User login
Get familiar with evidence on these supplements
NEW ORLEANS – With more than 10% of children receiving complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), you should be familiar with what does and doesn’t work when it comes to using supplements for various medical issues, said Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements with their uses and evidence at the American Academy of Pediatrics annual meeting. Most of the evidence comes from studies in adults, not children, and the evidence overall is sometimes scant, but it can guide physicians in discussing options with parents interested in CAM.
Butterbur
This root primarily is used to treat migraines via anti-inflammatory effects. The ideal dose is 50-75 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for children aged 8-9 years and 100-150 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for those aged 10 and older (Headache. 2005 Mar;45:196-203; Eur J Pain. 2008;12:301-13; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Adverse effects are mostly gastrointestinal, such as diarrhea and stomach upset, and dermal/allergic reactions, such as itchy eyes, asthma, and itching.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the most popular drug of choice for reducing drowsiness and increasing alertness and has the strongest evidence base, including for improving sports and work performance (J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Jan;24[1]:257-65). Regular caffeine use can lead to dependence, however, and it can cause anxiety, nervousness, irritability, insomnia, peptic ulcers, palpitations, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and tremors. Withdrawal can involve headaches, irritability, and anxiety.
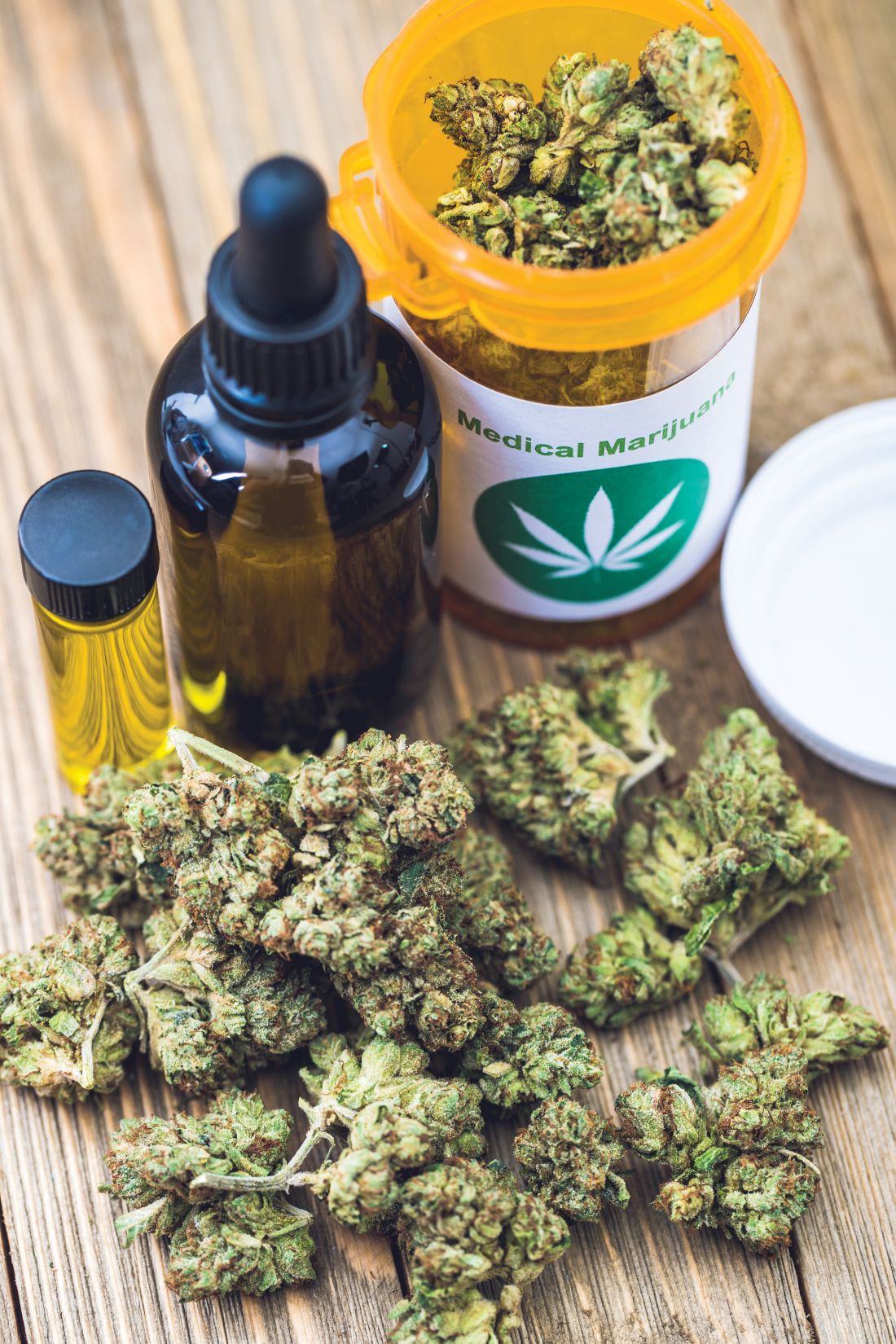
Cannabidiol
Marijuana has more than 80 cannabinoids, and a nonpsychoactive one, cannabidiol, makes up about 40% of cannabis extracts, Dr. Breuner said. It’s been used as an anticonvulsant and to combat anxiety, psychosis, nausea and rheumatoid arthritis pain. In a study using a rat model for arthritis, inflammation and pain-related behaviors decreased in rats that received cannabidiol (Eur J Pain. 2016 Jul;20[6]:936-48).
A human dose would be about 160-300 mg daily, but side effects can include dry mouth, hypotension, lightheadedness, psychomotor slowing, sedation, and sleepiness.
Coenzyme Q10
This antioxidant is fat-soluble and has a chemical structure similar to vitamin K. It has been used in people with autism, chronic fatigue syndrome, fatigue from chemotherapy, Lyme disease, and muscular dystrophy, but the evidence focuses on fibromyalgia. One study of patients with fibromyalgia found that a 300-mg daily dose for 40 days reduced pain by 52%-56%, fatigue by 47%, morning tiredness by 56%, and tender points by 44%, compared with baseline (Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19[12]:1356-61.)
In another, 200 mg of coenzyme Q10 with 200 mg ginkgo daily for 3 months resulted in improvement of quality of life measures, including physical fitness levels, emotional feelings, social activities, overall health, and pain (J Int Med Res. 2002;30:195-9).
Potential adverse effects of coenzyme Q10 include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, appetite suppression, and heartburn, albeit typically in less than 1% of patients.
Echinacea
Echinacea actually is approved in Germany for supportive therapy in treating upper respiratory tract infections, urogenital infections, and wound healing, Dr. Breuner said. Hypothesized mechanisms of action include stimulation of the alternate complement pathway, immune-modulating effects, activating nonspecific T cells, inhibiting viral replication, and enhancing phagocytosis.
However, in clinical studies, echinacea did not reduce the duration or severity of upper respiratory tract infections or the occurrence or severity of infection, compared with placebo (JAMA. 2003 Dec 3;290[21]:2824-30; N Engl J Med. 2005 Jul 28;353[4]:341-8); this was tested in children aged 2-11 years in the first study, and the mean age of the subjects in the second study was 21 years. A 2014 Cochrane review found no overall benefits for treating common colds but noted the possibility of “a weak benefit from some echinacea products” based on individual trials with consistently positive, yet nonsignificant, trends, albeit with “questionable clinical relevance” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 20;[2]:CD000530).
People with autoimmune conditions or who are immunocompromised should not use echinacea.
Magnesium
Magnesium also is used to treat migraines with a dose of 300-500 mg daily, although also it can be consumed in food, such as soy beans, black beans, tofu, seeds, nuts, whole grains, and shellfish (Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Mar;9[3]:369-79; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Side effects can include diarrhea and interactions with bisphosphonates, antibiotics] and diuretics. Taking proton pump inhibitors also may reduce magnesium levels.
Melatonin
Melatonin, a synthetic version of the hormone produced in humans to signal the onset of nighttime, has been studied extensively for jet lag, insomnia, shift-work disorder, circadian rhythm disorders, and withdrawal from benzodiazepine and nicotine.
Research shows that melatonin can improve sleep onset, duration, and quality. Some research has shown increased total sleep time (PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63773).
Some evidence suggests it has endocrine-disrupting adverse effects, such as inhibiting ovulation and impairing glucose utilization.
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)
Although it’s primarily an antidote for acetaminophen and carbon monoxide poisoning, NAC has been used for a wide range of conditions, including reducing lipoprotein levels with hyperlipidemia and reducing risk of cardiovascular events in people with end-stage renal disease and other conditions. It also has been used in people with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, PTSD, substance disorders, and Tourette syndrome.
“Some clinical research shows that taking NAC 900 mg daily for 4 weeks, followed by 900 mg twice daily for 4 weeks and then 900 mg three times daily for 4 weeks improves symptoms of irritability in children with autism,” Dr. Breuner said. Other research showed reduced irritability in children with autism when they took 1,200 mg of NAC daily with risperidone, compared with risperidone alone. One study also has found “that NAC adds to the effect of citalopram in improving resistance/control to compulsions in OCD children and adolescents” (Iran J Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;12[2]:134-141).
Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, and heartburn.
Omega-3 fatty acids: DHA and EHA
Docosahexanoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentanoic acid (EHA) have been used to treat ADHD, depression, heart disease, and also to lower the risk of macular degeneration.
A systematic review of 25 randomized controlled trials of more than 3,600 subjects found that “omega-3 supplementation generally correlated with improvements in blood biomarkers” (Nutrients. 2018 Aug 15;10[8]. pii: E1094). A small study in children with Tourette syndrome found that omega-3 fatty acids did not reduce tic scores, but “may be beneficial in reduction of tic-related impairment” for some children and teens (Pediatrics. 2012 Jun;129[6]:e1493-500).
Possible adverse effects include fishy taste, belching, nosebleeds, nausea, loose stools, and – at higher doses – decreased blood coagulation.
St. John’s wort
This herb has long been used to treat depression and appears to work by inhibiting serotonin reuptake, monoamine oxidase (MAO), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), dopamine, noradrenaline, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. A 2005 Cochrane review found St. John’s wort to work better than placebo with similar effectiveness as standard antidepressants for mild to moderate depression, but its benefit for major depression is questionable (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;[2]:CD000448).
An ideal dose is 300 mg daily, but physicians should be aware of the herb’s potential for certain drug interactions. It may increase metabolism of warfarin, cyclosporin, HIV protease inhibitors, theophylline, digoxin, and oral contraceptives (Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Jun;8[6]:691-708). Other potential side effects include decreased platelet aggregation, serotonin syndrome, and photosensitivity.
Turmeric (curcumin)
Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory agent used for a wide range of complaints, but research primarily has focused on its use for pain. No studies exist in children, but a handful of studies have found reduction in joint pain and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in adults with 500-mg doses twice daily (Phytother Res. 2012 Nov;26[11]:1719-25; J Med Food. 2017 Oct;20[10]:1022-30). One of these studies focused on a specific product, Instaflex, that contained turmeric among multiple other active ingredients (Nutr J. 2013 Nov 25;12[1]:154).
Potential adverse effects of turmeric/curcumin include constipation, dyspepsia, diarrhea, dissension, reflux, nausea, vomiting, itching, and hives.
Zinc
Like echinacea, zinc is commonly used to treat the common cold. A 2013 Cochrane review of randomized, controlled trials found that taking zinc “within 24 hours of onset of symptoms reduces the duration of common cold symptoms in healthy people, but some caution is needed due to the heterogeneity of the data” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 18;[6]:CD001364). The dose is 75 mg a day, and potential adverse effects include bad taste, nausea, and anosmia.
Dr. Breuner said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – With more than 10% of children receiving complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), you should be familiar with what does and doesn’t work when it comes to using supplements for various medical issues, said Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements with their uses and evidence at the American Academy of Pediatrics annual meeting. Most of the evidence comes from studies in adults, not children, and the evidence overall is sometimes scant, but it can guide physicians in discussing options with parents interested in CAM.
Butterbur
This root primarily is used to treat migraines via anti-inflammatory effects. The ideal dose is 50-75 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for children aged 8-9 years and 100-150 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for those aged 10 and older (Headache. 2005 Mar;45:196-203; Eur J Pain. 2008;12:301-13; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Adverse effects are mostly gastrointestinal, such as diarrhea and stomach upset, and dermal/allergic reactions, such as itchy eyes, asthma, and itching.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the most popular drug of choice for reducing drowsiness and increasing alertness and has the strongest evidence base, including for improving sports and work performance (J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Jan;24[1]:257-65). Regular caffeine use can lead to dependence, however, and it can cause anxiety, nervousness, irritability, insomnia, peptic ulcers, palpitations, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and tremors. Withdrawal can involve headaches, irritability, and anxiety.
Cannabidiol
Marijuana has more than 80 cannabinoids, and a nonpsychoactive one, cannabidiol, makes up about 40% of cannabis extracts, Dr. Breuner said. It’s been used as an anticonvulsant and to combat anxiety, psychosis, nausea and rheumatoid arthritis pain. In a study using a rat model for arthritis, inflammation and pain-related behaviors decreased in rats that received cannabidiol (Eur J Pain. 2016 Jul;20[6]:936-48).
A human dose would be about 160-300 mg daily, but side effects can include dry mouth, hypotension, lightheadedness, psychomotor slowing, sedation, and sleepiness.
Coenzyme Q10
This antioxidant is fat-soluble and has a chemical structure similar to vitamin K. It has been used in people with autism, chronic fatigue syndrome, fatigue from chemotherapy, Lyme disease, and muscular dystrophy, but the evidence focuses on fibromyalgia. One study of patients with fibromyalgia found that a 300-mg daily dose for 40 days reduced pain by 52%-56%, fatigue by 47%, morning tiredness by 56%, and tender points by 44%, compared with baseline (Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19[12]:1356-61.)
In another, 200 mg of coenzyme Q10 with 200 mg ginkgo daily for 3 months resulted in improvement of quality of life measures, including physical fitness levels, emotional feelings, social activities, overall health, and pain (J Int Med Res. 2002;30:195-9).
Potential adverse effects of coenzyme Q10 include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, appetite suppression, and heartburn, albeit typically in less than 1% of patients.
Echinacea
Echinacea actually is approved in Germany for supportive therapy in treating upper respiratory tract infections, urogenital infections, and wound healing, Dr. Breuner said. Hypothesized mechanisms of action include stimulation of the alternate complement pathway, immune-modulating effects, activating nonspecific T cells, inhibiting viral replication, and enhancing phagocytosis.
However, in clinical studies, echinacea did not reduce the duration or severity of upper respiratory tract infections or the occurrence or severity of infection, compared with placebo (JAMA. 2003 Dec 3;290[21]:2824-30; N Engl J Med. 2005 Jul 28;353[4]:341-8); this was tested in children aged 2-11 years in the first study, and the mean age of the subjects in the second study was 21 years. A 2014 Cochrane review found no overall benefits for treating common colds but noted the possibility of “a weak benefit from some echinacea products” based on individual trials with consistently positive, yet nonsignificant, trends, albeit with “questionable clinical relevance” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 20;[2]:CD000530).
People with autoimmune conditions or who are immunocompromised should not use echinacea.
Magnesium
Magnesium also is used to treat migraines with a dose of 300-500 mg daily, although also it can be consumed in food, such as soy beans, black beans, tofu, seeds, nuts, whole grains, and shellfish (Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Mar;9[3]:369-79; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Side effects can include diarrhea and interactions with bisphosphonates, antibiotics] and diuretics. Taking proton pump inhibitors also may reduce magnesium levels.
Melatonin
Melatonin, a synthetic version of the hormone produced in humans to signal the onset of nighttime, has been studied extensively for jet lag, insomnia, shift-work disorder, circadian rhythm disorders, and withdrawal from benzodiazepine and nicotine.
Research shows that melatonin can improve sleep onset, duration, and quality. Some research has shown increased total sleep time (PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63773).
Some evidence suggests it has endocrine-disrupting adverse effects, such as inhibiting ovulation and impairing glucose utilization.
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)
Although it’s primarily an antidote for acetaminophen and carbon monoxide poisoning, NAC has been used for a wide range of conditions, including reducing lipoprotein levels with hyperlipidemia and reducing risk of cardiovascular events in people with end-stage renal disease and other conditions. It also has been used in people with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, PTSD, substance disorders, and Tourette syndrome.
“Some clinical research shows that taking NAC 900 mg daily for 4 weeks, followed by 900 mg twice daily for 4 weeks and then 900 mg three times daily for 4 weeks improves symptoms of irritability in children with autism,” Dr. Breuner said. Other research showed reduced irritability in children with autism when they took 1,200 mg of NAC daily with risperidone, compared with risperidone alone. One study also has found “that NAC adds to the effect of citalopram in improving resistance/control to compulsions in OCD children and adolescents” (Iran J Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;12[2]:134-141).
Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, and heartburn.
Omega-3 fatty acids: DHA and EHA
Docosahexanoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentanoic acid (EHA) have been used to treat ADHD, depression, heart disease, and also to lower the risk of macular degeneration.
A systematic review of 25 randomized controlled trials of more than 3,600 subjects found that “omega-3 supplementation generally correlated with improvements in blood biomarkers” (Nutrients. 2018 Aug 15;10[8]. pii: E1094). A small study in children with Tourette syndrome found that omega-3 fatty acids did not reduce tic scores, but “may be beneficial in reduction of tic-related impairment” for some children and teens (Pediatrics. 2012 Jun;129[6]:e1493-500).
Possible adverse effects include fishy taste, belching, nosebleeds, nausea, loose stools, and – at higher doses – decreased blood coagulation.
St. John’s wort
This herb has long been used to treat depression and appears to work by inhibiting serotonin reuptake, monoamine oxidase (MAO), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), dopamine, noradrenaline, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. A 2005 Cochrane review found St. John’s wort to work better than placebo with similar effectiveness as standard antidepressants for mild to moderate depression, but its benefit for major depression is questionable (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;[2]:CD000448).
An ideal dose is 300 mg daily, but physicians should be aware of the herb’s potential for certain drug interactions. It may increase metabolism of warfarin, cyclosporin, HIV protease inhibitors, theophylline, digoxin, and oral contraceptives (Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Jun;8[6]:691-708). Other potential side effects include decreased platelet aggregation, serotonin syndrome, and photosensitivity.
Turmeric (curcumin)
Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory agent used for a wide range of complaints, but research primarily has focused on its use for pain. No studies exist in children, but a handful of studies have found reduction in joint pain and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in adults with 500-mg doses twice daily (Phytother Res. 2012 Nov;26[11]:1719-25; J Med Food. 2017 Oct;20[10]:1022-30). One of these studies focused on a specific product, Instaflex, that contained turmeric among multiple other active ingredients (Nutr J. 2013 Nov 25;12[1]:154).
Potential adverse effects of turmeric/curcumin include constipation, dyspepsia, diarrhea, dissension, reflux, nausea, vomiting, itching, and hives.
Zinc
Like echinacea, zinc is commonly used to treat the common cold. A 2013 Cochrane review of randomized, controlled trials found that taking zinc “within 24 hours of onset of symptoms reduces the duration of common cold symptoms in healthy people, but some caution is needed due to the heterogeneity of the data” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 18;[6]:CD001364). The dose is 75 mg a day, and potential adverse effects include bad taste, nausea, and anosmia.
Dr. Breuner said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – With more than 10% of children receiving complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), you should be familiar with what does and doesn’t work when it comes to using supplements for various medical issues, said Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements with their uses and evidence at the American Academy of Pediatrics annual meeting. Most of the evidence comes from studies in adults, not children, and the evidence overall is sometimes scant, but it can guide physicians in discussing options with parents interested in CAM.
Butterbur
This root primarily is used to treat migraines via anti-inflammatory effects. The ideal dose is 50-75 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for children aged 8-9 years and 100-150 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses for those aged 10 and older (Headache. 2005 Mar;45:196-203; Eur J Pain. 2008;12:301-13; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Adverse effects are mostly gastrointestinal, such as diarrhea and stomach upset, and dermal/allergic reactions, such as itchy eyes, asthma, and itching.
Caffeine
Caffeine is the most popular drug of choice for reducing drowsiness and increasing alertness and has the strongest evidence base, including for improving sports and work performance (J Strength Cond Res. 2010 Jan;24[1]:257-65). Regular caffeine use can lead to dependence, however, and it can cause anxiety, nervousness, irritability, insomnia, peptic ulcers, palpitations, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and tremors. Withdrawal can involve headaches, irritability, and anxiety.
Cannabidiol
Marijuana has more than 80 cannabinoids, and a nonpsychoactive one, cannabidiol, makes up about 40% of cannabis extracts, Dr. Breuner said. It’s been used as an anticonvulsant and to combat anxiety, psychosis, nausea and rheumatoid arthritis pain. In a study using a rat model for arthritis, inflammation and pain-related behaviors decreased in rats that received cannabidiol (Eur J Pain. 2016 Jul;20[6]:936-48).
A human dose would be about 160-300 mg daily, but side effects can include dry mouth, hypotension, lightheadedness, psychomotor slowing, sedation, and sleepiness.
Coenzyme Q10
This antioxidant is fat-soluble and has a chemical structure similar to vitamin K. It has been used in people with autism, chronic fatigue syndrome, fatigue from chemotherapy, Lyme disease, and muscular dystrophy, but the evidence focuses on fibromyalgia. One study of patients with fibromyalgia found that a 300-mg daily dose for 40 days reduced pain by 52%-56%, fatigue by 47%, morning tiredness by 56%, and tender points by 44%, compared with baseline (Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19[12]:1356-61.)
In another, 200 mg of coenzyme Q10 with 200 mg ginkgo daily for 3 months resulted in improvement of quality of life measures, including physical fitness levels, emotional feelings, social activities, overall health, and pain (J Int Med Res. 2002;30:195-9).
Potential adverse effects of coenzyme Q10 include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, appetite suppression, and heartburn, albeit typically in less than 1% of patients.
Echinacea
Echinacea actually is approved in Germany for supportive therapy in treating upper respiratory tract infections, urogenital infections, and wound healing, Dr. Breuner said. Hypothesized mechanisms of action include stimulation of the alternate complement pathway, immune-modulating effects, activating nonspecific T cells, inhibiting viral replication, and enhancing phagocytosis.
However, in clinical studies, echinacea did not reduce the duration or severity of upper respiratory tract infections or the occurrence or severity of infection, compared with placebo (JAMA. 2003 Dec 3;290[21]:2824-30; N Engl J Med. 2005 Jul 28;353[4]:341-8); this was tested in children aged 2-11 years in the first study, and the mean age of the subjects in the second study was 21 years. A 2014 Cochrane review found no overall benefits for treating common colds but noted the possibility of “a weak benefit from some echinacea products” based on individual trials with consistently positive, yet nonsignificant, trends, albeit with “questionable clinical relevance” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 20;[2]:CD000530).
People with autoimmune conditions or who are immunocompromised should not use echinacea.
Magnesium
Magnesium also is used to treat migraines with a dose of 300-500 mg daily, although also it can be consumed in food, such as soy beans, black beans, tofu, seeds, nuts, whole grains, and shellfish (Expert Rev Neurother. 2009 Mar;9[3]:369-79; Neurology. 2012 Apr 24;78[17]:1346-53).
Side effects can include diarrhea and interactions with bisphosphonates, antibiotics] and diuretics. Taking proton pump inhibitors also may reduce magnesium levels.
Melatonin
Melatonin, a synthetic version of the hormone produced in humans to signal the onset of nighttime, has been studied extensively for jet lag, insomnia, shift-work disorder, circadian rhythm disorders, and withdrawal from benzodiazepine and nicotine.
Research shows that melatonin can improve sleep onset, duration, and quality. Some research has shown increased total sleep time (PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63773).
Some evidence suggests it has endocrine-disrupting adverse effects, such as inhibiting ovulation and impairing glucose utilization.
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)
Although it’s primarily an antidote for acetaminophen and carbon monoxide poisoning, NAC has been used for a wide range of conditions, including reducing lipoprotein levels with hyperlipidemia and reducing risk of cardiovascular events in people with end-stage renal disease and other conditions. It also has been used in people with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, PTSD, substance disorders, and Tourette syndrome.
“Some clinical research shows that taking NAC 900 mg daily for 4 weeks, followed by 900 mg twice daily for 4 weeks and then 900 mg three times daily for 4 weeks improves symptoms of irritability in children with autism,” Dr. Breuner said. Other research showed reduced irritability in children with autism when they took 1,200 mg of NAC daily with risperidone, compared with risperidone alone. One study also has found “that NAC adds to the effect of citalopram in improving resistance/control to compulsions in OCD children and adolescents” (Iran J Psychiatry. 2017 Apr;12[2]:134-141).
Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, and heartburn.
Omega-3 fatty acids: DHA and EHA
Docosahexanoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentanoic acid (EHA) have been used to treat ADHD, depression, heart disease, and also to lower the risk of macular degeneration.
A systematic review of 25 randomized controlled trials of more than 3,600 subjects found that “omega-3 supplementation generally correlated with improvements in blood biomarkers” (Nutrients. 2018 Aug 15;10[8]. pii: E1094). A small study in children with Tourette syndrome found that omega-3 fatty acids did not reduce tic scores, but “may be beneficial in reduction of tic-related impairment” for some children and teens (Pediatrics. 2012 Jun;129[6]:e1493-500).
Possible adverse effects include fishy taste, belching, nosebleeds, nausea, loose stools, and – at higher doses – decreased blood coagulation.
St. John’s wort
This herb has long been used to treat depression and appears to work by inhibiting serotonin reuptake, monoamine oxidase (MAO), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), dopamine, noradrenaline, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. A 2005 Cochrane review found St. John’s wort to work better than placebo with similar effectiveness as standard antidepressants for mild to moderate depression, but its benefit for major depression is questionable (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;[2]:CD000448).
An ideal dose is 300 mg daily, but physicians should be aware of the herb’s potential for certain drug interactions. It may increase metabolism of warfarin, cyclosporin, HIV protease inhibitors, theophylline, digoxin, and oral contraceptives (Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Jun;8[6]:691-708). Other potential side effects include decreased platelet aggregation, serotonin syndrome, and photosensitivity.
Turmeric (curcumin)
Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory agent used for a wide range of complaints, but research primarily has focused on its use for pain. No studies exist in children, but a handful of studies have found reduction in joint pain and rheumatoid arthritis symptoms in adults with 500-mg doses twice daily (Phytother Res. 2012 Nov;26[11]:1719-25; J Med Food. 2017 Oct;20[10]:1022-30). One of these studies focused on a specific product, Instaflex, that contained turmeric among multiple other active ingredients (Nutr J. 2013 Nov 25;12[1]:154).
Potential adverse effects of turmeric/curcumin include constipation, dyspepsia, diarrhea, dissension, reflux, nausea, vomiting, itching, and hives.
Zinc
Like echinacea, zinc is commonly used to treat the common cold. A 2013 Cochrane review of randomized, controlled trials found that taking zinc “within 24 hours of onset of symptoms reduces the duration of common cold symptoms in healthy people, but some caution is needed due to the heterogeneity of the data” (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 18;[6]:CD001364). The dose is 75 mg a day, and potential adverse effects include bad taste, nausea, and anosmia.
Dr. Breuner said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 19
For pediatric use of supplements, rely on resources, evidence
NEW ORLEANS – More than 1 in 10 children (12%) have received complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), according to the 2012 National Health Interview Survey. It’s therefore vital that you are familiar with the options and evidence on these treatments, according to Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Use of CAM by a parent was strongly associated with the child’s use of CAM,” Dr. Breuner told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Parents of children using CAM were more likely to have a college education and to use prescription medication, the National Health Interview Survey found, and teens were more frequent users of CAM than infants.
The most common conditions treated in children with CAM were back and neck pain, colds, anxiety, stress, ADHD, insomnia, and general musculoskeletal conditions or complaints. Fish oil, melatonin, probiotics, and chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation were used more frequently than any other CAM treatments, but Dr. Breuner’s presentation focused specifically on supplements, including vitamins and herbs.
of how lax the law is when it comes to the safety and effectiveness of vitamins, minerals, herbs, and other dietary supplements.
“Products can go on the market with no testing of efficacy, and companies do not have to prove that their products are safe – only offer reasonable assurance of safety,” Dr. Breuner explained. “Supplements do not have to be manufactured to any standards, and FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approval is not needed for package or marketing claims,” although the reputable manufacturers favor standards.
She cited a 2011 study of popular supplement products on the market that found 75% of them did not include key safety messages (BMC Med. 2011 Aug 9;9:94). The study focused on St. John’s wort, ginkgo, ginseng, garlic, and echinacea products, and it’s likely other products lack such safety information as well. Yet researchers have identified a wide range of potential adverse effects from herbal medicines (Clin Med [Lond]. 2013 Feb;13[1]:7-12).
Physicians and consumers can rely on a handful of voluntary standards and online databases to guide therapeutic decisions and learn more about the evidence on specific products. The U.S. Pharmacopeia Dietary Supplement Verification Program is a seal consumers can look for on supplement products that indicates the product meets stricter standards than what the FDA allows.
Other resources include ConsumerLab.com, the Natural Medicines Research Collaboration, and the Pubmed Dietary Supplement Subset database from the National Institute of Medicine. The latter contains more than 676,000 unique scientific citations on published studies about vitamins, minerals, and botanicals, Dr. Breuner said.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements that included their uses and the evidence related to their use. Although not exhaustive, her list included the most common supplements for which some research has been done: butterbur, caffeine, cannabidiol, coenzyme Q10, echinacea, magnesium, melatonin, N-acetylcysteine, omega 3 fatty acids, St. John’s wort, turmeric (curcumin), and zinc.
The findings from these studies, however, vary greatly, and the studies themselves are often small and limited to adults. Shared decision making is key in working with families interested in using CAM, and families should be aware that supplements can have side effects just as FDA-approved drugs do.
Dr. Breuner reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – More than 1 in 10 children (12%) have received complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), according to the 2012 National Health Interview Survey. It’s therefore vital that you are familiar with the options and evidence on these treatments, according to Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Use of CAM by a parent was strongly associated with the child’s use of CAM,” Dr. Breuner told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Parents of children using CAM were more likely to have a college education and to use prescription medication, the National Health Interview Survey found, and teens were more frequent users of CAM than infants.
The most common conditions treated in children with CAM were back and neck pain, colds, anxiety, stress, ADHD, insomnia, and general musculoskeletal conditions or complaints. Fish oil, melatonin, probiotics, and chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation were used more frequently than any other CAM treatments, but Dr. Breuner’s presentation focused specifically on supplements, including vitamins and herbs.
of how lax the law is when it comes to the safety and effectiveness of vitamins, minerals, herbs, and other dietary supplements.
“Products can go on the market with no testing of efficacy, and companies do not have to prove that their products are safe – only offer reasonable assurance of safety,” Dr. Breuner explained. “Supplements do not have to be manufactured to any standards, and FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approval is not needed for package or marketing claims,” although the reputable manufacturers favor standards.
She cited a 2011 study of popular supplement products on the market that found 75% of them did not include key safety messages (BMC Med. 2011 Aug 9;9:94). The study focused on St. John’s wort, ginkgo, ginseng, garlic, and echinacea products, and it’s likely other products lack such safety information as well. Yet researchers have identified a wide range of potential adverse effects from herbal medicines (Clin Med [Lond]. 2013 Feb;13[1]:7-12).
Physicians and consumers can rely on a handful of voluntary standards and online databases to guide therapeutic decisions and learn more about the evidence on specific products. The U.S. Pharmacopeia Dietary Supplement Verification Program is a seal consumers can look for on supplement products that indicates the product meets stricter standards than what the FDA allows.
Other resources include ConsumerLab.com, the Natural Medicines Research Collaboration, and the Pubmed Dietary Supplement Subset database from the National Institute of Medicine. The latter contains more than 676,000 unique scientific citations on published studies about vitamins, minerals, and botanicals, Dr. Breuner said.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements that included their uses and the evidence related to their use. Although not exhaustive, her list included the most common supplements for which some research has been done: butterbur, caffeine, cannabidiol, coenzyme Q10, echinacea, magnesium, melatonin, N-acetylcysteine, omega 3 fatty acids, St. John’s wort, turmeric (curcumin), and zinc.
The findings from these studies, however, vary greatly, and the studies themselves are often small and limited to adults. Shared decision making is key in working with families interested in using CAM, and families should be aware that supplements can have side effects just as FDA-approved drugs do.
Dr. Breuner reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – More than 1 in 10 children (12%) have received complementary or alternative medicine (CAM), according to the 2012 National Health Interview Survey. It’s therefore vital that you are familiar with the options and evidence on these treatments, according to Cora Breuner, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington, Seattle, and attending physician at Seattle Children’s Hospital.
“Use of CAM by a parent was strongly associated with the child’s use of CAM,” Dr. Breuner told attendees at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics. Parents of children using CAM were more likely to have a college education and to use prescription medication, the National Health Interview Survey found, and teens were more frequent users of CAM than infants.
The most common conditions treated in children with CAM were back and neck pain, colds, anxiety, stress, ADHD, insomnia, and general musculoskeletal conditions or complaints. Fish oil, melatonin, probiotics, and chiropractic and osteopathic manipulation were used more frequently than any other CAM treatments, but Dr. Breuner’s presentation focused specifically on supplements, including vitamins and herbs.
of how lax the law is when it comes to the safety and effectiveness of vitamins, minerals, herbs, and other dietary supplements.
“Products can go on the market with no testing of efficacy, and companies do not have to prove that their products are safe – only offer reasonable assurance of safety,” Dr. Breuner explained. “Supplements do not have to be manufactured to any standards, and FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approval is not needed for package or marketing claims,” although the reputable manufacturers favor standards.
She cited a 2011 study of popular supplement products on the market that found 75% of them did not include key safety messages (BMC Med. 2011 Aug 9;9:94). The study focused on St. John’s wort, ginkgo, ginseng, garlic, and echinacea products, and it’s likely other products lack such safety information as well. Yet researchers have identified a wide range of potential adverse effects from herbal medicines (Clin Med [Lond]. 2013 Feb;13[1]:7-12).
Physicians and consumers can rely on a handful of voluntary standards and online databases to guide therapeutic decisions and learn more about the evidence on specific products. The U.S. Pharmacopeia Dietary Supplement Verification Program is a seal consumers can look for on supplement products that indicates the product meets stricter standards than what the FDA allows.
Other resources include ConsumerLab.com, the Natural Medicines Research Collaboration, and the Pubmed Dietary Supplement Subset database from the National Institute of Medicine. The latter contains more than 676,000 unique scientific citations on published studies about vitamins, minerals, and botanicals, Dr. Breuner said.
Dr. Breuner presented an overview of more than a dozen popular supplements that included their uses and the evidence related to their use. Although not exhaustive, her list included the most common supplements for which some research has been done: butterbur, caffeine, cannabidiol, coenzyme Q10, echinacea, magnesium, melatonin, N-acetylcysteine, omega 3 fatty acids, St. John’s wort, turmeric (curcumin), and zinc.
The findings from these studies, however, vary greatly, and the studies themselves are often small and limited to adults. Shared decision making is key in working with families interested in using CAM, and families should be aware that supplements can have side effects just as FDA-approved drugs do.
Dr. Breuner reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 19
Dietary flavonol intake linked to reduced risk of Alzheimer’s
Onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) was inversely associated with intake of flavonols, a subclass of flavonoids with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, according to the study authors.
The rate of developing AD was reduced by 50% among individuals reporting high intake of kaempferol, a flavonol plentiful in leafy green vegetables, and by 38% for high intake of the flavonols myricetin and isorhamnetin, researchers said in a report published in Neurology.
The findings are from the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP), a large, prospective study of older individuals in retirement communities and public housing in the Chicago area that has been ongoing since 1997.
“Although there is more work to be done, the associations that we observed are promising and deserve further study,” said Thomas M. Holland, MD, of the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging in Chicago, and coauthors.
Those associations between flavonol intake and AD help set the stage for U.S. POINTER and other randomized, controlled trials that seek to evaluate the effects of dietary interventions in a more rigorous way, according to Laura D. Baker, PhD, associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“This kind of data helps us feel like we are looking in the right direction in the randomized, controlled trials,” Dr. Baker said in an interview.
Dr. Baker is an investigator in the U.S. POINTER study, which will in part evaluate the impact of the MIND diet, which has been shown to slow cognitive decline with age in a previously published MAP study.
However, in the absence of randomized, controlled trial data, Dr. Baker cautioned against “prematurely advocating” for specific dietary approaches when speaking to patients and caregivers now.
“What I say is, we know for sure that the standard American Heart Association diet has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of heart disease, and in terms of brain health, if you can reduce risk of heart disease, you are protecting your brain,” she said in the interview.
The present MAP study linking a reduced rate of AD to flavonol consumption is believed to be the first of its kind, though two previous studies from the early 2000s did find inverse associations between incident AD and intake of flavonoids, of which flavonoids are just one subclass, said Dr. Holland and coinvestigators in their report.
Moreover, in a MAP study published in 2018, Martha Clare Morris, ScD, and coauthors concluded that consuming about a serving per day of green leafy vegetables and foods rich in kaempferol, among other nutrients and bioactive compounds, may help slow cognitive decline associated with aging.
To more specifically study the relationship between kaempferol and other flavonols and the development of AD, Dr. Holland and colleagues evaluated data for MAP participants who had completed a comprehensive food frequency questionnaire and underwent at least two evaluations to assess incidence of disease.
The mean age of the 921 individuals in the present analysis was 81 years, three-quarters were female, and over approximately 6 years of follow-up, 220 developed AD.
The rate of developing AD was 48% lower among participants reporting the highest total dietary intake of flavonols, compared with those reporting the lowest intake, Dr. Holland and coauthors reported.
Intake of the specific flavonols kaempferol, myricetin, and isorhamnetin were associated with incident AD reductions of 50%, 38%, and 38%, respectively. Another flavonol, quercetin, was by contrast not inversely associated with incident AD, according to the report.
Kaempferol was independently associated with AD in subsequent analyses, while there was no such independent association for myricetin, isorhamnetin, or quercetin, according to Dr. Holland and coinvestigators.
Further analyses of the data suggested the linkages between flavonols and AD were independent of lifestyle factors, dietary intakes, or cardiovascular conditions, they said in their report.
“Confirmation of these findings is warranted through other longitudinal epidemiologic studies and clinical trials, in addition to further elucidation of the biologic mechanisms,” they concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the USDA Agricultural Research Service. Dr. Holland and coauthors said that they had no disclosures relevant to their report.
SOURCE: Holland TM et al. Neurology. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008981.
Onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) was inversely associated with intake of flavonols, a subclass of flavonoids with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, according to the study authors.
The rate of developing AD was reduced by 50% among individuals reporting high intake of kaempferol, a flavonol plentiful in leafy green vegetables, and by 38% for high intake of the flavonols myricetin and isorhamnetin, researchers said in a report published in Neurology.
The findings are from the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP), a large, prospective study of older individuals in retirement communities and public housing in the Chicago area that has been ongoing since 1997.
“Although there is more work to be done, the associations that we observed are promising and deserve further study,” said Thomas M. Holland, MD, of the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging in Chicago, and coauthors.
Those associations between flavonol intake and AD help set the stage for U.S. POINTER and other randomized, controlled trials that seek to evaluate the effects of dietary interventions in a more rigorous way, according to Laura D. Baker, PhD, associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“This kind of data helps us feel like we are looking in the right direction in the randomized, controlled trials,” Dr. Baker said in an interview.
Dr. Baker is an investigator in the U.S. POINTER study, which will in part evaluate the impact of the MIND diet, which has been shown to slow cognitive decline with age in a previously published MAP study.
However, in the absence of randomized, controlled trial data, Dr. Baker cautioned against “prematurely advocating” for specific dietary approaches when speaking to patients and caregivers now.
“What I say is, we know for sure that the standard American Heart Association diet has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of heart disease, and in terms of brain health, if you can reduce risk of heart disease, you are protecting your brain,” she said in the interview.
The present MAP study linking a reduced rate of AD to flavonol consumption is believed to be the first of its kind, though two previous studies from the early 2000s did find inverse associations between incident AD and intake of flavonoids, of which flavonoids are just one subclass, said Dr. Holland and coinvestigators in their report.
Moreover, in a MAP study published in 2018, Martha Clare Morris, ScD, and coauthors concluded that consuming about a serving per day of green leafy vegetables and foods rich in kaempferol, among other nutrients and bioactive compounds, may help slow cognitive decline associated with aging.
To more specifically study the relationship between kaempferol and other flavonols and the development of AD, Dr. Holland and colleagues evaluated data for MAP participants who had completed a comprehensive food frequency questionnaire and underwent at least two evaluations to assess incidence of disease.
The mean age of the 921 individuals in the present analysis was 81 years, three-quarters were female, and over approximately 6 years of follow-up, 220 developed AD.
The rate of developing AD was 48% lower among participants reporting the highest total dietary intake of flavonols, compared with those reporting the lowest intake, Dr. Holland and coauthors reported.
Intake of the specific flavonols kaempferol, myricetin, and isorhamnetin were associated with incident AD reductions of 50%, 38%, and 38%, respectively. Another flavonol, quercetin, was by contrast not inversely associated with incident AD, according to the report.
Kaempferol was independently associated with AD in subsequent analyses, while there was no such independent association for myricetin, isorhamnetin, or quercetin, according to Dr. Holland and coinvestigators.
Further analyses of the data suggested the linkages between flavonols and AD were independent of lifestyle factors, dietary intakes, or cardiovascular conditions, they said in their report.
“Confirmation of these findings is warranted through other longitudinal epidemiologic studies and clinical trials, in addition to further elucidation of the biologic mechanisms,” they concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the USDA Agricultural Research Service. Dr. Holland and coauthors said that they had no disclosures relevant to their report.
SOURCE: Holland TM et al. Neurology. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008981.
Onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) was inversely associated with intake of flavonols, a subclass of flavonoids with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, according to the study authors.
The rate of developing AD was reduced by 50% among individuals reporting high intake of kaempferol, a flavonol plentiful in leafy green vegetables, and by 38% for high intake of the flavonols myricetin and isorhamnetin, researchers said in a report published in Neurology.
The findings are from the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP), a large, prospective study of older individuals in retirement communities and public housing in the Chicago area that has been ongoing since 1997.
“Although there is more work to be done, the associations that we observed are promising and deserve further study,” said Thomas M. Holland, MD, of the Rush Institute for Healthy Aging in Chicago, and coauthors.
Those associations between flavonol intake and AD help set the stage for U.S. POINTER and other randomized, controlled trials that seek to evaluate the effects of dietary interventions in a more rigorous way, according to Laura D. Baker, PhD, associate professor of internal medicine at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“This kind of data helps us feel like we are looking in the right direction in the randomized, controlled trials,” Dr. Baker said in an interview.
Dr. Baker is an investigator in the U.S. POINTER study, which will in part evaluate the impact of the MIND diet, which has been shown to slow cognitive decline with age in a previously published MAP study.
However, in the absence of randomized, controlled trial data, Dr. Baker cautioned against “prematurely advocating” for specific dietary approaches when speaking to patients and caregivers now.
“What I say is, we know for sure that the standard American Heart Association diet has been shown in clinical trials to reduce the risk of heart disease, and in terms of brain health, if you can reduce risk of heart disease, you are protecting your brain,” she said in the interview.
The present MAP study linking a reduced rate of AD to flavonol consumption is believed to be the first of its kind, though two previous studies from the early 2000s did find inverse associations between incident AD and intake of flavonoids, of which flavonoids are just one subclass, said Dr. Holland and coinvestigators in their report.
Moreover, in a MAP study published in 2018, Martha Clare Morris, ScD, and coauthors concluded that consuming about a serving per day of green leafy vegetables and foods rich in kaempferol, among other nutrients and bioactive compounds, may help slow cognitive decline associated with aging.
To more specifically study the relationship between kaempferol and other flavonols and the development of AD, Dr. Holland and colleagues evaluated data for MAP participants who had completed a comprehensive food frequency questionnaire and underwent at least two evaluations to assess incidence of disease.
The mean age of the 921 individuals in the present analysis was 81 years, three-quarters were female, and over approximately 6 years of follow-up, 220 developed AD.
The rate of developing AD was 48% lower among participants reporting the highest total dietary intake of flavonols, compared with those reporting the lowest intake, Dr. Holland and coauthors reported.
Intake of the specific flavonols kaempferol, myricetin, and isorhamnetin were associated with incident AD reductions of 50%, 38%, and 38%, respectively. Another flavonol, quercetin, was by contrast not inversely associated with incident AD, according to the report.
Kaempferol was independently associated with AD in subsequent analyses, while there was no such independent association for myricetin, isorhamnetin, or quercetin, according to Dr. Holland and coinvestigators.
Further analyses of the data suggested the linkages between flavonols and AD were independent of lifestyle factors, dietary intakes, or cardiovascular conditions, they said in their report.
“Confirmation of these findings is warranted through other longitudinal epidemiologic studies and clinical trials, in addition to further elucidation of the biologic mechanisms,” they concluded.
The study was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and the USDA Agricultural Research Service. Dr. Holland and coauthors said that they had no disclosures relevant to their report.
SOURCE: Holland TM et al. Neurology. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008981.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Celecoxib oral solution treats migraine effectively in randomized trial
, according to trial results published in the January issue of Headache.
Two hours after treatment, a significantly greater proportion of patients who received the liquid solution, known as DFN-15, had freedom from pain and freedom from their most bothersome accompanying symptom – nausea, photophobia, or phonophobia – compared with patients who received placebo. The pain freedom rates were 35.6% with celecoxib oral solution and 21.7% with placebo. The rates of freedom from the most bothersome symptom were 57.8% with celecoxib oral solution and 44.8% with placebo.
About 9% of patients who received celecoxib oral solution had treatment-emergent adverse events related to the study drug, the most common of which were dysgeusia (4.2%) and nausea (3.2%). In comparison, about 6% of patients who received placebo had treatment-emergent adverse events. There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events.
“DFN‐15 has the potential to become a reliable and convenient acute therapeutic option for patients with migraine,” said lead author Richard B. Lipton, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Lipton is affiliated with the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Assessing celecoxib in migraineurs
Evidence-based guidelines recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen, as effective acute migraine treatments, but these medications may increase the risk of adverse gastrointestinal events, the authors said. Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of acute pain in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, and rheumatoid arthritis. Although it produces analgesia similar to other NSAIDs, among patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, celecoxib is associated with significantly lower risk of gastrointestinal events, compared with naproxen and ibuprofen, and significantly lower risk of renal events, compared with ibuprofen.
Researchers have studied an oral capsule form of celecoxib (Celebrex, Pfizer) as an acute treatment for migraine in an open-label study that compared celecoxib with naproxen sodium. “While preliminary results suggest comparable efficacy but better tolerability than widely used and guideline-recommended NSAIDs, celecoxib is not currently approved for migraine,” the authors said.
Compared with the oral capsule formulation, the oral liquid solution DFN-15 has a faster median time to peak concentration under fasting conditions (within 1 hour vs. 2.5 hours), which “could translate into more rapid onset of pain relief,” the authors said. In addition, DFN-15 may have greater bioavailability, which could lower dose requirements and improve safety and tolerability. To compare the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of 120-mg DFN-15 with placebo for the acute treatment of migraine, researchers conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Participants used single-dose bottles
Researchers randomized 622 patients 1:1 to DFN-15 or placebo, and 567 treated a migraine during the trial. Patients had a mean age of 40 years, and 87% were female. Patients had episodic migraine with or without aura, no signs of medication overuse, and two-eight migraine attacks per month. For the trial, patients treated a single migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity within 1 hour of onset. “Each subject was given a single‐dose bottle of DFN‐15 120 mg or matching placebo containing 4.8 mL liquid,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said. “They were instructed to drink the entire contents of the bottle to ensure complete consumption of study medication.”
Freedom from pain and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours were the coprimary endpoints. “DFN‐15 was also significantly superior to placebo on multiple secondary 2‐hour endpoints, including freedom from photophobia, pain relief, change in functional disability from baseline, overall and 24‐hour satisfaction with treatment, and use of rescue medication,” they reported.
“A new COX‐2 inhibitor that is effective and rapidly absorbed could provide an important new option for a wide range of patients,” the authors said. “Though cross‐study comparisons are problematic, the current results for DFN‐15 indicate that its efficacy is similar to that of NSAIDs and small‐molecule calcitonin gene‐related peptide receptor antagonists (gepants), based on placebo‐subtracted rates pain freedom in acute treatment trials (14%‐21%). DFN‐15 may also be useful among triptan users, who are at elevated risk of medication‐overuse headache and for whom TEAEs within 24 hours postdose are common. ... The form and delivery system of DFN‐15 – a ready‐to‐use solution in a 4.8‐mL single‐use bottle – may support patient adherence.”
The trial had robust placebo response rates, which may have been influenced by “the novelty of a ready‐made oral solution, which has not been previously tested for the acute treatment of migraine,” the authors noted. In addition, the trial does not address the treatment of mild pain or treatment across multiple attacks.
The trial was supported by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, manufacturer of DFN-15. Two authors are employed by and own stock in Dr. Reddy’s. Dr. Lipton and a coauthor disclosed research support from and consulting for Dr. Reddy’s.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2020;60(1):58-70. doi: 10.1111/head.13663.
, according to trial results published in the January issue of Headache.
Two hours after treatment, a significantly greater proportion of patients who received the liquid solution, known as DFN-15, had freedom from pain and freedom from their most bothersome accompanying symptom – nausea, photophobia, or phonophobia – compared with patients who received placebo. The pain freedom rates were 35.6% with celecoxib oral solution and 21.7% with placebo. The rates of freedom from the most bothersome symptom were 57.8% with celecoxib oral solution and 44.8% with placebo.
About 9% of patients who received celecoxib oral solution had treatment-emergent adverse events related to the study drug, the most common of which were dysgeusia (4.2%) and nausea (3.2%). In comparison, about 6% of patients who received placebo had treatment-emergent adverse events. There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events.
“DFN‐15 has the potential to become a reliable and convenient acute therapeutic option for patients with migraine,” said lead author Richard B. Lipton, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Lipton is affiliated with the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Assessing celecoxib in migraineurs
Evidence-based guidelines recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen, as effective acute migraine treatments, but these medications may increase the risk of adverse gastrointestinal events, the authors said. Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of acute pain in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, and rheumatoid arthritis. Although it produces analgesia similar to other NSAIDs, among patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, celecoxib is associated with significantly lower risk of gastrointestinal events, compared with naproxen and ibuprofen, and significantly lower risk of renal events, compared with ibuprofen.
Researchers have studied an oral capsule form of celecoxib (Celebrex, Pfizer) as an acute treatment for migraine in an open-label study that compared celecoxib with naproxen sodium. “While preliminary results suggest comparable efficacy but better tolerability than widely used and guideline-recommended NSAIDs, celecoxib is not currently approved for migraine,” the authors said.
Compared with the oral capsule formulation, the oral liquid solution DFN-15 has a faster median time to peak concentration under fasting conditions (within 1 hour vs. 2.5 hours), which “could translate into more rapid onset of pain relief,” the authors said. In addition, DFN-15 may have greater bioavailability, which could lower dose requirements and improve safety and tolerability. To compare the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of 120-mg DFN-15 with placebo for the acute treatment of migraine, researchers conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Participants used single-dose bottles
Researchers randomized 622 patients 1:1 to DFN-15 or placebo, and 567 treated a migraine during the trial. Patients had a mean age of 40 years, and 87% were female. Patients had episodic migraine with or without aura, no signs of medication overuse, and two-eight migraine attacks per month. For the trial, patients treated a single migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity within 1 hour of onset. “Each subject was given a single‐dose bottle of DFN‐15 120 mg or matching placebo containing 4.8 mL liquid,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said. “They were instructed to drink the entire contents of the bottle to ensure complete consumption of study medication.”
Freedom from pain and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours were the coprimary endpoints. “DFN‐15 was also significantly superior to placebo on multiple secondary 2‐hour endpoints, including freedom from photophobia, pain relief, change in functional disability from baseline, overall and 24‐hour satisfaction with treatment, and use of rescue medication,” they reported.
“A new COX‐2 inhibitor that is effective and rapidly absorbed could provide an important new option for a wide range of patients,” the authors said. “Though cross‐study comparisons are problematic, the current results for DFN‐15 indicate that its efficacy is similar to that of NSAIDs and small‐molecule calcitonin gene‐related peptide receptor antagonists (gepants), based on placebo‐subtracted rates pain freedom in acute treatment trials (14%‐21%). DFN‐15 may also be useful among triptan users, who are at elevated risk of medication‐overuse headache and for whom TEAEs within 24 hours postdose are common. ... The form and delivery system of DFN‐15 – a ready‐to‐use solution in a 4.8‐mL single‐use bottle – may support patient adherence.”
The trial had robust placebo response rates, which may have been influenced by “the novelty of a ready‐made oral solution, which has not been previously tested for the acute treatment of migraine,” the authors noted. In addition, the trial does not address the treatment of mild pain or treatment across multiple attacks.
The trial was supported by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, manufacturer of DFN-15. Two authors are employed by and own stock in Dr. Reddy’s. Dr. Lipton and a coauthor disclosed research support from and consulting for Dr. Reddy’s.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2020;60(1):58-70. doi: 10.1111/head.13663.
, according to trial results published in the January issue of Headache.
Two hours after treatment, a significantly greater proportion of patients who received the liquid solution, known as DFN-15, had freedom from pain and freedom from their most bothersome accompanying symptom – nausea, photophobia, or phonophobia – compared with patients who received placebo. The pain freedom rates were 35.6% with celecoxib oral solution and 21.7% with placebo. The rates of freedom from the most bothersome symptom were 57.8% with celecoxib oral solution and 44.8% with placebo.
About 9% of patients who received celecoxib oral solution had treatment-emergent adverse events related to the study drug, the most common of which were dysgeusia (4.2%) and nausea (3.2%). In comparison, about 6% of patients who received placebo had treatment-emergent adverse events. There were no serious treatment-emergent adverse events.
“DFN‐15 has the potential to become a reliable and convenient acute therapeutic option for patients with migraine,” said lead author Richard B. Lipton, MD, and colleagues. Dr. Lipton is affiliated with the Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Assessing celecoxib in migraineurs
Evidence-based guidelines recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and naproxen, as effective acute migraine treatments, but these medications may increase the risk of adverse gastrointestinal events, the authors said. Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, is indicated for the treatment of acute pain in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, and rheumatoid arthritis. Although it produces analgesia similar to other NSAIDs, among patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, celecoxib is associated with significantly lower risk of gastrointestinal events, compared with naproxen and ibuprofen, and significantly lower risk of renal events, compared with ibuprofen.
Researchers have studied an oral capsule form of celecoxib (Celebrex, Pfizer) as an acute treatment for migraine in an open-label study that compared celecoxib with naproxen sodium. “While preliminary results suggest comparable efficacy but better tolerability than widely used and guideline-recommended NSAIDs, celecoxib is not currently approved for migraine,” the authors said.
Compared with the oral capsule formulation, the oral liquid solution DFN-15 has a faster median time to peak concentration under fasting conditions (within 1 hour vs. 2.5 hours), which “could translate into more rapid onset of pain relief,” the authors said. In addition, DFN-15 may have greater bioavailability, which could lower dose requirements and improve safety and tolerability. To compare the efficacy, tolerability, and safety of 120-mg DFN-15 with placebo for the acute treatment of migraine, researchers conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Participants used single-dose bottles
Researchers randomized 622 patients 1:1 to DFN-15 or placebo, and 567 treated a migraine during the trial. Patients had a mean age of 40 years, and 87% were female. Patients had episodic migraine with or without aura, no signs of medication overuse, and two-eight migraine attacks per month. For the trial, patients treated a single migraine attack of moderate to severe intensity within 1 hour of onset. “Each subject was given a single‐dose bottle of DFN‐15 120 mg or matching placebo containing 4.8 mL liquid,” Dr. Lipton and colleagues said. “They were instructed to drink the entire contents of the bottle to ensure complete consumption of study medication.”
Freedom from pain and freedom from the most bothersome symptom at 2 hours were the coprimary endpoints. “DFN‐15 was also significantly superior to placebo on multiple secondary 2‐hour endpoints, including freedom from photophobia, pain relief, change in functional disability from baseline, overall and 24‐hour satisfaction with treatment, and use of rescue medication,” they reported.
“A new COX‐2 inhibitor that is effective and rapidly absorbed could provide an important new option for a wide range of patients,” the authors said. “Though cross‐study comparisons are problematic, the current results for DFN‐15 indicate that its efficacy is similar to that of NSAIDs and small‐molecule calcitonin gene‐related peptide receptor antagonists (gepants), based on placebo‐subtracted rates pain freedom in acute treatment trials (14%‐21%). DFN‐15 may also be useful among triptan users, who are at elevated risk of medication‐overuse headache and for whom TEAEs within 24 hours postdose are common. ... The form and delivery system of DFN‐15 – a ready‐to‐use solution in a 4.8‐mL single‐use bottle – may support patient adherence.”
The trial had robust placebo response rates, which may have been influenced by “the novelty of a ready‐made oral solution, which has not been previously tested for the acute treatment of migraine,” the authors noted. In addition, the trial does not address the treatment of mild pain or treatment across multiple attacks.
The trial was supported by Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, manufacturer of DFN-15. Two authors are employed by and own stock in Dr. Reddy’s. Dr. Lipton and a coauthor disclosed research support from and consulting for Dr. Reddy’s.
SOURCE: Lipton RB et al. Headache. 2020;60(1):58-70. doi: 10.1111/head.13663.
FROM HEADACHE
Genetic factor linked to impaired memory after heading many soccer balls
according to authors of a recent longitudinal study. Worse verbal memory was linked to high levels of ball heading among those players who were APOE e4–positive, compared with those who were APOE e4–negative, according to the authors, led by Liane E. Hunter, PhD, of the Gruss Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
These findings, while preliminary, do raise the possibility that “safe levels for soccer heading” could be proposed to protect players from harm or that APOE e4-positive players might be advised to limit their exposure to head impacts, Dr. Hunter and coauthors wrote in a report in JAMA Neurology.
However, the findings should “in no way” be used to justify APOE testing to make clinical decisions regarding the safety of playing soccer, said Sarah J. Banks, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and Jesse Mez, MD, of Boston University in a related editorial (doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4451). “Like most good science, the study provides an important, but incremental, step to understanding gene-environment interactions in sports,” Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez wrote in their editorial.
While there are some studies tying APOE e4 to poorer neuropsychiatric performance in boxers and U.S. football players, there are no such studies looking at the role of APOE e4 in soccer players exposed to repetitive “subconcussive” ball heading, according to Dr. Hunter and coresearchers. Accordingly, they sought to analyze APOE e4 and neuropsychological performance in relation to ball heading in 352 adult amateur soccer players enrolled in the Einstein Soccer Study between November 2013 and January 2018. About three-quarters of the players were male, and the median age at enrollment was 23 years.
The players completed a computer-based questionnaire designed to estimate their exposure to soccer heading at enrollment and at follow-up visits every 3-6 months. To test verbal memory at each visit, players were asked to memorize a 12-item grocery list, and then asked to recall the items 20 minutes later.
High levels of heading were linked to poorer performance on the verbal memory task, similar to one previously reported study, investigators said.
There was no association overall of APOE e4 and heading with performance on the shopping list task, according to investigators. By contrast, there was a 4.1-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high heading exposure, compared with those with low exposure, investigators reported. Likewise, there was an 8.5-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high versus moderate heading exposure.
That said, the absolute difference in performance was “subtle” and difficult to interpret in the context of a cross-sectional study, Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez said in their editorial.
In absolute terms, the mean decrease in scores on the 13-point shopping list task between the high and low heading exposure was 1.13 points greater for the APOE e4–positive group, compared with the APOE e4–negative group, and the decrease between the high and moderate heading exposure groups was 0.98 points greater, according to the report.
“The effect size of our interaction is relatively small,” Dr. Hunter and colleagues acknowledged in their report. “However, similar to the widely cited model of disease evolution in Alzheimer disease, our findings may be evidence of early subclinical effects, which could accumulate in APOE e4–positive players over a protracted time frame and ultimately be associated with overt clinical dysfunction.”
Several study authors said they had received grants from the National Institutes of Health and affiliated institutes, the Migraine Research Foundation, and the National Headache Foundation. They reported disclosures related to Amgen, Avanir, Biohaven Holdings, Biovision, Boston Scientific, Eli Lilly, eNeura Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter LE et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4828.
according to authors of a recent longitudinal study. Worse verbal memory was linked to high levels of ball heading among those players who were APOE e4–positive, compared with those who were APOE e4–negative, according to the authors, led by Liane E. Hunter, PhD, of the Gruss Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
These findings, while preliminary, do raise the possibility that “safe levels for soccer heading” could be proposed to protect players from harm or that APOE e4-positive players might be advised to limit their exposure to head impacts, Dr. Hunter and coauthors wrote in a report in JAMA Neurology.
However, the findings should “in no way” be used to justify APOE testing to make clinical decisions regarding the safety of playing soccer, said Sarah J. Banks, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and Jesse Mez, MD, of Boston University in a related editorial (doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4451). “Like most good science, the study provides an important, but incremental, step to understanding gene-environment interactions in sports,” Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez wrote in their editorial.
While there are some studies tying APOE e4 to poorer neuropsychiatric performance in boxers and U.S. football players, there are no such studies looking at the role of APOE e4 in soccer players exposed to repetitive “subconcussive” ball heading, according to Dr. Hunter and coresearchers. Accordingly, they sought to analyze APOE e4 and neuropsychological performance in relation to ball heading in 352 adult amateur soccer players enrolled in the Einstein Soccer Study between November 2013 and January 2018. About three-quarters of the players were male, and the median age at enrollment was 23 years.
The players completed a computer-based questionnaire designed to estimate their exposure to soccer heading at enrollment and at follow-up visits every 3-6 months. To test verbal memory at each visit, players were asked to memorize a 12-item grocery list, and then asked to recall the items 20 minutes later.
High levels of heading were linked to poorer performance on the verbal memory task, similar to one previously reported study, investigators said.
There was no association overall of APOE e4 and heading with performance on the shopping list task, according to investigators. By contrast, there was a 4.1-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high heading exposure, compared with those with low exposure, investigators reported. Likewise, there was an 8.5-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high versus moderate heading exposure.
That said, the absolute difference in performance was “subtle” and difficult to interpret in the context of a cross-sectional study, Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez said in their editorial.
In absolute terms, the mean decrease in scores on the 13-point shopping list task between the high and low heading exposure was 1.13 points greater for the APOE e4–positive group, compared with the APOE e4–negative group, and the decrease between the high and moderate heading exposure groups was 0.98 points greater, according to the report.
“The effect size of our interaction is relatively small,” Dr. Hunter and colleagues acknowledged in their report. “However, similar to the widely cited model of disease evolution in Alzheimer disease, our findings may be evidence of early subclinical effects, which could accumulate in APOE e4–positive players over a protracted time frame and ultimately be associated with overt clinical dysfunction.”
Several study authors said they had received grants from the National Institutes of Health and affiliated institutes, the Migraine Research Foundation, and the National Headache Foundation. They reported disclosures related to Amgen, Avanir, Biohaven Holdings, Biovision, Boston Scientific, Eli Lilly, eNeura Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter LE et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4828.
according to authors of a recent longitudinal study. Worse verbal memory was linked to high levels of ball heading among those players who were APOE e4–positive, compared with those who were APOE e4–negative, according to the authors, led by Liane E. Hunter, PhD, of the Gruss Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
These findings, while preliminary, do raise the possibility that “safe levels for soccer heading” could be proposed to protect players from harm or that APOE e4-positive players might be advised to limit their exposure to head impacts, Dr. Hunter and coauthors wrote in a report in JAMA Neurology.
However, the findings should “in no way” be used to justify APOE testing to make clinical decisions regarding the safety of playing soccer, said Sarah J. Banks, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and Jesse Mez, MD, of Boston University in a related editorial (doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4451). “Like most good science, the study provides an important, but incremental, step to understanding gene-environment interactions in sports,” Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez wrote in their editorial.
While there are some studies tying APOE e4 to poorer neuropsychiatric performance in boxers and U.S. football players, there are no such studies looking at the role of APOE e4 in soccer players exposed to repetitive “subconcussive” ball heading, according to Dr. Hunter and coresearchers. Accordingly, they sought to analyze APOE e4 and neuropsychological performance in relation to ball heading in 352 adult amateur soccer players enrolled in the Einstein Soccer Study between November 2013 and January 2018. About three-quarters of the players were male, and the median age at enrollment was 23 years.
The players completed a computer-based questionnaire designed to estimate their exposure to soccer heading at enrollment and at follow-up visits every 3-6 months. To test verbal memory at each visit, players were asked to memorize a 12-item grocery list, and then asked to recall the items 20 minutes later.
High levels of heading were linked to poorer performance on the verbal memory task, similar to one previously reported study, investigators said.
There was no association overall of APOE e4 and heading with performance on the shopping list task, according to investigators. By contrast, there was a 4.1-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high heading exposure, compared with those with low exposure, investigators reported. Likewise, there was an 8.5-fold increased deficit in verbal memory for APOE e4–positive players with high versus moderate heading exposure.
That said, the absolute difference in performance was “subtle” and difficult to interpret in the context of a cross-sectional study, Dr. Banks and Dr. Mez said in their editorial.
In absolute terms, the mean decrease in scores on the 13-point shopping list task between the high and low heading exposure was 1.13 points greater for the APOE e4–positive group, compared with the APOE e4–negative group, and the decrease between the high and moderate heading exposure groups was 0.98 points greater, according to the report.
“The effect size of our interaction is relatively small,” Dr. Hunter and colleagues acknowledged in their report. “However, similar to the widely cited model of disease evolution in Alzheimer disease, our findings may be evidence of early subclinical effects, which could accumulate in APOE e4–positive players over a protracted time frame and ultimately be associated with overt clinical dysfunction.”
Several study authors said they had received grants from the National Institutes of Health and affiliated institutes, the Migraine Research Foundation, and the National Headache Foundation. They reported disclosures related to Amgen, Avanir, Biohaven Holdings, Biovision, Boston Scientific, Eli Lilly, eNeura Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Pfizer, among others.
SOURCE: Hunter LE et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4828.
FROM JAMA Neurology
Modafinil use in pregnancy tied to congenital malformations
Modafinil exposure during pregnancy was associated with an approximately tripled risk of congenital malformations in a large Danish registry-based study.
Modafinil (Provigil) is commonly prescribed to address daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and multiple sclerosis. An interim postmarketing safety analysis showed increased rates of major malformation in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, so the manufacturer issued an alert advising health care professionals of this safety signal in June 2019, wrote Per Damkier, MD, PhD, corresponding author of a JAMA research letter reporting the Danish study results. The postmarketing study had shown a major malformation rate of about 15% in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, much higher than the 3% background rate.
Dr. Damkier and Anne Broe, MD, PhD, both of the department of clinical biochemistry and pharmacology at Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, compared outcomes for pregnant women who were prescribed modafinil at any point during the first trimester of pregnancy with those who were prescribed an active comparator, methylphenidate, as well as with those who had neither exposure. Methylphenidate is not associated with congenital malformations and is used for indications similar to modafinil.
Looking at all pregnancies for whom complete records existed in Danish health registries between 2004 and 2017, the investigators found 49 modafinil-exposed pregnancies, 963 methylphenidate-exposed pregnancies, and 828,644 pregnancies with neither exposure.
Six major congenital malformations occurred in the modafinil-exposed group for an absolute risk of 12%. Major malformations occurred in 43 (4.5%) of the methylphenidate-exposed group and 32,466 (3.9%) of the unexposed group.
Using the extensive data available in public registries, the authors were able to perform logistic regression to adjust for concomitant use of other psychotropic medication; comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension; and demographic and anthropometric measures such as maternal age, smoking status, and body mass index.
After this statistical adjustment, the researchers found that modafinil exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy was associated with an odds ratio of 3.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-9.7) for major congenital malformation, compared with first-trimester methylphenidate exposure. Compared with the unexposed cohort, modafinil-exposed pregnancies had an adjusted odds ratio of 2.7 (95% CI, 1.1-6.9) for major congenital malformation.
A total of 13 (27%) women who took modafinil had multiple sclerosis, but the authors excluded women who’d received a prescription for the multiple sclerosis drug teriflunomide (Aubagio), a known teratogen. Sleep disorders were reported for 39% of modafinil users, compared with 4.5% of methylphenidate users. Rates of psychoactive drug use were 41% for the modafinil group and 30% for the methylphenidate group.
The authors acknowledged the possibility of residual confounders affecting their results, and of the statistical problems with the very small sample size of modafinil-exposed pregnancies. Also, actual medication use – rather than prescription redemption – wasn’t captured in the study.
The study was partially funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Damkier P, Broe A. JAMA. 2020;323(4):374-6.
Modafinil exposure during pregnancy was associated with an approximately tripled risk of congenital malformations in a large Danish registry-based study.
Modafinil (Provigil) is commonly prescribed to address daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and multiple sclerosis. An interim postmarketing safety analysis showed increased rates of major malformation in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, so the manufacturer issued an alert advising health care professionals of this safety signal in June 2019, wrote Per Damkier, MD, PhD, corresponding author of a JAMA research letter reporting the Danish study results. The postmarketing study had shown a major malformation rate of about 15% in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, much higher than the 3% background rate.
Dr. Damkier and Anne Broe, MD, PhD, both of the department of clinical biochemistry and pharmacology at Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, compared outcomes for pregnant women who were prescribed modafinil at any point during the first trimester of pregnancy with those who were prescribed an active comparator, methylphenidate, as well as with those who had neither exposure. Methylphenidate is not associated with congenital malformations and is used for indications similar to modafinil.
Looking at all pregnancies for whom complete records existed in Danish health registries between 2004 and 2017, the investigators found 49 modafinil-exposed pregnancies, 963 methylphenidate-exposed pregnancies, and 828,644 pregnancies with neither exposure.
Six major congenital malformations occurred in the modafinil-exposed group for an absolute risk of 12%. Major malformations occurred in 43 (4.5%) of the methylphenidate-exposed group and 32,466 (3.9%) of the unexposed group.
Using the extensive data available in public registries, the authors were able to perform logistic regression to adjust for concomitant use of other psychotropic medication; comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension; and demographic and anthropometric measures such as maternal age, smoking status, and body mass index.
After this statistical adjustment, the researchers found that modafinil exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy was associated with an odds ratio of 3.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-9.7) for major congenital malformation, compared with first-trimester methylphenidate exposure. Compared with the unexposed cohort, modafinil-exposed pregnancies had an adjusted odds ratio of 2.7 (95% CI, 1.1-6.9) for major congenital malformation.
A total of 13 (27%) women who took modafinil had multiple sclerosis, but the authors excluded women who’d received a prescription for the multiple sclerosis drug teriflunomide (Aubagio), a known teratogen. Sleep disorders were reported for 39% of modafinil users, compared with 4.5% of methylphenidate users. Rates of psychoactive drug use were 41% for the modafinil group and 30% for the methylphenidate group.
The authors acknowledged the possibility of residual confounders affecting their results, and of the statistical problems with the very small sample size of modafinil-exposed pregnancies. Also, actual medication use – rather than prescription redemption – wasn’t captured in the study.
The study was partially funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Damkier P, Broe A. JAMA. 2020;323(4):374-6.
Modafinil exposure during pregnancy was associated with an approximately tripled risk of congenital malformations in a large Danish registry-based study.
Modafinil (Provigil) is commonly prescribed to address daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and multiple sclerosis. An interim postmarketing safety analysis showed increased rates of major malformation in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, so the manufacturer issued an alert advising health care professionals of this safety signal in June 2019, wrote Per Damkier, MD, PhD, corresponding author of a JAMA research letter reporting the Danish study results. The postmarketing study had shown a major malformation rate of about 15% in modafinil-exposed pregnancies, much higher than the 3% background rate.
Dr. Damkier and Anne Broe, MD, PhD, both of the department of clinical biochemistry and pharmacology at Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, compared outcomes for pregnant women who were prescribed modafinil at any point during the first trimester of pregnancy with those who were prescribed an active comparator, methylphenidate, as well as with those who had neither exposure. Methylphenidate is not associated with congenital malformations and is used for indications similar to modafinil.
Looking at all pregnancies for whom complete records existed in Danish health registries between 2004 and 2017, the investigators found 49 modafinil-exposed pregnancies, 963 methylphenidate-exposed pregnancies, and 828,644 pregnancies with neither exposure.
Six major congenital malformations occurred in the modafinil-exposed group for an absolute risk of 12%. Major malformations occurred in 43 (4.5%) of the methylphenidate-exposed group and 32,466 (3.9%) of the unexposed group.
Using the extensive data available in public registries, the authors were able to perform logistic regression to adjust for concomitant use of other psychotropic medication; comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension; and demographic and anthropometric measures such as maternal age, smoking status, and body mass index.
After this statistical adjustment, the researchers found that modafinil exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy was associated with an odds ratio of 3.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-9.7) for major congenital malformation, compared with first-trimester methylphenidate exposure. Compared with the unexposed cohort, modafinil-exposed pregnancies had an adjusted odds ratio of 2.7 (95% CI, 1.1-6.9) for major congenital malformation.
A total of 13 (27%) women who took modafinil had multiple sclerosis, but the authors excluded women who’d received a prescription for the multiple sclerosis drug teriflunomide (Aubagio), a known teratogen. Sleep disorders were reported for 39% of modafinil users, compared with 4.5% of methylphenidate users. Rates of psychoactive drug use were 41% for the modafinil group and 30% for the methylphenidate group.
The authors acknowledged the possibility of residual confounders affecting their results, and of the statistical problems with the very small sample size of modafinil-exposed pregnancies. Also, actual medication use – rather than prescription redemption – wasn’t captured in the study.
The study was partially funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Damkier P, Broe A. JAMA. 2020;323(4):374-6.
FROM JAMA
BP levels during endovascular stroke therapy affect neurologic outcomes
For patients with acute ischemic stroke, prolonged durations of blood pressure above or below certain thresholds during endovascular therapy may be linked to poor functional outcome, results of a retrospective study suggest.
Mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) lower than 70 mm Hg for 10 minutes or more, or higher than 90 mm Hg for 45 minutes or more, represented “critical thresholds” associated with worse neurologic outcomes, the study authors wrote in JAMA Neurology.
“These results suggest MABP may be a modifiable therapeutic target to prevent or reduce poor functional outcome in patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke, and that MABP should possibly be maintained within such narrow limits, wrote the authors, led by Mads Rasmussen, MD, PhD, of the department of anesthesia at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital.
The findings come from an analysis of BP data from 365 patients with acute ischemic stroke enrolled in three randomized trials evaluating different strategies for anesthesia. Among those patients, the mean age was approximately 71 years, and about 45% were women.
The investigators looked at a variety of BP-related variables during endovascular therapy to assess their impact on functional outcome, based on modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 90 days.
Having an MABP below 70 mm Hg for a cumulative time of at least 10 minutes substantially increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores (odds ratio, 1.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-2.22), according to Dr. Rasmussen and colleagues. The number needed to harm (NNH) at this threshold was 10; in other words, to harm 1 patient, 10 patients are needed with procedural MABP below 70 mm Hg for at least 10 minutes.
Likewise, having an MABP above 90 mm Hg for a cumulated time of at least 45 minutes significantly increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores, with an OR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.02) and a number needed to harm of 10.
Odds of shifting toward a worse neurologic outcome increased by 62% for every continuous 10 minutes of MABP below 70 mm Hg, and by 8% for every continuous 10 minutes above 90 mm Hg.
The maximum MABP during the procedure was significantly associated with neurologic outcomes in the study, while by contrast, maximum procedural systolic BP was not, according to the investigators.
In general, the study findings suggest that MABP is “more sensitive” than systolic BP when assessing hypotension and hypertension in these patients. However, these findings are subject to a number of limitations, the investigators wrote, including the retrospective nature of the analysis and the selected group of patients enrolled in studies designed to evaluate anesthesia strategies, not hemodynamic management.
“Randomized studies are needed to determine the optimal blood pressure management strategy during endovascular therapy,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Rasmussen reported grant support from the Health Research Foundation of Central Denmark Region and the National Helicopter Emergency Medical Service Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grant support from the Novo Nordisk Foundation; a research award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and personal fees from Abbott Medical Sweden, I4L Innovation for Life, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Zoll.
SOURCE: Rasmussen M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4838.
For patients with acute ischemic stroke, prolonged durations of blood pressure above or below certain thresholds during endovascular therapy may be linked to poor functional outcome, results of a retrospective study suggest.
Mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) lower than 70 mm Hg for 10 minutes or more, or higher than 90 mm Hg for 45 minutes or more, represented “critical thresholds” associated with worse neurologic outcomes, the study authors wrote in JAMA Neurology.
“These results suggest MABP may be a modifiable therapeutic target to prevent or reduce poor functional outcome in patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke, and that MABP should possibly be maintained within such narrow limits, wrote the authors, led by Mads Rasmussen, MD, PhD, of the department of anesthesia at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital.
The findings come from an analysis of BP data from 365 patients with acute ischemic stroke enrolled in three randomized trials evaluating different strategies for anesthesia. Among those patients, the mean age was approximately 71 years, and about 45% were women.
The investigators looked at a variety of BP-related variables during endovascular therapy to assess their impact on functional outcome, based on modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 90 days.
Having an MABP below 70 mm Hg for a cumulative time of at least 10 minutes substantially increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores (odds ratio, 1.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-2.22), according to Dr. Rasmussen and colleagues. The number needed to harm (NNH) at this threshold was 10; in other words, to harm 1 patient, 10 patients are needed with procedural MABP below 70 mm Hg for at least 10 minutes.
Likewise, having an MABP above 90 mm Hg for a cumulated time of at least 45 minutes significantly increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores, with an OR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.02) and a number needed to harm of 10.
Odds of shifting toward a worse neurologic outcome increased by 62% for every continuous 10 minutes of MABP below 70 mm Hg, and by 8% for every continuous 10 minutes above 90 mm Hg.
The maximum MABP during the procedure was significantly associated with neurologic outcomes in the study, while by contrast, maximum procedural systolic BP was not, according to the investigators.
In general, the study findings suggest that MABP is “more sensitive” than systolic BP when assessing hypotension and hypertension in these patients. However, these findings are subject to a number of limitations, the investigators wrote, including the retrospective nature of the analysis and the selected group of patients enrolled in studies designed to evaluate anesthesia strategies, not hemodynamic management.
“Randomized studies are needed to determine the optimal blood pressure management strategy during endovascular therapy,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Rasmussen reported grant support from the Health Research Foundation of Central Denmark Region and the National Helicopter Emergency Medical Service Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grant support from the Novo Nordisk Foundation; a research award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and personal fees from Abbott Medical Sweden, I4L Innovation for Life, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Zoll.
SOURCE: Rasmussen M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4838.
For patients with acute ischemic stroke, prolonged durations of blood pressure above or below certain thresholds during endovascular therapy may be linked to poor functional outcome, results of a retrospective study suggest.
Mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) lower than 70 mm Hg for 10 minutes or more, or higher than 90 mm Hg for 45 minutes or more, represented “critical thresholds” associated with worse neurologic outcomes, the study authors wrote in JAMA Neurology.
“These results suggest MABP may be a modifiable therapeutic target to prevent or reduce poor functional outcome in patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke, and that MABP should possibly be maintained within such narrow limits, wrote the authors, led by Mads Rasmussen, MD, PhD, of the department of anesthesia at Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital.
The findings come from an analysis of BP data from 365 patients with acute ischemic stroke enrolled in three randomized trials evaluating different strategies for anesthesia. Among those patients, the mean age was approximately 71 years, and about 45% were women.
The investigators looked at a variety of BP-related variables during endovascular therapy to assess their impact on functional outcome, based on modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 90 days.
Having an MABP below 70 mm Hg for a cumulative time of at least 10 minutes substantially increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores (odds ratio, 1.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-2.22), according to Dr. Rasmussen and colleagues. The number needed to harm (NNH) at this threshold was 10; in other words, to harm 1 patient, 10 patients are needed with procedural MABP below 70 mm Hg for at least 10 minutes.
Likewise, having an MABP above 90 mm Hg for a cumulated time of at least 45 minutes significantly increased odds of higher 90-day mRS scores, with an OR of 1.49 (95% CI, 1.11-2.02) and a number needed to harm of 10.
Odds of shifting toward a worse neurologic outcome increased by 62% for every continuous 10 minutes of MABP below 70 mm Hg, and by 8% for every continuous 10 minutes above 90 mm Hg.
The maximum MABP during the procedure was significantly associated with neurologic outcomes in the study, while by contrast, maximum procedural systolic BP was not, according to the investigators.
In general, the study findings suggest that MABP is “more sensitive” than systolic BP when assessing hypotension and hypertension in these patients. However, these findings are subject to a number of limitations, the investigators wrote, including the retrospective nature of the analysis and the selected group of patients enrolled in studies designed to evaluate anesthesia strategies, not hemodynamic management.
“Randomized studies are needed to determine the optimal blood pressure management strategy during endovascular therapy,” the investigators wrote.
Dr. Rasmussen reported grant support from the Health Research Foundation of Central Denmark Region and the National Helicopter Emergency Medical Service Foundation. Coauthors reported receiving grant support from the Novo Nordisk Foundation; a research award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; and personal fees from Abbott Medical Sweden, I4L Innovation for Life, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and Zoll.
SOURCE: Rasmussen M et al. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 27. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4838.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Opioid deaths boost donor heart supply
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
SNOWMASS, COLO. – The tragic opioid epidemic has “one small bright spot”: an expanding pool of eligible donor hearts for transplantation, Akshay S. Desai, MD, said at the annual Cardiovascular Conference at Snowmass sponsored by the American College of Cardiology.
For decades, the annual volume of heart transplantations performed in the U.S. was static because of the huge mismatch between donor organ supply and demand. But heart transplant volume has increased steadily in the last few years – a result of the opioid epidemic.
Data from the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network show that the proportion of donor hearts obtained from individuals who died from drug intoxication climbed from a mere 1.5% in 1999 to 17.6% in 2017, the most recent year for which data are available. Meanwhile, the size of the heart transplant waiting list, which rose year after year in 2009-2015, has since declined (N Engl J Med. 2019 Feb 7;380[6]:597-9).
“What’s amazing is that, even though these patients might have historically been considered high risk in general, the organs recovered from these patients – and particularly the hearts – don’t seem to be any worse in terms of allograft survival than the organs recovered from patients who died from other causes, which are the traditional sources, like blunt head trauma, gunshot wounds, or stroke, that lead to brain death. In general, these organs are useful and do quite well,” according to Dr. Desai, medical director of the cardiomyopathy and heart failure program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
He highlighted several other recent developments in the field of cardiac transplantation that promise to further expand the donor heart pool, including acceptance of hepatitis C–infected donors and organ donation after circulatory rather than brain death. Dr. Desai also drew attention to the unintended perverse consequences of a recent redesign of the U.S. donor heart allocation system and discussed the impressive improvement in clinical outcomes with mechanical circulatory support. He noted that, while relatively few cardiologists practice in the highly specialized centers where heart transplants take place, virtually all cardiologists are affected by advances in heart transplantation since hundreds of thousands of the estimated 7 million Americans with heart failure have advanced disease.
Heart transplantation, he emphasized, is becoming increasingly complex. Recipients are on average older, sicker, and have more comorbidities than in times past. As a result, there is greater need for dual organ transplants: heart/lung, heart/liver, or heart/kidney. Plus, more patients come to transplantation after prior cardiac surgery for implantation of a ventricular assist device, so sensitization to blood products is a growing issue. And, of course, the pool of transplant candidates has expanded.
“We’re now forced to take patients previously considered to have contraindications to transplant; for example, diabetes was a contraindication to transplant in the early years, but now it’s the rule in 35%-40% of our patients who present with advanced heart failure,” the cardiologist noted.
Transplants from HCV-infected donors to uninfected recipients
Hearts and lungs from donors with hepatitis C viremia were traditionally deemed unsuitable for transplant. That’s all changed in the current era of highly effective direct-acting antiviral agents for the treatment of HCV infection.
In the DONATE HCV trial, Dr. Desai’s colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital showed that giving HCV-uninfected recipients of hearts or lungs from HCV-viremic donors a shortened 4-week course of treatment with sofosbuvir-velpatasvir (Epclusa) beginning within a few hours after transplantation uniformly blocked viral replication. Six months after transplantation, none of the study participants had a detectable HCV viral load, and all had excellent graft function (N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 25;380[17]:1606-17).
“This is effective prevention of HCV infection by aggressive upfront therapy,” Dr. Desai explained. “We can now take organs from HCV-viremic patients and use them in solid organ transplantation. This has led to a skyrocketing increase in donors with HCV infection, and those donations have helped us clear the waiting list.”
Donation after circulatory death
Australian transplant physicians have pioneered the use of donor hearts obtained after circulatory death in individuals with devastating neurologic injury who didn’t quite meet the criteria for brain death, which is the traditional prerequisite. In the new scenario, withdrawal of life-supporting therapy is followed by circulatory death, then the donor heart is procured and preserved via extracorporeal perfusion until transplantation.
The Australians report excellent outcomes, with rates of overall survival and rejection episodes similar to outcomes from brain-dead donors (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Apr 2;73[12]:1447-59). The first U.S. heart transplant involving donation after circulatory death took place at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina. A multicenter U.S. clinical trial of this practice is underway.
If the results are positive and the practice of donation after circulatory death becomes widely implemented, the U.S. heart donor pool could increase by 30%.
Recent overhaul of donor heart allocation system may have backfired
The U.S. donor heart allocation system was redesigned in the fall of 2018 in an effort to reduce waiting times. One of the biggest changes involved breaking down the category with the highest urgency status into three new subcategories based upon sickness. Now, the highest-urgency category is for patients in cardiogenic shock who are supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) or other temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
But an analysis of United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) data suggests this change has unintended adverse consequences for clinical outcomes.
Indeed, the investigators reported that the use of ECMO support is fourfold greater in the new system, the use of durable left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) as a bridge to transplant is down, and outcomes are worse. The 180-day rate of freedom from death or retransplantation was 77.9%, down significantly from 93.4% in the former system. In a multivariate analysis, patients transplanted in the new system had an adjusted 2.1-fold increased risk of death or retransplantation (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020 Jan;39[1]:1-4).
“When you create a new listing system, you create new incentives, and people start to manage patients differently,” Dr. Desai observed. “Increasingly now, the path direct to transplant is through temporary mechanical circulatory support rather than durable mechanical circulatory support. Is that a good idea? We don’t know, but if you look at the best data, those on ECMO or percutaneous VADs have the worst outcomes. So the question of whether we should take the sickest of sick patients directly to transplant as a standard strategy has come under scrutiny.”
Improved durable LVAD technology brings impressive clinical outcomes
Results of the landmark MOMENTUM 3 randomized trial showed that 2-year clinical outcomes with the magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow HeartMate 3 LVAD now rival those of percutaneous mitral valve repair using the MitraClip device. Two-year all-cause mortality in the LVAD recipients was 22% versus 29.1% with the MitraClip in the COAPT trial and 34.9% in the MITRA-FR trial. The HeartMate 3 reduces the hemocompatibility issues that plagued earlier-generation durable LVADs, with resultant lower rates of pump thrombosis, stroke, and GI bleeding. Indeed, the outcomes in MOMENTUM 3 were so good – and so similar – with the HeartMate 3, regardless of whether the intended treatment goal was as a bridge to transplant or as lifelong destination therapy, that the investigators have recently proposed doing away with those distinctions.
“It is possible that use of arbitrary categorizations based on current or future transplant eligibility should be clinically abandoned in favor of a single preimplant strategy: to extend the survival and improve the quality of life of patients with medically refractory heart failure,” according to the investigators (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jan 15. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2019.5323).
The next step forward in LVAD technology is already on the horizon: a fully implantable device that eliminates the transcutaneous drive-line for the power supply, which is prone to infection and diminishes overall quality of life. This investigational device utilizes wireless coplanar energy transfer, with a coil ring placed around the lung and fixed to the chest wall. The implanted battery provides more than 6 hours of power without a recharge (J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Apr;38[4]:339-43).
“The first LVAD patient has gone swimming in Kazakhstan,” according to Dr. Desai.
Myocardial recovery in LVAD recipients remains elusive
The initial hope for LVADs was that they would not only be able to serve as a bridge to transplantation or as lifetime therapy, but that the prolonged unloading of the ventricle would enable potent medical therapy to rescue myocardial function so that the device could eventually be explanted. That does happen, but only rarely. In a large registry study, myocardial recovery occurred in only about 1% of patients on mechanical circulatory support. Attempts to enhance the process by add-on stem cell therapy have thus far been ineffective.
“For the moment, recovery is still a hope, not a reality,” the cardiologist said.
He reported serving as a consultant to more than a dozen pharmaceutical or medical device companies and receiving research grants from Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, MyoKardia, and Novartis.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC SNOWMASS 2020
Zika virus: Birth defects rose fourfold in U.S. hardest-hit areas
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
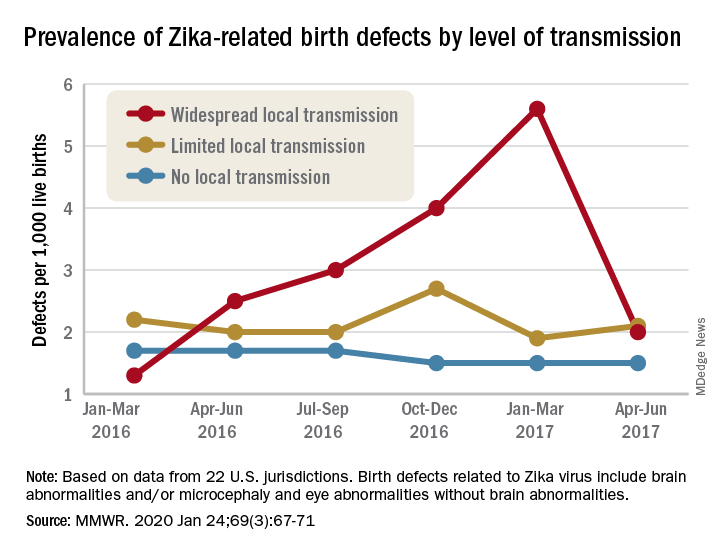
That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

That spike in the prevalence of brain abnormalities and/or microcephaly or eye abnormalities without brain abnormalities came during January through March 2017, about 6 months after the Zika outbreak’s reported peak in the jurisdictions with widespread local transmission, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, wrote Ashley N. Smoots, MPH, of the CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities and associates in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
In those two territories, the prevalence of birth defects potentially related to Zika virus infection was 5.6 per 1,000 live births during January through March 2017, compared with 1.3 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, they reported.
In the southern areas of Florida and Texas, where there was limited local Zika transmission, the highest prevalence of birth defects, 2.7 per 1,000, occurred during October through December 2016, and was only slightly greater than the baseline rate of 2.2 per 1,000 in January through March 2016, the investigators reported.
Among the other 19 jurisdictions (including Illinois, Louisiana, New Jersey, South Carolina, and Virginia) involved in the analysis, the rate of Zika virus–related birth defects never reached any higher than the 1.7 per 1,000 recorded at the start of the study period in January through March 2016, they said.
“Population-based birth defects surveillance is critical for identifying infants and fetuses with birth defects potentially related to Zika virus regardless of whether Zika virus testing was conducted, especially given the high prevalence of asymptomatic disease. These data can be used to inform follow-up care and services as well as strengthen surveillance,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE: Smoots AN et al. MMWR. 2020 Jan 24;69(3):67-71.
FROM MMWR
Cannabis for sleep: Short-term benefit, long-term disruption?
, new research shows.
Investigators found whole-plant medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with respect to waking up at night, but they also found that frequent medical cannabis use was associated with more problems initiating and maintaining sleep.
“Cannabis may improve overall sleep in the short term,” study investigator Sharon Sznitman, PhD, University of Haifa (Israel) Faculty of Social Welfare and Health Sciences, said in an interview. “But it’s also very interesting that when we looked at frequency of use in the group that used medical cannabis, individuals who had more frequent use also had poorer sleep in the long term.
“This suggests that while cannabis may improve overall sleep, it’s also possible that there is a tolerance that develops with either very frequent or long-term use,” she added.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in BMJ Supportive and Palliative Care.
A common problem
Estimates suggest chronic pain affects up to 37% of adults in the developed world. Individuals who suffer chronic pain often experience comorbid insomnia, which includes difficulty initiating sleep, sleep disruption, and early morning wakening.
For its part, medical cannabis to treat chronic pain symptoms and manage sleep problems has been widely reported as a prime motivation for medical cannabis use. Indeed, previous studies have concluded that the endocannabinoid system plays a role in sleep regulation, including sleep promotion and maintenance.
In recent years, investigators have reported the beneficial effects of medical cannabis for sleep. Nevertheless, some preclinical research has also concluded that chronic administration of tetrahydrocannabinol may result in tolerance to the sleep-enhancing effects of cannabis.
With that in mind, the researchers set out to examine the potential impact of whole-plant medicinal cannabis on sleep problems experienced by middle-aged patients suffering from chronic pain.
“People are self-reporting that they’re using cannabis for sleep and that it helps, but as we know, just because people are reporting that it works doesn’t mean that it will hold up in research,” Dr. Sznitman said.
The study included 128 individuals (mean age, 61±6 years; 51% females) with chronic neuropathic pain: 66 were medical cannabis users and 62 were not.
Three indicators of insomnia were measured using the 7-point Likert scale to assess issues with sleep initiation and maintenance.
In addition, investigators collected sociodemographic information, as well as data on daily consumption of tobacco, frequency of alcohol use, and pain severity. Finally, they collected patient data on the use of sleep-aid medications during the past month as well as tricyclic antidepressant use.
Frequent use, more sleep problems?
On average, medical cannabis users were 3 years younger than their nonusing counterparts (mean age, 60±6 vs. 63±6 years, respectively, P = .003) and more likely to be male (58% vs 40%, respectively, P = .038). Otherwise, the two groups were comparable.
Medical cannabis users reported taking the drug for an average of 4 years, at an average quantity of 31 g per month. The primary mode of administration was smoking (68.6%), followed by oil extracts (21.4%) and vaporization (20%).
Results showed that, of the total sample, 24.1% reported always waking up early and not falling back to sleep, 20.2% reported always having difficulty falling asleep, and 27.2% reported always waking up during the night.
After adjusting for patient age, sex, pain level, and use of sleep medications and antidepressants, medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with waking up at night, compared with nonmedical cannabis use. No differences were found between groups with respect to problems falling asleep or waking up early without being able to fall back to sleep, Dr. Sznitman and associates reported.
The final analysis of a subsample of patients that only included medical cannabis users showed frequency of medical cannabis use was associated with sleep problems, they said.
Specifically, more frequent cannabis use was associated with more problems related to waking up at night, as well as problems falling asleep.
Sleep problems associated with frequent medical cannabis use may signal the development of tolerance to the agent. However, frequent users of medical cannabis also maybsuffer pain or other comorbidities, which, in turn, may be linked to more sleep problems.
Either way, Dr. Sznitman said the study might open the door to another treatment option for patients suffering from chronic pain who struggle with sleep.
“If future research shows that the effect of medical cannabis on sleep is a consistent one, then we may be adding a new therapy for sleep problems, which are huge in society and especially in chronic pain patients,” she said.
Early days
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ryan G. Vandrey, PhD, who was not involved in the study, said the findings are in line with previous research.
“I think the results make sense with respect to the data I’ve collected and from what I’ve seen,” said Dr. Vandrey, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
“We typically only want to use sleep medications for short periods of time,” he continued. “When you think about recommended prescribing practices for any hypnotic medication, it’s usually short term, 2 weeks or less. Longer-term use often leads to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the medication is stopped, which leads to an exacerbation of disordered sleep,” Dr. Vandrey said.
Nevertheless, he urged caution when interpreting the results.
“I think the study warrants caution about long-term daily use of cannabinoids with respect to sleep,” he said. “But we need more detailed evaluations, as the trial wasn’t testing a defined product, specific dose, or dose regimen.
“In addition, this was all done in the context of people with chronic pain and not treating disordered sleep or insomnia, but the study highlights the importance of recognizing that long-term chronic use of cannabis is not likely to fully resolve sleep problems.”
Dr. Sznitman agreed that the research is still in its very early stages.
“We’re still far from saying we have the evidence to support the use of medical cannabis for sleep,” she said. “For in the end it was just a cross-sectional, observational study, so we cannot say anything about cause and effect. But if these results pan out, they could be far-reaching and exciting.”
The study was funded by the University of Haifa and Rambam Hospital in Israel, and by the Evelyn Lipper Foundation. Dr. Sznitman and Dr. Vandrey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Investigators found whole-plant medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with respect to waking up at night, but they also found that frequent medical cannabis use was associated with more problems initiating and maintaining sleep.
“Cannabis may improve overall sleep in the short term,” study investigator Sharon Sznitman, PhD, University of Haifa (Israel) Faculty of Social Welfare and Health Sciences, said in an interview. “But it’s also very interesting that when we looked at frequency of use in the group that used medical cannabis, individuals who had more frequent use also had poorer sleep in the long term.
“This suggests that while cannabis may improve overall sleep, it’s also possible that there is a tolerance that develops with either very frequent or long-term use,” she added.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in BMJ Supportive and Palliative Care.
A common problem
Estimates suggest chronic pain affects up to 37% of adults in the developed world. Individuals who suffer chronic pain often experience comorbid insomnia, which includes difficulty initiating sleep, sleep disruption, and early morning wakening.
For its part, medical cannabis to treat chronic pain symptoms and manage sleep problems has been widely reported as a prime motivation for medical cannabis use. Indeed, previous studies have concluded that the endocannabinoid system plays a role in sleep regulation, including sleep promotion and maintenance.
In recent years, investigators have reported the beneficial effects of medical cannabis for sleep. Nevertheless, some preclinical research has also concluded that chronic administration of tetrahydrocannabinol may result in tolerance to the sleep-enhancing effects of cannabis.
With that in mind, the researchers set out to examine the potential impact of whole-plant medicinal cannabis on sleep problems experienced by middle-aged patients suffering from chronic pain.
“People are self-reporting that they’re using cannabis for sleep and that it helps, but as we know, just because people are reporting that it works doesn’t mean that it will hold up in research,” Dr. Sznitman said.
The study included 128 individuals (mean age, 61±6 years; 51% females) with chronic neuropathic pain: 66 were medical cannabis users and 62 were not.
Three indicators of insomnia were measured using the 7-point Likert scale to assess issues with sleep initiation and maintenance.
In addition, investigators collected sociodemographic information, as well as data on daily consumption of tobacco, frequency of alcohol use, and pain severity. Finally, they collected patient data on the use of sleep-aid medications during the past month as well as tricyclic antidepressant use.
Frequent use, more sleep problems?
On average, medical cannabis users were 3 years younger than their nonusing counterparts (mean age, 60±6 vs. 63±6 years, respectively, P = .003) and more likely to be male (58% vs 40%, respectively, P = .038). Otherwise, the two groups were comparable.
Medical cannabis users reported taking the drug for an average of 4 years, at an average quantity of 31 g per month. The primary mode of administration was smoking (68.6%), followed by oil extracts (21.4%) and vaporization (20%).
Results showed that, of the total sample, 24.1% reported always waking up early and not falling back to sleep, 20.2% reported always having difficulty falling asleep, and 27.2% reported always waking up during the night.
After adjusting for patient age, sex, pain level, and use of sleep medications and antidepressants, medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with waking up at night, compared with nonmedical cannabis use. No differences were found between groups with respect to problems falling asleep or waking up early without being able to fall back to sleep, Dr. Sznitman and associates reported.
The final analysis of a subsample of patients that only included medical cannabis users showed frequency of medical cannabis use was associated with sleep problems, they said.
Specifically, more frequent cannabis use was associated with more problems related to waking up at night, as well as problems falling asleep.
Sleep problems associated with frequent medical cannabis use may signal the development of tolerance to the agent. However, frequent users of medical cannabis also maybsuffer pain or other comorbidities, which, in turn, may be linked to more sleep problems.
Either way, Dr. Sznitman said the study might open the door to another treatment option for patients suffering from chronic pain who struggle with sleep.
“If future research shows that the effect of medical cannabis on sleep is a consistent one, then we may be adding a new therapy for sleep problems, which are huge in society and especially in chronic pain patients,” she said.
Early days
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ryan G. Vandrey, PhD, who was not involved in the study, said the findings are in line with previous research.
“I think the results make sense with respect to the data I’ve collected and from what I’ve seen,” said Dr. Vandrey, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
“We typically only want to use sleep medications for short periods of time,” he continued. “When you think about recommended prescribing practices for any hypnotic medication, it’s usually short term, 2 weeks or less. Longer-term use often leads to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the medication is stopped, which leads to an exacerbation of disordered sleep,” Dr. Vandrey said.
Nevertheless, he urged caution when interpreting the results.
“I think the study warrants caution about long-term daily use of cannabinoids with respect to sleep,” he said. “But we need more detailed evaluations, as the trial wasn’t testing a defined product, specific dose, or dose regimen.
“In addition, this was all done in the context of people with chronic pain and not treating disordered sleep or insomnia, but the study highlights the importance of recognizing that long-term chronic use of cannabis is not likely to fully resolve sleep problems.”
Dr. Sznitman agreed that the research is still in its very early stages.
“We’re still far from saying we have the evidence to support the use of medical cannabis for sleep,” she said. “For in the end it was just a cross-sectional, observational study, so we cannot say anything about cause and effect. But if these results pan out, they could be far-reaching and exciting.”
The study was funded by the University of Haifa and Rambam Hospital in Israel, and by the Evelyn Lipper Foundation. Dr. Sznitman and Dr. Vandrey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Investigators found whole-plant medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with respect to waking up at night, but they also found that frequent medical cannabis use was associated with more problems initiating and maintaining sleep.
“Cannabis may improve overall sleep in the short term,” study investigator Sharon Sznitman, PhD, University of Haifa (Israel) Faculty of Social Welfare and Health Sciences, said in an interview. “But it’s also very interesting that when we looked at frequency of use in the group that used medical cannabis, individuals who had more frequent use also had poorer sleep in the long term.
“This suggests that while cannabis may improve overall sleep, it’s also possible that there is a tolerance that develops with either very frequent or long-term use,” she added.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in BMJ Supportive and Palliative Care.
A common problem
Estimates suggest chronic pain affects up to 37% of adults in the developed world. Individuals who suffer chronic pain often experience comorbid insomnia, which includes difficulty initiating sleep, sleep disruption, and early morning wakening.
For its part, medical cannabis to treat chronic pain symptoms and manage sleep problems has been widely reported as a prime motivation for medical cannabis use. Indeed, previous studies have concluded that the endocannabinoid system plays a role in sleep regulation, including sleep promotion and maintenance.
In recent years, investigators have reported the beneficial effects of medical cannabis for sleep. Nevertheless, some preclinical research has also concluded that chronic administration of tetrahydrocannabinol may result in tolerance to the sleep-enhancing effects of cannabis.
With that in mind, the researchers set out to examine the potential impact of whole-plant medicinal cannabis on sleep problems experienced by middle-aged patients suffering from chronic pain.
“People are self-reporting that they’re using cannabis for sleep and that it helps, but as we know, just because people are reporting that it works doesn’t mean that it will hold up in research,” Dr. Sznitman said.
The study included 128 individuals (mean age, 61±6 years; 51% females) with chronic neuropathic pain: 66 were medical cannabis users and 62 were not.
Three indicators of insomnia were measured using the 7-point Likert scale to assess issues with sleep initiation and maintenance.
In addition, investigators collected sociodemographic information, as well as data on daily consumption of tobacco, frequency of alcohol use, and pain severity. Finally, they collected patient data on the use of sleep-aid medications during the past month as well as tricyclic antidepressant use.
Frequent use, more sleep problems?
On average, medical cannabis users were 3 years younger than their nonusing counterparts (mean age, 60±6 vs. 63±6 years, respectively, P = .003) and more likely to be male (58% vs 40%, respectively, P = .038). Otherwise, the two groups were comparable.
Medical cannabis users reported taking the drug for an average of 4 years, at an average quantity of 31 g per month. The primary mode of administration was smoking (68.6%), followed by oil extracts (21.4%) and vaporization (20%).
Results showed that, of the total sample, 24.1% reported always waking up early and not falling back to sleep, 20.2% reported always having difficulty falling asleep, and 27.2% reported always waking up during the night.
After adjusting for patient age, sex, pain level, and use of sleep medications and antidepressants, medical cannabis use was associated with fewer problems with waking up at night, compared with nonmedical cannabis use. No differences were found between groups with respect to problems falling asleep or waking up early without being able to fall back to sleep, Dr. Sznitman and associates reported.
The final analysis of a subsample of patients that only included medical cannabis users showed frequency of medical cannabis use was associated with sleep problems, they said.
Specifically, more frequent cannabis use was associated with more problems related to waking up at night, as well as problems falling asleep.
Sleep problems associated with frequent medical cannabis use may signal the development of tolerance to the agent. However, frequent users of medical cannabis also maybsuffer pain or other comorbidities, which, in turn, may be linked to more sleep problems.
Either way, Dr. Sznitman said the study might open the door to another treatment option for patients suffering from chronic pain who struggle with sleep.
“If future research shows that the effect of medical cannabis on sleep is a consistent one, then we may be adding a new therapy for sleep problems, which are huge in society and especially in chronic pain patients,” she said.
Early days
Commenting on the findings in an interview, Ryan G. Vandrey, PhD, who was not involved in the study, said the findings are in line with previous research.
“I think the results make sense with respect to the data I’ve collected and from what I’ve seen,” said Dr. Vandrey, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins Medicine in Baltimore.
“We typically only want to use sleep medications for short periods of time,” he continued. “When you think about recommended prescribing practices for any hypnotic medication, it’s usually short term, 2 weeks or less. Longer-term use often leads to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the medication is stopped, which leads to an exacerbation of disordered sleep,” Dr. Vandrey said.
Nevertheless, he urged caution when interpreting the results.
“I think the study warrants caution about long-term daily use of cannabinoids with respect to sleep,” he said. “But we need more detailed evaluations, as the trial wasn’t testing a defined product, specific dose, or dose regimen.
“In addition, this was all done in the context of people with chronic pain and not treating disordered sleep or insomnia, but the study highlights the importance of recognizing that long-term chronic use of cannabis is not likely to fully resolve sleep problems.”
Dr. Sznitman agreed that the research is still in its very early stages.
“We’re still far from saying we have the evidence to support the use of medical cannabis for sleep,” she said. “For in the end it was just a cross-sectional, observational study, so we cannot say anything about cause and effect. But if these results pan out, they could be far-reaching and exciting.”
The study was funded by the University of Haifa and Rambam Hospital in Israel, and by the Evelyn Lipper Foundation. Dr. Sznitman and Dr. Vandrey have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMJ SUPPORTIVE AND PALLIATIVE CARE