User login
Prophylactic anticoagulation tied to lower death rate in COVID
Prophylactic anticoagulation to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE) was associated with reduced 60-day mortality in patients with COVID-19 who were ill enough to require hospitalization, a new report shows.
In a cohort study of more than 1,300 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection across 30 hospitals in Michigan, both prophylactic- and therapeutic-dose anticoagulation were associated with reduced in-hospital mortality; however, at 60 days, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality.
And adherence was key; nonadherence, or missing 2 days or more of anticoagulation, was linked to more deaths at 60 days.
The findings, which were published online June 11 in JAMA Network Open, are final proof that a prophylactic anticoagulation strategy for the hospitalized COVID population is, indeed, the right one, Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, director of hospital medicine research at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview.
“We’ve probably always known that patients with COVID need prophylaxis for VTE, but we found that early on, unfortunately, that wasn’t being done,” Dr. Vaughn said.
“Now, we see that prophylactic rates have increased. We always knew to use anticoagulation prophylactically in patients who were hospitalized with infection because of their risk for VTE, so this study just drives home that proper adherence to an anticoagulation protocol improves mortality,” she said.
Dr. Vaughn was on the front lines when COVID-19 came to Michigan, where the research was conducted.
“We probably should have been anticoagulating from the get-go, but you have to remember that in the early days of COVID, the hospitals in Michigan were being overwhelmed. They didn’t have PPE. They were taking care of patients outside of their typical hospital beds or setting up field hospitals,” she said. “It was not quite as bad as New York, but at the University of Michigan, we set up four or five ICUs outside of our normal care.”
They also converted the top floor of their pediatric hospital into an ICU to take care of patients with COVID during the first surge, she added. “We didn’t know much about this disease, but faced with this influx of patients, many of whom were dying with blood clots, we had to do something.”
Some hospitals began prophylactically anticoagulating their patients, but others hesitated before adopting the strategy. “But now we feel confident that prophylactic anticoagulation, done according to the right protocol, with no interruptions in the treatment, is beneficial,” Dr. Vaughn said.
The best medication choice is enoxaparin (Lovenox), which can be given once a day, as opposed to heparin, which needs to be given via injection three times a day, she said.
“Prophylactic dose anticoagulation is typically given by an injection under the skin, but a lot of times, I’ve had patients tell me they feel like a human pin cushion and have all these bruises from being stuck with needles every day, which I can totally relate to,” she said.
“It is important for us as clinicians to explain that we’re having to poke our patients because it is good for them and will help them fight COVID,” she added. “Also having the once-a-day option is going to be a lot better for adherence, and adherence to the protocol, not missing any days, is key to the better outcome.”
Dr. Vaughn and her team reviewed the charts of 1,351 patients (48% women, 49% Black, median age 64 [range 52-75]) who were hospitalized throughout Michigan during the first several months of the COVID-19 pandemic, from March to June 2020.
Only 18 patients (1.3%) had a confirmed VTE and 219 patients (16.2%) received treatment-dose anticoagulation.
The researchers noted that use of treatment-dose anticoagulation without imaging ranged from 0% to 29% across hospitals and increased significantly over time.
Of the 1,127 patients who received anticoagulation, 392 (34.8%) missed 2 days or more of prophylaxis.
In addition, there were varying rates of missed prophylaxis among the hospitals, from 11% to 61%, but these rates decreased markedly over time.
Missed doses were associated with a higher 60-day mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.67), but not in-hospital mortality (aHR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.91-1.03).
Compared with no anticoagulation, receiving any dose of anticoagulation was associated with lower in-hospital mortality.
However, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality at 60 days. The adjusted hazard ratio for prophylactic-dose anticoagulation was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.51-0.90), compared with 0.92 (95% CI, 0.63-1.35) for treatment-dose anticoagulation.
Study boosts confidence
Despite its limitations, the study should make clinicians more confident that the use of prophylactic anticoagulation is warranted for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, write Andrew B. Dicks, MD, and Ido Weinberg, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an invited commentary.
“Practically, we still lack the granular data we need to help guide us in patient-by-patient decision-making – such as anticoagulation agent choice, dosage, and duration of therapy – especially as dictated by acuity of patient illness,” Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg note.
“While we still await the data from randomized controlled trials to guide the optimal anticoagulation dose and duration, this study adds significant merit to the previously published recommendations from several different medical organizations regarding the use of prophylactic anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Dicks told this news organization.
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network as part of their Value Partnerships program. Dr. Vaughn has reported receiving speaking fees from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prophylactic anticoagulation to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE) was associated with reduced 60-day mortality in patients with COVID-19 who were ill enough to require hospitalization, a new report shows.
In a cohort study of more than 1,300 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection across 30 hospitals in Michigan, both prophylactic- and therapeutic-dose anticoagulation were associated with reduced in-hospital mortality; however, at 60 days, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality.
And adherence was key; nonadherence, or missing 2 days or more of anticoagulation, was linked to more deaths at 60 days.
The findings, which were published online June 11 in JAMA Network Open, are final proof that a prophylactic anticoagulation strategy for the hospitalized COVID population is, indeed, the right one, Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, director of hospital medicine research at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview.
“We’ve probably always known that patients with COVID need prophylaxis for VTE, but we found that early on, unfortunately, that wasn’t being done,” Dr. Vaughn said.
“Now, we see that prophylactic rates have increased. We always knew to use anticoagulation prophylactically in patients who were hospitalized with infection because of their risk for VTE, so this study just drives home that proper adherence to an anticoagulation protocol improves mortality,” she said.
Dr. Vaughn was on the front lines when COVID-19 came to Michigan, where the research was conducted.
“We probably should have been anticoagulating from the get-go, but you have to remember that in the early days of COVID, the hospitals in Michigan were being overwhelmed. They didn’t have PPE. They were taking care of patients outside of their typical hospital beds or setting up field hospitals,” she said. “It was not quite as bad as New York, but at the University of Michigan, we set up four or five ICUs outside of our normal care.”
They also converted the top floor of their pediatric hospital into an ICU to take care of patients with COVID during the first surge, she added. “We didn’t know much about this disease, but faced with this influx of patients, many of whom were dying with blood clots, we had to do something.”
Some hospitals began prophylactically anticoagulating their patients, but others hesitated before adopting the strategy. “But now we feel confident that prophylactic anticoagulation, done according to the right protocol, with no interruptions in the treatment, is beneficial,” Dr. Vaughn said.
The best medication choice is enoxaparin (Lovenox), which can be given once a day, as opposed to heparin, which needs to be given via injection three times a day, she said.
“Prophylactic dose anticoagulation is typically given by an injection under the skin, but a lot of times, I’ve had patients tell me they feel like a human pin cushion and have all these bruises from being stuck with needles every day, which I can totally relate to,” she said.
“It is important for us as clinicians to explain that we’re having to poke our patients because it is good for them and will help them fight COVID,” she added. “Also having the once-a-day option is going to be a lot better for adherence, and adherence to the protocol, not missing any days, is key to the better outcome.”
Dr. Vaughn and her team reviewed the charts of 1,351 patients (48% women, 49% Black, median age 64 [range 52-75]) who were hospitalized throughout Michigan during the first several months of the COVID-19 pandemic, from March to June 2020.
Only 18 patients (1.3%) had a confirmed VTE and 219 patients (16.2%) received treatment-dose anticoagulation.
The researchers noted that use of treatment-dose anticoagulation without imaging ranged from 0% to 29% across hospitals and increased significantly over time.
Of the 1,127 patients who received anticoagulation, 392 (34.8%) missed 2 days or more of prophylaxis.
In addition, there were varying rates of missed prophylaxis among the hospitals, from 11% to 61%, but these rates decreased markedly over time.
Missed doses were associated with a higher 60-day mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.67), but not in-hospital mortality (aHR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.91-1.03).
Compared with no anticoagulation, receiving any dose of anticoagulation was associated with lower in-hospital mortality.
However, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality at 60 days. The adjusted hazard ratio for prophylactic-dose anticoagulation was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.51-0.90), compared with 0.92 (95% CI, 0.63-1.35) for treatment-dose anticoagulation.
Study boosts confidence
Despite its limitations, the study should make clinicians more confident that the use of prophylactic anticoagulation is warranted for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, write Andrew B. Dicks, MD, and Ido Weinberg, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an invited commentary.
“Practically, we still lack the granular data we need to help guide us in patient-by-patient decision-making – such as anticoagulation agent choice, dosage, and duration of therapy – especially as dictated by acuity of patient illness,” Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg note.
“While we still await the data from randomized controlled trials to guide the optimal anticoagulation dose and duration, this study adds significant merit to the previously published recommendations from several different medical organizations regarding the use of prophylactic anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Dicks told this news organization.
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network as part of their Value Partnerships program. Dr. Vaughn has reported receiving speaking fees from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prophylactic anticoagulation to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE) was associated with reduced 60-day mortality in patients with COVID-19 who were ill enough to require hospitalization, a new report shows.
In a cohort study of more than 1,300 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection across 30 hospitals in Michigan, both prophylactic- and therapeutic-dose anticoagulation were associated with reduced in-hospital mortality; however, at 60 days, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality.
And adherence was key; nonadherence, or missing 2 days or more of anticoagulation, was linked to more deaths at 60 days.
The findings, which were published online June 11 in JAMA Network Open, are final proof that a prophylactic anticoagulation strategy for the hospitalized COVID population is, indeed, the right one, Valerie M. Vaughn, MD, director of hospital medicine research at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview.
“We’ve probably always known that patients with COVID need prophylaxis for VTE, but we found that early on, unfortunately, that wasn’t being done,” Dr. Vaughn said.
“Now, we see that prophylactic rates have increased. We always knew to use anticoagulation prophylactically in patients who were hospitalized with infection because of their risk for VTE, so this study just drives home that proper adherence to an anticoagulation protocol improves mortality,” she said.
Dr. Vaughn was on the front lines when COVID-19 came to Michigan, where the research was conducted.
“We probably should have been anticoagulating from the get-go, but you have to remember that in the early days of COVID, the hospitals in Michigan were being overwhelmed. They didn’t have PPE. They were taking care of patients outside of their typical hospital beds or setting up field hospitals,” she said. “It was not quite as bad as New York, but at the University of Michigan, we set up four or five ICUs outside of our normal care.”
They also converted the top floor of their pediatric hospital into an ICU to take care of patients with COVID during the first surge, she added. “We didn’t know much about this disease, but faced with this influx of patients, many of whom were dying with blood clots, we had to do something.”
Some hospitals began prophylactically anticoagulating their patients, but others hesitated before adopting the strategy. “But now we feel confident that prophylactic anticoagulation, done according to the right protocol, with no interruptions in the treatment, is beneficial,” Dr. Vaughn said.
The best medication choice is enoxaparin (Lovenox), which can be given once a day, as opposed to heparin, which needs to be given via injection three times a day, she said.
“Prophylactic dose anticoagulation is typically given by an injection under the skin, but a lot of times, I’ve had patients tell me they feel like a human pin cushion and have all these bruises from being stuck with needles every day, which I can totally relate to,” she said.
“It is important for us as clinicians to explain that we’re having to poke our patients because it is good for them and will help them fight COVID,” she added. “Also having the once-a-day option is going to be a lot better for adherence, and adherence to the protocol, not missing any days, is key to the better outcome.”
Dr. Vaughn and her team reviewed the charts of 1,351 patients (48% women, 49% Black, median age 64 [range 52-75]) who were hospitalized throughout Michigan during the first several months of the COVID-19 pandemic, from March to June 2020.
Only 18 patients (1.3%) had a confirmed VTE and 219 patients (16.2%) received treatment-dose anticoagulation.
The researchers noted that use of treatment-dose anticoagulation without imaging ranged from 0% to 29% across hospitals and increased significantly over time.
Of the 1,127 patients who received anticoagulation, 392 (34.8%) missed 2 days or more of prophylaxis.
In addition, there were varying rates of missed prophylaxis among the hospitals, from 11% to 61%, but these rates decreased markedly over time.
Missed doses were associated with a higher 60-day mortality (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.67), but not in-hospital mortality (aHR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.91-1.03).
Compared with no anticoagulation, receiving any dose of anticoagulation was associated with lower in-hospital mortality.
However, only prophylactic-dose anticoagulation remained associated with lower mortality at 60 days. The adjusted hazard ratio for prophylactic-dose anticoagulation was 0.71 (95% CI, 0.51-0.90), compared with 0.92 (95% CI, 0.63-1.35) for treatment-dose anticoagulation.
Study boosts confidence
Despite its limitations, the study should make clinicians more confident that the use of prophylactic anticoagulation is warranted for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, write Andrew B. Dicks, MD, and Ido Weinberg, MD, from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, in an invited commentary.
“Practically, we still lack the granular data we need to help guide us in patient-by-patient decision-making – such as anticoagulation agent choice, dosage, and duration of therapy – especially as dictated by acuity of patient illness,” Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg note.
“While we still await the data from randomized controlled trials to guide the optimal anticoagulation dose and duration, this study adds significant merit to the previously published recommendations from several different medical organizations regarding the use of prophylactic anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” Dr. Dicks told this news organization.
The study was supported by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Michigan and Blue Care Network as part of their Value Partnerships program. Dr. Vaughn has reported receiving speaking fees from Thermo Fisher Scientific. Dr. Dicks and Dr. Weinberg have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S., international MIS-C studies yield disparate results
That requires rapid pragmatic evaluation of therapies. Two real-world observational studies published online June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine do that, with differing results.
In the Overcoming COVID-19 study, investigators assessed initial therapy and outcomes for patients with MIS-C using surveillance data from 58 pediatric hospitals nationwide.
The results suggest that patients with MIS-C who were younger than 21 years of age and who were initially treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) plus glucocorticoids fared better in terms of cardiovascular function.
The study included 518 children (median age, 8.7 years) who were admitted to the hospital between March and October 2020 and who received at least one immunomodulatory therapy. In a propensity score–matched analysis, those given IVIG plus glucocorticoids (n = 103) had a lower risk for the primary outcome of cardiovascular dysfunction on or after day 2 than those given IVIG alone (n = 103), at 17% versus 31% (risk ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.34-0.94).
Risks for individual aspects of the study’s composite outcome were also lower with IVIG plus glucocorticoids. Left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 8% and 17%, respectively (RR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.19-1.15). Shock requiring vasopressor use emerged in 13% and 24%, respectively (RR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.29-1.00).
In addition, there were fewer cases in which adjunctive therapy was given on day one among those who received combination therapy than among those who received IVIG alone, at 34% versus 70% (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.36-0.65), but the risk for fever was not lower on or after day two (31% and 40%, respectively; RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.53-1.13).
Lead author Mary Beth F. Son, MD, director of the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is also associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, stressed that the study did not assess which MIS-C patients should receive treatment. “Rather, we studied children who had been treated with one of two initial regimens and then assessed short-term outcomes,” she told this news organization.
Going forward, it will be important to study which children should receive immunomodulatory treatment, Dr. Son said. “Specifically, can the less ill children receive IVIG alone or no treatment? This is an unanswered question at the moment, which could be addressed with a randomized controlled trial.”
Future directions, she added, will include assessing long-term cardiac outcomes for patients with MIS-C as well as studying outpatient regimens, especially those that involve steroids.
Earlier this year, French investigators found better outcomes with combined corticosteroids and IVIG than with IVIG alone. They suggested that combination therapy should be the standard of care, given the present state of therapeutic knowledge.
Maybe not so standard
Different results emerged, however, from an international study of MIS-C that compared three, rather than two, treatment approaches. Collaborators from the Best Available Treatment Study for MIS-C (BATS) evaluated data for 614 children with suspected MIS-C between June 2020 and February 2021 in 32 countries and found no substantial differences in recovery among children whose primary treatment was IVIG alone, IVIG plus glucocorticoids, or glucocorticoids alone.
The study by Andrew J. McArdle, MB BChir, MSC, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, and colleagues was published June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In the BATS cohort, 246 received IVIG alone, 208 received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, and 99 received glucocorticoids alone. Twenty-two patients received other combinations, including biologics, and 39 received no immunomodulatory therapy.
Among patients who were included in the primary analysis, death occurred or inotropic or ventilatory support was employed in 56 of 180 of the patients who received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, compared with 44 of 211 patients treated with IVIG alone, for an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.33-1.82). Among those who received glucocorticoids alone, 17 of 83 met the primary endpoint of death or inotropic or ventilatory support, for an aOR relative to IVIG alone of 0.54 (95% CI, 0.22-1.33).
After adjustments, the likelihood for reduced disease severity was similar in the two groups relative to IVIG alone, at 0.90 for IVIG plus glucocorticoids and 0.93 for glucocorticoids alone. Time to reduction in disease severity was also comparable across all groups.
Some of the differences between the U.S. study and the global studies could be the result of the larger size of the international cohort and possibly a difference in the strains of virus in the United States and abroad, according to S. Sexson Tejtel, MD, PhD, MPH, a pediatric cardiologist at Texas Children’s Hospital and an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas. “Some strains make children sicker than others, and they’re going to need more treatment,” said Dr. Sexson Tejtel, who was not involved in either study.
Dr. Sexson Tejtel also noted that the U.S. researchers did not assess outcomes among children treated with steroids alone. “It would be interesting to know what steroids alone look like in the U.S. MIS-C population,” she said in an interview.
BATS corresponding author Michael Levin, MBE, PhD, FRCPCH, an Imperial College professor of pediatrics and international child health, told this news organization that the differing results may have arisen because of the international study’s three-treatment focus, its wider spectrum of patients, and its different endpoints: Death and inotropic support on or after day 2, versus echocardiographic left ventricular dysfunction or inotropic usage.
Regardless of the differences between the two studies, neither establishes the most effective single or combination treatment, writes Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Children’s National Hospital and Research Institute and George Washington University, Washington, in an accompanying editorial. “Specifically, neither study was powered to include an evaluation of approaches that steer away from broad immunosuppression with glucocorticoids and that focus on more targeted and titratable treatments with biologic agents, such as anakinra and infliximab,” she writes.
Dr. DeBiasi adds that long-term follow-up studies of cardiac and noncardiac outcomes in these patients will launch soon. “Meanwhile, continued collaboration across centers is essential to decreasing the short-term incidence of death and complications,” she writes.
“It will be interesting as we apply results from these studies as they come out to see how they change our practice,” Dr. Sexson Tejtel said. “And it would be good to have some randomized clinical trials.”
For Dr. Levin, the bottom line is that all three treatments are associated with recovery for a majority of children. “This is good news for clinicians who have been guessing which treatment to use,” he said. “Both studies are attempts to provide doctors with some evidence on which to base treatment decisions and are not the final answer. Our study is ongoing, and with larger numbers of patients it may give clearer answers.”
The Overcoming COVID-19 study was funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Several coauthors have reported support from industry outside of the submitted work. BATS was funded by the European Union’s Horizons 2020 Program. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor’s spouse is employed by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. DeBiasi and Dr. Sexson Tejtel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That requires rapid pragmatic evaluation of therapies. Two real-world observational studies published online June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine do that, with differing results.
In the Overcoming COVID-19 study, investigators assessed initial therapy and outcomes for patients with MIS-C using surveillance data from 58 pediatric hospitals nationwide.
The results suggest that patients with MIS-C who were younger than 21 years of age and who were initially treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) plus glucocorticoids fared better in terms of cardiovascular function.
The study included 518 children (median age, 8.7 years) who were admitted to the hospital between March and October 2020 and who received at least one immunomodulatory therapy. In a propensity score–matched analysis, those given IVIG plus glucocorticoids (n = 103) had a lower risk for the primary outcome of cardiovascular dysfunction on or after day 2 than those given IVIG alone (n = 103), at 17% versus 31% (risk ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.34-0.94).
Risks for individual aspects of the study’s composite outcome were also lower with IVIG plus glucocorticoids. Left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 8% and 17%, respectively (RR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.19-1.15). Shock requiring vasopressor use emerged in 13% and 24%, respectively (RR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.29-1.00).
In addition, there were fewer cases in which adjunctive therapy was given on day one among those who received combination therapy than among those who received IVIG alone, at 34% versus 70% (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.36-0.65), but the risk for fever was not lower on or after day two (31% and 40%, respectively; RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.53-1.13).
Lead author Mary Beth F. Son, MD, director of the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is also associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, stressed that the study did not assess which MIS-C patients should receive treatment. “Rather, we studied children who had been treated with one of two initial regimens and then assessed short-term outcomes,” she told this news organization.
Going forward, it will be important to study which children should receive immunomodulatory treatment, Dr. Son said. “Specifically, can the less ill children receive IVIG alone or no treatment? This is an unanswered question at the moment, which could be addressed with a randomized controlled trial.”
Future directions, she added, will include assessing long-term cardiac outcomes for patients with MIS-C as well as studying outpatient regimens, especially those that involve steroids.
Earlier this year, French investigators found better outcomes with combined corticosteroids and IVIG than with IVIG alone. They suggested that combination therapy should be the standard of care, given the present state of therapeutic knowledge.
Maybe not so standard
Different results emerged, however, from an international study of MIS-C that compared three, rather than two, treatment approaches. Collaborators from the Best Available Treatment Study for MIS-C (BATS) evaluated data for 614 children with suspected MIS-C between June 2020 and February 2021 in 32 countries and found no substantial differences in recovery among children whose primary treatment was IVIG alone, IVIG plus glucocorticoids, or glucocorticoids alone.
The study by Andrew J. McArdle, MB BChir, MSC, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, and colleagues was published June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In the BATS cohort, 246 received IVIG alone, 208 received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, and 99 received glucocorticoids alone. Twenty-two patients received other combinations, including biologics, and 39 received no immunomodulatory therapy.
Among patients who were included in the primary analysis, death occurred or inotropic or ventilatory support was employed in 56 of 180 of the patients who received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, compared with 44 of 211 patients treated with IVIG alone, for an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.33-1.82). Among those who received glucocorticoids alone, 17 of 83 met the primary endpoint of death or inotropic or ventilatory support, for an aOR relative to IVIG alone of 0.54 (95% CI, 0.22-1.33).
After adjustments, the likelihood for reduced disease severity was similar in the two groups relative to IVIG alone, at 0.90 for IVIG plus glucocorticoids and 0.93 for glucocorticoids alone. Time to reduction in disease severity was also comparable across all groups.
Some of the differences between the U.S. study and the global studies could be the result of the larger size of the international cohort and possibly a difference in the strains of virus in the United States and abroad, according to S. Sexson Tejtel, MD, PhD, MPH, a pediatric cardiologist at Texas Children’s Hospital and an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas. “Some strains make children sicker than others, and they’re going to need more treatment,” said Dr. Sexson Tejtel, who was not involved in either study.
Dr. Sexson Tejtel also noted that the U.S. researchers did not assess outcomes among children treated with steroids alone. “It would be interesting to know what steroids alone look like in the U.S. MIS-C population,” she said in an interview.
BATS corresponding author Michael Levin, MBE, PhD, FRCPCH, an Imperial College professor of pediatrics and international child health, told this news organization that the differing results may have arisen because of the international study’s three-treatment focus, its wider spectrum of patients, and its different endpoints: Death and inotropic support on or after day 2, versus echocardiographic left ventricular dysfunction or inotropic usage.
Regardless of the differences between the two studies, neither establishes the most effective single or combination treatment, writes Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Children’s National Hospital and Research Institute and George Washington University, Washington, in an accompanying editorial. “Specifically, neither study was powered to include an evaluation of approaches that steer away from broad immunosuppression with glucocorticoids and that focus on more targeted and titratable treatments with biologic agents, such as anakinra and infliximab,” she writes.
Dr. DeBiasi adds that long-term follow-up studies of cardiac and noncardiac outcomes in these patients will launch soon. “Meanwhile, continued collaboration across centers is essential to decreasing the short-term incidence of death and complications,” she writes.
“It will be interesting as we apply results from these studies as they come out to see how they change our practice,” Dr. Sexson Tejtel said. “And it would be good to have some randomized clinical trials.”
For Dr. Levin, the bottom line is that all three treatments are associated with recovery for a majority of children. “This is good news for clinicians who have been guessing which treatment to use,” he said. “Both studies are attempts to provide doctors with some evidence on which to base treatment decisions and are not the final answer. Our study is ongoing, and with larger numbers of patients it may give clearer answers.”
The Overcoming COVID-19 study was funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Several coauthors have reported support from industry outside of the submitted work. BATS was funded by the European Union’s Horizons 2020 Program. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor’s spouse is employed by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. DeBiasi and Dr. Sexson Tejtel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That requires rapid pragmatic evaluation of therapies. Two real-world observational studies published online June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine do that, with differing results.
In the Overcoming COVID-19 study, investigators assessed initial therapy and outcomes for patients with MIS-C using surveillance data from 58 pediatric hospitals nationwide.
The results suggest that patients with MIS-C who were younger than 21 years of age and who were initially treated with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) plus glucocorticoids fared better in terms of cardiovascular function.
The study included 518 children (median age, 8.7 years) who were admitted to the hospital between March and October 2020 and who received at least one immunomodulatory therapy. In a propensity score–matched analysis, those given IVIG plus glucocorticoids (n = 103) had a lower risk for the primary outcome of cardiovascular dysfunction on or after day 2 than those given IVIG alone (n = 103), at 17% versus 31% (risk ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.34-0.94).
Risks for individual aspects of the study’s composite outcome were also lower with IVIG plus glucocorticoids. Left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 8% and 17%, respectively (RR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.19-1.15). Shock requiring vasopressor use emerged in 13% and 24%, respectively (RR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.29-1.00).
In addition, there were fewer cases in which adjunctive therapy was given on day one among those who received combination therapy than among those who received IVIG alone, at 34% versus 70% (RR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.36-0.65), but the risk for fever was not lower on or after day two (31% and 40%, respectively; RR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.53-1.13).
Lead author Mary Beth F. Son, MD, director of the rheumatology program at Boston Children’s Hospital, who is also associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, stressed that the study did not assess which MIS-C patients should receive treatment. “Rather, we studied children who had been treated with one of two initial regimens and then assessed short-term outcomes,” she told this news organization.
Going forward, it will be important to study which children should receive immunomodulatory treatment, Dr. Son said. “Specifically, can the less ill children receive IVIG alone or no treatment? This is an unanswered question at the moment, which could be addressed with a randomized controlled trial.”
Future directions, she added, will include assessing long-term cardiac outcomes for patients with MIS-C as well as studying outpatient regimens, especially those that involve steroids.
Earlier this year, French investigators found better outcomes with combined corticosteroids and IVIG than with IVIG alone. They suggested that combination therapy should be the standard of care, given the present state of therapeutic knowledge.
Maybe not so standard
Different results emerged, however, from an international study of MIS-C that compared three, rather than two, treatment approaches. Collaborators from the Best Available Treatment Study for MIS-C (BATS) evaluated data for 614 children with suspected MIS-C between June 2020 and February 2021 in 32 countries and found no substantial differences in recovery among children whose primary treatment was IVIG alone, IVIG plus glucocorticoids, or glucocorticoids alone.
The study by Andrew J. McArdle, MB BChir, MSC, a clinical research fellow at Imperial College London, and colleagues was published June 16 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
In the BATS cohort, 246 received IVIG alone, 208 received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, and 99 received glucocorticoids alone. Twenty-two patients received other combinations, including biologics, and 39 received no immunomodulatory therapy.
Among patients who were included in the primary analysis, death occurred or inotropic or ventilatory support was employed in 56 of 180 of the patients who received IVIG plus glucocorticoids, compared with 44 of 211 patients treated with IVIG alone, for an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 0.77 (95% CI, 0.33-1.82). Among those who received glucocorticoids alone, 17 of 83 met the primary endpoint of death or inotropic or ventilatory support, for an aOR relative to IVIG alone of 0.54 (95% CI, 0.22-1.33).
After adjustments, the likelihood for reduced disease severity was similar in the two groups relative to IVIG alone, at 0.90 for IVIG plus glucocorticoids and 0.93 for glucocorticoids alone. Time to reduction in disease severity was also comparable across all groups.
Some of the differences between the U.S. study and the global studies could be the result of the larger size of the international cohort and possibly a difference in the strains of virus in the United States and abroad, according to S. Sexson Tejtel, MD, PhD, MPH, a pediatric cardiologist at Texas Children’s Hospital and an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas. “Some strains make children sicker than others, and they’re going to need more treatment,” said Dr. Sexson Tejtel, who was not involved in either study.
Dr. Sexson Tejtel also noted that the U.S. researchers did not assess outcomes among children treated with steroids alone. “It would be interesting to know what steroids alone look like in the U.S. MIS-C population,” she said in an interview.
BATS corresponding author Michael Levin, MBE, PhD, FRCPCH, an Imperial College professor of pediatrics and international child health, told this news organization that the differing results may have arisen because of the international study’s three-treatment focus, its wider spectrum of patients, and its different endpoints: Death and inotropic support on or after day 2, versus echocardiographic left ventricular dysfunction or inotropic usage.
Regardless of the differences between the two studies, neither establishes the most effective single or combination treatment, writes Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases at Children’s National Hospital and Research Institute and George Washington University, Washington, in an accompanying editorial. “Specifically, neither study was powered to include an evaluation of approaches that steer away from broad immunosuppression with glucocorticoids and that focus on more targeted and titratable treatments with biologic agents, such as anakinra and infliximab,” she writes.
Dr. DeBiasi adds that long-term follow-up studies of cardiac and noncardiac outcomes in these patients will launch soon. “Meanwhile, continued collaboration across centers is essential to decreasing the short-term incidence of death and complications,” she writes.
“It will be interesting as we apply results from these studies as they come out to see how they change our practice,” Dr. Sexson Tejtel said. “And it would be good to have some randomized clinical trials.”
For Dr. Levin, the bottom line is that all three treatments are associated with recovery for a majority of children. “This is good news for clinicians who have been guessing which treatment to use,” he said. “Both studies are attempts to provide doctors with some evidence on which to base treatment decisions and are not the final answer. Our study is ongoing, and with larger numbers of patients it may give clearer answers.”
The Overcoming COVID-19 study was funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Several coauthors have reported support from industry outside of the submitted work. BATS was funded by the European Union’s Horizons 2020 Program. The study authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor’s spouse is employed by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. DeBiasi and Dr. Sexson Tejtel have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Foot rash and joint pain
A 21-year-old man presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 2-month history of joint pain, swelling, and difficulty walking that began with swelling of his right knee (FIGURE 1A). The patient said that over the course of several weeks, the swelling and joint pain spread to his left knee, followed by bilateral elbows and ankles. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin produced only modest improvement.
Two weeks prior to presentation, the patient also experienced widespread pruritus and conjunctivitis. His past medical history was significant for a sexual encounter that resulted in urinary tract infection (UTI)–like symptoms approximately 1 month prior to the onset of his joint symptoms. He did not seek care for the UTI-like symptoms.
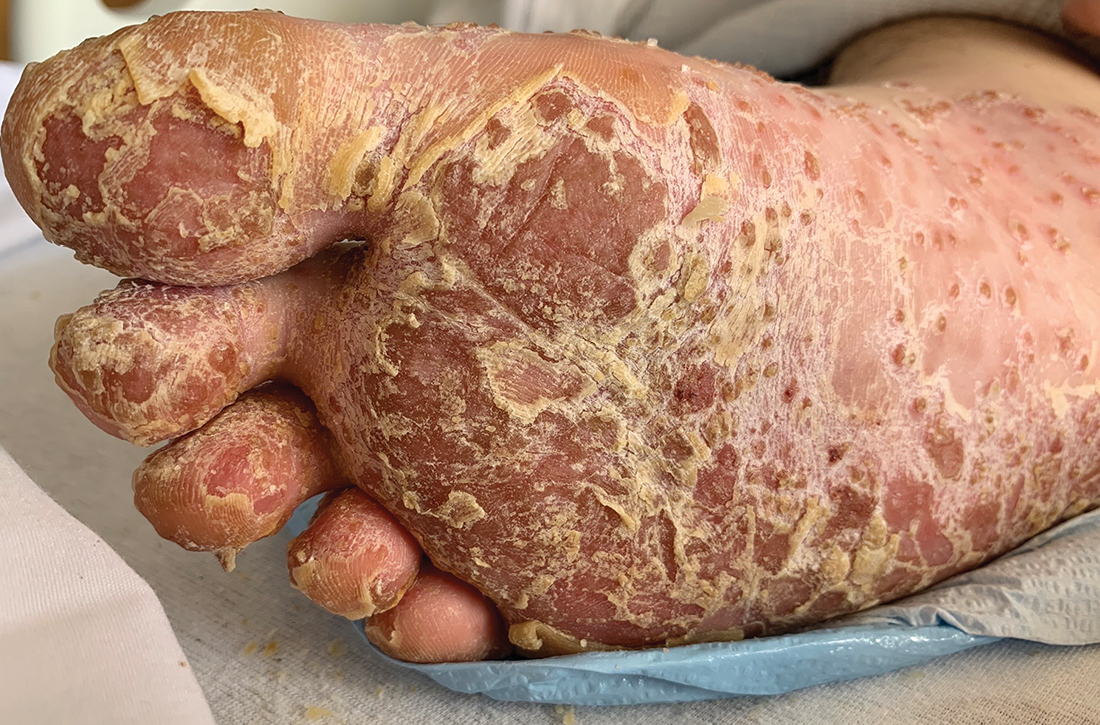
In the ED, the patient was febrile (102.1 °F) and tachycardic. Skin examination revealed erythematous papules, intact vesicles, and pustules with background hyperkeratosis and desquamation on his right foot (FIGURE 1B). The patient had spotty erythema on his palate and a 4-mm superficial erosion on the right penile shaft. Swelling and tenderness were noted over the elbows, knees, hands, and ankles. No inguinal lymphadenopathy was noted.

An arthrocentesis was performed on the right knee that demonstrated no organisms on Gram stain and a normal joint fluid cell count. A complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and urinalysis were ordered. A punch biopsy was performed on a scaly patch on the right elbow.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Keratoderma blenorrhagicum
The patient’s history, clinical findings, and lab results, including a positive Chlamydia trachomatis polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test from a urethral swab, pointed to a diagnosis of keratoderma blenorrhagicum in association with reactive arthritis (following infection with C trachomatis).
Relevant diagnostic findings included an elevated CRP of 26.5 mg/L (normal range, < 10 mg/L), an elevated ESR of 116 mm/h (normal range, < 15 mm/h) and as noted, a positive C trachomatis PCR test. The patient’s white blood cell count was 9.7/μL (normal range, 4.5-11 μL) and the rest of the CBC was within normal limits. Urinalysis was positive for leukocytes and rare bacteria. A treponemal antibody test was negative.
Additionally, the punch biopsy from the right elbow revealed acanthosis, intercellular spongiosis, and subcorneal pustules consistent with localized pustular psoriasis or keratoderma blenorrhagicum. After the diagnosis was made, human leukocyte antigen B27 allele (HLA-B27) testing was conducted and was positive.
A predisposition exacerbates the infection
Reactive arthritis, a type of spondyloarthropathy, features a triad of conjunctivitis, urethritis, and arthritis that follows either gastrointestinal or urogenital infection.1 Reactive arthritis occurs with a male predominance of 3:1, and the worldwide prevalence is 1 in 3000.1 Causative bacteria include C trachomatis, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile, and C pneumoniae.2 Patients with the HLA-B27 allele are 50 times more likely to develop reactive arthritis following infection with the aforementioned bacteria.1
Findings consistent with a diagnosis of reactive arthritis include a recent history of gastrointestinal or urogenital illness, joint pain, conjunctivitis, oral lesions, cutaneous changes, and genital lesions.3 Diagnostic tests should include arthrocentesis with cultures or PCR and cell count, ESR, CRP, CBC, and urinalysis. HLA-B27 can be used to support the diagnosis but is not routinely recommended.2
Pustules and psoriasiform scaling characterize this diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for the signs and symptoms seen in this patient include disseminated gonococcal arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and secondary syphilis.
Gonococcal arthritis manifests with painful, sterile joints as well as pustules on the palms and soles, but not with the psoriasiform scaling and desquamation that was seen in this case. A culture or PCR from urethral discharge or pustules on the palms and soles could be used to confirm this diagnosis.3
Continue to: Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis
Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis and the psoriasiform rashing of reactive arthritis (keratoderma blenorrhagicum) show similar histopathology; however, patients with psoriatic arthritis generally exhibit fewer constitutional symptoms.4
Rheumatoid arthritis also manifests with joint pain and swelling, especially in the hands, wrists, and knees. This diagnosis was unlikely in this patient, where small joints were largely uninvolved.4
Secondary syphilis also manifests with papular, scaly, erythematous lesions on the palms and soles along with pityriasis rosea–like rashing on the trunk. However, it rarely produces pustules or hyperkeratotic keratoderma.5 As noted earlier, a treponemal antibody test in this patient was negative.
Drug therapy is the best option
First-line therapy for reactive arthritis consists of NSAIDs. If the patient exhibits an inadequate response after a 2-week trial, intra-articular or systemic glucocorticoids may be considered.3 If the patient fails to respond to the steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be considered. Reactive arthritis is considered chronic if the disease lasts longer than 6 months, at which point, DMARDs or tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors may be utilized.3 For cutaneous manifestations, such as keratoderma blenorrhagicum, topical glucocorticoids twice daily may be used along with keratolytic agents.
Our patient received 2 doses of azithromycin (500 mg IV) and 1 dose of ceftriaxone (2 g IV) to treat his infection while in the ED. Over the course of his hospital stay, he received ceftriaxone (1 g IV daily) for 6 days and naproxen (500 mg tid po) which was tapered. Additionally, he received a week of methylprednisolone (60 mg IM daily) before tapering to oral prednisone. His taper consisted of 40 mg po for 1 week and was decreased by 10 mg each week. Augmented betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% cream and urea 20% cream were prescribed for twice-daily application for the hyperkeratotic scale on both of his feet.
1. Hayes KM, Hayes RJP, Turk MA, et al. Evolving patterns of reactive arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:2083-2088. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04522-4
2. Duba AS, Mathew SD. The seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Prim Care. 2018;45:271-287. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2018.02.005
3. Yu DT, van Tubergen A. Reactive arthritis. In: Joachim S, Romain PL, eds. UpToDate. Updated April 28, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/reactive-arthritis?search=reactive%20arthritis&topicRef=5571&source=see_link#H9
4. Barth WF, Segal K. Reactive arthritis (Reiter’s Syndrome). Am Fam Physician. 1999;60:499-503, 507.
5. Coleman E, Fiahlo A, Brateanu A. Secondary syphilis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:510-511. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.84a.16089
A 21-year-old man presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 2-month history of joint pain, swelling, and difficulty walking that began with swelling of his right knee (FIGURE 1A). The patient said that over the course of several weeks, the swelling and joint pain spread to his left knee, followed by bilateral elbows and ankles. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin produced only modest improvement.
Two weeks prior to presentation, the patient also experienced widespread pruritus and conjunctivitis. His past medical history was significant for a sexual encounter that resulted in urinary tract infection (UTI)–like symptoms approximately 1 month prior to the onset of his joint symptoms. He did not seek care for the UTI-like symptoms.
In the ED, the patient was febrile (102.1 °F) and tachycardic. Skin examination revealed erythematous papules, intact vesicles, and pustules with background hyperkeratosis and desquamation on his right foot (FIGURE 1B). The patient had spotty erythema on his palate and a 4-mm superficial erosion on the right penile shaft. Swelling and tenderness were noted over the elbows, knees, hands, and ankles. No inguinal lymphadenopathy was noted.

An arthrocentesis was performed on the right knee that demonstrated no organisms on Gram stain and a normal joint fluid cell count. A complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and urinalysis were ordered. A punch biopsy was performed on a scaly patch on the right elbow.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Keratoderma blenorrhagicum
The patient’s history, clinical findings, and lab results, including a positive Chlamydia trachomatis polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test from a urethral swab, pointed to a diagnosis of keratoderma blenorrhagicum in association with reactive arthritis (following infection with C trachomatis).
Relevant diagnostic findings included an elevated CRP of 26.5 mg/L (normal range, < 10 mg/L), an elevated ESR of 116 mm/h (normal range, < 15 mm/h) and as noted, a positive C trachomatis PCR test. The patient’s white blood cell count was 9.7/μL (normal range, 4.5-11 μL) and the rest of the CBC was within normal limits. Urinalysis was positive for leukocytes and rare bacteria. A treponemal antibody test was negative.
Additionally, the punch biopsy from the right elbow revealed acanthosis, intercellular spongiosis, and subcorneal pustules consistent with localized pustular psoriasis or keratoderma blenorrhagicum. After the diagnosis was made, human leukocyte antigen B27 allele (HLA-B27) testing was conducted and was positive.
A predisposition exacerbates the infection
Reactive arthritis, a type of spondyloarthropathy, features a triad of conjunctivitis, urethritis, and arthritis that follows either gastrointestinal or urogenital infection.1 Reactive arthritis occurs with a male predominance of 3:1, and the worldwide prevalence is 1 in 3000.1 Causative bacteria include C trachomatis, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile, and C pneumoniae.2 Patients with the HLA-B27 allele are 50 times more likely to develop reactive arthritis following infection with the aforementioned bacteria.1
Findings consistent with a diagnosis of reactive arthritis include a recent history of gastrointestinal or urogenital illness, joint pain, conjunctivitis, oral lesions, cutaneous changes, and genital lesions.3 Diagnostic tests should include arthrocentesis with cultures or PCR and cell count, ESR, CRP, CBC, and urinalysis. HLA-B27 can be used to support the diagnosis but is not routinely recommended.2
Pustules and psoriasiform scaling characterize this diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for the signs and symptoms seen in this patient include disseminated gonococcal arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and secondary syphilis.
Gonococcal arthritis manifests with painful, sterile joints as well as pustules on the palms and soles, but not with the psoriasiform scaling and desquamation that was seen in this case. A culture or PCR from urethral discharge or pustules on the palms and soles could be used to confirm this diagnosis.3
Continue to: Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis
Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis and the psoriasiform rashing of reactive arthritis (keratoderma blenorrhagicum) show similar histopathology; however, patients with psoriatic arthritis generally exhibit fewer constitutional symptoms.4
Rheumatoid arthritis also manifests with joint pain and swelling, especially in the hands, wrists, and knees. This diagnosis was unlikely in this patient, where small joints were largely uninvolved.4
Secondary syphilis also manifests with papular, scaly, erythematous lesions on the palms and soles along with pityriasis rosea–like rashing on the trunk. However, it rarely produces pustules or hyperkeratotic keratoderma.5 As noted earlier, a treponemal antibody test in this patient was negative.
Drug therapy is the best option
First-line therapy for reactive arthritis consists of NSAIDs. If the patient exhibits an inadequate response after a 2-week trial, intra-articular or systemic glucocorticoids may be considered.3 If the patient fails to respond to the steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be considered. Reactive arthritis is considered chronic if the disease lasts longer than 6 months, at which point, DMARDs or tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors may be utilized.3 For cutaneous manifestations, such as keratoderma blenorrhagicum, topical glucocorticoids twice daily may be used along with keratolytic agents.
Our patient received 2 doses of azithromycin (500 mg IV) and 1 dose of ceftriaxone (2 g IV) to treat his infection while in the ED. Over the course of his hospital stay, he received ceftriaxone (1 g IV daily) for 6 days and naproxen (500 mg tid po) which was tapered. Additionally, he received a week of methylprednisolone (60 mg IM daily) before tapering to oral prednisone. His taper consisted of 40 mg po for 1 week and was decreased by 10 mg each week. Augmented betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% cream and urea 20% cream were prescribed for twice-daily application for the hyperkeratotic scale on both of his feet.
A 21-year-old man presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 2-month history of joint pain, swelling, and difficulty walking that began with swelling of his right knee (FIGURE 1A). The patient said that over the course of several weeks, the swelling and joint pain spread to his left knee, followed by bilateral elbows and ankles. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin produced only modest improvement.
Two weeks prior to presentation, the patient also experienced widespread pruritus and conjunctivitis. His past medical history was significant for a sexual encounter that resulted in urinary tract infection (UTI)–like symptoms approximately 1 month prior to the onset of his joint symptoms. He did not seek care for the UTI-like symptoms.
In the ED, the patient was febrile (102.1 °F) and tachycardic. Skin examination revealed erythematous papules, intact vesicles, and pustules with background hyperkeratosis and desquamation on his right foot (FIGURE 1B). The patient had spotty erythema on his palate and a 4-mm superficial erosion on the right penile shaft. Swelling and tenderness were noted over the elbows, knees, hands, and ankles. No inguinal lymphadenopathy was noted.

An arthrocentesis was performed on the right knee that demonstrated no organisms on Gram stain and a normal joint fluid cell count. A complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and urinalysis were ordered. A punch biopsy was performed on a scaly patch on the right elbow.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Keratoderma blenorrhagicum
The patient’s history, clinical findings, and lab results, including a positive Chlamydia trachomatis polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test from a urethral swab, pointed to a diagnosis of keratoderma blenorrhagicum in association with reactive arthritis (following infection with C trachomatis).
Relevant diagnostic findings included an elevated CRP of 26.5 mg/L (normal range, < 10 mg/L), an elevated ESR of 116 mm/h (normal range, < 15 mm/h) and as noted, a positive C trachomatis PCR test. The patient’s white blood cell count was 9.7/μL (normal range, 4.5-11 μL) and the rest of the CBC was within normal limits. Urinalysis was positive for leukocytes and rare bacteria. A treponemal antibody test was negative.
Additionally, the punch biopsy from the right elbow revealed acanthosis, intercellular spongiosis, and subcorneal pustules consistent with localized pustular psoriasis or keratoderma blenorrhagicum. After the diagnosis was made, human leukocyte antigen B27 allele (HLA-B27) testing was conducted and was positive.
A predisposition exacerbates the infection
Reactive arthritis, a type of spondyloarthropathy, features a triad of conjunctivitis, urethritis, and arthritis that follows either gastrointestinal or urogenital infection.1 Reactive arthritis occurs with a male predominance of 3:1, and the worldwide prevalence is 1 in 3000.1 Causative bacteria include C trachomatis, Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile, and C pneumoniae.2 Patients with the HLA-B27 allele are 50 times more likely to develop reactive arthritis following infection with the aforementioned bacteria.1
Findings consistent with a diagnosis of reactive arthritis include a recent history of gastrointestinal or urogenital illness, joint pain, conjunctivitis, oral lesions, cutaneous changes, and genital lesions.3 Diagnostic tests should include arthrocentesis with cultures or PCR and cell count, ESR, CRP, CBC, and urinalysis. HLA-B27 can be used to support the diagnosis but is not routinely recommended.2
Pustules and psoriasiform scaling characterize this diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for the signs and symptoms seen in this patient include disseminated gonococcal arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and secondary syphilis.
Gonococcal arthritis manifests with painful, sterile joints as well as pustules on the palms and soles, but not with the psoriasiform scaling and desquamation that was seen in this case. A culture or PCR from urethral discharge or pustules on the palms and soles could be used to confirm this diagnosis.3
Continue to: Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis
Psoriasis in association with psoriatic arthritis and the psoriasiform rashing of reactive arthritis (keratoderma blenorrhagicum) show similar histopathology; however, patients with psoriatic arthritis generally exhibit fewer constitutional symptoms.4
Rheumatoid arthritis also manifests with joint pain and swelling, especially in the hands, wrists, and knees. This diagnosis was unlikely in this patient, where small joints were largely uninvolved.4
Secondary syphilis also manifests with papular, scaly, erythematous lesions on the palms and soles along with pityriasis rosea–like rashing on the trunk. However, it rarely produces pustules or hyperkeratotic keratoderma.5 As noted earlier, a treponemal antibody test in this patient was negative.
Drug therapy is the best option
First-line therapy for reactive arthritis consists of NSAIDs. If the patient exhibits an inadequate response after a 2-week trial, intra-articular or systemic glucocorticoids may be considered.3 If the patient fails to respond to the steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be considered. Reactive arthritis is considered chronic if the disease lasts longer than 6 months, at which point, DMARDs or tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors may be utilized.3 For cutaneous manifestations, such as keratoderma blenorrhagicum, topical glucocorticoids twice daily may be used along with keratolytic agents.
Our patient received 2 doses of azithromycin (500 mg IV) and 1 dose of ceftriaxone (2 g IV) to treat his infection while in the ED. Over the course of his hospital stay, he received ceftriaxone (1 g IV daily) for 6 days and naproxen (500 mg tid po) which was tapered. Additionally, he received a week of methylprednisolone (60 mg IM daily) before tapering to oral prednisone. His taper consisted of 40 mg po for 1 week and was decreased by 10 mg each week. Augmented betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% cream and urea 20% cream were prescribed for twice-daily application for the hyperkeratotic scale on both of his feet.
1. Hayes KM, Hayes RJP, Turk MA, et al. Evolving patterns of reactive arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:2083-2088. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04522-4
2. Duba AS, Mathew SD. The seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Prim Care. 2018;45:271-287. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2018.02.005
3. Yu DT, van Tubergen A. Reactive arthritis. In: Joachim S, Romain PL, eds. UpToDate. Updated April 28, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/reactive-arthritis?search=reactive%20arthritis&topicRef=5571&source=see_link#H9
4. Barth WF, Segal K. Reactive arthritis (Reiter’s Syndrome). Am Fam Physician. 1999;60:499-503, 507.
5. Coleman E, Fiahlo A, Brateanu A. Secondary syphilis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:510-511. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.84a.16089
1. Hayes KM, Hayes RJP, Turk MA, et al. Evolving patterns of reactive arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38:2083-2088. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04522-4
2. Duba AS, Mathew SD. The seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Prim Care. 2018;45:271-287. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2018.02.005
3. Yu DT, van Tubergen A. Reactive arthritis. In: Joachim S, Romain PL, eds. UpToDate. Updated April 28, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/reactive-arthritis?search=reactive%20arthritis&topicRef=5571&source=see_link#H9
4. Barth WF, Segal K. Reactive arthritis (Reiter’s Syndrome). Am Fam Physician. 1999;60:499-503, 507.
5. Coleman E, Fiahlo A, Brateanu A. Secondary syphilis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2017;84:510-511. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.84a.16089
Giving flu and COVID-19 shots at same time appears safe, effective: Study
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (Novavax) is showing 89.8% efficacy in an ongoing, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. When the researchers gave a smaller group of 431 volunteers from the same study an influenza shot at the same time, efficacy dropped slightly to 87.5%.
“These results demonstrate the promising opportunity for concomitant vaccination, which may lead to higher vaccination rates and further protection against both viruses,” said study coauthor Raja Rajaram, MD, medical affairs lead, Europe, Middle East, and Africa at Seqirus, the company that supplied the influenza vaccines for the research.
The research was published online June 13 as a medRxiv preprint.
“With these COVID-19 vaccines, there are essentially no concurrent use studies,” Paul A. Offit, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment.
Traditionally, how a new vaccine might interact with existing vaccines is studied before the product is cleared for use. That was not the case, however, with the COVID-19 vaccines made available through expedited emergency use authorization.
The researchers found no major safety concerns associated with concomitant vaccination, Dr. Rajaram said. In addition to safety, the aim of the current study was to determine whether either vaccine changes the immunogenicity or effectiveness of the other.
“It’s a small study, but it’s certainly encouraging to know that there didn’t seem to be a big decrease in immunogenicity either way and the safety profile was similar. Not identical, but similar,” added Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
Some adverse events were more common in the co-administration group. For example, injection-site tenderness was reported by 70%, versus 58% for those who got the COVID-19 shot alone. The same was true for pain at the injection site, 40% versus 29%; fatigue, 28% versus 19%; and muscle pain, 28% versus 21%.
Rates of unsolicited adverse events, adverse events that required medical attention, and serious adverse events were low and well balanced between groups.
Fewer antibodies important?
Although co-administering the two vaccines did not change the immune response for the influenza vaccine, the spike protein antibody response to the COVID-19 vaccine was less robust.
Antibody titer levels at day 35 were 46,678 among people in the Novavax vaccine alone group, compared with 31,236 titers in the participants who received both vaccines.
“This impact did not seem to be clinically meaningful as vaccine efficacy appeared to be preserved,” the researchers noted.
Gregory A. Poland, MD, an internist and part of the Vaccine Research Group at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., agreed. “I highly doubt that is significant,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Rajaram said the antibody findings are “slightly surprising but not completely unexpected” because the same observation has been made in other combination vaccine studies. He added that the antibody levels “remain very high, although we do not yet know what antibody levels are required to achieve protection against COVID-19.”
The decrease could become more concerning if people start with fewer antibodies and they drop over time with normal waning of protection, Dr. Poland said. This group could include people over age 65 or people who are immunocompromised. More data would be needed to confirm this, he added.
A boost for booster vaccines?
The research could carry implications for future COVID-19 booster shots, Dr. Poland said.
“Overall, the study results are reassuring and of potential practical importance if we have to give booster doses. It will make it easier to give them both in one visit,” said Dr. Poland, who was not affiliated with the research.
Although Novavax could be positioning itself as a logical choice for a COVID-19 booster based on the findings, Dr. Offit believes it is more important to focus on having more COVID-19 vaccine options available.
“There may be, as we say at the track, ‘courses for horses,’ ” he said, meaning that different vaccines may be better suited for different situations.
“It’s likely we’re going to find these vaccines have different safety profiles, they may have different populations for whom they work best, and they may have differences in terms of their long-term durability,” he added. Also, some may prove more effective against certain variants of concern.
The Novavax vaccine would add a new class of COVID-19 vaccine to the mRNA and adenovirus vaccines. NVX-CoV2373 is a recombinant spike protein vaccine.
“I think the more vaccines that are available here, the better,” Dr. Offit said.
Study limitations
Dr. Poland shared some caveats. The study was primarily conducted in adults aged 18-64 years, so there is less certainty on what could happen in people over 65. Furthermore, co-administration was evaluated after the first dose of the Novavax vaccine. “The reason I bring that up is most of the COVID-19 vaccine reactogenicity occurs with dose two, not dose one.
“All in all, it’s an important first step – but it’s only a first step,” Dr. Poland said. “We need more data, including in elderly people who are primarily at risk for morbidity and mortality from the flu.”
He suggested expanding the research to study co-administration of COVID-19 vaccines with different formulations of influenza vaccines.
The study was supported by Novavax. Dr. Offit had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Poland serves as a consultant to all of the COVID-19 vaccine companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Prediction rule identifies low infection risk in febrile infants
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A clinical prediction rule combining procalcitonin, absolute neutrophil count, and urinalysis effectively identified most febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections, based on data from 702 individuals
The clinical prediction rule (CPR) described in 2019 in JAMA Pediatrics was developed by the Febrile Infant Working Group of the Pediatric Emergency Care Applied Research Network (PECARN) to identify febrile infants at low risk for serious bacterial infections in order to reduce unnecessary procedures, antibiotics use, and hospitalization, according to April Clawson, MD, of Arkansas Children’s Hospital, Little Rock, and colleagues.
In a poster presented at the Pediatric Academic Societies annual meeting, the researchers conducted an external validation of the rule via a retrospective, observational study of febrile infants aged 60 days and younger who presented to an urban pediatric ED between October 2014 and June 2019. The study population included 702 infants with an average age of 36 days. Approximately 45% were female, and 60% were White. Fever was defined as 38° C or greater. Exclusion criteria were prematurity, receipt of antibiotics in the past 48 hours, presence of an indwelling medical device, and evidence of focal infection (not including otitis media); those who were critically ill at presentation or had a previous medical condition were excluded as well, the researchers said. A serious bacterial infection (SBI) was defined as a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, or bacterial meningitis.
Based on the CPR, a patient is considered low risk for an SBI if all the following criteria are met: normal urinalysis (defined as absence of leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and 5 or less white blood cells per high power field); an absolute neutrophil count of 4,090/mL or less; and procalcitonin of 1.71 ng/mL or less.
Overall, 62 infants (8.8%) were diagnosed with an SBI, similar to the 9.3% seen in the parent study of the CPR, Dr. Clawson said.
Of these, 42 had a UTI only (6%), 10 had bacteremia only (1.4%), and 1 had meningitis only (0.1%). Another five infants had UTI with bacteremia (0.7%), and four had bacteremia and meningitis (0.6%).
According to the CPR, 432 infants met criteria for low risk and 270 were considered high risk. A total of five infants who were classified as low risk had SBIs, including two with UTIs, two with bacteremia, and one with meningitis.
“The CPR derived and validated by Kupperman et al. had a decreased sensitivity for the patients in our study and missed some SBIs,” Dr. Clawson noted. “However, it had a strong negative predictive value, so it may still be a useful CPR.”
The sensitivity for the CPR in the parent study and the current study was 97.7 and 91.9, respectively; specificity was 60 and 66.7, respectively. The negative predictive values for the parent and current studies were 99.6 and 98.8, respectively, and the positive predictive values were 20.7 and 21.1.
The results support the potential of the CPR, but more external validation is needed, they said.
PECARN rule keeps it simple
“It has always been a challenge to identify infants with fever with serious bacterial infections when they are well-appearing,” Yashas Nathani, MD, of Oklahoma University, Oklahoma City, said in an interview. “The clinical prediction rule offers a simple, step-by-step approach for pediatricians and emergency medicine physicians to stratify infants in high or low risk categories for SBIs. However, as with everything, validation of protocols, guidelines and decision-making algorithms is extremely important, especially as more clinicians start to employ this CPR to their daily practice. This study objectively puts the CPR to the test and offers an independent external validation.
“Although this study had a lower sensitivity in identifying infants with SBI using the clinical prediction rule as compared to the original study, the robust validation of negative predictive value is extremely important and not surprising,” said Dr. Nathani. “The goal of this CPR is to identify infants with low-risk for SBI and the stated NPV helps clinicians in doing just that.”
Overall, “the clinical prediction rule is a fantastic resource for physicians to identify potentially sick infants with fever, especially the ones that appear well on initial evaluation,” said Dr. Nathani. However, “it is important to acknowledge that this is merely a guideline, and not an absolute rule. Clinicians also must remain cautious, as this rule does not incorporate the presence of viral pathogens as a factor.
“It is important to continue the scientific quest to refine our approach in identifying infants with serious bacterial infections when fever is the only presentation,” Dr. Nathani noted. “Additional research is needed to continue fine-tuning this CPR and the thresholds for procalcitonin and absolute neutrophil counts to improve the sensitivity and specificity.” Research also is needed to explore whether this CPR can be extended to incorporate viral testing, “as a large number of infants with fever have viral pathogens as the primary etiology,” he concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Nathani had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PAS 2021
As new cases fall, U.S. passes 4 million children with COVID-19
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.
Even as the number of new COVID-19 cases continues to drop, the United States reached the 4-million mark for infected children, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
. That weekly total, the lowest since June of 2020, comes from 49 states (excluding N.Y.), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Children represent 14.1% of all COVID-19 cases since the beginning of the pandemic, while the corresponding figure for the week ending June 10 was 19.0%. That weekly proportion of cases among children had been rising pretty steadily through the winter and early spring, but the situation has become much more volatile over the last month, the AAP/CHA data show.
Use of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children aged 16-17 years, of course, didn’t begin until April, and the vaccine wasn’t authorized for children aged 12-15 years until mid-May. The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have not received such authorization yet, but Moderna is in the process of seeking an emergency-use recommendation from the Food and Drug Administration.
In the younger group of children who are currently eligible, completion of the vaccine regimen took a big jump in the week ending June 14, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The cumulative share of those aged 12-15 years who had received a second dose jumped from 4.1% on June 7 to 11.4% on June 14, with comparable numbers for 16- and 17-year-olds coming in at 26.4% and 29.1%.
Activity over just the last 14 days, however, shows a slight decrease in children aged 12-15 getting a first dose: For just the 2 weeks ending June 7, 17.9% of all children in the age group initiated a first dose, but for the 14 days ending June 14, only 17.1% of the age group did so, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker site.
For children aged 16-17 years – of whom less than 30% have reached full vaccination – activity seems to have stagnated: 4.8% of all 16- to 17-year-olds initiated a first vaccination during the 14 days ending June 7, compared with 4.7% who did so during the 14 days ending June 14, the CDC reported.
Older age groups with higher completion rates are still producing greater vaccine initiation. As of June 14, those aged 25-39 years had a completion rate of 41.9% and 24.0% of the age group had received a first dose in the previous 2 weeks, while 61.4% of those aged 50-64 were fully vaccinated, and 18.0% had gotten their first dose, the CDC data indicate.
Third COVID-19 vaccine dose helped some transplant recipients
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
All of those with low titers before the third dose had high titers after receiving the additional shot, but only about 33% of those with negative initial responses had detectable antibodies after the third dose, according to the paper, published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, who keep a COVID-19 vaccine registry, perform antibody tests on all registry subjects and inform them of their results. Registry participants were asked to inform the research team if they received a third dose, and, the research team tracked the immune responses of those who did.
The participants in this case series had low antibody levels and received a third dose of the vaccine on their own between March 20 and May 10 of 2021.
Third dose results
In this cases series – thought to be the first to look at third vaccine shots in this type of patient group – all six of those who had low antibody titers before the third dose had high-positive titers after the third dose.
Of the 24 individuals who had negative antibody titers before the third dose, just 6 had high titers after the third dose.
Two of the participants had low-positive titers, and 16 were negative.
“Several of those boosted very nicely into ranges seen, using these assays, in healthy persons,” said William Werbel, MD, a fellow in infectious disease at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, who helped lead the study. Those with negative levels, even if they responded, tended to have lower titers, he said.
“The benefits at least from an antibody perspective were not the same for everybody and so this is obviously something that needs to be considered when thinking about selecting patients” for a COVID-19 prevention strategy, he said.
Reactions to the vaccine were low to moderate, such as some arm pain and fatigue.
“Showing that something is safe in that special, vulnerable population is important,” Dr. Werbel said. “We’re all wanting to make sure that we’re doing no harm.”
Dr. Werbel noted that there was no pattern in the small series based on the organ transplanted or in the vaccines used. As their third shot, 15 of the patients received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine; 9 received Moderna; and 6 received Pfizer-BioNTech.
Welcome news, but larger studies needed
“To think that a third dose could confer protection for a significant number of people is of course extremely welcome news,” said Christian Larsen, MD, DPhil, professor of surgery in the transplantation division at Emory University, Atlanta, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the easiest conceivable next intervention.”
He added, “We just want studies to confirm that – larger studies.”
Dr. Werbel stressed the importance of looking at third doses in these patients in a more controlled fashion in a randomized trial, to more carefully monitor safety and how patients fare when starting with one type of vaccine and switching to another, for example.
Richard Wender, MD, chair of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the findings are a reminder that there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and vaccination.
“We still don’t know who will or will not benefit from a third dose,” he said. “And our knowledge is evolving. For example, a recent study suggested that people with previous infection and who are vaccinated may have better and longer protection than people with vaccination alone. We’re still learning.”
He added that specialists, not primary care clinicians, should be relied upon to respond to this emerging vaccination data. Primary care doctors are very busy in other ways – such as in getting children caught up on vaccinations and helping adults return to managing their chronic diseases, Dr. Wender noted.
“Their focus needs to be on helping to overcome hesitancy, mistrust, lack of information, or antivaccination sentiment to help more people feel comfortable being vaccinated – this is a lot of work and needs constant focus. In short, primary care clinicians need to focus chiefly on the unvaccinated,” he said.
“Monitoring immunization recommendations for unique at-risk populations should be the chief responsibility of teams providing subspecialty care, [such as for] transplant patients, people with chronic kidney disease, cancer patients, and people with other chronic illnesses. This will allow primary care clinicians to tackle their many complex jobs.”
Possible solutions for those with low antibody responses
Dr. Larsen said that those with ongoing low antibody responses might still have other immune responses, such as a T-cell response. Such patients also could consider changing their vaccine type, he said.
“At the more significant intervention level, there may be circumstances where one could change the immunosuppressive drugs in a controlled way that might allow a better response,” suggested Dr. Larsen. “That’s obviously going to be something that requires a lot more thought and careful study.”
Dr. Werbel said that other options might need to be considered for those having no response following a third dose. One possibility is trying a vaccine with an adjuvant, such as the Novavax version, which might be more widely available soon.
“If you’re given a third dose of a very immunogenic vaccine – something that should work – and you just have no antibody development, it seems relatively unlikely that doing the same thing again is going to help you from that perspective, and for all we know might expose you to more risk,” Dr. Werbel noted.
Participant details
None of the 30 patients were thought to have ever had COVID-19. On average, patients had received their transplant 4.5 years before their original vaccination. In 25 patients, maintenance immunosuppression included tacrolimus or cyclosporine along with mycophenolate. Corticosteroids were also used for 24 patients, sirolimus was used for one patient, and belatacept was used for another patient.
Fifty-seven percent of patients had received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine originally, and 43% the Moderna vaccine. Most of the patients were kidney recipients, with two heart, three liver, one lung, one pancreas and one kidney-pancreas.
Dr. Werbel, Dr. Wender, and Dr. Larsen reported no relevant disclosures.
Infections in infants: An update
Converge 2021 session
Febrile Infant Update
Presenter
Russell J. McCulloh, MD
Session summary
Infections in infants aged younger than 90 days have been the subject of intense study in pediatric hospital medicine for many years. With the guidance of our talented presenter Dr. Russell McCulloh of Children’s Hospital & Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., the audience explored the historical perspective and evolution of this scientific question, including successes, special situations, newer screening tests, and description of cutting-edge scoring tools and platforms.
The challenge – Tens of thousands of infants present for care in the setting of fever each year. We know that our physical exam and history-taking skills are unlikely to be helpful in risk stratification. We have been guided by the desire to separate serious bacterial infection (SBI: bone infection, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, bacteremia, enteritis) from invasive bacterial infection (IBI: meningitis and bacteremia). Data has shown that no test is 100% sensitive or specific, therefore we have to balance risk of disease to cost and invasiveness of tests. Important questions include whether to test and how to stratify by age, who to admit, and who to provide antibiotics.
The wins and exceptions – Fortunately, the early Boston, Philadelphia, and Rochester criteria set the stage for safely reducing testing. The current American College of Emergency Physicians guidelines for infants aged 29-90 days allows for lumbar puncture to be optional knowing that a look back using prior criteria identified no cases of meningitis in the low risk group. Similarly, in low-risk infants aged less that 29 days in nearly 4,000 cases there were just 2 infants with meningitis. Universal screening of moms for Group B Streptococcus with delivery of antibiotics in appropriate cases has dramatically decreased incidence of SBI. The Hib and pneumovax vaccines have likewise decreased incidence of SBI. Exceptions persist, including knowledge that infants with herpes simplex virus disease will not have fever in 50% of cases and that risk of HSV transmission is highest (25%-60% transmission) in mothers with primary disease. Given risk of HSV CNS disease after 1 week of age, in any high-risk infant less than 21 days, the mantra remains to test and treat.
The cutting edge – Thanks to ongoing research, we now have the PECARN and REVISE study groups to further aid decision-making. With PECARN we know that SBI in infants is extremely unlikely (negative predictive value, 99.7%) with a negative urinalysis , absolute neutrophil count less than 4,090, and procalcitonin less than 1.71. REVISE has revealed that infants with positive viral testing are unlikely to have SBI (7%-12%), particularly with influenza and RSV disease. Procalcitonin has also recently been shown to be an effective tool to rule out disease with the highest negative predictive value among available inflammatory markers. The just-published Aronson rule identifies a scoring system for IBI (using age less than 21 days/1pt; temp 38-38.4° C/2pt; >38.5° C/4pt; abnormal urinalysis/3pt; and absolute neutrophil count >5185/2pt) where any score greater than2 provides a sensitivity of 98.8% and NPV in validation studies of 99.4%. Likewise, multiplex polymerase chain reaction testing of spinal fluid has allowed for additional insight in pretreated cases and has helped us to remove antibiotic treatment from cases where parechovirus and enterovirus are positive because of the low risk for concomitant bacterial meningitis. As we await the release of revised national American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines, it is safe to say great progress has been made in the care of young febrile infants with shorter length of stay and fewer tests for all.
Key takeaways
- Numerous screening tests, rules, and scoring tools have been created to improve identification of infants with IBI, a low-frequency, high-morbidity event. The most recent with negative predictive values of 99.7% and 99.4% are the PECARN and Aronson scoring tools.
- Recent studies of the febrile infant population indicate that the odds of UTI or bacteremia in infants with respiratory symptoms is low, particularly for RSV and influenza.
- Among newer tests developed, a negative procalcitonin has the highest negative predictive value.
- Viral pathogens identified on cerebrospinal fluid molecular testing can be helpful in pretreated cases and indicative of low likelihood of bacterial meningitis allowing for observation off of antibiotics.
Dr. King is a hospitalist, associate director for medical education and associate program director for the pediatrics residency program at Children’s Minnesota in Minneapolis. She has shared some of her resident teaching, presentation skills, and peer-coaching work on a national level.
Converge 2021 session
Febrile Infant Update
Presenter
Russell J. McCulloh, MD
Session summary
Infections in infants aged younger than 90 days have been the subject of intense study in pediatric hospital medicine for many years. With the guidance of our talented presenter Dr. Russell McCulloh of Children’s Hospital & Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., the audience explored the historical perspective and evolution of this scientific question, including successes, special situations, newer screening tests, and description of cutting-edge scoring tools and platforms.
The challenge – Tens of thousands of infants present for care in the setting of fever each year. We know that our physical exam and history-taking skills are unlikely to be helpful in risk stratification. We have been guided by the desire to separate serious bacterial infection (SBI: bone infection, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, bacteremia, enteritis) from invasive bacterial infection (IBI: meningitis and bacteremia). Data has shown that no test is 100% sensitive or specific, therefore we have to balance risk of disease to cost and invasiveness of tests. Important questions include whether to test and how to stratify by age, who to admit, and who to provide antibiotics.
The wins and exceptions – Fortunately, the early Boston, Philadelphia, and Rochester criteria set the stage for safely reducing testing. The current American College of Emergency Physicians guidelines for infants aged 29-90 days allows for lumbar puncture to be optional knowing that a look back using prior criteria identified no cases of meningitis in the low risk group. Similarly, in low-risk infants aged less that 29 days in nearly 4,000 cases there were just 2 infants with meningitis. Universal screening of moms for Group B Streptococcus with delivery of antibiotics in appropriate cases has dramatically decreased incidence of SBI. The Hib and pneumovax vaccines have likewise decreased incidence of SBI. Exceptions persist, including knowledge that infants with herpes simplex virus disease will not have fever in 50% of cases and that risk of HSV transmission is highest (25%-60% transmission) in mothers with primary disease. Given risk of HSV CNS disease after 1 week of age, in any high-risk infant less than 21 days, the mantra remains to test and treat.
The cutting edge – Thanks to ongoing research, we now have the PECARN and REVISE study groups to further aid decision-making. With PECARN we know that SBI in infants is extremely unlikely (negative predictive value, 99.7%) with a negative urinalysis , absolute neutrophil count less than 4,090, and procalcitonin less than 1.71. REVISE has revealed that infants with positive viral testing are unlikely to have SBI (7%-12%), particularly with influenza and RSV disease. Procalcitonin has also recently been shown to be an effective tool to rule out disease with the highest negative predictive value among available inflammatory markers. The just-published Aronson rule identifies a scoring system for IBI (using age less than 21 days/1pt; temp 38-38.4° C/2pt; >38.5° C/4pt; abnormal urinalysis/3pt; and absolute neutrophil count >5185/2pt) where any score greater than2 provides a sensitivity of 98.8% and NPV in validation studies of 99.4%. Likewise, multiplex polymerase chain reaction testing of spinal fluid has allowed for additional insight in pretreated cases and has helped us to remove antibiotic treatment from cases where parechovirus and enterovirus are positive because of the low risk for concomitant bacterial meningitis. As we await the release of revised national American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines, it is safe to say great progress has been made in the care of young febrile infants with shorter length of stay and fewer tests for all.
Key takeaways
- Numerous screening tests, rules, and scoring tools have been created to improve identification of infants with IBI, a low-frequency, high-morbidity event. The most recent with negative predictive values of 99.7% and 99.4% are the PECARN and Aronson scoring tools.
- Recent studies of the febrile infant population indicate that the odds of UTI or bacteremia in infants with respiratory symptoms is low, particularly for RSV and influenza.
- Among newer tests developed, a negative procalcitonin has the highest negative predictive value.
- Viral pathogens identified on cerebrospinal fluid molecular testing can be helpful in pretreated cases and indicative of low likelihood of bacterial meningitis allowing for observation off of antibiotics.
Dr. King is a hospitalist, associate director for medical education and associate program director for the pediatrics residency program at Children’s Minnesota in Minneapolis. She has shared some of her resident teaching, presentation skills, and peer-coaching work on a national level.
Converge 2021 session
Febrile Infant Update
Presenter
Russell J. McCulloh, MD
Session summary
Infections in infants aged younger than 90 days have been the subject of intense study in pediatric hospital medicine for many years. With the guidance of our talented presenter Dr. Russell McCulloh of Children’s Hospital & Medical Center in Omaha, Neb., the audience explored the historical perspective and evolution of this scientific question, including successes, special situations, newer screening tests, and description of cutting-edge scoring tools and platforms.
The challenge – Tens of thousands of infants present for care in the setting of fever each year. We know that our physical exam and history-taking skills are unlikely to be helpful in risk stratification. We have been guided by the desire to separate serious bacterial infection (SBI: bone infection, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, bacteremia, enteritis) from invasive bacterial infection (IBI: meningitis and bacteremia). Data has shown that no test is 100% sensitive or specific, therefore we have to balance risk of disease to cost and invasiveness of tests. Important questions include whether to test and how to stratify by age, who to admit, and who to provide antibiotics.
The wins and exceptions – Fortunately, the early Boston, Philadelphia, and Rochester criteria set the stage for safely reducing testing. The current American College of Emergency Physicians guidelines for infants aged 29-90 days allows for lumbar puncture to be optional knowing that a look back using prior criteria identified no cases of meningitis in the low risk group. Similarly, in low-risk infants aged less that 29 days in nearly 4,000 cases there were just 2 infants with meningitis. Universal screening of moms for Group B Streptococcus with delivery of antibiotics in appropriate cases has dramatically decreased incidence of SBI. The Hib and pneumovax vaccines have likewise decreased incidence of SBI. Exceptions persist, including knowledge that infants with herpes simplex virus disease will not have fever in 50% of cases and that risk of HSV transmission is highest (25%-60% transmission) in mothers with primary disease. Given risk of HSV CNS disease after 1 week of age, in any high-risk infant less than 21 days, the mantra remains to test and treat.
The cutting edge – Thanks to ongoing research, we now have the PECARN and REVISE study groups to further aid decision-making. With PECARN we know that SBI in infants is extremely unlikely (negative predictive value, 99.7%) with a negative urinalysis , absolute neutrophil count less than 4,090, and procalcitonin less than 1.71. REVISE has revealed that infants with positive viral testing are unlikely to have SBI (7%-12%), particularly with influenza and RSV disease. Procalcitonin has also recently been shown to be an effective tool to rule out disease with the highest negative predictive value among available inflammatory markers. The just-published Aronson rule identifies a scoring system for IBI (using age less than 21 days/1pt; temp 38-38.4° C/2pt; >38.5° C/4pt; abnormal urinalysis/3pt; and absolute neutrophil count >5185/2pt) where any score greater than2 provides a sensitivity of 98.8% and NPV in validation studies of 99.4%. Likewise, multiplex polymerase chain reaction testing of spinal fluid has allowed for additional insight in pretreated cases and has helped us to remove antibiotic treatment from cases where parechovirus and enterovirus are positive because of the low risk for concomitant bacterial meningitis. As we await the release of revised national American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines, it is safe to say great progress has been made in the care of young febrile infants with shorter length of stay and fewer tests for all.
Key takeaways
- Numerous screening tests, rules, and scoring tools have been created to improve identification of infants with IBI, a low-frequency, high-morbidity event. The most recent with negative predictive values of 99.7% and 99.4% are the PECARN and Aronson scoring tools.
- Recent studies of the febrile infant population indicate that the odds of UTI or bacteremia in infants with respiratory symptoms is low, particularly for RSV and influenza.
- Among newer tests developed, a negative procalcitonin has the highest negative predictive value.
- Viral pathogens identified on cerebrospinal fluid molecular testing can be helpful in pretreated cases and indicative of low likelihood of bacterial meningitis allowing for observation off of antibiotics.
Dr. King is a hospitalist, associate director for medical education and associate program director for the pediatrics residency program at Children’s Minnesota in Minneapolis. She has shared some of her resident teaching, presentation skills, and peer-coaching work on a national level.
FROM SHM CONVERGE 2021
COVID-19 death toll higher for international medical graduates
researchers report.
“I’ve always felt that international medical graduates [IMGs] in America are largely invisible,” said senior author Abraham Verghese, MD, MFA, an infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. “Everyone is aware that there are foreign doctors, but very few are aware of how many there are and also how vital they are to providing health care in America.”
IMGs made up 25% of all U.S. physicians in 2020 but accounted for 45% of those whose deaths had been attributed to COVID-19 through Nov. 23, 2020, Deendayal Dinakarpandian, MD, PhD, clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues report in JAMA Network Open.
IMGs are more likely to work in places where the incidence of COVID-19 is high and in facilities with fewer resources, Dr. Verghese said in an interview. “So, it’s not surprising that they were on the front lines when this thing came along,” he said.
To see whether their vulnerability affected their risk for death, Dr. Dinakarpandian and colleagues collected data from Nov. 23, 2020, from three sources of information regarding deaths among physicians: MedPage Today, which used investigative and voluntary reporting; Medscape, which used voluntary reporting of verifiable information; and a collaboration of The Guardian and Kaiser Health News, which used investigative reporting.
The Medscape project was launched on April 1, 2020. The MedPage Today and The Guardian/Kaiser Health News projects were launched on April 8, 2020.
Dr. Verghese and colleagues researched obituaries and news articles referenced by the three projects to verify their data. They used DocInfo to ascertain the deceased physicians’ medical schools.
After eliminating duplications from the lists, the researchers counted 132 physician deaths in 28 states. Of these, 59 physicians had graduated from medical schools outside the United States, a death toll 1.8 times higher than the proportion of IMGs among U.S. physicians (95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.21; P < .001).
New York, New Jersey, and Florida accounted for 66% of the deaths among IMGs but for only 45% of the deaths among U.S. medical school graduates.
Within each state, the proportion of IMGs among deceased physicians was not statistically different from their proportion among physicians in those states, with the exception of New York.
Two-thirds of the physicians’ deaths occurred in states where IMGs make up a larger proportion of physicians than in the nation as a whole. In these states, the incidence of COVID-19 was high at the start of the pandemic.
In New York, IMGs accounted for 60% of physician deaths, which was 1.62 times higher (95% CI, 1.26-2.09; P = .005) than the 37% among New York physicians overall.
Physicians who were trained abroad frequently can’t get into the most prestigious residency programs or into the highest paid specialties and are more likely to serve in primary care, Dr. Verghese said. Overall, 60% of the physicians who died of COVID-19 worked in primary care.
IMGs often staff hospitals serving low-income communities and communities of color, which were hardest hit by the pandemic and where personal protective equipment was hard to obtain, said Dr. Verghese.
In addition to these risks, IMGs sometimes endure racism, said Dr. Verghese, who obtained his medical degree at Madras Medical College, Chennai, India. “We’ve actually seen in the COVID era, in keeping with the sort of political tone that was set in Washington, that there’s been a lot more abuses of both foreign physicians and foreign looking physicians – even if they’re not foreign trained – and nurses by patients who have been given license. And I want to acknowledge the heroism of all these physicians.”
The study was partially funded by the Presence Center at Stanford. Dr. Verghese is a regular contributor to Medscape. He served on the advisory board for Gilead Sciences, serves as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Leigh Bureau, and receives royalties from Penguin Random House and Simon & Schuster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers report.
“I’ve always felt that international medical graduates [IMGs] in America are largely invisible,” said senior author Abraham Verghese, MD, MFA, an infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. “Everyone is aware that there are foreign doctors, but very few are aware of how many there are and also how vital they are to providing health care in America.”
IMGs made up 25% of all U.S. physicians in 2020 but accounted for 45% of those whose deaths had been attributed to COVID-19 through Nov. 23, 2020, Deendayal Dinakarpandian, MD, PhD, clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues report in JAMA Network Open.
IMGs are more likely to work in places where the incidence of COVID-19 is high and in facilities with fewer resources, Dr. Verghese said in an interview. “So, it’s not surprising that they were on the front lines when this thing came along,” he said.
To see whether their vulnerability affected their risk for death, Dr. Dinakarpandian and colleagues collected data from Nov. 23, 2020, from three sources of information regarding deaths among physicians: MedPage Today, which used investigative and voluntary reporting; Medscape, which used voluntary reporting of verifiable information; and a collaboration of The Guardian and Kaiser Health News, which used investigative reporting.
The Medscape project was launched on April 1, 2020. The MedPage Today and The Guardian/Kaiser Health News projects were launched on April 8, 2020.
Dr. Verghese and colleagues researched obituaries and news articles referenced by the three projects to verify their data. They used DocInfo to ascertain the deceased physicians’ medical schools.
After eliminating duplications from the lists, the researchers counted 132 physician deaths in 28 states. Of these, 59 physicians had graduated from medical schools outside the United States, a death toll 1.8 times higher than the proportion of IMGs among U.S. physicians (95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.21; P < .001).
New York, New Jersey, and Florida accounted for 66% of the deaths among IMGs but for only 45% of the deaths among U.S. medical school graduates.
Within each state, the proportion of IMGs among deceased physicians was not statistically different from their proportion among physicians in those states, with the exception of New York.
Two-thirds of the physicians’ deaths occurred in states where IMGs make up a larger proportion of physicians than in the nation as a whole. In these states, the incidence of COVID-19 was high at the start of the pandemic.
In New York, IMGs accounted for 60% of physician deaths, which was 1.62 times higher (95% CI, 1.26-2.09; P = .005) than the 37% among New York physicians overall.
Physicians who were trained abroad frequently can’t get into the most prestigious residency programs or into the highest paid specialties and are more likely to serve in primary care, Dr. Verghese said. Overall, 60% of the physicians who died of COVID-19 worked in primary care.
IMGs often staff hospitals serving low-income communities and communities of color, which were hardest hit by the pandemic and where personal protective equipment was hard to obtain, said Dr. Verghese.
In addition to these risks, IMGs sometimes endure racism, said Dr. Verghese, who obtained his medical degree at Madras Medical College, Chennai, India. “We’ve actually seen in the COVID era, in keeping with the sort of political tone that was set in Washington, that there’s been a lot more abuses of both foreign physicians and foreign looking physicians – even if they’re not foreign trained – and nurses by patients who have been given license. And I want to acknowledge the heroism of all these physicians.”
The study was partially funded by the Presence Center at Stanford. Dr. Verghese is a regular contributor to Medscape. He served on the advisory board for Gilead Sciences, serves as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Leigh Bureau, and receives royalties from Penguin Random House and Simon & Schuster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
researchers report.
“I’ve always felt that international medical graduates [IMGs] in America are largely invisible,” said senior author Abraham Verghese, MD, MFA, an infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University. “Everyone is aware that there are foreign doctors, but very few are aware of how many there are and also how vital they are to providing health care in America.”
IMGs made up 25% of all U.S. physicians in 2020 but accounted for 45% of those whose deaths had been attributed to COVID-19 through Nov. 23, 2020, Deendayal Dinakarpandian, MD, PhD, clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues report in JAMA Network Open.
IMGs are more likely to work in places where the incidence of COVID-19 is high and in facilities with fewer resources, Dr. Verghese said in an interview. “So, it’s not surprising that they were on the front lines when this thing came along,” he said.
To see whether their vulnerability affected their risk for death, Dr. Dinakarpandian and colleagues collected data from Nov. 23, 2020, from three sources of information regarding deaths among physicians: MedPage Today, which used investigative and voluntary reporting; Medscape, which used voluntary reporting of verifiable information; and a collaboration of The Guardian and Kaiser Health News, which used investigative reporting.
The Medscape project was launched on April 1, 2020. The MedPage Today and The Guardian/Kaiser Health News projects were launched on April 8, 2020.
Dr. Verghese and colleagues researched obituaries and news articles referenced by the three projects to verify their data. They used DocInfo to ascertain the deceased physicians’ medical schools.
After eliminating duplications from the lists, the researchers counted 132 physician deaths in 28 states. Of these, 59 physicians had graduated from medical schools outside the United States, a death toll 1.8 times higher than the proportion of IMGs among U.S. physicians (95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.21; P < .001).
New York, New Jersey, and Florida accounted for 66% of the deaths among IMGs but for only 45% of the deaths among U.S. medical school graduates.
Within each state, the proportion of IMGs among deceased physicians was not statistically different from their proportion among physicians in those states, with the exception of New York.
Two-thirds of the physicians’ deaths occurred in states where IMGs make up a larger proportion of physicians than in the nation as a whole. In these states, the incidence of COVID-19 was high at the start of the pandemic.
In New York, IMGs accounted for 60% of physician deaths, which was 1.62 times higher (95% CI, 1.26-2.09; P = .005) than the 37% among New York physicians overall.
Physicians who were trained abroad frequently can’t get into the most prestigious residency programs or into the highest paid specialties and are more likely to serve in primary care, Dr. Verghese said. Overall, 60% of the physicians who died of COVID-19 worked in primary care.
IMGs often staff hospitals serving low-income communities and communities of color, which were hardest hit by the pandemic and where personal protective equipment was hard to obtain, said Dr. Verghese.
In addition to these risks, IMGs sometimes endure racism, said Dr. Verghese, who obtained his medical degree at Madras Medical College, Chennai, India. “We’ve actually seen in the COVID era, in keeping with the sort of political tone that was set in Washington, that there’s been a lot more abuses of both foreign physicians and foreign looking physicians – even if they’re not foreign trained – and nurses by patients who have been given license. And I want to acknowledge the heroism of all these physicians.”
The study was partially funded by the Presence Center at Stanford. Dr. Verghese is a regular contributor to Medscape. He served on the advisory board for Gilead Sciences, serves as a speaker or a member of a speakers bureau for Leigh Bureau, and receives royalties from Penguin Random House and Simon & Schuster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More evidence links COVID vaccines to rare cases of myocarditis in youth
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expert reported on June 10, detailing data on cases of myocarditis and pericarditis detected through a government safety system.
The side effect seems to be more common in teen boys and young men than in older adults and women and may occur in 16 cases for every 1 million people who got a second dose, said Tom Shimabukuro, MD, MPH, deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Safety Office, who presented information on the cases at a meeting of an expert panel that advises the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on vaccines.
Telltale symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever.
William Schaffner, MD, an infectious diseases specialist from Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., thinks certain characteristics are pointing toward a “rare, but real” signal. First, the events are clustering, occurring within days of vaccination. Second, they tend to be more common in males and younger people. Third, he says, the number of events is above the so-called “background rate” – the cases that could be expected in this age group even without vaccination.
“I don’t think we’re quite there yet. We haven’t tied a ribbon around it, but I think the data are trending in that direction,” he said.
The issue of myocarditis weighed heavily on the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee’s considerations of what kind and how much data might be needed to green light use of a vaccine for COVID in children.
Because the rates of hospitalization for COVID are low in kids, some felt that the FDA should require at least a year of study of the vaccines in clinical trials, the amount of data typically required for full approval, instead of the 2 months currently required for emergency use authorization. Others wondered whether the risks of vaccination – as low as they are – might outweigh the benefits in this age group.
“I don’t really see this as an emergency in children,” said committee member Michael Kurilla, MD, PhD, the director of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Kurilla, however, did say he thought having an expanded access program for children at high risk might make sense.
Most of the young adults who experienced myocarditis recovered quickly, though three needed intensive care and rehabilitation after their episodes. Among cases with known outcomes, 81% got better and 19% still have ongoing symptoms.
Adverse events reports
The data on myocarditis come from the Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System, or VAERS, a database of health problems reported after vaccination. This reporting system, open to anyone, has benefits and limits. It gives the CDC and FDA the ability to rapidly detect potential safety issues, and it is large enough that it can detect rare events, something that’s beyond the power of even large clinical trials.
But it is observational, so that there’s no way to know if problems reported were caused by the vaccines or a coincidence.
But because VAERS works on an honor system, it can also be spammed, and it carries the bias of the person who’s doing the reporting, from clinicians to average patients. For that reason, Dr. Shimabukuro said they are actively investigating and confirming each report they get.
Out of more than 12 million doses administered to youth ages 16-24, the CDC says it has 275 reports of heart inflammation following vaccination in this age group. The CDC has analyzed a total 475 cases of myocarditis after vaccination in people under age 30 that were reported to VAERS.
The vaccines linked to the events are the mRNA vaccines made by Pfizer and Moderna. The only vaccines currently authorized for use in adolescents are made by Pfizer. Because the Pfizer vaccine was authorized for use in kids as young as 12 last month, there’s not yet enough data to draw conclusions about the risk of myocarditis in kids ages 12-15.
Younger age groups have only received about 9% of the total doses of the vaccine so far, but they represent about 50% of the myocarditis cases reported after vaccination. “We clearly have an imbalance there,” Dr. Shimabukuro said.
The number of events in this age group appears to be above the rate that would be expected for these age groups without vaccines in the picture, he said, explaining that the number of events are in line with similar adverse events seen in young people in Israel and reported by the Department of Defense. Israel found the incidence of myocarditis after vaccination was 50 cases per million for men ages 18-30.
More study needed
Another system tracking adverse events through hospitals, the Vaccine Safety Datalink, didn’t show reports of heart inflammation above numbers that are normally seen in the population, but it did show that inflammation was more likely after a second dose of the vaccine.
“Should this be included in informed consent?” asked Cody Meissner, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Tufts University, Boston, and a member of the FDA committee.
“I think it’s hard to deny there seem to be some [events that seem] to be occurring in terms of myocarditis,” he said.
Dr. Meissner said later in the committee’s discussion that his own hospital had recently admitted a 12-year-old boy who developed heart swelling 2 days after the second dose of vaccine with a high level of troponin, an enzyme that indicates damage to the heart. His level was over 9. “A very high level,” Dr. Meissner said.
“Will there be scarring to the myocardium? Will there be a predisposition to arrhythmias later on? Will there be an early onset of heart failure? We think that’s unlikely, but [we] don’t know that,” he said.
The CDC has scheduled an emergency meeting next week to convene an expert panel on immunization practices to further review the events.
In addition to the information presented at the FDA’s meeting, doctors at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, recently described seven cases in teens – all boys – who developed heart inflammation within 4 days of getting the second dose of the Pfizer vaccine.
The study was published June 10 in Pediatrics. All the boys were hospitalized and treated with anti-inflammatory medications including NSAIDs and steroids. Most were discharged within a few days and all recovered from their symptoms.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.