User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
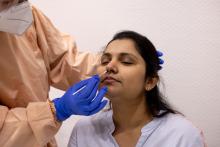
Study finds high rate of psychiatric burden in cosmetic dermatology patients
results from a large retrospective analysis showed.
“As the rate of cosmetic procedures continues to increase, it is crucial that physicians understand that many patients with a psychiatric disorder require clear communication and appropriate consultation visits,” lead study author Patricia Richey, MD, told this news organization.
While studies have displayed links between the desire for a cosmetic procedure and psychiatric stressors and disorders – most commonly mood disorders, personality disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and addiction-like behavior – the scarce literature on the subject mostly comes from the realm of plastic surgery.
“The relationship between psychiatric disease and the motivation for dermatologic cosmetic procedures has never been fully elucidated,” said Dr. Richey, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “A possible association between psychiatric disorder and the motivation for cosmetic procedures is critical to understand given increasing procedure rates and the need for clear communication and appropriate consultation visits with these patients.”
For the retrospective cohort study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Richey; Mathew Avram, MD, JD, director of the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at MGH; and Ryan W. Chapin, PharmD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, reviewed the medical records of 1,000 patients from a cosmetic dermatology clinic and 1,000 patients from a medical dermatology clinic, both at MGH. Those who crossed over between the two clinics were excluded from the analysis.
Patients in the cosmetic group were significantly younger than those in the medical group (a mean of 48 vs. 56 years, respectively; P < .0001), and there was a higher percentage of women than men in both groups (78.5% vs. 21.5% in the cosmetic group and 61.4% vs. 38.6% in the medical group; P < .00001).
The researchers found that 49% of patients in the cosmetic group had been diagnosed with at least one psychiatric disorder, compared with 33% in the medical group (P < .00001), most commonly anxiety, depression, ADHD, and insomnia. In addition, 39 patients in the cosmetic group had 2 or more psychiatric disorders, compared with 22 of those in the medical group.
Similarly, 44% of patients in the cosmetic group were on a psychiatric medication, compared with 28% in the medical group (P < .00001). The average number of medications among those on more than one psychiatric medication was 1.67 among those in the cosmetic dermatology group versus 1.48 among those in the medical dermatology group (P = .020).
By drug class, a higher percentage of patients in the cosmetic group, compared with those in the medical group, were taking antidepressants (33% vs. 21%, respectively; P < .00001), anxiolytics (26% vs. 13%; P < .00001), mood stabilizers (2.80% vs. 1.10%; P = .006), and stimulants (15.2% vs. 7.20%; P < .00001). The proportion of those taking antipsychotics was essentially even in the two groups (2.50% vs. 2.70%; P = .779).
Dr. Richey and colleagues also observed that patients in the cosmetic group had significantly higher rates of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and ADHD than those in the medical group. “This finding did not particularly surprise me,” she said, since she and her colleagues recently published a study on the association of stimulant use with psychocutaneous disease.
“Stimulants are used to treat ADHD and are also known to trigger OCD-like symptoms,” she said. “I was surprised that no patients had been diagnosed with body dysmorphic disorder, but we know that with increased patient access to medical records, physicians are often cautious in their documentation.”
She added that the overall results of the new study underscore the importance of consultation visits with cosmetic patients, including obtaining a full medication list and accurate medical history, if possible. “One could also consider well-studied screening tools mostly from the mood disorder realm, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire–2,” Dr. Richey said. “Much can be gained from simply talking to the patient and trying to understand him/her and underlying motivations prior to performing a procedure.”
Evan Rieder, MD, a New York City–based dermatologist and psychiatrist who was asked to comment on the study, characterized the analysis as demonstrating what medical and cosmetic dermatologists have been seeing in their practices for years. “While this study is limited by its single-center retrospective nature in an academic center that may not be representative of the general population, it does demonstrate a high burden of psychopathology and psychopharmacologic treatments in aesthetic patients,” Dr. Rieder said in an interview.
“While psychiatric illness is not a contraindication to cosmetic treatment, a high percentage of patients with ADHD, OCD, and likely [body dysmorphic disorder] in cosmetic dermatology practices should give us pause.” The nature of these diseases may indicate that some people are seeking aesthetic treatments for reasons yet to be elucidated, he added.
“It certainly indicates that dermatologists should be equipped to screen for, identify, and provide such patients with the appropriate resources for psychological treatment, regardless if they are deemed appropriate candidates for cosmetic intervention,” he said.
In an interview, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, noted that previous studies have demonstrated the interplay between mood disorders and dermatologic conditions for years, namely in acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and immune mediated disorders.
“In these conditions, the psychiatric stressors can worsen the skin condition and impede treatment,” Dr. Sodha said. “This study is an important segue into further elucidating our cosmetic patient population, and we should try to ask the next important question: how do we as physicians build a better rapport with these patients, understand their motivations for care, and effectively guide the patient through the consultation process to realistically address their concerns? It might help us both.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Rieder disclosed that he is a consultant for Allergan, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dr. Brandt, L’Oreal, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever.
results from a large retrospective analysis showed.
“As the rate of cosmetic procedures continues to increase, it is crucial that physicians understand that many patients with a psychiatric disorder require clear communication and appropriate consultation visits,” lead study author Patricia Richey, MD, told this news organization.
While studies have displayed links between the desire for a cosmetic procedure and psychiatric stressors and disorders – most commonly mood disorders, personality disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and addiction-like behavior – the scarce literature on the subject mostly comes from the realm of plastic surgery.
“The relationship between psychiatric disease and the motivation for dermatologic cosmetic procedures has never been fully elucidated,” said Dr. Richey, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “A possible association between psychiatric disorder and the motivation for cosmetic procedures is critical to understand given increasing procedure rates and the need for clear communication and appropriate consultation visits with these patients.”
For the retrospective cohort study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Richey; Mathew Avram, MD, JD, director of the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at MGH; and Ryan W. Chapin, PharmD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, reviewed the medical records of 1,000 patients from a cosmetic dermatology clinic and 1,000 patients from a medical dermatology clinic, both at MGH. Those who crossed over between the two clinics were excluded from the analysis.
Patients in the cosmetic group were significantly younger than those in the medical group (a mean of 48 vs. 56 years, respectively; P < .0001), and there was a higher percentage of women than men in both groups (78.5% vs. 21.5% in the cosmetic group and 61.4% vs. 38.6% in the medical group; P < .00001).
The researchers found that 49% of patients in the cosmetic group had been diagnosed with at least one psychiatric disorder, compared with 33% in the medical group (P < .00001), most commonly anxiety, depression, ADHD, and insomnia. In addition, 39 patients in the cosmetic group had 2 or more psychiatric disorders, compared with 22 of those in the medical group.
Similarly, 44% of patients in the cosmetic group were on a psychiatric medication, compared with 28% in the medical group (P < .00001). The average number of medications among those on more than one psychiatric medication was 1.67 among those in the cosmetic dermatology group versus 1.48 among those in the medical dermatology group (P = .020).
By drug class, a higher percentage of patients in the cosmetic group, compared with those in the medical group, were taking antidepressants (33% vs. 21%, respectively; P < .00001), anxiolytics (26% vs. 13%; P < .00001), mood stabilizers (2.80% vs. 1.10%; P = .006), and stimulants (15.2% vs. 7.20%; P < .00001). The proportion of those taking antipsychotics was essentially even in the two groups (2.50% vs. 2.70%; P = .779).
Dr. Richey and colleagues also observed that patients in the cosmetic group had significantly higher rates of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and ADHD than those in the medical group. “This finding did not particularly surprise me,” she said, since she and her colleagues recently published a study on the association of stimulant use with psychocutaneous disease.
“Stimulants are used to treat ADHD and are also known to trigger OCD-like symptoms,” she said. “I was surprised that no patients had been diagnosed with body dysmorphic disorder, but we know that with increased patient access to medical records, physicians are often cautious in their documentation.”
She added that the overall results of the new study underscore the importance of consultation visits with cosmetic patients, including obtaining a full medication list and accurate medical history, if possible. “One could also consider well-studied screening tools mostly from the mood disorder realm, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire–2,” Dr. Richey said. “Much can be gained from simply talking to the patient and trying to understand him/her and underlying motivations prior to performing a procedure.”
Evan Rieder, MD, a New York City–based dermatologist and psychiatrist who was asked to comment on the study, characterized the analysis as demonstrating what medical and cosmetic dermatologists have been seeing in their practices for years. “While this study is limited by its single-center retrospective nature in an academic center that may not be representative of the general population, it does demonstrate a high burden of psychopathology and psychopharmacologic treatments in aesthetic patients,” Dr. Rieder said in an interview.
“While psychiatric illness is not a contraindication to cosmetic treatment, a high percentage of patients with ADHD, OCD, and likely [body dysmorphic disorder] in cosmetic dermatology practices should give us pause.” The nature of these diseases may indicate that some people are seeking aesthetic treatments for reasons yet to be elucidated, he added.
“It certainly indicates that dermatologists should be equipped to screen for, identify, and provide such patients with the appropriate resources for psychological treatment, regardless if they are deemed appropriate candidates for cosmetic intervention,” he said.
In an interview, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, noted that previous studies have demonstrated the interplay between mood disorders and dermatologic conditions for years, namely in acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and immune mediated disorders.
“In these conditions, the psychiatric stressors can worsen the skin condition and impede treatment,” Dr. Sodha said. “This study is an important segue into further elucidating our cosmetic patient population, and we should try to ask the next important question: how do we as physicians build a better rapport with these patients, understand their motivations for care, and effectively guide the patient through the consultation process to realistically address their concerns? It might help us both.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Rieder disclosed that he is a consultant for Allergan, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dr. Brandt, L’Oreal, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever.
results from a large retrospective analysis showed.
“As the rate of cosmetic procedures continues to increase, it is crucial that physicians understand that many patients with a psychiatric disorder require clear communication and appropriate consultation visits,” lead study author Patricia Richey, MD, told this news organization.
While studies have displayed links between the desire for a cosmetic procedure and psychiatric stressors and disorders – most commonly mood disorders, personality disorders, body dysmorphic disorder, and addiction-like behavior – the scarce literature on the subject mostly comes from the realm of plastic surgery.
“The relationship between psychiatric disease and the motivation for dermatologic cosmetic procedures has never been fully elucidated,” said Dr. Richey, who practices Mohs surgery and cosmetic dermatology in Washington, D.C., and conducts research for the Wellman Center for Photomedicine and the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “A possible association between psychiatric disorder and the motivation for cosmetic procedures is critical to understand given increasing procedure rates and the need for clear communication and appropriate consultation visits with these patients.”
For the retrospective cohort study, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. Richey; Mathew Avram, MD, JD, director of the Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center at MGH; and Ryan W. Chapin, PharmD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, reviewed the medical records of 1,000 patients from a cosmetic dermatology clinic and 1,000 patients from a medical dermatology clinic, both at MGH. Those who crossed over between the two clinics were excluded from the analysis.
Patients in the cosmetic group were significantly younger than those in the medical group (a mean of 48 vs. 56 years, respectively; P < .0001), and there was a higher percentage of women than men in both groups (78.5% vs. 21.5% in the cosmetic group and 61.4% vs. 38.6% in the medical group; P < .00001).
The researchers found that 49% of patients in the cosmetic group had been diagnosed with at least one psychiatric disorder, compared with 33% in the medical group (P < .00001), most commonly anxiety, depression, ADHD, and insomnia. In addition, 39 patients in the cosmetic group had 2 or more psychiatric disorders, compared with 22 of those in the medical group.
Similarly, 44% of patients in the cosmetic group were on a psychiatric medication, compared with 28% in the medical group (P < .00001). The average number of medications among those on more than one psychiatric medication was 1.67 among those in the cosmetic dermatology group versus 1.48 among those in the medical dermatology group (P = .020).
By drug class, a higher percentage of patients in the cosmetic group, compared with those in the medical group, were taking antidepressants (33% vs. 21%, respectively; P < .00001), anxiolytics (26% vs. 13%; P < .00001), mood stabilizers (2.80% vs. 1.10%; P = .006), and stimulants (15.2% vs. 7.20%; P < .00001). The proportion of those taking antipsychotics was essentially even in the two groups (2.50% vs. 2.70%; P = .779).
Dr. Richey and colleagues also observed that patients in the cosmetic group had significantly higher rates of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and ADHD than those in the medical group. “This finding did not particularly surprise me,” she said, since she and her colleagues recently published a study on the association of stimulant use with psychocutaneous disease.
“Stimulants are used to treat ADHD and are also known to trigger OCD-like symptoms,” she said. “I was surprised that no patients had been diagnosed with body dysmorphic disorder, but we know that with increased patient access to medical records, physicians are often cautious in their documentation.”
She added that the overall results of the new study underscore the importance of consultation visits with cosmetic patients, including obtaining a full medication list and accurate medical history, if possible. “One could also consider well-studied screening tools mostly from the mood disorder realm, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire–2,” Dr. Richey said. “Much can be gained from simply talking to the patient and trying to understand him/her and underlying motivations prior to performing a procedure.”
Evan Rieder, MD, a New York City–based dermatologist and psychiatrist who was asked to comment on the study, characterized the analysis as demonstrating what medical and cosmetic dermatologists have been seeing in their practices for years. “While this study is limited by its single-center retrospective nature in an academic center that may not be representative of the general population, it does demonstrate a high burden of psychopathology and psychopharmacologic treatments in aesthetic patients,” Dr. Rieder said in an interview.
“While psychiatric illness is not a contraindication to cosmetic treatment, a high percentage of patients with ADHD, OCD, and likely [body dysmorphic disorder] in cosmetic dermatology practices should give us pause.” The nature of these diseases may indicate that some people are seeking aesthetic treatments for reasons yet to be elucidated, he added.
“It certainly indicates that dermatologists should be equipped to screen for, identify, and provide such patients with the appropriate resources for psychological treatment, regardless if they are deemed appropriate candidates for cosmetic intervention,” he said.
In an interview, Pooja Sodha, MD, director of the Center for Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, noted that previous studies have demonstrated the interplay between mood disorders and dermatologic conditions for years, namely in acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and immune mediated disorders.
“In these conditions, the psychiatric stressors can worsen the skin condition and impede treatment,” Dr. Sodha said. “This study is an important segue into further elucidating our cosmetic patient population, and we should try to ask the next important question: how do we as physicians build a better rapport with these patients, understand their motivations for care, and effectively guide the patient through the consultation process to realistically address their concerns? It might help us both.”
Neither the researchers nor Dr. Sodha reported having financial disclosures. Dr. Rieder disclosed that he is a consultant for Allergan, Almirall, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dr. Brandt, L’Oreal, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Have you heard the one about the emergency dept. that called 911?
Who watches the ED staff?
We heard a really great joke recently, one we simply have to share.
A man in Seattle went to a therapist. “I’m depressed,” he says. “Depressed, overworked, and lonely.”
“Oh dear, that sounds quite serious,” the therapist replies. “Tell me all about it.”
“Life just seems so harsh and cruel,” the man explains. “The pandemic has caused 300,000 health care workers across the country to leave the industry.”
“Such as the doctor typically filling this role in the joke,” the therapist, who is not licensed to prescribe medicine, nods.
“Exactly! And with so many respiratory viruses circulating and COVID still hanging around, emergency departments all over the country are facing massive backups. People are waiting outside the hospital for hours, hoping a bed will open up. Things got so bad at a hospital near Seattle in October that a nurse called 911 on her own ED. Told the 911 operator to send the fire department to help out, since they were ‘drowning’ and ‘in dire straits.’ They had 45 patients waiting and only five nurses to take care of them.”
“That is quite serious,” the therapist says, scribbling down unseen notes.
“The fire chief did send a crew out, and they cleaned rooms, changed beds, and took vitals for 90 minutes until the crisis passed,” the man says. “But it’s only a matter of time before it happens again. The hospital president said they have 300 open positions, and literally no one has applied to work in the emergency department. Not one person.”
“And how does all this make you feel?” the therapist asks.
“I feel all alone,” the man says. “This world feels so threatening, like no one cares, and I have no idea what will come next. It’s so vague and uncertain.”
“Ah, I think I have a solution for you,” the therapist says. “Go to the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center in Silverdale, near Seattle. They’ll get your bad mood all settled, and they’ll prescribe you the medicine you need to relax.”
The man bursts into tears. “You don’t understand,” he says. “I am the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center.”
Good joke. Everybody laugh. Roll on snare drum. Curtains.
Myth buster: Supplements for cholesterol lowering
When it comes to that nasty low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, some people swear by supplements over statins as a holistic approach. Well, we’re busting the myth that those heart-healthy supplements are even effective in comparison.
Which supplements are we talking about? These six are always on sale at the pharmacy: fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice.
In a study presented at the recent American Heart Association scientific sessions, researchers compared these supplements’ effectiveness in lowering LDL cholesterol with low-dose rosuvastatin or placebo among 199 adults aged 40-75 years who didn’t have a personal history of cardiovascular disease.
Participants who took the statin for 28 days had an average of 24% decrease in total cholesterol and a 38% reduction in LDL cholesterol, while 28 days’ worth of the supplements did no better than the placebo in either measure. Compared with placebo, the plant sterols supplement notably lowered HDL cholesterol and the garlic supplement notably increased LDL cholesterol.
Even though there are other studies showing the validity of plant sterols and red yeast rice to lower LDL cholesterol, author Luke J. Laffin, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic noted that this study shows how supplement results can vary and that more research is needed to see the effect they truly have on cholesterol over time.
So, should you stop taking or recommending supplements for heart health or healthy cholesterol levels? Well, we’re not going to come to your house and raid your medicine cabinet, but the authors of this study are definitely not saying that you should rely on them.
Consider this myth mostly busted.
COVID dept. of unintended consequences, part 2
The surveillance testing programs conducted in the first year of the pandemic were, in theory, meant to keep everyone safer. Someone, apparently, forgot to explain that to the students of the University of Wyoming and the University of Idaho.
We’re all familiar with the drill: Students at the two schools had to undergo frequent COVID screening to keep the virus from spreading, thereby making everyone safer. Duck your head now, because here comes the unintended consequence.
The students who didn’t get COVID eventually, and perhaps not so surprisingly, “perceived that the mandatory testing policy decreased their risk of contracting COVID-19, and … this perception led to higher participation in COVID-risky events,” Chian Jones Ritten, PhD, and associates said in PNAS Nexus.
They surveyed 757 students from the Univ. of Washington and 517 from the Univ. of Idaho and found that those who were tested more frequently perceived that they were less likely to contract the virus. Those respondents also more frequently attended indoor gatherings, both small and large, and spent more time in restaurants and bars.
The investigators did not mince words: “From a public health standpoint, such behavior is problematic.”
Current parents/participants in the workforce might have other ideas about an appropriate response to COVID.
At this point, we probably should mention that appropriation is the second-most sincere form of flattery.
Who watches the ED staff?
We heard a really great joke recently, one we simply have to share.
A man in Seattle went to a therapist. “I’m depressed,” he says. “Depressed, overworked, and lonely.”
“Oh dear, that sounds quite serious,” the therapist replies. “Tell me all about it.”
“Life just seems so harsh and cruel,” the man explains. “The pandemic has caused 300,000 health care workers across the country to leave the industry.”
“Such as the doctor typically filling this role in the joke,” the therapist, who is not licensed to prescribe medicine, nods.
“Exactly! And with so many respiratory viruses circulating and COVID still hanging around, emergency departments all over the country are facing massive backups. People are waiting outside the hospital for hours, hoping a bed will open up. Things got so bad at a hospital near Seattle in October that a nurse called 911 on her own ED. Told the 911 operator to send the fire department to help out, since they were ‘drowning’ and ‘in dire straits.’ They had 45 patients waiting and only five nurses to take care of them.”
“That is quite serious,” the therapist says, scribbling down unseen notes.
“The fire chief did send a crew out, and they cleaned rooms, changed beds, and took vitals for 90 minutes until the crisis passed,” the man says. “But it’s only a matter of time before it happens again. The hospital president said they have 300 open positions, and literally no one has applied to work in the emergency department. Not one person.”
“And how does all this make you feel?” the therapist asks.
“I feel all alone,” the man says. “This world feels so threatening, like no one cares, and I have no idea what will come next. It’s so vague and uncertain.”
“Ah, I think I have a solution for you,” the therapist says. “Go to the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center in Silverdale, near Seattle. They’ll get your bad mood all settled, and they’ll prescribe you the medicine you need to relax.”
The man bursts into tears. “You don’t understand,” he says. “I am the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center.”
Good joke. Everybody laugh. Roll on snare drum. Curtains.
Myth buster: Supplements for cholesterol lowering
When it comes to that nasty low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, some people swear by supplements over statins as a holistic approach. Well, we’re busting the myth that those heart-healthy supplements are even effective in comparison.
Which supplements are we talking about? These six are always on sale at the pharmacy: fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice.
In a study presented at the recent American Heart Association scientific sessions, researchers compared these supplements’ effectiveness in lowering LDL cholesterol with low-dose rosuvastatin or placebo among 199 adults aged 40-75 years who didn’t have a personal history of cardiovascular disease.
Participants who took the statin for 28 days had an average of 24% decrease in total cholesterol and a 38% reduction in LDL cholesterol, while 28 days’ worth of the supplements did no better than the placebo in either measure. Compared with placebo, the plant sterols supplement notably lowered HDL cholesterol and the garlic supplement notably increased LDL cholesterol.
Even though there are other studies showing the validity of plant sterols and red yeast rice to lower LDL cholesterol, author Luke J. Laffin, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic noted that this study shows how supplement results can vary and that more research is needed to see the effect they truly have on cholesterol over time.
So, should you stop taking or recommending supplements for heart health or healthy cholesterol levels? Well, we’re not going to come to your house and raid your medicine cabinet, but the authors of this study are definitely not saying that you should rely on them.
Consider this myth mostly busted.
COVID dept. of unintended consequences, part 2
The surveillance testing programs conducted in the first year of the pandemic were, in theory, meant to keep everyone safer. Someone, apparently, forgot to explain that to the students of the University of Wyoming and the University of Idaho.
We’re all familiar with the drill: Students at the two schools had to undergo frequent COVID screening to keep the virus from spreading, thereby making everyone safer. Duck your head now, because here comes the unintended consequence.
The students who didn’t get COVID eventually, and perhaps not so surprisingly, “perceived that the mandatory testing policy decreased their risk of contracting COVID-19, and … this perception led to higher participation in COVID-risky events,” Chian Jones Ritten, PhD, and associates said in PNAS Nexus.
They surveyed 757 students from the Univ. of Washington and 517 from the Univ. of Idaho and found that those who were tested more frequently perceived that they were less likely to contract the virus. Those respondents also more frequently attended indoor gatherings, both small and large, and spent more time in restaurants and bars.
The investigators did not mince words: “From a public health standpoint, such behavior is problematic.”
Current parents/participants in the workforce might have other ideas about an appropriate response to COVID.
At this point, we probably should mention that appropriation is the second-most sincere form of flattery.
Who watches the ED staff?
We heard a really great joke recently, one we simply have to share.
A man in Seattle went to a therapist. “I’m depressed,” he says. “Depressed, overworked, and lonely.”
“Oh dear, that sounds quite serious,” the therapist replies. “Tell me all about it.”
“Life just seems so harsh and cruel,” the man explains. “The pandemic has caused 300,000 health care workers across the country to leave the industry.”
“Such as the doctor typically filling this role in the joke,” the therapist, who is not licensed to prescribe medicine, nods.
“Exactly! And with so many respiratory viruses circulating and COVID still hanging around, emergency departments all over the country are facing massive backups. People are waiting outside the hospital for hours, hoping a bed will open up. Things got so bad at a hospital near Seattle in October that a nurse called 911 on her own ED. Told the 911 operator to send the fire department to help out, since they were ‘drowning’ and ‘in dire straits.’ They had 45 patients waiting and only five nurses to take care of them.”
“That is quite serious,” the therapist says, scribbling down unseen notes.
“The fire chief did send a crew out, and they cleaned rooms, changed beds, and took vitals for 90 minutes until the crisis passed,” the man says. “But it’s only a matter of time before it happens again. The hospital president said they have 300 open positions, and literally no one has applied to work in the emergency department. Not one person.”
“And how does all this make you feel?” the therapist asks.
“I feel all alone,” the man says. “This world feels so threatening, like no one cares, and I have no idea what will come next. It’s so vague and uncertain.”
“Ah, I think I have a solution for you,” the therapist says. “Go to the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center in Silverdale, near Seattle. They’ll get your bad mood all settled, and they’ll prescribe you the medicine you need to relax.”
The man bursts into tears. “You don’t understand,” he says. “I am the emergency department at St. Michael Medical Center.”
Good joke. Everybody laugh. Roll on snare drum. Curtains.
Myth buster: Supplements for cholesterol lowering
When it comes to that nasty low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, some people swear by supplements over statins as a holistic approach. Well, we’re busting the myth that those heart-healthy supplements are even effective in comparison.
Which supplements are we talking about? These six are always on sale at the pharmacy: fish oil, cinnamon, garlic, turmeric, plant sterols, and red yeast rice.
In a study presented at the recent American Heart Association scientific sessions, researchers compared these supplements’ effectiveness in lowering LDL cholesterol with low-dose rosuvastatin or placebo among 199 adults aged 40-75 years who didn’t have a personal history of cardiovascular disease.
Participants who took the statin for 28 days had an average of 24% decrease in total cholesterol and a 38% reduction in LDL cholesterol, while 28 days’ worth of the supplements did no better than the placebo in either measure. Compared with placebo, the plant sterols supplement notably lowered HDL cholesterol and the garlic supplement notably increased LDL cholesterol.
Even though there are other studies showing the validity of plant sterols and red yeast rice to lower LDL cholesterol, author Luke J. Laffin, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic noted that this study shows how supplement results can vary and that more research is needed to see the effect they truly have on cholesterol over time.
So, should you stop taking or recommending supplements for heart health or healthy cholesterol levels? Well, we’re not going to come to your house and raid your medicine cabinet, but the authors of this study are definitely not saying that you should rely on them.
Consider this myth mostly busted.
COVID dept. of unintended consequences, part 2
The surveillance testing programs conducted in the first year of the pandemic were, in theory, meant to keep everyone safer. Someone, apparently, forgot to explain that to the students of the University of Wyoming and the University of Idaho.
We’re all familiar with the drill: Students at the two schools had to undergo frequent COVID screening to keep the virus from spreading, thereby making everyone safer. Duck your head now, because here comes the unintended consequence.
The students who didn’t get COVID eventually, and perhaps not so surprisingly, “perceived that the mandatory testing policy decreased their risk of contracting COVID-19, and … this perception led to higher participation in COVID-risky events,” Chian Jones Ritten, PhD, and associates said in PNAS Nexus.
They surveyed 757 students from the Univ. of Washington and 517 from the Univ. of Idaho and found that those who were tested more frequently perceived that they were less likely to contract the virus. Those respondents also more frequently attended indoor gatherings, both small and large, and spent more time in restaurants and bars.
The investigators did not mince words: “From a public health standpoint, such behavior is problematic.”
Current parents/participants in the workforce might have other ideas about an appropriate response to COVID.
At this point, we probably should mention that appropriation is the second-most sincere form of flattery.
Traffic-related pollutant tied to increased dementia risk
Exposure to a traffic-related air pollutant significantly increases risk for dementia, new research suggests. Results from a meta-analysis, which included a total of more than 90 million people, showed
Particulate matter is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets from the burning of fossil fuels and nitrogen oxide, and also produced from road traffic exhaust.
While the research only showed an association between this type of air pollution and dementia risk, the estimates were consistent across the different analyses used.
“It’s rather sobering that there is this 3% relationship between incidence of dementia and the particulate matter and that it is such a precise estimate,” senior investigator Janet Martin, PharmD, MSc, associate professor of anesthesia & perioperative medicine and epidemiology & biostatistics at Western University’s, London, Ont., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Conflicting results in past studies
Air pollution is a known risk factor for dementia, but studies attempting to pinpoint its exact impact have yielded conflicting results.
Researchers analyzed data from 17 studies with a total of 91.4 million individuals, 6% of whom had dementia. In addition to PM2.5, the investigators also assessed nitrogen oxides, which form smog, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone exposure.
After adjustments for other known risk factors, such as age and gender, results showed that dementia risk increased by 3% for every 1 m3 rise in PM2.5 exposure (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.05).
The associations between dementia and exposure to nitrogen oxides (HR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.99-1.13), nitrogen dioxide (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.07) and ozone (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.91-1.11) did not reach statistical significance. However, the confidence intervals were wide enough that clinical relevance cannot be ruled out, Dr. Martin said.
The study did not examine how or if the duration of PM2.5 exposure affected dementia risk. In addition, the investigators were not able to identify a threshold above which dementia risk begins to rise.
The Environmental Pollution Agency considers average yearly exposures up to 12 mcg/m3 to be safe. The World Health Organization sets that limit lower, at 5 mcg/m3.
Dr. Martin noted that more studies are needed to explore those issues, as well as the mechanisms by which air pollutants contribute to the pathology of dementia. However, the clear link between fine particulate matter exposure and increased risk emphasizes the need to address air pollution as a modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“The rising tide of dementia is not something we can easily reverse,” Dr. Martin said. “The evidence has been so elusive for how to treat dementia once you have it, so our biggest opportunity is to prevent it.”
Results from a study published earlier in 2022 estimated that rates of dementia will triple worldwide and double in the United States by 2050 unless steps are taking to mitigate risk factors.
Research also suggests that improving air quality PM2.5 by just 10% results in a 14% decreased risk for dementia.
‘Impressive’ pattern
Paul Rosenberg, MD, codirector of the Memory and Alzheimer’s Treatment Center division of geriatric psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that air pollution “is the most prominent environmental risk we’ve found” for dementia. It also “adds to many other lifestyle and comorbidity risks, such as lack of exercise, obesity, depression, hearing loss, etc,” said Dr. Rosenberg, who was not involved with the research.
He noted what was “most impressive” was that in most of the pooled studies, small particulate air pollution was associated with dementia. “The overall pattern is most impressive and the effect sizes quite consistent over most of the studies,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
The meta-analysis was unfunded. Dr. Martin and Dr. Rosenberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposure to a traffic-related air pollutant significantly increases risk for dementia, new research suggests. Results from a meta-analysis, which included a total of more than 90 million people, showed
Particulate matter is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets from the burning of fossil fuels and nitrogen oxide, and also produced from road traffic exhaust.
While the research only showed an association between this type of air pollution and dementia risk, the estimates were consistent across the different analyses used.
“It’s rather sobering that there is this 3% relationship between incidence of dementia and the particulate matter and that it is such a precise estimate,” senior investigator Janet Martin, PharmD, MSc, associate professor of anesthesia & perioperative medicine and epidemiology & biostatistics at Western University’s, London, Ont., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Conflicting results in past studies
Air pollution is a known risk factor for dementia, but studies attempting to pinpoint its exact impact have yielded conflicting results.
Researchers analyzed data from 17 studies with a total of 91.4 million individuals, 6% of whom had dementia. In addition to PM2.5, the investigators also assessed nitrogen oxides, which form smog, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone exposure.
After adjustments for other known risk factors, such as age and gender, results showed that dementia risk increased by 3% for every 1 m3 rise in PM2.5 exposure (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.05).
The associations between dementia and exposure to nitrogen oxides (HR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.99-1.13), nitrogen dioxide (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.07) and ozone (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.91-1.11) did not reach statistical significance. However, the confidence intervals were wide enough that clinical relevance cannot be ruled out, Dr. Martin said.
The study did not examine how or if the duration of PM2.5 exposure affected dementia risk. In addition, the investigators were not able to identify a threshold above which dementia risk begins to rise.
The Environmental Pollution Agency considers average yearly exposures up to 12 mcg/m3 to be safe. The World Health Organization sets that limit lower, at 5 mcg/m3.
Dr. Martin noted that more studies are needed to explore those issues, as well as the mechanisms by which air pollutants contribute to the pathology of dementia. However, the clear link between fine particulate matter exposure and increased risk emphasizes the need to address air pollution as a modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“The rising tide of dementia is not something we can easily reverse,” Dr. Martin said. “The evidence has been so elusive for how to treat dementia once you have it, so our biggest opportunity is to prevent it.”
Results from a study published earlier in 2022 estimated that rates of dementia will triple worldwide and double in the United States by 2050 unless steps are taking to mitigate risk factors.
Research also suggests that improving air quality PM2.5 by just 10% results in a 14% decreased risk for dementia.
‘Impressive’ pattern
Paul Rosenberg, MD, codirector of the Memory and Alzheimer’s Treatment Center division of geriatric psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that air pollution “is the most prominent environmental risk we’ve found” for dementia. It also “adds to many other lifestyle and comorbidity risks, such as lack of exercise, obesity, depression, hearing loss, etc,” said Dr. Rosenberg, who was not involved with the research.
He noted what was “most impressive” was that in most of the pooled studies, small particulate air pollution was associated with dementia. “The overall pattern is most impressive and the effect sizes quite consistent over most of the studies,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
The meta-analysis was unfunded. Dr. Martin and Dr. Rosenberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Exposure to a traffic-related air pollutant significantly increases risk for dementia, new research suggests. Results from a meta-analysis, which included a total of more than 90 million people, showed
Particulate matter is a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets from the burning of fossil fuels and nitrogen oxide, and also produced from road traffic exhaust.
While the research only showed an association between this type of air pollution and dementia risk, the estimates were consistent across the different analyses used.
“It’s rather sobering that there is this 3% relationship between incidence of dementia and the particulate matter and that it is such a precise estimate,” senior investigator Janet Martin, PharmD, MSc, associate professor of anesthesia & perioperative medicine and epidemiology & biostatistics at Western University’s, London, Ont., told this news organization.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Conflicting results in past studies
Air pollution is a known risk factor for dementia, but studies attempting to pinpoint its exact impact have yielded conflicting results.
Researchers analyzed data from 17 studies with a total of 91.4 million individuals, 6% of whom had dementia. In addition to PM2.5, the investigators also assessed nitrogen oxides, which form smog, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone exposure.
After adjustments for other known risk factors, such as age and gender, results showed that dementia risk increased by 3% for every 1 m3 rise in PM2.5 exposure (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.02-1.05).
The associations between dementia and exposure to nitrogen oxides (HR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.99-1.13), nitrogen dioxide (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.07) and ozone (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.91-1.11) did not reach statistical significance. However, the confidence intervals were wide enough that clinical relevance cannot be ruled out, Dr. Martin said.
The study did not examine how or if the duration of PM2.5 exposure affected dementia risk. In addition, the investigators were not able to identify a threshold above which dementia risk begins to rise.
The Environmental Pollution Agency considers average yearly exposures up to 12 mcg/m3 to be safe. The World Health Organization sets that limit lower, at 5 mcg/m3.
Dr. Martin noted that more studies are needed to explore those issues, as well as the mechanisms by which air pollutants contribute to the pathology of dementia. However, the clear link between fine particulate matter exposure and increased risk emphasizes the need to address air pollution as a modifiable risk factor for dementia.
“The rising tide of dementia is not something we can easily reverse,” Dr. Martin said. “The evidence has been so elusive for how to treat dementia once you have it, so our biggest opportunity is to prevent it.”
Results from a study published earlier in 2022 estimated that rates of dementia will triple worldwide and double in the United States by 2050 unless steps are taking to mitigate risk factors.
Research also suggests that improving air quality PM2.5 by just 10% results in a 14% decreased risk for dementia.
‘Impressive’ pattern
Paul Rosenberg, MD, codirector of the Memory and Alzheimer’s Treatment Center division of geriatric psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said that air pollution “is the most prominent environmental risk we’ve found” for dementia. It also “adds to many other lifestyle and comorbidity risks, such as lack of exercise, obesity, depression, hearing loss, etc,” said Dr. Rosenberg, who was not involved with the research.
He noted what was “most impressive” was that in most of the pooled studies, small particulate air pollution was associated with dementia. “The overall pattern is most impressive and the effect sizes quite consistent over most of the studies,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
The meta-analysis was unfunded. Dr. Martin and Dr. Rosenberg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Physicians react: Climate change and other social issues
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around half of them rated climate change among their five most important issues. Slightly lower percentages of doctors prioritized domestic violence and immigration/refugee policies that highly, and about 40% did so regarding reproductive rights in the United States.
Survey responses and comments left on the Physicians’ Views on Today’s Divisive Social Issues 2022 report provide insights into doctors’ attitudes and thinking about these four social challenges.
Relevance of climate change to health care
In the Medscape report, 61% of physicians described themselves as “very concerned” or “concerned” about climate change, and about 7 in 10 agreed with the statement that it should be a top worldwide priority. “Climate change is the most pressing issue of this century,” a psychiatrist respondent wrote.
What about direct effects on patients’ health? An internist worried that rising temperatures will cause “pathogens to spread and infect disadvantaged people who do not have health access and have immunocompromised conditions.” A family medicine physician predicted “more weather disasters, more asthma, more hormonal changes, and more obesity.”
However, physician viewpoints ran the gamut with an issue that has become politically and emotionally charged. Descriptions such as “overblown,” “hysteria,” “hoax,” and “farce” were used. “Climate change is a natural phenomenon under God’s purview,” an emergency medicine physician said.
And there was some middle-ground thinking. “It’s overstated but quite real,” a pediatrician respondent wrote. Added an ophthalmologist: “It has gone on for ages. We must work to decrease man-made conditions that affect climate change, but it must be done in an intelligent fashion.”
Domestic violence: What physicians can do
About 7 in 10 physicians surveyed by Medscape said they don’t think the United States is adequately tackling domestic violence. “It is underrecognized and ignored,” a psychiatrist respondent argued. The problem is “rampant and unacceptable, pushed into a closet and normalized, with associated shame,” an emergency medicine doctor wrote.
Many respondents noted that physicians are under a mandate to report abuse of or a suspicious injury to a patient. Some shared anecdotes about how they reported action they had taken when they suspected it. “I’ve told patients who may be in dangerous situations that I’m a safe person and provide a safe space,” a radiologist added. An internist said, “I’ve recently started to ask about safety at home during triage on every patient.”
Other doctors bemoaned a lack of adequate education on detecting and managing domestic violence and abuse. “Domestic violence is often not recognized by health care providers,” a psychiatrist respondent observed.
Expanding legal immigration
In the Medscape report, 34% of physicians felt U.S. immigration/refugee policies need to be tougher, while 28% said they are too restrictive, and about a fifth saw them as appropriate.
“As an immigrant, I can tell you that the system is flawed and needs a complete overhaul, which will take a bipartisan effort,” an endocrinologist respondent wrote.
A number of respondents argued that it’s critical to simplify the process of obtaining U.S. citizenship so that fewer will feel forced to enter the country illegally. “For a country that relies very heavily on immigrants to sustain our health care system, we behave like idiots in denying safe harbor,” a nephrologist asserted.
A neurologist concurred. “Legal immigration needs to be encouraged. It should be easier to exchange visitor or student visa to immigrant visa in order to retain talent in the health care and technology fields, which would alleviate the shortage of workers in health care.”
Reproductive rights: No easy answers
Medscape’s survey was conducted before the U.S. Supreme Court in June reversed Roe v. Wade. In the report, 71% of physicians described themselves as very to somewhat concerned about women’s reproductive rights, but their viewpoints became nuanced after that. “There is a big disparity among physicians on this topic,” an oncologist respondent wrote.
At one end of the spectrum, 3% of doctors felt that abortions should never be permitted. “The human baby in the womb is an independent person with the right to life,” a pathologist said. At the other end, nearly one-fourth of physicians believed abortion should be accessible under all circumstances, regardless of trimester or reason. “I am just here to support the woman and make her decision a reality,” an internist said.
While saying an abortion should be granted after “fetal viability” only “in extenuating circumstances,” an ob.gyn. respondent said she is “extremely concerned” about attacks on abortion rights. “Some of us are old enough to remember women coming to the ER in extremis after illegal procedures, prior to Roe v. Wade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The danger when doctors don’t get mental health help
As medical professionals, you’re continually exposed to overwork, burnout, stressful situations, and challenging ethical decisions. Yet seeking help for mental health care may be last on your to-do list – or completely off your radar.
That’s sad and dangerous, since the American College of Emergency Physicians said 300-400 physicians die by suicide each year, and the stigma keeps 69% of female physicians from seeking mental health care, according to a prepandemic study.
In the 2022 Medscape Physician Suicide Report, 11% of female doctors and 9% of male doctors said they have had thoughts of suicide, and 64% experienced colloquial depression (feeling down, sad, or blue).
What’s more, physicians are typically seen as strong and capable and are often put on a pedestal by loved ones, patients, and the public and thought of as superhuman. No wonder it isn’t easy when you need to take time away to decompress and treat your mental well-being.
“There is a real fear for physicians when it comes to getting mental health care,” said Emil Tsai, MD, PhD, MAS, professor at the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, and an internationally reputed scientist in neurosciences and brain disorders.
The fear, said Dr. Tsai, comes from the stigma of mental health issues, potential repercussions to employment, and conceivable medical board suspension or revocation of your medical license.
Dr. Tsai said in an interview that to combat anxiety about “punishment” that many physicians fear when seeking care for their mental health, we must allow physicians to take time away from their day-to-day patient care for respite and treatment without reprisal.
Since the medical profession is high stress and has a high depression and suicide rate, finding solutions is imperative. And physicians must feel supported enough to seek treatment when needed. So how can we normalize seeking mental health care among physicians?
Get honest about stress and burnout
The only way to normalize any behavior is to be open and candid, Dr. Tsai said in an interview. The mental health conversation must occur across the board, not just within the medical profession.
“The greatest thing we can do to try and lift the burden that we place on physicians is to be willing to talk and be honest about the stress that physicians deal with and the importance of everyone feeling free to seek treatment and rest to strengthen their mental health,” said Dr. Tsai.
The more we talk about mental health and its treatment, the more we lessen the stigma, said Dr. Tsai. That could be more employer-employee check-ins, counseling as part of physician wellness, and programs structured so as not to construe a penal system.
“Mental health in the medical profession is a big issue and one that has to be met with the same compassion and care as it should be for any patient. We have annual physical checkups. Why don’t we offer annual mental health checkups for all, physicians included?” asked Dr. Tsai.
Evaluate the workload
Elizabeth Lombardo, PhD, psychologist, coach, and global keynote speaker, thinks that health care employers should reexamine their physicians’ workloads to see if they’re contributing to mental health issues.
The conversation on mental health in the workplace shouldn’t be about whether a certain person can handle stressors that are “normal” for health care settings. Instead, workplace managers in health care institutions should redefine workloads to ensure that physicians aren’t too heavily burdened with responsibilities that can cause overwork, burnout, and mental health problems,” she said.
Lessen the stigma
Even when physicians want to seek help for their psychological struggles, they may be weary of how their colleagues would react if they knew.
Raffaello Antonino, MD, clinical director at Therapy Central in London, said several underlying fears may exist at a physician’s core that prevent them from seeking care – being seen as weak, being judged as unfit to practice medicine, and the notion that “something is wrong with them.”
Dr. Antonino said we need to understand that physicians face challenges of bereavement and trauma derived from losing patients and the inability to save someone’s life. “These issues can easily develop into an accumulation of difficult, unprocessed emotions, later arising in symptoms and signs of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.”
Education is the best way to end this stigma, just like with any form of prejudice and stereotypes. For instance, we know that health care professionals are at risk of developing burnout. So, educating physicians on the symptoms and management of burnout and its consequences and prevention strategies is a must.
“Imagine what could happen if there were regular opportunities to work through the day’s events before signing out from a shift. The idea that individual weekly therapy is the only way to relieve mental distress is false,” said Lori McIsaac Bewsher, MSW, RSW, a trauma therapist and owner of a trauma-focused mental health clinic in New Brunswick.
“There are ways of integrating individual care into our doctor’s offices and hospitals that can be brief, effective, and confidential. The best way to introduce these interventions is early and collectively; no one is immune to the potential impact of exposure to trauma. The earlier these interventions can be accessed, the better the outcomes for everyone,” she said.
Dr. Antonino suggests, perhaps in the future, organizations can have “burnout checks” or mental health wellness checks for physicians akin to how we also have quick examinations for various physical ailments. What if physicians regularly answered a 10-question mental health survey as part of a burnout or trauma prevention strategy?
“Theirs is a profession and an identity which is often linked with a sense of strength, leadership and [benevolent] power: adjectives, which on the surface one might see as incompatible with what instead, unfortunately, and wrongly, may be associated with mental health issues,” said Dr. Antonino.
Keep it private
When it comes to removing the stigma from mental health care and treatment for physicians, privacy is top of mind. There needs to be some form of privacy protection for physicians who seek professional help for mental health reasons. Dr. Lombardo said physicians need to have the choice to keep their mental health journeys private. “Ideally, normalization should mean openly conversing about mental health, but for physicians, it can be a matter of life or death for their career, so the choice to remain private is something that should be afforded to them.”
Along those lines, the American Medical Association is pushing for system changes in legislative and regulatory arenas to support the mental health of practicing physicians, residents, and medical students. The organization is also urging health systems and state medical licensing bodies to remove questions on their applications that ask about prior treatment for mental health conditions.
Among many programs across the country, the Foundation of the Pennsylvania Medical Society has also created a Physicians’ Health Program, which provides confidential assessment, counseling, and referral services for physicians with mental health concerns.
“All of these initiatives are important in helping to destigmatize mental health issues among physicians,” said Harold Hong, MD, a board-certified psychiatrist in Raleigh, N.C.
Hail the benefits of treatment
Dr. Hong said to continue to destigmatize mental health among physicians and normalize its treatment, we not only have to emphasize how attending to mental health has individual benefits but also how it helps us help our patients.
“One key aspect that perhaps underpins this issue is the still present separation between mental and physical health, between mind and body, Dr. Hong said in an interview. “Feeling sad or angry or anxious should become a fact of life, a characteristic of being human, just like catching a cold or breaking a leg.”
It’s a normalization that, perhaps more than anything else, can lead the way for improving physicians’ mental health outcomes while also improving them for the rest of society. When society can finally see the health and well-being of someone in both their psychological and physical status, some of the stigmas may dissipate, and perhaps more physicians’ lives can be saved.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As medical professionals, you’re continually exposed to overwork, burnout, stressful situations, and challenging ethical decisions. Yet seeking help for mental health care may be last on your to-do list – or completely off your radar.
That’s sad and dangerous, since the American College of Emergency Physicians said 300-400 physicians die by suicide each year, and the stigma keeps 69% of female physicians from seeking mental health care, according to a prepandemic study.
In the 2022 Medscape Physician Suicide Report, 11% of female doctors and 9% of male doctors said they have had thoughts of suicide, and 64% experienced colloquial depression (feeling down, sad, or blue).
What’s more, physicians are typically seen as strong and capable and are often put on a pedestal by loved ones, patients, and the public and thought of as superhuman. No wonder it isn’t easy when you need to take time away to decompress and treat your mental well-being.
“There is a real fear for physicians when it comes to getting mental health care,” said Emil Tsai, MD, PhD, MAS, professor at the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, and an internationally reputed scientist in neurosciences and brain disorders.
The fear, said Dr. Tsai, comes from the stigma of mental health issues, potential repercussions to employment, and conceivable medical board suspension or revocation of your medical license.
Dr. Tsai said in an interview that to combat anxiety about “punishment” that many physicians fear when seeking care for their mental health, we must allow physicians to take time away from their day-to-day patient care for respite and treatment without reprisal.
Since the medical profession is high stress and has a high depression and suicide rate, finding solutions is imperative. And physicians must feel supported enough to seek treatment when needed. So how can we normalize seeking mental health care among physicians?
Get honest about stress and burnout
The only way to normalize any behavior is to be open and candid, Dr. Tsai said in an interview. The mental health conversation must occur across the board, not just within the medical profession.
“The greatest thing we can do to try and lift the burden that we place on physicians is to be willing to talk and be honest about the stress that physicians deal with and the importance of everyone feeling free to seek treatment and rest to strengthen their mental health,” said Dr. Tsai.
The more we talk about mental health and its treatment, the more we lessen the stigma, said Dr. Tsai. That could be more employer-employee check-ins, counseling as part of physician wellness, and programs structured so as not to construe a penal system.
“Mental health in the medical profession is a big issue and one that has to be met with the same compassion and care as it should be for any patient. We have annual physical checkups. Why don’t we offer annual mental health checkups for all, physicians included?” asked Dr. Tsai.
Evaluate the workload
Elizabeth Lombardo, PhD, psychologist, coach, and global keynote speaker, thinks that health care employers should reexamine their physicians’ workloads to see if they’re contributing to mental health issues.
The conversation on mental health in the workplace shouldn’t be about whether a certain person can handle stressors that are “normal” for health care settings. Instead, workplace managers in health care institutions should redefine workloads to ensure that physicians aren’t too heavily burdened with responsibilities that can cause overwork, burnout, and mental health problems,” she said.
Lessen the stigma
Even when physicians want to seek help for their psychological struggles, they may be weary of how their colleagues would react if they knew.
Raffaello Antonino, MD, clinical director at Therapy Central in London, said several underlying fears may exist at a physician’s core that prevent them from seeking care – being seen as weak, being judged as unfit to practice medicine, and the notion that “something is wrong with them.”
Dr. Antonino said we need to understand that physicians face challenges of bereavement and trauma derived from losing patients and the inability to save someone’s life. “These issues can easily develop into an accumulation of difficult, unprocessed emotions, later arising in symptoms and signs of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.”
Education is the best way to end this stigma, just like with any form of prejudice and stereotypes. For instance, we know that health care professionals are at risk of developing burnout. So, educating physicians on the symptoms and management of burnout and its consequences and prevention strategies is a must.
“Imagine what could happen if there were regular opportunities to work through the day’s events before signing out from a shift. The idea that individual weekly therapy is the only way to relieve mental distress is false,” said Lori McIsaac Bewsher, MSW, RSW, a trauma therapist and owner of a trauma-focused mental health clinic in New Brunswick.
“There are ways of integrating individual care into our doctor’s offices and hospitals that can be brief, effective, and confidential. The best way to introduce these interventions is early and collectively; no one is immune to the potential impact of exposure to trauma. The earlier these interventions can be accessed, the better the outcomes for everyone,” she said.
Dr. Antonino suggests, perhaps in the future, organizations can have “burnout checks” or mental health wellness checks for physicians akin to how we also have quick examinations for various physical ailments. What if physicians regularly answered a 10-question mental health survey as part of a burnout or trauma prevention strategy?
“Theirs is a profession and an identity which is often linked with a sense of strength, leadership and [benevolent] power: adjectives, which on the surface one might see as incompatible with what instead, unfortunately, and wrongly, may be associated with mental health issues,” said Dr. Antonino.
Keep it private
When it comes to removing the stigma from mental health care and treatment for physicians, privacy is top of mind. There needs to be some form of privacy protection for physicians who seek professional help for mental health reasons. Dr. Lombardo said physicians need to have the choice to keep their mental health journeys private. “Ideally, normalization should mean openly conversing about mental health, but for physicians, it can be a matter of life or death for their career, so the choice to remain private is something that should be afforded to them.”
Along those lines, the American Medical Association is pushing for system changes in legislative and regulatory arenas to support the mental health of practicing physicians, residents, and medical students. The organization is also urging health systems and state medical licensing bodies to remove questions on their applications that ask about prior treatment for mental health conditions.
Among many programs across the country, the Foundation of the Pennsylvania Medical Society has also created a Physicians’ Health Program, which provides confidential assessment, counseling, and referral services for physicians with mental health concerns.
“All of these initiatives are important in helping to destigmatize mental health issues among physicians,” said Harold Hong, MD, a board-certified psychiatrist in Raleigh, N.C.
Hail the benefits of treatment
Dr. Hong said to continue to destigmatize mental health among physicians and normalize its treatment, we not only have to emphasize how attending to mental health has individual benefits but also how it helps us help our patients.
“One key aspect that perhaps underpins this issue is the still present separation between mental and physical health, between mind and body, Dr. Hong said in an interview. “Feeling sad or angry or anxious should become a fact of life, a characteristic of being human, just like catching a cold or breaking a leg.”
It’s a normalization that, perhaps more than anything else, can lead the way for improving physicians’ mental health outcomes while also improving them for the rest of society. When society can finally see the health and well-being of someone in both their psychological and physical status, some of the stigmas may dissipate, and perhaps more physicians’ lives can be saved.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As medical professionals, you’re continually exposed to overwork, burnout, stressful situations, and challenging ethical decisions. Yet seeking help for mental health care may be last on your to-do list – or completely off your radar.
That’s sad and dangerous, since the American College of Emergency Physicians said 300-400 physicians die by suicide each year, and the stigma keeps 69% of female physicians from seeking mental health care, according to a prepandemic study.
In the 2022 Medscape Physician Suicide Report, 11% of female doctors and 9% of male doctors said they have had thoughts of suicide, and 64% experienced colloquial depression (feeling down, sad, or blue).
What’s more, physicians are typically seen as strong and capable and are often put on a pedestal by loved ones, patients, and the public and thought of as superhuman. No wonder it isn’t easy when you need to take time away to decompress and treat your mental well-being.
“There is a real fear for physicians when it comes to getting mental health care,” said Emil Tsai, MD, PhD, MAS, professor at the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles, and an internationally reputed scientist in neurosciences and brain disorders.
The fear, said Dr. Tsai, comes from the stigma of mental health issues, potential repercussions to employment, and conceivable medical board suspension or revocation of your medical license.
Dr. Tsai said in an interview that to combat anxiety about “punishment” that many physicians fear when seeking care for their mental health, we must allow physicians to take time away from their day-to-day patient care for respite and treatment without reprisal.
Since the medical profession is high stress and has a high depression and suicide rate, finding solutions is imperative. And physicians must feel supported enough to seek treatment when needed. So how can we normalize seeking mental health care among physicians?
Get honest about stress and burnout
The only way to normalize any behavior is to be open and candid, Dr. Tsai said in an interview. The mental health conversation must occur across the board, not just within the medical profession.
“The greatest thing we can do to try and lift the burden that we place on physicians is to be willing to talk and be honest about the stress that physicians deal with and the importance of everyone feeling free to seek treatment and rest to strengthen their mental health,” said Dr. Tsai.
The more we talk about mental health and its treatment, the more we lessen the stigma, said Dr. Tsai. That could be more employer-employee check-ins, counseling as part of physician wellness, and programs structured so as not to construe a penal system.
“Mental health in the medical profession is a big issue and one that has to be met with the same compassion and care as it should be for any patient. We have annual physical checkups. Why don’t we offer annual mental health checkups for all, physicians included?” asked Dr. Tsai.
Evaluate the workload
Elizabeth Lombardo, PhD, psychologist, coach, and global keynote speaker, thinks that health care employers should reexamine their physicians’ workloads to see if they’re contributing to mental health issues.
The conversation on mental health in the workplace shouldn’t be about whether a certain person can handle stressors that are “normal” for health care settings. Instead, workplace managers in health care institutions should redefine workloads to ensure that physicians aren’t too heavily burdened with responsibilities that can cause overwork, burnout, and mental health problems,” she said.
Lessen the stigma
Even when physicians want to seek help for their psychological struggles, they may be weary of how their colleagues would react if they knew.
Raffaello Antonino, MD, clinical director at Therapy Central in London, said several underlying fears may exist at a physician’s core that prevent them from seeking care – being seen as weak, being judged as unfit to practice medicine, and the notion that “something is wrong with them.”
Dr. Antonino said we need to understand that physicians face challenges of bereavement and trauma derived from losing patients and the inability to save someone’s life. “These issues can easily develop into an accumulation of difficult, unprocessed emotions, later arising in symptoms and signs of PTSD, anxiety, and depression.”
Education is the best way to end this stigma, just like with any form of prejudice and stereotypes. For instance, we know that health care professionals are at risk of developing burnout. So, educating physicians on the symptoms and management of burnout and its consequences and prevention strategies is a must.
“Imagine what could happen if there were regular opportunities to work through the day’s events before signing out from a shift. The idea that individual weekly therapy is the only way to relieve mental distress is false,” said Lori McIsaac Bewsher, MSW, RSW, a trauma therapist and owner of a trauma-focused mental health clinic in New Brunswick.
“There are ways of integrating individual care into our doctor’s offices and hospitals that can be brief, effective, and confidential. The best way to introduce these interventions is early and collectively; no one is immune to the potential impact of exposure to trauma. The earlier these interventions can be accessed, the better the outcomes for everyone,” she said.
Dr. Antonino suggests, perhaps in the future, organizations can have “burnout checks” or mental health wellness checks for physicians akin to how we also have quick examinations for various physical ailments. What if physicians regularly answered a 10-question mental health survey as part of a burnout or trauma prevention strategy?
“Theirs is a profession and an identity which is often linked with a sense of strength, leadership and [benevolent] power: adjectives, which on the surface one might see as incompatible with what instead, unfortunately, and wrongly, may be associated with mental health issues,” said Dr. Antonino.
Keep it private
When it comes to removing the stigma from mental health care and treatment for physicians, privacy is top of mind. There needs to be some form of privacy protection for physicians who seek professional help for mental health reasons. Dr. Lombardo said physicians need to have the choice to keep their mental health journeys private. “Ideally, normalization should mean openly conversing about mental health, but for physicians, it can be a matter of life or death for their career, so the choice to remain private is something that should be afforded to them.”
Along those lines, the American Medical Association is pushing for system changes in legislative and regulatory arenas to support the mental health of practicing physicians, residents, and medical students. The organization is also urging health systems and state medical licensing bodies to remove questions on their applications that ask about prior treatment for mental health conditions.
Among many programs across the country, the Foundation of the Pennsylvania Medical Society has also created a Physicians’ Health Program, which provides confidential assessment, counseling, and referral services for physicians with mental health concerns.
“All of these initiatives are important in helping to destigmatize mental health issues among physicians,” said Harold Hong, MD, a board-certified psychiatrist in Raleigh, N.C.
Hail the benefits of treatment
Dr. Hong said to continue to destigmatize mental health among physicians and normalize its treatment, we not only have to emphasize how attending to mental health has individual benefits but also how it helps us help our patients.
“One key aspect that perhaps underpins this issue is the still present separation between mental and physical health, between mind and body, Dr. Hong said in an interview. “Feeling sad or angry or anxious should become a fact of life, a characteristic of being human, just like catching a cold or breaking a leg.”
It’s a normalization that, perhaps more than anything else, can lead the way for improving physicians’ mental health outcomes while also improving them for the rest of society. When society can finally see the health and well-being of someone in both their psychological and physical status, some of the stigmas may dissipate, and perhaps more physicians’ lives can be saved.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Med students dismayed that residency match process won’t change
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– mostly medical students, residents, and fellows – who supported the change.
The program’s decision comes after nearly 3 months of feedback from the public, medical students, and education community. Although about 60% of public respondents believed the change could reduce stress and allow students more time for momentous career decisions, the program’s board of directors decided the disadvantages were “of greater consequence,” according to a Oct. 28 statement.
Those disadvantages included introducing application or interview behaviors that could increase students’ stress; potentially identifying partially matched or unmatched applicants, which could lead to bias; and extending the match process time for those applicants.
In addition, members of 12 medical education and student organizations raised other concerns, such as the proposed change not addressing high application numbers, according to the statement. NRMP has reported record numbers of applicants over the past few years, typically with more applicants than available program slots.
“While the testimony gave nod to the positive aspects of the proposal ... there was substantially more concern voiced about the potential negative consequences identified in the public comments,” NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN, told this news organization. Some of those issues could not be addressed without further study, so the board decided not to proceed with the proposal, she explained.
The proposal would have separated the Main Residency Match into two phases and replaced the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), in which unmatched or partially matched applicants apply for unfilled residency positions. Under the proposed change, each phase would have operated the same way, from rank order lists and using a matching algorithm to a pair of Match Days instead of a single day.
The two-phase process would have given students who didn’t match more time to carefully weigh residency programs – they can apply to up to 45 placements as part of SOAP – that will guide their career path for the next few years, PGY-1 intern Asim A., who asked not to be identified further, told this news organization. The alternative is a hasty decision once students learn which residency spots are available, he added. “Applicants would have breathing room to make a more informed decision.”
Asim, who is Canadian, said he is participating in a transitional year in internal medicine in the hopes of being matched into internal medicine or psychiatry. He said Canada’s two-phase match is a “lot less stressful” than the U.S. system.
Meanwhile, students on Reddit’s medical school community also questioned NRMP’s decision.
“A significant majority of those surveyed thought it would be beneficial. But NRMP decides to not go through with it,” one Reddit user wrote. Another posted, “The one thing that could have improved the match and they chose not to do it.”
Others supported the decision to retain a 1-day match.
“I think this was the right call,” Bryan Carmody, MD, an outspoken medical education blogger, tweeted after learning of NRMP’s decision. Dr. Carmody, a pediatric nephrologist, previously expressed to this news organization misgivings about whether the two-phase match would make it difficult for programs to thoroughly review candidates and vice versa. He was concerned that it would compress the interview season and pressure programs to rapidly review applicants and conduct interviews.
More than 8,000 people responded to the public survey that began in August and ran for a month. Nearly two-thirds of the respondents (60%) were students, residents, or fellows. About 25% included faculty, program directors, and staff. Among the survey findings, respondents were equally divided between whether the two-phase match would be modestly advantageous (30%) or significantly advantageous (30%) compared to 20% who viewed it as modestly or significantly disadvantageous.
The NRMP said it would continue engaging with the community through focus groups and other means to improve the match experience and transition to residency.
“It is important to remember that a proposal is just that,” Dr. Lamb told this news orgnization, “an opportunity to discuss the pros and cons of an idea or framework ... and to mitigate unwanted consequences determined to be detrimental to learners and programs.”
The NRMP will involve the community in future discussions “to continue to give learners a voice,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clozapine underutilized in treatment-resistant schizophrenia
, and when it is used, the drug is often delayed by several crucial years, reducing chances of efficacy.
“Despite being the only pharmacological therapy approved for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, clozapine is underutilized globally, even in developed countries, where only about 30% of patients who would benefit from the drug receive it,” said John M. Kane, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Zucker Hillside Hospital, Northwell Health, Glen Oaks, N.Y., in a presentation on the subject at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists in Cincinnati, Ohio.
Clozapine, a tricyclic dibenzodiazepine available in branded and various generic versions, is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a third-line therapy for severe, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, with studies showing benefits exceeding those of any other antipsychotics for the indication.
But while recommendations suggest use after a trial of two or more antipsychotics, with at least one being an atypical antipsychotic, one recent review finds delays in clozapine commencement ranging from 19.3 weeks to 5.5 years, and the duration of illness prior to clozapine use ranging from 1.1 to 9.7 years.
Blood monitoring, side effects
The key deterrents preventing many clinicians and patients from trying clozapine sooner are the drug’s safety and tolerability profiles, and notably the requirement of regular blood testing due to an increased risk of agranulocytosis.
Specifically, the blood testing is required every week for 6 months, then every other week for the next 6 months, and then once a month after that; however, “many of us think that that’s excessive at this point in time,” Dr. Kane noted.
Various other potential side effects are also of concern, including myocarditis, seizures, constipation, arrhythmia, hypersalivation, pneumonia, and metabolic symptoms including diabetes.
In terms of the common strategies that clinicians turn to when patients fail to respond to their current antipsychotic, including increasing doses, combining agents, or treatment switching, “none of the strategies likely rival clozapine in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Kane said.
Regarding higher dosing: “There is very little data suggesting that higher doses of antipsychotic drugs will work when the moderate or recommended dose has not worked,” he said.
Combination therapy strategies may provide benefits, but “they’re not a substitute for clozapine,” Dr. Kane added, noting that the combinations that do appear to be the most effective involve clozapine.
And regarding drug switching, studies suggest the likelihood of response in switching from one drug to another is “actually very low,” Dr. Kane added.
Clozapine also doesn’t work for all – the response rate runs between about 30% and 60%, Dr. Kane said, but when it is effective, the benefits can be profound.
“There are some patients who have a very pronounced response to clozapine – some patients describe it as life-changing,” he said.
Treatment delays reduce efficacy
Importantly, the delays before receiving clozapine are not inconsequential – data show that each outpatient antipsychotic trial prior to clozapine reduces the likelihood of response by 8%-11%, and each hospital admission further reduces the likelihood of response by 4%-8%, underscoring the need to identify treatment resistance as early as possible, Dr. Kane said.
“It’s critically important to try to identify treatment resistance earlier than we usually do because if we can get it under control sooner, we have a better chance of improving the patient’s outcome, and this has been shown in a number of studies,” he said.
“The longer you wait, the less likely you are to see a good response even to clozapine.”
Despite the concerns about clozapine, Dr. Kane notes that even the blood monitoring does not appear to be a big complaint for patients, especially they are improving.
“In our experience, the patients who benefit from clozapine don’t really have a problem with the monitoring,” he said.
“In fact, patients who benefit from clozapine are much more adherent to the medication than other patients that we see, which is understandable, because if you feel you’re really getting a benefit from medicine, you’re going to be much more motivated to take it even if it has side effects.”
A recent systematic review of 13 studies and 1,487 patients backs that up, concluding that “patients generally have a favorable experience when being treated with clozapine,” with the caveat that “conclusions are limited by the risk of bias, particularly survivorship bias.”
Preference for clozapine over other antipsychotic medications was reported by 54%-86% of patients in the review, with specific improvements in mood (11%-78%) and cognition (5%-68%).
Clinicians the biggest ‘obstacle’
Dr. Kane notes that an important factor in underutilization could indeed be the manner in which clinicians discuss clozapine with their patients – often opening the discussion by focusing on the negative aspects that, without the context of the potential benefits, can be deal-breakers for patient from the start.
“The clinicians in my opinion are really the obstacle,” Dr. Kane said. “What we always hear from clinicians is ‘I can’t do it because the patient refuses, or the patient doesn’t like the side effects’.”
Dr. Kane notes that most side effects can indeed be managed – regarding the risk for metabolic syndrome, for instance, he recommends that patients should be given metformin from the beginning when they’re started on clozapine.
He adds that in most cases, a 3-month trial is enough to answer the question of whether clozapine is working or not.
“Three months is a good trial, but it may not even tell you the total response to clozapine because that may actually accrue over time,” he said. “We’ve seen patients who actually get better and better beyond 3 months.”
Not offering the drug to patients, however, is doing them a serious disservice, Dr. Kane added.
“What I tell patients and families is that it would be a shame to miss this opportunity for a potential treatment that could be life-changing,” he said. “Does it have potential side effects? Yes. Do you have to get blood tests? Yes. And I can’t tell by evaluating a patient’s history or examining that patient whether or not they’re going to be a good responder. But would you really want to miss an opportunity to find that out?”
“To me the argument is – let’s try this drug for 3 months and see what effect it has, and at that point you’ll be in a much better position to make a decision about the benefits versus risk,” Dr. Kane said.
The only FDA-approved drug for treatment-resistant schizophrenia
Remarkably, clozapine isn’t just the only drug to currently have approval from the FDA for treatment-resistant schizophrenia – it has been for the last 3 decades.
“There have been attempts to develop medications with similar efficacy, but they have not succeeded,” Dr. Kane said in an interview. “We are still uncertain as to what accounts for clozapine’s unique qualities.”
Yet, with treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients representing some of the most dire mental illness cases clinicians may face, the need for better treatment decisions – and additional options – is pressing, Dr. Kane said.
“[The lack of any other drugs] is a big embarrassment to our field, in my opinion,” he said. “I’m a big proponent of clozapine, but we should have found another substance by now that could substitute for clozapine, which obviously has a lot of side effects and is not the easiest drug to use.”
Dr. Kane reported relationships either as a speaker or consultant/advisory board member and/or receives research grant support from Alkermes, Allergan, Click Therapeutics, Dainippon Sumitomo, H. Lundbeck, HLS Therapeutics, Indivior, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, LB Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Minerva, Neurocrine, Neumora Therapeutics, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka, Reviva, Roche, Saladax, Sunovion, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kane receives non-mutual funds stock ownership/stock options from LB Pharmaceuticals, Vanguard Research Group, and North Shore Therapeutics, and receives patent holder/royalties paid by UpToDate.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
, and when it is used, the drug is often delayed by several crucial years, reducing chances of efficacy.
“Despite being the only pharmacological therapy approved for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, clozapine is underutilized globally, even in developed countries, where only about 30% of patients who would benefit from the drug receive it,” said John M. Kane, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Zucker Hillside Hospital, Northwell Health, Glen Oaks, N.Y., in a presentation on the subject at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists in Cincinnati, Ohio.
Clozapine, a tricyclic dibenzodiazepine available in branded and various generic versions, is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a third-line therapy for severe, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, with studies showing benefits exceeding those of any other antipsychotics for the indication.
But while recommendations suggest use after a trial of two or more antipsychotics, with at least one being an atypical antipsychotic, one recent review finds delays in clozapine commencement ranging from 19.3 weeks to 5.5 years, and the duration of illness prior to clozapine use ranging from 1.1 to 9.7 years.
Blood monitoring, side effects
The key deterrents preventing many clinicians and patients from trying clozapine sooner are the drug’s safety and tolerability profiles, and notably the requirement of regular blood testing due to an increased risk of agranulocytosis.
Specifically, the blood testing is required every week for 6 months, then every other week for the next 6 months, and then once a month after that; however, “many of us think that that’s excessive at this point in time,” Dr. Kane noted.
Various other potential side effects are also of concern, including myocarditis, seizures, constipation, arrhythmia, hypersalivation, pneumonia, and metabolic symptoms including diabetes.
In terms of the common strategies that clinicians turn to when patients fail to respond to their current antipsychotic, including increasing doses, combining agents, or treatment switching, “none of the strategies likely rival clozapine in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Kane said.
Regarding higher dosing: “There is very little data suggesting that higher doses of antipsychotic drugs will work when the moderate or recommended dose has not worked,” he said.
Combination therapy strategies may provide benefits, but “they’re not a substitute for clozapine,” Dr. Kane added, noting that the combinations that do appear to be the most effective involve clozapine.
And regarding drug switching, studies suggest the likelihood of response in switching from one drug to another is “actually very low,” Dr. Kane added.
Clozapine also doesn’t work for all – the response rate runs between about 30% and 60%, Dr. Kane said, but when it is effective, the benefits can be profound.
“There are some patients who have a very pronounced response to clozapine – some patients describe it as life-changing,” he said.
Treatment delays reduce efficacy
Importantly, the delays before receiving clozapine are not inconsequential – data show that each outpatient antipsychotic trial prior to clozapine reduces the likelihood of response by 8%-11%, and each hospital admission further reduces the likelihood of response by 4%-8%, underscoring the need to identify treatment resistance as early as possible, Dr. Kane said.
“It’s critically important to try to identify treatment resistance earlier than we usually do because if we can get it under control sooner, we have a better chance of improving the patient’s outcome, and this has been shown in a number of studies,” he said.
“The longer you wait, the less likely you are to see a good response even to clozapine.”
Despite the concerns about clozapine, Dr. Kane notes that even the blood monitoring does not appear to be a big complaint for patients, especially they are improving.
“In our experience, the patients who benefit from clozapine don’t really have a problem with the monitoring,” he said.
“In fact, patients who benefit from clozapine are much more adherent to the medication than other patients that we see, which is understandable, because if you feel you’re really getting a benefit from medicine, you’re going to be much more motivated to take it even if it has side effects.”
A recent systematic review of 13 studies and 1,487 patients backs that up, concluding that “patients generally have a favorable experience when being treated with clozapine,” with the caveat that “conclusions are limited by the risk of bias, particularly survivorship bias.”
Preference for clozapine over other antipsychotic medications was reported by 54%-86% of patients in the review, with specific improvements in mood (11%-78%) and cognition (5%-68%).
Clinicians the biggest ‘obstacle’
Dr. Kane notes that an important factor in underutilization could indeed be the manner in which clinicians discuss clozapine with their patients – often opening the discussion by focusing on the negative aspects that, without the context of the potential benefits, can be deal-breakers for patient from the start.
“The clinicians in my opinion are really the obstacle,” Dr. Kane said. “What we always hear from clinicians is ‘I can’t do it because the patient refuses, or the patient doesn’t like the side effects’.”
Dr. Kane notes that most side effects can indeed be managed – regarding the risk for metabolic syndrome, for instance, he recommends that patients should be given metformin from the beginning when they’re started on clozapine.
He adds that in most cases, a 3-month trial is enough to answer the question of whether clozapine is working or not.
“Three months is a good trial, but it may not even tell you the total response to clozapine because that may actually accrue over time,” he said. “We’ve seen patients who actually get better and better beyond 3 months.”
Not offering the drug to patients, however, is doing them a serious disservice, Dr. Kane added.
“What I tell patients and families is that it would be a shame to miss this opportunity for a potential treatment that could be life-changing,” he said. “Does it have potential side effects? Yes. Do you have to get blood tests? Yes. And I can’t tell by evaluating a patient’s history or examining that patient whether or not they’re going to be a good responder. But would you really want to miss an opportunity to find that out?”
“To me the argument is – let’s try this drug for 3 months and see what effect it has, and at that point you’ll be in a much better position to make a decision about the benefits versus risk,” Dr. Kane said.
The only FDA-approved drug for treatment-resistant schizophrenia
Remarkably, clozapine isn’t just the only drug to currently have approval from the FDA for treatment-resistant schizophrenia – it has been for the last 3 decades.
“There have been attempts to develop medications with similar efficacy, but they have not succeeded,” Dr. Kane said in an interview. “We are still uncertain as to what accounts for clozapine’s unique qualities.”
Yet, with treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients representing some of the most dire mental illness cases clinicians may face, the need for better treatment decisions – and additional options – is pressing, Dr. Kane said.
“[The lack of any other drugs] is a big embarrassment to our field, in my opinion,” he said. “I’m a big proponent of clozapine, but we should have found another substance by now that could substitute for clozapine, which obviously has a lot of side effects and is not the easiest drug to use.”
Dr. Kane reported relationships either as a speaker or consultant/advisory board member and/or receives research grant support from Alkermes, Allergan, Click Therapeutics, Dainippon Sumitomo, H. Lundbeck, HLS Therapeutics, Indivior, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, LB Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Minerva, Neurocrine, Neumora Therapeutics, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka, Reviva, Roche, Saladax, Sunovion, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kane receives non-mutual funds stock ownership/stock options from LB Pharmaceuticals, Vanguard Research Group, and North Shore Therapeutics, and receives patent holder/royalties paid by UpToDate.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
, and when it is used, the drug is often delayed by several crucial years, reducing chances of efficacy.
“Despite being the only pharmacological therapy approved for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, clozapine is underutilized globally, even in developed countries, where only about 30% of patients who would benefit from the drug receive it,” said John M. Kane, MD, of the department of psychiatry, Zucker Hillside Hospital, Northwell Health, Glen Oaks, N.Y., in a presentation on the subject at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists in Cincinnati, Ohio.
Clozapine, a tricyclic dibenzodiazepine available in branded and various generic versions, is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a third-line therapy for severe, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, with studies showing benefits exceeding those of any other antipsychotics for the indication.
But while recommendations suggest use after a trial of two or more antipsychotics, with at least one being an atypical antipsychotic, one recent review finds delays in clozapine commencement ranging from 19.3 weeks to 5.5 years, and the duration of illness prior to clozapine use ranging from 1.1 to 9.7 years.
Blood monitoring, side effects
The key deterrents preventing many clinicians and patients from trying clozapine sooner are the drug’s safety and tolerability profiles, and notably the requirement of regular blood testing due to an increased risk of agranulocytosis.
Specifically, the blood testing is required every week for 6 months, then every other week for the next 6 months, and then once a month after that; however, “many of us think that that’s excessive at this point in time,” Dr. Kane noted.
Various other potential side effects are also of concern, including myocarditis, seizures, constipation, arrhythmia, hypersalivation, pneumonia, and metabolic symptoms including diabetes.
In terms of the common strategies that clinicians turn to when patients fail to respond to their current antipsychotic, including increasing doses, combining agents, or treatment switching, “none of the strategies likely rival clozapine in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Kane said.
Regarding higher dosing: “There is very little data suggesting that higher doses of antipsychotic drugs will work when the moderate or recommended dose has not worked,” he said.
Combination therapy strategies may provide benefits, but “they’re not a substitute for clozapine,” Dr. Kane added, noting that the combinations that do appear to be the most effective involve clozapine.
And regarding drug switching, studies suggest the likelihood of response in switching from one drug to another is “actually very low,” Dr. Kane added.
Clozapine also doesn’t work for all – the response rate runs between about 30% and 60%, Dr. Kane said, but when it is effective, the benefits can be profound.
“There are some patients who have a very pronounced response to clozapine – some patients describe it as life-changing,” he said.
Treatment delays reduce efficacy
Importantly, the delays before receiving clozapine are not inconsequential – data show that each outpatient antipsychotic trial prior to clozapine reduces the likelihood of response by 8%-11%, and each hospital admission further reduces the likelihood of response by 4%-8%, underscoring the need to identify treatment resistance as early as possible, Dr. Kane said.
“It’s critically important to try to identify treatment resistance earlier than we usually do because if we can get it under control sooner, we have a better chance of improving the patient’s outcome, and this has been shown in a number of studies,” he said.
“The longer you wait, the less likely you are to see a good response even to clozapine.”
Despite the concerns about clozapine, Dr. Kane notes that even the blood monitoring does not appear to be a big complaint for patients, especially they are improving.
“In our experience, the patients who benefit from clozapine don’t really have a problem with the monitoring,” he said.
“In fact, patients who benefit from clozapine are much more adherent to the medication than other patients that we see, which is understandable, because if you feel you’re really getting a benefit from medicine, you’re going to be much more motivated to take it even if it has side effects.”
A recent systematic review of 13 studies and 1,487 patients backs that up, concluding that “patients generally have a favorable experience when being treated with clozapine,” with the caveat that “conclusions are limited by the risk of bias, particularly survivorship bias.”
Preference for clozapine over other antipsychotic medications was reported by 54%-86% of patients in the review, with specific improvements in mood (11%-78%) and cognition (5%-68%).
Clinicians the biggest ‘obstacle’
Dr. Kane notes that an important factor in underutilization could indeed be the manner in which clinicians discuss clozapine with their patients – often opening the discussion by focusing on the negative aspects that, without the context of the potential benefits, can be deal-breakers for patient from the start.
“The clinicians in my opinion are really the obstacle,” Dr. Kane said. “What we always hear from clinicians is ‘I can’t do it because the patient refuses, or the patient doesn’t like the side effects’.”
Dr. Kane notes that most side effects can indeed be managed – regarding the risk for metabolic syndrome, for instance, he recommends that patients should be given metformin from the beginning when they’re started on clozapine.
He adds that in most cases, a 3-month trial is enough to answer the question of whether clozapine is working or not.
“Three months is a good trial, but it may not even tell you the total response to clozapine because that may actually accrue over time,” he said. “We’ve seen patients who actually get better and better beyond 3 months.”
Not offering the drug to patients, however, is doing them a serious disservice, Dr. Kane added.
“What I tell patients and families is that it would be a shame to miss this opportunity for a potential treatment that could be life-changing,” he said. “Does it have potential side effects? Yes. Do you have to get blood tests? Yes. And I can’t tell by evaluating a patient’s history or examining that patient whether or not they’re going to be a good responder. But would you really want to miss an opportunity to find that out?”
“To me the argument is – let’s try this drug for 3 months and see what effect it has, and at that point you’ll be in a much better position to make a decision about the benefits versus risk,” Dr. Kane said.
The only FDA-approved drug for treatment-resistant schizophrenia
Remarkably, clozapine isn’t just the only drug to currently have approval from the FDA for treatment-resistant schizophrenia – it has been for the last 3 decades.
“There have been attempts to develop medications with similar efficacy, but they have not succeeded,” Dr. Kane said in an interview. “We are still uncertain as to what accounts for clozapine’s unique qualities.”
Yet, with treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients representing some of the most dire mental illness cases clinicians may face, the need for better treatment decisions – and additional options – is pressing, Dr. Kane said.
“[The lack of any other drugs] is a big embarrassment to our field, in my opinion,” he said. “I’m a big proponent of clozapine, but we should have found another substance by now that could substitute for clozapine, which obviously has a lot of side effects and is not the easiest drug to use.”
Dr. Kane reported relationships either as a speaker or consultant/advisory board member and/or receives research grant support from Alkermes, Allergan, Click Therapeutics, Dainippon Sumitomo, H. Lundbeck, HLS Therapeutics, Indivior, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, LB Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Minerva, Neurocrine, Neumora Therapeutics, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka, Reviva, Roche, Saladax, Sunovion, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kane receives non-mutual funds stock ownership/stock options from LB Pharmaceuticals, Vanguard Research Group, and North Shore Therapeutics, and receives patent holder/royalties paid by UpToDate.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY UPDATE
FDA puts REMS requirements on hold to ensure continuity of care
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a Nov. 2 notice on its website, the FDA said it is aware that health care professionals and patients continue to experience ongoing difficulties with the clozapine REMS program, including issues with patient access to clozapine following discharge from inpatient care.
A chief concern is that inpatient pharmacies are only allowed to dispense a 7-days’ supply of clozapine to the patient upon discharge.
To address this issue, the FDA said it will now (temporarily) not object if inpatient pharmacies dispense a days’ supply of clozapine that aligns with the patient’s monitoring frequency.
For example, a 7-days’ supply for weekly monitoring, a 14-days’ supply for twice-monthly monitoring, and a 30-days’ supply for monthly monitoring upon discharge from an inpatient facility.
Clozapine is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia that is not well controlled with standard antipsychotics.
While clozapine can be highly effective in some patients, it also carries serious risks, including a decrease in neutrophil count, which can lead to severe neutropenia, serious infections, and death.
As a result, those taking the drug must undergo regular absolute neutrophil count monitoring. Clozapine REMS is intended to maximize the benefits of the drug and minimize risk.
The FDA says it will continue to exercise earlier enforcement discretion regarding the clozapine REMS program announced back in November 2021. This includes allowing pharmacists to dispense clozapine without a REMS dispense authorization and allowing wholesalers to ship clozapine to pharmacies and health care settings without confirming enrollment in the REMS.
“We understand that difficulties with the clozapine REMS program have caused frustration and have led to problems with patient access to clozapine. FDA takes these concerns seriously. Continuity of care, patient access to clozapine, and patient safety are our highest priorities,” the FDA says.
The agency is working closely with the clozapine REMS program administrators to address these challenges and avoid interruptions in patient care.
The FDA encourages pharmacists and prescribers to continue working with the clozapine REMS to complete certification and prescribers to enroll patients in the program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With a little help from your friends
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Novel drug eases Parkinson’s-related constipation in early trial
The findings are based on 135 patients who completed 7-25 days of treatment with a daily oral dose of the drug, ENT-01, or a placebo. Complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBMs), the primary efficacy endpoint, increased from a mean of 0.7 per week to 3.2 in individuals who took ENT-01 versus 1.2 in the placebo group.
The phase 2, multicenter, randomized trial showed that the drug “is safe and that it rapidly normalized bowel function in a dose-dependent fashion, with an effect that seems to persist for several weeks beyond the treatment period,” the researchers wrote in their paper on the research, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers hypothesized that displacing aggregated alpha-synuclein from nerve cells in the gastrointestinal tract may also “slow progression of neurologic symptoms” in patients with PD by arresting the abnormal development of alpha-nucleic aggregates in the brain.
Denise Barbut, MD, cofounder, president and chief medical officer of Enterin, the company developing ENT-01, said the next step is another phase 2 trial to determine whether the drug reverses dementia or psychosis in patients with PD, before conducting a phase 3 study.
“We want to treat all nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, not just constipation,” she said.
Constipation is an early PD symptom
Constipation is a common and persistent symptom of PD that often emerges years earlier than other symptoms such as motor deficits. Recent research has linked it to aggregates of alpha-synuclein that bind to cells in the enteric nervous system and may spread to the brain via the vagus nerve.
According to the researchers, ENT-01, a synthetic derivative of the antimicrobial compound squalamine, improves neural signaling in the gut by displacing alpha-synuclein aggregates.
In their double-blinded study, patients were randomized 3:1 to receive ENT-01 or a placebo and stratified by constipation severity to one of two starting doses: 75 mg or three placebo pills or 150 mg or six placebo pills. Doses increased until a patient reached a “prokinetic” dose, a maximum of 250 mg or 10 placebo pills, or the individual’s tolerability limit.
Dosing was fixed for the remainder of the 25 days, after which all patients took a placebo for 2 weeks followed by a 4-week washout.
In addition to more CSBMs, the treatment group had greater improvements in secondary endpoints of weekly spontaneous bowel movements (P = .002), better stool consistency (P < .001), improved ease of passage (P = .006), and less laxative use (P = .041).
There were no significant differences between the groups in scores on the Patient Assessment of Constipation Symptoms or the Patient Assessment of Constipation Quality of Life.
No deaths occurred, and there were no serious adverse events attributed to ENT-01. However, adverse events occurred in 61 (65.6%) of patients who took the drug versus 27 (47.4%) of those who took a placebo.
The most common problems were nausea, experienced by 32 (34%) in the ENT-01 group and 3 (5.3%) in the placebo group, and diarrhea, which occurred in 18 (9.4%) of those in the ENT-01 group and three (5.3%) who took the placebo.
Of 93 patients randomized to the drug (25.8%), 24 discontinued treatment before therapy ended, mostly because of nausea or diarrhea. That compared with 8 of 57 (14.1%) patients in the placebo group who stopped taking their pills before the end of the therapy period.
The researchers suggested that nausea and diarrhea might be alleviated by more gradual dosing escalation and the use of antinausea medication.
Dr. Barbut noted that a previous open-label trial of 50 patients with PD showed that ENT-01 acts locally in the gastrointestinal tract, which means it would not be absorbed into the bloodstream or interfere with other medications.
Targeting the underlying disease
Researchers noted that, in small subsets of patients with dementia or psychosis, greater improvements in those symptoms occurred among those who took ENT-01 versus those who took a placebo.
According to the study, among 11 patients with psychosis, average scores on the Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms adapted for PD dropped from 6.5 to 1.8 on a 45-point scale at the end of treatment in the ENT-01 group (n = 5) and from 6.3 to 3.4 in the placebo group (n = 6).
In 28 patients with dementia, scores on the Mini-Mental State Examination improved by 2.4 points on a 30-point scale, from 24.1 to 26.5, during the treatment period for the ENT-01 group (n = 14) versus an improvement of 0.9 points, from 24.8 to 25.7, in the placebo group (n = 14).
The researchers said the findings must be evaluated in future trials dedicated to studying ENT-01’s effects on PD-related psychosis and dementia.
He added that, if findings are reproduced in a large study, the drug could have “a major impact” not just in treating constipation, for which there are no PD-specific drugs, but also in addressing neurological dysfunctions that are cardinal features of PD. “That is what is exciting to me, because we’re now talking about reversing the disease itself,” he said.
However, Dr. Barbut said it’s been difficult to get across to the medical community and to investors that a drug that acts on nerve cells in the gut might reverse neurologic symptoms by improving direct gut-brain communication. “That’s a concept that is alien to most people’s thinking,” she said.
Enterin funded the study and was responsible for the design, data collection and analysis. Its employees also participated in the interpretation of data, writing of the report, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Dr. Barbut reported stock options in Enterin and patent interests in ENT-01. Fifteen other study investigators reported financial ties to Enterin and/or ENT-01 including employment, stock options, research funding, consulting fees and patent application ownership. Dr. Rao reported receiving honoraria from multiple companies that market drugs for general constipation.
The findings are based on 135 patients who completed 7-25 days of treatment with a daily oral dose of the drug, ENT-01, or a placebo. Complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBMs), the primary efficacy endpoint, increased from a mean of 0.7 per week to 3.2 in individuals who took ENT-01 versus 1.2 in the placebo group.
The phase 2, multicenter, randomized trial showed that the drug “is safe and that it rapidly normalized bowel function in a dose-dependent fashion, with an effect that seems to persist for several weeks beyond the treatment period,” the researchers wrote in their paper on the research, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers hypothesized that displacing aggregated alpha-synuclein from nerve cells in the gastrointestinal tract may also “slow progression of neurologic symptoms” in patients with PD by arresting the abnormal development of alpha-nucleic aggregates in the brain.
Denise Barbut, MD, cofounder, president and chief medical officer of Enterin, the company developing ENT-01, said the next step is another phase 2 trial to determine whether the drug reverses dementia or psychosis in patients with PD, before conducting a phase 3 study.
“We want to treat all nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, not just constipation,” she said.
Constipation is an early PD symptom
Constipation is a common and persistent symptom of PD that often emerges years earlier than other symptoms such as motor deficits. Recent research has linked it to aggregates of alpha-synuclein that bind to cells in the enteric nervous system and may spread to the brain via the vagus nerve.
According to the researchers, ENT-01, a synthetic derivative of the antimicrobial compound squalamine, improves neural signaling in the gut by displacing alpha-synuclein aggregates.
In their double-blinded study, patients were randomized 3:1 to receive ENT-01 or a placebo and stratified by constipation severity to one of two starting doses: 75 mg or three placebo pills or 150 mg or six placebo pills. Doses increased until a patient reached a “prokinetic” dose, a maximum of 250 mg or 10 placebo pills, or the individual’s tolerability limit.
Dosing was fixed for the remainder of the 25 days, after which all patients took a placebo for 2 weeks followed by a 4-week washout.
In addition to more CSBMs, the treatment group had greater improvements in secondary endpoints of weekly spontaneous bowel movements (P = .002), better stool consistency (P < .001), improved ease of passage (P = .006), and less laxative use (P = .041).
There were no significant differences between the groups in scores on the Patient Assessment of Constipation Symptoms or the Patient Assessment of Constipation Quality of Life.
No deaths occurred, and there were no serious adverse events attributed to ENT-01. However, adverse events occurred in 61 (65.6%) of patients who took the drug versus 27 (47.4%) of those who took a placebo.
The most common problems were nausea, experienced by 32 (34%) in the ENT-01 group and 3 (5.3%) in the placebo group, and diarrhea, which occurred in 18 (9.4%) of those in the ENT-01 group and three (5.3%) who took the placebo.
Of 93 patients randomized to the drug (25.8%), 24 discontinued treatment before therapy ended, mostly because of nausea or diarrhea. That compared with 8 of 57 (14.1%) patients in the placebo group who stopped taking their pills before the end of the therapy period.
The researchers suggested that nausea and diarrhea might be alleviated by more gradual dosing escalation and the use of antinausea medication.
Dr. Barbut noted that a previous open-label trial of 50 patients with PD showed that ENT-01 acts locally in the gastrointestinal tract, which means it would not be absorbed into the bloodstream or interfere with other medications.
Targeting the underlying disease
Researchers noted that, in small subsets of patients with dementia or psychosis, greater improvements in those symptoms occurred among those who took ENT-01 versus those who took a placebo.
According to the study, among 11 patients with psychosis, average scores on the Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms adapted for PD dropped from 6.5 to 1.8 on a 45-point scale at the end of treatment in the ENT-01 group (n = 5) and from 6.3 to 3.4 in the placebo group (n = 6).
In 28 patients with dementia, scores on the Mini-Mental State Examination improved by 2.4 points on a 30-point scale, from 24.1 to 26.5, during the treatment period for the ENT-01 group (n = 14) versus an improvement of 0.9 points, from 24.8 to 25.7, in the placebo group (n = 14).
The researchers said the findings must be evaluated in future trials dedicated to studying ENT-01’s effects on PD-related psychosis and dementia.
He added that, if findings are reproduced in a large study, the drug could have “a major impact” not just in treating constipation, for which there are no PD-specific drugs, but also in addressing neurological dysfunctions that are cardinal features of PD. “That is what is exciting to me, because we’re now talking about reversing the disease itself,” he said.
However, Dr. Barbut said it’s been difficult to get across to the medical community and to investors that a drug that acts on nerve cells in the gut might reverse neurologic symptoms by improving direct gut-brain communication. “That’s a concept that is alien to most people’s thinking,” she said.
Enterin funded the study and was responsible for the design, data collection and analysis. Its employees also participated in the interpretation of data, writing of the report, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Dr. Barbut reported stock options in Enterin and patent interests in ENT-01. Fifteen other study investigators reported financial ties to Enterin and/or ENT-01 including employment, stock options, research funding, consulting fees and patent application ownership. Dr. Rao reported receiving honoraria from multiple companies that market drugs for general constipation.
The findings are based on 135 patients who completed 7-25 days of treatment with a daily oral dose of the drug, ENT-01, or a placebo. Complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBMs), the primary efficacy endpoint, increased from a mean of 0.7 per week to 3.2 in individuals who took ENT-01 versus 1.2 in the placebo group.
The phase 2, multicenter, randomized trial showed that the drug “is safe and that it rapidly normalized bowel function in a dose-dependent fashion, with an effect that seems to persist for several weeks beyond the treatment period,” the researchers wrote in their paper on the research, which was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers hypothesized that displacing aggregated alpha-synuclein from nerve cells in the gastrointestinal tract may also “slow progression of neurologic symptoms” in patients with PD by arresting the abnormal development of alpha-nucleic aggregates in the brain.
Denise Barbut, MD, cofounder, president and chief medical officer of Enterin, the company developing ENT-01, said the next step is another phase 2 trial to determine whether the drug reverses dementia or psychosis in patients with PD, before conducting a phase 3 study.
“We want to treat all nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, not just constipation,” she said.
Constipation is an early PD symptom
Constipation is a common and persistent symptom of PD that often emerges years earlier than other symptoms such as motor deficits. Recent research has linked it to aggregates of alpha-synuclein that bind to cells in the enteric nervous system and may spread to the brain via the vagus nerve.
According to the researchers, ENT-01, a synthetic derivative of the antimicrobial compound squalamine, improves neural signaling in the gut by displacing alpha-synuclein aggregates.
In their double-blinded study, patients were randomized 3:1 to receive ENT-01 or a placebo and stratified by constipation severity to one of two starting doses: 75 mg or three placebo pills or 150 mg or six placebo pills. Doses increased until a patient reached a “prokinetic” dose, a maximum of 250 mg or 10 placebo pills, or the individual’s tolerability limit.
Dosing was fixed for the remainder of the 25 days, after which all patients took a placebo for 2 weeks followed by a 4-week washout.
In addition to more CSBMs, the treatment group had greater improvements in secondary endpoints of weekly spontaneous bowel movements (P = .002), better stool consistency (P < .001), improved ease of passage (P = .006), and less laxative use (P = .041).
There were no significant differences between the groups in scores on the Patient Assessment of Constipation Symptoms or the Patient Assessment of Constipation Quality of Life.
No deaths occurred, and there were no serious adverse events attributed to ENT-01. However, adverse events occurred in 61 (65.6%) of patients who took the drug versus 27 (47.4%) of those who took a placebo.
The most common problems were nausea, experienced by 32 (34%) in the ENT-01 group and 3 (5.3%) in the placebo group, and diarrhea, which occurred in 18 (9.4%) of those in the ENT-01 group and three (5.3%) who took the placebo.
Of 93 patients randomized to the drug (25.8%), 24 discontinued treatment before therapy ended, mostly because of nausea or diarrhea. That compared with 8 of 57 (14.1%) patients in the placebo group who stopped taking their pills before the end of the therapy period.
The researchers suggested that nausea and diarrhea might be alleviated by more gradual dosing escalation and the use of antinausea medication.
Dr. Barbut noted that a previous open-label trial of 50 patients with PD showed that ENT-01 acts locally in the gastrointestinal tract, which means it would not be absorbed into the bloodstream or interfere with other medications.
Targeting the underlying disease
Researchers noted that, in small subsets of patients with dementia or psychosis, greater improvements in those symptoms occurred among those who took ENT-01 versus those who took a placebo.
According to the study, among 11 patients with psychosis, average scores on the Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms adapted for PD dropped from 6.5 to 1.8 on a 45-point scale at the end of treatment in the ENT-01 group (n = 5) and from 6.3 to 3.4 in the placebo group (n = 6).
In 28 patients with dementia, scores on the Mini-Mental State Examination improved by 2.4 points on a 30-point scale, from 24.1 to 26.5, during the treatment period for the ENT-01 group (n = 14) versus an improvement of 0.9 points, from 24.8 to 25.7, in the placebo group (n = 14).
The researchers said the findings must be evaluated in future trials dedicated to studying ENT-01’s effects on PD-related psychosis and dementia.
He added that, if findings are reproduced in a large study, the drug could have “a major impact” not just in treating constipation, for which there are no PD-specific drugs, but also in addressing neurological dysfunctions that are cardinal features of PD. “That is what is exciting to me, because we’re now talking about reversing the disease itself,” he said.
However, Dr. Barbut said it’s been difficult to get across to the medical community and to investors that a drug that acts on nerve cells in the gut might reverse neurologic symptoms by improving direct gut-brain communication. “That’s a concept that is alien to most people’s thinking,” she said.
Enterin funded the study and was responsible for the design, data collection and analysis. Its employees also participated in the interpretation of data, writing of the report, and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Dr. Barbut reported stock options in Enterin and patent interests in ENT-01. Fifteen other study investigators reported financial ties to Enterin and/or ENT-01 including employment, stock options, research funding, consulting fees and patent application ownership. Dr. Rao reported receiving honoraria from multiple companies that market drugs for general constipation.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE