User login
Antigen tests: After pandemic success, time for bigger role?
Before the pandemic, most of the public probably had a fleeting and limited familiarity with lateral flow tests (LFTs), also known as rapid antigen tests. Perhaps they used, or awaited the results of, a lateral flow home pregnancy test, which detects human chorionic gonadotropin in urine.
Then came COVID-19, and the need for large-scale testing. By late 2022, more than 3 billion tests for SARS-CoV-2 had been done worldwide. Although testing with reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the gold standard for diagnosing COVID, LFTs made possible large-scale testing at low cost with rapid results.
As of Sept. 12, the Food and Drug Administration lists 32 rapid antigen tests with emergency use authorizations (EUAs) for home use.
Now, many experts conclude, it’s time to expand the role of LFTs so the technology can help detect a host of other diseases. In a Nature Reviews bioengineering report, global experts from the United States, the United Kingdom, and other countries pointed out that commercial LFTs are currently not available for four of the eight known priority diseases of epidemic potential: Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Nipah and other henipaviruses, and Rift Valley fever.
Expansion should not only include more tests for more diseases, some experts say, but also make use of existing technology to provide “full-circle” care. After a rapid test, for instance, users could download a mobile phone app, transmit the results to their health care provider, and then set up an appointment if needed or get a prescribed medication at the pharmacy.
Medical community on board
Clinicians support increased availability of LFTs, said Eric J. Topol, MD, professor and executive vice president of Scripps Research, La Jolla, Calif.“Rapid antigen tests are critical, made a big difference in the pandemic, and will be used increasingly for many other applications in the years ahead,” Dr. Topol said in an email.
Physicians welcome their potential, agreed William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. At the start of the pandemic, when he was briefed about a lateral flow device in development, he said, “I was blown away by the technology, ease of use, rapidity of getting a result, its reasonable accuracy and its anticipated relatively low price.”
Clinicians would probably see many advantages to having more LFTs for more diseases, Dr. Schaffner said, because they are of use not only at home but also in doctors’ offices and in emergency departments. Their increased use “would help [people] make quick decisions about treatment, especially for flu and COVID.”
How LFTs work
LFTs are capable of targeting antigens, such as for the COVID tests, and antibodies such as IgG or IgM. The tests are also capable of detecting nucleic acids, although the availability of these tests is currently rare.
First, a sample from blood, urine, saliva or other bodily sources is placed onto a sample pad. It travels to a conjugate pad containing antibodies. If the target being looked for is present, the target and antibodies bind and, as the sample moves along to the test line, produces a positive result line along with the control line (to show that the test worked).
Global market outlook
By 2030, the lateral flow assays market is predicted to rise to $14.1 billion, according to a report issued in September by the firm Research and Markets. In 2022, the market was estimated at $9.4 billion, with $3.6 billion of that in the United States.
The report details the performances of 55 major competitors, such as Abbott Laboratories, Siemens, and QuidelOrtho, but smaller companies and start-ups are also involved in LFT development.
LFTs: Pros and cons
Although LFTs give rapid results, their accuracy is lower than that of PCR, especially the sensitivity. For COVID antigen LFTs, the sensitivity ranges from 34.1% to 88.1%, with an overall specificity of 99.6%, according to a Cochrane Review report. The analytical sensitivity performance of PCR testing for COVID is near 100%.
Everyone acknowledges the accuracy challenge of LFTs. The technologies “are generally thought to have limitations of detection that for some applications may present a challenge,” said Douglas C. Bryant, president and CEO of QuidelOrtho, San Diego, which counts the QuickVue rapid test for COVID detection among its products.
However, Mr. Bryant added, “as we saw during the pandemic, there was a place for more sensitive PCR-based technologies that are often run in a lab and there was a place for the use of rapid tests: The key is knowing the strengths and best use cases when applying the different technologies.”
One strength, he said, was that the tests “were shown to be highly effective at detecting active, infectious cases of SARS-CoV-2 and the rapid turnaround time allowed patients to isolate themselves from others quickly to help curb the spread of infection to others.” Another advantage was the ability to screen high-risk populations such as nursing homes to detect positive cases and help prevent outbreaks.
The pandemic familiarized people with the tests, said Jeremy Stackawitz, CEO of Senzo, a start-up in vitro diagnostics company developing an amplified LFT platform for rapid tests for flu, tuberculosis, COVID, and Clostridioides difficile. People liked using them. Physicians generally accepted them. It works great with tele-doc. It works great with personalized medicine.
Now, he said, people used to the COVID self-tests are asking: “Where is my strep test? Where is my sexual health test?”
FDA’s perspective on LFTs
The FDA has no one-size-fits-all standard for evaluating LFTs.
“LFTs are evaluated with respect to their individual indications and the pathway under which they are being reviewed,” said James McKinney, an FDA spokesperson. “A performance recommendation for one type of lateral flow test may not be appropriate for another.”
EUAs, such as those given for the COVID at-home tests, require different levels of evidence than traditional premarket review, he said, whether de novo marketing authorization, 510(k) premarket notification, or premarket approval. The EUAs are evaluated with a risk-benefit analysis to speed up the time it takes to make the devices available.
And, Mr. McKinney said, for some devices, the FDA provides recommendations on the expected performance through guidance documents. For instance, for rapid devices developed to detect influenza A virus antigen, the FDA recommends including enough sample to generate sensitivity of greater than 60% and testing at least 50 samples.
LFTs: The potential, the challenges
Mr. Stackawitz predicted that, as more LFT self-tests become available, more people will seek care, just as they did with the COVID rapid tests. A 22-year-old who thinks he has chlamydia may balk at going to a doctor right away. However, “if he can go buy a soda and a test at CVS, it’s different, it really is. With a little anonymity, people will seek care.”
He has a vision shared by other experts: That testing technology will evolve so that after getting the results at home, people would follow through by sending those results to their health care provider and obtaining needed care or medication. In his opinion, this is superior to the traditional way, which often involves visiting a doctor with symptoms, going for tests, waiting for results, and then beginning treatment.
“It would make more sense if you came in knowing your results,” Mr. Stackawitz said. “It’s a much smarter pathway, gives better outcomes for the patient, is much quicker and at much less cost. And it frees up time for doctors. I think most physicians would embrace that.”
Although rapid testing is gaining well-deserved recognition, funding is an issue, according to the Nature Reviews report. Those experts warned that “a reduction in funding for LFT research post COVID-19 may hamper efforts to capitalize on gains in decentralized testing, especially self-testing, which may be critical to address future pandemic threats.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before the pandemic, most of the public probably had a fleeting and limited familiarity with lateral flow tests (LFTs), also known as rapid antigen tests. Perhaps they used, or awaited the results of, a lateral flow home pregnancy test, which detects human chorionic gonadotropin in urine.
Then came COVID-19, and the need for large-scale testing. By late 2022, more than 3 billion tests for SARS-CoV-2 had been done worldwide. Although testing with reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the gold standard for diagnosing COVID, LFTs made possible large-scale testing at low cost with rapid results.
As of Sept. 12, the Food and Drug Administration lists 32 rapid antigen tests with emergency use authorizations (EUAs) for home use.
Now, many experts conclude, it’s time to expand the role of LFTs so the technology can help detect a host of other diseases. In a Nature Reviews bioengineering report, global experts from the United States, the United Kingdom, and other countries pointed out that commercial LFTs are currently not available for four of the eight known priority diseases of epidemic potential: Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Nipah and other henipaviruses, and Rift Valley fever.
Expansion should not only include more tests for more diseases, some experts say, but also make use of existing technology to provide “full-circle” care. After a rapid test, for instance, users could download a mobile phone app, transmit the results to their health care provider, and then set up an appointment if needed or get a prescribed medication at the pharmacy.
Medical community on board
Clinicians support increased availability of LFTs, said Eric J. Topol, MD, professor and executive vice president of Scripps Research, La Jolla, Calif.“Rapid antigen tests are critical, made a big difference in the pandemic, and will be used increasingly for many other applications in the years ahead,” Dr. Topol said in an email.
Physicians welcome their potential, agreed William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. At the start of the pandemic, when he was briefed about a lateral flow device in development, he said, “I was blown away by the technology, ease of use, rapidity of getting a result, its reasonable accuracy and its anticipated relatively low price.”
Clinicians would probably see many advantages to having more LFTs for more diseases, Dr. Schaffner said, because they are of use not only at home but also in doctors’ offices and in emergency departments. Their increased use “would help [people] make quick decisions about treatment, especially for flu and COVID.”
How LFTs work
LFTs are capable of targeting antigens, such as for the COVID tests, and antibodies such as IgG or IgM. The tests are also capable of detecting nucleic acids, although the availability of these tests is currently rare.
First, a sample from blood, urine, saliva or other bodily sources is placed onto a sample pad. It travels to a conjugate pad containing antibodies. If the target being looked for is present, the target and antibodies bind and, as the sample moves along to the test line, produces a positive result line along with the control line (to show that the test worked).
Global market outlook
By 2030, the lateral flow assays market is predicted to rise to $14.1 billion, according to a report issued in September by the firm Research and Markets. In 2022, the market was estimated at $9.4 billion, with $3.6 billion of that in the United States.
The report details the performances of 55 major competitors, such as Abbott Laboratories, Siemens, and QuidelOrtho, but smaller companies and start-ups are also involved in LFT development.
LFTs: Pros and cons
Although LFTs give rapid results, their accuracy is lower than that of PCR, especially the sensitivity. For COVID antigen LFTs, the sensitivity ranges from 34.1% to 88.1%, with an overall specificity of 99.6%, according to a Cochrane Review report. The analytical sensitivity performance of PCR testing for COVID is near 100%.
Everyone acknowledges the accuracy challenge of LFTs. The technologies “are generally thought to have limitations of detection that for some applications may present a challenge,” said Douglas C. Bryant, president and CEO of QuidelOrtho, San Diego, which counts the QuickVue rapid test for COVID detection among its products.
However, Mr. Bryant added, “as we saw during the pandemic, there was a place for more sensitive PCR-based technologies that are often run in a lab and there was a place for the use of rapid tests: The key is knowing the strengths and best use cases when applying the different technologies.”
One strength, he said, was that the tests “were shown to be highly effective at detecting active, infectious cases of SARS-CoV-2 and the rapid turnaround time allowed patients to isolate themselves from others quickly to help curb the spread of infection to others.” Another advantage was the ability to screen high-risk populations such as nursing homes to detect positive cases and help prevent outbreaks.
The pandemic familiarized people with the tests, said Jeremy Stackawitz, CEO of Senzo, a start-up in vitro diagnostics company developing an amplified LFT platform for rapid tests for flu, tuberculosis, COVID, and Clostridioides difficile. People liked using them. Physicians generally accepted them. It works great with tele-doc. It works great with personalized medicine.
Now, he said, people used to the COVID self-tests are asking: “Where is my strep test? Where is my sexual health test?”
FDA’s perspective on LFTs
The FDA has no one-size-fits-all standard for evaluating LFTs.
“LFTs are evaluated with respect to their individual indications and the pathway under which they are being reviewed,” said James McKinney, an FDA spokesperson. “A performance recommendation for one type of lateral flow test may not be appropriate for another.”
EUAs, such as those given for the COVID at-home tests, require different levels of evidence than traditional premarket review, he said, whether de novo marketing authorization, 510(k) premarket notification, or premarket approval. The EUAs are evaluated with a risk-benefit analysis to speed up the time it takes to make the devices available.
And, Mr. McKinney said, for some devices, the FDA provides recommendations on the expected performance through guidance documents. For instance, for rapid devices developed to detect influenza A virus antigen, the FDA recommends including enough sample to generate sensitivity of greater than 60% and testing at least 50 samples.
LFTs: The potential, the challenges
Mr. Stackawitz predicted that, as more LFT self-tests become available, more people will seek care, just as they did with the COVID rapid tests. A 22-year-old who thinks he has chlamydia may balk at going to a doctor right away. However, “if he can go buy a soda and a test at CVS, it’s different, it really is. With a little anonymity, people will seek care.”
He has a vision shared by other experts: That testing technology will evolve so that after getting the results at home, people would follow through by sending those results to their health care provider and obtaining needed care or medication. In his opinion, this is superior to the traditional way, which often involves visiting a doctor with symptoms, going for tests, waiting for results, and then beginning treatment.
“It would make more sense if you came in knowing your results,” Mr. Stackawitz said. “It’s a much smarter pathway, gives better outcomes for the patient, is much quicker and at much less cost. And it frees up time for doctors. I think most physicians would embrace that.”
Although rapid testing is gaining well-deserved recognition, funding is an issue, according to the Nature Reviews report. Those experts warned that “a reduction in funding for LFT research post COVID-19 may hamper efforts to capitalize on gains in decentralized testing, especially self-testing, which may be critical to address future pandemic threats.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before the pandemic, most of the public probably had a fleeting and limited familiarity with lateral flow tests (LFTs), also known as rapid antigen tests. Perhaps they used, or awaited the results of, a lateral flow home pregnancy test, which detects human chorionic gonadotropin in urine.
Then came COVID-19, and the need for large-scale testing. By late 2022, more than 3 billion tests for SARS-CoV-2 had been done worldwide. Although testing with reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the gold standard for diagnosing COVID, LFTs made possible large-scale testing at low cost with rapid results.
As of Sept. 12, the Food and Drug Administration lists 32 rapid antigen tests with emergency use authorizations (EUAs) for home use.
Now, many experts conclude, it’s time to expand the role of LFTs so the technology can help detect a host of other diseases. In a Nature Reviews bioengineering report, global experts from the United States, the United Kingdom, and other countries pointed out that commercial LFTs are currently not available for four of the eight known priority diseases of epidemic potential: Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Nipah and other henipaviruses, and Rift Valley fever.
Expansion should not only include more tests for more diseases, some experts say, but also make use of existing technology to provide “full-circle” care. After a rapid test, for instance, users could download a mobile phone app, transmit the results to their health care provider, and then set up an appointment if needed or get a prescribed medication at the pharmacy.
Medical community on board
Clinicians support increased availability of LFTs, said Eric J. Topol, MD, professor and executive vice president of Scripps Research, La Jolla, Calif.“Rapid antigen tests are critical, made a big difference in the pandemic, and will be used increasingly for many other applications in the years ahead,” Dr. Topol said in an email.
Physicians welcome their potential, agreed William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. At the start of the pandemic, when he was briefed about a lateral flow device in development, he said, “I was blown away by the technology, ease of use, rapidity of getting a result, its reasonable accuracy and its anticipated relatively low price.”
Clinicians would probably see many advantages to having more LFTs for more diseases, Dr. Schaffner said, because they are of use not only at home but also in doctors’ offices and in emergency departments. Their increased use “would help [people] make quick decisions about treatment, especially for flu and COVID.”
How LFTs work
LFTs are capable of targeting antigens, such as for the COVID tests, and antibodies such as IgG or IgM. The tests are also capable of detecting nucleic acids, although the availability of these tests is currently rare.
First, a sample from blood, urine, saliva or other bodily sources is placed onto a sample pad. It travels to a conjugate pad containing antibodies. If the target being looked for is present, the target and antibodies bind and, as the sample moves along to the test line, produces a positive result line along with the control line (to show that the test worked).
Global market outlook
By 2030, the lateral flow assays market is predicted to rise to $14.1 billion, according to a report issued in September by the firm Research and Markets. In 2022, the market was estimated at $9.4 billion, with $3.6 billion of that in the United States.
The report details the performances of 55 major competitors, such as Abbott Laboratories, Siemens, and QuidelOrtho, but smaller companies and start-ups are also involved in LFT development.
LFTs: Pros and cons
Although LFTs give rapid results, their accuracy is lower than that of PCR, especially the sensitivity. For COVID antigen LFTs, the sensitivity ranges from 34.1% to 88.1%, with an overall specificity of 99.6%, according to a Cochrane Review report. The analytical sensitivity performance of PCR testing for COVID is near 100%.
Everyone acknowledges the accuracy challenge of LFTs. The technologies “are generally thought to have limitations of detection that for some applications may present a challenge,” said Douglas C. Bryant, president and CEO of QuidelOrtho, San Diego, which counts the QuickVue rapid test for COVID detection among its products.
However, Mr. Bryant added, “as we saw during the pandemic, there was a place for more sensitive PCR-based technologies that are often run in a lab and there was a place for the use of rapid tests: The key is knowing the strengths and best use cases when applying the different technologies.”
One strength, he said, was that the tests “were shown to be highly effective at detecting active, infectious cases of SARS-CoV-2 and the rapid turnaround time allowed patients to isolate themselves from others quickly to help curb the spread of infection to others.” Another advantage was the ability to screen high-risk populations such as nursing homes to detect positive cases and help prevent outbreaks.
The pandemic familiarized people with the tests, said Jeremy Stackawitz, CEO of Senzo, a start-up in vitro diagnostics company developing an amplified LFT platform for rapid tests for flu, tuberculosis, COVID, and Clostridioides difficile. People liked using them. Physicians generally accepted them. It works great with tele-doc. It works great with personalized medicine.
Now, he said, people used to the COVID self-tests are asking: “Where is my strep test? Where is my sexual health test?”
FDA’s perspective on LFTs
The FDA has no one-size-fits-all standard for evaluating LFTs.
“LFTs are evaluated with respect to their individual indications and the pathway under which they are being reviewed,” said James McKinney, an FDA spokesperson. “A performance recommendation for one type of lateral flow test may not be appropriate for another.”
EUAs, such as those given for the COVID at-home tests, require different levels of evidence than traditional premarket review, he said, whether de novo marketing authorization, 510(k) premarket notification, or premarket approval. The EUAs are evaluated with a risk-benefit analysis to speed up the time it takes to make the devices available.
And, Mr. McKinney said, for some devices, the FDA provides recommendations on the expected performance through guidance documents. For instance, for rapid devices developed to detect influenza A virus antigen, the FDA recommends including enough sample to generate sensitivity of greater than 60% and testing at least 50 samples.
LFTs: The potential, the challenges
Mr. Stackawitz predicted that, as more LFT self-tests become available, more people will seek care, just as they did with the COVID rapid tests. A 22-year-old who thinks he has chlamydia may balk at going to a doctor right away. However, “if he can go buy a soda and a test at CVS, it’s different, it really is. With a little anonymity, people will seek care.”
He has a vision shared by other experts: That testing technology will evolve so that after getting the results at home, people would follow through by sending those results to their health care provider and obtaining needed care or medication. In his opinion, this is superior to the traditional way, which often involves visiting a doctor with symptoms, going for tests, waiting for results, and then beginning treatment.
“It would make more sense if you came in knowing your results,” Mr. Stackawitz said. “It’s a much smarter pathway, gives better outcomes for the patient, is much quicker and at much less cost. And it frees up time for doctors. I think most physicians would embrace that.”
Although rapid testing is gaining well-deserved recognition, funding is an issue, according to the Nature Reviews report. Those experts warned that “a reduction in funding for LFT research post COVID-19 may hamper efforts to capitalize on gains in decentralized testing, especially self-testing, which may be critical to address future pandemic threats.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCPs prep for ‘less predictable’ respiratory virus season
Hospitalizations for COVID-19 in the United States have increased for 8 weeks in a row.
Data from Florida and Georgia signal that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season has begun.
As for flu shots, experts say patients with long COVID should get them in 2023, although federal health agencies have not addressed that specific question.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, an infectious disease consultant, said many patients in his primary care practice worry about “the big three” – COVID, influenza, and RSV.
They discussed how to handle COVID boosters, the use of Paxlovid, vaccine hesitancy, and the correct order of operations for patients getting vaccinated against all three diseases.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, clinical director of the division of infectious diseases and the Sherrilyn and Ken Fisher Professor of Medicine at Johns Hopkins University, BaltimoreQuestion: How should primary care physicians be preparing to handle what everyone is predicting will be a major surge in cases of respiratory infections?
Auwaerter: Although I’m an infectious disease consultant, I still have a small primary care practice. So, I field questions for my patients all the time, and many patients, especially those with health problems, are worried about the big three: RSV, COVID, and influenza – at least, my more motivated patients are.
People frequently ask if they need the COVID booster. I think that’s been something many people think maybe they can avoid. The good news is that the early in vitro data suggest that the XBB1.5x-based vaccine seems to offer sufficient neutralizing activity against the circulating newer variants since the vaccine was approved earlier this year. I am suggesting that everyone get a booster, especially those at high risk, because we know that the risk for hospitalization decreases based on earlier studies for 4-6 months after a COVID booster. We can simultaneously administer the revised COVID booster vaccine and the annual influenza vaccine. The timing is good, as influenza immunization should be accomplished by October or early November at the latest. Like many parts of the country, we in Maryland are in the middle of a COVID boomlet. I have issued more Paxlovid prescriptions since mid-August than I did all spring and early summer.
Q: Are you seeing a lot of rebound COVID in your patients taking Paxlovid [nirmatrelvir/ritonavir]?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think the frequency is probably around 10%. It has been quoted much higher – at 20% – but careful studies have put it down at just single digits. I think it just depends on symptomatology and how you ask the question. But I think it’s important that I try to persuade people to take a direct-acting antiviral if they’re in a high-risk category rather than tough it out. Increasing data suggest taking an antiviral also reduces the risk for long COVID. Also, we know that rebound symptoms are not always infectious virus. Sometimes, they’re just inflammatory. Unless a person is immune suppressed, they rarely have a culturable virus 7-8 days after onset of symptoms. So, for most people, I don’t administer second courses of Paxlovid, although I know some physicians do. One has to realize the risk for hospitalization from a rebound is tiny, and many people don’t even have infectious virus when they take the second course of a drug such as Paxlovid.
Q: You mentioned motivated patients, which seems to be an important factor to consider, particularly for new vaccines.
Dr. Auwaerter: There are always early adopters who are less afraid. And then some people say: This is a brand-new vaccine; I’m going to wait for a year to let this shake out, and make sure it seems safe. People more engaged in their health have asked me about the RSV vaccine. For anyone who has cardiopulmonary problems and other major health problems, I’ve advised it. But if someone’s in good health and 65 or 70, the RSV illness is probably pretty mild if they get it. For them, I would say the vaccine is optional.
For people over 75, I have been advising the RSV vaccine because that is a group we tend to see hospitalized with RSV; they’re the highest-risk group, similar to COVID. The older you are, the more likely this infection will land you in the hospital. You can acquire RSV even if you don’t have young grandchildren around.
Q: You have called respiratory virus seasons unstable? What does it mean, and what is the significance for clinicians?
Dr. Auwaerter: It’s less predictable than in the past. If you had a cough and fever, you could think it was influenza if you knew you had influenza circulating in your community. Maybe you thought about RSV for your immunocompromised or older patients, but we didn’t have any therapy for it anyway. I sometimes refer to the respiratory virus season as a cage match between the major infections. Last year, RSV came out first, and we got some influenza and COVID. What does the situation look like this year? I don’t know at this point, but we are seeing more COVID earlier. What’s different is we continue to have the emergence of viral variants of SARS-CoV-2. Also, with both influenza and COVID, it’s harder to make a clinical judgment about what people have.
I think we have to rely more on tests to treat these patients. Options include having point of care testing in the office for rapid results (molecular assays preferred) for both influenza and SARS-CoV-2 or home antigen testing. There are home kits that do test for both if influenza is known to be circulating significantly in the community. But there are still barriers. For one, COVID and COVID/influenza antigen kits are no longer free, although some health insurance companies do provide COVID kits free of charge. In offices, you don’t want to have ill people with respiratory infections in your waiting room unless you can isolate or have negative pressure rooms. Do you ask for masking in your offices? Telemedicine has been a big help since the pandemic in managing nonsevere respiratory infections at home; however, you must be licensed in the state to practice, which limits helping your out-of-state patients.
Q: How has the advent of in-home antigen tests changed practice?
Dr. Auwaerter: Home antigen tests have been groundbreaking in facilitating care. When I see patients via telemedicine, I don’t want to prescribe medications for influenza and COVID to people simultaneously. I want to pick one or the other – and now I’m able to ask for a COVID test or a COVID/influenza test if the patient or family is able to get a kit. Some offices do have real-time molecular testing, which is the ideal and the CDC-recommended approach, but they’re expensive, and not everyone has access to them.
Q: People talk about the “tripledemic,” but does doing so ignore the fourth horseman of the respiratory apocalypse: pneumococcal pneumonia?
Dr. Auwaerter: Pneumonia remains a leading cause of hospitalization, except we’ve seen much more viral than bacterial pneumonia in recent years of the pandemic. We’ve lost sight, and pneumococcal pneumonia is important, especially in older patients. What we have seen pretty clearly is a rise in group A streptococcal infections. This is another consequence of the pandemic, where people did not socialize for a year or 2. There was much less group A strep infection in younger children, and even in adults, the amount of invasive group A streptococcal infections has clearly taken a jump, according to the NHS in Great Britain. Our pediatric practices here at Johns Hopkins are seeing far more cases of acute rheumatic fever than they’ve seen in decades. And I think, again, this is a consequence of the frequency of group A strep infections definitely taking an uptick. And that was no doubt probably from social mitigation measures and just an interruption in normal circumstances that bacterial and respiratory pathogens tend to circulate and colonize.
Q: Do you have any concerns about immunogenicity or side effects associated with receiving several vaccines at once?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think three injections at once is only for the heroic, and there is actually no guidance for getting all three at the moment. COVID, RSV, and influenza are not live vaccines. I’ve been recommending the new COVID booster and flu together, and then wait 2 weeks and then get RSV or vice-versa. A part of the reason is RSV is new. People have gotten COVID and flu vaccines before; they’re no different than in the past in terms of anticipating adverse effects. But RSV is new, so I’ve usually been recommending that as a standalone to gauge if there are issues as an RSV booster may be recommended at some point down the road.
Q: Unfortunately, some people are going to see or hear misinformation that the COVID boosters have not been properly tested or proven safe. What’s your response to the patient who says something to that effect?
Dr. Auwaerter: My response is, the basic components of the vaccine are the same, right? If you have the mRNA vaccine, you’re getting the vaccine components, the lipids, and the mRNA coding for spike proteins, which has just been modified slightly to adjust to the Omicron subvariant composition. We do the same thing with the influenza vaccine every year, and we don’t see much change in the side effect profile. I think it’s important for my staff in the office and myself to be very comfortable to field questions such as these.
We try to inform all of our staff about a vaccine, especially a new one like RSV, just so they have some comfort level with it, whether they’re getting it or not. Vaccine-hesitant patients need very little to dissuade and to take a pass – to the probable detriment of their health and their family’s health. We know the influenza vaccine helps reduce absenteeism and transmission in addition to reducing serious illness in high-risk patients. Even COVID vaccine efficacy is not as robust as initially reported, falling from 95% to under 70% depending on the study – you are provided with protection against serious illness and hospitalization. The same goes for influenza, and that’s how we try to pitch it to people. Are they going to get the flu? Maybe, but you didn’t land in the hospital. That’s why it’s these vaccines are so important.
Spencer H. Durham, PharmD, associate clinical professor in the department of pharmacy practice at Auburn (Ala.) University, and clinical pharmacist, Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases, at the UAB Heersink School of Medicine in Huntsville.Q: What is known, if anything, about the risks/desirability of giving three vaccinations at once to patients (particularly older patients) – flu, COVID-19 and RSV? Any potential vaccine interactions physicians should know about?
Dr. Durham: There are currently no data about giving all three of these vaccines together at the same time. However, there is both data and practical experience of giving both the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time. The best approach right now for these three vaccines would be to get the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time, then give the RSV vaccine at a different date. In general, they should be separated by about 2 weeks, although it does not matter in what order they are given (that is, patients could get RSV first, then flu/COVID, or they could get flu/COVID first, followed by RSV).
Having said this, there is no theoretical reason why patients couldn’t get all three at once, so if there is only one opportunity to vaccinate a patient, then it would be okay to give all three. But, if the patient can come for two separate visits, the recommendation would currently be to separate these. In the future, there likely will be data on giving all three vaccines at once, so it may not be an issue to administer all three at the same time.
Lastly, I would point out that the RSV vaccine is not necessarily recommended for everyone age 60 and above. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends using shared clinical decision-making to determine if that vaccine is right for the patient. In general, the flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for everyone, although the specific COVID recommendations for fall 2023 have not yet been released. There are no particular vaccine interactions that are concerning with these vaccines.
Q: What if any special considerations are there regarding the storage, handling, and ordering of these vaccines? Should primary care practices take any special steps they might not already be taking?
Dr. Durham: I don’t think there are any special considerations that providers might not already be doing. All of the vaccines do require refrigeration, but each individual product may vary some on beyond-use dates or how long they are good after being reconstituted. All providers administering these vaccines should carefully examine the labeling of each individual product to ensure correct storage and handling. In addition, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has an online toolkit for vaccine storage and handling and can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/admin/storage/toolkit/index.html.
Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion, department of family and community medicine, and associate professor of family and community medicine, Northwestern University, ChicagoQ: What can primary care doctors/family physicians and their staff do to increase patient access to the vaccines? Any lessons learned from the earlier phases of the pandemic that might pertain not only to COVID-19 but also to RSV and/or influenza?
Dr. Wheat: I think the most important thing family physicians can do is speak with their patients about the importance of vaccines and specific recommendations they have for the situations of individuals and families. When vaccines started becoming available, I had many patients who wanted to hear from me – as their primary physician – what I truly thought and what I was planning to do for my own family.
I also think if our teams can know where vaccines are easily accessible, that makes it much easier for our patients. I have heard great stories and seen my own clinical support staff look at websites with patients to help them find the best location to get vaccines. In particular, about the RSV vaccine, I have had a handful of patients already come to ask me about my recommendations. When vaccines are available at my location, I find it much easier for my patients to be willing to get vaccinated. Similarly, if I am sending patients to pick up a prescription and they can get it at the same time, I have found success in them being willing to be vaccinated while picking up their prescription. In both instances, they do not need to make an additional stop; they are just able to be vaccinated while already at the clinic or pharmacy.
Q: Do you see any extra difficulties involved in trying to get groups of patients – in this case, older people – to be receptive to three vaccines, especially in this climate where it appears a growing number of people are hostile to immunization?
Dr. Wheat: Recently, I have found myself negotiating vaccines with patients not just with these, but as recommendations have changed for vaccines such as the pneumococcal vaccines and the hepatitis B vaccines. I think primary care providers can recommend all of them, but still help patients prioritize what is most important for that patient and family. For example, if welcoming a new baby soon, they might prioritize the vaccines for pertussis or influenza over the hepatitis vaccine with a plan to revisit the conversations later.
I have had some patients tell me they have gotten enough vaccines – and we know that even before the pandemic there was resistance to the influenza vaccine for some. I think we need to be prepared to address the concerns and, at times, the apathy. We also need to ask every time, because we never know which visit will be the one when a patient agrees.
Dr. Auwaerter reported financial relationships with Pfizer, Shionogi, Gilead, and Wellstat. Dr. Durham and Dr. Wheat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalizations for COVID-19 in the United States have increased for 8 weeks in a row.
Data from Florida and Georgia signal that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season has begun.
As for flu shots, experts say patients with long COVID should get them in 2023, although federal health agencies have not addressed that specific question.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, an infectious disease consultant, said many patients in his primary care practice worry about “the big three” – COVID, influenza, and RSV.
They discussed how to handle COVID boosters, the use of Paxlovid, vaccine hesitancy, and the correct order of operations for patients getting vaccinated against all three diseases.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, clinical director of the division of infectious diseases and the Sherrilyn and Ken Fisher Professor of Medicine at Johns Hopkins University, BaltimoreQuestion: How should primary care physicians be preparing to handle what everyone is predicting will be a major surge in cases of respiratory infections?
Auwaerter: Although I’m an infectious disease consultant, I still have a small primary care practice. So, I field questions for my patients all the time, and many patients, especially those with health problems, are worried about the big three: RSV, COVID, and influenza – at least, my more motivated patients are.
People frequently ask if they need the COVID booster. I think that’s been something many people think maybe they can avoid. The good news is that the early in vitro data suggest that the XBB1.5x-based vaccine seems to offer sufficient neutralizing activity against the circulating newer variants since the vaccine was approved earlier this year. I am suggesting that everyone get a booster, especially those at high risk, because we know that the risk for hospitalization decreases based on earlier studies for 4-6 months after a COVID booster. We can simultaneously administer the revised COVID booster vaccine and the annual influenza vaccine. The timing is good, as influenza immunization should be accomplished by October or early November at the latest. Like many parts of the country, we in Maryland are in the middle of a COVID boomlet. I have issued more Paxlovid prescriptions since mid-August than I did all spring and early summer.
Q: Are you seeing a lot of rebound COVID in your patients taking Paxlovid [nirmatrelvir/ritonavir]?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think the frequency is probably around 10%. It has been quoted much higher – at 20% – but careful studies have put it down at just single digits. I think it just depends on symptomatology and how you ask the question. But I think it’s important that I try to persuade people to take a direct-acting antiviral if they’re in a high-risk category rather than tough it out. Increasing data suggest taking an antiviral also reduces the risk for long COVID. Also, we know that rebound symptoms are not always infectious virus. Sometimes, they’re just inflammatory. Unless a person is immune suppressed, they rarely have a culturable virus 7-8 days after onset of symptoms. So, for most people, I don’t administer second courses of Paxlovid, although I know some physicians do. One has to realize the risk for hospitalization from a rebound is tiny, and many people don’t even have infectious virus when they take the second course of a drug such as Paxlovid.
Q: You mentioned motivated patients, which seems to be an important factor to consider, particularly for new vaccines.
Dr. Auwaerter: There are always early adopters who are less afraid. And then some people say: This is a brand-new vaccine; I’m going to wait for a year to let this shake out, and make sure it seems safe. People more engaged in their health have asked me about the RSV vaccine. For anyone who has cardiopulmonary problems and other major health problems, I’ve advised it. But if someone’s in good health and 65 or 70, the RSV illness is probably pretty mild if they get it. For them, I would say the vaccine is optional.
For people over 75, I have been advising the RSV vaccine because that is a group we tend to see hospitalized with RSV; they’re the highest-risk group, similar to COVID. The older you are, the more likely this infection will land you in the hospital. You can acquire RSV even if you don’t have young grandchildren around.
Q: You have called respiratory virus seasons unstable? What does it mean, and what is the significance for clinicians?
Dr. Auwaerter: It’s less predictable than in the past. If you had a cough and fever, you could think it was influenza if you knew you had influenza circulating in your community. Maybe you thought about RSV for your immunocompromised or older patients, but we didn’t have any therapy for it anyway. I sometimes refer to the respiratory virus season as a cage match between the major infections. Last year, RSV came out first, and we got some influenza and COVID. What does the situation look like this year? I don’t know at this point, but we are seeing more COVID earlier. What’s different is we continue to have the emergence of viral variants of SARS-CoV-2. Also, with both influenza and COVID, it’s harder to make a clinical judgment about what people have.
I think we have to rely more on tests to treat these patients. Options include having point of care testing in the office for rapid results (molecular assays preferred) for both influenza and SARS-CoV-2 or home antigen testing. There are home kits that do test for both if influenza is known to be circulating significantly in the community. But there are still barriers. For one, COVID and COVID/influenza antigen kits are no longer free, although some health insurance companies do provide COVID kits free of charge. In offices, you don’t want to have ill people with respiratory infections in your waiting room unless you can isolate or have negative pressure rooms. Do you ask for masking in your offices? Telemedicine has been a big help since the pandemic in managing nonsevere respiratory infections at home; however, you must be licensed in the state to practice, which limits helping your out-of-state patients.
Q: How has the advent of in-home antigen tests changed practice?
Dr. Auwaerter: Home antigen tests have been groundbreaking in facilitating care. When I see patients via telemedicine, I don’t want to prescribe medications for influenza and COVID to people simultaneously. I want to pick one or the other – and now I’m able to ask for a COVID test or a COVID/influenza test if the patient or family is able to get a kit. Some offices do have real-time molecular testing, which is the ideal and the CDC-recommended approach, but they’re expensive, and not everyone has access to them.
Q: People talk about the “tripledemic,” but does doing so ignore the fourth horseman of the respiratory apocalypse: pneumococcal pneumonia?
Dr. Auwaerter: Pneumonia remains a leading cause of hospitalization, except we’ve seen much more viral than bacterial pneumonia in recent years of the pandemic. We’ve lost sight, and pneumococcal pneumonia is important, especially in older patients. What we have seen pretty clearly is a rise in group A streptococcal infections. This is another consequence of the pandemic, where people did not socialize for a year or 2. There was much less group A strep infection in younger children, and even in adults, the amount of invasive group A streptococcal infections has clearly taken a jump, according to the NHS in Great Britain. Our pediatric practices here at Johns Hopkins are seeing far more cases of acute rheumatic fever than they’ve seen in decades. And I think, again, this is a consequence of the frequency of group A strep infections definitely taking an uptick. And that was no doubt probably from social mitigation measures and just an interruption in normal circumstances that bacterial and respiratory pathogens tend to circulate and colonize.
Q: Do you have any concerns about immunogenicity or side effects associated with receiving several vaccines at once?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think three injections at once is only for the heroic, and there is actually no guidance for getting all three at the moment. COVID, RSV, and influenza are not live vaccines. I’ve been recommending the new COVID booster and flu together, and then wait 2 weeks and then get RSV or vice-versa. A part of the reason is RSV is new. People have gotten COVID and flu vaccines before; they’re no different than in the past in terms of anticipating adverse effects. But RSV is new, so I’ve usually been recommending that as a standalone to gauge if there are issues as an RSV booster may be recommended at some point down the road.
Q: Unfortunately, some people are going to see or hear misinformation that the COVID boosters have not been properly tested or proven safe. What’s your response to the patient who says something to that effect?
Dr. Auwaerter: My response is, the basic components of the vaccine are the same, right? If you have the mRNA vaccine, you’re getting the vaccine components, the lipids, and the mRNA coding for spike proteins, which has just been modified slightly to adjust to the Omicron subvariant composition. We do the same thing with the influenza vaccine every year, and we don’t see much change in the side effect profile. I think it’s important for my staff in the office and myself to be very comfortable to field questions such as these.
We try to inform all of our staff about a vaccine, especially a new one like RSV, just so they have some comfort level with it, whether they’re getting it or not. Vaccine-hesitant patients need very little to dissuade and to take a pass – to the probable detriment of their health and their family’s health. We know the influenza vaccine helps reduce absenteeism and transmission in addition to reducing serious illness in high-risk patients. Even COVID vaccine efficacy is not as robust as initially reported, falling from 95% to under 70% depending on the study – you are provided with protection against serious illness and hospitalization. The same goes for influenza, and that’s how we try to pitch it to people. Are they going to get the flu? Maybe, but you didn’t land in the hospital. That’s why it’s these vaccines are so important.
Spencer H. Durham, PharmD, associate clinical professor in the department of pharmacy practice at Auburn (Ala.) University, and clinical pharmacist, Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases, at the UAB Heersink School of Medicine in Huntsville.Q: What is known, if anything, about the risks/desirability of giving three vaccinations at once to patients (particularly older patients) – flu, COVID-19 and RSV? Any potential vaccine interactions physicians should know about?
Dr. Durham: There are currently no data about giving all three of these vaccines together at the same time. However, there is both data and practical experience of giving both the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time. The best approach right now for these three vaccines would be to get the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time, then give the RSV vaccine at a different date. In general, they should be separated by about 2 weeks, although it does not matter in what order they are given (that is, patients could get RSV first, then flu/COVID, or they could get flu/COVID first, followed by RSV).
Having said this, there is no theoretical reason why patients couldn’t get all three at once, so if there is only one opportunity to vaccinate a patient, then it would be okay to give all three. But, if the patient can come for two separate visits, the recommendation would currently be to separate these. In the future, there likely will be data on giving all three vaccines at once, so it may not be an issue to administer all three at the same time.
Lastly, I would point out that the RSV vaccine is not necessarily recommended for everyone age 60 and above. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends using shared clinical decision-making to determine if that vaccine is right for the patient. In general, the flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for everyone, although the specific COVID recommendations for fall 2023 have not yet been released. There are no particular vaccine interactions that are concerning with these vaccines.
Q: What if any special considerations are there regarding the storage, handling, and ordering of these vaccines? Should primary care practices take any special steps they might not already be taking?
Dr. Durham: I don’t think there are any special considerations that providers might not already be doing. All of the vaccines do require refrigeration, but each individual product may vary some on beyond-use dates or how long they are good after being reconstituted. All providers administering these vaccines should carefully examine the labeling of each individual product to ensure correct storage and handling. In addition, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has an online toolkit for vaccine storage and handling and can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/admin/storage/toolkit/index.html.
Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion, department of family and community medicine, and associate professor of family and community medicine, Northwestern University, ChicagoQ: What can primary care doctors/family physicians and their staff do to increase patient access to the vaccines? Any lessons learned from the earlier phases of the pandemic that might pertain not only to COVID-19 but also to RSV and/or influenza?
Dr. Wheat: I think the most important thing family physicians can do is speak with their patients about the importance of vaccines and specific recommendations they have for the situations of individuals and families. When vaccines started becoming available, I had many patients who wanted to hear from me – as their primary physician – what I truly thought and what I was planning to do for my own family.
I also think if our teams can know where vaccines are easily accessible, that makes it much easier for our patients. I have heard great stories and seen my own clinical support staff look at websites with patients to help them find the best location to get vaccines. In particular, about the RSV vaccine, I have had a handful of patients already come to ask me about my recommendations. When vaccines are available at my location, I find it much easier for my patients to be willing to get vaccinated. Similarly, if I am sending patients to pick up a prescription and they can get it at the same time, I have found success in them being willing to be vaccinated while picking up their prescription. In both instances, they do not need to make an additional stop; they are just able to be vaccinated while already at the clinic or pharmacy.
Q: Do you see any extra difficulties involved in trying to get groups of patients – in this case, older people – to be receptive to three vaccines, especially in this climate where it appears a growing number of people are hostile to immunization?
Dr. Wheat: Recently, I have found myself negotiating vaccines with patients not just with these, but as recommendations have changed for vaccines such as the pneumococcal vaccines and the hepatitis B vaccines. I think primary care providers can recommend all of them, but still help patients prioritize what is most important for that patient and family. For example, if welcoming a new baby soon, they might prioritize the vaccines for pertussis or influenza over the hepatitis vaccine with a plan to revisit the conversations later.
I have had some patients tell me they have gotten enough vaccines – and we know that even before the pandemic there was resistance to the influenza vaccine for some. I think we need to be prepared to address the concerns and, at times, the apathy. We also need to ask every time, because we never know which visit will be the one when a patient agrees.
Dr. Auwaerter reported financial relationships with Pfizer, Shionogi, Gilead, and Wellstat. Dr. Durham and Dr. Wheat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitalizations for COVID-19 in the United States have increased for 8 weeks in a row.
Data from Florida and Georgia signal that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) season has begun.
As for flu shots, experts say patients with long COVID should get them in 2023, although federal health agencies have not addressed that specific question.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, an infectious disease consultant, said many patients in his primary care practice worry about “the big three” – COVID, influenza, and RSV.
They discussed how to handle COVID boosters, the use of Paxlovid, vaccine hesitancy, and the correct order of operations for patients getting vaccinated against all three diseases.
Paul G. Auwaerter, MD, MBA, clinical director of the division of infectious diseases and the Sherrilyn and Ken Fisher Professor of Medicine at Johns Hopkins University, BaltimoreQuestion: How should primary care physicians be preparing to handle what everyone is predicting will be a major surge in cases of respiratory infections?
Auwaerter: Although I’m an infectious disease consultant, I still have a small primary care practice. So, I field questions for my patients all the time, and many patients, especially those with health problems, are worried about the big three: RSV, COVID, and influenza – at least, my more motivated patients are.
People frequently ask if they need the COVID booster. I think that’s been something many people think maybe they can avoid. The good news is that the early in vitro data suggest that the XBB1.5x-based vaccine seems to offer sufficient neutralizing activity against the circulating newer variants since the vaccine was approved earlier this year. I am suggesting that everyone get a booster, especially those at high risk, because we know that the risk for hospitalization decreases based on earlier studies for 4-6 months after a COVID booster. We can simultaneously administer the revised COVID booster vaccine and the annual influenza vaccine. The timing is good, as influenza immunization should be accomplished by October or early November at the latest. Like many parts of the country, we in Maryland are in the middle of a COVID boomlet. I have issued more Paxlovid prescriptions since mid-August than I did all spring and early summer.
Q: Are you seeing a lot of rebound COVID in your patients taking Paxlovid [nirmatrelvir/ritonavir]?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think the frequency is probably around 10%. It has been quoted much higher – at 20% – but careful studies have put it down at just single digits. I think it just depends on symptomatology and how you ask the question. But I think it’s important that I try to persuade people to take a direct-acting antiviral if they’re in a high-risk category rather than tough it out. Increasing data suggest taking an antiviral also reduces the risk for long COVID. Also, we know that rebound symptoms are not always infectious virus. Sometimes, they’re just inflammatory. Unless a person is immune suppressed, they rarely have a culturable virus 7-8 days after onset of symptoms. So, for most people, I don’t administer second courses of Paxlovid, although I know some physicians do. One has to realize the risk for hospitalization from a rebound is tiny, and many people don’t even have infectious virus when they take the second course of a drug such as Paxlovid.
Q: You mentioned motivated patients, which seems to be an important factor to consider, particularly for new vaccines.
Dr. Auwaerter: There are always early adopters who are less afraid. And then some people say: This is a brand-new vaccine; I’m going to wait for a year to let this shake out, and make sure it seems safe. People more engaged in their health have asked me about the RSV vaccine. For anyone who has cardiopulmonary problems and other major health problems, I’ve advised it. But if someone’s in good health and 65 or 70, the RSV illness is probably pretty mild if they get it. For them, I would say the vaccine is optional.
For people over 75, I have been advising the RSV vaccine because that is a group we tend to see hospitalized with RSV; they’re the highest-risk group, similar to COVID. The older you are, the more likely this infection will land you in the hospital. You can acquire RSV even if you don’t have young grandchildren around.
Q: You have called respiratory virus seasons unstable? What does it mean, and what is the significance for clinicians?
Dr. Auwaerter: It’s less predictable than in the past. If you had a cough and fever, you could think it was influenza if you knew you had influenza circulating in your community. Maybe you thought about RSV for your immunocompromised or older patients, but we didn’t have any therapy for it anyway. I sometimes refer to the respiratory virus season as a cage match between the major infections. Last year, RSV came out first, and we got some influenza and COVID. What does the situation look like this year? I don’t know at this point, but we are seeing more COVID earlier. What’s different is we continue to have the emergence of viral variants of SARS-CoV-2. Also, with both influenza and COVID, it’s harder to make a clinical judgment about what people have.
I think we have to rely more on tests to treat these patients. Options include having point of care testing in the office for rapid results (molecular assays preferred) for both influenza and SARS-CoV-2 or home antigen testing. There are home kits that do test for both if influenza is known to be circulating significantly in the community. But there are still barriers. For one, COVID and COVID/influenza antigen kits are no longer free, although some health insurance companies do provide COVID kits free of charge. In offices, you don’t want to have ill people with respiratory infections in your waiting room unless you can isolate or have negative pressure rooms. Do you ask for masking in your offices? Telemedicine has been a big help since the pandemic in managing nonsevere respiratory infections at home; however, you must be licensed in the state to practice, which limits helping your out-of-state patients.
Q: How has the advent of in-home antigen tests changed practice?
Dr. Auwaerter: Home antigen tests have been groundbreaking in facilitating care. When I see patients via telemedicine, I don’t want to prescribe medications for influenza and COVID to people simultaneously. I want to pick one or the other – and now I’m able to ask for a COVID test or a COVID/influenza test if the patient or family is able to get a kit. Some offices do have real-time molecular testing, which is the ideal and the CDC-recommended approach, but they’re expensive, and not everyone has access to them.
Q: People talk about the “tripledemic,” but does doing so ignore the fourth horseman of the respiratory apocalypse: pneumococcal pneumonia?
Dr. Auwaerter: Pneumonia remains a leading cause of hospitalization, except we’ve seen much more viral than bacterial pneumonia in recent years of the pandemic. We’ve lost sight, and pneumococcal pneumonia is important, especially in older patients. What we have seen pretty clearly is a rise in group A streptococcal infections. This is another consequence of the pandemic, where people did not socialize for a year or 2. There was much less group A strep infection in younger children, and even in adults, the amount of invasive group A streptococcal infections has clearly taken a jump, according to the NHS in Great Britain. Our pediatric practices here at Johns Hopkins are seeing far more cases of acute rheumatic fever than they’ve seen in decades. And I think, again, this is a consequence of the frequency of group A strep infections definitely taking an uptick. And that was no doubt probably from social mitigation measures and just an interruption in normal circumstances that bacterial and respiratory pathogens tend to circulate and colonize.
Q: Do you have any concerns about immunogenicity or side effects associated with receiving several vaccines at once?
Dr. Auwaerter: I think three injections at once is only for the heroic, and there is actually no guidance for getting all three at the moment. COVID, RSV, and influenza are not live vaccines. I’ve been recommending the new COVID booster and flu together, and then wait 2 weeks and then get RSV or vice-versa. A part of the reason is RSV is new. People have gotten COVID and flu vaccines before; they’re no different than in the past in terms of anticipating adverse effects. But RSV is new, so I’ve usually been recommending that as a standalone to gauge if there are issues as an RSV booster may be recommended at some point down the road.
Q: Unfortunately, some people are going to see or hear misinformation that the COVID boosters have not been properly tested or proven safe. What’s your response to the patient who says something to that effect?
Dr. Auwaerter: My response is, the basic components of the vaccine are the same, right? If you have the mRNA vaccine, you’re getting the vaccine components, the lipids, and the mRNA coding for spike proteins, which has just been modified slightly to adjust to the Omicron subvariant composition. We do the same thing with the influenza vaccine every year, and we don’t see much change in the side effect profile. I think it’s important for my staff in the office and myself to be very comfortable to field questions such as these.
We try to inform all of our staff about a vaccine, especially a new one like RSV, just so they have some comfort level with it, whether they’re getting it or not. Vaccine-hesitant patients need very little to dissuade and to take a pass – to the probable detriment of their health and their family’s health. We know the influenza vaccine helps reduce absenteeism and transmission in addition to reducing serious illness in high-risk patients. Even COVID vaccine efficacy is not as robust as initially reported, falling from 95% to under 70% depending on the study – you are provided with protection against serious illness and hospitalization. The same goes for influenza, and that’s how we try to pitch it to people. Are they going to get the flu? Maybe, but you didn’t land in the hospital. That’s why it’s these vaccines are so important.
Spencer H. Durham, PharmD, associate clinical professor in the department of pharmacy practice at Auburn (Ala.) University, and clinical pharmacist, Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases, at the UAB Heersink School of Medicine in Huntsville.Q: What is known, if anything, about the risks/desirability of giving three vaccinations at once to patients (particularly older patients) – flu, COVID-19 and RSV? Any potential vaccine interactions physicians should know about?
Dr. Durham: There are currently no data about giving all three of these vaccines together at the same time. However, there is both data and practical experience of giving both the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time. The best approach right now for these three vaccines would be to get the flu and COVID vaccines at the same time, then give the RSV vaccine at a different date. In general, they should be separated by about 2 weeks, although it does not matter in what order they are given (that is, patients could get RSV first, then flu/COVID, or they could get flu/COVID first, followed by RSV).
Having said this, there is no theoretical reason why patients couldn’t get all three at once, so if there is only one opportunity to vaccinate a patient, then it would be okay to give all three. But, if the patient can come for two separate visits, the recommendation would currently be to separate these. In the future, there likely will be data on giving all three vaccines at once, so it may not be an issue to administer all three at the same time.
Lastly, I would point out that the RSV vaccine is not necessarily recommended for everyone age 60 and above. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends using shared clinical decision-making to determine if that vaccine is right for the patient. In general, the flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for everyone, although the specific COVID recommendations for fall 2023 have not yet been released. There are no particular vaccine interactions that are concerning with these vaccines.
Q: What if any special considerations are there regarding the storage, handling, and ordering of these vaccines? Should primary care practices take any special steps they might not already be taking?
Dr. Durham: I don’t think there are any special considerations that providers might not already be doing. All of the vaccines do require refrigeration, but each individual product may vary some on beyond-use dates or how long they are good after being reconstituted. All providers administering these vaccines should carefully examine the labeling of each individual product to ensure correct storage and handling. In addition, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has an online toolkit for vaccine storage and handling and can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/admin/storage/toolkit/index.html.
Santina J. G. Wheat, MD, MPH, vice chair of diversity, equity, and inclusion, department of family and community medicine, and associate professor of family and community medicine, Northwestern University, ChicagoQ: What can primary care doctors/family physicians and their staff do to increase patient access to the vaccines? Any lessons learned from the earlier phases of the pandemic that might pertain not only to COVID-19 but also to RSV and/or influenza?
Dr. Wheat: I think the most important thing family physicians can do is speak with their patients about the importance of vaccines and specific recommendations they have for the situations of individuals and families. When vaccines started becoming available, I had many patients who wanted to hear from me – as their primary physician – what I truly thought and what I was planning to do for my own family.
I also think if our teams can know where vaccines are easily accessible, that makes it much easier for our patients. I have heard great stories and seen my own clinical support staff look at websites with patients to help them find the best location to get vaccines. In particular, about the RSV vaccine, I have had a handful of patients already come to ask me about my recommendations. When vaccines are available at my location, I find it much easier for my patients to be willing to get vaccinated. Similarly, if I am sending patients to pick up a prescription and they can get it at the same time, I have found success in them being willing to be vaccinated while picking up their prescription. In both instances, they do not need to make an additional stop; they are just able to be vaccinated while already at the clinic or pharmacy.
Q: Do you see any extra difficulties involved in trying to get groups of patients – in this case, older people – to be receptive to three vaccines, especially in this climate where it appears a growing number of people are hostile to immunization?
Dr. Wheat: Recently, I have found myself negotiating vaccines with patients not just with these, but as recommendations have changed for vaccines such as the pneumococcal vaccines and the hepatitis B vaccines. I think primary care providers can recommend all of them, but still help patients prioritize what is most important for that patient and family. For example, if welcoming a new baby soon, they might prioritize the vaccines for pertussis or influenza over the hepatitis vaccine with a plan to revisit the conversations later.
I have had some patients tell me they have gotten enough vaccines – and we know that even before the pandemic there was resistance to the influenza vaccine for some. I think we need to be prepared to address the concerns and, at times, the apathy. We also need to ask every time, because we never know which visit will be the one when a patient agrees.
Dr. Auwaerter reported financial relationships with Pfizer, Shionogi, Gilead, and Wellstat. Dr. Durham and Dr. Wheat disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SGLT2 inhibitors: No benefit or harm in hospitalized COVID-19
A new meta-analysis has shown that SGLT2 inhibitors do not lead to lower 28-day all-cause mortality, compared with usual care or placebo, in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
However, no major safety issues were identified with the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in these acutely ill patients, the researchers report.
“While these findings do not support the use of SGLT2-inhibitors as standard of care for patients hospitalized with COVID-19, I think the most important take home message here is that the use of these medications appears to be safe even in really acutely ill hospitalized patients,” lead investigator of the meta-analysis, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., concluded.
He said this was important because the list of indications for SGLT2 inhibitors is rapidly growing.
“These medications are being used in more and more patients. And we know that when we discontinue medications in the hospital they frequently don’t get restarted, which can lead to real risks if SGLT2 inhibitors are stopped in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes. So, ,” he added.
The new meta-analysis was presented at the recent annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, held in Amsterdam.
Discussant of the presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, agreed with Dr. Kosiborod’s interpretation.
“Until today we have had very limited information on the safety of SGLT2-inhibitors in acute illness, as the pivotal trials which established the use of these drugs in diabetes and chronic kidney disease largely excluded patients who were hospitalized,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“While the overall results of this meta-analysis are neutral and SGLT2 inhibitors will not be added as drugs to be used in the primary care of patients with COVID-19, it certainly sends a strong message of safety in acutely ill patients,” he added.
Dr. Vaduganathan explained that from the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was great interest in repurposing established therapies for alternative indications for their use in the management of COVID-19.
“Conditions that strongly predispose to adverse COVID outcomes strongly overlap with established indications for SGLT2-inhibitors. So many wondered whether these drugs may be an ideal treatment candidate for the management of COVID-19. However, there have been many safety concerns about the use of SGLT2-inhibitors in this acute setting, with worries that they may induce hemodynamic changes such an excessive lowering of blood pressure, or metabolic changes such as ketoacidosis in acutely ill patients,” he noted.
The initial DARE-19 study investigating SGLT2-inhibitors in COVID-19, with 1,250 participants, found a 20% reduction in the primary outcome of organ dysfunction or death, but this did not reach statistical significance, and no safety issues were seen. This “intriguing” result led to two further larger trials – the ACTIV-4a and RECOVERY trials, Dr. Vaduganathan reported.
“Those early signals of benefit seen in DARE-19 were largely not substantiated in the ACTIV-4A and RECOVERY trials, or in this new meta-analysis, and now we have this much larger body of evidence and more stable estimates about the efficacy of these drugs in acutely ill COVID-19 patients,” he said.
“But the story that we will all take forward is one of safety. This set of trials was arguably conducted in some of the sickest patients we’ve seen who have been exposed to SGLT2-inhibitors, and they strongly affirm that these agents can be safely continued in the setting of acute illness, with very low rates of ketoacidosis and kidney injury, and there was no prolongation of hospital stay,” he commented.
In his presentation, Dr. Kosiborod explained that treatments targeting COVID-19 pathobiology such as dysregulated immune responses, endothelial damage, microvascular thrombosis, and inflammation have been shown to improve the key outcomes in this patient group.
SGLT2 inhibitors, which modulate similar pathobiology, provide cardiovascular protection and prevent the progression of kidney disease in patients at risk for these events, including those with type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and kidney disease, and may also lead to organ protection in a setting of acute illness such as COVID-19, he noted. However, the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 remains uncertain.
To address the need for more definitive efficacy data, the World Health Organization Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group conducted a prospective meta-analysis using data from the three randomized controlled trials, DARE-19, RECOVERY, and ACTIV-4a, evaluating SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Overall, these trials randomized 6,096 participants: 3,025 to SGLT2 inhibitors and 3,071 to usual care or placebo. The average age of participants ranged between 62 and 73 years across the trials, 39% were women, and 25% had type 2 diabetes.
By 28 days after randomization, all-cause mortality, the primary endpoint, had occurred in 11.6% of the SGLT2-inhibitor patients, compared with 12.4% of those randomized to usual care or placebo, giving an odds ratio of 0.93 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.08; P = .33) for SGLT2 inhibitors, with consistency across trials.
Data on in-hospital and 90-day all-cause mortality were only available for two out of three trials (DARE-19 and ACTIV-4a), but the results were similar to the primary endpoint showing nonsignificant trends toward a possible benefit in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
The results were also similar for the secondary outcomes of progression to acute kidney injury or requirement for dialysis or death, and progression to invasive mechanical ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or death, both assessed at 28 days.
The primary safety outcome of ketoacidosis by 28 days was observed in seven and two patients allocated to SGLT2 inhibitors and usual care or placebo, respectively, and overall, the incidence of reported serious adverse events was balanced between treatment groups.
The RECOVERY trial was supported by grants to the University of Oxford from UK Research and Innovation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Wellcome. The ACTIV-4a platform was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. DARE-19 was an investigator-initiated collaborative trial supported by AstraZeneca. Dr. Kosiborod reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new meta-analysis has shown that SGLT2 inhibitors do not lead to lower 28-day all-cause mortality, compared with usual care or placebo, in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
However, no major safety issues were identified with the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in these acutely ill patients, the researchers report.
“While these findings do not support the use of SGLT2-inhibitors as standard of care for patients hospitalized with COVID-19, I think the most important take home message here is that the use of these medications appears to be safe even in really acutely ill hospitalized patients,” lead investigator of the meta-analysis, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., concluded.
He said this was important because the list of indications for SGLT2 inhibitors is rapidly growing.
“These medications are being used in more and more patients. And we know that when we discontinue medications in the hospital they frequently don’t get restarted, which can lead to real risks if SGLT2 inhibitors are stopped in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes. So, ,” he added.
The new meta-analysis was presented at the recent annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, held in Amsterdam.
Discussant of the presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, agreed with Dr. Kosiborod’s interpretation.
“Until today we have had very limited information on the safety of SGLT2-inhibitors in acute illness, as the pivotal trials which established the use of these drugs in diabetes and chronic kidney disease largely excluded patients who were hospitalized,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“While the overall results of this meta-analysis are neutral and SGLT2 inhibitors will not be added as drugs to be used in the primary care of patients with COVID-19, it certainly sends a strong message of safety in acutely ill patients,” he added.
Dr. Vaduganathan explained that from the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was great interest in repurposing established therapies for alternative indications for their use in the management of COVID-19.
“Conditions that strongly predispose to adverse COVID outcomes strongly overlap with established indications for SGLT2-inhibitors. So many wondered whether these drugs may be an ideal treatment candidate for the management of COVID-19. However, there have been many safety concerns about the use of SGLT2-inhibitors in this acute setting, with worries that they may induce hemodynamic changes such an excessive lowering of blood pressure, or metabolic changes such as ketoacidosis in acutely ill patients,” he noted.
The initial DARE-19 study investigating SGLT2-inhibitors in COVID-19, with 1,250 participants, found a 20% reduction in the primary outcome of organ dysfunction or death, but this did not reach statistical significance, and no safety issues were seen. This “intriguing” result led to two further larger trials – the ACTIV-4a and RECOVERY trials, Dr. Vaduganathan reported.
“Those early signals of benefit seen in DARE-19 were largely not substantiated in the ACTIV-4A and RECOVERY trials, or in this new meta-analysis, and now we have this much larger body of evidence and more stable estimates about the efficacy of these drugs in acutely ill COVID-19 patients,” he said.
“But the story that we will all take forward is one of safety. This set of trials was arguably conducted in some of the sickest patients we’ve seen who have been exposed to SGLT2-inhibitors, and they strongly affirm that these agents can be safely continued in the setting of acute illness, with very low rates of ketoacidosis and kidney injury, and there was no prolongation of hospital stay,” he commented.
In his presentation, Dr. Kosiborod explained that treatments targeting COVID-19 pathobiology such as dysregulated immune responses, endothelial damage, microvascular thrombosis, and inflammation have been shown to improve the key outcomes in this patient group.
SGLT2 inhibitors, which modulate similar pathobiology, provide cardiovascular protection and prevent the progression of kidney disease in patients at risk for these events, including those with type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and kidney disease, and may also lead to organ protection in a setting of acute illness such as COVID-19, he noted. However, the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 remains uncertain.
To address the need for more definitive efficacy data, the World Health Organization Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group conducted a prospective meta-analysis using data from the three randomized controlled trials, DARE-19, RECOVERY, and ACTIV-4a, evaluating SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Overall, these trials randomized 6,096 participants: 3,025 to SGLT2 inhibitors and 3,071 to usual care or placebo. The average age of participants ranged between 62 and 73 years across the trials, 39% were women, and 25% had type 2 diabetes.
By 28 days after randomization, all-cause mortality, the primary endpoint, had occurred in 11.6% of the SGLT2-inhibitor patients, compared with 12.4% of those randomized to usual care or placebo, giving an odds ratio of 0.93 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.08; P = .33) for SGLT2 inhibitors, with consistency across trials.
Data on in-hospital and 90-day all-cause mortality were only available for two out of three trials (DARE-19 and ACTIV-4a), but the results were similar to the primary endpoint showing nonsignificant trends toward a possible benefit in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
The results were also similar for the secondary outcomes of progression to acute kidney injury or requirement for dialysis or death, and progression to invasive mechanical ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or death, both assessed at 28 days.
The primary safety outcome of ketoacidosis by 28 days was observed in seven and two patients allocated to SGLT2 inhibitors and usual care or placebo, respectively, and overall, the incidence of reported serious adverse events was balanced between treatment groups.
The RECOVERY trial was supported by grants to the University of Oxford from UK Research and Innovation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Wellcome. The ACTIV-4a platform was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. DARE-19 was an investigator-initiated collaborative trial supported by AstraZeneca. Dr. Kosiborod reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new meta-analysis has shown that SGLT2 inhibitors do not lead to lower 28-day all-cause mortality, compared with usual care or placebo, in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
However, no major safety issues were identified with the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in these acutely ill patients, the researchers report.
“While these findings do not support the use of SGLT2-inhibitors as standard of care for patients hospitalized with COVID-19, I think the most important take home message here is that the use of these medications appears to be safe even in really acutely ill hospitalized patients,” lead investigator of the meta-analysis, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., concluded.
He said this was important because the list of indications for SGLT2 inhibitors is rapidly growing.
“These medications are being used in more and more patients. And we know that when we discontinue medications in the hospital they frequently don’t get restarted, which can lead to real risks if SGLT2 inhibitors are stopped in patients with heart failure, chronic kidney disease, or diabetes. So, ,” he added.
The new meta-analysis was presented at the recent annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, held in Amsterdam.
Discussant of the presentation at the ESC Hotline session, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, agreed with Dr. Kosiborod’s interpretation.
“Until today we have had very limited information on the safety of SGLT2-inhibitors in acute illness, as the pivotal trials which established the use of these drugs in diabetes and chronic kidney disease largely excluded patients who were hospitalized,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“While the overall results of this meta-analysis are neutral and SGLT2 inhibitors will not be added as drugs to be used in the primary care of patients with COVID-19, it certainly sends a strong message of safety in acutely ill patients,” he added.
Dr. Vaduganathan explained that from the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was great interest in repurposing established therapies for alternative indications for their use in the management of COVID-19.
“Conditions that strongly predispose to adverse COVID outcomes strongly overlap with established indications for SGLT2-inhibitors. So many wondered whether these drugs may be an ideal treatment candidate for the management of COVID-19. However, there have been many safety concerns about the use of SGLT2-inhibitors in this acute setting, with worries that they may induce hemodynamic changes such an excessive lowering of blood pressure, or metabolic changes such as ketoacidosis in acutely ill patients,” he noted.
The initial DARE-19 study investigating SGLT2-inhibitors in COVID-19, with 1,250 participants, found a 20% reduction in the primary outcome of organ dysfunction or death, but this did not reach statistical significance, and no safety issues were seen. This “intriguing” result led to two further larger trials – the ACTIV-4a and RECOVERY trials, Dr. Vaduganathan reported.
“Those early signals of benefit seen in DARE-19 were largely not substantiated in the ACTIV-4A and RECOVERY trials, or in this new meta-analysis, and now we have this much larger body of evidence and more stable estimates about the efficacy of these drugs in acutely ill COVID-19 patients,” he said.
“But the story that we will all take forward is one of safety. This set of trials was arguably conducted in some of the sickest patients we’ve seen who have been exposed to SGLT2-inhibitors, and they strongly affirm that these agents can be safely continued in the setting of acute illness, with very low rates of ketoacidosis and kidney injury, and there was no prolongation of hospital stay,” he commented.
In his presentation, Dr. Kosiborod explained that treatments targeting COVID-19 pathobiology such as dysregulated immune responses, endothelial damage, microvascular thrombosis, and inflammation have been shown to improve the key outcomes in this patient group.
SGLT2 inhibitors, which modulate similar pathobiology, provide cardiovascular protection and prevent the progression of kidney disease in patients at risk for these events, including those with type 2 diabetes, heart failure, and kidney disease, and may also lead to organ protection in a setting of acute illness such as COVID-19, he noted. However, the role of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 remains uncertain.
To address the need for more definitive efficacy data, the World Health Organization Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group conducted a prospective meta-analysis using data from the three randomized controlled trials, DARE-19, RECOVERY, and ACTIV-4a, evaluating SGLT2 inhibitors in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Overall, these trials randomized 6,096 participants: 3,025 to SGLT2 inhibitors and 3,071 to usual care or placebo. The average age of participants ranged between 62 and 73 years across the trials, 39% were women, and 25% had type 2 diabetes.
By 28 days after randomization, all-cause mortality, the primary endpoint, had occurred in 11.6% of the SGLT2-inhibitor patients, compared with 12.4% of those randomized to usual care or placebo, giving an odds ratio of 0.93 (95% confidence interval, 0.79-1.08; P = .33) for SGLT2 inhibitors, with consistency across trials.
Data on in-hospital and 90-day all-cause mortality were only available for two out of three trials (DARE-19 and ACTIV-4a), but the results were similar to the primary endpoint showing nonsignificant trends toward a possible benefit in the SGLT2-inhibitor group.
The results were also similar for the secondary outcomes of progression to acute kidney injury or requirement for dialysis or death, and progression to invasive mechanical ventilation, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or death, both assessed at 28 days.
The primary safety outcome of ketoacidosis by 28 days was observed in seven and two patients allocated to SGLT2 inhibitors and usual care or placebo, respectively, and overall, the incidence of reported serious adverse events was balanced between treatment groups.
The RECOVERY trial was supported by grants to the University of Oxford from UK Research and Innovation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research, and Wellcome. The ACTIV-4a platform was sponsored by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. DARE-19 was an investigator-initiated collaborative trial supported by AstraZeneca. Dr. Kosiborod reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2023
Bad blood: Could brain bleeds be contagious?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
How do you tell if a condition is caused by an infection?
It seems like an obvious question, right? In the post–van Leeuwenhoek era we can look at whatever part of the body is diseased under a microscope and see microbes – you know, the usual suspects.
Except when we can’t. And there are plenty of cases where we can’t: where the microbe is too small to be seen without more advanced imaging techniques, like with viruses; or when the pathogen is sparsely populated or hard to culture, like Mycobacterium.
Finding out that a condition is the result of an infection is not only an exercise for 19th century physicians. After all, it was 2008 when Barry Marshall and Robin Warren won their Nobel Prize for proving that stomach ulcers, long thought to be due to “stress,” were actually caused by a tiny microbe called Helicobacter pylori.
And this week, we are looking at a study which, once again, begins to suggest that a condition thought to be more or less random – cerebral amyloid angiopathy – may actually be the result of an infectious disease.
We’re talking about this paper, appearing in JAMA, which is just a great example of old-fashioned shoe-leather epidemiology. But let’s get up to speed on cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) first.
CAA is characterized by the deposition of amyloid protein in the brain. While there are some genetic causes, they are quite rare, and most cases are thought to be idiopathic. Recent analyses suggest that somewhere between 5% and 7% of cognitively normal older adults have CAA, but the rate is much higher among those with intracerebral hemorrhage – brain bleeds. In fact, CAA is the second-most common cause of bleeding in the brain, second only to severe hypertension.
An article in Nature highlights cases that seemed to develop after the administration of cadaveric pituitary hormone.
Other studies have shown potential transmission via dura mater grafts and neurosurgical instruments. But despite those clues, no infectious organism has been identified. Some have suggested that the long latent period and difficulty of finding a responsible microbe points to a prion-like disease not yet known. But these studies are more or less case series. The new JAMA paper gives us, if not a smoking gun, a pretty decent set of fingerprints.
Here’s the idea: If CAA is caused by some infectious agent, it may be transmitted in the blood. We know that a decent percentage of people who have spontaneous brain bleeds have CAA. If those people donated blood in the past, maybe the people who received that blood would be at risk for brain bleeds too.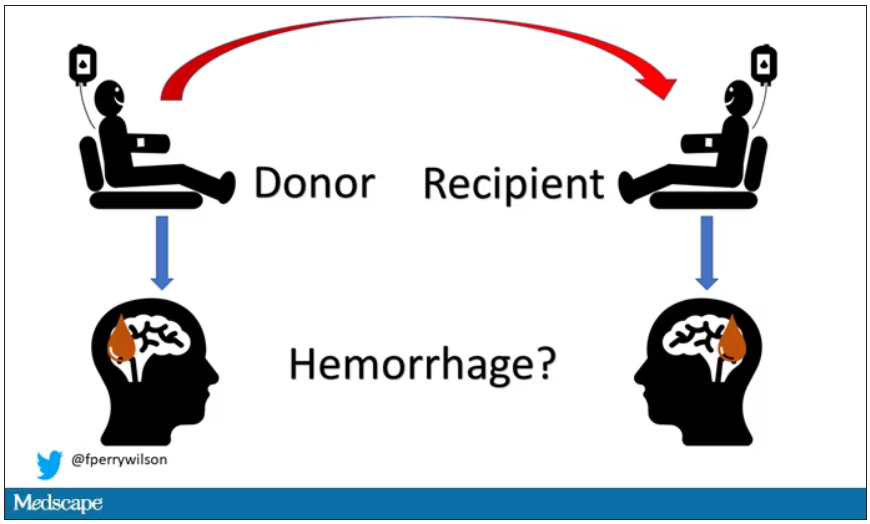
Of course, to really test that hypothesis, you’d need to know who every blood donor in a country was and every person who received that blood and all their subsequent diagnoses for basically their entire lives. No one has that kind of data, right?
Well, if you’ve been watching this space, you’ll know that a few countries do. Enter Sweden and Denmark, with their national electronic health record that captures all of this information, and much more, on every single person who lives or has lived in those countries since before 1970. Unbelievable.
So that’s exactly what the researchers, led by Jingchen Zhao at Karolinska (Sweden) University, did. They identified roughly 760,000 individuals in Sweden and 330,000 people in Denmark who had received a blood transfusion between 1970 and 2017.
Of course, most of those blood donors – 99% of them, actually – never went on to have any bleeding in the brain. It is a rare thing, fortunately.
But some of the donors did, on average within about 5 years of the time they donated blood. The researchers characterized each donor as either never having a brain bleed, having a single bleed, or having multiple bleeds. The latter is most strongly associated with CAA.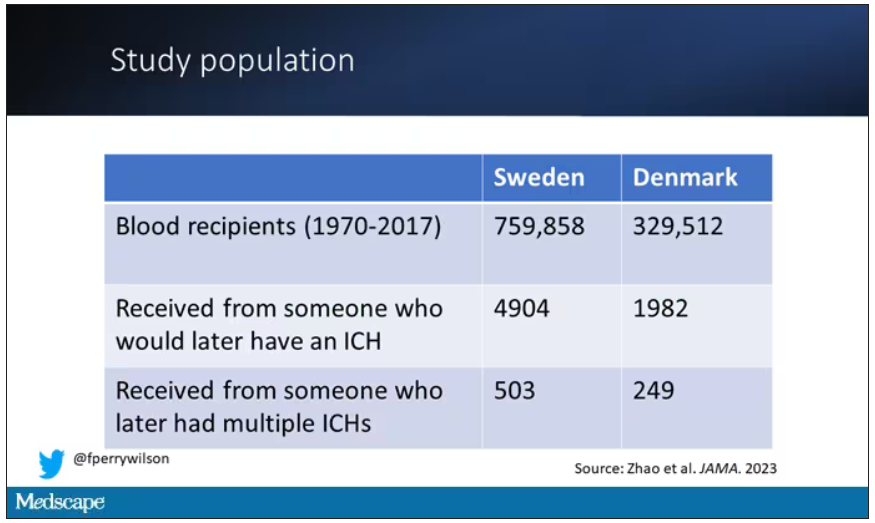
The big question: Would recipients who got blood from individuals who later on had brain bleeds, have brain bleeds themselves?
The answer is yes, though with an asterisk. You can see the results here. The risk of recipients having a brain bleed was lowest if the blood they received was from people who never had a brain bleed, higher if the individual had a single brain bleed, and highest if they got blood from a donor who would go on to have multiple brain bleeds.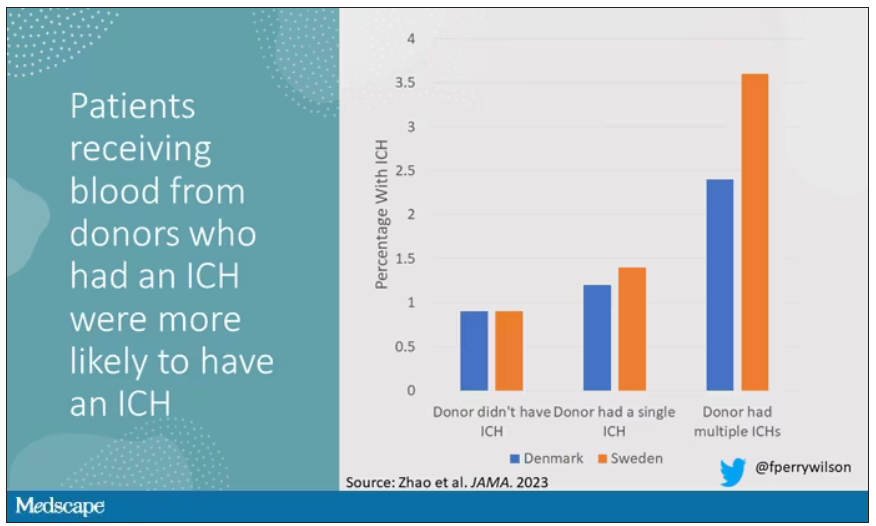
All in all, individuals who received blood from someone who would later have multiple hemorrhages were three times more likely to themselves develop bleeds themselves. It’s fairly compelling evidence of a transmissible agent.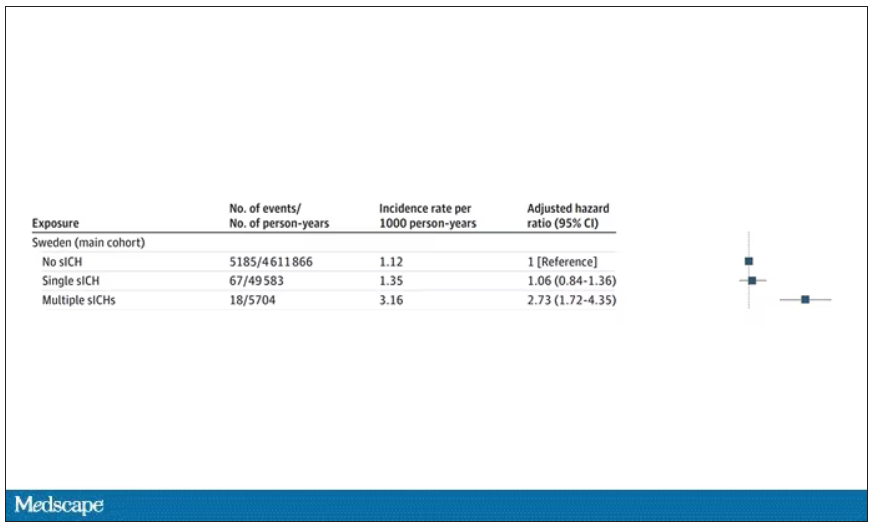
Of course, there are some potential confounders to consider here. Whose blood you get is not totally random. If, for example, people with type O blood are just more likely to have brain bleeds, then you could get results like this, as type O tends to donate to type O and both groups would have higher risk after donation. But the authors adjusted for blood type. They also adjusted for number of transfusions, calendar year, age, sex, and indication for transfusion.
Perhaps most compelling, and most clever, is that they used ischemic stroke as a negative control. Would people who received blood from someone who later had an ischemic stroke themselves be more likely to go on to have an ischemic stroke? No signal at all. It does not appear that there is a transmissible agent associated with ischemic stroke – only the brain bleeds.
I know what you’re thinking. What’s the agent? What’s the microbe, or virus, or prion, or toxin? The study gives us no insight there. These nationwide databases are awesome but they can only do so much. Because of the vagaries of medical coding and the difficulty of making the CAA diagnosis, the authors are using brain bleeds as a proxy here; we don’t even know for sure whether these were CAA-associated brain bleeds.
It’s also worth noting that there’s little we can do about this. None of the blood donors in this study had a brain bleed prior to donation; it’s not like we could screen people out of donating in the future. We have no test for whatever this agent is, if it even exists, nor do we have a potential treatment. Fortunately, whatever it is, it is extremely rare.
Still, this paper feels like a shot across the bow. At this point, the probability has shifted strongly away from CAA being a purely random disease and toward it being an infectious one. It may be time to round up some of the unusual suspects.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
How do you tell if a condition is caused by an infection?
It seems like an obvious question, right? In the post–van Leeuwenhoek era we can look at whatever part of the body is diseased under a microscope and see microbes – you know, the usual suspects.
Except when we can’t. And there are plenty of cases where we can’t: where the microbe is too small to be seen without more advanced imaging techniques, like with viruses; or when the pathogen is sparsely populated or hard to culture, like Mycobacterium.
Finding out that a condition is the result of an infection is not only an exercise for 19th century physicians. After all, it was 2008 when Barry Marshall and Robin Warren won their Nobel Prize for proving that stomach ulcers, long thought to be due to “stress,” were actually caused by a tiny microbe called Helicobacter pylori.
And this week, we are looking at a study which, once again, begins to suggest that a condition thought to be more or less random – cerebral amyloid angiopathy – may actually be the result of an infectious disease.
We’re talking about this paper, appearing in JAMA, which is just a great example of old-fashioned shoe-leather epidemiology. But let’s get up to speed on cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) first.
CAA is characterized by the deposition of amyloid protein in the brain. While there are some genetic causes, they are quite rare, and most cases are thought to be idiopathic. Recent analyses suggest that somewhere between 5% and 7% of cognitively normal older adults have CAA, but the rate is much higher among those with intracerebral hemorrhage – brain bleeds. In fact, CAA is the second-most common cause of bleeding in the brain, second only to severe hypertension.
An article in Nature highlights cases that seemed to develop after the administration of cadaveric pituitary hormone.
Other studies have shown potential transmission via dura mater grafts and neurosurgical instruments. But despite those clues, no infectious organism has been identified. Some have suggested that the long latent period and difficulty of finding a responsible microbe points to a prion-like disease not yet known. But these studies are more or less case series. The new JAMA paper gives us, if not a smoking gun, a pretty decent set of fingerprints.
Here’s the idea: If CAA is caused by some infectious agent, it may be transmitted in the blood. We know that a decent percentage of people who have spontaneous brain bleeds have CAA. If those people donated blood in the past, maybe the people who received that blood would be at risk for brain bleeds too.
Of course, to really test that hypothesis, you’d need to know who every blood donor in a country was and every person who received that blood and all their subsequent diagnoses for basically their entire lives. No one has that kind of data, right?
Well, if you’ve been watching this space, you’ll know that a few countries do. Enter Sweden and Denmark, with their national electronic health record that captures all of this information, and much more, on every single person who lives or has lived in those countries since before 1970. Unbelievable.
So that’s exactly what the researchers, led by Jingchen Zhao at Karolinska (Sweden) University, did. They identified roughly 760,000 individuals in Sweden and 330,000 people in Denmark who had received a blood transfusion between 1970 and 2017.
Of course, most of those blood donors – 99% of them, actually – never went on to have any bleeding in the brain. It is a rare thing, fortunately.
But some of the donors did, on average within about 5 years of the time they donated blood. The researchers characterized each donor as either never having a brain bleed, having a single bleed, or having multiple bleeds. The latter is most strongly associated with CAA.
The big question: Would recipients who got blood from individuals who later on had brain bleeds, have brain bleeds themselves?
The answer is yes, though with an asterisk. You can see the results here. The risk of recipients having a brain bleed was lowest if the blood they received was from people who never had a brain bleed, higher if the individual had a single brain bleed, and highest if they got blood from a donor who would go on to have multiple brain bleeds.
All in all, individuals who received blood from someone who would later have multiple hemorrhages were three times more likely to themselves develop bleeds themselves. It’s fairly compelling evidence of a transmissible agent.
Of course, there are some potential confounders to consider here. Whose blood you get is not totally random. If, for example, people with type O blood are just more likely to have brain bleeds, then you could get results like this, as type O tends to donate to type O and both groups would have higher risk after donation. But the authors adjusted for blood type. They also adjusted for number of transfusions, calendar year, age, sex, and indication for transfusion.
Perhaps most compelling, and most clever, is that they used ischemic stroke as a negative control. Would people who received blood from someone who later had an ischemic stroke themselves be more likely to go on to have an ischemic stroke? No signal at all. It does not appear that there is a transmissible agent associated with ischemic stroke – only the brain bleeds.
I know what you’re thinking. What’s the agent? What’s the microbe, or virus, or prion, or toxin? The study gives us no insight there. These nationwide databases are awesome but they can only do so much. Because of the vagaries of medical coding and the difficulty of making the CAA diagnosis, the authors are using brain bleeds as a proxy here; we don’t even know for sure whether these were CAA-associated brain bleeds.
It’s also worth noting that there’s little we can do about this. None of the blood donors in this study had a brain bleed prior to donation; it’s not like we could screen people out of donating in the future. We have no test for whatever this agent is, if it even exists, nor do we have a potential treatment. Fortunately, whatever it is, it is extremely rare.
Still, this paper feels like a shot across the bow. At this point, the probability has shifted strongly away from CAA being a purely random disease and toward it being an infectious one. It may be time to round up some of the unusual suspects.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
How do you tell if a condition is caused by an infection?
It seems like an obvious question, right? In the post–van Leeuwenhoek era we can look at whatever part of the body is diseased under a microscope and see microbes – you know, the usual suspects.
Except when we can’t. And there are plenty of cases where we can’t: where the microbe is too small to be seen without more advanced imaging techniques, like with viruses; or when the pathogen is sparsely populated or hard to culture, like Mycobacterium.
Finding out that a condition is the result of an infection is not only an exercise for 19th century physicians. After all, it was 2008 when Barry Marshall and Robin Warren won their Nobel Prize for proving that stomach ulcers, long thought to be due to “stress,” were actually caused by a tiny microbe called Helicobacter pylori.
And this week, we are looking at a study which, once again, begins to suggest that a condition thought to be more or less random – cerebral amyloid angiopathy – may actually be the result of an infectious disease.
We’re talking about this paper, appearing in JAMA, which is just a great example of old-fashioned shoe-leather epidemiology. But let’s get up to speed on cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) first.
CAA is characterized by the deposition of amyloid protein in the brain. While there are some genetic causes, they are quite rare, and most cases are thought to be idiopathic. Recent analyses suggest that somewhere between 5% and 7% of cognitively normal older adults have CAA, but the rate is much higher among those with intracerebral hemorrhage – brain bleeds. In fact, CAA is the second-most common cause of bleeding in the brain, second only to severe hypertension.
An article in Nature highlights cases that seemed to develop after the administration of cadaveric pituitary hormone.
Other studies have shown potential transmission via dura mater grafts and neurosurgical instruments. But despite those clues, no infectious organism has been identified. Some have suggested that the long latent period and difficulty of finding a responsible microbe points to a prion-like disease not yet known. But these studies are more or less case series. The new JAMA paper gives us, if not a smoking gun, a pretty decent set of fingerprints.
Here’s the idea: If CAA is caused by some infectious agent, it may be transmitted in the blood. We know that a decent percentage of people who have spontaneous brain bleeds have CAA. If those people donated blood in the past, maybe the people who received that blood would be at risk for brain bleeds too.
Of course, to really test that hypothesis, you’d need to know who every blood donor in a country was and every person who received that blood and all their subsequent diagnoses for basically their entire lives. No one has that kind of data, right?
Well, if you’ve been watching this space, you’ll know that a few countries do. Enter Sweden and Denmark, with their national electronic health record that captures all of this information, and much more, on every single person who lives or has lived in those countries since before 1970. Unbelievable.
So that’s exactly what the researchers, led by Jingchen Zhao at Karolinska (Sweden) University, did. They identified roughly 760,000 individuals in Sweden and 330,000 people in Denmark who had received a blood transfusion between 1970 and 2017.
Of course, most of those blood donors – 99% of them, actually – never went on to have any bleeding in the brain. It is a rare thing, fortunately.
But some of the donors did, on average within about 5 years of the time they donated blood. The researchers characterized each donor as either never having a brain bleed, having a single bleed, or having multiple bleeds. The latter is most strongly associated with CAA.
The big question: Would recipients who got blood from individuals who later on had brain bleeds, have brain bleeds themselves?
The answer is yes, though with an asterisk. You can see the results here. The risk of recipients having a brain bleed was lowest if the blood they received was from people who never had a brain bleed, higher if the individual had a single brain bleed, and highest if they got blood from a donor who would go on to have multiple brain bleeds.
All in all, individuals who received blood from someone who would later have multiple hemorrhages were three times more likely to themselves develop bleeds themselves. It’s fairly compelling evidence of a transmissible agent.
Of course, there are some potential confounders to consider here. Whose blood you get is not totally random. If, for example, people with type O blood are just more likely to have brain bleeds, then you could get results like this, as type O tends to donate to type O and both groups would have higher risk after donation. But the authors adjusted for blood type. They also adjusted for number of transfusions, calendar year, age, sex, and indication for transfusion.
Perhaps most compelling, and most clever, is that they used ischemic stroke as a negative control. Would people who received blood from someone who later had an ischemic stroke themselves be more likely to go on to have an ischemic stroke? No signal at all. It does not appear that there is a transmissible agent associated with ischemic stroke – only the brain bleeds.
I know what you’re thinking. What’s the agent? What’s the microbe, or virus, or prion, or toxin? The study gives us no insight there. These nationwide databases are awesome but they can only do so much. Because of the vagaries of medical coding and the difficulty of making the CAA diagnosis, the authors are using brain bleeds as a proxy here; we don’t even know for sure whether these were CAA-associated brain bleeds.
It’s also worth noting that there’s little we can do about this. None of the blood donors in this study had a brain bleed prior to donation; it’s not like we could screen people out of donating in the future. We have no test for whatever this agent is, if it even exists, nor do we have a potential treatment. Fortunately, whatever it is, it is extremely rare.
Still, this paper feels like a shot across the bow. At this point, the probability has shifted strongly away from CAA being a purely random disease and toward it being an infectious one. It may be time to round up some of the unusual suspects.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale University’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A White male presented with a purulent erythematous edematous plaque with central necrosis and ulceration on his right flank
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
Lyme disease is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne illness in the United States. This infection is typically transmitted through a bite by the Ixodes tick commonly found in the Midwest, Northeast, and mid-Atlantic regions; however, the geographical distribution continues to expand over time in the United States. Ticks must be attached for 24-48 hours to transmit the pathogen. There are three general stages of the disease: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated.
The most common presentation is the early localized disease, which manifests between 3 and 30 days after an infected tick bite. Approximately 70%-80% of cases feature a targetlike lesion that expands centrifugally at the site of the bite. Most commonly, lesions appear on the abdomen, groin, axilla, and popliteal fossa. The diagnosis of ECM requires lesions at least 5 cm in size. Lesions may be asymptomatic, although burning may occur in half of patients. Atypical presentations include bullous, vesicular, hemorrhagic, or necrotic lesions. Up to half of patients may develop multiple ECM lesions. Palms and soles are spared. Differential diagnoses include arthropod reactions, pyoderma gangrenosum, cellulitis, herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus, contact dermatitis, or granuloma annulare. The rash is often accompanied by systemic symptoms including fatigue, myalgia, headache, and fever.
The next two stages include early and late disseminated infection. Early disseminated infection often occurs 3-12 weeks after infection and is characterized by muscle pain, dizziness, headache, and cardiac symptoms. CNS involvement occurs in about 20% of patients. Joint involvement may include the knee, ankle, and wrist. If symptoms are only in one joint, septic arthritis is part of the differential diagnosis, so clinical correlation and labs must be considered. Late disseminated infection occurs months or years after initial infection and includes neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms including meningitis, Bell’s palsy, arthritis, and dysesthesia. Knee arthritis is a key feature of this stage. Patients commonly have radicular pain and fibromyalgia-type pain. More severe disease processes include encephalomyelitis, arrhythmias, and heart block.
ECM is often a clinical diagnosis because serologic testing may not be positive during the first 2 weeks of infection. The screening serologic test is the ELISA, and a Western blot confirms the results. Skin histopathology for Lyme disease is often nonspecific and reveals a perivascular infiltrate of histiocytes, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Silver stain or antibody testing may be used to identify the spirochete. In acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans, late Lyme disease presenting on the distal extremities, lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltrates are present. In borrelial lymphocytoma, a dense dermal lymphocytic infiltrate is present.
The standard for treatment of early localized disease is oral doxycycline in adults. Alternatives may be used if a patient is allergic or for children under 9. Disseminated disease may be treated with IV ceftriaxone and topical steroids are used if ocular symptoms are involved. Early treatment is often curative.
This patient’s antibodies were negative initially, but became positive after 6 weeks. He was treated empirically at the time of his office visit with doxycycline for 1 month.
This case and the photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Susannah Berke, MD, Three Rivers Dermatology, Coraopolis, Pa. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at MDedge.com/Dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Carriveau A et al. Nurs Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;54(2):261-75.
Skar GL and Simonsen KA. Lyme Disease. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: “StatPearls” [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
Tiger JB et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):e133-4.
New COVID vaccines force bivalents out
COVID vaccines will have a new formulation in 2023, according to a decision announced by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, that will focus efforts on circulating variants. The move pushes last year’s bivalent vaccines out of circulation because they will no longer be authorized for use in the United States.
The updated mRNA vaccines for 2023-2024 are being revised to include a single component that corresponds to the Omicron variant XBB.1.5. Like the bivalents offered before, the new monovalents are being manufactured by Moderna and Pfizer.
The new vaccines are authorized for use in individuals age 6 months and older. And the new options are being developed using a similar process as previous formulations, according to the FDA.
Targeting circulating variants
In recent studies, regulators point out the extent of neutralization observed by the updated vaccines against currently circulating viral variants causing COVID-19, including EG.5, BA.2.86, appears to be of a similar magnitude to the extent of neutralization observed with previous versions of the vaccines against corresponding prior variants.
“This suggests that the vaccines are a good match for protecting against the currently circulating COVID-19 variants,” according to the report.
Hundreds of millions of people in the United States have already received previously approved mRNA COVID vaccines, according to regulators who say the benefit-to-risk profile is well understood as they move forward with new formulations.
“Vaccination remains critical to public health and continued protection against serious consequences of COVID-19, including hospitalization and death,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement. “The public can be assured that these updated vaccines have met the agency’s rigorous scientific standards for safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing quality. We very much encourage those who are eligible to consider getting vaccinated.”
Timing the effort
On Sept. 12 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that everyone 6 months and older get an updated COVID-19 vaccine. Updated vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna will be available later this week, according to the agency.
This article was updated 9/14/23.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines will have a new formulation in 2023, according to a decision announced by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, that will focus efforts on circulating variants. The move pushes last year’s bivalent vaccines out of circulation because they will no longer be authorized for use in the United States.
The updated mRNA vaccines for 2023-2024 are being revised to include a single component that corresponds to the Omicron variant XBB.1.5. Like the bivalents offered before, the new monovalents are being manufactured by Moderna and Pfizer.
The new vaccines are authorized for use in individuals age 6 months and older. And the new options are being developed using a similar process as previous formulations, according to the FDA.
Targeting circulating variants
In recent studies, regulators point out the extent of neutralization observed by the updated vaccines against currently circulating viral variants causing COVID-19, including EG.5, BA.2.86, appears to be of a similar magnitude to the extent of neutralization observed with previous versions of the vaccines against corresponding prior variants.
“This suggests that the vaccines are a good match for protecting against the currently circulating COVID-19 variants,” according to the report.
Hundreds of millions of people in the United States have already received previously approved mRNA COVID vaccines, according to regulators who say the benefit-to-risk profile is well understood as they move forward with new formulations.
“Vaccination remains critical to public health and continued protection against serious consequences of COVID-19, including hospitalization and death,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement. “The public can be assured that these updated vaccines have met the agency’s rigorous scientific standards for safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing quality. We very much encourage those who are eligible to consider getting vaccinated.”
Timing the effort
On Sept. 12 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that everyone 6 months and older get an updated COVID-19 vaccine. Updated vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna will be available later this week, according to the agency.
This article was updated 9/14/23.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccines will have a new formulation in 2023, according to a decision announced by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, that will focus efforts on circulating variants. The move pushes last year’s bivalent vaccines out of circulation because they will no longer be authorized for use in the United States.
The updated mRNA vaccines for 2023-2024 are being revised to include a single component that corresponds to the Omicron variant XBB.1.5. Like the bivalents offered before, the new monovalents are being manufactured by Moderna and Pfizer.
The new vaccines are authorized for use in individuals age 6 months and older. And the new options are being developed using a similar process as previous formulations, according to the FDA.
Targeting circulating variants
In recent studies, regulators point out the extent of neutralization observed by the updated vaccines against currently circulating viral variants causing COVID-19, including EG.5, BA.2.86, appears to be of a similar magnitude to the extent of neutralization observed with previous versions of the vaccines against corresponding prior variants.
“This suggests that the vaccines are a good match for protecting against the currently circulating COVID-19 variants,” according to the report.
Hundreds of millions of people in the United States have already received previously approved mRNA COVID vaccines, according to regulators who say the benefit-to-risk profile is well understood as they move forward with new formulations.
“Vaccination remains critical to public health and continued protection against serious consequences of COVID-19, including hospitalization and death,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a statement. “The public can be assured that these updated vaccines have met the agency’s rigorous scientific standards for safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing quality. We very much encourage those who are eligible to consider getting vaccinated.”
Timing the effort
On Sept. 12 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended that everyone 6 months and older get an updated COVID-19 vaccine. Updated vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna will be available later this week, according to the agency.
This article was updated 9/14/23.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
RSV season has started, and this year could be different
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a national alert to health officials Sept. 5, urging them to offer new medicines that can prevent severe cases of the respiratory virus in very young children and in older people. Those two groups are at the highest risk of potentially deadly complications from RSV.
Typically, the CDC considers the start of RSV season to occur when the rate of positive tests for the virus goes above 3% for 2 consecutive weeks. In Florida, the rate has been around 5% in recent weeks, and in Georgia, there has been an increase in RSV-related hospitalizations. Most of the hospitalizations in Georgia have been among infants less than a year old.
“Historically, such regional increases have predicted the beginning of RSV season nationally, with increased RSV activity spreading north and west over the following 2-3 months,” the CDC said.
Most children have been infected with RSV by the time they are 2 years old. Historically, up to 80,000 children under 5 years old are hospitalized annually because of the virus, and between 100 and 300 die from complications each year.
Those figures could be drastically different this year because new preventive treatments are available.
The CDC recommends that all children under 8 months old receive the newly approved monoclonal antibody treatment nirsevimab (Beyfortus). Children up to 19 months old at high risk of severe complications from RSV are also eligible for the single-dose shot. In clinical trials, the treatment was 80% effective at preventing RSV infections from becoming so severe that children had to be hospitalized. The protection lasted about 5 months.
Older people are also at a heightened risk of severe illness from RSV, and two new vaccines are available this season. The vaccines are called Arexvy and Abrysvo, and the single-dose shots are approved for people ages 60 years and older. They are more than 80% effective at making severe lower respiratory complications less likely.
Last year’s RSV season started during the summer and peaked in October and November, which was earlier than usual. There’s no indication yet of when RSV season may peak this year. Last year and throughout the pandemic, RSV held its historical pattern of starting in Florida.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a national alert to health officials Sept. 5, urging them to offer new medicines that can prevent severe cases of the respiratory virus in very young children and in older people. Those two groups are at the highest risk of potentially deadly complications from RSV.
Typically, the CDC considers the start of RSV season to occur when the rate of positive tests for the virus goes above 3% for 2 consecutive weeks. In Florida, the rate has been around 5% in recent weeks, and in Georgia, there has been an increase in RSV-related hospitalizations. Most of the hospitalizations in Georgia have been among infants less than a year old.
“Historically, such regional increases have predicted the beginning of RSV season nationally, with increased RSV activity spreading north and west over the following 2-3 months,” the CDC said.
Most children have been infected with RSV by the time they are 2 years old. Historically, up to 80,000 children under 5 years old are hospitalized annually because of the virus, and between 100 and 300 die from complications each year.
Those figures could be drastically different this year because new preventive treatments are available.
The CDC recommends that all children under 8 months old receive the newly approved monoclonal antibody treatment nirsevimab (Beyfortus). Children up to 19 months old at high risk of severe complications from RSV are also eligible for the single-dose shot. In clinical trials, the treatment was 80% effective at preventing RSV infections from becoming so severe that children had to be hospitalized. The protection lasted about 5 months.
Older people are also at a heightened risk of severe illness from RSV, and two new vaccines are available this season. The vaccines are called Arexvy and Abrysvo, and the single-dose shots are approved for people ages 60 years and older. They are more than 80% effective at making severe lower respiratory complications less likely.
Last year’s RSV season started during the summer and peaked in October and November, which was earlier than usual. There’s no indication yet of when RSV season may peak this year. Last year and throughout the pandemic, RSV held its historical pattern of starting in Florida.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a national alert to health officials Sept. 5, urging them to offer new medicines that can prevent severe cases of the respiratory virus in very young children and in older people. Those two groups are at the highest risk of potentially deadly complications from RSV.
Typically, the CDC considers the start of RSV season to occur when the rate of positive tests for the virus goes above 3% for 2 consecutive weeks. In Florida, the rate has been around 5% in recent weeks, and in Georgia, there has been an increase in RSV-related hospitalizations. Most of the hospitalizations in Georgia have been among infants less than a year old.
“Historically, such regional increases have predicted the beginning of RSV season nationally, with increased RSV activity spreading north and west over the following 2-3 months,” the CDC said.
Most children have been infected with RSV by the time they are 2 years old. Historically, up to 80,000 children under 5 years old are hospitalized annually because of the virus, and between 100 and 300 die from complications each year.
Those figures could be drastically different this year because new preventive treatments are available.
The CDC recommends that all children under 8 months old receive the newly approved monoclonal antibody treatment nirsevimab (Beyfortus). Children up to 19 months old at high risk of severe complications from RSV are also eligible for the single-dose shot. In clinical trials, the treatment was 80% effective at preventing RSV infections from becoming so severe that children had to be hospitalized. The protection lasted about 5 months.
Older people are also at a heightened risk of severe illness from RSV, and two new vaccines are available this season. The vaccines are called Arexvy and Abrysvo, and the single-dose shots are approved for people ages 60 years and older. They are more than 80% effective at making severe lower respiratory complications less likely.
Last year’s RSV season started during the summer and peaked in October and November, which was earlier than usual. There’s no indication yet of when RSV season may peak this year. Last year and throughout the pandemic, RSV held its historical pattern of starting in Florida.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
New Moderna vaccine to work against recent COVID variant
“The company said its shot generated an 8.7-fold increase in neutralizing antibodies in humans against BA.2.86, which is being tracked by the World Health Organization and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,” Reuters reported.
“We think this is news people will want to hear as they prepare to go out and get their fall boosters,” Jacqueline Miller, Moderna head of infectious diseases, told the news agency.
The CDC said that the BA.2.86 variant might be more likely to infect people who have already had COVID or previous vaccinations. BA.2.86 is an Omicron variant. It has undergone more mutations than XBB.1.5, which has dominated most of this year and was the intended target of the updated shots.
BA.2.86 does not have a strong presence in the United States yet. However, officials are concerned about its high number of mutations, NBC News reported.
The FDA is expected to approve the new Moderna shot by early October.
Pfizer told NBC that its updated booster also generated a strong antibody response against Omicron variants, including BA.2.86.
COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations have been increasing in the U.S. because of the rise of several variants.
Experts told Reuters that BA.2.86 probably won’t cause a wave of severe disease and death because immunity has been built up around the world through previous infections and mass vaccinations.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
“The company said its shot generated an 8.7-fold increase in neutralizing antibodies in humans against BA.2.86, which is being tracked by the World Health Organization and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,” Reuters reported.
“We think this is news people will want to hear as they prepare to go out and get their fall boosters,” Jacqueline Miller, Moderna head of infectious diseases, told the news agency.
The CDC said that the BA.2.86 variant might be more likely to infect people who have already had COVID or previous vaccinations. BA.2.86 is an Omicron variant. It has undergone more mutations than XBB.1.5, which has dominated most of this year and was the intended target of the updated shots.
BA.2.86 does not have a strong presence in the United States yet. However, officials are concerned about its high number of mutations, NBC News reported.
The FDA is expected to approve the new Moderna shot by early October.
Pfizer told NBC that its updated booster also generated a strong antibody response against Omicron variants, including BA.2.86.
COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations have been increasing in the U.S. because of the rise of several variants.
Experts told Reuters that BA.2.86 probably won’t cause a wave of severe disease and death because immunity has been built up around the world through previous infections and mass vaccinations.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
“The company said its shot generated an 8.7-fold increase in neutralizing antibodies in humans against BA.2.86, which is being tracked by the World Health Organization and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,” Reuters reported.
“We think this is news people will want to hear as they prepare to go out and get their fall boosters,” Jacqueline Miller, Moderna head of infectious diseases, told the news agency.
The CDC said that the BA.2.86 variant might be more likely to infect people who have already had COVID or previous vaccinations. BA.2.86 is an Omicron variant. It has undergone more mutations than XBB.1.5, which has dominated most of this year and was the intended target of the updated shots.
BA.2.86 does not have a strong presence in the United States yet. However, officials are concerned about its high number of mutations, NBC News reported.
The FDA is expected to approve the new Moderna shot by early October.
Pfizer told NBC that its updated booster also generated a strong antibody response against Omicron variants, including BA.2.86.
COVID-19 cases and hospitalizations have been increasing in the U.S. because of the rise of several variants.
Experts told Reuters that BA.2.86 probably won’t cause a wave of severe disease and death because immunity has been built up around the world through previous infections and mass vaccinations.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Long COVID and new migraines: What’s the link?
.
“I’ve also noticed visual disturbances, like flickering lights or blurred vision, which I later learned are called auras,” the 30-year-old medical billing specialist in Seattle told this news organization.
Mr. Solomon isn’t alone. It’s estimated that 1 out of 8 people with COVID develop long COVID. Of those persons, 44% also experience headaches. Research has found that many of those headaches are migraines – and many patients who are afflicted say they had never had a migraine before. These migraines tend to persist for at least 5 or 6 months, according to data from the American Headache Society.
What’s more, other patients may suddenly have more frequent or intense versions of headaches they’ve not noticed before.
The mechanism as to how long COVID could manifest migraines is not yet fully understood, but many doctors believe that inflammation caused by the virus plays a key role.
“To understand why some patients have migraine in long COVID, we have to go back to understand the role of inflammation in COVID-19 itself,” says Emad Estemalik, MD, clinical assistant professor of neurology at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and section head of headache medicine at Cleveland Clinic.
In COVID-19, inflammation occurs because of a cytokine storm. Cytokines, which are proteins essential for a strong immune system, can be overproduced in a patient with COVID, which causes too much inflammation in any organ in the body, including the brain. This can result in new daily headache for some patients.
A new study from Italian researchers found that many patients who develop migraines for the first time while ill with long COVID are middle-aged women (traditionally a late point in life for a first migraine) who have a family history of migraine. Potential causes could have to do with the immune system remaining persistently activated from inflammation during long COVID, as well as the activation of the trigeminovascular system in the brain, which contains neurons that can trigger a migraine.
What treatments can work for migraines related to long COVID?
Long COVID usually causes a constellation of other symptoms at the same time as migraine.
“It’s so important for patients to take an interdisciplinary approach,” Dr. Estemalik stresses. “Patients should make sure their doctors are addressing all of their symptoms.”
When it comes to specifically targeting migraines, standard treatments can be effective.
“In terms of treating migraine in long COVID patients, we don’t do anything different or special,” says Matthew E. Fink, MD, chair of neurology at Weill Cornell Medical College and chief of the Division of Stroke and Critical Care Neurology at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “We treat these patients with standard migraine medications.”
Mr. Solomon is following this course of action.
“My doctor prescribed triptans, which have been somewhat effective in reducing the severity and duration of the migraines,” he says. A daily supplement of magnesium and a daily dose of aspirin can also work for some patients, according to Dr. Fink.
Lifestyle modification is also a great idea.
“Patients should keep regular sleep hours, getting up and going to bed at the same time every day,” Dr. Fink continues. “Daily exercise is also recommended.”
Mr. Solomon suggests tracking migraine triggers and patterns in a journal.
“Try to identify lifestyle changes that help, like managing stress and staying hydrated,” Mr. Solomon advises. “Seeking support from health care professionals and support groups can make a significant difference.”
The best news of all: for patients that are diligent in following these strategies, they’ve been proven to work.
“We doctors are very optimistic when it comes to good outcomes for patients with long COVID and migraine,” Dr. Fink says. “I reassure my patients by telling them, ‘You will get better long-term.’ ”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
“I’ve also noticed visual disturbances, like flickering lights or blurred vision, which I later learned are called auras,” the 30-year-old medical billing specialist in Seattle told this news organization.
Mr. Solomon isn’t alone. It’s estimated that 1 out of 8 people with COVID develop long COVID. Of those persons, 44% also experience headaches. Research has found that many of those headaches are migraines – and many patients who are afflicted say they had never had a migraine before. These migraines tend to persist for at least 5 or 6 months, according to data from the American Headache Society.
What’s more, other patients may suddenly have more frequent or intense versions of headaches they’ve not noticed before.
The mechanism as to how long COVID could manifest migraines is not yet fully understood, but many doctors believe that inflammation caused by the virus plays a key role.
“To understand why some patients have migraine in long COVID, we have to go back to understand the role of inflammation in COVID-19 itself,” says Emad Estemalik, MD, clinical assistant professor of neurology at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and section head of headache medicine at Cleveland Clinic.
In COVID-19, inflammation occurs because of a cytokine storm. Cytokines, which are proteins essential for a strong immune system, can be overproduced in a patient with COVID, which causes too much inflammation in any organ in the body, including the brain. This can result in new daily headache for some patients.
A new study from Italian researchers found that many patients who develop migraines for the first time while ill with long COVID are middle-aged women (traditionally a late point in life for a first migraine) who have a family history of migraine. Potential causes could have to do with the immune system remaining persistently activated from inflammation during long COVID, as well as the activation of the trigeminovascular system in the brain, which contains neurons that can trigger a migraine.
What treatments can work for migraines related to long COVID?
Long COVID usually causes a constellation of other symptoms at the same time as migraine.
“It’s so important for patients to take an interdisciplinary approach,” Dr. Estemalik stresses. “Patients should make sure their doctors are addressing all of their symptoms.”
When it comes to specifically targeting migraines, standard treatments can be effective.
“In terms of treating migraine in long COVID patients, we don’t do anything different or special,” says Matthew E. Fink, MD, chair of neurology at Weill Cornell Medical College and chief of the Division of Stroke and Critical Care Neurology at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “We treat these patients with standard migraine medications.”
Mr. Solomon is following this course of action.
“My doctor prescribed triptans, which have been somewhat effective in reducing the severity and duration of the migraines,” he says. A daily supplement of magnesium and a daily dose of aspirin can also work for some patients, according to Dr. Fink.
Lifestyle modification is also a great idea.
“Patients should keep regular sleep hours, getting up and going to bed at the same time every day,” Dr. Fink continues. “Daily exercise is also recommended.”
Mr. Solomon suggests tracking migraine triggers and patterns in a journal.
“Try to identify lifestyle changes that help, like managing stress and staying hydrated,” Mr. Solomon advises. “Seeking support from health care professionals and support groups can make a significant difference.”
The best news of all: for patients that are diligent in following these strategies, they’ve been proven to work.
“We doctors are very optimistic when it comes to good outcomes for patients with long COVID and migraine,” Dr. Fink says. “I reassure my patients by telling them, ‘You will get better long-term.’ ”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
.
“I’ve also noticed visual disturbances, like flickering lights or blurred vision, which I later learned are called auras,” the 30-year-old medical billing specialist in Seattle told this news organization.
Mr. Solomon isn’t alone. It’s estimated that 1 out of 8 people with COVID develop long COVID. Of those persons, 44% also experience headaches. Research has found that many of those headaches are migraines – and many patients who are afflicted say they had never had a migraine before. These migraines tend to persist for at least 5 or 6 months, according to data from the American Headache Society.
What’s more, other patients may suddenly have more frequent or intense versions of headaches they’ve not noticed before.
The mechanism as to how long COVID could manifest migraines is not yet fully understood, but many doctors believe that inflammation caused by the virus plays a key role.
“To understand why some patients have migraine in long COVID, we have to go back to understand the role of inflammation in COVID-19 itself,” says Emad Estemalik, MD, clinical assistant professor of neurology at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and section head of headache medicine at Cleveland Clinic.
In COVID-19, inflammation occurs because of a cytokine storm. Cytokines, which are proteins essential for a strong immune system, can be overproduced in a patient with COVID, which causes too much inflammation in any organ in the body, including the brain. This can result in new daily headache for some patients.
A new study from Italian researchers found that many patients who develop migraines for the first time while ill with long COVID are middle-aged women (traditionally a late point in life for a first migraine) who have a family history of migraine. Potential causes could have to do with the immune system remaining persistently activated from inflammation during long COVID, as well as the activation of the trigeminovascular system in the brain, which contains neurons that can trigger a migraine.
What treatments can work for migraines related to long COVID?
Long COVID usually causes a constellation of other symptoms at the same time as migraine.
“It’s so important for patients to take an interdisciplinary approach,” Dr. Estemalik stresses. “Patients should make sure their doctors are addressing all of their symptoms.”
When it comes to specifically targeting migraines, standard treatments can be effective.
“In terms of treating migraine in long COVID patients, we don’t do anything different or special,” says Matthew E. Fink, MD, chair of neurology at Weill Cornell Medical College and chief of the Division of Stroke and Critical Care Neurology at New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “We treat these patients with standard migraine medications.”
Mr. Solomon is following this course of action.
“My doctor prescribed triptans, which have been somewhat effective in reducing the severity and duration of the migraines,” he says. A daily supplement of magnesium and a daily dose of aspirin can also work for some patients, according to Dr. Fink.
Lifestyle modification is also a great idea.
“Patients should keep regular sleep hours, getting up and going to bed at the same time every day,” Dr. Fink continues. “Daily exercise is also recommended.”
Mr. Solomon suggests tracking migraine triggers and patterns in a journal.
“Try to identify lifestyle changes that help, like managing stress and staying hydrated,” Mr. Solomon advises. “Seeking support from health care professionals and support groups can make a significant difference.”
The best news of all: for patients that are diligent in following these strategies, they’ve been proven to work.
“We doctors are very optimistic when it comes to good outcomes for patients with long COVID and migraine,” Dr. Fink says. “I reassure my patients by telling them, ‘You will get better long-term.’ ”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
3D-printed meds customize the exact dose for sick children
Convincing kids to take their medicine could become much easier. Researchers at Texas A&M University are developing a new method of pharmaceutical 3D printing with pediatric patients in mind.
They hope to print precisely dosed tablets in child-friendly shapes and flavors. While the effort is focused on two drugs for pediatric AIDS, the process could be used to print other medicines, including for adults.
Researchers from Britain, Australia, and the University of Texas at Austin are also in the early stages of 3D-printed medication projects. It’s a promising venture in the broader pursuit of “personalized medicine,” tailoring treatments to each patient’s unique needs.
Drug mass production fails to address pediatric patients, who often need different dosages and combinations of medicines as they grow. As a result, adult tablets are often crushed and dissolved in liquid – known as compounding – and given to children. But this can harm drug quality and make doses less precise.
“Suppose the child needs 3.4 milligrams and only a 10-milligram tablet is available. Once you manipulate the dosage from solid to liquid, how do you ensure that it has the same amount of drug in it?” said co-principal investigator Mansoor Khan, PhD, a professor of pharmaceutical sciences at Texas A&M.
Most pharmacies lack the equipment to test compounded drug quality, he said. And liquified drugs taste bad because the pill coating has been ground away.
“Flavor is a big issue,” said Olive Eckstein, MD, an assistant professor of pediatric hematology-oncology at Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine, who is not involved in the research. “Hospitals will sometimes delay discharging pediatric patients because they can’t take their meds orally and have to get an IV formulation.”
Updating pharmaceutical 3D printing
The FDA approved a 3D-printed drug in 2015, but since then, progress has stalled, largely because the method relied on solvents to bind drug particles together. Over time, solvents can compromise shelf life, according to co-principal investigator Mathew Kuttolamadom, PhD, an associate professor of engineering at Texas A&M.
The Texas A&M team is using a different method, without solvents. First, they create a powder mixture of the drug, a biocompatible polymer (such as lactose), and a sheen, a pigment that colors the tablet and allows heat to be absorbed. Flavoring can also be added. Next, the mixture is heated in the printer chamber.
“The polymer should melt just enough. That gives the tablet structural strength. But it should not melt too much, whereby the drug can start dissolving into the polymer,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
The tablets are finished with precise applications of laser heat. Using computer-aided design software, the researchers can create tablets in almost any shape, such as “stars or teddy bears,” he said.
After much trial and error, the researchers have printed tablets that won’t break apart or become soggy.
Now they are testing how different laser scan speeds affect the structure of the tablet, which in turn affects the rate at which drugs dissolve. Slowing down the laser imparts more energy, strengthening the tablet structure and making drugs dissolve slower, for a longer release inside the body.
The researchers hope to develop machine learning models to test different laser speed combinations. Eventually, they could create tablets that combine drugs with different dissolve rates.
“The outside could be a rapid release, and the inside could be an extended release or a sustained release, or even a completely different drug,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
Older patients who take many daily medications could benefit from the technology. “Personalized tablets could be printed at your local pharmacy,” he said, “even before you leave your doctor’s office.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Convincing kids to take their medicine could become much easier. Researchers at Texas A&M University are developing a new method of pharmaceutical 3D printing with pediatric patients in mind.
They hope to print precisely dosed tablets in child-friendly shapes and flavors. While the effort is focused on two drugs for pediatric AIDS, the process could be used to print other medicines, including for adults.
Researchers from Britain, Australia, and the University of Texas at Austin are also in the early stages of 3D-printed medication projects. It’s a promising venture in the broader pursuit of “personalized medicine,” tailoring treatments to each patient’s unique needs.
Drug mass production fails to address pediatric patients, who often need different dosages and combinations of medicines as they grow. As a result, adult tablets are often crushed and dissolved in liquid – known as compounding – and given to children. But this can harm drug quality and make doses less precise.
“Suppose the child needs 3.4 milligrams and only a 10-milligram tablet is available. Once you manipulate the dosage from solid to liquid, how do you ensure that it has the same amount of drug in it?” said co-principal investigator Mansoor Khan, PhD, a professor of pharmaceutical sciences at Texas A&M.
Most pharmacies lack the equipment to test compounded drug quality, he said. And liquified drugs taste bad because the pill coating has been ground away.
“Flavor is a big issue,” said Olive Eckstein, MD, an assistant professor of pediatric hematology-oncology at Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine, who is not involved in the research. “Hospitals will sometimes delay discharging pediatric patients because they can’t take their meds orally and have to get an IV formulation.”
Updating pharmaceutical 3D printing
The FDA approved a 3D-printed drug in 2015, but since then, progress has stalled, largely because the method relied on solvents to bind drug particles together. Over time, solvents can compromise shelf life, according to co-principal investigator Mathew Kuttolamadom, PhD, an associate professor of engineering at Texas A&M.
The Texas A&M team is using a different method, without solvents. First, they create a powder mixture of the drug, a biocompatible polymer (such as lactose), and a sheen, a pigment that colors the tablet and allows heat to be absorbed. Flavoring can also be added. Next, the mixture is heated in the printer chamber.
“The polymer should melt just enough. That gives the tablet structural strength. But it should not melt too much, whereby the drug can start dissolving into the polymer,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
The tablets are finished with precise applications of laser heat. Using computer-aided design software, the researchers can create tablets in almost any shape, such as “stars or teddy bears,” he said.
After much trial and error, the researchers have printed tablets that won’t break apart or become soggy.
Now they are testing how different laser scan speeds affect the structure of the tablet, which in turn affects the rate at which drugs dissolve. Slowing down the laser imparts more energy, strengthening the tablet structure and making drugs dissolve slower, for a longer release inside the body.
The researchers hope to develop machine learning models to test different laser speed combinations. Eventually, they could create tablets that combine drugs with different dissolve rates.
“The outside could be a rapid release, and the inside could be an extended release or a sustained release, or even a completely different drug,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
Older patients who take many daily medications could benefit from the technology. “Personalized tablets could be printed at your local pharmacy,” he said, “even before you leave your doctor’s office.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Convincing kids to take their medicine could become much easier. Researchers at Texas A&M University are developing a new method of pharmaceutical 3D printing with pediatric patients in mind.
They hope to print precisely dosed tablets in child-friendly shapes and flavors. While the effort is focused on two drugs for pediatric AIDS, the process could be used to print other medicines, including for adults.
Researchers from Britain, Australia, and the University of Texas at Austin are also in the early stages of 3D-printed medication projects. It’s a promising venture in the broader pursuit of “personalized medicine,” tailoring treatments to each patient’s unique needs.
Drug mass production fails to address pediatric patients, who often need different dosages and combinations of medicines as they grow. As a result, adult tablets are often crushed and dissolved in liquid – known as compounding – and given to children. But this can harm drug quality and make doses less precise.
“Suppose the child needs 3.4 milligrams and only a 10-milligram tablet is available. Once you manipulate the dosage from solid to liquid, how do you ensure that it has the same amount of drug in it?” said co-principal investigator Mansoor Khan, PhD, a professor of pharmaceutical sciences at Texas A&M.
Most pharmacies lack the equipment to test compounded drug quality, he said. And liquified drugs taste bad because the pill coating has been ground away.
“Flavor is a big issue,” said Olive Eckstein, MD, an assistant professor of pediatric hematology-oncology at Texas Children’s Hospital and Baylor College of Medicine, who is not involved in the research. “Hospitals will sometimes delay discharging pediatric patients because they can’t take their meds orally and have to get an IV formulation.”
Updating pharmaceutical 3D printing
The FDA approved a 3D-printed drug in 2015, but since then, progress has stalled, largely because the method relied on solvents to bind drug particles together. Over time, solvents can compromise shelf life, according to co-principal investigator Mathew Kuttolamadom, PhD, an associate professor of engineering at Texas A&M.
The Texas A&M team is using a different method, without solvents. First, they create a powder mixture of the drug, a biocompatible polymer (such as lactose), and a sheen, a pigment that colors the tablet and allows heat to be absorbed. Flavoring can also be added. Next, the mixture is heated in the printer chamber.
“The polymer should melt just enough. That gives the tablet structural strength. But it should not melt too much, whereby the drug can start dissolving into the polymer,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
The tablets are finished with precise applications of laser heat. Using computer-aided design software, the researchers can create tablets in almost any shape, such as “stars or teddy bears,” he said.
After much trial and error, the researchers have printed tablets that won’t break apart or become soggy.
Now they are testing how different laser scan speeds affect the structure of the tablet, which in turn affects the rate at which drugs dissolve. Slowing down the laser imparts more energy, strengthening the tablet structure and making drugs dissolve slower, for a longer release inside the body.
The researchers hope to develop machine learning models to test different laser speed combinations. Eventually, they could create tablets that combine drugs with different dissolve rates.
“The outside could be a rapid release, and the inside could be an extended release or a sustained release, or even a completely different drug,” Dr. Kuttolamadom said.
Older patients who take many daily medications could benefit from the technology. “Personalized tablets could be printed at your local pharmacy,” he said, “even before you leave your doctor’s office.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.