User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Older age, r/r disease in lymphoma patients tied to increased COVID-19 death rate
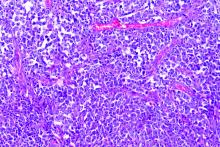
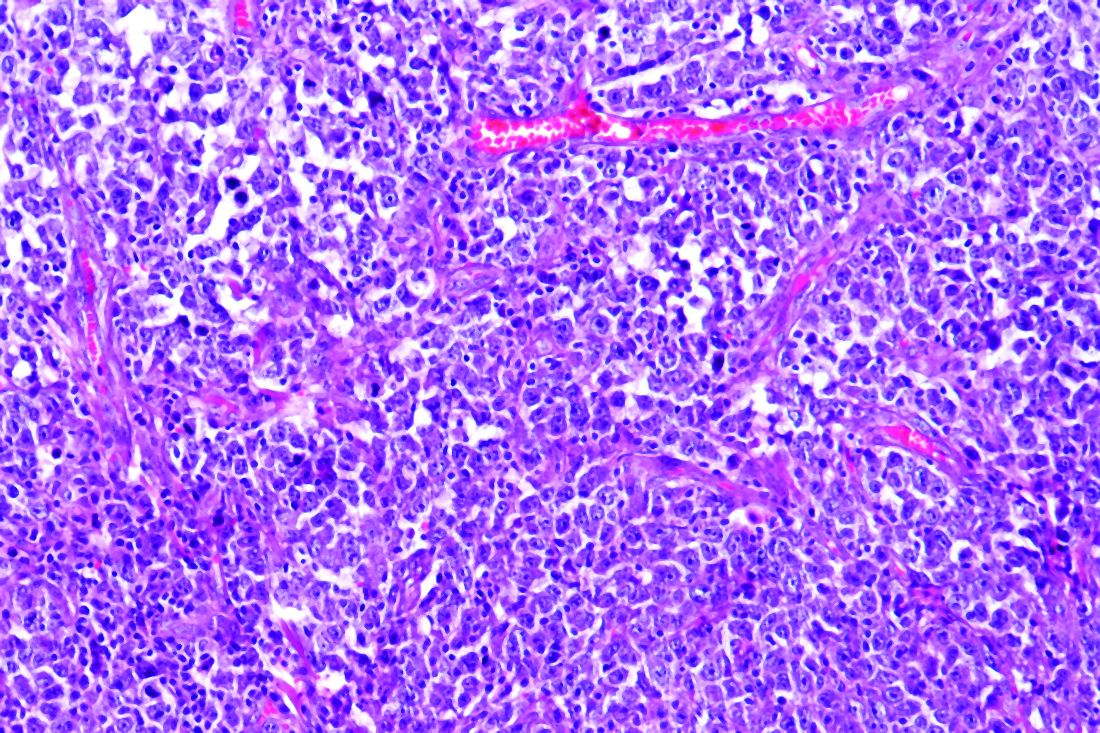
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
Patients with B-cell lymphoma are immunocompromised because of the disease and its treatments. This presents the question of their outcomes upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers assessed the characteristics of patients with lymphoma hospitalized for COVID-19 and analyzed determinants of mortality in a retrospective database study. The investigators looked at data from adult patients with lymphoma who were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020 in three French regions.
Older age and relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease in B-cell lymphoma patients were both found to be independent risk factors of increased death rate from COVID-19, according to the online report in EClinicalMedicine, published by The Lancet.
These results encourage “the application of standard Covid-19 treatment, including intubation, for lymphoma patients with Covid-19 lymphoma diagnosis, under first- or second-line chemotherapy, or in remission,” according to Sylvain Lamure, MD, of Montellier (France) University, and colleagues.
The study examined a series of 89 consecutive patients from three French regions who had lymphoma and were hospitalized for COVID-19 in March and April 2020. The population was homogeneous; most patients were diagnosed with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and had been treated for their lymphoma within 1 year.
Promising results for many
There were a significant associations between 30-day mortality and increasing age (over age 70 years) and r/r lymphoma. However, in the absence of those factors, mortality of the lymphoma patients with COVID-19 was comparable with that of the reference French COVID-19 population. In addition, there was no significant impact of active lymphoma treatment that had been given within 1 year, except for those patients who received bendamustine, which was associated with greater mortality, according to the researchers.
With a median follow-up of 33 days from admission, the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 30-day overall survival was 71% (95% confidence interval, 62%-81%). According to histological type of the lymphoma, 30-day overall survival rates were 80% (95% CI, 45%-100%) for Hodgkin lymphoma, 71% (95% CI, 61%-82%) for B-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and 71% (95% CI, 38%-100%) for T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
The main factors associated with mortality were age 70 years and older (hazard ratio, 3.78; 95% CI, 1.73-8.25; P = .0009), hypertension (HR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.06-4.59; P = .03), previous cancer (HR, 2.11; 95% CI, 0.90-4.92; P = .08), use of bendamustine within 12 months before admission to hospital (HR, 3.05; 95% CI, 1.31-7.11; P = .01), and r/r lymphoma (HR, 2.62; 95% CI, 1.20-5.72; P = .02).
Overall, the Kaplan-Meier estimates of 30-day overall survival were 61% for patients with r/r lymphoma, 52% in patients age 70 years with non–r/r lymphoma, and 88% for patients younger than 70 years with non–r/r, which was comparable with general population survival data among French populations, according to the researchers.
“Longer term clinical follow-up and biological monitoring of immune responses is warranted to explore the impact of lymphoma and its treatment on the immunity and prolonged outcome of Covid-19 patients,” they concluded.
The study was unsponsored. Several of the authors reported financial relationships with a number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Lamure S et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Oct 12. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100549.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
Blood group O linked to decreased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Blood group O was associated with a decreased risk for contracting SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to the results of large retrospective analysis of the Danish population.
Researchers Mike Bogetofte Barnkob, MD, of the Department of Clinical Immunology, Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort analysis of all Danish individuals with a known ABO blood group who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 between Feb. 27, 2020, and July 30, 2020.
Of the 841,327 people tested, ABO and RhD blood groups could be identified for 473,654 individuals. ABO and RhD data from 2,204,742 (38% of the entire Danish population) were used as a reference, according to the online report in Blood Advances.
The primary outcome was status of ABO and RhD blood groups and test results for SARS-CoV-2. The secondary outcomes followed were hospitalization and death from COVID-19.
Reduced prevalence
The study found that ABO blood groups varied significantly between patients and the reference group, with only 38.41% (95% confidence interval, 37.30%-39.50%) of the patients belonging to blood group O, compared with 41.70% (95% CI, 41.60%-41.80%) in the controls, corresponding to a relative risk of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.83-0.91) for acquiring COVID-19.
There was a slight, but statistically significant, difference in blood group distribution between the SARS-CoV-22 individuals and the reference population (P < .001), according to the authors.
Among the SARS-CoV-2 individuals, fewer group O individuals were found (P < .001); while more A, B, and AB individuals were seen (P < .001, P = .011, and P = .091, respectively). There was no significant difference seen among A, B, and AB blood groups (P = .30). The RR for contracting SARS-CoV-2 were 1.09 (95% CI, 1.04-1.14) for A group individuals; 1.06 (95% CI, 0.99-1.14) for B group; and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.03-1.27) for AB group, respectively.
There was no difference found in the RhD group between positive test cases and the reference population (P = .15). In addition, there was no statistical difference (all P > .40) between ABO blood groups and clinical severity of COVID-19 for nonhospitalized patients versus hospitalized patients or for deceased patients versus living patients, the researchers added.
Possible causes
The authors speculated on two possible causes of the lower prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the blood group O population. The first is that anti-A and anti-B antibodies may have an effect on neutralizing SARS-CoV viruses and that anti-A and anti-B are present on mucosal surfaces in some individuals lacking the corresponding ABO blood group. The second is that the association between ABO blood groups and levels of von Willebrand factor, which is higher in non-O individuals and is tied to an increased likelihood of arterial and venous thrombosis, could have an indirect or unknown impact on susceptibility to infection, according to the authors.
“Given the known increased risk of thrombosis in non-O individuals and the evolving central role for thrombosis in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, it is important to explore this aspect more closely in larger patient cohorts (e.g., by examining ABO blood type and viral load, the severity of symptoms, and the long-term effects following COVID-19),” the researchers concluded.
One author reported receiving fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche. The remaining authors reported they had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Barnkob MB et al. Blood Adv. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002657.
Blood group O was associated with a decreased risk for contracting SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to the results of large retrospective analysis of the Danish population.
Researchers Mike Bogetofte Barnkob, MD, of the Department of Clinical Immunology, Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort analysis of all Danish individuals with a known ABO blood group who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 between Feb. 27, 2020, and July 30, 2020.
Of the 841,327 people tested, ABO and RhD blood groups could be identified for 473,654 individuals. ABO and RhD data from 2,204,742 (38% of the entire Danish population) were used as a reference, according to the online report in Blood Advances.
The primary outcome was status of ABO and RhD blood groups and test results for SARS-CoV-2. The secondary outcomes followed were hospitalization and death from COVID-19.
Reduced prevalence
The study found that ABO blood groups varied significantly between patients and the reference group, with only 38.41% (95% confidence interval, 37.30%-39.50%) of the patients belonging to blood group O, compared with 41.70% (95% CI, 41.60%-41.80%) in the controls, corresponding to a relative risk of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.83-0.91) for acquiring COVID-19.
There was a slight, but statistically significant, difference in blood group distribution between the SARS-CoV-22 individuals and the reference population (P < .001), according to the authors.
Among the SARS-CoV-2 individuals, fewer group O individuals were found (P < .001); while more A, B, and AB individuals were seen (P < .001, P = .011, and P = .091, respectively). There was no significant difference seen among A, B, and AB blood groups (P = .30). The RR for contracting SARS-CoV-2 were 1.09 (95% CI, 1.04-1.14) for A group individuals; 1.06 (95% CI, 0.99-1.14) for B group; and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.03-1.27) for AB group, respectively.
There was no difference found in the RhD group between positive test cases and the reference population (P = .15). In addition, there was no statistical difference (all P > .40) between ABO blood groups and clinical severity of COVID-19 for nonhospitalized patients versus hospitalized patients or for deceased patients versus living patients, the researchers added.
Possible causes
The authors speculated on two possible causes of the lower prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the blood group O population. The first is that anti-A and anti-B antibodies may have an effect on neutralizing SARS-CoV viruses and that anti-A and anti-B are present on mucosal surfaces in some individuals lacking the corresponding ABO blood group. The second is that the association between ABO blood groups and levels of von Willebrand factor, which is higher in non-O individuals and is tied to an increased likelihood of arterial and venous thrombosis, could have an indirect or unknown impact on susceptibility to infection, according to the authors.
“Given the known increased risk of thrombosis in non-O individuals and the evolving central role for thrombosis in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, it is important to explore this aspect more closely in larger patient cohorts (e.g., by examining ABO blood type and viral load, the severity of symptoms, and the long-term effects following COVID-19),” the researchers concluded.
One author reported receiving fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche. The remaining authors reported they had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Barnkob MB et al. Blood Adv. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002657.
Blood group O was associated with a decreased risk for contracting SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to the results of large retrospective analysis of the Danish population.
Researchers Mike Bogetofte Barnkob, MD, of the Department of Clinical Immunology, Odense (Denmark) University Hospital, and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort analysis of all Danish individuals with a known ABO blood group who were tested for SARS-CoV-2 between Feb. 27, 2020, and July 30, 2020.
Of the 841,327 people tested, ABO and RhD blood groups could be identified for 473,654 individuals. ABO and RhD data from 2,204,742 (38% of the entire Danish population) were used as a reference, according to the online report in Blood Advances.
The primary outcome was status of ABO and RhD blood groups and test results for SARS-CoV-2. The secondary outcomes followed were hospitalization and death from COVID-19.
Reduced prevalence
The study found that ABO blood groups varied significantly between patients and the reference group, with only 38.41% (95% confidence interval, 37.30%-39.50%) of the patients belonging to blood group O, compared with 41.70% (95% CI, 41.60%-41.80%) in the controls, corresponding to a relative risk of 0.87 (95% CI, 0.83-0.91) for acquiring COVID-19.
There was a slight, but statistically significant, difference in blood group distribution between the SARS-CoV-22 individuals and the reference population (P < .001), according to the authors.
Among the SARS-CoV-2 individuals, fewer group O individuals were found (P < .001); while more A, B, and AB individuals were seen (P < .001, P = .011, and P = .091, respectively). There was no significant difference seen among A, B, and AB blood groups (P = .30). The RR for contracting SARS-CoV-2 were 1.09 (95% CI, 1.04-1.14) for A group individuals; 1.06 (95% CI, 0.99-1.14) for B group; and 1.15 (95% CI, 1.03-1.27) for AB group, respectively.
There was no difference found in the RhD group between positive test cases and the reference population (P = .15). In addition, there was no statistical difference (all P > .40) between ABO blood groups and clinical severity of COVID-19 for nonhospitalized patients versus hospitalized patients or for deceased patients versus living patients, the researchers added.
Possible causes
The authors speculated on two possible causes of the lower prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the blood group O population. The first is that anti-A and anti-B antibodies may have an effect on neutralizing SARS-CoV viruses and that anti-A and anti-B are present on mucosal surfaces in some individuals lacking the corresponding ABO blood group. The second is that the association between ABO blood groups and levels of von Willebrand factor, which is higher in non-O individuals and is tied to an increased likelihood of arterial and venous thrombosis, could have an indirect or unknown impact on susceptibility to infection, according to the authors.
“Given the known increased risk of thrombosis in non-O individuals and the evolving central role for thrombosis in the pathogenesis of COVID-19, it is important to explore this aspect more closely in larger patient cohorts (e.g., by examining ABO blood type and viral load, the severity of symptoms, and the long-term effects following COVID-19),” the researchers concluded.
One author reported receiving fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, and Roche. The remaining authors reported they had no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Barnkob MB et al. Blood Adv. 2020 Oct 14. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002657.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Trump signs Medicare loan relief bill delaying repayments
President Trump on Oct. 1 signed a bill to keep the federal government running through December 11. This “continuing resolution” (CR), which was approved by the Senate Wednesday on an 84-10 vote, according to The New York Times, includes provisions to delay repayment by physicians of pandemic-related Medicare loans and to reduce the loans’ interest rate.
In an earlier news release, the American Medical Association reported that Congress and the White House had agreed to include the provisions on Medicare loans in the CR.
Under the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payments (AAP) program, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services advanced money to physicians who were financially impacted by the pandemic. The program, created in March, was suspended in late April.
Physicians who received the Medicare loans were supposed to start paying them back 120 days after they were made. CMS planned to recoup the advances by offsetting them against Medicare claims payments due to physicians. Practices had up to 210 days (7 months) to repay the loans through this process before being asked to repay them directly with interest of 10.25%.
For the practices that received these advances, that meant their Medicare cash flow was scheduled to dry up, starting in August. However, CMS quietly abstained from collecting these payments when they came due, according to Modern Healthcare.
New terms
The amount to be recouped from each claim is reduced from 100% to 25% of the claim for the first 11 months and to 50% of claims withheld for an additional 6 months. If the loan is not repaid in full by then, the provider must pay the balance with interest of 4%.
More than 80% of the $100 billion that CMS loaned to healthcare providers through May 2 went to hospitals, Modern Healthcare calculated. Of the remainder, specialty or multispecialty practices received $3.5 billion, internal medicine specialists got $24 million, family physicians were loaned $15 million, and federally qualified health centers received $20 million.
In the AMA’s news release, AMA President Susan Bailey, MD, who assumed the post in June, called the original loan repayment plan an “economic sword hanging over physician practices.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Trump on Oct. 1 signed a bill to keep the federal government running through December 11. This “continuing resolution” (CR), which was approved by the Senate Wednesday on an 84-10 vote, according to The New York Times, includes provisions to delay repayment by physicians of pandemic-related Medicare loans and to reduce the loans’ interest rate.
In an earlier news release, the American Medical Association reported that Congress and the White House had agreed to include the provisions on Medicare loans in the CR.
Under the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payments (AAP) program, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services advanced money to physicians who were financially impacted by the pandemic. The program, created in March, was suspended in late April.
Physicians who received the Medicare loans were supposed to start paying them back 120 days after they were made. CMS planned to recoup the advances by offsetting them against Medicare claims payments due to physicians. Practices had up to 210 days (7 months) to repay the loans through this process before being asked to repay them directly with interest of 10.25%.
For the practices that received these advances, that meant their Medicare cash flow was scheduled to dry up, starting in August. However, CMS quietly abstained from collecting these payments when they came due, according to Modern Healthcare.
New terms
The amount to be recouped from each claim is reduced from 100% to 25% of the claim for the first 11 months and to 50% of claims withheld for an additional 6 months. If the loan is not repaid in full by then, the provider must pay the balance with interest of 4%.
More than 80% of the $100 billion that CMS loaned to healthcare providers through May 2 went to hospitals, Modern Healthcare calculated. Of the remainder, specialty or multispecialty practices received $3.5 billion, internal medicine specialists got $24 million, family physicians were loaned $15 million, and federally qualified health centers received $20 million.
In the AMA’s news release, AMA President Susan Bailey, MD, who assumed the post in June, called the original loan repayment plan an “economic sword hanging over physician practices.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Trump on Oct. 1 signed a bill to keep the federal government running through December 11. This “continuing resolution” (CR), which was approved by the Senate Wednesday on an 84-10 vote, according to The New York Times, includes provisions to delay repayment by physicians of pandemic-related Medicare loans and to reduce the loans’ interest rate.
In an earlier news release, the American Medical Association reported that Congress and the White House had agreed to include the provisions on Medicare loans in the CR.
Under the Medicare Accelerated and Advance Payments (AAP) program, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services advanced money to physicians who were financially impacted by the pandemic. The program, created in March, was suspended in late April.
Physicians who received the Medicare loans were supposed to start paying them back 120 days after they were made. CMS planned to recoup the advances by offsetting them against Medicare claims payments due to physicians. Practices had up to 210 days (7 months) to repay the loans through this process before being asked to repay them directly with interest of 10.25%.
For the practices that received these advances, that meant their Medicare cash flow was scheduled to dry up, starting in August. However, CMS quietly abstained from collecting these payments when they came due, according to Modern Healthcare.
New terms
The amount to be recouped from each claim is reduced from 100% to 25% of the claim for the first 11 months and to 50% of claims withheld for an additional 6 months. If the loan is not repaid in full by then, the provider must pay the balance with interest of 4%.
More than 80% of the $100 billion that CMS loaned to healthcare providers through May 2 went to hospitals, Modern Healthcare calculated. Of the remainder, specialty or multispecialty practices received $3.5 billion, internal medicine specialists got $24 million, family physicians were loaned $15 million, and federally qualified health centers received $20 million.
In the AMA’s news release, AMA President Susan Bailey, MD, who assumed the post in June, called the original loan repayment plan an “economic sword hanging over physician practices.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low VWF levels or blood group O not linked to intracerebral hemorrhage risk
In contrast to findings of previous research, low levels of von Willebrand Factor (VWF) and blood group O were not associated with a first-ever intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), according to a study published in Thrombosis Research.
The researchers compared 176 cases of ICH with 349 age- and sex-matched controls. The mean patient age was 57 years, and 50% were women. The median time from baseline blood sampling to the first ICH was 5.6 years, according to the study reported by Kristina Johansson of Umeå (Sweden) University and her colleagues.
Complicated picture
The level of VWF differed significantly among blood groups: In individuals with blood group O, the mean VWF level was 1.29 kIU/L; for blood group A, it was 1.52 kIU/L; for blood group AB, 1.59 kIU/L; and in blood group B, 1.76 kIU/L. However, there was no difference in VWF concentration between cases and controls.
The researchers found no association between blood group O and the risk of ICH, a finding previously seen in other studies. They did, however, find that, in the limited number of patients with blood group B there was an association with a lower risk of ICH, compared with blood group A (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.95).
“To our knowledge this is the largest prospective study investigating the association between VWF, ABO blood group and ICH. We found no association between VWF or blood group O and risk of future ICH,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by public institutions in Sweden. The authors declared that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Johansson K et al. Thromb Res. 2020 Jul 5;195:77-80.
In contrast to findings of previous research, low levels of von Willebrand Factor (VWF) and blood group O were not associated with a first-ever intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), according to a study published in Thrombosis Research.
The researchers compared 176 cases of ICH with 349 age- and sex-matched controls. The mean patient age was 57 years, and 50% were women. The median time from baseline blood sampling to the first ICH was 5.6 years, according to the study reported by Kristina Johansson of Umeå (Sweden) University and her colleagues.
Complicated picture
The level of VWF differed significantly among blood groups: In individuals with blood group O, the mean VWF level was 1.29 kIU/L; for blood group A, it was 1.52 kIU/L; for blood group AB, 1.59 kIU/L; and in blood group B, 1.76 kIU/L. However, there was no difference in VWF concentration between cases and controls.
The researchers found no association between blood group O and the risk of ICH, a finding previously seen in other studies. They did, however, find that, in the limited number of patients with blood group B there was an association with a lower risk of ICH, compared with blood group A (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.95).
“To our knowledge this is the largest prospective study investigating the association between VWF, ABO blood group and ICH. We found no association between VWF or blood group O and risk of future ICH,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by public institutions in Sweden. The authors declared that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Johansson K et al. Thromb Res. 2020 Jul 5;195:77-80.
In contrast to findings of previous research, low levels of von Willebrand Factor (VWF) and blood group O were not associated with a first-ever intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), according to a study published in Thrombosis Research.
The researchers compared 176 cases of ICH with 349 age- and sex-matched controls. The mean patient age was 57 years, and 50% were women. The median time from baseline blood sampling to the first ICH was 5.6 years, according to the study reported by Kristina Johansson of Umeå (Sweden) University and her colleagues.
Complicated picture
The level of VWF differed significantly among blood groups: In individuals with blood group O, the mean VWF level was 1.29 kIU/L; for blood group A, it was 1.52 kIU/L; for blood group AB, 1.59 kIU/L; and in blood group B, 1.76 kIU/L. However, there was no difference in VWF concentration between cases and controls.
The researchers found no association between blood group O and the risk of ICH, a finding previously seen in other studies. They did, however, find that, in the limited number of patients with blood group B there was an association with a lower risk of ICH, compared with blood group A (odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.95).
“To our knowledge this is the largest prospective study investigating the association between VWF, ABO blood group and ICH. We found no association between VWF or blood group O and risk of future ICH,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by public institutions in Sweden. The authors declared that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Johansson K et al. Thromb Res. 2020 Jul 5;195:77-80.
FROM THROMBOSIS RESEARCH
U.S. tops 500,000 COVID-19 cases in children
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
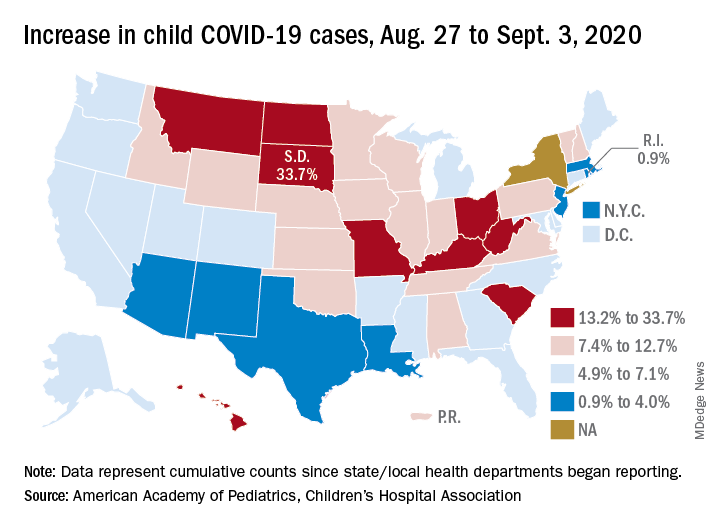
States have reported 513,415 cases of COVID-19 in children since the beginning of the pandemic, with almost 37,000 coming in the last week, the AAP and the CHA said Sept. 8 in the weekly report. That figure includes New York City – the rest of New York State is not reporting ages for COVID-19 patients – as well as Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, and Guam.
“These numbers are a chilling reminder of why we need to take this virus seriously,” AAP President Sara Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
Children now represent 9.8% of the almost 5.3 million cases that have been reported in Americans of all ages. The proportion of child cases has continued to increase as the pandemic has progressed – it was 8.0% as of mid-July and 5.2% in early June, the data show.
“Throughout the summer, surges in the virus have occurred in Southern, Western, and Midwestern states,” the AAP statement said.
The latest AAP/CHA report shows that, from Aug. 27 to Sept. 3, the total number of child cases jumped by 33.7% in South Dakota, more than any other state. North Dakota was next at 22.7%, followed by Hawaii (18.1%), Missouri (16.8%), and Kentucky (16.4%).
“This rapid rise in positive cases occurred over the summer, and as the weather cools, we know people will spend more time indoors,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. “The goal is to get children back into schools for in-person learning, but in many communities, this is not possible as the virus spreads unchecked.”
The smallest increase over the last week, just 0.9%, came in Rhode Island, with Massachusetts just a bit higher at 1.0%. Also at the low end of the increase scale are Arizona (3.3%) and Louisiana (4.0%), two states that have very high rates of cumulative cases: 1,380 per 100,000 children for Arizona and 1,234 per 100,000 for Louisiana, the report said.
To give those figures some context, Tennessee has the highest cumulative count of any state at 1,553 cases per 100,000 children and Vermont has the lowest at 151, based on the data gathered by the AAP and CHA.
“While much remains unknown about COVID-19, we do know that the spread among children reflects what is happening in the broader communities. A disproportionate number of cases are reported in Black and Hispanic children and in places where there is high poverty. We must work harder to address societal inequities that contribute to these disparities,” Dr. Goza said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

States have reported 513,415 cases of COVID-19 in children since the beginning of the pandemic, with almost 37,000 coming in the last week, the AAP and the CHA said Sept. 8 in the weekly report. That figure includes New York City – the rest of New York State is not reporting ages for COVID-19 patients – as well as Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, and Guam.
“These numbers are a chilling reminder of why we need to take this virus seriously,” AAP President Sara Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
Children now represent 9.8% of the almost 5.3 million cases that have been reported in Americans of all ages. The proportion of child cases has continued to increase as the pandemic has progressed – it was 8.0% as of mid-July and 5.2% in early June, the data show.
“Throughout the summer, surges in the virus have occurred in Southern, Western, and Midwestern states,” the AAP statement said.
The latest AAP/CHA report shows that, from Aug. 27 to Sept. 3, the total number of child cases jumped by 33.7% in South Dakota, more than any other state. North Dakota was next at 22.7%, followed by Hawaii (18.1%), Missouri (16.8%), and Kentucky (16.4%).
“This rapid rise in positive cases occurred over the summer, and as the weather cools, we know people will spend more time indoors,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. “The goal is to get children back into schools for in-person learning, but in many communities, this is not possible as the virus spreads unchecked.”
The smallest increase over the last week, just 0.9%, came in Rhode Island, with Massachusetts just a bit higher at 1.0%. Also at the low end of the increase scale are Arizona (3.3%) and Louisiana (4.0%), two states that have very high rates of cumulative cases: 1,380 per 100,000 children for Arizona and 1,234 per 100,000 for Louisiana, the report said.
To give those figures some context, Tennessee has the highest cumulative count of any state at 1,553 cases per 100,000 children and Vermont has the lowest at 151, based on the data gathered by the AAP and CHA.
“While much remains unknown about COVID-19, we do know that the spread among children reflects what is happening in the broader communities. A disproportionate number of cases are reported in Black and Hispanic children and in places where there is high poverty. We must work harder to address societal inequities that contribute to these disparities,” Dr. Goza said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

States have reported 513,415 cases of COVID-19 in children since the beginning of the pandemic, with almost 37,000 coming in the last week, the AAP and the CHA said Sept. 8 in the weekly report. That figure includes New York City – the rest of New York State is not reporting ages for COVID-19 patients – as well as Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, and Guam.
“These numbers are a chilling reminder of why we need to take this virus seriously,” AAP President Sara Goza, MD, said in a written statement.
Children now represent 9.8% of the almost 5.3 million cases that have been reported in Americans of all ages. The proportion of child cases has continued to increase as the pandemic has progressed – it was 8.0% as of mid-July and 5.2% in early June, the data show.
“Throughout the summer, surges in the virus have occurred in Southern, Western, and Midwestern states,” the AAP statement said.
The latest AAP/CHA report shows that, from Aug. 27 to Sept. 3, the total number of child cases jumped by 33.7% in South Dakota, more than any other state. North Dakota was next at 22.7%, followed by Hawaii (18.1%), Missouri (16.8%), and Kentucky (16.4%).
“This rapid rise in positive cases occurred over the summer, and as the weather cools, we know people will spend more time indoors,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, MPH, vice chair of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. “The goal is to get children back into schools for in-person learning, but in many communities, this is not possible as the virus spreads unchecked.”
The smallest increase over the last week, just 0.9%, came in Rhode Island, with Massachusetts just a bit higher at 1.0%. Also at the low end of the increase scale are Arizona (3.3%) and Louisiana (4.0%), two states that have very high rates of cumulative cases: 1,380 per 100,000 children for Arizona and 1,234 per 100,000 for Louisiana, the report said.
To give those figures some context, Tennessee has the highest cumulative count of any state at 1,553 cases per 100,000 children and Vermont has the lowest at 151, based on the data gathered by the AAP and CHA.
“While much remains unknown about COVID-19, we do know that the spread among children reflects what is happening in the broader communities. A disproportionate number of cases are reported in Black and Hispanic children and in places where there is high poverty. We must work harder to address societal inequities that contribute to these disparities,” Dr. Goza said.
Five reasons why medical meetings will never be the same
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the virtual medical meeting is now the norm. And while it’s admirable that key data are being disseminated (often for free), there is no escaping the fact that it is a fundamentally different and lesser experience.
Watching from home, most of us split our attention between live streams of the meeting and work and family obligations. There is far less urgency when early live presentations are recorded and can be viewed later.
In terms of discussing the data, Twitter may offer broader participation than a live meeting, yet only a small number of attendees actively engage online.
And the exhibit halls for these online meetings? With neither free coffee nor company-branded tchotchkes, I expect that they have virtual tumbleweeds blowing through and crickets chirping.
Even still, the virtual meeting experience, while inferior to the live one, is a tremendous advance. It should never be banished as a historical footnote but rather should remain an option. It’s analogous to watching the Super Bowl at home: Obviously, it’s not the same as being there, but it’s a terrific alternative. Like telemedicine, this pandemic has provided a critical proof of concept that there is a better model.
Reshaping the medical meeting
Let’s consider five reasons why medical meetings should be permanently reshaped by this pandemic.
This pandemic isn’t going away in 2020. While nearly every country has done a far better job than the United States of containing COVID-19 thus far, outbreaks remain a problem wherever crowds assemble. You’d be hard-pressed to devise a setting more conducive to mass spread than a conference of 20,000 attendees from all over the world sitting alongside each other cheek to jowl for 5 days. Worse yet is the thought of them returning home and infecting their patients, families, and friends. What medical society wants to be remembered for creating a COVID-19 superspreader event? Professional medical societies will need to offer this option as the safest alternative moving forward.
Virtual learning still conveys the most important content. Despite the many social benefits of a live meeting, its core purpose is to disseminate new research and current and emerging treatment options. Virtual meetings have proven that this format can effectively deliver the content, and not as a secondary offering but as the sole platform in real time.
Virtual learning levels the playing field. Traveling to attend conferences typically costs thousands of dollars, accounting for the registration fees, inflated hotel rates, ground transportation, and meals out for days on end. Most meetings also demand several days away from our work and families, forcing many of us to work extra in the days before we leave and upon our return. Parents and those with commitments at home also face special challenges. For international participants, the financial and time costs are even greater. A virtual meeting helps overcome these hurdles and erases barriers that have long precluded many from attending a conference.
Virtual learning is efficient and comfortable. Virtual meetings over the past 6 months have given us a glimpse of an astonishingly more efficient form. If the content seems of a lower magnitude without the fanfare of a live conference, it is in part because so much of a live meeting is spent walking a mile between session rooms, waiting in concession or taxi lines, sitting in traffic between venues, or simply waiting for a session to begin. All of that has been replaced with time that you can use productively in between video sessions viewed either live or on demand. And with a virtual meeting, you can comfortably watch the sessions. There’s no need to stand along the back wall of an overcrowded room or step over 10 people to squeeze into an open middle seat. You can be focused, rather than having an end-of-day presentation wash over you as your eyes cross because you’ve been running around for the past 12 hours.
Virtual learning and social media will only improve. While virtual meetings unquestionably have limitations, it’s important to acknowledge that the successes thus far still represent only the earliest forays into this endeavor. In-person meetings evolved to their present form over centuries. In contrast, virtual meetings are being cobbled together within a few weeks or months. They can only be expected to improve as presenters adapt their skills to the online audience and new tools improve virtual discussions.
I am not implying that live meetings will or should be replaced by virtual ones. We still need that experience of trainees and experts presenting to a live audience and discussing the results together, all while sharing the energy of the moment. But there should be room for both a live conference and a virtual version.
Practically speaking, it is unclear whether professional societies could forgo the revenue they receive from registration fees, meeting sponsorships, and corporate exhibits. Yet, there are certainly ways to obtain sponsorship revenue for a virtual program. Even if the virtual version of a conference costs far less than attending in person, there is plenty of room between that number and free. It costs remarkably little for a professional society to share its content, and virtual offerings further the mission of distributing this content broadly.
We should not rush to return to the previous status quo. Despite their limitations, virtual meetings have brought a new, higher standard of access and efficiency for sharing important new data and treatment options in medicine.
H. Jack West, MD, associate clinical professor and executive director of employer services at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, Calif., regularly comments on lung cancer for Medscape. West serves as web editor for JAMA Oncology, edits and writes several sections on lung cancer for UpToDate, and leads a wide range of continuing education programs and other educational programs, including hosting the audio podcast West Wind.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the virtual medical meeting is now the norm. And while it’s admirable that key data are being disseminated (often for free), there is no escaping the fact that it is a fundamentally different and lesser experience.
Watching from home, most of us split our attention between live streams of the meeting and work and family obligations. There is far less urgency when early live presentations are recorded and can be viewed later.
In terms of discussing the data, Twitter may offer broader participation than a live meeting, yet only a small number of attendees actively engage online.
And the exhibit halls for these online meetings? With neither free coffee nor company-branded tchotchkes, I expect that they have virtual tumbleweeds blowing through and crickets chirping.
Even still, the virtual meeting experience, while inferior to the live one, is a tremendous advance. It should never be banished as a historical footnote but rather should remain an option. It’s analogous to watching the Super Bowl at home: Obviously, it’s not the same as being there, but it’s a terrific alternative. Like telemedicine, this pandemic has provided a critical proof of concept that there is a better model.
Reshaping the medical meeting
Let’s consider five reasons why medical meetings should be permanently reshaped by this pandemic.
This pandemic isn’t going away in 2020. While nearly every country has done a far better job than the United States of containing COVID-19 thus far, outbreaks remain a problem wherever crowds assemble. You’d be hard-pressed to devise a setting more conducive to mass spread than a conference of 20,000 attendees from all over the world sitting alongside each other cheek to jowl for 5 days. Worse yet is the thought of them returning home and infecting their patients, families, and friends. What medical society wants to be remembered for creating a COVID-19 superspreader event? Professional medical societies will need to offer this option as the safest alternative moving forward.
Virtual learning still conveys the most important content. Despite the many social benefits of a live meeting, its core purpose is to disseminate new research and current and emerging treatment options. Virtual meetings have proven that this format can effectively deliver the content, and not as a secondary offering but as the sole platform in real time.
Virtual learning levels the playing field. Traveling to attend conferences typically costs thousands of dollars, accounting for the registration fees, inflated hotel rates, ground transportation, and meals out for days on end. Most meetings also demand several days away from our work and families, forcing many of us to work extra in the days before we leave and upon our return. Parents and those with commitments at home also face special challenges. For international participants, the financial and time costs are even greater. A virtual meeting helps overcome these hurdles and erases barriers that have long precluded many from attending a conference.
Virtual learning is efficient and comfortable. Virtual meetings over the past 6 months have given us a glimpse of an astonishingly more efficient form. If the content seems of a lower magnitude without the fanfare of a live conference, it is in part because so much of a live meeting is spent walking a mile between session rooms, waiting in concession or taxi lines, sitting in traffic between venues, or simply waiting for a session to begin. All of that has been replaced with time that you can use productively in between video sessions viewed either live or on demand. And with a virtual meeting, you can comfortably watch the sessions. There’s no need to stand along the back wall of an overcrowded room or step over 10 people to squeeze into an open middle seat. You can be focused, rather than having an end-of-day presentation wash over you as your eyes cross because you’ve been running around for the past 12 hours.
Virtual learning and social media will only improve. While virtual meetings unquestionably have limitations, it’s important to acknowledge that the successes thus far still represent only the earliest forays into this endeavor. In-person meetings evolved to their present form over centuries. In contrast, virtual meetings are being cobbled together within a few weeks or months. They can only be expected to improve as presenters adapt their skills to the online audience and new tools improve virtual discussions.
I am not implying that live meetings will or should be replaced by virtual ones. We still need that experience of trainees and experts presenting to a live audience and discussing the results together, all while sharing the energy of the moment. But there should be room for both a live conference and a virtual version.
Practically speaking, it is unclear whether professional societies could forgo the revenue they receive from registration fees, meeting sponsorships, and corporate exhibits. Yet, there are certainly ways to obtain sponsorship revenue for a virtual program. Even if the virtual version of a conference costs far less than attending in person, there is plenty of room between that number and free. It costs remarkably little for a professional society to share its content, and virtual offerings further the mission of distributing this content broadly.
We should not rush to return to the previous status quo. Despite their limitations, virtual meetings have brought a new, higher standard of access and efficiency for sharing important new data and treatment options in medicine.
H. Jack West, MD, associate clinical professor and executive director of employer services at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, Calif., regularly comments on lung cancer for Medscape. West serves as web editor for JAMA Oncology, edits and writes several sections on lung cancer for UpToDate, and leads a wide range of continuing education programs and other educational programs, including hosting the audio podcast West Wind.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the virtual medical meeting is now the norm. And while it’s admirable that key data are being disseminated (often for free), there is no escaping the fact that it is a fundamentally different and lesser experience.
Watching from home, most of us split our attention between live streams of the meeting and work and family obligations. There is far less urgency when early live presentations are recorded and can be viewed later.
In terms of discussing the data, Twitter may offer broader participation than a live meeting, yet only a small number of attendees actively engage online.
And the exhibit halls for these online meetings? With neither free coffee nor company-branded tchotchkes, I expect that they have virtual tumbleweeds blowing through and crickets chirping.
Even still, the virtual meeting experience, while inferior to the live one, is a tremendous advance. It should never be banished as a historical footnote but rather should remain an option. It’s analogous to watching the Super Bowl at home: Obviously, it’s not the same as being there, but it’s a terrific alternative. Like telemedicine, this pandemic has provided a critical proof of concept that there is a better model.
Reshaping the medical meeting
Let’s consider five reasons why medical meetings should be permanently reshaped by this pandemic.
This pandemic isn’t going away in 2020. While nearly every country has done a far better job than the United States of containing COVID-19 thus far, outbreaks remain a problem wherever crowds assemble. You’d be hard-pressed to devise a setting more conducive to mass spread than a conference of 20,000 attendees from all over the world sitting alongside each other cheek to jowl for 5 days. Worse yet is the thought of them returning home and infecting their patients, families, and friends. What medical society wants to be remembered for creating a COVID-19 superspreader event? Professional medical societies will need to offer this option as the safest alternative moving forward.
Virtual learning still conveys the most important content. Despite the many social benefits of a live meeting, its core purpose is to disseminate new research and current and emerging treatment options. Virtual meetings have proven that this format can effectively deliver the content, and not as a secondary offering but as the sole platform in real time.
Virtual learning levels the playing field. Traveling to attend conferences typically costs thousands of dollars, accounting for the registration fees, inflated hotel rates, ground transportation, and meals out for days on end. Most meetings also demand several days away from our work and families, forcing many of us to work extra in the days before we leave and upon our return. Parents and those with commitments at home also face special challenges. For international participants, the financial and time costs are even greater. A virtual meeting helps overcome these hurdles and erases barriers that have long precluded many from attending a conference.
Virtual learning is efficient and comfortable. Virtual meetings over the past 6 months have given us a glimpse of an astonishingly more efficient form. If the content seems of a lower magnitude without the fanfare of a live conference, it is in part because so much of a live meeting is spent walking a mile between session rooms, waiting in concession or taxi lines, sitting in traffic between venues, or simply waiting for a session to begin. All of that has been replaced with time that you can use productively in between video sessions viewed either live or on demand. And with a virtual meeting, you can comfortably watch the sessions. There’s no need to stand along the back wall of an overcrowded room or step over 10 people to squeeze into an open middle seat. You can be focused, rather than having an end-of-day presentation wash over you as your eyes cross because you’ve been running around for the past 12 hours.
Virtual learning and social media will only improve. While virtual meetings unquestionably have limitations, it’s important to acknowledge that the successes thus far still represent only the earliest forays into this endeavor. In-person meetings evolved to their present form over centuries. In contrast, virtual meetings are being cobbled together within a few weeks or months. They can only be expected to improve as presenters adapt their skills to the online audience and new tools improve virtual discussions.
I am not implying that live meetings will or should be replaced by virtual ones. We still need that experience of trainees and experts presenting to a live audience and discussing the results together, all while sharing the energy of the moment. But there should be room for both a live conference and a virtual version.
Practically speaking, it is unclear whether professional societies could forgo the revenue they receive from registration fees, meeting sponsorships, and corporate exhibits. Yet, there are certainly ways to obtain sponsorship revenue for a virtual program. Even if the virtual version of a conference costs far less than attending in person, there is plenty of room between that number and free. It costs remarkably little for a professional society to share its content, and virtual offerings further the mission of distributing this content broadly.
We should not rush to return to the previous status quo. Despite their limitations, virtual meetings have brought a new, higher standard of access and efficiency for sharing important new data and treatment options in medicine.
H. Jack West, MD, associate clinical professor and executive director of employer services at City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, Calif., regularly comments on lung cancer for Medscape. West serves as web editor for JAMA Oncology, edits and writes several sections on lung cancer for UpToDate, and leads a wide range of continuing education programs and other educational programs, including hosting the audio podcast West Wind.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study: 10% of pregnant women test positive for COVID-19, with most asymptomatic
according to a living systematic review from the PregCOV-19 Living Systematic Review Consortium.
The study, published in BMJ, shows an increased risk of preterm delivery, as well as the need for invasive ventilation in these women, wrote John Allotey, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) and colleagues. The findings “will produce a strong evidence base for living guidelines on COVID-19 and pregnancy,” they noted.
The systematic review included 77 studies, one-third each from the United States and China, with the remaining studies from Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, the Netherlands Portugal, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
The studies included women with COVID-19, of whom 13,118 were either pregnant or in the postpartum or postabortion period and 83,486 were of reproductive age but not pregnant. Some studies also included healthy pregnant women for comparison.
In the pregnant and recently pregnant women, the most common COVID-19 symptoms were fever (40%) and cough (39%), with lymphopenia (35%) and raised C reactive protein levels (49%) being the most common laboratory findings. Pregnant and recently pregnant women with COVID-19 were less likely to have fever (odds ratio, 0.43) and myalgia (OR, 0.48), compared with nonpregnant women of reproductive age with COVID-19, reported the authors.
The overall preterm and spontaneous preterm birth rates in the COVID-19–positive women were 17% and 6% respectively. Dr. Allotey and authors noted that “these preterm births could be medically indicated, as the overall rates of spontaneous preterm births in pregnant women with COVID-19 was broadly similar to those observed in the pre-pandemic period.” There were 18 stillbirths and 6 neonatal deaths in the COVID-19 cohort.
Overall, 73 (0.1%) of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 died from any cause, and severe COVID-19 infection was diagnosed in 13%. Maternal risk factors associated with severe infection included older age (OR, 1.78), high body mass index (OR, 2.3), chronic hypertension (OR, 2.0), and preexisting diabetes (OR, 2.51). Compared with nonpregnant women with COVID-19, pregnant or recently pregnant women with the infection were at increased risk of admission to intensive care (OR, 1.62) and needing invasive ventilation (OR, 1.88).
The report included studies published between December 1, 2019, and June 26, 2020, but the living systematic review will involve weekly search updates, with analysis performed every 2-4 weeks and reported through a dedicated website.
The value of a living meta-analysis
Asked to comment on the findings, Torri Metz, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, expressed surprise at the 10% rate of infection in the pregnant or recently pregnant population. “This is higher than currently observed at many hospitals in the United States,” she said in an interview. “This may overestimate the actual risk as many of these studies were published early in the pandemic and did not universally sample women who were pregnant for SARS-CoV-2.”
She noted the value of a living meta-analysis in that it will be updated on a regular basis as new evidence emerges. “During this time of rapidly accumulating publications about COVID-19 infection, clinicians will find it useful to have a resource in which the available data can be combined in one source.”
And there are still some outstanding questions that new studies hopefully will shed light on, she added. “The authors found that many of the risk factors for severe disease, like diabetes, obesity and high blood pressure, in nonpregnant adults are the same in the pregnant population. What remains unknown is if pregnant patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk than those who are not pregnant. The authors note that this information is still limited and largely influenced in this published analysis by a CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] study in which the majority of patients had unknown pregnancy status. We also do not know if COVID-19 infection is associated with any birth defects since the majority of women with COVID-19 infection in the first trimester have not yet delivered.”
Malavika Prabhu, MD, an obstetetrician/gyneologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City added that “this systematic review and meta analysis, which is a compilation of other studies done around the globe, confirms that pregnant women with preexisting medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 and that pregnant women with COVID-19 are at increased risk of invasive ventilation, compared to nonpregnant women with COVID-19, particularly if they have a preexisting medical condition.”
She said the preterm delivery rate of COVID-positive women is “challenging to interpret given that the total preterm birth rate potentially included many medically indicated preterm deliveries – which is to be expected – and there is no comparison group for spontaneous preterm birth presented”.
Other outstanding questions about COVID-19 pregnancies include whether they are associated with preeclampsia or smaller/growth restricted infants and why the cesarean delivery rate is high, she said. “But some of these questions are tough to answer with this data because it primarily reflects a COVID infection close to the delivery, not one that occurred several months prior to a delivery.”
Deborah Money, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, medicine, and the school of population and public health, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, commented that “this is a group that have been doing ongoing living systematic reviews of the literature scanning for pregnancy outcomes. They post their information in real time on their website, so many of us in this area follow these postings as their methodology is robust and they work hard to only include high-quality literature and avoid duplication of cases in multiple papers. There has been a problem of re-reporting the same severe cases of COVID-19 in the literature.”
This “amplifies the importance of collecting Canadian-specific data to ensure that we understand if these kind of outcomes will also be found in Canada. The data presented in this paper represent outcomes from a broad range of countries with different methods of collecting information on pregnancy and highly variable prenatal care systems. This makes our pan-Canadian study of outcomes of COVID-19 for pregnant women and their infants, CANCOVID-Preg, even more important,” she said.
“Globally, we all must continue to monitor outcomes of COVID-19 in pregnancy to minimize adverse impact on women and their infants,” said Dr. Money, who was not involved in the study.
The study was partially funded by the World Health Organization and supported by Katie’s Team, a dedicated patient and public involvement group in Women’s Health. Dr. Metz is principal investigator for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network COVID-19 study; the study is funded by NICHD and enrollment is ongoing. Dr. Prabhu had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Money received funding from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Public Health Agency of Canada and received a small grant from theBC Women’s Foundation for COVID-19 in pregnancy research.
SOURCE: Allotey J et al. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320.
according to a living systematic review from the PregCOV-19 Living Systematic Review Consortium.
The study, published in BMJ, shows an increased risk of preterm delivery, as well as the need for invasive ventilation in these women, wrote John Allotey, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) and colleagues. The findings “will produce a strong evidence base for living guidelines on COVID-19 and pregnancy,” they noted.
The systematic review included 77 studies, one-third each from the United States and China, with the remaining studies from Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, the Netherlands Portugal, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
The studies included women with COVID-19, of whom 13,118 were either pregnant or in the postpartum or postabortion period and 83,486 were of reproductive age but not pregnant. Some studies also included healthy pregnant women for comparison.
In the pregnant and recently pregnant women, the most common COVID-19 symptoms were fever (40%) and cough (39%), with lymphopenia (35%) and raised C reactive protein levels (49%) being the most common laboratory findings. Pregnant and recently pregnant women with COVID-19 were less likely to have fever (odds ratio, 0.43) and myalgia (OR, 0.48), compared with nonpregnant women of reproductive age with COVID-19, reported the authors.
The overall preterm and spontaneous preterm birth rates in the COVID-19–positive women were 17% and 6% respectively. Dr. Allotey and authors noted that “these preterm births could be medically indicated, as the overall rates of spontaneous preterm births in pregnant women with COVID-19 was broadly similar to those observed in the pre-pandemic period.” There were 18 stillbirths and 6 neonatal deaths in the COVID-19 cohort.
Overall, 73 (0.1%) of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 died from any cause, and severe COVID-19 infection was diagnosed in 13%. Maternal risk factors associated with severe infection included older age (OR, 1.78), high body mass index (OR, 2.3), chronic hypertension (OR, 2.0), and preexisting diabetes (OR, 2.51). Compared with nonpregnant women with COVID-19, pregnant or recently pregnant women with the infection were at increased risk of admission to intensive care (OR, 1.62) and needing invasive ventilation (OR, 1.88).
The report included studies published between December 1, 2019, and June 26, 2020, but the living systematic review will involve weekly search updates, with analysis performed every 2-4 weeks and reported through a dedicated website.
The value of a living meta-analysis
Asked to comment on the findings, Torri Metz, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, expressed surprise at the 10% rate of infection in the pregnant or recently pregnant population. “This is higher than currently observed at many hospitals in the United States,” she said in an interview. “This may overestimate the actual risk as many of these studies were published early in the pandemic and did not universally sample women who were pregnant for SARS-CoV-2.”
She noted the value of a living meta-analysis in that it will be updated on a regular basis as new evidence emerges. “During this time of rapidly accumulating publications about COVID-19 infection, clinicians will find it useful to have a resource in which the available data can be combined in one source.”
And there are still some outstanding questions that new studies hopefully will shed light on, she added. “The authors found that many of the risk factors for severe disease, like diabetes, obesity and high blood pressure, in nonpregnant adults are the same in the pregnant population. What remains unknown is if pregnant patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk than those who are not pregnant. The authors note that this information is still limited and largely influenced in this published analysis by a CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] study in which the majority of patients had unknown pregnancy status. We also do not know if COVID-19 infection is associated with any birth defects since the majority of women with COVID-19 infection in the first trimester have not yet delivered.”
Malavika Prabhu, MD, an obstetetrician/gyneologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City added that “this systematic review and meta analysis, which is a compilation of other studies done around the globe, confirms that pregnant women with preexisting medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 and that pregnant women with COVID-19 are at increased risk of invasive ventilation, compared to nonpregnant women with COVID-19, particularly if they have a preexisting medical condition.”
She said the preterm delivery rate of COVID-positive women is “challenging to interpret given that the total preterm birth rate potentially included many medically indicated preterm deliveries – which is to be expected – and there is no comparison group for spontaneous preterm birth presented”.
Other outstanding questions about COVID-19 pregnancies include whether they are associated with preeclampsia or smaller/growth restricted infants and why the cesarean delivery rate is high, she said. “But some of these questions are tough to answer with this data because it primarily reflects a COVID infection close to the delivery, not one that occurred several months prior to a delivery.”
Deborah Money, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, medicine, and the school of population and public health, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, commented that “this is a group that have been doing ongoing living systematic reviews of the literature scanning for pregnancy outcomes. They post their information in real time on their website, so many of us in this area follow these postings as their methodology is robust and they work hard to only include high-quality literature and avoid duplication of cases in multiple papers. There has been a problem of re-reporting the same severe cases of COVID-19 in the literature.”
This “amplifies the importance of collecting Canadian-specific data to ensure that we understand if these kind of outcomes will also be found in Canada. The data presented in this paper represent outcomes from a broad range of countries with different methods of collecting information on pregnancy and highly variable prenatal care systems. This makes our pan-Canadian study of outcomes of COVID-19 for pregnant women and their infants, CANCOVID-Preg, even more important,” she said.
“Globally, we all must continue to monitor outcomes of COVID-19 in pregnancy to minimize adverse impact on women and their infants,” said Dr. Money, who was not involved in the study.
The study was partially funded by the World Health Organization and supported by Katie’s Team, a dedicated patient and public involvement group in Women’s Health. Dr. Metz is principal investigator for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network COVID-19 study; the study is funded by NICHD and enrollment is ongoing. Dr. Prabhu had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Money received funding from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Public Health Agency of Canada and received a small grant from theBC Women’s Foundation for COVID-19 in pregnancy research.
SOURCE: Allotey J et al. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320.
according to a living systematic review from the PregCOV-19 Living Systematic Review Consortium.
The study, published in BMJ, shows an increased risk of preterm delivery, as well as the need for invasive ventilation in these women, wrote John Allotey, PhD, of the University of Birmingham (England) and colleagues. The findings “will produce a strong evidence base for living guidelines on COVID-19 and pregnancy,” they noted.
The systematic review included 77 studies, one-third each from the United States and China, with the remaining studies from Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, the Netherlands Portugal, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
The studies included women with COVID-19, of whom 13,118 were either pregnant or in the postpartum or postabortion period and 83,486 were of reproductive age but not pregnant. Some studies also included healthy pregnant women for comparison.
In the pregnant and recently pregnant women, the most common COVID-19 symptoms were fever (40%) and cough (39%), with lymphopenia (35%) and raised C reactive protein levels (49%) being the most common laboratory findings. Pregnant and recently pregnant women with COVID-19 were less likely to have fever (odds ratio, 0.43) and myalgia (OR, 0.48), compared with nonpregnant women of reproductive age with COVID-19, reported the authors.
The overall preterm and spontaneous preterm birth rates in the COVID-19–positive women were 17% and 6% respectively. Dr. Allotey and authors noted that “these preterm births could be medically indicated, as the overall rates of spontaneous preterm births in pregnant women with COVID-19 was broadly similar to those observed in the pre-pandemic period.” There were 18 stillbirths and 6 neonatal deaths in the COVID-19 cohort.
Overall, 73 (0.1%) of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 died from any cause, and severe COVID-19 infection was diagnosed in 13%. Maternal risk factors associated with severe infection included older age (OR, 1.78), high body mass index (OR, 2.3), chronic hypertension (OR, 2.0), and preexisting diabetes (OR, 2.51). Compared with nonpregnant women with COVID-19, pregnant or recently pregnant women with the infection were at increased risk of admission to intensive care (OR, 1.62) and needing invasive ventilation (OR, 1.88).
The report included studies published between December 1, 2019, and June 26, 2020, but the living systematic review will involve weekly search updates, with analysis performed every 2-4 weeks and reported through a dedicated website.
The value of a living meta-analysis
Asked to comment on the findings, Torri Metz, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, expressed surprise at the 10% rate of infection in the pregnant or recently pregnant population. “This is higher than currently observed at many hospitals in the United States,” she said in an interview. “This may overestimate the actual risk as many of these studies were published early in the pandemic and did not universally sample women who were pregnant for SARS-CoV-2.”
She noted the value of a living meta-analysis in that it will be updated on a regular basis as new evidence emerges. “During this time of rapidly accumulating publications about COVID-19 infection, clinicians will find it useful to have a resource in which the available data can be combined in one source.”
And there are still some outstanding questions that new studies hopefully will shed light on, she added. “The authors found that many of the risk factors for severe disease, like diabetes, obesity and high blood pressure, in nonpregnant adults are the same in the pregnant population. What remains unknown is if pregnant patients with COVID-19 infection are at higher risk than those who are not pregnant. The authors note that this information is still limited and largely influenced in this published analysis by a CDC [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] study in which the majority of patients had unknown pregnancy status. We also do not know if COVID-19 infection is associated with any birth defects since the majority of women with COVID-19 infection in the first trimester have not yet delivered.”
Malavika Prabhu, MD, an obstetetrician/gyneologist at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City added that “this systematic review and meta analysis, which is a compilation of other studies done around the globe, confirms that pregnant women with preexisting medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are at increased risk of severe COVID-19 and that pregnant women with COVID-19 are at increased risk of invasive ventilation, compared to nonpregnant women with COVID-19, particularly if they have a preexisting medical condition.”
She said the preterm delivery rate of COVID-positive women is “challenging to interpret given that the total preterm birth rate potentially included many medically indicated preterm deliveries – which is to be expected – and there is no comparison group for spontaneous preterm birth presented”.
Other outstanding questions about COVID-19 pregnancies include whether they are associated with preeclampsia or smaller/growth restricted infants and why the cesarean delivery rate is high, she said. “But some of these questions are tough to answer with this data because it primarily reflects a COVID infection close to the delivery, not one that occurred several months prior to a delivery.”
Deborah Money, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology, medicine, and the school of population and public health, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, commented that “this is a group that have been doing ongoing living systematic reviews of the literature scanning for pregnancy outcomes. They post their information in real time on their website, so many of us in this area follow these postings as their methodology is robust and they work hard to only include high-quality literature and avoid duplication of cases in multiple papers. There has been a problem of re-reporting the same severe cases of COVID-19 in the literature.”
This “amplifies the importance of collecting Canadian-specific data to ensure that we understand if these kind of outcomes will also be found in Canada. The data presented in this paper represent outcomes from a broad range of countries with different methods of collecting information on pregnancy and highly variable prenatal care systems. This makes our pan-Canadian study of outcomes of COVID-19 for pregnant women and their infants, CANCOVID-Preg, even more important,” she said.
“Globally, we all must continue to monitor outcomes of COVID-19 in pregnancy to minimize adverse impact on women and their infants,” said Dr. Money, who was not involved in the study.
The study was partially funded by the World Health Organization and supported by Katie’s Team, a dedicated patient and public involvement group in Women’s Health. Dr. Metz is principal investigator for the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network COVID-19 study; the study is funded by NICHD and enrollment is ongoing. Dr. Prabhu had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Money received funding from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Public Health Agency of Canada and received a small grant from theBC Women’s Foundation for COVID-19 in pregnancy research.
SOURCE: Allotey J et al. BMJ. 2020;370:m3320.
FROM BMJ
When viruses collide: Flu season during pandemic
The medical community is about to find out how prepared it is for the double whammy of influenza and COVID-19 that has been predicted for the fall of 2020. The complexities of diagnosis, management of vulnerable patients, and overflowing medical centers that have made the COVID-19 crisis so brutal may all be exacerbated by the arrival of seasonal influenza.
Lewis Jay Kaplan, MD, FCCP, a critical care surgeon at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has seen his share of critically ill COVID-19 patients in the surgical ICU that he oversees. He’s approaching the upcoming flu season, poised to collide with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, ready to listen to each patient’s story to distinguish one from the other and determine treatment.
“The patients that have underlying comorbidities all have a story, and it’s up to you to figure out which chapter you’re in and how far along you happen to be,” he said. “It’s a very interesting approach to care, medical storytelling.”
With flu season closing in, pulmonologists are ruminating about how they’ll distinguish symptoms of COVID-19 and traditional influenza and how they’ll manage the most vulnerable patients, namely those with underlying respiratory disease and children. Influenza kills 12,000-61,000 people a year, according to the Centers for Disease Control, and results in 140,000-810,00 hospitalizations. Having a flu season in the midst of a pandemic of a disease with multiple overlapping symptoms threatens to overwhelm practitioners, hospitals, and the health system.
Dr. Kaplan said each patient’s story can point to the correct clinical approach. “Instead of just sharing data when you are on rounds, you’re really telling someone’s story.” It arises from a series of questions about how the disease has impacted them, specifics of their presentation, how their signs and symptoms differ from the usual, and how they responded to treatment. “It also helps you to then take what you’re doing, which can seem very, very complicated to individuals who are not medically sophisticated, and then help them to understand why you’re doing what you’re doing at this point.”
That can help get through to a patient with respiratory disease who insists he or she has or doesn’t have COVID-19 rather than the flu. “They form a different group that brings with them different fears and concerns, and you have to help them navigate that, too: all of this data and your decision-making around testing and admissions, and what you can omit doing and what you must do help them to navigate their own story,” Dr. Kaplan said.
Benjamin D. Singer, MD, a pulmonologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, authored an editorial in Science Advances that addressed four factors that will determine the scope of flu spread in the upcoming season: rate of transmission; vaccination rates; coinfection rates; and health disparities in minority populations, which are prone to higher rates of flu as well as COVID-19.
Flu vaccine ‘extra important’
The convergence of COVID-19 and influenza has the potential to overwhelm the health system, said Daniel A. Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s in Boston. He coauthored a JAMA Insights clinical update on flu season during the COVID-19 pandemic that lists distinguishing and overlapping signs and symptoms of the two diseases.
The flu vaccine, he said, is “extra important this year,” especially in patients with existing respiratory disease, but COVID-19 has thrown up barriers to vaccination. Telemedicine has supplanted office visits. “People may miss that easy-touch opportunity to get the flu vaccine, so we have to be creative about making the flu vaccine highly accessible, maybe in nontraditional ways,” Dr. Solomon said. Some ideas he offered are pop-up vaccine fairs at schools and churches.
But just as COVID-19 may hinder flu vaccines, it may also be helping to mitigate flu transmission. “The interesting thing about transmission of the flu is that it’s transmitted the same way COVID is, so if we actually know how to decrease transmission of COVID, which we do – we’ve done it – we can actually decrease transmission of influenza as well,” Dr. Solomon said. Studies out of Hong Kong and Japan have reported a reduction in influenza cases during COVID-19 outbreaks in those places (Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e279-88; JAMA. 2020;323:1969-71).
Risks of coinfection
About one in four COVID-19 patients have been diagnosed with an additional respiratory infection, including influenza (JAMA. 2020:323:2085-6). Pulmonologists must keep that in mind when managing COVID-19 suspects, said Dr. Singer.
“While it is true that most of the time COVID-19 travels alone, we have numerous examples in the literature and in our own experience that COVID-19 is accompanied by either another virus or another bacterial infection, including influenza,” Dr. Singer said. “The distinction is important. One is just for diagnostic reasons and public reporting reasons, but also because flu and COVID-19 have different requirements for how you care for patients in terms of the health system.”
Clinical suspicion for coinfection should remain high if the community spread of both COVID-19 and influenza is high, said Megan Conroy, MD, chief pulmonary and critical care fellow at Ohio State University, Columbus. “As the coronavirus first took hold in the United States in March 2020, we were at the tail end of influenza season, so it’s hard to predict what the upcoming influenza season will really look like with regards to coinfection.”
Distinguishing COVID-19 from flu
Multiple signs and symptoms between COVID-19 and the flu overlap. They include fever, chills, headache, myalgia, cough, and fatigue. Nasal congestion and sore throat are characteristic of the flu; shortness of breath and loss of the sense of smell have been widely reported in COVID-19. “While many upper respiratory infections can result in loss of smell, this may be more prevalent in COVID-19,” Dr. Conroy said. Other symptoms unique to COVID-19 are GI symptoms such as diarrhea and skin rashes such as acral ischemia.
Testing, however, is the cornerstone of the differential diagnosis. “You can’t confidently distinguish between them on symptoms alone,” Dr. Conroy added.
“I think the challenge we’ll face as clinicians, is caring for people with nonspecific symptoms of a respiratory viral illness, especially in the early phase of the illness,” said Dr. Solomon.
But even after that, symptoms can be difficult to distinguish.
“Later in the illness, COVID is more associated with a hypercoagulable state,” he said. “It is more associated with viral pneumonia on chest imaging, like the diffuse ground-glass infiltrates that we’ve all gotten used to seeing – but flu can do both of those things as well. So, without a test, it’s impossible to distinguish between the two infections in the clinic.”
But testing can have its shortcomings when flu season clashes with the COVID-19 pandemic. “Getting the test is not the same as getting the test results,” Dr. Solomon added. “Though a lot of people can get a test, if it takes 7 or 8 days to get the test result back, the result is useless.”
Widespread, rapid testing also depends on having adequate supplies of viral media transport and swabs. “I think that this is what we should be focusing on now: scaling up access to rapid turnaround testing,” he said. Distinguishing between the two is also important to preserve hospital resources. COVID-19 has more rigorous standards than flu for personal protective equipment and isolation of patients within the hospital.
Having chronic lung disease isn’t necessarily a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 or the flu, or both, Dr. Solomon said. “It’s a risk factor for having severe disease.” Again, he noted that flu vaccines are still necessary in these patients, as well as patients of advanced age and underlying medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
In managing children, it’s important to keep in mind that they communicate differently about their illnesses than adults, said Dr. Kaplan. “They may not have the words to tell you the same kind of thing that the adult tells you.” That’s where family members can help to flesh out the history. “They may present with an initially much milder form, if you will, where they’re not as critical up front, but then that small proportion of them comes back with the multi-inflammatory syndrome and then they are profoundly ill.”
Younger people make up a larger share of COVID-19 patients now, compared with the initial wave that hit the Northeast in the spring, Dr. Kaplan said. “We don’t know if that’s because the virus is a little different or the people that are getting sick are a little bit different.”
The COVID-19 strain now emerging may be less virulent than the strain that hit in early spring, he said. “That doesn’t mean that there aren’t still profoundly critical ill people with COVID of many different age ranges, that is true, but there are a lot of people that we now see will test positive, but aren’t really as profoundly ill as when it first landed here in the United States.”
That may be somewhat welcome as flu season arrives.
The physicians interviewed have no relevant disclosures.
The medical community is about to find out how prepared it is for the double whammy of influenza and COVID-19 that has been predicted for the fall of 2020. The complexities of diagnosis, management of vulnerable patients, and overflowing medical centers that have made the COVID-19 crisis so brutal may all be exacerbated by the arrival of seasonal influenza.
Lewis Jay Kaplan, MD, FCCP, a critical care surgeon at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has seen his share of critically ill COVID-19 patients in the surgical ICU that he oversees. He’s approaching the upcoming flu season, poised to collide with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, ready to listen to each patient’s story to distinguish one from the other and determine treatment.
“The patients that have underlying comorbidities all have a story, and it’s up to you to figure out which chapter you’re in and how far along you happen to be,” he said. “It’s a very interesting approach to care, medical storytelling.”
With flu season closing in, pulmonologists are ruminating about how they’ll distinguish symptoms of COVID-19 and traditional influenza and how they’ll manage the most vulnerable patients, namely those with underlying respiratory disease and children. Influenza kills 12,000-61,000 people a year, according to the Centers for Disease Control, and results in 140,000-810,00 hospitalizations. Having a flu season in the midst of a pandemic of a disease with multiple overlapping symptoms threatens to overwhelm practitioners, hospitals, and the health system.
Dr. Kaplan said each patient’s story can point to the correct clinical approach. “Instead of just sharing data when you are on rounds, you’re really telling someone’s story.” It arises from a series of questions about how the disease has impacted them, specifics of their presentation, how their signs and symptoms differ from the usual, and how they responded to treatment. “It also helps you to then take what you’re doing, which can seem very, very complicated to individuals who are not medically sophisticated, and then help them to understand why you’re doing what you’re doing at this point.”
That can help get through to a patient with respiratory disease who insists he or she has or doesn’t have COVID-19 rather than the flu. “They form a different group that brings with them different fears and concerns, and you have to help them navigate that, too: all of this data and your decision-making around testing and admissions, and what you can omit doing and what you must do help them to navigate their own story,” Dr. Kaplan said.
Benjamin D. Singer, MD, a pulmonologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, authored an editorial in Science Advances that addressed four factors that will determine the scope of flu spread in the upcoming season: rate of transmission; vaccination rates; coinfection rates; and health disparities in minority populations, which are prone to higher rates of flu as well as COVID-19.
Flu vaccine ‘extra important’
The convergence of COVID-19 and influenza has the potential to overwhelm the health system, said Daniel A. Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s in Boston. He coauthored a JAMA Insights clinical update on flu season during the COVID-19 pandemic that lists distinguishing and overlapping signs and symptoms of the two diseases.
The flu vaccine, he said, is “extra important this year,” especially in patients with existing respiratory disease, but COVID-19 has thrown up barriers to vaccination. Telemedicine has supplanted office visits. “People may miss that easy-touch opportunity to get the flu vaccine, so we have to be creative about making the flu vaccine highly accessible, maybe in nontraditional ways,” Dr. Solomon said. Some ideas he offered are pop-up vaccine fairs at schools and churches.
But just as COVID-19 may hinder flu vaccines, it may also be helping to mitigate flu transmission. “The interesting thing about transmission of the flu is that it’s transmitted the same way COVID is, so if we actually know how to decrease transmission of COVID, which we do – we’ve done it – we can actually decrease transmission of influenza as well,” Dr. Solomon said. Studies out of Hong Kong and Japan have reported a reduction in influenza cases during COVID-19 outbreaks in those places (Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e279-88; JAMA. 2020;323:1969-71).
Risks of coinfection
About one in four COVID-19 patients have been diagnosed with an additional respiratory infection, including influenza (JAMA. 2020:323:2085-6). Pulmonologists must keep that in mind when managing COVID-19 suspects, said Dr. Singer.
“While it is true that most of the time COVID-19 travels alone, we have numerous examples in the literature and in our own experience that COVID-19 is accompanied by either another virus or another bacterial infection, including influenza,” Dr. Singer said. “The distinction is important. One is just for diagnostic reasons and public reporting reasons, but also because flu and COVID-19 have different requirements for how you care for patients in terms of the health system.”
Clinical suspicion for coinfection should remain high if the community spread of both COVID-19 and influenza is high, said Megan Conroy, MD, chief pulmonary and critical care fellow at Ohio State University, Columbus. “As the coronavirus first took hold in the United States in March 2020, we were at the tail end of influenza season, so it’s hard to predict what the upcoming influenza season will really look like with regards to coinfection.”
Distinguishing COVID-19 from flu
Multiple signs and symptoms between COVID-19 and the flu overlap. They include fever, chills, headache, myalgia, cough, and fatigue. Nasal congestion and sore throat are characteristic of the flu; shortness of breath and loss of the sense of smell have been widely reported in COVID-19. “While many upper respiratory infections can result in loss of smell, this may be more prevalent in COVID-19,” Dr. Conroy said. Other symptoms unique to COVID-19 are GI symptoms such as diarrhea and skin rashes such as acral ischemia.
Testing, however, is the cornerstone of the differential diagnosis. “You can’t confidently distinguish between them on symptoms alone,” Dr. Conroy added.
“I think the challenge we’ll face as clinicians, is caring for people with nonspecific symptoms of a respiratory viral illness, especially in the early phase of the illness,” said Dr. Solomon.
But even after that, symptoms can be difficult to distinguish.
“Later in the illness, COVID is more associated with a hypercoagulable state,” he said. “It is more associated with viral pneumonia on chest imaging, like the diffuse ground-glass infiltrates that we’ve all gotten used to seeing – but flu can do both of those things as well. So, without a test, it’s impossible to distinguish between the two infections in the clinic.”
But testing can have its shortcomings when flu season clashes with the COVID-19 pandemic. “Getting the test is not the same as getting the test results,” Dr. Solomon added. “Though a lot of people can get a test, if it takes 7 or 8 days to get the test result back, the result is useless.”
Widespread, rapid testing also depends on having adequate supplies of viral media transport and swabs. “I think that this is what we should be focusing on now: scaling up access to rapid turnaround testing,” he said. Distinguishing between the two is also important to preserve hospital resources. COVID-19 has more rigorous standards than flu for personal protective equipment and isolation of patients within the hospital.
Having chronic lung disease isn’t necessarily a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 or the flu, or both, Dr. Solomon said. “It’s a risk factor for having severe disease.” Again, he noted that flu vaccines are still necessary in these patients, as well as patients of advanced age and underlying medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
In managing children, it’s important to keep in mind that they communicate differently about their illnesses than adults, said Dr. Kaplan. “They may not have the words to tell you the same kind of thing that the adult tells you.” That’s where family members can help to flesh out the history. “They may present with an initially much milder form, if you will, where they’re not as critical up front, but then that small proportion of them comes back with the multi-inflammatory syndrome and then they are profoundly ill.”
Younger people make up a larger share of COVID-19 patients now, compared with the initial wave that hit the Northeast in the spring, Dr. Kaplan said. “We don’t know if that’s because the virus is a little different or the people that are getting sick are a little bit different.”
The COVID-19 strain now emerging may be less virulent than the strain that hit in early spring, he said. “That doesn’t mean that there aren’t still profoundly critical ill people with COVID of many different age ranges, that is true, but there are a lot of people that we now see will test positive, but aren’t really as profoundly ill as when it first landed here in the United States.”
That may be somewhat welcome as flu season arrives.
The physicians interviewed have no relevant disclosures.
The medical community is about to find out how prepared it is for the double whammy of influenza and COVID-19 that has been predicted for the fall of 2020. The complexities of diagnosis, management of vulnerable patients, and overflowing medical centers that have made the COVID-19 crisis so brutal may all be exacerbated by the arrival of seasonal influenza.
Lewis Jay Kaplan, MD, FCCP, a critical care surgeon at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, has seen his share of critically ill COVID-19 patients in the surgical ICU that he oversees. He’s approaching the upcoming flu season, poised to collide with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, ready to listen to each patient’s story to distinguish one from the other and determine treatment.
“The patients that have underlying comorbidities all have a story, and it’s up to you to figure out which chapter you’re in and how far along you happen to be,” he said. “It’s a very interesting approach to care, medical storytelling.”
With flu season closing in, pulmonologists are ruminating about how they’ll distinguish symptoms of COVID-19 and traditional influenza and how they’ll manage the most vulnerable patients, namely those with underlying respiratory disease and children. Influenza kills 12,000-61,000 people a year, according to the Centers for Disease Control, and results in 140,000-810,00 hospitalizations. Having a flu season in the midst of a pandemic of a disease with multiple overlapping symptoms threatens to overwhelm practitioners, hospitals, and the health system.
Dr. Kaplan said each patient’s story can point to the correct clinical approach. “Instead of just sharing data when you are on rounds, you’re really telling someone’s story.” It arises from a series of questions about how the disease has impacted them, specifics of their presentation, how their signs and symptoms differ from the usual, and how they responded to treatment. “It also helps you to then take what you’re doing, which can seem very, very complicated to individuals who are not medically sophisticated, and then help them to understand why you’re doing what you’re doing at this point.”
That can help get through to a patient with respiratory disease who insists he or she has or doesn’t have COVID-19 rather than the flu. “They form a different group that brings with them different fears and concerns, and you have to help them navigate that, too: all of this data and your decision-making around testing and admissions, and what you can omit doing and what you must do help them to navigate their own story,” Dr. Kaplan said.
Benjamin D. Singer, MD, a pulmonologist at Northwestern University, Chicago, authored an editorial in Science Advances that addressed four factors that will determine the scope of flu spread in the upcoming season: rate of transmission; vaccination rates; coinfection rates; and health disparities in minority populations, which are prone to higher rates of flu as well as COVID-19.
Flu vaccine ‘extra important’
The convergence of COVID-19 and influenza has the potential to overwhelm the health system, said Daniel A. Solomon, MD, of Brigham and Women’s in Boston. He coauthored a JAMA Insights clinical update on flu season during the COVID-19 pandemic that lists distinguishing and overlapping signs and symptoms of the two diseases.
The flu vaccine, he said, is “extra important this year,” especially in patients with existing respiratory disease, but COVID-19 has thrown up barriers to vaccination. Telemedicine has supplanted office visits. “People may miss that easy-touch opportunity to get the flu vaccine, so we have to be creative about making the flu vaccine highly accessible, maybe in nontraditional ways,” Dr. Solomon said. Some ideas he offered are pop-up vaccine fairs at schools and churches.
But just as COVID-19 may hinder flu vaccines, it may also be helping to mitigate flu transmission. “The interesting thing about transmission of the flu is that it’s transmitted the same way COVID is, so if we actually know how to decrease transmission of COVID, which we do – we’ve done it – we can actually decrease transmission of influenza as well,” Dr. Solomon said. Studies out of Hong Kong and Japan have reported a reduction in influenza cases during COVID-19 outbreaks in those places (Lancet Public Health. 2020;5:e279-88; JAMA. 2020;323:1969-71).
Risks of coinfection
About one in four COVID-19 patients have been diagnosed with an additional respiratory infection, including influenza (JAMA. 2020:323:2085-6). Pulmonologists must keep that in mind when managing COVID-19 suspects, said Dr. Singer.
“While it is true that most of the time COVID-19 travels alone, we have numerous examples in the literature and in our own experience that COVID-19 is accompanied by either another virus or another bacterial infection, including influenza,” Dr. Singer said. “The distinction is important. One is just for diagnostic reasons and public reporting reasons, but also because flu and COVID-19 have different requirements for how you care for patients in terms of the health system.”
Clinical suspicion for coinfection should remain high if the community spread of both COVID-19 and influenza is high, said Megan Conroy, MD, chief pulmonary and critical care fellow at Ohio State University, Columbus. “As the coronavirus first took hold in the United States in March 2020, we were at the tail end of influenza season, so it’s hard to predict what the upcoming influenza season will really look like with regards to coinfection.”
Distinguishing COVID-19 from flu
Multiple signs and symptoms between COVID-19 and the flu overlap. They include fever, chills, headache, myalgia, cough, and fatigue. Nasal congestion and sore throat are characteristic of the flu; shortness of breath and loss of the sense of smell have been widely reported in COVID-19. “While many upper respiratory infections can result in loss of smell, this may be more prevalent in COVID-19,” Dr. Conroy said. Other symptoms unique to COVID-19 are GI symptoms such as diarrhea and skin rashes such as acral ischemia.
Testing, however, is the cornerstone of the differential diagnosis. “You can’t confidently distinguish between them on symptoms alone,” Dr. Conroy added.
“I think the challenge we’ll face as clinicians, is caring for people with nonspecific symptoms of a respiratory viral illness, especially in the early phase of the illness,” said Dr. Solomon.
But even after that, symptoms can be difficult to distinguish.
“Later in the illness, COVID is more associated with a hypercoagulable state,” he said. “It is more associated with viral pneumonia on chest imaging, like the diffuse ground-glass infiltrates that we’ve all gotten used to seeing – but flu can do both of those things as well. So, without a test, it’s impossible to distinguish between the two infections in the clinic.”
But testing can have its shortcomings when flu season clashes with the COVID-19 pandemic. “Getting the test is not the same as getting the test results,” Dr. Solomon added. “Though a lot of people can get a test, if it takes 7 or 8 days to get the test result back, the result is useless.”
Widespread, rapid testing also depends on having adequate supplies of viral media transport and swabs. “I think that this is what we should be focusing on now: scaling up access to rapid turnaround testing,” he said. Distinguishing between the two is also important to preserve hospital resources. COVID-19 has more rigorous standards than flu for personal protective equipment and isolation of patients within the hospital.
Having chronic lung disease isn’t necessarily a risk factor for contracting COVID-19 or the flu, or both, Dr. Solomon said. “It’s a risk factor for having severe disease.” Again, he noted that flu vaccines are still necessary in these patients, as well as patients of advanced age and underlying medical conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
In managing children, it’s important to keep in mind that they communicate differently about their illnesses than adults, said Dr. Kaplan. “They may not have the words to tell you the same kind of thing that the adult tells you.” That’s where family members can help to flesh out the history. “They may present with an initially much milder form, if you will, where they’re not as critical up front, but then that small proportion of them comes back with the multi-inflammatory syndrome and then they are profoundly ill.”
Younger people make up a larger share of COVID-19 patients now, compared with the initial wave that hit the Northeast in the spring, Dr. Kaplan said. “We don’t know if that’s because the virus is a little different or the people that are getting sick are a little bit different.”
The COVID-19 strain now emerging may be less virulent than the strain that hit in early spring, he said. “That doesn’t mean that there aren’t still profoundly critical ill people with COVID of many different age ranges, that is true, but there are a lot of people that we now see will test positive, but aren’t really as profoundly ill as when it first landed here in the United States.”
That may be somewhat welcome as flu season arrives.
The physicians interviewed have no relevant disclosures.
Patient visits post COVID-19
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Has telemedicine found its footing?
Has telemedicine found its footing?
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
When Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone, he accomplished something that many telegraph devotees never thought possible: the synchronous, bidirectional transmission of voice over electrical lines.
This was an incredible milestone in the advancement of mankind and enabled true revolutions in commerce, scientific collaboration, and human interaction. But Mr. Bell knew his invention didn’t represent the final advancement in telecommunication; he was quite prescient in imagining a day when individuals could see each other while speaking on the phone.
Many years later, what was once only a dream is now commonplace, and children growing up today can’t imagine a world where apps such as FaceTime and Skype don’t exist. Until recently, however, the medical community has been slow to adopt the idea of video interactions. This has dramatically changed because of the pandemic and the need for social distancing. It appears that telemedicine has found its footing, but whether it will remain popular once patients feel safe going to see their doctors in person again remains to be seen. This month, we’ll examine a few key issues that will determine the future of virtual medical visits.
Collect calling
The pandemic has wrought both human and economic casualties. With fear, job loss, and regulations leading to decreased spending, many large and small businesses have been and will continue to be unable to survive. Companies, including Brooks Brothers, Hertz, Lord and Taylor, GNC, and J.C. Penney, have declared bankruptcy.1 Medical practices and hospitals have taken cuts to their bottom line, and we’ve heard of many physician groups that have had to enact substantial salary cuts or even lay off providers – something previously unheard of. Recent months have demonstrated the health care community’s commitment to put patients first, but we simply cannot survive if we aren’t adequately reimbursed. Traditionally, this has been a significant roadblock toward the widespread adoption of telemedicine.
In most cases, these visits were not reimbursed at all. Thankfully, shortly after the coronavirus hit our shores, Medicare and Medicaid changed their policies, offering equal payment for video and in-person patient encounters. Most private insurers have followed suit, but the commitment to this payment parity appears – thus far – to be temporary. It is unclear that the financial support of telemedicine will continue post COVID-19, and this has many physicians feeling uncomfortable. In the meantime, many patients have come to prefer virtual visits, appreciating the convenience and efficiency.
Physicians don’t always have the same experience. Telemedicine can be technically challenging and take just as much – or sometimes more – time to navigate and document. Unless they are reimbursed equitably, providers will be forced to limit their use of virtual visits or not offer them at all. This leads to another issue: reliability.
‘Can you hear me now?’
Over the past several months, we have had the opportunity to use telemedicine firsthand and have spoken to many other physicians and patients about their experiences with it. The reports are all quite consistent: Most have had generally positive things to say. Still, some common concerns emerge when diving a bit deeper. Most notably are complaints about usability and reliability of the software.
While there are large telemedicine companies that have developed world-class cross-platform products, many in use today are proprietary and EHR dependent. As a result, the quality varies widely. Many EHR vendors were caught completely off guard by the sudden demand for telemedicine and are playing catch-up as they develop their own virtual visit platforms. While these vendor-developed platforms promise tight integration with patient records, some have significant shortcomings in stability when taxed under high utilization, including choppy video and garbled voice. This simply won’t do if telemedicine is to survive. It is incumbent on software developers and health care providers to invest in high-quality, reliable platforms on which to build their virtual visit offerings. This will ensure a more rapid adoption and the “staying power” of the new technology.
Dialing ‘0’ for the operator
Once seen as a “novelty” offered by only a small number of medical providers, virtual visits now represent a significant and ever-increasing percentage of patient encounters. The technology therefore must be easy to use. Given confidentiality and documentation requirements, along with the broad variety of available computing platforms and devices (e.g., PC, Mac, iOS, and Android), the process is often far from problem free. Patients may need help downloading apps, setting up webcams, or registering for the service. Providers may face issues with Internet connectivity or EHR-related delays.
It is critical that help be available to make the connection seamless and the experience a positive one. We are fortunate to work for a health care institution that has made this a priority, dedicating a team of individuals to provide real-time support to patients and clinicians. Small independent practices may not have this luxury, but we would encourage all providers to engage with their telemedicine or EHR vendors to determine what resources are available when problems arise, as they undoubtedly will.
Answering the call
Like the invention of the telephone, the advent of telemedicine is another milestone on the journey toward better communication with our patients, and it appears to be here to stay. Virtual visits won’t completely replace in-person care, nor minimize the benefit of human interaction, but they will continue to play an important role in the care continuum. By addressing the above concerns, we’ll lay a solid foundation for success and create a positive experience for physicians and patients alike.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and chief medical officer of Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. They have no conflicts related to the content of this piece.
Reference
1. A running list of companies that have filed for bankruptcy during the coronavirus pandemic. Fortune.
Many children with COVID-19 present without classic symptoms
Most children who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 had no respiratory illness, according to data from a retrospective study of 22 patients at a single center.
To date, children account for less than 5% of COVID-19 cases in the United States, but details of the clinical presentations in children are limited, wrote Rabia Agha, MD, and colleagues of Maimonides Children’s Hospital, Brooklyn, N.Y.
In a study published in Hospital Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 22 children aged 0-18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and were admitted to a single hospital over a 4-week period from March 18, 2020, to April 15, 2020.
Of four patients requiring mechanical ventilation, two had underlying pulmonary disease. The other two patients who required intubation were one with cerebral palsy and status epilepticus and one who presented in a state of cardiac arrest.
The study population ranged from 11 days to 18 years of age, but 45% were infants younger than 1 year. None of the children had a travel history that might increase their risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection; 27% had confirmed exposure to the virus.
Most of the children (82%) were hospitalized within 3 days of the onset of symptoms, and no deaths occurred during the study period. The most common symptom was fever without a source in five (23%) otherwise healthy infants aged 11-35 days. All five of these children underwent a sepsis evaluation, received empiric antibiotics, and were discharged home with negative bacterial cultures within 48-72 hours. Another 10 children had fever in combination with other symptoms.
Other presenting symptoms were respiratory (9), fatigue (6), seizures (2), and headache (1).
Most children with respiratory illness were treated with supportive therapy and antibiotics, but three of those on mechanical ventilation also were treated with remdesivir; all three were ultimately extubated.
Neurological abnormalities occurred in two patients: an 11-year-old otherwise healthy boy who presented with fever, headache, confusion, and seizure but ultimately improved without short-term sequelae; and a 12-year-old girl with cerebral palsy who developed new onset seizures and required mechanical ventilation, but ultimately improved to baseline.
Positive PCR results were identified in seven patients (32%) during the second half of the study period who were initially hospitalized for non-COVID related symptoms; four with bacterial infections, two with illnesses of unknown etiology, and one with cardiac arrest. Another two children were completely asymptomatic at the time of admission but then tested positive by PCR; one child had been admitted for routine chemotherapy and the other for social reasons, Dr. Agha and associates said.
The study findings contrast with early data from China in which respiratory illness of varying severity was the major presentation in children with COVID-19, but support a more recent meta-analysis of 551 cases, the researchers noted. The findings also highlight the value of universal testing for children.
“Our initial testing strategy was according to the federal and local guidelines that recommended PCR testing for the symptoms of fever, cough and shortness of breath, or travel to certain countries or close contact with a confirmed case,” Dr. Agha and colleagues said.
“With the implementation of our universal screening strategy of all admitted pediatric patients, we identified 9 (41%) patients with COVID-19 that would have been missed, as they did not meet the then-recommended criteria for testing,” they wrote.
The results suggest the need for broader guidelines to test pediatric patients because children presenting with other illnesses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 as well, the researchers said.
“Testing of all hospitalized patients will not only identify cases early in the course of their admission process, but will also help prevent inadvertent exposure of other patients and health care workers, assist in cohorting infected patients, and aid in conservation of personal protective equipment,” Dr. Agha and associates concluded.
The current study is important as clinicians continue to learn about how infection with SARS-CoV-2 presents in different populations, Diana Lee, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“Understanding how it can present in the pediatric population is important in identifying children who may have the infection and developing strategies for testing,” she said.
“I was not surprised by the finding that most children did not present with the classic symptoms of COVID-19 in adults based on other published studies and my personal clinical experience taking care of hospitalized children in New York City,” said Dr. Lee. “Studies from the U.S. and other countries have reported that fewer children experience fever, cough, and shortness of breath [compared with] adults, and that most children have a milder clinical course, though there is a small percentage of children who can have severe or critical illness,” she said.
“A multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19 has also emerged and appears to be a postinfectious process with a presentation that often differs from classic COVID-19 infection in adults,” she added.
The take-home message for clinicians is the reminder that SARS-CoV-2 infection often presents differently in children than in adults, said Dr. Lee.
“Children who present to the hospital with non-classic COVID-19 symptoms or with other diagnoses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 on testing. Broadly testing hospitalized children for SARS-CoV-2 and instituting appropriate isolation precautions may help to protect other individuals from being exposed to the virus,” she said.
“Further research is needed to understand which individuals are contagious and how to accurately distinguish those who are infectious versus those who are not,” said Dr. Lee. “There have been individuals who persistently test positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (the genetic material of the virus), but were not found to have virus in their bodies that can replicate and thereby infect others,” she emphasized. “Further study is needed regarding the likelihood of household exposures in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection given that this study was done early in the epidemic in New York City when testing and contact tracing was less established,” she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Lee had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Agha R et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 July. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-000257.
Most children who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 had no respiratory illness, according to data from a retrospective study of 22 patients at a single center.
To date, children account for less than 5% of COVID-19 cases in the United States, but details of the clinical presentations in children are limited, wrote Rabia Agha, MD, and colleagues of Maimonides Children’s Hospital, Brooklyn, N.Y.
In a study published in Hospital Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 22 children aged 0-18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and were admitted to a single hospital over a 4-week period from March 18, 2020, to April 15, 2020.
Of four patients requiring mechanical ventilation, two had underlying pulmonary disease. The other two patients who required intubation were one with cerebral palsy and status epilepticus and one who presented in a state of cardiac arrest.
The study population ranged from 11 days to 18 years of age, but 45% were infants younger than 1 year. None of the children had a travel history that might increase their risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection; 27% had confirmed exposure to the virus.
Most of the children (82%) were hospitalized within 3 days of the onset of symptoms, and no deaths occurred during the study period. The most common symptom was fever without a source in five (23%) otherwise healthy infants aged 11-35 days. All five of these children underwent a sepsis evaluation, received empiric antibiotics, and were discharged home with negative bacterial cultures within 48-72 hours. Another 10 children had fever in combination with other symptoms.
Other presenting symptoms were respiratory (9), fatigue (6), seizures (2), and headache (1).
Most children with respiratory illness were treated with supportive therapy and antibiotics, but three of those on mechanical ventilation also were treated with remdesivir; all three were ultimately extubated.
Neurological abnormalities occurred in two patients: an 11-year-old otherwise healthy boy who presented with fever, headache, confusion, and seizure but ultimately improved without short-term sequelae; and a 12-year-old girl with cerebral palsy who developed new onset seizures and required mechanical ventilation, but ultimately improved to baseline.
Positive PCR results were identified in seven patients (32%) during the second half of the study period who were initially hospitalized for non-COVID related symptoms; four with bacterial infections, two with illnesses of unknown etiology, and one with cardiac arrest. Another two children were completely asymptomatic at the time of admission but then tested positive by PCR; one child had been admitted for routine chemotherapy and the other for social reasons, Dr. Agha and associates said.
The study findings contrast with early data from China in which respiratory illness of varying severity was the major presentation in children with COVID-19, but support a more recent meta-analysis of 551 cases, the researchers noted. The findings also highlight the value of universal testing for children.
“Our initial testing strategy was according to the federal and local guidelines that recommended PCR testing for the symptoms of fever, cough and shortness of breath, or travel to certain countries or close contact with a confirmed case,” Dr. Agha and colleagues said.
“With the implementation of our universal screening strategy of all admitted pediatric patients, we identified 9 (41%) patients with COVID-19 that would have been missed, as they did not meet the then-recommended criteria for testing,” they wrote.
The results suggest the need for broader guidelines to test pediatric patients because children presenting with other illnesses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 as well, the researchers said.
“Testing of all hospitalized patients will not only identify cases early in the course of their admission process, but will also help prevent inadvertent exposure of other patients and health care workers, assist in cohorting infected patients, and aid in conservation of personal protective equipment,” Dr. Agha and associates concluded.
The current study is important as clinicians continue to learn about how infection with SARS-CoV-2 presents in different populations, Diana Lee, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“Understanding how it can present in the pediatric population is important in identifying children who may have the infection and developing strategies for testing,” she said.
“I was not surprised by the finding that most children did not present with the classic symptoms of COVID-19 in adults based on other published studies and my personal clinical experience taking care of hospitalized children in New York City,” said Dr. Lee. “Studies from the U.S. and other countries have reported that fewer children experience fever, cough, and shortness of breath [compared with] adults, and that most children have a milder clinical course, though there is a small percentage of children who can have severe or critical illness,” she said.
“A multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19 has also emerged and appears to be a postinfectious process with a presentation that often differs from classic COVID-19 infection in adults,” she added.
The take-home message for clinicians is the reminder that SARS-CoV-2 infection often presents differently in children than in adults, said Dr. Lee.
“Children who present to the hospital with non-classic COVID-19 symptoms or with other diagnoses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 on testing. Broadly testing hospitalized children for SARS-CoV-2 and instituting appropriate isolation precautions may help to protect other individuals from being exposed to the virus,” she said.
“Further research is needed to understand which individuals are contagious and how to accurately distinguish those who are infectious versus those who are not,” said Dr. Lee. “There have been individuals who persistently test positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (the genetic material of the virus), but were not found to have virus in their bodies that can replicate and thereby infect others,” she emphasized. “Further study is needed regarding the likelihood of household exposures in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection given that this study was done early in the epidemic in New York City when testing and contact tracing was less established,” she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Lee had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Agha R et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 July. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-000257.
Most children who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 had no respiratory illness, according to data from a retrospective study of 22 patients at a single center.
To date, children account for less than 5% of COVID-19 cases in the United States, but details of the clinical presentations in children are limited, wrote Rabia Agha, MD, and colleagues of Maimonides Children’s Hospital, Brooklyn, N.Y.
In a study published in Hospital Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 22 children aged 0-18 years who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and were admitted to a single hospital over a 4-week period from March 18, 2020, to April 15, 2020.
Of four patients requiring mechanical ventilation, two had underlying pulmonary disease. The other two patients who required intubation were one with cerebral palsy and status epilepticus and one who presented in a state of cardiac arrest.
The study population ranged from 11 days to 18 years of age, but 45% were infants younger than 1 year. None of the children had a travel history that might increase their risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection; 27% had confirmed exposure to the virus.
Most of the children (82%) were hospitalized within 3 days of the onset of symptoms, and no deaths occurred during the study period. The most common symptom was fever without a source in five (23%) otherwise healthy infants aged 11-35 days. All five of these children underwent a sepsis evaluation, received empiric antibiotics, and were discharged home with negative bacterial cultures within 48-72 hours. Another 10 children had fever in combination with other symptoms.
Other presenting symptoms were respiratory (9), fatigue (6), seizures (2), and headache (1).
Most children with respiratory illness were treated with supportive therapy and antibiotics, but three of those on mechanical ventilation also were treated with remdesivir; all three were ultimately extubated.
Neurological abnormalities occurred in two patients: an 11-year-old otherwise healthy boy who presented with fever, headache, confusion, and seizure but ultimately improved without short-term sequelae; and a 12-year-old girl with cerebral palsy who developed new onset seizures and required mechanical ventilation, but ultimately improved to baseline.
Positive PCR results were identified in seven patients (32%) during the second half of the study period who were initially hospitalized for non-COVID related symptoms; four with bacterial infections, two with illnesses of unknown etiology, and one with cardiac arrest. Another two children were completely asymptomatic at the time of admission but then tested positive by PCR; one child had been admitted for routine chemotherapy and the other for social reasons, Dr. Agha and associates said.
The study findings contrast with early data from China in which respiratory illness of varying severity was the major presentation in children with COVID-19, but support a more recent meta-analysis of 551 cases, the researchers noted. The findings also highlight the value of universal testing for children.
“Our initial testing strategy was according to the federal and local guidelines that recommended PCR testing for the symptoms of fever, cough and shortness of breath, or travel to certain countries or close contact with a confirmed case,” Dr. Agha and colleagues said.
“With the implementation of our universal screening strategy of all admitted pediatric patients, we identified 9 (41%) patients with COVID-19 that would have been missed, as they did not meet the then-recommended criteria for testing,” they wrote.
The results suggest the need for broader guidelines to test pediatric patients because children presenting with other illnesses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 as well, the researchers said.
“Testing of all hospitalized patients will not only identify cases early in the course of their admission process, but will also help prevent inadvertent exposure of other patients and health care workers, assist in cohorting infected patients, and aid in conservation of personal protective equipment,” Dr. Agha and associates concluded.
The current study is important as clinicians continue to learn about how infection with SARS-CoV-2 presents in different populations, Diana Lee, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
“Understanding how it can present in the pediatric population is important in identifying children who may have the infection and developing strategies for testing,” she said.
“I was not surprised by the finding that most children did not present with the classic symptoms of COVID-19 in adults based on other published studies and my personal clinical experience taking care of hospitalized children in New York City,” said Dr. Lee. “Studies from the U.S. and other countries have reported that fewer children experience fever, cough, and shortness of breath [compared with] adults, and that most children have a milder clinical course, though there is a small percentage of children who can have severe or critical illness,” she said.
“A multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with COVID-19 has also emerged and appears to be a postinfectious process with a presentation that often differs from classic COVID-19 infection in adults,” she added.
The take-home message for clinicians is the reminder that SARS-CoV-2 infection often presents differently in children than in adults, said Dr. Lee.
“Children who present to the hospital with non-classic COVID-19 symptoms or with other diagnoses may be positive for SARS-CoV-2 on testing. Broadly testing hospitalized children for SARS-CoV-2 and instituting appropriate isolation precautions may help to protect other individuals from being exposed to the virus,” she said.
“Further research is needed to understand which individuals are contagious and how to accurately distinguish those who are infectious versus those who are not,” said Dr. Lee. “There have been individuals who persistently test positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (the genetic material of the virus), but were not found to have virus in their bodies that can replicate and thereby infect others,” she emphasized. “Further study is needed regarding the likelihood of household exposures in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection given that this study was done early in the epidemic in New York City when testing and contact tracing was less established,” she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Lee had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Agha R et al. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 July. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-000257.
FROM HOSPITAL PEDIATRICS