User login
Genetic tests prompt therapy adjustments in children with epilepsy
Physicians at a Boston hospital adjusted medical management for nearly three-quarters of patients with infantile- or childhood-onset epilepsy who were diagnosed with genetic epilepsy, researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. The findings provide new insight into the usefulness of genetic tests in children with epilepsy of unknown cause.
“. Genetic testing should be included as part of the standard evaluation of individuals with unexplained pediatric epilepsy as a means of achieving diagnostic precision and informing clinical management,” study lead author Isabel Haviland, MD, a neurologist with Boston Children’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Haviland, the causes of epilepsy are unexplained in an estimated two-thirds of pediatric epilepsy cases. “Increasingly, when genetic testing is available, previously unexplained cases of pediatric epilepsy are being found to have single-gene etiologies,” she said. “Though a genetic diagnosis in this population has implications for medical care, the direct impact on medical management in a clinical setting has not been measured. We aimed to describe the impact of genetic diagnosis on medical management in a cohort of individuals with pediatric epilepsy.”
Researchers tracked 602 patients at Boston Children’s Hospital who received next-generation gene sequencing testing from 2012 to 2019. Of those, Dr. Haviland said, 152 (25%) had a positive result that indicated genetic epilepsy (46% female, median age of onset = 6 months [2-15 months]). These patients were included in the study.
“We documented an impact on medical management in nearly three-fourths of participants (72%),” Dr. Haviland said. “A genetic diagnosis affected at least one of four categories of medical management, including care coordination (48%), treatment (45%), counseling about a change in prognosis (28%), and change in diagnosis for a few individuals who had a prior established diagnosis (1%).”
As examples, she mentioned three cases:
- Testing revealed that a subject has a disease-causing genetic variant in a gene called PRRT2. “This gene is involved in the release of neurotransmitters in the brain,” Dr. Haviland said. “Thanks to his diagnosis, he was treated with the antiseizure medication oxcarbazepine, which is often effective for epilepsy caused by variants in this gene. He had excellent response to the medication and later became seizure free.”
- A subject had a variation in the SCN1A gene that causes types of epilepsy. “At the time of his diagnosis, there was a trial for a medication called fenfluramine being offered for individuals with SCN1A variants, and his family elected to participate,” she said. “This medication was later approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for SCN1A-related epilepsy.”
- Testing identified disease-causing variant in the GRIN2A gene in another subject. “This gene is involved in brain cell communication,” Dr. Haviland said. “This individual was treated with memantine, which acts on the specific biological pathway affected by the gene. This treatment would not have been considered without the genetic diagnosis as it is currently only approved for Alzheimer’s disease.”
In addition, Dr. Haviland said, researchers found that “there was impact on medical management both in those with earlier age of epilepsy onset (under 2 years) and those with later age of onset, as well as both in those with developmental disorders (such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability and developmental delay) and those with normal development.
As for the cost of genetic tests, Dr. Haviland pointed to a 2019 study that she said estimated epilepsy panel testing runs from $1,500 to $7,500, and the whole exome sequencing from $4,500 to $7,000. “Insurers sometimes cover testing, but not always,” she said. “In some cases, insurance will only cover testing if it is documented that results will directly alter medical management, which highlights the importance of our findings.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Haviland and several other authors report no disclosures. One author reports consulting fees from Takeda, Zogenix, Marinus, and FOXG1 Research Foundation. Another author reports research support from the International Foundation for CDKL5 Research.
Physicians at a Boston hospital adjusted medical management for nearly three-quarters of patients with infantile- or childhood-onset epilepsy who were diagnosed with genetic epilepsy, researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. The findings provide new insight into the usefulness of genetic tests in children with epilepsy of unknown cause.
“. Genetic testing should be included as part of the standard evaluation of individuals with unexplained pediatric epilepsy as a means of achieving diagnostic precision and informing clinical management,” study lead author Isabel Haviland, MD, a neurologist with Boston Children’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Haviland, the causes of epilepsy are unexplained in an estimated two-thirds of pediatric epilepsy cases. “Increasingly, when genetic testing is available, previously unexplained cases of pediatric epilepsy are being found to have single-gene etiologies,” she said. “Though a genetic diagnosis in this population has implications for medical care, the direct impact on medical management in a clinical setting has not been measured. We aimed to describe the impact of genetic diagnosis on medical management in a cohort of individuals with pediatric epilepsy.”
Researchers tracked 602 patients at Boston Children’s Hospital who received next-generation gene sequencing testing from 2012 to 2019. Of those, Dr. Haviland said, 152 (25%) had a positive result that indicated genetic epilepsy (46% female, median age of onset = 6 months [2-15 months]). These patients were included in the study.
“We documented an impact on medical management in nearly three-fourths of participants (72%),” Dr. Haviland said. “A genetic diagnosis affected at least one of four categories of medical management, including care coordination (48%), treatment (45%), counseling about a change in prognosis (28%), and change in diagnosis for a few individuals who had a prior established diagnosis (1%).”
As examples, she mentioned three cases:
- Testing revealed that a subject has a disease-causing genetic variant in a gene called PRRT2. “This gene is involved in the release of neurotransmitters in the brain,” Dr. Haviland said. “Thanks to his diagnosis, he was treated with the antiseizure medication oxcarbazepine, which is often effective for epilepsy caused by variants in this gene. He had excellent response to the medication and later became seizure free.”
- A subject had a variation in the SCN1A gene that causes types of epilepsy. “At the time of his diagnosis, there was a trial for a medication called fenfluramine being offered for individuals with SCN1A variants, and his family elected to participate,” she said. “This medication was later approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for SCN1A-related epilepsy.”
- Testing identified disease-causing variant in the GRIN2A gene in another subject. “This gene is involved in brain cell communication,” Dr. Haviland said. “This individual was treated with memantine, which acts on the specific biological pathway affected by the gene. This treatment would not have been considered without the genetic diagnosis as it is currently only approved for Alzheimer’s disease.”
In addition, Dr. Haviland said, researchers found that “there was impact on medical management both in those with earlier age of epilepsy onset (under 2 years) and those with later age of onset, as well as both in those with developmental disorders (such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability and developmental delay) and those with normal development.
As for the cost of genetic tests, Dr. Haviland pointed to a 2019 study that she said estimated epilepsy panel testing runs from $1,500 to $7,500, and the whole exome sequencing from $4,500 to $7,000. “Insurers sometimes cover testing, but not always,” she said. “In some cases, insurance will only cover testing if it is documented that results will directly alter medical management, which highlights the importance of our findings.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Haviland and several other authors report no disclosures. One author reports consulting fees from Takeda, Zogenix, Marinus, and FOXG1 Research Foundation. Another author reports research support from the International Foundation for CDKL5 Research.
Physicians at a Boston hospital adjusted medical management for nearly three-quarters of patients with infantile- or childhood-onset epilepsy who were diagnosed with genetic epilepsy, researchers reported at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. The findings provide new insight into the usefulness of genetic tests in children with epilepsy of unknown cause.
“. Genetic testing should be included as part of the standard evaluation of individuals with unexplained pediatric epilepsy as a means of achieving diagnostic precision and informing clinical management,” study lead author Isabel Haviland, MD, a neurologist with Boston Children’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School, said in an interview.
According to Dr. Haviland, the causes of epilepsy are unexplained in an estimated two-thirds of pediatric epilepsy cases. “Increasingly, when genetic testing is available, previously unexplained cases of pediatric epilepsy are being found to have single-gene etiologies,” she said. “Though a genetic diagnosis in this population has implications for medical care, the direct impact on medical management in a clinical setting has not been measured. We aimed to describe the impact of genetic diagnosis on medical management in a cohort of individuals with pediatric epilepsy.”
Researchers tracked 602 patients at Boston Children’s Hospital who received next-generation gene sequencing testing from 2012 to 2019. Of those, Dr. Haviland said, 152 (25%) had a positive result that indicated genetic epilepsy (46% female, median age of onset = 6 months [2-15 months]). These patients were included in the study.
“We documented an impact on medical management in nearly three-fourths of participants (72%),” Dr. Haviland said. “A genetic diagnosis affected at least one of four categories of medical management, including care coordination (48%), treatment (45%), counseling about a change in prognosis (28%), and change in diagnosis for a few individuals who had a prior established diagnosis (1%).”
As examples, she mentioned three cases:
- Testing revealed that a subject has a disease-causing genetic variant in a gene called PRRT2. “This gene is involved in the release of neurotransmitters in the brain,” Dr. Haviland said. “Thanks to his diagnosis, he was treated with the antiseizure medication oxcarbazepine, which is often effective for epilepsy caused by variants in this gene. He had excellent response to the medication and later became seizure free.”
- A subject had a variation in the SCN1A gene that causes types of epilepsy. “At the time of his diagnosis, there was a trial for a medication called fenfluramine being offered for individuals with SCN1A variants, and his family elected to participate,” she said. “This medication was later approved by the [Food and Drug Administration] for SCN1A-related epilepsy.”
- Testing identified disease-causing variant in the GRIN2A gene in another subject. “This gene is involved in brain cell communication,” Dr. Haviland said. “This individual was treated with memantine, which acts on the specific biological pathway affected by the gene. This treatment would not have been considered without the genetic diagnosis as it is currently only approved for Alzheimer’s disease.”
In addition, Dr. Haviland said, researchers found that “there was impact on medical management both in those with earlier age of epilepsy onset (under 2 years) and those with later age of onset, as well as both in those with developmental disorders (such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability and developmental delay) and those with normal development.
As for the cost of genetic tests, Dr. Haviland pointed to a 2019 study that she said estimated epilepsy panel testing runs from $1,500 to $7,500, and the whole exome sequencing from $4,500 to $7,000. “Insurers sometimes cover testing, but not always,” she said. “In some cases, insurance will only cover testing if it is documented that results will directly alter medical management, which highlights the importance of our findings.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Haviland and several other authors report no disclosures. One author reports consulting fees from Takeda, Zogenix, Marinus, and FOXG1 Research Foundation. Another author reports research support from the International Foundation for CDKL5 Research.
FROM AES 2021
Ginger for migraine: A new review
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Diabetes tied to Parkinson’s risk, more rapid disease progression
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD) development, as well as more severe symptoms and more rapid disease progression, new research suggests.
In a systematic review, patients with type 2 diabetes were 34% more likely to develop PD than those without comorbid DM. In addition, patients with both conditions had significantly worse scores on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and worse cognitive performance.
Together, the results suggest that “DM may be a facilitating factor of neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators, led by Gennaro Pagano, MD, PhD, expert medical director at Roche Pharma Research and Early Development, in Basel, Switzerland.
The findings were published in a recent issue of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Unanswered questions
Researchers have long proposed a potential relationship between diabetes and PD. However, case-control studies have yielded conflicting results about this relationship – and previous systematic reviews have failed to clarify the question.
In the current systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators identified relevant studies in databases such as MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Scopus.
Eligible studies reported prevalence of DM in patients with PD, reported incidence of PD in those with and those without DM, and analyzed Parkinson’s phenotype and progression in those with and those without DM.
The researchers identified 3,829 articles in their initial search, evaluated 90 articles in detail, and included 43 studies in their analysis. Study quality was judged to be moderate or good, and the investigators did not find significant publication bias.
Twenty-one studies that encompassed 11,396 patients were examined to determine prevalence of DM in PD. This prevalence was calculated to be 10.02%, which is similar to the global prevalence of 9.3% reported in 2019.
The researchers also analyzed 12 cohort studies that included 17,797,221 patients to calculate risk for PD in patients with comorbid diabetes. The pooled summary odds ratio for incident PD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 1.34.
The evaluation of the effect of diabetes on PD severity was based on 10 studies that included 603 patients with both diseases. Because data on motor symptoms were not available for all studies, the researchers considered Hoehn and Yahr stage, UPDRS score, and cognitive impairment.
Patients with both conditions had a worse Hoehn and Yahr stage (standardized mean difference, 0.36; P < .001), and higher UPDRS score (SMD, 0.60; P < .001). In 7 of the 10 studies, diabetes was associated with worse cognitive performance in patients with PD.
Mechanisms uncertain
The mechanisms of the effect of diabetes on risk for and severity of PD are uncertain, but the researchers have developed hypotheses.
“Overlapping mechanisms between insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and alpha-synuclein expression could influence the development of the neurodegeneration process,” they wrote.
Because the current analysis demonstrated a trend toward more pronounced cognitive decline in patients with the comorbidities, clinicians should pay particular attention to the progression of motor and cognitive symptoms in patients with these diseases, the investigators noted.
“Additional studies are needed in order to better define the clinical phenotype of PD-DM patients and explore the role of antidiabetic drugs on PD progression,” they wrote.
They add that future studies also are needed to evaluate whether antidiabetic drugs might reduce risk for PD in these patients.
The investigators noted several limitations of their research. In many of the studies they examined, for example, diagnostic criteria of type 2 diabetes and PD were based only on medical records or self-reported health questionnaires. The diagnoses were rarely confirmed.
In addition, not all studies clearly stated that their populations presented with type 2 diabetes. Finally, patients with diabetes may be at increased risk for cardiovascular death, which could affect follow-up related to the development of PD, the investigators noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD) development, as well as more severe symptoms and more rapid disease progression, new research suggests.
In a systematic review, patients with type 2 diabetes were 34% more likely to develop PD than those without comorbid DM. In addition, patients with both conditions had significantly worse scores on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and worse cognitive performance.
Together, the results suggest that “DM may be a facilitating factor of neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators, led by Gennaro Pagano, MD, PhD, expert medical director at Roche Pharma Research and Early Development, in Basel, Switzerland.
The findings were published in a recent issue of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Unanswered questions
Researchers have long proposed a potential relationship between diabetes and PD. However, case-control studies have yielded conflicting results about this relationship – and previous systematic reviews have failed to clarify the question.
In the current systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators identified relevant studies in databases such as MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Scopus.
Eligible studies reported prevalence of DM in patients with PD, reported incidence of PD in those with and those without DM, and analyzed Parkinson’s phenotype and progression in those with and those without DM.
The researchers identified 3,829 articles in their initial search, evaluated 90 articles in detail, and included 43 studies in their analysis. Study quality was judged to be moderate or good, and the investigators did not find significant publication bias.
Twenty-one studies that encompassed 11,396 patients were examined to determine prevalence of DM in PD. This prevalence was calculated to be 10.02%, which is similar to the global prevalence of 9.3% reported in 2019.
The researchers also analyzed 12 cohort studies that included 17,797,221 patients to calculate risk for PD in patients with comorbid diabetes. The pooled summary odds ratio for incident PD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 1.34.
The evaluation of the effect of diabetes on PD severity was based on 10 studies that included 603 patients with both diseases. Because data on motor symptoms were not available for all studies, the researchers considered Hoehn and Yahr stage, UPDRS score, and cognitive impairment.
Patients with both conditions had a worse Hoehn and Yahr stage (standardized mean difference, 0.36; P < .001), and higher UPDRS score (SMD, 0.60; P < .001). In 7 of the 10 studies, diabetes was associated with worse cognitive performance in patients with PD.
Mechanisms uncertain
The mechanisms of the effect of diabetes on risk for and severity of PD are uncertain, but the researchers have developed hypotheses.
“Overlapping mechanisms between insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and alpha-synuclein expression could influence the development of the neurodegeneration process,” they wrote.
Because the current analysis demonstrated a trend toward more pronounced cognitive decline in patients with the comorbidities, clinicians should pay particular attention to the progression of motor and cognitive symptoms in patients with these diseases, the investigators noted.
“Additional studies are needed in order to better define the clinical phenotype of PD-DM patients and explore the role of antidiabetic drugs on PD progression,” they wrote.
They add that future studies also are needed to evaluate whether antidiabetic drugs might reduce risk for PD in these patients.
The investigators noted several limitations of their research. In many of the studies they examined, for example, diagnostic criteria of type 2 diabetes and PD were based only on medical records or self-reported health questionnaires. The diagnoses were rarely confirmed.
In addition, not all studies clearly stated that their populations presented with type 2 diabetes. Finally, patients with diabetes may be at increased risk for cardiovascular death, which could affect follow-up related to the development of PD, the investigators noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD) development, as well as more severe symptoms and more rapid disease progression, new research suggests.
In a systematic review, patients with type 2 diabetes were 34% more likely to develop PD than those without comorbid DM. In addition, patients with both conditions had significantly worse scores on the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and worse cognitive performance.
Together, the results suggest that “DM may be a facilitating factor of neurodegeneration,” wrote the investigators, led by Gennaro Pagano, MD, PhD, expert medical director at Roche Pharma Research and Early Development, in Basel, Switzerland.
The findings were published in a recent issue of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Unanswered questions
Researchers have long proposed a potential relationship between diabetes and PD. However, case-control studies have yielded conflicting results about this relationship – and previous systematic reviews have failed to clarify the question.
In the current systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators identified relevant studies in databases such as MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Scopus.
Eligible studies reported prevalence of DM in patients with PD, reported incidence of PD in those with and those without DM, and analyzed Parkinson’s phenotype and progression in those with and those without DM.
The researchers identified 3,829 articles in their initial search, evaluated 90 articles in detail, and included 43 studies in their analysis. Study quality was judged to be moderate or good, and the investigators did not find significant publication bias.
Twenty-one studies that encompassed 11,396 patients were examined to determine prevalence of DM in PD. This prevalence was calculated to be 10.02%, which is similar to the global prevalence of 9.3% reported in 2019.
The researchers also analyzed 12 cohort studies that included 17,797,221 patients to calculate risk for PD in patients with comorbid diabetes. The pooled summary odds ratio for incident PD among patients with type 2 diabetes was 1.34.
The evaluation of the effect of diabetes on PD severity was based on 10 studies that included 603 patients with both diseases. Because data on motor symptoms were not available for all studies, the researchers considered Hoehn and Yahr stage, UPDRS score, and cognitive impairment.
Patients with both conditions had a worse Hoehn and Yahr stage (standardized mean difference, 0.36; P < .001), and higher UPDRS score (SMD, 0.60; P < .001). In 7 of the 10 studies, diabetes was associated with worse cognitive performance in patients with PD.
Mechanisms uncertain
The mechanisms of the effect of diabetes on risk for and severity of PD are uncertain, but the researchers have developed hypotheses.
“Overlapping mechanisms between insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and alpha-synuclein expression could influence the development of the neurodegeneration process,” they wrote.
Because the current analysis demonstrated a trend toward more pronounced cognitive decline in patients with the comorbidities, clinicians should pay particular attention to the progression of motor and cognitive symptoms in patients with these diseases, the investigators noted.
“Additional studies are needed in order to better define the clinical phenotype of PD-DM patients and explore the role of antidiabetic drugs on PD progression,” they wrote.
They add that future studies also are needed to evaluate whether antidiabetic drugs might reduce risk for PD in these patients.
The investigators noted several limitations of their research. In many of the studies they examined, for example, diagnostic criteria of type 2 diabetes and PD were based only on medical records or self-reported health questionnaires. The diagnoses were rarely confirmed.
In addition, not all studies clearly stated that their populations presented with type 2 diabetes. Finally, patients with diabetes may be at increased risk for cardiovascular death, which could affect follow-up related to the development of PD, the investigators noted.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PARKINSON’S DISEASE
Are newer migraine therapies better? It depends
The findings, published in JAMA Network Open, “may imply that triptans will remain the current mainstay of specific acute migraine treatment,” suggested senior author Shuu-Jiun Wang, MD, from the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and the Taipei Veterans General Hospital, both in Taipei, Taiwan, and his coauthors. However, lasmiditan (a 5-hydroxytryptamine1F receptor agonist) and rimegepant and ubrogepant (both calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP] antagonists) might still have unique advantages, since triptans are contraindicated for patients with cardiovascular risks, they said.
The systemic review and meta-analysis showed that, for the outcome of pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours after the dose, the three newer agents worked better than placebo, but were inferior to most triptans. However, ubrogepant and rimegepant, which received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of acute migraine in adults in December 2019 and February 2020, respectively, might be associated with fewer risks of adverse events (AEs), compared with triptans. “These new effective therapeutic options enrich the therapeutic categories of specific acute migraine treatments and may provide an opportunity to decrease the risks of barbiturate or opioid overuse or addiction,” they wrote.
The meta-analysis included 64 randomized, controlled trials involving 46,442 participants (74%-87% female across studies; age range, 36-43 years). All studies examined clinically relevant outcomes in patients with International Headache Society criteria for migraine, and compared currently available migraine-specific acute treatments with each other or placebo. The drugs were examined at doses with widespread clinical use and included: ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant.
The findings showed that all drug treatments were associated with a higher odds ratio for pain freedom, compared with placebo, except for sumatriptan, 10-mg nasal spray. The most effective drug was eletriptan 40 mg (OR, 5.59), and the least effective was lasmiditan 50 mg (OR, 1.65). Most triptans were associated with higher ORs for both pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours, compared with lasmiditan, rimegepant, or ubrogepant, while comparisons between lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant for these outcomes showed no statistically significant difference, they reported.
Lasmiditan was associated with the highest risk of any AEs, “however, the AEs were tolerable and were not considered serious. … Therefore, we suggest that the benefits should be weighed against the risk of its AEs when considering the clinical application of lasmiditan,” they wrote. Certain triptans (rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan) were also associated with a higher risk of any AEs, compared with the CGRP antagonists. “Nevertheless, most of the AEs were mild to moderate, and the percentages of serious AEs were low (0.0%-2.1%).”
Finally, the authors noted that their observations of successful treatment with 5-hydroxytriptamine1F receptor agonists and CGRP antagonists “reveals that vasoconstriction is not essential for antimigraine therapy.” which could have implications for future pharmaceutical development.
Older and newer medications each have advantages
“Triptans will be around for a long time, but the newer medications are here to stay,” said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, in reaction to the study. “Before this publication, we knew that the 2-hour efficacy results of the newer medications were not quite as good as the faster-acting triptans; and after this network meta-analysis we are more sure of that,” said Dr. Rapoport, of the department of neurology at University of California, Los Angeles. “But the fact that the three newer medications do not constrict blood vessels and can easily be given even to patients with contraindications to triptans, or patients that simply are at greater risk due to obesity, smoking history, family history, diabetes, lack of exercise, or higher lipid levels, puts them into a desirable category.”
Calling it a “very carefully done” systematic review, Dr. Rapoport had a few caveats about the strength of the research. The trials that were included were not identically designed and were performed in different areas, by different investigators, on different patients, he noted. They were also not head-to-head trials “which ensures that the resultant data are more pure.” The studies also looked only at rapid results at 2 hours after dosing. “In my experience, patients are often satisfied with the response times from these newer agents; and doctors and patients both are happy that they are not vasoconstrictive,” he said. “The researchers also omitted studies looking at zolmitriptan nasal spray, which I have found to be rapid in onset and efficacious with few adverse events.”
Finally, Dr. Rapoport noted that one condition not examined in the review was medication overuse headache (MOH), which is “a major problem with patients that have high-frequency episodic migraine and chronic migraine. To our knowledge thus far, the two gepants (ubrogepant and rimegepant) do not appear to cause MOH when taken frequently, and these agents may end up being a treatment for this condition.”
Dr Wang reported receiving personal fees from Eli Lilly, Daiichi-Sankyo, Norvatis Taiwan, Biogen, Pfizer, and Bayer; and grants from AbbVie, Norvatis, Eli Lilly, Taiwan Ministry of Technology and Science, Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and Taipei Veterans General Hospital outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rapoport serves as an advisor for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano; he is on the Speakers Bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. He is Editor-in-Chief of Neurology Reviews.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Ministry of Education, Taiwan, and the Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University.
The findings, published in JAMA Network Open, “may imply that triptans will remain the current mainstay of specific acute migraine treatment,” suggested senior author Shuu-Jiun Wang, MD, from the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and the Taipei Veterans General Hospital, both in Taipei, Taiwan, and his coauthors. However, lasmiditan (a 5-hydroxytryptamine1F receptor agonist) and rimegepant and ubrogepant (both calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP] antagonists) might still have unique advantages, since triptans are contraindicated for patients with cardiovascular risks, they said.
The systemic review and meta-analysis showed that, for the outcome of pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours after the dose, the three newer agents worked better than placebo, but were inferior to most triptans. However, ubrogepant and rimegepant, which received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of acute migraine in adults in December 2019 and February 2020, respectively, might be associated with fewer risks of adverse events (AEs), compared with triptans. “These new effective therapeutic options enrich the therapeutic categories of specific acute migraine treatments and may provide an opportunity to decrease the risks of barbiturate or opioid overuse or addiction,” they wrote.
The meta-analysis included 64 randomized, controlled trials involving 46,442 participants (74%-87% female across studies; age range, 36-43 years). All studies examined clinically relevant outcomes in patients with International Headache Society criteria for migraine, and compared currently available migraine-specific acute treatments with each other or placebo. The drugs were examined at doses with widespread clinical use and included: ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant.
The findings showed that all drug treatments were associated with a higher odds ratio for pain freedom, compared with placebo, except for sumatriptan, 10-mg nasal spray. The most effective drug was eletriptan 40 mg (OR, 5.59), and the least effective was lasmiditan 50 mg (OR, 1.65). Most triptans were associated with higher ORs for both pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours, compared with lasmiditan, rimegepant, or ubrogepant, while comparisons between lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant for these outcomes showed no statistically significant difference, they reported.
Lasmiditan was associated with the highest risk of any AEs, “however, the AEs were tolerable and were not considered serious. … Therefore, we suggest that the benefits should be weighed against the risk of its AEs when considering the clinical application of lasmiditan,” they wrote. Certain triptans (rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan) were also associated with a higher risk of any AEs, compared with the CGRP antagonists. “Nevertheless, most of the AEs were mild to moderate, and the percentages of serious AEs were low (0.0%-2.1%).”
Finally, the authors noted that their observations of successful treatment with 5-hydroxytriptamine1F receptor agonists and CGRP antagonists “reveals that vasoconstriction is not essential for antimigraine therapy.” which could have implications for future pharmaceutical development.
Older and newer medications each have advantages
“Triptans will be around for a long time, but the newer medications are here to stay,” said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, in reaction to the study. “Before this publication, we knew that the 2-hour efficacy results of the newer medications were not quite as good as the faster-acting triptans; and after this network meta-analysis we are more sure of that,” said Dr. Rapoport, of the department of neurology at University of California, Los Angeles. “But the fact that the three newer medications do not constrict blood vessels and can easily be given even to patients with contraindications to triptans, or patients that simply are at greater risk due to obesity, smoking history, family history, diabetes, lack of exercise, or higher lipid levels, puts them into a desirable category.”
Calling it a “very carefully done” systematic review, Dr. Rapoport had a few caveats about the strength of the research. The trials that were included were not identically designed and were performed in different areas, by different investigators, on different patients, he noted. They were also not head-to-head trials “which ensures that the resultant data are more pure.” The studies also looked only at rapid results at 2 hours after dosing. “In my experience, patients are often satisfied with the response times from these newer agents; and doctors and patients both are happy that they are not vasoconstrictive,” he said. “The researchers also omitted studies looking at zolmitriptan nasal spray, which I have found to be rapid in onset and efficacious with few adverse events.”
Finally, Dr. Rapoport noted that one condition not examined in the review was medication overuse headache (MOH), which is “a major problem with patients that have high-frequency episodic migraine and chronic migraine. To our knowledge thus far, the two gepants (ubrogepant and rimegepant) do not appear to cause MOH when taken frequently, and these agents may end up being a treatment for this condition.”
Dr Wang reported receiving personal fees from Eli Lilly, Daiichi-Sankyo, Norvatis Taiwan, Biogen, Pfizer, and Bayer; and grants from AbbVie, Norvatis, Eli Lilly, Taiwan Ministry of Technology and Science, Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and Taipei Veterans General Hospital outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rapoport serves as an advisor for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano; he is on the Speakers Bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. He is Editor-in-Chief of Neurology Reviews.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Ministry of Education, Taiwan, and the Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University.
The findings, published in JAMA Network Open, “may imply that triptans will remain the current mainstay of specific acute migraine treatment,” suggested senior author Shuu-Jiun Wang, MD, from the National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and the Taipei Veterans General Hospital, both in Taipei, Taiwan, and his coauthors. However, lasmiditan (a 5-hydroxytryptamine1F receptor agonist) and rimegepant and ubrogepant (both calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP] antagonists) might still have unique advantages, since triptans are contraindicated for patients with cardiovascular risks, they said.
The systemic review and meta-analysis showed that, for the outcome of pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours after the dose, the three newer agents worked better than placebo, but were inferior to most triptans. However, ubrogepant and rimegepant, which received U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval for the treatment of acute migraine in adults in December 2019 and February 2020, respectively, might be associated with fewer risks of adverse events (AEs), compared with triptans. “These new effective therapeutic options enrich the therapeutic categories of specific acute migraine treatments and may provide an opportunity to decrease the risks of barbiturate or opioid overuse or addiction,” they wrote.
The meta-analysis included 64 randomized, controlled trials involving 46,442 participants (74%-87% female across studies; age range, 36-43 years). All studies examined clinically relevant outcomes in patients with International Headache Society criteria for migraine, and compared currently available migraine-specific acute treatments with each other or placebo. The drugs were examined at doses with widespread clinical use and included: ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, almotriptan, eletriptan, frovatriptan, lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant.
The findings showed that all drug treatments were associated with a higher odds ratio for pain freedom, compared with placebo, except for sumatriptan, 10-mg nasal spray. The most effective drug was eletriptan 40 mg (OR, 5.59), and the least effective was lasmiditan 50 mg (OR, 1.65). Most triptans were associated with higher ORs for both pain freedom and pain relief at 2 hours, compared with lasmiditan, rimegepant, or ubrogepant, while comparisons between lasmiditan, rimegepant, and ubrogepant for these outcomes showed no statistically significant difference, they reported.
Lasmiditan was associated with the highest risk of any AEs, “however, the AEs were tolerable and were not considered serious. … Therefore, we suggest that the benefits should be weighed against the risk of its AEs when considering the clinical application of lasmiditan,” they wrote. Certain triptans (rizatriptan, sumatriptan, and zolmitriptan) were also associated with a higher risk of any AEs, compared with the CGRP antagonists. “Nevertheless, most of the AEs were mild to moderate, and the percentages of serious AEs were low (0.0%-2.1%).”
Finally, the authors noted that their observations of successful treatment with 5-hydroxytriptamine1F receptor agonists and CGRP antagonists “reveals that vasoconstriction is not essential for antimigraine therapy.” which could have implications for future pharmaceutical development.
Older and newer medications each have advantages
“Triptans will be around for a long time, but the newer medications are here to stay,” said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, in reaction to the study. “Before this publication, we knew that the 2-hour efficacy results of the newer medications were not quite as good as the faster-acting triptans; and after this network meta-analysis we are more sure of that,” said Dr. Rapoport, of the department of neurology at University of California, Los Angeles. “But the fact that the three newer medications do not constrict blood vessels and can easily be given even to patients with contraindications to triptans, or patients that simply are at greater risk due to obesity, smoking history, family history, diabetes, lack of exercise, or higher lipid levels, puts them into a desirable category.”
Calling it a “very carefully done” systematic review, Dr. Rapoport had a few caveats about the strength of the research. The trials that were included were not identically designed and were performed in different areas, by different investigators, on different patients, he noted. They were also not head-to-head trials “which ensures that the resultant data are more pure.” The studies also looked only at rapid results at 2 hours after dosing. “In my experience, patients are often satisfied with the response times from these newer agents; and doctors and patients both are happy that they are not vasoconstrictive,” he said. “The researchers also omitted studies looking at zolmitriptan nasal spray, which I have found to be rapid in onset and efficacious with few adverse events.”
Finally, Dr. Rapoport noted that one condition not examined in the review was medication overuse headache (MOH), which is “a major problem with patients that have high-frequency episodic migraine and chronic migraine. To our knowledge thus far, the two gepants (ubrogepant and rimegepant) do not appear to cause MOH when taken frequently, and these agents may end up being a treatment for this condition.”
Dr Wang reported receiving personal fees from Eli Lilly, Daiichi-Sankyo, Norvatis Taiwan, Biogen, Pfizer, and Bayer; and grants from AbbVie, Norvatis, Eli Lilly, Taiwan Ministry of Technology and Science, Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University, and Taipei Veterans General Hospital outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rapoport serves as an advisor for AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Cala Health, Satsuma, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Theranica, Xoc and Zosano; he is on the Speakers Bureau of AbbVie, Amgen, Biohaven, Lundbeck and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries. He is Editor-in-Chief of Neurology Reviews.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Ministry of Education, Taiwan, and the Brain Research Center, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Treatment of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients
An opportunity for impact
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.
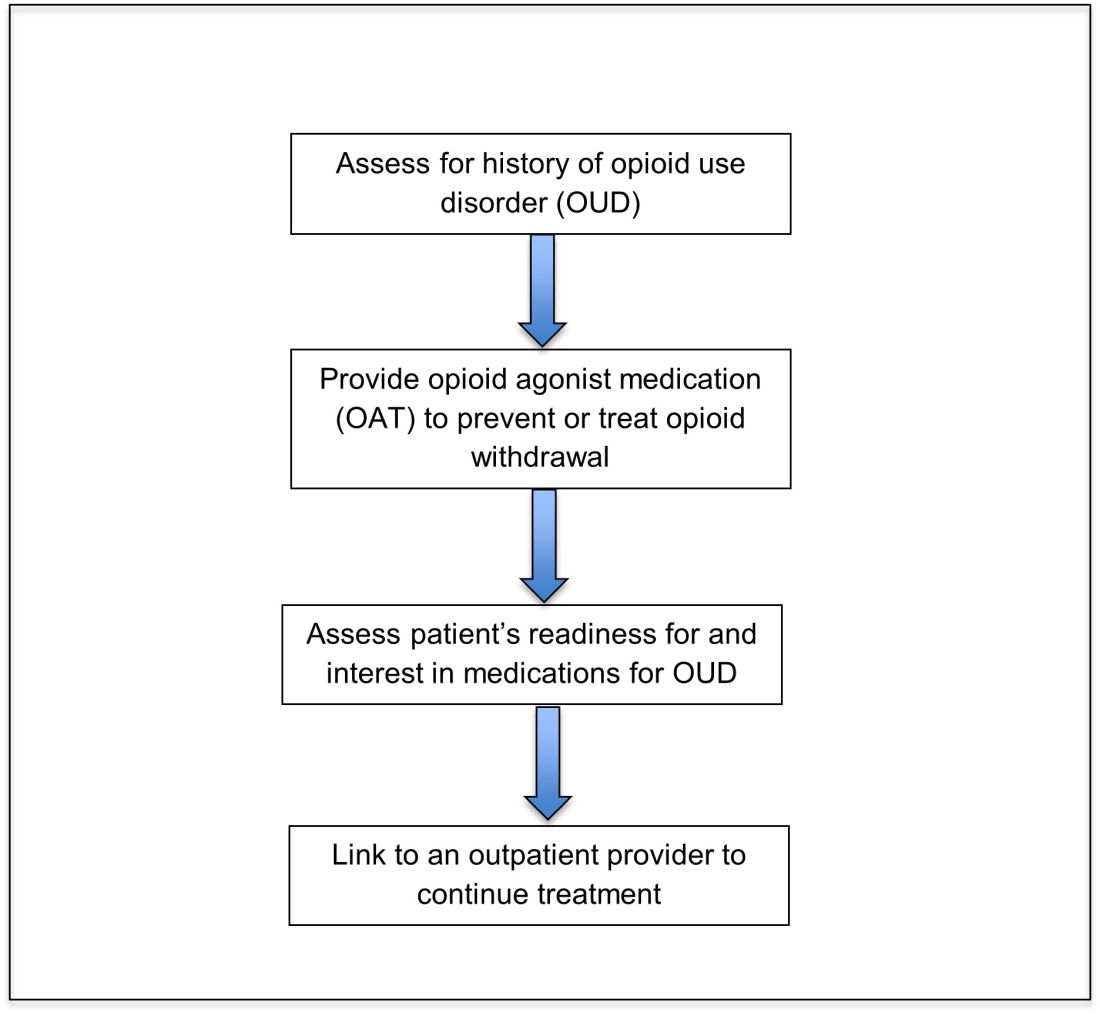
Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
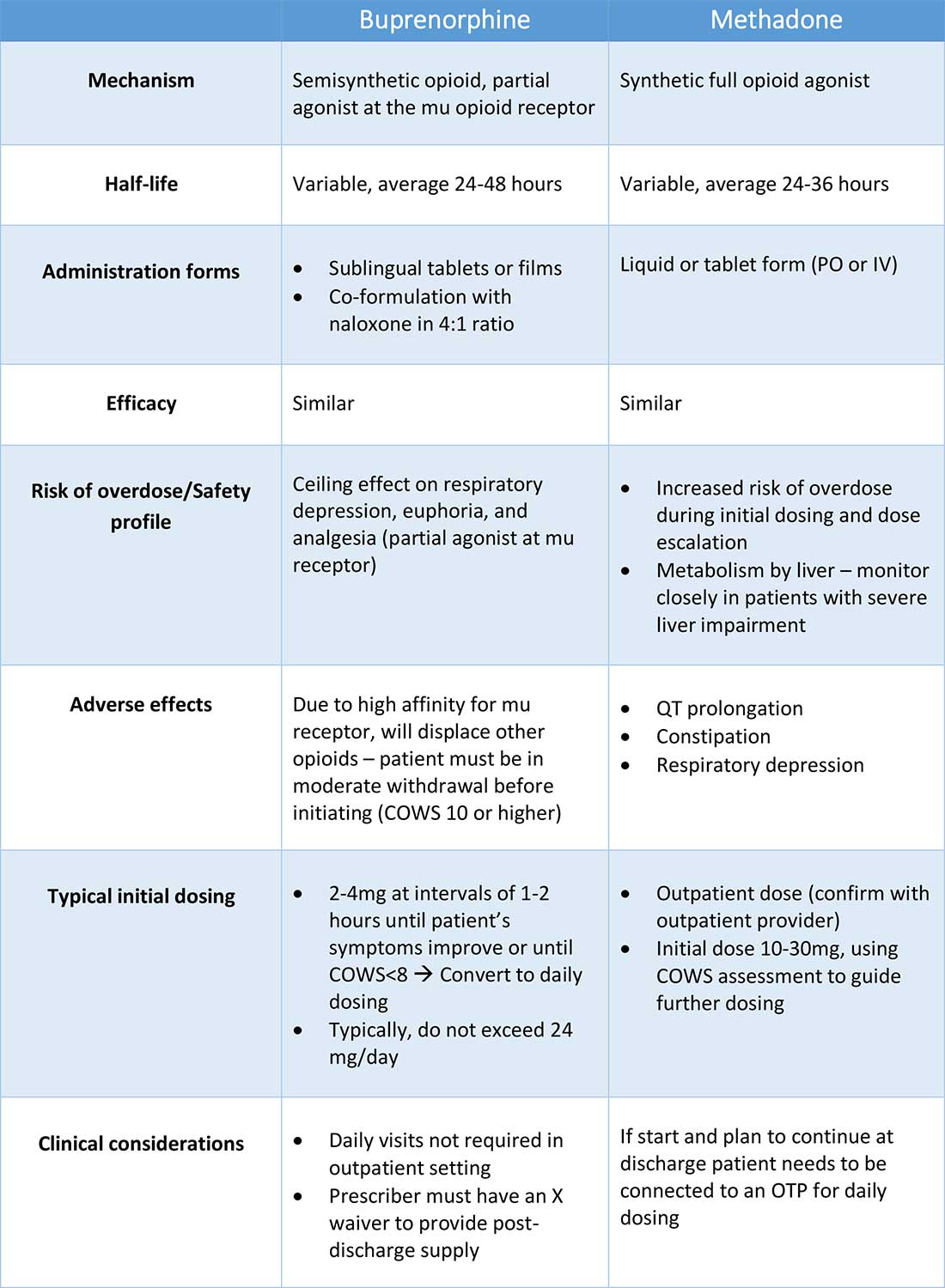
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.
Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
An opportunity for impact
An opportunity for impact
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.

Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.

Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.

Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.

Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
Yoga effective adjunct therapy in recurrent vasovagal syncope
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Yoga added to conventional therapy for vasovagal syncope (VVS), when patients faint after a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure, can reduce symptoms and improve quality of life, new research suggests.
A small, open-label trial conducted in New Delhi showed that participants practicing yoga reported an improvement in VVS symptoms after only 6 weeks, with a reduction of 1.82 events at 12 months. All those practicing yoga also showed significantly improved quality of life (QoL) scores by the end of the trial.
“Yoga as add-on therapy in VVS is superior to medical therapy in reducing syncopal and presyncopal events and in improving the QoL,” report Gautam Sharma, MD, DM, Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, and colleagues. “It may be useful to integrate a cost-effective and safe intervention such as yoga into the management of VVS.”
Results of the LIVE-Yoga study were published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Vasovagal syncope is a common and non–life-threatening condition, but given the severity and frequency of recurrence it can result in significant deterioration in a patient’s quality of life, the authors note. “Existing management therapies have been largely ineffective,” they write.
Recent trials have suggested some efficacy for yoga in diseases of autonomic imbalance, suggesting a possible use in VVS. To find out, the researchers enrolled adults with VVS between the ages of 15-70 years who had a positive head-up tilt test (HUTT) and at least two syncope or presyncope events within 3 months of enrollment. They also needed to be willing and able to practice yoga. Those with structural heart disease, accelerated hypertension, and underlying neurologic disorders were not included in the study.
A total of 55 patients were randomly assigned to receive either a specialized yoga training program in addition to guideline-based therapy, or guideline-based therapy alone. Standard care included physical counterpressure maneuvers, avoidance of known triggers, increased salt and water intake, and drug therapy or pacing at the discretion of the treating physician.
The primary outcome was a composite of the number of episodes of syncope and presyncope at 12 months.
Secondary outcomes including QoL, assessed using the World Health Organization Quality of Life Brief Field questionnaire (WHOQoL-BREF) and the Syncope Functional Status Questionnaire (SFSQ) at 12 months, a head-up tilt test, and heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
For the first 2 weeks, patients in the intervention group were enrolled in eight supervised yoga sessions conducted at the Centre for Integrative Medicine and Research at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. For the remainder of the trial, they continued a daily yoga practice at home at least 5 days a week.
The yoga module created for participants was designed with a view to the pathophysiology of VVS and featured postures, breathing, and relaxation techniques. Yoga classes were taught by qualified therapists under the guidance of physicians.
In addition to a booklet with a pictorial of the yoga regimen, participants received twice-monthly calls from the yoga center to encourage compliance. Results show that all participants adhered to their yoga routine for more than 80% of the 12-month trial.
At 12 months, the mean number of syncopal or presyncopal events was 0.7 ± 0.7 with the yoga intervention versus 2.52 ± 1.93 among patients in the control arm (P < .05). The reduction in events started as early as 6 weeks and continued to separate out to 12 months, the researchers note.
Thirteen of 30 (43.3%) intervention patients and 4 of 25 (16%) control patients remained event-free at 12 months, a statistically significant difference (P = .02). There was a trend toward fewer positive head-up tilt tests between groups that did not reach significance, and there was no difference in heart rate variability at 6 weeks.
No adverse events as a result of the yoga practice were reported, and no patient started drug therapy or received pacing therapy during the trial, they note.
The researchers point out that yoga postures can enhance vascular and muscle tone, especially in the lower limbs.
“Yoga breathing and relaxation techniques have been shown to increase vagal tone and improve autonomic balance, which could potentially curtail the sympathetic overdrive phase and interrupt the activation of the c-mechanoreceptors, which is a critical step in the syncope cascade,” they note.
“We postulate that positive effects of yoga in this study could be related to a multidimensional effect of this intervention acting through both central and peripheral mechanisms, including physical, psychological, and autonomic pathways,” the authors conclude.
Comprehensive regimen
Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, medical director for the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park, Kansas, says these results are in line with previous research indicating the benefits of yoga in improving cardiovascular function.
“All of this clearly shows that when you [include] a systematic diet of yoga for a reasonable amount of time to improve the plasticity of parasympathetic inputs into the chest and thereby the cardiovascular system ... you can help patients to improve their symptoms,” he said in an interview.
He already prescribes yoga in his own practice as part of a comprehensive therapeutic regimen, he said. “We have a handful of practitioners all around the city who work with us,” Dr. Lakkireddy said.
Both he and the study authors point the economic burden of VVS both in management and in loss of patient productivity. “A low-cost intervention in the form of yoga, which essentially requires only a mat, can reduce both direct and indirect costs significantly,” note the authors.
The trial was supported under the extramural research (EMR) scheme by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New insights into psychogenic seizures in teens
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results of a small study suggest.
The school experience of teens with PNES is overwhelmingly negative, study investigator Andrea Tanner, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University School of Nursing, Indianapolis.
She hopes this research will spur a collaborative effort between students, schools, families, and health care providers “to develop an effective plan to help these adolescents cope, to manage this condition, and hopefully reach seizure freedom.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Anxiety, perfectionism
Although psychogenic seizures resemble epileptic seizures, they have a psychological basis and, unlike epilepsy, are not caused by abnormal electrical brain activity.
While the school experience has previously been identified as a source of predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors for PNES, little is known about the school experience of adolescents with the disorder and the role it may play in PNES management, the investigators noted.
During her 20 years as a school nurse, Dr. Tanner saw firsthand how school staff struggled with responding appropriately to teens with PNES. “They wanted to call 911 every time; they wanted to respond as if it [were] an epileptic seizure.”
For the study, she interviewed 10 teens with PNES, aged 12 to 19 years, whom she found mostly through Facebook support groups but also through flyers. All participants had undergone video EEG and been diagnosed with PNES.
From the interviews, Dr. Tanner and colleagues conducted a qualitative content analysis and uncovered “overarching” themes.
A main theme was stress, some of which focused on bullying by peers or harassment by school personnel, much of which was related to accusations of the children “faking” seizures to get attention, said Dr. Tanner.
Some teens reported being banned from school events, such as field trips, out of concern they would be a “distraction,” which led to feelings of isolation and exclusion, said Dr. Tanner.
Research points to a growing incidence of PNES among adolescents. This may be because it is now better recognized, or it may stem from the unique stressors today’s teens face, said Dr. Tanner.
Adolescents discussed the pressures they feel to be the best at everything. “They wanted to be good in athletics; they wanted to be good in academics; they wanted to get into a good college,” said Dr. Tanner.
Some study participants had undergone psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, and others had investigated mindfulness-based therapy. However, not all were receiving treatment. For some, such care was inaccessible, while others had tried a mental health care intervention but had abandoned it.
Although all the study participants were female, Dr. Tanner has interviewed males outside this study and found their experiences are similar.
Her next research step is to try to quantify the findings. “I would like to begin to look at what would be the appropriate outcomes if I were to do an intervention to improve the school experience.”
Her message for doctors is to see school nurses as a “partner” or “liaison” who “can bridge the world of health care and education.”
Important, novel research
Commenting on the research, Barbara Dworetzky, MD, Chief, Epilepsy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, said it’s “important and novel.”
The study focuses on the main factors – or themes – that lead to increased stress, such as bullying, isolation, and “not being believed,” that are likely triggers for PNES, said Dr. Dworetzky.
The study is also important because it focuses on factors that help make the girls “feel supported and protected” – for example, having staff “take the episodes seriously,” she said.
The study’s qualitative measures “are a valid way of understanding these girls and giving them a voice,” said Dr. Dworetzky. She added the study provides “practical information” that could help target treatments to improve outcomes in this group.
A limitation of the study was that the very small cohort of teenage girls was selected only through families in Facebook support groups or flyers to school nurses, said Dr. Dworetzky.
“There are likely many other groups who don’t even have families trying to help them. Larger cohorts without this type of bias may be next steps.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From AES 2021
‘Alarming’ rate of abuse in pregnant women with epilepsy
, new research shows.
Study investigator Naveed Chaudhry, MD, a recent epilepsy fellow and assistant professor of neurology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, described the finding as “alarming” and called for more support for this patient population.
Investigators found that women with epilepsy are also more likely to report other stressors, including divorce, illness, lost pay, and partner discord, while expecting.
“As epilepsy physicians, it’s important that we ask the right questions and dive a little bit deeper with these patients, even if it’s uncomfortable and not something we’re used to,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Cause for concern
Women with epilepsy may be under stress for a variety of social and economic reasons. In some women, stress can trigger seizures, and during pregnancy, this can lead to complications such as preterm labor and low birth weight.
For the study, researchers tapped into the Center for Disease Control and Prevention Pregnancy Risk Assessment and Monitoring System (PRAMS). This database includes information from surveys asking women across the U.S. about their pregnancy and postpartum period.
Thirteen states collected data on stresses in women with and without epilepsy. Respondents were asked about 14 economic and other worries in the year prior to their baby’s birth, including the pregnancy period.
The analysis included 64,951 women, 1,140 of whom had epilepsy, who were included in surveys from 2012-2020. There were no significant demographic differences between those with and those without the disorder.
After adjusting for maternal age, race, ethnicity, marital status, education, and socioeconomic status, the study found that women with epilepsy experienced an average of 2.41 of the stressors compared with 1.72 for women without epilepsy.
Women with epilepsy were more likely to have experienced family illness, divorce, homelessness, partner job loss, reduced work or pay, increased arguments, having a partner in jail, drug use, and the death of someone close to them.
The results showed that unmarried and younger women as well as those with lower incomes were particularly prone to experience stress during pregnancy.
It’s not clear why women with epilepsy report more stressors. “Looking at the literature, no one has really looked at the exact reason for this, but we postulate it could be a lack of supports and support systems,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
Women were asked about physical, sexual, and emotional abuse. Results showed that substantially more women with epilepsy than those without the disorder reported such abuse during pregnancy – 10.6% versus 4.1%. The adjusted odds ratio for women with epilepsy reporting abuse was 2.78 (95% CI, 2.07-3.74).
“That raises our concern and needs to be looked at in more detail,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
It is unclear whether some women might have had psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES), which are linked to a higher rate of abuse, said Dr. Chaudhry. “But the prevalence of PNES in the general population is quite low, so we don’t think it’s contributing to a large extent to this finding.”
The findings highlight the importance of addressing stress in women with epilepsy during pregnancy, he said. “We need to have good support services and we need to counsel women to optimize good outcomes.”
This applies to all women of childbearing age. “We suspect abuse and stressors are going to be going on throughout that period,” said Dr. Chaudhry. “It’s important to ask about it and have appropriate support staff and social work and people available to help when an issue is identified.”
Stress a common seizure trigger
Commenting on the research, Kimford Meador, MD, professor, Department of Neurology and Neurological Sciences, Stanford University School of Medicine, noted the study was well conducted and had a large sample size.
The findings are important, as stress is a common trigger for seizures in people with epilepsy and is associated with mood and anxiety, which can affect quality of life, said Dr. Meador.
Results of his analysis from the Maternal Outcomes and Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (MONEAD) study, also presented at this year’s AES meeting, showed that women with epilepsy had more depressive symptoms during the postpartum period and more anxiety symptoms during pregnancy and postpartum in comparison with those without epilepsy.
Dr. Meador’s group also recently conducted a study that was published in JAMA Neurology, showing that in women with epilepsy during the postpartum period, anxiety is associated with lower cognitive ability in their children at age 2 years.
“All these findings highlight the importance of assessing and managing stress, anxiety, and mood in women with epilepsy,” said Dr. Meador. “Interventions could impact seizures and quality of life in pregnant women with epilepsy and long-term outcomes in their children.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Study investigator Naveed Chaudhry, MD, a recent epilepsy fellow and assistant professor of neurology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, described the finding as “alarming” and called for more support for this patient population.
Investigators found that women with epilepsy are also more likely to report other stressors, including divorce, illness, lost pay, and partner discord, while expecting.
“As epilepsy physicians, it’s important that we ask the right questions and dive a little bit deeper with these patients, even if it’s uncomfortable and not something we’re used to,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Cause for concern
Women with epilepsy may be under stress for a variety of social and economic reasons. In some women, stress can trigger seizures, and during pregnancy, this can lead to complications such as preterm labor and low birth weight.
For the study, researchers tapped into the Center for Disease Control and Prevention Pregnancy Risk Assessment and Monitoring System (PRAMS). This database includes information from surveys asking women across the U.S. about their pregnancy and postpartum period.
Thirteen states collected data on stresses in women with and without epilepsy. Respondents were asked about 14 economic and other worries in the year prior to their baby’s birth, including the pregnancy period.
The analysis included 64,951 women, 1,140 of whom had epilepsy, who were included in surveys from 2012-2020. There were no significant demographic differences between those with and those without the disorder.
After adjusting for maternal age, race, ethnicity, marital status, education, and socioeconomic status, the study found that women with epilepsy experienced an average of 2.41 of the stressors compared with 1.72 for women without epilepsy.
Women with epilepsy were more likely to have experienced family illness, divorce, homelessness, partner job loss, reduced work or pay, increased arguments, having a partner in jail, drug use, and the death of someone close to them.
The results showed that unmarried and younger women as well as those with lower incomes were particularly prone to experience stress during pregnancy.
It’s not clear why women with epilepsy report more stressors. “Looking at the literature, no one has really looked at the exact reason for this, but we postulate it could be a lack of supports and support systems,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
Women were asked about physical, sexual, and emotional abuse. Results showed that substantially more women with epilepsy than those without the disorder reported such abuse during pregnancy – 10.6% versus 4.1%. The adjusted odds ratio for women with epilepsy reporting abuse was 2.78 (95% CI, 2.07-3.74).
“That raises our concern and needs to be looked at in more detail,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
It is unclear whether some women might have had psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES), which are linked to a higher rate of abuse, said Dr. Chaudhry. “But the prevalence of PNES in the general population is quite low, so we don’t think it’s contributing to a large extent to this finding.”
The findings highlight the importance of addressing stress in women with epilepsy during pregnancy, he said. “We need to have good support services and we need to counsel women to optimize good outcomes.”
This applies to all women of childbearing age. “We suspect abuse and stressors are going to be going on throughout that period,” said Dr. Chaudhry. “It’s important to ask about it and have appropriate support staff and social work and people available to help when an issue is identified.”
Stress a common seizure trigger
Commenting on the research, Kimford Meador, MD, professor, Department of Neurology and Neurological Sciences, Stanford University School of Medicine, noted the study was well conducted and had a large sample size.
The findings are important, as stress is a common trigger for seizures in people with epilepsy and is associated with mood and anxiety, which can affect quality of life, said Dr. Meador.
Results of his analysis from the Maternal Outcomes and Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (MONEAD) study, also presented at this year’s AES meeting, showed that women with epilepsy had more depressive symptoms during the postpartum period and more anxiety symptoms during pregnancy and postpartum in comparison with those without epilepsy.
Dr. Meador’s group also recently conducted a study that was published in JAMA Neurology, showing that in women with epilepsy during the postpartum period, anxiety is associated with lower cognitive ability in their children at age 2 years.
“All these findings highlight the importance of assessing and managing stress, anxiety, and mood in women with epilepsy,” said Dr. Meador. “Interventions could impact seizures and quality of life in pregnant women with epilepsy and long-term outcomes in their children.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Study investigator Naveed Chaudhry, MD, a recent epilepsy fellow and assistant professor of neurology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, described the finding as “alarming” and called for more support for this patient population.
Investigators found that women with epilepsy are also more likely to report other stressors, including divorce, illness, lost pay, and partner discord, while expecting.
“As epilepsy physicians, it’s important that we ask the right questions and dive a little bit deeper with these patients, even if it’s uncomfortable and not something we’re used to,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society.
Cause for concern
Women with epilepsy may be under stress for a variety of social and economic reasons. In some women, stress can trigger seizures, and during pregnancy, this can lead to complications such as preterm labor and low birth weight.
For the study, researchers tapped into the Center for Disease Control and Prevention Pregnancy Risk Assessment and Monitoring System (PRAMS). This database includes information from surveys asking women across the U.S. about their pregnancy and postpartum period.
Thirteen states collected data on stresses in women with and without epilepsy. Respondents were asked about 14 economic and other worries in the year prior to their baby’s birth, including the pregnancy period.
The analysis included 64,951 women, 1,140 of whom had epilepsy, who were included in surveys from 2012-2020. There were no significant demographic differences between those with and those without the disorder.
After adjusting for maternal age, race, ethnicity, marital status, education, and socioeconomic status, the study found that women with epilepsy experienced an average of 2.41 of the stressors compared with 1.72 for women without epilepsy.
Women with epilepsy were more likely to have experienced family illness, divorce, homelessness, partner job loss, reduced work or pay, increased arguments, having a partner in jail, drug use, and the death of someone close to them.
The results showed that unmarried and younger women as well as those with lower incomes were particularly prone to experience stress during pregnancy.
It’s not clear why women with epilepsy report more stressors. “Looking at the literature, no one has really looked at the exact reason for this, but we postulate it could be a lack of supports and support systems,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
Women were asked about physical, sexual, and emotional abuse. Results showed that substantially more women with epilepsy than those without the disorder reported such abuse during pregnancy – 10.6% versus 4.1%. The adjusted odds ratio for women with epilepsy reporting abuse was 2.78 (95% CI, 2.07-3.74).
“That raises our concern and needs to be looked at in more detail,” said Dr. Chaudhry.
It is unclear whether some women might have had psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES), which are linked to a higher rate of abuse, said Dr. Chaudhry. “But the prevalence of PNES in the general population is quite low, so we don’t think it’s contributing to a large extent to this finding.”
The findings highlight the importance of addressing stress in women with epilepsy during pregnancy, he said. “We need to have good support services and we need to counsel women to optimize good outcomes.”
This applies to all women of childbearing age. “We suspect abuse and stressors are going to be going on throughout that period,” said Dr. Chaudhry. “It’s important to ask about it and have appropriate support staff and social work and people available to help when an issue is identified.”
Stress a common seizure trigger
Commenting on the research, Kimford Meador, MD, professor, Department of Neurology and Neurological Sciences, Stanford University School of Medicine, noted the study was well conducted and had a large sample size.
The findings are important, as stress is a common trigger for seizures in people with epilepsy and is associated with mood and anxiety, which can affect quality of life, said Dr. Meador.
Results of his analysis from the Maternal Outcomes and Neurodevelopmental Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs (MONEAD) study, also presented at this year’s AES meeting, showed that women with epilepsy had more depressive symptoms during the postpartum period and more anxiety symptoms during pregnancy and postpartum in comparison with those without epilepsy.
Dr. Meador’s group also recently conducted a study that was published in JAMA Neurology, showing that in women with epilepsy during the postpartum period, anxiety is associated with lower cognitive ability in their children at age 2 years.
“All these findings highlight the importance of assessing and managing stress, anxiety, and mood in women with epilepsy,” said Dr. Meador. “Interventions could impact seizures and quality of life in pregnant women with epilepsy and long-term outcomes in their children.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From AES 2021
Could Viagra help prevent Alzheimer’s?
published in the journal Nature Aging.
Patients who used the drug sildenafil, the generic name for Viagra, were 69% less likely to develop the disease than were nonusers.
“Sildenafil, which has been shown to significantly improve cognition and memory in preclinical models, presented as the best drug candidate,” Feixiong Cheng, PhD, the lead study author in the Cleveland Clinic’s Genomic Medicine Institute, said in a statement.
“Notably, we found that sildenafil use reduced the likelihood of Alzheimer’s in individuals with coronary artery disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, all of which are comorbidities significantly associated with risk of the disease, as well as in those without,” he said.
Alzheimer’s, which is the most common form of age-related dementia, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. The disease is expected to affect nearly 14 million Americans by 2050. There is no approved treatment for it.
Dr. Cheng and colleagues at the Cleveland Clinic used a large gene-mapping network to analyze whether more than 1,600 Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs could work against Alzheimer’s. They gave higher scores to drugs that target both amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, which are two hallmarks of the disease. Sildenafil appeared at the top of the list.
Then the researchers used a database of health insurance claims for more than 7 million people in the U.S. to understand the relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease outcomes. They compared sildenafil users to nonusers and found that those who used the drug were 69% less likely to have the neurodegenerative disease, even after 6 years of follow-up.
After that, the research team came up with a lab model that showed the sildenafil increased brain cell growth and targeted tau proteins. The lab model could indicate how the drug influences disease-related brain changes.
But Dr. Cheng cautioned against drawing strong conclusions. The study doesn’t demonstrate a causal relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers will need to conduct clinical trials with a placebo control to see how well the drug works.
Other researchers said the findings offer a new avenue for research but don’t yet provide solid answers.
“Being able to repurpose a drug already licensed for health conditions could help speed up the drug discovery process and bring about life-changing dementia treatments sooner,” Susan Kohlhaas, PhD, director of research at Alzheimer’s Research UK, told the Science Media Centre.
“Importantly, this research doesn’t prove that sildenafil is responsible for reducing dementia risk, or that it slows or stops the disease,” she continued. “If you want to discuss any treatments you are receiving, the first port of call is to speak to your doctor.”
And doctors won’t likely recommend it as a treatment just yet either.
“While these data are interesting scientifically, based on this study, I would not rush out to start taking sildenafil as a prevention for Alzheimer’s disease,” Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, deputy director of the Centre for Discovery Brain Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, told the Science Media Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
published in the journal Nature Aging.
Patients who used the drug sildenafil, the generic name for Viagra, were 69% less likely to develop the disease than were nonusers.
“Sildenafil, which has been shown to significantly improve cognition and memory in preclinical models, presented as the best drug candidate,” Feixiong Cheng, PhD, the lead study author in the Cleveland Clinic’s Genomic Medicine Institute, said in a statement.
“Notably, we found that sildenafil use reduced the likelihood of Alzheimer’s in individuals with coronary artery disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, all of which are comorbidities significantly associated with risk of the disease, as well as in those without,” he said.
Alzheimer’s, which is the most common form of age-related dementia, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. The disease is expected to affect nearly 14 million Americans by 2050. There is no approved treatment for it.
Dr. Cheng and colleagues at the Cleveland Clinic used a large gene-mapping network to analyze whether more than 1,600 Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs could work against Alzheimer’s. They gave higher scores to drugs that target both amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, which are two hallmarks of the disease. Sildenafil appeared at the top of the list.
Then the researchers used a database of health insurance claims for more than 7 million people in the U.S. to understand the relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease outcomes. They compared sildenafil users to nonusers and found that those who used the drug were 69% less likely to have the neurodegenerative disease, even after 6 years of follow-up.
After that, the research team came up with a lab model that showed the sildenafil increased brain cell growth and targeted tau proteins. The lab model could indicate how the drug influences disease-related brain changes.
But Dr. Cheng cautioned against drawing strong conclusions. The study doesn’t demonstrate a causal relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers will need to conduct clinical trials with a placebo control to see how well the drug works.
Other researchers said the findings offer a new avenue for research but don’t yet provide solid answers.
“Being able to repurpose a drug already licensed for health conditions could help speed up the drug discovery process and bring about life-changing dementia treatments sooner,” Susan Kohlhaas, PhD, director of research at Alzheimer’s Research UK, told the Science Media Centre.
“Importantly, this research doesn’t prove that sildenafil is responsible for reducing dementia risk, or that it slows or stops the disease,” she continued. “If you want to discuss any treatments you are receiving, the first port of call is to speak to your doctor.”
And doctors won’t likely recommend it as a treatment just yet either.
“While these data are interesting scientifically, based on this study, I would not rush out to start taking sildenafil as a prevention for Alzheimer’s disease,” Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, deputy director of the Centre for Discovery Brain Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, told the Science Media Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
published in the journal Nature Aging.
Patients who used the drug sildenafil, the generic name for Viagra, were 69% less likely to develop the disease than were nonusers.
“Sildenafil, which has been shown to significantly improve cognition and memory in preclinical models, presented as the best drug candidate,” Feixiong Cheng, PhD, the lead study author in the Cleveland Clinic’s Genomic Medicine Institute, said in a statement.
“Notably, we found that sildenafil use reduced the likelihood of Alzheimer’s in individuals with coronary artery disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, all of which are comorbidities significantly associated with risk of the disease, as well as in those without,” he said.
Alzheimer’s, which is the most common form of age-related dementia, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. The disease is expected to affect nearly 14 million Americans by 2050. There is no approved treatment for it.
Dr. Cheng and colleagues at the Cleveland Clinic used a large gene-mapping network to analyze whether more than 1,600 Food and Drug Administration–approved drugs could work against Alzheimer’s. They gave higher scores to drugs that target both amyloid and tau proteins in the brain, which are two hallmarks of the disease. Sildenafil appeared at the top of the list.
Then the researchers used a database of health insurance claims for more than 7 million people in the U.S. to understand the relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease outcomes. They compared sildenafil users to nonusers and found that those who used the drug were 69% less likely to have the neurodegenerative disease, even after 6 years of follow-up.
After that, the research team came up with a lab model that showed the sildenafil increased brain cell growth and targeted tau proteins. The lab model could indicate how the drug influences disease-related brain changes.
But Dr. Cheng cautioned against drawing strong conclusions. The study doesn’t demonstrate a causal relationship between sildenafil and Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers will need to conduct clinical trials with a placebo control to see how well the drug works.
Other researchers said the findings offer a new avenue for research but don’t yet provide solid answers.
“Being able to repurpose a drug already licensed for health conditions could help speed up the drug discovery process and bring about life-changing dementia treatments sooner,” Susan Kohlhaas, PhD, director of research at Alzheimer’s Research UK, told the Science Media Centre.
“Importantly, this research doesn’t prove that sildenafil is responsible for reducing dementia risk, or that it slows or stops the disease,” she continued. “If you want to discuss any treatments you are receiving, the first port of call is to speak to your doctor.”
And doctors won’t likely recommend it as a treatment just yet either.
“While these data are interesting scientifically, based on this study, I would not rush out to start taking sildenafil as a prevention for Alzheimer’s disease,” Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, deputy director of the Centre for Discovery Brain Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, told the Science Media Centre.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE AGING
Higher resting heart rate tied to increased dementia risk
independent of the presence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, new research shows.
“RHR is easy to measure and might be used to identify older people potentially at high risk of dementia and cognitive decline for early interventions,” Yume Imahori, MD, PhD, with the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview.
“Health care professionals should be aware of potential cognitive consequences associated with elevated RHR in older people and may advise older people with high RHR to have a follow-up assessment of cognitive function,” Dr. Imahori said.
The study was published online Dec. 3, 2021, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Heart-brain connection
The findings are based on 2,147 adults (62% women) aged 60 years and older (mean age, 70.6 years) from the population-based Swedish National Aging and Care in Kungsholmen (SNAC-K) study. All were free of dementia at baseline and were followed regularly from 2001-2004 to 2013-2016.
The average RHR at baseline was 65.7 bpm. Individuals in higher RHR groups were older, less educated, and were more likely to be smokers and sedentary and to have hypertension. There were no differences among RHR groups in the prevalence of CVD at baseline.
During a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 289 participants were diagnosed with dementia.
In the fully adjusted model, participants with RHR of 80 bpm or higher had a 55% increased risk of developing dementia, compared with peers with lower RHR of 60 to 69 bpm (hazard ratio, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.06-2.27).
“This association was not due to underlying cardiovascular diseases such as atrial fibrillation and heart failure, which is important because elevated RHR is often related to heart disease,” Dr. Imahori said in an interview.
Regarding cognitive function, Mini-Mental State Examination scores declined over time during the follow-up period in all RHR groups, but participants with RHR 70-79 and 80+ bpm had a greater decline, compared with those with lower RHR of 60-69 bpm.
Dr. Imahori said these findings are in line with data from the U.S. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study linking elevated RHR of 80+ bpm in midlife to dementia and cognitive decline in late life.
Public health implications
Reached for comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, said this study adds to the “growing body of research showing the health of the heart and brain are closely connected. However, this study only shows a correlation between resting heart rate and cognition, not causation. More research is needed.
“Evidence shows that other risk factors for cardiovascular disease and stroke – obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes – negatively impact your cognitive health,” Dr. Sexton said in an interview.
“The Alzheimer’s Association believes the conversation about heart health management is something everyone should be having with their doctor,” she said.
“There are things you can do today to lower your risk for cardiovascular disease, including regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet. Improving your heart health is an important step to maintaining your brain health as you age,” Dr. Sexton added.
SNAC-K is supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs and the participating county councils and municipalities and in part by additional grants from the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare. Dr. Imahori and Dr. Sexton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
independent of the presence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, new research shows.
“RHR is easy to measure and might be used to identify older people potentially at high risk of dementia and cognitive decline for early interventions,” Yume Imahori, MD, PhD, with the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview.
“Health care professionals should be aware of potential cognitive consequences associated with elevated RHR in older people and may advise older people with high RHR to have a follow-up assessment of cognitive function,” Dr. Imahori said.
The study was published online Dec. 3, 2021, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Heart-brain connection
The findings are based on 2,147 adults (62% women) aged 60 years and older (mean age, 70.6 years) from the population-based Swedish National Aging and Care in Kungsholmen (SNAC-K) study. All were free of dementia at baseline and were followed regularly from 2001-2004 to 2013-2016.
The average RHR at baseline was 65.7 bpm. Individuals in higher RHR groups were older, less educated, and were more likely to be smokers and sedentary and to have hypertension. There were no differences among RHR groups in the prevalence of CVD at baseline.
During a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 289 participants were diagnosed with dementia.
In the fully adjusted model, participants with RHR of 80 bpm or higher had a 55% increased risk of developing dementia, compared with peers with lower RHR of 60 to 69 bpm (hazard ratio, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.06-2.27).
“This association was not due to underlying cardiovascular diseases such as atrial fibrillation and heart failure, which is important because elevated RHR is often related to heart disease,” Dr. Imahori said in an interview.
Regarding cognitive function, Mini-Mental State Examination scores declined over time during the follow-up period in all RHR groups, but participants with RHR 70-79 and 80+ bpm had a greater decline, compared with those with lower RHR of 60-69 bpm.
Dr. Imahori said these findings are in line with data from the U.S. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study linking elevated RHR of 80+ bpm in midlife to dementia and cognitive decline in late life.
Public health implications
Reached for comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, said this study adds to the “growing body of research showing the health of the heart and brain are closely connected. However, this study only shows a correlation between resting heart rate and cognition, not causation. More research is needed.
“Evidence shows that other risk factors for cardiovascular disease and stroke – obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes – negatively impact your cognitive health,” Dr. Sexton said in an interview.
“The Alzheimer’s Association believes the conversation about heart health management is something everyone should be having with their doctor,” she said.
“There are things you can do today to lower your risk for cardiovascular disease, including regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet. Improving your heart health is an important step to maintaining your brain health as you age,” Dr. Sexton added.
SNAC-K is supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs and the participating county councils and municipalities and in part by additional grants from the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare. Dr. Imahori and Dr. Sexton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
independent of the presence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors, new research shows.
“RHR is easy to measure and might be used to identify older people potentially at high risk of dementia and cognitive decline for early interventions,” Yume Imahori, MD, PhD, with the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, said in an interview.
“Health care professionals should be aware of potential cognitive consequences associated with elevated RHR in older people and may advise older people with high RHR to have a follow-up assessment of cognitive function,” Dr. Imahori said.
The study was published online Dec. 3, 2021, in Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Heart-brain connection
The findings are based on 2,147 adults (62% women) aged 60 years and older (mean age, 70.6 years) from the population-based Swedish National Aging and Care in Kungsholmen (SNAC-K) study. All were free of dementia at baseline and were followed regularly from 2001-2004 to 2013-2016.
The average RHR at baseline was 65.7 bpm. Individuals in higher RHR groups were older, less educated, and were more likely to be smokers and sedentary and to have hypertension. There were no differences among RHR groups in the prevalence of CVD at baseline.
During a median follow-up of 11.4 years, 289 participants were diagnosed with dementia.
In the fully adjusted model, participants with RHR of 80 bpm or higher had a 55% increased risk of developing dementia, compared with peers with lower RHR of 60 to 69 bpm (hazard ratio, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.06-2.27).
“This association was not due to underlying cardiovascular diseases such as atrial fibrillation and heart failure, which is important because elevated RHR is often related to heart disease,” Dr. Imahori said in an interview.
Regarding cognitive function, Mini-Mental State Examination scores declined over time during the follow-up period in all RHR groups, but participants with RHR 70-79 and 80+ bpm had a greater decline, compared with those with lower RHR of 60-69 bpm.
Dr. Imahori said these findings are in line with data from the U.S. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study linking elevated RHR of 80+ bpm in midlife to dementia and cognitive decline in late life.
Public health implications
Reached for comment, Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, said this study adds to the “growing body of research showing the health of the heart and brain are closely connected. However, this study only shows a correlation between resting heart rate and cognition, not causation. More research is needed.
“Evidence shows that other risk factors for cardiovascular disease and stroke – obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes – negatively impact your cognitive health,” Dr. Sexton said in an interview.
“The Alzheimer’s Association believes the conversation about heart health management is something everyone should be having with their doctor,” she said.
“There are things you can do today to lower your risk for cardiovascular disease, including regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet. Improving your heart health is an important step to maintaining your brain health as you age,” Dr. Sexton added.
SNAC-K is supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs and the participating county councils and municipalities and in part by additional grants from the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare. Dr. Imahori and Dr. Sexton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ALZHEIMER’S & DEMENTIA






