope R, Simas V, Canetti E, Schram B, Orr R. The effects of early physiotherapy treatment on musculoskeletal injury outcomes in military personnel: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(20):13416. doi:10.3390/ijerph192013416
- Gurewich D, Shwartz M, Beilstein-Wedel E, Davila H, Rosen AK. Did access to care improve since passage of the veterans choice act? Differences between rural and urban veterans. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S270-S278. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001490
- Myers US, Birks A, Grubaugh AL, Axon RN. Flattening the curve by getting ahead of it: how the VA healthcare system is leveraging telehealth to provide continued access to care for rural veterans. J Rural Health. 2021;37(1):194-196. doi:10.1111/jrh.12449
- Hale-Gallardo JL, Kreider CM, Jia H, et al. Telerehabilitation for rural veterans: a qualitative assessment of barriers and facilitators to implementation. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:559-570. doi:10.2147/JMDH.S247267
- Kreider CM, Hale-Gallardo J, Kramer JC, et al. Providers’ shift to telerehabilitation at the U.S. Veterans Health Administration during COVID-19: practical applications. Front Public Health. 2022;10:831762. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.831762
- Cowper-Ripley DC, Jia H, Wang X, et al. Trends in VA telerehabilitation patients and encounters over time and by rurality. Fed Pract. 2019;36(3):122-128.
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. VHA Office of Rural Health. Updated August 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/index.asp
- National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Rural Veterans: 2021-2023. April 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.datahub.va.gov/stories/s/Rural-Veterans-FY2021-2023/kkh2-eymp/
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research & Development. Program Guide: 1200.21, VHA Operations Activities That May Constitute Research. January 9, 2019. https://www.research.va.gov/resources/policies/ProgramGuide-1200-21-VHA-Operations-Activities.pdf
- Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. J Nurs Care Qual. 2016;31(1):1-8. doi:10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000153
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration: Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Updated January 29, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- Stomberg C, Frost A, Becker C, Stang H, Windschitl M, Carrier E. Community Care referral dashboard [Data dashboard]. https://app.powerbigov.us/groups/me/reports/090d22a7-0e1f-4cc5-bea8-0a1b87aa0bd9/ReportSectionacfd03cdebd76ffca9ec [Source not verified]
- US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for community care outside VA. Updated May 30, 2024. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.va.gov/COMMUNITYCARE/programs/veterans/General_Care.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. How to define rurality fact sheet. Updated December 2023. Accessed January 28, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/docs/ORH_RuralityFactSheet_508.pdf
- Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes.aspx
- Gurewich D, Beilstein-Wedel E, Shwartz M, Davila H, Rosen AK. Disparities in wait times for care among US veterans by race and ethnici t y. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(1):e2252061. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.52061
- U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Office of Rural Health, Veterans Rural Health Resource Center-Gainesville, GeoSpatial Outcomes Division. VA and Community Healthcare, and VHA Rurality web map application. Published 2023. https://portal.vhagis.inv.vaec.va.gov/arcgis/apps/webappbuilder/index.html [source not verified]
- Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans: National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; November 2020. Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/research/findings/nhqrdr/chartbooks/veterans/index.html
- Lum HD, Nearing K, Pimentel CB, Levy CR, Hung WW. Anywhere to anywhere: use of telehealth to increase health care access for older, rural veterans. Public Policy Aging Rep. 2020;30(1):12-18. doi:10.1093/ppar/prz030
- Goulet JL, Kerns RD, Bair M, et al. The musculoskeletal diagnosis cohort: examining pain and pain care among veterans. Pain. 2016;157(8):1696-1703. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000567
- US Inflation Calculator. Health Care Inflation in the United States (1948-2024). Accessed September 23, 2024. https://www.usinflationcalculator.com/inflation/health-care-inflation-in-the-united-states/
- Cottrell MA, Galea OA, O’Leary SP, Hill AJ, Russell TG. Real-time telerehabilitation for the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions is effective and comparable to standard practice: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2017;31(5):625-638. doi:10.1177/0269215516645148
- Elor A, Conde S, Powel l M, Robbins A, Chen NN, Kurniawan S. Physical therapist impressions of telehealth and virtual reality needs amidst a pandemic. Front Virtual Real. 2022;3. doi:10.3389/frvir.2022.915332
- Lee AC, Harada N. Telehealth as a means of health care delivery for physical therapist practice. Phys Ther. 2012;92(3):463-468. doi:10.2522/ptj.20110100
- Hynes DM, Edwards S, Hickok A, et al. Veterans’ use of Veterans Health Administration primary care in an era of expanding choice. Med Care. 2021;59(Suppl 3):S292- S300. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001554
Utilization and Cost of Veterans Health Administration Referrals to Community Care-Based Physical Therapy
Utilization and Cost of Veterans Health Administration Referrals to Community Care-Based Physical Therapy
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.
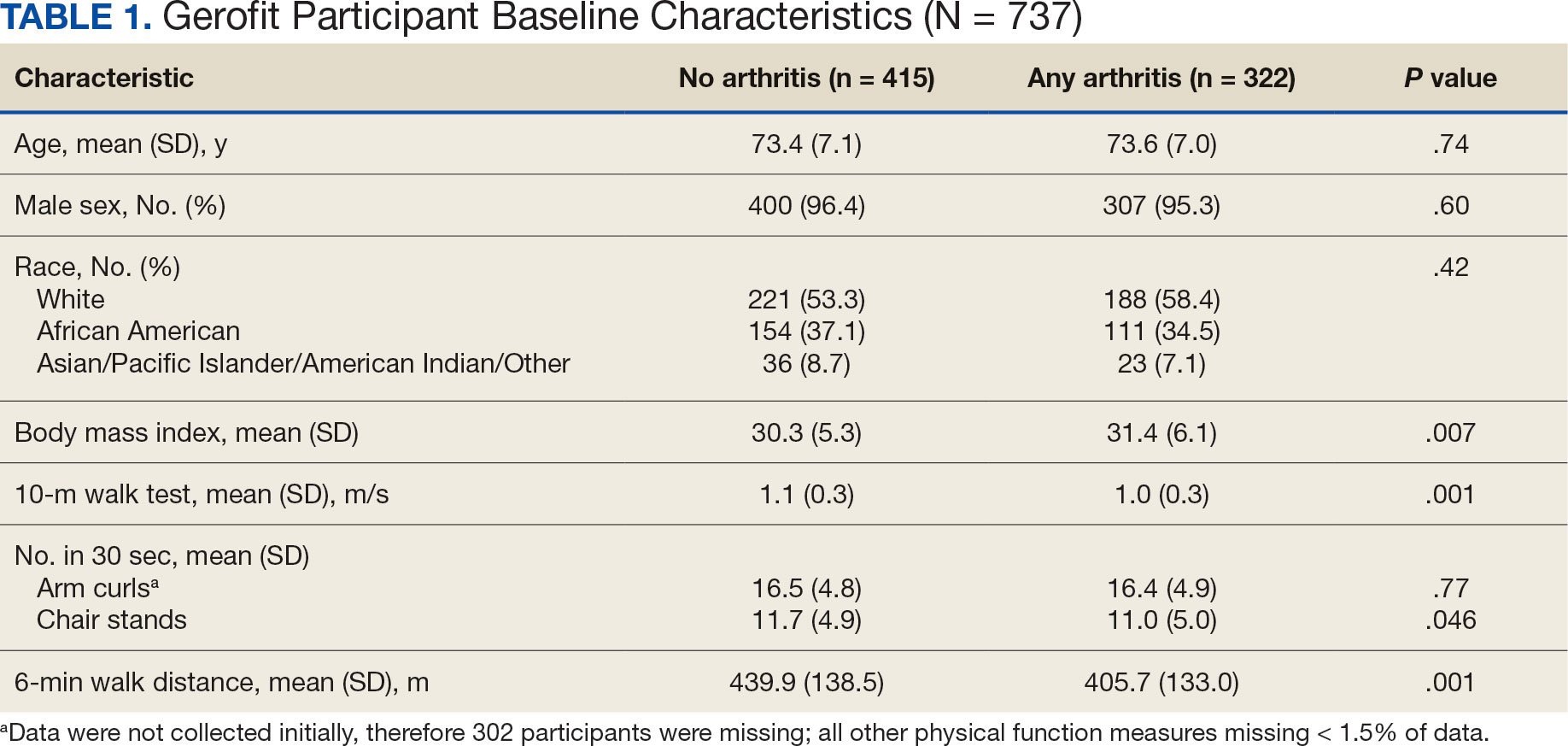
All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).
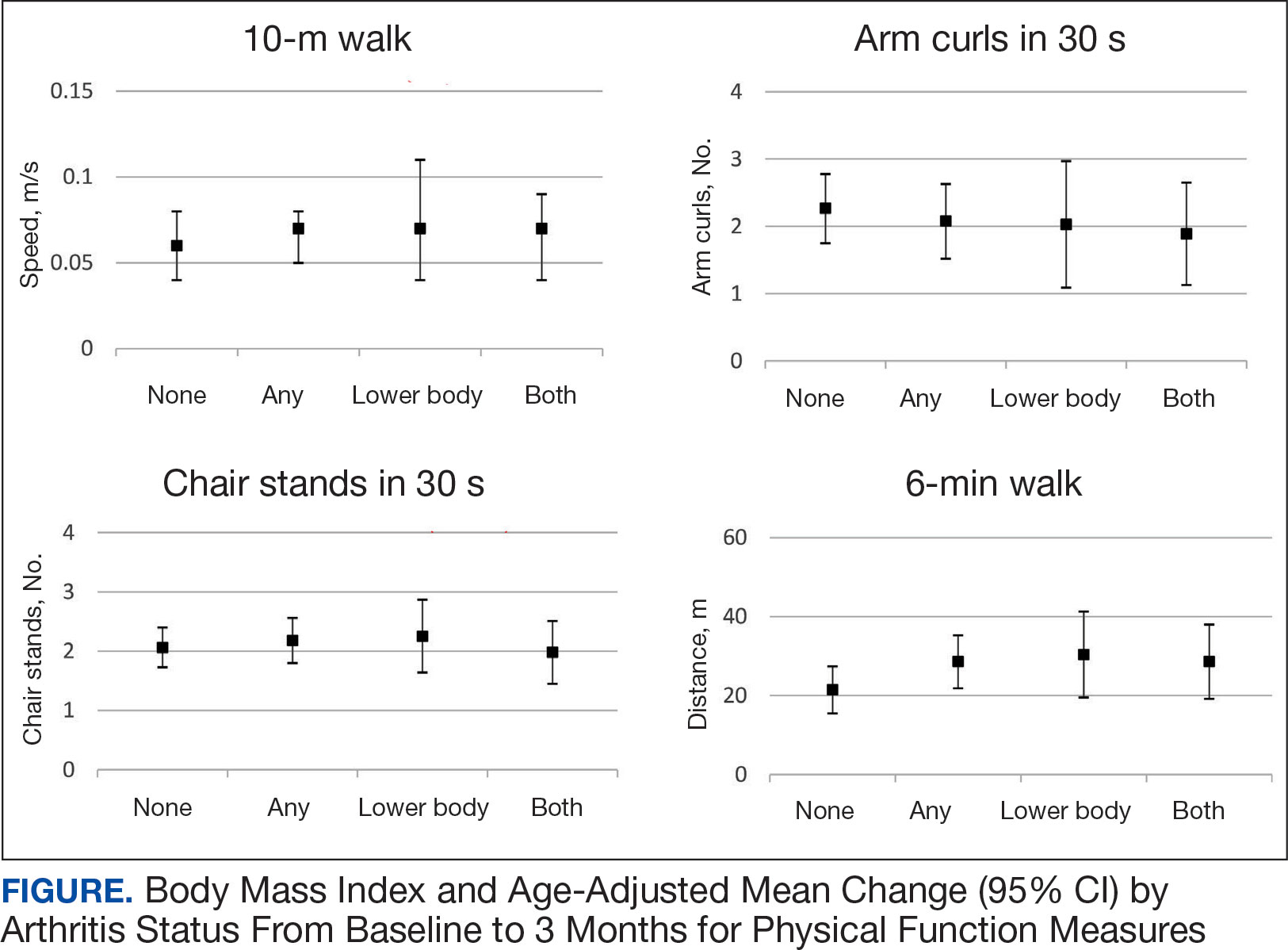
We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.
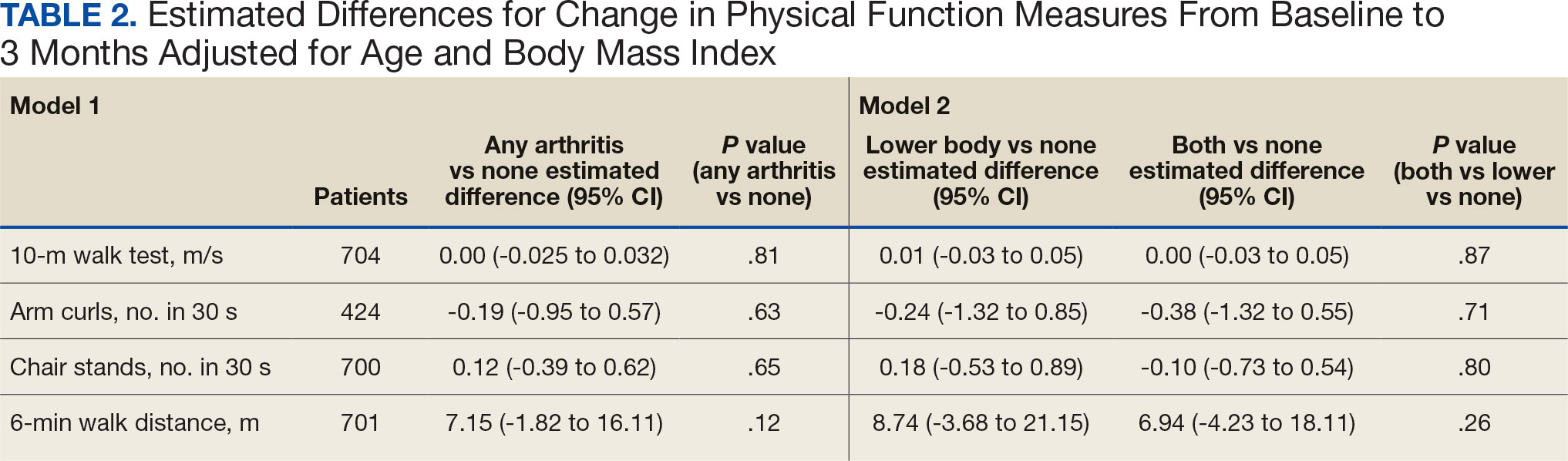
Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.

All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).

We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.

Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.

All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).

We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.

Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Improving High-Risk Osteoporosis Medication Adherence and Safety With an Automated Dashboard
Improving High-Risk Osteoporosis Medication Adherence and Safety With an Automated Dashboard
Osteoporotic fragility fractures constitute a significant public health concern, with 1 in 2 women and 1 in 5 men aged > 50 years sustaining an osteoporotic fracture.1 Osteoporotic fractures are costly and associated with reduced quality of life and impaired survival.2-6 Many interventions including fall mitigation, calcium, vitamin D supplementation, and osteoporosis—specific medications reduce fracture risk.7 New medications for treating osteoporosis, including anabolic therapies, are costly and require clinical oversight to ensure safe delivery. This includes laboratory monitoring, timing of in-clinic dosing and provision of sequence therapy.8,9 COVID-19 introduced numerous barriers to osteoporosis care, raising concerns for medication interruption and patients lost to follow-up, which made monitoring these high risk and costly medications even more important.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was an early adopter of using the electronic health record to analyze and implement system-wide processes for population management and quality improvement.10 This enabled the creation of clinical dashboards to display key performance indicator data that support quality improvement and patient care initiatives.11-15 The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) has a dedicated osteoporosis clinic focused on preventing and treating veterans at high risk for fracture. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, particularly those requiring timed sequential therapy to prevent bone mineral density loss and rebound osteoporotic fractures, close monitoring and follow-up is required. The COVID-19 pandemic made clear the need for proactive osteoporosis management. This article describes the creation and use of an automated clinic dashboard to identify and contact veterans with osteoporosis-related care needs, such as prescription refills, laboratory tests, and clinical visits.
Methods
An automated dashboard was created in partnership with VA pharmacy clinical informatics to display the osteoporosis medication prescription (including last refill), monitoring laboratory test values and most recent osteoporosis clinic visit for each clinic patient. Data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse were extracted. The resulting tables were used to create a patient cohort with ≥ 1 active medication for alendronate, zoledronic acid, the parathyroid hormone analogues (PTH) teriparatide or abaloparatide, denosumab, or romosozumab. Notably, alendronate was the only oral bisphosphonate prescribed in the clinic. These data were formatted and displayed using Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services. The secure and encrypted dashboard alerts the clinic staff when prescriptions, appointments, or laboratory tests, such as estimated glomerular filtration rate, 25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcium, and PTH are overdue or out of reference range. The dashboard tracked the most recent clinic visit or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan if performed within the VA. Overdue laboratory test alerts for bisphosphonates were flagged if delayed 12 months and 6 months for all other medications.
On March 20, 2021, the VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic was staffed by 1 endocrinologist, 1 geriatrician, 1 rheumatologist, and 1 registered nurse (RN) coordinator. Overdue or out-of-range alerts were reviewed weekly by the RN coordinator, who addressed alerts. For any overdue laboratory work or prescription refills, the RN coordinator alerted the primary osteoporosis physician via the electronic health record for updated orders. Patients were contacted by phone to schedule a clinic visit, complete ordered laboratory work, or discuss osteoporosis medication refills based on the need identified by the dashboard. A letter was mailed to the patient requesting they contact the osteoporosis clinic for patients who could not be reached by phone after 2 attempts. If 3 attempts (2 phone calls and a letter) were unsuccessful, the osteoporosis physician was alerted so they could either call the patient, alert the primary referring clinician, or discontinue the osteoporosis medication.
Results
As of March 20, 2021, 139 patients were included on the dashboard. Ninety-two patients (66%) had unmet care needs and 29% were female. Ages ranged from 40 to 100 years (Table). The dashboard alerted the team to 3 patients lost to follow-up, all of whom had transferred to care outside the clinic. Twenty-three patients (17%) had overdue medications, including 2 (9%) who had not refilled oral bisphosphonate and 18 (78%) who were overdue for intravenous bisphosphonate treatment. One veteran flagged as overdue for their denosumab injection was unable to receive it due to a significant change in health status. Two veterans were overdue for a PTH analogue refill, 1 of whom had completed their course and transitioned to bisphosphonate.
The most common alert was 40 patients (29%) with overdue laboratory tests, 37 of which were receiving bisphosphonates. One patient included on the dashboard was taking romosozumab and all their monitoring parameters were up to date, thus their data were not included in the Table to prevent possible identification.
Discussion
A dashboard alerted the osteoporosis clinic team to veterans who were overdue for visits, laboratory work, and prescription renewals. Overall, 92 patients (66%) had unmet care needs identified by the dashboard, all of which were addressed with phone calls and/or letters. Most of the overdue medication refills and laboratory tests were for patients taking bisphosphonates avoiding VAPSHCS during the COVID-19 pandemic. The dashboard enabled the RN coordinator to promptly contact the patient, facilitate coordination of care requirements, and guarantee the safe and efficient delivery of osteoporosis care.
The VA has historically been a leader in the creation of clinical dashboards to support health campaigns.11,12 These dashboards have successfully improved quality metrics towards the treatment of hepatitis C virus, heart failure, and highrisk opioid prescribing.13-15 Data have shown that successful clinical dashboard implementation must be done in conjunction with protected time or staff to support care improvements.16 Additionally, the time required for clinical dashboards can limit their sustainability and feasibility.17 A study aimed at improving osteoporosis care for patients with Parkinson disease found that weekly multidisciplinary review of at-risk patients resulted in all new patients and 91% of follow-up patients receiving evidence- based osteoporosis treatments.17 However, despite the benefits, the intervention required significant time and resources. In contrast, the osteoporosis dashboard implemented at VAPSHCS was not time or resource intensive, requiring about 1 hour per week for the RN coordinator to review the dashboard and coordinate patient care needs.
Limitations
This study setting is unique from other health care organizations or VA health care systems. Implementation of a similar dashboard in other clinical settings where patients receive medical care in multiple health care systems may differ. The VA dedicates resources to support veteran population health management, which may not be available in other health care systems.11,12 These issues may pose a barrier to implementing a similar osteoporosis dashboard in non-VA facilities. In addition, it is significant that while the dashboard can be reconfigured and adapted to track veterans across different VA facilities, certain complexities arise if essential data, such as laboratory tests and DXA imaging, are conducted outside of VA facilities. In such cases, manual entry of this information into the dashboard would be necessary. Because the dashboard was quickly developed during the COVID-19 pandemic, this study lacked preimplementation data on laboratory testing, medication refills, and DXA imaging, which would have enabled a comparison of adherence before and after dashboard implementation. Finally, we acknowledge the delay in publishing these findings; however, we believe sharing innovative approaches to providing care for high-risk populations is essential, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions
An osteoporosis clinic dashboard served as a valuable clinical support tool to ensure safe and effective osteoporosis medication delivery at VAPSHCS. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, this dashboard plays a vital role in facilitating care coordination for patients receiving these high-risk treatments.18 Use of the dashboard supported the effective use of high-cost osteoporosis medications and is likely to improve clinical osteoporosis outcomes.
Despite the known fracture risk reduction, osteoporosis medication adherence is low.19,20 Maintaining consistent pharmacotherapy for osteoporosis is essential not only for fracture prevention but also reducing health care costs related to osteoporosis and preserving patient independence and functionality.21-24 While initially developed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the dashboard remains useful. The VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic is now staffed by 2 physicians (endocrine and rheumatology) and the dashboard is still in use. The RN coordinator spends about 15 minutes per week using the dashboard and managing the 67 veterans on osteoporosis therapy. This dashboard represents a sustainable clinical tool with the capacity to minimize osteoporosis care gaps and improve outcomes.
- Johnell O, Kanis J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(suppl 2):S3-S7. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1702-6
- van Staa TP, Dennison EM, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone. 2001;29:517-522. doi:10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00614-7
- Dennison E, Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Horm Res. 2000;54(suppl 1):58-63. doi:10.1159/000063449
- Cooper C. Epidemiology and public health impact of osteoporosis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1993;7:459-477. doi:10.1016/s0950-3579(05)80073-1
- Dolan P, Torgerson DJ. The cost of treating osteoporotic fractures in the United Kingdom female population. Osteoporos Int. 1998;8:611-617. doi:10.1007/s001980050107
- Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:465-475. doi:10.1359/jbmr.061113
- Palacios S. Medical treatment of osteoporosis. Climacteric. 2022;25:43-49. doi:10.1080/13697137.2021.1951697
- Eastell R, Rosen CJ, Black DM, Cheung AM, Murad MH, Shoback D. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: an Endocrine Society* clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:1595-1622. doi:10.1210/jc.2019-00221
- Watts NB, Adler RA, Bilezikian JP, et al. Osteoporosis in men: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:1802-1822. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3045
- Lau MK, Bounthavong M, Kay CL, Harvey MA, Christopher MLD. Clinical dashboard development and use for academic detailing in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(2S):S96-S103.e3. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2018.12.006
- Mould DR, D’Haens G, Upton RN. Clinical decision support tools: the evolution of a revolution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;99:405-418. doi:10.1002/cpt.334
- Kizer KW, Fonseca ML, Long LM. The veterans healthcare system: preparing for the twenty-first century. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1997;42:283-298.
- Park A, Gonzalez R, Chartier M, et al. Screening and treating hepatitis c in the VA: achieving excellence using lean and system redesign. Fed Pract. 2018;35:24-29.
- Brownell N, Kay C, Parra D, et al. Development and optimization of the Veterans Affairs’ national heart failure dashboard for population health management. J Card Fail. 2024;30:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2023.08.024
- Lin LA, Bohnert ASB, Kerns RD, Clay MA, Ganoczy D, Ilgen MA. Impact of the opioid safety initiative on opioidrelated prescribing in veterans. Pain. 2017;158:833-839. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000837
- Twohig PA, Rivington JR, Gunzler D, Daprano J, Margolius D. Clinician dashboard views and improvement in preventative health outcome measures: a retrospective analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19:475. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4327-3
- Singh I, Fletcher R, Scanlon L, Tyler M, Aithal S. A quality improvement initiative on the management of osteoporosis in older people with Parkinsonism. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5:u210921.w5756. doi:10.1136/bmjquality.u210921.w5756
- Anastasilakis AD, Makras P, Yavropoulou MP, Tabacco G, Naciu AM, Palermo A. Denosumab discontinuation and the rebound phenomenon: a narrative review. J Clin Med. 2021;10:152. doi:10.3390/jcm10010152
- Sharman Moser S, Yu J, Goldshtein I, et al. Cost and consequences of nonadherence with oral bisphosphonate therapy: findings from a real-world data analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50:262-269. doi:10.1177/1060028015626935
- Olsen KR, Hansen C, Abrahamsen B. Association between refill compliance to oral bisphosphonate treatment, incident fractures, and health care costs--an analysis using national health databases. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2639-2647. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2365-y
- Blouin J, Dragomir A, Fredette M, Ste-Marie LG, Fernandes JC, Perreault S. Comparison of direct health care costs related to the pharmacological treatment of osteoporosis and to the management of osteoporotic fractures among compliant and noncompliant users of alendronate and risedronate: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:1571-1581. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0818-5
- Cotté F-E, De Pouvourville G. Cost of non-persistence with oral bisphosphonates in post-menopausal osteoporosis treatment in France. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:151. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-151
- Cho H, Byun J-H, Song I, et al. Effect of improved medication adherence on health care costs in osteoporosis patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11470. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000011470
- Li N, Cornelissen D, Silverman S, et al. An updated systematic review of cost-effectiveness analyses of drugs for osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39:181-209. doi:10.1007/s40273-020-00965-9
Osteoporotic fragility fractures constitute a significant public health concern, with 1 in 2 women and 1 in 5 men aged > 50 years sustaining an osteoporotic fracture.1 Osteoporotic fractures are costly and associated with reduced quality of life and impaired survival.2-6 Many interventions including fall mitigation, calcium, vitamin D supplementation, and osteoporosis—specific medications reduce fracture risk.7 New medications for treating osteoporosis, including anabolic therapies, are costly and require clinical oversight to ensure safe delivery. This includes laboratory monitoring, timing of in-clinic dosing and provision of sequence therapy.8,9 COVID-19 introduced numerous barriers to osteoporosis care, raising concerns for medication interruption and patients lost to follow-up, which made monitoring these high risk and costly medications even more important.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was an early adopter of using the electronic health record to analyze and implement system-wide processes for population management and quality improvement.10 This enabled the creation of clinical dashboards to display key performance indicator data that support quality improvement and patient care initiatives.11-15 The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) has a dedicated osteoporosis clinic focused on preventing and treating veterans at high risk for fracture. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, particularly those requiring timed sequential therapy to prevent bone mineral density loss and rebound osteoporotic fractures, close monitoring and follow-up is required. The COVID-19 pandemic made clear the need for proactive osteoporosis management. This article describes the creation and use of an automated clinic dashboard to identify and contact veterans with osteoporosis-related care needs, such as prescription refills, laboratory tests, and clinical visits.
Methods
An automated dashboard was created in partnership with VA pharmacy clinical informatics to display the osteoporosis medication prescription (including last refill), monitoring laboratory test values and most recent osteoporosis clinic visit for each clinic patient. Data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse were extracted. The resulting tables were used to create a patient cohort with ≥ 1 active medication for alendronate, zoledronic acid, the parathyroid hormone analogues (PTH) teriparatide or abaloparatide, denosumab, or romosozumab. Notably, alendronate was the only oral bisphosphonate prescribed in the clinic. These data were formatted and displayed using Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services. The secure and encrypted dashboard alerts the clinic staff when prescriptions, appointments, or laboratory tests, such as estimated glomerular filtration rate, 25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcium, and PTH are overdue or out of reference range. The dashboard tracked the most recent clinic visit or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan if performed within the VA. Overdue laboratory test alerts for bisphosphonates were flagged if delayed 12 months and 6 months for all other medications.
On March 20, 2021, the VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic was staffed by 1 endocrinologist, 1 geriatrician, 1 rheumatologist, and 1 registered nurse (RN) coordinator. Overdue or out-of-range alerts were reviewed weekly by the RN coordinator, who addressed alerts. For any overdue laboratory work or prescription refills, the RN coordinator alerted the primary osteoporosis physician via the electronic health record for updated orders. Patients were contacted by phone to schedule a clinic visit, complete ordered laboratory work, or discuss osteoporosis medication refills based on the need identified by the dashboard. A letter was mailed to the patient requesting they contact the osteoporosis clinic for patients who could not be reached by phone after 2 attempts. If 3 attempts (2 phone calls and a letter) were unsuccessful, the osteoporosis physician was alerted so they could either call the patient, alert the primary referring clinician, or discontinue the osteoporosis medication.
Results
As of March 20, 2021, 139 patients were included on the dashboard. Ninety-two patients (66%) had unmet care needs and 29% were female. Ages ranged from 40 to 100 years (Table). The dashboard alerted the team to 3 patients lost to follow-up, all of whom had transferred to care outside the clinic. Twenty-three patients (17%) had overdue medications, including 2 (9%) who had not refilled oral bisphosphonate and 18 (78%) who were overdue for intravenous bisphosphonate treatment. One veteran flagged as overdue for their denosumab injection was unable to receive it due to a significant change in health status. Two veterans were overdue for a PTH analogue refill, 1 of whom had completed their course and transitioned to bisphosphonate.

The most common alert was 40 patients (29%) with overdue laboratory tests, 37 of which were receiving bisphosphonates. One patient included on the dashboard was taking romosozumab and all their monitoring parameters were up to date, thus their data were not included in the Table to prevent possible identification.
Discussion
A dashboard alerted the osteoporosis clinic team to veterans who were overdue for visits, laboratory work, and prescription renewals. Overall, 92 patients (66%) had unmet care needs identified by the dashboard, all of which were addressed with phone calls and/or letters. Most of the overdue medication refills and laboratory tests were for patients taking bisphosphonates avoiding VAPSHCS during the COVID-19 pandemic. The dashboard enabled the RN coordinator to promptly contact the patient, facilitate coordination of care requirements, and guarantee the safe and efficient delivery of osteoporosis care.
The VA has historically been a leader in the creation of clinical dashboards to support health campaigns.11,12 These dashboards have successfully improved quality metrics towards the treatment of hepatitis C virus, heart failure, and highrisk opioid prescribing.13-15 Data have shown that successful clinical dashboard implementation must be done in conjunction with protected time or staff to support care improvements.16 Additionally, the time required for clinical dashboards can limit their sustainability and feasibility.17 A study aimed at improving osteoporosis care for patients with Parkinson disease found that weekly multidisciplinary review of at-risk patients resulted in all new patients and 91% of follow-up patients receiving evidence- based osteoporosis treatments.17 However, despite the benefits, the intervention required significant time and resources. In contrast, the osteoporosis dashboard implemented at VAPSHCS was not time or resource intensive, requiring about 1 hour per week for the RN coordinator to review the dashboard and coordinate patient care needs.
Limitations
This study setting is unique from other health care organizations or VA health care systems. Implementation of a similar dashboard in other clinical settings where patients receive medical care in multiple health care systems may differ. The VA dedicates resources to support veteran population health management, which may not be available in other health care systems.11,12 These issues may pose a barrier to implementing a similar osteoporosis dashboard in non-VA facilities. In addition, it is significant that while the dashboard can be reconfigured and adapted to track veterans across different VA facilities, certain complexities arise if essential data, such as laboratory tests and DXA imaging, are conducted outside of VA facilities. In such cases, manual entry of this information into the dashboard would be necessary. Because the dashboard was quickly developed during the COVID-19 pandemic, this study lacked preimplementation data on laboratory testing, medication refills, and DXA imaging, which would have enabled a comparison of adherence before and after dashboard implementation. Finally, we acknowledge the delay in publishing these findings; however, we believe sharing innovative approaches to providing care for high-risk populations is essential, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions
An osteoporosis clinic dashboard served as a valuable clinical support tool to ensure safe and effective osteoporosis medication delivery at VAPSHCS. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, this dashboard plays a vital role in facilitating care coordination for patients receiving these high-risk treatments.18 Use of the dashboard supported the effective use of high-cost osteoporosis medications and is likely to improve clinical osteoporosis outcomes.
Despite the known fracture risk reduction, osteoporosis medication adherence is low.19,20 Maintaining consistent pharmacotherapy for osteoporosis is essential not only for fracture prevention but also reducing health care costs related to osteoporosis and preserving patient independence and functionality.21-24 While initially developed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the dashboard remains useful. The VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic is now staffed by 2 physicians (endocrine and rheumatology) and the dashboard is still in use. The RN coordinator spends about 15 minutes per week using the dashboard and managing the 67 veterans on osteoporosis therapy. This dashboard represents a sustainable clinical tool with the capacity to minimize osteoporosis care gaps and improve outcomes.
Osteoporotic fragility fractures constitute a significant public health concern, with 1 in 2 women and 1 in 5 men aged > 50 years sustaining an osteoporotic fracture.1 Osteoporotic fractures are costly and associated with reduced quality of life and impaired survival.2-6 Many interventions including fall mitigation, calcium, vitamin D supplementation, and osteoporosis—specific medications reduce fracture risk.7 New medications for treating osteoporosis, including anabolic therapies, are costly and require clinical oversight to ensure safe delivery. This includes laboratory monitoring, timing of in-clinic dosing and provision of sequence therapy.8,9 COVID-19 introduced numerous barriers to osteoporosis care, raising concerns for medication interruption and patients lost to follow-up, which made monitoring these high risk and costly medications even more important.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) was an early adopter of using the electronic health record to analyze and implement system-wide processes for population management and quality improvement.10 This enabled the creation of clinical dashboards to display key performance indicator data that support quality improvement and patient care initiatives.11-15 The VA Puget Sound Health Care System (VAPSHCS) has a dedicated osteoporosis clinic focused on preventing and treating veterans at high risk for fracture. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, particularly those requiring timed sequential therapy to prevent bone mineral density loss and rebound osteoporotic fractures, close monitoring and follow-up is required. The COVID-19 pandemic made clear the need for proactive osteoporosis management. This article describes the creation and use of an automated clinic dashboard to identify and contact veterans with osteoporosis-related care needs, such as prescription refills, laboratory tests, and clinical visits.
Methods
An automated dashboard was created in partnership with VA pharmacy clinical informatics to display the osteoporosis medication prescription (including last refill), monitoring laboratory test values and most recent osteoporosis clinic visit for each clinic patient. Data from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse were extracted. The resulting tables were used to create a patient cohort with ≥ 1 active medication for alendronate, zoledronic acid, the parathyroid hormone analogues (PTH) teriparatide or abaloparatide, denosumab, or romosozumab. Notably, alendronate was the only oral bisphosphonate prescribed in the clinic. These data were formatted and displayed using Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services. The secure and encrypted dashboard alerts the clinic staff when prescriptions, appointments, or laboratory tests, such as estimated glomerular filtration rate, 25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcium, and PTH are overdue or out of reference range. The dashboard tracked the most recent clinic visit or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan if performed within the VA. Overdue laboratory test alerts for bisphosphonates were flagged if delayed 12 months and 6 months for all other medications.
On March 20, 2021, the VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic was staffed by 1 endocrinologist, 1 geriatrician, 1 rheumatologist, and 1 registered nurse (RN) coordinator. Overdue or out-of-range alerts were reviewed weekly by the RN coordinator, who addressed alerts. For any overdue laboratory work or prescription refills, the RN coordinator alerted the primary osteoporosis physician via the electronic health record for updated orders. Patients were contacted by phone to schedule a clinic visit, complete ordered laboratory work, or discuss osteoporosis medication refills based on the need identified by the dashboard. A letter was mailed to the patient requesting they contact the osteoporosis clinic for patients who could not be reached by phone after 2 attempts. If 3 attempts (2 phone calls and a letter) were unsuccessful, the osteoporosis physician was alerted so they could either call the patient, alert the primary referring clinician, or discontinue the osteoporosis medication.
Results
As of March 20, 2021, 139 patients were included on the dashboard. Ninety-two patients (66%) had unmet care needs and 29% were female. Ages ranged from 40 to 100 years (Table). The dashboard alerted the team to 3 patients lost to follow-up, all of whom had transferred to care outside the clinic. Twenty-three patients (17%) had overdue medications, including 2 (9%) who had not refilled oral bisphosphonate and 18 (78%) who were overdue for intravenous bisphosphonate treatment. One veteran flagged as overdue for their denosumab injection was unable to receive it due to a significant change in health status. Two veterans were overdue for a PTH analogue refill, 1 of whom had completed their course and transitioned to bisphosphonate.

The most common alert was 40 patients (29%) with overdue laboratory tests, 37 of which were receiving bisphosphonates. One patient included on the dashboard was taking romosozumab and all their monitoring parameters were up to date, thus their data were not included in the Table to prevent possible identification.
Discussion
A dashboard alerted the osteoporosis clinic team to veterans who were overdue for visits, laboratory work, and prescription renewals. Overall, 92 patients (66%) had unmet care needs identified by the dashboard, all of which were addressed with phone calls and/or letters. Most of the overdue medication refills and laboratory tests were for patients taking bisphosphonates avoiding VAPSHCS during the COVID-19 pandemic. The dashboard enabled the RN coordinator to promptly contact the patient, facilitate coordination of care requirements, and guarantee the safe and efficient delivery of osteoporosis care.
The VA has historically been a leader in the creation of clinical dashboards to support health campaigns.11,12 These dashboards have successfully improved quality metrics towards the treatment of hepatitis C virus, heart failure, and highrisk opioid prescribing.13-15 Data have shown that successful clinical dashboard implementation must be done in conjunction with protected time or staff to support care improvements.16 Additionally, the time required for clinical dashboards can limit their sustainability and feasibility.17 A study aimed at improving osteoporosis care for patients with Parkinson disease found that weekly multidisciplinary review of at-risk patients resulted in all new patients and 91% of follow-up patients receiving evidence- based osteoporosis treatments.17 However, despite the benefits, the intervention required significant time and resources. In contrast, the osteoporosis dashboard implemented at VAPSHCS was not time or resource intensive, requiring about 1 hour per week for the RN coordinator to review the dashboard and coordinate patient care needs.
Limitations
This study setting is unique from other health care organizations or VA health care systems. Implementation of a similar dashboard in other clinical settings where patients receive medical care in multiple health care systems may differ. The VA dedicates resources to support veteran population health management, which may not be available in other health care systems.11,12 These issues may pose a barrier to implementing a similar osteoporosis dashboard in non-VA facilities. In addition, it is significant that while the dashboard can be reconfigured and adapted to track veterans across different VA facilities, certain complexities arise if essential data, such as laboratory tests and DXA imaging, are conducted outside of VA facilities. In such cases, manual entry of this information into the dashboard would be necessary. Because the dashboard was quickly developed during the COVID-19 pandemic, this study lacked preimplementation data on laboratory testing, medication refills, and DXA imaging, which would have enabled a comparison of adherence before and after dashboard implementation. Finally, we acknowledge the delay in publishing these findings; however, we believe sharing innovative approaches to providing care for high-risk populations is essential, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusions
An osteoporosis clinic dashboard served as a valuable clinical support tool to ensure safe and effective osteoporosis medication delivery at VAPSHCS. Considering the growing utilization of osteoporosis medications, this dashboard plays a vital role in facilitating care coordination for patients receiving these high-risk treatments.18 Use of the dashboard supported the effective use of high-cost osteoporosis medications and is likely to improve clinical osteoporosis outcomes.
Despite the known fracture risk reduction, osteoporosis medication adherence is low.19,20 Maintaining consistent pharmacotherapy for osteoporosis is essential not only for fracture prevention but also reducing health care costs related to osteoporosis and preserving patient independence and functionality.21-24 While initially developed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the dashboard remains useful. The VAPSHCS osteoporosis clinic is now staffed by 2 physicians (endocrine and rheumatology) and the dashboard is still in use. The RN coordinator spends about 15 minutes per week using the dashboard and managing the 67 veterans on osteoporosis therapy. This dashboard represents a sustainable clinical tool with the capacity to minimize osteoporosis care gaps and improve outcomes.
- Johnell O, Kanis J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(suppl 2):S3-S7. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1702-6
- van Staa TP, Dennison EM, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone. 2001;29:517-522. doi:10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00614-7
- Dennison E, Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Horm Res. 2000;54(suppl 1):58-63. doi:10.1159/000063449
- Cooper C. Epidemiology and public health impact of osteoporosis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1993;7:459-477. doi:10.1016/s0950-3579(05)80073-1
- Dolan P, Torgerson DJ. The cost of treating osteoporotic fractures in the United Kingdom female population. Osteoporos Int. 1998;8:611-617. doi:10.1007/s001980050107
- Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:465-475. doi:10.1359/jbmr.061113
- Palacios S. Medical treatment of osteoporosis. Climacteric. 2022;25:43-49. doi:10.1080/13697137.2021.1951697
- Eastell R, Rosen CJ, Black DM, Cheung AM, Murad MH, Shoback D. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: an Endocrine Society* clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:1595-1622. doi:10.1210/jc.2019-00221
- Watts NB, Adler RA, Bilezikian JP, et al. Osteoporosis in men: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:1802-1822. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3045
- Lau MK, Bounthavong M, Kay CL, Harvey MA, Christopher MLD. Clinical dashboard development and use for academic detailing in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(2S):S96-S103.e3. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2018.12.006
- Mould DR, D’Haens G, Upton RN. Clinical decision support tools: the evolution of a revolution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;99:405-418. doi:10.1002/cpt.334
- Kizer KW, Fonseca ML, Long LM. The veterans healthcare system: preparing for the twenty-first century. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1997;42:283-298.
- Park A, Gonzalez R, Chartier M, et al. Screening and treating hepatitis c in the VA: achieving excellence using lean and system redesign. Fed Pract. 2018;35:24-29.
- Brownell N, Kay C, Parra D, et al. Development and optimization of the Veterans Affairs’ national heart failure dashboard for population health management. J Card Fail. 2024;30:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2023.08.024
- Lin LA, Bohnert ASB, Kerns RD, Clay MA, Ganoczy D, Ilgen MA. Impact of the opioid safety initiative on opioidrelated prescribing in veterans. Pain. 2017;158:833-839. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000837
- Twohig PA, Rivington JR, Gunzler D, Daprano J, Margolius D. Clinician dashboard views and improvement in preventative health outcome measures: a retrospective analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19:475. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4327-3
- Singh I, Fletcher R, Scanlon L, Tyler M, Aithal S. A quality improvement initiative on the management of osteoporosis in older people with Parkinsonism. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5:u210921.w5756. doi:10.1136/bmjquality.u210921.w5756
- Anastasilakis AD, Makras P, Yavropoulou MP, Tabacco G, Naciu AM, Palermo A. Denosumab discontinuation and the rebound phenomenon: a narrative review. J Clin Med. 2021;10:152. doi:10.3390/jcm10010152
- Sharman Moser S, Yu J, Goldshtein I, et al. Cost and consequences of nonadherence with oral bisphosphonate therapy: findings from a real-world data analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50:262-269. doi:10.1177/1060028015626935
- Olsen KR, Hansen C, Abrahamsen B. Association between refill compliance to oral bisphosphonate treatment, incident fractures, and health care costs--an analysis using national health databases. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2639-2647. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2365-y
- Blouin J, Dragomir A, Fredette M, Ste-Marie LG, Fernandes JC, Perreault S. Comparison of direct health care costs related to the pharmacological treatment of osteoporosis and to the management of osteoporotic fractures among compliant and noncompliant users of alendronate and risedronate: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:1571-1581. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0818-5
- Cotté F-E, De Pouvourville G. Cost of non-persistence with oral bisphosphonates in post-menopausal osteoporosis treatment in France. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:151. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-151
- Cho H, Byun J-H, Song I, et al. Effect of improved medication adherence on health care costs in osteoporosis patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11470. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000011470
- Li N, Cornelissen D, Silverman S, et al. An updated systematic review of cost-effectiveness analyses of drugs for osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39:181-209. doi:10.1007/s40273-020-00965-9
- Johnell O, Kanis J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(suppl 2):S3-S7. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1702-6
- van Staa TP, Dennison EM, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone. 2001;29:517-522. doi:10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00614-7
- Dennison E, Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures. Horm Res. 2000;54(suppl 1):58-63. doi:10.1159/000063449
- Cooper C. Epidemiology and public health impact of osteoporosis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1993;7:459-477. doi:10.1016/s0950-3579(05)80073-1
- Dolan P, Torgerson DJ. The cost of treating osteoporotic fractures in the United Kingdom female population. Osteoporos Int. 1998;8:611-617. doi:10.1007/s001980050107
- Burge R, Dawson-Hughes B, Solomon DH, Wong JB, King A, Tosteson A. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:465-475. doi:10.1359/jbmr.061113
- Palacios S. Medical treatment of osteoporosis. Climacteric. 2022;25:43-49. doi:10.1080/13697137.2021.1951697
- Eastell R, Rosen CJ, Black DM, Cheung AM, Murad MH, Shoback D. Pharmacological management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women: an Endocrine Society* clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104:1595-1622. doi:10.1210/jc.2019-00221
- Watts NB, Adler RA, Bilezikian JP, et al. Osteoporosis in men: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:1802-1822. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3045
- Lau MK, Bounthavong M, Kay CL, Harvey MA, Christopher MLD. Clinical dashboard development and use for academic detailing in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2019;59(2S):S96-S103.e3. doi:10.1016/j.japh.2018.12.006
- Mould DR, D’Haens G, Upton RN. Clinical decision support tools: the evolution of a revolution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016;99:405-418. doi:10.1002/cpt.334
- Kizer KW, Fonseca ML, Long LM. The veterans healthcare system: preparing for the twenty-first century. Hosp Health Serv Adm. 1997;42:283-298.
- Park A, Gonzalez R, Chartier M, et al. Screening and treating hepatitis c in the VA: achieving excellence using lean and system redesign. Fed Pract. 2018;35:24-29.
- Brownell N, Kay C, Parra D, et al. Development and optimization of the Veterans Affairs’ national heart failure dashboard for population health management. J Card Fail. 2024;30:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2023.08.024
- Lin LA, Bohnert ASB, Kerns RD, Clay MA, Ganoczy D, Ilgen MA. Impact of the opioid safety initiative on opioidrelated prescribing in veterans. Pain. 2017;158:833-839. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000837
- Twohig PA, Rivington JR, Gunzler D, Daprano J, Margolius D. Clinician dashboard views and improvement in preventative health outcome measures: a retrospective analysis. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19:475. doi:10.1186/s12913-019-4327-3
- Singh I, Fletcher R, Scanlon L, Tyler M, Aithal S. A quality improvement initiative on the management of osteoporosis in older people with Parkinsonism. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5:u210921.w5756. doi:10.1136/bmjquality.u210921.w5756
- Anastasilakis AD, Makras P, Yavropoulou MP, Tabacco G, Naciu AM, Palermo A. Denosumab discontinuation and the rebound phenomenon: a narrative review. J Clin Med. 2021;10:152. doi:10.3390/jcm10010152
- Sharman Moser S, Yu J, Goldshtein I, et al. Cost and consequences of nonadherence with oral bisphosphonate therapy: findings from a real-world data analysis. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50:262-269. doi:10.1177/1060028015626935
- Olsen KR, Hansen C, Abrahamsen B. Association between refill compliance to oral bisphosphonate treatment, incident fractures, and health care costs--an analysis using national health databases. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24:2639-2647. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2365-y
- Blouin J, Dragomir A, Fredette M, Ste-Marie LG, Fernandes JC, Perreault S. Comparison of direct health care costs related to the pharmacological treatment of osteoporosis and to the management of osteoporotic fractures among compliant and noncompliant users of alendronate and risedronate: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:1571-1581. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0818-5
- Cotté F-E, De Pouvourville G. Cost of non-persistence with oral bisphosphonates in post-menopausal osteoporosis treatment in France. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:151. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-11-151
- Cho H, Byun J-H, Song I, et al. Effect of improved medication adherence on health care costs in osteoporosis patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e11470. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000011470
- Li N, Cornelissen D, Silverman S, et al. An updated systematic review of cost-effectiveness analyses of drugs for osteoporosis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021;39:181-209. doi:10.1007/s40273-020-00965-9
Improving High-Risk Osteoporosis Medication Adherence and Safety With an Automated Dashboard
Improving High-Risk Osteoporosis Medication Adherence and Safety With an Automated Dashboard
Efficacy of Anti-Obesity Medications in Adult and Older Adult Veteran Populations
Efficacy of Anti-Obesity Medications in Adult and Older Adult Veteran Populations
The impact of obesity in the United States is significant. Between August 2021 and August 2023, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) in US adults was 40.3%.1 The prevalence of obesity in adults aged 40 to 59 years was 46.4%, higher than the prevalence in adults aged 20 to 39 years (35.5%) and those aged ≥ 60 years (38.9%).1 The excess annual medical costs associated with obesity in the US are estimated at nearly $173 billion.2
The first-line treatment for obesity is lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and exercise. When lifestyle modifications are not enough to achieve weight-loss goals, bariatric surgery and anti-obesity medications (AOMs) are often considered. Five medications were approved for the long-term tretament of obesity by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 2021 and 2023, when this study was conducted: semaglutide (Wegovy), liraglutide (Saxenda), phentermine and topiramate, naltrexone and bupropion, and orlistat. The clinically meaningful (and commonly accepted) weight-loss target for these medications is ≥ 5% from baseline by week 12 of the maximally tolerated dose of therapy. A 5% weight loss has been shown to be clinically significant in improving cardiometabolic risk factors.3,4 These medications are intended to be used as an adjunct to healthy diet and exercise. Of note, semaglutide and liraglutide carry brand names, which are associated with different dosing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
All 5 FDA-approved AOMs were available at the Veterans Affairs Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS) for the treatment of obesity at the time of the study. To qualify for an AOM, a veteran at VASFHCS must first work with a dietitian or be enrolled in the MOVE! clinic to participate in the weight management program, which focuses on dietary, exercise, and behavioral changes. At VASFHCS, AOMs are prescribed by primary care practitioners, clinical pharmacy providers, and advanced practitioners within the MOVE! program.
Ample data exist for the efficacy of AOMs. However, no published research has reported on AOM efficacy by age group (Appendix).5-11 While most of the AOM clinical trials included older adults, the average age of participants was typically between 40 and 50 years. It is well-known that pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes occur as age increases. Renal and hepatic clearance is reduced while the volume distribution and sensitivities to some medications may increase. 12 Although this study did not focus on specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes with respect to AOM, it is important to recognize that this may play a role in the efficacy and safety of AOMs in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective single-center chart review was performed using the VASFHCS Computerized Patient Record System to compare the efficacy of AOMs in older adults (aged ≥ 65 years) vs adults (aged < 65 years). The primary endpoint was the percent change in body weight from baseline to 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM therapy in the older adult vs adult population. Secondary endpoints included changes in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and blood pressure (BP) from baseline compared to 12 months on AOM therapy. HbA1c was assessed in patients with T2DM or prediabetes at the time of AOM initiation. Two safety endpoints were also explored to determine the incidence of medication adverse events (AEs) and subsequent discontinuation of AOM. A subset analysis was performed to determine whether there was a difference in percent change in body weight between patients in 3 age groups: 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
The study population included patients who were prescribed an AOM between January 1, 2021, and June 30, 2023. Patients were excluded if they did not continue AOM therapy for ≥ 6 months after initiation or if they underwent gastric bypass surgery while undergoing AOM therapy. Patients taking semaglutide (Ozempic) or liraglutide (Victoza) for both T2DM and weight loss who were eventually switched to the weight loss formulations (Wegovy or Saxenda) were included. Patients who switched between semaglutide and liraglutide for weight loss were also included. Those taking semaglutide or liraglutide solely for T2DM treatment were excluded because they are dosed differently.
Collected data included age, gender, race, weight (baseline, 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM), metabolic laboratory values/vital signs (HbA1c, LDL, and BP at baseline and 12 months after initiation of AOM), diagnosis of T2DM or prediabetes, reported AEs associated with AOM therapy, and date of AOM initiation and discontinuation (if applicable). Baseline values were defined at the time of medication initiation or values documented within 6 months prior to medication initiation if true baseline data were not reported. If values were not recorded at months 6 and 12 after AOM initiation, values documented closest to those targets were used. Weights were used for baseline, 6-, and 12-month data unless they were unavailable due to use of virtual care modalities. In these cases, patient-reported weights were used. Patients were included in the 6-month data, but not the 12-month data, if they were taking AOMs for > 6 months but not for 12 months. If patients had been on multiple AOMs, baseline data were recorded at the start of the first medication that was used for 6 months or longer. Twelve-month data were recorded after subsequent medication change. Twelve-month metabolic laboratory values/vital signs were recorded for patients included in the study even if they did not complete ≥ 12 months of AOM therapy.
Statistical Analysis
Data from patients who were prescribed an AOM from January 2021 to June 2023 and who remained on the medication for ≥ 6 months were analyzed. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The primary and secondary endpoints were evaluated using the t test. The safety endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. An analysis of variance test was used for the subset analysis. Results with P < .05 were statistically significant.
Results
A total of 144 participants were included in this study, 116 in the adult group (aged < 65 years) and 28 in the older adult group (aged ≥ 65 years). Sixty-seven patients were excluded due to prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Other than the predetermined mean age differences (48 years vs 71 years), there were multiple differences in patient baseline characteristics. When comparing older adults and adults, average weight (283 lb vs 269 lb) and White race (89% vs 87%) were slightly higher in the older adult group. Also, a higher prevalence of T2DM (54% and 18%) and a lower prevalence of prediabetes (21% and 33%) was noted in the older adult group. HbA1c and BP were similar between both groups at baseline, while LDL was slightly lower in the older adult group (Table 1).
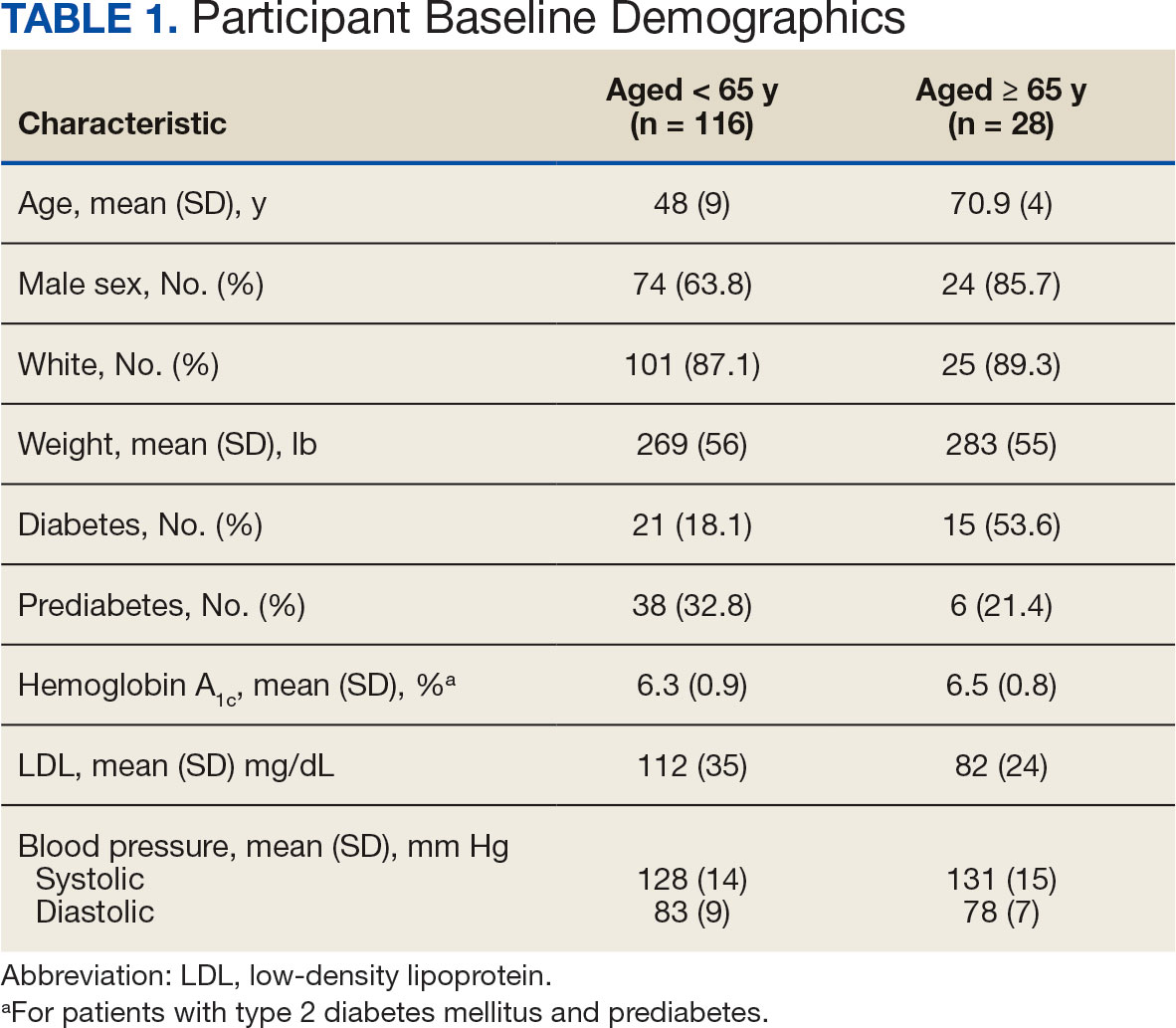
Patients in the adult group lost a mean 7.0% and 8.7% of body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively, while the older adult group lost 5.0% and 6.6% body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively. The difference in percent change in body weight was not statistically different at 6 (P = .08) or 12 (P = .26) months between patients in the adult group vs the older adult group or in the specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, ≥ 65 years) at 6 months (P = .24) or 12 months (P = .53) (Figure).
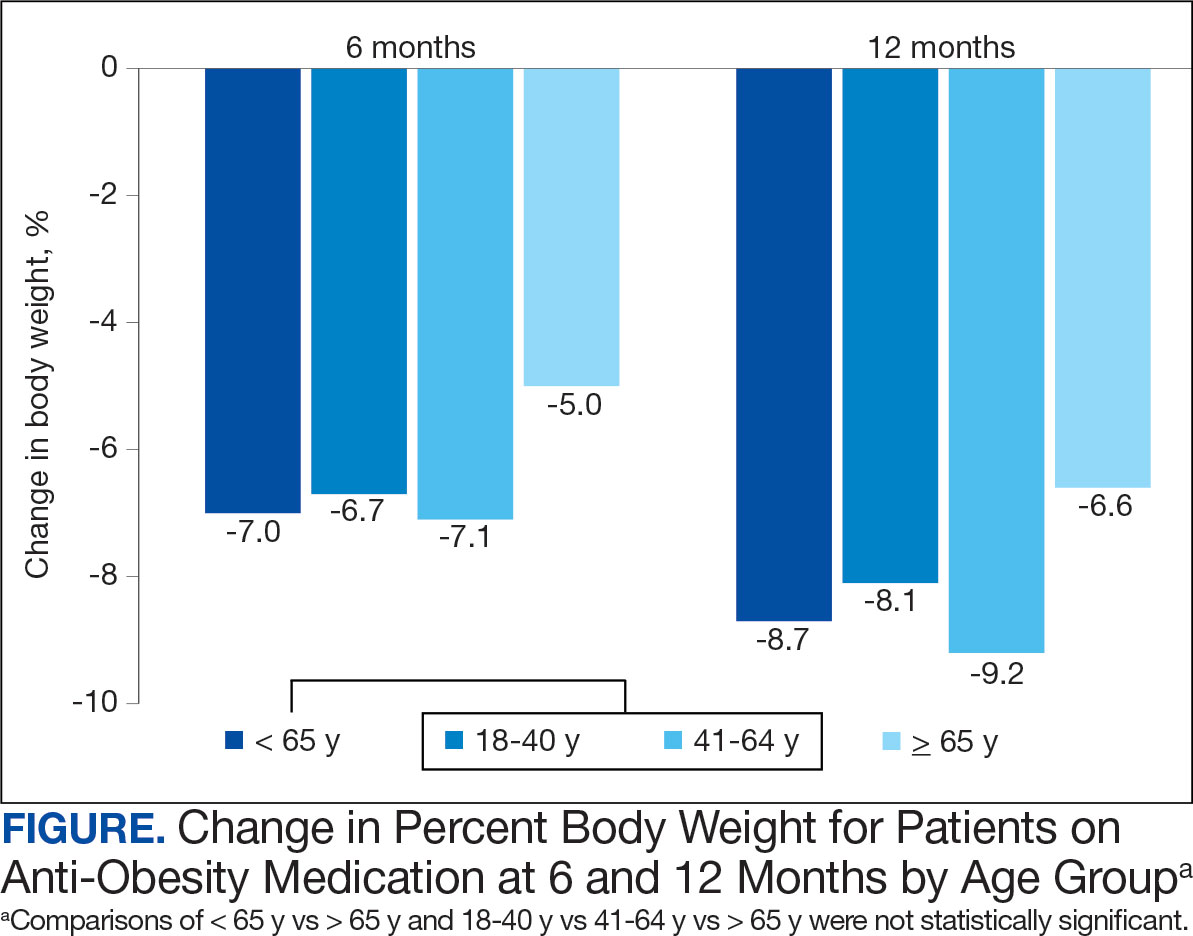
At 12 months, the difference between the adult group vs the older adult group was not statistically significant for HbA1c in patients with T2DM or prediabetes (P = .73), LDL (P = .95), systolic BP (P = .58), or diastolic BP (P = .51) (Table 2).
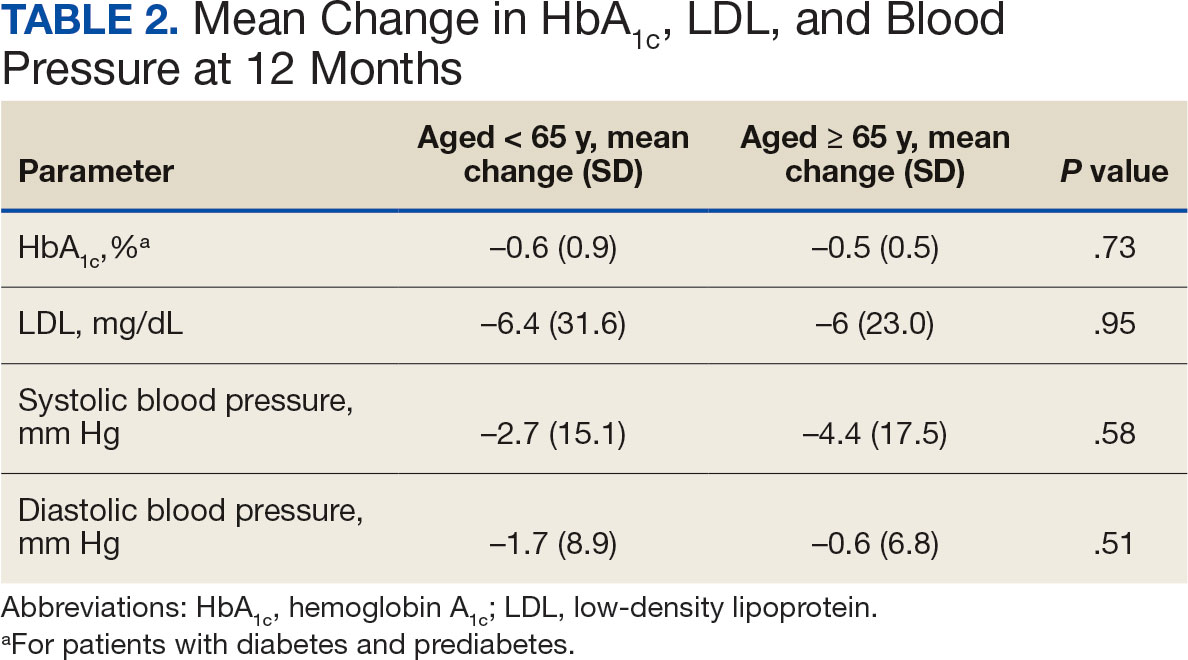
For the safety endpoint, the incidence of AEs was found to be different between groups. There were more reported AEs (61.2% vs 39.3%) and a greater increase in therapy discontinuation due to AEs (6.0% vs 0%) in the adult group compared to the older adult group (Table 3).

Discussion
Patients taking AOMs revealed no statistically significant difference in percent change in body weight at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. The subset analysis also showed no statistically significant difference in change in percent body weight between more narrowly defined age groups of 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years. This suggests that AOM may have similar efficacy for weight loss in all ages of adults.
Secondary endpoint findings showed no statistically significant difference in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL, or BP at 12 months between the 2 groups. Although this study did not differentiate secondary outcomes based on the individual AOM, the change in HbA1c in both groups was expected, given that 70% of the patients included in this study were taking a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (liraglutide and semaglutide) at some point during the study. It’s also worth noting that secondary endpoints were collected for patients who discontinued the AOM between 6 and 12 months. Therefore, the patients’ HbA1c, LDL, and BP may not have accurately reflected the change that could have been expected if they had continued AOM therapy beyond the 12-month period.
Due to the different mechanisms and range in efficacy that AOMs have in regard to weight loss, changes in all outcomes, including weight, HbA1c, LDL, and BP were expected to vary as patients were included even after switching AOM (collection of data started after ≥ 6 months on a single AOM). Switching of AOM after the first 6 months of therapy was recorded in 25% of the patients in the ≥ 65 years group and 330% of the patients in the < 65 years group.
The incidence of AEs and subsequent discontinuation of AOMs in this study was higher in the adult group. This study excluded patients who did not continue taking an AOM for at least 6 months. As a result, the incidence of AEs between the 2 groups within the first 6 months of AOM therapy remains unknown. It is possible that during the first 6 months of therapy, patients aged < 65 years were more willing to tolerate or had fewer severe AEs compared with the older adult group. It’s also possible that the smaller number of patients in the older adult group was due to increased AEs that led them to discontinue early (before completion of 6 months of therapy) and/or prescriber discomfort in using AOMs in the older adult population. In addition, because the specific medication(s) taken by patients in each group were not detailed, it is unknown whether the adult group was taking AOMs associated with a greater number of AEs.
Limitations
This was a retrospective study with a relatively small sample size. A larger sample size may have shown more precise differences between age groups and may be more representative of the general population. Additionally, data were reliant on appropriate documentation, and adherence to AOM therapy was not assessed due to the retrospective nature of this study. At times, the study relied on patient reported data points, such as weight, if a clinic weight was not available. Also, this study did not account for many potential confounding factors such as other medications taken by the patient, which can affect outcomes including weight, HbA1c, LDL, blood pressure, and AEs.
Conclusions
This retrospective study of patients taking AOMs showed no statistically significant difference in weight loss at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. A subset analysis found no statistically significant difference in change in body weight between specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, and ≥ 65 years). There was also no statistically significant difference in secondary outcomes, including change in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL or BP between age groups. The safety endpoints showed a higher incidence of medication AEs in the adult group, with more of these adults discontinuing therapy due to AEs. This study indicates that AOM may have similar outcomes for weight loss and metabolic laboratory values/vital sign changes between adults and older adults. Also, our findings suggest that patients aged < 65 years may experience more AEs than patients aged ≥ 65 years after ≥ 6 months of AOM therapy. Larger studies are needed to further evaluate these age-specific findings.
- Emmerich SD, Fryar CD, Stierman B, Ogden CL. Obesity and severe obesity prevalence in adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief No. 508. National Center for Health Statistics; 2024. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db508.htm
- Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Long MW, Gortmaker SL. Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0247307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247307
- Horn DB, Almandoz JP, Look M. What is clinically relevant weight loss for your patients and how can it be achieved? A narrative review. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(4):359-375. doi:10.1080/00325481.2022.2051366
- American Diabetes Association (ADA). Standards of care in diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(suppl 1):S128- S2139. doi:10.2337/dc23-S008
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Onceweekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
- Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, et al. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012;20(2):330-342. doi:10.1038/oby.2011.330
- Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, et al. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9774):1341-1352. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60205-5
- Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(2):297-308. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.024927
- Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, et al. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):595-605. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60888-4
- Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet. 1998;352(9123):167-172. doi:10.1016s0140-6736(97)11509-4
- Mangoni AA, Jackson SHD. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;57(1):6-14. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x
The impact of obesity in the United States is significant. Between August 2021 and August 2023, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) in US adults was 40.3%.1 The prevalence of obesity in adults aged 40 to 59 years was 46.4%, higher than the prevalence in adults aged 20 to 39 years (35.5%) and those aged ≥ 60 years (38.9%).1 The excess annual medical costs associated with obesity in the US are estimated at nearly $173 billion.2
The first-line treatment for obesity is lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and exercise. When lifestyle modifications are not enough to achieve weight-loss goals, bariatric surgery and anti-obesity medications (AOMs) are often considered. Five medications were approved for the long-term tretament of obesity by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 2021 and 2023, when this study was conducted: semaglutide (Wegovy), liraglutide (Saxenda), phentermine and topiramate, naltrexone and bupropion, and orlistat. The clinically meaningful (and commonly accepted) weight-loss target for these medications is ≥ 5% from baseline by week 12 of the maximally tolerated dose of therapy. A 5% weight loss has been shown to be clinically significant in improving cardiometabolic risk factors.3,4 These medications are intended to be used as an adjunct to healthy diet and exercise. Of note, semaglutide and liraglutide carry brand names, which are associated with different dosing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
All 5 FDA-approved AOMs were available at the Veterans Affairs Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS) for the treatment of obesity at the time of the study. To qualify for an AOM, a veteran at VASFHCS must first work with a dietitian or be enrolled in the MOVE! clinic to participate in the weight management program, which focuses on dietary, exercise, and behavioral changes. At VASFHCS, AOMs are prescribed by primary care practitioners, clinical pharmacy providers, and advanced practitioners within the MOVE! program.
Ample data exist for the efficacy of AOMs. However, no published research has reported on AOM efficacy by age group (Appendix).5-11 While most of the AOM clinical trials included older adults, the average age of participants was typically between 40 and 50 years. It is well-known that pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes occur as age increases. Renal and hepatic clearance is reduced while the volume distribution and sensitivities to some medications may increase. 12 Although this study did not focus on specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes with respect to AOM, it is important to recognize that this may play a role in the efficacy and safety of AOMs in older adults.

Methods
This retrospective single-center chart review was performed using the VASFHCS Computerized Patient Record System to compare the efficacy of AOMs in older adults (aged ≥ 65 years) vs adults (aged < 65 years). The primary endpoint was the percent change in body weight from baseline to 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM therapy in the older adult vs adult population. Secondary endpoints included changes in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and blood pressure (BP) from baseline compared to 12 months on AOM therapy. HbA1c was assessed in patients with T2DM or prediabetes at the time of AOM initiation. Two safety endpoints were also explored to determine the incidence of medication adverse events (AEs) and subsequent discontinuation of AOM. A subset analysis was performed to determine whether there was a difference in percent change in body weight between patients in 3 age groups: 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
The study population included patients who were prescribed an AOM between January 1, 2021, and June 30, 2023. Patients were excluded if they did not continue AOM therapy for ≥ 6 months after initiation or if they underwent gastric bypass surgery while undergoing AOM therapy. Patients taking semaglutide (Ozempic) or liraglutide (Victoza) for both T2DM and weight loss who were eventually switched to the weight loss formulations (Wegovy or Saxenda) were included. Patients who switched between semaglutide and liraglutide for weight loss were also included. Those taking semaglutide or liraglutide solely for T2DM treatment were excluded because they are dosed differently.
Collected data included age, gender, race, weight (baseline, 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM), metabolic laboratory values/vital signs (HbA1c, LDL, and BP at baseline and 12 months after initiation of AOM), diagnosis of T2DM or prediabetes, reported AEs associated with AOM therapy, and date of AOM initiation and discontinuation (if applicable). Baseline values were defined at the time of medication initiation or values documented within 6 months prior to medication initiation if true baseline data were not reported. If values were not recorded at months 6 and 12 after AOM initiation, values documented closest to those targets were used. Weights were used for baseline, 6-, and 12-month data unless they were unavailable due to use of virtual care modalities. In these cases, patient-reported weights were used. Patients were included in the 6-month data, but not the 12-month data, if they were taking AOMs for > 6 months but not for 12 months. If patients had been on multiple AOMs, baseline data were recorded at the start of the first medication that was used for 6 months or longer. Twelve-month data were recorded after subsequent medication change. Twelve-month metabolic laboratory values/vital signs were recorded for patients included in the study even if they did not complete ≥ 12 months of AOM therapy.
Statistical Analysis
Data from patients who were prescribed an AOM from January 2021 to June 2023 and who remained on the medication for ≥ 6 months were analyzed. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The primary and secondary endpoints were evaluated using the t test. The safety endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. An analysis of variance test was used for the subset analysis. Results with P < .05 were statistically significant.
Results
A total of 144 participants were included in this study, 116 in the adult group (aged < 65 years) and 28 in the older adult group (aged ≥ 65 years). Sixty-seven patients were excluded due to prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Other than the predetermined mean age differences (48 years vs 71 years), there were multiple differences in patient baseline characteristics. When comparing older adults and adults, average weight (283 lb vs 269 lb) and White race (89% vs 87%) were slightly higher in the older adult group. Also, a higher prevalence of T2DM (54% and 18%) and a lower prevalence of prediabetes (21% and 33%) was noted in the older adult group. HbA1c and BP were similar between both groups at baseline, while LDL was slightly lower in the older adult group (Table 1).

Patients in the adult group lost a mean 7.0% and 8.7% of body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively, while the older adult group lost 5.0% and 6.6% body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively. The difference in percent change in body weight was not statistically different at 6 (P = .08) or 12 (P = .26) months between patients in the adult group vs the older adult group or in the specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, ≥ 65 years) at 6 months (P = .24) or 12 months (P = .53) (Figure).

At 12 months, the difference between the adult group vs the older adult group was not statistically significant for HbA1c in patients with T2DM or prediabetes (P = .73), LDL (P = .95), systolic BP (P = .58), or diastolic BP (P = .51) (Table 2).

For the safety endpoint, the incidence of AEs was found to be different between groups. There were more reported AEs (61.2% vs 39.3%) and a greater increase in therapy discontinuation due to AEs (6.0% vs 0%) in the adult group compared to the older adult group (Table 3).

Discussion
Patients taking AOMs revealed no statistically significant difference in percent change in body weight at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. The subset analysis also showed no statistically significant difference in change in percent body weight between more narrowly defined age groups of 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years. This suggests that AOM may have similar efficacy for weight loss in all ages of adults.
Secondary endpoint findings showed no statistically significant difference in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL, or BP at 12 months between the 2 groups. Although this study did not differentiate secondary outcomes based on the individual AOM, the change in HbA1c in both groups was expected, given that 70% of the patients included in this study were taking a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (liraglutide and semaglutide) at some point during the study. It’s also worth noting that secondary endpoints were collected for patients who discontinued the AOM between 6 and 12 months. Therefore, the patients’ HbA1c, LDL, and BP may not have accurately reflected the change that could have been expected if they had continued AOM therapy beyond the 12-month period.
Due to the different mechanisms and range in efficacy that AOMs have in regard to weight loss, changes in all outcomes, including weight, HbA1c, LDL, and BP were expected to vary as patients were included even after switching AOM (collection of data started after ≥ 6 months on a single AOM). Switching of AOM after the first 6 months of therapy was recorded in 25% of the patients in the ≥ 65 years group and 330% of the patients in the < 65 years group.
The incidence of AEs and subsequent discontinuation of AOMs in this study was higher in the adult group. This study excluded patients who did not continue taking an AOM for at least 6 months. As a result, the incidence of AEs between the 2 groups within the first 6 months of AOM therapy remains unknown. It is possible that during the first 6 months of therapy, patients aged < 65 years were more willing to tolerate or had fewer severe AEs compared with the older adult group. It’s also possible that the smaller number of patients in the older adult group was due to increased AEs that led them to discontinue early (before completion of 6 months of therapy) and/or prescriber discomfort in using AOMs in the older adult population. In addition, because the specific medication(s) taken by patients in each group were not detailed, it is unknown whether the adult group was taking AOMs associated with a greater number of AEs.
Limitations
This was a retrospective study with a relatively small sample size. A larger sample size may have shown more precise differences between age groups and may be more representative of the general population. Additionally, data were reliant on appropriate documentation, and adherence to AOM therapy was not assessed due to the retrospective nature of this study. At times, the study relied on patient reported data points, such as weight, if a clinic weight was not available. Also, this study did not account for many potential confounding factors such as other medications taken by the patient, which can affect outcomes including weight, HbA1c, LDL, blood pressure, and AEs.
Conclusions
This retrospective study of patients taking AOMs showed no statistically significant difference in weight loss at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. A subset analysis found no statistically significant difference in change in body weight between specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, and ≥ 65 years). There was also no statistically significant difference in secondary outcomes, including change in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL or BP between age groups. The safety endpoints showed a higher incidence of medication AEs in the adult group, with more of these adults discontinuing therapy due to AEs. This study indicates that AOM may have similar outcomes for weight loss and metabolic laboratory values/vital sign changes between adults and older adults. Also, our findings suggest that patients aged < 65 years may experience more AEs than patients aged ≥ 65 years after ≥ 6 months of AOM therapy. Larger studies are needed to further evaluate these age-specific findings.
The impact of obesity in the United States is significant. Between August 2021 and August 2023, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥ 30) in US adults was 40.3%.1 The prevalence of obesity in adults aged 40 to 59 years was 46.4%, higher than the prevalence in adults aged 20 to 39 years (35.5%) and those aged ≥ 60 years (38.9%).1 The excess annual medical costs associated with obesity in the US are estimated at nearly $173 billion.2
The first-line treatment for obesity is lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and exercise. When lifestyle modifications are not enough to achieve weight-loss goals, bariatric surgery and anti-obesity medications (AOMs) are often considered. Five medications were approved for the long-term tretament of obesity by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 2021 and 2023, when this study was conducted: semaglutide (Wegovy), liraglutide (Saxenda), phentermine and topiramate, naltrexone and bupropion, and orlistat. The clinically meaningful (and commonly accepted) weight-loss target for these medications is ≥ 5% from baseline by week 12 of the maximally tolerated dose of therapy. A 5% weight loss has been shown to be clinically significant in improving cardiometabolic risk factors.3,4 These medications are intended to be used as an adjunct to healthy diet and exercise. Of note, semaglutide and liraglutide carry brand names, which are associated with different dosing for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
All 5 FDA-approved AOMs were available at the Veterans Affairs Sioux Falls Health Care System (VASFHCS) for the treatment of obesity at the time of the study. To qualify for an AOM, a veteran at VASFHCS must first work with a dietitian or be enrolled in the MOVE! clinic to participate in the weight management program, which focuses on dietary, exercise, and behavioral changes. At VASFHCS, AOMs are prescribed by primary care practitioners, clinical pharmacy providers, and advanced practitioners within the MOVE! program.
Ample data exist for the efficacy of AOMs. However, no published research has reported on AOM efficacy by age group (Appendix).5-11 While most of the AOM clinical trials included older adults, the average age of participants was typically between 40 and 50 years. It is well-known that pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes occur as age increases. Renal and hepatic clearance is reduced while the volume distribution and sensitivities to some medications may increase. 12 Although this study did not focus on specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic changes with respect to AOM, it is important to recognize that this may play a role in the efficacy and safety of AOMs in older adults.

Methods
This retrospective single-center chart review was performed using the VASFHCS Computerized Patient Record System to compare the efficacy of AOMs in older adults (aged ≥ 65 years) vs adults (aged < 65 years). The primary endpoint was the percent change in body weight from baseline to 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM therapy in the older adult vs adult population. Secondary endpoints included changes in low-density lipoprotein (LDL), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and blood pressure (BP) from baseline compared to 12 months on AOM therapy. HbA1c was assessed in patients with T2DM or prediabetes at the time of AOM initiation. Two safety endpoints were also explored to determine the incidence of medication adverse events (AEs) and subsequent discontinuation of AOM. A subset analysis was performed to determine whether there was a difference in percent change in body weight between patients in 3 age groups: 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years.
The study population included patients who were prescribed an AOM between January 1, 2021, and June 30, 2023. Patients were excluded if they did not continue AOM therapy for ≥ 6 months after initiation or if they underwent gastric bypass surgery while undergoing AOM therapy. Patients taking semaglutide (Ozempic) or liraglutide (Victoza) for both T2DM and weight loss who were eventually switched to the weight loss formulations (Wegovy or Saxenda) were included. Patients who switched between semaglutide and liraglutide for weight loss were also included. Those taking semaglutide or liraglutide solely for T2DM treatment were excluded because they are dosed differently.
Collected data included age, gender, race, weight (baseline, 6 and 12 months after initiation of AOM), metabolic laboratory values/vital signs (HbA1c, LDL, and BP at baseline and 12 months after initiation of AOM), diagnosis of T2DM or prediabetes, reported AEs associated with AOM therapy, and date of AOM initiation and discontinuation (if applicable). Baseline values were defined at the time of medication initiation or values documented within 6 months prior to medication initiation if true baseline data were not reported. If values were not recorded at months 6 and 12 after AOM initiation, values documented closest to those targets were used. Weights were used for baseline, 6-, and 12-month data unless they were unavailable due to use of virtual care modalities. In these cases, patient-reported weights were used. Patients were included in the 6-month data, but not the 12-month data, if they were taking AOMs for > 6 months but not for 12 months. If patients had been on multiple AOMs, baseline data were recorded at the start of the first medication that was used for 6 months or longer. Twelve-month data were recorded after subsequent medication change. Twelve-month metabolic laboratory values/vital signs were recorded for patients included in the study even if they did not complete ≥ 12 months of AOM therapy.
Statistical Analysis
Data from patients who were prescribed an AOM from January 2021 to June 2023 and who remained on the medication for ≥ 6 months were analyzed. Baseline characteristics were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The primary and secondary endpoints were evaluated using the t test. The safety endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. An analysis of variance test was used for the subset analysis. Results with P < .05 were statistically significant.
Results
A total of 144 participants were included in this study, 116 in the adult group (aged < 65 years) and 28 in the older adult group (aged ≥ 65 years). Sixty-seven patients were excluded due to prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Other than the predetermined mean age differences (48 years vs 71 years), there were multiple differences in patient baseline characteristics. When comparing older adults and adults, average weight (283 lb vs 269 lb) and White race (89% vs 87%) were slightly higher in the older adult group. Also, a higher prevalence of T2DM (54% and 18%) and a lower prevalence of prediabetes (21% and 33%) was noted in the older adult group. HbA1c and BP were similar between both groups at baseline, while LDL was slightly lower in the older adult group (Table 1).

Patients in the adult group lost a mean 7.0% and 8.7% of body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively, while the older adult group lost 5.0% and 6.6% body weight at 6 and 12 months, respectively. The difference in percent change in body weight was not statistically different at 6 (P = .08) or 12 (P = .26) months between patients in the adult group vs the older adult group or in the specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, ≥ 65 years) at 6 months (P = .24) or 12 months (P = .53) (Figure).

At 12 months, the difference between the adult group vs the older adult group was not statistically significant for HbA1c in patients with T2DM or prediabetes (P = .73), LDL (P = .95), systolic BP (P = .58), or diastolic BP (P = .51) (Table 2).

For the safety endpoint, the incidence of AEs was found to be different between groups. There were more reported AEs (61.2% vs 39.3%) and a greater increase in therapy discontinuation due to AEs (6.0% vs 0%) in the adult group compared to the older adult group (Table 3).

Discussion
Patients taking AOMs revealed no statistically significant difference in percent change in body weight at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. The subset analysis also showed no statistically significant difference in change in percent body weight between more narrowly defined age groups of 18 to 40 years, 41 to 64 years, and ≥ 65 years. This suggests that AOM may have similar efficacy for weight loss in all ages of adults.
Secondary endpoint findings showed no statistically significant difference in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL, or BP at 12 months between the 2 groups. Although this study did not differentiate secondary outcomes based on the individual AOM, the change in HbA1c in both groups was expected, given that 70% of the patients included in this study were taking a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (liraglutide and semaglutide) at some point during the study. It’s also worth noting that secondary endpoints were collected for patients who discontinued the AOM between 6 and 12 months. Therefore, the patients’ HbA1c, LDL, and BP may not have accurately reflected the change that could have been expected if they had continued AOM therapy beyond the 12-month period.
Due to the different mechanisms and range in efficacy that AOMs have in regard to weight loss, changes in all outcomes, including weight, HbA1c, LDL, and BP were expected to vary as patients were included even after switching AOM (collection of data started after ≥ 6 months on a single AOM). Switching of AOM after the first 6 months of therapy was recorded in 25% of the patients in the ≥ 65 years group and 330% of the patients in the < 65 years group.
The incidence of AEs and subsequent discontinuation of AOMs in this study was higher in the adult group. This study excluded patients who did not continue taking an AOM for at least 6 months. As a result, the incidence of AEs between the 2 groups within the first 6 months of AOM therapy remains unknown. It is possible that during the first 6 months of therapy, patients aged < 65 years were more willing to tolerate or had fewer severe AEs compared with the older adult group. It’s also possible that the smaller number of patients in the older adult group was due to increased AEs that led them to discontinue early (before completion of 6 months of therapy) and/or prescriber discomfort in using AOMs in the older adult population. In addition, because the specific medication(s) taken by patients in each group were not detailed, it is unknown whether the adult group was taking AOMs associated with a greater number of AEs.
Limitations
This was a retrospective study with a relatively small sample size. A larger sample size may have shown more precise differences between age groups and may be more representative of the general population. Additionally, data were reliant on appropriate documentation, and adherence to AOM therapy was not assessed due to the retrospective nature of this study. At times, the study relied on patient reported data points, such as weight, if a clinic weight was not available. Also, this study did not account for many potential confounding factors such as other medications taken by the patient, which can affect outcomes including weight, HbA1c, LDL, blood pressure, and AEs.
Conclusions
This retrospective study of patients taking AOMs showed no statistically significant difference in weight loss at 6 or 12 months between adults aged < 65 years and older adults aged ≥ 65 years. A subset analysis found no statistically significant difference in change in body weight between specific age groups (18-40 years, 41-64 years, and ≥ 65 years). There was also no statistically significant difference in secondary outcomes, including change in HbA1c (in patients with T2DM or prediabetes), LDL or BP between age groups. The safety endpoints showed a higher incidence of medication AEs in the adult group, with more of these adults discontinuing therapy due to AEs. This study indicates that AOM may have similar outcomes for weight loss and metabolic laboratory values/vital sign changes between adults and older adults. Also, our findings suggest that patients aged < 65 years may experience more AEs than patients aged ≥ 65 years after ≥ 6 months of AOM therapy. Larger studies are needed to further evaluate these age-specific findings.
- Emmerich SD, Fryar CD, Stierman B, Ogden CL. Obesity and severe obesity prevalence in adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief No. 508. National Center for Health Statistics; 2024. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db508.htm
- Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Long MW, Gortmaker SL. Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0247307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247307
- Horn DB, Almandoz JP, Look M. What is clinically relevant weight loss for your patients and how can it be achieved? A narrative review. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(4):359-375. doi:10.1080/00325481.2022.2051366
- American Diabetes Association (ADA). Standards of care in diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(suppl 1):S128- S2139. doi:10.2337/dc23-S008
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Onceweekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
- Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, et al. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012;20(2):330-342. doi:10.1038/oby.2011.330
- Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, et al. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9774):1341-1352. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60205-5
- Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(2):297-308. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.024927
- Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, et al. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):595-605. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60888-4
- Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet. 1998;352(9123):167-172. doi:10.1016s0140-6736(97)11509-4
- Mangoni AA, Jackson SHD. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;57(1):6-14. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x
- Emmerich SD, Fryar CD, Stierman B, Ogden CL. Obesity and severe obesity prevalence in adults: United States, August 2021-August 2023. NCHS Data Brief No. 508. National Center for Health Statistics; 2024. Accessed December 11, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db508.htm
- Ward ZJ, Bleich SN, Long MW, Gortmaker SL. Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0247307. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0247307
- Horn DB, Almandoz JP, Look M. What is clinically relevant weight loss for your patients and how can it be achieved? A narrative review. Postgrad Med. 2022;134(4):359-375. doi:10.1080/00325481.2022.2051366
- American Diabetes Association (ADA). Standards of care in diabetes–2023. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(suppl 1):S128- S2139. doi:10.2337/dc23-S008
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Onceweekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):11-22. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411892
- Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, et al. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012;20(2):330-342. doi:10.1038/oby.2011.330
- Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, et al. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9774):1341-1352. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60205-5
- Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, et al. Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(2):297-308. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.024927
- Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, et al. Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):595-605. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60888-4
- Sjöström L, Rissanen A, Andersen T, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss and prevention of weight regain in obese patients. European Multicentre Orlistat Study Group. Lancet. 1998;352(9123):167-172. doi:10.1016s0140-6736(97)11509-4
- Mangoni AA, Jackson SHD. Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;57(1):6-14. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x
Efficacy of Anti-Obesity Medications in Adult and Older Adult Veteran Populations
Efficacy of Anti-Obesity Medications in Adult and Older Adult Veteran Populations
Pruritus: Diagnosing and Treating Older Adults
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rethink Fall Risk Assessment When Choosing Between Gabapentin and Duloxetine for Older Adults
TOPLINE:
, with a weighted cumulative incidence of 84.44 vs 158.21 per 1000 person-years at 180 days. Incident gabapentin use showed a 48% lower hazard of falls at 6-month follow-up, with no increase in severe fall-related events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a new user, active comparator cohort study using IBM MarketScan Research Databases from January 2014 to December 2021.
- Analysis included 57,086 adults aged 65 years or older with postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, or fibromyalgia, excluding those with depression, anxiety, seizures, or cancer in the prior 365 days.
- The primary outcome measured the hazard of experiencing any fall-related visit in the 6 months after initiating gabapentin or duloxetine until treatment discontinuation.
- Secondary outcomes examined severe fall-related events, including falls with hip fractures or emergency department visits/hospitalizations associated with falls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analytic cohort included 52,152 gabapentin users and 4934 duloxetine users, with a median follow-up duration of 30 days (interquartile range, 30-90 days).
- Weighted cumulative incidence of fall-related visits per 1000 person-years at 30, 90, and 180 days was 103.60, 90.44, and 84.44 for gabapentin users vs 203.43, 177.73, and 158.21 for duloxetine users.
- At 6-month follow-up, incident gabapentin users demonstrated lower hazard of falls (hazard ratio, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.43-0.64), with no difference in hazards of severe falls.
- Results remained consistent across sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
IN PRACTICE:
“One bioplausible explanation for our results is that gabapentin is a highly titratable medication and many in our cohort started on low doses. Alternatively, duloxetine is usually titrated only once or twice. Thus, although it may be that gabapentin is simply safer than duloxetine from a falls perspective, it may also be likely that we are measuring specific clinical scenarios, the peri-initiation and titration period, in which gabapentin may be less likely to cause falls than duloxetine,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Chaitoff, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan School of Medicine in Ann Arbor, and Center for Healthcare Delivery Sciences, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston. It was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the design aimed at limiting confounding effects, the observational nature of the study introduces potential bias. Claims data may undercount falls for which patients do not seek care, though this limitation likely affects both medication groups equally. The commercial claims database includes only Medicare supplemental insurance beneficiaries, potentially limiting generalizability. Regional variations in prescribing patterns could not be accounted for in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was provided for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, with a weighted cumulative incidence of 84.44 vs 158.21 per 1000 person-years at 180 days. Incident gabapentin use showed a 48% lower hazard of falls at 6-month follow-up, with no increase in severe fall-related events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a new user, active comparator cohort study using IBM MarketScan Research Databases from January 2014 to December 2021.
- Analysis included 57,086 adults aged 65 years or older with postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, or fibromyalgia, excluding those with depression, anxiety, seizures, or cancer in the prior 365 days.
- The primary outcome measured the hazard of experiencing any fall-related visit in the 6 months after initiating gabapentin or duloxetine until treatment discontinuation.
- Secondary outcomes examined severe fall-related events, including falls with hip fractures or emergency department visits/hospitalizations associated with falls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analytic cohort included 52,152 gabapentin users and 4934 duloxetine users, with a median follow-up duration of 30 days (interquartile range, 30-90 days).
- Weighted cumulative incidence of fall-related visits per 1000 person-years at 30, 90, and 180 days was 103.60, 90.44, and 84.44 for gabapentin users vs 203.43, 177.73, and 158.21 for duloxetine users.
- At 6-month follow-up, incident gabapentin users demonstrated lower hazard of falls (hazard ratio, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.43-0.64), with no difference in hazards of severe falls.
- Results remained consistent across sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
IN PRACTICE:
“One bioplausible explanation for our results is that gabapentin is a highly titratable medication and many in our cohort started on low doses. Alternatively, duloxetine is usually titrated only once or twice. Thus, although it may be that gabapentin is simply safer than duloxetine from a falls perspective, it may also be likely that we are measuring specific clinical scenarios, the peri-initiation and titration period, in which gabapentin may be less likely to cause falls than duloxetine,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Chaitoff, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan School of Medicine in Ann Arbor, and Center for Healthcare Delivery Sciences, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston. It was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the design aimed at limiting confounding effects, the observational nature of the study introduces potential bias. Claims data may undercount falls for which patients do not seek care, though this limitation likely affects both medication groups equally. The commercial claims database includes only Medicare supplemental insurance beneficiaries, potentially limiting generalizability. Regional variations in prescribing patterns could not be accounted for in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was provided for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, with a weighted cumulative incidence of 84.44 vs 158.21 per 1000 person-years at 180 days. Incident gabapentin use showed a 48% lower hazard of falls at 6-month follow-up, with no increase in severe fall-related events.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a new user, active comparator cohort study using IBM MarketScan Research Databases from January 2014 to December 2021.
- Analysis included 57,086 adults aged 65 years or older with postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, or fibromyalgia, excluding those with depression, anxiety, seizures, or cancer in the prior 365 days.
- The primary outcome measured the hazard of experiencing any fall-related visit in the 6 months after initiating gabapentin or duloxetine until treatment discontinuation.
- Secondary outcomes examined severe fall-related events, including falls with hip fractures or emergency department visits/hospitalizations associated with falls.
TAKEAWAY:
- The analytic cohort included 52,152 gabapentin users and 4934 duloxetine users, with a median follow-up duration of 30 days (interquartile range, 30-90 days).
- Weighted cumulative incidence of fall-related visits per 1000 person-years at 30, 90, and 180 days was 103.60, 90.44, and 84.44 for gabapentin users vs 203.43, 177.73, and 158.21 for duloxetine users.
- At 6-month follow-up, incident gabapentin users demonstrated lower hazard of falls (hazard ratio, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.43-0.64), with no difference in hazards of severe falls.
- Results remained consistent across sensitivity and subgroup analyses.
IN PRACTICE:
“One bioplausible explanation for our results is that gabapentin is a highly titratable medication and many in our cohort started on low doses. Alternatively, duloxetine is usually titrated only once or twice. Thus, although it may be that gabapentin is simply safer than duloxetine from a falls perspective, it may also be likely that we are measuring specific clinical scenarios, the peri-initiation and titration period, in which gabapentin may be less likely to cause falls than duloxetine,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alexander Chaitoff, MD, MPH, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan School of Medicine in Ann Arbor, and Center for Healthcare Delivery Sciences, Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston. It was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite the design aimed at limiting confounding effects, the observational nature of the study introduces potential bias. Claims data may undercount falls for which patients do not seek care, though this limitation likely affects both medication groups equally. The commercial claims database includes only Medicare supplemental insurance beneficiaries, potentially limiting generalizability. Regional variations in prescribing patterns could not be accounted for in the analysis.
DISCLOSURES:
No funding was provided for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing of Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Geriatric Veterans
Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing of Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Geriatric Veterans
Low-dose aspirin commonly is used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) but is associated with an increased risk of major bleeding.1 The use of aspirin for primary prevention is largely extrapolated from clinical trials showing benefit in the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. However, results from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial challenged this practice.2 The ASPREE trial, conducted in the United States and Australia from 2010 to 2014, sought to determine whether daily 100 mg aspirin, was superior to placebo in promoting disability-free survival among older adults. Participants were aged ≥ 70 years (≥ 65 years for Hispanic and Black US participants), living in the community, and were free from preexisting CVD, cerebrovascular disease, or any chronic condition likely to limit survival to < 5 years. The study found no significant difference in the primary endpoints of death, dementia, or persistent physical disability, but there was a significantly higher risk of major hemorrhage in the aspirin group (3.8% vs 2.8%; hazard ratio, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.18-1.62; P < .001).
Several medical societies have updated their guideline recommendations for aspirin for primary prevention of CVD. The 2022 United States Public Service Task Force (USPSTF) provides a grade C recommendation (at least moderate certainty that the net benefit is small) to consider low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of CVD on an individual patient basis for adults aged 40 to 59 years who have a ≥ 10% 10-year CVD risk. For adults aged ≥ 60 years, the USPSTF recommendation is grade D (moderate or high certainty that the practice has no net benefit or that harms outweigh the benefits) for low-dose aspirin use.1,3 The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend considering low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) among select adults aged 40 to 70 years at higher CVD risk but not at increased risk of bleeding.4 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of CVD in patients with diabetes and additional risk factors such as family history of premature ASCVD, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, or chronic kidney disease, and who are not at higher risk of bleeding.5 The ADA standards also caution against the use of aspirin as primary prevention in patients aged > 70 years. Low-dose aspirin use is not recommended for the primary prevention of CVD in older adults or adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding.
Recent literature using the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse database confirms 86,555 of 1.8 million veterans aged > 70 years (5%) were taking low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD despite guideline recommendations.6 Higher risk of gastrointestinal and other major bleeding from low-dose aspirin has been reported in the literature.1 Major bleeds represent a significant burden to the health care system with an estimated mean $13,093 cost for gastrointestinal bleed hospitalization.7
Considering the large scale aspirin use without appropriate indication within the veteran population, the risk of adverse effects, and the significant cost to patients and the health care system, it is imperative to determine the best approach to efficiently deprescribe aspirin for primary prevention among geriatric patients. Deprescribing refers to the systematic and supervised process of dose reduction or drug discontinuation with the goal of improving health and/or reducing the risk of adverse effects.8 During patient visits, primary care practitioners (PCPs) have opportunities to discontinue aspirin, but these encounters are time-limited and deprescribing might be secondary to more acute primary care needs. The shortage of PCPs is expected to worsen in coming years, which could further reduce their availability to assess inappropriate aspirin use.9
VA clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) serve as medication experts and work autonomously under a broad scope of practice as part of the patient aligned care team.10-12 CPPs can free up time for PCPs and facilitate deprescribing efforts, especially for older adults. One retrospective cohort study conducted at a VA medical center found that CPPs deprescribed more potentially inappropriate medications among individuals aged ≥ 80 years compared with usual care with PCPs (26.8% vs 16.1%; P < .001).12,13 An aspirin deprescribing protocol conducted in 2022 resulted in nearly half of veterans aged ≥ 70 years contacted by phone agreeing to stop aspirin. Although this study supports the role pharmacists can play in reducing aspirin use in accordance with guidelines, the authors acknowledge that their interventions had a mean time of 12 minutes per patient and would require workflow changes.14 The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficiency of aspirin deprescribing through 2 approaches: direct deprescribing by pharmacists using populationlevel review compared with clinicians following a pharmacist-led education.
Methods
This was a single-center quality improvement cohort study at the Durham VA Health Care System (DVAHCS) in North Carolina. Patients included were aged ≥ 70 years without known ASCVD who received care at any of 3 DVAHCS community-based outpatient clinics and prescribed aspirin. Patient data was obtained using the VIONE (Deprescribing Dashboard called Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, and Every medication has a specific indication or diagnosis) dashboard.15 VIONE was developed to identify potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) that are eligible to deprescribe based on Beers Criteria, Screening Tool of Older Personsf Prescriptions criteria, and common clinical scenarios when clinicians determine the risk outweighs the benefit to continue a specific medication. 16,17 VIONE is used to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety, comfort, and medication adherence. Aspirin for patients aged ≥ 70 years without a history of ASCVD is a PIM identified by VIONE. Patients aged ≥ 70 years were chosen as an inclusion criteria in this study to match the ASPREE trial inclusion criteria and age inclusion criteria in the VIONE dashboard for aspirin deprescribing.2 Patient lists were generated for these potentially inappropriate aspirin prescriptions for 3 months before clinician staff education presentations, the day of the presentations, and 3 months after.
The primary endpoint was the number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed directly by 2 pharmacists over 12 weeks, divided by total patient care time spent, compared with the change in number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed by any DVAHCS physician, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or CPP over 12 weeks, divided by the total pharmacist time spent on PCP education. Secondary endpoints were the number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacists and CPPs, the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks before pharmacist-led education compared with the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks after CPP-led education, average and median pharmacist time spent per patient encounter, and time of direct patient encounters vs time spent on PCP education.
Pharmacists reviewed each patient who met the inclusion criteria from the list generated by VIONE on December 1, 2022, for aspirin appropriateness according to the ACC/AHA and USPSTF guidelines, with the goal to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD and no other indications.1,4 Pharmacists documented their visits using VIONE methodology in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) using a polypharmacy review note. CPPs contacted patients who were taking aspirin for primary prevention by unscheduled telephone call to assess for aspirin adherence, undocumented history of ASCVD, cardiovascular risk factors, and history of bleeding. Aspirin was discontinued if patients met guideline criteria recommendations and agreed to discontinuation. Risk-benefit discussions were completed when patients without known ASCVD were considered high risk because the ACC/AHA guidelines mention there is insufficient evidence of safety and efficacy of aspirin for primary prevention for patients with other known ASCVD risk factors (eg, strong family history of premature myocardial infarction, inability to achieve lipid, blood pressure, or glucose targets, or significant elevation in coronary artery calcium score).
High risk was defined as family history of premature ASCVD (in a male first-degree relative aged < 55 years or a female first-degree relative aged < 65 years), most recent blood pressure or 2 blood pressure results in the last 12 months > 160/100 mm Hg, recent hemoglobin A1c > 9%, and/or low-density lipoprotein > 190 mg/dL or not prescribed an indicated statin.3 Aspirin was continued or discontinued according to patient preference after the personalized risk-benefit discussion.
For patients with a clinical indication for aspirin use other than ASCVD (eg, atrial fibrillation not on anticoagulation, venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, carotid artery disease), CPPs documented their assessment and when appropriate deferred to the PCP for consideration of stopping aspirin. For patients with undocumented ASCVD, CPPs added their ASCVD history to their problem list and aspirin was continued. PCPs were notified by alert when aspirin was discontinued and when patients could not be reached by telephone.
presented a review of recent guideline updates and supporting literature at 2 online staff meetings. The education sessions lasted about 10 minutes and were presented to PCPs across 3 community-based outpatient clinics. An estimated 40 minutes were spent creating the PowerPoint education materials, seeking feedback, making edits, and answering questions or emails from PCPs after the presentation. During the presentation, pharmacists encouraged PCPs to discontinue aspirin (active VA prescriptions and reported over-the-counter use) for primary prevention of ASCVD in patients aged ≥ 70 years during their upcoming appointments and consider risk factors recommended by the ACC/AHA guidelines when applicable. PCPs were notified that CPPs planned to start a population review for discontinuing active VA aspirin prescriptions on December 1, 2022. The primary endpoint and secondary endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. All data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel.
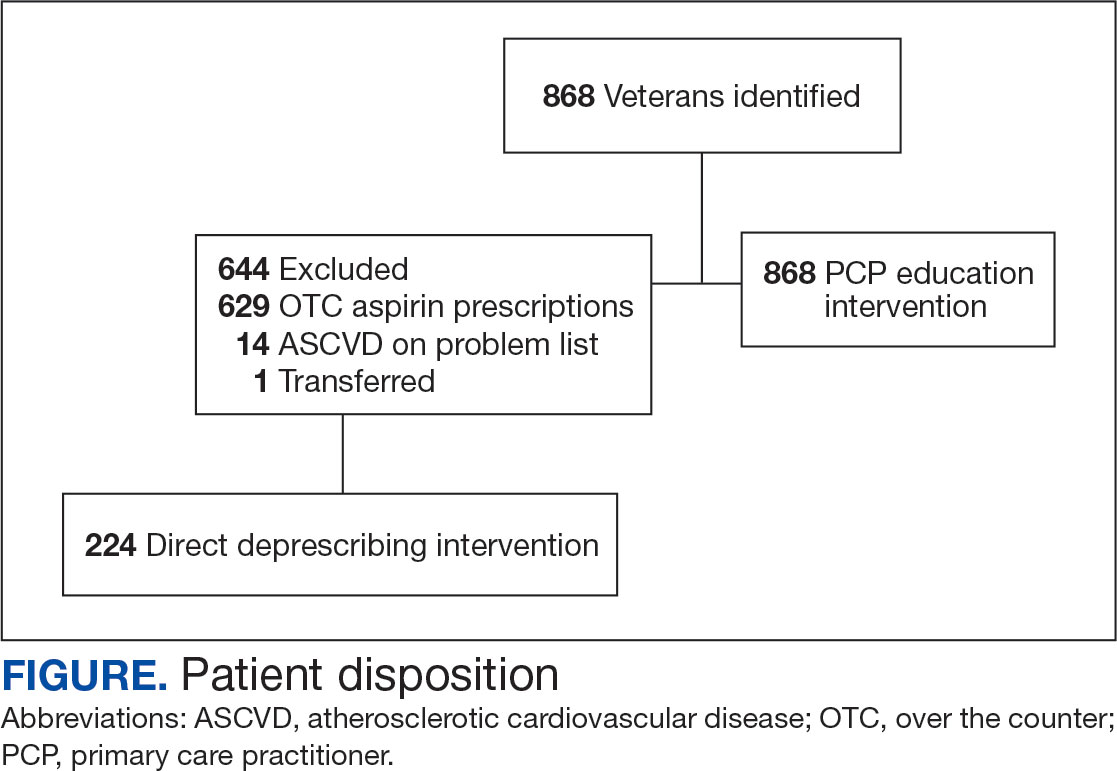
Results
A total of 868 patients aged ≥ 70 years with active prescriptions for aspirin were identified on December 1, 2022. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria for the pharmacist population review, 224 patients were included for cohort final analysis (Figure). All 868 patients were eligible for the CPP intervention. Primary reasons for exclusion from the CPP population included over-thecounter aspirin and a history of ASCVD in the patient’s problem list. All patients were male, with a mean (SD) age of 75 (4.4) years (Table 1). Most patients were prescribed aspirin, 81 mg daily (n = 220; 98%).
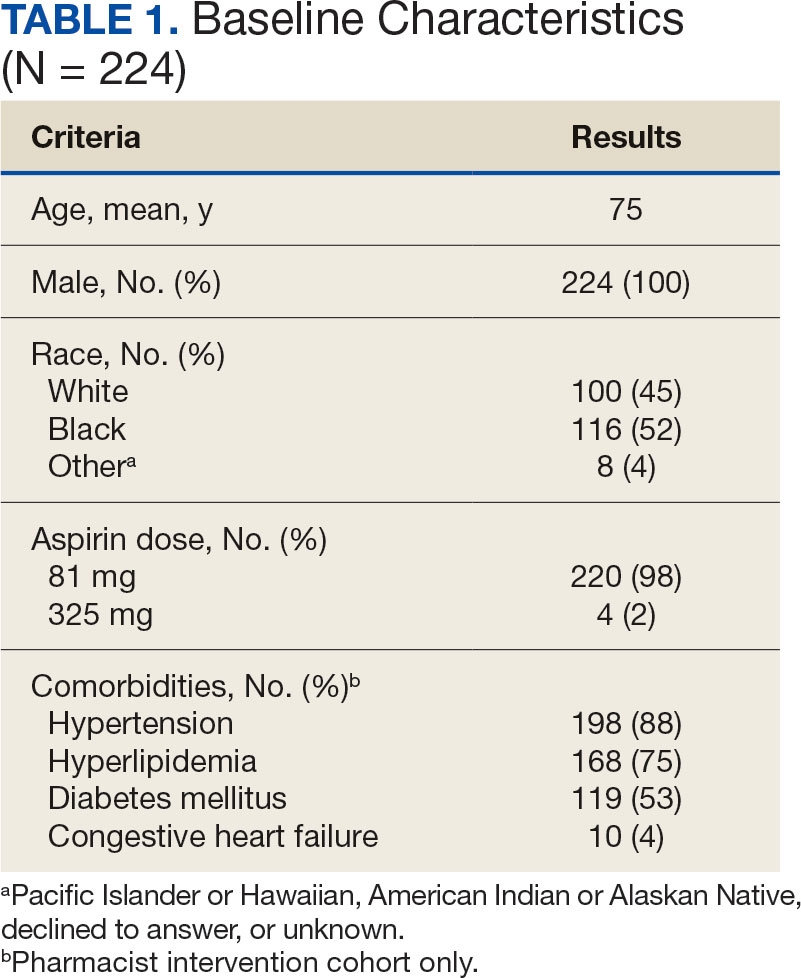
The direct CPP deprescribing intervention resulted in 2 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time and 67 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time via the PCP education intervention. CPPs discontinued 66 aspirin orders in the 12 weeks before the PCP education sessions. A total of 230 aspirin prescriptions were discontinued in the 12 weeks following the PCP education sessions, with 97 discontinued directly by CPPs and 133 discontinued by PCPs. The PCP education session yielded an additional 67 discontinued aspirin orders compared with the 12 weeks before the education sessions (Table 2).
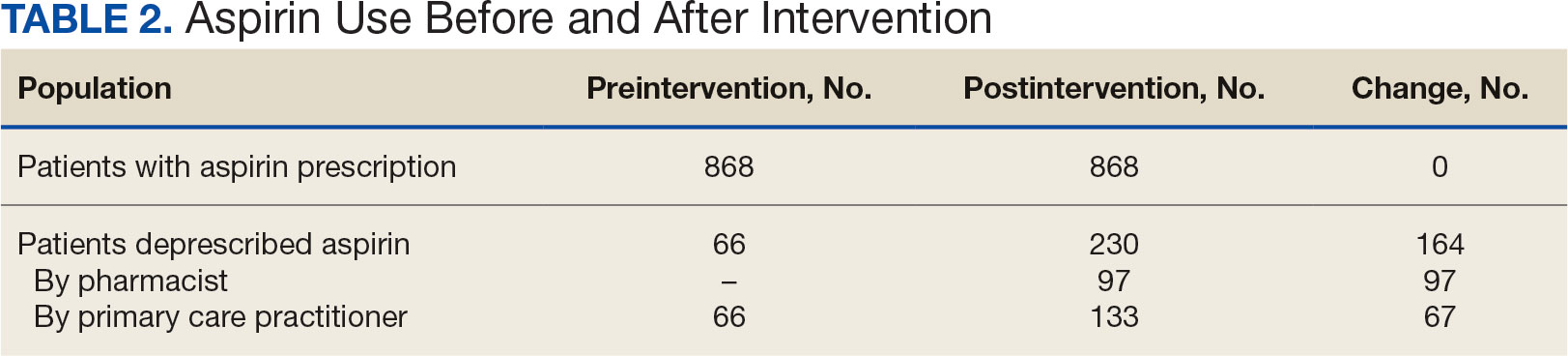
The CPP direct deprescribing intervention took about 48.3 hours, accounting for health record review and time interacting with patients. The PCP education intervention took about 60 minutes, which included time for preparing and delivering education materials (Table 3). CPP deprescribing encounter types, interventions, and related subcategories, and other identified indications to continue aspirin are listed in Table 4.

Discussion
Compared with direct deprescribing by pharmacists, the PCP education intervention was more efficient based on number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacist time. PCPs discontinued twice as many aspirin prescriptions in the 12 weeks after pharmacist-led education compared with the 12 weeks before.
Patients were primarily contacted by telephone (73%) for deprescribing. Among the 163 patients reached by phone and encouraged to discontinue aspirin, 97 patients (60%) accepted the recommendation, which was similar to the acceptance rates found in the literature (48% to 55%).14,18 Although many veterans continued taking aspirin (78%), most had indications for its continued use, such as a history of ASCVD, atrial fibrillation without anticoagulation, and carotid artery stenosis, and complex comorbidities that required further discussion with their PCP. Less common uses for aspirin were identified through CPRS review or patient reports included cerebral small vessel disease without history of ASCVD, subclavian artery stenosis, thrombocytosis, bioprosthetic valve replacement, giant cell arteritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and prevention of second eye involvement of ischemic optic neuropathy.
to describe the benefit of clinical pharmacy services for deprescribing aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD through PCP education. Previously published literature has assessed alternative ways to identify or discontinue PIMs—including aspirin—among geriatric patients. One study evaluated the use of marking inappropriate aspirin prescriptions in the electronic health database, leading to a significant reduction in incidence of inappropriate aspirin prescribing; however, it did not assess changes in discontinuation rates of existing aspirin prescriptions.19 The previous VA pharmacist aspirin deprescribing protocol demonstrated pharmacists’ aptitude at discontinuing aspirin for primary prevention but only used direct patient contact and did not compare efficiency with other methods, including PCP education.14
This quality improvement project contributes new data to the existing literature to support the use of clinical pharmacists to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention and suggests a strong role for pharmacists as educators on clinical guidelines, in addition to their roles directly deprescribing PIMs in clinical practice. This study is further strengthened by its use of VIONE, which previously has demonstrated effectiveness in deprescribing a variety of PIMs in primary care settings.20
Despite using VIONE for generating a list of patients eligible for deprescription, our CPRS review found that this list was frequently inaccurate. For example, a small portion of patients were on the VIONE generated list indicating they had no ASCVD history, but had transient ischemic attack listed in their problem lists. Patient problem lists often were missing documented ASCVD history that was revealed by patient interview or CPRS review. It is possible that patients interviewed might have omitted relevant ASCVD history because of low health literacy, conditions affecting memory, or use of health care services outside the VA system.
There were several instances of aspirin used for other non-ASCVD indications, such as primary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. The ACC/AHA atrial fibrillation guidelines previously provided a Class IIb recommendation (benefit is greater than risk but additional studies are needed) for considering no antithrombic therapy or treatment with oral anticoagulant or aspirin for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with CHA2DS2-VASc (Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age [> 65 y, 1 point; > 75 y, 2 points], Diabetes, previous Stroke/transient ischemic attack [2 points]) score of 1.21 The ACC/ AHA guidelines were updated in 2023 to recommend against antiplatelet therapy as an alternative to anticoagulation for reducing cardioembolic stroke risk among patients with atrial fibrillation with no indication for antiplatelet therapy because of risk of harm.22 If a patient has no risk factors for stroke, aspirin is not recommended to prevent thromboembolic events because of a lack of benefit. Interventions from this quality improvement study were completed before the 2023 atrial fibrillation guideline was published and therefore in this study aspirin was not discontinued when used for atrial fibrillation. Aspirin use for atrial fibrillation might benefit from similar discontinuation efforts analyzed within this study. Beyond atrial fibrillation, major guidelines do not comment on the use of aspirin for any other indications in the absence of clinical ASCVD.
Limitations
This study is limited by the lack of clinical consensus for complex patients and demonstrates the importance of individualized patient assessment when considering discontinuing aspirin. Because of the project’s relatively short intervention period, aspirin deprescribing rates could decrease over time and repeated education efforts might be necessary to see lasting impact. Health care professionals from services outside of primary care also might have discontinued aspirin during the study period unrelated to the education and these discontinued aspirin prescriptions could contribute to the higher rate observed among PCPs. This study included a specific population cohort of male, US veterans and might not reflect other populations where these interventions could be implemented.
The measurement of time spent by pharmacists and PCPs is an additional limitation. Although it is expected that PCPs attempt to discontinue aspirin during their existing patient care appointments, the time spent during visits was not measured or documented. Direct deprescribing by pharmacist CPRS review required a significant amount of time and could be a barrier to successful intervention by CPPs in patient aligned care teams.
To reduce the time pharmacists spent completing CPRS reviews, an aspirin deprescribing clinical reminder tool could be used to assess use and appropriate indication quickly during any primary care visit led by a PCP or CPP. In addition, it is recommended that pharmacists regularly educate health care professionals on guideline recommendations for aspirin use among geriatric patients. Future studies of the incidence of major cardiovascular events after aspirin deprescribing among geriatric patients and a longitudinal cost/benefit analysis could support these initiatives.
Conclusions
In this study, pharmacists successfully deprescribed inappropriate medications, such as aspirin. However, pharmacist-led PCP education is more efficient compared with direct deprescribing using a population-level review. PCP education requires less time and could allow ambulatory care pharmacists to spend more time on other direct patient care interventions to improve quality and access to care in primary care clinics. This study’s results further support the role of pharmacists in deprescribing PIMs for older adults and the use of a deprescribing tool, such as VIONE, in a primary care setting.
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Aspirin use to prevent cardiovascular disease: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2022;327(16):1577-1584. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.4983
- McNeil JJ, Nelson MR, Woods RL, et al. Effect of aspirin on all-cause mortality in the healthy elderly. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(16):1519-1528. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1803955
- Barry MJ, Wolff TA, Pbert L, et al. Putting evidence into practice: an update on the US Preventive Services Task Force methods for developing recommendations for preventive services. Ann Fam Med. 2023;21(2):165-171. doi:10.1370/afm.2946
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S179-S218. doi:10.2337/dc24-S010
- Ong SY, Chui P, Bhargava A, Justice A, Hauser RG. Estimating aspirin overuse for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (from a nationwide healthcare system). Am J Cardiol. 2020;137:25-30. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.09.042
- Weiss AJ, Jiang HJ. Overview of clinical conditions with frequent and costly hospital readmissions by payer, 2018. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); July 20, 2021.
- Krishnaswami A, Steinman MA, Goyal P, et al. Deprescribing in older adults with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(20):2584-2595. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.467
- Association of American Medical Colleges. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2019 to 2034. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/54681/download
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1108.07(1): General pharmacy service requirements. November 28, 2022. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10045
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1108.11(3): Clinical pharmacy services. July 1, 2015. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) to improve access to and quality of care August 2021. August 2021. Accessed May 19, 2023. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/CPPO/Documents/ExternalFactSheet_OptimizingtheCPPToImproveAccess_508.pdf
- Ammerman CA, Simpkins BA, Warman N, Downs TN. Potentially inappropriate medications in older adults: Deprescribing with a clinical pharmacist. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(1):115-118. doi:10.1111/jgs.15623
- Rothbauer K, Siodlak M, Dreischmeier E, Ranola TS, Welch L. Evaluation of a pharmacist-driven ambulatory aspirin deprescribing protocol. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 5):S37- S41a. doi:10.12788/fp.0294
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VIONE changes the way VA handles prescriptions. January 25, 2020. Accessed May 21, 2023. https://news.va.gov/70709/vione-changes-way-va-handles-prescriptions/
- 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052- 2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- O’Mahony D, Cherubini A, Guiteras AR, et al. STOPP/ START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: version 3. Eur Geriatr Med. 2023;14(4):625- 632. doi:10.1007/s41999-023-00777-y
- Draeger C, Lodhi F, Geissinger N, Larson T, Griesbach S. Interdisciplinary deprescribing of aspirin through prescriber education and provision of patient-specific recommendations. WMJ. 2022;121(3):220-225
- de Lusignan S, Hinton W, Seidu S, et al. Dashboards to reduce inappropriate prescribing of metformin and aspirin: A quality assurance programme in a primary care sentinel network. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021;15(6):1075-1079. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.06.003
- Nelson MW, Downs TN, Puglisi GM, Simpkins BA, Collier AS. Use of a deprescribing tool in an interdisciplinary primary-care patient-aligned care team. Sr Care Pharm. 2022;37(1):34-43. doi:10.4140/TCP.n.2022.34
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-e267. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000041
- Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/ AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines Circulation. 2024;149(1):e1- e156. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001193
Low-dose aspirin commonly is used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) but is associated with an increased risk of major bleeding.1 The use of aspirin for primary prevention is largely extrapolated from clinical trials showing benefit in the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. However, results from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial challenged this practice.2 The ASPREE trial, conducted in the United States and Australia from 2010 to 2014, sought to determine whether daily 100 mg aspirin, was superior to placebo in promoting disability-free survival among older adults. Participants were aged ≥ 70 years (≥ 65 years for Hispanic and Black US participants), living in the community, and were free from preexisting CVD, cerebrovascular disease, or any chronic condition likely to limit survival to < 5 years. The study found no significant difference in the primary endpoints of death, dementia, or persistent physical disability, but there was a significantly higher risk of major hemorrhage in the aspirin group (3.8% vs 2.8%; hazard ratio, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.18-1.62; P < .001).
Several medical societies have updated their guideline recommendations for aspirin for primary prevention of CVD. The 2022 United States Public Service Task Force (USPSTF) provides a grade C recommendation (at least moderate certainty that the net benefit is small) to consider low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of CVD on an individual patient basis for adults aged 40 to 59 years who have a ≥ 10% 10-year CVD risk. For adults aged ≥ 60 years, the USPSTF recommendation is grade D (moderate or high certainty that the practice has no net benefit or that harms outweigh the benefits) for low-dose aspirin use.1,3 The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend considering low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) among select adults aged 40 to 70 years at higher CVD risk but not at increased risk of bleeding.4 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of CVD in patients with diabetes and additional risk factors such as family history of premature ASCVD, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, or chronic kidney disease, and who are not at higher risk of bleeding.5 The ADA standards also caution against the use of aspirin as primary prevention in patients aged > 70 years. Low-dose aspirin use is not recommended for the primary prevention of CVD in older adults or adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding.
Recent literature using the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse database confirms 86,555 of 1.8 million veterans aged > 70 years (5%) were taking low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD despite guideline recommendations.6 Higher risk of gastrointestinal and other major bleeding from low-dose aspirin has been reported in the literature.1 Major bleeds represent a significant burden to the health care system with an estimated mean $13,093 cost for gastrointestinal bleed hospitalization.7
Considering the large scale aspirin use without appropriate indication within the veteran population, the risk of adverse effects, and the significant cost to patients and the health care system, it is imperative to determine the best approach to efficiently deprescribe aspirin for primary prevention among geriatric patients. Deprescribing refers to the systematic and supervised process of dose reduction or drug discontinuation with the goal of improving health and/or reducing the risk of adverse effects.8 During patient visits, primary care practitioners (PCPs) have opportunities to discontinue aspirin, but these encounters are time-limited and deprescribing might be secondary to more acute primary care needs. The shortage of PCPs is expected to worsen in coming years, which could further reduce their availability to assess inappropriate aspirin use.9
VA clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) serve as medication experts and work autonomously under a broad scope of practice as part of the patient aligned care team.10-12 CPPs can free up time for PCPs and facilitate deprescribing efforts, especially for older adults. One retrospective cohort study conducted at a VA medical center found that CPPs deprescribed more potentially inappropriate medications among individuals aged ≥ 80 years compared with usual care with PCPs (26.8% vs 16.1%; P < .001).12,13 An aspirin deprescribing protocol conducted in 2022 resulted in nearly half of veterans aged ≥ 70 years contacted by phone agreeing to stop aspirin. Although this study supports the role pharmacists can play in reducing aspirin use in accordance with guidelines, the authors acknowledge that their interventions had a mean time of 12 minutes per patient and would require workflow changes.14 The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficiency of aspirin deprescribing through 2 approaches: direct deprescribing by pharmacists using populationlevel review compared with clinicians following a pharmacist-led education.
Methods
This was a single-center quality improvement cohort study at the Durham VA Health Care System (DVAHCS) in North Carolina. Patients included were aged ≥ 70 years without known ASCVD who received care at any of 3 DVAHCS community-based outpatient clinics and prescribed aspirin. Patient data was obtained using the VIONE (Deprescribing Dashboard called Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, and Every medication has a specific indication or diagnosis) dashboard.15 VIONE was developed to identify potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) that are eligible to deprescribe based on Beers Criteria, Screening Tool of Older Personsf Prescriptions criteria, and common clinical scenarios when clinicians determine the risk outweighs the benefit to continue a specific medication. 16,17 VIONE is used to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety, comfort, and medication adherence. Aspirin for patients aged ≥ 70 years without a history of ASCVD is a PIM identified by VIONE. Patients aged ≥ 70 years were chosen as an inclusion criteria in this study to match the ASPREE trial inclusion criteria and age inclusion criteria in the VIONE dashboard for aspirin deprescribing.2 Patient lists were generated for these potentially inappropriate aspirin prescriptions for 3 months before clinician staff education presentations, the day of the presentations, and 3 months after.
The primary endpoint was the number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed directly by 2 pharmacists over 12 weeks, divided by total patient care time spent, compared with the change in number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed by any DVAHCS physician, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or CPP over 12 weeks, divided by the total pharmacist time spent on PCP education. Secondary endpoints were the number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacists and CPPs, the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks before pharmacist-led education compared with the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks after CPP-led education, average and median pharmacist time spent per patient encounter, and time of direct patient encounters vs time spent on PCP education.
Pharmacists reviewed each patient who met the inclusion criteria from the list generated by VIONE on December 1, 2022, for aspirin appropriateness according to the ACC/AHA and USPSTF guidelines, with the goal to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD and no other indications.1,4 Pharmacists documented their visits using VIONE methodology in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) using a polypharmacy review note. CPPs contacted patients who were taking aspirin for primary prevention by unscheduled telephone call to assess for aspirin adherence, undocumented history of ASCVD, cardiovascular risk factors, and history of bleeding. Aspirin was discontinued if patients met guideline criteria recommendations and agreed to discontinuation. Risk-benefit discussions were completed when patients without known ASCVD were considered high risk because the ACC/AHA guidelines mention there is insufficient evidence of safety and efficacy of aspirin for primary prevention for patients with other known ASCVD risk factors (eg, strong family history of premature myocardial infarction, inability to achieve lipid, blood pressure, or glucose targets, or significant elevation in coronary artery calcium score).
High risk was defined as family history of premature ASCVD (in a male first-degree relative aged < 55 years or a female first-degree relative aged < 65 years), most recent blood pressure or 2 blood pressure results in the last 12 months > 160/100 mm Hg, recent hemoglobin A1c > 9%, and/or low-density lipoprotein > 190 mg/dL or not prescribed an indicated statin.3 Aspirin was continued or discontinued according to patient preference after the personalized risk-benefit discussion.
For patients with a clinical indication for aspirin use other than ASCVD (eg, atrial fibrillation not on anticoagulation, venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, carotid artery disease), CPPs documented their assessment and when appropriate deferred to the PCP for consideration of stopping aspirin. For patients with undocumented ASCVD, CPPs added their ASCVD history to their problem list and aspirin was continued. PCPs were notified by alert when aspirin was discontinued and when patients could not be reached by telephone.
presented a review of recent guideline updates and supporting literature at 2 online staff meetings. The education sessions lasted about 10 minutes and were presented to PCPs across 3 community-based outpatient clinics. An estimated 40 minutes were spent creating the PowerPoint education materials, seeking feedback, making edits, and answering questions or emails from PCPs after the presentation. During the presentation, pharmacists encouraged PCPs to discontinue aspirin (active VA prescriptions and reported over-the-counter use) for primary prevention of ASCVD in patients aged ≥ 70 years during their upcoming appointments and consider risk factors recommended by the ACC/AHA guidelines when applicable. PCPs were notified that CPPs planned to start a population review for discontinuing active VA aspirin prescriptions on December 1, 2022. The primary endpoint and secondary endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. All data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel.

Results
A total of 868 patients aged ≥ 70 years with active prescriptions for aspirin were identified on December 1, 2022. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria for the pharmacist population review, 224 patients were included for cohort final analysis (Figure). All 868 patients were eligible for the CPP intervention. Primary reasons for exclusion from the CPP population included over-thecounter aspirin and a history of ASCVD in the patient’s problem list. All patients were male, with a mean (SD) age of 75 (4.4) years (Table 1). Most patients were prescribed aspirin, 81 mg daily (n = 220; 98%).

The direct CPP deprescribing intervention resulted in 2 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time and 67 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time via the PCP education intervention. CPPs discontinued 66 aspirin orders in the 12 weeks before the PCP education sessions. A total of 230 aspirin prescriptions were discontinued in the 12 weeks following the PCP education sessions, with 97 discontinued directly by CPPs and 133 discontinued by PCPs. The PCP education session yielded an additional 67 discontinued aspirin orders compared with the 12 weeks before the education sessions (Table 2).

The CPP direct deprescribing intervention took about 48.3 hours, accounting for health record review and time interacting with patients. The PCP education intervention took about 60 minutes, which included time for preparing and delivering education materials (Table 3). CPP deprescribing encounter types, interventions, and related subcategories, and other identified indications to continue aspirin are listed in Table 4.


Discussion
Compared with direct deprescribing by pharmacists, the PCP education intervention was more efficient based on number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacist time. PCPs discontinued twice as many aspirin prescriptions in the 12 weeks after pharmacist-led education compared with the 12 weeks before.
Patients were primarily contacted by telephone (73%) for deprescribing. Among the 163 patients reached by phone and encouraged to discontinue aspirin, 97 patients (60%) accepted the recommendation, which was similar to the acceptance rates found in the literature (48% to 55%).14,18 Although many veterans continued taking aspirin (78%), most had indications for its continued use, such as a history of ASCVD, atrial fibrillation without anticoagulation, and carotid artery stenosis, and complex comorbidities that required further discussion with their PCP. Less common uses for aspirin were identified through CPRS review or patient reports included cerebral small vessel disease without history of ASCVD, subclavian artery stenosis, thrombocytosis, bioprosthetic valve replacement, giant cell arteritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and prevention of second eye involvement of ischemic optic neuropathy.
to describe the benefit of clinical pharmacy services for deprescribing aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD through PCP education. Previously published literature has assessed alternative ways to identify or discontinue PIMs—including aspirin—among geriatric patients. One study evaluated the use of marking inappropriate aspirin prescriptions in the electronic health database, leading to a significant reduction in incidence of inappropriate aspirin prescribing; however, it did not assess changes in discontinuation rates of existing aspirin prescriptions.19 The previous VA pharmacist aspirin deprescribing protocol demonstrated pharmacists’ aptitude at discontinuing aspirin for primary prevention but only used direct patient contact and did not compare efficiency with other methods, including PCP education.14
This quality improvement project contributes new data to the existing literature to support the use of clinical pharmacists to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention and suggests a strong role for pharmacists as educators on clinical guidelines, in addition to their roles directly deprescribing PIMs in clinical practice. This study is further strengthened by its use of VIONE, which previously has demonstrated effectiveness in deprescribing a variety of PIMs in primary care settings.20
Despite using VIONE for generating a list of patients eligible for deprescription, our CPRS review found that this list was frequently inaccurate. For example, a small portion of patients were on the VIONE generated list indicating they had no ASCVD history, but had transient ischemic attack listed in their problem lists. Patient problem lists often were missing documented ASCVD history that was revealed by patient interview or CPRS review. It is possible that patients interviewed might have omitted relevant ASCVD history because of low health literacy, conditions affecting memory, or use of health care services outside the VA system.
There were several instances of aspirin used for other non-ASCVD indications, such as primary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. The ACC/AHA atrial fibrillation guidelines previously provided a Class IIb recommendation (benefit is greater than risk but additional studies are needed) for considering no antithrombic therapy or treatment with oral anticoagulant or aspirin for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with CHA2DS2-VASc (Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age [> 65 y, 1 point; > 75 y, 2 points], Diabetes, previous Stroke/transient ischemic attack [2 points]) score of 1.21 The ACC/ AHA guidelines were updated in 2023 to recommend against antiplatelet therapy as an alternative to anticoagulation for reducing cardioembolic stroke risk among patients with atrial fibrillation with no indication for antiplatelet therapy because of risk of harm.22 If a patient has no risk factors for stroke, aspirin is not recommended to prevent thromboembolic events because of a lack of benefit. Interventions from this quality improvement study were completed before the 2023 atrial fibrillation guideline was published and therefore in this study aspirin was not discontinued when used for atrial fibrillation. Aspirin use for atrial fibrillation might benefit from similar discontinuation efforts analyzed within this study. Beyond atrial fibrillation, major guidelines do not comment on the use of aspirin for any other indications in the absence of clinical ASCVD.
Limitations
This study is limited by the lack of clinical consensus for complex patients and demonstrates the importance of individualized patient assessment when considering discontinuing aspirin. Because of the project’s relatively short intervention period, aspirin deprescribing rates could decrease over time and repeated education efforts might be necessary to see lasting impact. Health care professionals from services outside of primary care also might have discontinued aspirin during the study period unrelated to the education and these discontinued aspirin prescriptions could contribute to the higher rate observed among PCPs. This study included a specific population cohort of male, US veterans and might not reflect other populations where these interventions could be implemented.
The measurement of time spent by pharmacists and PCPs is an additional limitation. Although it is expected that PCPs attempt to discontinue aspirin during their existing patient care appointments, the time spent during visits was not measured or documented. Direct deprescribing by pharmacist CPRS review required a significant amount of time and could be a barrier to successful intervention by CPPs in patient aligned care teams.
To reduce the time pharmacists spent completing CPRS reviews, an aspirin deprescribing clinical reminder tool could be used to assess use and appropriate indication quickly during any primary care visit led by a PCP or CPP. In addition, it is recommended that pharmacists regularly educate health care professionals on guideline recommendations for aspirin use among geriatric patients. Future studies of the incidence of major cardiovascular events after aspirin deprescribing among geriatric patients and a longitudinal cost/benefit analysis could support these initiatives.
Conclusions
In this study, pharmacists successfully deprescribed inappropriate medications, such as aspirin. However, pharmacist-led PCP education is more efficient compared with direct deprescribing using a population-level review. PCP education requires less time and could allow ambulatory care pharmacists to spend more time on other direct patient care interventions to improve quality and access to care in primary care clinics. This study’s results further support the role of pharmacists in deprescribing PIMs for older adults and the use of a deprescribing tool, such as VIONE, in a primary care setting.
Low-dose aspirin commonly is used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) but is associated with an increased risk of major bleeding.1 The use of aspirin for primary prevention is largely extrapolated from clinical trials showing benefit in the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. However, results from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) trial challenged this practice.2 The ASPREE trial, conducted in the United States and Australia from 2010 to 2014, sought to determine whether daily 100 mg aspirin, was superior to placebo in promoting disability-free survival among older adults. Participants were aged ≥ 70 years (≥ 65 years for Hispanic and Black US participants), living in the community, and were free from preexisting CVD, cerebrovascular disease, or any chronic condition likely to limit survival to < 5 years. The study found no significant difference in the primary endpoints of death, dementia, or persistent physical disability, but there was a significantly higher risk of major hemorrhage in the aspirin group (3.8% vs 2.8%; hazard ratio, 1.38; 95% CI, 1.18-1.62; P < .001).
Several medical societies have updated their guideline recommendations for aspirin for primary prevention of CVD. The 2022 United States Public Service Task Force (USPSTF) provides a grade C recommendation (at least moderate certainty that the net benefit is small) to consider low-dose aspirin for the primary prevention of CVD on an individual patient basis for adults aged 40 to 59 years who have a ≥ 10% 10-year CVD risk. For adults aged ≥ 60 years, the USPSTF recommendation is grade D (moderate or high certainty that the practice has no net benefit or that harms outweigh the benefits) for low-dose aspirin use.1,3 The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend considering low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) among select adults aged 40 to 70 years at higher CVD risk but not at increased risk of bleeding.4 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of CVD in patients with diabetes and additional risk factors such as family history of premature ASCVD, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, or chronic kidney disease, and who are not at higher risk of bleeding.5 The ADA standards also caution against the use of aspirin as primary prevention in patients aged > 70 years. Low-dose aspirin use is not recommended for the primary prevention of CVD in older adults or adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding.
Recent literature using the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse database confirms 86,555 of 1.8 million veterans aged > 70 years (5%) were taking low-dose aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD despite guideline recommendations.6 Higher risk of gastrointestinal and other major bleeding from low-dose aspirin has been reported in the literature.1 Major bleeds represent a significant burden to the health care system with an estimated mean $13,093 cost for gastrointestinal bleed hospitalization.7
Considering the large scale aspirin use without appropriate indication within the veteran population, the risk of adverse effects, and the significant cost to patients and the health care system, it is imperative to determine the best approach to efficiently deprescribe aspirin for primary prevention among geriatric patients. Deprescribing refers to the systematic and supervised process of dose reduction or drug discontinuation with the goal of improving health and/or reducing the risk of adverse effects.8 During patient visits, primary care practitioners (PCPs) have opportunities to discontinue aspirin, but these encounters are time-limited and deprescribing might be secondary to more acute primary care needs. The shortage of PCPs is expected to worsen in coming years, which could further reduce their availability to assess inappropriate aspirin use.9
VA clinical pharmacist practitioners (CPPs) serve as medication experts and work autonomously under a broad scope of practice as part of the patient aligned care team.10-12 CPPs can free up time for PCPs and facilitate deprescribing efforts, especially for older adults. One retrospective cohort study conducted at a VA medical center found that CPPs deprescribed more potentially inappropriate medications among individuals aged ≥ 80 years compared with usual care with PCPs (26.8% vs 16.1%; P < .001).12,13 An aspirin deprescribing protocol conducted in 2022 resulted in nearly half of veterans aged ≥ 70 years contacted by phone agreeing to stop aspirin. Although this study supports the role pharmacists can play in reducing aspirin use in accordance with guidelines, the authors acknowledge that their interventions had a mean time of 12 minutes per patient and would require workflow changes.14 The purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficiency of aspirin deprescribing through 2 approaches: direct deprescribing by pharmacists using populationlevel review compared with clinicians following a pharmacist-led education.
Methods
This was a single-center quality improvement cohort study at the Durham VA Health Care System (DVAHCS) in North Carolina. Patients included were aged ≥ 70 years without known ASCVD who received care at any of 3 DVAHCS community-based outpatient clinics and prescribed aspirin. Patient data was obtained using the VIONE (Deprescribing Dashboard called Vital, Important, Optional, Not indicated, and Every medication has a specific indication or diagnosis) dashboard.15 VIONE was developed to identify potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) that are eligible to deprescribe based on Beers Criteria, Screening Tool of Older Personsf Prescriptions criteria, and common clinical scenarios when clinicians determine the risk outweighs the benefit to continue a specific medication. 16,17 VIONE is used to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety, comfort, and medication adherence. Aspirin for patients aged ≥ 70 years without a history of ASCVD is a PIM identified by VIONE. Patients aged ≥ 70 years were chosen as an inclusion criteria in this study to match the ASPREE trial inclusion criteria and age inclusion criteria in the VIONE dashboard for aspirin deprescribing.2 Patient lists were generated for these potentially inappropriate aspirin prescriptions for 3 months before clinician staff education presentations, the day of the presentations, and 3 months after.
The primary endpoint was the number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed directly by 2 pharmacists over 12 weeks, divided by total patient care time spent, compared with the change in number of veterans with aspirin deprescribed by any DVAHCS physician, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or CPP over 12 weeks, divided by the total pharmacist time spent on PCP education. Secondary endpoints were the number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacists and CPPs, the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks before pharmacist-led education compared with the number of aspirin orders discontinued 12 weeks after CPP-led education, average and median pharmacist time spent per patient encounter, and time of direct patient encounters vs time spent on PCP education.
Pharmacists reviewed each patient who met the inclusion criteria from the list generated by VIONE on December 1, 2022, for aspirin appropriateness according to the ACC/AHA and USPSTF guidelines, with the goal to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD and no other indications.1,4 Pharmacists documented their visits using VIONE methodology in the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) using a polypharmacy review note. CPPs contacted patients who were taking aspirin for primary prevention by unscheduled telephone call to assess for aspirin adherence, undocumented history of ASCVD, cardiovascular risk factors, and history of bleeding. Aspirin was discontinued if patients met guideline criteria recommendations and agreed to discontinuation. Risk-benefit discussions were completed when patients without known ASCVD were considered high risk because the ACC/AHA guidelines mention there is insufficient evidence of safety and efficacy of aspirin for primary prevention for patients with other known ASCVD risk factors (eg, strong family history of premature myocardial infarction, inability to achieve lipid, blood pressure, or glucose targets, or significant elevation in coronary artery calcium score).
High risk was defined as family history of premature ASCVD (in a male first-degree relative aged < 55 years or a female first-degree relative aged < 65 years), most recent blood pressure or 2 blood pressure results in the last 12 months > 160/100 mm Hg, recent hemoglobin A1c > 9%, and/or low-density lipoprotein > 190 mg/dL or not prescribed an indicated statin.3 Aspirin was continued or discontinued according to patient preference after the personalized risk-benefit discussion.
For patients with a clinical indication for aspirin use other than ASCVD (eg, atrial fibrillation not on anticoagulation, venous thromboembolism prophylaxis, carotid artery disease), CPPs documented their assessment and when appropriate deferred to the PCP for consideration of stopping aspirin. For patients with undocumented ASCVD, CPPs added their ASCVD history to their problem list and aspirin was continued. PCPs were notified by alert when aspirin was discontinued and when patients could not be reached by telephone.
presented a review of recent guideline updates and supporting literature at 2 online staff meetings. The education sessions lasted about 10 minutes and were presented to PCPs across 3 community-based outpatient clinics. An estimated 40 minutes were spent creating the PowerPoint education materials, seeking feedback, making edits, and answering questions or emails from PCPs after the presentation. During the presentation, pharmacists encouraged PCPs to discontinue aspirin (active VA prescriptions and reported over-the-counter use) for primary prevention of ASCVD in patients aged ≥ 70 years during their upcoming appointments and consider risk factors recommended by the ACC/AHA guidelines when applicable. PCPs were notified that CPPs planned to start a population review for discontinuing active VA aspirin prescriptions on December 1, 2022. The primary endpoint and secondary endpoints were analyzed using descriptive statistics. All data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel.

Results
A total of 868 patients aged ≥ 70 years with active prescriptions for aspirin were identified on December 1, 2022. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria for the pharmacist population review, 224 patients were included for cohort final analysis (Figure). All 868 patients were eligible for the CPP intervention. Primary reasons for exclusion from the CPP population included over-thecounter aspirin and a history of ASCVD in the patient’s problem list. All patients were male, with a mean (SD) age of 75 (4.4) years (Table 1). Most patients were prescribed aspirin, 81 mg daily (n = 220; 98%).

The direct CPP deprescribing intervention resulted in 2 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time and 67 aspirin prescriptions discontinued per hour of pharmacist time via the PCP education intervention. CPPs discontinued 66 aspirin orders in the 12 weeks before the PCP education sessions. A total of 230 aspirin prescriptions were discontinued in the 12 weeks following the PCP education sessions, with 97 discontinued directly by CPPs and 133 discontinued by PCPs. The PCP education session yielded an additional 67 discontinued aspirin orders compared with the 12 weeks before the education sessions (Table 2).

The CPP direct deprescribing intervention took about 48.3 hours, accounting for health record review and time interacting with patients. The PCP education intervention took about 60 minutes, which included time for preparing and delivering education materials (Table 3). CPP deprescribing encounter types, interventions, and related subcategories, and other identified indications to continue aspirin are listed in Table 4.


Discussion
Compared with direct deprescribing by pharmacists, the PCP education intervention was more efficient based on number of aspirin orders discontinued by pharmacist time. PCPs discontinued twice as many aspirin prescriptions in the 12 weeks after pharmacist-led education compared with the 12 weeks before.
Patients were primarily contacted by telephone (73%) for deprescribing. Among the 163 patients reached by phone and encouraged to discontinue aspirin, 97 patients (60%) accepted the recommendation, which was similar to the acceptance rates found in the literature (48% to 55%).14,18 Although many veterans continued taking aspirin (78%), most had indications for its continued use, such as a history of ASCVD, atrial fibrillation without anticoagulation, and carotid artery stenosis, and complex comorbidities that required further discussion with their PCP. Less common uses for aspirin were identified through CPRS review or patient reports included cerebral small vessel disease without history of ASCVD, subclavian artery stenosis, thrombocytosis, bioprosthetic valve replacement, giant cell arteritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and prevention of second eye involvement of ischemic optic neuropathy.
to describe the benefit of clinical pharmacy services for deprescribing aspirin for primary prevention of ASCVD through PCP education. Previously published literature has assessed alternative ways to identify or discontinue PIMs—including aspirin—among geriatric patients. One study evaluated the use of marking inappropriate aspirin prescriptions in the electronic health database, leading to a significant reduction in incidence of inappropriate aspirin prescribing; however, it did not assess changes in discontinuation rates of existing aspirin prescriptions.19 The previous VA pharmacist aspirin deprescribing protocol demonstrated pharmacists’ aptitude at discontinuing aspirin for primary prevention but only used direct patient contact and did not compare efficiency with other methods, including PCP education.14
This quality improvement project contributes new data to the existing literature to support the use of clinical pharmacists to discontinue aspirin for primary prevention and suggests a strong role for pharmacists as educators on clinical guidelines, in addition to their roles directly deprescribing PIMs in clinical practice. This study is further strengthened by its use of VIONE, which previously has demonstrated effectiveness in deprescribing a variety of PIMs in primary care settings.20
Despite using VIONE for generating a list of patients eligible for deprescription, our CPRS review found that this list was frequently inaccurate. For example, a small portion of patients were on the VIONE generated list indicating they had no ASCVD history, but had transient ischemic attack listed in their problem lists. Patient problem lists often were missing documented ASCVD history that was revealed by patient interview or CPRS review. It is possible that patients interviewed might have omitted relevant ASCVD history because of low health literacy, conditions affecting memory, or use of health care services outside the VA system.
There were several instances of aspirin used for other non-ASCVD indications, such as primary stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. The ACC/AHA atrial fibrillation guidelines previously provided a Class IIb recommendation (benefit is greater than risk but additional studies are needed) for considering no antithrombic therapy or treatment with oral anticoagulant or aspirin for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation with CHA2DS2-VASc (Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age [> 65 y, 1 point; > 75 y, 2 points], Diabetes, previous Stroke/transient ischemic attack [2 points]) score of 1.21 The ACC/ AHA guidelines were updated in 2023 to recommend against antiplatelet therapy as an alternative to anticoagulation for reducing cardioembolic stroke risk among patients with atrial fibrillation with no indication for antiplatelet therapy because of risk of harm.22 If a patient has no risk factors for stroke, aspirin is not recommended to prevent thromboembolic events because of a lack of benefit. Interventions from this quality improvement study were completed before the 2023 atrial fibrillation guideline was published and therefore in this study aspirin was not discontinued when used for atrial fibrillation. Aspirin use for atrial fibrillation might benefit from similar discontinuation efforts analyzed within this study. Beyond atrial fibrillation, major guidelines do not comment on the use of aspirin for any other indications in the absence of clinical ASCVD.
Limitations
This study is limited by the lack of clinical consensus for complex patients and demonstrates the importance of individualized patient assessment when considering discontinuing aspirin. Because of the project’s relatively short intervention period, aspirin deprescribing rates could decrease over time and repeated education efforts might be necessary to see lasting impact. Health care professionals from services outside of primary care also might have discontinued aspirin during the study period unrelated to the education and these discontinued aspirin prescriptions could contribute to the higher rate observed among PCPs. This study included a specific population cohort of male, US veterans and might not reflect other populations where these interventions could be implemented.
The measurement of time spent by pharmacists and PCPs is an additional limitation. Although it is expected that PCPs attempt to discontinue aspirin during their existing patient care appointments, the time spent during visits was not measured or documented. Direct deprescribing by pharmacist CPRS review required a significant amount of time and could be a barrier to successful intervention by CPPs in patient aligned care teams.
To reduce the time pharmacists spent completing CPRS reviews, an aspirin deprescribing clinical reminder tool could be used to assess use and appropriate indication quickly during any primary care visit led by a PCP or CPP. In addition, it is recommended that pharmacists regularly educate health care professionals on guideline recommendations for aspirin use among geriatric patients. Future studies of the incidence of major cardiovascular events after aspirin deprescribing among geriatric patients and a longitudinal cost/benefit analysis could support these initiatives.
Conclusions
In this study, pharmacists successfully deprescribed inappropriate medications, such as aspirin. However, pharmacist-led PCP education is more efficient compared with direct deprescribing using a population-level review. PCP education requires less time and could allow ambulatory care pharmacists to spend more time on other direct patient care interventions to improve quality and access to care in primary care clinics. This study’s results further support the role of pharmacists in deprescribing PIMs for older adults and the use of a deprescribing tool, such as VIONE, in a primary care setting.
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Aspirin use to prevent cardiovascular disease: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2022;327(16):1577-1584. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.4983
- McNeil JJ, Nelson MR, Woods RL, et al. Effect of aspirin on all-cause mortality in the healthy elderly. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(16):1519-1528. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1803955
- Barry MJ, Wolff TA, Pbert L, et al. Putting evidence into practice: an update on the US Preventive Services Task Force methods for developing recommendations for preventive services. Ann Fam Med. 2023;21(2):165-171. doi:10.1370/afm.2946
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S179-S218. doi:10.2337/dc24-S010
- Ong SY, Chui P, Bhargava A, Justice A, Hauser RG. Estimating aspirin overuse for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (from a nationwide healthcare system). Am J Cardiol. 2020;137:25-30. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.09.042
- Weiss AJ, Jiang HJ. Overview of clinical conditions with frequent and costly hospital readmissions by payer, 2018. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); July 20, 2021.
- Krishnaswami A, Steinman MA, Goyal P, et al. Deprescribing in older adults with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(20):2584-2595. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.467
- Association of American Medical Colleges. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2019 to 2034. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/54681/download
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1108.07(1): General pharmacy service requirements. November 28, 2022. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10045
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1108.11(3): Clinical pharmacy services. July 1, 2015. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) to improve access to and quality of care August 2021. August 2021. Accessed May 19, 2023. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/CPPO/Documents/ExternalFactSheet_OptimizingtheCPPToImproveAccess_508.pdf
- Ammerman CA, Simpkins BA, Warman N, Downs TN. Potentially inappropriate medications in older adults: Deprescribing with a clinical pharmacist. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(1):115-118. doi:10.1111/jgs.15623
- Rothbauer K, Siodlak M, Dreischmeier E, Ranola TS, Welch L. Evaluation of a pharmacist-driven ambulatory aspirin deprescribing protocol. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 5):S37- S41a. doi:10.12788/fp.0294
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VIONE changes the way VA handles prescriptions. January 25, 2020. Accessed May 21, 2023. https://news.va.gov/70709/vione-changes-way-va-handles-prescriptions/
- 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052- 2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- O’Mahony D, Cherubini A, Guiteras AR, et al. STOPP/ START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: version 3. Eur Geriatr Med. 2023;14(4):625- 632. doi:10.1007/s41999-023-00777-y
- Draeger C, Lodhi F, Geissinger N, Larson T, Griesbach S. Interdisciplinary deprescribing of aspirin through prescriber education and provision of patient-specific recommendations. WMJ. 2022;121(3):220-225
- de Lusignan S, Hinton W, Seidu S, et al. Dashboards to reduce inappropriate prescribing of metformin and aspirin: A quality assurance programme in a primary care sentinel network. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021;15(6):1075-1079. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.06.003
- Nelson MW, Downs TN, Puglisi GM, Simpkins BA, Collier AS. Use of a deprescribing tool in an interdisciplinary primary-care patient-aligned care team. Sr Care Pharm. 2022;37(1):34-43. doi:10.4140/TCP.n.2022.34
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-e267. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000041
- Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/ AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines Circulation. 2024;149(1):e1- e156. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001193
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Aspirin use to prevent cardiovascular disease: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2022;327(16):1577-1584. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.4983
- McNeil JJ, Nelson MR, Woods RL, et al. Effect of aspirin on all-cause mortality in the healthy elderly. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(16):1519-1528. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1803955
- Barry MJ, Wolff TA, Pbert L, et al. Putting evidence into practice: an update on the US Preventive Services Task Force methods for developing recommendations for preventive services. Ann Fam Med. 2023;21(2):165-171. doi:10.1370/afm.2946
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S179-S218. doi:10.2337/dc24-S010
- Ong SY, Chui P, Bhargava A, Justice A, Hauser RG. Estimating aspirin overuse for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (from a nationwide healthcare system). Am J Cardiol. 2020;137:25-30. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.09.042
- Weiss AJ, Jiang HJ. Overview of clinical conditions with frequent and costly hospital readmissions by payer, 2018. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); July 20, 2021.
- Krishnaswami A, Steinman MA, Goyal P, et al. Deprescribing in older adults with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(20):2584-2595. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.467
- Association of American Medical Colleges. The complexities of physician supply and demand: projections from 2019 to 2034. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/media/54681/download
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1108.07(1): General pharmacy service requirements. November 28, 2022. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10045
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1108.11(3): Clinical pharmacy services. July 1, 2015. Accessed March 17, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) to improve access to and quality of care August 2021. August 2021. Accessed May 19, 2023. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/CPPO/Documents/ExternalFactSheet_OptimizingtheCPPToImproveAccess_508.pdf
- Ammerman CA, Simpkins BA, Warman N, Downs TN. Potentially inappropriate medications in older adults: Deprescribing with a clinical pharmacist. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(1):115-118. doi:10.1111/jgs.15623
- Rothbauer K, Siodlak M, Dreischmeier E, Ranola TS, Welch L. Evaluation of a pharmacist-driven ambulatory aspirin deprescribing protocol. Fed Pract. 2022;39(suppl 5):S37- S41a. doi:10.12788/fp.0294
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VIONE changes the way VA handles prescriptions. January 25, 2020. Accessed May 21, 2023. https://news.va.gov/70709/vione-changes-way-va-handles-prescriptions/
- 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052- 2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- O’Mahony D, Cherubini A, Guiteras AR, et al. STOPP/ START criteria for potentially inappropriate prescribing in older people: version 3. Eur Geriatr Med. 2023;14(4):625- 632. doi:10.1007/s41999-023-00777-y
- Draeger C, Lodhi F, Geissinger N, Larson T, Griesbach S. Interdisciplinary deprescribing of aspirin through prescriber education and provision of patient-specific recommendations. WMJ. 2022;121(3):220-225
- de Lusignan S, Hinton W, Seidu S, et al. Dashboards to reduce inappropriate prescribing of metformin and aspirin: A quality assurance programme in a primary care sentinel network. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021;15(6):1075-1079. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2021.06.003
- Nelson MW, Downs TN, Puglisi GM, Simpkins BA, Collier AS. Use of a deprescribing tool in an interdisciplinary primary-care patient-aligned care team. Sr Care Pharm. 2022;37(1):34-43. doi:10.4140/TCP.n.2022.34
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2014;130(23):e199-e267. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000041
- Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/ AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines Circulation. 2024;149(1):e1- e156. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000001193
Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing of Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Geriatric Veterans
Pharmacist-Led Deprescribing of Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Among Geriatric Veterans
Loneliness, Isolation Affect One Third of US Adults Over 50
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About one third of US adults aged 50-80 years report feeling lonely and socially isolated, a new study of data from 2018-2024 shows. While the levels have returned to the prepandemic range, investigators say the findings suggest clinicians should screen for loneliness and isolation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a nationally representative survey of US adults aged 50-80 years through the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging at six timepoints between 2018 and 2024.
- Data collection involved online surveys conducted using the Ipsos KnowledgePanel from 2018 to 2021, transitioning to online and phone surveys conducted using the National Opinion Research Center AmeriSpeak panel from 2022 to 2024.
- Sample sizes ranged between 2051 and 2576 respondents, with completion rates ranging from 61% to 78% across the survey periods.
TAKEAWAY:
- Loneliness rates among adults aged 50-80 years showed notable fluctuation, starting at 34% (95% CI, 31.7%-36.2%) in 2018, rising to 41% (95% CI, 39.1%-43.7%) in 2020, and returning to 33% (95% CI, 31.7%-35.1%) by 2024.
- Social isolation showed a similar pattern in the study group, starting at 27% (95% CI, 24.5%-28.8%) in 2018, peaking at 56% (95% CI, 53.4%-58.1%) in 2020, and declining to 29% (95% CI, 27.5%-30.9%) by 2024.
- Higher loneliness and social isolation rates were frequently reported among individuals who did not work, lived alone, had lower household incomes, and had self-reported fair and poor physical and mental health than those who reported excellent, very good, or good health.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings suggest that “much like routinely asking about diet and exercise, clinicians should consider screening older adults for loneliness and social isolation and connect them with appropriate resources,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Preeti N. Malani, MD, MSJ, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor. It was published online on December 9 in JAMA.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by possible recall bias, reliance on self-reported data, lack of longitudinal results, and differences in survey timing, panels, and question framing across years. The findings may not have been applicable to excluded groups such as nursing home residents or individuals aged > 80 years, which limited their generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by AARP and Michigan Medicine and the Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, and Health Systems Research. One author reported receiving consulting fees and honoraria from various organizations. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.