User login
Survey: Supportive oncodermatology program improves QOL for cancer patients
according to a cross-sectional survey of participants.
The average quality of life score prior to program participation in 34 adult patients enrolled in the George Washington University Supportive Oncodermatology Clinic who responded to the survey was 6.5, indicating a moderate effect of their dermatologic symptoms on quality of life. After the beginning of treatment, the average score declined significantly to 3.8, indicating a small effect of the symptoms on quality of life, Leora Aizman, a medical student at George Washington University, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
“On average, [quality of life] total scores were significantly reduced by 2.7 points after joining the supportive oncodermatology clinic,” the authors wrote.
Decreases were seen across all quality of life categories, including physical symptoms, embarrassment, clothes, social/leisure, work/school, and close relationships; the only score that didn’t decrease significantly was for physical symptoms of itch, pain, or soreness (1.43 vs. 1.1 before and after therapy), whereas the category that showed the greatest difference was embarrassment about the dermatologic condition (1.57 vs. 0.83 before and after therapy).
As for satisfaction with the program, the average participant satisfaction score was 4.15, indicating satisfaction with the program. The lowest – an average of 3.67, indicating neutral to satisfied – was related to the effects of the program on treatment adherence.
Survey respondents were adults aged over 18 years who received dermatologic care between the opening of the clinic in May 2017 and Nov. 1, 2019. The online survey included questions adapted from the Dermatology Life Quality Index and Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire.
The findings, though limited by the potential for recall bias and other factors inherent in a survey-based study, suggest that participation in a comprehensive, supportive program could be of benefit for cancer patients experiencing dermatologic conditions from cancer treatment, the authors wrote, explaining that such conditions can be disabling and are associated with negative psychosocial effects. In fact, more than half of all cancer patients experience treatment interruption because of such events.
The findings also underscore the importance of a close partnerships between dermatologists and oncologists as nearly 90% of the surveyed patients were referred to the clinic by their oncologist, the authors wrote. However, the uncertainty that survey respondents experienced with respect to the effects of program participation on treatment adherence highlights a need for further study.
“Our results highlight that supportive oncodermatology interventions improve the psychosocial wellness of patients but require further research on evidence-based preventive and active management strategies,” they wrote.
Additionally, more work is needed to “optimize treatment of secondary toxicities and allow for the continuation of life-prolonging anticancer therapy,” they noted, adding that “prospective, multicenter studies on the management of [dermatologic adverse events] are critical to better understand the effectiveness of these clinics.”
This study was funded by a La Roche–Posay grant. Ms. Aizman reported having no disclosures. One coauthor reported relationships involving consulting and/or honoraria with several companies, including La Roche–Posay.
SOURCE: Aizman L et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.36849/JDD.2020.5040.
according to a cross-sectional survey of participants.
The average quality of life score prior to program participation in 34 adult patients enrolled in the George Washington University Supportive Oncodermatology Clinic who responded to the survey was 6.5, indicating a moderate effect of their dermatologic symptoms on quality of life. After the beginning of treatment, the average score declined significantly to 3.8, indicating a small effect of the symptoms on quality of life, Leora Aizman, a medical student at George Washington University, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
“On average, [quality of life] total scores were significantly reduced by 2.7 points after joining the supportive oncodermatology clinic,” the authors wrote.
Decreases were seen across all quality of life categories, including physical symptoms, embarrassment, clothes, social/leisure, work/school, and close relationships; the only score that didn’t decrease significantly was for physical symptoms of itch, pain, or soreness (1.43 vs. 1.1 before and after therapy), whereas the category that showed the greatest difference was embarrassment about the dermatologic condition (1.57 vs. 0.83 before and after therapy).
As for satisfaction with the program, the average participant satisfaction score was 4.15, indicating satisfaction with the program. The lowest – an average of 3.67, indicating neutral to satisfied – was related to the effects of the program on treatment adherence.
Survey respondents were adults aged over 18 years who received dermatologic care between the opening of the clinic in May 2017 and Nov. 1, 2019. The online survey included questions adapted from the Dermatology Life Quality Index and Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire.
The findings, though limited by the potential for recall bias and other factors inherent in a survey-based study, suggest that participation in a comprehensive, supportive program could be of benefit for cancer patients experiencing dermatologic conditions from cancer treatment, the authors wrote, explaining that such conditions can be disabling and are associated with negative psychosocial effects. In fact, more than half of all cancer patients experience treatment interruption because of such events.
The findings also underscore the importance of a close partnerships between dermatologists and oncologists as nearly 90% of the surveyed patients were referred to the clinic by their oncologist, the authors wrote. However, the uncertainty that survey respondents experienced with respect to the effects of program participation on treatment adherence highlights a need for further study.
“Our results highlight that supportive oncodermatology interventions improve the psychosocial wellness of patients but require further research on evidence-based preventive and active management strategies,” they wrote.
Additionally, more work is needed to “optimize treatment of secondary toxicities and allow for the continuation of life-prolonging anticancer therapy,” they noted, adding that “prospective, multicenter studies on the management of [dermatologic adverse events] are critical to better understand the effectiveness of these clinics.”
This study was funded by a La Roche–Posay grant. Ms. Aizman reported having no disclosures. One coauthor reported relationships involving consulting and/or honoraria with several companies, including La Roche–Posay.
SOURCE: Aizman L et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.36849/JDD.2020.5040.
according to a cross-sectional survey of participants.
The average quality of life score prior to program participation in 34 adult patients enrolled in the George Washington University Supportive Oncodermatology Clinic who responded to the survey was 6.5, indicating a moderate effect of their dermatologic symptoms on quality of life. After the beginning of treatment, the average score declined significantly to 3.8, indicating a small effect of the symptoms on quality of life, Leora Aizman, a medical student at George Washington University, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology.
“On average, [quality of life] total scores were significantly reduced by 2.7 points after joining the supportive oncodermatology clinic,” the authors wrote.
Decreases were seen across all quality of life categories, including physical symptoms, embarrassment, clothes, social/leisure, work/school, and close relationships; the only score that didn’t decrease significantly was for physical symptoms of itch, pain, or soreness (1.43 vs. 1.1 before and after therapy), whereas the category that showed the greatest difference was embarrassment about the dermatologic condition (1.57 vs. 0.83 before and after therapy).
As for satisfaction with the program, the average participant satisfaction score was 4.15, indicating satisfaction with the program. The lowest – an average of 3.67, indicating neutral to satisfied – was related to the effects of the program on treatment adherence.
Survey respondents were adults aged over 18 years who received dermatologic care between the opening of the clinic in May 2017 and Nov. 1, 2019. The online survey included questions adapted from the Dermatology Life Quality Index and Patient Satisfaction Questionnaire.
The findings, though limited by the potential for recall bias and other factors inherent in a survey-based study, suggest that participation in a comprehensive, supportive program could be of benefit for cancer patients experiencing dermatologic conditions from cancer treatment, the authors wrote, explaining that such conditions can be disabling and are associated with negative psychosocial effects. In fact, more than half of all cancer patients experience treatment interruption because of such events.
The findings also underscore the importance of a close partnerships between dermatologists and oncologists as nearly 90% of the surveyed patients were referred to the clinic by their oncologist, the authors wrote. However, the uncertainty that survey respondents experienced with respect to the effects of program participation on treatment adherence highlights a need for further study.
“Our results highlight that supportive oncodermatology interventions improve the psychosocial wellness of patients but require further research on evidence-based preventive and active management strategies,” they wrote.
Additionally, more work is needed to “optimize treatment of secondary toxicities and allow for the continuation of life-prolonging anticancer therapy,” they noted, adding that “prospective, multicenter studies on the management of [dermatologic adverse events] are critical to better understand the effectiveness of these clinics.”
This study was funded by a La Roche–Posay grant. Ms. Aizman reported having no disclosures. One coauthor reported relationships involving consulting and/or honoraria with several companies, including La Roche–Posay.
SOURCE: Aizman L et al. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.36849/JDD.2020.5040.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF DRUGS IN DERMATOLOGY
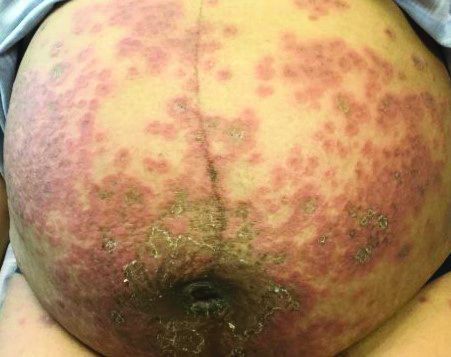
Itchy, vesicular rash
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
Pemphigoid gestationis
It typically presents with the abrupt onset of very pruritic urticarial plaques and papules, which start around the umbilicus and then spread to involve the trunk and extremities. The papules and plaques evolve to generalized tense blisters, which typically spare the face, palms, soles, and mucous membranes. Half of affected patients may present in an atypical distribution involving the extremities, palms, or soles. Patients may be at an increased risk for the development of Graves disease.
The cause of pemphigoid gestationis is a factor known as “herpes gestationis factor” that induces C3 deposition along the dermal-epidermal junction. As in bullous pemphigoid, patients with pemphigoid gestationis have antibodies to a transmembrane hemidesmosomal protein called BPAG2/BP180/collagen XVII.
Three-quarters of patients worsen at the time of delivery and up to 10% of newborns will have bullous lesions secondary to placental transfer of antibodies. In most cases, lesions will spontaneously resolve over a few weeks following delivery. Recurrence with future pregnancies is common, with severity increasing with each pregnancy. Recurrence with menstruation and with the use of oral contraceptives can also occur. Although there is no increase in maternal mortality, onset in the first or second trimester and presence of blisters is associated with decreased gestational age of baby at delivery and lower-birth-weight infants. There is no increase in fetal mortality.
Histopathology reveals a subepidermal vesicle and perivascular infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils. Diagnosis can be confirmed with direct immunofluorescence showing C3 in a linear band along the basement membrane zone. IgG may be present as well. Complement added indirect immunofluorescence reveals circulating anti–basement zone IgG, which allows differentiation from pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy.
Treatment for localized disease includes class I topical steroids and oral antihistamines. More severe cases require systemic corticosteroid treatment. Systemic steroids may cause lower-birth-weight infants.
This case and the photos were submitted by Dr. Hanson of Associated Skin Care Specialists in Eden Prairie, Minn. The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
The resurgence of Plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine)
Two of the most unusual dermatologic drugs have resurged as possible first-line therapy for rescue treatment of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2, despite extremely limited clinical data supporting their efficacy, optimal dose, treatment duration, and potential adverse effects.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine were introduced as treatment and prophylaxis of malaria and approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1949 and 1955, respectively. They belong to a class of drugs called 4-aminoquinolones and have a flat aromatic core and a basic side chain. The basic property of these drugs contribute to their ability to accumulate in lysosomes. They have a large volume of distribution in the blood and a half-life of 40-60 days. Important interactions include use with tamoxifen, proton pump inhibitors, and with smoking. Although both drugs cross the placenta, they don’t have any notable effects on the fetus.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine enter the cell and accumulate in the lysosomes along a pH gradient. Within the lysosome, they increase the pH, thereby stabilizing lysosomes and inhibiting eosinophil and neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytic activity. They also inhibit complement-mediated hemolysis, reduce acute phase reactants, and prevent MHC class II–mediated auto antigen presentation. Additionally, they decrease cell-mediated immunity by decreasing the production of interleukin-1 and plasma cell synthesis. Hydroxychloroquine can also accumulate in endosomes and inhibit toll-like receptor signaling, thereby reducing the production of proinflammatory cytokines.
One of the ways SARS-CoV-2 enters cells is by up-regulating and binding to ACE2. Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine reduce glycosylation of ACE2 and thus inhibit viral entry. Additionally, by increasing the endosomal pH, they potentially inactivate enzymes that viruses require for replication. Their lifesaving benefits, however, are thought to involve blocking the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and suppressing the cytokine storm thought to induce acute respiratory distress syndrome. Interestingly, chloroquine has also been shown to allow zinc ions into the cell, and zinc is a potent inhibitor of coronavirus RNA polymerase.
Side effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine include GI upset, retinal toxicity with long-term use, hypoglycemia, cardiomyopathy, QT prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and renal and liver toxicity. Adverse effects have been observed with long-term daily doses of more than 3.5 mg/kg of chloroquine or more than 6.5 mg/kg of hydroxychloroquine. Cutaneous effects include pruritus, morbilliform rashes (in an estimated 10% of those treated) and psoriasis flares, and blue-black hyperpigmentation (in about 25%) of the shins, face, oral palate, and nails.
Initial In February 2020, the first clinical results of 100 patients treated with chloroquine were reported in a news briefing by the Chinese government. On March 20, the first clinical trial was published offering guidelines for the treatment of COVID-19 using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin combination therapy – albeit with many limitations and reported biases in the study. Despite the poorly designed studies and inconclusive evidence, on March 28, the FDA issued an Emergency Use Authorization that allows providers to request a supply of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are unable to join a clinical trial.
On April 2, the first clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 began at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. The ORCHID trial (Outcomes Related to COVID-19 Treated With Hydroxychloroquine Among In-patients With Symptomatic Disease), funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. This blinded, placebo-controlled study is evaluating hydroxychloroquine treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in hopes of treating the severe complications of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Participants are randomly assigned to receive 400 mg hydroxychloroquine twice daily as a loading dose and then 200 mg twice daily thereafter on days 2-5. As of this writing, this study is currently underway and outcomes are expected in the upcoming weeks.
There is now a shortage of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in patients who have severe dermatologic and rheumatologic diseases, which include some who been in remission for years because of these medications and are in grave danger of recurrence. During this crisis, we desperately need well-controlled, randomized studies to test the efficacy and prolonged safety profile of these drugs in COVID-19 patients, as well as appropriate funding to source these medications for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients in need.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. They had no relevant disclosures. Write to them at [email protected].
Sources
Liu J et al. Cell Discov. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0.
Vincent MJ et al. Virol J. 2005 Aug 22;2:69.
Gautret P et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949.
Devaux CA et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 12:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938.
Aronson J et al. COVID-19 trials registered up to 8 March 2020 – an analysis of 382 studies. 2020. Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.net/oxford-covid-19/covid-19-registered-trials-and-analysis/
Savarino A et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003 Nov;3(11):722-7.
Yazdany J, Kim AHJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 31. doi: 10.7326/M20-1334.
Xue J et al. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 1;9(10):e109180.
te Velthuis AJ et al. PLoS Pathog. 2010 Nov 4;6(11):e1001176.
Two of the most unusual dermatologic drugs have resurged as possible first-line therapy for rescue treatment of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2, despite extremely limited clinical data supporting their efficacy, optimal dose, treatment duration, and potential adverse effects.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine were introduced as treatment and prophylaxis of malaria and approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1949 and 1955, respectively. They belong to a class of drugs called 4-aminoquinolones and have a flat aromatic core and a basic side chain. The basic property of these drugs contribute to their ability to accumulate in lysosomes. They have a large volume of distribution in the blood and a half-life of 40-60 days. Important interactions include use with tamoxifen, proton pump inhibitors, and with smoking. Although both drugs cross the placenta, they don’t have any notable effects on the fetus.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine enter the cell and accumulate in the lysosomes along a pH gradient. Within the lysosome, they increase the pH, thereby stabilizing lysosomes and inhibiting eosinophil and neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytic activity. They also inhibit complement-mediated hemolysis, reduce acute phase reactants, and prevent MHC class II–mediated auto antigen presentation. Additionally, they decrease cell-mediated immunity by decreasing the production of interleukin-1 and plasma cell synthesis. Hydroxychloroquine can also accumulate in endosomes and inhibit toll-like receptor signaling, thereby reducing the production of proinflammatory cytokines.
One of the ways SARS-CoV-2 enters cells is by up-regulating and binding to ACE2. Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine reduce glycosylation of ACE2 and thus inhibit viral entry. Additionally, by increasing the endosomal pH, they potentially inactivate enzymes that viruses require for replication. Their lifesaving benefits, however, are thought to involve blocking the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and suppressing the cytokine storm thought to induce acute respiratory distress syndrome. Interestingly, chloroquine has also been shown to allow zinc ions into the cell, and zinc is a potent inhibitor of coronavirus RNA polymerase.
Side effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine include GI upset, retinal toxicity with long-term use, hypoglycemia, cardiomyopathy, QT prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and renal and liver toxicity. Adverse effects have been observed with long-term daily doses of more than 3.5 mg/kg of chloroquine or more than 6.5 mg/kg of hydroxychloroquine. Cutaneous effects include pruritus, morbilliform rashes (in an estimated 10% of those treated) and psoriasis flares, and blue-black hyperpigmentation (in about 25%) of the shins, face, oral palate, and nails.
Initial In February 2020, the first clinical results of 100 patients treated with chloroquine were reported in a news briefing by the Chinese government. On March 20, the first clinical trial was published offering guidelines for the treatment of COVID-19 using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin combination therapy – albeit with many limitations and reported biases in the study. Despite the poorly designed studies and inconclusive evidence, on March 28, the FDA issued an Emergency Use Authorization that allows providers to request a supply of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are unable to join a clinical trial.
On April 2, the first clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 began at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. The ORCHID trial (Outcomes Related to COVID-19 Treated With Hydroxychloroquine Among In-patients With Symptomatic Disease), funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. This blinded, placebo-controlled study is evaluating hydroxychloroquine treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in hopes of treating the severe complications of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Participants are randomly assigned to receive 400 mg hydroxychloroquine twice daily as a loading dose and then 200 mg twice daily thereafter on days 2-5. As of this writing, this study is currently underway and outcomes are expected in the upcoming weeks.
There is now a shortage of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in patients who have severe dermatologic and rheumatologic diseases, which include some who been in remission for years because of these medications and are in grave danger of recurrence. During this crisis, we desperately need well-controlled, randomized studies to test the efficacy and prolonged safety profile of these drugs in COVID-19 patients, as well as appropriate funding to source these medications for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients in need.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. They had no relevant disclosures. Write to them at [email protected].
Sources
Liu J et al. Cell Discov. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0.
Vincent MJ et al. Virol J. 2005 Aug 22;2:69.
Gautret P et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949.
Devaux CA et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 12:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938.
Aronson J et al. COVID-19 trials registered up to 8 March 2020 – an analysis of 382 studies. 2020. Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.net/oxford-covid-19/covid-19-registered-trials-and-analysis/
Savarino A et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003 Nov;3(11):722-7.
Yazdany J, Kim AHJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 31. doi: 10.7326/M20-1334.
Xue J et al. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 1;9(10):e109180.
te Velthuis AJ et al. PLoS Pathog. 2010 Nov 4;6(11):e1001176.
Two of the most unusual dermatologic drugs have resurged as possible first-line therapy for rescue treatment of hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2, despite extremely limited clinical data supporting their efficacy, optimal dose, treatment duration, and potential adverse effects.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine were introduced as treatment and prophylaxis of malaria and approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1949 and 1955, respectively. They belong to a class of drugs called 4-aminoquinolones and have a flat aromatic core and a basic side chain. The basic property of these drugs contribute to their ability to accumulate in lysosomes. They have a large volume of distribution in the blood and a half-life of 40-60 days. Important interactions include use with tamoxifen, proton pump inhibitors, and with smoking. Although both drugs cross the placenta, they don’t have any notable effects on the fetus.
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine enter the cell and accumulate in the lysosomes along a pH gradient. Within the lysosome, they increase the pH, thereby stabilizing lysosomes and inhibiting eosinophil and neutrophil chemotaxis and phagocytic activity. They also inhibit complement-mediated hemolysis, reduce acute phase reactants, and prevent MHC class II–mediated auto antigen presentation. Additionally, they decrease cell-mediated immunity by decreasing the production of interleukin-1 and plasma cell synthesis. Hydroxychloroquine can also accumulate in endosomes and inhibit toll-like receptor signaling, thereby reducing the production of proinflammatory cytokines.
One of the ways SARS-CoV-2 enters cells is by up-regulating and binding to ACE2. Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine reduce glycosylation of ACE2 and thus inhibit viral entry. Additionally, by increasing the endosomal pH, they potentially inactivate enzymes that viruses require for replication. Their lifesaving benefits, however, are thought to involve blocking the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and suppressing the cytokine storm thought to induce acute respiratory distress syndrome. Interestingly, chloroquine has also been shown to allow zinc ions into the cell, and zinc is a potent inhibitor of coronavirus RNA polymerase.
Side effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine include GI upset, retinal toxicity with long-term use, hypoglycemia, cardiomyopathy, QT prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and renal and liver toxicity. Adverse effects have been observed with long-term daily doses of more than 3.5 mg/kg of chloroquine or more than 6.5 mg/kg of hydroxychloroquine. Cutaneous effects include pruritus, morbilliform rashes (in an estimated 10% of those treated) and psoriasis flares, and blue-black hyperpigmentation (in about 25%) of the shins, face, oral palate, and nails.
Initial In February 2020, the first clinical results of 100 patients treated with chloroquine were reported in a news briefing by the Chinese government. On March 20, the first clinical trial was published offering guidelines for the treatment of COVID-19 using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin combination therapy – albeit with many limitations and reported biases in the study. Despite the poorly designed studies and inconclusive evidence, on March 28, the FDA issued an Emergency Use Authorization that allows providers to request a supply of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who are unable to join a clinical trial.
On April 2, the first clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 began at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. The ORCHID trial (Outcomes Related to COVID-19 Treated With Hydroxychloroquine Among In-patients With Symptomatic Disease), funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. This blinded, placebo-controlled study is evaluating hydroxychloroquine treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in hopes of treating the severe complications of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Participants are randomly assigned to receive 400 mg hydroxychloroquine twice daily as a loading dose and then 200 mg twice daily thereafter on days 2-5. As of this writing, this study is currently underway and outcomes are expected in the upcoming weeks.
There is now a shortage of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in patients who have severe dermatologic and rheumatologic diseases, which include some who been in remission for years because of these medications and are in grave danger of recurrence. During this crisis, we desperately need well-controlled, randomized studies to test the efficacy and prolonged safety profile of these drugs in COVID-19 patients, as well as appropriate funding to source these medications for hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients in need.
Dr. Wesley and Dr. Talakoub are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. They had no relevant disclosures. Write to them at [email protected].
Sources
Liu J et al. Cell Discov. 2020 Mar 18. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-0156-0.
Vincent MJ et al. Virol J. 2005 Aug 22;2:69.
Gautret P et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949.
Devaux CA et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Mar 12:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105938.
Aronson J et al. COVID-19 trials registered up to 8 March 2020 – an analysis of 382 studies. 2020. Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. https://www.cebm.net/oxford-covid-19/covid-19-registered-trials-and-analysis/
Savarino A et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003 Nov;3(11):722-7.
Yazdany J, Kim AHJ. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Mar 31. doi: 10.7326/M20-1334.
Xue J et al. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 1;9(10):e109180.
te Velthuis AJ et al. PLoS Pathog. 2010 Nov 4;6(11):e1001176.
COVID-19 PPE-related skin effects described in survey of Chinese doctors, nurses
Almost 75% of doctors and nurses in and around Wuhan, China, where the outbreak first emerged, reported skin problems during a single week in early February 2020, in a survey of health care workers (HCW) caring for COVID-19 patients at five university and five regional hospitals. Hands, cheeks, and the nasal bridge were the most commonly affected areas, with skin dryness, maceration, papules, and erythema the most common problems, according to research published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
In New York City, masks in particular are “really an issue,” said Ellen Marmur, MD, a dermatologist in private practice and an associate clinical professor at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York.
She’s dealing with patients who have abrasions and skin infections at the tip of the nose, bruising from the metal strap that goes across the bridge of the nose, and skin irritation from the straps. “Rosacea is [also] definitely flaring up, [and] people’s acne is definitely flaring up, not only because of the stress, but because of the sweat and humidity” that builds up under the masks, she said.
“It’s not a life-threatening thing, but it’s definitely something we’ve been helping people with,” she said. This includes her husband, a cardiologist pulling 12-hour shifts in a New York City hospital wearing an N95 mask; when he comes home, the tip of his nose is red and abraded.
Treatment entails first aid skin care: a dab of a gentle ointment like Aquaphor to prevent abrasions while the mask is on and to help them heal after it’s off, and bacitracin if infection is a worry. For acne and rosacea flares, a course of minocycline or topical clindamycin might help, Dr. Marmur said.
Although almost 75% of the doctors and nurses in the Chinese study reported skin problems, the response rate was low, just 376 of the 1,000 surveyed (37.6%). That might have tilted the results to providers who actually ran into problems, wrote the investigators, led by Ping Lin of the department of dermatology and venereology at Peking University First Hospital, Beijing.
Still, 280 (74.5%) reported adverse skin reactions from caring for COVID-19 patients. “Of note, this rate was much higher than the rate of occupational contact dermatitis (31.5%) in HCWs under normal working condition[s], and that of adverse skin reactions (21.4%-35.5%)” during the outbreak of another coronavirus in 2003, severe acute respiratory syndrome, they wrote.
Most providers in the study washed their hands more than 10 times a day, but only about 22% applied hand cream afterwards, they reported.
On multivariate analysis, working in hospitals harder hit by the pandemic (odds ratio, 2.41; P = .001), working on inpatient wards (OR, 2.44; P = .003), wearing full-body personal protective equipment over 6 hours (OR, 4.26; P < .001), and female sex (OR, 1.87; P = .038) increased the risk of adverse skin reactions. The team suggested moisturizers would help to protect against hand dermatitis, and alcohol-based products instead of soaps “as the former show high antimicrobial activity and low risks of skin damage.” Also, “restricting duration of wearing” of protection gear “to no more than 6 hours would help.”
The study investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lin P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19089.
Almost 75% of doctors and nurses in and around Wuhan, China, where the outbreak first emerged, reported skin problems during a single week in early February 2020, in a survey of health care workers (HCW) caring for COVID-19 patients at five university and five regional hospitals. Hands, cheeks, and the nasal bridge were the most commonly affected areas, with skin dryness, maceration, papules, and erythema the most common problems, according to research published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
In New York City, masks in particular are “really an issue,” said Ellen Marmur, MD, a dermatologist in private practice and an associate clinical professor at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York.
She’s dealing with patients who have abrasions and skin infections at the tip of the nose, bruising from the metal strap that goes across the bridge of the nose, and skin irritation from the straps. “Rosacea is [also] definitely flaring up, [and] people’s acne is definitely flaring up, not only because of the stress, but because of the sweat and humidity” that builds up under the masks, she said.
“It’s not a life-threatening thing, but it’s definitely something we’ve been helping people with,” she said. This includes her husband, a cardiologist pulling 12-hour shifts in a New York City hospital wearing an N95 mask; when he comes home, the tip of his nose is red and abraded.
Treatment entails first aid skin care: a dab of a gentle ointment like Aquaphor to prevent abrasions while the mask is on and to help them heal after it’s off, and bacitracin if infection is a worry. For acne and rosacea flares, a course of minocycline or topical clindamycin might help, Dr. Marmur said.
Although almost 75% of the doctors and nurses in the Chinese study reported skin problems, the response rate was low, just 376 of the 1,000 surveyed (37.6%). That might have tilted the results to providers who actually ran into problems, wrote the investigators, led by Ping Lin of the department of dermatology and venereology at Peking University First Hospital, Beijing.
Still, 280 (74.5%) reported adverse skin reactions from caring for COVID-19 patients. “Of note, this rate was much higher than the rate of occupational contact dermatitis (31.5%) in HCWs under normal working condition[s], and that of adverse skin reactions (21.4%-35.5%)” during the outbreak of another coronavirus in 2003, severe acute respiratory syndrome, they wrote.
Most providers in the study washed their hands more than 10 times a day, but only about 22% applied hand cream afterwards, they reported.
On multivariate analysis, working in hospitals harder hit by the pandemic (odds ratio, 2.41; P = .001), working on inpatient wards (OR, 2.44; P = .003), wearing full-body personal protective equipment over 6 hours (OR, 4.26; P < .001), and female sex (OR, 1.87; P = .038) increased the risk of adverse skin reactions. The team suggested moisturizers would help to protect against hand dermatitis, and alcohol-based products instead of soaps “as the former show high antimicrobial activity and low risks of skin damage.” Also, “restricting duration of wearing” of protection gear “to no more than 6 hours would help.”
The study investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lin P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19089.
Almost 75% of doctors and nurses in and around Wuhan, China, where the outbreak first emerged, reported skin problems during a single week in early February 2020, in a survey of health care workers (HCW) caring for COVID-19 patients at five university and five regional hospitals. Hands, cheeks, and the nasal bridge were the most commonly affected areas, with skin dryness, maceration, papules, and erythema the most common problems, according to research published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
In New York City, masks in particular are “really an issue,” said Ellen Marmur, MD, a dermatologist in private practice and an associate clinical professor at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York.
She’s dealing with patients who have abrasions and skin infections at the tip of the nose, bruising from the metal strap that goes across the bridge of the nose, and skin irritation from the straps. “Rosacea is [also] definitely flaring up, [and] people’s acne is definitely flaring up, not only because of the stress, but because of the sweat and humidity” that builds up under the masks, she said.
“It’s not a life-threatening thing, but it’s definitely something we’ve been helping people with,” she said. This includes her husband, a cardiologist pulling 12-hour shifts in a New York City hospital wearing an N95 mask; when he comes home, the tip of his nose is red and abraded.
Treatment entails first aid skin care: a dab of a gentle ointment like Aquaphor to prevent abrasions while the mask is on and to help them heal after it’s off, and bacitracin if infection is a worry. For acne and rosacea flares, a course of minocycline or topical clindamycin might help, Dr. Marmur said.
Although almost 75% of the doctors and nurses in the Chinese study reported skin problems, the response rate was low, just 376 of the 1,000 surveyed (37.6%). That might have tilted the results to providers who actually ran into problems, wrote the investigators, led by Ping Lin of the department of dermatology and venereology at Peking University First Hospital, Beijing.
Still, 280 (74.5%) reported adverse skin reactions from caring for COVID-19 patients. “Of note, this rate was much higher than the rate of occupational contact dermatitis (31.5%) in HCWs under normal working condition[s], and that of adverse skin reactions (21.4%-35.5%)” during the outbreak of another coronavirus in 2003, severe acute respiratory syndrome, they wrote.
Most providers in the study washed their hands more than 10 times a day, but only about 22% applied hand cream afterwards, they reported.
On multivariate analysis, working in hospitals harder hit by the pandemic (odds ratio, 2.41; P = .001), working on inpatient wards (OR, 2.44; P = .003), wearing full-body personal protective equipment over 6 hours (OR, 4.26; P < .001), and female sex (OR, 1.87; P = .038) increased the risk of adverse skin reactions. The team suggested moisturizers would help to protect against hand dermatitis, and alcohol-based products instead of soaps “as the former show high antimicrobial activity and low risks of skin damage.” Also, “restricting duration of wearing” of protection gear “to no more than 6 hours would help.”
The study investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lin P et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19089.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
A case of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis attributed to HIV treatment
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
arising in an affected patient, Jessica Kalen, MD, advised during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology.
The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a presentation entitled, “When HAART [highly active antiretroviral therapy] Hurts,” Dr. Kalen, a dermatology resident at the university, presented a case report involving a 65-year-old man who presented with juicy red edematous papules and plaques on his scalp and ears. He was on the three-drug combination of rilpivirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor), and the NRTIs tenofovir, and emtricitabine (Odefsey) for treatment of HIV infection, which was well controlled, with no detectable viral load.
The patient was also on insulin detemir for diabetes; pravastatin, amlodipine, and lisinopril for hypertension; and episodic acyclovir for recurrent herpes simplex outbreaks. However, none of those drugs has been associated with NEH. In contrast, Dr. Kalen found three published case reports describing a link between NRTIs and NEH.
Lesional biopsy of her patient showed the classic features of NEH: a dermal neutrophilic infiltrate surrounding the eccrine secretory coils and ducts, with vacuolar degeneration that spared the acrosyringium.
The most common causes of NEH, a rare dermatologic disorder first described in 1982, are hematologic malignancies and some of the chemotherapeutic agents used in treating them. Particularly prominent are acute myelogenous leukemia and cytarabine, which are often prescribed for that cancer. Carbamazepine, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, and BRAF inhibitors have also been associated with NEH.
The pathogenesis of NEH is not fully worked out; however, NRTIs are secreted via eccrine structures, and that close contact could potentially promote an environment favoring inflammation and destruction of the eccrine coils. Also, NRTIs inhibit DNA polymerase, as does cytarabine, Dr. Kalen noted.
Her patient’s NEH was treated with triamcinolone. His skin condition resolved completely while he remained on NRTI therapy, with no relapses to date.
Dr. Kalen reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
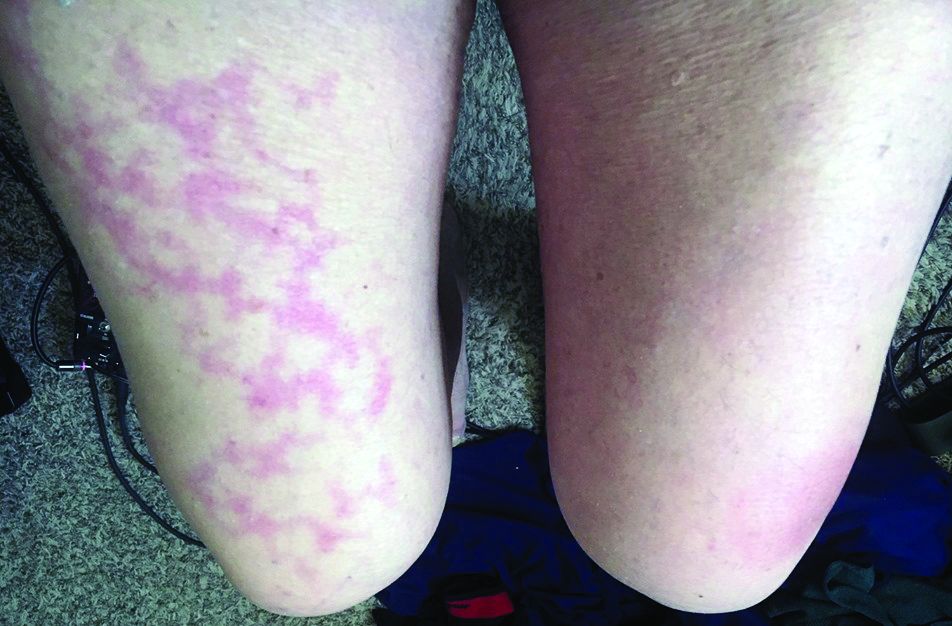
When to suspect calciphylaxis and what to do about it
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
If the shoe fits a presumptive clinical diagnosis of calciphylaxis, wear it – and don’t assume that ordering imaging studies or histology will make for a better fit or is even necessary.
That was the key message of Karl M. Saardi, MD, during his video presentation at a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations that had been slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“ said Dr. Saardi, a dermatology resident at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C.
He presented a single-center, retrospective study that underscored the diagnostic challenges posed by calciphylaxis, a condition for which there are no generally accepted clinical, radiographic, or histologic diagnostic criteria.
The rare skin condition is characterized by calcium deposition in small arterioles and capillaries in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. It’s most common in patients with end-stage renal disease who are on dialysis; however, there is also an increasingly recognized nonuremic variant that’s associated with the use of warfarin, chronic steroids, obesity, and possibly with being antiphospholipid antibody positive.
Calciphylaxis is an extremely painful condition – the pain is ischemic in nature – and it’s associated with substantial morbidity as well as a mortality rate that in many series exceeds 50%. Affected individuals typically present with progressive, painful retiform purpura on the legs, belly, buttocks, and other fatty body sites.
Dr. Saardi’s study entailed a retrospective look at the medical records and pathologic reports of 57 patients who underwent skin biopsy for suspected calciphylaxis. Of the 57, 18 had no antecedent imaging studies done during the preceding 3 months; 8 of those 18 (40%), had a confirmatory positive biopsy. A total of 39 patients did have imaging studies, deemed positive for calciphylaxis in 11 cases, which in only 5 of the 11 imaging-positive cases (45%) were subsequently confirmed by positive biopsy.
And finally, of the 28 patients with negative imaging studies, 10 (36%), had a positive biopsy. Those positive biopsy rates, ranging from 36% to 45%, did not differ statistically. Thus, whether an imaging study was positive or negative, or wasn’t even done, made no difference in terms of the ultimate diagnosis.
“You may not need imaging studies, because imaging has often been done before the consultation is requested because people are looking for things like arterial thrombus, cellulitis, [deep vein thrombosis] or something like that,” Dr. Saardi noted. “In our series, the indication was never calciphylaxis, it was always something like pain, infection, swelling, suspected [deep vein thrombosis], things like that.”
The classic signature of calciphylaxis on plain x-ray is net-like calcifications in skin and subcutaneous tissue. In one study, this often-subtle finding was associated with a 830% increased likelihood of a positive biopsy, with a specificity of 90%; however, these x-ray changes were only found in 13 of 29 patients with biopsy-confirmed calciphylaxis.
“It’s really important when you request plain films in these patients to review the images yourself or together with the radiologist because oftentimes the indication for imaging will be very different from what we’re looking for. Radiologists often won’t know to look for this specifically,” Dr. Saardi said.
The classic histopathologic finding is calcification of the small- and medium-sized vessels in the dermis and subcutaneous soft tissue. However, sometimes all that’s present are small intravascular inflammatory thrombi with intimal hyperplasia.
Skin biopsies are not infrequently falsely negative or nondiagnostic. To maximize the utility of the procedure, it’s important to go deep and gather a tissue sample that extends into subcutaneous tissue.
“You need to do a very deep punch or double-punch biopsy,” he said. “Another key is to avoid biopsy if the pretest probability of calciphylaxis is high because a negative biopsy shouldn’t necessarily reassure you or cause you to withhold treatment. And with the concern about pathergy or Koebnerization of the area causing a wound that’s never going to heal, sometimes a biopsy is not needed if the pretest suspicion is high enough.”
Other investigators have shown that the likelihood of an informative biopsy is enhanced by using a calcium stain on the specimen and having an experienced dermatopathologist do the evaluation. Also, the use of a radiographically guided core needle biopsy to ensure that the physician is getting sufficiently deep into subcutaneous fat is now under evaluation.
In addition to plain radiographs, other imaging methods that are sometimes used to evaluate soft-tissue sites for suspected calciphylaxis included CT and ultrasound. Dr. Saardi is particularly intrigued by reports from investigators at Harvard University regarding the utility of nuclear bone scintigraphy; in one study, this form of imaging was positive in 16 of 18 patients with clinically diagnosed calciphylaxis, versus just 1 of 31 controls with end-stage renal disease.
“We’ve started doing this in situations where biopsy is not desirable or feasible at that moment,” he said.
Dr. Saardi reported having no financial conflicts regarding his presentation.
D.C.-area blacks face increased risk of mortality from SJS/TEN
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
(TEN), compared with nonblack patients, results from a single-center study showed.

Adam Swigost, MD, presented data on behalf of the study’s principal investigator, Helena B. Pasieka, MD, and associates at MedStar Health Georgetown University in Washington in a video presentation during a virtual meeting held by the George Washington University department of dermatology. The virtual meeting included presentations slated for the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, which was canceled because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
According to the 2009-2012 Nationwide Inpatient Survey, there were 12,195 cases of SJS, 2,373 cases of SJS/TEN overlap, and 2,675 cases of TEN. In 2016, researchers led by Derek Y. Hsu, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, found that SJS/TEN was associated with nonwhite race, particularly Asians (odds ratio, 3.27) and blacks (OR, 2.01) (J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136[7]:1387-97).
“This led Dr. Pasieka and our team to ask the question: Are there differences in SJS/TEN outcomes in self-reported blacks in the U.S.?” said Dr. Swigost, a resident in the department of dermatology at MedStar Health Georgetown University.
To find out, he and his colleagues retrospectively analyzed records from 74 patients with SJS/TEN who were treated at Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., from 2009 to 2019. They drew data from clinical diagnoses with histopathologic evaluation, when available, and performed a multivariate analysis adjusted for age, HIV status, black race, and offending drug category.
Of the 75 patients, 43 were female, 45 were black, 16 were white, 6 were Asian, 5 were Indian, 1 was Native American, and 1 was South Asian. Multivariate analysis revealed that black race was the only significant variable associated with an elevated risk of mortality from SJS/TEN (OR, 4.81; P = .04).
Of the 45 black patients in the study, 33 were HIV negative and 12 were HIV positive. “While this variable was not statistically significant, it did seem to have an elevated risk for mortality in HIV-positive patients [4 of 12; 33%], compared with 8 of 33 HIV-negative patients [25%],” Dr. Swigost said.
Next, the researchers investigated the culprit medications in the black patients. As a reference, they compared their data with a 2015 study that set out to document the clinical profile, etiologies, and outcomes of SJS and TEN in hospitals in four sub-Saharan African countries (Int J Dermatol. 2013 May;52[5]:575-9). In the 2015 study, sulfonamides were the most-used drugs (38%) followed by the antiretroviral drug nevirapine (20%) and tuberculosis drugs (6%). In the study by Dr. Swigost and colleagues, the most frequently implicated drugs were sulfonamides (24%), followed by other antibiotics (24%), and anticonvulsants (17%).
“Our patients at MedStar Washington Hospital Center are going to have different comorbidities and medical problems that dictate different medications being used in different proportions,” Dr. Swigost explained.
Delayed detection is one possible reason for the increased mortality observed in black patients. “Dermatology education on a national level is biased most commonly toward white skin,” he said. “Often, diseases can be missed in skin of color. It’s possible that the diagnoses are being delayed and so treatment is being delayed.”
Socioeconomics and access to health care could also play a role in the poor outcome we observed. “Those are variables we want to further analyze in this data,” Dr. Swigost said. “Other things to consider are genetic variations between African and American black patient populations, because in the U.S. our black population is likely more heterogeneous than African patient populations are. It’s possible that there are HLA [human leukocyte antigen] differences that are contributing. Lastly, further characterization and stratification of SJS/TEN risk factors are required.”
Dr. Swigost and Dr. Pasieka reported having no disclosures.
Skin manifestations are emerging in the coronavirus pandemic
Dermatologists there were pulled from their usual duty to help with the pandemic and looked at what was going on with the skin in 148 COVID-19 inpatients. They excluded 60 who had started new drugs within 15 days to rule out acute drug reactions, then reported what they saw (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16387).
Of the 88 COVID-19 patients, 20.5% developed skin manifestations. Eight of the 18 (44%) had skin eruptions at symptom onset, and the rest after hospitalization. Fourteen (78%) had red rashes, three had widespread urticaria, and one had chickenpox-like vesicles. The most commonly affected area was the trunk. Itching was mild or absent, and lesions usually healed up in a few days. Most importantly, skin manifestations did not correlate with disease severity.
These skin manifestations “are similar to cutaneous involvement occurring during common viral infections,” said the author of the report, Sebastiano Recalcati, MD, a dermatologist at Alessandro Manzoni Hospital.
COVID-19 skin manifestations can cloud the diagnosis, according to the authors of another report from Thailand, where the first case of COVID-19 outside of China was reported.
They described a case of a COVID-19 infection in a Bangkok hospital that masqueraded as dengue fever. A person there presented with only a skin rash, petechiae, and a low platelet count, and was diagnosed with Dengue because that’s exactly what it looked like, the authors wrote (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar 22. pii: S0190-9622[20]30454-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036).
The correct diagnosis, COVID-19, was made at a tertiary care center after the patient was admitted with respiratory problems.
“There is a possibility that a COVID-19 patient might initially present with a skin rash that can be misdiagnosed as another common disease. ... The practitioner should recognize the possibility that the patient might have only a skin rash” at first, said the lead author of that report, Beuy Joob, PhD, of the Sanitation1 Medical Academic Center, Bangkok, and a coauthor.
There are similar reports in the United States, too. “Many have wondered if COVID-19 presents with any particular skin changes. The answer is yes,” said Randy Jacobs, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Riverside, who also has a private practice in southern California.
“COVID-19 can feature signs of small blood vessel occlusion. These can be petechiae or tiny bruises, and transient livedoid eruptions,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Jacobs had a 67-year-old patient who presented with a low fever, nasal congestion, postnasal drip, and a wet cough but no shortness of breath. It looked like a common cold. But a week later, the man had a nonpruritic blanching livedoid vascular eruption on his right anterior thigh, and blood in his urine, and he felt weak. The vascular eruption and bloody urine resolved in 24 hours, but the COVID-19 test came back positive and his cough became dry and hacking, and the weakness persisted. He’s in a hospital now and on oxygen, but not ventilated so far.
“Another dermatologist friend of mine also reported a similar transient COVID-19 unilateral livedoid eruption,” Dr. Jacobs said.
It suggests vaso-occlusion. Whether it’s neurogenic, microthrombotic, or immune complex mediated is unknown, but it’s “a skin finding that can help clinicians as they work up their patients with COVID-19 symptoms,” he noted.
Dr. Jacobs and the authors of the studies had no disclosures.
Dermatologists there were pulled from their usual duty to help with the pandemic and looked at what was going on with the skin in 148 COVID-19 inpatients. They excluded 60 who had started new drugs within 15 days to rule out acute drug reactions, then reported what they saw (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16387).
Of the 88 COVID-19 patients, 20.5% developed skin manifestations. Eight of the 18 (44%) had skin eruptions at symptom onset, and the rest after hospitalization. Fourteen (78%) had red rashes, three had widespread urticaria, and one had chickenpox-like vesicles. The most commonly affected area was the trunk. Itching was mild or absent, and lesions usually healed up in a few days. Most importantly, skin manifestations did not correlate with disease severity.
These skin manifestations “are similar to cutaneous involvement occurring during common viral infections,” said the author of the report, Sebastiano Recalcati, MD, a dermatologist at Alessandro Manzoni Hospital.
COVID-19 skin manifestations can cloud the diagnosis, according to the authors of another report from Thailand, where the first case of COVID-19 outside of China was reported.
They described a case of a COVID-19 infection in a Bangkok hospital that masqueraded as dengue fever. A person there presented with only a skin rash, petechiae, and a low platelet count, and was diagnosed with Dengue because that’s exactly what it looked like, the authors wrote (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar 22. pii: S0190-9622[20]30454-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036).
The correct diagnosis, COVID-19, was made at a tertiary care center after the patient was admitted with respiratory problems.
“There is a possibility that a COVID-19 patient might initially present with a skin rash that can be misdiagnosed as another common disease. ... The practitioner should recognize the possibility that the patient might have only a skin rash” at first, said the lead author of that report, Beuy Joob, PhD, of the Sanitation1 Medical Academic Center, Bangkok, and a coauthor.
There are similar reports in the United States, too. “Many have wondered if COVID-19 presents with any particular skin changes. The answer is yes,” said Randy Jacobs, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Riverside, who also has a private practice in southern California.
“COVID-19 can feature signs of small blood vessel occlusion. These can be petechiae or tiny bruises, and transient livedoid eruptions,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Jacobs had a 67-year-old patient who presented with a low fever, nasal congestion, postnasal drip, and a wet cough but no shortness of breath. It looked like a common cold. But a week later, the man had a nonpruritic blanching livedoid vascular eruption on his right anterior thigh, and blood in his urine, and he felt weak. The vascular eruption and bloody urine resolved in 24 hours, but the COVID-19 test came back positive and his cough became dry and hacking, and the weakness persisted. He’s in a hospital now and on oxygen, but not ventilated so far.
“Another dermatologist friend of mine also reported a similar transient COVID-19 unilateral livedoid eruption,” Dr. Jacobs said.
It suggests vaso-occlusion. Whether it’s neurogenic, microthrombotic, or immune complex mediated is unknown, but it’s “a skin finding that can help clinicians as they work up their patients with COVID-19 symptoms,” he noted.
Dr. Jacobs and the authors of the studies had no disclosures.
Dermatologists there were pulled from their usual duty to help with the pandemic and looked at what was going on with the skin in 148 COVID-19 inpatients. They excluded 60 who had started new drugs within 15 days to rule out acute drug reactions, then reported what they saw (J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16387).
Of the 88 COVID-19 patients, 20.5% developed skin manifestations. Eight of the 18 (44%) had skin eruptions at symptom onset, and the rest after hospitalization. Fourteen (78%) had red rashes, three had widespread urticaria, and one had chickenpox-like vesicles. The most commonly affected area was the trunk. Itching was mild or absent, and lesions usually healed up in a few days. Most importantly, skin manifestations did not correlate with disease severity.
These skin manifestations “are similar to cutaneous involvement occurring during common viral infections,” said the author of the report, Sebastiano Recalcati, MD, a dermatologist at Alessandro Manzoni Hospital.
COVID-19 skin manifestations can cloud the diagnosis, according to the authors of another report from Thailand, where the first case of COVID-19 outside of China was reported.
They described a case of a COVID-19 infection in a Bangkok hospital that masqueraded as dengue fever. A person there presented with only a skin rash, petechiae, and a low platelet count, and was diagnosed with Dengue because that’s exactly what it looked like, the authors wrote (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Mar 22. pii: S0190-9622[20]30454-0. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036).
The correct diagnosis, COVID-19, was made at a tertiary care center after the patient was admitted with respiratory problems.
“There is a possibility that a COVID-19 patient might initially present with a skin rash that can be misdiagnosed as another common disease. ... The practitioner should recognize the possibility that the patient might have only a skin rash” at first, said the lead author of that report, Beuy Joob, PhD, of the Sanitation1 Medical Academic Center, Bangkok, and a coauthor.
There are similar reports in the United States, too. “Many have wondered if COVID-19 presents with any particular skin changes. The answer is yes,” said Randy Jacobs, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology at the University of California, Riverside, who also has a private practice in southern California.
“COVID-19 can feature signs of small blood vessel occlusion. These can be petechiae or tiny bruises, and transient livedoid eruptions,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Jacobs had a 67-year-old patient who presented with a low fever, nasal congestion, postnasal drip, and a wet cough but no shortness of breath. It looked like a common cold. But a week later, the man had a nonpruritic blanching livedoid vascular eruption on his right anterior thigh, and blood in his urine, and he felt weak. The vascular eruption and bloody urine resolved in 24 hours, but the COVID-19 test came back positive and his cough became dry and hacking, and the weakness persisted. He’s in a hospital now and on oxygen, but not ventilated so far.
“Another dermatologist friend of mine also reported a similar transient COVID-19 unilateral livedoid eruption,” Dr. Jacobs said.
It suggests vaso-occlusion. Whether it’s neurogenic, microthrombotic, or immune complex mediated is unknown, but it’s “a skin finding that can help clinicians as they work up their patients with COVID-19 symptoms,” he noted.
Dr. Jacobs and the authors of the studies had no disclosures.
Stage I mycosis fungoides is the general dermatologist’s bailiwick
LAHAINA, HAWAII – without bringing in a medical oncologist, Trilokraj Tejasvi, MBBS, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
This approach is in the best interest of patients with stage I mycosis fungoides, the skin-limited, patch/plaque form of the disease that generally responds well to skin-directed therapies without needing to resort to the medical oncologist’s arsenal of toxic treatments.
“For many medical oncologists, a lymphoma is a lymphoma. The first thing they give is CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), and all the variants of CHOP,” cautioned Dr. Tejasvi, a dermatologist who is director of the cutaneous lymphoma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and chief of the dermatology service at the Ann Arbor Veteran Affairs Hospital.
Stage IA mycosis fungoides is defined under the TNMB (tumor, node, metastasis, blood) classification as patches and/or plaques covering less than 10% of body surface area along with negative nodes, no metastases, and no or low burden of disease in the blood. Stage IB differs only in that it features 10% or greater body surface area involvement. The extent of body surface area involvement can be estimated by hands-on measurement in which the area of one of the patient’s hands – palm plus fingers – is considered equivalent to 1% of that individual’s total body surface area.
The first question patients newly diagnosed with a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma ask concerns their prognosis. For those with stage IA or IB mycosis fungoides, the news is very good, as highlighted in a retrospective study of nearly 1,400 patients with mycosis fungoides, 71% of whom presented with patch/plaque stage disease (J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28[31]:4730-9).
The median overall survival was 35.5 years in patients with stage IA disease and 21.5 years in those with stage IB disease.
“I tell patients with stage IA disease that whether we treat it or not will not change the course of their life,” Dr. Tejasvri said.
His message to patients with stage IB disease is that, because of their 38% risk of disease progression, he wants to see them in follow-up annually for the rest of their life.
Stage IIA disease – that is, patches and/or plaques with lymph node involvement with no effacement – is a tipping point at which serious consideration should be given to possible referral to a specialized multidisciplinary lymphoma center, in his view. That’s because the 10-year overall survival rate is only 52%.
Topical therapies
Topical corticosteroids remain the time-honored first-line skin-directed treatment. The mechanism of benefit involves induction of apoptosis and inhibition of lymphocyte binding. In one prospective study, clobetasol propionate achieved a 94% overall response rate in patients with stage IA or B disease, with minimal toxicity.
Alternatives include topical 5% imiquimod (Aldara), with an overall response rate of 80% and complete response rate of 45% in a 20-patient study. A newer formulation of mechlorethamine gel (Valchlor), is reported to have a 59% overall response rate and a sustained response in 86% of initial responders. For refractory skin lesions, 1% bexarotene gel (Targretin) is an option, with overall response rates of 44%-63% reported in prospective trials.
“I like it if the patient’s insurance covers it. Otherwise, it’s like buying a Prius: it’s $30,000 for a 45-g tube, which is insane,” Dr. Tejasvi commented.
Narrow-band UVB phototherapy is an effective modality for thin plaques and patches, as is PUVA for thicker ones. Dr. Tejasvi typically treats with topical steroids and/or phototherapy for at least 3 months before tapering.
When to suspect mycosis fungoides
“Mycosis fungoides is a great masquerader,” the dermatologist observed. For that reason, it deserves to be included in the differential diagnosis of an atypical psoriasiform or eczematoid rash, any new-onset rash in an elderly patient, or a rash with fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss in a patient of any age. Generalized erythema with severe itching is another red flag.
“This pruritus is so severe that the only other condition which in my clinical practice would match it is Norwegian scabies,” according to Dr. Tejasvi.
Polychromatic patches or plaques in skin of color warrant further investigation as possible mycosis fungoides, he added.
Dr. Tejasvi reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAHAINA, HAWAII – without bringing in a medical oncologist, Trilokraj Tejasvi, MBBS, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
This approach is in the best interest of patients with stage I mycosis fungoides, the skin-limited, patch/plaque form of the disease that generally responds well to skin-directed therapies without needing to resort to the medical oncologist’s arsenal of toxic treatments.
“For many medical oncologists, a lymphoma is a lymphoma. The first thing they give is CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), and all the variants of CHOP,” cautioned Dr. Tejasvi, a dermatologist who is director of the cutaneous lymphoma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and chief of the dermatology service at the Ann Arbor Veteran Affairs Hospital.
Stage IA mycosis fungoides is defined under the TNMB (tumor, node, metastasis, blood) classification as patches and/or plaques covering less than 10% of body surface area along with negative nodes, no metastases, and no or low burden of disease in the blood. Stage IB differs only in that it features 10% or greater body surface area involvement. The extent of body surface area involvement can be estimated by hands-on measurement in which the area of one of the patient’s hands – palm plus fingers – is considered equivalent to 1% of that individual’s total body surface area.
The first question patients newly diagnosed with a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma ask concerns their prognosis. For those with stage IA or IB mycosis fungoides, the news is very good, as highlighted in a retrospective study of nearly 1,400 patients with mycosis fungoides, 71% of whom presented with patch/plaque stage disease (J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28[31]:4730-9).
The median overall survival was 35.5 years in patients with stage IA disease and 21.5 years in those with stage IB disease.
“I tell patients with stage IA disease that whether we treat it or not will not change the course of their life,” Dr. Tejasvri said.
His message to patients with stage IB disease is that, because of their 38% risk of disease progression, he wants to see them in follow-up annually for the rest of their life.
Stage IIA disease – that is, patches and/or plaques with lymph node involvement with no effacement – is a tipping point at which serious consideration should be given to possible referral to a specialized multidisciplinary lymphoma center, in his view. That’s because the 10-year overall survival rate is only 52%.
Topical therapies
Topical corticosteroids remain the time-honored first-line skin-directed treatment. The mechanism of benefit involves induction of apoptosis and inhibition of lymphocyte binding. In one prospective study, clobetasol propionate achieved a 94% overall response rate in patients with stage IA or B disease, with minimal toxicity.
Alternatives include topical 5% imiquimod (Aldara), with an overall response rate of 80% and complete response rate of 45% in a 20-patient study. A newer formulation of mechlorethamine gel (Valchlor), is reported to have a 59% overall response rate and a sustained response in 86% of initial responders. For refractory skin lesions, 1% bexarotene gel (Targretin) is an option, with overall response rates of 44%-63% reported in prospective trials.
“I like it if the patient’s insurance covers it. Otherwise, it’s like buying a Prius: it’s $30,000 for a 45-g tube, which is insane,” Dr. Tejasvi commented.
Narrow-band UVB phototherapy is an effective modality for thin plaques and patches, as is PUVA for thicker ones. Dr. Tejasvi typically treats with topical steroids and/or phototherapy for at least 3 months before tapering.
When to suspect mycosis fungoides
“Mycosis fungoides is a great masquerader,” the dermatologist observed. For that reason, it deserves to be included in the differential diagnosis of an atypical psoriasiform or eczematoid rash, any new-onset rash in an elderly patient, or a rash with fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss in a patient of any age. Generalized erythema with severe itching is another red flag.
“This pruritus is so severe that the only other condition which in my clinical practice would match it is Norwegian scabies,” according to Dr. Tejasvi.
Polychromatic patches or plaques in skin of color warrant further investigation as possible mycosis fungoides, he added.
Dr. Tejasvi reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAHAINA, HAWAII – without bringing in a medical oncologist, Trilokraj Tejasvi, MBBS, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
This approach is in the best interest of patients with stage I mycosis fungoides, the skin-limited, patch/plaque form of the disease that generally responds well to skin-directed therapies without needing to resort to the medical oncologist’s arsenal of toxic treatments.
“For many medical oncologists, a lymphoma is a lymphoma. The first thing they give is CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), and all the variants of CHOP,” cautioned Dr. Tejasvi, a dermatologist who is director of the cutaneous lymphoma program at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and chief of the dermatology service at the Ann Arbor Veteran Affairs Hospital.
Stage IA mycosis fungoides is defined under the TNMB (tumor, node, metastasis, blood) classification as patches and/or plaques covering less than 10% of body surface area along with negative nodes, no metastases, and no or low burden of disease in the blood. Stage IB differs only in that it features 10% or greater body surface area involvement. The extent of body surface area involvement can be estimated by hands-on measurement in which the area of one of the patient’s hands – palm plus fingers – is considered equivalent to 1% of that individual’s total body surface area.
The first question patients newly diagnosed with a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma ask concerns their prognosis. For those with stage IA or IB mycosis fungoides, the news is very good, as highlighted in a retrospective study of nearly 1,400 patients with mycosis fungoides, 71% of whom presented with patch/plaque stage disease (J Clin Oncol. 2010 Nov 1;28[31]:4730-9).
The median overall survival was 35.5 years in patients with stage IA disease and 21.5 years in those with stage IB disease.
“I tell patients with stage IA disease that whether we treat it or not will not change the course of their life,” Dr. Tejasvri said.
His message to patients with stage IB disease is that, because of their 38% risk of disease progression, he wants to see them in follow-up annually for the rest of their life.
Stage IIA disease – that is, patches and/or plaques with lymph node involvement with no effacement – is a tipping point at which serious consideration should be given to possible referral to a specialized multidisciplinary lymphoma center, in his view. That’s because the 10-year overall survival rate is only 52%.
Topical therapies
Topical corticosteroids remain the time-honored first-line skin-directed treatment. The mechanism of benefit involves induction of apoptosis and inhibition of lymphocyte binding. In one prospective study, clobetasol propionate achieved a 94% overall response rate in patients with stage IA or B disease, with minimal toxicity.
Alternatives include topical 5% imiquimod (Aldara), with an overall response rate of 80% and complete response rate of 45% in a 20-patient study. A newer formulation of mechlorethamine gel (Valchlor), is reported to have a 59% overall response rate and a sustained response in 86% of initial responders. For refractory skin lesions, 1% bexarotene gel (Targretin) is an option, with overall response rates of 44%-63% reported in prospective trials.
“I like it if the patient’s insurance covers it. Otherwise, it’s like buying a Prius: it’s $30,000 for a 45-g tube, which is insane,” Dr. Tejasvi commented.
Narrow-band UVB phototherapy is an effective modality for thin plaques and patches, as is PUVA for thicker ones. Dr. Tejasvi typically treats with topical steroids and/or phototherapy for at least 3 months before tapering.
When to suspect mycosis fungoides
“Mycosis fungoides is a great masquerader,” the dermatologist observed. For that reason, it deserves to be included in the differential diagnosis of an atypical psoriasiform or eczematoid rash, any new-onset rash in an elderly patient, or a rash with fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss in a patient of any age. Generalized erythema with severe itching is another red flag.
“This pruritus is so severe that the only other condition which in my clinical practice would match it is Norwegian scabies,” according to Dr. Tejasvi.
Polychromatic patches or plaques in skin of color warrant further investigation as possible mycosis fungoides, he added.
Dr. Tejasvi reported having no financial conflicts of interest regarding his presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
REPORTING FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Don’t call it perioral dermatitis
LAHAINA, HAWAII – , according to Jessica Sprague, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital.
Years ago, some of her senior colleagues at the children’s hospital carried out a retrospective study of 79 patients, aged 6 months to 18 years, who were treated for what’s typically called perioral dermatitis. Of note, only 40% of patients had isolated perioral involvement, while 30% of the patients had no perioral lesions at all. Perinasal lesions were present in 43%, and 25% had periocular involvement, she noted at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
The peak incidence of periorificial dermatitis in this series was under age 5 years. At presentation, the rash had been present for an average of 8 months. Seventy-two percent of patients had a history of exposure to corticosteroids, most often in the form of topical steroids, but in some cases inhaled or systemic steroids.
“Obviously you want to discontinue the topical steroid. Sometimes you need to taper them off, or you can switch to a topical calcineurin inhibitor [TCI] because they tend to flare a lot when you stop their topical steroid, although there are cases of TCIs precipitating periorificial dermatitis, so keep that in mind,” Dr. Sprague said.
If a patient is on inhaled steroids by mask for asthma, switching to a tube can sometimes limit the exposure, she continued.
Her first-line therapy for mild to moderate periorificial dermatitis, and the one supported by the strongest evidence base, is metronidazole cream. Other topical agents shown to be effective include azelaic acid, sulfacetamide, clindamycin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
Oral therapy is a good option for more extensive or recalcitrant cases.
“If parents are very anxious, like before school photos or holiday photos, sometimes I’ll use oral therapy as well. In younger kids, I prefer erythromycin at 30 mg/kg per day t.i.d. for 3-6 weeks. In kids 8 years old and up you can use doxycycline at 50-100 mg b.i.d., again for 3-6 weeks. And you have to tell them it’s going to take a while for this to go away,” Dr. Sprague said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAHAINA, HAWAII – , according to Jessica Sprague, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital.
Years ago, some of her senior colleagues at the children’s hospital carried out a retrospective study of 79 patients, aged 6 months to 18 years, who were treated for what’s typically called perioral dermatitis. Of note, only 40% of patients had isolated perioral involvement, while 30% of the patients had no perioral lesions at all. Perinasal lesions were present in 43%, and 25% had periocular involvement, she noted at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
The peak incidence of periorificial dermatitis in this series was under age 5 years. At presentation, the rash had been present for an average of 8 months. Seventy-two percent of patients had a history of exposure to corticosteroids, most often in the form of topical steroids, but in some cases inhaled or systemic steroids.
“Obviously you want to discontinue the topical steroid. Sometimes you need to taper them off, or you can switch to a topical calcineurin inhibitor [TCI] because they tend to flare a lot when you stop their topical steroid, although there are cases of TCIs precipitating periorificial dermatitis, so keep that in mind,” Dr. Sprague said.
If a patient is on inhaled steroids by mask for asthma, switching to a tube can sometimes limit the exposure, she continued.
Her first-line therapy for mild to moderate periorificial dermatitis, and the one supported by the strongest evidence base, is metronidazole cream. Other topical agents shown to be effective include azelaic acid, sulfacetamide, clindamycin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
Oral therapy is a good option for more extensive or recalcitrant cases.
“If parents are very anxious, like before school photos or holiday photos, sometimes I’ll use oral therapy as well. In younger kids, I prefer erythromycin at 30 mg/kg per day t.i.d. for 3-6 weeks. In kids 8 years old and up you can use doxycycline at 50-100 mg b.i.d., again for 3-6 weeks. And you have to tell them it’s going to take a while for this to go away,” Dr. Sprague said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAHAINA, HAWAII – , according to Jessica Sprague, MD, a pediatric dermatologist at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital.
Years ago, some of her senior colleagues at the children’s hospital carried out a retrospective study of 79 patients, aged 6 months to 18 years, who were treated for what’s typically called perioral dermatitis. Of note, only 40% of patients had isolated perioral involvement, while 30% of the patients had no perioral lesions at all. Perinasal lesions were present in 43%, and 25% had periocular involvement, she noted at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Education Foundation.
The peak incidence of periorificial dermatitis in this series was under age 5 years. At presentation, the rash had been present for an average of 8 months. Seventy-two percent of patients had a history of exposure to corticosteroids, most often in the form of topical steroids, but in some cases inhaled or systemic steroids.
“Obviously you want to discontinue the topical steroid. Sometimes you need to taper them off, or you can switch to a topical calcineurin inhibitor [TCI] because they tend to flare a lot when you stop their topical steroid, although there are cases of TCIs precipitating periorificial dermatitis, so keep that in mind,” Dr. Sprague said.
If a patient is on inhaled steroids by mask for asthma, switching to a tube can sometimes limit the exposure, she continued.
Her first-line therapy for mild to moderate periorificial dermatitis, and the one supported by the strongest evidence base, is metronidazole cream. Other topical agents shown to be effective include azelaic acid, sulfacetamide, clindamycin, and topical calcineurin inhibitors.
Oral therapy is a good option for more extensive or recalcitrant cases.
“If parents are very anxious, like before school photos or holiday photos, sometimes I’ll use oral therapy as well. In younger kids, I prefer erythromycin at 30 mg/kg per day t.i.d. for 3-6 weeks. In kids 8 years old and up you can use doxycycline at 50-100 mg b.i.d., again for 3-6 weeks. And you have to tell them it’s going to take a while for this to go away,” Dr. Sprague said.
She reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
SDEF/Global Academy for Medical Education and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
REPORTING FROM SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR