User login
Preparing for the viral trifecta: RSV, influenza, and COVID-19
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
No need to restrict hep C DAA therapy based on alcohol use
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
As U.S. syphilis cases rise, those at the epicenter scramble
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Three antibiotic regimens show similar effectiveness for CAP
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CHEST
Creatine may improve key long COVID symptoms: Small study
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM FOOD, SCIENCE & NUTRITION
Cat Scratch Disease Presenting With Concurrent Pityriasis Rosea in a 10-Year-Old Girl
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

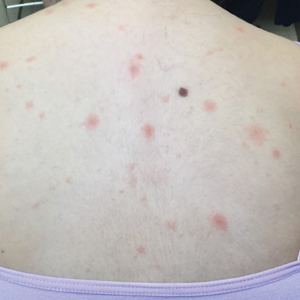
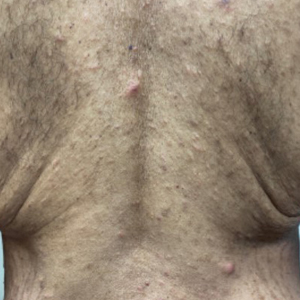
A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.
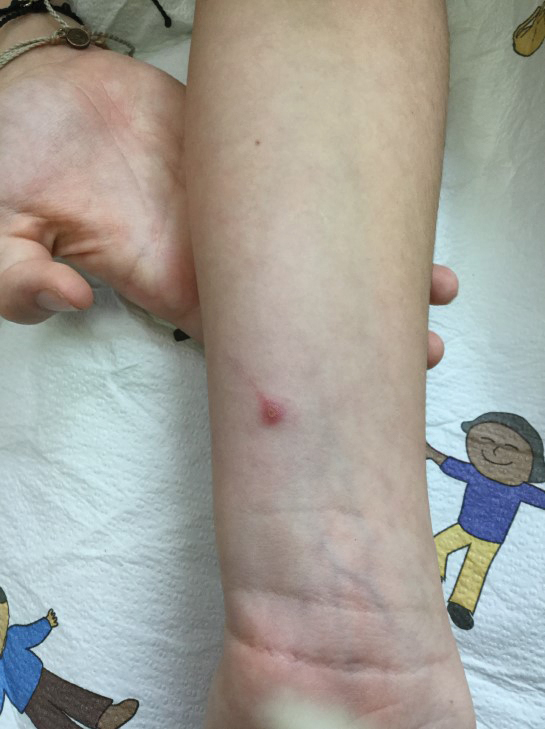
The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.

The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
To the Editor:
Cat scratch disease (CSD) is caused by Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae bacteria transferred from cats to humans that results in an inflamed inoculation site and tender lymphadenopathy. Pityriasis rosea (PR) and PR-like eruptions are self-limited, acute exanthems that have been associated with infections, vaccinations, and medications. We report a case of PR occurring in a 10-year-old girl with CSD, which may suggest an association between the 2 diseases.

A 10-year-old girl who was otherwise healthy presented in the winter with a rash of 5 days’ duration. Fourteen days prior to the rash, the patient reported being scratched by a new kitten and noted a pinpoint “puncture” on the left forearm that developed into a red papule over the following week. Seven days after the cat scratch, the patient experienced pain and swelling in the left axilla. Approximately 1 week after the onset of lymphadenopathy, the patient developed an asymptomatic rash that started with a large spot on the left chest, followed by smaller spots appearing over the next 2 days and spreading to the rest of the trunk. Four days after the rash onset, the patient experienced a mild headache, low-grade subjective fever, and chills. She denied any recent travel, bug bites, sore throat, and diarrhea. She was up-to-date on all vaccinations and had not received any vaccines preceding the symptoms. Physical examination revealed a 2-cm pink, scaly, thin plaque with a collarette of scale on the left upper chest (herald patch), along with multiple thin pink papules and small plaques with central scale on the trunk (Figure 1). A pustule with adjacent linear erosion was present on the left ventral forearm (Figure 2). The patient had a tender subcutaneous nodule in the left axilla as well as bilateral anterior and posterior cervical-chain subcutaneous tender nodules. There was no involvement of the palms, soles, or mucosae.

The patient was empirically treated for CSD with azithromycin (200 mg/5 mL), 404 mg on day 1 followed by 202 mg daily for 4 days. The rash was treated with hydrocortisone cream 2.5% twice daily for 2 weeks. A wound culture of the pustule on the left forearm was negative for neutrophils and organisms. Antibody serologies obtained 4 weeks after presentation were notable for an elevated B henselae IgG titer of 1:640, confirming the diagnosis of CSD. Following treatment with azithromycin and hydrocortisone, all of the patient’s symptoms resolved after 1 to 2 weeks.
Cat scratch disease is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacteria B henselae and the more recently described pathogen B clarridgeiae. Cat fleas spread these bacteria among cats, which subsequently inoculate the bacteria into humans through bites and scratches. The incidence of CSD in the United States is estimated to be 4.5 to 9.3 per 100,000 individuals in the outpatient setting and 0.19 to 0.86 per 100,000 individuals in the inpatient setting.1 Geographic variance can occur based on flea populations, resulting in higher incidence in warm humid climates and lower incidence in mountainous arid climates. The incidence of CSD in the pediatric population is highest in children aged 5 to 9 years. A national representative survey (N=3011) from 2017 revealed that 37.2% of primary care providers had diagnosed CSD in the prior year.1
Classic CSD presents as an erythematous papule at the inoculation site lasting days to weeks, with progression to tender lymphadenopathy lasting weeks to months. Fever, malaise, and chills also can be seen. Atypical CSD occurs in up to 24% of cases in immunocompetent patients.1 Atypical and systemic presentations are varied and can include fever of unknown origin, neuroretinitis, uveitis, retinal vessel occlusion, encephalitis, hepatosplenic lesions, Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis.1,2 Atypical dermatologic presentations of CSD include maculopapular rash in 7% of cases and erythema nodosum in 2.5% of cases, as well as rare reports of cutaneous vasculitis, urticaria, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, and papuloedematous eruption.3 Treatment guidelines for CSD vary widely depending on the clinical presentation as well as the immunocompetence of the infected individual. Our patient had limited regional lymphadenopathy with no signs of dissemination or neurologic involvement and was successfully treated with a 5-day course of oral azithromycin (weight based, 10 mg/kg). More extensive disease such as hepatosplenic or neurologic CSD may require multiple antibiotics for up to 6 weeks. Alternative or additional antibiotics used for CSD include rifampin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, gentamicin, and clarithromycin. Opinions vary as to whether all patients or just those with complicated infections warrant antibiotic therapy.4-6
Pityriasis rosea is a self-limited acute exanthematous disease that is classically associated with a systemic reactivation of human herpesvirus (HHV) 6 and/or HHV-7. The incidence of PR is estimated to be 480 per 100,000 dermatologic patients. It is slightly more common in females and occurs most often in patients aged 10 to 35 years.7 Clinically, PR appears with the abrupt onset of a single erythematous scaly patch (termed the herald patch), followed by a secondary eruption of smaller erythematous scaly macules and patches along the trunk’s cleavage lines. The secondary eruption on the back is sometimes termed a Christmas or fir tree pattern.7,8
In addition to the classic presentation of PR, there have been reports of numerous atypical clinical presentations. The herald patch, which classically presents on the trunk, also has been reported to present on the extremities; PR of the extremities is defined by lesions that appear as large scaly plaques on the extremities only. Inverse PR presents with lesions occurring in flexural areas and acral surfaces but not on the trunk. There also is an acral PR variant in which lesions appear only on the palms, wrists, and soles. Purpuric or hemorrhagic PR has been described and presents with purpura and petechiae with or without collarettes of scale in diffuse locations, including the palate. Oral PR presents more commonly in patients of color as erosions, ulcers, hemorrhagic lesions, bullae, or geographic tongue. Erythema multiforme–like PR appears with targetoid lesions on the trunk, face, neck, and arms without a history of herpes simplex virus infection. A large pear-shaped herald patch has been reported and characterizes the gigantea PR of Darier variant. Irritated PR occurs with typical PR findings, but afflicted patients report severe pain and burning with diaphoresis. Relapsing PR can occur within 1 year of a prior episode of PR and presents without a herald patch. Persistent PR is defined by PR lasting more than 3 months, and most reported cases have included oral lesions. Finally, other PR variants that have been described include urticarial, papular, follicular, vesicular, and hypopigmented types.7-9
Furthermore, there have been reports of multiple atypical presentations occurring simultaneously in the same patient.10 Although PR classically has been associated with HHV-6 and/or HHV-7 reactivation, it has been reported with a few other clinical situations and conditions. Pityriasislike eruption specifically refers to an exanthem secondary to drugs or vaccination that resembles PR but shows clinical differences, including diffuse and confluent dusky-red macules and/or plaques with or without desquamation on the trunk, extremities, and face. Drugs that have been implicated as triggers include ACE inhibitors, gold, isotretinoin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, omeprazole, terbinafine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Smallpox, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis B virus, pneumococcus, papillomavirus, yellow fever, and pertussis vaccinations also have been associated with PR.7,11,12 Additionally, PR has been reported to occur with active systemic infections, specifically H1N1 influenza, though it is rare.13 Because of its self-limited course, treatment of PR most often involves only reassurance. Topical corticosteroids may be appropriate for pruritus.7,8
Pediatric health care providers including dermatologists should be familiar with both CSD and PR because they are common diseases that more often are encountered in the pediatric population. We present a unique case of CSD presenting with concurrent PR, which highlights a potential new etiology for PR and a rare cutaneous manifestation of CSD. Further investigation into a possible relationship between CSD and PR may be warranted. Patients with any signs and symptoms of fever, tender lymphadenopathy, worsening rash, or exposure to cats warrant a thorough history and physical examination to ensure that neither entity is overlooked.
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
- Nelson CA, Moore AR, Perea AE, et al. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge [published online July 14, 2017]. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018;65:67-73. doi:10.1111/zph.12368
- Habot-Wilner Z, Trivizki O, Goldstein M, et al. Cat-scratch disease: ocular manifestations and treatment outcome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96:E524-E532. doi:10.1111/aos.13684
- Schattner A, Uliel L, Dubin I. The cat did it: erythema nodosum and additional atypical presentations of Bartonella henselae infection in immunocompetent hosts [published online February 16, 2018]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222511
- Shorbatli L, Koranyi K, Nahata M. Effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in pediatric patients with cat scratch disease. Int J Clin Pharm. 2018;40:1458-1461. doi: 10.1007/s11096-018-0746-1
- Bass JW, Freitas BC, Freitas AD, et al. Prospective randomized double blind placebo-controlled evaluation of azithromycin for treatment of cat-scratch disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:447-452. doi:10.1097/00006454-199806000-00002
- Spach DH, Kaplan SL. Treatment of cat scratch disease. UpToDate. Updated December 9, 2021. Accessed September 12, 2023. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-of-cat-scratch-disease
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, et al. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431-437. doi:10.1159/000445375
- Urbina F, Das A, Sudy E. Clinical variants of pityriasis rosea. World J Clin Cases. 2017;5:203-211. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.203
- Alzahrani NA, Al Jasser MI. Geographic tonguelike presentation in a child with pityriasis rosea: case report and review of oral manifestations of pityriasis rosea. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:E124-E127. doi:10.1111/pde.13417
- Sinha S, Sardana K, Garg V. Coexistence of two atypical variants of pityriasis rosea: a case report and review of literature. Pediatr Dermatol. 2012;29:538-540. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2011.01549.x
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: how to distinguish them? JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:800-801. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.04.002
- Drago F, Ciccarese G, Javor S, et al. Vaccine-induced pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:544-545. doi:10.1111/jdv.12942
- Mubki TF, Bin Dayel SA, Kadry R. A case of pityriasis rosea concurrent with the novel influenza A (H1N1) infection. Pediatr Dermatol. 2011;28:341-342. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2010.01090.x
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should familiarize themselves with the physical examination findings of cat scratch disease.
- There are numerous clinical variants and triggers of pityriasis rosea (PR).
- There may be a new infectious trigger for PR, and exposure to cats prior to a classic PR eruption should raise one’s suspicion as a possible cause.
Primary care clinicians should spearhead HIV prevention
HIV continues to be a significant public health concern in the United States, with an estimated 1.2 million people currently living with the virus and more than 30,000 new diagnoses in 2020 alone.
Primary care clinicians can help decrease rates of HIV infection by prescribing pre-exposure prophylaxis to people who are sexually active.
But many do not.
“In medical school, we don’t spend much time discussing sexuality, sexual behavior, sexually transmitted infections, and such, so providers may feel uncomfortable asking what kind of sex their patient is having and with whom, whether they use a condom, and other basics,” said Matthew M. Hamill, MBChB, PhD, MPH, a specialist in sexually transmitted diseases at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) is an antiviral medication that cuts the risk of contracting HIV through sex by around 99% when taken as prescribed, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Many people who would benefit from PrEP are not receiving this highly effective medication,” said John B. Wong, MD, a primary care internist and professor of medicine at Tufts University, Boston. The gap is particularly acute among Black, Hispanic, and Latino people, who are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with HIV but are much less likely than Whites to receive PrEP, he said.
Dr. Wong, a member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, helped write the group’s new PrEP recommendations. Published in August, the guidelines call for clinicians to prescribe the drugs to adolescents and adults who do not have HIV but are at an increased risk for infection.
“Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to prescribe PrEP for their patients because they have longitudinal relationships: They get to know their patients, and hopefully their patients feel comfortable talking with them about their sexual health,” said Brandon Pollak, MD, a primary care physician and HIV specialist at the Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Dr. Pollak, who was not involved with the USPSTF recommendations, cares for patients who are heterosexual and living with HIV.
Clinicians should consider PrEP for all patients who have sex with someone who has HIV, do not use condoms, or have had a sexually transmitted infection within the previous 6 months. Men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject illicit drugs or engage in transactional sex, and Black, Hispanic, and Latino individuals also are at increased risk for the infection.
“The vast majority of patients on PrEP in any form sail through with no problems; they have regular lab work and can follow up in person or by telemedicine,” Dr. Hamill said. “They tend to be young, fit people without complicated medical histories, and the medications are very well-tolerated, particularly if people expect some short-term side effects.”
What you need to know when prescribing PrEP
Prescribing PrEP is similar in complexity to prescribing hypertension or diabetes medications, Dr. Hamill said.
Because taking the medications while already infected with the virus can lead to the emergence of drug-resistant HIV, patients must have a negative HIV test before starting PrEP. In addition, the USPSTF recommends testing for other sexually transmitted infections and for pregnancy, if appropriate. The task force also recommends conducting kidney function and hepatitis B tests, and a lipid profile before starting specific types of PrEP.
HIV screening is also recommended at 3-month intervals.
“Providers may order labs done at 3- to 4-month intervals but only see patients in clinic once or twice per year, depending on patient needs and risk behaviors,” said Jill S. Blumenthal, MD, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health.
Clinicians should consider medication adherence and whether a patient is likely to take a pill once a day or could benefit from receiving an injection every 2 months. Patients may experience side effects such as diarrhea or headache with oral PrEP or soreness at the injection site. In rare cases, some of the drugs may cause kidney toxicity or bone mineral loss, according to Dr. Hamill.
Three similarly effective forms of PrEP approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enable clinicians to tailor the medications to the specific needs and preferences of each patient. Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) and Descovy (emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide) are both daily tablets, although the latter is not advised for people assigned female sex at birth who have receptive vaginal sex. Apretude (cabotegravir), an injectable agent, is not recommended for people who inject illegal drugs.
Patients with renal or bone disease are not good candidates for Truvada.
“Truvada can decrease bone density, so for someone with osteoporosis, you might choose Descovy or Apretude,” Dr. Pollak said. “For someone with chronic kidney disease, consider Descovy or Apretude. “If a patient has hepatitis B, Truvada or Descovy are appropriate, because hepatitis B is treatable.”
Patients taking an injectable PrEP may need more attention, because the concentration of the medication in the body decreases slowly and may linger for many months at low levels that don’t prevent HIV, according to Dr. Hamill. Someone who acquires HIV during that “tail” period might develop resistance to PrEP.
New research also showed that Descovy users were at elevated risk of developing hypertension and statin initiation, especially among those over age 40 years.
Primary care physicians may want to consult with renal specialists about medication safety in patients with severe kidney disease or with rheumatologists or endocrinologists about metabolic bone disease concerns, Dr. Hamill said.
Meanwhile, if a person begins a monogamous relationship and their risk for HIV drops, “it’s fine to stop taking PrEP tablets,” Dr. Pollak said. “I would still recommend routine HIV screening every 6 or 12 months or however often, depending on other risk factors.”
Caring for these patients entails ensuring labs are completed, monitoring adherence, ordering refills, and scheduling regular follow-up visits.
“For the vast majority of patients, the primary care physician is perfectly equipped for their care through the entire PrEP journey, from discussion and initiation to provision of PrEP,” and most cases do not require specialist care, Dr. Hamill said.
However, “if PrEP fails, which is exceedingly rare, primary care physicians should refer patients immediately, preferably with a warm handoff, for linkage to HIV care,” Dr. Blumenthal said.
Talking about PrEP opens the door to conversations with patients about sexual health and broader health issues, Dr. Hamill said. Although these may not come naturally to primary care clinicians, training is available. The National Network of STD Clinical Prevention Training Centers, funded by the CDC, trains providers on how to overcome their anxiety and have open, inclusive conversations about sexuality and sexual behaviors with transgender and gender-diverse, nonbinary people.
“People worry about saying the wrong thing, about causing offense,” Dr. Hamill said. “But once you get comfortable discussing sexuality, you may open conversations around other health issues.”
Barriers for patients
The task force identified several barriers to PrEP access for patients because of lack of trusting relationships with health care, the effects of structural racism on health disparities, and persistent biases within the health care system.
Racial and ethnic disparities in HIV incidence persist, with 42% of new diagnoses occurring among Black people, 27% among Hispanic or Latino people, and 26% among White people in 2020.
Rates of PrEP usage for a year or longer are also low. Sometimes the patient no longer needs PrEP, but barriers often involve the costs of taking time off from work and arranging transportation to clinic visits.
Although nearly all insurance plans and state Medicaid programs cover PrEP, if a patient does not have coverage, the drugs and required tests and office visits can be expensive.
“One of the biggest barriers for all providers is navigating our complicated health system and drug assistance programs,” said Mehri S. McKellar, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, N.C.
But lower-cost FDA-approved generic emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is now available, and clinicians can direct patients to programs that help provide the medications at low or no cost.
“Providing PrEP care is straightforward, beneficial, and satisfying,” Dr. Hamill said. “You help people protect themselves from a life-changing diagnosis, and the health system doesn’t need to pay the cost of treating HIV. Everyone wins.”
Dr. Hamill, Dr. McKellar, Dr. Pollak, and Dr. Wong have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blumenthal has reported a financial relationship with Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV continues to be a significant public health concern in the United States, with an estimated 1.2 million people currently living with the virus and more than 30,000 new diagnoses in 2020 alone.
Primary care clinicians can help decrease rates of HIV infection by prescribing pre-exposure prophylaxis to people who are sexually active.
But many do not.
“In medical school, we don’t spend much time discussing sexuality, sexual behavior, sexually transmitted infections, and such, so providers may feel uncomfortable asking what kind of sex their patient is having and with whom, whether they use a condom, and other basics,” said Matthew M. Hamill, MBChB, PhD, MPH, a specialist in sexually transmitted diseases at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) is an antiviral medication that cuts the risk of contracting HIV through sex by around 99% when taken as prescribed, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Many people who would benefit from PrEP are not receiving this highly effective medication,” said John B. Wong, MD, a primary care internist and professor of medicine at Tufts University, Boston. The gap is particularly acute among Black, Hispanic, and Latino people, who are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with HIV but are much less likely than Whites to receive PrEP, he said.
Dr. Wong, a member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, helped write the group’s new PrEP recommendations. Published in August, the guidelines call for clinicians to prescribe the drugs to adolescents and adults who do not have HIV but are at an increased risk for infection.
“Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to prescribe PrEP for their patients because they have longitudinal relationships: They get to know their patients, and hopefully their patients feel comfortable talking with them about their sexual health,” said Brandon Pollak, MD, a primary care physician and HIV specialist at the Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Dr. Pollak, who was not involved with the USPSTF recommendations, cares for patients who are heterosexual and living with HIV.
Clinicians should consider PrEP for all patients who have sex with someone who has HIV, do not use condoms, or have had a sexually transmitted infection within the previous 6 months. Men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject illicit drugs or engage in transactional sex, and Black, Hispanic, and Latino individuals also are at increased risk for the infection.
“The vast majority of patients on PrEP in any form sail through with no problems; they have regular lab work and can follow up in person or by telemedicine,” Dr. Hamill said. “They tend to be young, fit people without complicated medical histories, and the medications are very well-tolerated, particularly if people expect some short-term side effects.”
What you need to know when prescribing PrEP
Prescribing PrEP is similar in complexity to prescribing hypertension or diabetes medications, Dr. Hamill said.
Because taking the medications while already infected with the virus can lead to the emergence of drug-resistant HIV, patients must have a negative HIV test before starting PrEP. In addition, the USPSTF recommends testing for other sexually transmitted infections and for pregnancy, if appropriate. The task force also recommends conducting kidney function and hepatitis B tests, and a lipid profile before starting specific types of PrEP.
HIV screening is also recommended at 3-month intervals.
“Providers may order labs done at 3- to 4-month intervals but only see patients in clinic once or twice per year, depending on patient needs and risk behaviors,” said Jill S. Blumenthal, MD, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health.
Clinicians should consider medication adherence and whether a patient is likely to take a pill once a day or could benefit from receiving an injection every 2 months. Patients may experience side effects such as diarrhea or headache with oral PrEP or soreness at the injection site. In rare cases, some of the drugs may cause kidney toxicity or bone mineral loss, according to Dr. Hamill.
Three similarly effective forms of PrEP approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enable clinicians to tailor the medications to the specific needs and preferences of each patient. Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) and Descovy (emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide) are both daily tablets, although the latter is not advised for people assigned female sex at birth who have receptive vaginal sex. Apretude (cabotegravir), an injectable agent, is not recommended for people who inject illegal drugs.
Patients with renal or bone disease are not good candidates for Truvada.
“Truvada can decrease bone density, so for someone with osteoporosis, you might choose Descovy or Apretude,” Dr. Pollak said. “For someone with chronic kidney disease, consider Descovy or Apretude. “If a patient has hepatitis B, Truvada or Descovy are appropriate, because hepatitis B is treatable.”
Patients taking an injectable PrEP may need more attention, because the concentration of the medication in the body decreases slowly and may linger for many months at low levels that don’t prevent HIV, according to Dr. Hamill. Someone who acquires HIV during that “tail” period might develop resistance to PrEP.
New research also showed that Descovy users were at elevated risk of developing hypertension and statin initiation, especially among those over age 40 years.
Primary care physicians may want to consult with renal specialists about medication safety in patients with severe kidney disease or with rheumatologists or endocrinologists about metabolic bone disease concerns, Dr. Hamill said.
Meanwhile, if a person begins a monogamous relationship and their risk for HIV drops, “it’s fine to stop taking PrEP tablets,” Dr. Pollak said. “I would still recommend routine HIV screening every 6 or 12 months or however often, depending on other risk factors.”
Caring for these patients entails ensuring labs are completed, monitoring adherence, ordering refills, and scheduling regular follow-up visits.
“For the vast majority of patients, the primary care physician is perfectly equipped for their care through the entire PrEP journey, from discussion and initiation to provision of PrEP,” and most cases do not require specialist care, Dr. Hamill said.
However, “if PrEP fails, which is exceedingly rare, primary care physicians should refer patients immediately, preferably with a warm handoff, for linkage to HIV care,” Dr. Blumenthal said.
Talking about PrEP opens the door to conversations with patients about sexual health and broader health issues, Dr. Hamill said. Although these may not come naturally to primary care clinicians, training is available. The National Network of STD Clinical Prevention Training Centers, funded by the CDC, trains providers on how to overcome their anxiety and have open, inclusive conversations about sexuality and sexual behaviors with transgender and gender-diverse, nonbinary people.
“People worry about saying the wrong thing, about causing offense,” Dr. Hamill said. “But once you get comfortable discussing sexuality, you may open conversations around other health issues.”
Barriers for patients
The task force identified several barriers to PrEP access for patients because of lack of trusting relationships with health care, the effects of structural racism on health disparities, and persistent biases within the health care system.
Racial and ethnic disparities in HIV incidence persist, with 42% of new diagnoses occurring among Black people, 27% among Hispanic or Latino people, and 26% among White people in 2020.
Rates of PrEP usage for a year or longer are also low. Sometimes the patient no longer needs PrEP, but barriers often involve the costs of taking time off from work and arranging transportation to clinic visits.
Although nearly all insurance plans and state Medicaid programs cover PrEP, if a patient does not have coverage, the drugs and required tests and office visits can be expensive.
“One of the biggest barriers for all providers is navigating our complicated health system and drug assistance programs,” said Mehri S. McKellar, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, N.C.
But lower-cost FDA-approved generic emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is now available, and clinicians can direct patients to programs that help provide the medications at low or no cost.
“Providing PrEP care is straightforward, beneficial, and satisfying,” Dr. Hamill said. “You help people protect themselves from a life-changing diagnosis, and the health system doesn’t need to pay the cost of treating HIV. Everyone wins.”
Dr. Hamill, Dr. McKellar, Dr. Pollak, and Dr. Wong have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blumenthal has reported a financial relationship with Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HIV continues to be a significant public health concern in the United States, with an estimated 1.2 million people currently living with the virus and more than 30,000 new diagnoses in 2020 alone.
Primary care clinicians can help decrease rates of HIV infection by prescribing pre-exposure prophylaxis to people who are sexually active.
But many do not.
“In medical school, we don’t spend much time discussing sexuality, sexual behavior, sexually transmitted infections, and such, so providers may feel uncomfortable asking what kind of sex their patient is having and with whom, whether they use a condom, and other basics,” said Matthew M. Hamill, MBChB, PhD, MPH, a specialist in sexually transmitted diseases at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) is an antiviral medication that cuts the risk of contracting HIV through sex by around 99% when taken as prescribed, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Many people who would benefit from PrEP are not receiving this highly effective medication,” said John B. Wong, MD, a primary care internist and professor of medicine at Tufts University, Boston. The gap is particularly acute among Black, Hispanic, and Latino people, who are significantly more likely to be diagnosed with HIV but are much less likely than Whites to receive PrEP, he said.
Dr. Wong, a member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, helped write the group’s new PrEP recommendations. Published in August, the guidelines call for clinicians to prescribe the drugs to adolescents and adults who do not have HIV but are at an increased risk for infection.
“Primary care physicians are ideally positioned to prescribe PrEP for their patients because they have longitudinal relationships: They get to know their patients, and hopefully their patients feel comfortable talking with them about their sexual health,” said Brandon Pollak, MD, a primary care physician and HIV specialist at the Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Dr. Pollak, who was not involved with the USPSTF recommendations, cares for patients who are heterosexual and living with HIV.
Clinicians should consider PrEP for all patients who have sex with someone who has HIV, do not use condoms, or have had a sexually transmitted infection within the previous 6 months. Men who have sex with men, transgender women who have sex with men, people who inject illicit drugs or engage in transactional sex, and Black, Hispanic, and Latino individuals also are at increased risk for the infection.
“The vast majority of patients on PrEP in any form sail through with no problems; they have regular lab work and can follow up in person or by telemedicine,” Dr. Hamill said. “They tend to be young, fit people without complicated medical histories, and the medications are very well-tolerated, particularly if people expect some short-term side effects.”
What you need to know when prescribing PrEP
Prescribing PrEP is similar in complexity to prescribing hypertension or diabetes medications, Dr. Hamill said.
Because taking the medications while already infected with the virus can lead to the emergence of drug-resistant HIV, patients must have a negative HIV test before starting PrEP. In addition, the USPSTF recommends testing for other sexually transmitted infections and for pregnancy, if appropriate. The task force also recommends conducting kidney function and hepatitis B tests, and a lipid profile before starting specific types of PrEP.
HIV screening is also recommended at 3-month intervals.
“Providers may order labs done at 3- to 4-month intervals but only see patients in clinic once or twice per year, depending on patient needs and risk behaviors,” said Jill S. Blumenthal, MD, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health.
Clinicians should consider medication adherence and whether a patient is likely to take a pill once a day or could benefit from receiving an injection every 2 months. Patients may experience side effects such as diarrhea or headache with oral PrEP or soreness at the injection site. In rare cases, some of the drugs may cause kidney toxicity or bone mineral loss, according to Dr. Hamill.
Three similarly effective forms of PrEP approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration enable clinicians to tailor the medications to the specific needs and preferences of each patient. Truvada (emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) and Descovy (emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide) are both daily tablets, although the latter is not advised for people assigned female sex at birth who have receptive vaginal sex. Apretude (cabotegravir), an injectable agent, is not recommended for people who inject illegal drugs.
Patients with renal or bone disease are not good candidates for Truvada.
“Truvada can decrease bone density, so for someone with osteoporosis, you might choose Descovy or Apretude,” Dr. Pollak said. “For someone with chronic kidney disease, consider Descovy or Apretude. “If a patient has hepatitis B, Truvada or Descovy are appropriate, because hepatitis B is treatable.”
Patients taking an injectable PrEP may need more attention, because the concentration of the medication in the body decreases slowly and may linger for many months at low levels that don’t prevent HIV, according to Dr. Hamill. Someone who acquires HIV during that “tail” period might develop resistance to PrEP.
New research also showed that Descovy users were at elevated risk of developing hypertension and statin initiation, especially among those over age 40 years.
Primary care physicians may want to consult with renal specialists about medication safety in patients with severe kidney disease or with rheumatologists or endocrinologists about metabolic bone disease concerns, Dr. Hamill said.
Meanwhile, if a person begins a monogamous relationship and their risk for HIV drops, “it’s fine to stop taking PrEP tablets,” Dr. Pollak said. “I would still recommend routine HIV screening every 6 or 12 months or however often, depending on other risk factors.”
Caring for these patients entails ensuring labs are completed, monitoring adherence, ordering refills, and scheduling regular follow-up visits.
“For the vast majority of patients, the primary care physician is perfectly equipped for their care through the entire PrEP journey, from discussion and initiation to provision of PrEP,” and most cases do not require specialist care, Dr. Hamill said.
However, “if PrEP fails, which is exceedingly rare, primary care physicians should refer patients immediately, preferably with a warm handoff, for linkage to HIV care,” Dr. Blumenthal said.
Talking about PrEP opens the door to conversations with patients about sexual health and broader health issues, Dr. Hamill said. Although these may not come naturally to primary care clinicians, training is available. The National Network of STD Clinical Prevention Training Centers, funded by the CDC, trains providers on how to overcome their anxiety and have open, inclusive conversations about sexuality and sexual behaviors with transgender and gender-diverse, nonbinary people.
“People worry about saying the wrong thing, about causing offense,” Dr. Hamill said. “But once you get comfortable discussing sexuality, you may open conversations around other health issues.”
Barriers for patients
The task force identified several barriers to PrEP access for patients because of lack of trusting relationships with health care, the effects of structural racism on health disparities, and persistent biases within the health care system.
Racial and ethnic disparities in HIV incidence persist, with 42% of new diagnoses occurring among Black people, 27% among Hispanic or Latino people, and 26% among White people in 2020.
Rates of PrEP usage for a year or longer are also low. Sometimes the patient no longer needs PrEP, but barriers often involve the costs of taking time off from work and arranging transportation to clinic visits.
Although nearly all insurance plans and state Medicaid programs cover PrEP, if a patient does not have coverage, the drugs and required tests and office visits can be expensive.
“One of the biggest barriers for all providers is navigating our complicated health system and drug assistance programs,” said Mehri S. McKellar, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, N.C.
But lower-cost FDA-approved generic emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is now available, and clinicians can direct patients to programs that help provide the medications at low or no cost.
“Providing PrEP care is straightforward, beneficial, and satisfying,” Dr. Hamill said. “You help people protect themselves from a life-changing diagnosis, and the health system doesn’t need to pay the cost of treating HIV. Everyone wins.”
Dr. Hamill, Dr. McKellar, Dr. Pollak, and Dr. Wong have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Blumenthal has reported a financial relationship with Gilead Sciences.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diffuse Pruritic Eruption in an Immunocompromised Patient
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.
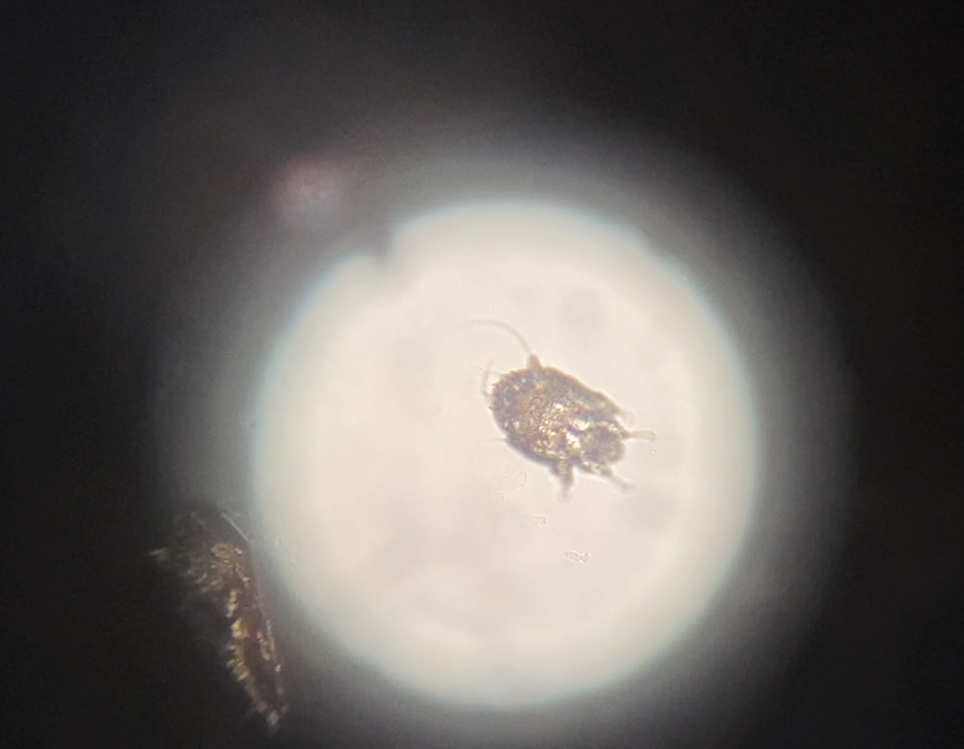
Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.

Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
The Diagnosis: Scabies Infestation
Direct microscopy revealed the presence of a live scabies mite and numerous eggs (Figure), confirming the diagnosis of a scabies infestation. Scabies, caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis mite, characteristically presents in adults as pruritic hyperkeratotic plaques of the interdigital web spaces of the hands, flexor surfaces of the wrists and elbows, axillae, male genitalia, and breasts; however, an atypical presentation is common in immunocompromised or immunosuppressed individuals, such as our patient. In children, the palms, soles, and head (ie, face, scalp, neck) are common sites of involvement. Although dermatologists generally are familiar with severe atypical presentations such as Norwegian crusted scabies or bullous scabies, it is important that they are aware of other atypical presentations, such as the diffuse papulonodular variant observed in our patient.1 As such, a low threshold of suspicion for scabies infestations should be employed in immunocompromised patients with new-onset pruritic eruptions.

Direct microscopy is widely accepted as the gold standard for the diagnosis of scabies infestations; it is a fast and low-cost diagnostic tool. However, this technique displays variable sensitivity in clinical practice, requiring experience and a skilled hand.1,2 Other more sensitive diagnostic options for suspected scabies infestations include histopathology, serology, and molecular-based techniques such as DNA isolation and polymerase chain reaction. Although these tests do demonstrate greater sensitivity, they also are more invasive, time intensive, and costly.2 Therefore, they typically are not the first choice for a suspected scabies infestation. Dermoscopy has emerged as another tool to aid in the diagnosis of a suspected scabies infestation, enabling visualization of scaly burrows, eggs, and live mites. Classically, findings resembling a delta wing with contrail are seen on dermoscopic examination. The delta wing represents the brown triangular structure of the pigmented scabies mite head and anterior legs; the contrail is the lighter linear structures streaming behind the scabies mite (similar to visible vapor streams occurring behind flying jets), representing the burrow of the mite.
Although treatment of scabies infestations typically can be accomplished with permethrin cream 5%, the diffuse nature of our patient’s lesions in combination with his immunocompromised state made oral therapy a more appropriate choice. Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommendations, the patient received 2 doses of oral weight-based ivermectin (200 μg/kg per dose) administered 1 week apart.1,3 The initial dose at day 1 serves to eliminate any scabies mites that are present, while the second dose 1 week later eliminates any residual eggs. Our patient experienced complete resolution of the symptoms following this treatment regimen.
It was important to differentiate our patient’s scabies infestation from other intensely pruritic conditions and morphologic mimics including papular urticaria, lichenoid drug eruptions, tinea corporis, and prurigo nodularis. Papular urticaria is an intensely pruritic hypersensitivity reaction to insect bites that commonly affects the extremities or other exposed areas. Visible puncta may be present.4 Our patient’s lesion distribution involved areas covered by clothing, no puncta were present, and he had no history of a recent arthropod assault, making the diagnosis of papular urticaria less likely.
Lichenoid drug eruptions classically present with symmetric, diffuse, pruritic, violaceous, scaling papules and plaques that present 2 to 3 months after exposure to an offending agent.5 Our patient’s eruption was papulonodular with no violaceous plaques, and he did not report changes to his medications, making a lichenoid drug eruption less likely.
Tinea corporis is another intensely pruritic condition that should be considered, especially in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by dermatophytes and classically presents as erythematous pruritic plaques with an annular, advancing, scaling border.6 Although immunocompromised patients may display extensive involvement, our patient’s lesions were papulonodular with no annular morphology or scale, rendering tinea corporis less likely.
Prurigo nodularis is a chronic condition characterized by pruritic, violaceous, dome-shaped, smooth or crusted nodules secondary to repeated scratching or pressure. Although prurigo nodules can develop as a secondary change due to chronic excoriations in scabies infestations, prurigo nodules usually do not develop in areas such as the midline of the back that are not easily reached by the fingernails,7 which made prurigo nodularis less likely in our patient.
This case describes a unique papulonodular variant of scabies presenting in an immunocompromised cancer patient. Timely recognition and diagnosis of atypical scabies infestations can decrease morbidity and improve the quality of life of these patients.
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
- Chandler DJ, Fuller LC. A review of scabies: an infestation more than skin deep. Dermatology. 2019;235:79-90. doi:10.1159/000495290
- Siddig EE, Hay R. Laboratory-based diagnosis of scabies: a review of the current status. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2022;116:4-9. doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab049
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites—scabies. medications. Accessed September 19, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ scabies/health_professionals/meds.html
- Örnek S, Zuberbier T, Kocatürk E. Annular urticarial lesions. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:480-504. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol .2021.12.010
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruptions, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Leung AK, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Tinea corporis: an updated review. Drugs Context. 2020;9:2020-5-6. doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-6
- Kwon CD, Khanna R, Williams KA, et al. Diagnostic workup and evaluation of patients with prurigo nodularis. Medicines (Basel). 2019;6:97. doi:10.3390/medicines6040097
A 54-year-old man presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of a widespread intensely pruritic rash of 4 weeks’ duration. Calamine lotion and oral hydroxyzine provided minimal relief. He was being treated for a myeloproliferative disorder with immunosuppressive therapy consisting of a combination of cladribine, low-dose cytarabine, and fedratinib. Physical examination revealed multiple excoriated papules and indurated nodules on the extensor and flexor surfaces of the arms and legs (top), chest, midline of the back (bottom), and groin. No lesions were noted on the volar aspect of the patient’s wrists or interdigital spaces, and no central puncta or scales were present. He denied any preceding arthropod bites, trauma, new environmental exposures, or changes to his medications. Scrapings from several representative lesions were obtained for mineral oil preparation and microscopic evaluation.
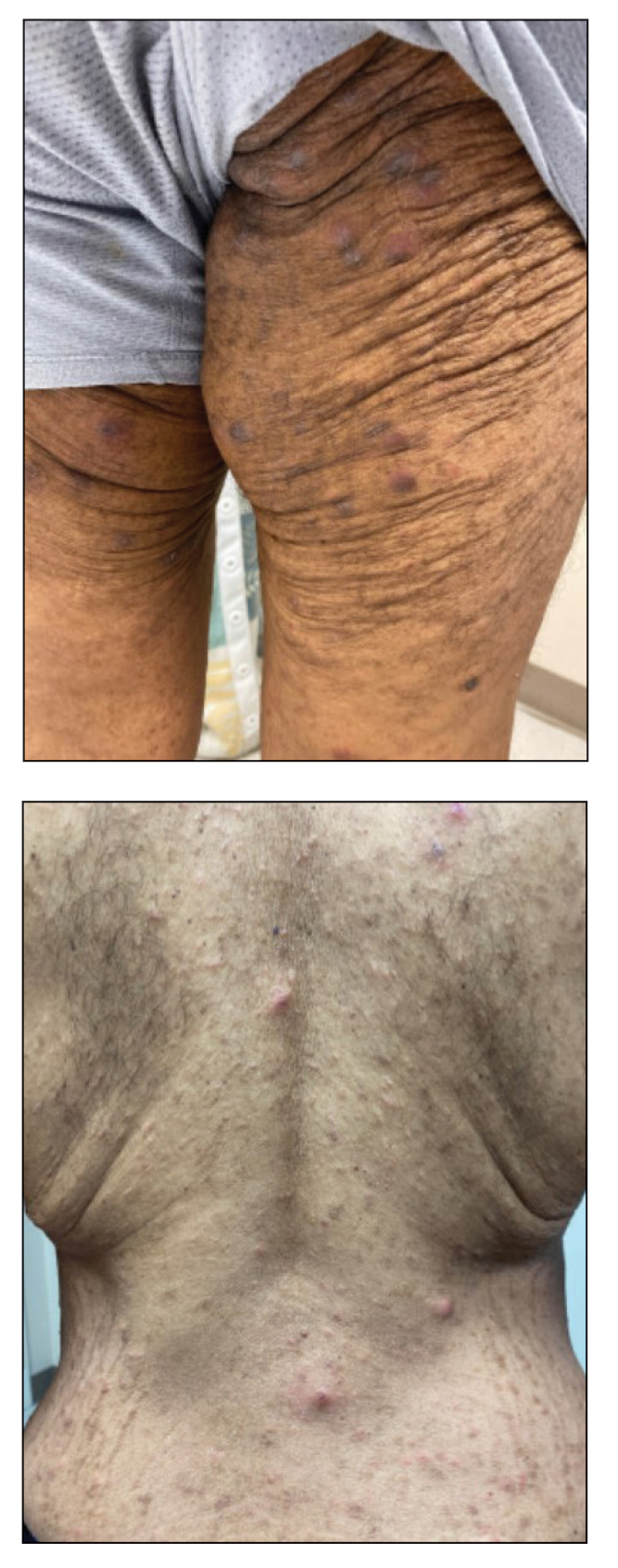
Paxlovid and Lagevrio benefit COVID outpatients in Omicron era
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
The American College of Physicians has issued an updated version of its living, rapid practice point guideline on the best treatment options for outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 in the era of the dominant Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. The recommendations in version 2 apply to persons presenting with mild to moderate infection and symptom onset in the past 5 days who are at high risk for progression to severe disease and potential hospitalization or death.
Version 1 appeared in late 2022.
While outpatient management is appropriate for most patients, treatment should be personalized and based on careful risk stratification and informed decision-making, said the guideline authors, led by Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, MHA, vice president of clinical policy and the Center for Evidence Reviews at the ACP in Philadelphia.
Practice points
- Consider the oral antivirals nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) or molnupiravir (Lagevrio) for symptomatic outpatients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 who are within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
New evidence for the Omicron variant suggests a possible net benefit of the antiviral molnupiravir versus standard or no treatment in terms of reducing recovery time if treatment is initiated within 5 days of symptom onset. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with reductions in COVID-19 hospitalization and all-cause mortality.
“The practice points only address [whether] treatments work compared to placebo, no treatment, or usual care,” cautioned Linda L. Humphrey, MD, MPH, MACP, chair of the ACP’s Population Health and Medical Science Committee and a professor of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University VA Portland Health Care System. The ACP continues to monitor the evidence. “Once enough evidence has emerged, it will be possible to compare treatments to each other. Until that time we are unable to determine if there is an advantage to using one treatment over another.”
- Do not use the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol) or the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab (Xevudy) to treat this patient population. “It is not expected to be effective against the Omicron variant,” Dr. Humphrey said.
There was no evidence to support the use of medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, antihistamines, SSRIs, and multiple other agents.
“The guideline is not a departure from previous knowledge and reflects what appears in other guidelines and is already being done generally in practice,” said Mirella Salvatore, MD, an associate professor of medicine and population health sciences at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, who was not involved in the ACP statement. It is therefore unlikely the recommendations will trigger controversy or negative feedback, added Dr. Salvatore, who is also a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. “We believe that our evidence-based approach, which considers the balance of benefits and harms of various treatments, will be embraced by the physician community,” Dr. Humphrey said.
The updated recommendations are based on new data from the evidence review of multiple treatments, which concluded that both nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and molnupiravir likely improve outcomes for outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19. The review was conducted after the emergence of the Omicron variant by the ACP Center for Evidence Reviews at Cochrane Austria/University for Continuing Education Krems (Austria).
Review details
Inclusion criteria were modified to focus on the Omicron variant by limiting eligible studies to only those enrolling patients on or after Nov. 26, 2021. The investigators included two randomized controlled trials and six retrospective cohort studies and ranked quality of evidence for the effectiveness of the following treatments, compared with usual care or no treatment: azithromycin, camostat mesylate, chloroquine-hydroxychloroquine, chlorpheniramine, colchicine, convalescent plasma, corticosteroids, ensitrelvir, favipiravir, fluvoxamine, ivermectin, lopinavir-ritonavir, molnupiravir, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, metformin, niclosamide, nitazoxanide, nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, and remdesivir.
It compared results for all-cause and COVID-specific mortality, recovery, time to recovery, COVID hospitalization, and adverse and serious adverse events.
Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir was associated with a reduction in hospitalization caused by COVID-19 of 0.7% versus 1.2% (moderate certainty of evidence [COE]) and a reduction in all-cause mortality of less than 0.1% versus 0.2% (moderate COE).
Molnupiravir led to a higher recovery rate of 31.8% versus 22.6% (moderate COE) and a reduced time to recovery of 9 versus 15 median days (moderate COE). It had no effect, however, on all-cause mortality: 0.02% versus 0.04% (moderate COE). Nor did it affect the incidence of serious adverse events: 0.4% versus 0.3% (moderate COE).
“There have been no head-to-head comparative studies of these two treatments, but nirmatrelvir-ritonavir appears to be the preferred treatment,” Dr. Salvatore said. She noted that molnupiravir cannot be used in pregnant women or young persons under age 18, while nirmatrelvir-ritonavir carries the risk of drug interactions. Viral rebound and recurrence of symptoms have been reported in some patients receiving nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
In other review findings, ivermectin had no effect on time to recovery (moderate COE) and adverse events versus placebo (low COE). Sotrovimab resulted in no difference in all-cause mortality, compared with no treatment (low COE). There were no eligible studies for all of the other treatments of interest nor were there any that specifically evaluated the benefits and harms of treatments for the Omicron variant.
The panel pointed to the need for more evaluation of the efficacy, effectiveness, and comparative effectiveness, as well as harms of pharmacologic and biologic treatments of COVID-19 in the outpatient setting, particularly in the context of changing dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants and subvariants.
Another area requiring further research is the effectiveness of retreatment in patients with previous COVID-19 infection. Subgroup analyses are also needed to assess whether the efficacy and effectiveness of outpatient treatments vary by age, sex, socioeconomic status, and comorbid conditions – or by SARS-CoV-2 variant, immunity status (prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination status, or time since infection or vaccination), symptom duration, or disease severity.
Dr. Salvatore agreed that more research is needed in special convalescent groups. “For instance, those with cancer who are immunocompromised may need longer treatment and adjunctive treatment with convalescent plasma. But is difficult to find a large enough study with 5,000 immunocompromised patients.”
Financial support for the development of the practice points came exclusively from the ACP operating budget. The evidence review was funded by the ACP. The authors disclosed no relevant high-level competing interests with regard to this guidance, although several authors reported intellectual interests in various areas of research. Dr. Salvatore disclosed no conflicts of interest relevant to her comments but is engaged in influenza research for Genentech.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
New antibiotic could combat multidrug-resistant superbugs
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health problem. Few new molecules are in development, but a new antibiotic called clovibactin brings hope.
The drug was discovered and has been studied by scientists from Utrecht University in the Netherlands, the University of Bonn in Germany, the German Center for Infection Research, Northeastern University in Boston, and NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals in Cambridge, Mass.
Their research was published in Cell.
“Since clovibactin was isolated from bacteria that could not be grown before, pathogenic bacteria have not seen such an antibiotic before and had no time to develop resistance,” Markus Weingarth, MD, PhD, a researcher in Utrecht University’s chemistry department, said in a press release.
Microbial “dark matter”
Researchers isolated clovibactin from sandy soil from North Carolina and studied it using the iChip device, which was developed in 2015. This technique allowed them to grow “bacterial dark matter,” so-called unculturable bacteria, which compose a group to which 99% of bacteria belong.
This device also paved the way for the discovery of the antibiotic teixobactin in 2020. Teixobactin is effective against gram-positive bacteria and is one of the first truly new antibiotics in decades. Its mechanism of action is like that of clovibactin.
Combats resistant bacteria
In the Cell article, the researchers showed that clovibactin acts via several mechanisms and that it successfully treated mice infected with the superbug Staphylococcus aureus.
Clovibactin exhibited antibacterial activity against a broad range of gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus, daptomycin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus strains, and difficult-to-treat vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and E faecium (vancomycin-resistant enterococci). Escherichia coli was only marginally affected “compared with an outer membrane deficient E. coli WO153 strain, probably reflecting insufficient penetration of the compound,” the authors wrote.
Original mechanism of action
Clovibactin acts not on one but three molecules, all of which are essential to the construction of bacterial walls: C55PP, lipid II, and lipid IIIWTA, which are from different cell wall biosynthetic pathways. Clovibactin binds to the pyrophosphate portion of these precursors.
“Clovibactin wraps around the pyrophosphate like [a] tight glove, like a cage that encloses its target,” said Dr. Weingarth. This is what gives clovibactin its name, which is derived from Greek word klouvi, meaning cage.
The remarkable aspect of clovibactin’s mechanism is that it only binds to the immutable pyrophosphate that is common to cell wall precursors, but it also ignores the variable sugar-peptide part of the targets. The bacteria therefore have a much harder time developing resistance against it. “In fact, we did not observe any resistance to clovibactin in our studies,” Dr. Weingarth confirmed.
Upon binding the target molecules, it self-assembles into large fibrils on the surface of bacterial membranes. These fibrils are stable for a long time and thereby ensure that the target molecules remain sequestered for as long as necessary to kill bacteria.
Few side effects
Because of the mechanism of action of the antibiotic, few side effects are predicted. Indeed, clovibactin targets bacteria cells but not human cells.
“Since these fibrils only form on bacterial membranes and not on human membranes, they are presumably also the reason why clovibactin selectively damages bacterial cells but is not toxic to human cells,” said Dr. Weingarth.
Other studies – in particular, studies in humans – are needed before the antibiotic can be considered a potential treatment. In the meantime, regulations regarding the proper use of antibiotics must continue to be applied to limit antibiotic resistance.
In 2019, 4.95 million deaths worldwide were associated with bacterial antimicrobial resistance, including 1.27 million deaths directly attributable to bacterial antimicrobial resistance. If this trend continues without new medicines becoming available to treat bacterial infections, it is estimated that by 2050, 10 million people will die every year from antimicrobial drug resistance.
This article was translated from the Medscape French Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health problem. Few new molecules are in development, but a new antibiotic called clovibactin brings hope.
The drug was discovered and has been studied by scientists from Utrecht University in the Netherlands, the University of Bonn in Germany, the German Center for Infection Research, Northeastern University in Boston, and NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals in Cambridge, Mass.
Their research was published in Cell.
“Since clovibactin was isolated from bacteria that could not be grown before, pathogenic bacteria have not seen such an antibiotic before and had no time to develop resistance,” Markus Weingarth, MD, PhD, a researcher in Utrecht University’s chemistry department, said in a press release.
Microbial “dark matter”
Researchers isolated clovibactin from sandy soil from North Carolina and studied it using the iChip device, which was developed in 2015. This technique allowed them to grow “bacterial dark matter,” so-called unculturable bacteria, which compose a group to which 99% of bacteria belong.
This device also paved the way for the discovery of the antibiotic teixobactin in 2020. Teixobactin is effective against gram-positive bacteria and is one of the first truly new antibiotics in decades. Its mechanism of action is like that of clovibactin.
Combats resistant bacteria
In the Cell article, the researchers showed that clovibactin acts via several mechanisms and that it successfully treated mice infected with the superbug Staphylococcus aureus.
Clovibactin exhibited antibacterial activity against a broad range of gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus, daptomycin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus strains, and difficult-to-treat vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and E faecium (vancomycin-resistant enterococci). Escherichia coli was only marginally affected “compared with an outer membrane deficient E. coli WO153 strain, probably reflecting insufficient penetration of the compound,” the authors wrote.
Original mechanism of action
Clovibactin acts not on one but three molecules, all of which are essential to the construction of bacterial walls: C55PP, lipid II, and lipid IIIWTA, which are from different cell wall biosynthetic pathways. Clovibactin binds to the pyrophosphate portion of these precursors.
“Clovibactin wraps around the pyrophosphate like [a] tight glove, like a cage that encloses its target,” said Dr. Weingarth. This is what gives clovibactin its name, which is derived from Greek word klouvi, meaning cage.
The remarkable aspect of clovibactin’s mechanism is that it only binds to the immutable pyrophosphate that is common to cell wall precursors, but it also ignores the variable sugar-peptide part of the targets. The bacteria therefore have a much harder time developing resistance against it. “In fact, we did not observe any resistance to clovibactin in our studies,” Dr. Weingarth confirmed.
Upon binding the target molecules, it self-assembles into large fibrils on the surface of bacterial membranes. These fibrils are stable for a long time and thereby ensure that the target molecules remain sequestered for as long as necessary to kill bacteria.
Few side effects
Because of the mechanism of action of the antibiotic, few side effects are predicted. Indeed, clovibactin targets bacteria cells but not human cells.
“Since these fibrils only form on bacterial membranes and not on human membranes, they are presumably also the reason why clovibactin selectively damages bacterial cells but is not toxic to human cells,” said Dr. Weingarth.
Other studies – in particular, studies in humans – are needed before the antibiotic can be considered a potential treatment. In the meantime, regulations regarding the proper use of antibiotics must continue to be applied to limit antibiotic resistance.
In 2019, 4.95 million deaths worldwide were associated with bacterial antimicrobial resistance, including 1.27 million deaths directly attributable to bacterial antimicrobial resistance. If this trend continues without new medicines becoming available to treat bacterial infections, it is estimated that by 2050, 10 million people will die every year from antimicrobial drug resistance.
This article was translated from the Medscape French Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health problem. Few new molecules are in development, but a new antibiotic called clovibactin brings hope.
The drug was discovered and has been studied by scientists from Utrecht University in the Netherlands, the University of Bonn in Germany, the German Center for Infection Research, Northeastern University in Boston, and NovoBiotic Pharmaceuticals in Cambridge, Mass.
Their research was published in Cell.
“Since clovibactin was isolated from bacteria that could not be grown before, pathogenic bacteria have not seen such an antibiotic before and had no time to develop resistance,” Markus Weingarth, MD, PhD, a researcher in Utrecht University’s chemistry department, said in a press release.
Microbial “dark matter”
Researchers isolated clovibactin from sandy soil from North Carolina and studied it using the iChip device, which was developed in 2015. This technique allowed them to grow “bacterial dark matter,” so-called unculturable bacteria, which compose a group to which 99% of bacteria belong.
This device also paved the way for the discovery of the antibiotic teixobactin in 2020. Teixobactin is effective against gram-positive bacteria and is one of the first truly new antibiotics in decades. Its mechanism of action is like that of clovibactin.
Combats resistant bacteria
In the Cell article, the researchers showed that clovibactin acts via several mechanisms and that it successfully treated mice infected with the superbug Staphylococcus aureus.
Clovibactin exhibited antibacterial activity against a broad range of gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus, daptomycin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus strains, and difficult-to-treat vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and E faecium (vancomycin-resistant enterococci). Escherichia coli was only marginally affected “compared with an outer membrane deficient E. coli WO153 strain, probably reflecting insufficient penetration of the compound,” the authors wrote.
Original mechanism of action
Clovibactin acts not on one but three molecules, all of which are essential to the construction of bacterial walls: C55PP, lipid II, and lipid IIIWTA, which are from different cell wall biosynthetic pathways. Clovibactin binds to the pyrophosphate portion of these precursors.
“Clovibactin wraps around the pyrophosphate like [a] tight glove, like a cage that encloses its target,” said Dr. Weingarth. This is what gives clovibactin its name, which is derived from Greek word klouvi, meaning cage.
The remarkable aspect of clovibactin’s mechanism is that it only binds to the immutable pyrophosphate that is common to cell wall precursors, but it also ignores the variable sugar-peptide part of the targets. The bacteria therefore have a much harder time developing resistance against it. “In fact, we did not observe any resistance to clovibactin in our studies,” Dr. Weingarth confirmed.
Upon binding the target molecules, it self-assembles into large fibrils on the surface of bacterial membranes. These fibrils are stable for a long time and thereby ensure that the target molecules remain sequestered for as long as necessary to kill bacteria.
Few side effects
Because of the mechanism of action of the antibiotic, few side effects are predicted. Indeed, clovibactin targets bacteria cells but not human cells.
“Since these fibrils only form on bacterial membranes and not on human membranes, they are presumably also the reason why clovibactin selectively damages bacterial cells but is not toxic to human cells,” said Dr. Weingarth.
Other studies – in particular, studies in humans – are needed before the antibiotic can be considered a potential treatment. In the meantime, regulations regarding the proper use of antibiotics must continue to be applied to limit antibiotic resistance.
In 2019, 4.95 million deaths worldwide were associated with bacterial antimicrobial resistance, including 1.27 million deaths directly attributable to bacterial antimicrobial resistance. If this trend continues without new medicines becoming available to treat bacterial infections, it is estimated that by 2050, 10 million people will die every year from antimicrobial drug resistance.
This article was translated from the Medscape French Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL