User login
Using Telehealth to Increase Lung Cancer Screening Referrals for At-Risk Veterans in Rural Communities
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
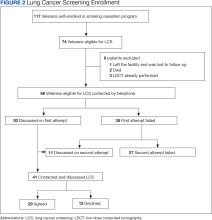
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
Annual lung cancer screening (LCS) with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) of the chest has been shown to reduce mortality rates for individuals at risk for lung cancer.1 Despite the benefits, < 5% of those who were eligible for LCS in the United States were screened in 2022.2 Implementation of a LCS program in rural communities is especially challenging because they are sparsely populated, medically underserved, and located far from urban centers.2-7 It is estimated that 1 in 5 people live in rural areas. Rates of tobacco smoking and cancer are higher in rural communities when compared with urban communities.8,9 The scarcity of physicians in rural areas who are familiar with LCS may further impede individuals who are at risk from accessing this life saving service.5,6 As a result, these individuals may not regularly undergo LCS as recommended.9
Telehealth, or the remote delivery of health care services via telecommunications, is an emerging approach for addressing unmet medical needs in rural communities and is being utilized widely by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA).4,10-15 The Veterans Integrated Service Network 12 (Great Lakes Network) has established the Clinical Resource Hub (CRH), a telehealth network comprising of licensed independent physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, and ancillary staff. The CRH offers regular, remote health care services to several community-based outpatient clinics (CBOC) primary care clinics located in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.10,14
The utility of telehealth in promoting LCS among at-risk veterans living in rural communities has not been firmly established.4-6 To address this issue, we conducted a proof-of-principle quality improvement project to determine whether a telehealth intervention would increase referrals among at-risk veterans who reside in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan who are self-enrolled in a CBOC smoking cessation program in Green Bay, Wisconsin. The CBOC provides primary health care to veterans residing in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as defined by US Department of Agriculture rural-urban commuting area codes.16 The intervention aimed to refer these individuals to the closest available and centralized LCS program, which is located at the Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center (CJZVAMC) in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
METHODS
We reviewed electronic health records (EHR) of LCS-eligible veterans treated by 2 authors (SH and TB) who were self-enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the Green Bay CBOC between October 1, 2020, and September 30, 2021. The program provides comprehensive evidence-based tobacco use treatment, online self-help resources, behavioral counseling, and medicines for smoking cessation.17 Veterans aged 50 to 80 years with a smoking history of ≥ 20 pack-years, who currently smoke cigarettes or quit within the past 15 years, were considered at risk for lung cancer and eligible for LCS. After confirming eligibility, pertinent demographic data were abstracted from each EHR.
Telehealth Intervention
The CJZVAMC centralized LCS program manages all delivery processes and has been previously shown to increase uptake of LCS and improve patient outcomes among veterans as compared to a decentralized approach.18,19 In the centralized approach, eligible veterans were referred by a CBOC primary care practitioner (PCP) to a designated centralized LCS program. The centralized LCS program provides further evaluation and disposition, which includes structured and shared decision making, ordering LDCT of the chest, reporting LDCT results to the patient and PCP, devising a goal-directed care plan, and managing follow-up LDCTs as indicated (Figure 1).18,19
This intervention was initiated before other measures aimed to increase the LCS enrollment for at-risk rural veterans at the CBOC, (eg, mailing LCS education fact sheet to veterans).20 After reviewing prospective veterans’ EHRs, 1 author (TB) contacted LCS-eligible veterans by telephone and left a voicemail if contact could not be established. A second telephone call was placed within 2 months of the initial call if no call back was documented in the EHR. When verbal contact was established, the goals of the centralized LCS program were described and the veteran was invited to participate.21
Veterans were seen at CBOCs affiliated with CJZVAMC. The CJZVAMC LCS coordinator was notified whenever a veteran agreed to enroll into LCS and then ordered LDCT, which was performed and read at CJZVAMC. Once LDCT has been ordered, 1 author (TB) reviewed the veteran’s EHR for LDCT completion over the next 4 months.Upon conclusion of the intervention period, the number of veterans referred for LDCT and the number of LDCTs performed were recorded. Each LDCT was reviewed and coded by medical imaging clinicians according to Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) version 1.1 and coded as 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 based on the nodule with the highest degree of suspicion.22 The LDCT and reports were also reviewed by pulmonary physicians at the CJZVAMC Lung Nodule Clinic with recommendations issued and reported to the PCP treating the veteran, such as annual follow-up with LDCT or referral to specialty care for further evaluation as indicated.
RESULTS
Of 117 veterans enrolled in the smoking cessation program at the CBOC during the intervention period, 74 (63%) were eligible to undergo LCS, and 68 (58%) were contacted by telephone (Figure 2). Eligible patients were primarily White male veterans; their mean (SD) age was 65.0 years (7.6). Participation in LCS was discussed with 41 (60%) veterans either during the initial or second telephone call of which 29 (71%) agreed to enroll and 12 (29%) declined. Veterans did not provide reasons for declining participation at the time of the telephone call.
Among the 74 eligible veterans who attended the smoking cessation program, only 3 had LDCT performed before initiation of this project (4%). At the conclusion of the telehealth intervention period, 19 veterans had LDCT performed (26%). Ten LDCTs were coded Lung-RADS 1, 7 Lung-RADS 2, 1 Lung-RADS 3, and 1 Lung-RADS 4B. In each case, annual follow-up LDCT or referral to a LCS clinician was pursued as indicated.22
DISCUSSION
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that a high percentage (66%) of individuals in rural communities who were contacted via telehealth agreed to participate in a regional LCS program. The program reviewed LDCT results, ordered follow-up LDCTs, and recommended further evaluations.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process could also promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians, if abnormal imaging findings are detected, remains unclear.
It has been well established LDCT LCS reduces lung cancer-specific and overall mortality rates among eligible current and former smokers.1,9,23 The 5-year relative survival rate of veterans diagnosed with localized non-small cell lung cancer is 63%; that number drops to 7% in those with advanced disease attesting to the utility of LCS in detecting early stage lung cancer.2 Despite these favorable observations, however, screening rates with free LDCT remains low in rural communities.3-7
This proof-of-principle quality improvement project found that telehealth intervention may increase referrals of at-risk veterans who reside in rural communities to the closest centralized LCS program located at aregional VAMC. This program is responsible for reviewing the results of the initial LDCT, ordering follow-up LDCT, and recommending further evaluation as indicated.18,19 Whether this centralized LCS process would promote adherence with subsequent annual LDCT and/or scheduled clinic appointments with designated clinicians if abnormal imaging findings are detected is yet to be determined.
We found that among 74 LCS-eligible rural veterans attending a CBOC-based smoking cessation program, only 3 (4%) underwent LDCT screening before this telehealth intervention was launched. This low LCS rate among veterans attempting to quit smoking may have been related, in part, to a lack of awareness of this intervention and/or barriers to LCS access.7,10,21,24 Deploying a telehealth intervention targeting LCS could address this life threatening and unmet medical need in rural communities.25 The results of this proof-of-principle quality improvement project support this contention with the reported increased referrals to and completion of initial LDCT within 4 months of the telehealth encounter.
Limitations
This was a small, single site project composed of predominantly White male rural veterans participating in a smoking cessation program associated with a VA facility.26,27 It is not clear whether similar outcomes would be observed in at-risk veterans who do not participate in a smoking cessation program or in more diverse communities. We were unable to contact 40% of LCS-eligible rural veterans by telephone. Twelve veterans reached by telephone declined to participate in LCS without providing a reason, and only 19 of 68 eligible veterans (28%) underwent LDCT screening during the 4-month telehealth intervention. The reasons underlying this overall low accrual rate and whether rural veterans prefer other means of personal communication regarding LCS were not determined. Lastly, generalizability of our initial observations to other veterans living in rural communities is limited because the project was conducted only in rural northern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Conclusions
At-risk rural veterans may be willing to participate in a centralized LCS program at a regional VA medical facility when contacted and coordinated using telehealth modalities. These findings offer support for future prospective, multisite, VA telehealth-based studies to be conducted in rural areas. The results of this project also suggest that telehealth intervention could increase referrals of at-risk rural veterans to the closest centralized LCS program located at a regional VA medical facility.
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
1. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team, Aberle DR, Adams AM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395-409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
2. State of Lung Cancer: 2023 Report. American Lung Association. November 14, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.lung.org/getmedia/186786b6-18c3-46a9-a7e7-810f3ce4deda/SOLC-2023-Print-Report.pdf
3. Okereke IC, Nishi S, Zhou J, Goodwin JS. Trends in lung cancer screening in the United States, 2016-2017. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11(3):873-881. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.01.105
4. Petraglia AF, Olazagasti JM, Strong A, Dunn B, Anderson RT, Hanley M. Establishing satellite lung cancer screening sites with telehealth to address disparities between high-risk smokers and American College of Radiology-approved Centers of Designation. J Thorac Imaging. 2021;36(1):2-5. doi:10.1097/RTI.0000000000000520
5. Odahowski CL, Zahnd WE, Eberth JM. Challenges and opportunities for lung cancer screening in rural America. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(4 Pt B):590-595. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.01.001
6. Rohatgi KW, Marx CM, Lewis-Thames MW, Liu J, Colditz GA, James AS. Urban-rural disparities in access to low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening in Missouri and Illinois. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E140. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200202
7. Boudreau JH, Miller DR, Qian S, Nunez ER, Caverly TJ, Wiener RS. Access to lung cancer screening in the Veterans Health Administration: does geographic distribution match need in the population? Chest. 2021;160(1):358-367. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.016
8. Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al, eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. National Cancer Institute, US Dept of Health and Human Services; April 15, 2020. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2017/index.html
9. US Preventive Services Task Force, Krist AH, Davidson KW, et al. Screening for Lung Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(10):962-970. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1117
10. Gopal RK, Solanki P, Bokhour BG, et al. Provider, staff, and patient perspectives on medical visits using clinical video telehealth: a foundation for educational initiatives to improve medical care in telehealth. J Nurse Pract. 2021;17(5):582-587. doi:10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.02.020
11. Yacoub JH, Swanson CE, Jay AK, Cooper C, Spies J, Krishnan P. The radiology virtual reading room: during and beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. J Digit Imaging. 2021;34(2):308-319. doi:10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4
12. Beswick DM, Vashi A, Song Y, et al. Consultation via telemedicine and access to operative care for patients with head and neck cancer in a Veterans Health Administration population. Head Neck. 2016;38(6):925-929. doi:10.1002/hed.24386
13. Ruco A, Dossa F, Tinmouth J, et al. Social media and mHealth technology for cancer screening: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(7):e26759. doi:10.2196/26759
14. Raza T, Joshi M, Schapira RM, Agha Z. Pulmonary telemedicine - a model to access the subspecialist services in underserved rural areas. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78(1):53-59. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.010
15. Chen A, Ayub MH, Mishuris RG, et al. Telehealth policy, practice, and education: a position statement of the Society of General Internal Medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2613-2620. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08190-8
16. Rural-Urban Commuting Area Codes. Economic Research Service, US Dept of Agriculture. Updated September 25, 2023. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-commuting-area-codes/
17. VHA Directive 1056: National Smoking and Tobacco Use Cessation Program. Veterans Health Administration, US Dept of Veterans Affairs; September 5, 2019. Accessed June 4, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=8488
18. Smith HB, Ward R, Frazier C, Angotti J, Tanner NT. Guideline-recommended lung cancer screening adherence is superior with a centralized approach. Chest. 2022;161(3):818-825. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2021.09.002
19. Lewis JA, Samuels LR, Denton J, et al. The association of health care system resources with lung cancer screening implementation: a cohort study. Chest. 2022;162(3):701-711. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2022.03.050
20. US Dept of Veterans Affairs. Lung cancer screening: patient education fact sheet. Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.cancer.va.gov/assets/pdf/survey/LCSflyer.pdf
21. Melzer AC, Golden SE, Ono SS, Datta S, Crothers K, Slatore CG. What exactly is shared decision-making? A qualitative study of shared decision-making in lung cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35(2):546-553. doi:10.1007/s11606-019-05516-3
22. Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA, Christensen JD, Dyer DS, White CS. Lung-RADS Version 1.1: challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021;216(6):1411-1422. doi:10.2214/AJR.20.24807
23. Ritzwoller DP, Meza R, Carroll NM, et al. Evaluation of population-level changes associated with the 2021 US Preventive Services Task Force lung cancer screening recommendations in community-based health care systems. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(10):e2128176. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28176
24. Golden SE, Ono SS, Thakurta SG, et al. “I’m putting my trust in their hands”: a qualitative study of patients’ views on clinician initial communication about lung cancer screening. Chest. 2020;158(3):1260-1267. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.072
25. Park ER, Chiles C, Cinciripini PM, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on telehealth research in cancer prevention and care: a call to sustain telehealth advances. Cancer. 2021;127(3):334-338. doi:10.1002/cncr.33227
26. Tremblay A, Taghizadeh N, Huang J, et al. A randomized controlled study of integrated smoking cessation in a lung cancer screening program. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1528-1537. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.04.024
27. Neil JM, Marotta C, Gonzalez I, et al. Integrating tobacco treatment into lung cancer screening practices: study protocol for the Screen ASSIST randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2021;111:106586. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2021.106586
Greater Transparency of Oncologists’ Pharma Relationships Needed
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
The findings reflect limited awareness in low-income countries about what scenarios constitute a conflict of interest, first author, Khalid El Bairi, MD, said during an interview. “There is a lack of training in ethics and integrity in medical schools [in countries in Africa], so people are not informed about conflicts of interest,” continued Dr. El Bairi, who presented the new research at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. “There is also a lack of policies in universities and hospitals to guide clinicians about conflict of interest reporting.”
Overall, 58.5% of survey participants categorized honoraria as a conflict of interest that required disclosure, while 50% said the same of gifts from pharmaceutical representatives, and 44.5% identified travel grants for attending conferences as conflicts of interests. The report was published in JCO Global Oncology. Less often considered conflicts of interest were personal and institutional research funding, trips to conferences, consulting or advisory roles, food and beverages, expert testimony, and sample drugs provided by the pharmaceutical industry.
Just 24% of participants indicated that all of the listed items were deemed conflicts of interest. The survey — called Oncology Transparency Under Scrutiny and Tracking, or ONCOTRUST-1 — considered the perceptions of 200 oncologists, about 70% of whom practice in low- and middle-income countries.
What’s more, 37.5% of respondents identified fear of losing financial support as a reason not to report a conflict of interest. Still, 75% indicated that industry-sponsored speaking does not affect treatment decisions, and 60% said conflicts of interest do not impair objective appraisal of clinical trials.
Dr. El Bairi, a research associate in the department of medical oncology at Mohammed VI University Hospital, Oujda, Morocco, and his colleagues undertook the study in part because of an editorial published in The Lancet Oncology last year. First author Fidel Rubagumya, MD, a consultant oncologist and director of research at Rwanda Military Hospital, Kigali, and colleagues called for more research on the ties between oncologists and industry in Africa. The ONCOTRUST-1 findings set the stage for a planned follow-up study, which aims to compare views surrounding conflicts of interests between oncologists in different economic settings.
Open Payments Houses US Physicians’ Conflicts of Interest
To be sure, many authors of research published in major US journals are based outside of the United States. According to JAMA Network Open, 69% of submissions to the journal are from international authors. However, Dr. El Bairi also raised other potential signs of industry influence that he said need global discussion, such as the role of pharmaceutical companies in presentations of clinical trial findings at large cancer societies’ conferences, a shift toward progression-free survival as the endpoint in clinical cancer trials, and the rise of third-party writing assistance.
“There are two sides of the story,” Dr. El Bairi said. “The good side is that unfortunately, sometimes [industry money is] the only way for African oncologists to go abroad for training, to conferences for their continuous medical education. The bad is now we may harm patients, we might harm science by having conflicts of interest not reported.”
Unlike other countries, the United States has plentiful data on the scale of physicians’ financial conflicts of interest in the form of the Open Payments platform. Championed by Sen. Chuck Grassley (R-Iowa), the federal repository of payments to doctors and teaching hospitals by drug and medical device companies was established as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
The health care reform law, which passed in 2010, requires pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers to report this information.
From 2013 to 2021, the pharmaceutical and medical device industry paid physicians $12.1 billion, according to a research letter published in JAMA in March of 2024 that reviewed Open Payments data.
Ranked by specialty, hematologists and oncologists received the fourth-largest amount of money in aggregate, the study shows. Their total of $825.8 million trailed only physicians in orthopedics ($1.36 billion), neurology and psychiatry ($1.32 billion) and cardiology ($1.29 billion). What’s more, this specialty had the biggest share of physicians taking industry money, with 74.2% of hematologists and oncologists receiving payments.
The payments from industry include fees for consulting services and speaking, as well as food and beverages, travel and lodging, education, gifts, grants, and honoraria.
Joseph S. Ross, MD, MHS, one of the JAMA study’s coauthors, said in an interview that the continued prevalence of such funding runs counter to the expectation behind the measure, which was that transparency would lead to physicians’ becoming less likely to accept a payment.
“We as a profession need to take a cold hard look in the mirror,” he said, referring to physicians in general.
Dr. Ross, professor of medicine at Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, said he hopes that the profession will self-police, and that patients will make a bigger deal of the issue. Still, he acknowledged that “the vast majority” of patient advocacy groups, too, are funded by the pharmaceutical industry.
Exposing Industry Payments May Have Perverse Effect
A growing body of research explores the effect that physicians’ financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies can have on their prescribing practices. Indeed, oncologists taking industry payments seem to be more likely to prescribe nonrecommended and low-value drugs in some clinical settings, according to a study published in The BMJ last year.
That study’s first author, Aaron P. Mitchell, MD, a medical oncologist and assistant attending physician at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York City, suggested in an interview that exposing industry payments to the sunlight may have had a perverse effect on physicians.
“There’s this idea of having license to do something,” Dr. Mitchell said, speaking broadly about human psychology rather than drawing on empirical data. “You might feel a little less bad about then prescribing more of that company’s drug, because the disclosure has already been done.”
The influence of pharmaceutical industry money on oncologists goes beyond what’s prescribed to which treatments get studied, approved, and recommended by guidelines, Dr. Mitchell said. He was also first author of a 2016 paper published in JAMA Oncology that found 86% of authors of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines had at least one conflict of interest reported on Open Systems in 2014.
Meanwhile, the fact that physicians’ payments from industry are a matter of public record on Open Systems has not guaranteed that doctors will disclose their conflicts of interest in other forums. A study published in JAMA earlier this year, for which Dr. Mitchell served as first author, found that almost one in three physicians endorsing drugs and devices on the social media platform X failed to disclose that the manufacturer paid them.
The lack of disclosure seems to extend beyond social media. A 2018 study published in JAMA Oncology found that 32% of oncologist authors of clinical drug trials for drugs approved over a 20-month period from 2016 to 2017 did not fully disclose payments from the trial sponsor when checked against the Open Payments database.
A lion’s share of industry payments within oncology appears to be going to a small group of high-profile physicians, suggested a 2022 study published in JCO Oncology Practice. It found that just 1% of all US oncologists accounted for 37% of industry payments, with each receiving more than $100,000 a year.
Experts: Professional Societies Should Further Limit Industry Payments
While partnerships between drug companies and physicians are necessary and have often been positive, more than disclosure is needed to minimize the risk of patient harm, according to an editorial published in March in JCO Oncology Practice. In it, Nina Niu Sanford, MD, a radiation oncologist UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist at Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, argue that following a specific blueprint could help mitigate financial conflicts of interest.
For starters, Dr. Sanford and Dr. Gyawali contend in the editorial that the maximum general payment NCCN members are allowed to receive from industry should be $0, compared with a current bar of $20,000 from a single entity or $50,000 from all external entities combined. They also urge professional societies to follow the current policy of the American Society of Clinical Oncology and ban members serving in their leadership from receiving any general payments from the industry.
The authors further suggest that investigators of clinical trials should be barred from holding stock for the drug or product while it is under study and that editorialists should not have conflicts of interest with the company whose drug or product they are discussing.
Pharmaceutical money can harm patients in ways that are not always obvious, Dr. Gyawali said in an interview.
“It can dominate the conversation by removing critical viewpoints from these top people about certain drugs,” he said. “It’s not always about saying good things about the drug.”
For instance, he suggested, a doctor receiving payments from Pfizer might openly criticize perceived flaws in drugs from other companies but refrain from weighing in negatively on a Pfizer drug.
From 2016 to 2018, industry made general payments to more than 52,000 physicians for 137 unique cancer drugs, according to a separate 2021 study published in the Journal of Cancer Policy, for which Dr. Gyawali served as one of the coauthors.
The results suggest that pharmaceutical money affects the entire cancer system, not relatively few oncology leaders. The amounts and dollar values grew each year covered by the study, to nearly 466,000 payments totaling $98.5 million in 2018.
Adriane Fugh-Berman, MD, professor of pharmacology and physiology at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, and director of PharmedOut, a Georgetown-based project that advances evidence-based prescribing and educates healthcare professionals about pharmaceutical marketing practices, has called for a ban on industry gifts to physicians.
When a publication asks physicians to disclose relevant conflicts of interest, physicians may choose not to disclose, because they don’t feel that their conflicts are relevant, Dr. Fugh-Berman said. Drug and device makers have also grown sophisticated about how they work with physicians, she suggested. “It’s illegal to market a drug before it comes on the market, but it’s not illegal to market the disease,” said Dr. Fugh-Berman, noting that drugmakers often work on long timelines.
“The doctor is going around saying we don’t have good therapies. They’re not pushing a drug. And so they feel totally fine about it.”
Anecdotally, Dr. Fugh-Berman noted that, if anything, speaking fees and similar payments only improve doctors’ reputations. She said that’s especially true if the physicians are paid by multiple companies, on the supposed theory that their conflicts of interest cancel each other out.
“I’m not defending this,” added Dr. Fugh-Berman, observing that, at the end of the day, such conflicts may go against the interests of patients.
“Sometimes the best drugs are older, generic, cheap drugs, and if oncologists or other specialists are only choosing among the most promoted drugs, they’re not necessarily choosing the best drugs.”
Beyond any prestige, doctors have other possible nonfinancial incentives for receiving industry payments. “It’s the relationships,” Dr. Fugh-Berman said. “Companies are very good at offering friendship.”
Dr. El Bairi reported NCODA leadership and honoraria along with expert testimony through techspert.io. Dr. Ross reported that he is a deputy editor of JAMA but was not involved in decisions regarding acceptance of or the review of the manuscript he authored and discussed in this article. Dr. Ross also reported receiving grants from the Food and Drug Administration, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Device Innovation Consortium, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. He was an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen that was settled in 2022. Dr. Mitchell reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gyawali reported a consulting or advisory role with Vivio Health. Dr. Fugh-Berman reported being an expert witness for plaintiffs in complaints about drug and device marketing practices.
FROM ASCO 2024
Should Cancer Trial Eligibility Become More Inclusive?
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, published online in Clinical Cancer Research, highlighted the potential benefits of broadening eligibility criteria for clinical trials.
“It is well known that results in an ‘ideal’ population do not always translate to the real-world population,” senior author Hans Gelderblom, MD, chair of the Department of Medical Oncology at the Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, the Netherlands, said in a press release. “Eligibility criteria are often too strict, and educated exemptions by experienced investigators can help individual patients, especially in a last-resort trial.”
Although experts have expressed interest in improving trial inclusivity, it’s unclear how doing so might impact treatment safety and efficacy.
In the Drug Rediscovery Protocol (DRUP), Dr. Gelderblom and colleagues examined the impact of broadening trial eligibility on patient outcomes. DRUP is an ongoing Dutch national, multicenter, pan-cancer, nonrandomized clinical trial in which patients are treated off-label with approved molecularly targeted or immunotherapies.
In the trial, 1019 patients with treatment-refractory disease were matched to one of the available study drugs based on their tumor molecular profile and enrolled in parallel cohorts. Cohorts were defined by tumor type, molecular profile, and study drug.
Among these patients, 82 patients — 8% of the cohort — were granted waivers to participate. Most waivers (45%) were granted as exceptions to general- or drug-related eligibility criteria, often because of out-of-range lab results. Other categories included treatment and testing exceptions, as well as out-of-window testing.
The researchers then compared safety and efficacy outcomes between the 82 participants granted waivers and the 937 who did not receive waivers.
Overall, Dr. Gelderblom’s team found that the rate of serious adverse events was similar between patients who received a waiver and those who did not: 39% vs 41%, respectively.
A relationship between waivers and serious adverse events was deemed “unlikely” for 86% of patients and “possible” for 14%. In two cases concerning a direct relationship, for instance, patients who received waivers for decreased hemoglobin levels developed anemia.
The rate of clinical benefit — defined as an objective response or stable disease for at least 16 weeks — was similar between the groups. Overall, 40% of patients who received a waiver (33 of 82) had a clinical benefit vs 33% of patients without a waiver (P = .43). Median overall survival for patients that received a waiver was also similar — 11 months in the waiver group and 8 months in the nonwaiver group (hazard ratio, 0.87; P = .33).
“Safety and clinical benefit were preserved in patients for whom a waiver was granted,” the authors concluded.
The study had several limitations. The diversity of cancer types, treatments, and reasons for protocol exemptions precluded subgroup analyses. In addition, because the decision to grant waivers depended in large part on the likelihood of clinical benefit, “it is possible that patients who received waivers were positively selected for clinical benefit compared with the general study population,” the authors wrote.
So, “although the clinical benefit rate of the patient group for whom a waiver was granted appears to be slightly higher, this difference might be explained by the selection process of the central study team, in which each waiver request was carefully considered, weighing the risks and potential benefits for the patient in question,” the authors explained.
Overall, “these findings advocate for a broader and more inclusive design when establishing novel trials, paving the way for a more effective and tailored application of cancer therapies in patients with advanced or refractory disease,” Dr. Gelderblom said.
Commenting on the study, Bishal Gyawali, MD, PhD, said that “relaxing eligibility criteria is important, and I support this. Trials should include patients that are more representative of the real-world, so that results are generalizable.”
However, “the paper overemphasized efficacy,” said Dr. Gyawali, from Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. The sample size of waiver-granted patients was small, plus “the clinical benefit rate is not a marker of efficacy.
“The response rate is somewhat better, but for a heterogeneous study with multiple targets and drugs, it is difficult to say much about treatment effects here,” Dr. Gyawali added. Overall, “we shouldn’t read too much into treatment benefits based on these numbers.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Stelvio for Life Foundation, the Dutch Cancer Society, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, pharma&, Eisai Co., Ipsen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. Dr. Gelderblom declared no conflicts of interest, and Dr. Gyawali declared no conflicts of interest related to his comment.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Quitting Smoking Boosts Life Expectancy at Any Age
TOPLINE:
Quitting smoking at any age increases life expectancy, with the most significant increases observed in younger individuals. But people who quit over age 65 can extend life expectancy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the detrimental effects of smoking and the positive impacts of cessation on life expectancy in individuals aged 35-75 years.
- Age-specific death rates by smoking status were calculated using the relative risks for all-cause mortality derived from the Cancer Prevention Study II data, 2018 National Health Interview Survey smoking prevalence data, and 2018 all-cause mortality rates.
- Life tables were constructed to obtain information on the life expectancies of people who never smoked, those who currently smoked, and those who previously smoked but quit at various ages.
- Estimates of years lost due to smoking and years gained by quitting smoking were calculated for people starting at age 35 and over 10-year increments.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with people who never smoked, those who smoked at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years and continued smoking throughout their lives would lose 9.1, 8.3, 7.3, 5.9, and 4.4 years, respectively.
- People who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would have life expectancies that are shorter by 1.2, 2.7, 3.9, 4.2, and 3.7 years, respectively, than those of same-age individuals who never smoked.
- Individuals who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would experience an additional 8.0, 5.6, 3.4, 1.7, and 0.7 years of life expectancy compared with those who continued smoking.
- People who quit at ages 65 and 75 years would have a 23.4% and 14.2% chance of gaining at least 1 additional year of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“This cessation benefit is not limited to young- and middle-aged adults who smoke; this study demonstrates its applicability to seniors as well. These findings may be valuable for clinicians seeking scientific evidence to motivate their patients who smoke to quit,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Thuy T.T. Le, PhD, from the Department of Health Management and Policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor and published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s estimates were according to data from 2018 and may not reflect current trends. The estimates also did not account for variability in smoking intensity among individuals.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute of the US National Institutes of Health and the US Food and Drug Administration Center for Tobacco Products. The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Quitting smoking at any age increases life expectancy, with the most significant increases observed in younger individuals. But people who quit over age 65 can extend life expectancy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the detrimental effects of smoking and the positive impacts of cessation on life expectancy in individuals aged 35-75 years.
- Age-specific death rates by smoking status were calculated using the relative risks for all-cause mortality derived from the Cancer Prevention Study II data, 2018 National Health Interview Survey smoking prevalence data, and 2018 all-cause mortality rates.
- Life tables were constructed to obtain information on the life expectancies of people who never smoked, those who currently smoked, and those who previously smoked but quit at various ages.
- Estimates of years lost due to smoking and years gained by quitting smoking were calculated for people starting at age 35 and over 10-year increments.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with people who never smoked, those who smoked at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years and continued smoking throughout their lives would lose 9.1, 8.3, 7.3, 5.9, and 4.4 years, respectively.
- People who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would have life expectancies that are shorter by 1.2, 2.7, 3.9, 4.2, and 3.7 years, respectively, than those of same-age individuals who never smoked.
- Individuals who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would experience an additional 8.0, 5.6, 3.4, 1.7, and 0.7 years of life expectancy compared with those who continued smoking.
- People who quit at ages 65 and 75 years would have a 23.4% and 14.2% chance of gaining at least 1 additional year of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“This cessation benefit is not limited to young- and middle-aged adults who smoke; this study demonstrates its applicability to seniors as well. These findings may be valuable for clinicians seeking scientific evidence to motivate their patients who smoke to quit,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Thuy T.T. Le, PhD, from the Department of Health Management and Policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor and published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s estimates were according to data from 2018 and may not reflect current trends. The estimates also did not account for variability in smoking intensity among individuals.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute of the US National Institutes of Health and the US Food and Drug Administration Center for Tobacco Products. The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Quitting smoking at any age increases life expectancy, with the most significant increases observed in younger individuals. But people who quit over age 65 can extend life expectancy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed the detrimental effects of smoking and the positive impacts of cessation on life expectancy in individuals aged 35-75 years.
- Age-specific death rates by smoking status were calculated using the relative risks for all-cause mortality derived from the Cancer Prevention Study II data, 2018 National Health Interview Survey smoking prevalence data, and 2018 all-cause mortality rates.
- Life tables were constructed to obtain information on the life expectancies of people who never smoked, those who currently smoked, and those who previously smoked but quit at various ages.
- Estimates of years lost due to smoking and years gained by quitting smoking were calculated for people starting at age 35 and over 10-year increments.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with people who never smoked, those who smoked at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years and continued smoking throughout their lives would lose 9.1, 8.3, 7.3, 5.9, and 4.4 years, respectively.
- People who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would have life expectancies that are shorter by 1.2, 2.7, 3.9, 4.2, and 3.7 years, respectively, than those of same-age individuals who never smoked.
- Individuals who quit smoking at ages 35, 45, 55, 65, and 75 years would experience an additional 8.0, 5.6, 3.4, 1.7, and 0.7 years of life expectancy compared with those who continued smoking.
- People who quit at ages 65 and 75 years would have a 23.4% and 14.2% chance of gaining at least 1 additional year of life.
IN PRACTICE:
“This cessation benefit is not limited to young- and middle-aged adults who smoke; this study demonstrates its applicability to seniors as well. These findings may be valuable for clinicians seeking scientific evidence to motivate their patients who smoke to quit,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Thuy T.T. Le, PhD, from the Department of Health Management and Policy at the University of Michigan School of Public Health in Ann Arbor and published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s estimates were according to data from 2018 and may not reflect current trends. The estimates also did not account for variability in smoking intensity among individuals.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute of the US National Institutes of Health and the US Food and Drug Administration Center for Tobacco Products. The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Weight Loss Drugs Cut Cancer Risk in Diabetes Patients
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Recent research on popular weight loss drugs has uncovered surprising benefits beyond their intended use, like lowering the risk of fatal heart attacks. And now there may be another unforeseen advantage:
That’s according to a study published July 5 in JAMA Network Open where researchers studied glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists (known as GLP-1RAs), a class of drugs used to treat diabetes and obesity. Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound, which have become well-known recently because they are linked to rapid weight loss, contain GLP-1RAs.
For the study, they looked at electronic health records of 1.7 million patients who had type 2 diabetes, no prior diagnosis of obesity-related cancers, and had been prescribed GLP-1RAs, insulins, or metformin from March 2005 to November 2018.
The scientists found that compared to patients who took insulin, people who took GLP-1RAs had a “significant risk reduction” in 10 of 13 obesity-related cancers. Those 10 cancers were esophageal, colorectal, endometrial, gallbladder, kidney, liver, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers, as well as meningioma and multiple myeloma.
Compared with patients taking insulin, patients taking GLP-1RAs showed no statistically significant reduction in stomach cancer and no reduced risk of breast and thyroid cancers, the study said.
But the study found no decrease in cancer risk with GLP-1RAs compared with metformin.
While the study results suggest that these drugs may reduce the risk of certain obesity-related cancers better than insulins, more research is needed, they said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Urticaria Linked to Higher Cancer Risk, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
which decreased to 6% in subsequent years, in a cohort study using Danish healthcare databases.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from Danish healthcare registries and compared the incident cancer risk between patients with urticaria and the risk in the general population.
- They identified 87,507 patients (58% women) with a primary or secondary first-time hospital outpatient clinic, emergency room, or inpatient diagnosis of urticaria between 1980 and 2022, who were followed for a median of 10.1 years.
- Incident cancers, including nonmelanoma skin cancer, were identified using the Danish Cancer Registry and classified by the extent of spread at the time of diagnosis.
- This study computed the absolute cancer risk within the first year of an urticaria diagnosis and standardized incidence ratios (SIRs), with 95% CIs standardized to Danish national cancer rates.
TAKEAWAY:
- For the first year of follow-up, the absolute risk for all cancer types was 0.7%, and it was 29.5% for subsequent years. The overall SIR for all types of cancer was 1.09 (95% CI, 1.06-1.11), which was based on 7788 observed cancer cases compared with 7161 cases expected over the entire follow-up period.
- Within the first year of follow-up, 588 patients with urticaria were diagnosed with cancer, for an SIR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.38-1.62) for all cancer types.
- After the first year, the SIR for all cancer sites decreased and stabilized at 1.06 (95% CI, 1.04-1.09), with 7200 observed cancer cases.
- The risk was highest for hematological cancers in the first year, particularly Hodgkin lymphoma (SIR, 5.35; 95% CI, 2.56-9.85).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study suggests that urticaria may be a marker of occult cancer and that it is associated with a slightly increased long-term cancer risk,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sissel B.T. Sørensen, departments of dermatology and rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark. It was published online on June 27, 2024, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study is limited by its observational design and reliance on registry data, which may be subject to misclassification or incomplete information. In addition, the study could not assess individual patient factors such as lifestyle or genetic predispositions that may influence cancer risk, and the results may not be generalizable to other populations. Finally, the exact biologic mechanisms linking urticaria and cancer remain unclear, warranting further investigation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not receive any funding. The authors reported that they had no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Time Warp: Fax Machines Still Common in Oncology Practice. Why?
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One minute, he’s working on sequencing a tumor genome. The next, he’s sifting through pages of disorganized data from a device that has been around for decades: the fax machine.
“If two doctors’ offices aren’t on the same electronic medical record, one of the main ways to transfer records is still by fax,” said Dr. Lewis, director of gastrointestinal oncology at Intermountain Healthcare in Murray, Utah. “I can go from cutting-edge innovation to relying on, at best, 1980s information technology. It just boggles my mind.”
Dr. Lewis, who has posted about his frustration with fax machines, is far from alone. Oncologists are among the many specialists across the country at the mercy of telecopiers.
According to a 2021 report by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology, fax and mail continue to be the most common methods for hospitals and health systems to exchange care record summaries. In 2019, nearly 8 in 10 hospitals used mail or fax to send and receive health information, the report found.
Fax machines are still commonplace across the healthcare spectrum, said Robert Havasy, MS, senior director for informatics strategy at the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). Inertia, cost, and more pressing priorities for hospitals and medical institutions contribute to the technology sticking around, he explained.
“Post-COVID, my guess is we’re still at over 50% of healthcare practices using fax for some reason, on a daily basis,” Mr. Havasy said in an interview. “A lot of hospitals just don’t have the time, the money, or the staff to fix that problem because there’s always something a little higher up the priority chain they need to focus on.”
If, for instance, “you’re going to do a process redesign to reduce hospital total acquired infections, your fax machine replacement might be 10th or 12th on the list. It just never gets up to 1 or 2 because it’s ‘not that much of a problem,’ ” he added.
Or is it?
Administrators may not view fax machines as a top concern, but clinicians who deal with the machines daily see it differently.
“What worries me is we’re taking records out of an electronic storehouse [and] converting them to a paper medium,” Dr. Lewis said. “And then we are scanning into another electronic storehouse. The more steps, the more can be lost.”
And when information is lost, patient care can be compromised.
Slower Workflows, Care Concerns
Although there are no published data on fax machine use in oncology specifically, this outdated technology does come into play in a variety of ways along the cancer care continuum.
Radiation oncologist David R. Penberthy, MD, said patients often seek his cancer center’s expertise for second opinions, and that requires collecting patient records from many different practices.
“Ideally, it would come electronically, but sometimes it does come by fax,” said Dr. Penberthy, program director of radiation oncology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville. “The quality of the fax is not always the best. Sometimes it’s literally a fax of a fax. You’re reading something that’s very difficult to read.”
Orders for new tests are also typically sent and received via fax temporarily while IT teams work to integrate them into the electronic health record (EHR), Dr. Penberthy said.
Insurers and third-party laboratories often send test results back by fax as well.
“Even if I haven’t actually sent my patient out of our institution, this crucial result may only be entered back into the record as a scanned document from a fax, which is not great because it can get lost in the other results that are reported electronically,” Dr. Lewis said. The risk here is that an ordering physician won’t see these results, which can lead to delayed or overlooked care for patients, he explained.
“To me, it’s like a blind spot,” Dr. Lewis said. “Every time we use a fax, I see it actually as an opportunity for oversight and missed opportunity to collect data.”
Dr. Penberthy said faxing can slow things down at his practice, particularly if he faxes a document to another office but receives no confirmation and has to track down what happened.
As for cybersecurity, data that are in transit during faxing are generally considered secure and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), said Mr. Havasy of HIMSS. However, the Privacy Rule also requires that data remain secure while at rest, which isn’t always possible, he added.
“That’s where faxes fall down, because generally fax machines are in public, if you will, or open areas in a hospital,” he said. “They just sit on a desk. I don’t know that the next nurse who comes up and looks through that stack was the nurse who was treating the patient.”
Important decisions or results can also be missed when sent by fax, creating headaches for physicians and care problems for patients.
Dr. Lewis recently experienced an insurance-related fax mishap over Memorial Day weekend. He believed his patient had access to the antinausea medication he had prescribed. When Dr. Lewis happened to check the fax machine over the weekend, he found a coverage denial for the medication from the insurer but, at that point, had no recourse to appeal because it was a long holiday weekend.
“Had the denial been sent by an electronic means that was quicker and more readily available, it would have been possible to appeal before the holiday weekend,” he said.
Hematologist Aaron Goodman, MD, encountered a similar problem after an insurer denied coverage of an expensive cancer drug for a patient and faxed over its reason for the denial. Dr. Goodman was not directly notified that the information arrived and didn’t learn about the denial for a week, he said.
“There’s no ‘ding’ in my inbox if something is faxed over and scanned,” said Dr. Goodman, associate professor of medicine at UC San Diego Health. “Once I realized it was denied, I was able to rectify it, but it wasted a week of a patient not getting a drug that I felt would be beneficial for them.”
Broader Health Policy Impacts
The use of outdated technology, such as fax machines, also creates ripple effects that burden the health system, health policy experts say.
Duplicate testing and unnecessary care are top impacts, said Julia Adler-Milstein, PhD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of clinical informatics and digital transformation at the University of California, San Francisco.
Studies show that 20%-30% of the $65 billion spent annually on lab tests is used on unnecessary duplicate tests, and another estimated $30 billion is spent each year on unnecessary duplicate medical imaging. These duplicate tests may be mitigated if hospitals adopt certified EHR technology, research shows.
Still, without EHR interoperability between institutions, new providers may be unaware that tests or past labs for patients exist, leading to repeat tests, said Dr. Adler-Milstein, who researches health IT policy with a focus on EHRs. Patients can sometimes fill in the gaps, but not always.
“Fax machines only help close information gaps if the clinician is aware of where to seek out the information and there is someone at the other organization to locate and transmit the information in a timely manner,” Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Old technology and poor interoperability also greatly affect data collection for disease surveillance and monitoring, said Janet Hamilton, MPH, executive director for the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists. This issue was keenly demonstrated during the pandemic, Ms. Hamilton said.
“It was tragic, quite honestly,” she said. “There was such an immense amount of data that needed to be moved quickly, and that’s when computers are at their best.”
But, she said, “we didn’t have the level of systems in place to do it well.”
Specifically, the lack of electronic case reporting in place during the pandemic — where diagnoses are documented in the record and then immediately sent to the public health system — led to reports that were delayed, not made, or had missing or incomplete information, such as patients’ race and ethnicity or other health conditions, Ms. Hamilton said.
Incomplete or missing data hampered the ability of public health officials and researchers to understand how the virus might affect different patients.
“If you had a chronic condition like cancer, you were less likely to have a positive outcome with COVID,” Ms. Hamilton said. “But because electronic case reporting was not in place, we didn’t get some of those additional pieces of information. We didn’t have people’s underlying oncology status to then say, ‘Here are individuals with these types of characteristics, and these are the things that happen if they also have a cancer.’”
Slow, but Steady, Improvements
Efforts at the state and federal levels have targeted improved health information exchange, but progress takes time, Dr. Adler-Milstein said.
Most states have some form of health information exchange, such as statewide exchanges, regional health information organizations, or clinical data registries. Maryland is often held up as a notable example for its health information exchange, Dr. Adler-Milstein noted.
According to Maryland law, all hospitals under the jurisdiction of the Maryland Health Care Commission are required to electronically connect to the state-designated health information exchange. In 2012, Maryland became the first state to connect all its 46 acute care hospitals in the sharing of real-time data.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act provided federal-enhanced Medicaid matching funds to states through 2021 to support efforts to advance electronic exchange. Nearly all states used these funds, and most have identified other sources to sustain the efforts, according to a recent US Government Accountability Office (GAO) report. However, GAO found that small and rural providers are less likely to have the financial and technological resources to participate in or maintain electronic exchange capabilities.
Nationally, several recent initiatives have targeted health data interoperability, including for cancer care. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Data Modernization Initiative is a multiyear, multi–billion-dollar effort to improve data sharing across the federal and state public health landscape.
Meanwhile, in March 2024, the Biden-Harris administration launched United States Core Data for Interoperability Plus Cancer. The program will define a recommended minimum set of cancer-related data to be included in a patient’s EHR to enhance data exchange for research and clinical care.
EHR vendors are also key to improving the landscape, said Dr. Adler-Milstein. Vendors such as Epic have developed strong sharing capabilities for transmitting health information from site to site, but of course, that only helps if providers have Epic, she said.
“That’s where these national frameworks should help, because we don’t want it to break down by what EHR vendor you have,” she said. “It’s a patchwork. You can go to some places and hear success stories because they have Epic or a state health information exchange, but it’s very heterogeneous. In some places, they have nothing and are using a fax machine.”
Mr. Havasy believes fax machines will ultimately go extinct, particularly as a younger, more digitally savvy generation enters the healthcare workforce. He also foresees that the growing use of artificial intelligence will help eradicate the outdated technology.
But, Ms. Hamilton noted, “unless we have consistent, ongoing, sustained funding, it is very hard to move off [an older] technology that can work. That’s one of the biggest barriers.”
“Public health is about protecting the lives of every single person everywhere,” Ms. Hamilton said, “but when we don’t have the data that comes into the system, we can’t achieve our mission.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer Drug Shortages Continue in the US, Survey Finds
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nearly 90% of the 28 NCCN member centers who responded to the survey, conducted between May 28 and June 11, said they were experiencing a shortage of at least one drug.
“Many drugs that are currently in shortage form the backbones of effective multiagent regimens across both curative and palliative treatment settings,” NCCN’s CEO Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, said in an interview.
The good news is that carboplatin and cisplatin shortages have fallen dramatically since 2023. At the peak of the shortage in 2023, 93% of centers surveyed reported experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and 70% were experiencing a shortage of cisplatin, whereas in 2024, only 11% reported a carboplatin shortage and 7% reported a cisplatin shortage.
“Thankfully, the shortages for carboplatin and cisplatin are mostly resolved at this time,” Dr. Denlinger said.
However, all three NCCN surveys conducted in the past year, including the most recent one, have found shortages of various chemotherapies and supportive care medications, which suggests this is an ongoing issue affecting a significant spectrum of generic drugs.
“The acute crisis associated with the shortage of carboplatin and cisplatin was a singular event that brought the issue into the national spotlight,” but it’s “important to note that the current broad drug shortages found on this survey are not new,” said Dr. Denlinger.
In the latest survey, 89% of NCCN centers continue to report shortages of one or more drugs, and 75% said they are experiencing shortages of two or more drugs.
Overall, 57% of centers are short on vinblastine, 46% are short on etoposide, and 43% are short on topotecan. Other common chemotherapy and supportive care agents in short supply include dacarbazine (18% of centers) as well as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and methotrexate (14% of centers).
In 2023, however, shortages of methotrexate and 5-FU were worse, with 67% of centers reporting shortages of methotrexate and 26% of 5-FU.
In the current survey, 75% of NCCN centers also noted they were aware of drug shortages within community practices in their area, and more than one in four centers reported treatment delays requiring additional prior authorization.
Cancer drug shortages impact not only routine treatments but also clinical trials. The recent survey found that 43% of respondents said drug shortages disrupted clinical trials at their center. The biggest issues centers flagged included greater administrative burdens, lower patient enrollment, and fewer open trials.
How are centers dealing with ongoing supply issues?
Top mitigation strategies include reducing waste, limiting use of current stock, and adjusting the timing and dosage within evidence-based ranges.
“The current situation underscores the need for sustainable, long-term solutions that ensure a stable supply of high-quality cancer medications,” Alyssa Schatz, MSW, NCCN senior director of policy and advocacy, said in a news release.
Three-quarters (75%) of survey respondents said they would like to see economic incentives put in place to encourage the high-quality manufacturing of medications, especially generic versions that are often in short supply. Nearly two-thirds (64%) cited a need for a broader buffer stock payment, and the same percentage would like to see more information on user experiences with various generic suppliers to help hospitals contract with those engaging in high-quality practices.
The NCCN also continues to work with federal regulators, agencies, and lawmakers to implement long-term solutions to cancer drug shortages.
“The federal government has a key role to play in addressing this issue,” Ms. Schatz said. “Establishing economic incentives, such as tax breaks or manufacturing grants for generic drugmakers, will help support a robust and resilient supply chain — ultimately safeguarding care for people with cancer across the country.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Top reads from the CHEST journal portfolio
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Primary Care: Try These Steps to Boost Lung Cancer Screens
A few years ago, Kim Lori Sandler, MD, realized many patients newly diagnosed with lung cancer had never been screened for the disease — they received CT scans only because they were symptomatic.
But Dr. Sandler, a radiologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, could see in medical charts that most of these patients had been eligible for a screening before becoming symptomatic. And for women, most had received decades worth of mammograms. She saw an opportunity and launched a study to find out if an intervention would work.
Low-dose CT and mammography services often are available in the same imaging facility, so women who qualified for a lung cancer screening were offered the scan during their mammography visit. Over a 3-year period, monthly rates of lung scans in women rose by 50% at one facility and 36% at the other.
“What we found is that women are really receptive, if you talk to them about it,” Dr. Sandler said. “I don’t think that lung cancer is thought of as a disease in women.”
Although lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine found only 18% of eligible patients were screened in 2022, a far cry from the rates of 72% for colon cancer — which itself falls short of goals from US medical groups like the American Cancer Society (ACS). Among those eligible, rates of lung screenings were lowest among younger people without comorbid conditions, who did not have health insurance or a usual source of care, and those living in southern states and states that did not expand Medicaid as part of the Affordable Care Act.
Getting patients screened is lifesaving: 27% of people with lung cancer survive 5 years after diagnosis. But the survival rate rises to 63% when cases are diagnosed at an early stage.
Increasing Uptake
The formal recommendation to use low-dose chest CT to screen for lung cancer is only a decade old. The approach was first endorsed by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) on the basis of an influential trial that found such testing was linked to a 20% reduction in mortality from the disease. Updated 2021 USPSTF guidelines call for annual screening of people aged 50-80 years who have a 20 pack-year history of smoking and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
But implementing the recommendation is not always simple. Unlike a colorectal or breast cancer screening, which is recommended primarily on patient age, eligibility for a lung cancer screening requires calculating pack-years of smoking, and, for past smokers, knowledge of when they quit.
The structured fields in most electronic medical records (EMRs) inquire about current or past use of cigarettes and the number of daily packs smoked. But few EMRs can calculate when a patient starts smoking two cigarettes a day but then increases to a pack a day and cuts down again. EMRs also do not track when a patient has stopped smoking permanently. Individual clinicians or health systems must identify patients who are eligible for screening, but the lack of automated calculations makes that job more difficult.
Dr. Sandler and colleagues turned to the informatics team at Vanderbilt to develop a natural language processing approach that extracts smoking data directly from clinician notes instead of using standard variables in their EMR.
The number of patients identified as needing a screening using the algorithm nearly doubled from baseline, from 5887 to 10,231 over a 3-year period, according to results from another study that Dr. Sandler published.
Although the algorithm may occasionally flag someone who does not need screening as eligible, “you can always have a conversation with the patient to determine if they actually meet eligibility criteria,” Dr. Sandler said.
Patient Navigators to the Rescue?
About a decade ago, Travis Baggett, MD, MPH, an associate professor of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, received pilot funding from the ACS to study cancer epidemiology among patients at Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program (BHCHP), which serves nearly 10,000 patients at a variety of Boston-area clinics each year.
“We found that both the incidence and mortality rates for lung cancer were more than twofold higher than in the general population,” Dr. Baggett, who is also the director of research at BHCHP, said.
He also discovered that BHCHP patients were diagnosed at significantly later stages than people in the general population for malignancies like breast and colorectal cancer.
Screening for lung cancer was a new recommendation at the time. With additional funding from the ACS, he launched a clinical trial in 2020 that randomized patients who were eligible for lung cancer screening to either work with a patient navigator or receive usual care.
The navigators eased the burden on primary care clinicians: They facilitated shared decision-making visits, helped participants make and attend appointments for low-dose CT, assisted with transportation, and arranged follow-up as needed.
The 3-year study found 43% of patients who received navigation services underwent screening for lung cancer, compared with 9% in the usual-care arm. Participants said the navigators played a critical role in educating them about the importance of screening, coordinating care, and providing emotional support.
“At the root of it all, it was quite clear that one thing that made the navigator successful was their interpersonal qualities and having someone that the patient could trust to help guide them through the process,” Dr. Baggett said.
The navigator program, however, stopped when the funding for the study ended.
But another health system has implemented navigators in a sustainable way through a quality improvement project. Michael Gieske, MD, director of lung cancer screening at St. Elizabeth Healthcare in Edgewood, Kentucky, starts his Friday morning meeting with a multidisciplinary group, including a thoracic surgeon, radiologist, pulmonologist, and several screening nurse navigators. They review the week’s chest CTs, with approximately one-third from patients who underwent lung cancer screening.
Nurse navigators at St. Elizabeth Healthcare follow up with any patient whose scan is suspicious for lung cancer and guide them through the process of seeing specialists and obtaining additional testing.
“They essentially hold the patient’s hand through this scary time in their life and make sure that everything flows smoothly and efficiently,” said Dr. Gieske, a family medicine physician.
St. Elizabeth’s program also draws on several evidence-based strategies used for other cancer screening programs, such as patient and provider education and quarterly feedback to their 194 primary care clinicians on rates of lung cancer screening among their eligible patients.
Several requirements for reimbursement for a lung cancer screening from the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services can also serve as barriers to getting patients screened: Clinicians must identify who is eligible, provide tobacco cessation counseling, and document the shared decision-making process.
To streamline the steps, St. Elizabeth’s clinicians use an EMR smart set that reminds clinicians to verify smoking history and helps them document the required counseling.
Last year, 47% of eligible patients received their recommended screening, and Dr. Gieske said he expects even more improvement.
“We’re on track this year to complete 60% uptake if things continue,” he said, adding that 76% of the new cases of lung cancer are now diagnosed in stage I, with only 5% diagnosed in stage IV.
Dr. Gieske has shared his experience with many clinics in Appalachia, home to some of the highest rates of mortality from lung cancer in the country. A major part of his role with the Appalachian Community Cancer Alliance is helping educate primary care clinicians in the region about the importance of early detection of lung cancer.
“I think one of the most important things is just to convey a message of hope,” he said. “We’re trying to get the good word out there that if you screen individuals, you’re going to catch it early, when you have an extremely high chance of curing the lung cancer.”
Dr. Baggett reported support from grants from the ACS and the Massachusetts General Hospital Research Scholars Program. Dr. Sandler and Dr. Gieske reported no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A few years ago, Kim Lori Sandler, MD, realized many patients newly diagnosed with lung cancer had never been screened for the disease — they received CT scans only because they were symptomatic.
But Dr. Sandler, a radiologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, could see in medical charts that most of these patients had been eligible for a screening before becoming symptomatic. And for women, most had received decades worth of mammograms. She saw an opportunity and launched a study to find out if an intervention would work.
Low-dose CT and mammography services often are available in the same imaging facility, so women who qualified for a lung cancer screening were offered the scan during their mammography visit. Over a 3-year period, monthly rates of lung scans in women rose by 50% at one facility and 36% at the other.
“What we found is that women are really receptive, if you talk to them about it,” Dr. Sandler said. “I don’t think that lung cancer is thought of as a disease in women.”
Although lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine found only 18% of eligible patients were screened in 2022, a far cry from the rates of 72% for colon cancer — which itself falls short of goals from US medical groups like the American Cancer Society (ACS). Among those eligible, rates of lung screenings were lowest among younger people without comorbid conditions, who did not have health insurance or a usual source of care, and those living in southern states and states that did not expand Medicaid as part of the Affordable Care Act.
Getting patients screened is lifesaving: 27% of people with lung cancer survive 5 years after diagnosis. But the survival rate rises to 63% when cases are diagnosed at an early stage.
Increasing Uptake
The formal recommendation to use low-dose chest CT to screen for lung cancer is only a decade old. The approach was first endorsed by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) on the basis of an influential trial that found such testing was linked to a 20% reduction in mortality from the disease. Updated 2021 USPSTF guidelines call for annual screening of people aged 50-80 years who have a 20 pack-year history of smoking and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
But implementing the recommendation is not always simple. Unlike a colorectal or breast cancer screening, which is recommended primarily on patient age, eligibility for a lung cancer screening requires calculating pack-years of smoking, and, for past smokers, knowledge of when they quit.
The structured fields in most electronic medical records (EMRs) inquire about current or past use of cigarettes and the number of daily packs smoked. But few EMRs can calculate when a patient starts smoking two cigarettes a day but then increases to a pack a day and cuts down again. EMRs also do not track when a patient has stopped smoking permanently. Individual clinicians or health systems must identify patients who are eligible for screening, but the lack of automated calculations makes that job more difficult.
Dr. Sandler and colleagues turned to the informatics team at Vanderbilt to develop a natural language processing approach that extracts smoking data directly from clinician notes instead of using standard variables in their EMR.
The number of patients identified as needing a screening using the algorithm nearly doubled from baseline, from 5887 to 10,231 over a 3-year period, according to results from another study that Dr. Sandler published.
Although the algorithm may occasionally flag someone who does not need screening as eligible, “you can always have a conversation with the patient to determine if they actually meet eligibility criteria,” Dr. Sandler said.
Patient Navigators to the Rescue?
About a decade ago, Travis Baggett, MD, MPH, an associate professor of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, received pilot funding from the ACS to study cancer epidemiology among patients at Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program (BHCHP), which serves nearly 10,000 patients at a variety of Boston-area clinics each year.
“We found that both the incidence and mortality rates for lung cancer were more than twofold higher than in the general population,” Dr. Baggett, who is also the director of research at BHCHP, said.
He also discovered that BHCHP patients were diagnosed at significantly later stages than people in the general population for malignancies like breast and colorectal cancer.
Screening for lung cancer was a new recommendation at the time. With additional funding from the ACS, he launched a clinical trial in 2020 that randomized patients who were eligible for lung cancer screening to either work with a patient navigator or receive usual care.
The navigators eased the burden on primary care clinicians: They facilitated shared decision-making visits, helped participants make and attend appointments for low-dose CT, assisted with transportation, and arranged follow-up as needed.
The 3-year study found 43% of patients who received navigation services underwent screening for lung cancer, compared with 9% in the usual-care arm. Participants said the navigators played a critical role in educating them about the importance of screening, coordinating care, and providing emotional support.
“At the root of it all, it was quite clear that one thing that made the navigator successful was their interpersonal qualities and having someone that the patient could trust to help guide them through the process,” Dr. Baggett said.
The navigator program, however, stopped when the funding for the study ended.
But another health system has implemented navigators in a sustainable way through a quality improvement project. Michael Gieske, MD, director of lung cancer screening at St. Elizabeth Healthcare in Edgewood, Kentucky, starts his Friday morning meeting with a multidisciplinary group, including a thoracic surgeon, radiologist, pulmonologist, and several screening nurse navigators. They review the week’s chest CTs, with approximately one-third from patients who underwent lung cancer screening.
Nurse navigators at St. Elizabeth Healthcare follow up with any patient whose scan is suspicious for lung cancer and guide them through the process of seeing specialists and obtaining additional testing.
“They essentially hold the patient’s hand through this scary time in their life and make sure that everything flows smoothly and efficiently,” said Dr. Gieske, a family medicine physician.
St. Elizabeth’s program also draws on several evidence-based strategies used for other cancer screening programs, such as patient and provider education and quarterly feedback to their 194 primary care clinicians on rates of lung cancer screening among their eligible patients.
Several requirements for reimbursement for a lung cancer screening from the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services can also serve as barriers to getting patients screened: Clinicians must identify who is eligible, provide tobacco cessation counseling, and document the shared decision-making process.
To streamline the steps, St. Elizabeth’s clinicians use an EMR smart set that reminds clinicians to verify smoking history and helps them document the required counseling.
Last year, 47% of eligible patients received their recommended screening, and Dr. Gieske said he expects even more improvement.
“We’re on track this year to complete 60% uptake if things continue,” he said, adding that 76% of the new cases of lung cancer are now diagnosed in stage I, with only 5% diagnosed in stage IV.
Dr. Gieske has shared his experience with many clinics in Appalachia, home to some of the highest rates of mortality from lung cancer in the country. A major part of his role with the Appalachian Community Cancer Alliance is helping educate primary care clinicians in the region about the importance of early detection of lung cancer.
“I think one of the most important things is just to convey a message of hope,” he said. “We’re trying to get the good word out there that if you screen individuals, you’re going to catch it early, when you have an extremely high chance of curing the lung cancer.”
Dr. Baggett reported support from grants from the ACS and the Massachusetts General Hospital Research Scholars Program. Dr. Sandler and Dr. Gieske reported no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A few years ago, Kim Lori Sandler, MD, realized many patients newly diagnosed with lung cancer had never been screened for the disease — they received CT scans only because they were symptomatic.
But Dr. Sandler, a radiologist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, could see in medical charts that most of these patients had been eligible for a screening before becoming symptomatic. And for women, most had received decades worth of mammograms. She saw an opportunity and launched a study to find out if an intervention would work.
Low-dose CT and mammography services often are available in the same imaging facility, so women who qualified for a lung cancer screening were offered the scan during their mammography visit. Over a 3-year period, monthly rates of lung scans in women rose by 50% at one facility and 36% at the other.
“What we found is that women are really receptive, if you talk to them about it,” Dr. Sandler said. “I don’t think that lung cancer is thought of as a disease in women.”
Although lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine found only 18% of eligible patients were screened in 2022, a far cry from the rates of 72% for colon cancer — which itself falls short of goals from US medical groups like the American Cancer Society (ACS). Among those eligible, rates of lung screenings were lowest among younger people without comorbid conditions, who did not have health insurance or a usual source of care, and those living in southern states and states that did not expand Medicaid as part of the Affordable Care Act.
Getting patients screened is lifesaving: 27% of people with lung cancer survive 5 years after diagnosis. But the survival rate rises to 63% when cases are diagnosed at an early stage.
Increasing Uptake
The formal recommendation to use low-dose chest CT to screen for lung cancer is only a decade old. The approach was first endorsed by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) on the basis of an influential trial that found such testing was linked to a 20% reduction in mortality from the disease. Updated 2021 USPSTF guidelines call for annual screening of people aged 50-80 years who have a 20 pack-year history of smoking and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
But implementing the recommendation is not always simple. Unlike a colorectal or breast cancer screening, which is recommended primarily on patient age, eligibility for a lung cancer screening requires calculating pack-years of smoking, and, for past smokers, knowledge of when they quit.
The structured fields in most electronic medical records (EMRs) inquire about current or past use of cigarettes and the number of daily packs smoked. But few EMRs can calculate when a patient starts smoking two cigarettes a day but then increases to a pack a day and cuts down again. EMRs also do not track when a patient has stopped smoking permanently. Individual clinicians or health systems must identify patients who are eligible for screening, but the lack of automated calculations makes that job more difficult.
Dr. Sandler and colleagues turned to the informatics team at Vanderbilt to develop a natural language processing approach that extracts smoking data directly from clinician notes instead of using standard variables in their EMR.
The number of patients identified as needing a screening using the algorithm nearly doubled from baseline, from 5887 to 10,231 over a 3-year period, according to results from another study that Dr. Sandler published.
Although the algorithm may occasionally flag someone who does not need screening as eligible, “you can always have a conversation with the patient to determine if they actually meet eligibility criteria,” Dr. Sandler said.
Patient Navigators to the Rescue?
About a decade ago, Travis Baggett, MD, MPH, an associate professor of internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, received pilot funding from the ACS to study cancer epidemiology among patients at Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program (BHCHP), which serves nearly 10,000 patients at a variety of Boston-area clinics each year.
“We found that both the incidence and mortality rates for lung cancer were more than twofold higher than in the general population,” Dr. Baggett, who is also the director of research at BHCHP, said.
He also discovered that BHCHP patients were diagnosed at significantly later stages than people in the general population for malignancies like breast and colorectal cancer.
Screening for lung cancer was a new recommendation at the time. With additional funding from the ACS, he launched a clinical trial in 2020 that randomized patients who were eligible for lung cancer screening to either work with a patient navigator or receive usual care.
The navigators eased the burden on primary care clinicians: They facilitated shared decision-making visits, helped participants make and attend appointments for low-dose CT, assisted with transportation, and arranged follow-up as needed.
The 3-year study found 43% of patients who received navigation services underwent screening for lung cancer, compared with 9% in the usual-care arm. Participants said the navigators played a critical role in educating them about the importance of screening, coordinating care, and providing emotional support.
“At the root of it all, it was quite clear that one thing that made the navigator successful was their interpersonal qualities and having someone that the patient could trust to help guide them through the process,” Dr. Baggett said.
The navigator program, however, stopped when the funding for the study ended.
But another health system has implemented navigators in a sustainable way through a quality improvement project. Michael Gieske, MD, director of lung cancer screening at St. Elizabeth Healthcare in Edgewood, Kentucky, starts his Friday morning meeting with a multidisciplinary group, including a thoracic surgeon, radiologist, pulmonologist, and several screening nurse navigators. They review the week’s chest CTs, with approximately one-third from patients who underwent lung cancer screening.
Nurse navigators at St. Elizabeth Healthcare follow up with any patient whose scan is suspicious for lung cancer and guide them through the process of seeing specialists and obtaining additional testing.
“They essentially hold the patient’s hand through this scary time in their life and make sure that everything flows smoothly and efficiently,” said Dr. Gieske, a family medicine physician.
St. Elizabeth’s program also draws on several evidence-based strategies used for other cancer screening programs, such as patient and provider education and quarterly feedback to their 194 primary care clinicians on rates of lung cancer screening among their eligible patients.
Several requirements for reimbursement for a lung cancer screening from the US Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services can also serve as barriers to getting patients screened: Clinicians must identify who is eligible, provide tobacco cessation counseling, and document the shared decision-making process.
To streamline the steps, St. Elizabeth’s clinicians use an EMR smart set that reminds clinicians to verify smoking history and helps them document the required counseling.
Last year, 47% of eligible patients received their recommended screening, and Dr. Gieske said he expects even more improvement.
“We’re on track this year to complete 60% uptake if things continue,” he said, adding that 76% of the new cases of lung cancer are now diagnosed in stage I, with only 5% diagnosed in stage IV.
Dr. Gieske has shared his experience with many clinics in Appalachia, home to some of the highest rates of mortality from lung cancer in the country. A major part of his role with the Appalachian Community Cancer Alliance is helping educate primary care clinicians in the region about the importance of early detection of lung cancer.
“I think one of the most important things is just to convey a message of hope,” he said. “We’re trying to get the good word out there that if you screen individuals, you’re going to catch it early, when you have an extremely high chance of curing the lung cancer.”
Dr. Baggett reported support from grants from the ACS and the Massachusetts General Hospital Research Scholars Program. Dr. Sandler and Dr. Gieske reported no financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.