User login
Most e-consults not followed by specialist visit
Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
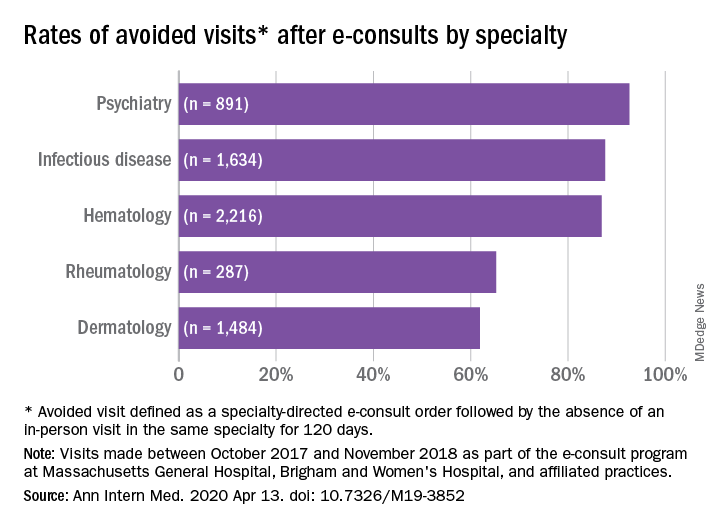
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.

Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.

Studies have shown that e-consults increase access to specialist care and primary care physician (PCP) education, according to research published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2020. Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852) by Salman Ahmed, MD, and colleagues.
These resources are already being frequently used by physicians, but more often by general internists and hospitalists than by subspecialists, according to a recent survey by the American College of Physicians. That survey found that 42% of its respondents are using e-consults and that subspecialists’ use is less common primarily because of the lack of access to e-consult technology.
What hasn’t been widely researched are the effects of large-scale e-consult programs, said Dr. Ahmed, who is associate physician in the renal division at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an interview.
For frontline providers such as PCPs, e-consults are a way to quickly seek out answers to clinical questions from specialists. In turn, the specialist can help a wider pool of participants, he noted.
The findings of Dr. Ahmed’s study, which included several academic centers and hospitals affiliated with Partners HealthCare System, a nonprofit network in eastern Massachusetts that includes Brigham and Women’s Hospital, used several metrics to analyze the appropriateness and utility of e-consults across a range of specialties. An e-consult was considered useful if it resulted in the avoidance of a visit to a specialist, which was defined as the absence of an in-person visit to the type of specialist consulted electronically for 120 days. An e-consult was considered appropriate if it met the following four criteria.
- It could not be answered by referring to society guidelines or widely available, evidence-based summary sources.
- It did not seek logistic information, such as where to have a specific laboratory test done.
- It did not include a question of high urgency.
- The medical complexity of the clinical situation was not substantial enough to warrant an in-person consultation.
The investigators examined e-consult inquiries to mostly physician health care providers in five specialties – hematology, infectious disease, dermatology, rheumatology, and psychiatry – over a year.
High rates of appropriateness
The search spanned 6,512 eligible e-consults from 1,096 referring providers to 121 specialist consultants. Narrowing their search to 741 records with complete data, the investigators found that 70.2% of these consults met the criteria for appropriateness. In an analysis of four reviewers blinded to each other’s results, raters agreed on the appropriateness of 94% of e-consults.
Across specialties, more than 81% of e-consults were associated with avoided in-person visits.
The reasons for most e-consults were to seek answers to questions about diagnosis, therapeutics, or patient inquiries, or to request further education by PCPs.
“Across all specialties, the most common reasons an e-consult was not considered appropriate were failing the point-of-care resource test and asking a question of inappropriately high complexity,” the authors summarized.
Physicians and PCPs from tertiary care practices made up the majority of referring providers, with turnaround time for consults averaging 24 hours across specialties.
Rates of appropriateness, content, patient demographics, and timeliness of e-consult responses varied among the four specialties. Those with high avoidance of visits rates tended to have high appropriateness rates, indicating that some specialties may be more conducive to e-consults than others, the authors noted. Psychiatry and hematology had the highest proportion of appropriate e-consults (77.9% and 73.3% respectively). Rheumatology had the lowest proportion of appropriate e-consults and one of the lowest rates of avoided in-person visits, and dermatology had the lowest rate of avoided in-person visits, at 61.9%.
The majority (93%) of e-consults sought in psychiatry were therapy related, whereas 88.4% of the e-consult questions in rheumatology related to diagnosis.
“Questions about diagnosis were less likely to be answerable via e-consult, which suggests that to provide diagnoses, consultants may wish to engage with the patient directly,” Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
Infectious disease specialists seemed to be the fastest responders, with nearly 90% of their consultations having been answered within a day. Dermatology specialists had the distinction of having the youngest e-consult patients (mean age, 38.6 years).
PCPs weigh in on results
Physicians said in interviews that the study data reflects their own positive experiences with e-consults.
“Although I don’t always think [an e-consult] is able to fully prevent the specialist visit, it does allow the specialist to provide recommendations for work-up that can be done prior to the specialist visit,” said Santina Wheat MD, a family physician at Erie Family Health Center in Chicago. This reduces the time in which the consult is placed to when effective treatment can take place.
Patients who may have to wait months or even years to see a specialty doctor, benefit from e-consults, said Dr. Wheat, who is also a member of the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. “As part of an organization that does e-consults to another hospital with a different electronic medical record, the e-consult increases the likelihood that all of the clinical information reaches the specialists and prevents tests from being repeated.”
Starting an e-consult may also increase the likelihood that the patient quickly sees a specialist at the contracted hospital, she added.
Sarah G. Candler, MD, said in an interview that she also sees e-consults as an essential tool. “When patients present with rare, complex, or atypical pictures, I find it helpful to have specialists weigh in. The e-consult helps me ensure that I work to the top of my abilities as an internist,” said Dr. Candler, who is practice medical director and physician director of academic relations at Iora Primary Care, Northside Clinic, Houston. However, she did not agree with the study’s avoided in-person visits metric for assessing utility.
“In some cases, the end result of an e-consult is a referral for an in-person evaluation, and the role of the e-consult is to ensure that I have done my due diligence as a primary care doctor asking the correct questions, getting the appropriate work-up completed, and referring to the appropriate specialty for next steps, when necessary,” noted Dr. Candler, who also serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Financial considerations
The study’s authors suggested taking a closer look at standardizing payment for the use of e-consults and developing appropriateness criteria for them.
Health systems could use such criteria to study what makes an e-consult useful and how to best utilize this tool, Dr. Ahmed said in an interview.
“Compensation models that promote high-quality, effective, and efficient e-consults are needed to reinforce the ability of health systems to optimize the mix of e-consults and in-person visits,” Dr. Ahmed and colleagues suggested.
Because not all patient care requires e-consults, the model makes the most sense in practices that already participate in value-based payment programs. In these types of programs, the cost can be shared according to the variable risk and patient need for the service, Dr. Candler explained.
“I have been fortunate to work in two different systems that function in this way, which means that e-consults have been readily available and encouraged-both to improve patient care and decrease overall cost by decreasing unnecessary testing or specialist referral,” she said.
Dr. Wheat said that the managed care organization affiliated with her practice seems to be saving money with e-consults, as it decreases the need to pay for specialist visits in some instances and for repeated work-ups.
Future studies
The study’s cohort represented just one large health care system with a shared electronic health record. “Single-system descriptive studies, such as that of Ahmed and colleagues, are particularly useful for local evaluation and quality improvement efforts,” Varsha G. Vimalananda, MD, and B. Graeme Fincke, MD, both of the Center for Healthcare Organization and Implementation Research at Bedford (Mass.) Veterans Affairs Hospital, wrote in a related editorial.
“However, we need innovative approaches to evaluation that estimate the effect of e-consults on quality and cost of care across health care systems and over time. Implementation studies can help to identify key contributors to success,” the editorialists wrote.
One of the study authors, reported receiving personal fees from Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors of the paper and the authors of the editorial reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Candler said her employer contracts with an e-consult service, but that she is not compensated for use of the service. She is also a coeditor of Annals of Internal Medicine’s blog, “Fresh Look.”
SOURCE: Ahmed S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.7326/M19-3852.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
SARS-CoV-2 may confound seasons, persist in warmer months, report shows
Although conflicting, the available data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 could continue to spread in warmer spring and summer months in the US, according to a new report from the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NAS).
Current data suggest that the novel coronavirus may be transmitted less efficiently in higher temperatures and humidity, but the studies are not conclusive because of poor data quality, confounding factors, and the relatively short existence of the pandemic, which makes it difficult to determine its true course, writes David A. Relman, MD, a member of the NAS’ Standing Committee on Emerging Infectious Diseases and 21st Century Health Threats, in a rapid expert consultation letter to the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy on April 7.
A number of factors could influence whether SARS-CoV-2 follows the same seasonal pattern as the influenza virus and other seasonal coronaviruses, which wane during warmer months, writes Relman, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Stanford University in California.
But he pointed out that previous coronavirus strains that have caused serious illness – SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV – “have not demonstrated any evidence of seasonality following their emergence.”
Relman cites an example from the current outbreak: “Given that countries currently in ‘summer’ climates, such as Australia and Iran, are experiencing rapid virus spread, a decrease in cases with increases in humidity and temperature elsewhere should not be assumed…Additional studies as the pandemic unfolds could shed more light on the effects of climate on transmission,” he writes.
And even if SARS-CoV-2 turns out to be less infectious in warmer months, “given the lack of host immunity globally, this reduction in transmission efficiency may not lead to a significant reduction in disease spread without the concomitant adoption of major public health interventions,” writes Relman.
Conflicting Data
Relman cites a handful of studies indicating that, on the one hand, SARS-CoV-2 has declined with increasing humidity and temperatures, but that conversely, infectivity has increased in warmer, more humid climates.
A recent study in China, published on the repository and international journal site SSRN, found that while increased temperatures and humidity decreased the infectivity, “the average R0 (R naught) was still close to 2 at maximum temperatures and humidity in their data set, suggesting that the virus will still spread exponentially at higher temperatures and humidity,” said Relman.
Several other studies found higher growth rates in temperate regions. One study, still in preprint on MedRxiv, looked at 310 geographic regions across 116 countries, and shows an inverse relationship between temperature and humidity and the incidence of COVID-19.
All the available studies so far have significant limitations, including limitation in time and location, confounding factors having to do with geography, access to and the quality of public health and health care systems, human behavior, and the availability of testing, said Relman.
However, he said, “it is useful to note that pandemic influenza strains have not exhibited the typical seasonal pattern of endemic/epidemic strains,” and, regardless of whether they started in a warmer or a cooler month, “all had a peak second wave approximately six months after the emergence in the human population.”
Worrisome Persistence on Masks
Seasonality can also be potentially gauged in the laboratory. Most of the studies on environmental persistence of SARS-CoV-2 have been conducted using virus grown in tissue culture. But that, too, is an imperfect method.
Virus disseminated into the environment from naturally infected humans likely has different survival properties than virus grown in culture, said Relman.
In addition, many labs cannot, or fail to, control and vary relative humidity, the committee letter noted. The aerosol studies so far have used humidity levels of 50% to 65%, which is more favorable to decay, while respiratory fluid is more likely to protect against infectivity, and the 20%-to-40% wintertime indoor humidity in temperate regions is more favorable for virus survival.
Even with these caveats, the committee cited worrisome studies on SARS-CoV-2 survival.
In a study published April 2 online in The Lancet, Hong Kong researchers reported significant reductions in virus in culture starting with temperatures at 37°C (98.6°F) or above.
On surfaces at a room temperature of 22°C (71.6°F) with a relative humidity of 65%, there was no infectious virus on printing paper or tissue papers after just 3 hours. It took 4 days for an infectious level to break down on glass and money, and 7 days for stainless steel and plastic. But after 7 days, investigators found 0.1% of the original inoculum on the outside of a surgical mask.
“The persistence of infectious virus on PPE is concerning,” writes Relman, noting that more studies are needed to guide healthcare workers, especially on what might be used to disinfect personal protective equipment “when they cannot be discarded after single use.”
Chad Roy, PhD, a researcher from Tulane University National Primate Research Center in New Orleans, Louisiana, told Relman by phone that in experiments where the virus was suspended as an aerosol at a temperature of 23°C (73.4° F) and about 50% humidity, SARS-CoV-2 had a longer half-life than the influenza virus, SARS-CoV-1, monkeypox virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
“This result is also concerning, but quite preliminary,” writes Relman.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although conflicting, the available data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 could continue to spread in warmer spring and summer months in the US, according to a new report from the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NAS).
Current data suggest that the novel coronavirus may be transmitted less efficiently in higher temperatures and humidity, but the studies are not conclusive because of poor data quality, confounding factors, and the relatively short existence of the pandemic, which makes it difficult to determine its true course, writes David A. Relman, MD, a member of the NAS’ Standing Committee on Emerging Infectious Diseases and 21st Century Health Threats, in a rapid expert consultation letter to the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy on April 7.
A number of factors could influence whether SARS-CoV-2 follows the same seasonal pattern as the influenza virus and other seasonal coronaviruses, which wane during warmer months, writes Relman, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Stanford University in California.
But he pointed out that previous coronavirus strains that have caused serious illness – SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV – “have not demonstrated any evidence of seasonality following their emergence.”
Relman cites an example from the current outbreak: “Given that countries currently in ‘summer’ climates, such as Australia and Iran, are experiencing rapid virus spread, a decrease in cases with increases in humidity and temperature elsewhere should not be assumed…Additional studies as the pandemic unfolds could shed more light on the effects of climate on transmission,” he writes.
And even if SARS-CoV-2 turns out to be less infectious in warmer months, “given the lack of host immunity globally, this reduction in transmission efficiency may not lead to a significant reduction in disease spread without the concomitant adoption of major public health interventions,” writes Relman.
Conflicting Data
Relman cites a handful of studies indicating that, on the one hand, SARS-CoV-2 has declined with increasing humidity and temperatures, but that conversely, infectivity has increased in warmer, more humid climates.
A recent study in China, published on the repository and international journal site SSRN, found that while increased temperatures and humidity decreased the infectivity, “the average R0 (R naught) was still close to 2 at maximum temperatures and humidity in their data set, suggesting that the virus will still spread exponentially at higher temperatures and humidity,” said Relman.
Several other studies found higher growth rates in temperate regions. One study, still in preprint on MedRxiv, looked at 310 geographic regions across 116 countries, and shows an inverse relationship between temperature and humidity and the incidence of COVID-19.
All the available studies so far have significant limitations, including limitation in time and location, confounding factors having to do with geography, access to and the quality of public health and health care systems, human behavior, and the availability of testing, said Relman.
However, he said, “it is useful to note that pandemic influenza strains have not exhibited the typical seasonal pattern of endemic/epidemic strains,” and, regardless of whether they started in a warmer or a cooler month, “all had a peak second wave approximately six months after the emergence in the human population.”
Worrisome Persistence on Masks
Seasonality can also be potentially gauged in the laboratory. Most of the studies on environmental persistence of SARS-CoV-2 have been conducted using virus grown in tissue culture. But that, too, is an imperfect method.
Virus disseminated into the environment from naturally infected humans likely has different survival properties than virus grown in culture, said Relman.
In addition, many labs cannot, or fail to, control and vary relative humidity, the committee letter noted. The aerosol studies so far have used humidity levels of 50% to 65%, which is more favorable to decay, while respiratory fluid is more likely to protect against infectivity, and the 20%-to-40% wintertime indoor humidity in temperate regions is more favorable for virus survival.
Even with these caveats, the committee cited worrisome studies on SARS-CoV-2 survival.
In a study published April 2 online in The Lancet, Hong Kong researchers reported significant reductions in virus in culture starting with temperatures at 37°C (98.6°F) or above.
On surfaces at a room temperature of 22°C (71.6°F) with a relative humidity of 65%, there was no infectious virus on printing paper or tissue papers after just 3 hours. It took 4 days for an infectious level to break down on glass and money, and 7 days for stainless steel and plastic. But after 7 days, investigators found 0.1% of the original inoculum on the outside of a surgical mask.
“The persistence of infectious virus on PPE is concerning,” writes Relman, noting that more studies are needed to guide healthcare workers, especially on what might be used to disinfect personal protective equipment “when they cannot be discarded after single use.”
Chad Roy, PhD, a researcher from Tulane University National Primate Research Center in New Orleans, Louisiana, told Relman by phone that in experiments where the virus was suspended as an aerosol at a temperature of 23°C (73.4° F) and about 50% humidity, SARS-CoV-2 had a longer half-life than the influenza virus, SARS-CoV-1, monkeypox virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
“This result is also concerning, but quite preliminary,” writes Relman.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although conflicting, the available data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 could continue to spread in warmer spring and summer months in the US, according to a new report from the National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine (NAS).
Current data suggest that the novel coronavirus may be transmitted less efficiently in higher temperatures and humidity, but the studies are not conclusive because of poor data quality, confounding factors, and the relatively short existence of the pandemic, which makes it difficult to determine its true course, writes David A. Relman, MD, a member of the NAS’ Standing Committee on Emerging Infectious Diseases and 21st Century Health Threats, in a rapid expert consultation letter to the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy on April 7.
A number of factors could influence whether SARS-CoV-2 follows the same seasonal pattern as the influenza virus and other seasonal coronaviruses, which wane during warmer months, writes Relman, a professor of microbiology and immunology at Stanford University in California.
But he pointed out that previous coronavirus strains that have caused serious illness – SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV – “have not demonstrated any evidence of seasonality following their emergence.”
Relman cites an example from the current outbreak: “Given that countries currently in ‘summer’ climates, such as Australia and Iran, are experiencing rapid virus spread, a decrease in cases with increases in humidity and temperature elsewhere should not be assumed…Additional studies as the pandemic unfolds could shed more light on the effects of climate on transmission,” he writes.
And even if SARS-CoV-2 turns out to be less infectious in warmer months, “given the lack of host immunity globally, this reduction in transmission efficiency may not lead to a significant reduction in disease spread without the concomitant adoption of major public health interventions,” writes Relman.
Conflicting Data
Relman cites a handful of studies indicating that, on the one hand, SARS-CoV-2 has declined with increasing humidity and temperatures, but that conversely, infectivity has increased in warmer, more humid climates.
A recent study in China, published on the repository and international journal site SSRN, found that while increased temperatures and humidity decreased the infectivity, “the average R0 (R naught) was still close to 2 at maximum temperatures and humidity in their data set, suggesting that the virus will still spread exponentially at higher temperatures and humidity,” said Relman.
Several other studies found higher growth rates in temperate regions. One study, still in preprint on MedRxiv, looked at 310 geographic regions across 116 countries, and shows an inverse relationship between temperature and humidity and the incidence of COVID-19.
All the available studies so far have significant limitations, including limitation in time and location, confounding factors having to do with geography, access to and the quality of public health and health care systems, human behavior, and the availability of testing, said Relman.
However, he said, “it is useful to note that pandemic influenza strains have not exhibited the typical seasonal pattern of endemic/epidemic strains,” and, regardless of whether they started in a warmer or a cooler month, “all had a peak second wave approximately six months after the emergence in the human population.”
Worrisome Persistence on Masks
Seasonality can also be potentially gauged in the laboratory. Most of the studies on environmental persistence of SARS-CoV-2 have been conducted using virus grown in tissue culture. But that, too, is an imperfect method.
Virus disseminated into the environment from naturally infected humans likely has different survival properties than virus grown in culture, said Relman.
In addition, many labs cannot, or fail to, control and vary relative humidity, the committee letter noted. The aerosol studies so far have used humidity levels of 50% to 65%, which is more favorable to decay, while respiratory fluid is more likely to protect against infectivity, and the 20%-to-40% wintertime indoor humidity in temperate regions is more favorable for virus survival.
Even with these caveats, the committee cited worrisome studies on SARS-CoV-2 survival.
In a study published April 2 online in The Lancet, Hong Kong researchers reported significant reductions in virus in culture starting with temperatures at 37°C (98.6°F) or above.
On surfaces at a room temperature of 22°C (71.6°F) with a relative humidity of 65%, there was no infectious virus on printing paper or tissue papers after just 3 hours. It took 4 days for an infectious level to break down on glass and money, and 7 days for stainless steel and plastic. But after 7 days, investigators found 0.1% of the original inoculum on the outside of a surgical mask.
“The persistence of infectious virus on PPE is concerning,” writes Relman, noting that more studies are needed to guide healthcare workers, especially on what might be used to disinfect personal protective equipment “when they cannot be discarded after single use.”
Chad Roy, PhD, a researcher from Tulane University National Primate Research Center in New Orleans, Louisiana, told Relman by phone that in experiments where the virus was suspended as an aerosol at a temperature of 23°C (73.4° F) and about 50% humidity, SARS-CoV-2 had a longer half-life than the influenza virus, SARS-CoV-1, monkeypox virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
“This result is also concerning, but quite preliminary,” writes Relman.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What do early remdesivir data suggest?
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data on the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir (Gilead) suggest clinical improvement in 36 of 53 patients (68%) hospitalized for severe COVID-19, according to a new study published online April 10 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
But experts are warning that these data come from compassionate use in a wide variety of patients, with no randomization and no control group.
“It is impossible to know the outcome for this relatively small group of patients had they not received remdesivir,” commented Stephen Griffin, PhD, associate professor at the University of Leeds School of Medicine, United Kingdom, who was not involved with the study.
“As the authors point out, a randomized clinical trial is necessary to determine the true effectiveness of this drug,” Griffin added in comments he provided to the Science Media Centre in London. Such trials are underway.
“The data from this paper are almost uninterpretable,” said Stephen Evans, MSc, FRCP, professor of pharmacoepidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, who provided comments to the Science Media Centre.
Evans notes that the authors describe multiple caveats that limit interpretation of the results, including the small sample size, the relatively short follow-up, missing data, no follow-up on eight patients, and lack of a randomized control group.
Meanwhile, Josh Farkas, MD, who writes the PulmCrit blog, details his criticisms in a piece entitled, “Eleven reasons the NEJM paper on remdesivir reveals nothing.” Beyond the issues the authors list, he points out several more, including cherry picking of patients. “Remdesivir was aggressively sought-after by thousands of patients with COVID-19,” he writes. “Of these patients, 61 ended up receiving the drug. Why did these patients receive medication, out of scores of patients applying to receive it?”
Also, there are no follow-up data for 8 of the 61 patients who received an initial dose of the drug, leaving 53 for the published analysis, continues Farkas, who is an assistant professor of pulmonary and critical care medicine at the University of Vermont in Burlington.
“What happened to these patients? Did they die from anaphylaxis? Did they get well, sign out against medical advice, and go party? This is unknown — but I’m worried that these patients actually didn’t fare so well,” Farkas writes.
Farkas, like Evans and Griffin, concludes that the data are largely unusable. “Until [a randomized controlled trial] is performed, further compassionate use of remdesivir probably isn’t justified,” he writes.
Data from Compassionate Use Program
The data in the NEJM article come from a compassionate use program set up by Gilead. The company says it has provided emergency access to remdesivir for several hundred patients in the United States, Europe, and Japan.
The authors, led by Jonathan Grein, MD, from Cedars–Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, report on 61 patients who received remdesivir as part of this program.
The authors, several of whom are employees of Gilead, note that data on 8 patients could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no posttreatment data and 1 with a dosing error).
Of the 53 patients whose data were included, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan.
These were patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who had confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air, or who were receiving oxygen support.
Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment.
At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 (57%) of 30 patients receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated.
A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
While the authors acknowledge limitations of the data they collected, they nevertheless comment that “comparisons with contemporaneous cohorts from the literature, in whom general care is expected to be consistent with that of our cohort, suggest that remdesivir may have clinical benefit in patients with severe COVID-19.”
“Currently there is no proven treatment for COVID-19. We cannot draw definitive conclusions from these data, but the observations from this group of hospitalized patients who received remdesivir are hopeful,” said Grein in a Cedars–Sinai press release. “We look forward to the results of controlled clinical trials to potentially validate these findings.”
Experts are not convinced, however.
“The drug was being used in patients who were severely ill, but reporting on 61 out of several hundred makes it clear that generalizations about the efficacy and safety must be treated with great caution,” said Evans. “There is some evidence suggesting efficacy, but we simply do not know what would have happened to these patients had they not been given the drug.”
“I would say it’s impossible to discern whether there is a treatment effect or not,” said Duncan Richards, MA, DM, FRCP, clinical pharmacologist and professor of clinical therapeutics, University of Oxford, UK. “This is in part due to the mixed patient population, ranging from those needing low dose oxygen, who are more likely to survive anyway, to much more severe cases ... [who] show a much more mixed picture.”
“There are ongoing large international randomized controlled trials with remdesivir — we really need to see those data, “ he said in comments to Science Media Centre. “Safe and effective treatments for COVID-19 are critically needed and should be expedited wherever possible, but it’s important not to compromise on the quality of the research.”
Multiple coauthors are employees of Gilead, the company developing remdesivir. Griffin, Evans, and Farkas have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Richards consults for GlaxoSmithKline in the field of drug safety. GSK does not manufacture any of the products mentioned.
N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 10. Full text.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Remdesivir tops list of promising COVID-19 treatments in review of nearly 300 trials
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
, according to authors of a recent review covering nearly 300 active clinical treatment trials underway for the disease.
Remdesivir, which has potent in vitro activity against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration and is currently being tested in randomized trials, according to the review authors, led by James M. Sanders, PhD, of the department of pharmacy at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
By contrast, oseltamivir has not demonstrated efficacy against the virus, corticosteroids are not recommended, and promising data from a small French hydroxychloroquine study are balanced by “several major limitations” including small sample size and exclusion of early dropouts from the analysis, among others, Dr. Sanders and coauthors said in their report.
“These limitations coupled with concerns of additive cardiotoxicity with combination therapy [i.e., hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin] do not support adoption of this regimen without additional studies,” the researchers wrote. Their report is in JAMA.
Dr. Sanders and colleagues identified 291 COVID-19–specific studies listed in ClinicalTrials.gov through April 2, including 29 placebo-controlled trials.
This might represent just a sliver of the treatments that could combat COVID-19, according to the researchers, who said more than 3,000 small-molecule drug candidates with potential activity against human coronaviruses have been identified.
“This large amount of potential agents will hopefully yield more candidate therapeutics in the race to find effective treatments or preventive strategies against COVID-19,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
Remdesivir for COVID-19
Remdesivir, an investigational nucleotide analog, is one promising agent because of its broad-spectrum and potent activity against SARS-CoV-2 and other novel coronaviruses, they said, adding that phase 1 trials demonstrated the drug was well tolerated without observed liver or kidney toxicity.
There have been “successful” case reports of remdesivir use in COVID-19, and at least five ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the drug’s safety and antiviral activity in this disease. Among those studies is a National Institutes of Health–sponsored adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that will provide data on the use of remdesivir versus supportive care.
“As the results from randomized controlled trials are anticipated, inclusion of this agent for treatment of COVID-19 may be considered,” Dr. Sanders and colleagues wrote in their report. To date, remdesivir remains investigational and needs to be obtained via compassionate use, through expanded access, or by participating in a clinical trial, they added.
Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine
Among the published hydroxychloroquine studies is a “promising” 36-patient open-label nonrandomized French study, in which the antimalarial agent given every 8 hours improved virologic clearance by day 6 versus controls (70% vs. 12.5%, respectively), the review authors said. Moreover, viral clearance was 100% for 6 patients who received hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin, compared to 57% (8 of 14) for patients treated with hydroxychloroquine alone. However, that study had several important limitations, including the small sample size, variable viral loads at baseline between groups, and a lack of safety and clinical outcomes reporting, according to the investigators. Moreover, six patients in the hydroxychloroquine group were taken out of the analysis because of early treatment stoppage due to medical intolerance or critical illness, the authors noted.
One prospective study including 30 patients in China demonstrated no difference in virologic outcomes for patients randomized to hydroxychloroquine plus standard of care versus standard of care alone, they added. There is also a case series of more than 100 patients with COVID-19 that reportedly improved viral clearance and reduced disease progression, though they said results haven’t been published or presented beyond a news briefing in China.
Randomized, controlled trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 treatment are underway, and studies are planned or enrolling to look at chloroquine prophylaxis in health care personnel and hydroxychloroquine for postexposure prophylaxis, authors said.
In results from one of those randomized trials, just reported, a higher dose of chloroquine was associated with a cardiac adverse event and an increased mortality risk, leading to the closure of that study arm. In the parallel, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial, patients in Brazil with SARS-CoV-2 infection received low or high doses of chloroquine plus ceftriaxone and azithromycin. According to the preprint publication, a higher rate of heart rate–corrected QT interval (QTc) prolongation and a “trend toward higher lethality” was observed in the high-dose group, leading investigators to “strongly recommend” the higher dose be abandoned.
“No apparent benefit of chloroquine was seen regarding lethality in our patients so far, but we will still enroll patients in the low chloroquine dose group to complete the originally planned sample size,” said investigators of the study, which at the time of the report had enrolled 81 out of an anticipated 440 patients.
Other COVID-19 pharmacologic therapies under study
Treatments of note in the review included the following:
- Tocilizumab. This monoclonal antibody IL-6 receptor antagonist, approved by the FDA for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and for cytokine release syndrome related to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, has yielded success in small series of patients with severe cases of COVID-19, according to authors. In one 21-patient report, 91% had clinical improvement, usually after a single dose. In China, tocilizumab is included in COVID-19 treatment guidelines, and several randomized clinical trials are underway in China including patients with COVID-19 with severe pneumonia.
- Immunoglobulin therapy. Antibodies from recovered COVID-19 patients could help with free virus and infected cell immune clearance, the authors said, adding that further studies are warranted beyond a few small published case series that suggest promise. Furthermore, on March 24 the FDA released guidance for screening donors for COVID-19 convalescent plasma and on emergency investigational new drug applications based on this modality.
- Lopinavir/ritonavir. Despite demonstrated in vitro activity against other novel coronaviruses, there is no published in vitro data for lopinavir/ritonavir in SARS-CoV-2, and likely a “limited role” for this combination anticipated in treating COVID-19, according to the review authors. In an open-label randomized clinical trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282), there were no differences in clinical improvement, viral clearance, or mortality for antiviral treatment versus standard care. Delayed treatment initiation may explain the ineffectiveness, though a subgroup analysis didn’t show a shorter time to clinical improvement for those who got the treatment earlier.
- Ribavirin. Likewise, this antiviral medication has efficacy and safety data suggesting “limited value” for treatment of COVID-19. Treatment of SARS yielded “inconclusive results” for ribavirin, which was also associated with substantial toxicity that included hemolytic anemia in 60% of SARS patients.
- Oseltamivir. While it may treat influenza, it has no documented activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro: “This agent has no role in the management of COVID-19 once influenza has been excluded,” said Dr. Sanders and coauthors.
- Corticosteroids. They could decrease inflammatory responses in the lung, but they could also lead to delays in viral clearance and increases in secondary infection risk. Guidelines for COVID-19 say to avoid corticosteroids, and the authors of the review concur, saying that potential harms and lack of proven benefit mean they usually should not be used outside of a randomized clinical trial setting.
- Vaccines. Clearly, vaccines represent the “most effective long-term strategy” to prevent future COVID-19 outbreaks, though at least 12-18 months would be required until vaccines can be widely deployed, authors said.
Dr. Sanders reported no potential conflicts. Senior author James B. Cutrell, MD, also of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, reported nonfinancial support from Gilead and Regeneron outside of the study. No other authors reported disclosures.
FROM JAMA
COVID-19 pandemic brings unexpected pediatric consequences
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
As physicians and advanced practitioners, we have been preparing to face COVID-19 – anticipating increasing volumes of patients with fevers, cough, and shortness of breath, and potential surges in emergency departments (EDs) and primary care offices. Fortunately, while COVID-19 has demonstrated more mild symptoms in pediatric patients, the heightened public health fears and mandated social isolation have created some unforeseen consequences for pediatric patients. This article presents cases encountered over the course of 2 weeks in our ED that shed light on the unexpected ramifications of living in the time of a pandemic. These encounters should remind us as providers to be diligent and thorough in giving guidance to families during a time when face-to-face medicine has become increasingly difficult and limited.
These stories have been modified to protect patient confidentiality.
Case 1
A 2-week-old full-term infant arrived in the ED after having a fever for 48 hours. The patient’s mother reported that she had called the pediatrician yesterday to ask for advice on treating the fever and was instructed to give acetaminophen and bring the infant into the ED for testing.
When we asked mom why she did not bring the infant in yesterday, she stated that the fever went down with acetaminophen, and the baby was drinking well and urinating normally. Mostly, she was afraid to bring the child into the ED given concern for COVID-19; however, when the fever persisted today, she came in. During the work-up, the infant was noted to have focal seizures and was ultimately diagnosed with bacterial meningitis.
Takeaway: Families may be hesitant to follow pediatrician’s advice to seek medical attention at an ED or doctor’s office because of the fear of being exposed to COVID-19.
- If something is urgent or emergent, be sure to stress the importance to families that the advice is non-negotiable for their child’s health.
- Attempt to call ahead for patients who might be more vulnerable in waiting rooms or overcrowded hospitals.
Case 2
A 5-month-old baby presented to the ED with new-onset seizures. Immediate bedside blood work performed demonstrated a normal blood glucose, but the baby was profoundly hyponatremic. Upon asking the mother if the baby has had any vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty tolerating feeds, she says that she has been diluting formula because all the stores were out of formula. Today, she gave the baby plain water because they were completely out of formula.
Takeaway: With economists estimating unemployment rates in the United States at 13% at press time (the worst since the Great Depression), many families may lack resources to purchase necessities.
- Even if families have the ability to purchase necessities, they may be difficult to find or unavailable (e.g., formula, medications, diapers).
- Consider reaching out to patients in your practice to ask about their ability to find essentials and with advice on what to do if they run out of formula or diapers, or who they should contact if they cannot refill a medication.
- Are you in a position to speak with your mayor or local council to ensure there are regulations on the hoarding of essential items?
- In a time when breast milk or formula is not available for children younger than 1 year of age, what will you recommend for families? There are no current American Academy of Pediatrics’ guidelines.
Case 3
A school-aged girl was helping her mother sanitize the home during the COVID-19 pandemic. She had her gloves on, her commercial antiseptic cleaner ready to go, but it was not spraying. She turned the bottle around to check the nozzle and sprayed herself in the eyes. The family presented to the ED for alkaline burn to her eyes, which required copious irrigation.
Takeaway: Children are spending more time in the house with access to button batteries, choking hazards, and cleaning supplies.
- Cleaning products can cause chemical burns. These products should not be used by young children.
Case 4
A school-aged boy arrived via emergency medical services (EMS) for altered mental status. He told his father he was feeling dizzy and then lost consciousness. EMS noticed that he had some tonic movements of his lower extremities, and when he arrived in the ED, he had eye deviation and was unresponsive.
Work-up ultimately demonstrated that this patient had a seizure and a dangerously elevated ethanol level from drinking an entire bottle of hand sanitizer. Hand sanitizer may contain high concentrations of ethyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, which when ingested can cause intoxication or poisoning.
Takeaway: Many products that we may view as harmless can be toxic if ingested in large amounts.
- Consider making a list of products that families may have acquired and have around the home during this COVID-19 pandemic and instruct families to make sure dangerous items (e.g., acetaminophen, aspirin, hand sanitizer, lighters, firearms, batteries) are locked up and/or out of reach of children.
- Make sure families know the Poison Control phone number (800-222-1222).
Case 5
An adolescent female currently being treated with immunosuppressants arrived from home with fever. Her medical history revealed that the patient’s guardian recently passed away from suspected COVID-19. The patient was tested and is herself found to be positive for COVID-19. The patient is currently being cared for by relatives who also live in the same home. They require extensive education and teaching regarding the patient’s medication regimen, while also dealing with the loss of their loved one and the fear of personal exposure.
Takeaway: Communicate with families – especially those with special health care needs – about issues of guardianship in case a child’s primary caretaker falls ill.
- Discuss with families about having easily accessible lists of medications and medical conditions.
- Involve social work and child life specialists to help children and their families deal with life-altering changes and losses suffered during this time, as well as fears related to mortality and exposure.
Case 6
A 3-year-old boy arrived covered in bruises and complaining of stomachache. While the mother denies any known abuse, she states that her significant other has been getting more and more “worked up having to deal with the child’s behavior all day every day.” The preschool the child previously attended has closed due to the pandemic.
Takeaway: Abuse is more common when the parents perceive that there is little community support and when families feel a lack of connection to the community.1 Huang et al. examined the relationship between the economy and nonaccidental trauma, showing a doubling in the rate of nonaccidental head trauma during economic recession.2
- Allow families to know that they are not alone and that child care is difficult
- Offer advice on what caretakers can do if they feel alone or at their mental or physical limit.
- Provide strategies on your practice’s website if a situation at home becomes tense and strained.
Case 7
An adolescent female arrived to the ED with increased suicidality. She normally follows with her psychiatrist once a month and her therapist once a week. Since the beginning of COVID-19 restrictions, she has been using telemedicine for her therapy visits. While previously doing well, she reports that her suicidal ideations have worsened because of feeling isolated from her friends now that school is out and she is not allowed to see them. Although compliant with her medications, her thoughts have increased to the point where she has to be admitted to inpatient psychiatry.
Takeaway: Anxiety, depression, and suicide may increase in a down economy. After the 2008 global economic crisis, rates of suicide drastically increased.3
- Recognize the limitations of telemedicine (technology limitations, patient cooperation, etc.)
- Social isolation may contribute to worsening mental health
- Know when to advise patients to seek in-person evaluation and care for medical and mental health concerns.
Pediatricians are at the forefront of preventative medicine. Families rely on pediatricians for trustworthy and accurate anticipatory guidance, a need that is only heightened during times of local and national stress. The social isolation, fear, and lack of resources accompanying this pandemic have serious consequences for our families. What can you and your practice do to keep children safe in the time of COVID-19?
Dr. Angelica DesPain is a pediatric emergency medicine fellow at Children’s National Hospital in Washington. Dr. Rachel Hatcliffe is an attending physician at the hospital. Neither physician had any relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. DesPain and/or Dr. Hatcliffe at [email protected].
References
1. Child Dev. 1978;49:604-16.
2. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2011 Aug;8(2):171-6.
3. BMJ 2013;347:f5239.
COVID-19: Managing resource crunch and ethical challenges
COVID-19 has been a watershed event in medical history of epic proportions. With this fast-spreading pandemic stretching resources at health care institutions, practical considerations for management of a disease about which we are still learning has been a huge challenge.
Although many guidelines have been made available by medical societies and experts worldwide, there appear to be very few which throw light on management in a resource-poor setup. The hospitalist, as a front-line provider, is likely expected to lead the planning and management of resources in order to deliver appropriate care.
As per American Hospital Association data, there are 2,704 community hospitals that can deliver ICU care in the United States. There are 534,964 acute care beds with 96,596 ICU beds. Additionally, there are 25,157 step-down beds and 1,183 burn unit beds. Of the 2,704 hospitals, 74% are in metropolitan areas (> 50,000 population), 17% (464) are in micropolitan areas (10,000-49,999 population), and the remaining 9% (244) are in rural areas. Only 7% (36,453) of hospital beds and 5% (4715) of ICU beds are in micropolitan areas. Two percent of acute care hospital beds and 1% of ICU beds are in rural areas. Although the US has the highest per capita number of ICU beds in the world, this may not be sufficient as these are concentrated in highly populated metropolitan areas.
Infrastructure and human power resource augmentation will be important. Infrastructure can be ramped up by:
- Canceling elective procedures
- Using the operating room and perioperative room ventilators and beds
- Servicing and using older functioning hospitals, medical wards, and ventilators.
As ventilators are expected to be in short supply, while far from ideal, other resources may include using ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile, renting from vendors, and using state-owned stockpiles. Use of non-invasive ventilators, such as CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure), BiPAP (bi-level positive airway pressure), and HFNC (high-flow nasal cannula) may be considered in addition to full-featured ventilators. Rapidly manufacturing new ventilators with government direction is also being undertaken.
Although estimates vary based on the model used, about 1 million people are expected to need ventilatory support. However, in addition to infrastructural shortcomings, trained persons to care for these patients are lacking. Approximately 48% of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, and there are only 28,808 intensivists as per 2015 AHA data. In order to increase the amount of skilled manpower needed to staff ICUs, a model from the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Fundamental Disaster Management Program can be adopted. This involves an intensivist overseeing four different teams, with each team caring for 24 patients. Each team is led by a non-ICU physician or an ICU advanced practice provider (APP) who in turn cares for the patient with respiratory therapists, pharmacists, ICU nurses, and other non-ICU health professionals.
It is essential that infrastructure and human power be augmented and optimized, as well as contingency plans, including triage based on ethical and legal considerations, put in place if demand overwhelms capacity.
Lack of PPE and fear among health care staff
There have been widespread reports in the media, and several anecdotal reports, about severe shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE), and as a result, an increase in fear and anxiety among frontline health care workers.
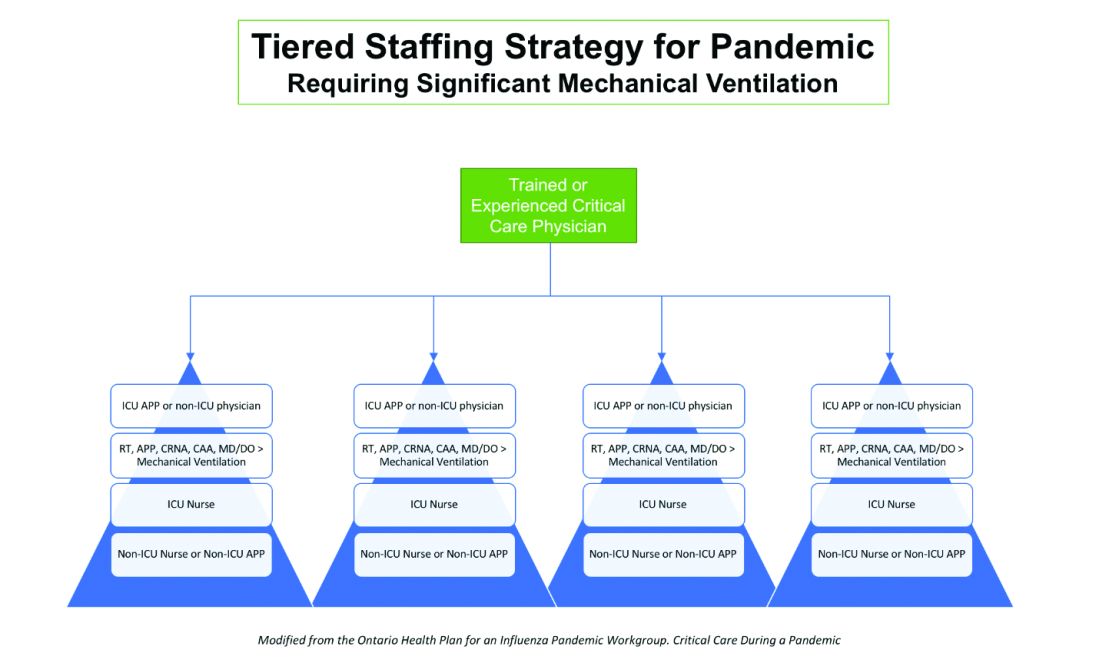
In addition, there also have been reports about hospital administrators disciplining medical and nursing staff for voicing their concerns about PPE shortages to the general public and the media. This likely stems from the narrow “optics” and public relations concerns of health care facilities.
It is evident that the size and magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic was grossly underestimated, and preparations were inadequate. But according to past surveys of health care workers, a good number of them believe that medical and nursing staff have a duty to deliver care to sick people even if it exposes them to personal danger.
Given the special skills and privileges that health care professionals possess, they do have a moral and ethical responsibility to take care of sick patients even if a danger to themselves exists. However, society also has a responsibility to provide for the safety of these health care workers by supplying them with appropriate safety gear. Given the unprecedented nature of this pandemic, it is obvious that federal and state governments, public health officials, and hospital administrators (along with health care professionals) are still learning how to appropriately respond to the challenge.
It would be reasonable and appropriate for everyone concerned to understand and acknowledge that there is a shortage of PPE, and while arranging for this to be replenished, undertake and implement measures that maximize the safety of all health care workers. An open forum, mutually agreed-upon policy and procedures, along with mechanisms to address concerns should be formulated.
In addition, health care workers who test positive for COVID-19 can be a source of infection for other health care workers and non-infected patients. Therefore, health care workers have the responsibility of reporting their symptoms, the right to have themselves tested, and they must follow agreed-upon procedures that would limit their ability to infect other people, including mandated absenteeism from work. Every individual has a right to safety at the workplace and this right cannot be compromised, as otherwise this will lead to a suboptimal response to the pandemic. The government, hospital administrators, and health care workers will need to come together and work cohesively.
Ethical issues surrounding resource allocation
At the time of hospital admission, any suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patient should have his or her wishes recorded with the admitting team regarding the goals of care and code status. During any critical illness, goals evolve depending on discussions, reflections of the patient with family, and clinical response to therapy. A patient who does not want any kind of life support obviously should not be offered an ICU level of care.
On the other hand, in the event of resources becoming overwhelmed by demand as can be expected during this pandemic, careful ethical considerations will need to be applied.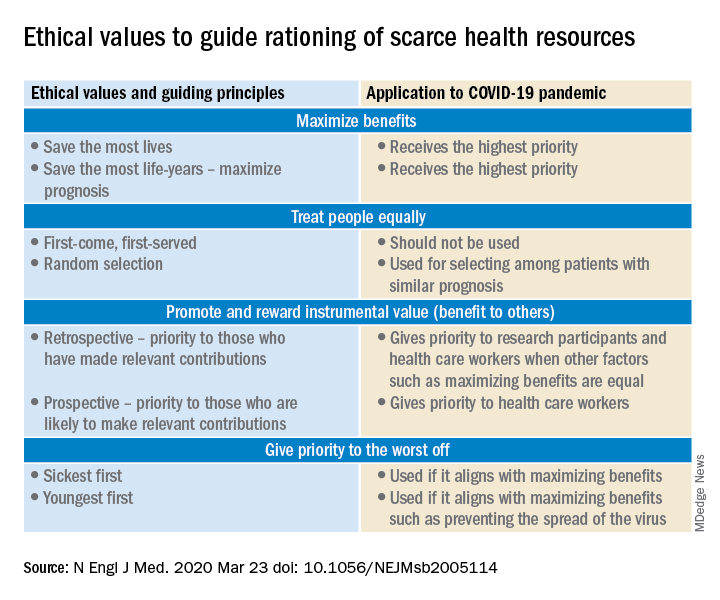
A carefully crafted transparent ethical framework, with a clear understanding of the decision-making process, that involves all stakeholders – including government entities, public health officials, health care workers, ethics specialists, and members of the community – is essential. Ideally, allocation of resources should be made according to a well-written plan, by a triage team that can include a nontreating physician, bioethicists, legal personnel, and religious representatives. It should not be left to the front-line treating physician, who is unlikely to be trained to make these decisions and who has an ethical responsibility to advocate for the patient under his care.
Ethical principles that deserve consideration
The “principle of utility” provides the maximum possible benefit to the maximum number of people. It should not only save the greatest number of lives but also maximize improvements in individuals’ posttreatment length of life.
The “principle of equity” requires that resources are allocated on a nondiscriminatory basis with a fair distribution of benefits and burdens. When conflicts arise between these two principles, a balanced approach likely will help when handled with a transparent decision-making process, with decisions to be applied consistently. Most experts would agree on not only saving more lives but also in preserving more years of life.
The distribution of medical resources should not be based on age or disability. Frailty and functional status are important considerations; however, priority is to be given to sicker patients who have lesser comorbidities and are also likely to survive longer. This could entail that younger, healthier patients will access scarce resources based on the principle of maximizing benefits.
Another consideration is “preservation of functioning of the society.” Those individuals who are important for providing important public services, health care services, and the functioning of other key aspects of society can be considered for prioritization of resources. While this may not satisfy the classic utilitarian principle of doing maximum good to the maximum number of people, it will help to continue augmenting the fight against the pandemic because of the critical role that such individuals play.
For patients with a similar prognosis, the principle of equality comes into play, and distribution should be done by way of random allocation, like a lottery. Distribution based on the principle of “first come, first served” is unlikely to be a fair process, as it would likely discriminate against patients based on their ability to access care.
Care should also be taken not to discriminate among people who have COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 health conditions that require medical care. Distribution should never be done based on an individual’s political influence, celebrity, or financial status, as occurred in the early days of the pandemic regarding access to testing.
Resuscitation or not?
Should a COVID-19 positive patient be offered CPR in case of cardiac arrest? The concern is that CPR is a high-level aerosolizing procedure and PPE is in short supply with the worsening of the pandemic. This will depend more on local policies and resource availability, along with goals of care that have to be determined at the time of admission and subsequent conversations.
The American Hospital Association has issued a general guideline and as more data become available, we can have more informed discussions with patients and families. At this point, all due precautions that prevent the infection of health care personnel are applicable.
Ethical considerations often do not have answers that are a universal fit, and the challenge is always to promote the best interest of the patient with a balance of judiciously utilizing scarce community resources.
Although many states have had discussions and some even have written policies, they have never been implemented. The organization and application of a judicious ethical “crisis level of care” is extremely challenging and likely to test the foundation and fabric of the society.
Dr. Jain is senior associate consultant, hospital & critical care medicine, at Mayo Clinic in Mankato, Minn. He is a board-certified internal medicine, pulmonary, and critical care physician, and has special interests in rural medicine and ethical issues involving critical care medicine. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of keystone infectious diseases/HIV in Chambersburg and is currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro Hospitals, all in Pennsylvania. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
1. United States Resource Availability for COVID-19. SCCM Blog.
2. Intensive care medicine: Triage in case of bottlenecks. l
3. Interim Guidance for Healthcare Providers during COVID-19 Outbreak.
4. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020 Mar 23.doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
5. Devnani M et al. Planning and response to the influenza A (H1N1) pandemic: Ethics, equity and justice. Indian J Med Ethics. 2011 Oct-Dec;8(4):237-40.
6. Alexander C and Wynia M. Ready and willing? Physicians’ sense of preparedness for bioterrorism. Health Aff (Millwood). 2003 Sep-Oct;22(5):189-97.
7. Damery S et al. Healthcare workers’ perceptions of the duty to work during an influenza pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2010 Jan;36(1):12-8.
COVID-19 has been a watershed event in medical history of epic proportions. With this fast-spreading pandemic stretching resources at health care institutions, practical considerations for management of a disease about which we are still learning has been a huge challenge.
Although many guidelines have been made available by medical societies and experts worldwide, there appear to be very few which throw light on management in a resource-poor setup. The hospitalist, as a front-line provider, is likely expected to lead the planning and management of resources in order to deliver appropriate care.
As per American Hospital Association data, there are 2,704 community hospitals that can deliver ICU care in the United States. There are 534,964 acute care beds with 96,596 ICU beds. Additionally, there are 25,157 step-down beds and 1,183 burn unit beds. Of the 2,704 hospitals, 74% are in metropolitan areas (> 50,000 population), 17% (464) are in micropolitan areas (10,000-49,999 population), and the remaining 9% (244) are in rural areas. Only 7% (36,453) of hospital beds and 5% (4715) of ICU beds are in micropolitan areas. Two percent of acute care hospital beds and 1% of ICU beds are in rural areas. Although the US has the highest per capita number of ICU beds in the world, this may not be sufficient as these are concentrated in highly populated metropolitan areas.
Infrastructure and human power resource augmentation will be important. Infrastructure can be ramped up by:
- Canceling elective procedures
- Using the operating room and perioperative room ventilators and beds
- Servicing and using older functioning hospitals, medical wards, and ventilators.
As ventilators are expected to be in short supply, while far from ideal, other resources may include using ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile, renting from vendors, and using state-owned stockpiles. Use of non-invasive ventilators, such as CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure), BiPAP (bi-level positive airway pressure), and HFNC (high-flow nasal cannula) may be considered in addition to full-featured ventilators. Rapidly manufacturing new ventilators with government direction is also being undertaken.
Although estimates vary based on the model used, about 1 million people are expected to need ventilatory support. However, in addition to infrastructural shortcomings, trained persons to care for these patients are lacking. Approximately 48% of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, and there are only 28,808 intensivists as per 2015 AHA data. In order to increase the amount of skilled manpower needed to staff ICUs, a model from the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Fundamental Disaster Management Program can be adopted. This involves an intensivist overseeing four different teams, with each team caring for 24 patients. Each team is led by a non-ICU physician or an ICU advanced practice provider (APP) who in turn cares for the patient with respiratory therapists, pharmacists, ICU nurses, and other non-ICU health professionals.
It is essential that infrastructure and human power be augmented and optimized, as well as contingency plans, including triage based on ethical and legal considerations, put in place if demand overwhelms capacity.
Lack of PPE and fear among health care staff
There have been widespread reports in the media, and several anecdotal reports, about severe shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE), and as a result, an increase in fear and anxiety among frontline health care workers.

In addition, there also have been reports about hospital administrators disciplining medical and nursing staff for voicing their concerns about PPE shortages to the general public and the media. This likely stems from the narrow “optics” and public relations concerns of health care facilities.
It is evident that the size and magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic was grossly underestimated, and preparations were inadequate. But according to past surveys of health care workers, a good number of them believe that medical and nursing staff have a duty to deliver care to sick people even if it exposes them to personal danger.
Given the special skills and privileges that health care professionals possess, they do have a moral and ethical responsibility to take care of sick patients even if a danger to themselves exists. However, society also has a responsibility to provide for the safety of these health care workers by supplying them with appropriate safety gear. Given the unprecedented nature of this pandemic, it is obvious that federal and state governments, public health officials, and hospital administrators (along with health care professionals) are still learning how to appropriately respond to the challenge.
It would be reasonable and appropriate for everyone concerned to understand and acknowledge that there is a shortage of PPE, and while arranging for this to be replenished, undertake and implement measures that maximize the safety of all health care workers. An open forum, mutually agreed-upon policy and procedures, along with mechanisms to address concerns should be formulated.
In addition, health care workers who test positive for COVID-19 can be a source of infection for other health care workers and non-infected patients. Therefore, health care workers have the responsibility of reporting their symptoms, the right to have themselves tested, and they must follow agreed-upon procedures that would limit their ability to infect other people, including mandated absenteeism from work. Every individual has a right to safety at the workplace and this right cannot be compromised, as otherwise this will lead to a suboptimal response to the pandemic. The government, hospital administrators, and health care workers will need to come together and work cohesively.
Ethical issues surrounding resource allocation
At the time of hospital admission, any suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patient should have his or her wishes recorded with the admitting team regarding the goals of care and code status. During any critical illness, goals evolve depending on discussions, reflections of the patient with family, and clinical response to therapy. A patient who does not want any kind of life support obviously should not be offered an ICU level of care.
On the other hand, in the event of resources becoming overwhelmed by demand as can be expected during this pandemic, careful ethical considerations will need to be applied.
A carefully crafted transparent ethical framework, with a clear understanding of the decision-making process, that involves all stakeholders – including government entities, public health officials, health care workers, ethics specialists, and members of the community – is essential. Ideally, allocation of resources should be made according to a well-written plan, by a triage team that can include a nontreating physician, bioethicists, legal personnel, and religious representatives. It should not be left to the front-line treating physician, who is unlikely to be trained to make these decisions and who has an ethical responsibility to advocate for the patient under his care.
Ethical principles that deserve consideration
The “principle of utility” provides the maximum possible benefit to the maximum number of people. It should not only save the greatest number of lives but also maximize improvements in individuals’ posttreatment length of life.
The “principle of equity” requires that resources are allocated on a nondiscriminatory basis with a fair distribution of benefits and burdens. When conflicts arise between these two principles, a balanced approach likely will help when handled with a transparent decision-making process, with decisions to be applied consistently. Most experts would agree on not only saving more lives but also in preserving more years of life.
The distribution of medical resources should not be based on age or disability. Frailty and functional status are important considerations; however, priority is to be given to sicker patients who have lesser comorbidities and are also likely to survive longer. This could entail that younger, healthier patients will access scarce resources based on the principle of maximizing benefits.
Another consideration is “preservation of functioning of the society.” Those individuals who are important for providing important public services, health care services, and the functioning of other key aspects of society can be considered for prioritization of resources. While this may not satisfy the classic utilitarian principle of doing maximum good to the maximum number of people, it will help to continue augmenting the fight against the pandemic because of the critical role that such individuals play.
For patients with a similar prognosis, the principle of equality comes into play, and distribution should be done by way of random allocation, like a lottery. Distribution based on the principle of “first come, first served” is unlikely to be a fair process, as it would likely discriminate against patients based on their ability to access care.
Care should also be taken not to discriminate among people who have COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 health conditions that require medical care. Distribution should never be done based on an individual’s political influence, celebrity, or financial status, as occurred in the early days of the pandemic regarding access to testing.
Resuscitation or not?
Should a COVID-19 positive patient be offered CPR in case of cardiac arrest? The concern is that CPR is a high-level aerosolizing procedure and PPE is in short supply with the worsening of the pandemic. This will depend more on local policies and resource availability, along with goals of care that have to be determined at the time of admission and subsequent conversations.
The American Hospital Association has issued a general guideline and as more data become available, we can have more informed discussions with patients and families. At this point, all due precautions that prevent the infection of health care personnel are applicable.
Ethical considerations often do not have answers that are a universal fit, and the challenge is always to promote the best interest of the patient with a balance of judiciously utilizing scarce community resources.
Although many states have had discussions and some even have written policies, they have never been implemented. The organization and application of a judicious ethical “crisis level of care” is extremely challenging and likely to test the foundation and fabric of the society.
Dr. Jain is senior associate consultant, hospital & critical care medicine, at Mayo Clinic in Mankato, Minn. He is a board-certified internal medicine, pulmonary, and critical care physician, and has special interests in rural medicine and ethical issues involving critical care medicine. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of keystone infectious diseases/HIV in Chambersburg and is currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro Hospitals, all in Pennsylvania. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
1. United States Resource Availability for COVID-19. SCCM Blog.
2. Intensive care medicine: Triage in case of bottlenecks. l
3. Interim Guidance for Healthcare Providers during COVID-19 Outbreak.
4. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020 Mar 23.doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
5. Devnani M et al. Planning and response to the influenza A (H1N1) pandemic: Ethics, equity and justice. Indian J Med Ethics. 2011 Oct-Dec;8(4):237-40.
6. Alexander C and Wynia M. Ready and willing? Physicians’ sense of preparedness for bioterrorism. Health Aff (Millwood). 2003 Sep-Oct;22(5):189-97.
7. Damery S et al. Healthcare workers’ perceptions of the duty to work during an influenza pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2010 Jan;36(1):12-8.
COVID-19 has been a watershed event in medical history of epic proportions. With this fast-spreading pandemic stretching resources at health care institutions, practical considerations for management of a disease about which we are still learning has been a huge challenge.
Although many guidelines have been made available by medical societies and experts worldwide, there appear to be very few which throw light on management in a resource-poor setup. The hospitalist, as a front-line provider, is likely expected to lead the planning and management of resources in order to deliver appropriate care.
As per American Hospital Association data, there are 2,704 community hospitals that can deliver ICU care in the United States. There are 534,964 acute care beds with 96,596 ICU beds. Additionally, there are 25,157 step-down beds and 1,183 burn unit beds. Of the 2,704 hospitals, 74% are in metropolitan areas (> 50,000 population), 17% (464) are in micropolitan areas (10,000-49,999 population), and the remaining 9% (244) are in rural areas. Only 7% (36,453) of hospital beds and 5% (4715) of ICU beds are in micropolitan areas. Two percent of acute care hospital beds and 1% of ICU beds are in rural areas. Although the US has the highest per capita number of ICU beds in the world, this may not be sufficient as these are concentrated in highly populated metropolitan areas.
Infrastructure and human power resource augmentation will be important. Infrastructure can be ramped up by:
- Canceling elective procedures
- Using the operating room and perioperative room ventilators and beds
- Servicing and using older functioning hospitals, medical wards, and ventilators.
As ventilators are expected to be in short supply, while far from ideal, other resources may include using ventilators from the Strategic National Stockpile, renting from vendors, and using state-owned stockpiles. Use of non-invasive ventilators, such as CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure), BiPAP (bi-level positive airway pressure), and HFNC (high-flow nasal cannula) may be considered in addition to full-featured ventilators. Rapidly manufacturing new ventilators with government direction is also being undertaken.
Although estimates vary based on the model used, about 1 million people are expected to need ventilatory support. However, in addition to infrastructural shortcomings, trained persons to care for these patients are lacking. Approximately 48% of acute care hospitals have no intensivists, and there are only 28,808 intensivists as per 2015 AHA data. In order to increase the amount of skilled manpower needed to staff ICUs, a model from the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Fundamental Disaster Management Program can be adopted. This involves an intensivist overseeing four different teams, with each team caring for 24 patients. Each team is led by a non-ICU physician or an ICU advanced practice provider (APP) who in turn cares for the patient with respiratory therapists, pharmacists, ICU nurses, and other non-ICU health professionals.
It is essential that infrastructure and human power be augmented and optimized, as well as contingency plans, including triage based on ethical and legal considerations, put in place if demand overwhelms capacity.
Lack of PPE and fear among health care staff
There have been widespread reports in the media, and several anecdotal reports, about severe shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE), and as a result, an increase in fear and anxiety among frontline health care workers.

In addition, there also have been reports about hospital administrators disciplining medical and nursing staff for voicing their concerns about PPE shortages to the general public and the media. This likely stems from the narrow “optics” and public relations concerns of health care facilities.
It is evident that the size and magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic was grossly underestimated, and preparations were inadequate. But according to past surveys of health care workers, a good number of them believe that medical and nursing staff have a duty to deliver care to sick people even if it exposes them to personal danger.
Given the special skills and privileges that health care professionals possess, they do have a moral and ethical responsibility to take care of sick patients even if a danger to themselves exists. However, society also has a responsibility to provide for the safety of these health care workers by supplying them with appropriate safety gear. Given the unprecedented nature of this pandemic, it is obvious that federal and state governments, public health officials, and hospital administrators (along with health care professionals) are still learning how to appropriately respond to the challenge.
It would be reasonable and appropriate for everyone concerned to understand and acknowledge that there is a shortage of PPE, and while arranging for this to be replenished, undertake and implement measures that maximize the safety of all health care workers. An open forum, mutually agreed-upon policy and procedures, along with mechanisms to address concerns should be formulated.
In addition, health care workers who test positive for COVID-19 can be a source of infection for other health care workers and non-infected patients. Therefore, health care workers have the responsibility of reporting their symptoms, the right to have themselves tested, and they must follow agreed-upon procedures that would limit their ability to infect other people, including mandated absenteeism from work. Every individual has a right to safety at the workplace and this right cannot be compromised, as otherwise this will lead to a suboptimal response to the pandemic. The government, hospital administrators, and health care workers will need to come together and work cohesively.
Ethical issues surrounding resource allocation
At the time of hospital admission, any suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patient should have his or her wishes recorded with the admitting team regarding the goals of care and code status. During any critical illness, goals evolve depending on discussions, reflections of the patient with family, and clinical response to therapy. A patient who does not want any kind of life support obviously should not be offered an ICU level of care.
On the other hand, in the event of resources becoming overwhelmed by demand as can be expected during this pandemic, careful ethical considerations will need to be applied.
A carefully crafted transparent ethical framework, with a clear understanding of the decision-making process, that involves all stakeholders – including government entities, public health officials, health care workers, ethics specialists, and members of the community – is essential. Ideally, allocation of resources should be made according to a well-written plan, by a triage team that can include a nontreating physician, bioethicists, legal personnel, and religious representatives. It should not be left to the front-line treating physician, who is unlikely to be trained to make these decisions and who has an ethical responsibility to advocate for the patient under his care.
Ethical principles that deserve consideration
The “principle of utility” provides the maximum possible benefit to the maximum number of people. It should not only save the greatest number of lives but also maximize improvements in individuals’ posttreatment length of life.
The “principle of equity” requires that resources are allocated on a nondiscriminatory basis with a fair distribution of benefits and burdens. When conflicts arise between these two principles, a balanced approach likely will help when handled with a transparent decision-making process, with decisions to be applied consistently. Most experts would agree on not only saving more lives but also in preserving more years of life.
The distribution of medical resources should not be based on age or disability. Frailty and functional status are important considerations; however, priority is to be given to sicker patients who have lesser comorbidities and are also likely to survive longer. This could entail that younger, healthier patients will access scarce resources based on the principle of maximizing benefits.
Another consideration is “preservation of functioning of the society.” Those individuals who are important for providing important public services, health care services, and the functioning of other key aspects of society can be considered for prioritization of resources. While this may not satisfy the classic utilitarian principle of doing maximum good to the maximum number of people, it will help to continue augmenting the fight against the pandemic because of the critical role that such individuals play.
For patients with a similar prognosis, the principle of equality comes into play, and distribution should be done by way of random allocation, like a lottery. Distribution based on the principle of “first come, first served” is unlikely to be a fair process, as it would likely discriminate against patients based on their ability to access care.
Care should also be taken not to discriminate among people who have COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 health conditions that require medical care. Distribution should never be done based on an individual’s political influence, celebrity, or financial status, as occurred in the early days of the pandemic regarding access to testing.
Resuscitation or not?
Should a COVID-19 positive patient be offered CPR in case of cardiac arrest? The concern is that CPR is a high-level aerosolizing procedure and PPE is in short supply with the worsening of the pandemic. This will depend more on local policies and resource availability, along with goals of care that have to be determined at the time of admission and subsequent conversations.
The American Hospital Association has issued a general guideline and as more data become available, we can have more informed discussions with patients and families. At this point, all due precautions that prevent the infection of health care personnel are applicable.
Ethical considerations often do not have answers that are a universal fit, and the challenge is always to promote the best interest of the patient with a balance of judiciously utilizing scarce community resources.
Although many states have had discussions and some even have written policies, they have never been implemented. The organization and application of a judicious ethical “crisis level of care” is extremely challenging and likely to test the foundation and fabric of the society.
Dr. Jain is senior associate consultant, hospital & critical care medicine, at Mayo Clinic in Mankato, Minn. He is a board-certified internal medicine, pulmonary, and critical care physician, and has special interests in rural medicine and ethical issues involving critical care medicine. Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of keystone infectious diseases/HIV in Chambersburg and is currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro Hospitals, all in Pennsylvania. Dr. Palabindala is hospital medicine division chief at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, and a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Sources
1. United States Resource Availability for COVID-19. SCCM Blog.
2. Intensive care medicine: Triage in case of bottlenecks. l
3. Interim Guidance for Healthcare Providers during COVID-19 Outbreak.
4. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020 Mar 23.doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
5. Devnani M et al. Planning and response to the influenza A (H1N1) pandemic: Ethics, equity and justice. Indian J Med Ethics. 2011 Oct-Dec;8(4):237-40.
6. Alexander C and Wynia M. Ready and willing? Physicians’ sense of preparedness for bioterrorism. Health Aff (Millwood). 2003 Sep-Oct;22(5):189-97.
7. Damery S et al. Healthcare workers’ perceptions of the duty to work during an influenza pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2010 Jan;36(1):12-8.
COVID 19: Confessions of an outpatient psychiatrist during the pandemic
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
It seems that some glitches would be inevitable. With a sudden shift to videoconferencing in private psychiatric practices, there were bound to be issues with both technology and privacy. One friend told me of such a glitch on the very first day she started telemental health: She was meeting with a patient who was sitting at her kitchen table. Unbeknownst to the patient, her husband walked into the kitchen behind her, fully naked, to get something from the refrigerator. “There was a full moon shot!” my friend said, initially quite shocked, and then eventually amused. As we all cope with a national tragedy and the total upheaval to our personal and professional lives, the stories just keep coming.
I left work on Friday, March 13, with plans to return on the following Monday to see patients. I had no idea that, by Sunday evening, I would be persuaded that for the safety of all I would need to shut down my real-life psychiatric practice and switch to a videoconferencing venue. I, along with many psychiatrists in Maryland, made this decision after Amy Huberman, MD, posted the following on the Maryland Psychiatric Society (MPS) listserv on Sunday, March 15:
“I want to make a case for starting video sessions with all your patients NOW. There is increasing evidence that the spread of coronavirus is driven primarily by asymptomatic or mildly ill people infected with the virus. Because of this, it’s not good enough to tell your patients not to come in if they have symptoms, or for you not to come into work if you have no symptoms. Even after I sent out a letter two weeks ago warning people not to come in if they had symptoms or had potentially come in contact with someone with COVID-19, several patients with coughs still came to my office, as well as several people who had just been on trips to New York City.
If we want to help slow the spread of this illness so that our health system has a better chance of being able to offer ventilators to the people who need them, we must limit all contacts as much as possible – even of asymptomatic people, given the emerging data.
I am planning to send out a message to all my patients today that they should do the same. Without the president or the media giving clear advice to people about what to do, it’s our job as physicians to do it.”
By that night, I had set up a home office with a blank wall behind me, windows in front of me, and books propping my computer at a height that would not have my patients looking up my nose. For the first time in over 20 years, I dusted my son’s Little League trophies, moved them and a 40,000 baseball card collection against the wall, carried a desk, chair, rug, houseplant, and a small Buddha into a room in which I would have some privacy, and my telepsychiatry practice found a home.
After some research, I registered for a free site called Doxy.me because it was HIPAA compliant and did not require patients to download an application; anyone with a camera on any Internet-enabled phone, computer, or tablet, could click on a link and enter my virtual waiting room. I soon discovered that images on the Doxy.me site are sometimes grainy and sometimes freeze up; in some sessions, we ended up switching to FaceTime, and as government mandates for HIPAA compliance relaxed, I offered to meet on any site that my patients might be comfortable with: if not Doxy.me (which remains my starting place for most sessions), Facetime, Skype, Zoom, or Whatsapp. I have not offered Bluejeans, Google Hangouts, or WebEx, and no one has requested those applications. I keep the phone next to the computer, and some sessions include a few minutes of tech support as I help patients (or they help me) navigate the various sites. In a few sessions, we could not get the audio to work and we used video on one venue while we talked on the phone. I haven’t figured out if the variations in the quality of the connection has to do with my Comcast connection, the fact that these websites are overloaded with users, or that my household now consists of three people, two large monitors, three laptops, two tablets, three cell phone lines (not to mention one dog and a transplanted cat), all going at the same time. The pets do not require any bandwidth, but all the people are talking to screens throughout the workday.
As my colleagues embarked on the same journey, the listserv questions and comments came quickly. What were the best platforms? Was it a good thing or a bad thing to suddenly be in people’s homes? Some felt the extraneous background to be helpful, others found it distracting and intrusive.
How do these sessions get coded for the purpose of billing? There was a tremendous amount of confusion over that, with the initial verdict being that Medicare wanted the place of service changed to “02” and that private insurers want one of two modifiers, and it was anyone’s guess which company wanted which modifier. Then there was the concern that Medicare was paying 25% less, until the MPS staff clarified that full fees would be paid, but the place of service should be filled in as “11” – not “02” – as with regular office visits, and the modifier “95” should be added on the Health Care Finance Administration claim form. We were left to wait and see what gets reimbursed and for what fees.
Could new patients be seen by videoconferencing? Could patients from other states be seen this way if the psychiatrist was not licensed in the state where the patient was calling from? One psychiatrist reported he had a patient in an adjacent state drive over the border into Maryland, but the patient brought her mother and the evaluation included unwanted input from the mom as the session consisted of the patient and her mother yelling at both each other in the car and at the psychiatrist on the screen!
Psychiatrists on the listserv began to comment that treatment sessions were intense and exhausting. I feel the literal face-to-face contact of another person’s head just inches from my own, with full eye contact, often gets to be a lot. No one asks why I’ve moved a trinket (ah, there are no trinkets) or gazes off around the room. I sometimes sit for long periods of time as I don’t even stand to see the patients to the door. Other patients move about or bounce their devices on their laps, and my stomach starts to feel queasy until I ask to have the device adjusted. In some sessions, I find I’m talking to partial heads, or that computer icons cover the patient’s mouth.
Being in people’s lives via screen has been interesting. Unlike my colleague, I have not had any streaking spouses, but I’ve greeted a few family members – often those serving as technical support – and I’ve toured part of a farm, met dogs, guinea pigs, and even a goat. I’ve made brief daily “visits” to a frightened patient in isolation on a COVID hospital unit and had the joy of celebrating the discharge to home. It’s odd to be in a bedroom with a patient, even virtually, and it is interesting to note where they choose to hold their sessions; I’ve had several patients hold sessions from their cars. Seeing my own image in the corner of the screen is also a bit distracting, and in one session, as I saw my own reaction, my patient said, “I knew you were going to make that face!”
The pandemic has usurped most of the activities of all of our lives, and without social interactions, travel, and work in the usual way, life does not hold its usual richness. In a few cases, I have ended the session after half the time as the patient insisted there was nothing to talk about. Many talk about the medical problems they can’t be seen for, what they are doing to keep safe (or not), how they are washing down their groceries, and who they are meeting with by Zoom. Of those who were terribly anxious before, some feel oddly calmer – the world has ramped up to meet their level of anxiety and they feel vindicated. No one thinks they are odd for worrying about germs on door knobs or elevator buttons. What were once neurotic fears are now our real-life reality. Others have been triggered by a paralyzing fear, often with panic attacks, and these sessions are certainly challenging as I figure out which medications will best help, while responding to requests for reassurance. And there is the troublesome aspect of trying to care for others who are fearful while living with the reality that these fears are not extraneous to our own lives: We, too, are scared for ourselves and our families.
For some people, stay-at-home mandates have been easier than for others. People who are naturally introverted, or those with social anxiety, have told me they find this time at home to be a relief. They no longer feel pressured to go out; there is permission to be alone, to read, or watch Netflix. No one is pressuring them to go to parties or look for a Tinder date. For others, the isolation and loneliness have been devastating, causing a range of emotions from being “stir crazy,” to triggering episodes of major depression and severe anxiety.
Health care workers in therapy talk about their fears of being contaminated with coronavirus, about the exposures they’ve had, their fears of bringing the virus home to family, and about the anger – sometimes rage – that their employers are not doing more to protect them.
Few people these past weeks are looking for insight into their patterns of behavior and emotion. Most of life has come to be about survival and not about personal striving. Students who are driven to excel are disappointed to have their scholastic worlds have switched to pass/fail. And for those struggling with milder forms of depression and anxiety, both the patients and I have all been a bit perplexed by losing the usual measures of what feelings are normal in a tragic world and we no longer use socializing as the hallmark that heralds a return to normalcy after a period of withdrawal.
In some aspects, it is not all been bad. I’ve enjoyed watching my neighbors walk by with their dogs through the window behind my computer screen and I’ve felt part of the daily evolution as the cherry tree outside that same window turns from dead brown wood to vibrant pink blossoms. I like the flexibility of my schedule and the sensation I always carry of being rushed has quelled. I take more walks and spend more time with the family members who are held captive with me. The dog, who no longer is left alone for hours each day, is certainly a winner.
Some of my colleagues tell me they are overwhelmed – patients they have not seen for years have returned, people are asking for more frequent sessions, and they are suddenly trying to work at home while homeschooling children. I have had only a few of those requests for crisis care, while new referrals are much quieter than normal. Some of my patients have even said that they simply aren’t comfortable meeting this way and they will see me at the other end of the pandemic. A few people I would have expected to hear from I have not, and I fear that those who have lost their jobs may avoiding the cost of treatment – this group I will reach out to in the coming weeks. A little extra time, however, has given me the opportunity to join the Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health team. And my first attempt at teaching a resident seminar by Zoom has gone well.
For some in the medical field, this has been a horrible and traumatic time; they are worked to exhaustion, and surrounded by distress, death, and personal fear with every shift. For others, life has come to a standstill as the elective procedures that fill their days have virtually stopped. For outpatient psychiatry, it’s been a bit of an in-between, we may feel an odd mix of relevant and useless all at the same time, as our services are appreciated by our patients, but as actual soldiers caring for the ill COVID patients, we are leaving that to our colleagues in the EDs, COVID units, and ICUs. As a physician who has not treated a patient in an ICU for decades, I wish I had something more concrete to contribute to the effort, and at the same time, I’m relieved that I don’t.
And what about the patients? How are they doing with remote psychiatry? Some are clearly flustered or frustrated by the technology issues. Other times sessions go smoothly, and the fact that we are talking through screens gets forgotten. Some like the convenience of not having to drive a far distance and no one misses my crowded parking lot.
Kristen, another doctor’s patient in Illinois, commented: “I appreciate the continuity in care, especially if the alternative is delaying appointments. I think that’s most important. The interaction helps manage added anxiety from isolating as well. I don’t think it diminishes the care I receive; it makes me feel that my doctor is still accessible. One other point, since I have had both telemedicine and in-person appointments with my current psychiatrist, is that during in-person meetings, he is usually on his computer and rarely looks at me or makes eye contact. In virtual meetings, I feel he is much more engaged with me.”
In normal times, I spend a good deal of time encouraging patients to work on building their relationships and community – these connections lead people to healthy and fulfilling lives – and now we talk about how to best be socially distant. We see each other as vectors of disease and to greet a friend with a handshake, much less a hug, would be unthinkable. Will our collective psyches ever recover? For those of us who will survive, that remains to be seen. In the meantime, perhaps we are all being forced to be more flexible and innovative.
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore.
Presymptomatic or asymptomatic? ID experts on shifting terminology
They also addressed racial disparities surrounding COVID-19, and announced new IDSA guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of the illness.
Regarding the shifting thinking on symptoms and transmission of the novel coronavirus, when it comes to presymptomatic or asymptomatic, “pre” is really the right terminology, Carlos del Rio, MD, professor of medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, said during the briefing, because it’s not that people are asymptomatic but that they develop symptoms later and start transmitting the virus 24 to 48 hours before they develop symptoms.
“Clearly, this plays a role in transmission,” with some studies suggesting that 6% to 12% of transmissions occur during this presymptomatic stage, he explained.
Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted that early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the presymptomatic phase “could have been missed because we didn’t realize the wide ranging symptoms this disease has.”
This is turning out to be a “very interesting” virus with “fascinating” symptoms, she told reporters on the call.
The virus seems to have capacity to affect far more than just the respiratory tract. Initially, however, it was viewed “very much like a classic respiratory viral infection. As a result, a lot of people were refused testing because they were not showing the classic signs” of respiratory infection, Marrazzo noted.
It’s now clear that the range of symptoms is quite different, she said.
Notably, loss of smell seems to be “very characteristic and very specific to this infection. I can’t think of another common viral infection that causes loss of smell before you start to see other things,” Marrazzo said.
Data also suggest that gastrointestinal symptoms are common with COVID-19. Early data suggest that diarrhea probably occurs in about one third of patients. Some people have reported abdominal pain as the first sign, she said.
“Now that we know about the more wide range of symptoms associated [with COVID-19], we are being much more open to considering people perhaps having this infection. There is a lower index of suspicion and much lower threshold for diagnostic testing,” Marrazzo said, adding that there are still many barriers to testing and getting test results.
Stark Racial Disparities Need Greater Understanding
The second major topic of discussion at the briefing was the growing realization of racial disparities in COVID-19.
“Racial disparities in our country are not new but racial disparities in this disease are pretty stark,” del Rio said. “We live in a country where disparities have really colored a lot of what our diseases are, from HIV to diabetes to hypertension, and it’s not surprising that we are seeing this now with COVID-19.”
Marrazzo noted that, in Alabama, around 20% of the population is African American, yet almost 40% of COVID-19 deaths are occurring in this population. “The most stark statistics are coming out of Illinois and Michigan, where less than around 15% of the population is African American and yet 70% of the deaths are occurring in that group,” she said.
Both del Rio and Marrazzo agreed that understanding the racial differences in COVID-19 deaths is going to require a lot of analysis in the coming months.
Part of it likely reflects the challenge of social distancing in urban areas, Marrazzo said. “Social distancing is a luxury afforded by having a really big space, and space is money.”
The other long-standing challenge of unequal access to healthcare also likely plays a role, she said. This includes missing out on preventive health appointments and screenings, which can translate into more comorbidities, particularly hypertension.
The evolving evidence about the virus, and the stark conditions that frontline clinicians face, make this an especially challenging public health crisis, del Rio said.
“Taking care of these patients is incredibly taxing and my hat is off to physicians, residents, nurses, everybody working on this in the hospitals because they are really doing a yeoman’s work,” he said.
“These are not easy patients to take care of. Not only are [the frontline clinicians] providing care, they are caring for the patient and providing a comfort and someone to listen to when family can’t be present,” del Rio emphasized.
New Guidelines
The IDSA just released new guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19.
“We are learning new things every day about this virus. Things are rapidly changing, and as we learn new things we have to adapt and make changes,” del Rio said.
del Rio noted that the guildelines “will evolve and change as more information comes out.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They also addressed racial disparities surrounding COVID-19, and announced new IDSA guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of the illness.
Regarding the shifting thinking on symptoms and transmission of the novel coronavirus, when it comes to presymptomatic or asymptomatic, “pre” is really the right terminology, Carlos del Rio, MD, professor of medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, said during the briefing, because it’s not that people are asymptomatic but that they develop symptoms later and start transmitting the virus 24 to 48 hours before they develop symptoms.
“Clearly, this plays a role in transmission,” with some studies suggesting that 6% to 12% of transmissions occur during this presymptomatic stage, he explained.
Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted that early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the presymptomatic phase “could have been missed because we didn’t realize the wide ranging symptoms this disease has.”
This is turning out to be a “very interesting” virus with “fascinating” symptoms, she told reporters on the call.
The virus seems to have capacity to affect far more than just the respiratory tract. Initially, however, it was viewed “very much like a classic respiratory viral infection. As a result, a lot of people were refused testing because they were not showing the classic signs” of respiratory infection, Marrazzo noted.
It’s now clear that the range of symptoms is quite different, she said.
Notably, loss of smell seems to be “very characteristic and very specific to this infection. I can’t think of another common viral infection that causes loss of smell before you start to see other things,” Marrazzo said.
Data also suggest that gastrointestinal symptoms are common with COVID-19. Early data suggest that diarrhea probably occurs in about one third of patients. Some people have reported abdominal pain as the first sign, she said.
“Now that we know about the more wide range of symptoms associated [with COVID-19], we are being much more open to considering people perhaps having this infection. There is a lower index of suspicion and much lower threshold for diagnostic testing,” Marrazzo said, adding that there are still many barriers to testing and getting test results.
Stark Racial Disparities Need Greater Understanding
The second major topic of discussion at the briefing was the growing realization of racial disparities in COVID-19.
“Racial disparities in our country are not new but racial disparities in this disease are pretty stark,” del Rio said. “We live in a country where disparities have really colored a lot of what our diseases are, from HIV to diabetes to hypertension, and it’s not surprising that we are seeing this now with COVID-19.”
Marrazzo noted that, in Alabama, around 20% of the population is African American, yet almost 40% of COVID-19 deaths are occurring in this population. “The most stark statistics are coming out of Illinois and Michigan, where less than around 15% of the population is African American and yet 70% of the deaths are occurring in that group,” she said.
Both del Rio and Marrazzo agreed that understanding the racial differences in COVID-19 deaths is going to require a lot of analysis in the coming months.
Part of it likely reflects the challenge of social distancing in urban areas, Marrazzo said. “Social distancing is a luxury afforded by having a really big space, and space is money.”
The other long-standing challenge of unequal access to healthcare also likely plays a role, she said. This includes missing out on preventive health appointments and screenings, which can translate into more comorbidities, particularly hypertension.
The evolving evidence about the virus, and the stark conditions that frontline clinicians face, make this an especially challenging public health crisis, del Rio said.
“Taking care of these patients is incredibly taxing and my hat is off to physicians, residents, nurses, everybody working on this in the hospitals because they are really doing a yeoman’s work,” he said.
“These are not easy patients to take care of. Not only are [the frontline clinicians] providing care, they are caring for the patient and providing a comfort and someone to listen to when family can’t be present,” del Rio emphasized.
New Guidelines
The IDSA just released new guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19.
“We are learning new things every day about this virus. Things are rapidly changing, and as we learn new things we have to adapt and make changes,” del Rio said.
del Rio noted that the guildelines “will evolve and change as more information comes out.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They also addressed racial disparities surrounding COVID-19, and announced new IDSA guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of the illness.
Regarding the shifting thinking on symptoms and transmission of the novel coronavirus, when it comes to presymptomatic or asymptomatic, “pre” is really the right terminology, Carlos del Rio, MD, professor of medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, said during the briefing, because it’s not that people are asymptomatic but that they develop symptoms later and start transmitting the virus 24 to 48 hours before they develop symptoms.
“Clearly, this plays a role in transmission,” with some studies suggesting that 6% to 12% of transmissions occur during this presymptomatic stage, he explained.
Jeanne Marrazzo, MD, MPH, director of the Division of Infectious Diseases at University of Alabama at Birmingham, noted that early in the COVID-19 pandemic, the presymptomatic phase “could have been missed because we didn’t realize the wide ranging symptoms this disease has.”
This is turning out to be a “very interesting” virus with “fascinating” symptoms, she told reporters on the call.
The virus seems to have capacity to affect far more than just the respiratory tract. Initially, however, it was viewed “very much like a classic respiratory viral infection. As a result, a lot of people were refused testing because they were not showing the classic signs” of respiratory infection, Marrazzo noted.
It’s now clear that the range of symptoms is quite different, she said.
Notably, loss of smell seems to be “very characteristic and very specific to this infection. I can’t think of another common viral infection that causes loss of smell before you start to see other things,” Marrazzo said.
Data also suggest that gastrointestinal symptoms are common with COVID-19. Early data suggest that diarrhea probably occurs in about one third of patients. Some people have reported abdominal pain as the first sign, she said.
“Now that we know about the more wide range of symptoms associated [with COVID-19], we are being much more open to considering people perhaps having this infection. There is a lower index of suspicion and much lower threshold for diagnostic testing,” Marrazzo said, adding that there are still many barriers to testing and getting test results.
Stark Racial Disparities Need Greater Understanding
The second major topic of discussion at the briefing was the growing realization of racial disparities in COVID-19.
“Racial disparities in our country are not new but racial disparities in this disease are pretty stark,” del Rio said. “We live in a country where disparities have really colored a lot of what our diseases are, from HIV to diabetes to hypertension, and it’s not surprising that we are seeing this now with COVID-19.”
Marrazzo noted that, in Alabama, around 20% of the population is African American, yet almost 40% of COVID-19 deaths are occurring in this population. “The most stark statistics are coming out of Illinois and Michigan, where less than around 15% of the population is African American and yet 70% of the deaths are occurring in that group,” she said.
Both del Rio and Marrazzo agreed that understanding the racial differences in COVID-19 deaths is going to require a lot of analysis in the coming months.
Part of it likely reflects the challenge of social distancing in urban areas, Marrazzo said. “Social distancing is a luxury afforded by having a really big space, and space is money.”
The other long-standing challenge of unequal access to healthcare also likely plays a role, she said. This includes missing out on preventive health appointments and screenings, which can translate into more comorbidities, particularly hypertension.
The evolving evidence about the virus, and the stark conditions that frontline clinicians face, make this an especially challenging public health crisis, del Rio said.
“Taking care of these patients is incredibly taxing and my hat is off to physicians, residents, nurses, everybody working on this in the hospitals because they are really doing a yeoman’s work,” he said.
“These are not easy patients to take care of. Not only are [the frontline clinicians] providing care, they are caring for the patient and providing a comfort and someone to listen to when family can’t be present,” del Rio emphasized.
New Guidelines
The IDSA just released new guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19.
“We are learning new things every day about this virus. Things are rapidly changing, and as we learn new things we have to adapt and make changes,” del Rio said.
del Rio noted that the guildelines “will evolve and change as more information comes out.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NYC hospitals require health care workers to report in person, even for phone and telehealth work
A social worker in New York City was home, caring for his sick son, when the hospital at which he works ordered him to report back to work. His son had COVID-19, yet his hospital told him he had to show up in person.
The social worker’s situation is just one of many NYC Health + Hospitals employees who could work remotely yet are required to report in person. His circumstances were described in a letter sent by Lichten & Bright, a law firm representing the New York City Health Services Employees Union, Local 768.
“Despite the fact that all or virtually all of the work social workers perform can be done remotely, only a handful…are being permitted to work from home,” said the letter, which was written on behalf of about 1000 social workers and 150 medical records specialists and addressed to NYC H+H CEO Mitchell Katz, MD.
Most social workers stopped seeing patients in person in early March. But many still face crowded conditions at several points during their work day. They take public transportation to work, come face-to-face with other health care workers and patients in elevators, and some attend daily meetings with up to 10 employees in conference rooms too small to stay six feet apart, the letter says.
“The social workers are scared to go to work,” said Daniel Bright, the letter’s author. “They’re baffled by the lack of any management response that would allow them to work from home. They are worried about getting exposed to the coronavirus while riding the subway or the bus to work or at work from a doctor or nurse or patient, and getting sick themselves or taking it home to their families.”
There is no good reason that the social workers should be compelled to be physically at work during the COVID-19 pandemic, Bright said. The handful of social workers at NYC H+H’s World Trade Center Environmental Health Center clinic at Bellevue who have been allowed to work from home on an ad hoc basis, he said, have done so successfully.
In response to Bright’s letter, the hospital system issued a statement that seemed to downplay workers’ assessment of the situation, and included the following: “NYC Health + Hospital social workers…play different roles in our system, from acting as front-line providers to navigating safe discharges and helping patients and families with important health care decisions. Depending on the facility, the department, and the role they play, decisions are made by our hospital leaders on whether their critical work could be done remotely.”
Recently, many medical associations have issued statements supporting the rights of health care workers to speak up without fear of repercussion. But NYC H+H social workers have been complying with the orders because they say they’re scared of retaliation: In daily video conference calls, an administrator at one of NYC H+H’s hospitals has shown exasperation when asked about working from home, multiple employees told Medscape Medical News. And other questions, they said, such as whether staff could receive hazard pay, were scoffed at. Instead, the administration mentioned disciplinary action for those who didn’t show up to work.
During Thursday’s call, a recording of which was obtained by Medscape, the CEO of one NYC H+H hospital chastised his employees for taking their concerns to the press.
“People are just taking things and you know, using things for their benefit to be able to create problems for us who are trying to do our jobs,” he said, adding that he refuses to be bullied or blackmailed and that he’ll continue to do what he needs to do as CEO — but he wanted people to know “some of the garbage I have to deal with.”
He also reminded employees of documentation people need to provide if they don’t come in to work for being sick or taking a personal leave so the hospital can verify that “you have a condition that warrants you being out.”
Christopher Miller, a spokesperson for the hospital system, said that “some employees in certain functions may be approved to telecommute.” But employees contacted by Medscape who see all of their clients remotely said their requests to telecommute have not been approved.
At this point, it’s no longer a theoretical problem. COVID-19 appears to have spread among a cluster of people reporting to work in one of the H+H hospitals, employees said. In some cases, employees’ family members also became ill.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A social worker in New York City was home, caring for his sick son, when the hospital at which he works ordered him to report back to work. His son had COVID-19, yet his hospital told him he had to show up in person.
The social worker’s situation is just one of many NYC Health + Hospitals employees who could work remotely yet are required to report in person. His circumstances were described in a letter sent by Lichten & Bright, a law firm representing the New York City Health Services Employees Union, Local 768.
“Despite the fact that all or virtually all of the work social workers perform can be done remotely, only a handful…are being permitted to work from home,” said the letter, which was written on behalf of about 1000 social workers and 150 medical records specialists and addressed to NYC H+H CEO Mitchell Katz, MD.
Most social workers stopped seeing patients in person in early March. But many still face crowded conditions at several points during their work day. They take public transportation to work, come face-to-face with other health care workers and patients in elevators, and some attend daily meetings with up to 10 employees in conference rooms too small to stay six feet apart, the letter says.
“The social workers are scared to go to work,” said Daniel Bright, the letter’s author. “They’re baffled by the lack of any management response that would allow them to work from home. They are worried about getting exposed to the coronavirus while riding the subway or the bus to work or at work from a doctor or nurse or patient, and getting sick themselves or taking it home to their families.”
There is no good reason that the social workers should be compelled to be physically at work during the COVID-19 pandemic, Bright said. The handful of social workers at NYC H+H’s World Trade Center Environmental Health Center clinic at Bellevue who have been allowed to work from home on an ad hoc basis, he said, have done so successfully.
In response to Bright’s letter, the hospital system issued a statement that seemed to downplay workers’ assessment of the situation, and included the following: “NYC Health + Hospital social workers…play different roles in our system, from acting as front-line providers to navigating safe discharges and helping patients and families with important health care decisions. Depending on the facility, the department, and the role they play, decisions are made by our hospital leaders on whether their critical work could be done remotely.”
Recently, many medical associations have issued statements supporting the rights of health care workers to speak up without fear of repercussion. But NYC H+H social workers have been complying with the orders because they say they’re scared of retaliation: In daily video conference calls, an administrator at one of NYC H+H’s hospitals has shown exasperation when asked about working from home, multiple employees told Medscape Medical News. And other questions, they said, such as whether staff could receive hazard pay, were scoffed at. Instead, the administration mentioned disciplinary action for those who didn’t show up to work.
During Thursday’s call, a recording of which was obtained by Medscape, the CEO of one NYC H+H hospital chastised his employees for taking their concerns to the press.
“People are just taking things and you know, using things for their benefit to be able to create problems for us who are trying to do our jobs,” he said, adding that he refuses to be bullied or blackmailed and that he’ll continue to do what he needs to do as CEO — but he wanted people to know “some of the garbage I have to deal with.”
He also reminded employees of documentation people need to provide if they don’t come in to work for being sick or taking a personal leave so the hospital can verify that “you have a condition that warrants you being out.”
Christopher Miller, a spokesperson for the hospital system, said that “some employees in certain functions may be approved to telecommute.” But employees contacted by Medscape who see all of their clients remotely said their requests to telecommute have not been approved.
At this point, it’s no longer a theoretical problem. COVID-19 appears to have spread among a cluster of people reporting to work in one of the H+H hospitals, employees said. In some cases, employees’ family members also became ill.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A social worker in New York City was home, caring for his sick son, when the hospital at which he works ordered him to report back to work. His son had COVID-19, yet his hospital told him he had to show up in person.
The social worker’s situation is just one of many NYC Health + Hospitals employees who could work remotely yet are required to report in person. His circumstances were described in a letter sent by Lichten & Bright, a law firm representing the New York City Health Services Employees Union, Local 768.
“Despite the fact that all or virtually all of the work social workers perform can be done remotely, only a handful…are being permitted to work from home,” said the letter, which was written on behalf of about 1000 social workers and 150 medical records specialists and addressed to NYC H+H CEO Mitchell Katz, MD.
Most social workers stopped seeing patients in person in early March. But many still face crowded conditions at several points during their work day. They take public transportation to work, come face-to-face with other health care workers and patients in elevators, and some attend daily meetings with up to 10 employees in conference rooms too small to stay six feet apart, the letter says.
“The social workers are scared to go to work,” said Daniel Bright, the letter’s author. “They’re baffled by the lack of any management response that would allow them to work from home. They are worried about getting exposed to the coronavirus while riding the subway or the bus to work or at work from a doctor or nurse or patient, and getting sick themselves or taking it home to their families.”
There is no good reason that the social workers should be compelled to be physically at work during the COVID-19 pandemic, Bright said. The handful of social workers at NYC H+H’s World Trade Center Environmental Health Center clinic at Bellevue who have been allowed to work from home on an ad hoc basis, he said, have done so successfully.
In response to Bright’s letter, the hospital system issued a statement that seemed to downplay workers’ assessment of the situation, and included the following: “NYC Health + Hospital social workers…play different roles in our system, from acting as front-line providers to navigating safe discharges and helping patients and families with important health care decisions. Depending on the facility, the department, and the role they play, decisions are made by our hospital leaders on whether their critical work could be done remotely.”
Recently, many medical associations have issued statements supporting the rights of health care workers to speak up without fear of repercussion. But NYC H+H social workers have been complying with the orders because they say they’re scared of retaliation: In daily video conference calls, an administrator at one of NYC H+H’s hospitals has shown exasperation when asked about working from home, multiple employees told Medscape Medical News. And other questions, they said, such as whether staff could receive hazard pay, were scoffed at. Instead, the administration mentioned disciplinary action for those who didn’t show up to work.
During Thursday’s call, a recording of which was obtained by Medscape, the CEO of one NYC H+H hospital chastised his employees for taking their concerns to the press.
“People are just taking things and you know, using things for their benefit to be able to create problems for us who are trying to do our jobs,” he said, adding that he refuses to be bullied or blackmailed and that he’ll continue to do what he needs to do as CEO — but he wanted people to know “some of the garbage I have to deal with.”
He also reminded employees of documentation people need to provide if they don’t come in to work for being sick or taking a personal leave so the hospital can verify that “you have a condition that warrants you being out.”
Christopher Miller, a spokesperson for the hospital system, said that “some employees in certain functions may be approved to telecommute.” But employees contacted by Medscape who see all of their clients remotely said their requests to telecommute have not been approved.
At this point, it’s no longer a theoretical problem. COVID-19 appears to have spread among a cluster of people reporting to work in one of the H+H hospitals, employees said. In some cases, employees’ family members also became ill.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doing things right vs. doing the right things
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 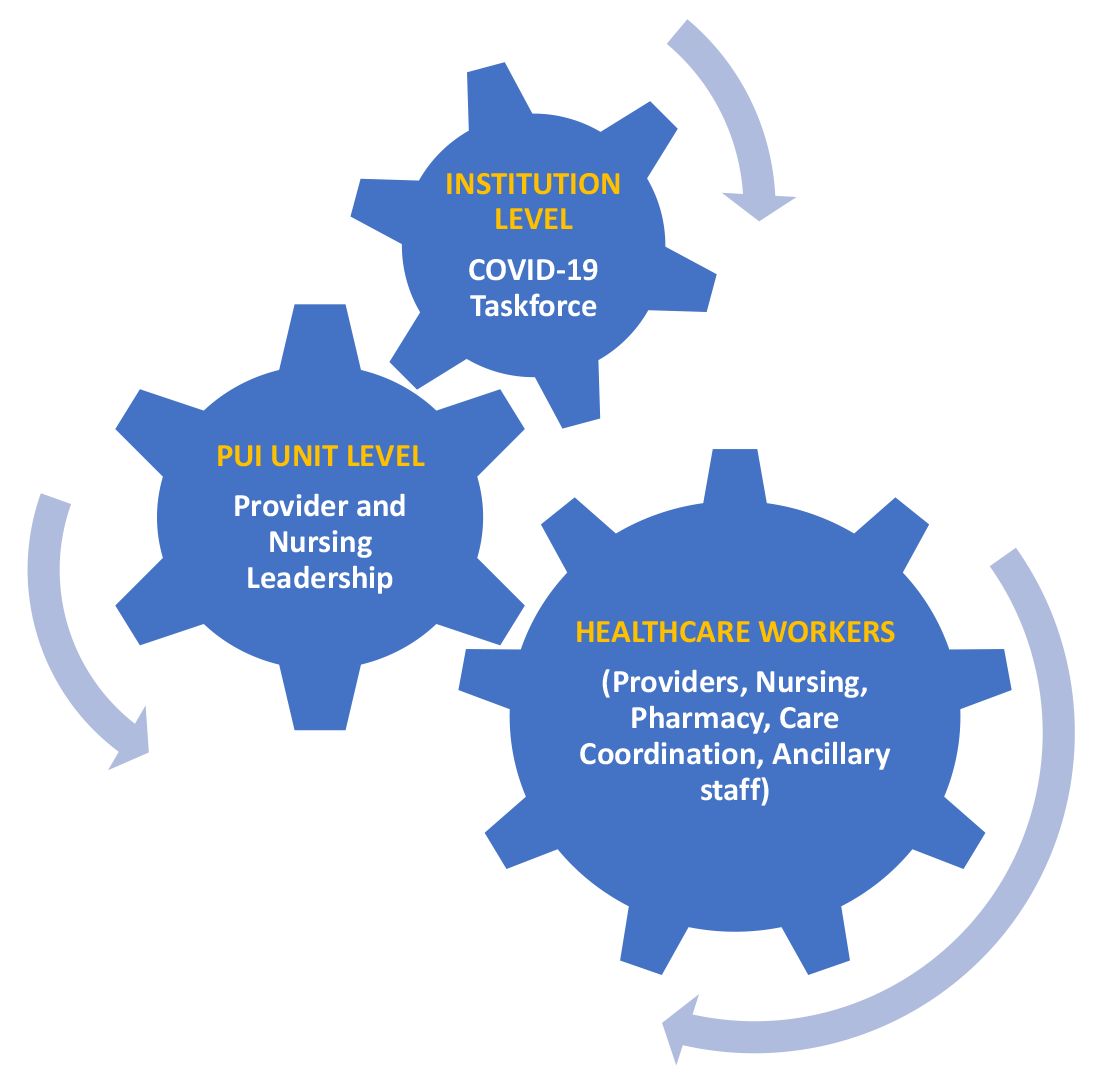
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
A framework for a COVID-19 Person Under Investigation unit
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.
The current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic shocked the world with its rapid spread despite stringent containment efforts, and it continues to wreak havoc. The surrounding uncertainty due to the novelty of this virus has prompted significant investigation to determine proper containment, treatment, and eradication efforts.1,2 In addition, health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and a shortage of resources resulting in lower quality care for patients and putting health care workers (HCWs) at risk for infection.3,4
While there is a lot of emerging clinical and basic science research in this area, there has been inconsistent guidance in regard to the containment and prevention of spread in health care systems. An initiative to minimize HCW exposure risk and to provide the highest quality care to patients was implemented by the Section of Hospital Medicine at our large academic medical center. We used a hospital medicine medical-surgical unit and converted it into a Person Under Investigation (PUI) unit for patients suspected of COVID-19.
Unit goals
- Deliver dedicated, comprehensive, and high-quality care to our PUI patients suspected of COVID-19.
- Minimize cross contamination with healthy patients on other hospital units.
- Provide clear and direct communications with our HCWs.
- Educate HCWs on optimal donning and doffing techniques.
- Minimize our HCW exposure risk.
- Efficiently use our personal protective equipment (PPE) supply.
Unit and team characteristics
We used a preexisting 24-bed hospital medicine medical-surgical unit with a dyad rounding model of an attending physician and advanced practice provider (APP). Other team members include a designated care coordinator (social worker/case manager), pharmacist, respiratory therapist, physical/occupational therapist, speech language pathologist, unit medical director, and nurse manager. A daily multidisciplinary huddle with all the team members was held to discuss the care of the PUI patients.
Administrative leadership
A COVID-19 task force composed of the medical director of clinical operations from the Section of Hospital Medicine, infectious disease, infection prevention, and several other important stakeholders conducted a daily conference call. This call allowed for the dissemination of information, including any treatment updates based on literature review or care processes. This information was then relayed to the HCWs following the meeting through the PUI unit medical director and nurse manager, who also facilitated feedback from the HCWs to the COVID-19 task force during the daily conference call. (See Figure 1.) 
Patient flow
Hospital medicine was designated as the default service for all PUI patients suspected of COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19 cases requiring hospitalization. These patients were admitted to this PUI unit directly from the emergency department (ED), or as transfers from outside institutions with assistance from our patient placement specialist team. Those patients admitted from our ED were tested for COVID-19 prior to arriving on the unit. Other suspected COVID-19 patients arriving as transfers from outside institutions were screened by the patient placement specialist team asking the following questions about the patient:
- “Has the patient had a fever or cough and been in contact with a laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 patient?”
- “Has the patient had a fever and cough?”
If the answer to either screening question was “yes,” then the patient was accepted to the PUI unit and tested upon arrival. Lastly, patients who were found to be COVID-19 positive at the outside institution, but who required transfer for other clinical reasons, were placed on this PUI unit as well.
Mechanisms to efficiently utilize PPE and mitigate HCW exposure risk
Our objectives are reducing the number of HCWs encountering PUI patients, reducing the number of encounters the HCWs have with PUI patients, and reducing the amount of time HCWs spent with PUI patients.
First, we maintained a log outside each patient’s room to track the details of staff encounters. Second, there was only one medical provider (either the attending physician or APP) assigned to each patient to limit personnel exposure. Third, we removed all learners (e.g. residents and students) from this unit. Fourth, we limited the number of entries into patient rooms to only critical staff directly involved in patient care (e.g. dietary and other ancillary staff were not allowed to enter the rooms) and provided updates to the patients by calling into the rooms. In addition, care coordination, pharmacy, and other staff members also utilized the same approach of calling into the room to speak with the patient regarding updates to minimize the duration of time spent in the room. Furthermore, our medical providers – with the help of the pharmacist and nursing – timed a patient’s medications to help reduce the number of entries into the room.
The medical providers also eliminated any unnecessary blood draws, imaging, and other procedures to minimize the number of encounters our HCWs had with the PUI. Lastly, the medical providers also avoided using any nebulizer treatments and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation to reduce any aerosol transmission of the virus. These measures not only helped to minimize our HCWs exposures, but also helped with the preservation of PPE.
Other efforts involved collaboration with infection prevention. They assisted with the training of our HCWs on proper PPE donning and doffing skills. This included watching a video and having an infection prevention specialist guide the HCWs throughout the entire process. We felt this was vital given the high amount of active failures with PPE use (up to 87%) reported in the literature.5 Furthermore, to ensure adequate mastery of these skills, infection prevention performed daily direct observation checks and provided real-time feedback to our HCWs.
Other things to consider for your PUI unit
There are several ideas that were not implemented in our PUI unit, but something to consider for your PUI unit, including:
- The use of elongated intravenous (IV) tubing, such that the IV poles and pumps were stationed outside the patient’s room, would be useful in reducing the amount of PPE required as well as HCW exposure to the patient.
- Having designated chest radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging scanners for these PUI patients to help minimize contamination with our non-PUI patients and to standardize the cleaning process.
- Supply our HCWs with designated scrubs at the beginning of their shifts, such that they can discard them at the end of their shifts for decontamination/sterilization purposes. This would help reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Supply our HCWs with a designated place to stay, such as a hotel or other living quarters, to reduce HCWs fear of potentially exposing their families at home.
- Although we encouraged providers and staff to utilize designated phones to conduct patient history and review of systems information-gathering, to decrease the time spent in the room, the availability of more sophisticated audiovisual equipment could also improve the quality of the interview.
Conclusions
The increasing incidence in suspected COVID-19 patients has led to significant strain on health care systems of the world along with the associated economic and social crisis. Some health care facilities are facing surge capacity issues and inadequate resources, while others are facing a humanitarian crisis. Overall, we are all being affected by this pandemic, but are most concerned about its effects on our HCWs and our patients.
To address the concerns of low-quality care to our patients and anxiety levels among HCWs, we created this dedicated PUI unit in an effort to provide high-quality care for these suspected (and confirmed) COVID-19 patients and to maintain clear direct and constant communication with our HCWs.
Dr. Sunkara ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C. He is the medical director for Hospital Medicine Units and the newly established PUI Unit, and is the corresponding author for this article. Dr. Lippert ([email protected]) is assistant professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Morris ([email protected]) is a PGY-3 internal medicine resident at Wake Forest School of Medicine. Dr. Huang ([email protected]) is associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
References
1. Food and Drug Administration. Recommendations for investigational COVID-19 convalescent plasma. 2020 Apr 8.
2. Fauci AS et al. Covid-19 – Navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2002387. 3. Emanuel EJ et al. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb2005114.
4. Li Ran et al. Risk factors of healthcare workers with corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study in a designated hospital of Wuhan in China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 17. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa287.
5. Krein SL et al. Identification and characterization of failures in infectious agent transmission precaution practices in hospitals: A qualitative study. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(8):1016-57. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.1898.