User login
Survey: Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccine dips below 50%
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
Less than half of Americans now say that they would get a coronavirus vaccine if one became available, according to a survey conducted Oct. 8-10.
the lowest number since the weekly survey began at the end of February, digital media company Morning Consult reported.
Americans’ willingness to receive such a vaccine reached its high point, 72%, in early April but has been steadily dropping. “Overall willingness has hovered around 50% throughout September, fueled primarily by a sharp drop among Democrats since mid-August, around the time reports of White House interference at the Food and Drug Administration and other federal health agencies began to command more public attention,” Morning Consult noted.
Despite that drop, a majority of Democrats (55%) are still willing to get a COVID-19 vaccine, compared with 48% of Republicans and just 41% of independents. The willingness gap between the two parties was quite a bit wider in the previous poll, conducted Oct. 1-4: 60% of Democrats versus 48% for Republicans, the company said.
“Keeping with longstanding trends, the survey also shows women were less likely to say they’d seek a vaccine than men (42% to 55%), as were people with lower education levels and those who live in rural areas,” the news outlet added.
The latest poll results also show that 33% of respondents (43% of Republicans/25% of Democrats) are socializing in public places. The overall number was just 8% in mid-April but was up to 27% by mid-June. The proportion of all adults who believe in the effectiveness of face masks has been around 80% since April, but there is a significant gap between those who strongly approve of President Trump (66%) and those who strongly disapprove (95%), Morning Consult said.
When the only clinical choices are ‘lose-lose’
Among the many tolls inflicted on health care workers by COVID-19 is one that is not as easily measured as rates of death or disease, but is no less tangible: moral injury. This is the term by which we describe the psychological, social, and spiritual impact of high-stakes situations that lead to the betrayal or transgression of our own deeply held moral beliefs and values.
The current pandemic has provided innumerable such situations that can increase the risk for moral injury, whether we deal directly with patients infected by the coronavirus or not. Telling family members they cannot visit critically ill loved ones. Delaying code activities, even momentarily, to get fully protected with personal protective equipment. Seeing patients who have delayed their necessary or preventive care. Using video rather than touch to reassure people.
Knowing that we are following guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not stop our feelings of guilt. The longer this pandemic goes on, the more likely it is that these situations will begin to take a toll on us.
For most of us, being exposed to moral injuries is new; they have historically been most associated with severe traumatic wartime experiences. Soldiers, philosophers, and writers have described the ethical dilemmas inherent in war for as long as recorded history. But the use of this term is a more recent development, which the Moral Injury Project at Syracuse (N.Y.) University describes as probably originating in the Vietnam War–era writings of veteran and peace activist Camillo “Mac” Bica and psychiatrist Jonathan Shay. Examples of wartime events that have been thought to lead to moral injury include: causing the harm or death of civilians, knowingly but without alternatives, or accidentally; failing to provide medical aid to an injured civilian or service member; and following orders that were illegal, immoral, and/or against the rules of engagement or the Geneva Conventions.
However, the occurrence of moral injuries in modern health care is increasingly being reported, primarily as an adverse effect of health care inefficiencies that can contribute to burnout. COVID-19 has now provided an array of additional stressors that can cause moral injuries among health care workers. A recent guidance document on moral injury published by the American Psychiatric Association noted that, in the context of a public health disaster, such as COVID-19, it is sometimes necessary to transition from ordinary standards of care to those more appropriate in a crisis, as in wartime. This forces us all to confront challenging questions for which there may be no clear answers, and to make “lose-lose” choices in which no one involved – patients, family, or clinicians – ends up feeling satisfied or even comfortable.
Our lives have been altered significantly, and for many, completely turned upside down by enormous sacrifices and tragic losses. Globally, physicians account for over half of healthcare worker deaths. In the United States alone, over 900 health care workers have died of COVID-19.
Most of us have felt the symptoms of moral injury: frustration, anger, disgust, guilt. A recent report describes three levels of stressors in health care occurring during the pandemic, which are not dissimilar to those wartime events described previously.
- Severe moral stressors, such as the denial of treatment to a COVID-19 patient owing to lack of resources, the inability to provide optimal care to non–COVID-19 patients for many reasons, and concern about passing COVID to loved ones.
- Moderate moral stressors, such as preventing visitors, especially to dying patients, triaging patients for healthcare services with inadequate information, and trying to solve the tension between the need for self-preservation and the need to treat.
- Lower-level but common moral challenges, especially in the community – for example, seeing others not protecting the community by hoarding food, gathering for large parties, and not social distancing or wearing masks. Such stressors lead to frustration and contempt, especially from healthcare workers making personal sacrifices and who may be at risk for infection caused by these behaviors.
Every one of us is affected by these stressors. I certainly am.
What are the outcomes? We know that moral injuries are a risk factor for the development of mental health problems and burnout, and not surprisingly we are seeing that mental health problems, suicidality, and substance use disorders have increased markedly during COVID-19, as recently detailed by the CDC.
Common emotions that occur in response to moral injuries are: feelings of guilt, shame, anger, sadness, anxiety, and disgust; intrapersonal outcomes, including lowered self-esteem, high self-criticism, and beliefs about being bad, damaged, unworthy, failing, or weak; interpersonal outcomes, including loss of faith in people, avoidance of intimacy, and lack of trust in authority figures; and existential and spiritual outcomes, including loss of faith in previous religious beliefs and no longer believing in a just world.
Moral injuries tend to originate primarily from systems-based problems, as we have seen with the lack of concerted national approaches to the pandemic. On the positive side, solutions typically also involve systems-based changes, which in this case may mean changes in leadership styles nationally and locally, as well as changes in the culture of medicine and the way healthcare is practiced and managed in the modern era. We are starting to see some of those changes with the increased use of telemedicine and health technologies, as well as more of a focus on the well-being of health care workers, now deemed “essential.”
As individuals, we are not helpless. There are things we can do in our workplaces to create change. I suggest:
- Acknowledge that you, like me, are affected by these stressors. This is not a secret, and you should not be ashamed of your feelings.
- Talk with your colleagues, loved ones, and friends about how you and they are affected. You are not alone. Encourage others to share their thoughts, stories, and feelings.
- Put this topic on your meeting and departmental agendas and discuss these moral issues openly with your colleagues. Allow sufficient time to engage in open dialogue.
- Work out ways of assisting those who are in high-risk situations, especially for moderate to severe injuries. Be supportive toward those affected.
- Modify policies and change rosters and rotate staff between high- and low-stress roles. Protect and support at-risk colleagues.
- Think about difficult ethical decisions in advance so they can be made by groups, not individuals, and certainly not “on the fly.”
- Keep everyone in your workplace constantly informed, especially of impending staff or equipment shortages.
- Maintain your inherent self-care and resilience with rest, good nutrition, sleep, exercise, love, caring, socialization, and work-life balance.
- Be prepared to access the many professional support services available in our community if you are intensely distressed or if the above suggestions are not enough.
Remember, we are in this together and will find strength in each other. This too will pass.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the many tolls inflicted on health care workers by COVID-19 is one that is not as easily measured as rates of death or disease, but is no less tangible: moral injury. This is the term by which we describe the psychological, social, and spiritual impact of high-stakes situations that lead to the betrayal or transgression of our own deeply held moral beliefs and values.
The current pandemic has provided innumerable such situations that can increase the risk for moral injury, whether we deal directly with patients infected by the coronavirus or not. Telling family members they cannot visit critically ill loved ones. Delaying code activities, even momentarily, to get fully protected with personal protective equipment. Seeing patients who have delayed their necessary or preventive care. Using video rather than touch to reassure people.
Knowing that we are following guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not stop our feelings of guilt. The longer this pandemic goes on, the more likely it is that these situations will begin to take a toll on us.
For most of us, being exposed to moral injuries is new; they have historically been most associated with severe traumatic wartime experiences. Soldiers, philosophers, and writers have described the ethical dilemmas inherent in war for as long as recorded history. But the use of this term is a more recent development, which the Moral Injury Project at Syracuse (N.Y.) University describes as probably originating in the Vietnam War–era writings of veteran and peace activist Camillo “Mac” Bica and psychiatrist Jonathan Shay. Examples of wartime events that have been thought to lead to moral injury include: causing the harm or death of civilians, knowingly but without alternatives, or accidentally; failing to provide medical aid to an injured civilian or service member; and following orders that were illegal, immoral, and/or against the rules of engagement or the Geneva Conventions.
However, the occurrence of moral injuries in modern health care is increasingly being reported, primarily as an adverse effect of health care inefficiencies that can contribute to burnout. COVID-19 has now provided an array of additional stressors that can cause moral injuries among health care workers. A recent guidance document on moral injury published by the American Psychiatric Association noted that, in the context of a public health disaster, such as COVID-19, it is sometimes necessary to transition from ordinary standards of care to those more appropriate in a crisis, as in wartime. This forces us all to confront challenging questions for which there may be no clear answers, and to make “lose-lose” choices in which no one involved – patients, family, or clinicians – ends up feeling satisfied or even comfortable.
Our lives have been altered significantly, and for many, completely turned upside down by enormous sacrifices and tragic losses. Globally, physicians account for over half of healthcare worker deaths. In the United States alone, over 900 health care workers have died of COVID-19.
Most of us have felt the symptoms of moral injury: frustration, anger, disgust, guilt. A recent report describes three levels of stressors in health care occurring during the pandemic, which are not dissimilar to those wartime events described previously.
- Severe moral stressors, such as the denial of treatment to a COVID-19 patient owing to lack of resources, the inability to provide optimal care to non–COVID-19 patients for many reasons, and concern about passing COVID to loved ones.
- Moderate moral stressors, such as preventing visitors, especially to dying patients, triaging patients for healthcare services with inadequate information, and trying to solve the tension between the need for self-preservation and the need to treat.
- Lower-level but common moral challenges, especially in the community – for example, seeing others not protecting the community by hoarding food, gathering for large parties, and not social distancing or wearing masks. Such stressors lead to frustration and contempt, especially from healthcare workers making personal sacrifices and who may be at risk for infection caused by these behaviors.
Every one of us is affected by these stressors. I certainly am.
What are the outcomes? We know that moral injuries are a risk factor for the development of mental health problems and burnout, and not surprisingly we are seeing that mental health problems, suicidality, and substance use disorders have increased markedly during COVID-19, as recently detailed by the CDC.
Common emotions that occur in response to moral injuries are: feelings of guilt, shame, anger, sadness, anxiety, and disgust; intrapersonal outcomes, including lowered self-esteem, high self-criticism, and beliefs about being bad, damaged, unworthy, failing, or weak; interpersonal outcomes, including loss of faith in people, avoidance of intimacy, and lack of trust in authority figures; and existential and spiritual outcomes, including loss of faith in previous religious beliefs and no longer believing in a just world.
Moral injuries tend to originate primarily from systems-based problems, as we have seen with the lack of concerted national approaches to the pandemic. On the positive side, solutions typically also involve systems-based changes, which in this case may mean changes in leadership styles nationally and locally, as well as changes in the culture of medicine and the way healthcare is practiced and managed in the modern era. We are starting to see some of those changes with the increased use of telemedicine and health technologies, as well as more of a focus on the well-being of health care workers, now deemed “essential.”
As individuals, we are not helpless. There are things we can do in our workplaces to create change. I suggest:
- Acknowledge that you, like me, are affected by these stressors. This is not a secret, and you should not be ashamed of your feelings.
- Talk with your colleagues, loved ones, and friends about how you and they are affected. You are not alone. Encourage others to share their thoughts, stories, and feelings.
- Put this topic on your meeting and departmental agendas and discuss these moral issues openly with your colleagues. Allow sufficient time to engage in open dialogue.
- Work out ways of assisting those who are in high-risk situations, especially for moderate to severe injuries. Be supportive toward those affected.
- Modify policies and change rosters and rotate staff between high- and low-stress roles. Protect and support at-risk colleagues.
- Think about difficult ethical decisions in advance so they can be made by groups, not individuals, and certainly not “on the fly.”
- Keep everyone in your workplace constantly informed, especially of impending staff or equipment shortages.
- Maintain your inherent self-care and resilience with rest, good nutrition, sleep, exercise, love, caring, socialization, and work-life balance.
- Be prepared to access the many professional support services available in our community if you are intensely distressed or if the above suggestions are not enough.
Remember, we are in this together and will find strength in each other. This too will pass.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the many tolls inflicted on health care workers by COVID-19 is one that is not as easily measured as rates of death or disease, but is no less tangible: moral injury. This is the term by which we describe the psychological, social, and spiritual impact of high-stakes situations that lead to the betrayal or transgression of our own deeply held moral beliefs and values.
The current pandemic has provided innumerable such situations that can increase the risk for moral injury, whether we deal directly with patients infected by the coronavirus or not. Telling family members they cannot visit critically ill loved ones. Delaying code activities, even momentarily, to get fully protected with personal protective equipment. Seeing patients who have delayed their necessary or preventive care. Using video rather than touch to reassure people.
Knowing that we are following guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not stop our feelings of guilt. The longer this pandemic goes on, the more likely it is that these situations will begin to take a toll on us.
For most of us, being exposed to moral injuries is new; they have historically been most associated with severe traumatic wartime experiences. Soldiers, philosophers, and writers have described the ethical dilemmas inherent in war for as long as recorded history. But the use of this term is a more recent development, which the Moral Injury Project at Syracuse (N.Y.) University describes as probably originating in the Vietnam War–era writings of veteran and peace activist Camillo “Mac” Bica and psychiatrist Jonathan Shay. Examples of wartime events that have been thought to lead to moral injury include: causing the harm or death of civilians, knowingly but without alternatives, or accidentally; failing to provide medical aid to an injured civilian or service member; and following orders that were illegal, immoral, and/or against the rules of engagement or the Geneva Conventions.
However, the occurrence of moral injuries in modern health care is increasingly being reported, primarily as an adverse effect of health care inefficiencies that can contribute to burnout. COVID-19 has now provided an array of additional stressors that can cause moral injuries among health care workers. A recent guidance document on moral injury published by the American Psychiatric Association noted that, in the context of a public health disaster, such as COVID-19, it is sometimes necessary to transition from ordinary standards of care to those more appropriate in a crisis, as in wartime. This forces us all to confront challenging questions for which there may be no clear answers, and to make “lose-lose” choices in which no one involved – patients, family, or clinicians – ends up feeling satisfied or even comfortable.
Our lives have been altered significantly, and for many, completely turned upside down by enormous sacrifices and tragic losses. Globally, physicians account for over half of healthcare worker deaths. In the United States alone, over 900 health care workers have died of COVID-19.
Most of us have felt the symptoms of moral injury: frustration, anger, disgust, guilt. A recent report describes three levels of stressors in health care occurring during the pandemic, which are not dissimilar to those wartime events described previously.
- Severe moral stressors, such as the denial of treatment to a COVID-19 patient owing to lack of resources, the inability to provide optimal care to non–COVID-19 patients for many reasons, and concern about passing COVID to loved ones.
- Moderate moral stressors, such as preventing visitors, especially to dying patients, triaging patients for healthcare services with inadequate information, and trying to solve the tension between the need for self-preservation and the need to treat.
- Lower-level but common moral challenges, especially in the community – for example, seeing others not protecting the community by hoarding food, gathering for large parties, and not social distancing or wearing masks. Such stressors lead to frustration and contempt, especially from healthcare workers making personal sacrifices and who may be at risk for infection caused by these behaviors.
Every one of us is affected by these stressors. I certainly am.
What are the outcomes? We know that moral injuries are a risk factor for the development of mental health problems and burnout, and not surprisingly we are seeing that mental health problems, suicidality, and substance use disorders have increased markedly during COVID-19, as recently detailed by the CDC.
Common emotions that occur in response to moral injuries are: feelings of guilt, shame, anger, sadness, anxiety, and disgust; intrapersonal outcomes, including lowered self-esteem, high self-criticism, and beliefs about being bad, damaged, unworthy, failing, or weak; interpersonal outcomes, including loss of faith in people, avoidance of intimacy, and lack of trust in authority figures; and existential and spiritual outcomes, including loss of faith in previous religious beliefs and no longer believing in a just world.
Moral injuries tend to originate primarily from systems-based problems, as we have seen with the lack of concerted national approaches to the pandemic. On the positive side, solutions typically also involve systems-based changes, which in this case may mean changes in leadership styles nationally and locally, as well as changes in the culture of medicine and the way healthcare is practiced and managed in the modern era. We are starting to see some of those changes with the increased use of telemedicine and health technologies, as well as more of a focus on the well-being of health care workers, now deemed “essential.”
As individuals, we are not helpless. There are things we can do in our workplaces to create change. I suggest:
- Acknowledge that you, like me, are affected by these stressors. This is not a secret, and you should not be ashamed of your feelings.
- Talk with your colleagues, loved ones, and friends about how you and they are affected. You are not alone. Encourage others to share their thoughts, stories, and feelings.
- Put this topic on your meeting and departmental agendas and discuss these moral issues openly with your colleagues. Allow sufficient time to engage in open dialogue.
- Work out ways of assisting those who are in high-risk situations, especially for moderate to severe injuries. Be supportive toward those affected.
- Modify policies and change rosters and rotate staff between high- and low-stress roles. Protect and support at-risk colleagues.
- Think about difficult ethical decisions in advance so they can be made by groups, not individuals, and certainly not “on the fly.”
- Keep everyone in your workplace constantly informed, especially of impending staff or equipment shortages.
- Maintain your inherent self-care and resilience with rest, good nutrition, sleep, exercise, love, caring, socialization, and work-life balance.
- Be prepared to access the many professional support services available in our community if you are intensely distressed or if the above suggestions are not enough.
Remember, we are in this together and will find strength in each other. This too will pass.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Latest week brings 44,000 more children with COVID-19
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
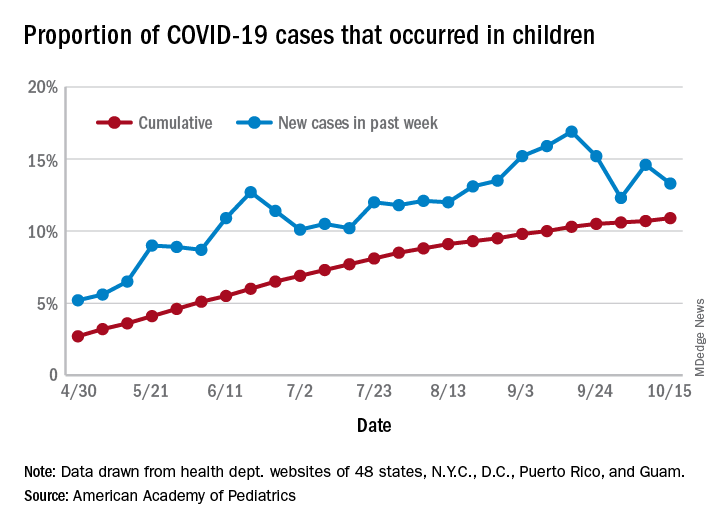
The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
in the United States, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The total number of COVID-19 cases among children was 741,891 as of Oct. 15, which puts the cumulative proportion at 10.9% of the 6.8 million cases reported in all ages by 49 states (New York does not report ages), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The 44,258 new cases in children represented 13.3% of all cases reported during the week ending Oct. 15, down from 14.6% the previous week (children make up almost 23% of the total U.S. population), the AAP/CHA data show.
Those data also indicate that there have been almost 986 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children in the United States. Corresponding rates among the states range from 181 per 100,000 in Vermont to 2,581 per 100,000 in North Dakota. Tennessee (2,277) and South Carolina (2,212) are the only other states above 2,000, according to the report.
California has reported the most child cases, 89,843 (1,010 per 100,000 children), so far, followed by Florida (44,199), Illinois (42,132), and Tennessee (40,137). Seven other states have had over 20,000 cases each, the AAP and CHA noted.
Measures of severe illness continue to be low, although the data are less comprehensive. Children represent only 1.7% of all COVID-19 hospitalizations (24 states and N.Y.C. reporting) and 0.07% of all deaths (42 states and N.Y.C. reporting). Thirteen states and D.C. have had no deaths yet, while Texas has reported three times as many (27) as any other state (Arizona is next with 9, although N.Y.C. has had 15), the AAP/CHA report said.
COVID-19 antibody response not reduced with diabetes
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Neither diabetes per se nor hyperglycemia appear to impair the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2, suggesting that a COVID-19 vaccine would be just as effective in people with diabetes as in those without, new research finds.
Results from a study involving 480 patients with confirmed COVID-19 seen at an Italian hospital between February 25 and April 19 were published online October 8 in Diabetologia by Vito Lampasona, MD, and colleagues.
Antibody responses against multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens among the 27% of patients with COVID-19 and diabetes (preexisting and newly diagnosed) were similar with regard to timing, titers, and classes to those of patients with COVID-19 and without diabetes, and the results did not differ by glucose levels.
Moreover, positivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) against the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) was associated with improved survival regardless of diabetes status.
And as previously shown, high blood glucose levels were strongly associated with greater COVID-19 mortality even in those without diabetes.
This is the first study of the immunologic humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with hyperglycemia, the authors say.
“The immunological response to a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine will be assessed when the vaccine becomes available. However, our data allow a cautious optimism regarding effective immunization in individuals with diabetes, as well as in the general population,” wrote Dr. Lampasona of San Raffaele Diabetes Research Institute, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele in Milan, and colleagues.
Diabetes and hyperglycemia worsen COVID-19 outcomes
The investigators analyzed the presence of three types of antibody to multiple SARS-CoV-2 antigens in 509 participants: IgG, which is evidence of past infection; IgM, which indicates more recent or current infection; and IgA, which is involved in the mucosal immune response, for example, in the nose where the virus enters the body.
Overall, 452 (88.8%) patients were hospitalized, 79 (15.5%) patients were admitted to intensive care, and 93 (18.3%) patients died during follow-up.
Of the 139 patients with diabetes, 90 (17.7% of the study cohort) already had a diagnosis of diabetes, and 49 (9.6%) were newly diagnosed.
Those with diabetes were older, had a higher body mass index (BMI), and were more likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. As has been previously reported for diabetes and COVID-19, diabetes was also associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, hypercoagulopathy, leukocytosis, and neutrophilia.
In multivariate analysis, diabetes status (hazard ratio, 2.32; P = .001), mean fasting plasma glucose (P < .001), and glucose variability (P = .002) were all independently associated with increased mortality and ICU admission. And fasting plasma glucose was associated with increased mortality risk even among those without diabetes (P < .001).
Antibody response similar in patients with and without diabetes
The humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with diabetes was present and superimposable in terms of timing and antibody titers to that of patients without diabetes, with marginal differences, and was not influenced by glucose levels.
After adjustment for sex, age, and diabetes status and stratification by symptom duration at time of sampling, the development of SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG antibodies was associated with improved survival, with an HR for time to death of 0.4 (P = .002).
“Of the measured antibody responses, positivity for IgG against the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD was predictive of survival rate, both in the presence or absence of diabetes,” the authors stressed, with similar HRs for those with diabetes (0.37; P = .013) and without diabetes (0.43; P = .038).
These data confirm “the relevance for patient survival rate of the specific antigen response against spike RBD even in the presence of diabetes, and it underlines how the mechanism explaining the worse clinical outcome in patients with diabetes is unrelated to the antibody response,” they explain.
They added, “This, together with evidence that increased blood glucose levels do predict a poor prognosis even in nondiabetic individuals and the association with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers and hypercoagulopathy, as well as leukocytosis and neutrophilia, support the speculation that glucose per se could be an independent biological negative factor, acting as a direct regulator of innate immunity.”
“The observed increased severity and mortality risk of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with hyperglycemia was not the result of an impaired humoral response against SARS-CoV-2.”
“RBD IgG positivity was associated with a remarkable protective effect, allowing for a cautious optimism about the efficacy of future vaccines against SARS-COV-2 in people with diabetes,” they reiterated.
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Survey: Doctors lonely, burned out in COVID-19
Patrick Ross, MD, a critical care physician at Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, was plagued with increasing worry about his health and that of his family, patients, and colleagues. While distancing from his wife and daughter, he became terrified of falling ill and dying alone.
As he grew more anxious, Ross withdrew from family, colleagues, and friends, although his clinical and academic responsibilities were unaffected. He barely ate; his weight plummeted, and he began to have suicidal thoughts.
Rebecca Margolis, DO, a pediatric anesthesiologist whom Ross was mentoring, noticed something was amiss and suggested that he go to a therapist. That suggestion may have saved him.
“Once I started therapy, I no longer had suicidal ideations, but I still remained anxious on a day-to-day basis,” said Ross, who is an associate professor of clinical anesthesiology and pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “As soon as I learned to manage or mitigate the anxiety, I was no longer consumed to the degree I had been by the sense of day-to-day threat.”
Ross openly shares his story because “many other physicians may be going through versions of what I experienced, and I want to encourage them to get help if they’re feeling stressed, anxious, lonely, depressed, or burned out, and to recognize that they are not alone.”
Physicians feel a sense of betrayal
Ross’ experience, although extreme, is not unique. According to a Medscape survey of almost 7,500 physicians, about two-thirds (64%) of U.S. physicians reported experiencing more intense burnout, and close to half (46%) reported feeling more lonely and isolated during the pandemic.
“We know that stress, which was already significant in physicians, has increased dramatically for many physicians during the pandemic. That’s understandable, given the circumstances they’ve been working under,” said Christine A. Sinsky, MD, vice president of professional satisfaction at the American Medical Association.
Physicians are stressed about potentially contracting the virus or infecting family members; being overworked and fatigued; witnessing wrenching scenes of patients dying alone; grieving the loss of patients, colleagues, or family members; and sometimes lacking adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), she said.
Lack of PPE has been identified as one of the most significant contributors to burnout and stress among physicians and other health care professionals. In all eight countries surveyed by Medscape, a significant number of respondents reported lacking appropriate PPE “sometimes,” “often,” or “always” when treating COVID-19 patients. Only 54% of U.S. respondents said they were always adequately protected.
The PPE shortage not only jeopardizes physical health but also has a negative effect on mental health and morale. A U.S.-based rheumatologist said, “The fact that we were sent to take care of infectious patients without proper PPE makes me feel we were betrayed in this fight.”
Not what they signed up for
Many physicians expressed fear regarding their personal safety, but that was often superseded by concern for family – especially elderly relatives or young children. (Medscape’s survey found that 9% of US respondents had immediate family members who had been diagnosed with COVID-19.)
Larissa Thomas, MD, MPH, University of California, San Francisco, said her greatest fear was bringing the virus home to her new baby and other vulnerable family members. Thomas is associate clinical professor of medicine and is a faculty hospitalist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital.
“Although physicians assume risk in our work, we didn’t sign up to care for patients without adequate protection, and our families certainly didn’t sign up for that risk, so the concern was acutely stressful,” said Thomas, who is also associate program director for the UCSF Internal Medicine Residency Program and is director of well-being for UCSF Graduate Medical Education.
The impact of stay-at-home restrictions on family members’ mental health also affected many physicians.
David Marcus, MD, residency director of the Combined Program in Emergency/Internal/Critical Care Medicine and chair of the GME Physician Wellbeing Committee at Northwell Health, Long Island, New York, said that a large stressor during the pandemic was having an elderly father with multiple comorbidities who lived alone and was unable to go out because of stay-at-home restrictions.
“I was worried not only for his physical health but also that his cognition might slip due to lack of socialization,” said Marcus.
Marcus was also worried about his preschool-age daughter, who seemed to be regressing and becoming desocialized from no longer being at school. “Fortunately, school has reopened, but it was a constant weight on my wife and me to see the impact of the lockdown on her development,” he said.
New situations create more anxiety
Being redeployed to new clinical roles in settings such as the emergency department or intensive care, which were not in their area of specialty, created much stress for physicians, Thomas said.
Physicians in private practice also had to adjust to new ways of practicing. In Medscape’s survey, 39% of U.S. physicians reported that their medical practice never closed during the pandemic. Keeping a practice open often meant learning to see patients virtually or becoming extremely vigilant about reducing the risk for contagion when seeing patients in person.
Relationships became more challenging
Social distancing during the pandemic had a negative effect on personal relationships for 44% of respondents, both in the United States and abroad.
One physician described her relationship with her partner as “more stressful” and argumentative. A rheumatologist reported experiencing frustration at having college-aged children living at home. Another respondent said that being with young children 24/7 left her “short-tempered,” and an emergency medicine physician respondent said she and her family were “driving each other crazy.”
Social distancing was not the only challenge to relationships. An orthopedist identified long, taxing work hours as contributing to a “decline in spousal harmony.”
On the other hand, some physicians said their relationships improved by developing shared insight. An emergency medicine physician wrote that he and his wife were “having more quarrels” but were “trying very hard and succeeding at understanding that much of this is due to the changes in our living situation.”
As a volunteer with New York City’s Medical Reserve Corps, Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, chose to keep his Teaneck, New Jersey–based office open and was taking overnight shifts at Lincoln Hospital in New York City during the acute physician shortage. “After my regular hospital job treating psychiatric patients and seeing patients in my private practice, I sometimes pulled 12-hour nights caring for very ill patients. It was grueling, and I came home drained and exhausted,” he recalled.
Raby’s wife, a surgical nurse, had been redeployed to care for COVID-19 patients in the ICU – a situation she found grueling as well. Adding to the stress were the “rigorous distancing and sanitation precautions we needed to practice at home.” Fear of contagion, together with exhaustion, resulted in “occasional moments of friction,” Raby acknowledged.
Still, some physicians managed to find a bit of a silver lining. “We tried to relax, get as much sleep as possible, and keep things simple, not taking on extra tasks that could be postponed,” Raby said. “It helped that we both recognized how difficult it was to reassure each other when we were stressed and scared, so we faced the crisis together, and I think it ultimately brought us closer.”
Thomas said that the pandemic has helped her to recognize what she can and cannot control and how to take things one day at a time.
“When my husband and I can both work from home, we are grateful to have that ability and grateful for the things that we do have. These small moments of gratitude have sustained us day to day,” Thomas said.
Socializing outside the box
Several physicians expressed a sense of loneliness because stay-at-home guidelines and social distancing prevented them from socializing with friends. In all countries, physician respondents to the Medscape survey reported feeling “more lonely” than prior to the pandemic. Over half (51%) of Portuguese physicians reported feeling lonelier; 48% of physicians in Brazil felt that way. The United States came in third, at 46%.
Many physicians feel cut off, even from other physicians, and are reluctant to share feelings of distress.
“Talking to colleagues about distress is an important human connection,” Margolis emphasized. “We need to rely on each other to commiserate and receive validation and comfort.”
Some institutions have formalized this process by instituting a “battle buddy” model – a term borrowed from the military – which involves pairing clinicians of similar specialty, career stage, and life circumstances to provide mutual peer support, Margolis said. A partner who notices concerning signs in the other partner can refer the person to resources for help.
Sinsky said that an organization called PeerRxMed offers physicians a chance to sign up for a “buddy,” even outside their own institution.
The importance of ‘fixing’ the workplace
Close to half (43%) of U.S. respondents to Medscape’s survey reported that their workplace offers activities to help physicians deal with grief and stress, but 39% said that their workplace does not offer this type of support, and 18% were not sure whether these services were offered.
At times of crisis, organizations need to offer “stress first aid,” Sinsky said. This includes providing for basic needs, such as child care, transportation, and healthy food, and having “open, transparent, and honest communication” from leadership regarding what is known and not known about the pandemic, clinician responsibilities, and stress reduction measures.
Marcus notes that, at his institution, psychiatric residents and other members of the psychiatry department have “stepped up and crafted process groups and peer support contexts to debrief, engage, explore productive outlets for feelings, and facilitate communication.” In particular, residents have found cognitive-behavioral therapy to be useful.
Despite the difficult situation, seeking help can be challenging for some physicians. One reason, Marcus says, is that doctors tend to think of themselves as being at the giving rather than the receiving end of help – especially during a crisis. “We do what we need to do, and we often don’t see the toll it takes on us,” he noted. Moreover, the pressure to be at the “giving” end can lead to stigma in acknowledging vulnerability.
Ross said he hopes his story will help to destigmatize reaching out for help. “It is possible that a silver lining of this terrible crisis is to normalize physicians receiving help for mental health issues.”
Marcus likewise openly shares his own experiences about struggles with burnout and depressive symptoms. “As a physician educator, I think it’s important for me to be public about these things, which validates help-seeking for residents and colleagues.”
For physicians seeking help not offered in their workplace, the Physician Support Line is a useful resource, added Margolis. She noted that its services are free and confidential.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patrick Ross, MD, a critical care physician at Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, was plagued with increasing worry about his health and that of his family, patients, and colleagues. While distancing from his wife and daughter, he became terrified of falling ill and dying alone.
As he grew more anxious, Ross withdrew from family, colleagues, and friends, although his clinical and academic responsibilities were unaffected. He barely ate; his weight plummeted, and he began to have suicidal thoughts.
Rebecca Margolis, DO, a pediatric anesthesiologist whom Ross was mentoring, noticed something was amiss and suggested that he go to a therapist. That suggestion may have saved him.
“Once I started therapy, I no longer had suicidal ideations, but I still remained anxious on a day-to-day basis,” said Ross, who is an associate professor of clinical anesthesiology and pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “As soon as I learned to manage or mitigate the anxiety, I was no longer consumed to the degree I had been by the sense of day-to-day threat.”
Ross openly shares his story because “many other physicians may be going through versions of what I experienced, and I want to encourage them to get help if they’re feeling stressed, anxious, lonely, depressed, or burned out, and to recognize that they are not alone.”
Physicians feel a sense of betrayal
Ross’ experience, although extreme, is not unique. According to a Medscape survey of almost 7,500 physicians, about two-thirds (64%) of U.S. physicians reported experiencing more intense burnout, and close to half (46%) reported feeling more lonely and isolated during the pandemic.
“We know that stress, which was already significant in physicians, has increased dramatically for many physicians during the pandemic. That’s understandable, given the circumstances they’ve been working under,” said Christine A. Sinsky, MD, vice president of professional satisfaction at the American Medical Association.
Physicians are stressed about potentially contracting the virus or infecting family members; being overworked and fatigued; witnessing wrenching scenes of patients dying alone; grieving the loss of patients, colleagues, or family members; and sometimes lacking adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), she said.
Lack of PPE has been identified as one of the most significant contributors to burnout and stress among physicians and other health care professionals. In all eight countries surveyed by Medscape, a significant number of respondents reported lacking appropriate PPE “sometimes,” “often,” or “always” when treating COVID-19 patients. Only 54% of U.S. respondents said they were always adequately protected.
The PPE shortage not only jeopardizes physical health but also has a negative effect on mental health and morale. A U.S.-based rheumatologist said, “The fact that we were sent to take care of infectious patients without proper PPE makes me feel we were betrayed in this fight.”
Not what they signed up for
Many physicians expressed fear regarding their personal safety, but that was often superseded by concern for family – especially elderly relatives or young children. (Medscape’s survey found that 9% of US respondents had immediate family members who had been diagnosed with COVID-19.)
Larissa Thomas, MD, MPH, University of California, San Francisco, said her greatest fear was bringing the virus home to her new baby and other vulnerable family members. Thomas is associate clinical professor of medicine and is a faculty hospitalist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital.
“Although physicians assume risk in our work, we didn’t sign up to care for patients without adequate protection, and our families certainly didn’t sign up for that risk, so the concern was acutely stressful,” said Thomas, who is also associate program director for the UCSF Internal Medicine Residency Program and is director of well-being for UCSF Graduate Medical Education.
The impact of stay-at-home restrictions on family members’ mental health also affected many physicians.
David Marcus, MD, residency director of the Combined Program in Emergency/Internal/Critical Care Medicine and chair of the GME Physician Wellbeing Committee at Northwell Health, Long Island, New York, said that a large stressor during the pandemic was having an elderly father with multiple comorbidities who lived alone and was unable to go out because of stay-at-home restrictions.
“I was worried not only for his physical health but also that his cognition might slip due to lack of socialization,” said Marcus.
Marcus was also worried about his preschool-age daughter, who seemed to be regressing and becoming desocialized from no longer being at school. “Fortunately, school has reopened, but it was a constant weight on my wife and me to see the impact of the lockdown on her development,” he said.
New situations create more anxiety
Being redeployed to new clinical roles in settings such as the emergency department or intensive care, which were not in their area of specialty, created much stress for physicians, Thomas said.
Physicians in private practice also had to adjust to new ways of practicing. In Medscape’s survey, 39% of U.S. physicians reported that their medical practice never closed during the pandemic. Keeping a practice open often meant learning to see patients virtually or becoming extremely vigilant about reducing the risk for contagion when seeing patients in person.
Relationships became more challenging
Social distancing during the pandemic had a negative effect on personal relationships for 44% of respondents, both in the United States and abroad.
One physician described her relationship with her partner as “more stressful” and argumentative. A rheumatologist reported experiencing frustration at having college-aged children living at home. Another respondent said that being with young children 24/7 left her “short-tempered,” and an emergency medicine physician respondent said she and her family were “driving each other crazy.”
Social distancing was not the only challenge to relationships. An orthopedist identified long, taxing work hours as contributing to a “decline in spousal harmony.”
On the other hand, some physicians said their relationships improved by developing shared insight. An emergency medicine physician wrote that he and his wife were “having more quarrels” but were “trying very hard and succeeding at understanding that much of this is due to the changes in our living situation.”
As a volunteer with New York City’s Medical Reserve Corps, Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, chose to keep his Teaneck, New Jersey–based office open and was taking overnight shifts at Lincoln Hospital in New York City during the acute physician shortage. “After my regular hospital job treating psychiatric patients and seeing patients in my private practice, I sometimes pulled 12-hour nights caring for very ill patients. It was grueling, and I came home drained and exhausted,” he recalled.
Raby’s wife, a surgical nurse, had been redeployed to care for COVID-19 patients in the ICU – a situation she found grueling as well. Adding to the stress were the “rigorous distancing and sanitation precautions we needed to practice at home.” Fear of contagion, together with exhaustion, resulted in “occasional moments of friction,” Raby acknowledged.
Still, some physicians managed to find a bit of a silver lining. “We tried to relax, get as much sleep as possible, and keep things simple, not taking on extra tasks that could be postponed,” Raby said. “It helped that we both recognized how difficult it was to reassure each other when we were stressed and scared, so we faced the crisis together, and I think it ultimately brought us closer.”
Thomas said that the pandemic has helped her to recognize what she can and cannot control and how to take things one day at a time.
“When my husband and I can both work from home, we are grateful to have that ability and grateful for the things that we do have. These small moments of gratitude have sustained us day to day,” Thomas said.
Socializing outside the box
Several physicians expressed a sense of loneliness because stay-at-home guidelines and social distancing prevented them from socializing with friends. In all countries, physician respondents to the Medscape survey reported feeling “more lonely” than prior to the pandemic. Over half (51%) of Portuguese physicians reported feeling lonelier; 48% of physicians in Brazil felt that way. The United States came in third, at 46%.
Many physicians feel cut off, even from other physicians, and are reluctant to share feelings of distress.
“Talking to colleagues about distress is an important human connection,” Margolis emphasized. “We need to rely on each other to commiserate and receive validation and comfort.”
Some institutions have formalized this process by instituting a “battle buddy” model – a term borrowed from the military – which involves pairing clinicians of similar specialty, career stage, and life circumstances to provide mutual peer support, Margolis said. A partner who notices concerning signs in the other partner can refer the person to resources for help.
Sinsky said that an organization called PeerRxMed offers physicians a chance to sign up for a “buddy,” even outside their own institution.
The importance of ‘fixing’ the workplace
Close to half (43%) of U.S. respondents to Medscape’s survey reported that their workplace offers activities to help physicians deal with grief and stress, but 39% said that their workplace does not offer this type of support, and 18% were not sure whether these services were offered.
At times of crisis, organizations need to offer “stress first aid,” Sinsky said. This includes providing for basic needs, such as child care, transportation, and healthy food, and having “open, transparent, and honest communication” from leadership regarding what is known and not known about the pandemic, clinician responsibilities, and stress reduction measures.
Marcus notes that, at his institution, psychiatric residents and other members of the psychiatry department have “stepped up and crafted process groups and peer support contexts to debrief, engage, explore productive outlets for feelings, and facilitate communication.” In particular, residents have found cognitive-behavioral therapy to be useful.
Despite the difficult situation, seeking help can be challenging for some physicians. One reason, Marcus says, is that doctors tend to think of themselves as being at the giving rather than the receiving end of help – especially during a crisis. “We do what we need to do, and we often don’t see the toll it takes on us,” he noted. Moreover, the pressure to be at the “giving” end can lead to stigma in acknowledging vulnerability.
Ross said he hopes his story will help to destigmatize reaching out for help. “It is possible that a silver lining of this terrible crisis is to normalize physicians receiving help for mental health issues.”
Marcus likewise openly shares his own experiences about struggles with burnout and depressive symptoms. “As a physician educator, I think it’s important for me to be public about these things, which validates help-seeking for residents and colleagues.”
For physicians seeking help not offered in their workplace, the Physician Support Line is a useful resource, added Margolis. She noted that its services are free and confidential.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patrick Ross, MD, a critical care physician at Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles, was plagued with increasing worry about his health and that of his family, patients, and colleagues. While distancing from his wife and daughter, he became terrified of falling ill and dying alone.
As he grew more anxious, Ross withdrew from family, colleagues, and friends, although his clinical and academic responsibilities were unaffected. He barely ate; his weight plummeted, and he began to have suicidal thoughts.
Rebecca Margolis, DO, a pediatric anesthesiologist whom Ross was mentoring, noticed something was amiss and suggested that he go to a therapist. That suggestion may have saved him.
“Once I started therapy, I no longer had suicidal ideations, but I still remained anxious on a day-to-day basis,” said Ross, who is an associate professor of clinical anesthesiology and pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “As soon as I learned to manage or mitigate the anxiety, I was no longer consumed to the degree I had been by the sense of day-to-day threat.”
Ross openly shares his story because “many other physicians may be going through versions of what I experienced, and I want to encourage them to get help if they’re feeling stressed, anxious, lonely, depressed, or burned out, and to recognize that they are not alone.”
Physicians feel a sense of betrayal
Ross’ experience, although extreme, is not unique. According to a Medscape survey of almost 7,500 physicians, about two-thirds (64%) of U.S. physicians reported experiencing more intense burnout, and close to half (46%) reported feeling more lonely and isolated during the pandemic.
“We know that stress, which was already significant in physicians, has increased dramatically for many physicians during the pandemic. That’s understandable, given the circumstances they’ve been working under,” said Christine A. Sinsky, MD, vice president of professional satisfaction at the American Medical Association.
Physicians are stressed about potentially contracting the virus or infecting family members; being overworked and fatigued; witnessing wrenching scenes of patients dying alone; grieving the loss of patients, colleagues, or family members; and sometimes lacking adequate personal protective equipment (PPE), she said.
Lack of PPE has been identified as one of the most significant contributors to burnout and stress among physicians and other health care professionals. In all eight countries surveyed by Medscape, a significant number of respondents reported lacking appropriate PPE “sometimes,” “often,” or “always” when treating COVID-19 patients. Only 54% of U.S. respondents said they were always adequately protected.
The PPE shortage not only jeopardizes physical health but also has a negative effect on mental health and morale. A U.S.-based rheumatologist said, “The fact that we were sent to take care of infectious patients without proper PPE makes me feel we were betrayed in this fight.”
Not what they signed up for
Many physicians expressed fear regarding their personal safety, but that was often superseded by concern for family – especially elderly relatives or young children. (Medscape’s survey found that 9% of US respondents had immediate family members who had been diagnosed with COVID-19.)
Larissa Thomas, MD, MPH, University of California, San Francisco, said her greatest fear was bringing the virus home to her new baby and other vulnerable family members. Thomas is associate clinical professor of medicine and is a faculty hospitalist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital.
“Although physicians assume risk in our work, we didn’t sign up to care for patients without adequate protection, and our families certainly didn’t sign up for that risk, so the concern was acutely stressful,” said Thomas, who is also associate program director for the UCSF Internal Medicine Residency Program and is director of well-being for UCSF Graduate Medical Education.
The impact of stay-at-home restrictions on family members’ mental health also affected many physicians.
David Marcus, MD, residency director of the Combined Program in Emergency/Internal/Critical Care Medicine and chair of the GME Physician Wellbeing Committee at Northwell Health, Long Island, New York, said that a large stressor during the pandemic was having an elderly father with multiple comorbidities who lived alone and was unable to go out because of stay-at-home restrictions.
“I was worried not only for his physical health but also that his cognition might slip due to lack of socialization,” said Marcus.
Marcus was also worried about his preschool-age daughter, who seemed to be regressing and becoming desocialized from no longer being at school. “Fortunately, school has reopened, but it was a constant weight on my wife and me to see the impact of the lockdown on her development,” he said.
New situations create more anxiety
Being redeployed to new clinical roles in settings such as the emergency department or intensive care, which were not in their area of specialty, created much stress for physicians, Thomas said.
Physicians in private practice also had to adjust to new ways of practicing. In Medscape’s survey, 39% of U.S. physicians reported that their medical practice never closed during the pandemic. Keeping a practice open often meant learning to see patients virtually or becoming extremely vigilant about reducing the risk for contagion when seeing patients in person.
Relationships became more challenging
Social distancing during the pandemic had a negative effect on personal relationships for 44% of respondents, both in the United States and abroad.
One physician described her relationship with her partner as “more stressful” and argumentative. A rheumatologist reported experiencing frustration at having college-aged children living at home. Another respondent said that being with young children 24/7 left her “short-tempered,” and an emergency medicine physician respondent said she and her family were “driving each other crazy.”
Social distancing was not the only challenge to relationships. An orthopedist identified long, taxing work hours as contributing to a “decline in spousal harmony.”
On the other hand, some physicians said their relationships improved by developing shared insight. An emergency medicine physician wrote that he and his wife were “having more quarrels” but were “trying very hard and succeeding at understanding that much of this is due to the changes in our living situation.”
As a volunteer with New York City’s Medical Reserve Corps, Wilfrid Noel Raby, PhD, MD, adjunct clinical professor of psychiatry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City, chose to keep his Teaneck, New Jersey–based office open and was taking overnight shifts at Lincoln Hospital in New York City during the acute physician shortage. “After my regular hospital job treating psychiatric patients and seeing patients in my private practice, I sometimes pulled 12-hour nights caring for very ill patients. It was grueling, and I came home drained and exhausted,” he recalled.
Raby’s wife, a surgical nurse, had been redeployed to care for COVID-19 patients in the ICU – a situation she found grueling as well. Adding to the stress were the “rigorous distancing and sanitation precautions we needed to practice at home.” Fear of contagion, together with exhaustion, resulted in “occasional moments of friction,” Raby acknowledged.
Still, some physicians managed to find a bit of a silver lining. “We tried to relax, get as much sleep as possible, and keep things simple, not taking on extra tasks that could be postponed,” Raby said. “It helped that we both recognized how difficult it was to reassure each other when we were stressed and scared, so we faced the crisis together, and I think it ultimately brought us closer.”
Thomas said that the pandemic has helped her to recognize what she can and cannot control and how to take things one day at a time.
“When my husband and I can both work from home, we are grateful to have that ability and grateful for the things that we do have. These small moments of gratitude have sustained us day to day,” Thomas said.
Socializing outside the box
Several physicians expressed a sense of loneliness because stay-at-home guidelines and social distancing prevented them from socializing with friends. In all countries, physician respondents to the Medscape survey reported feeling “more lonely” than prior to the pandemic. Over half (51%) of Portuguese physicians reported feeling lonelier; 48% of physicians in Brazil felt that way. The United States came in third, at 46%.
Many physicians feel cut off, even from other physicians, and are reluctant to share feelings of distress.
“Talking to colleagues about distress is an important human connection,” Margolis emphasized. “We need to rely on each other to commiserate and receive validation and comfort.”
Some institutions have formalized this process by instituting a “battle buddy” model – a term borrowed from the military – which involves pairing clinicians of similar specialty, career stage, and life circumstances to provide mutual peer support, Margolis said. A partner who notices concerning signs in the other partner can refer the person to resources for help.
Sinsky said that an organization called PeerRxMed offers physicians a chance to sign up for a “buddy,” even outside their own institution.
The importance of ‘fixing’ the workplace
Close to half (43%) of U.S. respondents to Medscape’s survey reported that their workplace offers activities to help physicians deal with grief and stress, but 39% said that their workplace does not offer this type of support, and 18% were not sure whether these services were offered.
At times of crisis, organizations need to offer “stress first aid,” Sinsky said. This includes providing for basic needs, such as child care, transportation, and healthy food, and having “open, transparent, and honest communication” from leadership regarding what is known and not known about the pandemic, clinician responsibilities, and stress reduction measures.
Marcus notes that, at his institution, psychiatric residents and other members of the psychiatry department have “stepped up and crafted process groups and peer support contexts to debrief, engage, explore productive outlets for feelings, and facilitate communication.” In particular, residents have found cognitive-behavioral therapy to be useful.
Despite the difficult situation, seeking help can be challenging for some physicians. One reason, Marcus says, is that doctors tend to think of themselves as being at the giving rather than the receiving end of help – especially during a crisis. “We do what we need to do, and we often don’t see the toll it takes on us,” he noted. Moreover, the pressure to be at the “giving” end can lead to stigma in acknowledging vulnerability.
Ross said he hopes his story will help to destigmatize reaching out for help. “It is possible that a silver lining of this terrible crisis is to normalize physicians receiving help for mental health issues.”
Marcus likewise openly shares his own experiences about struggles with burnout and depressive symptoms. “As a physician educator, I think it’s important for me to be public about these things, which validates help-seeking for residents and colleagues.”
For physicians seeking help not offered in their workplace, the Physician Support Line is a useful resource, added Margolis. She noted that its services are free and confidential.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low IgA levels associated with increased infection risk in SLE patients
A new study of immunoglobulin levels in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has found that acquired low levels of IgA are associated with a higher risk of infection.
To the knowledge of first author Ibrahim Almaghlouth, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Toronto, and colleagues, “this is the first dedicated study to examine the relationship between acquired low immunoglobulins and infection risk in adult patients with SLE.” But as to whether there may be a “protective role for immunoglobulins and the potential effect of immunoglobulin replacement in a setting of recurrent or severe infection among SLE patients requires further study.”
To determine if the risk of infection was tied to acquired low immunoglobulin levels, the researchers launched a retrospective analysis of data from a prospective cohort study of adult SLE patients from a Toronto lupus cohort that was established in 1970. The study was published in Rheumatology.
A total of 448 patients with at least two low immunoglobulin tests were matched with 656 SLE patients with no low immunoglobulins according to enrollment decade. The average age of the low-immunoglobulin group was 41.8 years, compared with 39.3 years in the control group. Average disease duration was 11.2 years in the low-immunoglobulin group and 7.6 years in the control group.
Of the patients in the low-immunoglobulin group, 221 had consecutive low tests and 227 had nonconsecutive low tests. Overall, 98 of those patients had low IgG, 251 patients had low IgM, and 51 patients had low IgA. Only 48 patients had overlapping low levels, including 5 with all three.
Average levels among the low-immunoglobulin group at baseline were 11.5 (standard deviation, 6.1) g/L of IgG, 0.8 (1.1) g/L of IgM, and 2.4 (1.6) g/L of IgA, while average levels among the control group were 16.3 (6.4) g/L of IgG, 1.8 (1.2) g/L of IgM, and 3.2 (1.5) g/L of IgA. In the primary analysis, after adjustment using propensity scoring, there were 97 infections: 47 in the low-immunoglobulin group and 50 in the control group. The most common types were respiratory and urinary tract infections, and the rate of infection was higher in patients with low IgA. The IgA level associated with risk of infection was less than 0.75 g/L.
After Cox regression analysis, the only variable that significantly increased infection risk was a low IgA level (hazard ratio, 3.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-8.71), not a low IgG level (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 0.77-4.54) or low IgM level (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.34-1.17). In regard to recovery among the low-immunoglobulin group, 11 patients (2.5%) recovered from low immunoglobulins within in the first year, followed by 36 (8.2%) in the second year, 44 (10.1%) in the third year, and 80 (18.4%) in the fourth year. All told, 60% (263) of patients with acquired hypogammaglobulinemia recovered over a 4-year period.
Is there clinical relevance to low IgA?
“I don’t see us using this clinically immediately,” Karen Costenbader, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview. “We do test immunoglobulins often, especially in patients who’ve had biologic therapy. Will we start thinking about their IgA levels? It’s not clear, and the researchers leave it up in the air as to what this means, beyond them being at high risk.”
That said, she added, “IgA levels are interesting, especially in a time of COVID, because they’re associated with mucosal immunity. Is this subset of patients going to be at particularly high risk for the coronavirus?”
She also noted that, though immunoglobulin replacement has been helpful in her patients, it’s an expensive therapy to recommend for low IgA levels without knowing exactly what is causing these deficiencies. “My question is, would it be useful to follow these levels in lupus patients, even we don’t know what to do about them?” she asked. “We know there are a lot of risk factors for infections, so is the IgA going to be useful above and beyond that, and then what can we do about it?”
The authors acknowledged their study’s potential limitations, including low infection rates and yearly measurements of immunoglobulin levels, which could’ve led to misclassifying a lab error as true low immunoglobulin. They also highlighted its strengths, including using various methods to reduce selection and confounding bias while also reporting consistent results after examining multiple definitions of low immunoglobulins and outcomes.
The study received no specific funding, and the authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Almaghlouth I et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Oct 2. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa641.
A new study of immunoglobulin levels in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has found that acquired low levels of IgA are associated with a higher risk of infection.
To the knowledge of first author Ibrahim Almaghlouth, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Toronto, and colleagues, “this is the first dedicated study to examine the relationship between acquired low immunoglobulins and infection risk in adult patients with SLE.” But as to whether there may be a “protective role for immunoglobulins and the potential effect of immunoglobulin replacement in a setting of recurrent or severe infection among SLE patients requires further study.”
To determine if the risk of infection was tied to acquired low immunoglobulin levels, the researchers launched a retrospective analysis of data from a prospective cohort study of adult SLE patients from a Toronto lupus cohort that was established in 1970. The study was published in Rheumatology.
A total of 448 patients with at least two low immunoglobulin tests were matched with 656 SLE patients with no low immunoglobulins according to enrollment decade. The average age of the low-immunoglobulin group was 41.8 years, compared with 39.3 years in the control group. Average disease duration was 11.2 years in the low-immunoglobulin group and 7.6 years in the control group.
Of the patients in the low-immunoglobulin group, 221 had consecutive low tests and 227 had nonconsecutive low tests. Overall, 98 of those patients had low IgG, 251 patients had low IgM, and 51 patients had low IgA. Only 48 patients had overlapping low levels, including 5 with all three.
Average levels among the low-immunoglobulin group at baseline were 11.5 (standard deviation, 6.1) g/L of IgG, 0.8 (1.1) g/L of IgM, and 2.4 (1.6) g/L of IgA, while average levels among the control group were 16.3 (6.4) g/L of IgG, 1.8 (1.2) g/L of IgM, and 3.2 (1.5) g/L of IgA. In the primary analysis, after adjustment using propensity scoring, there were 97 infections: 47 in the low-immunoglobulin group and 50 in the control group. The most common types were respiratory and urinary tract infections, and the rate of infection was higher in patients with low IgA. The IgA level associated with risk of infection was less than 0.75 g/L.
After Cox regression analysis, the only variable that significantly increased infection risk was a low IgA level (hazard ratio, 3.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-8.71), not a low IgG level (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 0.77-4.54) or low IgM level (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.34-1.17). In regard to recovery among the low-immunoglobulin group, 11 patients (2.5%) recovered from low immunoglobulins within in the first year, followed by 36 (8.2%) in the second year, 44 (10.1%) in the third year, and 80 (18.4%) in the fourth year. All told, 60% (263) of patients with acquired hypogammaglobulinemia recovered over a 4-year period.
Is there clinical relevance to low IgA?
“I don’t see us using this clinically immediately,” Karen Costenbader, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview. “We do test immunoglobulins often, especially in patients who’ve had biologic therapy. Will we start thinking about their IgA levels? It’s not clear, and the researchers leave it up in the air as to what this means, beyond them being at high risk.”
That said, she added, “IgA levels are interesting, especially in a time of COVID, because they’re associated with mucosal immunity. Is this subset of patients going to be at particularly high risk for the coronavirus?”
She also noted that, though immunoglobulin replacement has been helpful in her patients, it’s an expensive therapy to recommend for low IgA levels without knowing exactly what is causing these deficiencies. “My question is, would it be useful to follow these levels in lupus patients, even we don’t know what to do about them?” she asked. “We know there are a lot of risk factors for infections, so is the IgA going to be useful above and beyond that, and then what can we do about it?”
The authors acknowledged their study’s potential limitations, including low infection rates and yearly measurements of immunoglobulin levels, which could’ve led to misclassifying a lab error as true low immunoglobulin. They also highlighted its strengths, including using various methods to reduce selection and confounding bias while also reporting consistent results after examining multiple definitions of low immunoglobulins and outcomes.
The study received no specific funding, and the authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Almaghlouth I et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Oct 2. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa641.
A new study of immunoglobulin levels in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has found that acquired low levels of IgA are associated with a higher risk of infection.
To the knowledge of first author Ibrahim Almaghlouth, MD, of the division of rheumatology at the University of Toronto, and colleagues, “this is the first dedicated study to examine the relationship between acquired low immunoglobulins and infection risk in adult patients with SLE.” But as to whether there may be a “protective role for immunoglobulins and the potential effect of immunoglobulin replacement in a setting of recurrent or severe infection among SLE patients requires further study.”
To determine if the risk of infection was tied to acquired low immunoglobulin levels, the researchers launched a retrospective analysis of data from a prospective cohort study of adult SLE patients from a Toronto lupus cohort that was established in 1970. The study was published in Rheumatology.
A total of 448 patients with at least two low immunoglobulin tests were matched with 656 SLE patients with no low immunoglobulins according to enrollment decade. The average age of the low-immunoglobulin group was 41.8 years, compared with 39.3 years in the control group. Average disease duration was 11.2 years in the low-immunoglobulin group and 7.6 years in the control group.
Of the patients in the low-immunoglobulin group, 221 had consecutive low tests and 227 had nonconsecutive low tests. Overall, 98 of those patients had low IgG, 251 patients had low IgM, and 51 patients had low IgA. Only 48 patients had overlapping low levels, including 5 with all three.
Average levels among the low-immunoglobulin group at baseline were 11.5 (standard deviation, 6.1) g/L of IgG, 0.8 (1.1) g/L of IgM, and 2.4 (1.6) g/L of IgA, while average levels among the control group were 16.3 (6.4) g/L of IgG, 1.8 (1.2) g/L of IgM, and 3.2 (1.5) g/L of IgA. In the primary analysis, after adjustment using propensity scoring, there were 97 infections: 47 in the low-immunoglobulin group and 50 in the control group. The most common types were respiratory and urinary tract infections, and the rate of infection was higher in patients with low IgA. The IgA level associated with risk of infection was less than 0.75 g/L.
After Cox regression analysis, the only variable that significantly increased infection risk was a low IgA level (hazard ratio, 3.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.17-8.71), not a low IgG level (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 0.77-4.54) or low IgM level (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.34-1.17). In regard to recovery among the low-immunoglobulin group, 11 patients (2.5%) recovered from low immunoglobulins within in the first year, followed by 36 (8.2%) in the second year, 44 (10.1%) in the third year, and 80 (18.4%) in the fourth year. All told, 60% (263) of patients with acquired hypogammaglobulinemia recovered over a 4-year period.
Is there clinical relevance to low IgA?
“I don’t see us using this clinically immediately,” Karen Costenbader, MD, a rheumatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview. “We do test immunoglobulins often, especially in patients who’ve had biologic therapy. Will we start thinking about their IgA levels? It’s not clear, and the researchers leave it up in the air as to what this means, beyond them being at high risk.”
That said, she added, “IgA levels are interesting, especially in a time of COVID, because they’re associated with mucosal immunity. Is this subset of patients going to be at particularly high risk for the coronavirus?”
She also noted that, though immunoglobulin replacement has been helpful in her patients, it’s an expensive therapy to recommend for low IgA levels without knowing exactly what is causing these deficiencies. “My question is, would it be useful to follow these levels in lupus patients, even we don’t know what to do about them?” she asked. “We know there are a lot of risk factors for infections, so is the IgA going to be useful above and beyond that, and then what can we do about it?”
The authors acknowledged their study’s potential limitations, including low infection rates and yearly measurements of immunoglobulin levels, which could’ve led to misclassifying a lab error as true low immunoglobulin. They also highlighted its strengths, including using various methods to reduce selection and confounding bias while also reporting consistent results after examining multiple definitions of low immunoglobulins and outcomes.
The study received no specific funding, and the authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Almaghlouth I et al. Rheumatology. 2020 Oct 2. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa641.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY
Fauci: Cautious optimism for COVID-19 vaccine by end of 2020
with distribution of first doses possible before the end of the year, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.
“Given the rate of infection that’s going on in this country, and the distribution of the clinical trial sites involving tens of thousands of volunteers, we project that we will have an answer as to whether or not we have a safe and effective vaccine by November or December,” Dr. Fauci said today in his virtual keynote address during the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It may come earlier -- this month, in October,” he added in his remarks. “That is unlikely – it is more likely that we’ll have an answer in November and December.”
If that timing does come to pass, Dr. Fauci said, it’s possible that distribution of doses could start at the end of the year, continuing throughout the beginning and middle of 2021.
Although there are no guarantees, Dr. Fauci said he is “cautiously optimistic” regarding the timeline.
He said that his optimism is based in part on animal studies and phase 1 data that demonstrate robust neutralizing antibody responses to a vaccine that are equivalent to, if not greater than, natural infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
Rapid development gives reason for hope
Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, a critical care and infectious disease specialist at Naval Medical Center San Diego, said there is reason to be hopeful that a vaccine will be available by the end of the calendar year. He cautioned, however, that this timing is based on the assumption that one of the vaccines will be proven safe and effective very soon.
“We’re lucky to have multiple phase 3 trials using multiple vaccine technologies in different platforms,” Dr. Maves said in a panel discussion following Dr. Fauci’s remarks. “I think the odds are very high that one of them will be effective.”
“I’m hoping that multiple vaccines will be effective,” Dr. Maves added. “Then we’ll be in a good position of determining which is the best of several good options, as a society and as a world.”
COVID-19 vaccine development over the past year has been remarkably fast, especially given the previous record set by the mumps vaccine, which took about four years to go from initial steps to rollout, Dr. Maves noted.
Dr. Fauci said the federal government has taken a “strategic approach” to the COVID-19 vaccine that includes direct involvement in the research and development of six different vaccine candidates, five of which are now in phase 3 trials.
As part of that strategic approach, the study protocols are harmonized to have a common data and safety monitoring board, common primary and secondary endpoints, and an independent statistical group to determine correlates of protection, Dr. Fauci said.
Prioritizing COVID-19 vaccine distribution
Who gets COVID-19 vaccine first will be a challenge for governmental organizations as well as bioethicists, who have proposed different strategies for fairly prioritizing different groups for access.
Reaching communities of color will be an important consideration for prioritization, according to Dr. Maves, given the disproportionate burden of disease on Black and Hispanic individuals, among other such populations.
COVID-19–related hospitalization rates have been substantially higher in communities of color, Dr. Fauci said in his keynote address. Age-adjusted hospitalization rates for Hispanic/Latinx and Black populations are 375 to 368 per 100,000, respectively, compared with just 82 per 100,000 for White non-Hispanics, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Outreach to those communities should include building trust in those populations that they will benefit from a safe and effective vaccine, and making sure that the vaccine is available to those communities as quickly as possible, Dr. Maves said.
Dr. Fauci and Dr. Maves provided no disclosures related to their presentations.
with distribution of first doses possible before the end of the year, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.
“Given the rate of infection that’s going on in this country, and the distribution of the clinical trial sites involving tens of thousands of volunteers, we project that we will have an answer as to whether or not we have a safe and effective vaccine by November or December,” Dr. Fauci said today in his virtual keynote address during the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It may come earlier -- this month, in October,” he added in his remarks. “That is unlikely – it is more likely that we’ll have an answer in November and December.”
If that timing does come to pass, Dr. Fauci said, it’s possible that distribution of doses could start at the end of the year, continuing throughout the beginning and middle of 2021.
Although there are no guarantees, Dr. Fauci said he is “cautiously optimistic” regarding the timeline.
He said that his optimism is based in part on animal studies and phase 1 data that demonstrate robust neutralizing antibody responses to a vaccine that are equivalent to, if not greater than, natural infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
Rapid development gives reason for hope
Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, a critical care and infectious disease specialist at Naval Medical Center San Diego, said there is reason to be hopeful that a vaccine will be available by the end of the calendar year. He cautioned, however, that this timing is based on the assumption that one of the vaccines will be proven safe and effective very soon.
“We’re lucky to have multiple phase 3 trials using multiple vaccine technologies in different platforms,” Dr. Maves said in a panel discussion following Dr. Fauci’s remarks. “I think the odds are very high that one of them will be effective.”
“I’m hoping that multiple vaccines will be effective,” Dr. Maves added. “Then we’ll be in a good position of determining which is the best of several good options, as a society and as a world.”
COVID-19 vaccine development over the past year has been remarkably fast, especially given the previous record set by the mumps vaccine, which took about four years to go from initial steps to rollout, Dr. Maves noted.
Dr. Fauci said the federal government has taken a “strategic approach” to the COVID-19 vaccine that includes direct involvement in the research and development of six different vaccine candidates, five of which are now in phase 3 trials.
As part of that strategic approach, the study protocols are harmonized to have a common data and safety monitoring board, common primary and secondary endpoints, and an independent statistical group to determine correlates of protection, Dr. Fauci said.
Prioritizing COVID-19 vaccine distribution
Who gets COVID-19 vaccine first will be a challenge for governmental organizations as well as bioethicists, who have proposed different strategies for fairly prioritizing different groups for access.
Reaching communities of color will be an important consideration for prioritization, according to Dr. Maves, given the disproportionate burden of disease on Black and Hispanic individuals, among other such populations.
COVID-19–related hospitalization rates have been substantially higher in communities of color, Dr. Fauci said in his keynote address. Age-adjusted hospitalization rates for Hispanic/Latinx and Black populations are 375 to 368 per 100,000, respectively, compared with just 82 per 100,000 for White non-Hispanics, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Outreach to those communities should include building trust in those populations that they will benefit from a safe and effective vaccine, and making sure that the vaccine is available to those communities as quickly as possible, Dr. Maves said.
Dr. Fauci and Dr. Maves provided no disclosures related to their presentations.
with distribution of first doses possible before the end of the year, according to Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.
“Given the rate of infection that’s going on in this country, and the distribution of the clinical trial sites involving tens of thousands of volunteers, we project that we will have an answer as to whether or not we have a safe and effective vaccine by November or December,” Dr. Fauci said today in his virtual keynote address during the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
“It may come earlier -- this month, in October,” he added in his remarks. “That is unlikely – it is more likely that we’ll have an answer in November and December.”
If that timing does come to pass, Dr. Fauci said, it’s possible that distribution of doses could start at the end of the year, continuing throughout the beginning and middle of 2021.
Although there are no guarantees, Dr. Fauci said he is “cautiously optimistic” regarding the timeline.
He said that his optimism is based in part on animal studies and phase 1 data that demonstrate robust neutralizing antibody responses to a vaccine that are equivalent to, if not greater than, natural infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
Rapid development gives reason for hope
Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, a critical care and infectious disease specialist at Naval Medical Center San Diego, said there is reason to be hopeful that a vaccine will be available by the end of the calendar year. He cautioned, however, that this timing is based on the assumption that one of the vaccines will be proven safe and effective very soon.
“We’re lucky to have multiple phase 3 trials using multiple vaccine technologies in different platforms,” Dr. Maves said in a panel discussion following Dr. Fauci’s remarks. “I think the odds are very high that one of them will be effective.”
“I’m hoping that multiple vaccines will be effective,” Dr. Maves added. “Then we’ll be in a good position of determining which is the best of several good options, as a society and as a world.”
COVID-19 vaccine development over the past year has been remarkably fast, especially given the previous record set by the mumps vaccine, which took about four years to go from initial steps to rollout, Dr. Maves noted.
Dr. Fauci said the federal government has taken a “strategic approach” to the COVID-19 vaccine that includes direct involvement in the research and development of six different vaccine candidates, five of which are now in phase 3 trials.
As part of that strategic approach, the study protocols are harmonized to have a common data and safety monitoring board, common primary and secondary endpoints, and an independent statistical group to determine correlates of protection, Dr. Fauci said.
Prioritizing COVID-19 vaccine distribution
Who gets COVID-19 vaccine first will be a challenge for governmental organizations as well as bioethicists, who have proposed different strategies for fairly prioritizing different groups for access.
Reaching communities of color will be an important consideration for prioritization, according to Dr. Maves, given the disproportionate burden of disease on Black and Hispanic individuals, among other such populations.
COVID-19–related hospitalization rates have been substantially higher in communities of color, Dr. Fauci said in his keynote address. Age-adjusted hospitalization rates for Hispanic/Latinx and Black populations are 375 to 368 per 100,000, respectively, compared with just 82 per 100,000 for White non-Hispanics, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Outreach to those communities should include building trust in those populations that they will benefit from a safe and effective vaccine, and making sure that the vaccine is available to those communities as quickly as possible, Dr. Maves said.
Dr. Fauci and Dr. Maves provided no disclosures related to their presentations.
FROM CHEST 2020
Four-week, 8-week CAB/RPV injections safe, effective in women
according to results from the ATLAS-2M study, presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Conference, held October 5-8. The women also reported high satisfaction with the regimen, compared with daily oral antiretroviral therapy.
Previously reported results had shown that the two-drug combination administered every 8 weeks (600 mg cabotegravir and 900 mg rilpivirine) was noninferior to injections every 4 weeks (400 mg cabotegravir and 600 mg rilpivirine) in adults with HIV during the open-label phase 3b ATLAS-2M trial. Further, the ATLAS and FLAIR phase 3 trials had shown the 4-week administration of the therapy to be noninferior to a daily oral three-drug antiretroviral therapy.
Paul Benn, MBBS, of ViiV Healthcare (which is seeking regulatory approval for CAB/RPV treatment), and his colleagues completed a planned subgroup analysis of women in the ATLAS-2M trial. The primary endpoint was the proportion of intention-to-treat participants with plasma HIV-1 RNA of at least 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 4% at 48 weeks. The secondary endpoint was the proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 10%.
Among the 280 women enrolled, 137 were randomly assigned to receive injections every 8 weeks, and 143 to receive injections every 4 weeks. A majority of the women (56%) were White, the median age was 44 years, and just over half (53%) were treatment naive with cabotegravir and rilpivirine.
At 48 weeks, 3.6% of women in the 8-week group and 0% of women in the 4-week group had at least 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA. In both arms, 91% of participants had HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL. Plasma concentrations of cabotegravir and rilpivirine were similar between the women and the overall study population.
Confirmed virologic failure occurred in five women, all before week 24. Three of the women were subtype A/A1, and four of them had archived nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance–associated mutations.
There were no significant differences in the safety profile between the groups; 99% of injection site reactions that occurred were mild to moderate and lasted a median 3-4 days. Fewer than 4% of participants discontinued because of adverse events – five women in the 8-week group and five women in the 4-week group. Four women cited injection site reactions as the reason for discontinuation.
Women not previously treated with CAB/RPV reported increased treatment satisfaction on the HIV Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire, a score of 5.4 in the 8-week group and 3.9 in the 4-week group. Among those with prior CAB/RPV treatment, 88% preferred the 8-weekly injections, 8% preferred the 4-weekly injections, and 2% preferred oral dosing.
Long-acting CAB/RPV is an investigational formulation. In December 2019, the Food and Drug Administration denied approval to the formulation on the basis of manufacturing and chemistry concerns, according to a company press release.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results from the ATLAS-2M study, presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Conference, held October 5-8. The women also reported high satisfaction with the regimen, compared with daily oral antiretroviral therapy.
Previously reported results had shown that the two-drug combination administered every 8 weeks (600 mg cabotegravir and 900 mg rilpivirine) was noninferior to injections every 4 weeks (400 mg cabotegravir and 600 mg rilpivirine) in adults with HIV during the open-label phase 3b ATLAS-2M trial. Further, the ATLAS and FLAIR phase 3 trials had shown the 4-week administration of the therapy to be noninferior to a daily oral three-drug antiretroviral therapy.
Paul Benn, MBBS, of ViiV Healthcare (which is seeking regulatory approval for CAB/RPV treatment), and his colleagues completed a planned subgroup analysis of women in the ATLAS-2M trial. The primary endpoint was the proportion of intention-to-treat participants with plasma HIV-1 RNA of at least 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 4% at 48 weeks. The secondary endpoint was the proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 10%.
Among the 280 women enrolled, 137 were randomly assigned to receive injections every 8 weeks, and 143 to receive injections every 4 weeks. A majority of the women (56%) were White, the median age was 44 years, and just over half (53%) were treatment naive with cabotegravir and rilpivirine.
At 48 weeks, 3.6% of women in the 8-week group and 0% of women in the 4-week group had at least 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA. In both arms, 91% of participants had HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL. Plasma concentrations of cabotegravir and rilpivirine were similar between the women and the overall study population.
Confirmed virologic failure occurred in five women, all before week 24. Three of the women were subtype A/A1, and four of them had archived nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance–associated mutations.
There were no significant differences in the safety profile between the groups; 99% of injection site reactions that occurred were mild to moderate and lasted a median 3-4 days. Fewer than 4% of participants discontinued because of adverse events – five women in the 8-week group and five women in the 4-week group. Four women cited injection site reactions as the reason for discontinuation.
Women not previously treated with CAB/RPV reported increased treatment satisfaction on the HIV Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire, a score of 5.4 in the 8-week group and 3.9 in the 4-week group. Among those with prior CAB/RPV treatment, 88% preferred the 8-weekly injections, 8% preferred the 4-weekly injections, and 2% preferred oral dosing.
Long-acting CAB/RPV is an investigational formulation. In December 2019, the Food and Drug Administration denied approval to the formulation on the basis of manufacturing and chemistry concerns, according to a company press release.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results from the ATLAS-2M study, presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Conference, held October 5-8. The women also reported high satisfaction with the regimen, compared with daily oral antiretroviral therapy.
Previously reported results had shown that the two-drug combination administered every 8 weeks (600 mg cabotegravir and 900 mg rilpivirine) was noninferior to injections every 4 weeks (400 mg cabotegravir and 600 mg rilpivirine) in adults with HIV during the open-label phase 3b ATLAS-2M trial. Further, the ATLAS and FLAIR phase 3 trials had shown the 4-week administration of the therapy to be noninferior to a daily oral three-drug antiretroviral therapy.
Paul Benn, MBBS, of ViiV Healthcare (which is seeking regulatory approval for CAB/RPV treatment), and his colleagues completed a planned subgroup analysis of women in the ATLAS-2M trial. The primary endpoint was the proportion of intention-to-treat participants with plasma HIV-1 RNA of at least 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 4% at 48 weeks. The secondary endpoint was the proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL with a noninferiority margin of 10%.
Among the 280 women enrolled, 137 were randomly assigned to receive injections every 8 weeks, and 143 to receive injections every 4 weeks. A majority of the women (56%) were White, the median age was 44 years, and just over half (53%) were treatment naive with cabotegravir and rilpivirine.
At 48 weeks, 3.6% of women in the 8-week group and 0% of women in the 4-week group had at least 50 copies/mL of HIV-1 RNA. In both arms, 91% of participants had HIV-1 RNA under 50 copies/mL. Plasma concentrations of cabotegravir and rilpivirine were similar between the women and the overall study population.
Confirmed virologic failure occurred in five women, all before week 24. Three of the women were subtype A/A1, and four of them had archived nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance–associated mutations.
There were no significant differences in the safety profile between the groups; 99% of injection site reactions that occurred were mild to moderate and lasted a median 3-4 days. Fewer than 4% of participants discontinued because of adverse events – five women in the 8-week group and five women in the 4-week group. Four women cited injection site reactions as the reason for discontinuation.
Women not previously treated with CAB/RPV reported increased treatment satisfaction on the HIV Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire, a score of 5.4 in the 8-week group and 3.9 in the 4-week group. Among those with prior CAB/RPV treatment, 88% preferred the 8-weekly injections, 8% preferred the 4-weekly injections, and 2% preferred oral dosing.
Long-acting CAB/RPV is an investigational formulation. In December 2019, the Food and Drug Administration denied approval to the formulation on the basis of manufacturing and chemistry concerns, according to a company press release.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Social factors predicted peripartum depressive symptoms in Black women with HIV
Women with high-risk pregnancies because of chronic conditions are at increased risk for developing postpartum depression, and HIV may be one such risk. However, risk factors for women living with HIV, particularly Black women, have not been well studied, wrote Emmanuela Nneamaka Ojukwu of the University of Miami School of Nursing, and colleagues.
Data suggest that as many as half of cases of postpartum depression (PPD) begin before delivery, the researchers noted. “Therefore, for this study, the symptoms of both PND (prenatal depression) and PPD have been classified in what we have termed peripartum depressive symptoms (PDS),” and defined as depressive symptoms during pregnancy and within 1 year postpartum, they said.
In a study published in the Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, the researchers conducted a secondary analysis of 143 Black women living with HIV seen at specialty prenatal and women’s health clinics in Miami.
Overall, 81 women (57%) reported either perinatal or postpartum depressive symptoms, or both. “Some of the symptoms prevalent among women in our study included restlessness, depressed mood, apathy, guilt, hopelessness, and social isolation,” the researchers said.
Social factors show significant impact
In a multivariate analysis, low income, intimate partner violence, and childcare burden were significant predictors of PDS (P less than .05). Women who reported intimate partner violence or abuse were 6.5 times more likely to experience PDS than were women who did not report abuse, and women with a childcare burden involving two children were 4.6 times more likely to experience PDS than were women with no childcare burden or only one child needing child care.
The average age of the women studied was 29 years, and 59% were above the federal poverty level. Nearly two-thirds (62%) were Black and 38% were Haitian; 63% were unemployed, 62% had a high school diploma or less, and 59% received care through Medicaid.
The researchers assessed four categories of health: HIV-related, gynecologic, obstetric, and psychosocial. The average viral load among the patients was 22,359 copies/mL at baseline, and they averaged 2.5 medical comorbidities. The most common comorbid conditions were other sexually transmitted infections and blood disorders, followed by cardiovascular and metabolic conditions.
Quantitative studies needed
Larger quantitative studies of Black pregnant women living with HIV are needed to analyze social factors at multiple levels, the researchers said. “To address depression among Black women living with HIV, local and federal governments should enact measures that increase the family income and diminish the prevalence of [intimate partner violence] among these women,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including retrospective design and use of self-reports, as well as the small sample size and lack of generalizability to women living with HIV of other races or from other regions, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the value of early screening and referral to improve well being for Black women living with HIV, as well as the importance of comprehensive medical care, they said.
“Women should be counseled that postpartum physical and psychological changes (and the stresses and demands of caring for a new baby) may make [antiretroviral] adherence more difficult and that additional support may be needed during this period,” the researchers wrote.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ojukwu EN et al. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2020.05.004.
Women with high-risk pregnancies because of chronic conditions are at increased risk for developing postpartum depression, and HIV may be one such risk. However, risk factors for women living with HIV, particularly Black women, have not been well studied, wrote Emmanuela Nneamaka Ojukwu of the University of Miami School of Nursing, and colleagues.
Data suggest that as many as half of cases of postpartum depression (PPD) begin before delivery, the researchers noted. “Therefore, for this study, the symptoms of both PND (prenatal depression) and PPD have been classified in what we have termed peripartum depressive symptoms (PDS),” and defined as depressive symptoms during pregnancy and within 1 year postpartum, they said.
In a study published in the Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, the researchers conducted a secondary analysis of 143 Black women living with HIV seen at specialty prenatal and women’s health clinics in Miami.
Overall, 81 women (57%) reported either perinatal or postpartum depressive symptoms, or both. “Some of the symptoms prevalent among women in our study included restlessness, depressed mood, apathy, guilt, hopelessness, and social isolation,” the researchers said.
Social factors show significant impact
In a multivariate analysis, low income, intimate partner violence, and childcare burden were significant predictors of PDS (P less than .05). Women who reported intimate partner violence or abuse were 6.5 times more likely to experience PDS than were women who did not report abuse, and women with a childcare burden involving two children were 4.6 times more likely to experience PDS than were women with no childcare burden or only one child needing child care.
The average age of the women studied was 29 years, and 59% were above the federal poverty level. Nearly two-thirds (62%) were Black and 38% were Haitian; 63% were unemployed, 62% had a high school diploma or less, and 59% received care through Medicaid.
The researchers assessed four categories of health: HIV-related, gynecologic, obstetric, and psychosocial. The average viral load among the patients was 22,359 copies/mL at baseline, and they averaged 2.5 medical comorbidities. The most common comorbid conditions were other sexually transmitted infections and blood disorders, followed by cardiovascular and metabolic conditions.
Quantitative studies needed
Larger quantitative studies of Black pregnant women living with HIV are needed to analyze social factors at multiple levels, the researchers said. “To address depression among Black women living with HIV, local and federal governments should enact measures that increase the family income and diminish the prevalence of [intimate partner violence] among these women,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including retrospective design and use of self-reports, as well as the small sample size and lack of generalizability to women living with HIV of other races or from other regions, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the value of early screening and referral to improve well being for Black women living with HIV, as well as the importance of comprehensive medical care, they said.
“Women should be counseled that postpartum physical and psychological changes (and the stresses and demands of caring for a new baby) may make [antiretroviral] adherence more difficult and that additional support may be needed during this period,” the researchers wrote.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ojukwu EN et al. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2020.05.004.
Women with high-risk pregnancies because of chronic conditions are at increased risk for developing postpartum depression, and HIV may be one such risk. However, risk factors for women living with HIV, particularly Black women, have not been well studied, wrote Emmanuela Nneamaka Ojukwu of the University of Miami School of Nursing, and colleagues.
Data suggest that as many as half of cases of postpartum depression (PPD) begin before delivery, the researchers noted. “Therefore, for this study, the symptoms of both PND (prenatal depression) and PPD have been classified in what we have termed peripartum depressive symptoms (PDS),” and defined as depressive symptoms during pregnancy and within 1 year postpartum, they said.
In a study published in the Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, the researchers conducted a secondary analysis of 143 Black women living with HIV seen at specialty prenatal and women’s health clinics in Miami.
Overall, 81 women (57%) reported either perinatal or postpartum depressive symptoms, or both. “Some of the symptoms prevalent among women in our study included restlessness, depressed mood, apathy, guilt, hopelessness, and social isolation,” the researchers said.
Social factors show significant impact
In a multivariate analysis, low income, intimate partner violence, and childcare burden were significant predictors of PDS (P less than .05). Women who reported intimate partner violence or abuse were 6.5 times more likely to experience PDS than were women who did not report abuse, and women with a childcare burden involving two children were 4.6 times more likely to experience PDS than were women with no childcare burden or only one child needing child care.
The average age of the women studied was 29 years, and 59% were above the federal poverty level. Nearly two-thirds (62%) were Black and 38% were Haitian; 63% were unemployed, 62% had a high school diploma or less, and 59% received care through Medicaid.
The researchers assessed four categories of health: HIV-related, gynecologic, obstetric, and psychosocial. The average viral load among the patients was 22,359 copies/mL at baseline, and they averaged 2.5 medical comorbidities. The most common comorbid conditions were other sexually transmitted infections and blood disorders, followed by cardiovascular and metabolic conditions.
Quantitative studies needed
Larger quantitative studies of Black pregnant women living with HIV are needed to analyze social factors at multiple levels, the researchers said. “To address depression among Black women living with HIV, local and federal governments should enact measures that increase the family income and diminish the prevalence of [intimate partner violence] among these women,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including retrospective design and use of self-reports, as well as the small sample size and lack of generalizability to women living with HIV of other races or from other regions, the researchers noted. However, the results reflect data from previous studies and support the value of early screening and referral to improve well being for Black women living with HIV, as well as the importance of comprehensive medical care, they said.
“Women should be counseled that postpartum physical and psychological changes (and the stresses and demands of caring for a new baby) may make [antiretroviral] adherence more difficult and that additional support may be needed during this period,” the researchers wrote.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Ojukwu EN et al. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2020.05.004.
FROM ARCHIVES OF PSYCHIATRIC NURSING
Heterosexual men likely to have unmet HIV treatment needs
according to findings presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Meeting. MSM had better overall health outcomes than the other two groups, the study found, suggesting that MSW and women have unmet needs that require providers’ attention.
Chinyere Okoli of ViiV Healthcare Global Medical Affairs in Brentford, England, and her associates administered a Web-based survey about HIV-related perceptions and behaviors to 2,389 adults with HIV in 25 countries. The respondents included 1,018 MSM, 479 MSW, and 696 women.
In high-income countries, MSM respondents had been diagnosed a median 9 years earlier, MSW respondents a median 4 years earlier, and women respondents a median 5 years earlier. In middle-income countries, diagnosis was a median 3 years ago for MSM respondents and a median 6 years for MSW and women respondents.
Rates of suboptimal adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) were lowest (15.5%) among MSM, compared with MSW (38.8%) and women (28%). Similarly, viral nonsuppression had occurred in only 10.9% of MSM, whereas it had occurred in 43.2% of MSW and 37.1% of women. A little more than one-third (36.5%) of MSM had suboptimal overall health, whereas 47.2% of MSW and 46.2% of women had suboptimal overall health (P < .05).
A similar percentage of MSM (38%) and women (38.2%) reported polypharmacy; both percentages were significantly lower than for MSW (45.1%; P = .020). Yet MSW were less likely than the other two groups to have comorbidities unrelated to HIV: 46.1%, compared with 64.6% of MSM and 56.7% of women (P < .001).
Although a higher proportion (63%) of MSW than MSM (44%) or women (55%) were receiving a multitablet ART regimen, MSW were least likely to consider the impact of side effects when they began ART and were most likely to experience side effects. Only 45% of MSW prioritized minimizing side effects when they began receiving ART, and more than half (52%) were experiencing side effects with their current regimen.
By contrast, a majority of MSM (60%) prioritized minimizing side effects at ART initiation, and only 35% currently had side effects. Women fell in the middle with 48% considering side effects when starting ART and 49% reporting current side effects.
The proportion of respondents who said ART side effects were affecting their lives was not significantly different: 69% of MSM, 73% of MSW, and 74% of women. However, 56% of MSW reported skipping at least one dose in the past month because of side effects, which was more than twice the percentage of MSM (24%; P < .001). One-third of women (33%) reported skipping at least one dose.
MSW were also least comfortable talking to their health care provider about ART side effects: 55% reported discomfort, compared with 34% of MSM and 43% of women. A high majority of MSW (87.9%) said they experienced barriers to talking to their providers about relevant health concerns. The proportion who reported barriers was lower for MSM (59%) and women (72.7%; P < .001).
The substantial differences between MSM and MSW, which were even greater than those between MSW and women, suggest this population has the greatest amount of unmet needs, the researchers concluded. “Acknowledging these differences when planning/administering care can help narrow disparities,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to findings presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Meeting. MSM had better overall health outcomes than the other two groups, the study found, suggesting that MSW and women have unmet needs that require providers’ attention.
Chinyere Okoli of ViiV Healthcare Global Medical Affairs in Brentford, England, and her associates administered a Web-based survey about HIV-related perceptions and behaviors to 2,389 adults with HIV in 25 countries. The respondents included 1,018 MSM, 479 MSW, and 696 women.
In high-income countries, MSM respondents had been diagnosed a median 9 years earlier, MSW respondents a median 4 years earlier, and women respondents a median 5 years earlier. In middle-income countries, diagnosis was a median 3 years ago for MSM respondents and a median 6 years for MSW and women respondents.
Rates of suboptimal adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) were lowest (15.5%) among MSM, compared with MSW (38.8%) and women (28%). Similarly, viral nonsuppression had occurred in only 10.9% of MSM, whereas it had occurred in 43.2% of MSW and 37.1% of women. A little more than one-third (36.5%) of MSM had suboptimal overall health, whereas 47.2% of MSW and 46.2% of women had suboptimal overall health (P < .05).
A similar percentage of MSM (38%) and women (38.2%) reported polypharmacy; both percentages were significantly lower than for MSW (45.1%; P = .020). Yet MSW were less likely than the other two groups to have comorbidities unrelated to HIV: 46.1%, compared with 64.6% of MSM and 56.7% of women (P < .001).
Although a higher proportion (63%) of MSW than MSM (44%) or women (55%) were receiving a multitablet ART regimen, MSW were least likely to consider the impact of side effects when they began ART and were most likely to experience side effects. Only 45% of MSW prioritized minimizing side effects when they began receiving ART, and more than half (52%) were experiencing side effects with their current regimen.
By contrast, a majority of MSM (60%) prioritized minimizing side effects at ART initiation, and only 35% currently had side effects. Women fell in the middle with 48% considering side effects when starting ART and 49% reporting current side effects.
The proportion of respondents who said ART side effects were affecting their lives was not significantly different: 69% of MSM, 73% of MSW, and 74% of women. However, 56% of MSW reported skipping at least one dose in the past month because of side effects, which was more than twice the percentage of MSM (24%; P < .001). One-third of women (33%) reported skipping at least one dose.
MSW were also least comfortable talking to their health care provider about ART side effects: 55% reported discomfort, compared with 34% of MSM and 43% of women. A high majority of MSW (87.9%) said they experienced barriers to talking to their providers about relevant health concerns. The proportion who reported barriers was lower for MSM (59%) and women (72.7%; P < .001).
The substantial differences between MSM and MSW, which were even greater than those between MSW and women, suggest this population has the greatest amount of unmet needs, the researchers concluded. “Acknowledging these differences when planning/administering care can help narrow disparities,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to findings presented at the HIV Glasgow 2020 Virtual Meeting. MSM had better overall health outcomes than the other two groups, the study found, suggesting that MSW and women have unmet needs that require providers’ attention.
Chinyere Okoli of ViiV Healthcare Global Medical Affairs in Brentford, England, and her associates administered a Web-based survey about HIV-related perceptions and behaviors to 2,389 adults with HIV in 25 countries. The respondents included 1,018 MSM, 479 MSW, and 696 women.
In high-income countries, MSM respondents had been diagnosed a median 9 years earlier, MSW respondents a median 4 years earlier, and women respondents a median 5 years earlier. In middle-income countries, diagnosis was a median 3 years ago for MSM respondents and a median 6 years for MSW and women respondents.
Rates of suboptimal adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) were lowest (15.5%) among MSM, compared with MSW (38.8%) and women (28%). Similarly, viral nonsuppression had occurred in only 10.9% of MSM, whereas it had occurred in 43.2% of MSW and 37.1% of women. A little more than one-third (36.5%) of MSM had suboptimal overall health, whereas 47.2% of MSW and 46.2% of women had suboptimal overall health (P < .05).
A similar percentage of MSM (38%) and women (38.2%) reported polypharmacy; both percentages were significantly lower than for MSW (45.1%; P = .020). Yet MSW were less likely than the other two groups to have comorbidities unrelated to HIV: 46.1%, compared with 64.6% of MSM and 56.7% of women (P < .001).
Although a higher proportion (63%) of MSW than MSM (44%) or women (55%) were receiving a multitablet ART regimen, MSW were least likely to consider the impact of side effects when they began ART and were most likely to experience side effects. Only 45% of MSW prioritized minimizing side effects when they began receiving ART, and more than half (52%) were experiencing side effects with their current regimen.
By contrast, a majority of MSM (60%) prioritized minimizing side effects at ART initiation, and only 35% currently had side effects. Women fell in the middle with 48% considering side effects when starting ART and 49% reporting current side effects.
The proportion of respondents who said ART side effects were affecting their lives was not significantly different: 69% of MSM, 73% of MSW, and 74% of women. However, 56% of MSW reported skipping at least one dose in the past month because of side effects, which was more than twice the percentage of MSM (24%; P < .001). One-third of women (33%) reported skipping at least one dose.
MSW were also least comfortable talking to their health care provider about ART side effects: 55% reported discomfort, compared with 34% of MSM and 43% of women. A high majority of MSW (87.9%) said they experienced barriers to talking to their providers about relevant health concerns. The proportion who reported barriers was lower for MSM (59%) and women (72.7%; P < .001).
The substantial differences between MSM and MSW, which were even greater than those between MSW and women, suggest this population has the greatest amount of unmet needs, the researchers concluded. “Acknowledging these differences when planning/administering care can help narrow disparities,” they wrote.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.







