User login
TAPs top epidurals in ventral hernia repair
, according to a review of 246 cases at the Greenville Health System, in South Carolina.
“Regional anesthesia using TAP block[s] provides an effective alternative to epidural analgesia or opioid use alone for perioperative pain control ... In light of these findings, use of TAP block should be strongly considered as an adjunct to abdominal surgery,” wrote investigators led by general surgeon Jeremy Warren, MD, of the University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville, in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Prompted by favorable reports in the literature, the team switched from epidural analgesia to TAP blocks in early 2017. To see how it’s worked out, they reviewed all patients who had ventral hernia repairs at the Greenville Health System from Feb. 2015 to March 2018. They were all mesh cases, without parastomal hernias or enterostomy reversal.
Seventy-four patients had TAP blocks, which were placed in the OR after anesthesia induction and consisted of 200 mg ropivacaine, 100 mcg epinephrine, and 100 mcg clonidine in 60 ml saline, with 30 ml injected on each side under ultrasound guidance.
Their outcomes were compared with 172 patients who received epidurals, which were placed preoperatively and consisted of 0.125% bupivacaine initiated shortly before patients came out of anesthesia, at a rate of 8-12 ml/hr.
Hospital lengths of stay were significantly shorter in the TAP group, a median of 2.4 versus 4.5 days (P less than .001), and TAP patients received fewer opioids, a mean of 40 versus 54.1 morphine milligram equivalents (MME) on postop day 1, and 36.1 versus 52.5 MME on postop day 2 (P = .018).
There were no differences in the rates of surgical site infections or other wound complications. The mean duration of epidural infusion was 49.5 hours.
The shorter length of stay with TAP block was probably related to side effects of epidurals, which can include leg paresthesias, hypotension, and urinary retention, all of which get in the way of early ambulation. “Additionally, the decision of when to discontinue epidural analgesia in our series was left to the judgment of the pain management and surgical team based on reporting of patient pain, rather than duration determined by a protocol,” which may have also played a role, the study team said.
Overall, the results mirror outcomes from previous TAP block studies, but there were caveats. Epidural patients had wider hernias (median 10.8 cm versus 8.8 cm); required more myofascial releases; and had longer operative times, “indicating a higher degree of complexity that may influence the need for longer hospitalization and greater opioid use,” the investigators said.
Also, a greater number of TAP block patients received non-opioid pain killers, including ketorolac and acetaminophen.
The study was conducted within the health system’s enhanced recovery after surgery protocol, which includes a preoperative cocktail of pregabalin 75 mg, celecoxib 400 mg, and acetaminophen 1,000 mg, given within 1-2 hours of surgery. Post-operative management includes intravenous ketamine infusions at sub-anesthetic doses, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen, among other measures. The approach has pretty much eliminated patient-controlled analgesia.
There were slightly more men than women in the review. Study participants, on average, were in their late 50s. There were no significant differences in comorbidities.
No funding was reported, and the investigators didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Warren JA et al., J Am Coll Surg. 2019 Jan 7. pii: S1072-7515(19)30014-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.12.017
, according to a review of 246 cases at the Greenville Health System, in South Carolina.
“Regional anesthesia using TAP block[s] provides an effective alternative to epidural analgesia or opioid use alone for perioperative pain control ... In light of these findings, use of TAP block should be strongly considered as an adjunct to abdominal surgery,” wrote investigators led by general surgeon Jeremy Warren, MD, of the University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville, in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Prompted by favorable reports in the literature, the team switched from epidural analgesia to TAP blocks in early 2017. To see how it’s worked out, they reviewed all patients who had ventral hernia repairs at the Greenville Health System from Feb. 2015 to March 2018. They were all mesh cases, without parastomal hernias or enterostomy reversal.
Seventy-four patients had TAP blocks, which were placed in the OR after anesthesia induction and consisted of 200 mg ropivacaine, 100 mcg epinephrine, and 100 mcg clonidine in 60 ml saline, with 30 ml injected on each side under ultrasound guidance.
Their outcomes were compared with 172 patients who received epidurals, which were placed preoperatively and consisted of 0.125% bupivacaine initiated shortly before patients came out of anesthesia, at a rate of 8-12 ml/hr.
Hospital lengths of stay were significantly shorter in the TAP group, a median of 2.4 versus 4.5 days (P less than .001), and TAP patients received fewer opioids, a mean of 40 versus 54.1 morphine milligram equivalents (MME) on postop day 1, and 36.1 versus 52.5 MME on postop day 2 (P = .018).
There were no differences in the rates of surgical site infections or other wound complications. The mean duration of epidural infusion was 49.5 hours.
The shorter length of stay with TAP block was probably related to side effects of epidurals, which can include leg paresthesias, hypotension, and urinary retention, all of which get in the way of early ambulation. “Additionally, the decision of when to discontinue epidural analgesia in our series was left to the judgment of the pain management and surgical team based on reporting of patient pain, rather than duration determined by a protocol,” which may have also played a role, the study team said.
Overall, the results mirror outcomes from previous TAP block studies, but there were caveats. Epidural patients had wider hernias (median 10.8 cm versus 8.8 cm); required more myofascial releases; and had longer operative times, “indicating a higher degree of complexity that may influence the need for longer hospitalization and greater opioid use,” the investigators said.
Also, a greater number of TAP block patients received non-opioid pain killers, including ketorolac and acetaminophen.
The study was conducted within the health system’s enhanced recovery after surgery protocol, which includes a preoperative cocktail of pregabalin 75 mg, celecoxib 400 mg, and acetaminophen 1,000 mg, given within 1-2 hours of surgery. Post-operative management includes intravenous ketamine infusions at sub-anesthetic doses, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen, among other measures. The approach has pretty much eliminated patient-controlled analgesia.
There were slightly more men than women in the review. Study participants, on average, were in their late 50s. There were no significant differences in comorbidities.
No funding was reported, and the investigators didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Warren JA et al., J Am Coll Surg. 2019 Jan 7. pii: S1072-7515(19)30014-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.12.017
, according to a review of 246 cases at the Greenville Health System, in South Carolina.
“Regional anesthesia using TAP block[s] provides an effective alternative to epidural analgesia or opioid use alone for perioperative pain control ... In light of these findings, use of TAP block should be strongly considered as an adjunct to abdominal surgery,” wrote investigators led by general surgeon Jeremy Warren, MD, of the University of South Carolina School of Medicine, Greenville, in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons.
Prompted by favorable reports in the literature, the team switched from epidural analgesia to TAP blocks in early 2017. To see how it’s worked out, they reviewed all patients who had ventral hernia repairs at the Greenville Health System from Feb. 2015 to March 2018. They were all mesh cases, without parastomal hernias or enterostomy reversal.
Seventy-four patients had TAP blocks, which were placed in the OR after anesthesia induction and consisted of 200 mg ropivacaine, 100 mcg epinephrine, and 100 mcg clonidine in 60 ml saline, with 30 ml injected on each side under ultrasound guidance.
Their outcomes were compared with 172 patients who received epidurals, which were placed preoperatively and consisted of 0.125% bupivacaine initiated shortly before patients came out of anesthesia, at a rate of 8-12 ml/hr.
Hospital lengths of stay were significantly shorter in the TAP group, a median of 2.4 versus 4.5 days (P less than .001), and TAP patients received fewer opioids, a mean of 40 versus 54.1 morphine milligram equivalents (MME) on postop day 1, and 36.1 versus 52.5 MME on postop day 2 (P = .018).
There were no differences in the rates of surgical site infections or other wound complications. The mean duration of epidural infusion was 49.5 hours.
The shorter length of stay with TAP block was probably related to side effects of epidurals, which can include leg paresthesias, hypotension, and urinary retention, all of which get in the way of early ambulation. “Additionally, the decision of when to discontinue epidural analgesia in our series was left to the judgment of the pain management and surgical team based on reporting of patient pain, rather than duration determined by a protocol,” which may have also played a role, the study team said.
Overall, the results mirror outcomes from previous TAP block studies, but there were caveats. Epidural patients had wider hernias (median 10.8 cm versus 8.8 cm); required more myofascial releases; and had longer operative times, “indicating a higher degree of complexity that may influence the need for longer hospitalization and greater opioid use,” the investigators said.
Also, a greater number of TAP block patients received non-opioid pain killers, including ketorolac and acetaminophen.
The study was conducted within the health system’s enhanced recovery after surgery protocol, which includes a preoperative cocktail of pregabalin 75 mg, celecoxib 400 mg, and acetaminophen 1,000 mg, given within 1-2 hours of surgery. Post-operative management includes intravenous ketamine infusions at sub-anesthetic doses, NSAIDs, and acetaminophen, among other measures. The approach has pretty much eliminated patient-controlled analgesia.
There were slightly more men than women in the review. Study participants, on average, were in their late 50s. There were no significant differences in comorbidities.
No funding was reported, and the investigators didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Warren JA et al., J Am Coll Surg. 2019 Jan 7. pii: S1072-7515(19)30014-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.12.017
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS
Key clinical point: TAP blocks are better than epidurals for pain control after ventral hernia repair.
Major finding: Hospital lengths of stay were significantly shorter in the TAP group, a median of 2.4 versus 4.5 days (P less than .001), and TAP patients received fewer opioids, a mean of 40 versus 54.1 morphine milligram equivalents (MME) on postop day 1.
Study details: Review of 246 repairs
Disclosures: No funding was reported, and the investigators didn’t have any relevant disclosures.
Source: Warren JA et al., J Am Coll Surg. 2019 Jan 7. pii: S1072-7515(19)30014-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.12.017
FDA labeling templates smooth way for OTC naloxone
Drug facts labels (DFLs) are required for all OTC drugs, and it’s usually up to manufacturers to develop and test their own to ensure that consumers understand how to use their products.
“Some stakeholders have identified the requirement ... as a barrier to development of OTC naloxone products,” so the agency developed two DFLs on its own – one for nasal spray naloxone, the other for auto-injectors – and completed the necessary label comprehension testing, according to an announcement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD.
There’s not much else manufactures have to do, except deal with the details of their own products. They “can now focus their efforts on ... how well consumers understand the product-specific information that hasn’t been already tested in the model” DFLs, according to the announcement.
As deaths from opioid abuse continue to climb, the FDA is committed to increasing access to naloxone, which currently requires a prescription. The new DFLs “should jump-start the development of OTC naloxone products ... I personally urge companies to take notice of this pathway that the FDA has opened for them and come to the Agency with applications as soon as possible,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
Comprehension was assessed in more than 700 people, including heroin and prescription opioid users, their friends and families, and adolescents. “Overall, the study demonstrated that” the DFLs are “well-understood by consumers” and acceptable “for use by manufacturers in support of their ... development programs,” according to the announcement.
In a press statement, the American Medical Association applauded the agency’s move “to provide labeling that would allow for over-the-counter availability of naloxone, a move that will save people from opioid-related overdose ... The action should spur efforts by naloxone manufacturers to submit applications for their products to receive over-the-counter status.”
Drug facts labels (DFLs) are required for all OTC drugs, and it’s usually up to manufacturers to develop and test their own to ensure that consumers understand how to use their products.
“Some stakeholders have identified the requirement ... as a barrier to development of OTC naloxone products,” so the agency developed two DFLs on its own – one for nasal spray naloxone, the other for auto-injectors – and completed the necessary label comprehension testing, according to an announcement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD.
There’s not much else manufactures have to do, except deal with the details of their own products. They “can now focus their efforts on ... how well consumers understand the product-specific information that hasn’t been already tested in the model” DFLs, according to the announcement.
As deaths from opioid abuse continue to climb, the FDA is committed to increasing access to naloxone, which currently requires a prescription. The new DFLs “should jump-start the development of OTC naloxone products ... I personally urge companies to take notice of this pathway that the FDA has opened for them and come to the Agency with applications as soon as possible,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
Comprehension was assessed in more than 700 people, including heroin and prescription opioid users, their friends and families, and adolescents. “Overall, the study demonstrated that” the DFLs are “well-understood by consumers” and acceptable “for use by manufacturers in support of their ... development programs,” according to the announcement.
In a press statement, the American Medical Association applauded the agency’s move “to provide labeling that would allow for over-the-counter availability of naloxone, a move that will save people from opioid-related overdose ... The action should spur efforts by naloxone manufacturers to submit applications for their products to receive over-the-counter status.”
Drug facts labels (DFLs) are required for all OTC drugs, and it’s usually up to manufacturers to develop and test their own to ensure that consumers understand how to use their products.
“Some stakeholders have identified the requirement ... as a barrier to development of OTC naloxone products,” so the agency developed two DFLs on its own – one for nasal spray naloxone, the other for auto-injectors – and completed the necessary label comprehension testing, according to an announcement from FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD.
There’s not much else manufactures have to do, except deal with the details of their own products. They “can now focus their efforts on ... how well consumers understand the product-specific information that hasn’t been already tested in the model” DFLs, according to the announcement.
As deaths from opioid abuse continue to climb, the FDA is committed to increasing access to naloxone, which currently requires a prescription. The new DFLs “should jump-start the development of OTC naloxone products ... I personally urge companies to take notice of this pathway that the FDA has opened for them and come to the Agency with applications as soon as possible,” Dr. Gottlieb said.
Comprehension was assessed in more than 700 people, including heroin and prescription opioid users, their friends and families, and adolescents. “Overall, the study demonstrated that” the DFLs are “well-understood by consumers” and acceptable “for use by manufacturers in support of their ... development programs,” according to the announcement.
In a press statement, the American Medical Association applauded the agency’s move “to provide labeling that would allow for over-the-counter availability of naloxone, a move that will save people from opioid-related overdose ... The action should spur efforts by naloxone manufacturers to submit applications for their products to receive over-the-counter status.”
Courts stop contraceptive mandate
Too much sleep and too little sleep are linked to atherosclerosis, there is no drop in gout prevalence, but there isn’t an increase either, and back pain persists in one in five patients.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Too much sleep and too little sleep are linked to atherosclerosis, there is no drop in gout prevalence, but there isn’t an increase either, and back pain persists in one in five patients.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Too much sleep and too little sleep are linked to atherosclerosis, there is no drop in gout prevalence, but there isn’t an increase either, and back pain persists in one in five patients.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
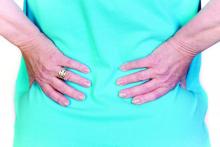
Back pain persists in one in five patients
according to data from a population-based study of more than 12,000 adults in Canada.
“Given that back pain [BP] is often recurrent, it is important to understand the course of back pain over time as this can provide additional insights on risk factors for nonfavorable outcomes,” wrote Mayilee Canizares, PhD, and her colleagues at the University Health Network’s Krembil Research Institute in Toronto.
In a longitudinal study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators followed 12,782 adults from 1994 to 2011. The study population was a representative sample of the Canadian population via the National Population Health Survey, which collected data every 2 years for a total of nine cycles of data. They included people aged 15 years or older in 1994-1995 who had at least three cycles of data from baseline onward.
Over the 16-year study period, 46% of the participants reported at least one episode of back pain. Of these, 18% were identified as persistent, 28% as developing, 21% as recovering, and 33% as occasional.
“A major finding from this study is the negative impact of persistent BP on a range of health-related outcomes, including health care use, after adjustments for sociodemographic, behavior-related factors, and comorbidities,” the researchers wrote.
They examined several sociodemographic variables, including age, gender, educational level, and household income, as well as behavior-related variables including physical activity, work activity, smoking status, and obesity. The average age of the participants at baseline was 39 years; 51% were female.
Individuals who reported any back pain were more likely than those with no back pain to be overweight or obese, to smoke, to engage in moderate to heavy physical activity each day, and to have chronic conditions, including arthritis, depression, high blood pressure, and migraine.
Overall, individuals with persistent or developing BP had more pain, disability, health care visits, and medication use, compared with those in the recovery and occasional BP groups. However, individuals in the recovery group showed increased use of opioids and antidepressants over time as well, suggesting a need for long-term monitoring of back pain patients.
The trend in general disability was greatest for individuals in the persistent group followed by the developing group, recovery group, and occasional BP group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of self-reports, potential selection bias, and the inability to differentiate the specific types of back pain, the researchers noted. However, the results support and extend data from previous studies and provide clinical implications for understanding back pain.
The researchers concluded that “the different trajectory patterns potentially represent subgroups in the population that may require different interventions. In light of the trend of marked worsening outcomes, particularly for the persistent and developing groups, studies are needed to determine the nature of these groups.”
The authors reported no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Canizares M et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/acr.23811.
according to data from a population-based study of more than 12,000 adults in Canada.
“Given that back pain [BP] is often recurrent, it is important to understand the course of back pain over time as this can provide additional insights on risk factors for nonfavorable outcomes,” wrote Mayilee Canizares, PhD, and her colleagues at the University Health Network’s Krembil Research Institute in Toronto.
In a longitudinal study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators followed 12,782 adults from 1994 to 2011. The study population was a representative sample of the Canadian population via the National Population Health Survey, which collected data every 2 years for a total of nine cycles of data. They included people aged 15 years or older in 1994-1995 who had at least three cycles of data from baseline onward.
Over the 16-year study period, 46% of the participants reported at least one episode of back pain. Of these, 18% were identified as persistent, 28% as developing, 21% as recovering, and 33% as occasional.
“A major finding from this study is the negative impact of persistent BP on a range of health-related outcomes, including health care use, after adjustments for sociodemographic, behavior-related factors, and comorbidities,” the researchers wrote.
They examined several sociodemographic variables, including age, gender, educational level, and household income, as well as behavior-related variables including physical activity, work activity, smoking status, and obesity. The average age of the participants at baseline was 39 years; 51% were female.
Individuals who reported any back pain were more likely than those with no back pain to be overweight or obese, to smoke, to engage in moderate to heavy physical activity each day, and to have chronic conditions, including arthritis, depression, high blood pressure, and migraine.
Overall, individuals with persistent or developing BP had more pain, disability, health care visits, and medication use, compared with those in the recovery and occasional BP groups. However, individuals in the recovery group showed increased use of opioids and antidepressants over time as well, suggesting a need for long-term monitoring of back pain patients.
The trend in general disability was greatest for individuals in the persistent group followed by the developing group, recovery group, and occasional BP group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of self-reports, potential selection bias, and the inability to differentiate the specific types of back pain, the researchers noted. However, the results support and extend data from previous studies and provide clinical implications for understanding back pain.
The researchers concluded that “the different trajectory patterns potentially represent subgroups in the population that may require different interventions. In light of the trend of marked worsening outcomes, particularly for the persistent and developing groups, studies are needed to determine the nature of these groups.”
The authors reported no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Canizares M et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/acr.23811.
according to data from a population-based study of more than 12,000 adults in Canada.
“Given that back pain [BP] is often recurrent, it is important to understand the course of back pain over time as this can provide additional insights on risk factors for nonfavorable outcomes,” wrote Mayilee Canizares, PhD, and her colleagues at the University Health Network’s Krembil Research Institute in Toronto.
In a longitudinal study published in Arthritis Care & Research, the investigators followed 12,782 adults from 1994 to 2011. The study population was a representative sample of the Canadian population via the National Population Health Survey, which collected data every 2 years for a total of nine cycles of data. They included people aged 15 years or older in 1994-1995 who had at least three cycles of data from baseline onward.
Over the 16-year study period, 46% of the participants reported at least one episode of back pain. Of these, 18% were identified as persistent, 28% as developing, 21% as recovering, and 33% as occasional.
“A major finding from this study is the negative impact of persistent BP on a range of health-related outcomes, including health care use, after adjustments for sociodemographic, behavior-related factors, and comorbidities,” the researchers wrote.
They examined several sociodemographic variables, including age, gender, educational level, and household income, as well as behavior-related variables including physical activity, work activity, smoking status, and obesity. The average age of the participants at baseline was 39 years; 51% were female.
Individuals who reported any back pain were more likely than those with no back pain to be overweight or obese, to smoke, to engage in moderate to heavy physical activity each day, and to have chronic conditions, including arthritis, depression, high blood pressure, and migraine.
Overall, individuals with persistent or developing BP had more pain, disability, health care visits, and medication use, compared with those in the recovery and occasional BP groups. However, individuals in the recovery group showed increased use of opioids and antidepressants over time as well, suggesting a need for long-term monitoring of back pain patients.
The trend in general disability was greatest for individuals in the persistent group followed by the developing group, recovery group, and occasional BP group.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the use of self-reports, potential selection bias, and the inability to differentiate the specific types of back pain, the researchers noted. However, the results support and extend data from previous studies and provide clinical implications for understanding back pain.
The researchers concluded that “the different trajectory patterns potentially represent subgroups in the population that may require different interventions. In light of the trend of marked worsening outcomes, particularly for the persistent and developing groups, studies are needed to determine the nature of these groups.”
The authors reported no relevant financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Canizares M et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/acr.23811.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Key clinical point: Back pain is a common health problem, and one in five Canadian adults reported persistent back pain.
Major finding: Approximately half (46%) of Canadian adults reported some type of back pain over a 16-year period.
Study details: The data come from a population-based study of 12,782 adults followed from 1994 to 2011.
Disclosures: The authors reported no relevant financial conflicts.
Source: Canizares M et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2019 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/acr.23811.
Opioid crisis offers poignant lessons for public health
Populations and circumstances matter
As a medical student in New York City in the mid-1980s, I did several of my clinical clerkships at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. One night during my general surgery rotation, there was a young woman with anal cancer who complained of pain.
My resident did not want to give her more medication and I asked why. After all, this was a cancer center with progressive ideas about pain management, this patient was suffering, and she was ill enough to be hospitalized.
The resident responded to my inquiry: “She doesn’t have a terminal condition and she has an addictive personality.” It seemed to me a draconian (and perhaps sexist) response in a hospital where patient-controlled analgesia was becoming routine and, as an aspiring psychiatrist, I didn’t quite trust the surgical resident’s evaluation of the patient’s personality or his ability to predict if she might become addicted to opiates.
This encounter happened about 6 years after Jane Porter and Hershel Jink, MD, had published a letter titled, “Addiction Rare in Patients Treated with Narcotics” in the New England Journal of Medicine (1980 Jan 10;302:123) with the following finding: “... of 11,800 patients given narcotic painkillers while in hospital, only four developed an addiction to those drugs.” This fragment of a sentence, published as a one-paragraph letter and not as a full, peer-reviewed study, was in the process of changing how all of American medicine responded to pain.
In his book, “Dreamland: The True Tale of America’s Opiate Epidemic” (Bloomsbury Press, 2015), journalist Sam Quinones was quick to point out that these findings were made at a time when doctors, like my surgical resident, were hesitant to use opiates for fear of addiction. Their use was limited to cancer patients, postoperative patients, and those suffering from an acute injury. This finding that prescribed opiates did not cause addiction was true in these hospitalized patients, at a time when pills were doled out with caution for short-term use, and their use for chronic pain had not yet been tested.
Nearly 40 years later, we know that the answer to that national experiment did not work out so well: A proportion of patients given long-term, sometimes high-dose, opiates for chronic pain do sometimes become addicted. Some chronic pain patients received narcotics at “pill mills,” and some went on to use heroin obtained illegally. Furthermore, the widespread use of these medicines made them more readily available to those looking for something besides pain relief.
I would like to suggest that the opioid epidemic is not solely the fault of the medical community: We had drug addiction long before we had the Porter and Jink paragraph and not all addiction starts with a prescription pad. Still, the lesson for public health is a poignant one: Populations and circumstances matter. Be careful with generalizations.
Still, we see these generalizations all the time. I am sometimes surprised at how many people have “the answer.” Whether it’s more widespread availability of Narcan, medication-assisted treatment (MAT), safe injection sites, 12-step programs, or “Just Say No,” every method has its proponents. I always wonder when I see public health officials propose safe injection sites as something that would surely save thousands of lives, citing data out of cities such as Vancouver, as well as in Europe, and Australia, if results in those places would transfer to my city – Baltimore – where drug addiction, violence, and poverty are rampant. Perhaps they would, and I would love to see Baltimore try anything that might work. But I hope cities that do set up such sites will follow the numbers and halt any program that does not offer robust results.
I wonder, as well, why, with the clear success of MAT strategies in reducing mortality, we don’t experiment with ways of making these methods more accessible. Might Suboxone work if doctors could prescribe it as easily as they can prescribe oxycodone, with no 8-hour course or DEA waiver? Might methadone both work and be more acceptable to patients if given in a way that didn’t require daily travel to a clinic for administration? With such a deadly pervasive epidemic, I wonder also about our focus on treating addiction, when it seems we should have a parallel focus on understanding and addressing the factors that cause addiction. Medical prescribing is but one avenue to addiction, yet we have no understanding as to why some people become addicted when others do not. Shouldn’t we be able to prevent addiction? From Richard Nixon’s “war on drugs” to Donald Trump’s physical border wall, there are many answers, but few solutions.
There are other public health issues that suffer from the same generalizations. In psychiatry, advocacy groups tout involuntary outpatient treatment as a successful way of getting treatment to vulnerable individuals who will not willingly negotiate their own care. While a pilot study at Bellevue showed no benefit to mandated care, a follow-up study showed that mandated treatment was effective at reducing hospital days. While outpatient commitment studies look at rates of hospitalization, incarceration, and quality-of-life measures, mandated treatment is often cited as a means to prevent all forms of violence, including mass shootings, while there is no evidence to support these ideas. Still, 47 states and the District of Columbia now have outpatient commitment laws.
Does involuntary care benefit those with substance use disorders? In Massachusetts, Section 35 allows for civil commitment for drug treatment, and many of the treatment facilities are run by the Department of Corrections. It would be good to know if these measures worked. So far, it looks like opioid deaths in Massachusetts have stabilized, while the overdose death rate continues to rise in other states. Whether this is a result of Section 35 or other measures is unknown.
I’m not against innovation, and desperate situations call for creative responses. We need to be careful that our responses are measured and these experiments are contained while ascertaining what really does work and what does not cause unintended harms. Will a concrete wall stem the flow of illegal heroin? I imagine a new world of drones making drug drops.
Sometimes our innovative best guesses don’t work, and sometimes they do. Despite easy access to antidepressant medications, a national suicide hotline, increased numbers of mental health professionals, and anti-stigma/awareness campaigns, suicide rates continue to rise. Efforts to end smoking, however, have been quite successful, as have measures to get Americans to buckle their seat belts, and these measures have decreased mortality rates. The recommendation for healthy women to take hormone therapy is a good example: It was an innovative recommendation to help cardiac and orthopedic outcomes, yet studies that were run alongside these recommendations were quick to show an unintended increased risk of breast and uterine cancer.
I don’t know what happened to the young woman on my surgical rotation. If the decision were mine, I would have given her more pain medication, even now, but I don’t know if that would have been the right thing to do., and to look carefully at our outcomes in a variety of populations and circumstances.
Dr. Miller is the coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore.
Populations and circumstances matter
Populations and circumstances matter
As a medical student in New York City in the mid-1980s, I did several of my clinical clerkships at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. One night during my general surgery rotation, there was a young woman with anal cancer who complained of pain.
My resident did not want to give her more medication and I asked why. After all, this was a cancer center with progressive ideas about pain management, this patient was suffering, and she was ill enough to be hospitalized.
The resident responded to my inquiry: “She doesn’t have a terminal condition and she has an addictive personality.” It seemed to me a draconian (and perhaps sexist) response in a hospital where patient-controlled analgesia was becoming routine and, as an aspiring psychiatrist, I didn’t quite trust the surgical resident’s evaluation of the patient’s personality or his ability to predict if she might become addicted to opiates.
This encounter happened about 6 years after Jane Porter and Hershel Jink, MD, had published a letter titled, “Addiction Rare in Patients Treated with Narcotics” in the New England Journal of Medicine (1980 Jan 10;302:123) with the following finding: “... of 11,800 patients given narcotic painkillers while in hospital, only four developed an addiction to those drugs.” This fragment of a sentence, published as a one-paragraph letter and not as a full, peer-reviewed study, was in the process of changing how all of American medicine responded to pain.
In his book, “Dreamland: The True Tale of America’s Opiate Epidemic” (Bloomsbury Press, 2015), journalist Sam Quinones was quick to point out that these findings were made at a time when doctors, like my surgical resident, were hesitant to use opiates for fear of addiction. Their use was limited to cancer patients, postoperative patients, and those suffering from an acute injury. This finding that prescribed opiates did not cause addiction was true in these hospitalized patients, at a time when pills were doled out with caution for short-term use, and their use for chronic pain had not yet been tested.
Nearly 40 years later, we know that the answer to that national experiment did not work out so well: A proportion of patients given long-term, sometimes high-dose, opiates for chronic pain do sometimes become addicted. Some chronic pain patients received narcotics at “pill mills,” and some went on to use heroin obtained illegally. Furthermore, the widespread use of these medicines made them more readily available to those looking for something besides pain relief.
I would like to suggest that the opioid epidemic is not solely the fault of the medical community: We had drug addiction long before we had the Porter and Jink paragraph and not all addiction starts with a prescription pad. Still, the lesson for public health is a poignant one: Populations and circumstances matter. Be careful with generalizations.
Still, we see these generalizations all the time. I am sometimes surprised at how many people have “the answer.” Whether it’s more widespread availability of Narcan, medication-assisted treatment (MAT), safe injection sites, 12-step programs, or “Just Say No,” every method has its proponents. I always wonder when I see public health officials propose safe injection sites as something that would surely save thousands of lives, citing data out of cities such as Vancouver, as well as in Europe, and Australia, if results in those places would transfer to my city – Baltimore – where drug addiction, violence, and poverty are rampant. Perhaps they would, and I would love to see Baltimore try anything that might work. But I hope cities that do set up such sites will follow the numbers and halt any program that does not offer robust results.
I wonder, as well, why, with the clear success of MAT strategies in reducing mortality, we don’t experiment with ways of making these methods more accessible. Might Suboxone work if doctors could prescribe it as easily as they can prescribe oxycodone, with no 8-hour course or DEA waiver? Might methadone both work and be more acceptable to patients if given in a way that didn’t require daily travel to a clinic for administration? With such a deadly pervasive epidemic, I wonder also about our focus on treating addiction, when it seems we should have a parallel focus on understanding and addressing the factors that cause addiction. Medical prescribing is but one avenue to addiction, yet we have no understanding as to why some people become addicted when others do not. Shouldn’t we be able to prevent addiction? From Richard Nixon’s “war on drugs” to Donald Trump’s physical border wall, there are many answers, but few solutions.
There are other public health issues that suffer from the same generalizations. In psychiatry, advocacy groups tout involuntary outpatient treatment as a successful way of getting treatment to vulnerable individuals who will not willingly negotiate their own care. While a pilot study at Bellevue showed no benefit to mandated care, a follow-up study showed that mandated treatment was effective at reducing hospital days. While outpatient commitment studies look at rates of hospitalization, incarceration, and quality-of-life measures, mandated treatment is often cited as a means to prevent all forms of violence, including mass shootings, while there is no evidence to support these ideas. Still, 47 states and the District of Columbia now have outpatient commitment laws.
Does involuntary care benefit those with substance use disorders? In Massachusetts, Section 35 allows for civil commitment for drug treatment, and many of the treatment facilities are run by the Department of Corrections. It would be good to know if these measures worked. So far, it looks like opioid deaths in Massachusetts have stabilized, while the overdose death rate continues to rise in other states. Whether this is a result of Section 35 or other measures is unknown.
I’m not against innovation, and desperate situations call for creative responses. We need to be careful that our responses are measured and these experiments are contained while ascertaining what really does work and what does not cause unintended harms. Will a concrete wall stem the flow of illegal heroin? I imagine a new world of drones making drug drops.
Sometimes our innovative best guesses don’t work, and sometimes they do. Despite easy access to antidepressant medications, a national suicide hotline, increased numbers of mental health professionals, and anti-stigma/awareness campaigns, suicide rates continue to rise. Efforts to end smoking, however, have been quite successful, as have measures to get Americans to buckle their seat belts, and these measures have decreased mortality rates. The recommendation for healthy women to take hormone therapy is a good example: It was an innovative recommendation to help cardiac and orthopedic outcomes, yet studies that were run alongside these recommendations were quick to show an unintended increased risk of breast and uterine cancer.
I don’t know what happened to the young woman on my surgical rotation. If the decision were mine, I would have given her more pain medication, even now, but I don’t know if that would have been the right thing to do., and to look carefully at our outcomes in a variety of populations and circumstances.
Dr. Miller is the coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore.
As a medical student in New York City in the mid-1980s, I did several of my clinical clerkships at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. One night during my general surgery rotation, there was a young woman with anal cancer who complained of pain.
My resident did not want to give her more medication and I asked why. After all, this was a cancer center with progressive ideas about pain management, this patient was suffering, and she was ill enough to be hospitalized.
The resident responded to my inquiry: “She doesn’t have a terminal condition and she has an addictive personality.” It seemed to me a draconian (and perhaps sexist) response in a hospital where patient-controlled analgesia was becoming routine and, as an aspiring psychiatrist, I didn’t quite trust the surgical resident’s evaluation of the patient’s personality or his ability to predict if she might become addicted to opiates.
This encounter happened about 6 years after Jane Porter and Hershel Jink, MD, had published a letter titled, “Addiction Rare in Patients Treated with Narcotics” in the New England Journal of Medicine (1980 Jan 10;302:123) with the following finding: “... of 11,800 patients given narcotic painkillers while in hospital, only four developed an addiction to those drugs.” This fragment of a sentence, published as a one-paragraph letter and not as a full, peer-reviewed study, was in the process of changing how all of American medicine responded to pain.
In his book, “Dreamland: The True Tale of America’s Opiate Epidemic” (Bloomsbury Press, 2015), journalist Sam Quinones was quick to point out that these findings were made at a time when doctors, like my surgical resident, were hesitant to use opiates for fear of addiction. Their use was limited to cancer patients, postoperative patients, and those suffering from an acute injury. This finding that prescribed opiates did not cause addiction was true in these hospitalized patients, at a time when pills were doled out with caution for short-term use, and their use for chronic pain had not yet been tested.
Nearly 40 years later, we know that the answer to that national experiment did not work out so well: A proportion of patients given long-term, sometimes high-dose, opiates for chronic pain do sometimes become addicted. Some chronic pain patients received narcotics at “pill mills,” and some went on to use heroin obtained illegally. Furthermore, the widespread use of these medicines made them more readily available to those looking for something besides pain relief.
I would like to suggest that the opioid epidemic is not solely the fault of the medical community: We had drug addiction long before we had the Porter and Jink paragraph and not all addiction starts with a prescription pad. Still, the lesson for public health is a poignant one: Populations and circumstances matter. Be careful with generalizations.
Still, we see these generalizations all the time. I am sometimes surprised at how many people have “the answer.” Whether it’s more widespread availability of Narcan, medication-assisted treatment (MAT), safe injection sites, 12-step programs, or “Just Say No,” every method has its proponents. I always wonder when I see public health officials propose safe injection sites as something that would surely save thousands of lives, citing data out of cities such as Vancouver, as well as in Europe, and Australia, if results in those places would transfer to my city – Baltimore – where drug addiction, violence, and poverty are rampant. Perhaps they would, and I would love to see Baltimore try anything that might work. But I hope cities that do set up such sites will follow the numbers and halt any program that does not offer robust results.
I wonder, as well, why, with the clear success of MAT strategies in reducing mortality, we don’t experiment with ways of making these methods more accessible. Might Suboxone work if doctors could prescribe it as easily as they can prescribe oxycodone, with no 8-hour course or DEA waiver? Might methadone both work and be more acceptable to patients if given in a way that didn’t require daily travel to a clinic for administration? With such a deadly pervasive epidemic, I wonder also about our focus on treating addiction, when it seems we should have a parallel focus on understanding and addressing the factors that cause addiction. Medical prescribing is but one avenue to addiction, yet we have no understanding as to why some people become addicted when others do not. Shouldn’t we be able to prevent addiction? From Richard Nixon’s “war on drugs” to Donald Trump’s physical border wall, there are many answers, but few solutions.
There are other public health issues that suffer from the same generalizations. In psychiatry, advocacy groups tout involuntary outpatient treatment as a successful way of getting treatment to vulnerable individuals who will not willingly negotiate their own care. While a pilot study at Bellevue showed no benefit to mandated care, a follow-up study showed that mandated treatment was effective at reducing hospital days. While outpatient commitment studies look at rates of hospitalization, incarceration, and quality-of-life measures, mandated treatment is often cited as a means to prevent all forms of violence, including mass shootings, while there is no evidence to support these ideas. Still, 47 states and the District of Columbia now have outpatient commitment laws.
Does involuntary care benefit those with substance use disorders? In Massachusetts, Section 35 allows for civil commitment for drug treatment, and many of the treatment facilities are run by the Department of Corrections. It would be good to know if these measures worked. So far, it looks like opioid deaths in Massachusetts have stabilized, while the overdose death rate continues to rise in other states. Whether this is a result of Section 35 or other measures is unknown.
I’m not against innovation, and desperate situations call for creative responses. We need to be careful that our responses are measured and these experiments are contained while ascertaining what really does work and what does not cause unintended harms. Will a concrete wall stem the flow of illegal heroin? I imagine a new world of drones making drug drops.
Sometimes our innovative best guesses don’t work, and sometimes they do. Despite easy access to antidepressant medications, a national suicide hotline, increased numbers of mental health professionals, and anti-stigma/awareness campaigns, suicide rates continue to rise. Efforts to end smoking, however, have been quite successful, as have measures to get Americans to buckle their seat belts, and these measures have decreased mortality rates. The recommendation for healthy women to take hormone therapy is a good example: It was an innovative recommendation to help cardiac and orthopedic outcomes, yet studies that were run alongside these recommendations were quick to show an unintended increased risk of breast and uterine cancer.
I don’t know what happened to the young woman on my surgical rotation. If the decision were mine, I would have given her more pain medication, even now, but I don’t know if that would have been the right thing to do., and to look carefully at our outcomes in a variety of populations and circumstances.
Dr. Miller is the coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice in Baltimore.
Think outside lower body for pelvic pain
Also today, treating obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure decreased amyloid levels, spending on medical marketing increased by more than $12 billion over that past two decades, and one expert has advice on how you can get your work published.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, treating obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure decreased amyloid levels, spending on medical marketing increased by more than $12 billion over that past two decades, and one expert has advice on how you can get your work published.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, treating obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure decreased amyloid levels, spending on medical marketing increased by more than $12 billion over that past two decades, and one expert has advice on how you can get your work published.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
AAP guidance: How to ask about military service
Knee pathologies predict accelerated knee osteoarthritis, patients with a poor-prognosis cancer have a higher risk of suicide in the first year, and Nuedexta is mainly being prescribed for dementia and Parkinson’s.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Knee pathologies predict accelerated knee osteoarthritis, patients with a poor-prognosis cancer have a higher risk of suicide in the first year, and Nuedexta is mainly being prescribed for dementia and Parkinson’s.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Knee pathologies predict accelerated knee osteoarthritis, patients with a poor-prognosis cancer have a higher risk of suicide in the first year, and Nuedexta is mainly being prescribed for dementia and Parkinson’s.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
For pelvic pain, think outside the lower body
LAS VEGAS – An estimated 15%-25% of women aged 18-50 years suffer from chronic pelvic pain, a condition that commonly leads to sick days, reduced activity, and higher medication use. Treatments like surgery and opioids may seem feasible, but an obstetrician-gynecologist who studies pain urged colleagues to think twice.
In some cases, pelvic pain patients may suffer from centralized pain syndromes, conditions linked to the central nervous system that may not respond well to those common treatments, said Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor.
“If we have laser vision on the pelvis, we may help some patients, but many of us will do harm,” said Dr. As-Sanie, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Endometriosis is frequently linked to pelvic pain. But, she said, the link between the two is fuzzier than has been assumed.
“It would make sense that endometriosis or pelvic adhesions would activate nociceptive pain, and [there are] a lot of data to support that this is, in part, how endometriosis causes pain,” she said. “But I would argue it really isn’t that simple because the relationship between endometriosis and pelvic pain is very complex and not explained entirely by the lesion.” For example, “we know that pain recurs after medical and surgical therapy, often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis.” And, there’s little relationship between pain symptoms and the location or extent of endometriosis.
What’s going on? Dr. As-Sanie suggested central pain syndromes can play a significant role in pelvic pain. These syndromes are 1.5-2 times more common in women than men, and are triggered or exacerbated by stressors.
She also emphasized the wide-ranging effects of these syndromes. “We focus on pain, but it’s clearly not a just a pain disorder,” noting that patients can report fatigue, poor sleep, greater sensitivity to light and sound, and memory difficulties that produce “fibromyalgia fog.”
Research suggests that patients with central pain syndromes experience changes in both brain structure and function, she said. As for pelvic pain specifically, studies have linked it to increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function regardless of whether endometriosis is present.
How should patients with pelvic pain be treated in light of this information? Dr. As-Sanie suggests first trying “gold standard” approaches to treat contributing factors whether they’re gynecologic, urologic, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal or nerve related.
If those strategies don’t work, she said, “consider treating centralized pain” with a blend of approaches: behavioral (such as diet and cognitive-behavior therapy), medical (such as hormone modulation), and interventional (such as physical therapy and surgery).
Also consider pharmacologic therapies, said Dr. As-Sanie, who identified dual reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine [Effexor] and duloxetine [Cymbalta] are a class of antidepressants that block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine) and anticonvulsants as drugs with strong evidence as treatments for central pain syndromes.
“Start at low doses and titrate up,” she advised, and “if at any point a given medication doesn’t work, we should try another.”
The Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Dr. As-Sanie discloses she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
LAS VEGAS – An estimated 15%-25% of women aged 18-50 years suffer from chronic pelvic pain, a condition that commonly leads to sick days, reduced activity, and higher medication use. Treatments like surgery and opioids may seem feasible, but an obstetrician-gynecologist who studies pain urged colleagues to think twice.
In some cases, pelvic pain patients may suffer from centralized pain syndromes, conditions linked to the central nervous system that may not respond well to those common treatments, said Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor.
“If we have laser vision on the pelvis, we may help some patients, but many of us will do harm,” said Dr. As-Sanie, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Endometriosis is frequently linked to pelvic pain. But, she said, the link between the two is fuzzier than has been assumed.
“It would make sense that endometriosis or pelvic adhesions would activate nociceptive pain, and [there are] a lot of data to support that this is, in part, how endometriosis causes pain,” she said. “But I would argue it really isn’t that simple because the relationship between endometriosis and pelvic pain is very complex and not explained entirely by the lesion.” For example, “we know that pain recurs after medical and surgical therapy, often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis.” And, there’s little relationship between pain symptoms and the location or extent of endometriosis.
What’s going on? Dr. As-Sanie suggested central pain syndromes can play a significant role in pelvic pain. These syndromes are 1.5-2 times more common in women than men, and are triggered or exacerbated by stressors.
She also emphasized the wide-ranging effects of these syndromes. “We focus on pain, but it’s clearly not a just a pain disorder,” noting that patients can report fatigue, poor sleep, greater sensitivity to light and sound, and memory difficulties that produce “fibromyalgia fog.”
Research suggests that patients with central pain syndromes experience changes in both brain structure and function, she said. As for pelvic pain specifically, studies have linked it to increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function regardless of whether endometriosis is present.
How should patients with pelvic pain be treated in light of this information? Dr. As-Sanie suggests first trying “gold standard” approaches to treat contributing factors whether they’re gynecologic, urologic, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal or nerve related.
If those strategies don’t work, she said, “consider treating centralized pain” with a blend of approaches: behavioral (such as diet and cognitive-behavior therapy), medical (such as hormone modulation), and interventional (such as physical therapy and surgery).
Also consider pharmacologic therapies, said Dr. As-Sanie, who identified dual reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine [Effexor] and duloxetine [Cymbalta] are a class of antidepressants that block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine) and anticonvulsants as drugs with strong evidence as treatments for central pain syndromes.
“Start at low doses and titrate up,” she advised, and “if at any point a given medication doesn’t work, we should try another.”
The Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Dr. As-Sanie discloses she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
LAS VEGAS – An estimated 15%-25% of women aged 18-50 years suffer from chronic pelvic pain, a condition that commonly leads to sick days, reduced activity, and higher medication use. Treatments like surgery and opioids may seem feasible, but an obstetrician-gynecologist who studies pain urged colleagues to think twice.
In some cases, pelvic pain patients may suffer from centralized pain syndromes, conditions linked to the central nervous system that may not respond well to those common treatments, said Sawsan As-Sanie, MD, MPH, director of the University of Michigan Endometriosis Center, Ann Arbor.
“If we have laser vision on the pelvis, we may help some patients, but many of us will do harm,” said Dr. As-Sanie, who spoke at the Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium.
Endometriosis is frequently linked to pelvic pain. But, she said, the link between the two is fuzzier than has been assumed.
“It would make sense that endometriosis or pelvic adhesions would activate nociceptive pain, and [there are] a lot of data to support that this is, in part, how endometriosis causes pain,” she said. “But I would argue it really isn’t that simple because the relationship between endometriosis and pelvic pain is very complex and not explained entirely by the lesion.” For example, “we know that pain recurs after medical and surgical therapy, often without evidence of recurrent endometriosis.” And, there’s little relationship between pain symptoms and the location or extent of endometriosis.
What’s going on? Dr. As-Sanie suggested central pain syndromes can play a significant role in pelvic pain. These syndromes are 1.5-2 times more common in women than men, and are triggered or exacerbated by stressors.
She also emphasized the wide-ranging effects of these syndromes. “We focus on pain, but it’s clearly not a just a pain disorder,” noting that patients can report fatigue, poor sleep, greater sensitivity to light and sound, and memory difficulties that produce “fibromyalgia fog.”
Research suggests that patients with central pain syndromes experience changes in both brain structure and function, she said. As for pelvic pain specifically, studies have linked it to increased pain sensitivity and altered central nervous system structure and function regardless of whether endometriosis is present.
How should patients with pelvic pain be treated in light of this information? Dr. As-Sanie suggests first trying “gold standard” approaches to treat contributing factors whether they’re gynecologic, urologic, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal or nerve related.
If those strategies don’t work, she said, “consider treating centralized pain” with a blend of approaches: behavioral (such as diet and cognitive-behavior therapy), medical (such as hormone modulation), and interventional (such as physical therapy and surgery).
Also consider pharmacologic therapies, said Dr. As-Sanie, who identified dual reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine [Effexor] and duloxetine [Cymbalta] are a class of antidepressants that block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine) and anticonvulsants as drugs with strong evidence as treatments for central pain syndromes.
“Start at low doses and titrate up,” she advised, and “if at any point a given medication doesn’t work, we should try another.”
The Pelvic Anatomy and Gynecologic Surgery Symposium was jointly provided by Global Academy for Medical Education and the University of Cincinnati. Global Academy and this news organization are owned by the same company.
Dr. As-Sanie discloses she is a consultant for AbbVie and Myovant.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PAGS
Prenatal valproate and ADHD
Also today, one expert calls for better ways to preserve beta cell function in youth, synthetic opioids drive a spike in the number of fatal overdoses, and mothers may play a role in the link between depression in fathers and daughters.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, one expert calls for better ways to preserve beta cell function in youth, synthetic opioids drive a spike in the number of fatal overdoses, and mothers may play a role in the link between depression in fathers and daughters.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, one expert calls for better ways to preserve beta cell function in youth, synthetic opioids drive a spike in the number of fatal overdoses, and mothers may play a role in the link between depression in fathers and daughters.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Cerebral small vessel and cognitive impairment
Also today, antidepressants are tied to greater hip fracture incidence, a hospital readmission reduction program may be doing more harm than good, and the flu season rages on with 19 states showing high activity in the final week of 2018.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, antidepressants are tied to greater hip fracture incidence, a hospital readmission reduction program may be doing more harm than good, and the flu season rages on with 19 states showing high activity in the final week of 2018.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, antidepressants are tied to greater hip fracture incidence, a hospital readmission reduction program may be doing more harm than good, and the flu season rages on with 19 states showing high activity in the final week of 2018.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify