User login
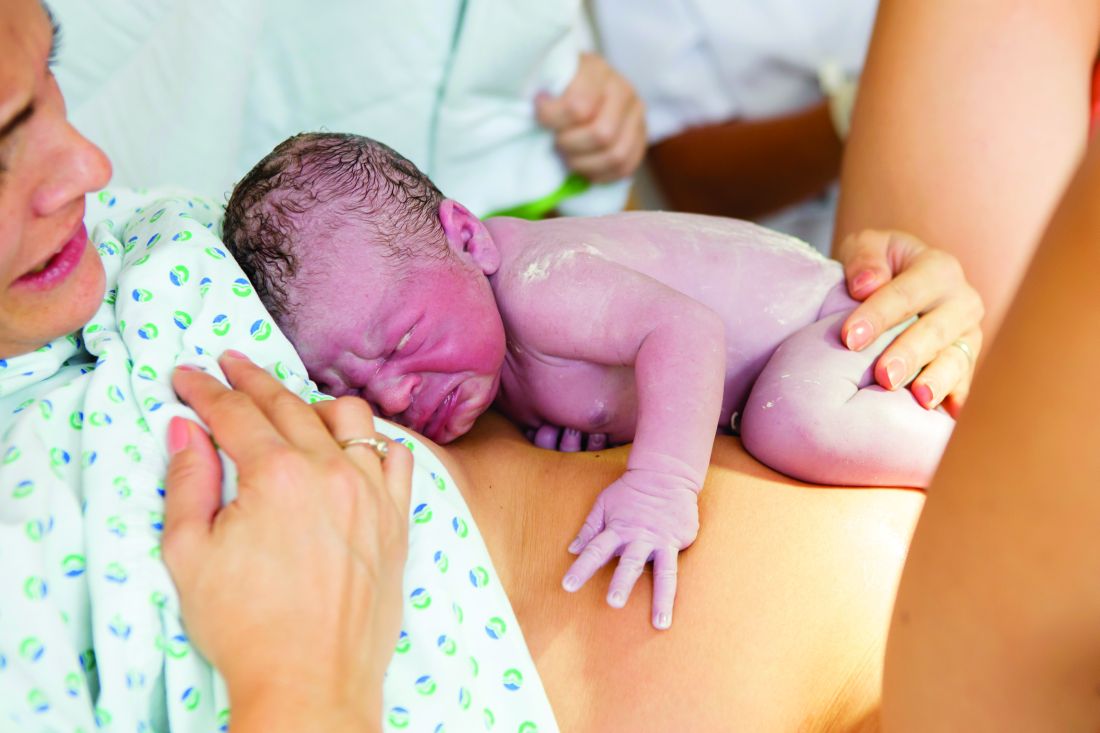
Poor parent-infant relationship may affect a child’s motor skill development
TORONTO – In what is believed to be a landmark finding, researchers have shown than modifiable risk factors, such as parent-infant relationships, may play a role in preventing children from developing high motor problems during early life.
“Our findings suggest that early health and clinical problems, such as neonatal complications and abnormal neonatal neurological status, are useful indicators to help identify children at risk of poor motor development,” lead study author Nicole Baumann said in an interview in advance of the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting. “Additionally, as a possible implication, children may benefit in motor development from early interventions that incorporate and focus on improving parent-infant relationships.”
For the current study, she and her associates investigated motor development using data from two different cohorts: the Bavarian Longitudinal Study in Germany (BLS) and the Arvo Ylppö Longitudinal Study in Finland (AYLS). A total of 4,741 and 1,423 children, respectively, underwent assessment from birth to age 56 months. Motor functioning was evaluated via standard physical and neurological assessments at birth and at 5, 20, and 56 months. Perinatal, neonatal, and early environmental information was collected at birth and at 5 months via medical records and reports from parents and research nurses.
The researchers identified two distinct trajectories of motor development problems from birth to 56 months: low (94.3% of BLS and 97.3% of AYLS) and high (5.7% of BLS and 2.7% of AYLS) motor problems.
In the BLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was predicted by poor parent-infant relationship, such as the mother feeling insecure when taking care of the infant at home (OR 1.52); abnormal neonatal neurological status (odds ratio, 1.16); neonatal complications (OR, 1.12); and duration of initial hospitalization (OR, 1.02).
In the AYLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was also predicted by abnormal neonatal neurological status (OR, 1.69) and duration of hospitalization (OR, 1.02). Although neonatal complications (OR, 1.08) and poor parent-infant relationship (OR, 1.09) did not significantly predict high motor problem trajectory in the AYLS cohort, trends identified were comparable with those obtained from the BLS cohort.
“Most surprising was that one of the four risk factors that remained as independent predictors of high motor problem trajectory was poor parent-infant relationship,” Ms. Baumann said. “As far as we are aware, parent-infant relationship has not been previously reported as a predictor of poor motor development.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that nearly 33% of children could not be assessed throughout the study period because of dropout. “Families with children who had poor health and were socially disadvantaged were less likely to continue participation, and may even suggest that our findings have an even larger effect than reported,” Ms. Baumann said. “This is a problem that affects many longitudinal studies, and it may affect group comparisons. However, simulations have shown that even when dropout is selective or correlated with the outcome that predictions only marginally change (Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195[3]:249-56).”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
TORONTO – In what is believed to be a landmark finding, researchers have shown than modifiable risk factors, such as parent-infant relationships, may play a role in preventing children from developing high motor problems during early life.
“Our findings suggest that early health and clinical problems, such as neonatal complications and abnormal neonatal neurological status, are useful indicators to help identify children at risk of poor motor development,” lead study author Nicole Baumann said in an interview in advance of the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting. “Additionally, as a possible implication, children may benefit in motor development from early interventions that incorporate and focus on improving parent-infant relationships.”
For the current study, she and her associates investigated motor development using data from two different cohorts: the Bavarian Longitudinal Study in Germany (BLS) and the Arvo Ylppö Longitudinal Study in Finland (AYLS). A total of 4,741 and 1,423 children, respectively, underwent assessment from birth to age 56 months. Motor functioning was evaluated via standard physical and neurological assessments at birth and at 5, 20, and 56 months. Perinatal, neonatal, and early environmental information was collected at birth and at 5 months via medical records and reports from parents and research nurses.
The researchers identified two distinct trajectories of motor development problems from birth to 56 months: low (94.3% of BLS and 97.3% of AYLS) and high (5.7% of BLS and 2.7% of AYLS) motor problems.
In the BLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was predicted by poor parent-infant relationship, such as the mother feeling insecure when taking care of the infant at home (OR 1.52); abnormal neonatal neurological status (odds ratio, 1.16); neonatal complications (OR, 1.12); and duration of initial hospitalization (OR, 1.02).
In the AYLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was also predicted by abnormal neonatal neurological status (OR, 1.69) and duration of hospitalization (OR, 1.02). Although neonatal complications (OR, 1.08) and poor parent-infant relationship (OR, 1.09) did not significantly predict high motor problem trajectory in the AYLS cohort, trends identified were comparable with those obtained from the BLS cohort.
“Most surprising was that one of the four risk factors that remained as independent predictors of high motor problem trajectory was poor parent-infant relationship,” Ms. Baumann said. “As far as we are aware, parent-infant relationship has not been previously reported as a predictor of poor motor development.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that nearly 33% of children could not be assessed throughout the study period because of dropout. “Families with children who had poor health and were socially disadvantaged were less likely to continue participation, and may even suggest that our findings have an even larger effect than reported,” Ms. Baumann said. “This is a problem that affects many longitudinal studies, and it may affect group comparisons. However, simulations have shown that even when dropout is selective or correlated with the outcome that predictions only marginally change (Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195[3]:249-56).”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
TORONTO – In what is believed to be a landmark finding, researchers have shown than modifiable risk factors, such as parent-infant relationships, may play a role in preventing children from developing high motor problems during early life.
“Our findings suggest that early health and clinical problems, such as neonatal complications and abnormal neonatal neurological status, are useful indicators to help identify children at risk of poor motor development,” lead study author Nicole Baumann said in an interview in advance of the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting. “Additionally, as a possible implication, children may benefit in motor development from early interventions that incorporate and focus on improving parent-infant relationships.”
For the current study, she and her associates investigated motor development using data from two different cohorts: the Bavarian Longitudinal Study in Germany (BLS) and the Arvo Ylppö Longitudinal Study in Finland (AYLS). A total of 4,741 and 1,423 children, respectively, underwent assessment from birth to age 56 months. Motor functioning was evaluated via standard physical and neurological assessments at birth and at 5, 20, and 56 months. Perinatal, neonatal, and early environmental information was collected at birth and at 5 months via medical records and reports from parents and research nurses.
The researchers identified two distinct trajectories of motor development problems from birth to 56 months: low (94.3% of BLS and 97.3% of AYLS) and high (5.7% of BLS and 2.7% of AYLS) motor problems.
In the BLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was predicted by poor parent-infant relationship, such as the mother feeling insecure when taking care of the infant at home (OR 1.52); abnormal neonatal neurological status (odds ratio, 1.16); neonatal complications (OR, 1.12); and duration of initial hospitalization (OR, 1.02).
In the AYLS cohort, high motor problem trajectory was also predicted by abnormal neonatal neurological status (OR, 1.69) and duration of hospitalization (OR, 1.02). Although neonatal complications (OR, 1.08) and poor parent-infant relationship (OR, 1.09) did not significantly predict high motor problem trajectory in the AYLS cohort, trends identified were comparable with those obtained from the BLS cohort.
“Most surprising was that one of the four risk factors that remained as independent predictors of high motor problem trajectory was poor parent-infant relationship,” Ms. Baumann said. “As far as we are aware, parent-infant relationship has not been previously reported as a predictor of poor motor development.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that nearly 33% of children could not be assessed throughout the study period because of dropout. “Families with children who had poor health and were socially disadvantaged were less likely to continue participation, and may even suggest that our findings have an even larger effect than reported,” Ms. Baumann said. “This is a problem that affects many longitudinal studies, and it may affect group comparisons. However, simulations have shown that even when dropout is selective or correlated with the outcome that predictions only marginally change (Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195[3]:249-56).”
She reported having no financial disclosures.
AT PAS 2018
Key clinical point: Four risk factors are independent predictors of high motor problem trajectory in young children.
Major finding: In the Bavarian Longitudinal Study cohort, high motor problem trajectory was predicted by abnormal neonatal neurological status (odds ratio, 1.16), duration of initial hospitalization (OR 1.02), neonatal complications (OR 1.12), and poor parent-infant relationship (OR 1.52).
Study details: A longitudinal analysis of 4,741 children from the Bavarian Longitudinal Study in Germany and 1,423 children from the Arvo Ylppö Longitudinal Study in Finland.
Disclosures: Ms. Baumann reported having no financial disclosures.
MDedge Daily News: Fewer smokes mean fewer strokes
Are biopsy’s days numbered for diagnosing celiac disease? The perils of endoscopic therapy for Barrett’s esophagus. And is your EHR preventing breastfeeding?
Listen to the MDedge Daily News podcast for all the details on today’s top news.
Are biopsy’s days numbered for diagnosing celiac disease? The perils of endoscopic therapy for Barrett’s esophagus. And is your EHR preventing breastfeeding?
Listen to the MDedge Daily News podcast for all the details on today’s top news.
Are biopsy’s days numbered for diagnosing celiac disease? The perils of endoscopic therapy for Barrett’s esophagus. And is your EHR preventing breastfeeding?
Listen to the MDedge Daily News podcast for all the details on today’s top news.
VIDEO: To boost newborn breastfeeding rates, hide the EHR formula order
AUSTIN, TEXAS – When the check box for ordering formula for newborns was removed as a standard newborn order option in the electronic health record (EHR), rates of exclusive breastfeeding climbed significantly in Los Angeles County hospitals, according to a recent study.
“The saying, ‘out of sight, out of mind’ cannot be overstated when it comes to physician order entry,” wrote Ramy Eskander, MD, and his colleagues in the poster accompanying the presentation at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a video interview, Dr. Eskander said that he and his colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, were looking for an intervention that would use the EHR as a quality improvement tool.
What they decided to do was to see “how could we possibly ‘get in the way’ and have an intervention between the provider and the patient that didn’t necessarily involve much work on the provider’s end, that had a significant impact on the back end,” he said. What they ended up doing was remove the order to request formula for mothers from the physician order set in the EHR.
Study data were collected in three stages for the academic tertiary care hospital within the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services system.
First, Dr. Eskander and his colleagues collected baseline data from January to July of 2016. Then, data were collected from July to the end of 2016, while a campaign was underway to bring staff and patients up to speed on the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding. There were no statistically significant differences in the rates of exclusive breastfeeding on discharge between these two time periods, when rates hovered between 30% and 40%.
The final data collection period began in January 2017. At that time, the option to order formula for a newborn was removed as an option for the EHR newborn order set.
“When we did that, providers weren’t looking at the possibility of having that easy check box right there to fill in … and we know that when people have to go through more steps, they invariably don’t do it,” Dr. Eskander said.
He and his colleagues saw an almost immediate . Once the formula order was removed, breastfeeding rates rose from 40.57% to 53.90% (P less than .001). Rates have been sustained since the removal of the EHR option for formula.
There was no difference in how infants fared after the intervention, said Dr. Eskander. “The outcomes for those infants was identical. There were no increased NICU admissions, there were no increased poor outcomes.”
Length of stay remained the same as well. “The babies were being discharged in the same state of health, just more of them were getting breast milk only, and we know the benefits that tends to portend,” he added.
There was some initial grumbling when the formula order was pulled from the newborn order set, he conceded. “The providers were not very happy about having to look for the newborn order for formula.” However, it took just about a month for the new workflow to seem normal, he said.
Dr. Eskander envisions a future where the EHR is “smart” enough to prompt appropriate orders and interventions for serious conditions such as preeclampsia. The electronic record, he said, could recognize the maternal diagnosis “and immediately create a system and structure around that mother to be able to help protect her and her baby. ... then having those diagnoses be able to drive outcomes can be very significant.”
Dr. Eskander reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Eskander, R et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 31I.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – When the check box for ordering formula for newborns was removed as a standard newborn order option in the electronic health record (EHR), rates of exclusive breastfeeding climbed significantly in Los Angeles County hospitals, according to a recent study.
“The saying, ‘out of sight, out of mind’ cannot be overstated when it comes to physician order entry,” wrote Ramy Eskander, MD, and his colleagues in the poster accompanying the presentation at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a video interview, Dr. Eskander said that he and his colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, were looking for an intervention that would use the EHR as a quality improvement tool.
What they decided to do was to see “how could we possibly ‘get in the way’ and have an intervention between the provider and the patient that didn’t necessarily involve much work on the provider’s end, that had a significant impact on the back end,” he said. What they ended up doing was remove the order to request formula for mothers from the physician order set in the EHR.
Study data were collected in three stages for the academic tertiary care hospital within the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services system.
First, Dr. Eskander and his colleagues collected baseline data from January to July of 2016. Then, data were collected from July to the end of 2016, while a campaign was underway to bring staff and patients up to speed on the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding. There were no statistically significant differences in the rates of exclusive breastfeeding on discharge between these two time periods, when rates hovered between 30% and 40%.
The final data collection period began in January 2017. At that time, the option to order formula for a newborn was removed as an option for the EHR newborn order set.
“When we did that, providers weren’t looking at the possibility of having that easy check box right there to fill in … and we know that when people have to go through more steps, they invariably don’t do it,” Dr. Eskander said.
He and his colleagues saw an almost immediate . Once the formula order was removed, breastfeeding rates rose from 40.57% to 53.90% (P less than .001). Rates have been sustained since the removal of the EHR option for formula.
There was no difference in how infants fared after the intervention, said Dr. Eskander. “The outcomes for those infants was identical. There were no increased NICU admissions, there were no increased poor outcomes.”
Length of stay remained the same as well. “The babies were being discharged in the same state of health, just more of them were getting breast milk only, and we know the benefits that tends to portend,” he added.
There was some initial grumbling when the formula order was pulled from the newborn order set, he conceded. “The providers were not very happy about having to look for the newborn order for formula.” However, it took just about a month for the new workflow to seem normal, he said.
Dr. Eskander envisions a future where the EHR is “smart” enough to prompt appropriate orders and interventions for serious conditions such as preeclampsia. The electronic record, he said, could recognize the maternal diagnosis “and immediately create a system and structure around that mother to be able to help protect her and her baby. ... then having those diagnoses be able to drive outcomes can be very significant.”
Dr. Eskander reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Eskander, R et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 31I.
AUSTIN, TEXAS – When the check box for ordering formula for newborns was removed as a standard newborn order option in the electronic health record (EHR), rates of exclusive breastfeeding climbed significantly in Los Angeles County hospitals, according to a recent study.
“The saying, ‘out of sight, out of mind’ cannot be overstated when it comes to physician order entry,” wrote Ramy Eskander, MD, and his colleagues in the poster accompanying the presentation at the annual clinical and scientific sessions of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
In a video interview, Dr. Eskander said that he and his colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, were looking for an intervention that would use the EHR as a quality improvement tool.
What they decided to do was to see “how could we possibly ‘get in the way’ and have an intervention between the provider and the patient that didn’t necessarily involve much work on the provider’s end, that had a significant impact on the back end,” he said. What they ended up doing was remove the order to request formula for mothers from the physician order set in the EHR.
Study data were collected in three stages for the academic tertiary care hospital within the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services system.
First, Dr. Eskander and his colleagues collected baseline data from January to July of 2016. Then, data were collected from July to the end of 2016, while a campaign was underway to bring staff and patients up to speed on the benefits of exclusive breastfeeding. There were no statistically significant differences in the rates of exclusive breastfeeding on discharge between these two time periods, when rates hovered between 30% and 40%.
The final data collection period began in January 2017. At that time, the option to order formula for a newborn was removed as an option for the EHR newborn order set.
“When we did that, providers weren’t looking at the possibility of having that easy check box right there to fill in … and we know that when people have to go through more steps, they invariably don’t do it,” Dr. Eskander said.
He and his colleagues saw an almost immediate . Once the formula order was removed, breastfeeding rates rose from 40.57% to 53.90% (P less than .001). Rates have been sustained since the removal of the EHR option for formula.
There was no difference in how infants fared after the intervention, said Dr. Eskander. “The outcomes for those infants was identical. There were no increased NICU admissions, there were no increased poor outcomes.”
Length of stay remained the same as well. “The babies were being discharged in the same state of health, just more of them were getting breast milk only, and we know the benefits that tends to portend,” he added.
There was some initial grumbling when the formula order was pulled from the newborn order set, he conceded. “The providers were not very happy about having to look for the newborn order for formula.” However, it took just about a month for the new workflow to seem normal, he said.
Dr. Eskander envisions a future where the EHR is “smart” enough to prompt appropriate orders and interventions for serious conditions such as preeclampsia. The electronic record, he said, could recognize the maternal diagnosis “and immediately create a system and structure around that mother to be able to help protect her and her baby. ... then having those diagnoses be able to drive outcomes can be very significant.”
Dr. Eskander reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Eskander, R et al. ACOG 2018, Abstract 31I.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2018
Pot peaks in breast milk 1 hour after smoking
The levels of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in breast milk peak around 1 hour after smoking, according to a pilot pharmacokinetic study.
Eight mothers who were either occasional or chronic cannabis smokers, and who exclusively breastfed their infants, were directed to smoke a preweighed, standardized amount of “Prezidential Kush” from a preselected Denver dispensary after initially discontinuing for 24 hours. Researchers collected breast milk samples from just before smoking, and at 20 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours after smoking, according to a paper published in the May issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
This translated to an estimated relative infant dose of 2.5% of the maternal dose, or 8 mcg per kilogram per day.
“It remains unclear what exposure to cannabis products during this critical neurobehavioral development period will mean for the infant,” wrote Teresa Baker, MD, of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, and her coauthors. “These questions will require an enormous effort to determine.”
Concentrations of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites 11-OH-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-Nor-9-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol were too low to be detected.
The authors noted that these metabolites are known to be more water soluble and polar than delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol itself, which may make it more difficult for them to enter the breast milk compartment.
Two of the participants had a low but measurable concentration of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol at zero time (the samples collected just before smoking), suggesting some residual accumulation of it from prior heavy use or use close to the start of breast milk collection.
“Although the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into the plasma compartment is almost instantaneous, the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into breast milk in our study appears to be slightly slower than the transfer into the plasma compartment,” the authors wrote.
The women in the study were all 2-5 months postpartum. The authors noted that in these women who were exclusively breastfeeding, the breast milk compartment, along with drug entry and exit, “remains fairly consistent.”
The researchers also noted that the lack of corresponding plasma samples was a major limitation of the study, but because of the nature of the study, anonymity was important.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Baker T et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:783-8.
The levels of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in breast milk peak around 1 hour after smoking, according to a pilot pharmacokinetic study.
Eight mothers who were either occasional or chronic cannabis smokers, and who exclusively breastfed their infants, were directed to smoke a preweighed, standardized amount of “Prezidential Kush” from a preselected Denver dispensary after initially discontinuing for 24 hours. Researchers collected breast milk samples from just before smoking, and at 20 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours after smoking, according to a paper published in the May issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
This translated to an estimated relative infant dose of 2.5% of the maternal dose, or 8 mcg per kilogram per day.
“It remains unclear what exposure to cannabis products during this critical neurobehavioral development period will mean for the infant,” wrote Teresa Baker, MD, of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, and her coauthors. “These questions will require an enormous effort to determine.”
Concentrations of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites 11-OH-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-Nor-9-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol were too low to be detected.
The authors noted that these metabolites are known to be more water soluble and polar than delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol itself, which may make it more difficult for them to enter the breast milk compartment.
Two of the participants had a low but measurable concentration of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol at zero time (the samples collected just before smoking), suggesting some residual accumulation of it from prior heavy use or use close to the start of breast milk collection.
“Although the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into the plasma compartment is almost instantaneous, the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into breast milk in our study appears to be slightly slower than the transfer into the plasma compartment,” the authors wrote.
The women in the study were all 2-5 months postpartum. The authors noted that in these women who were exclusively breastfeeding, the breast milk compartment, along with drug entry and exit, “remains fairly consistent.”
The researchers also noted that the lack of corresponding plasma samples was a major limitation of the study, but because of the nature of the study, anonymity was important.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Baker T et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:783-8.
The levels of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in breast milk peak around 1 hour after smoking, according to a pilot pharmacokinetic study.
Eight mothers who were either occasional or chronic cannabis smokers, and who exclusively breastfed their infants, were directed to smoke a preweighed, standardized amount of “Prezidential Kush” from a preselected Denver dispensary after initially discontinuing for 24 hours. Researchers collected breast milk samples from just before smoking, and at 20 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours after smoking, according to a paper published in the May issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
This translated to an estimated relative infant dose of 2.5% of the maternal dose, or 8 mcg per kilogram per day.
“It remains unclear what exposure to cannabis products during this critical neurobehavioral development period will mean for the infant,” wrote Teresa Baker, MD, of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, and her coauthors. “These questions will require an enormous effort to determine.”
Concentrations of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites 11-OH-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-Nor-9-carboxy-delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol were too low to be detected.
The authors noted that these metabolites are known to be more water soluble and polar than delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol itself, which may make it more difficult for them to enter the breast milk compartment.
Two of the participants had a low but measurable concentration of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol at zero time (the samples collected just before smoking), suggesting some residual accumulation of it from prior heavy use or use close to the start of breast milk collection.
“Although the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into the plasma compartment is almost instantaneous, the transfer of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol into breast milk in our study appears to be slightly slower than the transfer into the plasma compartment,” the authors wrote.
The women in the study were all 2-5 months postpartum. The authors noted that in these women who were exclusively breastfeeding, the breast milk compartment, along with drug entry and exit, “remains fairly consistent.”
The researchers also noted that the lack of corresponding plasma samples was a major limitation of the study, but because of the nature of the study, anonymity was important.
No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Baker T et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:783-8.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Key clinical point: Cannabinoid levels peak in breast milk 1 hour after smoking.
Major finding: Breastfeeding infants ingest around 2.5% of the maternal dose in breast milk.
Study details: A pilot pharmacokinetic study in eight women.
Disclosures: No conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Baker T et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:783-8.
Caffeine for apnea of prematurity found safe, effective at 11 years
Caffeine for apnea of prematurity was neurobehaviorally safe and significantly improved fine motor coordination, visuomotor integration, visual perception, and visuospatial organization at 11-year follow-up, according to the results of a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
“There was little evidence for differences between the caffeine and placebo groups on tests of general intelligence, attention, executive function, and behavior. This highlights the long-term safety and efficacy of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight neonates,” wrote Ines M. Mürner-Lavanchy, PhD, of Monash University, Clayton, Australia, and her associates. The Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity (CAP) trial, the first to assess long-term neurobehavioral outcomes of neonatal caffeine therapy, was published online April 11 in Pediatrics.
Neonatal caffeine therapy significantly lowered the risk of death before 18 months, cerebral palsy, cognitive delay, severe hearing loss, and bilateral blindness, as has been reported (N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1893-902). By 5 years, caffeine no longer showed significant benefits, apart from improved motor performance, Dr. Mürner-Lavanchy and her associates noted.
At 11 years, available data from 870 patients showed generally similar neurobehavioral outcomes between groups, although the caffeine group scored higher on most scales. The most apparent benefits included visuomotor integration (mean difference from placebo, 1.8; 95% confidence interval, 0.0-3.7; P less than .05), visual perception (2.0; 95% CI, 0.3-3.8; P = .02), fine motor coordination (2.9; 95% CI, 0.7-5.1; P = .01), and Rey Complex Figure copy accuracy, a measure of visuospatial organization (1.2; 95% CI, 0.4-2.0; P = .003).
Eleven-year follow-up data were missing for 22% of patients, but their birth characteristics and childhood outcomes resembled those of patients with available data, the investigators said. “Therefore, we are confident that the outcomes of the whole cohort are reflected in the present results with sufficient accuracy.”
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research provided funding. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mürner-Lavanchy IM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-4047.
Caffeine for apnea of prematurity was neurobehaviorally safe and significantly improved fine motor coordination, visuomotor integration, visual perception, and visuospatial organization at 11-year follow-up, according to the results of a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
“There was little evidence for differences between the caffeine and placebo groups on tests of general intelligence, attention, executive function, and behavior. This highlights the long-term safety and efficacy of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight neonates,” wrote Ines M. Mürner-Lavanchy, PhD, of Monash University, Clayton, Australia, and her associates. The Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity (CAP) trial, the first to assess long-term neurobehavioral outcomes of neonatal caffeine therapy, was published online April 11 in Pediatrics.
Neonatal caffeine therapy significantly lowered the risk of death before 18 months, cerebral palsy, cognitive delay, severe hearing loss, and bilateral blindness, as has been reported (N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1893-902). By 5 years, caffeine no longer showed significant benefits, apart from improved motor performance, Dr. Mürner-Lavanchy and her associates noted.
At 11 years, available data from 870 patients showed generally similar neurobehavioral outcomes between groups, although the caffeine group scored higher on most scales. The most apparent benefits included visuomotor integration (mean difference from placebo, 1.8; 95% confidence interval, 0.0-3.7; P less than .05), visual perception (2.0; 95% CI, 0.3-3.8; P = .02), fine motor coordination (2.9; 95% CI, 0.7-5.1; P = .01), and Rey Complex Figure copy accuracy, a measure of visuospatial organization (1.2; 95% CI, 0.4-2.0; P = .003).
Eleven-year follow-up data were missing for 22% of patients, but their birth characteristics and childhood outcomes resembled those of patients with available data, the investigators said. “Therefore, we are confident that the outcomes of the whole cohort are reflected in the present results with sufficient accuracy.”
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research provided funding. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mürner-Lavanchy IM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-4047.
Caffeine for apnea of prematurity was neurobehaviorally safe and significantly improved fine motor coordination, visuomotor integration, visual perception, and visuospatial organization at 11-year follow-up, according to the results of a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.
“There was little evidence for differences between the caffeine and placebo groups on tests of general intelligence, attention, executive function, and behavior. This highlights the long-term safety and efficacy of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity in very-low-birth-weight neonates,” wrote Ines M. Mürner-Lavanchy, PhD, of Monash University, Clayton, Australia, and her associates. The Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity (CAP) trial, the first to assess long-term neurobehavioral outcomes of neonatal caffeine therapy, was published online April 11 in Pediatrics.
Neonatal caffeine therapy significantly lowered the risk of death before 18 months, cerebral palsy, cognitive delay, severe hearing loss, and bilateral blindness, as has been reported (N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1893-902). By 5 years, caffeine no longer showed significant benefits, apart from improved motor performance, Dr. Mürner-Lavanchy and her associates noted.
At 11 years, available data from 870 patients showed generally similar neurobehavioral outcomes between groups, although the caffeine group scored higher on most scales. The most apparent benefits included visuomotor integration (mean difference from placebo, 1.8; 95% confidence interval, 0.0-3.7; P less than .05), visual perception (2.0; 95% CI, 0.3-3.8; P = .02), fine motor coordination (2.9; 95% CI, 0.7-5.1; P = .01), and Rey Complex Figure copy accuracy, a measure of visuospatial organization (1.2; 95% CI, 0.4-2.0; P = .003).
Eleven-year follow-up data were missing for 22% of patients, but their birth characteristics and childhood outcomes resembled those of patients with available data, the investigators said. “Therefore, we are confident that the outcomes of the whole cohort are reflected in the present results with sufficient accuracy.”
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research provided funding. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mürner-Lavanchy IM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-4047.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At 11 years, the caffeine group outperformed the placebo group on measures of fine motor coordination (P = .01), visuomotor integration (P less than .05), visual perception (P = .02), and visuospatial organization (P = .003).
Study details: The Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity (CAP) trial, a double-blind, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of 870 very-low-birth-weight infants (500-1,250 g).
Disclosures: The Canadian Institutes of Health Research provided funding. The investigators reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
Source: Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-4047.
Language difficulties persist until age 13 for very preterm infants
Children born very preterm continue to display language difficulties compared with term controls at 13 years of age, with no evidence of developmental “catch up.”
Given the functional implications associated with language deficits, early language-based interventions should be considered for children born VP, investigators wrote in Pediatrics.
“Difficulties in language functioning in this cohort of children born VP remained stable from 2 to 13 years of age. Although generalized language deficits were observed, the VP group had marked difficulties on expressive components of language,” wrote Thi-Nhu-Ngoc Nguyen, BSc, of Monash University, Melbourne, and her associates.
Read the full story here.
Children born very preterm continue to display language difficulties compared with term controls at 13 years of age, with no evidence of developmental “catch up.”
Given the functional implications associated with language deficits, early language-based interventions should be considered for children born VP, investigators wrote in Pediatrics.
“Difficulties in language functioning in this cohort of children born VP remained stable from 2 to 13 years of age. Although generalized language deficits were observed, the VP group had marked difficulties on expressive components of language,” wrote Thi-Nhu-Ngoc Nguyen, BSc, of Monash University, Melbourne, and her associates.
Read the full story here.
Children born very preterm continue to display language difficulties compared with term controls at 13 years of age, with no evidence of developmental “catch up.”
Given the functional implications associated with language deficits, early language-based interventions should be considered for children born VP, investigators wrote in Pediatrics.
“Difficulties in language functioning in this cohort of children born VP remained stable from 2 to 13 years of age. Although generalized language deficits were observed, the VP group had marked difficulties on expressive components of language,” wrote Thi-Nhu-Ngoc Nguyen, BSc, of Monash University, Melbourne, and her associates.
Read the full story here.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Evaluating fever in the first 90 days of life
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
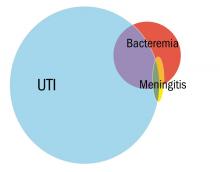
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.
Fever in the youngest of infants creates a challenge for the pediatric clinician. Fever is a common presentation for serious bacterial infection (SBI) although most fevers are due to viral infection. However, the clinical presentation does not necessarily differ, and the risk for a poor outcome in this age group is substantial.
In the early stages of my pediatric career, most febrile infants less than 90 days of age were evaluated for sepsis, admitted, and treated with antibiotics pending culture results. Group B streptococcal sepsis or Escherichia coli sepsis were common in the first month of life, and Haemophilus influenza type B or Streptococcus pneumoniae in the second and third months of life. The approach to fever in the first 90 days has changed following both the introduction of haemophilus and pneumococcal conjugate vaccines, the experience with risk stratification criteria for identifying infants at low risk for SBI, and the recognition of urinary tract infection (UTI) as a common source of infection in this age group as well as development of criteria for diagnosis.
A further nuance was subsequently added with the introduction of rapid diagnostics for viral infection. Byington et al. found that the majority of febrile infants less than 90 days of age had viral infection with enterovirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza or rotavirus.1 Using the Rochester risk stratification and the presence or absence of viral infection, she demonstrated that the risk of SBI was reduced in both high- and low-risk infants in the presence of viral infection; in low risk infants with viral infection, SBI was identified in 1.8%, compared with 3.1% in those without viral infection, and in high-risk infants. 5.5% has SBI when viral infection was found, compared to 16.7% in the absence of viral infection. She also proposed risk features to identify those infected with herpes simplex virus; age less than 42 days, vesicular rash, elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), CSF pleocytosis, and seizure or twitching.
Greenhow et al. reported on the experience with “serious” bacterial infection in infants less than 90 days of age receiving care at Northern California Kaiser Permanente during the period 2005-2011.2 As pictured, the majority of children have UTI, and smaller numbers have bacteremia or meningitis. A small group of children with UTI have urosepsis as well; those with urosepsis can be differentiated from those with only UTI by age (less than 21 days), clinical exam (ill appearing), and elevated C reactive protein (greater than 20 mg/L) or elevated procalcitonin (greater than 0.5 ng/mL).3 Further evaluation of procalcitonin by other groups appears to validate its role in identifying children at low risk of SBI (procalcitonin less than 0.3 ng/mL).4
Currently, studies of febrile infants less than 90 days of age demonstrate that E. coli dominates in bacteremia, UTI, and meningitis, with Group B streptococcus as the next most frequent pathogen identified.2 Increasingly ampicillin resistance has been reported among E. coli isolates from both early- and late-onset disease as well as rare isolates that are resistant to third generation cephalosporins or gentamicin. Surveillance to identify changes in antimicrobial susceptibility will need to be ongoing to ensure that current approaches for initial therapy in high-risk infants aligns with current susceptibility patterns.
Dr. Pelton is chief of the section of pediatric infectious diseases and coordinator of the maternal-child HIV program at Boston Medical Center. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatrics. 2004 Jun;113(6):1662-6.
2. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Jun;33(6):595-9.
3. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015 Jan;34(1):17-21.
4. JAMA Pediatr. 2016;170(1):17-18.
5. “AAP Proposes Update to Evaluating, Managing Febrile Infants Guideline,” The Hospitalist, 2016.
PPIs, H2RAs in infants raise later allergy risk
Children prescribed histamine2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs), proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or antibiotics during the first 6 months of life may be at greater risk of developing allergic disease, research suggests.
A retrospective cohort study looked at the incidence of subsequent allergic disease in 792,130 children, 7.6% of whom were prescribed an H2RA, 1.7% were prescribed a PPI, and 16.6% were prescribed an antibiotic during the first 6 months of life.
Children who were prescribed a H2RA or a PPI had a greater than twofold higher incidence of food allergy (adjusted hazard ratios 2.18 and 2.59, respectively), reported Edward Mitre, MD, of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., and his coauthors, reported in the April 2 online edition of JAMA Pediatrics.
In particular, the use of acid-suppressing medications was associated with a 2.4-fold increase in the risk of being diagnosed with cow’s milk allergy, while the risk of egg allergy was 74% higher in children prescribed an H2RA and 35% higher in children prescribed a PPI. In children prescribed an H2RA, the risk of peanut allergy was 21% higher, and in children prescribed a PPI, it was 27% higher.
There also was a dose-dependent interaction between the duration of medication and risk of food allergy. Children who were prescribed more than 60 days of PPIs had a 52% higher risk than did those who were prescribed 1-60 days, and a similar but slightly lower increased risk was seen in those prescribed more than 60 days of H2RAs (hazard ratio, 1.32).
Acid-suppressing medication use also was associated with an increased risk of nonfood allergies, in particular medication allergy (adjusted HR, 1.70 for H2RAs and 1.84 for PPIs), allergic rhinitis (aHR, 1.50 for H2RAs and 1.44 for PPIs), anaphylaxis (aHR, 1.51 for H2RAs and 1.45 for PPIs).
Infants prescribed acid-suppressing medication also showed higher rates of asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, and urticaria during childhood.
The use of antibiotics in the first 6 months of life was associated with a 14% higher incidence of food allergy but with a 24% higher risk of cow’s milk allergy and egg allergy. Children prescribed antibiotics also had a twofold greater risk of asthma, a 51% higher risk of anaphylaxis, 42% higher risk of allergic conjunctivitis, and a 34% higher risk of medication allergy.
“This study adds to the mounting evidence that agents that disrupt the normal intestinal microbiome during infancy may increase the development of allergic disease,” said Dr. Mitre and his coauthors. “Thus, this study provides further impetus that antibiotics and acid-suppressive medications should be used during infancy only in situations of clear clinical benefit.”
No funding source or conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mitre E et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.0315.
Children prescribed histamine2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs), proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or antibiotics during the first 6 months of life may be at greater risk of developing allergic disease, research suggests.
A retrospective cohort study looked at the incidence of subsequent allergic disease in 792,130 children, 7.6% of whom were prescribed an H2RA, 1.7% were prescribed a PPI, and 16.6% were prescribed an antibiotic during the first 6 months of life.
Children who were prescribed a H2RA or a PPI had a greater than twofold higher incidence of food allergy (adjusted hazard ratios 2.18 and 2.59, respectively), reported Edward Mitre, MD, of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., and his coauthors, reported in the April 2 online edition of JAMA Pediatrics.
In particular, the use of acid-suppressing medications was associated with a 2.4-fold increase in the risk of being diagnosed with cow’s milk allergy, while the risk of egg allergy was 74% higher in children prescribed an H2RA and 35% higher in children prescribed a PPI. In children prescribed an H2RA, the risk of peanut allergy was 21% higher, and in children prescribed a PPI, it was 27% higher.
There also was a dose-dependent interaction between the duration of medication and risk of food allergy. Children who were prescribed more than 60 days of PPIs had a 52% higher risk than did those who were prescribed 1-60 days, and a similar but slightly lower increased risk was seen in those prescribed more than 60 days of H2RAs (hazard ratio, 1.32).
Acid-suppressing medication use also was associated with an increased risk of nonfood allergies, in particular medication allergy (adjusted HR, 1.70 for H2RAs and 1.84 for PPIs), allergic rhinitis (aHR, 1.50 for H2RAs and 1.44 for PPIs), anaphylaxis (aHR, 1.51 for H2RAs and 1.45 for PPIs).
Infants prescribed acid-suppressing medication also showed higher rates of asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, and urticaria during childhood.
The use of antibiotics in the first 6 months of life was associated with a 14% higher incidence of food allergy but with a 24% higher risk of cow’s milk allergy and egg allergy. Children prescribed antibiotics also had a twofold greater risk of asthma, a 51% higher risk of anaphylaxis, 42% higher risk of allergic conjunctivitis, and a 34% higher risk of medication allergy.
“This study adds to the mounting evidence that agents that disrupt the normal intestinal microbiome during infancy may increase the development of allergic disease,” said Dr. Mitre and his coauthors. “Thus, this study provides further impetus that antibiotics and acid-suppressive medications should be used during infancy only in situations of clear clinical benefit.”
No funding source or conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mitre E et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.0315.
Children prescribed histamine2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs), proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or antibiotics during the first 6 months of life may be at greater risk of developing allergic disease, research suggests.
A retrospective cohort study looked at the incidence of subsequent allergic disease in 792,130 children, 7.6% of whom were prescribed an H2RA, 1.7% were prescribed a PPI, and 16.6% were prescribed an antibiotic during the first 6 months of life.
Children who were prescribed a H2RA or a PPI had a greater than twofold higher incidence of food allergy (adjusted hazard ratios 2.18 and 2.59, respectively), reported Edward Mitre, MD, of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Md., and his coauthors, reported in the April 2 online edition of JAMA Pediatrics.
In particular, the use of acid-suppressing medications was associated with a 2.4-fold increase in the risk of being diagnosed with cow’s milk allergy, while the risk of egg allergy was 74% higher in children prescribed an H2RA and 35% higher in children prescribed a PPI. In children prescribed an H2RA, the risk of peanut allergy was 21% higher, and in children prescribed a PPI, it was 27% higher.
There also was a dose-dependent interaction between the duration of medication and risk of food allergy. Children who were prescribed more than 60 days of PPIs had a 52% higher risk than did those who were prescribed 1-60 days, and a similar but slightly lower increased risk was seen in those prescribed more than 60 days of H2RAs (hazard ratio, 1.32).
Acid-suppressing medication use also was associated with an increased risk of nonfood allergies, in particular medication allergy (adjusted HR, 1.70 for H2RAs and 1.84 for PPIs), allergic rhinitis (aHR, 1.50 for H2RAs and 1.44 for PPIs), anaphylaxis (aHR, 1.51 for H2RAs and 1.45 for PPIs).
Infants prescribed acid-suppressing medication also showed higher rates of asthma, allergic conjunctivitis, and urticaria during childhood.
The use of antibiotics in the first 6 months of life was associated with a 14% higher incidence of food allergy but with a 24% higher risk of cow’s milk allergy and egg allergy. Children prescribed antibiotics also had a twofold greater risk of asthma, a 51% higher risk of anaphylaxis, 42% higher risk of allergic conjunctivitis, and a 34% higher risk of medication allergy.
“This study adds to the mounting evidence that agents that disrupt the normal intestinal microbiome during infancy may increase the development of allergic disease,” said Dr. Mitre and his coauthors. “Thus, this study provides further impetus that antibiotics and acid-suppressive medications should be used during infancy only in situations of clear clinical benefit.”
No funding source or conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Mitre E et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.0315.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Children prescribed acid-suppressing medications before 6 months had a greater than twofold higher incidence of food allergy.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study in 792,130 children between Oct. 1, 2001, and Sept. 30, 2013.
Disclosures: No funding source or conflicts of interest were declared.
Source: Mitre E et al. JAMA Pediatrics. 2018 Apr 2. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.0315.
QI initiative reduces antibiotic use in chorioamnionitis-exposed newborns
A hospital quality improvement initiative reduced antibiotic use by more than half when well-appearing newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis were initially monitored for symptoms instead of routinely given antibiotics, found a study in Pediatrics.
“The reduction in both antibiotic use and laboratory testing occurred without clinically relevant delays in care or poor outcomes,” wrote Neha S. Joshi, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and her associates.
At Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital Stanford, about half of all antibiotic use for late-preterm or term infants went to newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis. The hospital developed a quality improvement initiative to safely reduce unnecessary antibiotic use in these patients and to decrease unnecessary lab testing given the weak clinical relevance of CBC counts and C-reactive protein labs for determining whether to give a well-appearing child antibiotics, the study authors explained.
Before the initiative began, standard practice included admitting all infants to the neonatal ICU who were at least 34 weeks’ gestation and exposed to chorioamnionitis. They were treated with ampicillin and gentamicin until early-onset sepsis was excluded. Lab evaluations included a CBC count, blood culture, and multiple C-reactive protein labs.
Under the new protocol, symptomatic newborns still had the same labs and received empirical antibiotics. Well-appearing, late-preterm or term infants exposed to chorioamnionitis first spent 2 hours of skin-to-skin contact with their mothers and then were monitored clinically in a level II nursery for at least 24 hours. Unless clinical symptoms developed in that time, the infants then were returned to their mothers until discharge without labs or antibiotics. Those who did develop potentially septic signs/symptoms, as determined by the treating physician, were evaluated and then received antibiotics if deemed appropriate.
During the first 15 months of the quality improvement initiative, 310 infants (5.7% of the 5,425 total births with at least 34 weeks’ gestation) were exposed to chorioamnionitis. Of these, 23 (7.4%) were symptomatic and began antibiotics; another 10 (3.2%) were admitted to the neonatal ICU for a congenital anomaly.
The researchers collected data on antibiotic use, lab tests, cultures, and clinical outcomes from the remaining 277 well-appearing newborns; 88% did not receive antibiotics during their hospital stay, and 83% underwent no laboratory testing. Only 17% of infants had lab testing for sepsis; none had culture result–positive, early-onset sepsis.
Only 12% of infants who initially appeared well developed signs/symptoms of sepsis, underwent laboratory testing, and received antibiotics. Nearly half of these (5% of all infants) received antibiotic treatment for at least 5 days despite negative cultures, while the other 7% received antibiotics for less than 48 hours, Dr. Joshi and her colleagues reported.
Infants with at least 34 weeks’ gestation receiving antibiotics at the hospital dropped from 12.3% before the initiative to 5.5% afterward, a 55% decrease (95% confidence interval, 40%-60%), the researchers said. Study limitations included a lack of postdischarge follow-up, the variability in physician decisions about which infants were symptomatic and which ones needed antibiotics, and an inability to generalize findings to institutions without 24/7 availability of neonatal hospitalists.
Past studies have found that all newborns with positive cultures showed symptoms at birth and needed resuscitation, continuous positive airway pressure, or intubation.
“An infant who is well-appearing at birth likely has an even lower risk of early-onset sepsis even in the setting of chorioamnionitis, and an empirical antibiotic treatment strategy for chorioamnionitis-exposed infants will result in a large number of uninfected infants being treated,” Dr. Joshi and her associates said. “Updated treatment approaches are needed to reduce unnecessary antibiotic exposure and provide higher-value care in this population.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joshi NS et al. Pediatrics. 2018;141(4):e20172056.
A hospital quality improvement initiative reduced antibiotic use by more than half when well-appearing newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis were initially monitored for symptoms instead of routinely given antibiotics, found a study in Pediatrics.
“The reduction in both antibiotic use and laboratory testing occurred without clinically relevant delays in care or poor outcomes,” wrote Neha S. Joshi, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and her associates.
At Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital Stanford, about half of all antibiotic use for late-preterm or term infants went to newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis. The hospital developed a quality improvement initiative to safely reduce unnecessary antibiotic use in these patients and to decrease unnecessary lab testing given the weak clinical relevance of CBC counts and C-reactive protein labs for determining whether to give a well-appearing child antibiotics, the study authors explained.
Before the initiative began, standard practice included admitting all infants to the neonatal ICU who were at least 34 weeks’ gestation and exposed to chorioamnionitis. They were treated with ampicillin and gentamicin until early-onset sepsis was excluded. Lab evaluations included a CBC count, blood culture, and multiple C-reactive protein labs.
Under the new protocol, symptomatic newborns still had the same labs and received empirical antibiotics. Well-appearing, late-preterm or term infants exposed to chorioamnionitis first spent 2 hours of skin-to-skin contact with their mothers and then were monitored clinically in a level II nursery for at least 24 hours. Unless clinical symptoms developed in that time, the infants then were returned to their mothers until discharge without labs or antibiotics. Those who did develop potentially septic signs/symptoms, as determined by the treating physician, were evaluated and then received antibiotics if deemed appropriate.
During the first 15 months of the quality improvement initiative, 310 infants (5.7% of the 5,425 total births with at least 34 weeks’ gestation) were exposed to chorioamnionitis. Of these, 23 (7.4%) were symptomatic and began antibiotics; another 10 (3.2%) were admitted to the neonatal ICU for a congenital anomaly.
The researchers collected data on antibiotic use, lab tests, cultures, and clinical outcomes from the remaining 277 well-appearing newborns; 88% did not receive antibiotics during their hospital stay, and 83% underwent no laboratory testing. Only 17% of infants had lab testing for sepsis; none had culture result–positive, early-onset sepsis.
Only 12% of infants who initially appeared well developed signs/symptoms of sepsis, underwent laboratory testing, and received antibiotics. Nearly half of these (5% of all infants) received antibiotic treatment for at least 5 days despite negative cultures, while the other 7% received antibiotics for less than 48 hours, Dr. Joshi and her colleagues reported.
Infants with at least 34 weeks’ gestation receiving antibiotics at the hospital dropped from 12.3% before the initiative to 5.5% afterward, a 55% decrease (95% confidence interval, 40%-60%), the researchers said. Study limitations included a lack of postdischarge follow-up, the variability in physician decisions about which infants were symptomatic and which ones needed antibiotics, and an inability to generalize findings to institutions without 24/7 availability of neonatal hospitalists.
Past studies have found that all newborns with positive cultures showed symptoms at birth and needed resuscitation, continuous positive airway pressure, or intubation.
“An infant who is well-appearing at birth likely has an even lower risk of early-onset sepsis even in the setting of chorioamnionitis, and an empirical antibiotic treatment strategy for chorioamnionitis-exposed infants will result in a large number of uninfected infants being treated,” Dr. Joshi and her associates said. “Updated treatment approaches are needed to reduce unnecessary antibiotic exposure and provide higher-value care in this population.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joshi NS et al. Pediatrics. 2018;141(4):e20172056.
A hospital quality improvement initiative reduced antibiotic use by more than half when well-appearing newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis were initially monitored for symptoms instead of routinely given antibiotics, found a study in Pediatrics.
“The reduction in both antibiotic use and laboratory testing occurred without clinically relevant delays in care or poor outcomes,” wrote Neha S. Joshi, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and her associates.
At Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital Stanford, about half of all antibiotic use for late-preterm or term infants went to newborns exposed to chorioamnionitis. The hospital developed a quality improvement initiative to safely reduce unnecessary antibiotic use in these patients and to decrease unnecessary lab testing given the weak clinical relevance of CBC counts and C-reactive protein labs for determining whether to give a well-appearing child antibiotics, the study authors explained.
Before the initiative began, standard practice included admitting all infants to the neonatal ICU who were at least 34 weeks’ gestation and exposed to chorioamnionitis. They were treated with ampicillin and gentamicin until early-onset sepsis was excluded. Lab evaluations included a CBC count, blood culture, and multiple C-reactive protein labs.
Under the new protocol, symptomatic newborns still had the same labs and received empirical antibiotics. Well-appearing, late-preterm or term infants exposed to chorioamnionitis first spent 2 hours of skin-to-skin contact with their mothers and then were monitored clinically in a level II nursery for at least 24 hours. Unless clinical symptoms developed in that time, the infants then were returned to their mothers until discharge without labs or antibiotics. Those who did develop potentially septic signs/symptoms, as determined by the treating physician, were evaluated and then received antibiotics if deemed appropriate.
During the first 15 months of the quality improvement initiative, 310 infants (5.7% of the 5,425 total births with at least 34 weeks’ gestation) were exposed to chorioamnionitis. Of these, 23 (7.4%) were symptomatic and began antibiotics; another 10 (3.2%) were admitted to the neonatal ICU for a congenital anomaly.
The researchers collected data on antibiotic use, lab tests, cultures, and clinical outcomes from the remaining 277 well-appearing newborns; 88% did not receive antibiotics during their hospital stay, and 83% underwent no laboratory testing. Only 17% of infants had lab testing for sepsis; none had culture result–positive, early-onset sepsis.
Only 12% of infants who initially appeared well developed signs/symptoms of sepsis, underwent laboratory testing, and received antibiotics. Nearly half of these (5% of all infants) received antibiotic treatment for at least 5 days despite negative cultures, while the other 7% received antibiotics for less than 48 hours, Dr. Joshi and her colleagues reported.
Infants with at least 34 weeks’ gestation receiving antibiotics at the hospital dropped from 12.3% before the initiative to 5.5% afterward, a 55% decrease (95% confidence interval, 40%-60%), the researchers said. Study limitations included a lack of postdischarge follow-up, the variability in physician decisions about which infants were symptomatic and which ones needed antibiotics, and an inability to generalize findings to institutions without 24/7 availability of neonatal hospitalists.
Past studies have found that all newborns with positive cultures showed symptoms at birth and needed resuscitation, continuous positive airway pressure, or intubation.
“An infant who is well-appearing at birth likely has an even lower risk of early-onset sepsis even in the setting of chorioamnionitis, and an empirical antibiotic treatment strategy for chorioamnionitis-exposed infants will result in a large number of uninfected infants being treated,” Dr. Joshi and her associates said. “Updated treatment approaches are needed to reduce unnecessary antibiotic exposure and provide higher-value care in this population.”
The study did not use external funding. The authors had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Joshi NS et al. Pediatrics. 2018;141(4):e20172056.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After a quality improvement initiative was implemented, 55% fewer late-preterm and term, chorioamnionitis-exposed infants received antibiotics without an increase in negative outcomes.
Data source: A study of 310 chorioamnionitis-exposed newborns who were late preterm or term at a California hospital.
Disclosures: The study did not use external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Joshi NS et al. Pediatrics. 2018;141(4):e20172056.
Time to HIV rebound in infants off ART linked to birth health
BOSTON – For infants with HIV infection, baseline immune function and birth health appear to influence viral control after the discontinuation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), an analysis of data from the landmark CHER trial shows.
Among 183 children diagnosed with HIV between 6 and 12 weeks of age who were started on early, time-limited ART, longer time to viral rebound after treatment discontinuation was associated with higher baseline CD4 percentages, higher birth weight, and with achievement of viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART, reported Man Chan, PhD, of the Medical Research Council clinical trials unit at University College London.
The CHER trial compared South African infants with HIV on either 40 or 96 weeks of immediate ART with those on deferred ART. The results showed that early time-limited ART was associated with better clinical and immunologic outcomes than was deferred ART and influenced a change in treatment guidelines (Lancet 2013 Nov 9;382[9904]:1555-63).
In the current analysis, investigators examined viral control after treatment interruption in early-treated children and looked for factors that could influence time to viral rebound after ART cessation.
They measured viral load from stored samples at 1.8 weeks after ART interruption and then every 12 weeks thereafter. They defined viral rebound as two consecutive samples with 400 or more copies/mL.
Of the 183 children in the sample, 177 had a rebound; the remaining six children were censored from the analysis, five because they had restarted ART, and one child who remained in viral suppression with an undetectable viral load and was asymptomatic for 8.5 years off ART.
The estimated cumulative probability of rebound was 70% at 2 months following ART interruption, 80% at 4 months, 94% at 6 months, and 99% at 8 months.
In multivariable analysis, factors significantly associated with longer time to viral rebound included higher baseline CD4 counts (P = .03), higher birth weight (P = .032), and viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART (P = .028)
In contrast, there were no significant associations with other factors in the multivariate model, including sex, baseline viral load, baseline CD8 percentage, HIV stage, status of therapy to prevent mother-to-child transmission, age at ART initiation, length of therapy, or treatment center.
Sensitivity analyses of a few cases in which there was a 4-7 month gap between rebound and the last viral load below 400 copies/mL before rebound showed similar results, Dr. Chan noted.
The study was the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chan reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Violari A et al. CROI 2018, Abstract 137
BOSTON – For infants with HIV infection, baseline immune function and birth health appear to influence viral control after the discontinuation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), an analysis of data from the landmark CHER trial shows.
Among 183 children diagnosed with HIV between 6 and 12 weeks of age who were started on early, time-limited ART, longer time to viral rebound after treatment discontinuation was associated with higher baseline CD4 percentages, higher birth weight, and with achievement of viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART, reported Man Chan, PhD, of the Medical Research Council clinical trials unit at University College London.
The CHER trial compared South African infants with HIV on either 40 or 96 weeks of immediate ART with those on deferred ART. The results showed that early time-limited ART was associated with better clinical and immunologic outcomes than was deferred ART and influenced a change in treatment guidelines (Lancet 2013 Nov 9;382[9904]:1555-63).
In the current analysis, investigators examined viral control after treatment interruption in early-treated children and looked for factors that could influence time to viral rebound after ART cessation.
They measured viral load from stored samples at 1.8 weeks after ART interruption and then every 12 weeks thereafter. They defined viral rebound as two consecutive samples with 400 or more copies/mL.
Of the 183 children in the sample, 177 had a rebound; the remaining six children were censored from the analysis, five because they had restarted ART, and one child who remained in viral suppression with an undetectable viral load and was asymptomatic for 8.5 years off ART.
The estimated cumulative probability of rebound was 70% at 2 months following ART interruption, 80% at 4 months, 94% at 6 months, and 99% at 8 months.
In multivariable analysis, factors significantly associated with longer time to viral rebound included higher baseline CD4 counts (P = .03), higher birth weight (P = .032), and viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART (P = .028)
In contrast, there were no significant associations with other factors in the multivariate model, including sex, baseline viral load, baseline CD8 percentage, HIV stage, status of therapy to prevent mother-to-child transmission, age at ART initiation, length of therapy, or treatment center.
Sensitivity analyses of a few cases in which there was a 4-7 month gap between rebound and the last viral load below 400 copies/mL before rebound showed similar results, Dr. Chan noted.
The study was the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chan reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Violari A et al. CROI 2018, Abstract 137
BOSTON – For infants with HIV infection, baseline immune function and birth health appear to influence viral control after the discontinuation of antiretroviral therapy (ART), an analysis of data from the landmark CHER trial shows.
Among 183 children diagnosed with HIV between 6 and 12 weeks of age who were started on early, time-limited ART, longer time to viral rebound after treatment discontinuation was associated with higher baseline CD4 percentages, higher birth weight, and with achievement of viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART, reported Man Chan, PhD, of the Medical Research Council clinical trials unit at University College London.
The CHER trial compared South African infants with HIV on either 40 or 96 weeks of immediate ART with those on deferred ART. The results showed that early time-limited ART was associated with better clinical and immunologic outcomes than was deferred ART and influenced a change in treatment guidelines (Lancet 2013 Nov 9;382[9904]:1555-63).
In the current analysis, investigators examined viral control after treatment interruption in early-treated children and looked for factors that could influence time to viral rebound after ART cessation.
They measured viral load from stored samples at 1.8 weeks after ART interruption and then every 12 weeks thereafter. They defined viral rebound as two consecutive samples with 400 or more copies/mL.
Of the 183 children in the sample, 177 had a rebound; the remaining six children were censored from the analysis, five because they had restarted ART, and one child who remained in viral suppression with an undetectable viral load and was asymptomatic for 8.5 years off ART.
The estimated cumulative probability of rebound was 70% at 2 months following ART interruption, 80% at 4 months, 94% at 6 months, and 99% at 8 months.
In multivariable analysis, factors significantly associated with longer time to viral rebound included higher baseline CD4 counts (P = .03), higher birth weight (P = .032), and viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting on ART (P = .028)
In contrast, there were no significant associations with other factors in the multivariate model, including sex, baseline viral load, baseline CD8 percentage, HIV stage, status of therapy to prevent mother-to-child transmission, age at ART initiation, length of therapy, or treatment center.
Sensitivity analyses of a few cases in which there was a 4-7 month gap between rebound and the last viral load below 400 copies/mL before rebound showed similar results, Dr. Chan noted.
The study was the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chan reported having nothing to disclose.
SOURCE: Violari A et al. CROI 2018, Abstract 137
FROM CROI 2018
Key clinical point: Early initiation of antiretroviral therapy in infants is associated with better outcomes.
Major finding: Longer time to viral rebound was associated with higher baseline CD4, higher birth weight, and viral suppression within 40 weeks of starting ART.
Study details: Analysis of outcomes in 183 infants with HIV infection in the CHER trial.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Chan reported having nothing to disclose.
Source: Violari A et al. CROI 2018, Abstract 137.