User login
Mortality trends in childhood after infant bacterial meningitis
Among infants younger than 1 year of age, bacterial meningitis is associated with worse long-term mortality, even after recovery from the initial infection. Heightened mortality risk stretched out to 10 years, and was highest in the wake of infection from Streptococcus agalactiae, according to a retrospective analysis of children in the Netherlands.
“The adjusted hazard rates were high for the whole group of bacterial meningitis, especially within the first year after onset. (Staphylococcus agalactiae) meningitis has the highest mortality risk within one year of disease onset,” Linde Snoek said during her presentation of the study (abstract 913) at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Ms. Snoek is a PhD student at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
Over longer time periods, the mortality associations were different. “The adjusted hazard rates were highest for pneumococcal meningitis compared to the other pathogens. And this was the case for 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years after disease onset,” said Ms. Snoek.
The study appears to be the first to look at extended mortality following bacterial meningitis in this age group, according to Marie Rohr, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
“In a quick review of the literature I did not find any [equivalent] study concerning short- and long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis in under 1 year of age,” said Dr. Rohr, a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at University Hospitals of Geneva. But the message to physicians is clear. “Children with history of bacterial meningitis have a higher long-term mortality than children without a history of bacterial meningitis,” said Dr. Rohr.
The study did have a key limitation: For matched controls, it relied on anonymous data from the Municipal Personal Records Database in Statistics Netherlands. “Important information like cause of death is lacking,” said Dr. Rohr.
Bacterial meningitis is associated with significant mortality and morbidity. Pathogens behind the infections vary with age group and geographic location, as well as immunization status.
To examine long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis, the researchers collected 1,646 records from an exposed cohort, with a date range of 1995 to 2018, from the Netherlands Reference Laboratory for Bacterial Meningitis. Included patients had a positive culture diagnosis of bacterial meningitis during the first year of life. Each exposed subject was compared to 10 controls matched by birth month, birth year, and sex, who had no exposure to bacterial meningitis.
Staphylococcus pneumoniae accounted for the most cases, at 32.0% (median age of onset, 180 days), followed by Neisseria meningitidis at 29.0% (median age of onset, 203 days). Other pathogens included S. agalactiae (19.7%, 10 days), Escherichia coli (8.8%, 13 days), and Haemophilus influenzae (5.4%, 231 days).
The mortality risk within 1 year of disease onset was higher for all pathogens (6.2% vs. 0.2% unexposed). The highest mortality risk was seen for S. agalactiae (8.7%), followed by E. coli (6.4%), N. meningitidis (4.9%), and H. influenzae (3.4%).
Hazard ratios (HR) for mortality were also higher, particularly in the first year after disease onset. For all pathogens, mortality rates were higher within 1 year (HR, 39.2), 5 years (HR, 28.7), and 10 years (HR, 24.1). The consistently highest mortality rates were associated with S. pneumoniae over 1-year, 5-year, and 10-year follow-up (HR, 42.8; HR, 45.6; HR, 40.6, respectively). Within 1 year, the highest mortality rate was associated with N. meningitidis (HR, 58.4).
Ms. Snoek and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
Among infants younger than 1 year of age, bacterial meningitis is associated with worse long-term mortality, even after recovery from the initial infection. Heightened mortality risk stretched out to 10 years, and was highest in the wake of infection from Streptococcus agalactiae, according to a retrospective analysis of children in the Netherlands.
“The adjusted hazard rates were high for the whole group of bacterial meningitis, especially within the first year after onset. (Staphylococcus agalactiae) meningitis has the highest mortality risk within one year of disease onset,” Linde Snoek said during her presentation of the study (abstract 913) at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Ms. Snoek is a PhD student at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
Over longer time periods, the mortality associations were different. “The adjusted hazard rates were highest for pneumococcal meningitis compared to the other pathogens. And this was the case for 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years after disease onset,” said Ms. Snoek.
The study appears to be the first to look at extended mortality following bacterial meningitis in this age group, according to Marie Rohr, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
“In a quick review of the literature I did not find any [equivalent] study concerning short- and long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis in under 1 year of age,” said Dr. Rohr, a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at University Hospitals of Geneva. But the message to physicians is clear. “Children with history of bacterial meningitis have a higher long-term mortality than children without a history of bacterial meningitis,” said Dr. Rohr.
The study did have a key limitation: For matched controls, it relied on anonymous data from the Municipal Personal Records Database in Statistics Netherlands. “Important information like cause of death is lacking,” said Dr. Rohr.
Bacterial meningitis is associated with significant mortality and morbidity. Pathogens behind the infections vary with age group and geographic location, as well as immunization status.
To examine long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis, the researchers collected 1,646 records from an exposed cohort, with a date range of 1995 to 2018, from the Netherlands Reference Laboratory for Bacterial Meningitis. Included patients had a positive culture diagnosis of bacterial meningitis during the first year of life. Each exposed subject was compared to 10 controls matched by birth month, birth year, and sex, who had no exposure to bacterial meningitis.
Staphylococcus pneumoniae accounted for the most cases, at 32.0% (median age of onset, 180 days), followed by Neisseria meningitidis at 29.0% (median age of onset, 203 days). Other pathogens included S. agalactiae (19.7%, 10 days), Escherichia coli (8.8%, 13 days), and Haemophilus influenzae (5.4%, 231 days).
The mortality risk within 1 year of disease onset was higher for all pathogens (6.2% vs. 0.2% unexposed). The highest mortality risk was seen for S. agalactiae (8.7%), followed by E. coli (6.4%), N. meningitidis (4.9%), and H. influenzae (3.4%).
Hazard ratios (HR) for mortality were also higher, particularly in the first year after disease onset. For all pathogens, mortality rates were higher within 1 year (HR, 39.2), 5 years (HR, 28.7), and 10 years (HR, 24.1). The consistently highest mortality rates were associated with S. pneumoniae over 1-year, 5-year, and 10-year follow-up (HR, 42.8; HR, 45.6; HR, 40.6, respectively). Within 1 year, the highest mortality rate was associated with N. meningitidis (HR, 58.4).
Ms. Snoek and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
Among infants younger than 1 year of age, bacterial meningitis is associated with worse long-term mortality, even after recovery from the initial infection. Heightened mortality risk stretched out to 10 years, and was highest in the wake of infection from Streptococcus agalactiae, according to a retrospective analysis of children in the Netherlands.
“The adjusted hazard rates were high for the whole group of bacterial meningitis, especially within the first year after onset. (Staphylococcus agalactiae) meningitis has the highest mortality risk within one year of disease onset,” Linde Snoek said during her presentation of the study (abstract 913) at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. Ms. Snoek is a PhD student at Amsterdam University Medical Center.
Over longer time periods, the mortality associations were different. “The adjusted hazard rates were highest for pneumococcal meningitis compared to the other pathogens. And this was the case for 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years after disease onset,” said Ms. Snoek.
The study appears to be the first to look at extended mortality following bacterial meningitis in this age group, according to Marie Rohr, MD, who comoderated the session where the research was presented.
“In a quick review of the literature I did not find any [equivalent] study concerning short- and long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis in under 1 year of age,” said Dr. Rohr, a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at University Hospitals of Geneva. But the message to physicians is clear. “Children with history of bacterial meningitis have a higher long-term mortality than children without a history of bacterial meningitis,” said Dr. Rohr.
The study did have a key limitation: For matched controls, it relied on anonymous data from the Municipal Personal Records Database in Statistics Netherlands. “Important information like cause of death is lacking,” said Dr. Rohr.
Bacterial meningitis is associated with significant mortality and morbidity. Pathogens behind the infections vary with age group and geographic location, as well as immunization status.
To examine long-term mortality after bacterial meningitis, the researchers collected 1,646 records from an exposed cohort, with a date range of 1995 to 2018, from the Netherlands Reference Laboratory for Bacterial Meningitis. Included patients had a positive culture diagnosis of bacterial meningitis during the first year of life. Each exposed subject was compared to 10 controls matched by birth month, birth year, and sex, who had no exposure to bacterial meningitis.
Staphylococcus pneumoniae accounted for the most cases, at 32.0% (median age of onset, 180 days), followed by Neisseria meningitidis at 29.0% (median age of onset, 203 days). Other pathogens included S. agalactiae (19.7%, 10 days), Escherichia coli (8.8%, 13 days), and Haemophilus influenzae (5.4%, 231 days).
The mortality risk within 1 year of disease onset was higher for all pathogens (6.2% vs. 0.2% unexposed). The highest mortality risk was seen for S. agalactiae (8.7%), followed by E. coli (6.4%), N. meningitidis (4.9%), and H. influenzae (3.4%).
Hazard ratios (HR) for mortality were also higher, particularly in the first year after disease onset. For all pathogens, mortality rates were higher within 1 year (HR, 39.2), 5 years (HR, 28.7), and 10 years (HR, 24.1). The consistently highest mortality rates were associated with S. pneumoniae over 1-year, 5-year, and 10-year follow-up (HR, 42.8; HR, 45.6; HR, 40.6, respectively). Within 1 year, the highest mortality rate was associated with N. meningitidis (HR, 58.4).
Ms. Snoek and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ESPID 2021
FDA approves secukinumab in psoriasis patients age six and older
The who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. The expanded indication marks the first time the drug has been available for a pediatric population in the United States.
Children with plaque psoriasis are often undertreated because of fear of side effects of therapies, according to Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “Now, more and more medicines are being tested for safety and efficacy in children, and we no longer have to rely on adult studies to inform treatment choices for children,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization.
The FDA approval of secukinumab for children aged 6 and older with moderate to severe psoriasis “is a welcome addition to the therapeutic toolbox for pediatric psoriasis,” she said. “We’ve entered an era where severe pediatric psoriasis has become a condition that can be adequately controlled with minimal risk and with the convenience of intermittent injections. This has changed the playing field for these children and their families completely. Given the potential short- and long-term negative impact of chronic inflammation on the body of a growing child, we now have approved treatments that can safely offset the risks of undertreated severe psoriasis on the functional and psychological health of the child.”
The approved pediatric dosing for secukinumab is 75 mg or 150 mg depending on the child’s weight at the time of dosing, and it is administered by subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks after an initial loading regimen. According to a press release from Novartis, the FDA approval came on the heels of two phase 3 studies that evaluated the use of secukinumab in children aged 6 to younger than 18 years with plaque psoriasis. The first was a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study which included 162 children 6 years of age and older with severe plaque psoriasis. The doses evaluated were 75 mg for children who weighed less than 50 kg and 150 mg for those 50 kg or greater.
At week 12, the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI)-75 response was 55% among children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 10% in the placebo group and 86% in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 19% in the placebo group.
Meanwhile, the Investigator’s Global Assessment modified 2011 (IGA) “clear” response was achieved in 32% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group and in 81% of children in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group. An IGA “almost clear” skin response was achieved in 81% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group.
The second phase 3 study was a randomized open-label, 208-week trial of 84 subjects 6 years of age and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. According to the Novartis press release, the safety profile reported in both trials was consistent with the safety profile reported in adult plaque psoriasis trials and no new safety signals were observed. The updated prescribing information for secukinumab can be found here.
“When considering treatment with a systemic agent such as a biologic, it is important to consider objective measures of severity, such as extent of disease and involvement of joints but also subjective indicators of severity such as impact beyond the skin on psychological well-being,” Dr. Cordoro said in the interview. “Kids with psoriasis in visible locations may socially isolate themselves due to embarrassment or bullying. Therefore, the impact of moderate to severe psoriasis not only on overall health but on self-esteem and identity formation can be significant, and therefore adequately treating children of all ages to prevent the downstream negative consequences of childhood psoriasis is critical.”
Dr. Cordoro reported having no financial disclosures.
The who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. The expanded indication marks the first time the drug has been available for a pediatric population in the United States.
Children with plaque psoriasis are often undertreated because of fear of side effects of therapies, according to Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “Now, more and more medicines are being tested for safety and efficacy in children, and we no longer have to rely on adult studies to inform treatment choices for children,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization.
The FDA approval of secukinumab for children aged 6 and older with moderate to severe psoriasis “is a welcome addition to the therapeutic toolbox for pediatric psoriasis,” she said. “We’ve entered an era where severe pediatric psoriasis has become a condition that can be adequately controlled with minimal risk and with the convenience of intermittent injections. This has changed the playing field for these children and their families completely. Given the potential short- and long-term negative impact of chronic inflammation on the body of a growing child, we now have approved treatments that can safely offset the risks of undertreated severe psoriasis on the functional and psychological health of the child.”
The approved pediatric dosing for secukinumab is 75 mg or 150 mg depending on the child’s weight at the time of dosing, and it is administered by subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks after an initial loading regimen. According to a press release from Novartis, the FDA approval came on the heels of two phase 3 studies that evaluated the use of secukinumab in children aged 6 to younger than 18 years with plaque psoriasis. The first was a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study which included 162 children 6 years of age and older with severe plaque psoriasis. The doses evaluated were 75 mg for children who weighed less than 50 kg and 150 mg for those 50 kg or greater.
At week 12, the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI)-75 response was 55% among children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 10% in the placebo group and 86% in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 19% in the placebo group.
Meanwhile, the Investigator’s Global Assessment modified 2011 (IGA) “clear” response was achieved in 32% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group and in 81% of children in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group. An IGA “almost clear” skin response was achieved in 81% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group.
The second phase 3 study was a randomized open-label, 208-week trial of 84 subjects 6 years of age and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. According to the Novartis press release, the safety profile reported in both trials was consistent with the safety profile reported in adult plaque psoriasis trials and no new safety signals were observed. The updated prescribing information for secukinumab can be found here.
“When considering treatment with a systemic agent such as a biologic, it is important to consider objective measures of severity, such as extent of disease and involvement of joints but also subjective indicators of severity such as impact beyond the skin on psychological well-being,” Dr. Cordoro said in the interview. “Kids with psoriasis in visible locations may socially isolate themselves due to embarrassment or bullying. Therefore, the impact of moderate to severe psoriasis not only on overall health but on self-esteem and identity formation can be significant, and therefore adequately treating children of all ages to prevent the downstream negative consequences of childhood psoriasis is critical.”
Dr. Cordoro reported having no financial disclosures.
The who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. The expanded indication marks the first time the drug has been available for a pediatric population in the United States.
Children with plaque psoriasis are often undertreated because of fear of side effects of therapies, according to Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “Now, more and more medicines are being tested for safety and efficacy in children, and we no longer have to rely on adult studies to inform treatment choices for children,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization.
The FDA approval of secukinumab for children aged 6 and older with moderate to severe psoriasis “is a welcome addition to the therapeutic toolbox for pediatric psoriasis,” she said. “We’ve entered an era where severe pediatric psoriasis has become a condition that can be adequately controlled with minimal risk and with the convenience of intermittent injections. This has changed the playing field for these children and their families completely. Given the potential short- and long-term negative impact of chronic inflammation on the body of a growing child, we now have approved treatments that can safely offset the risks of undertreated severe psoriasis on the functional and psychological health of the child.”
The approved pediatric dosing for secukinumab is 75 mg or 150 mg depending on the child’s weight at the time of dosing, and it is administered by subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks after an initial loading regimen. According to a press release from Novartis, the FDA approval came on the heels of two phase 3 studies that evaluated the use of secukinumab in children aged 6 to younger than 18 years with plaque psoriasis. The first was a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study which included 162 children 6 years of age and older with severe plaque psoriasis. The doses evaluated were 75 mg for children who weighed less than 50 kg and 150 mg for those 50 kg or greater.
At week 12, the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI)-75 response was 55% among children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 10% in the placebo group and 86% in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 19% in the placebo group.
Meanwhile, the Investigator’s Global Assessment modified 2011 (IGA) “clear” response was achieved in 32% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group and in 81% of children in the 150-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group. An IGA “almost clear” skin response was achieved in 81% of children in the 75-mg dosing group vs. 5% in the placebo group.
The second phase 3 study was a randomized open-label, 208-week trial of 84 subjects 6 years of age and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. According to the Novartis press release, the safety profile reported in both trials was consistent with the safety profile reported in adult plaque psoriasis trials and no new safety signals were observed. The updated prescribing information for secukinumab can be found here.
“When considering treatment with a systemic agent such as a biologic, it is important to consider objective measures of severity, such as extent of disease and involvement of joints but also subjective indicators of severity such as impact beyond the skin on psychological well-being,” Dr. Cordoro said in the interview. “Kids with psoriasis in visible locations may socially isolate themselves due to embarrassment or bullying. Therefore, the impact of moderate to severe psoriasis not only on overall health but on self-esteem and identity formation can be significant, and therefore adequately treating children of all ages to prevent the downstream negative consequences of childhood psoriasis is critical.”
Dr. Cordoro reported having no financial disclosures.
Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica Associated With Raynaud Phenomenon, Segmental Nevi, Hyperhidrosis, and Scoliosis
To the Editor:
Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (PPK) is a rare epidermal nevus syndrome complicated by multiple extracutaneous anomalies, including skeletal defects and neurologic anomalies. Less common associations include lateral curvature of the spine and hyperhidrosis. We present a patient with PPK and unilateral Raynaud phenomenon in addition to a segmental distribution of melanocytic nevi, hyperhidrosis, and scoliosis.
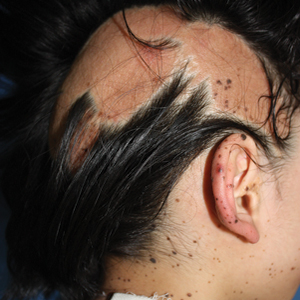
A 9-year-old girl was born with a yellow-orange alopecic plaque on the right side of the scalp (Figure 1). There also were 2 large, irregularly pigmented patches localized on the right side of the upper back and buttock. Over 3 years, numerous papular nevi developed within these pigmented patches and were diagnosed as speckled lentiginous nevi (Figure 2). In addition, numerous nevi of various sizes affected the right face, right shoulder, right arm (Figure 3), and right neck and were clearly demarcated along the midline. Several nevi also were noted within the nevus sebaceous on the right scalp. These skin lesions expanded progressively with age. At 6 years of age, she was diagnosed with hyperhidrosis of the right half of the body, which was most pronounced on the face. Raynaud phenomenon restricted to the right hand also was noted (Figure 4). Upon cold exposure, the digits become pale white, cold, and numb; then blue; and finally red. She lacked other features of connective tissue disease, and autoantibody testing was negative. She also was noted to have an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine (scoliosis). Auditory, ocular, and neurologic examinations were normal. Cranial and cerebral magnetic resonance imaging showed no central nervous system abnormalities. Her family history was negative for nevus spilus, nevus sebaceous, and neurofibromatosis. The clinical findings in our patient led to the diagnosis of PPK.
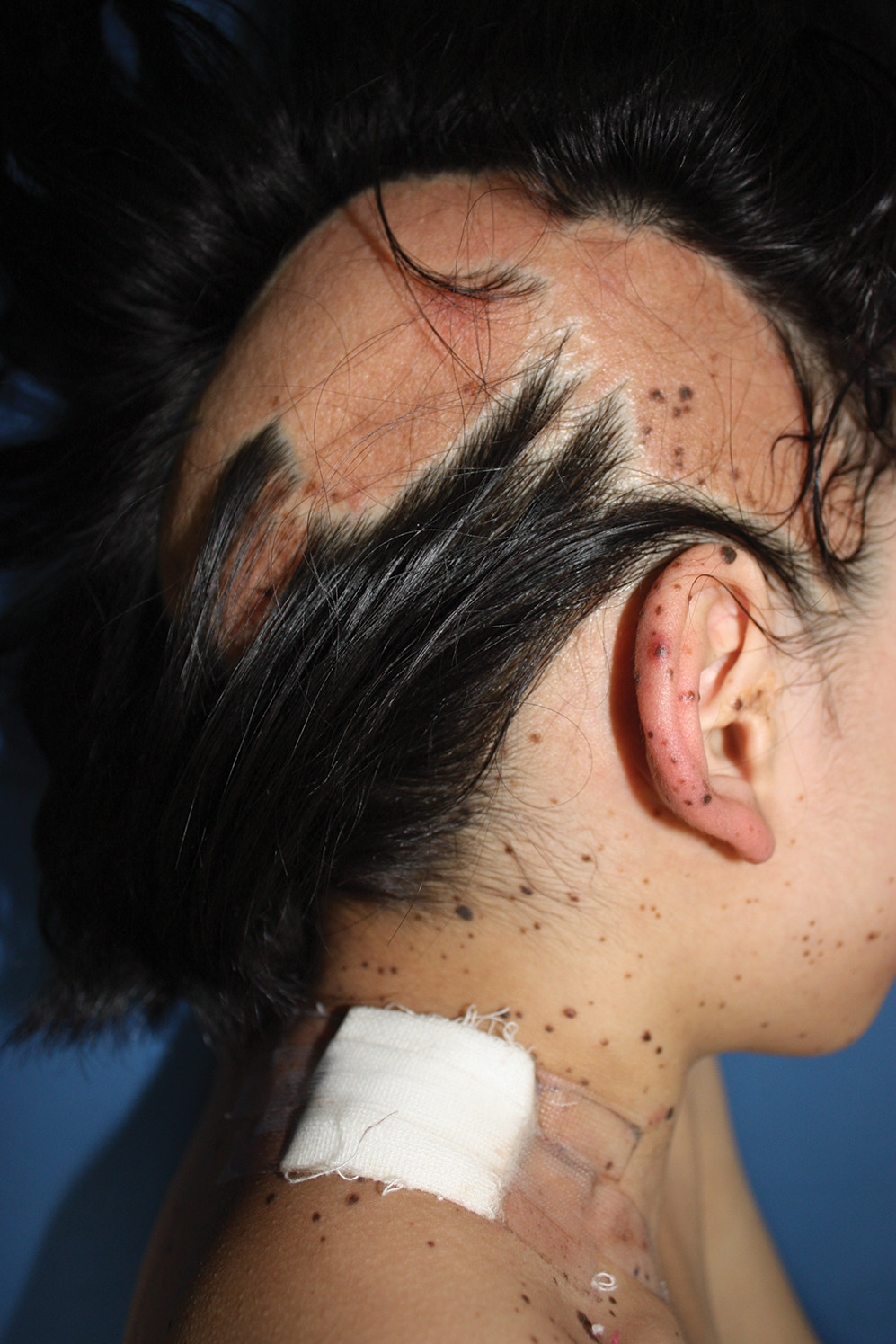
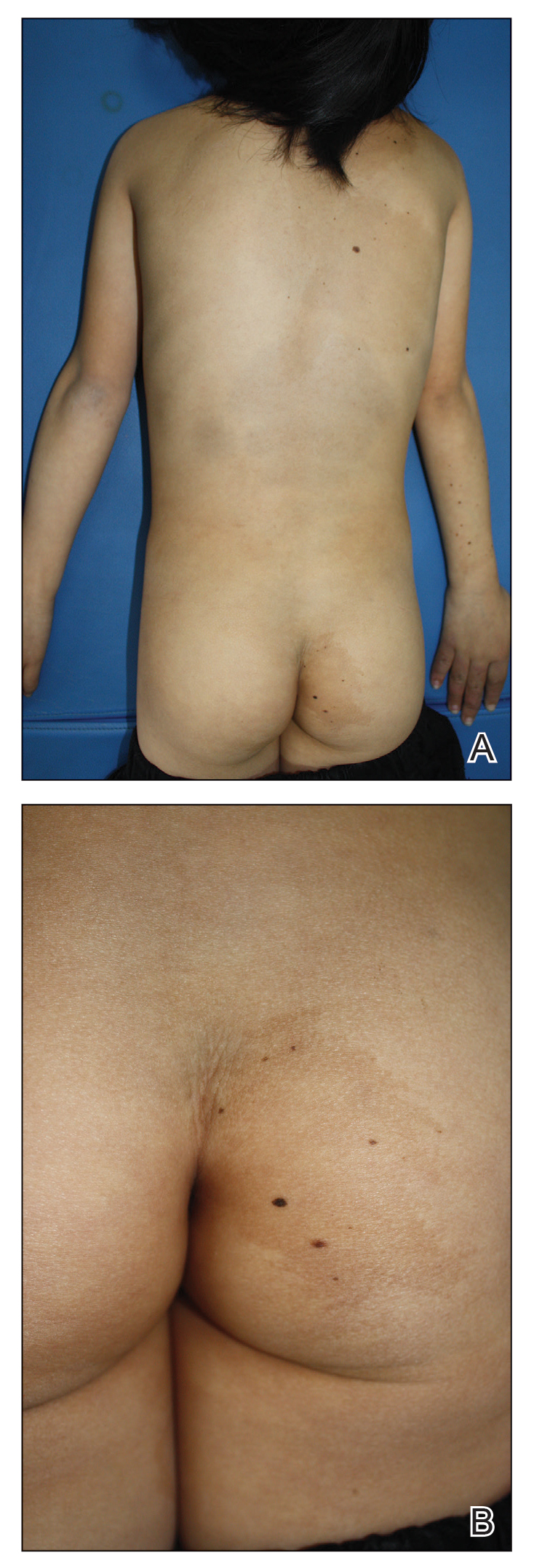
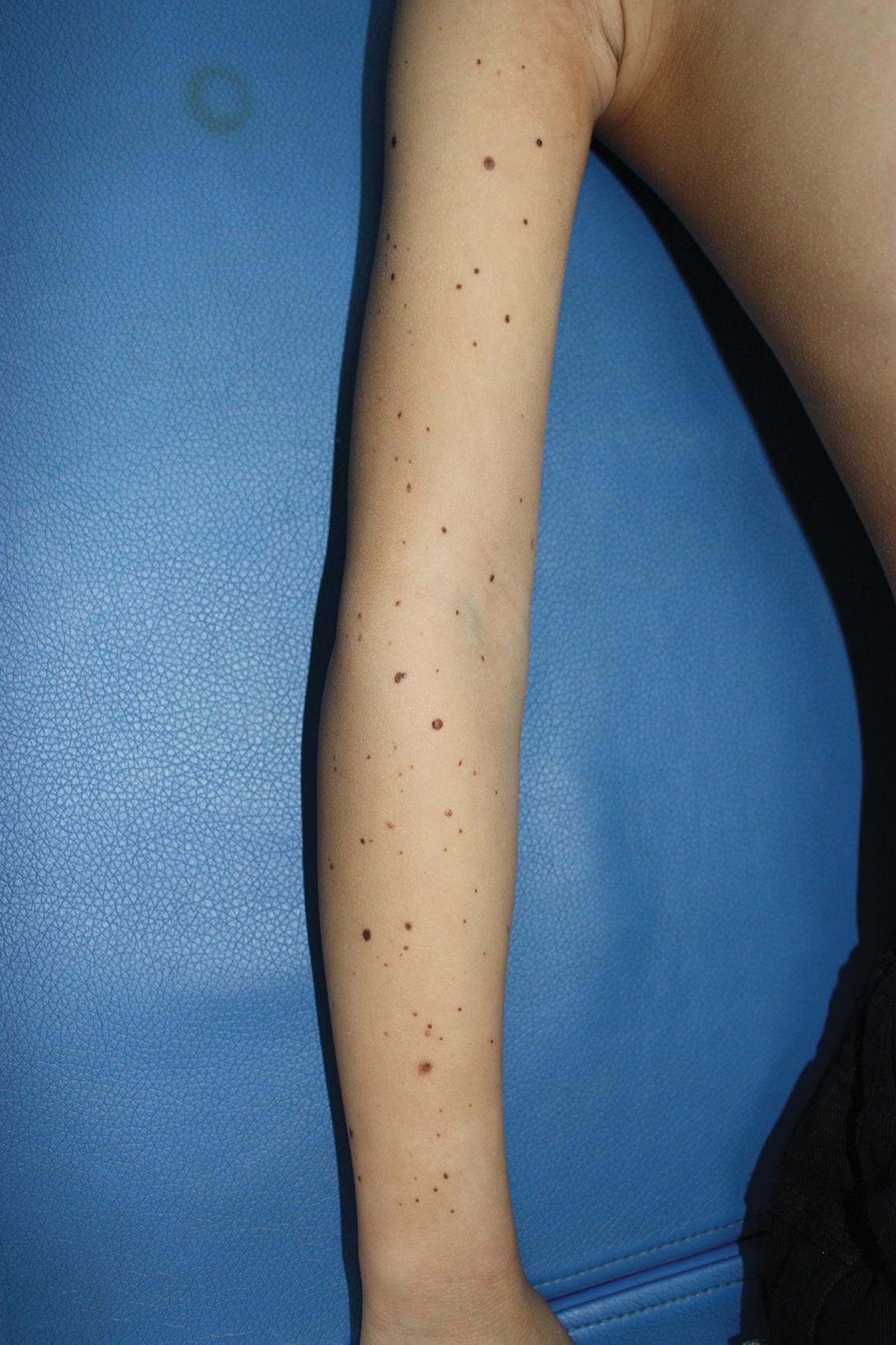
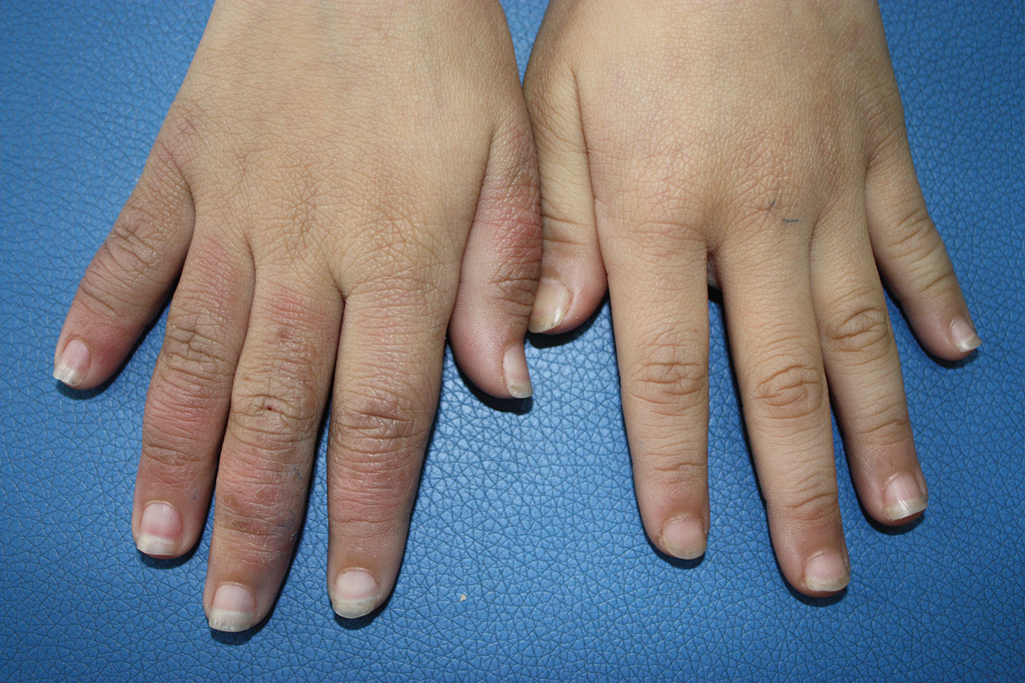
Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is a distinctive epidermal nevus syndrome characterized by the coexistence of a speckled lentiginous nevus, also known as a nevus spilus, and a nevus sebaceous1; PPK frequently is complicated by skeletal, ophthalmic, or neurologic abnormalities.2 Most cases reported are sporadic, and a postzygotic mosaic HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase, HRAS, mutation has been demonstrated in some patients and may contribute to the phenotype of PPK.3,4
Other anomalies have included ichthyosislike diffuse hyperkeratosis, laxity of the hands, pelvic hypoplasia, glaucoma, psychomotor retardation, and hypophosphatemic rickets. These patients also should be monitored for the development of malignant neoplasms within the nevus sebaceous.5 Segmental hyperhidrosis may be seen in association with the nevus spilus component.2
Raynaud phenomenon involving only the right hand was a unique finding in our patient. In 3 years of follow-up, our patient developed no evidence of connective tissue disease or other systemic illness. We speculate that Raynaud phenomenon of the right hand along with hyperhidrosis of the right side of the body could be a result of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. We propose that Raynaud phenomenon represents an unusual manifestation of PPK and may broaden the spectrum of extracutaneous anomalies associated with the disease. The finding of segmental nevi outside of the confines of the nevus spilus was another unusual manifestation of mosaicism.
- Happle R, Hoffmann R, Restano L, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a melanocytic-epidermal twin nevus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996;65:363-365.
- Happle R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes part I. well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:1-22, 23-24.
- Groesser L, Herschberger E, Sagrera A, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is caused by a postzygotic HRAS mutation in a multipotent progenitor cell. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1998-2003.
- Martin RJ, Arefi M, Splitt M, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica and precocious puberty associated with HRAS mutation. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:289-291.
- Chu GY, Wu CY. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a follow-up report with fatal outcome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:467-468.
To the Editor:
Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (PPK) is a rare epidermal nevus syndrome complicated by multiple extracutaneous anomalies, including skeletal defects and neurologic anomalies. Less common associations include lateral curvature of the spine and hyperhidrosis. We present a patient with PPK and unilateral Raynaud phenomenon in addition to a segmental distribution of melanocytic nevi, hyperhidrosis, and scoliosis.
A 9-year-old girl was born with a yellow-orange alopecic plaque on the right side of the scalp (Figure 1). There also were 2 large, irregularly pigmented patches localized on the right side of the upper back and buttock. Over 3 years, numerous papular nevi developed within these pigmented patches and were diagnosed as speckled lentiginous nevi (Figure 2). In addition, numerous nevi of various sizes affected the right face, right shoulder, right arm (Figure 3), and right neck and were clearly demarcated along the midline. Several nevi also were noted within the nevus sebaceous on the right scalp. These skin lesions expanded progressively with age. At 6 years of age, she was diagnosed with hyperhidrosis of the right half of the body, which was most pronounced on the face. Raynaud phenomenon restricted to the right hand also was noted (Figure 4). Upon cold exposure, the digits become pale white, cold, and numb; then blue; and finally red. She lacked other features of connective tissue disease, and autoantibody testing was negative. She also was noted to have an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine (scoliosis). Auditory, ocular, and neurologic examinations were normal. Cranial and cerebral magnetic resonance imaging showed no central nervous system abnormalities. Her family history was negative for nevus spilus, nevus sebaceous, and neurofibromatosis. The clinical findings in our patient led to the diagnosis of PPK.




Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is a distinctive epidermal nevus syndrome characterized by the coexistence of a speckled lentiginous nevus, also known as a nevus spilus, and a nevus sebaceous1; PPK frequently is complicated by skeletal, ophthalmic, or neurologic abnormalities.2 Most cases reported are sporadic, and a postzygotic mosaic HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase, HRAS, mutation has been demonstrated in some patients and may contribute to the phenotype of PPK.3,4
Other anomalies have included ichthyosislike diffuse hyperkeratosis, laxity of the hands, pelvic hypoplasia, glaucoma, psychomotor retardation, and hypophosphatemic rickets. These patients also should be monitored for the development of malignant neoplasms within the nevus sebaceous.5 Segmental hyperhidrosis may be seen in association with the nevus spilus component.2
Raynaud phenomenon involving only the right hand was a unique finding in our patient. In 3 years of follow-up, our patient developed no evidence of connective tissue disease or other systemic illness. We speculate that Raynaud phenomenon of the right hand along with hyperhidrosis of the right side of the body could be a result of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. We propose that Raynaud phenomenon represents an unusual manifestation of PPK and may broaden the spectrum of extracutaneous anomalies associated with the disease. The finding of segmental nevi outside of the confines of the nevus spilus was another unusual manifestation of mosaicism.
To the Editor:
Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (PPK) is a rare epidermal nevus syndrome complicated by multiple extracutaneous anomalies, including skeletal defects and neurologic anomalies. Less common associations include lateral curvature of the spine and hyperhidrosis. We present a patient with PPK and unilateral Raynaud phenomenon in addition to a segmental distribution of melanocytic nevi, hyperhidrosis, and scoliosis.
A 9-year-old girl was born with a yellow-orange alopecic plaque on the right side of the scalp (Figure 1). There also were 2 large, irregularly pigmented patches localized on the right side of the upper back and buttock. Over 3 years, numerous papular nevi developed within these pigmented patches and were diagnosed as speckled lentiginous nevi (Figure 2). In addition, numerous nevi of various sizes affected the right face, right shoulder, right arm (Figure 3), and right neck and were clearly demarcated along the midline. Several nevi also were noted within the nevus sebaceous on the right scalp. These skin lesions expanded progressively with age. At 6 years of age, she was diagnosed with hyperhidrosis of the right half of the body, which was most pronounced on the face. Raynaud phenomenon restricted to the right hand also was noted (Figure 4). Upon cold exposure, the digits become pale white, cold, and numb; then blue; and finally red. She lacked other features of connective tissue disease, and autoantibody testing was negative. She also was noted to have an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine (scoliosis). Auditory, ocular, and neurologic examinations were normal. Cranial and cerebral magnetic resonance imaging showed no central nervous system abnormalities. Her family history was negative for nevus spilus, nevus sebaceous, and neurofibromatosis. The clinical findings in our patient led to the diagnosis of PPK.




Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is a distinctive epidermal nevus syndrome characterized by the coexistence of a speckled lentiginous nevus, also known as a nevus spilus, and a nevus sebaceous1; PPK frequently is complicated by skeletal, ophthalmic, or neurologic abnormalities.2 Most cases reported are sporadic, and a postzygotic mosaic HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase, HRAS, mutation has been demonstrated in some patients and may contribute to the phenotype of PPK.3,4
Other anomalies have included ichthyosislike diffuse hyperkeratosis, laxity of the hands, pelvic hypoplasia, glaucoma, psychomotor retardation, and hypophosphatemic rickets. These patients also should be monitored for the development of malignant neoplasms within the nevus sebaceous.5 Segmental hyperhidrosis may be seen in association with the nevus spilus component.2
Raynaud phenomenon involving only the right hand was a unique finding in our patient. In 3 years of follow-up, our patient developed no evidence of connective tissue disease or other systemic illness. We speculate that Raynaud phenomenon of the right hand along with hyperhidrosis of the right side of the body could be a result of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. We propose that Raynaud phenomenon represents an unusual manifestation of PPK and may broaden the spectrum of extracutaneous anomalies associated with the disease. The finding of segmental nevi outside of the confines of the nevus spilus was another unusual manifestation of mosaicism.
- Happle R, Hoffmann R, Restano L, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a melanocytic-epidermal twin nevus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996;65:363-365.
- Happle R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes part I. well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:1-22, 23-24.
- Groesser L, Herschberger E, Sagrera A, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is caused by a postzygotic HRAS mutation in a multipotent progenitor cell. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1998-2003.
- Martin RJ, Arefi M, Splitt M, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica and precocious puberty associated with HRAS mutation. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:289-291.
- Chu GY, Wu CY. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a follow-up report with fatal outcome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:467-468.
- Happle R, Hoffmann R, Restano L, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a melanocytic-epidermal twin nevus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996;65:363-365.
- Happle R. The group of epidermal nevus syndromes part I. well defined phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:1-22, 23-24.
- Groesser L, Herschberger E, Sagrera A, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica is caused by a postzygotic HRAS mutation in a multipotent progenitor cell. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:1998-2003.
- Martin RJ, Arefi M, Splitt M, et al. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica and precocious puberty associated with HRAS mutation. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:289-291.
- Chu GY, Wu CY. Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica: a follow-up report with fatal outcome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94:467-468.
Practice Points
- Phacomatosis pigmentokeratotica (PPK) is characterized by the coexistence of speckled lentiginous nevus and nevus sebaceous.
- Raynaud phenomenon may be an unreported association with PPK.
FDA approves diagnostic device for autism spectrum disorder
The Food and Drug Administration has approved marketing for a device that will help diagnose autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old who exhibit potential symptoms.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid is a machine learning–based software program that receives information from parents or caregivers, video analysts, and health care providers to assist physicians in evaluating whether a child is at risk of having autism.
Autism is a developmental disorder that can cause social, communication, and behavioral challenges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The disorder affects about 1 in 54 children. The disorder is difficult to diagnose because there isn’t a medical test to diagnose the it. Instead, physicians have to look at a child’s developmental history and behavior to make a diagnosis.
Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the FDA.
“[ASD] can delay a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development, including motor skill development, learning, communication, and interacting with others. The earlier ASD can be diagnosed, the more quickly intervention strategies and appropriate therapies can begin,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a statement. “Today’s marketing authorization provides a new tool for helping diagnose children with ASD.”
The safety and efficacy of the Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid was assessed in a study of 425 patients between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old. For the study, researchers compared the diagnostic assessments made by the device to those made by a panel of clinical experts who used the current standard ASD diagnostic process. The device diagnosed 32% of the children with either a “Positive for ASD” or a “Negative for ASD” result. Researchers found that the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 81% of the patients who received a positive diagnosis. For those who received a negative diagnosis, the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 98% of the patients. In addition, the device made an accurate ASD determination in 98.4% of patients with the condition and in 78.9% of patients without the condition.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid has three main components. One component includes a mobile app for caregivers to answer questions about the child’s behavioral problems and to upload videos of the child. The next component is a video analysis portal for specialists to view and analyze uploaded videos of patients. Another component is a portal for health care providers that allows them to enter answers to preloaded questions about behavior problems, track the information provided by parents, and review a report of the results.
After the machine learning–based device processes the information provided by parents and health care providers, it reports either a positive or a negative diagnosis. If there is insufficient information to make either a positive or a negative diagnosis, the ASD Diagnostic AID will report that no result can be generated.
Some of the risks associated with this device include misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis of ASD because of a false-positive or false-negative result, or when no result is generated. Researchers said a false-positive result occurred in 15 out of 303 study subjects without ASD and a false-negative result occurred in 1 out of 122 study subjects with ASD.
The FDA emphasized that the device is indicated to aid physicians in the process of diagnosing ASD in children. This means it shouldn’t be treated as a standalone diagnostic device, but as an adjunct to the diagnostic process.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved marketing for a device that will help diagnose autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old who exhibit potential symptoms.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid is a machine learning–based software program that receives information from parents or caregivers, video analysts, and health care providers to assist physicians in evaluating whether a child is at risk of having autism.
Autism is a developmental disorder that can cause social, communication, and behavioral challenges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The disorder affects about 1 in 54 children. The disorder is difficult to diagnose because there isn’t a medical test to diagnose the it. Instead, physicians have to look at a child’s developmental history and behavior to make a diagnosis.
Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the FDA.
“[ASD] can delay a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development, including motor skill development, learning, communication, and interacting with others. The earlier ASD can be diagnosed, the more quickly intervention strategies and appropriate therapies can begin,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a statement. “Today’s marketing authorization provides a new tool for helping diagnose children with ASD.”
The safety and efficacy of the Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid was assessed in a study of 425 patients between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old. For the study, researchers compared the diagnostic assessments made by the device to those made by a panel of clinical experts who used the current standard ASD diagnostic process. The device diagnosed 32% of the children with either a “Positive for ASD” or a “Negative for ASD” result. Researchers found that the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 81% of the patients who received a positive diagnosis. For those who received a negative diagnosis, the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 98% of the patients. In addition, the device made an accurate ASD determination in 98.4% of patients with the condition and in 78.9% of patients without the condition.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid has three main components. One component includes a mobile app for caregivers to answer questions about the child’s behavioral problems and to upload videos of the child. The next component is a video analysis portal for specialists to view and analyze uploaded videos of patients. Another component is a portal for health care providers that allows them to enter answers to preloaded questions about behavior problems, track the information provided by parents, and review a report of the results.
After the machine learning–based device processes the information provided by parents and health care providers, it reports either a positive or a negative diagnosis. If there is insufficient information to make either a positive or a negative diagnosis, the ASD Diagnostic AID will report that no result can be generated.
Some of the risks associated with this device include misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis of ASD because of a false-positive or false-negative result, or when no result is generated. Researchers said a false-positive result occurred in 15 out of 303 study subjects without ASD and a false-negative result occurred in 1 out of 122 study subjects with ASD.
The FDA emphasized that the device is indicated to aid physicians in the process of diagnosing ASD in children. This means it shouldn’t be treated as a standalone diagnostic device, but as an adjunct to the diagnostic process.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved marketing for a device that will help diagnose autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old who exhibit potential symptoms.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid is a machine learning–based software program that receives information from parents or caregivers, video analysts, and health care providers to assist physicians in evaluating whether a child is at risk of having autism.
Autism is a developmental disorder that can cause social, communication, and behavioral challenges, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The disorder affects about 1 in 54 children. The disorder is difficult to diagnose because there isn’t a medical test to diagnose the it. Instead, physicians have to look at a child’s developmental history and behavior to make a diagnosis.
Many children are not diagnosed with ASD until later in childhood, which in some cases delays treatment and early intervention. ASD may be detected as early as 18 months, but the average age of diagnosis for ASD is 4.3 years, according to the FDA.
“[ASD] can delay a child’s physical, cognitive, and social development, including motor skill development, learning, communication, and interacting with others. The earlier ASD can be diagnosed, the more quickly intervention strategies and appropriate therapies can begin,” Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, said in a statement. “Today’s marketing authorization provides a new tool for helping diagnose children with ASD.”
The safety and efficacy of the Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid was assessed in a study of 425 patients between the ages of 18 months and 5 years old. For the study, researchers compared the diagnostic assessments made by the device to those made by a panel of clinical experts who used the current standard ASD diagnostic process. The device diagnosed 32% of the children with either a “Positive for ASD” or a “Negative for ASD” result. Researchers found that the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 81% of the patients who received a positive diagnosis. For those who received a negative diagnosis, the device matched the panel’s conclusions for 98% of the patients. In addition, the device made an accurate ASD determination in 98.4% of patients with the condition and in 78.9% of patients without the condition.
Cognoa ASD Diagnosis Aid has three main components. One component includes a mobile app for caregivers to answer questions about the child’s behavioral problems and to upload videos of the child. The next component is a video analysis portal for specialists to view and analyze uploaded videos of patients. Another component is a portal for health care providers that allows them to enter answers to preloaded questions about behavior problems, track the information provided by parents, and review a report of the results.
After the machine learning–based device processes the information provided by parents and health care providers, it reports either a positive or a negative diagnosis. If there is insufficient information to make either a positive or a negative diagnosis, the ASD Diagnostic AID will report that no result can be generated.
Some of the risks associated with this device include misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis of ASD because of a false-positive or false-negative result, or when no result is generated. Researchers said a false-positive result occurred in 15 out of 303 study subjects without ASD and a false-negative result occurred in 1 out of 122 study subjects with ASD.
The FDA emphasized that the device is indicated to aid physicians in the process of diagnosing ASD in children. This means it shouldn’t be treated as a standalone diagnostic device, but as an adjunct to the diagnostic process.
Benzene found in some sunscreen products, online pharmacy says
Valisure, an online pharmacy known for testing every batch of medication it sells, announced that it has
The company tested 294 batches from 69 companies and found benzene in 27% – many in major national brands like Neutrogena and Banana Boat. Some batches contained as much as three times the emergency FDA limit of 2 parts per million.
Long-term exposure to benzene is known to cause cancer in humans.
“This is especially concerning with sunscreen because multiple FDA studies have shown that sunscreen ingredients absorb through the skin and end up in the blood at high levels,” said David Light, CEO of Valisure.
The FDA is seeking more information about the potential risks from common sunscreen ingredients.
“There is not a safe level of benzene that can exist in sunscreen products,” Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in Valisure’s FDA petition. “The total mass of sunscreen required to cover and protect the human body, in single daily application or repeated applications daily, means that even benzene at 0.1 ppm in a sunscreen could expose people to excessively high nanogram amounts of benzene.”
Valisure’s testing previously led to FDA recalls of heartburn medications and hand sanitizers.
Examining sunscreen’s environmental impact
Chemicals in sunscreen may be harmful to other forms of life, too. For years, scientists have been examining whether certain chemicals in sunscreen could be causing damage to marine life, in particular the world’s coral reefs. Specific ingredients, including oxybenzone, benzophenone-1, benzophenone-8, OD-PABA, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, 3-benzylidene camphor, nano-titanium dioxide, nano-zinc oxide, octinoxate, and octocrylene, have been identified as potential risks.
Earlier this year, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine created a committee to review the existing science about the potential environmental hazards. Over the next 2 years, they’ll also consider the public health implications if people stopped using sunscreen.
Valisure’s announcement included this message: “It is important to note that not all sunscreen products contain benzene and that uncontaminated products are available, should continue to be used, and are important for protecting against potentially harmful solar radiation.”
Using sunscreen with SPF 15 every day can lower risk of squamous cell carcinoma by around 40% and melanoma by 50%. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Valisure, an online pharmacy known for testing every batch of medication it sells, announced that it has
The company tested 294 batches from 69 companies and found benzene in 27% – many in major national brands like Neutrogena and Banana Boat. Some batches contained as much as three times the emergency FDA limit of 2 parts per million.
Long-term exposure to benzene is known to cause cancer in humans.
“This is especially concerning with sunscreen because multiple FDA studies have shown that sunscreen ingredients absorb through the skin and end up in the blood at high levels,” said David Light, CEO of Valisure.
The FDA is seeking more information about the potential risks from common sunscreen ingredients.
“There is not a safe level of benzene that can exist in sunscreen products,” Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in Valisure’s FDA petition. “The total mass of sunscreen required to cover and protect the human body, in single daily application or repeated applications daily, means that even benzene at 0.1 ppm in a sunscreen could expose people to excessively high nanogram amounts of benzene.”
Valisure’s testing previously led to FDA recalls of heartburn medications and hand sanitizers.
Examining sunscreen’s environmental impact
Chemicals in sunscreen may be harmful to other forms of life, too. For years, scientists have been examining whether certain chemicals in sunscreen could be causing damage to marine life, in particular the world’s coral reefs. Specific ingredients, including oxybenzone, benzophenone-1, benzophenone-8, OD-PABA, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, 3-benzylidene camphor, nano-titanium dioxide, nano-zinc oxide, octinoxate, and octocrylene, have been identified as potential risks.
Earlier this year, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine created a committee to review the existing science about the potential environmental hazards. Over the next 2 years, they’ll also consider the public health implications if people stopped using sunscreen.
Valisure’s announcement included this message: “It is important to note that not all sunscreen products contain benzene and that uncontaminated products are available, should continue to be used, and are important for protecting against potentially harmful solar radiation.”
Using sunscreen with SPF 15 every day can lower risk of squamous cell carcinoma by around 40% and melanoma by 50%. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Valisure, an online pharmacy known for testing every batch of medication it sells, announced that it has
The company tested 294 batches from 69 companies and found benzene in 27% – many in major national brands like Neutrogena and Banana Boat. Some batches contained as much as three times the emergency FDA limit of 2 parts per million.
Long-term exposure to benzene is known to cause cancer in humans.
“This is especially concerning with sunscreen because multiple FDA studies have shown that sunscreen ingredients absorb through the skin and end up in the blood at high levels,” said David Light, CEO of Valisure.
The FDA is seeking more information about the potential risks from common sunscreen ingredients.
“There is not a safe level of benzene that can exist in sunscreen products,” Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in Valisure’s FDA petition. “The total mass of sunscreen required to cover and protect the human body, in single daily application or repeated applications daily, means that even benzene at 0.1 ppm in a sunscreen could expose people to excessively high nanogram amounts of benzene.”
Valisure’s testing previously led to FDA recalls of heartburn medications and hand sanitizers.
Examining sunscreen’s environmental impact
Chemicals in sunscreen may be harmful to other forms of life, too. For years, scientists have been examining whether certain chemicals in sunscreen could be causing damage to marine life, in particular the world’s coral reefs. Specific ingredients, including oxybenzone, benzophenone-1, benzophenone-8, OD-PABA, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, 3-benzylidene camphor, nano-titanium dioxide, nano-zinc oxide, octinoxate, and octocrylene, have been identified as potential risks.
Earlier this year, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine created a committee to review the existing science about the potential environmental hazards. Over the next 2 years, they’ll also consider the public health implications if people stopped using sunscreen.
Valisure’s announcement included this message: “It is important to note that not all sunscreen products contain benzene and that uncontaminated products are available, should continue to be used, and are important for protecting against potentially harmful solar radiation.”
Using sunscreen with SPF 15 every day can lower risk of squamous cell carcinoma by around 40% and melanoma by 50%. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a broad-spectrum, water-resistant sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In Zambia, PCR tracks pertussis
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
In the periurban slum of Lusaka, Zambia, asymptomatic pertussis infections were common among both mothers and infants, a surprising finding since asymptomatic infections are assumed to be rare in infants. The findings suggested that pertussis should be considered in cases of chronic cough, and that current standards of treating pertussis infections in low-resource settings may need to be reexamined.
The results come from testing of 1,320 infant-mother pairs who were first enrolled at a public health clinic, then followed over at least four visits. The researchers tracked pertussis infection using quantitative PCR (qPCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs. Over the course of the study, 8.9% tested positive, although only one infant developed clinical pertussis during the study.
The study was presented by Christian Gunning, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Georgia, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year. The group also included researchers at Boston University and the University of Zambia, where PCR tests were conducted.
“That was amazing,” said session moderator Vana Spoulou, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases at National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, who is associated with Aghia Sofia Children’s Hospital of Athens. She noted that the study found that many physicians misdiagnosed coughs, believing them to be caused by another agent. “It was very interesting that there was so much pertussis spreading around in that community, and that nobody knew that it was around,” said Dr. Spoulou.
It’s important that physicians provide appropriate treatment, since ampicillin, which is typically prescribed for childhood upper respiratory illnesses, is believed to be ineffective against pertussis, while macrolides are effective and can prevent transmission.
Dr. Spoulou also noted that Zambia uses a whole cell vaccine, which is contraindicated in pregnant women because of potential side effects. “The good thing, despite that there was [a lot of] infection, there were no deaths, which means that maybe because the mother was infected, maybe some antibodies of the mother had passed to the child and could help the child to develop milder symptoms. So these are the pros and cons of natural infection,” said Dr. Spoulou.
The study took place in 2015, and participants were seen at the Chawama Public Health Clinic from about age 1 week to 4 months (with a target of seven clinic visits). Researchers recorded respiratory symptoms and antibiotics use at each visit, and collected a nasopharyngeal swab that was tested retrospectively using qPCR for Bordetella pertussis.
Real-time PCR analysis of the samples yields the CT value, which represents the number of amplification cycles that the PCR test must complete before Bordetella pertussis is detectable. The fewer the cycles (and the lower the CT value), the more infectious particles must have been present in the sample. For pertussis testing, a value below 35 is considered a clinically positive result. Tests that come back with higher CT values are increasingly likely to be false positives.
The researchers plotted a value called evidence for infection (EFI), which combined a range of CT values with the number of positive tests over the seven clinic visits to group patients into none, weak, or strong EFI. Among infants with no symptoms, 77% were in the no EFI category, 16% were in the weak category, and 7% were in the strong EFI group. Of infants with minimal respiratory symptoms, 18% were in the strong group, and 20% with moderate to severe symptoms were in the strong EFI group. Among mothers, 13% with no symptoms were in the strong group. 19% in the minimal symptom group were categorized as strong EFI, as were 11% in the moderate to severe symptom group.
The study used a full range of CT, not just positive test results (for pertussis, CT ≤ 35). Beyond contributing to composite measures such as EFI, CT values can serve as leading indicators of infectious disease outbreaks in a population, according to Dr. Gunning. That’s because weaker qPCR signals (CT > 35) can provide additional information within a large sample population. Higher CT values are successively more prone to false positives, but that’s less important for disease surveillance where sensitivity is of the highest importance. The false positive “noise” tends to cancel out over time. “It may be the case that you don’t make that call (correctly) 100% of the time for 100% of the people, but if you get it right in 80 out of 100 people, that’s sufficient to say we see this pathogen circulating in the population,” said Dr. Gunning.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Gunning and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ESPID 2021
Children aged 12-15 years continue to close COVID-19 vaccination gap
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
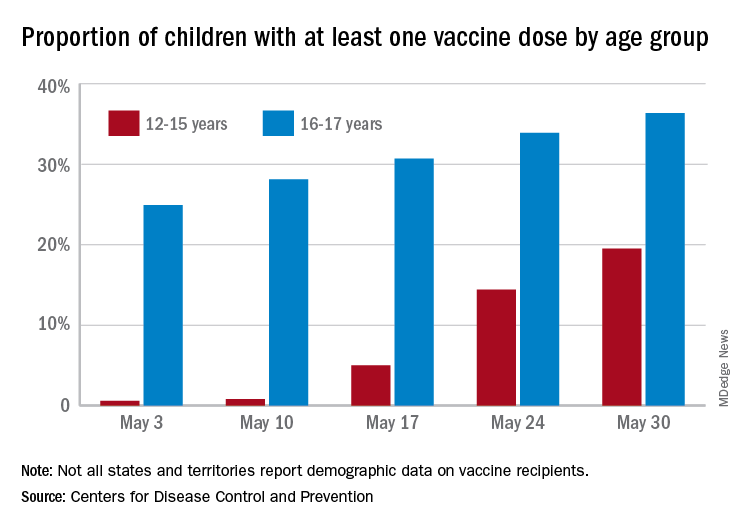
with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.
Sickle cell disease: Epidemiological change in bacterial infections
Among children with sickle cell disease who have not undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Salmonella is now the leading cause of invasive bacterial infection (IBI), according to a new retrospective study (BACT-SPRING) conducted in Europe. Streptococcus pneumoniae was the second most common source of infection, marking a shift from years past, when S. pneumoniae was the most common source. The epidemiology of IBI in Europe has been altered by adoption of prophylaxis and the introduction of the pneumococcal conjugated vaccine (PCV13) in 2009.
Previous studies of IBI have been single center with small sample sizes, and few have been conducted since 2016, said Jean Gaschignard, MD, PhD, during his presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Dr. Gaschignard is head of pediatrics at Groupe Hospitalier Nord Essonne in Longjumeau, France.
The study produced some unexpected results. “We were surprised,” said Dr. Gaschignard, by results indicating that not all children aged under 10 years were undergoing prophylaxis. Instead, the figures were closer to 80% or 90%. Among children over 10, the rate of prophylaxis varies between countries. “Our study is a clue to discuss again the indications for the age limit for prophylaxis against pneumococcus,” said Dr. Gauschignard, during the question-and-answer session following his talk.
The data give clinicians an updated picture of the epidemiology in this population following introduction of the PCV13 vaccine. “It was very important to have new data on microbiology after this implementation,” said Marie Rohr, MD, who is a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at the University Hospitals of Geneva. Dr. Rohr moderated the session where the study was presented.
Dr. Rohr noted the shift from the dominant cause of IBI after the introduction of the PCV10/13 vaccine, from S. pneumoniae to Salmonella. The researchers also found a preponderance of bacteremia and osteoarticular infections. “The mortality and morbidity are still considerable despite infection preventive measures,” said Dr. Rohr.
The results should also prompt a second look at prevention strategies. “Even if the antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed for a large [proportion of children with sickle cell disease] under 10 years old, the median age of invasive bacterial infection is 7 years old. This calls into question systematic antibiotic prophylaxis and case-control studies are needed to evaluate this and possibly modify antibiotic prophylaxis recommendations in the future,” said Dr. Rohr.
The BACT-SPRING study was conducted between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 31, 2019, using online data. It included 217 IBI episodes from 26 centers in five European countries. Just over half were from France, while about a quarter occurred in Spain. Other countries included Belgium, Portugal, and Great Britain. Participants were younger than 18 and had an IBI confirmed by bacterial culture or PCR from normally sterile fluid.
Thirty-eight episodes occurred in children who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), and 179 in children who had not undergone HSCT. The presentation focused exclusively on the latter group.
Among episodes in children without HSCT, the mean age was 7. Forty-eight patients had a history of acute chest syndrome, 47 had a history of ICU admission, 29 had a history of IBI, and 27 had a history of acute splenic sequestration. Thirteen underwent a splenectomy. Almost half of children had none of these characteristics, while about one-fourth had two or more.
In the HSCT group, 141 children were on prophylaxis at the time of the infection; 74 were on hydroxyurea, and 36 were currently or previously on a transfusion program. Sixty-eight cases were primary bacteremia and 55 were osteoarticular. Other syndromes included pneumonia empyema (n = 18), and meningitis (n = 17), among others. In 44 cases, the isolated bacteria was Salmonella, followed by S. pneumoniae in 32 cases. Escherichia coli accounted for 22. Haemophilus influenza was identified in six episodes, and group A Streptococcus in three.
The study is the first large European epidemiologic study investigating IBI in children with sickle cell disease, and one of its strengths was the strict inclusion criteria. However, it was limited by its retrospective nature.
Dr. Gaschignard and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
Among children with sickle cell disease who have not undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Salmonella is now the leading cause of invasive bacterial infection (IBI), according to a new retrospective study (BACT-SPRING) conducted in Europe. Streptococcus pneumoniae was the second most common source of infection, marking a shift from years past, when S. pneumoniae was the most common source. The epidemiology of IBI in Europe has been altered by adoption of prophylaxis and the introduction of the pneumococcal conjugated vaccine (PCV13) in 2009.
Previous studies of IBI have been single center with small sample sizes, and few have been conducted since 2016, said Jean Gaschignard, MD, PhD, during his presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Dr. Gaschignard is head of pediatrics at Groupe Hospitalier Nord Essonne in Longjumeau, France.
The study produced some unexpected results. “We were surprised,” said Dr. Gaschignard, by results indicating that not all children aged under 10 years were undergoing prophylaxis. Instead, the figures were closer to 80% or 90%. Among children over 10, the rate of prophylaxis varies between countries. “Our study is a clue to discuss again the indications for the age limit for prophylaxis against pneumococcus,” said Dr. Gauschignard, during the question-and-answer session following his talk.
The data give clinicians an updated picture of the epidemiology in this population following introduction of the PCV13 vaccine. “It was very important to have new data on microbiology after this implementation,” said Marie Rohr, MD, who is a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at the University Hospitals of Geneva. Dr. Rohr moderated the session where the study was presented.
Dr. Rohr noted the shift from the dominant cause of IBI after the introduction of the PCV10/13 vaccine, from S. pneumoniae to Salmonella. The researchers also found a preponderance of bacteremia and osteoarticular infections. “The mortality and morbidity are still considerable despite infection preventive measures,” said Dr. Rohr.
The results should also prompt a second look at prevention strategies. “Even if the antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed for a large [proportion of children with sickle cell disease] under 10 years old, the median age of invasive bacterial infection is 7 years old. This calls into question systematic antibiotic prophylaxis and case-control studies are needed to evaluate this and possibly modify antibiotic prophylaxis recommendations in the future,” said Dr. Rohr.
The BACT-SPRING study was conducted between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 31, 2019, using online data. It included 217 IBI episodes from 26 centers in five European countries. Just over half were from France, while about a quarter occurred in Spain. Other countries included Belgium, Portugal, and Great Britain. Participants were younger than 18 and had an IBI confirmed by bacterial culture or PCR from normally sterile fluid.
Thirty-eight episodes occurred in children who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), and 179 in children who had not undergone HSCT. The presentation focused exclusively on the latter group.
Among episodes in children without HSCT, the mean age was 7. Forty-eight patients had a history of acute chest syndrome, 47 had a history of ICU admission, 29 had a history of IBI, and 27 had a history of acute splenic sequestration. Thirteen underwent a splenectomy. Almost half of children had none of these characteristics, while about one-fourth had two or more.
In the HSCT group, 141 children were on prophylaxis at the time of the infection; 74 were on hydroxyurea, and 36 were currently or previously on a transfusion program. Sixty-eight cases were primary bacteremia and 55 were osteoarticular. Other syndromes included pneumonia empyema (n = 18), and meningitis (n = 17), among others. In 44 cases, the isolated bacteria was Salmonella, followed by S. pneumoniae in 32 cases. Escherichia coli accounted for 22. Haemophilus influenza was identified in six episodes, and group A Streptococcus in three.
The study is the first large European epidemiologic study investigating IBI in children with sickle cell disease, and one of its strengths was the strict inclusion criteria. However, it was limited by its retrospective nature.
Dr. Gaschignard and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
Among children with sickle cell disease who have not undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplant, Salmonella is now the leading cause of invasive bacterial infection (IBI), according to a new retrospective study (BACT-SPRING) conducted in Europe. Streptococcus pneumoniae was the second most common source of infection, marking a shift from years past, when S. pneumoniae was the most common source. The epidemiology of IBI in Europe has been altered by adoption of prophylaxis and the introduction of the pneumococcal conjugated vaccine (PCV13) in 2009.
Previous studies of IBI have been single center with small sample sizes, and few have been conducted since 2016, said Jean Gaschignard, MD, PhD, during his presentation of the study at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Dr. Gaschignard is head of pediatrics at Groupe Hospitalier Nord Essonne in Longjumeau, France.
The study produced some unexpected results. “We were surprised,” said Dr. Gaschignard, by results indicating that not all children aged under 10 years were undergoing prophylaxis. Instead, the figures were closer to 80% or 90%. Among children over 10, the rate of prophylaxis varies between countries. “Our study is a clue to discuss again the indications for the age limit for prophylaxis against pneumococcus,” said Dr. Gauschignard, during the question-and-answer session following his talk.
The data give clinicians an updated picture of the epidemiology in this population following introduction of the PCV13 vaccine. “It was very important to have new data on microbiology after this implementation,” said Marie Rohr, MD, who is a fellow in pediatric infectious diseases at the University Hospitals of Geneva. Dr. Rohr moderated the session where the study was presented.
Dr. Rohr noted the shift from the dominant cause of IBI after the introduction of the PCV10/13 vaccine, from S. pneumoniae to Salmonella. The researchers also found a preponderance of bacteremia and osteoarticular infections. “The mortality and morbidity are still considerable despite infection preventive measures,” said Dr. Rohr.
The results should also prompt a second look at prevention strategies. “Even if the antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed for a large [proportion of children with sickle cell disease] under 10 years old, the median age of invasive bacterial infection is 7 years old. This calls into question systematic antibiotic prophylaxis and case-control studies are needed to evaluate this and possibly modify antibiotic prophylaxis recommendations in the future,” said Dr. Rohr.
The BACT-SPRING study was conducted between Jan. 1, 2014, and Dec. 31, 2019, using online data. It included 217 IBI episodes from 26 centers in five European countries. Just over half were from France, while about a quarter occurred in Spain. Other countries included Belgium, Portugal, and Great Britain. Participants were younger than 18 and had an IBI confirmed by bacterial culture or PCR from normally sterile fluid.
Thirty-eight episodes occurred in children who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), and 179 in children who had not undergone HSCT. The presentation focused exclusively on the latter group.
Among episodes in children without HSCT, the mean age was 7. Forty-eight patients had a history of acute chest syndrome, 47 had a history of ICU admission, 29 had a history of IBI, and 27 had a history of acute splenic sequestration. Thirteen underwent a splenectomy. Almost half of children had none of these characteristics, while about one-fourth had two or more.
In the HSCT group, 141 children were on prophylaxis at the time of the infection; 74 were on hydroxyurea, and 36 were currently or previously on a transfusion program. Sixty-eight cases were primary bacteremia and 55 were osteoarticular. Other syndromes included pneumonia empyema (n = 18), and meningitis (n = 17), among others. In 44 cases, the isolated bacteria was Salmonella, followed by S. pneumoniae in 32 cases. Escherichia coli accounted for 22. Haemophilus influenza was identified in six episodes, and group A Streptococcus in three.
The study is the first large European epidemiologic study investigating IBI in children with sickle cell disease, and one of its strengths was the strict inclusion criteria. However, it was limited by its retrospective nature.
Dr. Gaschignard and Dr. Rohr have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ESPID 2021
Antiviral may improve hearing loss in congenital CMV
Infants with isolated sensorineural hearing loss as a result of congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection may benefit from treatment with valganciclovir, according to results from the CONCERT nonrandomized trial.
Subjects were found through the Newborn Hearing Screening program, using dried blood spot screening to confirm cCMV Infection. As a result of 6 weeks of therapy, more patients in the treatment group had improvements in hearing at age 20 months, and fewer had deterioration compared with untreated controls.
There is a general consensus that symptomatic cCMV should be treated with valganciclovir for 6 weeks or 6 months, but treatment of patients with only hearing loss is still under debate. The average age of participants was 8 weeks.
The study was presented by Pui Khi Chung, MD, a clinical microbiologist at the Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Out of 1,377 NHS-referred infants, 59 were diagnosed with cCMV (4.3%), and 35 were included in the study. Twenty-five patients received 6 weeks of valganciclovir, while 10 patients received placebo. The control group was expanded to 12 when two additional subjects were identified retrospectively and were successfully followed up at 20 months. Subjects in the treatment group were an average of 8 weeks old when treatment began. Both groups had similar neurodevelopmental outcomes at 20 months, as measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development (BSID-III) and the Child Development Inventory (CDI). There were no serious adverse events associated with treatment.
To measure efficacy, the researchers used a random intercept, random slope model that accounted for repeated measurements. The differences in slopes for analyses of the best ear were significantly different between the treatment and control groups (estimated difference in slopes, –0.93; P = .0071). Further analyses of total hearing found that improvement was more common in the treatment group, and deterioration/no change was more common in the nontreatment group (P = .044). In another analysis that excluded the most profoundly impaired ears (> 70 db hearing loss), none in the control group experienced improvement and almost half deteriorated. In the treatment group, most were unchanged and a small number improved, with almost none deteriorating (P = .006).
Asked whether the treatment has any effect on the most profoundly impaired ears, Dr. Chung said she had not yet completed that analysis, but the hypothesis is that the treatment is unlikely to lead to any improvement. “When you take out the severely impaired ears, you can see a greater [treatment] effect, so it does suggest that it doesn’t do anything for those ears,” Dr. Chung said during the Q&A session following her talk.
She was also asked why the treatment period was 6 weeks, rather than 6 months – a period of treatment that has shown a better effect on long-term hearing and developmental outcomes than 6 weeks of treatment in symptomatic patients. Dr. Chung replied that she wasn’t involved in the study design, but said that at her center, the 6-month regimen is not standard.
There were two key weaknesses in the study. One was the small sample size, and the other was its nonrandomized nature, which could have led to bias in the treated versus untreated group. “Although we don’t see any baseline differences between the groups, we have to be wary in analyses. Unfortunately, an RCT proved impossible in our setting. The CONCERT Trial started as randomized but this was amended to nonrandomized, as both parents and pediatricians had a clear preference for treatment,” said Dr. Chung.
The study could provide useful information about the timing of oral antiviral medication, according to Vana Spoulou, MD, who moderated the session where the research was presented. “The earliest you can give it is best, but sometimes it’s not easy to get them diagnosed immediately after birth. What they showed us is that even giving it so late, there was some improvement,” Dr. Spoulou said in an interview.
Dr. Spoulou isn’t ready to change practice based on the results, because she noted that some other studies have shown no benefit of treatment at 3 months. “But this was a hint that maybe even in these later diagnosed cases there could be some benefit,” she said.
Dr. Chung and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
Infants with isolated sensorineural hearing loss as a result of congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection may benefit from treatment with valganciclovir, according to results from the CONCERT nonrandomized trial.
Subjects were found through the Newborn Hearing Screening program, using dried blood spot screening to confirm cCMV Infection. As a result of 6 weeks of therapy, more patients in the treatment group had improvements in hearing at age 20 months, and fewer had deterioration compared with untreated controls.
There is a general consensus that symptomatic cCMV should be treated with valganciclovir for 6 weeks or 6 months, but treatment of patients with only hearing loss is still under debate. The average age of participants was 8 weeks.
The study was presented by Pui Khi Chung, MD, a clinical microbiologist at the Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Out of 1,377 NHS-referred infants, 59 were diagnosed with cCMV (4.3%), and 35 were included in the study. Twenty-five patients received 6 weeks of valganciclovir, while 10 patients received placebo. The control group was expanded to 12 when two additional subjects were identified retrospectively and were successfully followed up at 20 months. Subjects in the treatment group were an average of 8 weeks old when treatment began. Both groups had similar neurodevelopmental outcomes at 20 months, as measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development (BSID-III) and the Child Development Inventory (CDI). There were no serious adverse events associated with treatment.
To measure efficacy, the researchers used a random intercept, random slope model that accounted for repeated measurements. The differences in slopes for analyses of the best ear were significantly different between the treatment and control groups (estimated difference in slopes, –0.93; P = .0071). Further analyses of total hearing found that improvement was more common in the treatment group, and deterioration/no change was more common in the nontreatment group (P = .044). In another analysis that excluded the most profoundly impaired ears (> 70 db hearing loss), none in the control group experienced improvement and almost half deteriorated. In the treatment group, most were unchanged and a small number improved, with almost none deteriorating (P = .006).
Asked whether the treatment has any effect on the most profoundly impaired ears, Dr. Chung said she had not yet completed that analysis, but the hypothesis is that the treatment is unlikely to lead to any improvement. “When you take out the severely impaired ears, you can see a greater [treatment] effect, so it does suggest that it doesn’t do anything for those ears,” Dr. Chung said during the Q&A session following her talk.
She was also asked why the treatment period was 6 weeks, rather than 6 months – a period of treatment that has shown a better effect on long-term hearing and developmental outcomes than 6 weeks of treatment in symptomatic patients. Dr. Chung replied that she wasn’t involved in the study design, but said that at her center, the 6-month regimen is not standard.
There were two key weaknesses in the study. One was the small sample size, and the other was its nonrandomized nature, which could have led to bias in the treated versus untreated group. “Although we don’t see any baseline differences between the groups, we have to be wary in analyses. Unfortunately, an RCT proved impossible in our setting. The CONCERT Trial started as randomized but this was amended to nonrandomized, as both parents and pediatricians had a clear preference for treatment,” said Dr. Chung.
The study could provide useful information about the timing of oral antiviral medication, according to Vana Spoulou, MD, who moderated the session where the research was presented. “The earliest you can give it is best, but sometimes it’s not easy to get them diagnosed immediately after birth. What they showed us is that even giving it so late, there was some improvement,” Dr. Spoulou said in an interview.
Dr. Spoulou isn’t ready to change practice based on the results, because she noted that some other studies have shown no benefit of treatment at 3 months. “But this was a hint that maybe even in these later diagnosed cases there could be some benefit,” she said.
Dr. Chung and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
Infants with isolated sensorineural hearing loss as a result of congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection may benefit from treatment with valganciclovir, according to results from the CONCERT nonrandomized trial.
Subjects were found through the Newborn Hearing Screening program, using dried blood spot screening to confirm cCMV Infection. As a result of 6 weeks of therapy, more patients in the treatment group had improvements in hearing at age 20 months, and fewer had deterioration compared with untreated controls.
There is a general consensus that symptomatic cCMV should be treated with valganciclovir for 6 weeks or 6 months, but treatment of patients with only hearing loss is still under debate. The average age of participants was 8 weeks.
The study was presented by Pui Khi Chung, MD, a clinical microbiologist at the Leiden University Medical Center, the Netherlands, at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases, held virtually this year.
Out of 1,377 NHS-referred infants, 59 were diagnosed with cCMV (4.3%), and 35 were included in the study. Twenty-five patients received 6 weeks of valganciclovir, while 10 patients received placebo. The control group was expanded to 12 when two additional subjects were identified retrospectively and were successfully followed up at 20 months. Subjects in the treatment group were an average of 8 weeks old when treatment began. Both groups had similar neurodevelopmental outcomes at 20 months, as measured by the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development (BSID-III) and the Child Development Inventory (CDI). There were no serious adverse events associated with treatment.
To measure efficacy, the researchers used a random intercept, random slope model that accounted for repeated measurements. The differences in slopes for analyses of the best ear were significantly different between the treatment and control groups (estimated difference in slopes, –0.93; P = .0071). Further analyses of total hearing found that improvement was more common in the treatment group, and deterioration/no change was more common in the nontreatment group (P = .044). In another analysis that excluded the most profoundly impaired ears (> 70 db hearing loss), none in the control group experienced improvement and almost half deteriorated. In the treatment group, most were unchanged and a small number improved, with almost none deteriorating (P = .006).
Asked whether the treatment has any effect on the most profoundly impaired ears, Dr. Chung said she had not yet completed that analysis, but the hypothesis is that the treatment is unlikely to lead to any improvement. “When you take out the severely impaired ears, you can see a greater [treatment] effect, so it does suggest that it doesn’t do anything for those ears,” Dr. Chung said during the Q&A session following her talk.
She was also asked why the treatment period was 6 weeks, rather than 6 months – a period of treatment that has shown a better effect on long-term hearing and developmental outcomes than 6 weeks of treatment in symptomatic patients. Dr. Chung replied that she wasn’t involved in the study design, but said that at her center, the 6-month regimen is not standard.
There were two key weaknesses in the study. One was the small sample size, and the other was its nonrandomized nature, which could have led to bias in the treated versus untreated group. “Although we don’t see any baseline differences between the groups, we have to be wary in analyses. Unfortunately, an RCT proved impossible in our setting. The CONCERT Trial started as randomized but this was amended to nonrandomized, as both parents and pediatricians had a clear preference for treatment,” said Dr. Chung.
The study could provide useful information about the timing of oral antiviral medication, according to Vana Spoulou, MD, who moderated the session where the research was presented. “The earliest you can give it is best, but sometimes it’s not easy to get them diagnosed immediately after birth. What they showed us is that even giving it so late, there was some improvement,” Dr. Spoulou said in an interview.
Dr. Spoulou isn’t ready to change practice based on the results, because she noted that some other studies have shown no benefit of treatment at 3 months. “But this was a hint that maybe even in these later diagnosed cases there could be some benefit,” she said.
Dr. Chung and Dr. Spoulou have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ESPID 2021
How early can laser treatment for port wine stains in infants be initiated?
without any complications, results from a single-center study showed.
“The current modality of choice for the treatment of port wine birthmarks is pulsed dye laser,” Chelsea Grimes Fidai, MD, said during the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “When performed by a highly trained expert at efficient frequencies, PDL is a safe, effective treatment that is successful in the majority of patients. We know that earlier treatment yields maximal clearance. However, just how early can you initiate treatment?”
To find out, Dr. Fidai, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, and colleagues at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of New York, conducted a retrospective chart review of 39 infants with port wine birthmarks who were treated with a 595-nm PDL between 2015 and 2020 at the center. Of the 39 infants, the average age at first treatment was 18 days, with a range from 5 to 29 days. The youngest patient was born prematurely at 35 weeks’ gestation and presented for his first treatment even before his expected due date. Most (74%) had facial lesions with the remaining distributed on the trunk or extremities. The average number of treatments was 15 over the course of 15 months.
The initial settings chosen for facial lesions were a 10-mm spot size, a fluence of 8.0 J/cm2, and a 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. For body lesions, the typical initial settings were a 12-mm spot size, a fluence of 6.7 J/cm2, and 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. Corneal eye shields were placed for all cases with port wine birthmarks approaching the eyelid. “We do recommend a treatment interval of every 2-3 weeks, with longer intervals for patients of darker skin type until the child is 2 years old, at which time the interval is increased to every 3-6 months,” said Dr. Fidai.
Patients in the study experienced the expected short-term side effects of erythema, edema, purpura, and mild transient postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, but there were no cases of atrophy, scarring, infection, or permanent pigmentary change.
“Families seeking early treatment of port wine birthmarks can be reassured that it can be safely initiated within the first few days after birth,” Dr. Fidai concluded. “This procedure can be quickly and confidently performed as an in-office procedure without any complications. The early intervention allows for treatment without general anesthesia and it maximizes the chance of significant clearance as early in life as possible.”
During a question-and-answer session, the abstract section chair, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, expressed concern about the effect of PDL on developing infants. “We do repeated treatments at this young age without any type of anesthesia,” said Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at the Netherlands Institute for Pigment Disorders, department of dermatology, University of Amsterdam.
“Will that influence the development of the child, especially when I hear there might be 15 or 20 treatments done within the first year of life? I think this is a problem where we need to ask the experts in the field of pain management in children, like pediatric anesthesiologists, to find the right way, because I think that the results that you showed are fantastic. I don’t think we can achieve that at a later age, although there’s no direct comparison at this moment.”
Dr. Fidai said that she understood the concern, but pointed to a 2020 article by Dr. Geronemus and colleagues that assessed treatment tolerance and parental perspective of outpatient PDL treatment for port-wine birthmarks without general anesthesia in infants and toddlers. “The kids recover pretty quickly after the treatment,” she said. “There has never been any longstanding issue from the parents’ perspective.”
Dr. Fidai reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial conflicts with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Lumenis and InCyte and equipment from Humeca and PerfAction Technologies. He has also received grant funding from Novartis and InCyte and he is a member of InCyte’s advisory board.
without any complications, results from a single-center study showed.
“The current modality of choice for the treatment of port wine birthmarks is pulsed dye laser,” Chelsea Grimes Fidai, MD, said during the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “When performed by a highly trained expert at efficient frequencies, PDL is a safe, effective treatment that is successful in the majority of patients. We know that earlier treatment yields maximal clearance. However, just how early can you initiate treatment?”
To find out, Dr. Fidai, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, and colleagues at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of New York, conducted a retrospective chart review of 39 infants with port wine birthmarks who were treated with a 595-nm PDL between 2015 and 2020 at the center. Of the 39 infants, the average age at first treatment was 18 days, with a range from 5 to 29 days. The youngest patient was born prematurely at 35 weeks’ gestation and presented for his first treatment even before his expected due date. Most (74%) had facial lesions with the remaining distributed on the trunk or extremities. The average number of treatments was 15 over the course of 15 months.
The initial settings chosen for facial lesions were a 10-mm spot size, a fluence of 8.0 J/cm2, and a 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. For body lesions, the typical initial settings were a 12-mm spot size, a fluence of 6.7 J/cm2, and 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. Corneal eye shields were placed for all cases with port wine birthmarks approaching the eyelid. “We do recommend a treatment interval of every 2-3 weeks, with longer intervals for patients of darker skin type until the child is 2 years old, at which time the interval is increased to every 3-6 months,” said Dr. Fidai.
Patients in the study experienced the expected short-term side effects of erythema, edema, purpura, and mild transient postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, but there were no cases of atrophy, scarring, infection, or permanent pigmentary change.
“Families seeking early treatment of port wine birthmarks can be reassured that it can be safely initiated within the first few days after birth,” Dr. Fidai concluded. “This procedure can be quickly and confidently performed as an in-office procedure without any complications. The early intervention allows for treatment without general anesthesia and it maximizes the chance of significant clearance as early in life as possible.”
During a question-and-answer session, the abstract section chair, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, expressed concern about the effect of PDL on developing infants. “We do repeated treatments at this young age without any type of anesthesia,” said Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at the Netherlands Institute for Pigment Disorders, department of dermatology, University of Amsterdam.
“Will that influence the development of the child, especially when I hear there might be 15 or 20 treatments done within the first year of life? I think this is a problem where we need to ask the experts in the field of pain management in children, like pediatric anesthesiologists, to find the right way, because I think that the results that you showed are fantastic. I don’t think we can achieve that at a later age, although there’s no direct comparison at this moment.”
Dr. Fidai said that she understood the concern, but pointed to a 2020 article by Dr. Geronemus and colleagues that assessed treatment tolerance and parental perspective of outpatient PDL treatment for port-wine birthmarks without general anesthesia in infants and toddlers. “The kids recover pretty quickly after the treatment,” she said. “There has never been any longstanding issue from the parents’ perspective.”
Dr. Fidai reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial conflicts with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Lumenis and InCyte and equipment from Humeca and PerfAction Technologies. He has also received grant funding from Novartis and InCyte and he is a member of InCyte’s advisory board.
without any complications, results from a single-center study showed.
“The current modality of choice for the treatment of port wine birthmarks is pulsed dye laser,” Chelsea Grimes Fidai, MD, said during the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “When performed by a highly trained expert at efficient frequencies, PDL is a safe, effective treatment that is successful in the majority of patients. We know that earlier treatment yields maximal clearance. However, just how early can you initiate treatment?”
To find out, Dr. Fidai, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, and colleagues at the Laser and Skin Surgery Center of New York, conducted a retrospective chart review of 39 infants with port wine birthmarks who were treated with a 595-nm PDL between 2015 and 2020 at the center. Of the 39 infants, the average age at first treatment was 18 days, with a range from 5 to 29 days. The youngest patient was born prematurely at 35 weeks’ gestation and presented for his first treatment even before his expected due date. Most (74%) had facial lesions with the remaining distributed on the trunk or extremities. The average number of treatments was 15 over the course of 15 months.
The initial settings chosen for facial lesions were a 10-mm spot size, a fluence of 8.0 J/cm2, and a 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. For body lesions, the typical initial settings were a 12-mm spot size, a fluence of 6.7 J/cm2, and 1.5-millisecond pulse duration. Corneal eye shields were placed for all cases with port wine birthmarks approaching the eyelid. “We do recommend a treatment interval of every 2-3 weeks, with longer intervals for patients of darker skin type until the child is 2 years old, at which time the interval is increased to every 3-6 months,” said Dr. Fidai.
Patients in the study experienced the expected short-term side effects of erythema, edema, purpura, and mild transient postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, but there were no cases of atrophy, scarring, infection, or permanent pigmentary change.
“Families seeking early treatment of port wine birthmarks can be reassured that it can be safely initiated within the first few days after birth,” Dr. Fidai concluded. “This procedure can be quickly and confidently performed as an in-office procedure without any complications. The early intervention allows for treatment without general anesthesia and it maximizes the chance of significant clearance as early in life as possible.”
During a question-and-answer session, the abstract section chair, Albert Wolkerstorfer, MD, PhD, expressed concern about the effect of PDL on developing infants. “We do repeated treatments at this young age without any type of anesthesia,” said Dr. Wolkerstorfer, a dermatologist at the Netherlands Institute for Pigment Disorders, department of dermatology, University of Amsterdam.
“Will that influence the development of the child, especially when I hear there might be 15 or 20 treatments done within the first year of life? I think this is a problem where we need to ask the experts in the field of pain management in children, like pediatric anesthesiologists, to find the right way, because I think that the results that you showed are fantastic. I don’t think we can achieve that at a later age, although there’s no direct comparison at this moment.”
Dr. Fidai said that she understood the concern, but pointed to a 2020 article by Dr. Geronemus and colleagues that assessed treatment tolerance and parental perspective of outpatient PDL treatment for port-wine birthmarks without general anesthesia in infants and toddlers. “The kids recover pretty quickly after the treatment,” she said. “There has never been any longstanding issue from the parents’ perspective.”
Dr. Fidai reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial conflicts with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Wolkerstorfer disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Lumenis and InCyte and equipment from Humeca and PerfAction Technologies. He has also received grant funding from Novartis and InCyte and he is a member of InCyte’s advisory board.
FROM ASLMS 2021