User login
The Return of the Plague: A Primer on Pandemic Ethics
I am writing this editorial on a beautiful day in the high desert of the Southwest: a bright blue clear sky such as you see only in the mountain air, a sun warm and comforting, and birds singing as if they had not a care in the world. Spring has come early as if to dramatize the cognitive dissonance between this idyllic scene and a seemingly invincible winter of disease and death that has gripped the globe.
For now, my editorials will focus on the most threatening infectious disease outbreak since, perhaps, 1918. I have been teaching public health and pandemic ethics to health care professionals and trainees for more than a decade. I always tell the medical students, “it is not if but when” the next viral wave overwhelms society. It is human nature to disbelieve this inevitability and to ignore, dismiss, or even attack the infectious disease experts and science journalists who, like Cassandra, warn us of the return of the plague.1
In the early 2000s, virologists were concerned that Avian influenza with a mortality rate of > 60% would mutate into a virus capable of jumping the species barrier with sustained human transmission; however, that threat has not materialized (yet).2 Instead, in 2009 the H1N1 influenza pandemic struck viciously. The always capricious genetic mutations of viral combinations outwitted vaccine manufacturers, offering little protection, resulting in an estimated 12,469 deaths, tragically many of them children, young, and middle-aged people.3 In between, there were periodic eruptions of the deadly Ebola virus in Africa. In 2014, 11 Americans who had either served as health care workers or traveled in the region were treated in the US.4
This much abridged survey of recent pandemics reminds us of how wrong were those who returning victorious from World War II with newly developed antibiotics and at the zenith of American military medicine argued that we would also beat infectious disease.5 As my Army pediatrician father would tell me, “the bugs will always be smarter than the drugs.” For now, COVID-19 is outwitting those in science and medicine who are engaged in a desperate race to discover a vaccine or a drug to “stop the virus in its tracks” as the media is so fond of saying.6 Irresponsible news outlets are giving a panicked citizenry false hope. Experts recently testified before the US House of Representatives that according to the most optimistic estimates, a vaccine is a year away.7 Yet information is a double-edged sword, as the Internet also is able to communicate accurate lifesaving information from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments with unprecedented speed and reach.
The best chance for civilization to “flatten the curve” of the pandemic is, as it has been so many times before, through precautionary measures and preventive public health efforts. There is a reason that in 2007, readers of the prestigious British Journal of Medicine ranked public health interventions as the most important advances in medical history.8
The initial installment of this pandemic series will offer a primer in public health ethics. Just as almost everything else in daily life has rapidly and radically changed, from cancelled church services to school closures, so too public health ethics is significantly different in many important aspects from the clinical health ethics we are accustomed to in our practice.
The first difference is focus. In clinical health ethics the focus of the individual health care practitioner is the individual patient, but public health ethics focuses on “what we as a society do to keep people healthy.”9 In a pandemic when decisions must be made (to paraphrase Mr. Spock) “for the good of the many” this creates an intrinsic ethical tension for the health care practitioner whose ethos is to advocate for his or her patient.
The second difference is that in order to accomplish these communitarian aims, the law and political and cultural factors have much more influence in medical decision making than within the ideal dyad of a health care practitioner and the patient engaged in shared decision making about the patient’s health. This is nowhere more evident than in the President’s recent declaration of a public health emergency. “The Federal Government, along with State and Local governments, has taken preventive and proactive measures to slow the spread of the virus and treat those affected. . .”10 Federal and state governments can exercise wide-ranging powers that can restrict individual liberties in ways that would never be legal or ethically justifiable in the course of routine clinical care.
The third difference relates to the ethical principles that guide public health care decision making in comparison with those of clinical ethics. The primacy of autonomy in modern American medical ethics must for the health of the public sometimes yield to the overarching goal of preventing serious harm to the public and mitigating the transmission of the infection. Values such as nonmaleficence and justice become even more important than individual self-determination especially as the pandemic worsens and the demand for scarce ventilators and other life-saving resources outstrips the supply.11
The fourth difference is that in nonemergent care, whether in the clinic or the hospital, the health care provider bears the primary responsibility for making decisions. Practitioners bring their knowledge and experience and patients their values and preferences to arrive at a mutually acceptable treatment plan. In stark contrast the profound and tragic life and death decisions made in a pandemic should not be left to the individual clinician who to the degree possible should remain faithful to the individual patient’s interests to preserve his or her professional integrity. Instead, decisions should be in the hands of highly trained and respected committees with diverse membership and expertise in accordance with evidence-based scientific protocols that are in response to changing pandemic conditions and the best available evidence. This process ensures that the values of consistency, transparency, and fairness which take center place in a public health emergency are the moral basis of decisions rather than ad hoc decisions that risk bias and inequity especially regarding vulnerable populations.11
There is one characteristic of medical decision making that does not change whether in a routine checkup or resource allocation in an intensive care unit in a pandemic: the need to respect individual human dignity and to show compassion for the suffering of those who will not survive. In the Star Trek episode “Wrath of Khan,” Spock sacrificed himself to save his ship, his comrades, and his friends who mourned his death and honored his life.
1. Garrett L. The Coming Plague: Newly Emerging Diseases in a World Out of Balance. New York: Penguin Books, 1995.
2. World Health Organization. FAQS: H5N1 influenza. https://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/avian_influenza/h5n1_research/faqs/en/. Accessed March 20, 2020.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009 H1N1 pandemic. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pandemic-resources/2009-h1n1-pandemic.html. Updated June 11, 2019. Accessed March 20, 2020.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak in West Africa. https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/2014-2016-outbreak/index.html. Updated March 8, 2019. March 20, 2020.
5. Pier GB. On the greatly exaggerated reports of the death of infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(8):1113-1114.
6. Digital staff. Coronavirus Australia: researchers say they are close to a cure. https://7news.com.au/sunrise/on-the-show/coronavirus-australia-researchers-say-theyre-close-to-a-cure-c-746508. Published March 15, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
7. Hoetz P. Testimony of Peter Hoetz, M.D, Ph.D. Before the House Committee on Space, Science and Technology of the United States House of Representatives, March 5, 2020. https://science.house.gov/imo/media/doc/Hotez%20Testimony.pdf. Accessed March 15, 2020.
8. Ferriman A. BMJ readers choose the “sanitary revolution” as greatest medical advance since 1840. BMJ. 2007;334(7585):111.
9. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Assuring the Health of the Public in the 21st Century. The Future of the Public’s Health in the 21st Century. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2002.
10. Trump DJ. Proclamation on declaring a national emergency concerning the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease outbreak. https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/proclamation-declaring-national-emergency-concerning-novel-coronavirus-disease-covid-19-outbreak/. Published March 13, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Ethics in Health Care. Meeting the challenge of pandemic influenza: ethical guidance for leaders and health care professionals in the Veterans Health Administration. https://www.ethics.va.gov/activities/pandemic_influenza_preparedness.asp. Published July 2010. Accessed March 20, 2020.
I am writing this editorial on a beautiful day in the high desert of the Southwest: a bright blue clear sky such as you see only in the mountain air, a sun warm and comforting, and birds singing as if they had not a care in the world. Spring has come early as if to dramatize the cognitive dissonance between this idyllic scene and a seemingly invincible winter of disease and death that has gripped the globe.
For now, my editorials will focus on the most threatening infectious disease outbreak since, perhaps, 1918. I have been teaching public health and pandemic ethics to health care professionals and trainees for more than a decade. I always tell the medical students, “it is not if but when” the next viral wave overwhelms society. It is human nature to disbelieve this inevitability and to ignore, dismiss, or even attack the infectious disease experts and science journalists who, like Cassandra, warn us of the return of the plague.1
In the early 2000s, virologists were concerned that Avian influenza with a mortality rate of > 60% would mutate into a virus capable of jumping the species barrier with sustained human transmission; however, that threat has not materialized (yet).2 Instead, in 2009 the H1N1 influenza pandemic struck viciously. The always capricious genetic mutations of viral combinations outwitted vaccine manufacturers, offering little protection, resulting in an estimated 12,469 deaths, tragically many of them children, young, and middle-aged people.3 In between, there were periodic eruptions of the deadly Ebola virus in Africa. In 2014, 11 Americans who had either served as health care workers or traveled in the region were treated in the US.4
This much abridged survey of recent pandemics reminds us of how wrong were those who returning victorious from World War II with newly developed antibiotics and at the zenith of American military medicine argued that we would also beat infectious disease.5 As my Army pediatrician father would tell me, “the bugs will always be smarter than the drugs.” For now, COVID-19 is outwitting those in science and medicine who are engaged in a desperate race to discover a vaccine or a drug to “stop the virus in its tracks” as the media is so fond of saying.6 Irresponsible news outlets are giving a panicked citizenry false hope. Experts recently testified before the US House of Representatives that according to the most optimistic estimates, a vaccine is a year away.7 Yet information is a double-edged sword, as the Internet also is able to communicate accurate lifesaving information from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments with unprecedented speed and reach.
The best chance for civilization to “flatten the curve” of the pandemic is, as it has been so many times before, through precautionary measures and preventive public health efforts. There is a reason that in 2007, readers of the prestigious British Journal of Medicine ranked public health interventions as the most important advances in medical history.8
The initial installment of this pandemic series will offer a primer in public health ethics. Just as almost everything else in daily life has rapidly and radically changed, from cancelled church services to school closures, so too public health ethics is significantly different in many important aspects from the clinical health ethics we are accustomed to in our practice.
The first difference is focus. In clinical health ethics the focus of the individual health care practitioner is the individual patient, but public health ethics focuses on “what we as a society do to keep people healthy.”9 In a pandemic when decisions must be made (to paraphrase Mr. Spock) “for the good of the many” this creates an intrinsic ethical tension for the health care practitioner whose ethos is to advocate for his or her patient.
The second difference is that in order to accomplish these communitarian aims, the law and political and cultural factors have much more influence in medical decision making than within the ideal dyad of a health care practitioner and the patient engaged in shared decision making about the patient’s health. This is nowhere more evident than in the President’s recent declaration of a public health emergency. “The Federal Government, along with State and Local governments, has taken preventive and proactive measures to slow the spread of the virus and treat those affected. . .”10 Federal and state governments can exercise wide-ranging powers that can restrict individual liberties in ways that would never be legal or ethically justifiable in the course of routine clinical care.
The third difference relates to the ethical principles that guide public health care decision making in comparison with those of clinical ethics. The primacy of autonomy in modern American medical ethics must for the health of the public sometimes yield to the overarching goal of preventing serious harm to the public and mitigating the transmission of the infection. Values such as nonmaleficence and justice become even more important than individual self-determination especially as the pandemic worsens and the demand for scarce ventilators and other life-saving resources outstrips the supply.11
The fourth difference is that in nonemergent care, whether in the clinic or the hospital, the health care provider bears the primary responsibility for making decisions. Practitioners bring their knowledge and experience and patients their values and preferences to arrive at a mutually acceptable treatment plan. In stark contrast the profound and tragic life and death decisions made in a pandemic should not be left to the individual clinician who to the degree possible should remain faithful to the individual patient’s interests to preserve his or her professional integrity. Instead, decisions should be in the hands of highly trained and respected committees with diverse membership and expertise in accordance with evidence-based scientific protocols that are in response to changing pandemic conditions and the best available evidence. This process ensures that the values of consistency, transparency, and fairness which take center place in a public health emergency are the moral basis of decisions rather than ad hoc decisions that risk bias and inequity especially regarding vulnerable populations.11
There is one characteristic of medical decision making that does not change whether in a routine checkup or resource allocation in an intensive care unit in a pandemic: the need to respect individual human dignity and to show compassion for the suffering of those who will not survive. In the Star Trek episode “Wrath of Khan,” Spock sacrificed himself to save his ship, his comrades, and his friends who mourned his death and honored his life.
I am writing this editorial on a beautiful day in the high desert of the Southwest: a bright blue clear sky such as you see only in the mountain air, a sun warm and comforting, and birds singing as if they had not a care in the world. Spring has come early as if to dramatize the cognitive dissonance between this idyllic scene and a seemingly invincible winter of disease and death that has gripped the globe.
For now, my editorials will focus on the most threatening infectious disease outbreak since, perhaps, 1918. I have been teaching public health and pandemic ethics to health care professionals and trainees for more than a decade. I always tell the medical students, “it is not if but when” the next viral wave overwhelms society. It is human nature to disbelieve this inevitability and to ignore, dismiss, or even attack the infectious disease experts and science journalists who, like Cassandra, warn us of the return of the plague.1
In the early 2000s, virologists were concerned that Avian influenza with a mortality rate of > 60% would mutate into a virus capable of jumping the species barrier with sustained human transmission; however, that threat has not materialized (yet).2 Instead, in 2009 the H1N1 influenza pandemic struck viciously. The always capricious genetic mutations of viral combinations outwitted vaccine manufacturers, offering little protection, resulting in an estimated 12,469 deaths, tragically many of them children, young, and middle-aged people.3 In between, there were periodic eruptions of the deadly Ebola virus in Africa. In 2014, 11 Americans who had either served as health care workers or traveled in the region were treated in the US.4
This much abridged survey of recent pandemics reminds us of how wrong were those who returning victorious from World War II with newly developed antibiotics and at the zenith of American military medicine argued that we would also beat infectious disease.5 As my Army pediatrician father would tell me, “the bugs will always be smarter than the drugs.” For now, COVID-19 is outwitting those in science and medicine who are engaged in a desperate race to discover a vaccine or a drug to “stop the virus in its tracks” as the media is so fond of saying.6 Irresponsible news outlets are giving a panicked citizenry false hope. Experts recently testified before the US House of Representatives that according to the most optimistic estimates, a vaccine is a year away.7 Yet information is a double-edged sword, as the Internet also is able to communicate accurate lifesaving information from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention and state health departments with unprecedented speed and reach.
The best chance for civilization to “flatten the curve” of the pandemic is, as it has been so many times before, through precautionary measures and preventive public health efforts. There is a reason that in 2007, readers of the prestigious British Journal of Medicine ranked public health interventions as the most important advances in medical history.8
The initial installment of this pandemic series will offer a primer in public health ethics. Just as almost everything else in daily life has rapidly and radically changed, from cancelled church services to school closures, so too public health ethics is significantly different in many important aspects from the clinical health ethics we are accustomed to in our practice.
The first difference is focus. In clinical health ethics the focus of the individual health care practitioner is the individual patient, but public health ethics focuses on “what we as a society do to keep people healthy.”9 In a pandemic when decisions must be made (to paraphrase Mr. Spock) “for the good of the many” this creates an intrinsic ethical tension for the health care practitioner whose ethos is to advocate for his or her patient.
The second difference is that in order to accomplish these communitarian aims, the law and political and cultural factors have much more influence in medical decision making than within the ideal dyad of a health care practitioner and the patient engaged in shared decision making about the patient’s health. This is nowhere more evident than in the President’s recent declaration of a public health emergency. “The Federal Government, along with State and Local governments, has taken preventive and proactive measures to slow the spread of the virus and treat those affected. . .”10 Federal and state governments can exercise wide-ranging powers that can restrict individual liberties in ways that would never be legal or ethically justifiable in the course of routine clinical care.
The third difference relates to the ethical principles that guide public health care decision making in comparison with those of clinical ethics. The primacy of autonomy in modern American medical ethics must for the health of the public sometimes yield to the overarching goal of preventing serious harm to the public and mitigating the transmission of the infection. Values such as nonmaleficence and justice become even more important than individual self-determination especially as the pandemic worsens and the demand for scarce ventilators and other life-saving resources outstrips the supply.11
The fourth difference is that in nonemergent care, whether in the clinic or the hospital, the health care provider bears the primary responsibility for making decisions. Practitioners bring their knowledge and experience and patients their values and preferences to arrive at a mutually acceptable treatment plan. In stark contrast the profound and tragic life and death decisions made in a pandemic should not be left to the individual clinician who to the degree possible should remain faithful to the individual patient’s interests to preserve his or her professional integrity. Instead, decisions should be in the hands of highly trained and respected committees with diverse membership and expertise in accordance with evidence-based scientific protocols that are in response to changing pandemic conditions and the best available evidence. This process ensures that the values of consistency, transparency, and fairness which take center place in a public health emergency are the moral basis of decisions rather than ad hoc decisions that risk bias and inequity especially regarding vulnerable populations.11
There is one characteristic of medical decision making that does not change whether in a routine checkup or resource allocation in an intensive care unit in a pandemic: the need to respect individual human dignity and to show compassion for the suffering of those who will not survive. In the Star Trek episode “Wrath of Khan,” Spock sacrificed himself to save his ship, his comrades, and his friends who mourned his death and honored his life.
1. Garrett L. The Coming Plague: Newly Emerging Diseases in a World Out of Balance. New York: Penguin Books, 1995.
2. World Health Organization. FAQS: H5N1 influenza. https://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/avian_influenza/h5n1_research/faqs/en/. Accessed March 20, 2020.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009 H1N1 pandemic. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pandemic-resources/2009-h1n1-pandemic.html. Updated June 11, 2019. Accessed March 20, 2020.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak in West Africa. https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/2014-2016-outbreak/index.html. Updated March 8, 2019. March 20, 2020.
5. Pier GB. On the greatly exaggerated reports of the death of infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(8):1113-1114.
6. Digital staff. Coronavirus Australia: researchers say they are close to a cure. https://7news.com.au/sunrise/on-the-show/coronavirus-australia-researchers-say-theyre-close-to-a-cure-c-746508. Published March 15, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
7. Hoetz P. Testimony of Peter Hoetz, M.D, Ph.D. Before the House Committee on Space, Science and Technology of the United States House of Representatives, March 5, 2020. https://science.house.gov/imo/media/doc/Hotez%20Testimony.pdf. Accessed March 15, 2020.
8. Ferriman A. BMJ readers choose the “sanitary revolution” as greatest medical advance since 1840. BMJ. 2007;334(7585):111.
9. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Assuring the Health of the Public in the 21st Century. The Future of the Public’s Health in the 21st Century. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2002.
10. Trump DJ. Proclamation on declaring a national emergency concerning the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease outbreak. https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/proclamation-declaring-national-emergency-concerning-novel-coronavirus-disease-covid-19-outbreak/. Published March 13, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Ethics in Health Care. Meeting the challenge of pandemic influenza: ethical guidance for leaders and health care professionals in the Veterans Health Administration. https://www.ethics.va.gov/activities/pandemic_influenza_preparedness.asp. Published July 2010. Accessed March 20, 2020.
1. Garrett L. The Coming Plague: Newly Emerging Diseases in a World Out of Balance. New York: Penguin Books, 1995.
2. World Health Organization. FAQS: H5N1 influenza. https://www.who.int/influenza/human_animal_interface/avian_influenza/h5n1_research/faqs/en/. Accessed March 20, 2020.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009 H1N1 pandemic. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/pandemic-resources/2009-h1n1-pandemic.html. Updated June 11, 2019. Accessed March 20, 2020.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2014-2016 Ebola outbreak in West Africa. https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/2014-2016-outbreak/index.html. Updated March 8, 2019. March 20, 2020.
5. Pier GB. On the greatly exaggerated reports of the death of infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(8):1113-1114.
6. Digital staff. Coronavirus Australia: researchers say they are close to a cure. https://7news.com.au/sunrise/on-the-show/coronavirus-australia-researchers-say-theyre-close-to-a-cure-c-746508. Published March 15, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
7. Hoetz P. Testimony of Peter Hoetz, M.D, Ph.D. Before the House Committee on Space, Science and Technology of the United States House of Representatives, March 5, 2020. https://science.house.gov/imo/media/doc/Hotez%20Testimony.pdf. Accessed March 15, 2020.
8. Ferriman A. BMJ readers choose the “sanitary revolution” as greatest medical advance since 1840. BMJ. 2007;334(7585):111.
9. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Assuring the Health of the Public in the 21st Century. The Future of the Public’s Health in the 21st Century. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2002.
10. Trump DJ. Proclamation on declaring a national emergency concerning the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) disease outbreak. https://www.whitehouse.gov/presidential-actions/proclamation-declaring-national-emergency-concerning-novel-coronavirus-disease-covid-19-outbreak/. Published March 13, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Ethics in Health Care. Meeting the challenge of pandemic influenza: ethical guidance for leaders and health care professionals in the Veterans Health Administration. https://www.ethics.va.gov/activities/pandemic_influenza_preparedness.asp. Published July 2010. Accessed March 20, 2020.
Use of an Electronic Alert Tool to Prevent Readmissions Following Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
From the University of North Carolina at Wilmington School of Nursing (Dr. Smith and Dr. Turrise), the New Hanover Regional Medical Center Heart Center (Mr. Jordan), the Coastal Carolinas Health Alliance and Coastal Connect Health Information Exchange (Ms. Robertson), and Coastal Thoracic Surgical Associates (Dr. Kane), Wilmington, NC.
Abstract
Objective: Cardiothoracic (CT) surgeons at our medical center were not receiving timely notification when their coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery patients were admitted to the medical center or to other hospitals. The CT surgical team worked with a health alliance in southeastern North Carolina to implement health information exchange (HIE) real-time electronic notifications for their CABG patients who presented to the hospital’s emergency department (ED) or any ED affiliated with the medical center. The alert tool notifies team members about patient encounters, driving timely clinical engagement.
Methods: The CT team provided the HIE team with the names of CABG surgery patients, which were loaded into the alert tool. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED or its affiliates, the alert tool sent a real-time electronic notification to the Cardiac Surgical Services nurse coordinator. This intervention prompted the assessment and disposition of CABG patients, while in the ED, by the CT surgical team.
Results: Over a 16-month period (September 2017-December 2018), the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; 44 were readmitted for inpatient care; and 492 did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Following implementation of this practice change, the 30-day readmission rate for patients who underwent CABG at our institution decreased from 10% to 7.2%.
Conclusion: Utilizing a real-time alert tool resulted in immediate notification of the CT team when 1 of their patients presented to the ED. This afforded the CT surgical team an opportunity to intervene in the care of their patients, which in turn led to improved quality of care, physician communication and collaboration, and patient outcomes, such as preventable 30-day readmissions.
Keywords: electronic health record; real-time electronic notification; CABG; process improvement.
Unplanned 30-day hospital readmissions of patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery contribute to higher overall health care costs. CABG is 1 of the conditions/procedures that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) monitors for excess readmissions.1 Readmission rates for CABG-related conditions at 30 days post-surgery are reported to be between 16% and 20% for US hospitals.2 Readmissions are not only financially costly, but also have been associated with worse patient outcomes and decreased patient satisfaction.3 Common diagnoses for post-CABG admission include atrial fibrillation, pleural effusion, and wound infection.
The facility where this project was implemented had a 10% post-CABG admission rate for patients across all payers. While this rate is below the national average of 13.2%, the cardiothoracic (CT) surgical team was not being notified in a timely manner when their post-CABG patients were readmitted. The Lean team used the A3 problem-solving process to develop strategies that would reduce these readmissions and improve the care of their patients.
We explored the use of electronic alerts in managing post-CABG patients by conducting a literature search using the terms electronic alerts in patient care, patient engagement in the emergency department, electronic alerts in CABG, real-time notifications to prevent readmission, and CABG readmission. Databases searched were PubMed, Google Scholar, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect. This search resulted in studies focused on the use of electronic health record (EHR) alerts as a clinical decision-support tool; for example, patient demographic and assessment data are entered into the EHR, and the clinician is prompted with “performance” recommendations (eg, consider electrocardiogram and aspirin).4 In a paper by Engelman and Benjamin,5 the authors discuss the importance of the engaged physician and note that, in their emergency department (ED), an electronic notification is sent when a postoperative patient presents; however, the notification goes to the inpatient service for timely review and disposition. There was no literature that discussed the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy that resulted in a practice change specific to the CT surgical team.
Our process improvement project focused on alerting the CT surgical team when a post-CABG patient presented to the ED, allowing them to evaluate the patient in real time and determine whether the chief complaint was related to the CABG and whether further evaluation by the CT surgeon was required. Specifically, we wanted to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. During this project, alerts were sent to the CT surgical team notifying them of a post-CABG patient presenting to the ED or being directly admitted from home on physician orders, a provider’s office, or inpatient rehabilitation; however, the focus of this article is specifically on the notification regarding post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
Prior to implementing the electronic notification project, the team developed and implemented several internal and external readmission reduction and prevention strategies for CABG patients. An in-house strategy involved a process whereby patients would receive their discharge medications prior to being discharged from the hospital post-CABG, thereby avoiding potential delays in the patient obtaining medications. When examining post-CABG patient readmissions, the primary conditions that led to readmission were fluid overload, pleural effusion, and atrial fibrillation. As such, a second in-house strategy was developed for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED with atrial fibrillation. The newly established protocol allowed patients to be monitored and treated in the cardiac observation unit. In addition, external strategies, including an outpatient furosemide protocol for home health nurses and an outpatient thoracentesis program and order set, were established (eg, for patients with congestive heart failure, shortness of breath).
Methods
Setting
The regional medical center where this project was implemented is the ninth largest hospital in North Carolina and the largest county-owned public hospital in the state. It is a tertiary care center and teaching hospital with 3 hospital campuses and 855 licensed beds. The medical center was included in the 100 Safecare Hospitals list by the Safecare Group; received a grade “A” Hospital Safety Score from the Leapfrog Group; and is 1 of America’s Top 100 Hospitals for Patient Experience.
Real-Time Notification Project
A regional hospital alliance in southeastern North Carolina established a health information exchange (HIE) with its member hospitals and office-based physicians to enable electronic exchange of patient information to improve quality, safety, and efficiency in health care delivery. Our medical center is part of this alliance. The HIE is a digital platform that facilitates the sharing of information between disparate connected EHR systems, and offers a portal for practices and hospitals to access patient information across North Carolina, South Carolina (via SC HIE), and nationwide (select dialysis centers). More specifically, approved providers and team members are able to access, in real time, patient-care encounter documents from other care settings (eg, acute, post-acute, ambulatory) via the HIE. Additionally, approved care entities can query-retrieve web portal information to support patient outcome improvement strategies. A partnership discussion highlighted the opportunity to utilize the HIE’s capabilities, such as real-time notification, to facilitate workflow (eg, when a patient presents to the ED, the HIE can provide access to health information at the point of care). In this capacity, the alert tool notifies care team members about patient encounters to drive timely clinical engagement for care transitions.
In January 2017, we began discussions on using the HIE to facilitate real-time electronic tracking in the Cardiac Surgical Services department at our medical center. Persons involved in these discussions included the cardiovascular (CV) team (comprised of case managers, department managers and coordinators, program coordinators, administrators, and support services [eg, pre-admission testing and home health staff]) and CT surgeons. At that time, CABG readmissions were manually tracked, and the real-time notification tool was being used in other departments (eg, in case management for tracking readmissions). The entire team was part of the initial decision meeting to pursue this possibility. The CV team reached consensus in June 2017 and proposed extending the use of the alert tool to the post-CABG population presenting to the ED (or any ED affiliated with the medical center) or admitted directly to the medical center.
The HIE staff met with the Cardiac Surgical Services team to tailor and develop the logistics of the project, such as who would be notified and how. The goals of the project were to support appropriate care intervention, reduce preventable hospital readmissions, and improve quality of care through enhanced provider communication and engagement. To achieve these goals, on the day of discharge the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator provided the HIE team with the names of patients who had undergone CABG surgery. This patient list was loaded into the alert tool and continually updated. At 31 days, patient names were removed from the list. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED, the alert tool sent 2 real-time electronic notifications, an email and a text message, to the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, noting that a patient event occurred. Personal information was not included in the alert in order to protect patient information and comply with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations.
The alert prompted the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator to securely access patient information to identify and, if necessary, visit the patient. Then, based on the information gathered by the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, a Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation report was relayed to the CT surgeon, who then determined whether intervention by the CT surgical team was warranted. This process, on average, took approximately 30 minutes to complete. This was a key change in processes, one that allowed post-CABG patients to be seen by the CT surgical team while in the ED. If the issue was related to the CABG surgery, the CT surgeons could then determine an appropriate course of action, including admission or implementation of another protocol, such as the home furosemide protocol. For patients directly admitted, the surgeon contacted the admitting provider to discuss the level of care required (ie, observation or inpatient admission and treatment).
Biweekly CV team meetings were conducted during the implementation of the real-time notification alert tool. At each meeting, updates were provided on notifications received, patients who were missed by the notification process, and how well the real-time alerts were working to enhance care and appropriate disposition.
Measurements
Clinical performance data included total notifications, total number of ED visits, ED disposition (inpatient admission, observation, discharge), total number of direct admissions, direct admissions to observation, direct inpatient admissions, and patients missed by the notification process (eg, due to data entry errors, omissions of information [suffix of junior or senior], as well as programming bugs). Finally, the number of observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions was collected and further analyzed to inform needed process changes.
The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator collected, entered, and maintained data using Excel. Data were obtained from the EHR, recorded in Excel, and analyzed using basic descriptive statistics in an ongoing fashion. Particular attention was focused on problems with the notification process (eg, patients being missed due to errors in data entry) and summarizing information to keep the Cardiac Surgical Services team updated on the progress of the process improvement. This project did not require staff protections or considerations, and because this was not a research study Institutional Review Board approval was not required.
Results
This practice change was implemented in September 2017 and led to improvements in care quality, as evidenced by improved physician communication and collaboration. In the 16-month period from implementation through December 2018, the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; and 44 were readmitted for inpatient care. The remaining 492 patients did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Clinical performance data from this period included 70 ED visits, 21 direct admissions, 19 direct admissions to observation, 5 patients missed by the notification process, and 4 observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions. A reduction in the CABG readmission rate from 10% in September 2017 to 7.2% in December 2018 was also noted.
Discussion
The aim of this process improvement project was to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. This practice change has been successful, following 16 months of implementation and process refinement. Integrating a real-time electronic alert with a supporting action plan and care protocols resulted in timely patient engagement and avoidance of readmission of post-CABG patients.
Early notification of possible post-CABG readmissions became a standard-of-care process within the Cardiac Surgical Services department, with expansion to all CT post-op patients. Leveraging HIE technology to support quality improvement processes was also viewed by other departments as relevant and beneficial. For example, the hospital stroke and orthopedic-spine teams established their own processes for receiving real-time alerts.
There were several lessons learned during this project. First, gaining 100% physician buy-in to collaborative communication proved to be critical to the project’s success. The CV team was surprised by the length of time (approximately 8-10 months) it took for the practice change to be adopted by the physicians. In part, some of this delay in adoption resulted from medical staff turnover, primarily in the medical resident training rotations. Collaborative communication was key. The CT surgeons spoke with ED leadership and hospitalist services to explain the readmission reduction project and the use of an electronic alert tool. The CT surgeons also communicated to the ED physicians, hospitalists, and cardiologists that the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator would be involved in the process and discussions regarding patientss care. Additionally, the CT surgeons authored the furosemide protocol and then committed to its use in the home health setting, further highlighting the role of collaborative communication in avoiding readmissions.
Another key step in this quality improvement project was determining who should receive the alert notifications. At the onset of the project, all notifications were sent to 1 person, the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator. While this seemed logical in the initial stage of the project, it was unsustainable, as the receipt of the alert and the subsequent notification of the CT surgeon depended on 1 person and their availability. Approximately 10 months into the project, the notification process was further refined, with the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse becoming the point of contact for the alerts. The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, in collaboration with nursing leaders and CT surgeons, completed a Lean Standard Work template outlining the major steps and the associated responsibilities (for the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse, CT surgeon and on-call surgeon, Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator) in the process of receiving notifications, collecting patient assessment data, and reporting notifications to the CT surgeons.
Establishing adequate support mechanisms during a practice change is also important. For instance, we had to dedicate personnel time for data collection and analysis and involve additional nursing or other qualified personnel in the new process to avoid depending on a single person for the project’s success. Additional considerations were establishing criteria for surgeon notification and defining an appropriate time frame for notification (eg, urgent versus next-day notifications). We accomplished these activities approximately 10 months into the project, after it became apparent at CV team meeting discussions that further clarification of criteria and timelines was needed.
Some aspects of the project unfolded as planned, while others presented opportunities for improvement. For example, the alert notification process worked as envisioned; however, as previously mentioned, the process needed to be more inclusive to ensure there is always a charge nurse on duty to receive the alert notification, rather than just the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, who may not always be at the hospital. The outpatient thoracentesis program was well planned and effectively implemented. This program provided an avenue for patients who had symptoms of pleural effusion to be treated in an outpatient setting, rather than requiring an inpatient stay. Opportunities for improvement included addressing the inconsistent use of the home health furosemide protocol (developed in 2016), and the need for continued interprofessional and interdepartmental communication and coordination. For example, we had to inform the ED physicians and staff who rotate or are new to the ED about established processes and protocols in place for managing post-CABG patients who present to the ED.
The primary limitation of this project was the inability to measure the enhanced patient experience, which was 1 of the stated project goals. This goal became secondary because of more pressing issues, specifically, interorganizational collaboration (eg, hospital EHR, HIE, and CT surgical team) and tailoring the functionality of the electronic alert tool to the project. Developing and implementing measures of enhanced patient experience were not feasible during this implementation. Additionally, because this was not a research study, it was not possible to determine cause and effect or to control for confounders, such as a sicker, older cohort with more comorbid conditions, during the comparison period. Finally, although this process improvement project was conducted at a regional medical center that is the only facility performing CABG within the region, patients may have presented to another facility for an event that led to a readmission. Because readmissions to other facilities could not be captured, it is possible that the actual readmission rate was higher than the rate reported here.
Conclusions and Implications
Utilizing a real-time alert from the HIE to the CT surgical team resulted in CT surgeons being immediately made aware when their patients presented to the ED, allowing the CT surgical team the opportunity to intervene, as appropriate, in the care of their patients. Furthermore, this real-time notification and intervention resulted in timely patient engagement and, in some cases, avoidance of readmissions. Currently, patients are monitored for readmission within 30 days of discharge. In the future, the time will expand to 91 days, in preparation for participation in the CMS bundle payment program for CABG surgery.
This practice change can be used in organizations that do not have or participate in a HIE. In fact, these real-time alert applications may be available through an EHR already in use within the organization. The use of the alert requires collaborative communication and having supporting protocols in place to guide decision-making and care of post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
There appears to be a gap in the literature discussing the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED. As such, this project contributes important results and lessons learned for other hospital service lines/departments that might consider implementing a similar process. Next steps include designing and conducting methodologically rigorous research studies based on this process improvement project to examine mortality rates as an outcome, and designing a more specific measure of patient experience, as the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey only provides hospital-level data.
Corresponding author: Stephanie D. Smith, PhD, RN, UNCW School of Nursing, 601 South College Road, Wilmington, NC 28403; [email protected].
Funding disclosures: None.
1. Hannan EL, Zhong Y, Lahey SJ, et al. 30-day readmissions after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in New York State. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:569-576.
2. Feng TR, White R, Gaber-Baylis L, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft readmission rates and risk factors- A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;54 (Part A):7-17.
3. Donndorf P, Kaminski A. “Return to sender” or “consider it done”?! The importance of reducing hospital readmission after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:1298-1299.
4. Sequist TD, Morong SM, Marston A, et al. Electronic risk alerts to improve primary care management of chest pain: A randomized, controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27:438-444.
5. Engelman D, Benjamin EM. Physician engagement: The “secret sauce” to success in bundled health care. Am J Med Qual. 2018;33:100-102.
From the University of North Carolina at Wilmington School of Nursing (Dr. Smith and Dr. Turrise), the New Hanover Regional Medical Center Heart Center (Mr. Jordan), the Coastal Carolinas Health Alliance and Coastal Connect Health Information Exchange (Ms. Robertson), and Coastal Thoracic Surgical Associates (Dr. Kane), Wilmington, NC.
Abstract
Objective: Cardiothoracic (CT) surgeons at our medical center were not receiving timely notification when their coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery patients were admitted to the medical center or to other hospitals. The CT surgical team worked with a health alliance in southeastern North Carolina to implement health information exchange (HIE) real-time electronic notifications for their CABG patients who presented to the hospital’s emergency department (ED) or any ED affiliated with the medical center. The alert tool notifies team members about patient encounters, driving timely clinical engagement.
Methods: The CT team provided the HIE team with the names of CABG surgery patients, which were loaded into the alert tool. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED or its affiliates, the alert tool sent a real-time electronic notification to the Cardiac Surgical Services nurse coordinator. This intervention prompted the assessment and disposition of CABG patients, while in the ED, by the CT surgical team.
Results: Over a 16-month period (September 2017-December 2018), the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; 44 were readmitted for inpatient care; and 492 did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Following implementation of this practice change, the 30-day readmission rate for patients who underwent CABG at our institution decreased from 10% to 7.2%.
Conclusion: Utilizing a real-time alert tool resulted in immediate notification of the CT team when 1 of their patients presented to the ED. This afforded the CT surgical team an opportunity to intervene in the care of their patients, which in turn led to improved quality of care, physician communication and collaboration, and patient outcomes, such as preventable 30-day readmissions.
Keywords: electronic health record; real-time electronic notification; CABG; process improvement.
Unplanned 30-day hospital readmissions of patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery contribute to higher overall health care costs. CABG is 1 of the conditions/procedures that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) monitors for excess readmissions.1 Readmission rates for CABG-related conditions at 30 days post-surgery are reported to be between 16% and 20% for US hospitals.2 Readmissions are not only financially costly, but also have been associated with worse patient outcomes and decreased patient satisfaction.3 Common diagnoses for post-CABG admission include atrial fibrillation, pleural effusion, and wound infection.
The facility where this project was implemented had a 10% post-CABG admission rate for patients across all payers. While this rate is below the national average of 13.2%, the cardiothoracic (CT) surgical team was not being notified in a timely manner when their post-CABG patients were readmitted. The Lean team used the A3 problem-solving process to develop strategies that would reduce these readmissions and improve the care of their patients.
We explored the use of electronic alerts in managing post-CABG patients by conducting a literature search using the terms electronic alerts in patient care, patient engagement in the emergency department, electronic alerts in CABG, real-time notifications to prevent readmission, and CABG readmission. Databases searched were PubMed, Google Scholar, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect. This search resulted in studies focused on the use of electronic health record (EHR) alerts as a clinical decision-support tool; for example, patient demographic and assessment data are entered into the EHR, and the clinician is prompted with “performance” recommendations (eg, consider electrocardiogram and aspirin).4 In a paper by Engelman and Benjamin,5 the authors discuss the importance of the engaged physician and note that, in their emergency department (ED), an electronic notification is sent when a postoperative patient presents; however, the notification goes to the inpatient service for timely review and disposition. There was no literature that discussed the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy that resulted in a practice change specific to the CT surgical team.
Our process improvement project focused on alerting the CT surgical team when a post-CABG patient presented to the ED, allowing them to evaluate the patient in real time and determine whether the chief complaint was related to the CABG and whether further evaluation by the CT surgeon was required. Specifically, we wanted to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. During this project, alerts were sent to the CT surgical team notifying them of a post-CABG patient presenting to the ED or being directly admitted from home on physician orders, a provider’s office, or inpatient rehabilitation; however, the focus of this article is specifically on the notification regarding post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
Prior to implementing the electronic notification project, the team developed and implemented several internal and external readmission reduction and prevention strategies for CABG patients. An in-house strategy involved a process whereby patients would receive their discharge medications prior to being discharged from the hospital post-CABG, thereby avoiding potential delays in the patient obtaining medications. When examining post-CABG patient readmissions, the primary conditions that led to readmission were fluid overload, pleural effusion, and atrial fibrillation. As such, a second in-house strategy was developed for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED with atrial fibrillation. The newly established protocol allowed patients to be monitored and treated in the cardiac observation unit. In addition, external strategies, including an outpatient furosemide protocol for home health nurses and an outpatient thoracentesis program and order set, were established (eg, for patients with congestive heart failure, shortness of breath).
Methods
Setting
The regional medical center where this project was implemented is the ninth largest hospital in North Carolina and the largest county-owned public hospital in the state. It is a tertiary care center and teaching hospital with 3 hospital campuses and 855 licensed beds. The medical center was included in the 100 Safecare Hospitals list by the Safecare Group; received a grade “A” Hospital Safety Score from the Leapfrog Group; and is 1 of America’s Top 100 Hospitals for Patient Experience.
Real-Time Notification Project
A regional hospital alliance in southeastern North Carolina established a health information exchange (HIE) with its member hospitals and office-based physicians to enable electronic exchange of patient information to improve quality, safety, and efficiency in health care delivery. Our medical center is part of this alliance. The HIE is a digital platform that facilitates the sharing of information between disparate connected EHR systems, and offers a portal for practices and hospitals to access patient information across North Carolina, South Carolina (via SC HIE), and nationwide (select dialysis centers). More specifically, approved providers and team members are able to access, in real time, patient-care encounter documents from other care settings (eg, acute, post-acute, ambulatory) via the HIE. Additionally, approved care entities can query-retrieve web portal information to support patient outcome improvement strategies. A partnership discussion highlighted the opportunity to utilize the HIE’s capabilities, such as real-time notification, to facilitate workflow (eg, when a patient presents to the ED, the HIE can provide access to health information at the point of care). In this capacity, the alert tool notifies care team members about patient encounters to drive timely clinical engagement for care transitions.
In January 2017, we began discussions on using the HIE to facilitate real-time electronic tracking in the Cardiac Surgical Services department at our medical center. Persons involved in these discussions included the cardiovascular (CV) team (comprised of case managers, department managers and coordinators, program coordinators, administrators, and support services [eg, pre-admission testing and home health staff]) and CT surgeons. At that time, CABG readmissions were manually tracked, and the real-time notification tool was being used in other departments (eg, in case management for tracking readmissions). The entire team was part of the initial decision meeting to pursue this possibility. The CV team reached consensus in June 2017 and proposed extending the use of the alert tool to the post-CABG population presenting to the ED (or any ED affiliated with the medical center) or admitted directly to the medical center.
The HIE staff met with the Cardiac Surgical Services team to tailor and develop the logistics of the project, such as who would be notified and how. The goals of the project were to support appropriate care intervention, reduce preventable hospital readmissions, and improve quality of care through enhanced provider communication and engagement. To achieve these goals, on the day of discharge the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator provided the HIE team with the names of patients who had undergone CABG surgery. This patient list was loaded into the alert tool and continually updated. At 31 days, patient names were removed from the list. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED, the alert tool sent 2 real-time electronic notifications, an email and a text message, to the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, noting that a patient event occurred. Personal information was not included in the alert in order to protect patient information and comply with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations.
The alert prompted the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator to securely access patient information to identify and, if necessary, visit the patient. Then, based on the information gathered by the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, a Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation report was relayed to the CT surgeon, who then determined whether intervention by the CT surgical team was warranted. This process, on average, took approximately 30 minutes to complete. This was a key change in processes, one that allowed post-CABG patients to be seen by the CT surgical team while in the ED. If the issue was related to the CABG surgery, the CT surgeons could then determine an appropriate course of action, including admission or implementation of another protocol, such as the home furosemide protocol. For patients directly admitted, the surgeon contacted the admitting provider to discuss the level of care required (ie, observation or inpatient admission and treatment).
Biweekly CV team meetings were conducted during the implementation of the real-time notification alert tool. At each meeting, updates were provided on notifications received, patients who were missed by the notification process, and how well the real-time alerts were working to enhance care and appropriate disposition.
Measurements
Clinical performance data included total notifications, total number of ED visits, ED disposition (inpatient admission, observation, discharge), total number of direct admissions, direct admissions to observation, direct inpatient admissions, and patients missed by the notification process (eg, due to data entry errors, omissions of information [suffix of junior or senior], as well as programming bugs). Finally, the number of observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions was collected and further analyzed to inform needed process changes.
The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator collected, entered, and maintained data using Excel. Data were obtained from the EHR, recorded in Excel, and analyzed using basic descriptive statistics in an ongoing fashion. Particular attention was focused on problems with the notification process (eg, patients being missed due to errors in data entry) and summarizing information to keep the Cardiac Surgical Services team updated on the progress of the process improvement. This project did not require staff protections or considerations, and because this was not a research study Institutional Review Board approval was not required.
Results
This practice change was implemented in September 2017 and led to improvements in care quality, as evidenced by improved physician communication and collaboration. In the 16-month period from implementation through December 2018, the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; and 44 were readmitted for inpatient care. The remaining 492 patients did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Clinical performance data from this period included 70 ED visits, 21 direct admissions, 19 direct admissions to observation, 5 patients missed by the notification process, and 4 observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions. A reduction in the CABG readmission rate from 10% in September 2017 to 7.2% in December 2018 was also noted.
Discussion
The aim of this process improvement project was to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. This practice change has been successful, following 16 months of implementation and process refinement. Integrating a real-time electronic alert with a supporting action plan and care protocols resulted in timely patient engagement and avoidance of readmission of post-CABG patients.
Early notification of possible post-CABG readmissions became a standard-of-care process within the Cardiac Surgical Services department, with expansion to all CT post-op patients. Leveraging HIE technology to support quality improvement processes was also viewed by other departments as relevant and beneficial. For example, the hospital stroke and orthopedic-spine teams established their own processes for receiving real-time alerts.
There were several lessons learned during this project. First, gaining 100% physician buy-in to collaborative communication proved to be critical to the project’s success. The CV team was surprised by the length of time (approximately 8-10 months) it took for the practice change to be adopted by the physicians. In part, some of this delay in adoption resulted from medical staff turnover, primarily in the medical resident training rotations. Collaborative communication was key. The CT surgeons spoke with ED leadership and hospitalist services to explain the readmission reduction project and the use of an electronic alert tool. The CT surgeons also communicated to the ED physicians, hospitalists, and cardiologists that the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator would be involved in the process and discussions regarding patientss care. Additionally, the CT surgeons authored the furosemide protocol and then committed to its use in the home health setting, further highlighting the role of collaborative communication in avoiding readmissions.
Another key step in this quality improvement project was determining who should receive the alert notifications. At the onset of the project, all notifications were sent to 1 person, the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator. While this seemed logical in the initial stage of the project, it was unsustainable, as the receipt of the alert and the subsequent notification of the CT surgeon depended on 1 person and their availability. Approximately 10 months into the project, the notification process was further refined, with the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse becoming the point of contact for the alerts. The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, in collaboration with nursing leaders and CT surgeons, completed a Lean Standard Work template outlining the major steps and the associated responsibilities (for the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse, CT surgeon and on-call surgeon, Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator) in the process of receiving notifications, collecting patient assessment data, and reporting notifications to the CT surgeons.
Establishing adequate support mechanisms during a practice change is also important. For instance, we had to dedicate personnel time for data collection and analysis and involve additional nursing or other qualified personnel in the new process to avoid depending on a single person for the project’s success. Additional considerations were establishing criteria for surgeon notification and defining an appropriate time frame for notification (eg, urgent versus next-day notifications). We accomplished these activities approximately 10 months into the project, after it became apparent at CV team meeting discussions that further clarification of criteria and timelines was needed.
Some aspects of the project unfolded as planned, while others presented opportunities for improvement. For example, the alert notification process worked as envisioned; however, as previously mentioned, the process needed to be more inclusive to ensure there is always a charge nurse on duty to receive the alert notification, rather than just the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, who may not always be at the hospital. The outpatient thoracentesis program was well planned and effectively implemented. This program provided an avenue for patients who had symptoms of pleural effusion to be treated in an outpatient setting, rather than requiring an inpatient stay. Opportunities for improvement included addressing the inconsistent use of the home health furosemide protocol (developed in 2016), and the need for continued interprofessional and interdepartmental communication and coordination. For example, we had to inform the ED physicians and staff who rotate or are new to the ED about established processes and protocols in place for managing post-CABG patients who present to the ED.
The primary limitation of this project was the inability to measure the enhanced patient experience, which was 1 of the stated project goals. This goal became secondary because of more pressing issues, specifically, interorganizational collaboration (eg, hospital EHR, HIE, and CT surgical team) and tailoring the functionality of the electronic alert tool to the project. Developing and implementing measures of enhanced patient experience were not feasible during this implementation. Additionally, because this was not a research study, it was not possible to determine cause and effect or to control for confounders, such as a sicker, older cohort with more comorbid conditions, during the comparison period. Finally, although this process improvement project was conducted at a regional medical center that is the only facility performing CABG within the region, patients may have presented to another facility for an event that led to a readmission. Because readmissions to other facilities could not be captured, it is possible that the actual readmission rate was higher than the rate reported here.
Conclusions and Implications
Utilizing a real-time alert from the HIE to the CT surgical team resulted in CT surgeons being immediately made aware when their patients presented to the ED, allowing the CT surgical team the opportunity to intervene, as appropriate, in the care of their patients. Furthermore, this real-time notification and intervention resulted in timely patient engagement and, in some cases, avoidance of readmissions. Currently, patients are monitored for readmission within 30 days of discharge. In the future, the time will expand to 91 days, in preparation for participation in the CMS bundle payment program for CABG surgery.
This practice change can be used in organizations that do not have or participate in a HIE. In fact, these real-time alert applications may be available through an EHR already in use within the organization. The use of the alert requires collaborative communication and having supporting protocols in place to guide decision-making and care of post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
There appears to be a gap in the literature discussing the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED. As such, this project contributes important results and lessons learned for other hospital service lines/departments that might consider implementing a similar process. Next steps include designing and conducting methodologically rigorous research studies based on this process improvement project to examine mortality rates as an outcome, and designing a more specific measure of patient experience, as the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey only provides hospital-level data.
Corresponding author: Stephanie D. Smith, PhD, RN, UNCW School of Nursing, 601 South College Road, Wilmington, NC 28403; [email protected].
Funding disclosures: None.
From the University of North Carolina at Wilmington School of Nursing (Dr. Smith and Dr. Turrise), the New Hanover Regional Medical Center Heart Center (Mr. Jordan), the Coastal Carolinas Health Alliance and Coastal Connect Health Information Exchange (Ms. Robertson), and Coastal Thoracic Surgical Associates (Dr. Kane), Wilmington, NC.
Abstract
Objective: Cardiothoracic (CT) surgeons at our medical center were not receiving timely notification when their coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery patients were admitted to the medical center or to other hospitals. The CT surgical team worked with a health alliance in southeastern North Carolina to implement health information exchange (HIE) real-time electronic notifications for their CABG patients who presented to the hospital’s emergency department (ED) or any ED affiliated with the medical center. The alert tool notifies team members about patient encounters, driving timely clinical engagement.
Methods: The CT team provided the HIE team with the names of CABG surgery patients, which were loaded into the alert tool. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED or its affiliates, the alert tool sent a real-time electronic notification to the Cardiac Surgical Services nurse coordinator. This intervention prompted the assessment and disposition of CABG patients, while in the ED, by the CT surgical team.
Results: Over a 16-month period (September 2017-December 2018), the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; 44 were readmitted for inpatient care; and 492 did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Following implementation of this practice change, the 30-day readmission rate for patients who underwent CABG at our institution decreased from 10% to 7.2%.
Conclusion: Utilizing a real-time alert tool resulted in immediate notification of the CT team when 1 of their patients presented to the ED. This afforded the CT surgical team an opportunity to intervene in the care of their patients, which in turn led to improved quality of care, physician communication and collaboration, and patient outcomes, such as preventable 30-day readmissions.
Keywords: electronic health record; real-time electronic notification; CABG; process improvement.
Unplanned 30-day hospital readmissions of patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery contribute to higher overall health care costs. CABG is 1 of the conditions/procedures that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) monitors for excess readmissions.1 Readmission rates for CABG-related conditions at 30 days post-surgery are reported to be between 16% and 20% for US hospitals.2 Readmissions are not only financially costly, but also have been associated with worse patient outcomes and decreased patient satisfaction.3 Common diagnoses for post-CABG admission include atrial fibrillation, pleural effusion, and wound infection.
The facility where this project was implemented had a 10% post-CABG admission rate for patients across all payers. While this rate is below the national average of 13.2%, the cardiothoracic (CT) surgical team was not being notified in a timely manner when their post-CABG patients were readmitted. The Lean team used the A3 problem-solving process to develop strategies that would reduce these readmissions and improve the care of their patients.
We explored the use of electronic alerts in managing post-CABG patients by conducting a literature search using the terms electronic alerts in patient care, patient engagement in the emergency department, electronic alerts in CABG, real-time notifications to prevent readmission, and CABG readmission. Databases searched were PubMed, Google Scholar, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect. This search resulted in studies focused on the use of electronic health record (EHR) alerts as a clinical decision-support tool; for example, patient demographic and assessment data are entered into the EHR, and the clinician is prompted with “performance” recommendations (eg, consider electrocardiogram and aspirin).4 In a paper by Engelman and Benjamin,5 the authors discuss the importance of the engaged physician and note that, in their emergency department (ED), an electronic notification is sent when a postoperative patient presents; however, the notification goes to the inpatient service for timely review and disposition. There was no literature that discussed the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy that resulted in a practice change specific to the CT surgical team.
Our process improvement project focused on alerting the CT surgical team when a post-CABG patient presented to the ED, allowing them to evaluate the patient in real time and determine whether the chief complaint was related to the CABG and whether further evaluation by the CT surgeon was required. Specifically, we wanted to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. During this project, alerts were sent to the CT surgical team notifying them of a post-CABG patient presenting to the ED or being directly admitted from home on physician orders, a provider’s office, or inpatient rehabilitation; however, the focus of this article is specifically on the notification regarding post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
Prior to implementing the electronic notification project, the team developed and implemented several internal and external readmission reduction and prevention strategies for CABG patients. An in-house strategy involved a process whereby patients would receive their discharge medications prior to being discharged from the hospital post-CABG, thereby avoiding potential delays in the patient obtaining medications. When examining post-CABG patient readmissions, the primary conditions that led to readmission were fluid overload, pleural effusion, and atrial fibrillation. As such, a second in-house strategy was developed for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED with atrial fibrillation. The newly established protocol allowed patients to be monitored and treated in the cardiac observation unit. In addition, external strategies, including an outpatient furosemide protocol for home health nurses and an outpatient thoracentesis program and order set, were established (eg, for patients with congestive heart failure, shortness of breath).
Methods
Setting
The regional medical center where this project was implemented is the ninth largest hospital in North Carolina and the largest county-owned public hospital in the state. It is a tertiary care center and teaching hospital with 3 hospital campuses and 855 licensed beds. The medical center was included in the 100 Safecare Hospitals list by the Safecare Group; received a grade “A” Hospital Safety Score from the Leapfrog Group; and is 1 of America’s Top 100 Hospitals for Patient Experience.
Real-Time Notification Project
A regional hospital alliance in southeastern North Carolina established a health information exchange (HIE) with its member hospitals and office-based physicians to enable electronic exchange of patient information to improve quality, safety, and efficiency in health care delivery. Our medical center is part of this alliance. The HIE is a digital platform that facilitates the sharing of information between disparate connected EHR systems, and offers a portal for practices and hospitals to access patient information across North Carolina, South Carolina (via SC HIE), and nationwide (select dialysis centers). More specifically, approved providers and team members are able to access, in real time, patient-care encounter documents from other care settings (eg, acute, post-acute, ambulatory) via the HIE. Additionally, approved care entities can query-retrieve web portal information to support patient outcome improvement strategies. A partnership discussion highlighted the opportunity to utilize the HIE’s capabilities, such as real-time notification, to facilitate workflow (eg, when a patient presents to the ED, the HIE can provide access to health information at the point of care). In this capacity, the alert tool notifies care team members about patient encounters to drive timely clinical engagement for care transitions.
In January 2017, we began discussions on using the HIE to facilitate real-time electronic tracking in the Cardiac Surgical Services department at our medical center. Persons involved in these discussions included the cardiovascular (CV) team (comprised of case managers, department managers and coordinators, program coordinators, administrators, and support services [eg, pre-admission testing and home health staff]) and CT surgeons. At that time, CABG readmissions were manually tracked, and the real-time notification tool was being used in other departments (eg, in case management for tracking readmissions). The entire team was part of the initial decision meeting to pursue this possibility. The CV team reached consensus in June 2017 and proposed extending the use of the alert tool to the post-CABG population presenting to the ED (or any ED affiliated with the medical center) or admitted directly to the medical center.
The HIE staff met with the Cardiac Surgical Services team to tailor and develop the logistics of the project, such as who would be notified and how. The goals of the project were to support appropriate care intervention, reduce preventable hospital readmissions, and improve quality of care through enhanced provider communication and engagement. To achieve these goals, on the day of discharge the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator provided the HIE team with the names of patients who had undergone CABG surgery. This patient list was loaded into the alert tool and continually updated. At 31 days, patient names were removed from the list. When a patient on the list presented to the hospital ED, the alert tool sent 2 real-time electronic notifications, an email and a text message, to the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, noting that a patient event occurred. Personal information was not included in the alert in order to protect patient information and comply with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act regulations.
The alert prompted the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator to securely access patient information to identify and, if necessary, visit the patient. Then, based on the information gathered by the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, a Situation-Background-Assessment-Recommendation report was relayed to the CT surgeon, who then determined whether intervention by the CT surgical team was warranted. This process, on average, took approximately 30 minutes to complete. This was a key change in processes, one that allowed post-CABG patients to be seen by the CT surgical team while in the ED. If the issue was related to the CABG surgery, the CT surgeons could then determine an appropriate course of action, including admission or implementation of another protocol, such as the home furosemide protocol. For patients directly admitted, the surgeon contacted the admitting provider to discuss the level of care required (ie, observation or inpatient admission and treatment).
Biweekly CV team meetings were conducted during the implementation of the real-time notification alert tool. At each meeting, updates were provided on notifications received, patients who were missed by the notification process, and how well the real-time alerts were working to enhance care and appropriate disposition.
Measurements
Clinical performance data included total notifications, total number of ED visits, ED disposition (inpatient admission, observation, discharge), total number of direct admissions, direct admissions to observation, direct inpatient admissions, and patients missed by the notification process (eg, due to data entry errors, omissions of information [suffix of junior or senior], as well as programming bugs). Finally, the number of observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions was collected and further analyzed to inform needed process changes.
The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator collected, entered, and maintained data using Excel. Data were obtained from the EHR, recorded in Excel, and analyzed using basic descriptive statistics in an ongoing fashion. Particular attention was focused on problems with the notification process (eg, patients being missed due to errors in data entry) and summarizing information to keep the Cardiac Surgical Services team updated on the progress of the process improvement. This project did not require staff protections or considerations, and because this was not a research study Institutional Review Board approval was not required.
Results
This practice change was implemented in September 2017 and led to improvements in care quality, as evidenced by improved physician communication and collaboration. In the 16-month period from implementation through December 2018, the names of 614 post-CABG patients were input into the HIE for tracking. Of these patients, 47 were treated and discharged from the ED; 31 were admitted for observation; and 44 were readmitted for inpatient care. The remaining 492 patients did not have a qualifying event requiring a notification alert. Clinical performance data from this period included 70 ED visits, 21 direct admissions, 19 direct admissions to observation, 5 patients missed by the notification process, and 4 observation admissions converted to inpatient admissions. A reduction in the CABG readmission rate from 10% in September 2017 to 7.2% in December 2018 was also noted.
Discussion
The aim of this process improvement project was to determine whether a real-time electronic alert that notified the CT surgical team about post-op CABG patients presenting to the ED would result in timely patient engagement, avoidance of readmissions, and an enhanced patient experience. This practice change has been successful, following 16 months of implementation and process refinement. Integrating a real-time electronic alert with a supporting action plan and care protocols resulted in timely patient engagement and avoidance of readmission of post-CABG patients.
Early notification of possible post-CABG readmissions became a standard-of-care process within the Cardiac Surgical Services department, with expansion to all CT post-op patients. Leveraging HIE technology to support quality improvement processes was also viewed by other departments as relevant and beneficial. For example, the hospital stroke and orthopedic-spine teams established their own processes for receiving real-time alerts.
There were several lessons learned during this project. First, gaining 100% physician buy-in to collaborative communication proved to be critical to the project’s success. The CV team was surprised by the length of time (approximately 8-10 months) it took for the practice change to be adopted by the physicians. In part, some of this delay in adoption resulted from medical staff turnover, primarily in the medical resident training rotations. Collaborative communication was key. The CT surgeons spoke with ED leadership and hospitalist services to explain the readmission reduction project and the use of an electronic alert tool. The CT surgeons also communicated to the ED physicians, hospitalists, and cardiologists that the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator would be involved in the process and discussions regarding patientss care. Additionally, the CT surgeons authored the furosemide protocol and then committed to its use in the home health setting, further highlighting the role of collaborative communication in avoiding readmissions.
Another key step in this quality improvement project was determining who should receive the alert notifications. At the onset of the project, all notifications were sent to 1 person, the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator. While this seemed logical in the initial stage of the project, it was unsustainable, as the receipt of the alert and the subsequent notification of the CT surgeon depended on 1 person and their availability. Approximately 10 months into the project, the notification process was further refined, with the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse becoming the point of contact for the alerts. The Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, in collaboration with nursing leaders and CT surgeons, completed a Lean Standard Work template outlining the major steps and the associated responsibilities (for the cardiovascular intensive care unit charge nurse, CT surgeon and on-call surgeon, Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator) in the process of receiving notifications, collecting patient assessment data, and reporting notifications to the CT surgeons.
Establishing adequate support mechanisms during a practice change is also important. For instance, we had to dedicate personnel time for data collection and analysis and involve additional nursing or other qualified personnel in the new process to avoid depending on a single person for the project’s success. Additional considerations were establishing criteria for surgeon notification and defining an appropriate time frame for notification (eg, urgent versus next-day notifications). We accomplished these activities approximately 10 months into the project, after it became apparent at CV team meeting discussions that further clarification of criteria and timelines was needed.
Some aspects of the project unfolded as planned, while others presented opportunities for improvement. For example, the alert notification process worked as envisioned; however, as previously mentioned, the process needed to be more inclusive to ensure there is always a charge nurse on duty to receive the alert notification, rather than just the Cardiac Surgical Services coordinator, who may not always be at the hospital. The outpatient thoracentesis program was well planned and effectively implemented. This program provided an avenue for patients who had symptoms of pleural effusion to be treated in an outpatient setting, rather than requiring an inpatient stay. Opportunities for improvement included addressing the inconsistent use of the home health furosemide protocol (developed in 2016), and the need for continued interprofessional and interdepartmental communication and coordination. For example, we had to inform the ED physicians and staff who rotate or are new to the ED about established processes and protocols in place for managing post-CABG patients who present to the ED.
The primary limitation of this project was the inability to measure the enhanced patient experience, which was 1 of the stated project goals. This goal became secondary because of more pressing issues, specifically, interorganizational collaboration (eg, hospital EHR, HIE, and CT surgical team) and tailoring the functionality of the electronic alert tool to the project. Developing and implementing measures of enhanced patient experience were not feasible during this implementation. Additionally, because this was not a research study, it was not possible to determine cause and effect or to control for confounders, such as a sicker, older cohort with more comorbid conditions, during the comparison period. Finally, although this process improvement project was conducted at a regional medical center that is the only facility performing CABG within the region, patients may have presented to another facility for an event that led to a readmission. Because readmissions to other facilities could not be captured, it is possible that the actual readmission rate was higher than the rate reported here.
Conclusions and Implications
Utilizing a real-time alert from the HIE to the CT surgical team resulted in CT surgeons being immediately made aware when their patients presented to the ED, allowing the CT surgical team the opportunity to intervene, as appropriate, in the care of their patients. Furthermore, this real-time notification and intervention resulted in timely patient engagement and, in some cases, avoidance of readmissions. Currently, patients are monitored for readmission within 30 days of discharge. In the future, the time will expand to 91 days, in preparation for participation in the CMS bundle payment program for CABG surgery.
This practice change can be used in organizations that do not have or participate in a HIE. In fact, these real-time alert applications may be available through an EHR already in use within the organization. The use of the alert requires collaborative communication and having supporting protocols in place to guide decision-making and care of post-CABG patients presenting to the ED.
There appears to be a gap in the literature discussing the use of an electronic alert tool as a real-time patient engagement strategy for post-CABG patients presenting to the ED. As such, this project contributes important results and lessons learned for other hospital service lines/departments that might consider implementing a similar process. Next steps include designing and conducting methodologically rigorous research studies based on this process improvement project to examine mortality rates as an outcome, and designing a more specific measure of patient experience, as the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey only provides hospital-level data.
Corresponding author: Stephanie D. Smith, PhD, RN, UNCW School of Nursing, 601 South College Road, Wilmington, NC 28403; [email protected].
Funding disclosures: None.
1. Hannan EL, Zhong Y, Lahey SJ, et al. 30-day readmissions after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in New York State. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:569-576.
2. Feng TR, White R, Gaber-Baylis L, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft readmission rates and risk factors- A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;54 (Part A):7-17.
3. Donndorf P, Kaminski A. “Return to sender” or “consider it done”?! The importance of reducing hospital readmission after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:1298-1299.
4. Sequist TD, Morong SM, Marston A, et al. Electronic risk alerts to improve primary care management of chest pain: A randomized, controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27:438-444.
5. Engelman D, Benjamin EM. Physician engagement: The “secret sauce” to success in bundled health care. Am J Med Qual. 2018;33:100-102.
1. Hannan EL, Zhong Y, Lahey SJ, et al. 30-day readmissions after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in New York State. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4:569-576.
2. Feng TR, White R, Gaber-Baylis L, et al. Coronary artery bypass graft readmission rates and risk factors- A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2018;54 (Part A):7-17.
3. Donndorf P, Kaminski A. “Return to sender” or “consider it done”?! The importance of reducing hospital readmission after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:1298-1299.
4. Sequist TD, Morong SM, Marston A, et al. Electronic risk alerts to improve primary care management of chest pain: A randomized, controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27:438-444.
5. Engelman D, Benjamin EM. Physician engagement: The “secret sauce” to success in bundled health care. Am J Med Qual. 2018;33:100-102.
Factors Associated With Lower-Extremity Amputation in Patients With Diabetic Foot Ulcers
From Northwell Health System, Lake Success, NY.
Abstract
- Objective: To explore factors associated with lower-extremity amputation (LEA) in patients with diabetic foot ulcers using data from the Online Wound Electronic Medical Record Database.
- Design: Retrospective analysis of medical records.
- Setting and participants: Data from 169 individuals with previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus who received wound care for a 6-month period within a span of 2 years was analyzed. A baseline evaluation was obtained and wound(s) were treated, managed, and monitored.
Treatment continued until the patient healed, required an LEA, or phased out of the study, neither healing nor undergoing an amputation. Of the 149 patients who completed the study, 38 had healed ulcers, 14 underwent amputation, and 97 neither healed nor underwent an amputation. All patients were treated under the care of vascular and/or podiatric surgeons. - Measurements: Variables included wound status (healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated); size of wound area; age, gender, race, and ethnicity; white blood cell (WBC) count, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI); and presence of osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease.
- Results: As compared to the healed and unhealed/non-amputated group, the group of patients who underwent LEA was older and had higher percentages of males, Hispanics, and African Americans; had a higher WBC count, larger wound area, and higher rates of wound infection, osteomyelitis, and neuropathy; and had lower average values of HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease.
- Conclusion: The association between HbA1c and LEA highlights a window of relative safety among an at-risk population. By identifying and focusing on factors associated with LEA, health care professionals may be able to decrease the prevalence of LEA in patients with diabetes.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer; lower-extremity amputation; risk factors; HbA1c.
An estimated 30.3 million people, or 9.4% of the US population, has diabetes. In 2014, approximately 108,000 amputations were performed on adults with diagnosed diabetes.1 Furthermore, patients with diabetes have a 10-fold increased risk for lower-extremity amputation (LEA), as compared with patients without diabetes.2 The frequency of amputations in the diabetic population is a public health crisis.
Amputation has significant, life-altering consequences. Patients who undergo LEA often face debilitation in their daily activities and must undergo intense rehabilitation to learn basic tasks. Amputations can also impact individuals’ psychological well-being as they come to terms with their altered body and may face challenges in self-perception, confidence, self-esteem, work life, and relationships. In addition, the mortality rate for patients with diabetes 5 years after undergoing LEA is 30%.2 However, public health studies estimate that more than half of LEAs in patients with diabetes are preventable.3
Although studies have explored the relationship between diabetes and LEA, few have sought to identify factors directly correlated with wound care. In the United States, patients with diabetic ulcerations are typically treated in wound care facilities; however, previous studies have concentrated on the conditions that lead to the formation of an ulcer or amputation, viewing amputation and ulcer as 2 separate entities. Our study took into account systemic variables, patient demographics, and specific wound characteristics to explore factors associated with LEA in a high-risk group of patients with diabetes. This study was designed to assess ailments that are prevalent in patients who require a LEA.
Methods
Patients and Setting
A total of 169 patients who were treated at the Comprehensive Wound Healing and Hyperbaric Center (Lake Success, NY), a tertiary facility of the Northwell Health system, participated in this retrospective study. The data for this study were obtained in conjunction with the development of the New York University School of Medicine’s Online Wound Electronic Medical Record to Decrease Limb Amputations in Persons with Diabetes (OWEMR) database. The OWEMR collects individual patient data from satellite locations across the country. Using this database, researchers can analyze similarities and differences between patients who undergo LEA.
This study utilized patient data specific to the Northwell Health facility. All of the patients in our study were enrolled under the criteria of the OWEMR database. In order to be included in the OWEMR database, patients had to be diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes; have a break in the skin ≥ 0.5 cm2; be 18 years of age or older; and have a measured hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) value within the past 120 days. Study patients signed an informed consent and committed to being available for follow-up visits to the wound care facility for 6 months after entering the study. Patients were enrolled between 2012 and 2014, and each patient was monitored for a period of 6 months within this time period. Participants were treated with current standards of care using diet, lifestyle, and pharmacologic interventions. This study was approved by the Northwell Health System Institutional Review Board Human Research Protection Program (Manhasset, NY).
Data Collection
On their first visit to the facility, patients were given a physical examination and initial interview regarding their medical history. Clinicians were required to select 1 ulcer that would be examined for the duration of the study. The selection of the ulcer was based on a point system that awarded points for pedal pulses, the ability to be probed to the bone, the location of the ulcer (ie, located on the foot rather than a toe), and the presence of multiple ulcerations. The ulcer with the highest score was selected for the study. If numerous ulcers were evaluated with the same score, the largest and deepest was selected. Wagner classification of the wound was recorded at baseline and taken at each subsequent patient visit. In addition, peripheral sensation was assessed for signs of neuropathy using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing.
Once selected, the wound was clinically evaluated, samples for culture were obtained, and blood tests were performed to detect the presence of wound infection. The patient’s blood was drawn for a full laboratory analysis, including white blood cell (WBC) count and measurement of blood glucose and HbA1c levels. Bone biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging, and bone scans were used to detect the presence of osteomyelitis at the discretion of the health care provider. Wounds suspected of infection, underlying osteomyelitis, or gangrene at baseline were excluded. Patients would then return for follow-up visits at least once every 6 weeks, plus or minus 2 weeks, for a maximum of 6 months.
Statistical Analysis
Utilizing SAS version 9.3 (Cary, NC), descriptive statistics (minimum, maximum, mean, median, and SD) were calculated for the following variables: age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI). These variables were collected for each patient as per the OWEMR protocol and provided a basis for which to compare patients who underwent amputation and those who did not. Twenty patients were lost to follow-up, and therefore we altered the window of our statistics from 6 months to 3 months to provide the most accurate data, as 6-month follow-up data were limited. The patients were classified into the following categories: healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated. Descriptive statistics were calculated for these 3 groups, analyzing the same variables (age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI). Additional statistical computations were utilized in order to show the prevalence and frequency of our categorical variables: gender, race, ethnicity, osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease. The baseline values of WBC count, HbA1c, wound area, and BMI of the 3 groups were analyzed with descriptive statistics for comparison. A multinomial logistic regression was then performed using a 3-level outcome variable: healed, amputated, or unhealed/non-amputated. Each predictor variable was analyzed independently due to the small sample size.
Results
Of the 169 registered patients treated at the Northwell Health facility, all qualified for the OWEMR study and met the study criteria. In the original 169 patients, there were 19 amputations: 6 toe, 6 trans-metatarsal, 6 below knee, and 1 above knee (Table 1). 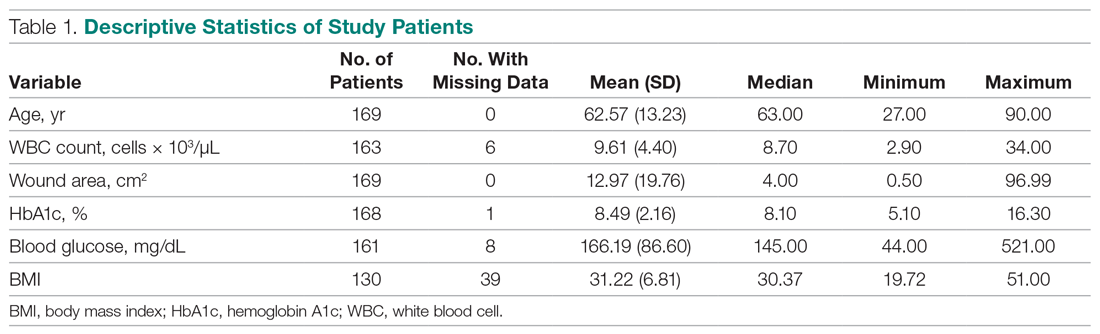
The descriptive statistics of 149 patients grouped into 3 categories (healed, amputated, unhealed/non-amputated) are shown in Table 2.
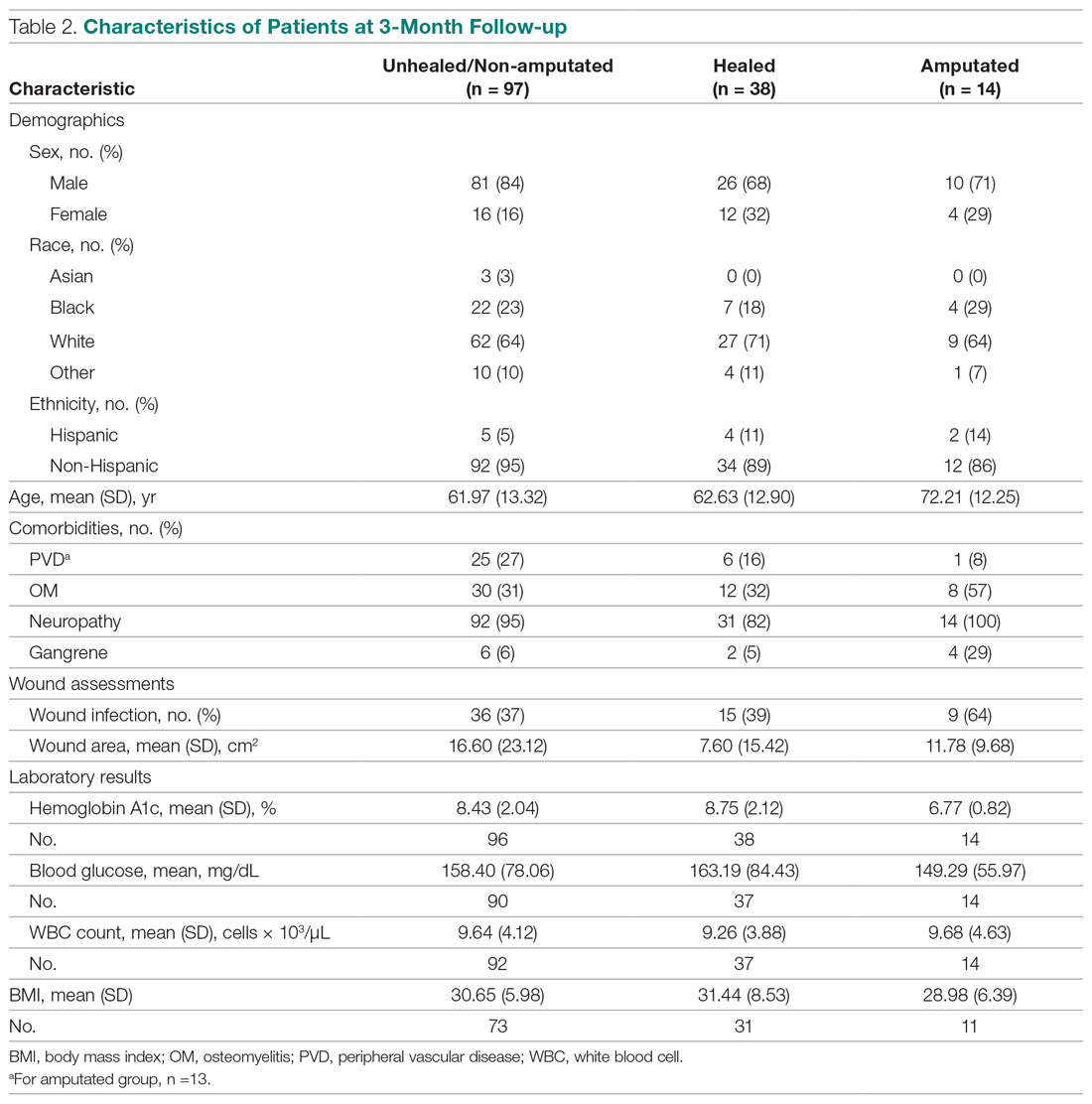
The results of the logistic regression exploring the differences between the amputation and healed groups and the unhealed/non-amputated group are shown in Table 3. The amputation group had a higher mean age and WBC count and greater wound area. Increased age was determined to be a significant predictor of the odds of amputation (P = 0.0089). For each year increase in age, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5% (odds ratio, 1.07 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 1.02-1.12]). Patients in the amputation group were more likely to be male, Hispanic, and African American and to have wound infections and comorbidities (osteomyelitis, neuropathy, and gangrene).
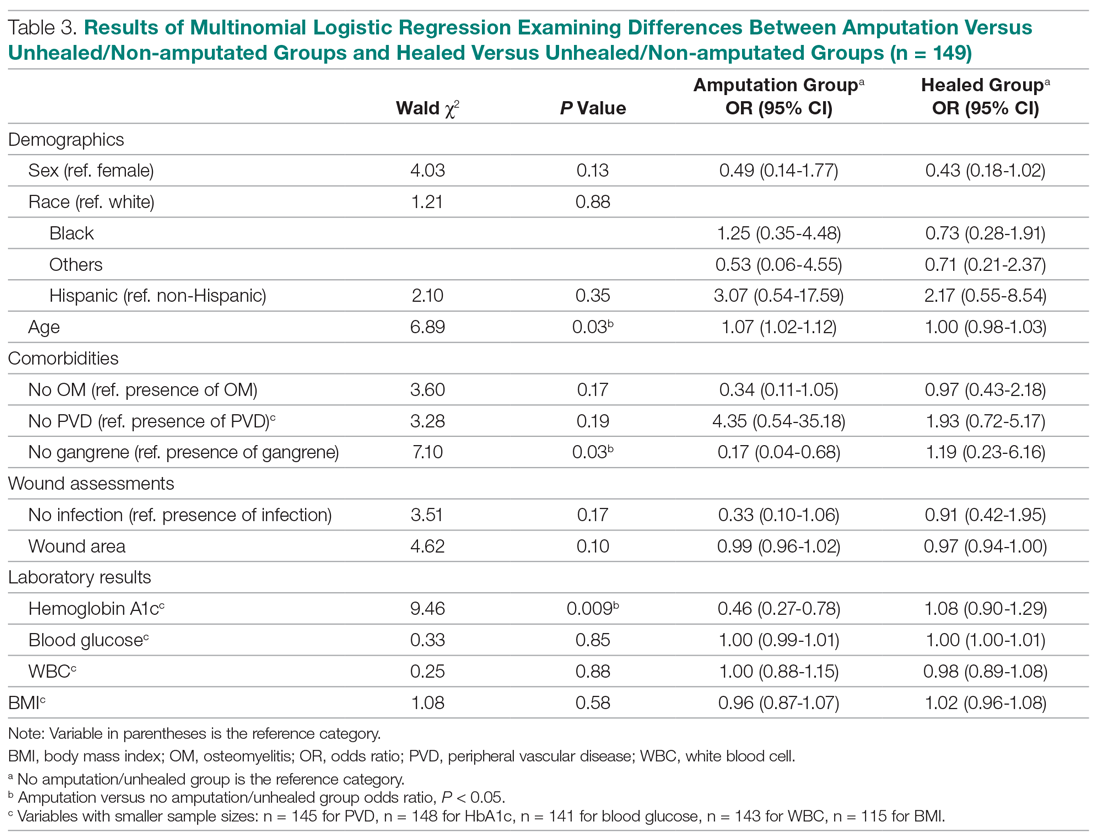
The presence of gangrene was significantly associated with LEA (P = 0.03). Specifically, the odds of patients without gangrene undergoing a LEA were substantially lower compared with their counterparts with gangrene (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.04-0.68; P = 0.0131). However, the presence of gangrene was not associated with the odds of healing compared with the odds of neither healing nor undergoing amputation (P = 0.84; not shown in Table 3).
The amputation group had lower mean values for HbA1c, BMI, and blood glucose levels and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease. Only the relationship between lower HbA1c and increased odds of amputation versus not healing/non-amputation was found to be statistically significant (95% CI, 0.27-0.78; P = 0.009).
Discussion
This retrospective study was undertaken to evaluate factors associated with LEA in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with diabetes being treated at a wound care facility often require continuous surgical and metabolic intervention to promote optimal healing: drainage, surgical debridement, irrigation, culturing for infection, and monitoring of blood glucose levels. This treatment requires strict compliance with medical directions and, oftentimes, additional care, such as home-care nursing visits, to maintain a curative environment for the wound. Frequently, wounds on the lower extremity further complicate the healing process by reducing the patient’s mobility and daily life. Due to these factors, many patients progress to LEA. The link between diabetic ulcers and amputation has already been well described in previous studies, with studies showing that history of diabetic foot ulcer significantly predisposes an individual to LEA.4 However, few studies have further investigated demographic factors associated with risk for an amputation. Our study analyzed several categories of patient data taken from a baseline visit. We found that those with highly elevated HbA1c values were less likely to have an amputation than persons with relatively lower levels, a finding that is contrary to previous studies.
Our study’s findings suggest a higher risk for LEA with increased age. The amputation group was, on average, 7 years older than the other 2 groups. A recent study showed that risk for amputation is directly correlated to patient age, as is the mortality rate after undergoing LEA (2.3%; P < 0.05).5 Our study found that with each increase in age of 1 year, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5%. However, recent evidence on LEA risk and aging suggests that age is of less consequence than the duration of diabetes. One study found that the propensity to develop diabetic foot ulcers increases with the duration of diabetes.6 The same study found that prevalence of ulceration was correlated with age, but the relationship between age and LEA was less significant. A follow-up study for LEA could be done to examine the role of disease duration versus age in LEA.
A consensus among previous studies is that men have a higher risk for LEA.5,7 Men comprised the majority in all 3 groups in our study. In addition, the amputation group in our study had the lowest BMI. Higher BMI generally is associated with an increased risk for health complications. However, a past study conducted in Taiwan reported that obese patients with diabetes were less likely to undergo LEA than those within the normal range for BMI.8 Neither study suggests that obesity is a deterrent for LEA, but both studies may suggest that risk of amputation may approach a maximum frequency at a specific BMI range, and then decrease. This unconfirmed “cyclic” relationship should be evaluated further in a larger sample size.
Most patients in our analysis were Caucasian, followed by African American and South Asian. African Americans were the only racial group with an increased frequency in the amputation group. This finding is supported by a previous study that found that the rate of LEA among patients with diabetes in low-income, predominantly African-American neighborhoods was nearly double that in wealthier, predominantly Caucasian areas.9 A potential problem in the comparison between our data with previous studies is that the studies did not analyze patients with our inclusion criteria. All patients with diabetes in previous investigations were grouped by race, but were not necessarily required to have 1 or more ulcers. Multiple ulcers may predispose an individual to a greater risk for amputation.
Multinomial logistic regression did not suggest an association between initial size of a patient’s wound and the risk of amputation. However, the descriptive data suggests a trend. Patients who did not heal or require an amputation had the largest average wound area. This finding is not surprising in that our study followed individuals for only 3 months. Many wounds require a long course of treatment, especially in patients with diabetes, who may have poor vascularization. However, in comparison to the healed patients, the patients who required an amputation had a larger average wound area. A larger wound requires a plentiful vascular supply for the delivery of clotting factors and nutrients to the damaged area. As wound size increases, an individual’s body must transmit an increased quantity of these factors and nutrients for the regeneration of tissue. In addition, wounds that possess a larger surface area require more debridement and present a greater opportunity for infection. This may also foreshadow a longer, more costly course of treatment. Additionally, individuals coping with large ulcerations are burdened by more elaborate and complex wound dressings.
Elevated levels of HbA1c are associated with increased adverse effects of diabetes, including end-stage renal disease, neuropathy, and infection.10 In a previous study, the risk for amputation was 1.2 times higher in patients with elevated HbA1c.11 In contrast, our study suggested the odds of LEA versus not healing/not undergoing amputation decreased as HbA1c increased. As a patient’s HbA1c level increased by a value of 1, their odds for LEA decreased by 54.3%. This finding contradicts prior studies that have found a positive association between HbA1c and LEA risk, including a study where each percentage increase in HbA1c correlated with a 13% to 15% increased risk of LEA.12 The finding that patients who underwent amputation in our study had lower levels of HbA1c and blood glucose cannot be fully explained. The maximum HbA1c value in the amputated group was 7.9%. The average values for healed patients and those who underwent LEA were 8.75% and 6.77%, respectively.
Blood glucose levels were also found to be the lowest in the amputated group in our study (mean, 149.29 mg/dL vs 163.19 mg/dL in the healed group). Similar results were found in a Brazilian study, in which patients who did not require amputation had higher HbA1c levels. This study also found an association between blood glucose levels above 200 mg/dL and amputations.3 These findings provide interesting opportunities for repeat studies, preferably with a larger number of participants.
Our study is limited by the small sample size. The sample population had to be reduced, as many patients were lost to follow-up. Although this paring down of the sample size can introduce bias, we are confident that our study is representative of the demographic of patients treated in our facility. The loss of patients to follow-up in turn caused the window of analysis to be narrowed, as long-term outcome data were not available. A multisite study observing various population samples can better explore the relationship between HbA1c and risk of amputation.
Conclusion
This retrospective study exploring factors associated with LEA was unique in that all our participants had 1 or more diabetic foot ulcerations, and thus already had an extremely high risk for amputation, in contrast to previous studies that followed persons at risk for developing diabetic foot ulcerations. In contrast to several previous studies, we found that the risk for amputation actually decreased as baseline measurements of HbA1c increased. The results of this study offer many opportunities for future investigations, preferably with a larger sample size. By further isolating and scrutinizing specific factors associated with LEA, researchers can help clinicians focus on providing wound care that promotes limb salvage.
Corresponding author: Alisha Oropallo, MD, MS, Northwell Health Comprehensive Wound Care Healing Center and Hyperbarics, 1999 Marcus Avenue, Suite M6, Lake Success, NY 11042; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: Funding for this research was provided by a multi-institutional AHRQ governmental grant.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States, 2017. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017.
2. Uccioli L, Giurato L, Meloni M, et al. Comment on Hoffstad et al. Diabetes, lower-extremity amputation, and death. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1852-1857.
3. Gamba MA, Gotlieb SLD, Bergamaschi DP, Vianna LAC. Lower extremity amputations in diabetic patients: a case-control study. Rev Saúde Pública. 2004;38:399-404.
4. Martins-Mendes D, Monteiro-Soares M, Boyko EJ, et al. The independent contribution of diabetic foot ulcer on lower extremity amputation and mortality risk. J Diabetes Complications. 2014;28:632-638.
5. Lipsky BA, Weigelt JA, Sun X, et al. Developing and validating a risk score for lower-extremity amputation in patients hospitalized for a diabetic foot infection. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1695-1700.
6. Al-Rubeaan K, Al Derwish M, Ouizi S, et al. Diabetic foot complications and their risk factors from a large retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124446.
7. Pickwell K, Siersma V, Kars M, et al. Predictors of lower-extremity amputation in patients with an infected diabetic foot ulcer. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:852-857.
8. Lin C, Hsu BR, Tsai J, et al. Effect of limb preservation status and body mass index on the survival of patients with limb-threatening diabetic foot ulcers. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31:180-185.
9. Stevens CD, Schriger DL, Raffetto B, et al. Geographic clustering of diabetic lower-extremity amputations in low-income regions of California. Health Aff. 2014;33:1383-1390.
10. Liao L, Li C, Liu C, et al. Extreme levels of HbA1c increase incident ESRD risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: competing risk analysis in national cohort of Taiwan diabetes study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0130828.
11. Miyajima S, Shirai A, Yamamoto S, et al. Risk factors for major limb amputations in diabetic foot gangrene patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71:272-279.
12. Zhao W, Katzmarzyk PT, Horswell R, et al. HbA1c and lower-extremity amputation risk in low-income patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3591-3598.
From Northwell Health System, Lake Success, NY.
Abstract
- Objective: To explore factors associated with lower-extremity amputation (LEA) in patients with diabetic foot ulcers using data from the Online Wound Electronic Medical Record Database.
- Design: Retrospective analysis of medical records.
- Setting and participants: Data from 169 individuals with previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus who received wound care for a 6-month period within a span of 2 years was analyzed. A baseline evaluation was obtained and wound(s) were treated, managed, and monitored.
Treatment continued until the patient healed, required an LEA, or phased out of the study, neither healing nor undergoing an amputation. Of the 149 patients who completed the study, 38 had healed ulcers, 14 underwent amputation, and 97 neither healed nor underwent an amputation. All patients were treated under the care of vascular and/or podiatric surgeons. - Measurements: Variables included wound status (healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated); size of wound area; age, gender, race, and ethnicity; white blood cell (WBC) count, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI); and presence of osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease.
- Results: As compared to the healed and unhealed/non-amputated group, the group of patients who underwent LEA was older and had higher percentages of males, Hispanics, and African Americans; had a higher WBC count, larger wound area, and higher rates of wound infection, osteomyelitis, and neuropathy; and had lower average values of HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease.
- Conclusion: The association between HbA1c and LEA highlights a window of relative safety among an at-risk population. By identifying and focusing on factors associated with LEA, health care professionals may be able to decrease the prevalence of LEA in patients with diabetes.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer; lower-extremity amputation; risk factors; HbA1c.
An estimated 30.3 million people, or 9.4% of the US population, has diabetes. In 2014, approximately 108,000 amputations were performed on adults with diagnosed diabetes.1 Furthermore, patients with diabetes have a 10-fold increased risk for lower-extremity amputation (LEA), as compared with patients without diabetes.2 The frequency of amputations in the diabetic population is a public health crisis.
Amputation has significant, life-altering consequences. Patients who undergo LEA often face debilitation in their daily activities and must undergo intense rehabilitation to learn basic tasks. Amputations can also impact individuals’ psychological well-being as they come to terms with their altered body and may face challenges in self-perception, confidence, self-esteem, work life, and relationships. In addition, the mortality rate for patients with diabetes 5 years after undergoing LEA is 30%.2 However, public health studies estimate that more than half of LEAs in patients with diabetes are preventable.3
Although studies have explored the relationship between diabetes and LEA, few have sought to identify factors directly correlated with wound care. In the United States, patients with diabetic ulcerations are typically treated in wound care facilities; however, previous studies have concentrated on the conditions that lead to the formation of an ulcer or amputation, viewing amputation and ulcer as 2 separate entities. Our study took into account systemic variables, patient demographics, and specific wound characteristics to explore factors associated with LEA in a high-risk group of patients with diabetes. This study was designed to assess ailments that are prevalent in patients who require a LEA.
Methods
Patients and Setting
A total of 169 patients who were treated at the Comprehensive Wound Healing and Hyperbaric Center (Lake Success, NY), a tertiary facility of the Northwell Health system, participated in this retrospective study. The data for this study were obtained in conjunction with the development of the New York University School of Medicine’s Online Wound Electronic Medical Record to Decrease Limb Amputations in Persons with Diabetes (OWEMR) database. The OWEMR collects individual patient data from satellite locations across the country. Using this database, researchers can analyze similarities and differences between patients who undergo LEA.
This study utilized patient data specific to the Northwell Health facility. All of the patients in our study were enrolled under the criteria of the OWEMR database. In order to be included in the OWEMR database, patients had to be diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes; have a break in the skin ≥ 0.5 cm2; be 18 years of age or older; and have a measured hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) value within the past 120 days. Study patients signed an informed consent and committed to being available for follow-up visits to the wound care facility for 6 months after entering the study. Patients were enrolled between 2012 and 2014, and each patient was monitored for a period of 6 months within this time period. Participants were treated with current standards of care using diet, lifestyle, and pharmacologic interventions. This study was approved by the Northwell Health System Institutional Review Board Human Research Protection Program (Manhasset, NY).
Data Collection
On their first visit to the facility, patients were given a physical examination and initial interview regarding their medical history. Clinicians were required to select 1 ulcer that would be examined for the duration of the study. The selection of the ulcer was based on a point system that awarded points for pedal pulses, the ability to be probed to the bone, the location of the ulcer (ie, located on the foot rather than a toe), and the presence of multiple ulcerations. The ulcer with the highest score was selected for the study. If numerous ulcers were evaluated with the same score, the largest and deepest was selected. Wagner classification of the wound was recorded at baseline and taken at each subsequent patient visit. In addition, peripheral sensation was assessed for signs of neuropathy using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing.
Once selected, the wound was clinically evaluated, samples for culture were obtained, and blood tests were performed to detect the presence of wound infection. The patient’s blood was drawn for a full laboratory analysis, including white blood cell (WBC) count and measurement of blood glucose and HbA1c levels. Bone biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging, and bone scans were used to detect the presence of osteomyelitis at the discretion of the health care provider. Wounds suspected of infection, underlying osteomyelitis, or gangrene at baseline were excluded. Patients would then return for follow-up visits at least once every 6 weeks, plus or minus 2 weeks, for a maximum of 6 months.
Statistical Analysis
Utilizing SAS version 9.3 (Cary, NC), descriptive statistics (minimum, maximum, mean, median, and SD) were calculated for the following variables: age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI). These variables were collected for each patient as per the OWEMR protocol and provided a basis for which to compare patients who underwent amputation and those who did not. Twenty patients were lost to follow-up, and therefore we altered the window of our statistics from 6 months to 3 months to provide the most accurate data, as 6-month follow-up data were limited. The patients were classified into the following categories: healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated. Descriptive statistics were calculated for these 3 groups, analyzing the same variables (age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI). Additional statistical computations were utilized in order to show the prevalence and frequency of our categorical variables: gender, race, ethnicity, osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease. The baseline values of WBC count, HbA1c, wound area, and BMI of the 3 groups were analyzed with descriptive statistics for comparison. A multinomial logistic regression was then performed using a 3-level outcome variable: healed, amputated, or unhealed/non-amputated. Each predictor variable was analyzed independently due to the small sample size.
Results
Of the 169 registered patients treated at the Northwell Health facility, all qualified for the OWEMR study and met the study criteria. In the original 169 patients, there were 19 amputations: 6 toe, 6 trans-metatarsal, 6 below knee, and 1 above knee (Table 1). 
The descriptive statistics of 149 patients grouped into 3 categories (healed, amputated, unhealed/non-amputated) are shown in Table 2.

The results of the logistic regression exploring the differences between the amputation and healed groups and the unhealed/non-amputated group are shown in Table 3. The amputation group had a higher mean age and WBC count and greater wound area. Increased age was determined to be a significant predictor of the odds of amputation (P = 0.0089). For each year increase in age, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5% (odds ratio, 1.07 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 1.02-1.12]). Patients in the amputation group were more likely to be male, Hispanic, and African American and to have wound infections and comorbidities (osteomyelitis, neuropathy, and gangrene).

The presence of gangrene was significantly associated with LEA (P = 0.03). Specifically, the odds of patients without gangrene undergoing a LEA were substantially lower compared with their counterparts with gangrene (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.04-0.68; P = 0.0131). However, the presence of gangrene was not associated with the odds of healing compared with the odds of neither healing nor undergoing amputation (P = 0.84; not shown in Table 3).
The amputation group had lower mean values for HbA1c, BMI, and blood glucose levels and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease. Only the relationship between lower HbA1c and increased odds of amputation versus not healing/non-amputation was found to be statistically significant (95% CI, 0.27-0.78; P = 0.009).
Discussion
This retrospective study was undertaken to evaluate factors associated with LEA in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with diabetes being treated at a wound care facility often require continuous surgical and metabolic intervention to promote optimal healing: drainage, surgical debridement, irrigation, culturing for infection, and monitoring of blood glucose levels. This treatment requires strict compliance with medical directions and, oftentimes, additional care, such as home-care nursing visits, to maintain a curative environment for the wound. Frequently, wounds on the lower extremity further complicate the healing process by reducing the patient’s mobility and daily life. Due to these factors, many patients progress to LEA. The link between diabetic ulcers and amputation has already been well described in previous studies, with studies showing that history of diabetic foot ulcer significantly predisposes an individual to LEA.4 However, few studies have further investigated demographic factors associated with risk for an amputation. Our study analyzed several categories of patient data taken from a baseline visit. We found that those with highly elevated HbA1c values were less likely to have an amputation than persons with relatively lower levels, a finding that is contrary to previous studies.
Our study’s findings suggest a higher risk for LEA with increased age. The amputation group was, on average, 7 years older than the other 2 groups. A recent study showed that risk for amputation is directly correlated to patient age, as is the mortality rate after undergoing LEA (2.3%; P < 0.05).5 Our study found that with each increase in age of 1 year, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5%. However, recent evidence on LEA risk and aging suggests that age is of less consequence than the duration of diabetes. One study found that the propensity to develop diabetic foot ulcers increases with the duration of diabetes.6 The same study found that prevalence of ulceration was correlated with age, but the relationship between age and LEA was less significant. A follow-up study for LEA could be done to examine the role of disease duration versus age in LEA.
A consensus among previous studies is that men have a higher risk for LEA.5,7 Men comprised the majority in all 3 groups in our study. In addition, the amputation group in our study had the lowest BMI. Higher BMI generally is associated with an increased risk for health complications. However, a past study conducted in Taiwan reported that obese patients with diabetes were less likely to undergo LEA than those within the normal range for BMI.8 Neither study suggests that obesity is a deterrent for LEA, but both studies may suggest that risk of amputation may approach a maximum frequency at a specific BMI range, and then decrease. This unconfirmed “cyclic” relationship should be evaluated further in a larger sample size.
Most patients in our analysis were Caucasian, followed by African American and South Asian. African Americans were the only racial group with an increased frequency in the amputation group. This finding is supported by a previous study that found that the rate of LEA among patients with diabetes in low-income, predominantly African-American neighborhoods was nearly double that in wealthier, predominantly Caucasian areas.9 A potential problem in the comparison between our data with previous studies is that the studies did not analyze patients with our inclusion criteria. All patients with diabetes in previous investigations were grouped by race, but were not necessarily required to have 1 or more ulcers. Multiple ulcers may predispose an individual to a greater risk for amputation.
Multinomial logistic regression did not suggest an association between initial size of a patient’s wound and the risk of amputation. However, the descriptive data suggests a trend. Patients who did not heal or require an amputation had the largest average wound area. This finding is not surprising in that our study followed individuals for only 3 months. Many wounds require a long course of treatment, especially in patients with diabetes, who may have poor vascularization. However, in comparison to the healed patients, the patients who required an amputation had a larger average wound area. A larger wound requires a plentiful vascular supply for the delivery of clotting factors and nutrients to the damaged area. As wound size increases, an individual’s body must transmit an increased quantity of these factors and nutrients for the regeneration of tissue. In addition, wounds that possess a larger surface area require more debridement and present a greater opportunity for infection. This may also foreshadow a longer, more costly course of treatment. Additionally, individuals coping with large ulcerations are burdened by more elaborate and complex wound dressings.
Elevated levels of HbA1c are associated with increased adverse effects of diabetes, including end-stage renal disease, neuropathy, and infection.10 In a previous study, the risk for amputation was 1.2 times higher in patients with elevated HbA1c.11 In contrast, our study suggested the odds of LEA versus not healing/not undergoing amputation decreased as HbA1c increased. As a patient’s HbA1c level increased by a value of 1, their odds for LEA decreased by 54.3%. This finding contradicts prior studies that have found a positive association between HbA1c and LEA risk, including a study where each percentage increase in HbA1c correlated with a 13% to 15% increased risk of LEA.12 The finding that patients who underwent amputation in our study had lower levels of HbA1c and blood glucose cannot be fully explained. The maximum HbA1c value in the amputated group was 7.9%. The average values for healed patients and those who underwent LEA were 8.75% and 6.77%, respectively.
Blood glucose levels were also found to be the lowest in the amputated group in our study (mean, 149.29 mg/dL vs 163.19 mg/dL in the healed group). Similar results were found in a Brazilian study, in which patients who did not require amputation had higher HbA1c levels. This study also found an association between blood glucose levels above 200 mg/dL and amputations.3 These findings provide interesting opportunities for repeat studies, preferably with a larger number of participants.
Our study is limited by the small sample size. The sample population had to be reduced, as many patients were lost to follow-up. Although this paring down of the sample size can introduce bias, we are confident that our study is representative of the demographic of patients treated in our facility. The loss of patients to follow-up in turn caused the window of analysis to be narrowed, as long-term outcome data were not available. A multisite study observing various population samples can better explore the relationship between HbA1c and risk of amputation.
Conclusion
This retrospective study exploring factors associated with LEA was unique in that all our participants had 1 or more diabetic foot ulcerations, and thus already had an extremely high risk for amputation, in contrast to previous studies that followed persons at risk for developing diabetic foot ulcerations. In contrast to several previous studies, we found that the risk for amputation actually decreased as baseline measurements of HbA1c increased. The results of this study offer many opportunities for future investigations, preferably with a larger sample size. By further isolating and scrutinizing specific factors associated with LEA, researchers can help clinicians focus on providing wound care that promotes limb salvage.
Corresponding author: Alisha Oropallo, MD, MS, Northwell Health Comprehensive Wound Care Healing Center and Hyperbarics, 1999 Marcus Avenue, Suite M6, Lake Success, NY 11042; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: Funding for this research was provided by a multi-institutional AHRQ governmental grant.
From Northwell Health System, Lake Success, NY.
Abstract
- Objective: To explore factors associated with lower-extremity amputation (LEA) in patients with diabetic foot ulcers using data from the Online Wound Electronic Medical Record Database.
- Design: Retrospective analysis of medical records.
- Setting and participants: Data from 169 individuals with previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus who received wound care for a 6-month period within a span of 2 years was analyzed. A baseline evaluation was obtained and wound(s) were treated, managed, and monitored.
Treatment continued until the patient healed, required an LEA, or phased out of the study, neither healing nor undergoing an amputation. Of the 149 patients who completed the study, 38 had healed ulcers, 14 underwent amputation, and 97 neither healed nor underwent an amputation. All patients were treated under the care of vascular and/or podiatric surgeons. - Measurements: Variables included wound status (healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated); size of wound area; age, gender, race, and ethnicity; white blood cell (WBC) count, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI); and presence of osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease.
- Results: As compared to the healed and unhealed/non-amputated group, the group of patients who underwent LEA was older and had higher percentages of males, Hispanics, and African Americans; had a higher WBC count, larger wound area, and higher rates of wound infection, osteomyelitis, and neuropathy; and had lower average values of HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease.
- Conclusion: The association between HbA1c and LEA highlights a window of relative safety among an at-risk population. By identifying and focusing on factors associated with LEA, health care professionals may be able to decrease the prevalence of LEA in patients with diabetes.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer; lower-extremity amputation; risk factors; HbA1c.
An estimated 30.3 million people, or 9.4% of the US population, has diabetes. In 2014, approximately 108,000 amputations were performed on adults with diagnosed diabetes.1 Furthermore, patients with diabetes have a 10-fold increased risk for lower-extremity amputation (LEA), as compared with patients without diabetes.2 The frequency of amputations in the diabetic population is a public health crisis.
Amputation has significant, life-altering consequences. Patients who undergo LEA often face debilitation in their daily activities and must undergo intense rehabilitation to learn basic tasks. Amputations can also impact individuals’ psychological well-being as they come to terms with their altered body and may face challenges in self-perception, confidence, self-esteem, work life, and relationships. In addition, the mortality rate for patients with diabetes 5 years after undergoing LEA is 30%.2 However, public health studies estimate that more than half of LEAs in patients with diabetes are preventable.3
Although studies have explored the relationship between diabetes and LEA, few have sought to identify factors directly correlated with wound care. In the United States, patients with diabetic ulcerations are typically treated in wound care facilities; however, previous studies have concentrated on the conditions that lead to the formation of an ulcer or amputation, viewing amputation and ulcer as 2 separate entities. Our study took into account systemic variables, patient demographics, and specific wound characteristics to explore factors associated with LEA in a high-risk group of patients with diabetes. This study was designed to assess ailments that are prevalent in patients who require a LEA.
Methods
Patients and Setting
A total of 169 patients who were treated at the Comprehensive Wound Healing and Hyperbaric Center (Lake Success, NY), a tertiary facility of the Northwell Health system, participated in this retrospective study. The data for this study were obtained in conjunction with the development of the New York University School of Medicine’s Online Wound Electronic Medical Record to Decrease Limb Amputations in Persons with Diabetes (OWEMR) database. The OWEMR collects individual patient data from satellite locations across the country. Using this database, researchers can analyze similarities and differences between patients who undergo LEA.
This study utilized patient data specific to the Northwell Health facility. All of the patients in our study were enrolled under the criteria of the OWEMR database. In order to be included in the OWEMR database, patients had to be diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes; have a break in the skin ≥ 0.5 cm2; be 18 years of age or older; and have a measured hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) value within the past 120 days. Study patients signed an informed consent and committed to being available for follow-up visits to the wound care facility for 6 months after entering the study. Patients were enrolled between 2012 and 2014, and each patient was monitored for a period of 6 months within this time period. Participants were treated with current standards of care using diet, lifestyle, and pharmacologic interventions. This study was approved by the Northwell Health System Institutional Review Board Human Research Protection Program (Manhasset, NY).
Data Collection
On their first visit to the facility, patients were given a physical examination and initial interview regarding their medical history. Clinicians were required to select 1 ulcer that would be examined for the duration of the study. The selection of the ulcer was based on a point system that awarded points for pedal pulses, the ability to be probed to the bone, the location of the ulcer (ie, located on the foot rather than a toe), and the presence of multiple ulcerations. The ulcer with the highest score was selected for the study. If numerous ulcers were evaluated with the same score, the largest and deepest was selected. Wagner classification of the wound was recorded at baseline and taken at each subsequent patient visit. In addition, peripheral sensation was assessed for signs of neuropathy using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing.
Once selected, the wound was clinically evaluated, samples for culture were obtained, and blood tests were performed to detect the presence of wound infection. The patient’s blood was drawn for a full laboratory analysis, including white blood cell (WBC) count and measurement of blood glucose and HbA1c levels. Bone biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging, and bone scans were used to detect the presence of osteomyelitis at the discretion of the health care provider. Wounds suspected of infection, underlying osteomyelitis, or gangrene at baseline were excluded. Patients would then return for follow-up visits at least once every 6 weeks, plus or minus 2 weeks, for a maximum of 6 months.
Statistical Analysis
Utilizing SAS version 9.3 (Cary, NC), descriptive statistics (minimum, maximum, mean, median, and SD) were calculated for the following variables: age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and body mass index (BMI). These variables were collected for each patient as per the OWEMR protocol and provided a basis for which to compare patients who underwent amputation and those who did not. Twenty patients were lost to follow-up, and therefore we altered the window of our statistics from 6 months to 3 months to provide the most accurate data, as 6-month follow-up data were limited. The patients were classified into the following categories: healed, amputated, and unhealed/non-amputated. Descriptive statistics were calculated for these 3 groups, analyzing the same variables (age, WBC count, wound area, HbA1c, blood glucose, and BMI). Additional statistical computations were utilized in order to show the prevalence and frequency of our categorical variables: gender, race, ethnicity, osteomyelitis, gangrene, and peripheral vascular disease. The baseline values of WBC count, HbA1c, wound area, and BMI of the 3 groups were analyzed with descriptive statistics for comparison. A multinomial logistic regression was then performed using a 3-level outcome variable: healed, amputated, or unhealed/non-amputated. Each predictor variable was analyzed independently due to the small sample size.
Results
Of the 169 registered patients treated at the Northwell Health facility, all qualified for the OWEMR study and met the study criteria. In the original 169 patients, there were 19 amputations: 6 toe, 6 trans-metatarsal, 6 below knee, and 1 above knee (Table 1). 
The descriptive statistics of 149 patients grouped into 3 categories (healed, amputated, unhealed/non-amputated) are shown in Table 2.

The results of the logistic regression exploring the differences between the amputation and healed groups and the unhealed/non-amputated group are shown in Table 3. The amputation group had a higher mean age and WBC count and greater wound area. Increased age was determined to be a significant predictor of the odds of amputation (P = 0.0089). For each year increase in age, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5% (odds ratio, 1.07 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 1.02-1.12]). Patients in the amputation group were more likely to be male, Hispanic, and African American and to have wound infections and comorbidities (osteomyelitis, neuropathy, and gangrene).

The presence of gangrene was significantly associated with LEA (P = 0.03). Specifically, the odds of patients without gangrene undergoing a LEA were substantially lower compared with their counterparts with gangrene (odds ratio, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.04-0.68; P = 0.0131). However, the presence of gangrene was not associated with the odds of healing compared with the odds of neither healing nor undergoing amputation (P = 0.84; not shown in Table 3).
The amputation group had lower mean values for HbA1c, BMI, and blood glucose levels and a lower rate of peripheral vascular disease. Only the relationship between lower HbA1c and increased odds of amputation versus not healing/non-amputation was found to be statistically significant (95% CI, 0.27-0.78; P = 0.009).
Discussion
This retrospective study was undertaken to evaluate factors associated with LEA in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with diabetes being treated at a wound care facility often require continuous surgical and metabolic intervention to promote optimal healing: drainage, surgical debridement, irrigation, culturing for infection, and monitoring of blood glucose levels. This treatment requires strict compliance with medical directions and, oftentimes, additional care, such as home-care nursing visits, to maintain a curative environment for the wound. Frequently, wounds on the lower extremity further complicate the healing process by reducing the patient’s mobility and daily life. Due to these factors, many patients progress to LEA. The link between diabetic ulcers and amputation has already been well described in previous studies, with studies showing that history of diabetic foot ulcer significantly predisposes an individual to LEA.4 However, few studies have further investigated demographic factors associated with risk for an amputation. Our study analyzed several categories of patient data taken from a baseline visit. We found that those with highly elevated HbA1c values were less likely to have an amputation than persons with relatively lower levels, a finding that is contrary to previous studies.
Our study’s findings suggest a higher risk for LEA with increased age. The amputation group was, on average, 7 years older than the other 2 groups. A recent study showed that risk for amputation is directly correlated to patient age, as is the mortality rate after undergoing LEA (2.3%; P < 0.05).5 Our study found that with each increase in age of 1 year, the odds of amputation increased by 6.5%. However, recent evidence on LEA risk and aging suggests that age is of less consequence than the duration of diabetes. One study found that the propensity to develop diabetic foot ulcers increases with the duration of diabetes.6 The same study found that prevalence of ulceration was correlated with age, but the relationship between age and LEA was less significant. A follow-up study for LEA could be done to examine the role of disease duration versus age in LEA.
A consensus among previous studies is that men have a higher risk for LEA.5,7 Men comprised the majority in all 3 groups in our study. In addition, the amputation group in our study had the lowest BMI. Higher BMI generally is associated with an increased risk for health complications. However, a past study conducted in Taiwan reported that obese patients with diabetes were less likely to undergo LEA than those within the normal range for BMI.8 Neither study suggests that obesity is a deterrent for LEA, but both studies may suggest that risk of amputation may approach a maximum frequency at a specific BMI range, and then decrease. This unconfirmed “cyclic” relationship should be evaluated further in a larger sample size.
Most patients in our analysis were Caucasian, followed by African American and South Asian. African Americans were the only racial group with an increased frequency in the amputation group. This finding is supported by a previous study that found that the rate of LEA among patients with diabetes in low-income, predominantly African-American neighborhoods was nearly double that in wealthier, predominantly Caucasian areas.9 A potential problem in the comparison between our data with previous studies is that the studies did not analyze patients with our inclusion criteria. All patients with diabetes in previous investigations were grouped by race, but were not necessarily required to have 1 or more ulcers. Multiple ulcers may predispose an individual to a greater risk for amputation.
Multinomial logistic regression did not suggest an association between initial size of a patient’s wound and the risk of amputation. However, the descriptive data suggests a trend. Patients who did not heal or require an amputation had the largest average wound area. This finding is not surprising in that our study followed individuals for only 3 months. Many wounds require a long course of treatment, especially in patients with diabetes, who may have poor vascularization. However, in comparison to the healed patients, the patients who required an amputation had a larger average wound area. A larger wound requires a plentiful vascular supply for the delivery of clotting factors and nutrients to the damaged area. As wound size increases, an individual’s body must transmit an increased quantity of these factors and nutrients for the regeneration of tissue. In addition, wounds that possess a larger surface area require more debridement and present a greater opportunity for infection. This may also foreshadow a longer, more costly course of treatment. Additionally, individuals coping with large ulcerations are burdened by more elaborate and complex wound dressings.
Elevated levels of HbA1c are associated with increased adverse effects of diabetes, including end-stage renal disease, neuropathy, and infection.10 In a previous study, the risk for amputation was 1.2 times higher in patients with elevated HbA1c.11 In contrast, our study suggested the odds of LEA versus not healing/not undergoing amputation decreased as HbA1c increased. As a patient’s HbA1c level increased by a value of 1, their odds for LEA decreased by 54.3%. This finding contradicts prior studies that have found a positive association between HbA1c and LEA risk, including a study where each percentage increase in HbA1c correlated with a 13% to 15% increased risk of LEA.12 The finding that patients who underwent amputation in our study had lower levels of HbA1c and blood glucose cannot be fully explained. The maximum HbA1c value in the amputated group was 7.9%. The average values for healed patients and those who underwent LEA were 8.75% and 6.77%, respectively.
Blood glucose levels were also found to be the lowest in the amputated group in our study (mean, 149.29 mg/dL vs 163.19 mg/dL in the healed group). Similar results were found in a Brazilian study, in which patients who did not require amputation had higher HbA1c levels. This study also found an association between blood glucose levels above 200 mg/dL and amputations.3 These findings provide interesting opportunities for repeat studies, preferably with a larger number of participants.
Our study is limited by the small sample size. The sample population had to be reduced, as many patients were lost to follow-up. Although this paring down of the sample size can introduce bias, we are confident that our study is representative of the demographic of patients treated in our facility. The loss of patients to follow-up in turn caused the window of analysis to be narrowed, as long-term outcome data were not available. A multisite study observing various population samples can better explore the relationship between HbA1c and risk of amputation.
Conclusion
This retrospective study exploring factors associated with LEA was unique in that all our participants had 1 or more diabetic foot ulcerations, and thus already had an extremely high risk for amputation, in contrast to previous studies that followed persons at risk for developing diabetic foot ulcerations. In contrast to several previous studies, we found that the risk for amputation actually decreased as baseline measurements of HbA1c increased. The results of this study offer many opportunities for future investigations, preferably with a larger sample size. By further isolating and scrutinizing specific factors associated with LEA, researchers can help clinicians focus on providing wound care that promotes limb salvage.
Corresponding author: Alisha Oropallo, MD, MS, Northwell Health Comprehensive Wound Care Healing Center and Hyperbarics, 1999 Marcus Avenue, Suite M6, Lake Success, NY 11042; [email protected].
Financial disclosures: Funding for this research was provided by a multi-institutional AHRQ governmental grant.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States, 2017. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017.
2. Uccioli L, Giurato L, Meloni M, et al. Comment on Hoffstad et al. Diabetes, lower-extremity amputation, and death. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1852-1857.
3. Gamba MA, Gotlieb SLD, Bergamaschi DP, Vianna LAC. Lower extremity amputations in diabetic patients: a case-control study. Rev Saúde Pública. 2004;38:399-404.
4. Martins-Mendes D, Monteiro-Soares M, Boyko EJ, et al. The independent contribution of diabetic foot ulcer on lower extremity amputation and mortality risk. J Diabetes Complications. 2014;28:632-638.
5. Lipsky BA, Weigelt JA, Sun X, et al. Developing and validating a risk score for lower-extremity amputation in patients hospitalized for a diabetic foot infection. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1695-1700.
6. Al-Rubeaan K, Al Derwish M, Ouizi S, et al. Diabetic foot complications and their risk factors from a large retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124446.
7. Pickwell K, Siersma V, Kars M, et al. Predictors of lower-extremity amputation in patients with an infected diabetic foot ulcer. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:852-857.
8. Lin C, Hsu BR, Tsai J, et al. Effect of limb preservation status and body mass index on the survival of patients with limb-threatening diabetic foot ulcers. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31:180-185.
9. Stevens CD, Schriger DL, Raffetto B, et al. Geographic clustering of diabetic lower-extremity amputations in low-income regions of California. Health Aff. 2014;33:1383-1390.
10. Liao L, Li C, Liu C, et al. Extreme levels of HbA1c increase incident ESRD risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: competing risk analysis in national cohort of Taiwan diabetes study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0130828.
11. Miyajima S, Shirai A, Yamamoto S, et al. Risk factors for major limb amputations in diabetic foot gangrene patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71:272-279.
12. Zhao W, Katzmarzyk PT, Horswell R, et al. HbA1c and lower-extremity amputation risk in low-income patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3591-3598.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States, 2017. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2017.
2. Uccioli L, Giurato L, Meloni M, et al. Comment on Hoffstad et al. Diabetes, lower-extremity amputation, and death. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1852-1857.
3. Gamba MA, Gotlieb SLD, Bergamaschi DP, Vianna LAC. Lower extremity amputations in diabetic patients: a case-control study. Rev Saúde Pública. 2004;38:399-404.
4. Martins-Mendes D, Monteiro-Soares M, Boyko EJ, et al. The independent contribution of diabetic foot ulcer on lower extremity amputation and mortality risk. J Diabetes Complications. 2014;28:632-638.
5. Lipsky BA, Weigelt JA, Sun X, et al. Developing and validating a risk score for lower-extremity amputation in patients hospitalized for a diabetic foot infection. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1695-1700.
6. Al-Rubeaan K, Al Derwish M, Ouizi S, et al. Diabetic foot complications and their risk factors from a large retrospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124446.
7. Pickwell K, Siersma V, Kars M, et al. Predictors of lower-extremity amputation in patients with an infected diabetic foot ulcer. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:852-857.
8. Lin C, Hsu BR, Tsai J, et al. Effect of limb preservation status and body mass index on the survival of patients with limb-threatening diabetic foot ulcers. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31:180-185.
9. Stevens CD, Schriger DL, Raffetto B, et al. Geographic clustering of diabetic lower-extremity amputations in low-income regions of California. Health Aff. 2014;33:1383-1390.
10. Liao L, Li C, Liu C, et al. Extreme levels of HbA1c increase incident ESRD risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: competing risk analysis in national cohort of Taiwan diabetes study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0130828.
11. Miyajima S, Shirai A, Yamamoto S, et al. Risk factors for major limb amputations in diabetic foot gangrene patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;71:272-279.
12. Zhao W, Katzmarzyk PT, Horswell R, et al. HbA1c and lower-extremity amputation risk in low-income patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3591-3598.
Impact of Hospitalists on Care Outcomes in a Large Integrated Health System in British Columbia
From the Fraser Health Authority, Surrey, British Columbia, Canada.
Abstract
- Objective: To study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to traditional providers.
- Design: Retrospective review of administrative data.
- Setting and participants: Patients from a large integrated health care system in British Columbia in western Canada admitted and cared for by 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018: hospitalists, family physicians (FP), and internal medicine (IM) physicians:
- Measurements: Average total length of stay (LOS), 30-day readmission, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR) were the study outcome measures. Multiple logistic regression or generalized regression were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and outcomes.
- Results: A total of 248,412 hospitalizations were included. Compared to patients admitted to hospitalists, patients admitted to other providers had higher odds of mortality (odds ratio [OR] for FP, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Compared to hospitalist care, FP care was associated with higher readmission (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.33), while IM care showed lower odds of readmission (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Patients admitted to the IM group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to patients admitted to hospitalists (mean, 7.37 days; CI, 7.26-7.49) and FPs (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41). In a subgroup analysis of patients presenting with congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and pneumonia, these general tendencies broadly persisted for mortality and LOS comparisons between FPs and hospitalists, but results were mixed for hospital readmissions.
- Conclusion: Care provided by hospitalists was associated with lower mortality and readmission rates compared with care provided by FPs, despite similar LOS. These findings may reflect differences in volume of services delivered by individual physicians, on-site availability to address urgent medical issues, and evolving specialization of clinical and nonclinical care processes in the acute care setting.
Keywords: hospital medicine; length of stay; readmission; mortality.
The hospitalist model of care has undergone rapid growth globally in recent years.1 The first hospitalist programs in Canada began around the same time as those in the United States and share many similarities in design and operations with their counterparts.2-4 However, unlike in the United States, where the hospitalist model has successfully established itself as an emerging specialty, debates about the merits of the model and its value proposition continue among Canadian observers.5-9
Historically, the type of physicians who acted as the most responsible provider (MRP) in Canadian hospitals depended on setting and geography.10 In large urban areas, groups of general internists or specialists have historically looked after general medicine patients as part of university-affiliated teaching services.11,12 Patients admitted to community hospitals have traditionally been cared for by their own primary care providers, typically general practitioners or family physicians (FPs). In the mid-1990s, many primary care providers in urban centers began to withdraw from inpatient care and primarily focused their practices in the outpatient setting.13-15 Hospitalist programs emerged as health care administrators sought to fill the resulting gap in MRP coverage.2,10
To date, attempts to understand the impact of hospitalist programs in Canada have been limited. A number of early studies aimed to describe16 the role of hospitalists in Canada and suggested improvements in length of stay (LOS) and staff satisfaction.17 However, these studies relied on unadjusted before-after comparisons and lacked methodological rigor to draw robust conclusions. More recently, a few studies have evaluated care outcomes associated with hospitalists using administrative databases, which attempted to control for potential confounding factors.18-21
While these studies are beginning to shed some light on the impact of hospital medicine programs in Canada, there are a number of issues that limit their generalizability. For example, the majority of studies to date focus on hospital medicine programs in Canada’s largest province (Ontario), and most describe experiences from single institutions. Since each of the 13 provincial and territorial governments organizes its health care system differently,22 results from 1 province may not be generalizable to other parts of the country. Moreover, hospitalists in Ontario are more diverse in their training backgrounds, with a larger percentage having trained in general internal medicine (IM), as compared to other parts of Canada, where the majority of hospitalists are overwhelmingly trained as FPs.3
We aimed to study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to “traditional” providers (community-based FPs and IM specialists) in a large integrated health care system in the province of British Columbia in western Canada. The hospital medicine services in this network span a range of community and academic hospitals, and collectively constitute 1 of the largest regional programs in the country. This provides a unique opportunity to understand the impact of hospitalists on outcome measures across a range of acute care institutions.
Methods
Setting and Population
Fraser Health Authority is 1 of 5 regional health authorities in British Columbia that emerged in 2001.23,24 It operates a network of hospitalist programs in 10 of its 12 acute care hospitals. In addition to hospitalists, there are a variable number of “traditional” physician providers who continue to act as MRPs. These include community-based FPs who continue to see their own patients in the hospital, either as part of a solo-practice model or a clinic-based call group. There are also a number of general internists and other subspecialists who accept MRP roles for general medicine patients who may present with higher-acuity conditions. As a result, patients requiring hospitalization due to nonsurgical or noncritical care conditions at each Fraser Health hospital may be cared for by a physician belonging to 1 of 3 groups, depending on local circumstances: an FP, a hospitalist, or an internist.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In order to evaluate comparative outcomes associated with hospitalist care, we included all patients admitted to a physician in each of the 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. We chose this time period for 2 reasons: first, we wanted to ensure comparability over an extended period of time, given the methodological changes implemented in 2009 by the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI), the federal organization in the country responsible for setting standards for health care measures.25 Second, previous internal reviews had suggested that data quality prior to this year was inconsistent. We only considered hospitalizations where patients were admitted to and discharged by the same service, and excluded 2 acute care facilities and 1 free-standing rehabilitation facility without a hospitalist service during this period. We also excluded patients who resided in a location beyond the geographic catchment area of Fraser Health. Further details about data collection are outlined in the Appendix.
Measures
We used the framework developed by White and Glazier26 to inform the selection of our outcome measures, as well as relevant variables that may impact them. This framework proposes that the design of the inpatient care model (structures and processes of care) directly affects care outcomes. The model also proposes that patient and provider attributes can modulate this relationship, and suggests that a comprehensive evaluation of hospitalist performance needs to take these factors into account. We identified average total LOS, 30-day readmission rate, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR)27 as primary outcome measures. HSMR is defined as actual over expected mortality and is measured by CIHI through a formula that takes into account patient illness attributes (eg, the most responsible diagnosis, comorbidity levels) and baseline population mortality rates.27 We chose these measures because they are clinically relevant and easy to obtain and have been utilized in previous similar studies in Canada and the United States.18-21,26
Statistical Analysis
Baseline demographic and clinical differences in patient outcomes were examined using independent t-tests or chi-square tests. Furthermore, baseline differences based on provider groups were explored using analysis of variance or chi-square tests. Multiple logistic regression analyses were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and readmission and mortality, while the relationship between provider groups and hospital LOS was determined with generalized linear regression (using gamma distribution and a log link). Gamma distribution with a log link analysis is appropriate with outcome measures that are positively skewed (eg, hospital LOS). It assumes that data are sampled from an exponential family of distributions, thus mimicking a log-normal distribution, and minimizes estimation bias and standard errors. These analyses were completed while controlling for the effects of age, gender, and other potential confounding factors.
We initially attempted to control for case mix by incorporating case-mix groups (CMGs) in our multivariate analysis. However, we identified 475 CMGs with at least 1 patient in our study population. We then explored the inclusion of major clinical categories (MCCs) that broadly group CMGs into various higher order/organ-system level categories (eg, diseases of the respiratory system); however, we could not aggregate them into sufficiently homogenous groups to be entered into regression models. Instead, we conducted subgroup analyses on patients in our study population who were hospitalized with 1 of the following 3 CMGs: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, n = 11,404 patients), congestive heart failure without coronary angiography (CHF, n = 7680), and pneumonia (itself an aggregate of 3 separate CMGs: aspiration pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, viral/unspecified pneumonia, n = 11,155). We chose these CMGs as they are among the top 8 presentations for all 3 provider groups.
For all outcome measures, we excluded atypical patients (defined by CIHI as those with atypically long stays) and patients who had been transferred between facilities. For the readmission analysis, we also excluded patients who died in the hospital (Appendix A). Data analyses were completed in IBM SPSS, version 21. For all analyses, significance was determined using 2-tailed test and alpha < 0.05.
Ethics
The Fraser Health Department of Research and Evaluation reviewed this project to determine need for formal Ethics Review Board review, and granted an exemption based on institutional guidelines for program evaluations.
Results
A total of 132,178 patients were admitted to and discharged by 1 of the 3 study provider groups during the study period, accounting for a total of 248,412 hospitalizations. After excluding patients cared for in Fraser Health facilities without a hospitalist service and those who resided in a geographic area beyond Fraser Health, a total of 224,214 admissions were included in the final analysis.
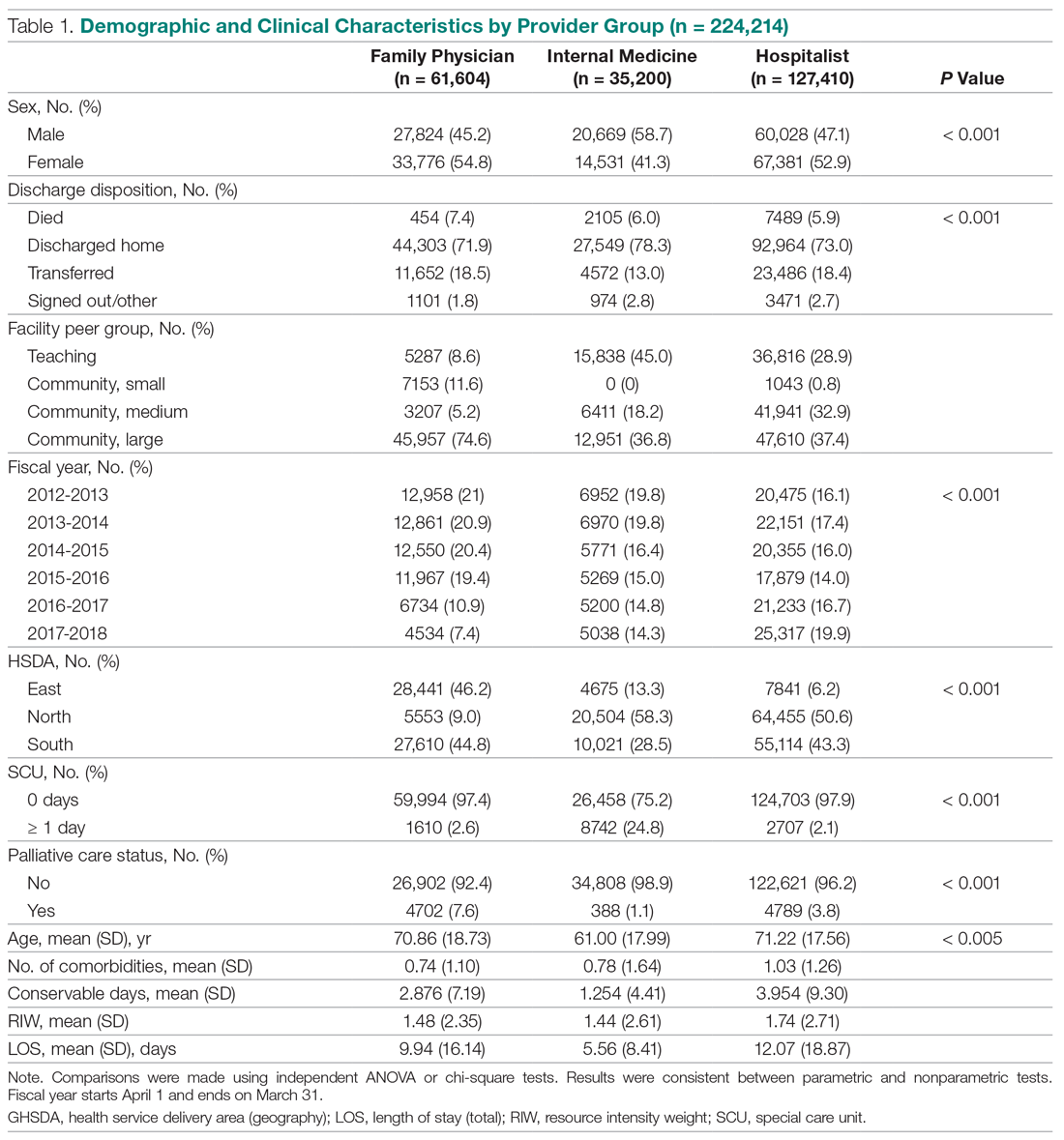
Patient Characteristics
The demographic and clinical characteristics of patients by provider group are summarized in Table 1. Patients admitted to IM providers were substantially younger than those admitted to either FPs or hospitalists (61.00 vs 70.86 and 71.22 years, respectively; P < 0.005). However, patients admitted to hospitalists had higher degrees of complexity (as measured by higher comorbidity levels, number of secondary diagnoses, and higher resource intensity weights [RIWs]; P < 000.1 for all comparisons). Overall, the most common CMGs seen by FPs and hospitalists were similar, while IM providers primarily saw patients with cardiac conditions (Table 2).
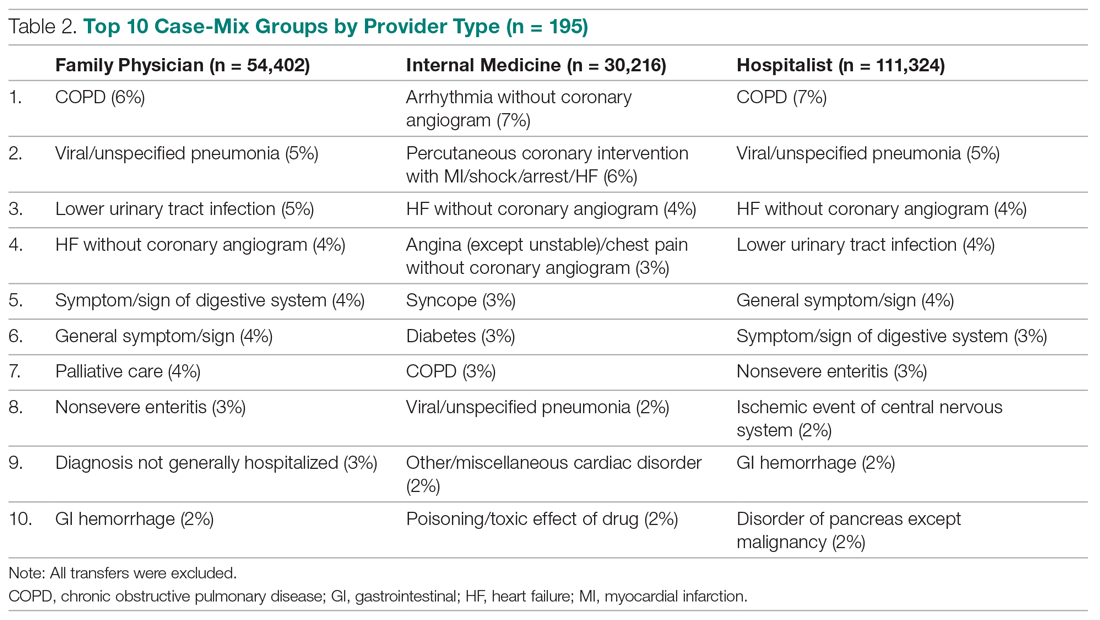
Trends Over Time
During the study period, the number of patients admitted to the hospitalist services increased by 24%, while admissions to FPs and IM providers declined steadily (Figure). During this time, LOS for hospitalists progressively declined, while LOS for FPs and IM providers increased. Similar trends were observed for measures of mortality, while readmission rates remained constant for FPs, despite a decline observed for other providers.
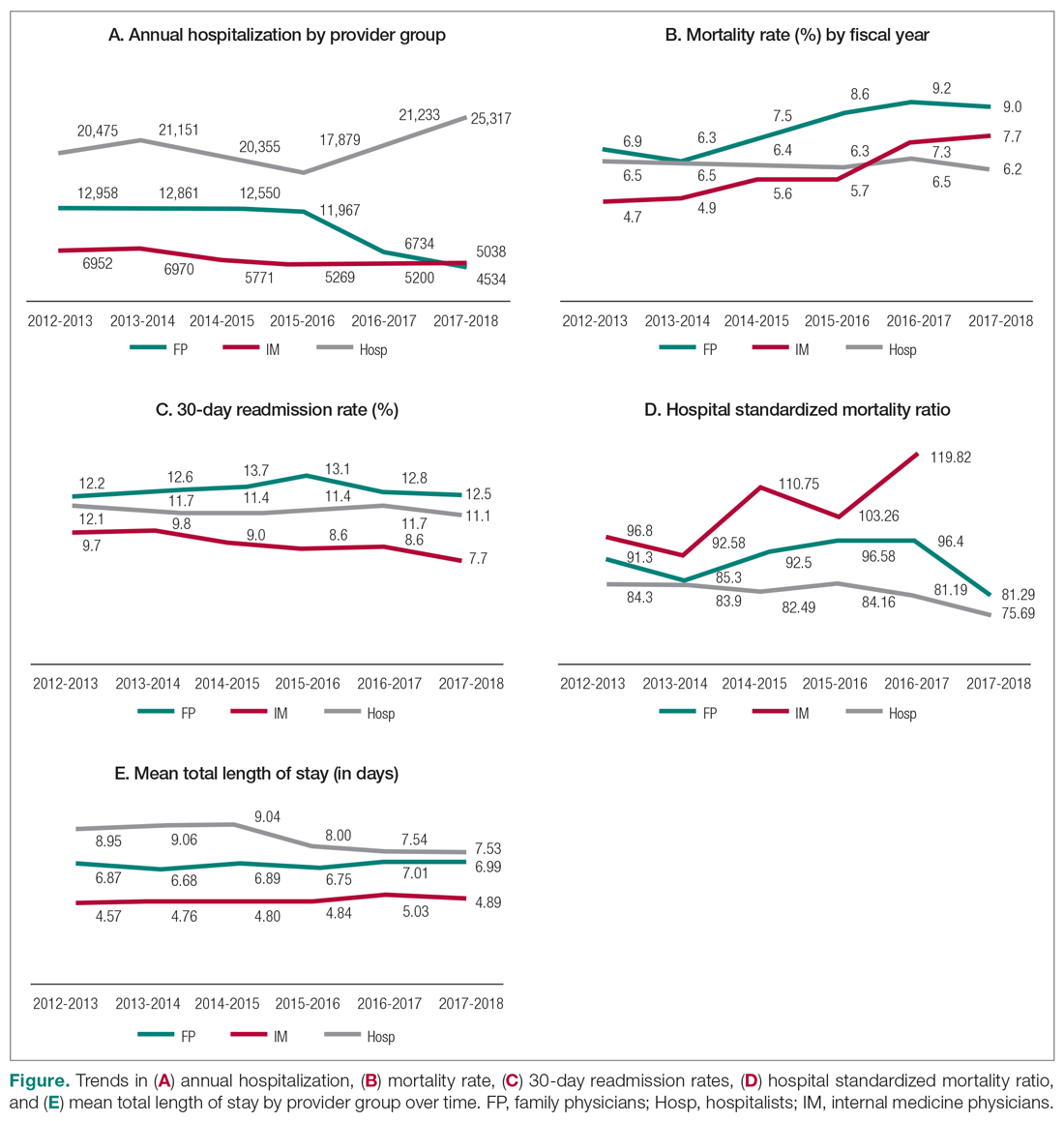
Mortality
Table 3 summarizes the relationship between provider groups and in-hospital mortality (n = 183,779). Controlling for other variables, patients admitted to FP and IM providers had higher odds of mortality when compared to hospitalists (odds ratio [OR] for FPs, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Older age, higher comorbidity level, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher use of hospital resources (as measured by RIWs), longer than expected hospital stay (as measured by conservable days), and male gender were also associated with higher mortality. Similarly, patients receiving palliative care and those who spent at least 1 day in a special care unit (critical care, observation, and monitored care units) also had higher odds of mortality. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching medium facilities and longer hospital stay were associated with lower mortality. Compared to the first year of this analysis, lower mortality rates were observed in subsequent fiscal years. Finally, there appear to be geographic variations in mortality within Fraser Health.
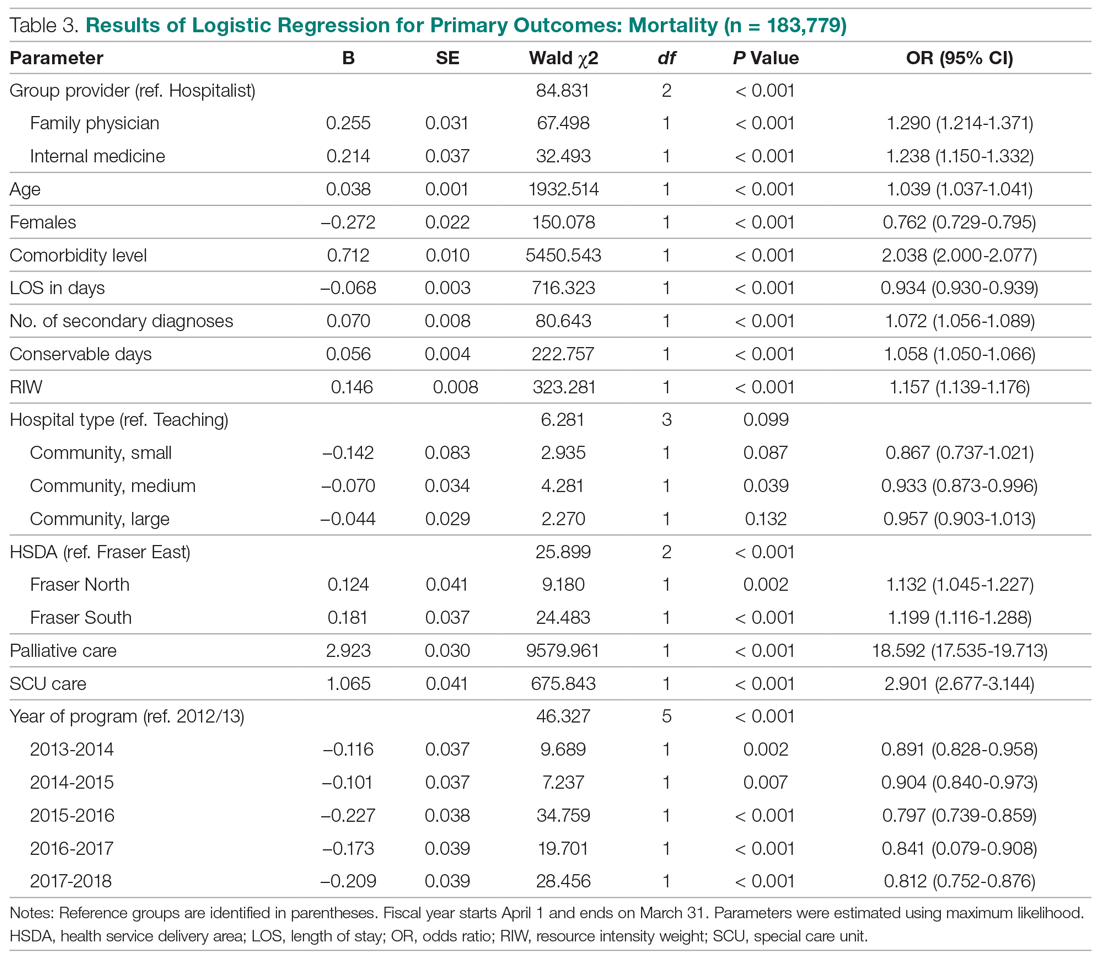
Our analysis of patients with COPD, CHF, and pneumonia showed mixed results (Table 4). Patients admitted to the FP provider group with CHF and pneumonia had higher mortality compared to hospitalists (OR for CHF, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.38-2.27; OR for pneumonia, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.25-1.88), with a similar but nonstatistically significant trend observed for patients with COPD (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.99-1.70). On the other hand, the higher observed mortality associated with the IM provider group in the overall study population only persisted for patients with COPD (OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.94-3.80), with no statistically significant differences for patients with CHF (OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.84-1.65) and pneumonia (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.69-1.25).
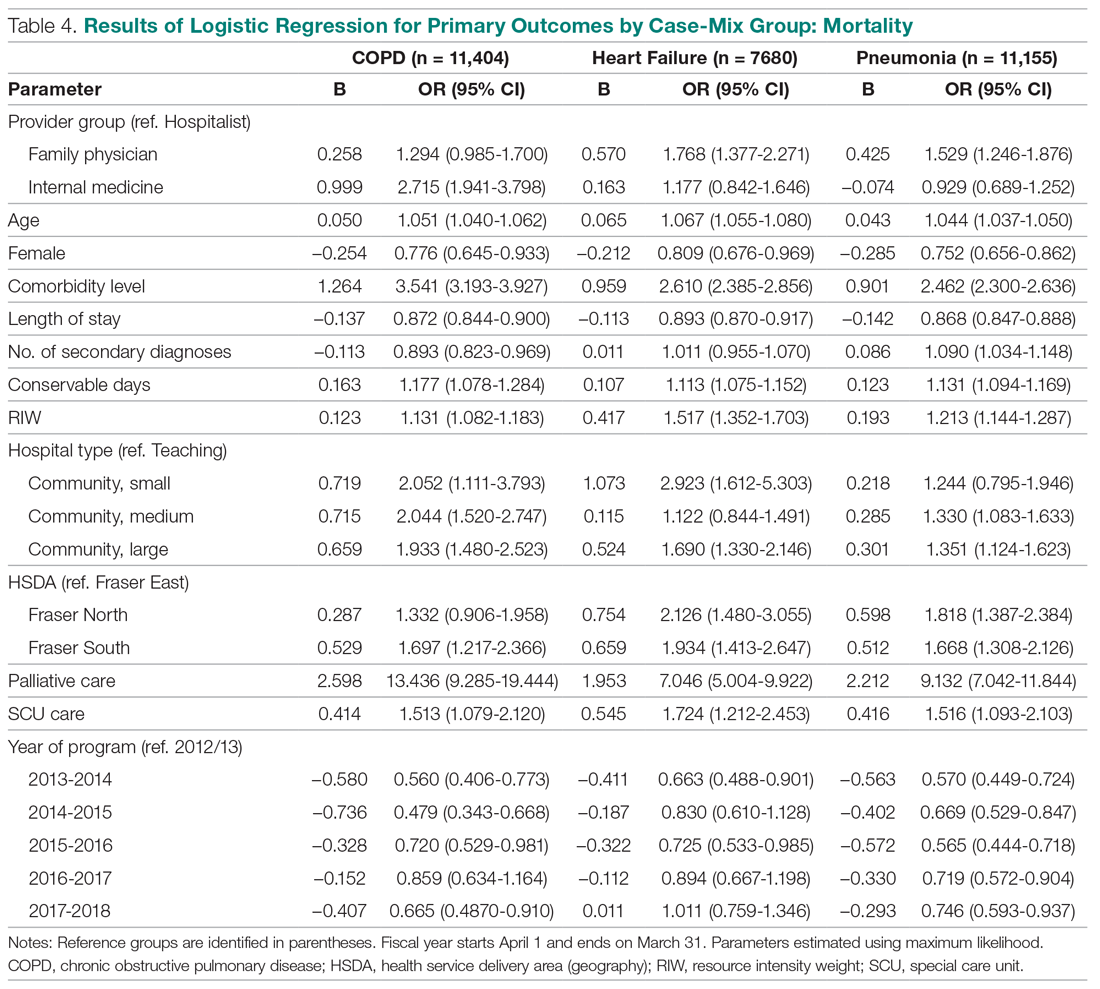
We also studied adjusted mortality as measured by HSMRs. Currently, our Health Information Management system calculates an HSMR value for each patient admitted to our acute care facilities using the methodology developed by CIHI. Prior internal audits demonstrated that our internal calculations closely approximate those reported nationally. Our analysis suggests that over time, HSMR rates for the 3 provider groups have diverged, with patients admitted to IM providers having a higher mortality rate than what would be expected based on the presenting clinical conditions and comorbidity levels (Figure, part D).
Readmission
The results of our multiple logistic regression for readmission are summarized in Table 5 (n = 166,042). The impact of provider group on 30-day readmission is mixed, with higher odds associated with FPs compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.34) and lower odds associated with IM physicians (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Gender and RIW did not show any significant associations, but increasing age, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher comorbidity levels, and longer than expected LOS (as measure by conservable days) were associated with higher odds of readmission. Conversely, longer hospitalization, admission to a large community hospital, palliative status, admission to a special care unit, geography, and fiscal year were associated with lower odds of readmission.
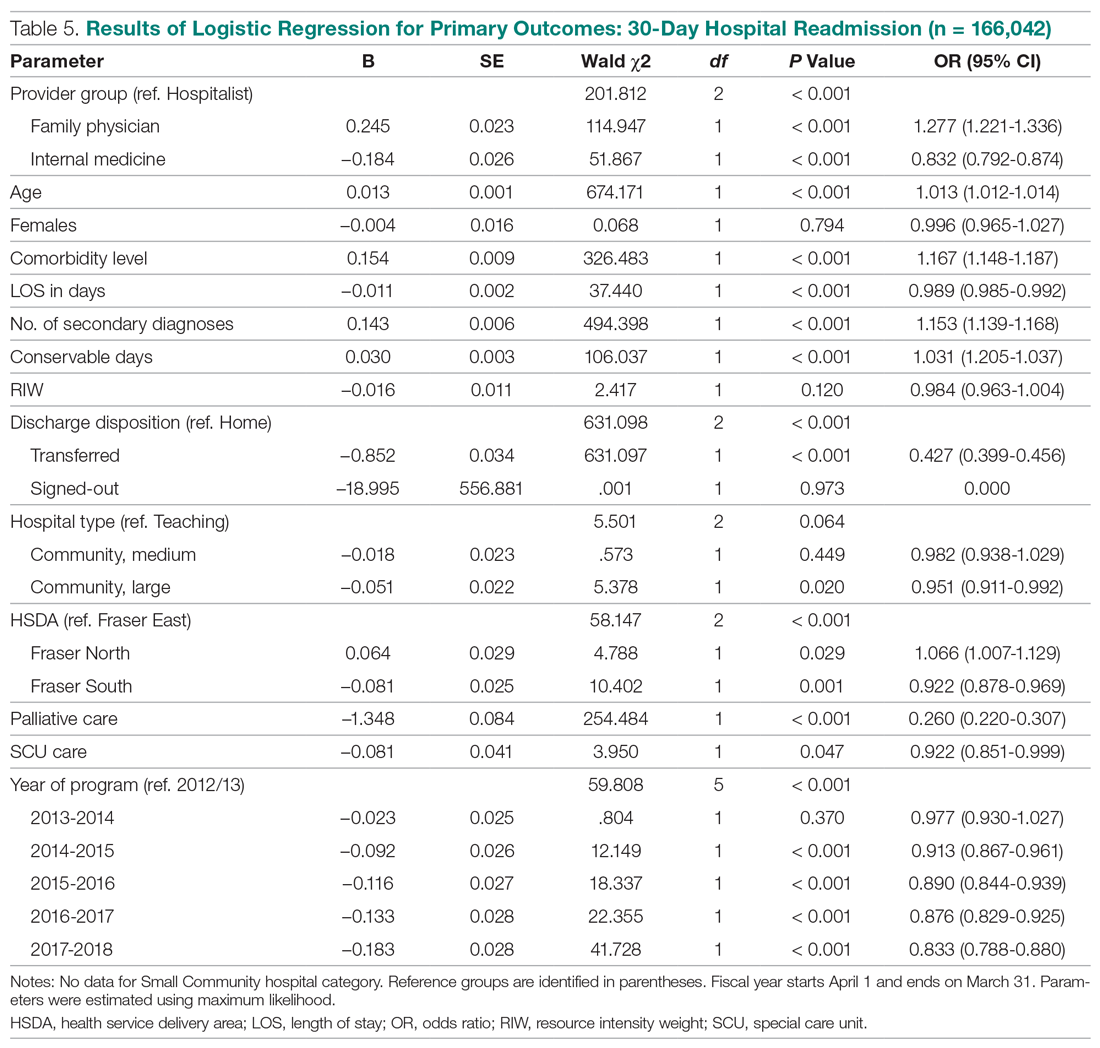
The above differences between provider groups were no longer consistently present when we analyzed patients presenting with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias (Table 6). Only patients admitted to the FP provider group with pneumonia had higher odds of readmission compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54). Conversely, only patients admitted to the IM provider group with CHF showed lower readmission (OR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62-0.92).
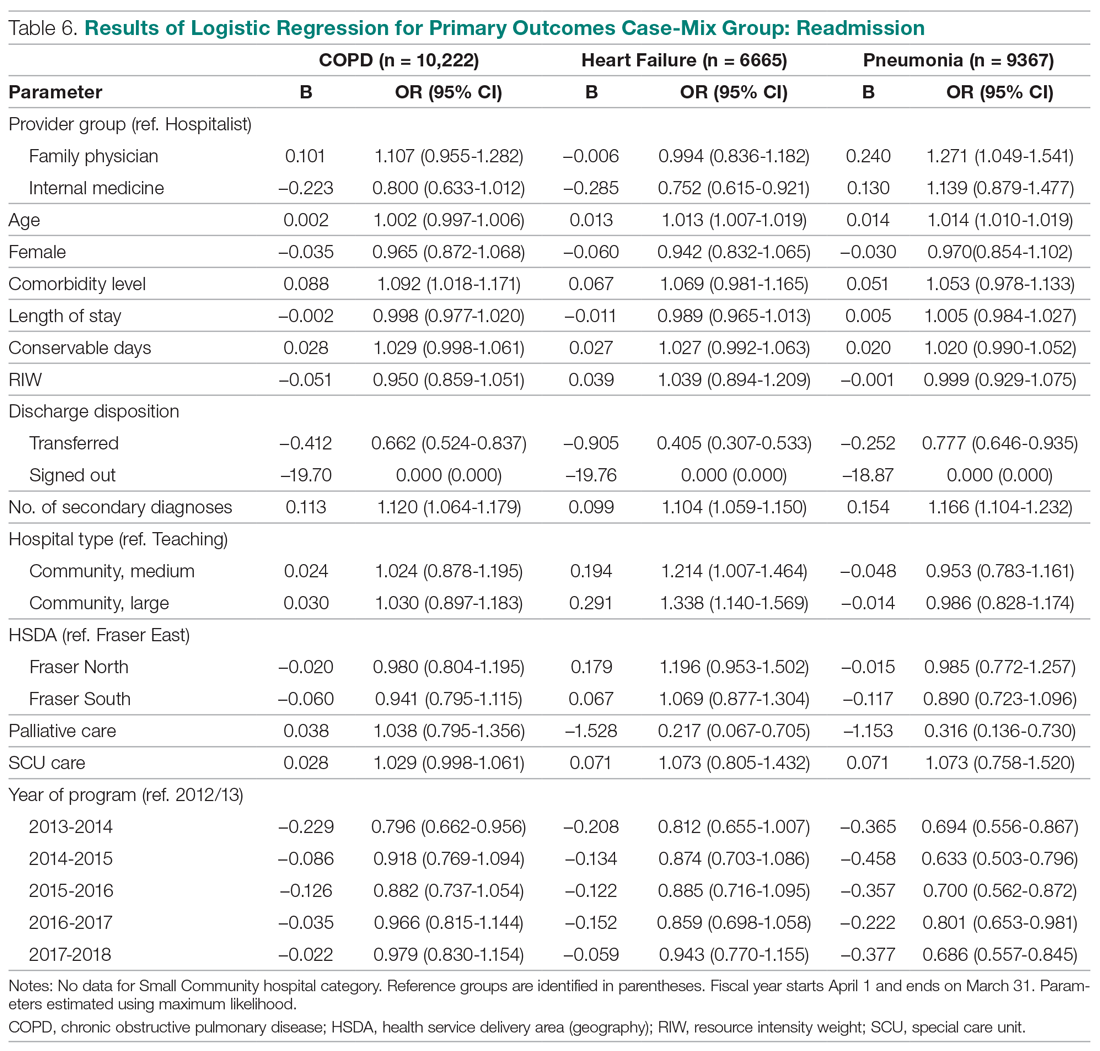
Total LOS
Results using generalized linear regressions for total LOS are presented in Table 7 (n = 183,779). Patients admitted to the IM provider group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to the hospitalist (mean, 7.37 days; 95% CI, 7.26-7.49) and FP (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41) groups, with no significant differences between the latter 2 groups. Older patients, females, patients with higher comorbidity levels or number of secondary diagnoses, higher RIW, palliative patients, and discharge to a facility other than the patient’s home were associated with a significantly longer LOS. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching hospitals and admission to a special care unit was associated with lower LOS.
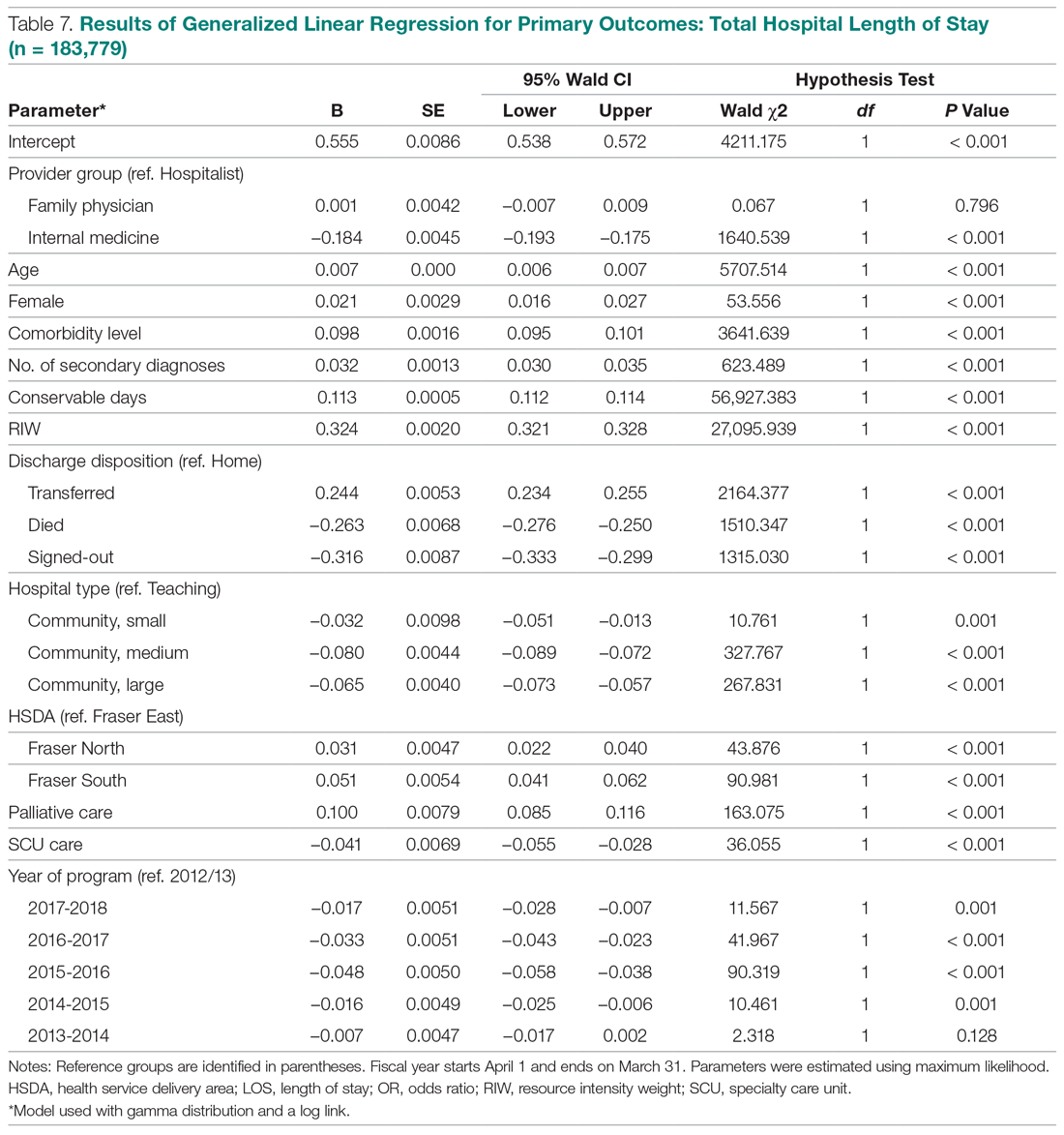
When we compared total LOS for patients admitted with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias, the same differences observed for the broader comparisons persisted: IM patients consistently showed shorter LOS compared to hospitalist patients, while LOS associated with FP patients was similar (Table 8).
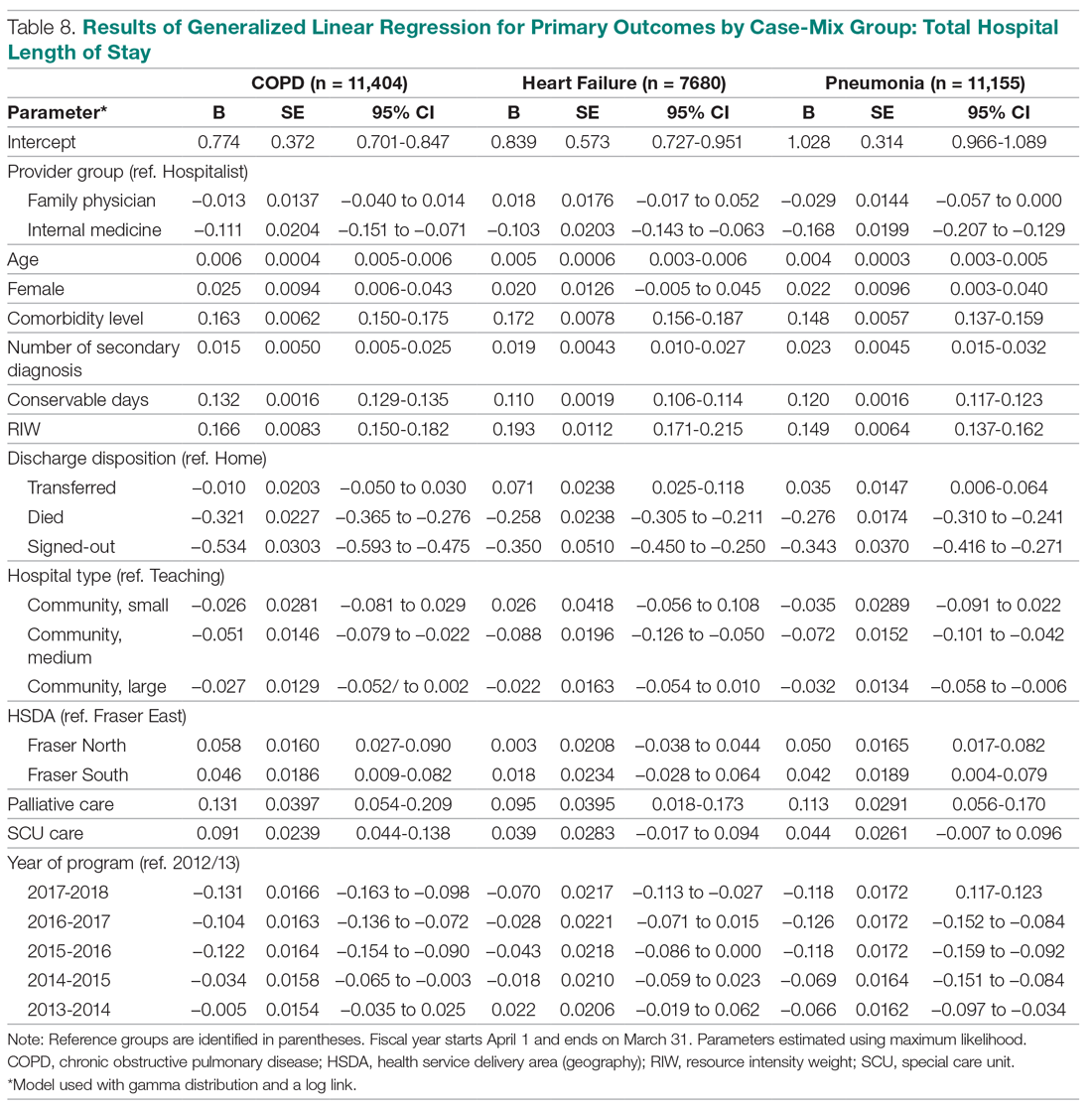
Discussion
To our knowledge, our evaluation is the largest study to date designed to understand outcomes associated with hospitalist care in Canada. Our analyses suggest that patients admitted to our large network of hospitalist services present with clinical conditions that are very similar to those of general medicine patients in other Canadian provinces.28,29 They also show that patients cared for by hospitalists experience lower mortality rates compared to those cared for by FPs. Our findings are similar to previous studies, which have suggested a 12% to 75% reduction in odds of mortality associated with hospitalist care.18,19 These differences persisted even when we focused on patients presenting with specific clinical conditions (CHF, COPD, and pneumonias).
White and colleagues have previously demonstrated that generalist physicians who had higher volumes of inpatient care activity also had lower mortality rates compared to those who cared for hospitalized patients less frequently.19 An association between higher physician caseloads and better outcomes has been established for many surgical and medical conditions.30-32 Given that 85% of hospitalists in our program have post-graduate medical training in family medicine (internal department surveys, data not shown), it is less likely that training background can explain differences in outcomes. Instead, differences in patient volumes and the dedicated focus of hospitalists on acute care are likely more important contributors to lower mortality. In our program, a full-time hospitalist spends an average of 2000 hours annually providing services in the hospital setting. The continuous on-site presence of hospitalists enhances their clinical experience with regards to the management of common medical conditions, and increases their exposure to less common presentations of illnesses. The ability to respond to deteriorating patients in a timely manner may be another factor in explaining the differences in mortality rates between dedicated hospital-based generalist providers and similarly trained physicians with a primarily community-based focus.
In our study, hospitalist care was also broadly associated with lower mortality compared to the IM providers, although these differences were not consistently present when patients with specific diagnoses were compared. This may be partly explained by the relationship between caseload and outcomes, but other factors may also be important. For example, patients admitted by IM providers spend significantly more time in specialized units. They also predominantly present with cardiac conditions, and as such may have higher acuity levels and require more invasive interventions. While this may explain the higher observed mortality, a within-group comparison still suggests higher than expected mortality for IM patients. The HSMR methodology measures actual mortality rates compared to what would be expected based on clinical presentation and baseline population characteristics. Calculating HSMR is highly dependent on proper documentation and chart abstraction,33,34 and it is possible that some of the differences observed are due to incomplete physician documentation. However, a more in-depth analysis of care processes will be required to clarify the observed trends.
Compared to hospitalists, patients cared for by FPs also had higher odds of readmission within 30 days, which is consistent with prior studies.18,19 One of the criticisms of the hospitalist model has been the inherent discontinuity of care that is built into the model, which can contribute to suboptimal transitions of care between the acute and community settings.35 The expectation is that FPs who admit their own patients do not face this challenge, and as a result their patients should be readmitted less frequently after discharge. Our data and those from previous studies do not support this hypothesis. At the same time, when we studied patients with specific clinical diagnoses, only those hospitalized for pneumonias continued to demonstrate higher readmission odds. This suggests that hospital readmission rate is a complex measure that may be influenced by a multitude of hospital and community factors, and may be different for patients who present with different clinical diagnoses. Further research is required to better understand the relationship between provider type and experience with hospital readmission for patients with various clinical presentations.
Unlike the United States, where hospitalist care has been associated with reductions in LOS,26,36 studies in the Canadian health care setting have shown mixed results.17-21 In our evaluation, hospitalist care is not associated with reductions in total LOS compared to care provided by FPs or IM physicians. This could be due to a number of factors. First, unlike FPs, who know their patients, hospitalists may have a more conservative risk tolerance in discharging patients with whom they are not familiar. Similarly, physicians who have trained in IM may have a lower threshold for discharging patients than hospitalists, whose training background is mainly rooted in family medicine.3 Second, discontinuity of care has been associated with longer LOS for hospitalized patients.37,38 Hospitalists generally work for 7- to 10-day rotations. As a result, a patient may see a number of different hospitalists during the same hospital stay, which could nullify any gains in LOS that may be expected from better familiarity with hospital processes. Third, whereas a FP or an internist may only have a few inpatients under their care at any given time, each hospitalist typically cares for 17 to 22 patients every day. Increasing hospitalist workload has been shown to negatively impact LOS and may result in lower efficiency.39 Finally, many patients in our health system who require more time to recuperate or need complex discharge planning are usually transferred to the care of the hospitalist service from other services, or are preferentially admitted to hospitalists from the emergency department. As a result, hospitalists may look after a disproportionately higher number of long-stay patients. Despite all this, hospitalists in our population perform similarly to FPs, regardless of the clinical diagnoses of hospitalized patients.
Our study has a number of notable limitations. First, we used administrative data to conduct our evaluation and could only control for factors that are available in our data systems. As a result, some potential confounders may not have been taken into consideration. For example, our databases do not contain provider characteristics (eg, age, years of clinical experience) that have been deemed to be relevant by White and Glazier.26 Similarly, we did not have all the necessary information about the characteristics of the various MRP programs (eg, number of physicians involved in group practices, the schedule model of community FP call groups) and were not able to account for the potential impact of these on observed outcomes. Second, although our findings mirror prior studies from other parts of Canada, they may not be applicable to hospitalist programs in other jurisdictions or in health systems that are not regionalized or integrated. Third, our IM provider group is heterogeneous, with a number of different IM subspecialties (cardiologists, gastroenterologists, general internists) grouped under the IM category in our database. As a result, comparisons between the IM provider group and the other 2 provider groups, which are more homogenous, should be interpreted with caution.
Finally, we included only patients admitted to facilities in which a hospitalist service existed during the study period. As a result, a medium-size community hospital without a hospitalist service where patients are cared for exclusively by FPs and IM physicians was not included in the comparisons, and in 4 of the 10 facilities included, the number of FP patients was less than 10% of total hospitalized patients at the site (Appendix A). This may have resulted in an under-representation of FP patients.
Conclusion
Debates about the merits of the hospitalist model in Canada continue, and are in part fueled by a paucity of robust evidence about its impact on care outcomes compared to more traditional ways of providing inpatient care. In our evaluation, care provided by hospitalists is associated with lower mortality and readmission rates, despite similar LOS compared with FPs. Hospitalist care is also associated with lower mortality compared to IM providers. Hospitalists also demonstrated progressive improvement over time, with decreasing LOS and mortality rates and a stable readmission rate. Our results suggest that physicians with a focus on inpatient care can have positive contributions to quality and efficiency of care in Canada.
Corresponding author: Vandad Yousefi MD, CCFP, FHM, Fraser Health Authority, 400, 13450–102 Avenue, Surrey BC V3T 0H1, Canada.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Kisuule F, Howell E. Hospital medicine beyond the United States. Int J Gen Med. 2018;11:65-71.
2. Yousefi V, Wilton D. Dedesigning hospital care: learning from the experience of hospital medicine in Canada. J Global Health Care Syst. 2011;1(3).
3. Soong C, Fan E, Howell E, et al. Characteristics of hospitalists and hospitalist programs in the United States and Canada. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2009;16:69-76.
4. Yousefi V. How Canadian hospitalists spend their time - A work-sampling study within a hospital medicine program in Ontario. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2011;18:159-166.
5. Wilson G. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors? No. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1101-1103.
6. Samoil D. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors: Yes? Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1100-1101.
7. Nicolson B. Where’s Marcus Welby when you need him? BC Medical J. 2016;58:63-64.
8. Lemire F. Enhanced skills in family medicine: Update. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:160.
9. Lerner J. Wanting family medicine without primary care. Can Fam Physician. 2018; 64:155.
10. Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine. Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine - Care of the Medical Inpatient. 2015.
11. Redelmeier DA. A Canadian perspective on the American hospitalist movement. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1665-1668.
12. Ghali WA, Greenberg PB, Mejia R, et al. International perspectives on general internal medicine and the case for “globalization” of a discipline. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:197-200.
13. Day A, MacMillan L. Neglect of the inpatient: The hospitalist movement in Canada responds. Hosp Q. 2001;4:36.
14. Sullivan P. Enter the hospitalist: New type of patient creating a new type of specialist. CMAJ. 2000;162:1345-1346.
15. Chan BTB. The declining comprehensiveness of primary care. CMAJ. 2002;166:429-434.
16. Abenhaim HA, Kahn SR, Raffoul J, Becker MR. Program description: A hospitalist-run, medical short-stay unit in a teaching hospital. CMAJ. 2000;163:1477-1480.
17. McGowan B, Nightingale M. The hospitalist program a new specialty on the horizon in acute care medicine a hospital case study. BC Med J. 2003;45:391-394.
18. Yousefi V, Chong C. Does implementation of a hospitalist program in a Canadian community hospital improve measures of quality of care and utilization? An observational comparative analysis of hospitalists vs. traditional care providers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:204.
19. White HL. Assessing the prevalence, penetration and performance of hospital physicians in Ontario: Implications for the quality and efficiency of inpatient care. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing; 2016.
20. Gutierrez CA, Norris M, Chail M. Impact of a newly established hospitalist training program on patient LOS and RIW. Poster presented at the 9th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference, September 23-25, 2011; Banff, Alberta.
21. Seth P, Nicholson K, Habbous S, Menard J. Implementation of a hospitalist medicine model in a full-service community hospital: Examining impact two years post-implementation on health resource use andpatient satisfaction. Poster presented at the 13th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference. 2015; Niagara Falls, Ontario.
22. Lewis S. A system in name only--access, variation, and reform in Canada’s provinces. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:497-500.
23. Lewis S, Kouri D. Regionalization: Making sense of the Canadian experience. Healthcare Papers. 2004;5:12-31.
24. Fraser Health Authority. About Fraser health. www.fraserhealth.ca/about-us/about-fraser-health#.XFJrl9JKiUk. Updated 2018. Accessed January 30, 2019.
25. Canadian Institute for Health Information. CMG+. https://www.cihi.ca/en/cmg. Accessed January 30, 2019.
26. White HL, Glazier RH. Do hospitalist physicians improve the quality of inpatient care delivery? A systematic review of process, efficiency and outcome measures. BMC Med. 2011;9:58.
27. Canadian Institute for Health Information. Hospital standardized mortality ratio technical notes. 2008. www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/hsmr-tech-notes_en_0.pdf.
28. McAlister FA, Youngson E, Bakal JA, et al. Physician experience and outcomes among patients admitted to general internal medicine teaching wards. CMAJ. 2015;187:1041-1048.
29. Verma AA, Guo Y, Kwan JL, et al. Patient characteristics, resource use and outcomes associated with general internal medicine hospital care: The general medicine inpatient initiative (GEMINI) retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open. 2017;5:E849.
30. Morche J, Mathes T, Pieper D. Relationship between surgeon volume and outcomes: A systematic review of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:204.
31. Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:511-520.
32. Chen CH, Chen YH, Lin HC, Lin HC. Association between physician caseload and patient outcome for sepsis treatment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30:556-562.
33. van Gestel YR, Lemmens VE, Lingsma HF, et al. The hospital standardized mortality ratio fallacy: A narrative review. Med Care. 2012;50:662-667.
34. Scott IA, Brand CA, Phelps GE, et al. Using hospital standardised mortality ratios to assess quality of care—proceed with extreme caution. Med J Aust. 2011; 194:645-648.
35. Wachter RM. Hospitalists in the United States -- mission accomplished or work in progress? N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1935-1936.
36. Peterson MC. A systematic review of outcomes and quality measures in adult patients cared for by hospitalists vs nonhospitalists. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84:248-254.
37. Chandra S, Wright SM, Howell EE. The creating incentives and continuity leading to efficiency staffing model: A quality improvement initiative in hospital medicine. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:364-371.
38. Epstein K, Juarez E, Epstein A, et al. The impact of fragmentation of hospitalist care on length of stay. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:335-338.
39. Elliott DJ, Young RS, Brice J, et al. Effect of hospitalist workload on the quality and efficiency of care. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:786-793.
From the Fraser Health Authority, Surrey, British Columbia, Canada.
Abstract
- Objective: To study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to traditional providers.
- Design: Retrospective review of administrative data.
- Setting and participants: Patients from a large integrated health care system in British Columbia in western Canada admitted and cared for by 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018: hospitalists, family physicians (FP), and internal medicine (IM) physicians:
- Measurements: Average total length of stay (LOS), 30-day readmission, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR) were the study outcome measures. Multiple logistic regression or generalized regression were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and outcomes.
- Results: A total of 248,412 hospitalizations were included. Compared to patients admitted to hospitalists, patients admitted to other providers had higher odds of mortality (odds ratio [OR] for FP, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Compared to hospitalist care, FP care was associated with higher readmission (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.33), while IM care showed lower odds of readmission (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Patients admitted to the IM group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to patients admitted to hospitalists (mean, 7.37 days; CI, 7.26-7.49) and FPs (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41). In a subgroup analysis of patients presenting with congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and pneumonia, these general tendencies broadly persisted for mortality and LOS comparisons between FPs and hospitalists, but results were mixed for hospital readmissions.
- Conclusion: Care provided by hospitalists was associated with lower mortality and readmission rates compared with care provided by FPs, despite similar LOS. These findings may reflect differences in volume of services delivered by individual physicians, on-site availability to address urgent medical issues, and evolving specialization of clinical and nonclinical care processes in the acute care setting.
Keywords: hospital medicine; length of stay; readmission; mortality.
The hospitalist model of care has undergone rapid growth globally in recent years.1 The first hospitalist programs in Canada began around the same time as those in the United States and share many similarities in design and operations with their counterparts.2-4 However, unlike in the United States, where the hospitalist model has successfully established itself as an emerging specialty, debates about the merits of the model and its value proposition continue among Canadian observers.5-9
Historically, the type of physicians who acted as the most responsible provider (MRP) in Canadian hospitals depended on setting and geography.10 In large urban areas, groups of general internists or specialists have historically looked after general medicine patients as part of university-affiliated teaching services.11,12 Patients admitted to community hospitals have traditionally been cared for by their own primary care providers, typically general practitioners or family physicians (FPs). In the mid-1990s, many primary care providers in urban centers began to withdraw from inpatient care and primarily focused their practices in the outpatient setting.13-15 Hospitalist programs emerged as health care administrators sought to fill the resulting gap in MRP coverage.2,10
To date, attempts to understand the impact of hospitalist programs in Canada have been limited. A number of early studies aimed to describe16 the role of hospitalists in Canada and suggested improvements in length of stay (LOS) and staff satisfaction.17 However, these studies relied on unadjusted before-after comparisons and lacked methodological rigor to draw robust conclusions. More recently, a few studies have evaluated care outcomes associated with hospitalists using administrative databases, which attempted to control for potential confounding factors.18-21
While these studies are beginning to shed some light on the impact of hospital medicine programs in Canada, there are a number of issues that limit their generalizability. For example, the majority of studies to date focus on hospital medicine programs in Canada’s largest province (Ontario), and most describe experiences from single institutions. Since each of the 13 provincial and territorial governments organizes its health care system differently,22 results from 1 province may not be generalizable to other parts of the country. Moreover, hospitalists in Ontario are more diverse in their training backgrounds, with a larger percentage having trained in general internal medicine (IM), as compared to other parts of Canada, where the majority of hospitalists are overwhelmingly trained as FPs.3
We aimed to study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to “traditional” providers (community-based FPs and IM specialists) in a large integrated health care system in the province of British Columbia in western Canada. The hospital medicine services in this network span a range of community and academic hospitals, and collectively constitute 1 of the largest regional programs in the country. This provides a unique opportunity to understand the impact of hospitalists on outcome measures across a range of acute care institutions.
Methods
Setting and Population
Fraser Health Authority is 1 of 5 regional health authorities in British Columbia that emerged in 2001.23,24 It operates a network of hospitalist programs in 10 of its 12 acute care hospitals. In addition to hospitalists, there are a variable number of “traditional” physician providers who continue to act as MRPs. These include community-based FPs who continue to see their own patients in the hospital, either as part of a solo-practice model or a clinic-based call group. There are also a number of general internists and other subspecialists who accept MRP roles for general medicine patients who may present with higher-acuity conditions. As a result, patients requiring hospitalization due to nonsurgical or noncritical care conditions at each Fraser Health hospital may be cared for by a physician belonging to 1 of 3 groups, depending on local circumstances: an FP, a hospitalist, or an internist.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In order to evaluate comparative outcomes associated with hospitalist care, we included all patients admitted to a physician in each of the 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. We chose this time period for 2 reasons: first, we wanted to ensure comparability over an extended period of time, given the methodological changes implemented in 2009 by the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI), the federal organization in the country responsible for setting standards for health care measures.25 Second, previous internal reviews had suggested that data quality prior to this year was inconsistent. We only considered hospitalizations where patients were admitted to and discharged by the same service, and excluded 2 acute care facilities and 1 free-standing rehabilitation facility without a hospitalist service during this period. We also excluded patients who resided in a location beyond the geographic catchment area of Fraser Health. Further details about data collection are outlined in the Appendix.
Measures
We used the framework developed by White and Glazier26 to inform the selection of our outcome measures, as well as relevant variables that may impact them. This framework proposes that the design of the inpatient care model (structures and processes of care) directly affects care outcomes. The model also proposes that patient and provider attributes can modulate this relationship, and suggests that a comprehensive evaluation of hospitalist performance needs to take these factors into account. We identified average total LOS, 30-day readmission rate, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR)27 as primary outcome measures. HSMR is defined as actual over expected mortality and is measured by CIHI through a formula that takes into account patient illness attributes (eg, the most responsible diagnosis, comorbidity levels) and baseline population mortality rates.27 We chose these measures because they are clinically relevant and easy to obtain and have been utilized in previous similar studies in Canada and the United States.18-21,26
Statistical Analysis
Baseline demographic and clinical differences in patient outcomes were examined using independent t-tests or chi-square tests. Furthermore, baseline differences based on provider groups were explored using analysis of variance or chi-square tests. Multiple logistic regression analyses were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and readmission and mortality, while the relationship between provider groups and hospital LOS was determined with generalized linear regression (using gamma distribution and a log link). Gamma distribution with a log link analysis is appropriate with outcome measures that are positively skewed (eg, hospital LOS). It assumes that data are sampled from an exponential family of distributions, thus mimicking a log-normal distribution, and minimizes estimation bias and standard errors. These analyses were completed while controlling for the effects of age, gender, and other potential confounding factors.
We initially attempted to control for case mix by incorporating case-mix groups (CMGs) in our multivariate analysis. However, we identified 475 CMGs with at least 1 patient in our study population. We then explored the inclusion of major clinical categories (MCCs) that broadly group CMGs into various higher order/organ-system level categories (eg, diseases of the respiratory system); however, we could not aggregate them into sufficiently homogenous groups to be entered into regression models. Instead, we conducted subgroup analyses on patients in our study population who were hospitalized with 1 of the following 3 CMGs: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, n = 11,404 patients), congestive heart failure without coronary angiography (CHF, n = 7680), and pneumonia (itself an aggregate of 3 separate CMGs: aspiration pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, viral/unspecified pneumonia, n = 11,155). We chose these CMGs as they are among the top 8 presentations for all 3 provider groups.
For all outcome measures, we excluded atypical patients (defined by CIHI as those with atypically long stays) and patients who had been transferred between facilities. For the readmission analysis, we also excluded patients who died in the hospital (Appendix A). Data analyses were completed in IBM SPSS, version 21. For all analyses, significance was determined using 2-tailed test and alpha < 0.05.
Ethics
The Fraser Health Department of Research and Evaluation reviewed this project to determine need for formal Ethics Review Board review, and granted an exemption based on institutional guidelines for program evaluations.
Results
A total of 132,178 patients were admitted to and discharged by 1 of the 3 study provider groups during the study period, accounting for a total of 248,412 hospitalizations. After excluding patients cared for in Fraser Health facilities without a hospitalist service and those who resided in a geographic area beyond Fraser Health, a total of 224,214 admissions were included in the final analysis.

Patient Characteristics
The demographic and clinical characteristics of patients by provider group are summarized in Table 1. Patients admitted to IM providers were substantially younger than those admitted to either FPs or hospitalists (61.00 vs 70.86 and 71.22 years, respectively; P < 0.005). However, patients admitted to hospitalists had higher degrees of complexity (as measured by higher comorbidity levels, number of secondary diagnoses, and higher resource intensity weights [RIWs]; P < 000.1 for all comparisons). Overall, the most common CMGs seen by FPs and hospitalists were similar, while IM providers primarily saw patients with cardiac conditions (Table 2).

Trends Over Time
During the study period, the number of patients admitted to the hospitalist services increased by 24%, while admissions to FPs and IM providers declined steadily (Figure). During this time, LOS for hospitalists progressively declined, while LOS for FPs and IM providers increased. Similar trends were observed for measures of mortality, while readmission rates remained constant for FPs, despite a decline observed for other providers.

Mortality
Table 3 summarizes the relationship between provider groups and in-hospital mortality (n = 183,779). Controlling for other variables, patients admitted to FP and IM providers had higher odds of mortality when compared to hospitalists (odds ratio [OR] for FPs, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Older age, higher comorbidity level, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher use of hospital resources (as measured by RIWs), longer than expected hospital stay (as measured by conservable days), and male gender were also associated with higher mortality. Similarly, patients receiving palliative care and those who spent at least 1 day in a special care unit (critical care, observation, and monitored care units) also had higher odds of mortality. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching medium facilities and longer hospital stay were associated with lower mortality. Compared to the first year of this analysis, lower mortality rates were observed in subsequent fiscal years. Finally, there appear to be geographic variations in mortality within Fraser Health.

Our analysis of patients with COPD, CHF, and pneumonia showed mixed results (Table 4). Patients admitted to the FP provider group with CHF and pneumonia had higher mortality compared to hospitalists (OR for CHF, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.38-2.27; OR for pneumonia, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.25-1.88), with a similar but nonstatistically significant trend observed for patients with COPD (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.99-1.70). On the other hand, the higher observed mortality associated with the IM provider group in the overall study population only persisted for patients with COPD (OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.94-3.80), with no statistically significant differences for patients with CHF (OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.84-1.65) and pneumonia (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.69-1.25).

We also studied adjusted mortality as measured by HSMRs. Currently, our Health Information Management system calculates an HSMR value for each patient admitted to our acute care facilities using the methodology developed by CIHI. Prior internal audits demonstrated that our internal calculations closely approximate those reported nationally. Our analysis suggests that over time, HSMR rates for the 3 provider groups have diverged, with patients admitted to IM providers having a higher mortality rate than what would be expected based on the presenting clinical conditions and comorbidity levels (Figure, part D).
Readmission
The results of our multiple logistic regression for readmission are summarized in Table 5 (n = 166,042). The impact of provider group on 30-day readmission is mixed, with higher odds associated with FPs compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.34) and lower odds associated with IM physicians (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Gender and RIW did not show any significant associations, but increasing age, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher comorbidity levels, and longer than expected LOS (as measure by conservable days) were associated with higher odds of readmission. Conversely, longer hospitalization, admission to a large community hospital, palliative status, admission to a special care unit, geography, and fiscal year were associated with lower odds of readmission.

The above differences between provider groups were no longer consistently present when we analyzed patients presenting with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias (Table 6). Only patients admitted to the FP provider group with pneumonia had higher odds of readmission compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54). Conversely, only patients admitted to the IM provider group with CHF showed lower readmission (OR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62-0.92).

Total LOS
Results using generalized linear regressions for total LOS are presented in Table 7 (n = 183,779). Patients admitted to the IM provider group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to the hospitalist (mean, 7.37 days; 95% CI, 7.26-7.49) and FP (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41) groups, with no significant differences between the latter 2 groups. Older patients, females, patients with higher comorbidity levels or number of secondary diagnoses, higher RIW, palliative patients, and discharge to a facility other than the patient’s home were associated with a significantly longer LOS. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching hospitals and admission to a special care unit was associated with lower LOS.

When we compared total LOS for patients admitted with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias, the same differences observed for the broader comparisons persisted: IM patients consistently showed shorter LOS compared to hospitalist patients, while LOS associated with FP patients was similar (Table 8).

Discussion
To our knowledge, our evaluation is the largest study to date designed to understand outcomes associated with hospitalist care in Canada. Our analyses suggest that patients admitted to our large network of hospitalist services present with clinical conditions that are very similar to those of general medicine patients in other Canadian provinces.28,29 They also show that patients cared for by hospitalists experience lower mortality rates compared to those cared for by FPs. Our findings are similar to previous studies, which have suggested a 12% to 75% reduction in odds of mortality associated with hospitalist care.18,19 These differences persisted even when we focused on patients presenting with specific clinical conditions (CHF, COPD, and pneumonias).
White and colleagues have previously demonstrated that generalist physicians who had higher volumes of inpatient care activity also had lower mortality rates compared to those who cared for hospitalized patients less frequently.19 An association between higher physician caseloads and better outcomes has been established for many surgical and medical conditions.30-32 Given that 85% of hospitalists in our program have post-graduate medical training in family medicine (internal department surveys, data not shown), it is less likely that training background can explain differences in outcomes. Instead, differences in patient volumes and the dedicated focus of hospitalists on acute care are likely more important contributors to lower mortality. In our program, a full-time hospitalist spends an average of 2000 hours annually providing services in the hospital setting. The continuous on-site presence of hospitalists enhances their clinical experience with regards to the management of common medical conditions, and increases their exposure to less common presentations of illnesses. The ability to respond to deteriorating patients in a timely manner may be another factor in explaining the differences in mortality rates between dedicated hospital-based generalist providers and similarly trained physicians with a primarily community-based focus.
In our study, hospitalist care was also broadly associated with lower mortality compared to the IM providers, although these differences were not consistently present when patients with specific diagnoses were compared. This may be partly explained by the relationship between caseload and outcomes, but other factors may also be important. For example, patients admitted by IM providers spend significantly more time in specialized units. They also predominantly present with cardiac conditions, and as such may have higher acuity levels and require more invasive interventions. While this may explain the higher observed mortality, a within-group comparison still suggests higher than expected mortality for IM patients. The HSMR methodology measures actual mortality rates compared to what would be expected based on clinical presentation and baseline population characteristics. Calculating HSMR is highly dependent on proper documentation and chart abstraction,33,34 and it is possible that some of the differences observed are due to incomplete physician documentation. However, a more in-depth analysis of care processes will be required to clarify the observed trends.
Compared to hospitalists, patients cared for by FPs also had higher odds of readmission within 30 days, which is consistent with prior studies.18,19 One of the criticisms of the hospitalist model has been the inherent discontinuity of care that is built into the model, which can contribute to suboptimal transitions of care between the acute and community settings.35 The expectation is that FPs who admit their own patients do not face this challenge, and as a result their patients should be readmitted less frequently after discharge. Our data and those from previous studies do not support this hypothesis. At the same time, when we studied patients with specific clinical diagnoses, only those hospitalized for pneumonias continued to demonstrate higher readmission odds. This suggests that hospital readmission rate is a complex measure that may be influenced by a multitude of hospital and community factors, and may be different for patients who present with different clinical diagnoses. Further research is required to better understand the relationship between provider type and experience with hospital readmission for patients with various clinical presentations.
Unlike the United States, where hospitalist care has been associated with reductions in LOS,26,36 studies in the Canadian health care setting have shown mixed results.17-21 In our evaluation, hospitalist care is not associated with reductions in total LOS compared to care provided by FPs or IM physicians. This could be due to a number of factors. First, unlike FPs, who know their patients, hospitalists may have a more conservative risk tolerance in discharging patients with whom they are not familiar. Similarly, physicians who have trained in IM may have a lower threshold for discharging patients than hospitalists, whose training background is mainly rooted in family medicine.3 Second, discontinuity of care has been associated with longer LOS for hospitalized patients.37,38 Hospitalists generally work for 7- to 10-day rotations. As a result, a patient may see a number of different hospitalists during the same hospital stay, which could nullify any gains in LOS that may be expected from better familiarity with hospital processes. Third, whereas a FP or an internist may only have a few inpatients under their care at any given time, each hospitalist typically cares for 17 to 22 patients every day. Increasing hospitalist workload has been shown to negatively impact LOS and may result in lower efficiency.39 Finally, many patients in our health system who require more time to recuperate or need complex discharge planning are usually transferred to the care of the hospitalist service from other services, or are preferentially admitted to hospitalists from the emergency department. As a result, hospitalists may look after a disproportionately higher number of long-stay patients. Despite all this, hospitalists in our population perform similarly to FPs, regardless of the clinical diagnoses of hospitalized patients.
Our study has a number of notable limitations. First, we used administrative data to conduct our evaluation and could only control for factors that are available in our data systems. As a result, some potential confounders may not have been taken into consideration. For example, our databases do not contain provider characteristics (eg, age, years of clinical experience) that have been deemed to be relevant by White and Glazier.26 Similarly, we did not have all the necessary information about the characteristics of the various MRP programs (eg, number of physicians involved in group practices, the schedule model of community FP call groups) and were not able to account for the potential impact of these on observed outcomes. Second, although our findings mirror prior studies from other parts of Canada, they may not be applicable to hospitalist programs in other jurisdictions or in health systems that are not regionalized or integrated. Third, our IM provider group is heterogeneous, with a number of different IM subspecialties (cardiologists, gastroenterologists, general internists) grouped under the IM category in our database. As a result, comparisons between the IM provider group and the other 2 provider groups, which are more homogenous, should be interpreted with caution.
Finally, we included only patients admitted to facilities in which a hospitalist service existed during the study period. As a result, a medium-size community hospital without a hospitalist service where patients are cared for exclusively by FPs and IM physicians was not included in the comparisons, and in 4 of the 10 facilities included, the number of FP patients was less than 10% of total hospitalized patients at the site (Appendix A). This may have resulted in an under-representation of FP patients.
Conclusion
Debates about the merits of the hospitalist model in Canada continue, and are in part fueled by a paucity of robust evidence about its impact on care outcomes compared to more traditional ways of providing inpatient care. In our evaluation, care provided by hospitalists is associated with lower mortality and readmission rates, despite similar LOS compared with FPs. Hospitalist care is also associated with lower mortality compared to IM providers. Hospitalists also demonstrated progressive improvement over time, with decreasing LOS and mortality rates and a stable readmission rate. Our results suggest that physicians with a focus on inpatient care can have positive contributions to quality and efficiency of care in Canada.
Corresponding author: Vandad Yousefi MD, CCFP, FHM, Fraser Health Authority, 400, 13450–102 Avenue, Surrey BC V3T 0H1, Canada.
Financial disclosures: None.
From the Fraser Health Authority, Surrey, British Columbia, Canada.
Abstract
- Objective: To study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to traditional providers.
- Design: Retrospective review of administrative data.
- Setting and participants: Patients from a large integrated health care system in British Columbia in western Canada admitted and cared for by 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018: hospitalists, family physicians (FP), and internal medicine (IM) physicians:
- Measurements: Average total length of stay (LOS), 30-day readmission, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR) were the study outcome measures. Multiple logistic regression or generalized regression were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and outcomes.
- Results: A total of 248,412 hospitalizations were included. Compared to patients admitted to hospitalists, patients admitted to other providers had higher odds of mortality (odds ratio [OR] for FP, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Compared to hospitalist care, FP care was associated with higher readmission (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.33), while IM care showed lower odds of readmission (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Patients admitted to the IM group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to patients admitted to hospitalists (mean, 7.37 days; CI, 7.26-7.49) and FPs (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41). In a subgroup analysis of patients presenting with congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and pneumonia, these general tendencies broadly persisted for mortality and LOS comparisons between FPs and hospitalists, but results were mixed for hospital readmissions.
- Conclusion: Care provided by hospitalists was associated with lower mortality and readmission rates compared with care provided by FPs, despite similar LOS. These findings may reflect differences in volume of services delivered by individual physicians, on-site availability to address urgent medical issues, and evolving specialization of clinical and nonclinical care processes in the acute care setting.
Keywords: hospital medicine; length of stay; readmission; mortality.
The hospitalist model of care has undergone rapid growth globally in recent years.1 The first hospitalist programs in Canada began around the same time as those in the United States and share many similarities in design and operations with their counterparts.2-4 However, unlike in the United States, where the hospitalist model has successfully established itself as an emerging specialty, debates about the merits of the model and its value proposition continue among Canadian observers.5-9
Historically, the type of physicians who acted as the most responsible provider (MRP) in Canadian hospitals depended on setting and geography.10 In large urban areas, groups of general internists or specialists have historically looked after general medicine patients as part of university-affiliated teaching services.11,12 Patients admitted to community hospitals have traditionally been cared for by their own primary care providers, typically general practitioners or family physicians (FPs). In the mid-1990s, many primary care providers in urban centers began to withdraw from inpatient care and primarily focused their practices in the outpatient setting.13-15 Hospitalist programs emerged as health care administrators sought to fill the resulting gap in MRP coverage.2,10
To date, attempts to understand the impact of hospitalist programs in Canada have been limited. A number of early studies aimed to describe16 the role of hospitalists in Canada and suggested improvements in length of stay (LOS) and staff satisfaction.17 However, these studies relied on unadjusted before-after comparisons and lacked methodological rigor to draw robust conclusions. More recently, a few studies have evaluated care outcomes associated with hospitalists using administrative databases, which attempted to control for potential confounding factors.18-21
While these studies are beginning to shed some light on the impact of hospital medicine programs in Canada, there are a number of issues that limit their generalizability. For example, the majority of studies to date focus on hospital medicine programs in Canada’s largest province (Ontario), and most describe experiences from single institutions. Since each of the 13 provincial and territorial governments organizes its health care system differently,22 results from 1 province may not be generalizable to other parts of the country. Moreover, hospitalists in Ontario are more diverse in their training backgrounds, with a larger percentage having trained in general internal medicine (IM), as compared to other parts of Canada, where the majority of hospitalists are overwhelmingly trained as FPs.3
We aimed to study care outcomes associated with a network of hospitalist services compared to “traditional” providers (community-based FPs and IM specialists) in a large integrated health care system in the province of British Columbia in western Canada. The hospital medicine services in this network span a range of community and academic hospitals, and collectively constitute 1 of the largest regional programs in the country. This provides a unique opportunity to understand the impact of hospitalists on outcome measures across a range of acute care institutions.
Methods
Setting and Population
Fraser Health Authority is 1 of 5 regional health authorities in British Columbia that emerged in 2001.23,24 It operates a network of hospitalist programs in 10 of its 12 acute care hospitals. In addition to hospitalists, there are a variable number of “traditional” physician providers who continue to act as MRPs. These include community-based FPs who continue to see their own patients in the hospital, either as part of a solo-practice model or a clinic-based call group. There are also a number of general internists and other subspecialists who accept MRP roles for general medicine patients who may present with higher-acuity conditions. As a result, patients requiring hospitalization due to nonsurgical or noncritical care conditions at each Fraser Health hospital may be cared for by a physician belonging to 1 of 3 groups, depending on local circumstances: an FP, a hospitalist, or an internist.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In order to evaluate comparative outcomes associated with hospitalist care, we included all patients admitted to a physician in each of the 3 provider groups between April 1, 2012, and March 31, 2018. We chose this time period for 2 reasons: first, we wanted to ensure comparability over an extended period of time, given the methodological changes implemented in 2009 by the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI), the federal organization in the country responsible for setting standards for health care measures.25 Second, previous internal reviews had suggested that data quality prior to this year was inconsistent. We only considered hospitalizations where patients were admitted to and discharged by the same service, and excluded 2 acute care facilities and 1 free-standing rehabilitation facility without a hospitalist service during this period. We also excluded patients who resided in a location beyond the geographic catchment area of Fraser Health. Further details about data collection are outlined in the Appendix.
Measures
We used the framework developed by White and Glazier26 to inform the selection of our outcome measures, as well as relevant variables that may impact them. This framework proposes that the design of the inpatient care model (structures and processes of care) directly affects care outcomes. The model also proposes that patient and provider attributes can modulate this relationship, and suggests that a comprehensive evaluation of hospitalist performance needs to take these factors into account. We identified average total LOS, 30-day readmission rate, in-hospital mortality, and hospital standardized mortality ratio (HSMR)27 as primary outcome measures. HSMR is defined as actual over expected mortality and is measured by CIHI through a formula that takes into account patient illness attributes (eg, the most responsible diagnosis, comorbidity levels) and baseline population mortality rates.27 We chose these measures because they are clinically relevant and easy to obtain and have been utilized in previous similar studies in Canada and the United States.18-21,26
Statistical Analysis
Baseline demographic and clinical differences in patient outcomes were examined using independent t-tests or chi-square tests. Furthermore, baseline differences based on provider groups were explored using analysis of variance or chi-square tests. Multiple logistic regression analyses were completed to determine the relationship between provider groups and readmission and mortality, while the relationship between provider groups and hospital LOS was determined with generalized linear regression (using gamma distribution and a log link). Gamma distribution with a log link analysis is appropriate with outcome measures that are positively skewed (eg, hospital LOS). It assumes that data are sampled from an exponential family of distributions, thus mimicking a log-normal distribution, and minimizes estimation bias and standard errors. These analyses were completed while controlling for the effects of age, gender, and other potential confounding factors.
We initially attempted to control for case mix by incorporating case-mix groups (CMGs) in our multivariate analysis. However, we identified 475 CMGs with at least 1 patient in our study population. We then explored the inclusion of major clinical categories (MCCs) that broadly group CMGs into various higher order/organ-system level categories (eg, diseases of the respiratory system); however, we could not aggregate them into sufficiently homogenous groups to be entered into regression models. Instead, we conducted subgroup analyses on patients in our study population who were hospitalized with 1 of the following 3 CMGs: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, n = 11,404 patients), congestive heart failure without coronary angiography (CHF, n = 7680), and pneumonia (itself an aggregate of 3 separate CMGs: aspiration pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, viral/unspecified pneumonia, n = 11,155). We chose these CMGs as they are among the top 8 presentations for all 3 provider groups.
For all outcome measures, we excluded atypical patients (defined by CIHI as those with atypically long stays) and patients who had been transferred between facilities. For the readmission analysis, we also excluded patients who died in the hospital (Appendix A). Data analyses were completed in IBM SPSS, version 21. For all analyses, significance was determined using 2-tailed test and alpha < 0.05.
Ethics
The Fraser Health Department of Research and Evaluation reviewed this project to determine need for formal Ethics Review Board review, and granted an exemption based on institutional guidelines for program evaluations.
Results
A total of 132,178 patients were admitted to and discharged by 1 of the 3 study provider groups during the study period, accounting for a total of 248,412 hospitalizations. After excluding patients cared for in Fraser Health facilities without a hospitalist service and those who resided in a geographic area beyond Fraser Health, a total of 224,214 admissions were included in the final analysis.

Patient Characteristics
The demographic and clinical characteristics of patients by provider group are summarized in Table 1. Patients admitted to IM providers were substantially younger than those admitted to either FPs or hospitalists (61.00 vs 70.86 and 71.22 years, respectively; P < 0.005). However, patients admitted to hospitalists had higher degrees of complexity (as measured by higher comorbidity levels, number of secondary diagnoses, and higher resource intensity weights [RIWs]; P < 000.1 for all comparisons). Overall, the most common CMGs seen by FPs and hospitalists were similar, while IM providers primarily saw patients with cardiac conditions (Table 2).

Trends Over Time
During the study period, the number of patients admitted to the hospitalist services increased by 24%, while admissions to FPs and IM providers declined steadily (Figure). During this time, LOS for hospitalists progressively declined, while LOS for FPs and IM providers increased. Similar trends were observed for measures of mortality, while readmission rates remained constant for FPs, despite a decline observed for other providers.

Mortality
Table 3 summarizes the relationship between provider groups and in-hospital mortality (n = 183,779). Controlling for other variables, patients admitted to FP and IM providers had higher odds of mortality when compared to hospitalists (odds ratio [OR] for FPs, 1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.21-1.37; OR for IM, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.15-1.33). Older age, higher comorbidity level, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher use of hospital resources (as measured by RIWs), longer than expected hospital stay (as measured by conservable days), and male gender were also associated with higher mortality. Similarly, patients receiving palliative care and those who spent at least 1 day in a special care unit (critical care, observation, and monitored care units) also had higher odds of mortality. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching medium facilities and longer hospital stay were associated with lower mortality. Compared to the first year of this analysis, lower mortality rates were observed in subsequent fiscal years. Finally, there appear to be geographic variations in mortality within Fraser Health.

Our analysis of patients with COPD, CHF, and pneumonia showed mixed results (Table 4). Patients admitted to the FP provider group with CHF and pneumonia had higher mortality compared to hospitalists (OR for CHF, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.38-2.27; OR for pneumonia, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.25-1.88), with a similar but nonstatistically significant trend observed for patients with COPD (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.99-1.70). On the other hand, the higher observed mortality associated with the IM provider group in the overall study population only persisted for patients with COPD (OR, 2.71; 95% CI, 1.94-3.80), with no statistically significant differences for patients with CHF (OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.84-1.65) and pneumonia (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.69-1.25).

We also studied adjusted mortality as measured by HSMRs. Currently, our Health Information Management system calculates an HSMR value for each patient admitted to our acute care facilities using the methodology developed by CIHI. Prior internal audits demonstrated that our internal calculations closely approximate those reported nationally. Our analysis suggests that over time, HSMR rates for the 3 provider groups have diverged, with patients admitted to IM providers having a higher mortality rate than what would be expected based on the presenting clinical conditions and comorbidity levels (Figure, part D).
Readmission
The results of our multiple logistic regression for readmission are summarized in Table 5 (n = 166,042). The impact of provider group on 30-day readmission is mixed, with higher odds associated with FPs compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.22-1.34) and lower odds associated with IM physicians (OR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.79-0.87). Gender and RIW did not show any significant associations, but increasing age, higher number of secondary diagnoses, higher comorbidity levels, and longer than expected LOS (as measure by conservable days) were associated with higher odds of readmission. Conversely, longer hospitalization, admission to a large community hospital, palliative status, admission to a special care unit, geography, and fiscal year were associated with lower odds of readmission.

The above differences between provider groups were no longer consistently present when we analyzed patients presenting with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias (Table 6). Only patients admitted to the FP provider group with pneumonia had higher odds of readmission compared to hospitalists (OR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.05-1.54). Conversely, only patients admitted to the IM provider group with CHF showed lower readmission (OR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62-0.92).

Total LOS
Results using generalized linear regressions for total LOS are presented in Table 7 (n = 183,779). Patients admitted to the IM provider group had significantly lower total LOS (mean, 5.13 days; 95% CI, 5.04-5.21) compared to the hospitalist (mean, 7.37 days; 95% CI, 7.26-7.49) and FP (mean, 7.30 days; 95% CI, 7.19-7.41) groups, with no significant differences between the latter 2 groups. Older patients, females, patients with higher comorbidity levels or number of secondary diagnoses, higher RIW, palliative patients, and discharge to a facility other than the patient’s home were associated with a significantly longer LOS. On the other hand, admission to nonteaching hospitals and admission to a special care unit was associated with lower LOS.

When we compared total LOS for patients admitted with COPD, CHF, and pneumonias, the same differences observed for the broader comparisons persisted: IM patients consistently showed shorter LOS compared to hospitalist patients, while LOS associated with FP patients was similar (Table 8).

Discussion
To our knowledge, our evaluation is the largest study to date designed to understand outcomes associated with hospitalist care in Canada. Our analyses suggest that patients admitted to our large network of hospitalist services present with clinical conditions that are very similar to those of general medicine patients in other Canadian provinces.28,29 They also show that patients cared for by hospitalists experience lower mortality rates compared to those cared for by FPs. Our findings are similar to previous studies, which have suggested a 12% to 75% reduction in odds of mortality associated with hospitalist care.18,19 These differences persisted even when we focused on patients presenting with specific clinical conditions (CHF, COPD, and pneumonias).
White and colleagues have previously demonstrated that generalist physicians who had higher volumes of inpatient care activity also had lower mortality rates compared to those who cared for hospitalized patients less frequently.19 An association between higher physician caseloads and better outcomes has been established for many surgical and medical conditions.30-32 Given that 85% of hospitalists in our program have post-graduate medical training in family medicine (internal department surveys, data not shown), it is less likely that training background can explain differences in outcomes. Instead, differences in patient volumes and the dedicated focus of hospitalists on acute care are likely more important contributors to lower mortality. In our program, a full-time hospitalist spends an average of 2000 hours annually providing services in the hospital setting. The continuous on-site presence of hospitalists enhances their clinical experience with regards to the management of common medical conditions, and increases their exposure to less common presentations of illnesses. The ability to respond to deteriorating patients in a timely manner may be another factor in explaining the differences in mortality rates between dedicated hospital-based generalist providers and similarly trained physicians with a primarily community-based focus.
In our study, hospitalist care was also broadly associated with lower mortality compared to the IM providers, although these differences were not consistently present when patients with specific diagnoses were compared. This may be partly explained by the relationship between caseload and outcomes, but other factors may also be important. For example, patients admitted by IM providers spend significantly more time in specialized units. They also predominantly present with cardiac conditions, and as such may have higher acuity levels and require more invasive interventions. While this may explain the higher observed mortality, a within-group comparison still suggests higher than expected mortality for IM patients. The HSMR methodology measures actual mortality rates compared to what would be expected based on clinical presentation and baseline population characteristics. Calculating HSMR is highly dependent on proper documentation and chart abstraction,33,34 and it is possible that some of the differences observed are due to incomplete physician documentation. However, a more in-depth analysis of care processes will be required to clarify the observed trends.
Compared to hospitalists, patients cared for by FPs also had higher odds of readmission within 30 days, which is consistent with prior studies.18,19 One of the criticisms of the hospitalist model has been the inherent discontinuity of care that is built into the model, which can contribute to suboptimal transitions of care between the acute and community settings.35 The expectation is that FPs who admit their own patients do not face this challenge, and as a result their patients should be readmitted less frequently after discharge. Our data and those from previous studies do not support this hypothesis. At the same time, when we studied patients with specific clinical diagnoses, only those hospitalized for pneumonias continued to demonstrate higher readmission odds. This suggests that hospital readmission rate is a complex measure that may be influenced by a multitude of hospital and community factors, and may be different for patients who present with different clinical diagnoses. Further research is required to better understand the relationship between provider type and experience with hospital readmission for patients with various clinical presentations.
Unlike the United States, where hospitalist care has been associated with reductions in LOS,26,36 studies in the Canadian health care setting have shown mixed results.17-21 In our evaluation, hospitalist care is not associated with reductions in total LOS compared to care provided by FPs or IM physicians. This could be due to a number of factors. First, unlike FPs, who know their patients, hospitalists may have a more conservative risk tolerance in discharging patients with whom they are not familiar. Similarly, physicians who have trained in IM may have a lower threshold for discharging patients than hospitalists, whose training background is mainly rooted in family medicine.3 Second, discontinuity of care has been associated with longer LOS for hospitalized patients.37,38 Hospitalists generally work for 7- to 10-day rotations. As a result, a patient may see a number of different hospitalists during the same hospital stay, which could nullify any gains in LOS that may be expected from better familiarity with hospital processes. Third, whereas a FP or an internist may only have a few inpatients under their care at any given time, each hospitalist typically cares for 17 to 22 patients every day. Increasing hospitalist workload has been shown to negatively impact LOS and may result in lower efficiency.39 Finally, many patients in our health system who require more time to recuperate or need complex discharge planning are usually transferred to the care of the hospitalist service from other services, or are preferentially admitted to hospitalists from the emergency department. As a result, hospitalists may look after a disproportionately higher number of long-stay patients. Despite all this, hospitalists in our population perform similarly to FPs, regardless of the clinical diagnoses of hospitalized patients.
Our study has a number of notable limitations. First, we used administrative data to conduct our evaluation and could only control for factors that are available in our data systems. As a result, some potential confounders may not have been taken into consideration. For example, our databases do not contain provider characteristics (eg, age, years of clinical experience) that have been deemed to be relevant by White and Glazier.26 Similarly, we did not have all the necessary information about the characteristics of the various MRP programs (eg, number of physicians involved in group practices, the schedule model of community FP call groups) and were not able to account for the potential impact of these on observed outcomes. Second, although our findings mirror prior studies from other parts of Canada, they may not be applicable to hospitalist programs in other jurisdictions or in health systems that are not regionalized or integrated. Third, our IM provider group is heterogeneous, with a number of different IM subspecialties (cardiologists, gastroenterologists, general internists) grouped under the IM category in our database. As a result, comparisons between the IM provider group and the other 2 provider groups, which are more homogenous, should be interpreted with caution.
Finally, we included only patients admitted to facilities in which a hospitalist service existed during the study period. As a result, a medium-size community hospital without a hospitalist service where patients are cared for exclusively by FPs and IM physicians was not included in the comparisons, and in 4 of the 10 facilities included, the number of FP patients was less than 10% of total hospitalized patients at the site (Appendix A). This may have resulted in an under-representation of FP patients.
Conclusion
Debates about the merits of the hospitalist model in Canada continue, and are in part fueled by a paucity of robust evidence about its impact on care outcomes compared to more traditional ways of providing inpatient care. In our evaluation, care provided by hospitalists is associated with lower mortality and readmission rates, despite similar LOS compared with FPs. Hospitalist care is also associated with lower mortality compared to IM providers. Hospitalists also demonstrated progressive improvement over time, with decreasing LOS and mortality rates and a stable readmission rate. Our results suggest that physicians with a focus on inpatient care can have positive contributions to quality and efficiency of care in Canada.
Corresponding author: Vandad Yousefi MD, CCFP, FHM, Fraser Health Authority, 400, 13450–102 Avenue, Surrey BC V3T 0H1, Canada.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Kisuule F, Howell E. Hospital medicine beyond the United States. Int J Gen Med. 2018;11:65-71.
2. Yousefi V, Wilton D. Dedesigning hospital care: learning from the experience of hospital medicine in Canada. J Global Health Care Syst. 2011;1(3).
3. Soong C, Fan E, Howell E, et al. Characteristics of hospitalists and hospitalist programs in the United States and Canada. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2009;16:69-76.
4. Yousefi V. How Canadian hospitalists spend their time - A work-sampling study within a hospital medicine program in Ontario. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2011;18:159-166.
5. Wilson G. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors? No. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1101-1103.
6. Samoil D. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors: Yes? Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1100-1101.
7. Nicolson B. Where’s Marcus Welby when you need him? BC Medical J. 2016;58:63-64.
8. Lemire F. Enhanced skills in family medicine: Update. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:160.
9. Lerner J. Wanting family medicine without primary care. Can Fam Physician. 2018; 64:155.
10. Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine. Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine - Care of the Medical Inpatient. 2015.
11. Redelmeier DA. A Canadian perspective on the American hospitalist movement. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1665-1668.
12. Ghali WA, Greenberg PB, Mejia R, et al. International perspectives on general internal medicine and the case for “globalization” of a discipline. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:197-200.
13. Day A, MacMillan L. Neglect of the inpatient: The hospitalist movement in Canada responds. Hosp Q. 2001;4:36.
14. Sullivan P. Enter the hospitalist: New type of patient creating a new type of specialist. CMAJ. 2000;162:1345-1346.
15. Chan BTB. The declining comprehensiveness of primary care. CMAJ. 2002;166:429-434.
16. Abenhaim HA, Kahn SR, Raffoul J, Becker MR. Program description: A hospitalist-run, medical short-stay unit in a teaching hospital. CMAJ. 2000;163:1477-1480.
17. McGowan B, Nightingale M. The hospitalist program a new specialty on the horizon in acute care medicine a hospital case study. BC Med J. 2003;45:391-394.
18. Yousefi V, Chong C. Does implementation of a hospitalist program in a Canadian community hospital improve measures of quality of care and utilization? An observational comparative analysis of hospitalists vs. traditional care providers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:204.
19. White HL. Assessing the prevalence, penetration and performance of hospital physicians in Ontario: Implications for the quality and efficiency of inpatient care. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing; 2016.
20. Gutierrez CA, Norris M, Chail M. Impact of a newly established hospitalist training program on patient LOS and RIW. Poster presented at the 9th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference, September 23-25, 2011; Banff, Alberta.
21. Seth P, Nicholson K, Habbous S, Menard J. Implementation of a hospitalist medicine model in a full-service community hospital: Examining impact two years post-implementation on health resource use andpatient satisfaction. Poster presented at the 13th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference. 2015; Niagara Falls, Ontario.
22. Lewis S. A system in name only--access, variation, and reform in Canada’s provinces. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:497-500.
23. Lewis S, Kouri D. Regionalization: Making sense of the Canadian experience. Healthcare Papers. 2004;5:12-31.
24. Fraser Health Authority. About Fraser health. www.fraserhealth.ca/about-us/about-fraser-health#.XFJrl9JKiUk. Updated 2018. Accessed January 30, 2019.
25. Canadian Institute for Health Information. CMG+. https://www.cihi.ca/en/cmg. Accessed January 30, 2019.
26. White HL, Glazier RH. Do hospitalist physicians improve the quality of inpatient care delivery? A systematic review of process, efficiency and outcome measures. BMC Med. 2011;9:58.
27. Canadian Institute for Health Information. Hospital standardized mortality ratio technical notes. 2008. www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/hsmr-tech-notes_en_0.pdf.
28. McAlister FA, Youngson E, Bakal JA, et al. Physician experience and outcomes among patients admitted to general internal medicine teaching wards. CMAJ. 2015;187:1041-1048.
29. Verma AA, Guo Y, Kwan JL, et al. Patient characteristics, resource use and outcomes associated with general internal medicine hospital care: The general medicine inpatient initiative (GEMINI) retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open. 2017;5:E849.
30. Morche J, Mathes T, Pieper D. Relationship between surgeon volume and outcomes: A systematic review of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:204.
31. Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:511-520.
32. Chen CH, Chen YH, Lin HC, Lin HC. Association between physician caseload and patient outcome for sepsis treatment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30:556-562.
33. van Gestel YR, Lemmens VE, Lingsma HF, et al. The hospital standardized mortality ratio fallacy: A narrative review. Med Care. 2012;50:662-667.
34. Scott IA, Brand CA, Phelps GE, et al. Using hospital standardised mortality ratios to assess quality of care—proceed with extreme caution. Med J Aust. 2011; 194:645-648.
35. Wachter RM. Hospitalists in the United States -- mission accomplished or work in progress? N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1935-1936.
36. Peterson MC. A systematic review of outcomes and quality measures in adult patients cared for by hospitalists vs nonhospitalists. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84:248-254.
37. Chandra S, Wright SM, Howell EE. The creating incentives and continuity leading to efficiency staffing model: A quality improvement initiative in hospital medicine. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:364-371.
38. Epstein K, Juarez E, Epstein A, et al. The impact of fragmentation of hospitalist care on length of stay. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:335-338.
39. Elliott DJ, Young RS, Brice J, et al. Effect of hospitalist workload on the quality and efficiency of care. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:786-793.
1. Kisuule F, Howell E. Hospital medicine beyond the United States. Int J Gen Med. 2018;11:65-71.
2. Yousefi V, Wilton D. Dedesigning hospital care: learning from the experience of hospital medicine in Canada. J Global Health Care Syst. 2011;1(3).
3. Soong C, Fan E, Howell E, et al. Characteristics of hospitalists and hospitalist programs in the United States and Canada. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2009;16:69-76.
4. Yousefi V. How Canadian hospitalists spend their time - A work-sampling study within a hospital medicine program in Ontario. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2011;18:159-166.
5. Wilson G. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors? No. Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1101-1103.
6. Samoil D. Are inpatients’ needs better served by hospitalists than by their family doctors: Yes? Can Fam Physician. 2008;54:1100-1101.
7. Nicolson B. Where’s Marcus Welby when you need him? BC Medical J. 2016;58:63-64.
8. Lemire F. Enhanced skills in family medicine: Update. Can Fam Physician. 2018;64:160.
9. Lerner J. Wanting family medicine without primary care. Can Fam Physician. 2018; 64:155.
10. Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine. Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine - Care of the Medical Inpatient. 2015.
11. Redelmeier DA. A Canadian perspective on the American hospitalist movement. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1665-1668.
12. Ghali WA, Greenberg PB, Mejia R, et al. International perspectives on general internal medicine and the case for “globalization” of a discipline. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:197-200.
13. Day A, MacMillan L. Neglect of the inpatient: The hospitalist movement in Canada responds. Hosp Q. 2001;4:36.
14. Sullivan P. Enter the hospitalist: New type of patient creating a new type of specialist. CMAJ. 2000;162:1345-1346.
15. Chan BTB. The declining comprehensiveness of primary care. CMAJ. 2002;166:429-434.
16. Abenhaim HA, Kahn SR, Raffoul J, Becker MR. Program description: A hospitalist-run, medical short-stay unit in a teaching hospital. CMAJ. 2000;163:1477-1480.
17. McGowan B, Nightingale M. The hospitalist program a new specialty on the horizon in acute care medicine a hospital case study. BC Med J. 2003;45:391-394.
18. Yousefi V, Chong C. Does implementation of a hospitalist program in a Canadian community hospital improve measures of quality of care and utilization? An observational comparative analysis of hospitalists vs. traditional care providers. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:204.
19. White HL. Assessing the prevalence, penetration and performance of hospital physicians in Ontario: Implications for the quality and efficiency of inpatient care. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing; 2016.
20. Gutierrez CA, Norris M, Chail M. Impact of a newly established hospitalist training program on patient LOS and RIW. Poster presented at the 9th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference, September 23-25, 2011; Banff, Alberta.
21. Seth P, Nicholson K, Habbous S, Menard J. Implementation of a hospitalist medicine model in a full-service community hospital: Examining impact two years post-implementation on health resource use andpatient satisfaction. Poster presented at the 13th Annual Canadian Society of Hospital Medicine Conference. 2015; Niagara Falls, Ontario.
22. Lewis S. A system in name only--access, variation, and reform in Canada’s provinces. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:497-500.
23. Lewis S, Kouri D. Regionalization: Making sense of the Canadian experience. Healthcare Papers. 2004;5:12-31.
24. Fraser Health Authority. About Fraser health. www.fraserhealth.ca/about-us/about-fraser-health#.XFJrl9JKiUk. Updated 2018. Accessed January 30, 2019.
25. Canadian Institute for Health Information. CMG+. https://www.cihi.ca/en/cmg. Accessed January 30, 2019.
26. White HL, Glazier RH. Do hospitalist physicians improve the quality of inpatient care delivery? A systematic review of process, efficiency and outcome measures. BMC Med. 2011;9:58.
27. Canadian Institute for Health Information. Hospital standardized mortality ratio technical notes. 2008. www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/hsmr-tech-notes_en_0.pdf.
28. McAlister FA, Youngson E, Bakal JA, et al. Physician experience and outcomes among patients admitted to general internal medicine teaching wards. CMAJ. 2015;187:1041-1048.
29. Verma AA, Guo Y, Kwan JL, et al. Patient characteristics, resource use and outcomes associated with general internal medicine hospital care: The general medicine inpatient initiative (GEMINI) retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open. 2017;5:E849.
30. Morche J, Mathes T, Pieper D. Relationship between surgeon volume and outcomes: A systematic review of systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5:204.
31. Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:511-520.
32. Chen CH, Chen YH, Lin HC, Lin HC. Association between physician caseload and patient outcome for sepsis treatment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009;30:556-562.
33. van Gestel YR, Lemmens VE, Lingsma HF, et al. The hospital standardized mortality ratio fallacy: A narrative review. Med Care. 2012;50:662-667.
34. Scott IA, Brand CA, Phelps GE, et al. Using hospital standardised mortality ratios to assess quality of care—proceed with extreme caution. Med J Aust. 2011; 194:645-648.
35. Wachter RM. Hospitalists in the United States -- mission accomplished or work in progress? N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1935-1936.
36. Peterson MC. A systematic review of outcomes and quality measures in adult patients cared for by hospitalists vs nonhospitalists. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84:248-254.
37. Chandra S, Wright SM, Howell EE. The creating incentives and continuity leading to efficiency staffing model: A quality improvement initiative in hospital medicine. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:364-371.
38. Epstein K, Juarez E, Epstein A, et al. The impact of fragmentation of hospitalist care on length of stay. J Hosp Med. 2010;5:335-338.
39. Elliott DJ, Young RS, Brice J, et al. Effect of hospitalist workload on the quality and efficiency of care. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:786-793.
FDA okays emergency use of convalescent plasma for seriously ill COVID-19 patients
As the proportion of patients infected with COVID-19 continues to rise in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is facilitating access to COVID-19 convalescent plasma for use in patients with serious or immediately life-threatening COVID-19 infections.
While clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of administering convalescent plasma to patients with COVID-19, the FDA is granting clinicians permission for use of investigational convalescent plasma under single-patient emergency Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs), since no known cure exists and a vaccine is more than 1 year away from becoming available.
This allows the use of an investigational drug for the treatment of an individual patient by a licensed physician upon FDA authorization. This does not include the use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma for the prevention of infection, according to a statement issued by the agency on March 24.
“It is possible that convalescent plasma that contains antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) might be effective against the infection,” the FDA statement reads. “Use of convalescent plasma has been studied in outbreaks of other respiratory infections, including the 2009-2010 H1N1 influenza virus pandemic, 2003 SARS-CoV-1 epidemic, and the 2012 MERS-CoV epidemic. Although promising, convalescent plasma has not been shown to be effective in every disease studied.”
“I think the FDA got caught initially a little flat-footed when it came to the development of COVID-19 tests, but they’re quickly catching up,” Peter J. Pitts, who was the FDA’s associate commissioner from 2002 to 2004, said in an interview. “I think that the attitude now is, ‘If it’s safe, let’s create a pathway to see how these things work in the real world.’ I think that’s going to be as true for treatments to lessen the symptoms and shorten the duration of the disease, as well as convalescent plasma as a potential alternative to a yet-to-be-developed vaccine.”
At the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Terry B. Gernsheimer, MD, and her colleagues are recruiting recovered COVID-19 patients to donate plasma for seriously ill patients affected with the virus. “The thought of using convalescent plasma makes total sense, because it’s immediately available, and it’s something that we can try to give people,” said Dr. Gernsheimer, a hematologist who is professor of medicine at the medical school. “It’s been used in China, and reports should be coming out shortly about their experience with this.”
In a case series that appeared in JAMA on March 27 (doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783), Chinese researchers led by Chenguang Shen, PhD, reported findings from five critically ill COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome who received a transfusion with convalescent plasma at Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital 10 and 22 days after hospital admission. The patients ranged in age from 36 to 73 years, three were men, and all were receiving mechanical ventilation at the time of treatment.
Dr. Shen and colleagues reported that viral loads decreased and became negative within 12 days following the transfusion. Three of the patients were discharged from the hospital after a length of stay that ranged from 51 to 55 days, and two remain in stable condition at 37 days after the transfusion. The researchers pointed out that all patients received antiviral agents, including interferon and lopinavir/ritonavir, during and following convalescent plasma treatment, “which also may have contributed to the viral clearance observed.”
Under the FDA policy on emergency IND use, COVID-19 convalescent plasma must only be collected from recovered individuals if they are eligible to donate blood, required testing must be performed, and the donation must be found suitable.
Potential donors “are going to be screened the way all blood donors are screened,” Dr. Gernsheimer said. “It’s not going to be any less safe than any unit of plasma that’s on the shelf that comes from our volunteer donors. There are always transfusion reactions that we have to worry about, [and] there are potentially unknown pathogens that we don’t yet know about that we are not yet testing for. It’s the regular risk we see with any unit of plasma.”
She added that COVID-19 survivors appear to start increasing their titer of the antibody around day 28. “We’ll be looking for recovered individuals who have had a documented infection, and whose symptoms started about 28 days before we collect,” she said.
The FDA advises clinicians to address several considerations for donor eligibility, including prior diagnosis of COVID-19 documented by a laboratory test; complete resolution of symptoms at least 14 days prior to donation; female donors negative for HLA antibodies or male donors, and negative results for COVID-19 either from one or more nasopharyngeal swab specimens or by a molecular diagnostic test from blood. [A partial list of available tests can be accessed on the FDA website.] The agency also advises that donors have defined SARS-CoV-2–neutralizing antibody titers, if testing can be conducted (optimally greater than 1:320).
Patients eligible to receive COVID-19 convalescent plasma must have a severe or immediately life-threatening infection with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19. The agency defines severe disease as dyspnea, respiratory frequency of 30 per minute or greater, blood oxygen saturation of 93% or less, partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio of less than 300, and/or lung infiltrates of greater than 50% within 24-48 hours. Life-threatening disease is defined as respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction or failure. Patients must provide informed consent.
The potential risks of receiving COVID-19 convalescent plasma remain unknown, according to Dr. Gernsheimer. “What some people have thought about is, could there be such an inflammatory response with the virus that we would initially see these patients get worse?” she said. “My understanding is that has not occurred in China yet, but we don’t have all those data. But we always worry if we have something that’s going to cause inflammation around an infection, for example, that could initially make it more difficult to breathe if it’s a lung infection. So far, my understanding is that has not been seen.”
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response within 4-8 hours, requesting clinicians may complete form 3296 and submit it by email to [email protected].
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response in less than 4 hours, or if the clinician is unable to complete and submit form 3926 because of extenuating circumstances, verbal authorization can be sought by calling the FDA’s Office of Emergency Operations at 1-866-300-4374.
The FDA is working with the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and other government partners to develop protocols for use by multiple investigators in order to coordinate the collection and use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma.
“It’s crucial that data be captured for every patient so that we really understand what safety and effectiveness looks like on as close to a real-world level as we can, as quickly as we can,” said Mr. Pitts, who is president and cofounder of the Center for Medicine in the Public Interest, and who also does consulting work for the FDA. “I understand that health care professionals are overworked and overburdened right now. I applaud them for their heroic work. But that doesn’t mean that we can shirk off collecting the data. When I was at the FDA, I helped address the SARS epidemic. The agency attitude at that point was, ‘Let’s get things that just might work through the process, as long as the cure isn’t going to be worse than the disease.’ I think that’s the attitude that’s leading the charge today.”
As the proportion of patients infected with COVID-19 continues to rise in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is facilitating access to COVID-19 convalescent plasma for use in patients with serious or immediately life-threatening COVID-19 infections.
While clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of administering convalescent plasma to patients with COVID-19, the FDA is granting clinicians permission for use of investigational convalescent plasma under single-patient emergency Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs), since no known cure exists and a vaccine is more than 1 year away from becoming available.
This allows the use of an investigational drug for the treatment of an individual patient by a licensed physician upon FDA authorization. This does not include the use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma for the prevention of infection, according to a statement issued by the agency on March 24.
“It is possible that convalescent plasma that contains antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) might be effective against the infection,” the FDA statement reads. “Use of convalescent plasma has been studied in outbreaks of other respiratory infections, including the 2009-2010 H1N1 influenza virus pandemic, 2003 SARS-CoV-1 epidemic, and the 2012 MERS-CoV epidemic. Although promising, convalescent plasma has not been shown to be effective in every disease studied.”
“I think the FDA got caught initially a little flat-footed when it came to the development of COVID-19 tests, but they’re quickly catching up,” Peter J. Pitts, who was the FDA’s associate commissioner from 2002 to 2004, said in an interview. “I think that the attitude now is, ‘If it’s safe, let’s create a pathway to see how these things work in the real world.’ I think that’s going to be as true for treatments to lessen the symptoms and shorten the duration of the disease, as well as convalescent plasma as a potential alternative to a yet-to-be-developed vaccine.”
At the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Terry B. Gernsheimer, MD, and her colleagues are recruiting recovered COVID-19 patients to donate plasma for seriously ill patients affected with the virus. “The thought of using convalescent plasma makes total sense, because it’s immediately available, and it’s something that we can try to give people,” said Dr. Gernsheimer, a hematologist who is professor of medicine at the medical school. “It’s been used in China, and reports should be coming out shortly about their experience with this.”
In a case series that appeared in JAMA on March 27 (doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783), Chinese researchers led by Chenguang Shen, PhD, reported findings from five critically ill COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome who received a transfusion with convalescent plasma at Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital 10 and 22 days after hospital admission. The patients ranged in age from 36 to 73 years, three were men, and all were receiving mechanical ventilation at the time of treatment.
Dr. Shen and colleagues reported that viral loads decreased and became negative within 12 days following the transfusion. Three of the patients were discharged from the hospital after a length of stay that ranged from 51 to 55 days, and two remain in stable condition at 37 days after the transfusion. The researchers pointed out that all patients received antiviral agents, including interferon and lopinavir/ritonavir, during and following convalescent plasma treatment, “which also may have contributed to the viral clearance observed.”
Under the FDA policy on emergency IND use, COVID-19 convalescent plasma must only be collected from recovered individuals if they are eligible to donate blood, required testing must be performed, and the donation must be found suitable.
Potential donors “are going to be screened the way all blood donors are screened,” Dr. Gernsheimer said. “It’s not going to be any less safe than any unit of plasma that’s on the shelf that comes from our volunteer donors. There are always transfusion reactions that we have to worry about, [and] there are potentially unknown pathogens that we don’t yet know about that we are not yet testing for. It’s the regular risk we see with any unit of plasma.”
She added that COVID-19 survivors appear to start increasing their titer of the antibody around day 28. “We’ll be looking for recovered individuals who have had a documented infection, and whose symptoms started about 28 days before we collect,” she said.
The FDA advises clinicians to address several considerations for donor eligibility, including prior diagnosis of COVID-19 documented by a laboratory test; complete resolution of symptoms at least 14 days prior to donation; female donors negative for HLA antibodies or male donors, and negative results for COVID-19 either from one or more nasopharyngeal swab specimens or by a molecular diagnostic test from blood. [A partial list of available tests can be accessed on the FDA website.] The agency also advises that donors have defined SARS-CoV-2–neutralizing antibody titers, if testing can be conducted (optimally greater than 1:320).
Patients eligible to receive COVID-19 convalescent plasma must have a severe or immediately life-threatening infection with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19. The agency defines severe disease as dyspnea, respiratory frequency of 30 per minute or greater, blood oxygen saturation of 93% or less, partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio of less than 300, and/or lung infiltrates of greater than 50% within 24-48 hours. Life-threatening disease is defined as respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction or failure. Patients must provide informed consent.
The potential risks of receiving COVID-19 convalescent plasma remain unknown, according to Dr. Gernsheimer. “What some people have thought about is, could there be such an inflammatory response with the virus that we would initially see these patients get worse?” she said. “My understanding is that has not occurred in China yet, but we don’t have all those data. But we always worry if we have something that’s going to cause inflammation around an infection, for example, that could initially make it more difficult to breathe if it’s a lung infection. So far, my understanding is that has not been seen.”
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response within 4-8 hours, requesting clinicians may complete form 3296 and submit it by email to [email protected].
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response in less than 4 hours, or if the clinician is unable to complete and submit form 3926 because of extenuating circumstances, verbal authorization can be sought by calling the FDA’s Office of Emergency Operations at 1-866-300-4374.
The FDA is working with the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and other government partners to develop protocols for use by multiple investigators in order to coordinate the collection and use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma.
“It’s crucial that data be captured for every patient so that we really understand what safety and effectiveness looks like on as close to a real-world level as we can, as quickly as we can,” said Mr. Pitts, who is president and cofounder of the Center for Medicine in the Public Interest, and who also does consulting work for the FDA. “I understand that health care professionals are overworked and overburdened right now. I applaud them for their heroic work. But that doesn’t mean that we can shirk off collecting the data. When I was at the FDA, I helped address the SARS epidemic. The agency attitude at that point was, ‘Let’s get things that just might work through the process, as long as the cure isn’t going to be worse than the disease.’ I think that’s the attitude that’s leading the charge today.”
As the proportion of patients infected with COVID-19 continues to rise in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is facilitating access to COVID-19 convalescent plasma for use in patients with serious or immediately life-threatening COVID-19 infections.
While clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of administering convalescent plasma to patients with COVID-19, the FDA is granting clinicians permission for use of investigational convalescent plasma under single-patient emergency Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs), since no known cure exists and a vaccine is more than 1 year away from becoming available.
This allows the use of an investigational drug for the treatment of an individual patient by a licensed physician upon FDA authorization. This does not include the use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma for the prevention of infection, according to a statement issued by the agency on March 24.
“It is possible that convalescent plasma that contains antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) might be effective against the infection,” the FDA statement reads. “Use of convalescent plasma has been studied in outbreaks of other respiratory infections, including the 2009-2010 H1N1 influenza virus pandemic, 2003 SARS-CoV-1 epidemic, and the 2012 MERS-CoV epidemic. Although promising, convalescent plasma has not been shown to be effective in every disease studied.”
“I think the FDA got caught initially a little flat-footed when it came to the development of COVID-19 tests, but they’re quickly catching up,” Peter J. Pitts, who was the FDA’s associate commissioner from 2002 to 2004, said in an interview. “I think that the attitude now is, ‘If it’s safe, let’s create a pathway to see how these things work in the real world.’ I think that’s going to be as true for treatments to lessen the symptoms and shorten the duration of the disease, as well as convalescent plasma as a potential alternative to a yet-to-be-developed vaccine.”
At the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Terry B. Gernsheimer, MD, and her colleagues are recruiting recovered COVID-19 patients to donate plasma for seriously ill patients affected with the virus. “The thought of using convalescent plasma makes total sense, because it’s immediately available, and it’s something that we can try to give people,” said Dr. Gernsheimer, a hematologist who is professor of medicine at the medical school. “It’s been used in China, and reports should be coming out shortly about their experience with this.”
In a case series that appeared in JAMA on March 27 (doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4783), Chinese researchers led by Chenguang Shen, PhD, reported findings from five critically ill COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome who received a transfusion with convalescent plasma at Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital 10 and 22 days after hospital admission. The patients ranged in age from 36 to 73 years, three were men, and all were receiving mechanical ventilation at the time of treatment.
Dr. Shen and colleagues reported that viral loads decreased and became negative within 12 days following the transfusion. Three of the patients were discharged from the hospital after a length of stay that ranged from 51 to 55 days, and two remain in stable condition at 37 days after the transfusion. The researchers pointed out that all patients received antiviral agents, including interferon and lopinavir/ritonavir, during and following convalescent plasma treatment, “which also may have contributed to the viral clearance observed.”
Under the FDA policy on emergency IND use, COVID-19 convalescent plasma must only be collected from recovered individuals if they are eligible to donate blood, required testing must be performed, and the donation must be found suitable.
Potential donors “are going to be screened the way all blood donors are screened,” Dr. Gernsheimer said. “It’s not going to be any less safe than any unit of plasma that’s on the shelf that comes from our volunteer donors. There are always transfusion reactions that we have to worry about, [and] there are potentially unknown pathogens that we don’t yet know about that we are not yet testing for. It’s the regular risk we see with any unit of plasma.”
She added that COVID-19 survivors appear to start increasing their titer of the antibody around day 28. “We’ll be looking for recovered individuals who have had a documented infection, and whose symptoms started about 28 days before we collect,” she said.
The FDA advises clinicians to address several considerations for donor eligibility, including prior diagnosis of COVID-19 documented by a laboratory test; complete resolution of symptoms at least 14 days prior to donation; female donors negative for HLA antibodies or male donors, and negative results for COVID-19 either from one or more nasopharyngeal swab specimens or by a molecular diagnostic test from blood. [A partial list of available tests can be accessed on the FDA website.] The agency also advises that donors have defined SARS-CoV-2–neutralizing antibody titers, if testing can be conducted (optimally greater than 1:320).
Patients eligible to receive COVID-19 convalescent plasma must have a severe or immediately life-threatening infection with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19. The agency defines severe disease as dyspnea, respiratory frequency of 30 per minute or greater, blood oxygen saturation of 93% or less, partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio of less than 300, and/or lung infiltrates of greater than 50% within 24-48 hours. Life-threatening disease is defined as respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction or failure. Patients must provide informed consent.
The potential risks of receiving COVID-19 convalescent plasma remain unknown, according to Dr. Gernsheimer. “What some people have thought about is, could there be such an inflammatory response with the virus that we would initially see these patients get worse?” she said. “My understanding is that has not occurred in China yet, but we don’t have all those data. But we always worry if we have something that’s going to cause inflammation around an infection, for example, that could initially make it more difficult to breathe if it’s a lung infection. So far, my understanding is that has not been seen.”
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response within 4-8 hours, requesting clinicians may complete form 3296 and submit it by email to [email protected].
For COVID-19 convalescent plasma authorization requests that require a response in less than 4 hours, or if the clinician is unable to complete and submit form 3926 because of extenuating circumstances, verbal authorization can be sought by calling the FDA’s Office of Emergency Operations at 1-866-300-4374.
The FDA is working with the National Institutes of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and other government partners to develop protocols for use by multiple investigators in order to coordinate the collection and use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma.
“It’s crucial that data be captured for every patient so that we really understand what safety and effectiveness looks like on as close to a real-world level as we can, as quickly as we can,” said Mr. Pitts, who is president and cofounder of the Center for Medicine in the Public Interest, and who also does consulting work for the FDA. “I understand that health care professionals are overworked and overburdened right now. I applaud them for their heroic work. But that doesn’t mean that we can shirk off collecting the data. When I was at the FDA, I helped address the SARS epidemic. The agency attitude at that point was, ‘Let’s get things that just might work through the process, as long as the cure isn’t going to be worse than the disease.’ I think that’s the attitude that’s leading the charge today.”
Wilkie and the VA vs COVID-19: Who’s Winning?
US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Secretary Robert Wilkie is finding out what it means to be on wartime footing against a virus. He is overseeing the VA’s internal response to COVID-19 while deciding how to fulfil the VA’s fourth mission: providing reinforcement for the nation’s healthcare system in a national emergency. Meanwhile, he’s facing hostilities on a third front: criticism of his efforts so far.
In late February, when lawmakers asked whether the VA needed more resources to fight COVID-19, Wilkie said no. He told NPR on March 19 that “we are poised for the onslaught.” But on March 13, 2020, the VA was being attacked for not releasing a comprehensive emergency response to the incipient pandemic. Wilkie countered, “Before there was a single confirmed case in the US,” he wrote in a recent op-ed piece for Military Times, “the VA was already conducting emergency preparedness exercises.”
In the NPR interview, Wilkie said the VA had undertaken “a very aggressive public health response at an early stage.” Now, the VA has added other measures. The VA, he said, was the first health system to stop people from entering its facilities without being questioned or tested, and the first to adopt the “hard decision” of a no-visitor rule for veterans in nursing homes. Every veteran who comes to a VA facility with flu-like symptoms is screened. Further, via tweets and blog posts, Wilkie is “inviting” retired medical personnel back to work to help deal with the pandemic.
The VA is also the “buttress force,” Wilkie says, for the Federal Emergency Management Agency and the US Department of Health and Human Services if they need medical professionals for crises. “We plan for that every day,” he says. “We are gaming out emergency preparedness scenarios and we stand ready when the President needs us to expand our mission.” But in The American Prospect, Suzanne Gordon and Jasper Craven, both fellows at the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute, write that “one quiet action is ominous”—the VA website has deleted any mention of the department’s credo of caring for civilians in times of crisis.
According to Gordon and Craven, on Wednesday Wilkie “came out of the woodwork” to express the department’s readiness to help in the crisis. The VA has established 19 emergency operations centers across the country, Wilkie says, and has stopped elective surgeries to free up thousands of beds. He touts the agency’s flexibility, saying it’s prepared to move resources around the country as needed. “Some veterans hospitals have not been impacted [by the virus],” Wilkie said. “So, I’m not going to keep 500 respirators in the middle of a state that has one veteran with the infection, when I can use that in Seattle or New Orleans, or New York City.”
Wilkie says the VA has stockpiled equipment and its supply chain is stable. However, in the NPR interview, Mary Louise Kelly said the NPR VA correspondent had been hearing complaints about lack of gear, such as masks. When pressed on his claim that the VA had adequate protective supplies, Wilkie said those complaints “have not reached us.” In fact, he said, “I can tell you that the arrangements that we have made on both the masks side and also on the testing side—we’re in a very good place.”
Nonetheless, on March 16, the employee unions representing nearly 350,000 VA healthcare workers issued a joint statement that called on VHA management to “work with us to ensure the nation’s VA health facilities can safely handle COVID-19.” It’s time, said Everett Kelley, National President of the American Federation of Government Employees, “for the VA to invite our members to the table, instead of kicking them off the property, so we can finally work together on a solution….”
“Instead of relaxing standards and efforts,” the unions said, “like we have seen the CDC do [in allowing healthcare workers to reuse facemasks and rely on simple surgical facemasks], “we need to be stepping it up.”
It all takes money. After weeks of debate, the US Senate has just released details of the $2 trillion coronavirus aid package. The US Department of Defense (DoD) seems about to get $10.5 billion in emergency funding and the VA another $19.6 billion. The money includes funding for National Guard deployments to help state governments respond to emerging health needs, the expansion of military hospitals and mobile medical centers if needed, and help with production of medical supplies. Nearly $16 billion will be used for direct care specifically in response to veterans’ health needs, covering treatment for COVID-19 in VA hospitals, community urgent care clinics and emergency departments; overtime for clinical staff; and purchase of protective equipment, tests, and other supplies.
Despite having one of the best telehealth systems in the US, the VA has also come under fire for its telehealth preparations to meet the current pandemic-related demand. Former VA Under Secretary of Health Kenneth Kizer wrote in an op-ed for Military Times, “Regrettably, so far, there is no coordinated strategy for ramping up and optimizing the use of telehealth to combat the growing epidemic in the US.” The relief package proposes $3 billion for new telemedicine efforts, including staffing and equipping mobile treatment sites.
In mid-March, the VA had 3,000 coronavirus test kits but still had not used roughly 90%, an article in Mother Jones charged. At a White house press conference around that time, Wilkie was asked how many veterans of those who needed to be tested had been. “We believe we’ve caught most of them,” he replied.
But that was in the early days of the crisis.
With results from the 322 tests administered by Mar. 18, the VA had confirmed five positive cases, was tracking 33 presumptive cases, and acknowledged the first veteran death linked to COVID-19. As of Mar. 26, the VA had administered roughly 7,500 COVID-19 tests nationwide.
Secretary Wilkie has promised that the department’s first focus will always be caring for veterans. In an interview with Military Times, he said, “We don’t release any beds if veterans are needing them. The veterans still are primary. We are a [health] bridge for the larger community, but that’s only after veterans are taken care of.”
US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Secretary Robert Wilkie is finding out what it means to be on wartime footing against a virus. He is overseeing the VA’s internal response to COVID-19 while deciding how to fulfil the VA’s fourth mission: providing reinforcement for the nation’s healthcare system in a national emergency. Meanwhile, he’s facing hostilities on a third front: criticism of his efforts so far.
In late February, when lawmakers asked whether the VA needed more resources to fight COVID-19, Wilkie said no. He told NPR on March 19 that “we are poised for the onslaught.” But on March 13, 2020, the VA was being attacked for not releasing a comprehensive emergency response to the incipient pandemic. Wilkie countered, “Before there was a single confirmed case in the US,” he wrote in a recent op-ed piece for Military Times, “the VA was already conducting emergency preparedness exercises.”
In the NPR interview, Wilkie said the VA had undertaken “a very aggressive public health response at an early stage.” Now, the VA has added other measures. The VA, he said, was the first health system to stop people from entering its facilities without being questioned or tested, and the first to adopt the “hard decision” of a no-visitor rule for veterans in nursing homes. Every veteran who comes to a VA facility with flu-like symptoms is screened. Further, via tweets and blog posts, Wilkie is “inviting” retired medical personnel back to work to help deal with the pandemic.
The VA is also the “buttress force,” Wilkie says, for the Federal Emergency Management Agency and the US Department of Health and Human Services if they need medical professionals for crises. “We plan for that every day,” he says. “We are gaming out emergency preparedness scenarios and we stand ready when the President needs us to expand our mission.” But in The American Prospect, Suzanne Gordon and Jasper Craven, both fellows at the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute, write that “one quiet action is ominous”—the VA website has deleted any mention of the department’s credo of caring for civilians in times of crisis.
According to Gordon and Craven, on Wednesday Wilkie “came out of the woodwork” to express the department’s readiness to help in the crisis. The VA has established 19 emergency operations centers across the country, Wilkie says, and has stopped elective surgeries to free up thousands of beds. He touts the agency’s flexibility, saying it’s prepared to move resources around the country as needed. “Some veterans hospitals have not been impacted [by the virus],” Wilkie said. “So, I’m not going to keep 500 respirators in the middle of a state that has one veteran with the infection, when I can use that in Seattle or New Orleans, or New York City.”
Wilkie says the VA has stockpiled equipment and its supply chain is stable. However, in the NPR interview, Mary Louise Kelly said the NPR VA correspondent had been hearing complaints about lack of gear, such as masks. When pressed on his claim that the VA had adequate protective supplies, Wilkie said those complaints “have not reached us.” In fact, he said, “I can tell you that the arrangements that we have made on both the masks side and also on the testing side—we’re in a very good place.”
Nonetheless, on March 16, the employee unions representing nearly 350,000 VA healthcare workers issued a joint statement that called on VHA management to “work with us to ensure the nation’s VA health facilities can safely handle COVID-19.” It’s time, said Everett Kelley, National President of the American Federation of Government Employees, “for the VA to invite our members to the table, instead of kicking them off the property, so we can finally work together on a solution….”
“Instead of relaxing standards and efforts,” the unions said, “like we have seen the CDC do [in allowing healthcare workers to reuse facemasks and rely on simple surgical facemasks], “we need to be stepping it up.”
It all takes money. After weeks of debate, the US Senate has just released details of the $2 trillion coronavirus aid package. The US Department of Defense (DoD) seems about to get $10.5 billion in emergency funding and the VA another $19.6 billion. The money includes funding for National Guard deployments to help state governments respond to emerging health needs, the expansion of military hospitals and mobile medical centers if needed, and help with production of medical supplies. Nearly $16 billion will be used for direct care specifically in response to veterans’ health needs, covering treatment for COVID-19 in VA hospitals, community urgent care clinics and emergency departments; overtime for clinical staff; and purchase of protective equipment, tests, and other supplies.
Despite having one of the best telehealth systems in the US, the VA has also come under fire for its telehealth preparations to meet the current pandemic-related demand. Former VA Under Secretary of Health Kenneth Kizer wrote in an op-ed for Military Times, “Regrettably, so far, there is no coordinated strategy for ramping up and optimizing the use of telehealth to combat the growing epidemic in the US.” The relief package proposes $3 billion for new telemedicine efforts, including staffing and equipping mobile treatment sites.
In mid-March, the VA had 3,000 coronavirus test kits but still had not used roughly 90%, an article in Mother Jones charged. At a White house press conference around that time, Wilkie was asked how many veterans of those who needed to be tested had been. “We believe we’ve caught most of them,” he replied.
But that was in the early days of the crisis.
With results from the 322 tests administered by Mar. 18, the VA had confirmed five positive cases, was tracking 33 presumptive cases, and acknowledged the first veteran death linked to COVID-19. As of Mar. 26, the VA had administered roughly 7,500 COVID-19 tests nationwide.
Secretary Wilkie has promised that the department’s first focus will always be caring for veterans. In an interview with Military Times, he said, “We don’t release any beds if veterans are needing them. The veterans still are primary. We are a [health] bridge for the larger community, but that’s only after veterans are taken care of.”
US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Secretary Robert Wilkie is finding out what it means to be on wartime footing against a virus. He is overseeing the VA’s internal response to COVID-19 while deciding how to fulfil the VA’s fourth mission: providing reinforcement for the nation’s healthcare system in a national emergency. Meanwhile, he’s facing hostilities on a third front: criticism of his efforts so far.
In late February, when lawmakers asked whether the VA needed more resources to fight COVID-19, Wilkie said no. He told NPR on March 19 that “we are poised for the onslaught.” But on March 13, 2020, the VA was being attacked for not releasing a comprehensive emergency response to the incipient pandemic. Wilkie countered, “Before there was a single confirmed case in the US,” he wrote in a recent op-ed piece for Military Times, “the VA was already conducting emergency preparedness exercises.”
In the NPR interview, Wilkie said the VA had undertaken “a very aggressive public health response at an early stage.” Now, the VA has added other measures. The VA, he said, was the first health system to stop people from entering its facilities without being questioned or tested, and the first to adopt the “hard decision” of a no-visitor rule for veterans in nursing homes. Every veteran who comes to a VA facility with flu-like symptoms is screened. Further, via tweets and blog posts, Wilkie is “inviting” retired medical personnel back to work to help deal with the pandemic.
The VA is also the “buttress force,” Wilkie says, for the Federal Emergency Management Agency and the US Department of Health and Human Services if they need medical professionals for crises. “We plan for that every day,” he says. “We are gaming out emergency preparedness scenarios and we stand ready when the President needs us to expand our mission.” But in The American Prospect, Suzanne Gordon and Jasper Craven, both fellows at the Veterans Healthcare Policy Institute, write that “one quiet action is ominous”—the VA website has deleted any mention of the department’s credo of caring for civilians in times of crisis.
According to Gordon and Craven, on Wednesday Wilkie “came out of the woodwork” to express the department’s readiness to help in the crisis. The VA has established 19 emergency operations centers across the country, Wilkie says, and has stopped elective surgeries to free up thousands of beds. He touts the agency’s flexibility, saying it’s prepared to move resources around the country as needed. “Some veterans hospitals have not been impacted [by the virus],” Wilkie said. “So, I’m not going to keep 500 respirators in the middle of a state that has one veteran with the infection, when I can use that in Seattle or New Orleans, or New York City.”
Wilkie says the VA has stockpiled equipment and its supply chain is stable. However, in the NPR interview, Mary Louise Kelly said the NPR VA correspondent had been hearing complaints about lack of gear, such as masks. When pressed on his claim that the VA had adequate protective supplies, Wilkie said those complaints “have not reached us.” In fact, he said, “I can tell you that the arrangements that we have made on both the masks side and also on the testing side—we’re in a very good place.”
Nonetheless, on March 16, the employee unions representing nearly 350,000 VA healthcare workers issued a joint statement that called on VHA management to “work with us to ensure the nation’s VA health facilities can safely handle COVID-19.” It’s time, said Everett Kelley, National President of the American Federation of Government Employees, “for the VA to invite our members to the table, instead of kicking them off the property, so we can finally work together on a solution….”
“Instead of relaxing standards and efforts,” the unions said, “like we have seen the CDC do [in allowing healthcare workers to reuse facemasks and rely on simple surgical facemasks], “we need to be stepping it up.”
It all takes money. After weeks of debate, the US Senate has just released details of the $2 trillion coronavirus aid package. The US Department of Defense (DoD) seems about to get $10.5 billion in emergency funding and the VA another $19.6 billion. The money includes funding for National Guard deployments to help state governments respond to emerging health needs, the expansion of military hospitals and mobile medical centers if needed, and help with production of medical supplies. Nearly $16 billion will be used for direct care specifically in response to veterans’ health needs, covering treatment for COVID-19 in VA hospitals, community urgent care clinics and emergency departments; overtime for clinical staff; and purchase of protective equipment, tests, and other supplies.
Despite having one of the best telehealth systems in the US, the VA has also come under fire for its telehealth preparations to meet the current pandemic-related demand. Former VA Under Secretary of Health Kenneth Kizer wrote in an op-ed for Military Times, “Regrettably, so far, there is no coordinated strategy for ramping up and optimizing the use of telehealth to combat the growing epidemic in the US.” The relief package proposes $3 billion for new telemedicine efforts, including staffing and equipping mobile treatment sites.
In mid-March, the VA had 3,000 coronavirus test kits but still had not used roughly 90%, an article in Mother Jones charged. At a White house press conference around that time, Wilkie was asked how many veterans of those who needed to be tested had been. “We believe we’ve caught most of them,” he replied.
But that was in the early days of the crisis.
With results from the 322 tests administered by Mar. 18, the VA had confirmed five positive cases, was tracking 33 presumptive cases, and acknowledged the first veteran death linked to COVID-19. As of Mar. 26, the VA had administered roughly 7,500 COVID-19 tests nationwide.
Secretary Wilkie has promised that the department’s first focus will always be caring for veterans. In an interview with Military Times, he said, “We don’t release any beds if veterans are needing them. The veterans still are primary. We are a [health] bridge for the larger community, but that’s only after veterans are taken care of.”
Less pain with a cancer drug to treat anal HPV, but it’s expensive
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
At the end of 6 months of low-dose pomalidomide (Pomalyst), more than half of men who have sex with men had partial or complete clearance of long-standing, grade 3 anal lesions from human papillomavirus, irrespective of HIV status; the number increased to almost two-thirds when they were checked at 12 months, according to a 26-subject study said in video presentation of his research during the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections, which was presented online this year. CROI organizers chose to hold a virtual meeting because of concerns about the spread of COVID-19.
“Therapy induced durable and continuous clearance of anal HSIL [high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions]. Further study in HPV-associated premalignancy is warranted to follow up this small, single arm study,” said study lead Mark Polizzotto, MD, PhD, head of the therapeutic and vaccine research program at the Kirby Institute in Sydney.
HPV anal lesions, and subsequent HSIL and progression to anal cancer, are prevalent among men who have sex with men. The risk increases with chronic lesions and concomitant HIV infection.
Pomalidomide is potentially a less painful alternative to options such as freezing and laser ablation, and it may have a lower rate of recurrence, but it’s expensive. Copays range upward from $5,000 for a month supply, according to GoodRx. Celgene, the maker of the drug, offers financial assistance.
Pomalidomide is a derivative of thalidomide that’s approved for multiple myeloma and also has shown effect against a viral lesion associated with HIV, Kaposi sarcoma. The drug is a T-cell activator, and since T-cell activation also is key to spontaneous anal HSIL clearance, Dr. Polizzotto and team wanted to take a look to see if it could help, he said.
The men in the study were at high risk for progression to anal cancer. With a median lesion duration of more than 3 years, and at least one case out past 7 years, spontaneous clearance wasn’t in the cards. The lesions were all grade 3 HSIL, which means severe dysplasia, and more than half of the subjects had HPV genotype 16, and the rest had other risky genotypes. Ten subjects also had HIV, which also increases the risk of anal cancer.
Pomalidomide was given in back-to-back cycles for 6 months, each consisting of 2 mg orally for 3 weeks, then 1 week off, along with a thrombolytic, usually aspirin, given the black box warning of blood clots. The dose was half the 5-mg cycle for Kaposi’s.
The overall response rate – complete clearance or a partial clearance of at least a 50% on high-resolution anoscopy – was 50% at 6 months (12/24), including four complete responses (4/15, 27%) in subjects without HIV, as well as four in the HIV group (4/9, 44%).
On follow-up at month 12, “we saw something we did not expect. Strikingly, with no additional therapy in the interim, we saw a deepening of response in a number of subjects.” The overall response rate climbed to 63% (15/24), including 33% complete response in the HIV-free group (5/15) and HIV-positive group (3/9).
Some did lose their response in the interim, however, and the study team is working to figure out if it was do to a recurrence or a new infection.
A general pattern of immune activation on treatment, including increased systemic CD4+ T-cell responses to HPV during therapy, supported the investigator’s hunch of an immunologic mechanism of action, Dr. Polizzotto said.
There were four instances of grade 3 neutropenia over eight treatment cycles, and one possibly related angina attack, but other than that, adverse reactions were generally mild and self-limited, mostly to grade 1 or 2 neutropenia, constipation, fatigue, and rash, with no idiosyncratic reactions in the HIV group or loss of viral suppression, and no discontinuations because of side effects.
The men in the study were aged 40-50 years, with a median age of 54 years; all but one were white. The median lesion involved a quarter of the anal ring, but sometimes more than half.
The work was funded by the Cancer Institute of New South Wales, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Celgene. Dr. Polizzotto disclosed patents with Celgene and research funding from the company.
SOURCE: Polizzotto M et al. CROI 2020. Abstract 70
FROM CROI 2020
FDA to allow alternative respiratory devices to treat COVID-19
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
“Whenever possible, health care facilities should use FDA-cleared conventional/standard full-featured ventilators when necessary to support patients with respiratory failure, or a device subject to an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), if any,” FDA stated in a guidance document issued March 22.
“However, to help ensure the availability of the greatest possible number of devices for this purpose, ... FDA does not intend to object to limited modifications to indications, claims, functionality, or to the hardware, software, or materials of FDA-cleared devices used to support patients with respiratory failure or respiratory insufficiency, without prior submission of a premarket notification” for the duration of the declared national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement that the agency is doing everything it can to support patients, health care professionals, and others during this pandemic.
“One of the most impactful steps we can take is to help with access and availability to life-saving medical treatments,” he said. “Our policy issued today demonstrates our ability to react and adapt quickly during this pandemic and help very ill patients access the lifesaving ventilator support they need. To do that, we are providing maximum regulatory flexibility to facilitate an increase in ventilator inventory, while still providing crucial FDA oversight. We believe this action will immediately increase ventilator availability.”
The document identified examples of where modifications would not create undue risk, including the use of powered emergency ventilators and anesthesia gas machines for patients needing mechanical ventilation; the use of ventilators outside of their cleared environment; the use of devices used to treat patients with sleep apnea, such as CPAPs and BiPAPs, to treat respiratory insufficiency when appropriate design mitigations are in place to minimize aerosolization; and the use of oxygen concentrators for primary supply when medically necessary and clinically appropriate.
The agency also is allowing for changes to the hardware, software, and materials to FDA-cleared ventilators and anesthesia gas machines, such as modifications to motors, batteries, or other electrical components; material changes to components in the gas pathways or with other patient tissue contact; the introduction of filtration to minimize aerosolization; and other hardware and software modifications.
FDA is also allowing for products to be used past their indicated shelf life.
Tribes Outperform Federal Government in COVID-19 Response
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Several days ago, Rodney Bordeaux, president of the Rosebud Sioux Tribe in South Dakota, sent a strongly worded SOS to the directors of the World Health Organization and the Pan American Health Organization about COVID-19, saying, “We have approximately 30,000 tribal members living in south central South Dakota with access to fewer than 200 beds within our reservation.”
Not only were beds woefully inadequate to the needs of potential COVID-19 victims, but tests to find out who might need the beds also were lacking. “We believe that some kits have been sent to the states,” Bordeaux wrote, “but it is the states that have been determining who gets a test and who does not.”
In Michigan, Aaron Payment, chair of the Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians, told the Native America Calling radio show, “We’re the largest tribe east of the Mississippi, and we have two test kits.”
The “chronically underfunded” Indian Health Service (IHS) was underprepared for handling virus response, Melissa Riley, PhD, executive director of Indigenous Women Rising, charged in a March 24 opinion piece in Rewire News. “If IHS can barely keep up with broken bones and preventive care,” she wrote, “what makes our people across the country think IHS can handle the outbreak of COVID-19?”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) does not break down data on cases according to race or ethnicity, but according to the IHS website, 42 people in the agency’s jurisdiction had tested positive for COVID-19 as of Mar. 24. Of those, 29 were in Navajo Country. By the evening of that day, according to Native News Online, the number of Navajos testing positive had risen to 49. Given the often-invisible spread of the virus, many more are likely to be infected.
The IHS website directs visitors to visit CDC pages for more information. However, these pages do not provide information “in a culturally literate and responsive manner,” Riley says, that explain ways to stay indoors, nor do they offer contacts for indigenous people—despite the fact, she adds, that on the West Coast they were among the first to contract the virus and to reach out with questions.
For its part, the IHS has said it “continues to work closely with our tribal partners to coordinate a comprehensive public health response to COVID-19,” holding weekly conference calls with tribal and urban Indian health organization leaders to “provide updates, answer questions, and hear concerns.” It also is in constant contact with the White House and the CDC, IHS says. IHS facilities “generally” have access to testing for individuals who may have COVID-19, the website says: However, “there are nationwide shortages of materials that may temporarily affect the availability of COVID-19 testing at a particular location.” Tribes, the website recommends, should first follow their usual process for ordering supplies. If they can’t access supplies, they should contact their IHS Area Office, which can access supplies through the IH National Supply Service Center.
Bordeaux, Payment, and Riley are not alone in their criticisms and concerns. Native Americans and Alaska Natives were hit disproportionately during the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: The death rate was 4 times higher than in all other racial and ethnic groups combined. The NIH says AI/ANs are particularly vulnerable to epidemic infections, due to poverty, underlying chronic illnesses (including asthma), and delayed access to care.
Tribes began taking steps early on to protect their members, even before the federal and state governments began requiring such measures. Lummi Nation leaders, in the Pacific Northwest, for instance, began preparing when the virus first appeared in Wuhan in late 2019, according to an article in The Guardian, and declared a state of emergency on March 3—10 days before President Trump did.
The tribe has been “beefing up” emergency plans, reorganizing services, and gathering medical supplies. It also approved $1 million for emergency response, including repurposing a community fitness center into a field hospital. “We quickly recognized the need to make sacrifices for the greater good, in order to protect our people and the wider community,” Dr. Dakotah Lane, medical director of the tribal health service, said in the Guardian interview.
On March 17, the Navajo Nation shut down its 4 casinos after an Arizona tribe member was diagnosed with the virus. President Jonathan Nez says the tribe stands to lose $3 million to $5 million in revenue. But “[t]he health and well-being of our Navajo people is of utmost importance and not just profit,” Nez said in a Navajo Times interview.
In the meantime, bending to pressure from Rep. Deb Haaland (D-NM) and “a handful” of other lawmakers, according to an article in The Guardian, Congress designated $40 million for tribal health and Urban Indian Health organizations as part of the emergency federal relief legislation.
While the states received the emergency funds immediately, the CDC disburses the money to tribes, who have yet to receive any. Haaland, the first Native American woman elected to Congress, says the tribes needed the money “yesterday.”
Three COVID-19 rapid diagnostic tests get FDA thumbs-up
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.
The first authorization, announced by the agency on March 21, was for the Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 test, a rapid molecular diagnostic test for qualitative detection of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19.
The test, manufactured by Cepheid, has a detection time of 45 minutes and has been designed to operate on any of the company’s more than 23,000 automated GeneXpert Systems worldwide, according to a statement from the company.
The agency said in its EUA approval document the test is for a “qualitative detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swab and/or nasal wash/aspirate specimens collected from patients who are suspected of having COVID-19 infection.” Positive results are indicative of an infection but do not rule out other potential infections, it noted.
The company plans to roll out the test by March 30, according to the FDA.
Cepheid said in a statement that it has almost 5,000 GeneXpert systems in the United States that are capable of point-of-care testing and ready for use in hospitals. “Our automated systems do not require users to have specialty training to perform testing – they are capable of running 24/7, with many systems already doing so today,” Warren Kocmond, the company’s president, said in the statement.
FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD said in a statement that the authorization marked “an important step in expanding the availability of testing and, importantly, rapid results. Point-of-care testing means that results are delivered to the patient in the patient-care settings, like hospitals, urgent care centers, and emergency rooms, instead of samples being sent to a laboratory. With today’s authorization, there is now an option for testing at the point of care, which enables patient access to more immediate results.”
On March 23, the agency issued an emergency use authorization to bioMerieux subsidiary BioFire Defense LLC for its BIOFIRE COVID-19 test, which detects SARS-CoV-2 from a nasopharyngeal swab in about 45 minutes.
The test was developed with funding from the U.S. Department of Defense.
“Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status,” the agency said in its approval document. It again noted that positive results did not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.
Also on March 23, the agency issued an EUA to Mesa Biotech for its Accula SARS-CoV-2 test, which gives COVID-19 diagnostic results in 30 minutes.
The test is indicated for “qualitative, visual detection of nucleic acid from the SARS-CoV-2 in throat swab and nasal swab specimens combined, collected from patients suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider,” according to the FDA approval document. “The SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid is generally detectable in throat and nasal swab specimens during the acute phase of infection. Positive results are indicative of the presence of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; clinical correlation with patient history and other diagnostic information is necessary to determine patient infection status. Positive results do not rule out bacterial infection or coinfection with other viruses.”
Mesa Biotech said in a statement that the test is designed for point-of-care use, including at temporary screening facilities, physician office labs, urgent care, and long-term nursing facilities.
“Our test will provide a highly accessible means for health care professionals to access laboratory quality results close in their office to aid in the decision to isolate, treat, or dismiss potential carriers of the virus,” Hong Cai, the CEO and cofounder of Mesa Biotech, said in a statement. “The potential to reduce the growing strain on our nation’s hospitals is tremendous.”
In separate letters to the three companies notifying them of the authorizations, the FDA said the emergency use of the products met the criteria for issuances of authorization because the SARS-CoV-2 can cause a serious or life-threatening disease or condition; it was “reasonable to believe
that [the] product may be effective in diagnosing COVID-19; and there is no “adequate, approved, and available alternative” to the emergency use of the three products.


