User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Poorly controlled asthma predicts COVID-19 hospitalization in children
Children and adolescents with poorly controlled asthma were three to six times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19 infections, based on data from a national study of more than 750,000 children in Scotland.
Although the majority of COVID-19 cases in children have been mild, some children require hospitalization, wrote Ting Shi, PhD, of the University of Edinburgh (Scotland) and colleagues.
Vaccination policies to potentially reduce infection and hospitalization of children remain inconsistent, the researchers said. Identifying which school-age children would derive the greatest benefit from vaccination “could help to reduce the risk of infection and consequently the need for children to have time off school; and might also reduce the risk of spread of SARS-CoV-2 within schools and households,” but the potential benefits of vaccination for children with asthma in particular have not been well studied, they wrote.
The United Kingdom’s Joint Commission on Vaccination and Immunisation commissioned research on the rates of hospitalization among children with poorly controlled asthma. In a national incidence cohort study published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from all children aged 5-17 years in Scotland who were enrolled in the linked dataset of Early Pandemic Evaluation and Enhanced Surveillance of COVID-19 (EAVE II). The total number of children in the dataset was 752,867, and 63,463 (8.4%) of these had diagnosed asthma. Among the children with asthma, 4,339 (6.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections between March 1, 2020, and July 27, 2021. A total of 67 infected children were hospitalized. Of the 689,404 children without asthma, 40,231 (5.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections, and 382 (0.9%) of these children were hospitalized.
Overall, hospital admission rates for COVID-19 were significantly higher among children with asthma, compared to those without asthma (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.49), and the rates increased among children with poorly controlled asthma.
The researchers used previous hospital admission for asthma as a measure of uncontrolled asthma, and found that hospitalization was at least six times as likely for children with poorly controlled asthma, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 6.40), although children with well-controlled asthma also had an increased risk of hospitalization, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 1.36).
When the researchers used oral corticosteroid prescriptions as an indicator of uncontrolled asthma, the adjusted hazard ratios were 3.38, 3.53, 1.52, and 1.34 for children with prescribed corticosteroid courses of three or more, two, one, and none, respectively, compared with children with no asthma.
These hazard ratios remained significant after controlling for factors including age, sex, socioeconomic status, comorbidity, and previous hospital admission, the researchers wrote.
In an age-based analysis, results were similar for children aged 12-17 years, but in children aged 5-11 years, the hospitalization risk decreased for those with one course of corticosteroids and reached the highest rate for those with three or more courses, rather than two courses.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and deaths in children with asthma, the researchers noted. Other limitations include potential changes in asthma control over the study period, and lack of data on certain confounders such as tobacco use, unsuitable housing, and ethnicity, they noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a large, national dataset, and access to electronic health records, they said.
The findings reflect data from previous studies suggesting increased risk of hospitalization for patients with respiratory illness who develop COVID-19 infections, the researchers wrote.
The results emphasize the importance of good asthma control to protect children from severe COVID-19, and careful monitoring of children with poorly controlled asthma who do become infected, they added.
“The findings from this linkage of multiple data sources have helped inform the prioritisation of school-aged children with poorly controlled asthma for vaccines,” they concluded.
Findings support value of vaccination for children with asthma
“Pediatricians see many children who suffer from asthma, and although one could assume that these children would have more serious consequences from contracting COVID-19, the current study examines a large database in a way not possible in the United States to address the severity question,” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “The authors used prior hospitalization rate or two prescriptions for oral corticosteroids as markers of asthma severity prior to the onset of COVID-19 in Scotland, and they collected retrospective data for 16 months of the pandemic through July of 2021, showing a significant increase in hospitalization for those children,” she said. Dr. Boulter said she was not surprised by this finding, given the impact of COVID-19 on the respiratory system.
“Pediatricians have found significant challenges from some groups of parents when discussing the indications and need for vaccination in their patients,” said Dr. Boulter. “Having this data on the increased risk of morbidity and mortality in children with asthma might help parents who are uncertain about the risk/benefit ratio of the vaccine make their decision,” she said.
Dr. Boulter said she hoped that additional studies will yield ongoing information about hospitalization rates for COVID-19 not only about asthma, but also other diagnoses affecting children in the United States and worldwide.
“It would also be important to see a breakdown of ethnic factors and adverse childhood experiences and how they relate to hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Dr. Boulter said.
“The results of this study are not surprising, as we have known for a long time that children with severe asthma are more susceptible to severe respiratory viruses,” Francis E. Rushton, MD, a pediatrician in Beaufort, S.C., said in an interview. “But the study is still important, as it helps us determine which children are most urgently in need of protection from COVID-19 in any of its forms,” he emphasized. In particular, the current study underlines the importance of vaccinating children with unstable asthma, Dr. Rushton said.
Going forward, “it would be interesting to do additional studies looking at other markers for poor asthma control that could guide our vaccine efforts so that they are focused on those most at risk,” he added.
The study was supported by the UK Research and Innovation (Medical Research Council), Research and Innovation Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, Health Data Research UK, and the Scottish Government. Lead author Dr. Shi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rushton and Dr. Boulter had no financial conflicts to disclose, but each serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
Children and adolescents with poorly controlled asthma were three to six times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19 infections, based on data from a national study of more than 750,000 children in Scotland.
Although the majority of COVID-19 cases in children have been mild, some children require hospitalization, wrote Ting Shi, PhD, of the University of Edinburgh (Scotland) and colleagues.
Vaccination policies to potentially reduce infection and hospitalization of children remain inconsistent, the researchers said. Identifying which school-age children would derive the greatest benefit from vaccination “could help to reduce the risk of infection and consequently the need for children to have time off school; and might also reduce the risk of spread of SARS-CoV-2 within schools and households,” but the potential benefits of vaccination for children with asthma in particular have not been well studied, they wrote.
The United Kingdom’s Joint Commission on Vaccination and Immunisation commissioned research on the rates of hospitalization among children with poorly controlled asthma. In a national incidence cohort study published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from all children aged 5-17 years in Scotland who were enrolled in the linked dataset of Early Pandemic Evaluation and Enhanced Surveillance of COVID-19 (EAVE II). The total number of children in the dataset was 752,867, and 63,463 (8.4%) of these had diagnosed asthma. Among the children with asthma, 4,339 (6.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections between March 1, 2020, and July 27, 2021. A total of 67 infected children were hospitalized. Of the 689,404 children without asthma, 40,231 (5.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections, and 382 (0.9%) of these children were hospitalized.
Overall, hospital admission rates for COVID-19 were significantly higher among children with asthma, compared to those without asthma (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.49), and the rates increased among children with poorly controlled asthma.
The researchers used previous hospital admission for asthma as a measure of uncontrolled asthma, and found that hospitalization was at least six times as likely for children with poorly controlled asthma, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 6.40), although children with well-controlled asthma also had an increased risk of hospitalization, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 1.36).
When the researchers used oral corticosteroid prescriptions as an indicator of uncontrolled asthma, the adjusted hazard ratios were 3.38, 3.53, 1.52, and 1.34 for children with prescribed corticosteroid courses of three or more, two, one, and none, respectively, compared with children with no asthma.
These hazard ratios remained significant after controlling for factors including age, sex, socioeconomic status, comorbidity, and previous hospital admission, the researchers wrote.
In an age-based analysis, results were similar for children aged 12-17 years, but in children aged 5-11 years, the hospitalization risk decreased for those with one course of corticosteroids and reached the highest rate for those with three or more courses, rather than two courses.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and deaths in children with asthma, the researchers noted. Other limitations include potential changes in asthma control over the study period, and lack of data on certain confounders such as tobacco use, unsuitable housing, and ethnicity, they noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a large, national dataset, and access to electronic health records, they said.
The findings reflect data from previous studies suggesting increased risk of hospitalization for patients with respiratory illness who develop COVID-19 infections, the researchers wrote.
The results emphasize the importance of good asthma control to protect children from severe COVID-19, and careful monitoring of children with poorly controlled asthma who do become infected, they added.
“The findings from this linkage of multiple data sources have helped inform the prioritisation of school-aged children with poorly controlled asthma for vaccines,” they concluded.
Findings support value of vaccination for children with asthma
“Pediatricians see many children who suffer from asthma, and although one could assume that these children would have more serious consequences from contracting COVID-19, the current study examines a large database in a way not possible in the United States to address the severity question,” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “The authors used prior hospitalization rate or two prescriptions for oral corticosteroids as markers of asthma severity prior to the onset of COVID-19 in Scotland, and they collected retrospective data for 16 months of the pandemic through July of 2021, showing a significant increase in hospitalization for those children,” she said. Dr. Boulter said she was not surprised by this finding, given the impact of COVID-19 on the respiratory system.
“Pediatricians have found significant challenges from some groups of parents when discussing the indications and need for vaccination in their patients,” said Dr. Boulter. “Having this data on the increased risk of morbidity and mortality in children with asthma might help parents who are uncertain about the risk/benefit ratio of the vaccine make their decision,” she said.
Dr. Boulter said she hoped that additional studies will yield ongoing information about hospitalization rates for COVID-19 not only about asthma, but also other diagnoses affecting children in the United States and worldwide.
“It would also be important to see a breakdown of ethnic factors and adverse childhood experiences and how they relate to hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Dr. Boulter said.
“The results of this study are not surprising, as we have known for a long time that children with severe asthma are more susceptible to severe respiratory viruses,” Francis E. Rushton, MD, a pediatrician in Beaufort, S.C., said in an interview. “But the study is still important, as it helps us determine which children are most urgently in need of protection from COVID-19 in any of its forms,” he emphasized. In particular, the current study underlines the importance of vaccinating children with unstable asthma, Dr. Rushton said.
Going forward, “it would be interesting to do additional studies looking at other markers for poor asthma control that could guide our vaccine efforts so that they are focused on those most at risk,” he added.
The study was supported by the UK Research and Innovation (Medical Research Council), Research and Innovation Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, Health Data Research UK, and the Scottish Government. Lead author Dr. Shi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rushton and Dr. Boulter had no financial conflicts to disclose, but each serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
Children and adolescents with poorly controlled asthma were three to six times more likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19 infections, based on data from a national study of more than 750,000 children in Scotland.
Although the majority of COVID-19 cases in children have been mild, some children require hospitalization, wrote Ting Shi, PhD, of the University of Edinburgh (Scotland) and colleagues.
Vaccination policies to potentially reduce infection and hospitalization of children remain inconsistent, the researchers said. Identifying which school-age children would derive the greatest benefit from vaccination “could help to reduce the risk of infection and consequently the need for children to have time off school; and might also reduce the risk of spread of SARS-CoV-2 within schools and households,” but the potential benefits of vaccination for children with asthma in particular have not been well studied, they wrote.
The United Kingdom’s Joint Commission on Vaccination and Immunisation commissioned research on the rates of hospitalization among children with poorly controlled asthma. In a national incidence cohort study published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, the researchers reviewed data from all children aged 5-17 years in Scotland who were enrolled in the linked dataset of Early Pandemic Evaluation and Enhanced Surveillance of COVID-19 (EAVE II). The total number of children in the dataset was 752,867, and 63,463 (8.4%) of these had diagnosed asthma. Among the children with asthma, 4,339 (6.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections between March 1, 2020, and July 27, 2021. A total of 67 infected children were hospitalized. Of the 689,404 children without asthma, 40,231 (5.8%) had confirmed COVID-19 infections, and 382 (0.9%) of these children were hospitalized.
Overall, hospital admission rates for COVID-19 were significantly higher among children with asthma, compared to those without asthma (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.49), and the rates increased among children with poorly controlled asthma.
The researchers used previous hospital admission for asthma as a measure of uncontrolled asthma, and found that hospitalization was at least six times as likely for children with poorly controlled asthma, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 6.40), although children with well-controlled asthma also had an increased risk of hospitalization, compared with those with no asthma (aHR, 1.36).
When the researchers used oral corticosteroid prescriptions as an indicator of uncontrolled asthma, the adjusted hazard ratios were 3.38, 3.53, 1.52, and 1.34 for children with prescribed corticosteroid courses of three or more, two, one, and none, respectively, compared with children with no asthma.
These hazard ratios remained significant after controlling for factors including age, sex, socioeconomic status, comorbidity, and previous hospital admission, the researchers wrote.
In an age-based analysis, results were similar for children aged 12-17 years, but in children aged 5-11 years, the hospitalization risk decreased for those with one course of corticosteroids and reached the highest rate for those with three or more courses, rather than two courses.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small numbers of COVID-19 hospitalizations, ICU admissions, and deaths in children with asthma, the researchers noted. Other limitations include potential changes in asthma control over the study period, and lack of data on certain confounders such as tobacco use, unsuitable housing, and ethnicity, they noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a large, national dataset, and access to electronic health records, they said.
The findings reflect data from previous studies suggesting increased risk of hospitalization for patients with respiratory illness who develop COVID-19 infections, the researchers wrote.
The results emphasize the importance of good asthma control to protect children from severe COVID-19, and careful monitoring of children with poorly controlled asthma who do become infected, they added.
“The findings from this linkage of multiple data sources have helped inform the prioritisation of school-aged children with poorly controlled asthma for vaccines,” they concluded.
Findings support value of vaccination for children with asthma
“Pediatricians see many children who suffer from asthma, and although one could assume that these children would have more serious consequences from contracting COVID-19, the current study examines a large database in a way not possible in the United States to address the severity question,” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “The authors used prior hospitalization rate or two prescriptions for oral corticosteroids as markers of asthma severity prior to the onset of COVID-19 in Scotland, and they collected retrospective data for 16 months of the pandemic through July of 2021, showing a significant increase in hospitalization for those children,” she said. Dr. Boulter said she was not surprised by this finding, given the impact of COVID-19 on the respiratory system.
“Pediatricians have found significant challenges from some groups of parents when discussing the indications and need for vaccination in their patients,” said Dr. Boulter. “Having this data on the increased risk of morbidity and mortality in children with asthma might help parents who are uncertain about the risk/benefit ratio of the vaccine make their decision,” she said.
Dr. Boulter said she hoped that additional studies will yield ongoing information about hospitalization rates for COVID-19 not only about asthma, but also other diagnoses affecting children in the United States and worldwide.
“It would also be important to see a breakdown of ethnic factors and adverse childhood experiences and how they relate to hospitalization and death from COVID-19,” Dr. Boulter said.
“The results of this study are not surprising, as we have known for a long time that children with severe asthma are more susceptible to severe respiratory viruses,” Francis E. Rushton, MD, a pediatrician in Beaufort, S.C., said in an interview. “But the study is still important, as it helps us determine which children are most urgently in need of protection from COVID-19 in any of its forms,” he emphasized. In particular, the current study underlines the importance of vaccinating children with unstable asthma, Dr. Rushton said.
Going forward, “it would be interesting to do additional studies looking at other markers for poor asthma control that could guide our vaccine efforts so that they are focused on those most at risk,” he added.
The study was supported by the UK Research and Innovation (Medical Research Council), Research and Innovation Industrial Strategy Challenge Fund, Health Data Research UK, and the Scottish Government. Lead author Dr. Shi had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Rushton and Dr. Boulter had no financial conflicts to disclose, but each serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
FROM THE LANCET
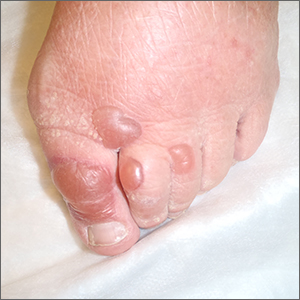
Bullae on elderly woman’s toes
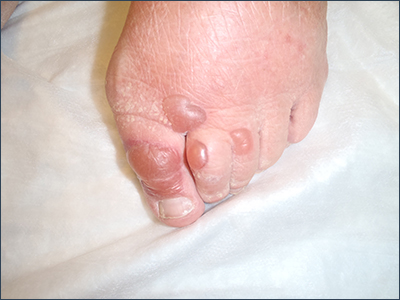
A biopsy was performed and sent for immunofluorescence; the results were negative. This, along with the patient’s history of diabetes, led us to the diagnosis of bullosis diabeticorum (BD). This condition, also known as bullous disease of diabetes, is characterized by abrupt development of noninflammatory bullae on acral areas in patients with diabetes.
The etiology of BD is unknown. The acral location suggests that trauma may be a contributing factor. Although electron microscopy has suggested an abnormality in anchoring fibrils, this cellular change does not fully explain the development of multiple blisters at varying sites.
A diagnosis of BD can be made when biopsy with immunofluorescence excludes other histologically similar diagnoses such as epidermolysis bullosa, noninflammatory bullous pemphigoid, and porphyria cutanea tarda. And, while immunofluorescence findings are typically negative, elevated levels of immunoglobulin M and C3 have, on occasion, been reported.1,2 Cultures are warranted only if a secondary infection is suspected.
The distribution of lesions and the presence—or absence—of systemic symptoms go a long way toward narrowing the differential of blistering diseases. The presence of generalized blistering and systemic symptoms would suggest conditions related to medication exposure, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis; infectious etiologies (eg, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome); autoimmune causes; or underlying malignancy.3 Generalized blistering in the absence of systemic symptoms would support diagnoses such as bullous impetigo and pemphigoid.3
The blisters associated with BD spontaneously resolve over several weeks without treatment but tend to recur. The lesions typically heal without significant scarring, although they may have a darker pigmentation after the first occurrence. Treatment may be warranted if a patient develops a secondary infection. For this patient, the bullae resolved within 2 weeks without treatment, although mild hyperpigmentation remained.
This case was adapted from: Mims L, Savage A, Chessman A. Blisters on an elderly woman’s toes. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:273-274.
1. James WD, Odom RB, Goette DK. Bullous eruption of diabetes. A case with positive immunofluorescence microscopy findings. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:1191-1192.
2. Basarab T, Munn SE, McGrath J, et al. Bullous diabeticorum. A case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995;20:218-220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1995.tb01305.x
3. Hull C, Zone JJ. Approach to the patient with cutaneous blisters. UpToDate. Updated July 30, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-patient-with-cutaneous-blisters

A biopsy was performed and sent for immunofluorescence; the results were negative. This, along with the patient’s history of diabetes, led us to the diagnosis of bullosis diabeticorum (BD). This condition, also known as bullous disease of diabetes, is characterized by abrupt development of noninflammatory bullae on acral areas in patients with diabetes.
The etiology of BD is unknown. The acral location suggests that trauma may be a contributing factor. Although electron microscopy has suggested an abnormality in anchoring fibrils, this cellular change does not fully explain the development of multiple blisters at varying sites.
A diagnosis of BD can be made when biopsy with immunofluorescence excludes other histologically similar diagnoses such as epidermolysis bullosa, noninflammatory bullous pemphigoid, and porphyria cutanea tarda. And, while immunofluorescence findings are typically negative, elevated levels of immunoglobulin M and C3 have, on occasion, been reported.1,2 Cultures are warranted only if a secondary infection is suspected.
The distribution of lesions and the presence—or absence—of systemic symptoms go a long way toward narrowing the differential of blistering diseases. The presence of generalized blistering and systemic symptoms would suggest conditions related to medication exposure, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis; infectious etiologies (eg, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome); autoimmune causes; or underlying malignancy.3 Generalized blistering in the absence of systemic symptoms would support diagnoses such as bullous impetigo and pemphigoid.3
The blisters associated with BD spontaneously resolve over several weeks without treatment but tend to recur. The lesions typically heal without significant scarring, although they may have a darker pigmentation after the first occurrence. Treatment may be warranted if a patient develops a secondary infection. For this patient, the bullae resolved within 2 weeks without treatment, although mild hyperpigmentation remained.
This case was adapted from: Mims L, Savage A, Chessman A. Blisters on an elderly woman’s toes. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:273-274.

A biopsy was performed and sent for immunofluorescence; the results were negative. This, along with the patient’s history of diabetes, led us to the diagnosis of bullosis diabeticorum (BD). This condition, also known as bullous disease of diabetes, is characterized by abrupt development of noninflammatory bullae on acral areas in patients with diabetes.
The etiology of BD is unknown. The acral location suggests that trauma may be a contributing factor. Although electron microscopy has suggested an abnormality in anchoring fibrils, this cellular change does not fully explain the development of multiple blisters at varying sites.
A diagnosis of BD can be made when biopsy with immunofluorescence excludes other histologically similar diagnoses such as epidermolysis bullosa, noninflammatory bullous pemphigoid, and porphyria cutanea tarda. And, while immunofluorescence findings are typically negative, elevated levels of immunoglobulin M and C3 have, on occasion, been reported.1,2 Cultures are warranted only if a secondary infection is suspected.
The distribution of lesions and the presence—or absence—of systemic symptoms go a long way toward narrowing the differential of blistering diseases. The presence of generalized blistering and systemic symptoms would suggest conditions related to medication exposure, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis; infectious etiologies (eg, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome); autoimmune causes; or underlying malignancy.3 Generalized blistering in the absence of systemic symptoms would support diagnoses such as bullous impetigo and pemphigoid.3
The blisters associated with BD spontaneously resolve over several weeks without treatment but tend to recur. The lesions typically heal without significant scarring, although they may have a darker pigmentation after the first occurrence. Treatment may be warranted if a patient develops a secondary infection. For this patient, the bullae resolved within 2 weeks without treatment, although mild hyperpigmentation remained.
This case was adapted from: Mims L, Savage A, Chessman A. Blisters on an elderly woman’s toes. J Fam Pract. 2014;63:273-274.
1. James WD, Odom RB, Goette DK. Bullous eruption of diabetes. A case with positive immunofluorescence microscopy findings. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:1191-1192.
2. Basarab T, Munn SE, McGrath J, et al. Bullous diabeticorum. A case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995;20:218-220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1995.tb01305.x
3. Hull C, Zone JJ. Approach to the patient with cutaneous blisters. UpToDate. Updated July 30, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-patient-with-cutaneous-blisters
1. James WD, Odom RB, Goette DK. Bullous eruption of diabetes. A case with positive immunofluorescence microscopy findings. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:1191-1192.
2. Basarab T, Munn SE, McGrath J, et al. Bullous diabeticorum. A case report and literature review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995;20:218-220. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1995.tb01305.x
3. Hull C, Zone JJ. Approach to the patient with cutaneous blisters. UpToDate. Updated July 30, 2019. Accessed September 14, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-patient-with-cutaneous-blisters
First Omicron variant case identified in U.S.
He or she was fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and experienced only “mild symptoms that are improving,” officials with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The patient, who was not named in the CDC’s announcement of the first U.S. case of the Omicron variant Dec. 1, is self-quarantining.
“All close contacts have been contacted and have tested negative,” officials said.
The announcement comes as no surprise to many as the Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa, has been reported in countries around the world in recent days. Hong Kong, the United Kingdom, and Germany each reported this variant, as have Italy and the Netherlands. Over the weekend, the first North American cases were identified in Canada.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, announced over the weekend that this newest variant was likely already in the United States, telling ABC’s This Week its appearance here was “inevitable.”
Similar to previous variants, this new strain likely started circulating in the United States before scientists could do genetic tests to confirm its presence.
The World Health Organization named Omicron a “variant of concern” on Nov. 26, even though much remains unknown about how well it spreads, how severe it can be, and how it may resist vaccines. In the meantime, the United States enacted travel bans from multiple South African countries.
It remains to be seen if Omicron will follow the pattern of the Delta variant, which was first identified in the United States in May and became the dominant strain by July. It’s also possible it will follow the path taken by the Mu variant. Mu emerged in March and April to much concern, only to fizzle out by September because it was unable to compete with the Delta variant.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
He or she was fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and experienced only “mild symptoms that are improving,” officials with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The patient, who was not named in the CDC’s announcement of the first U.S. case of the Omicron variant Dec. 1, is self-quarantining.
“All close contacts have been contacted and have tested negative,” officials said.
The announcement comes as no surprise to many as the Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa, has been reported in countries around the world in recent days. Hong Kong, the United Kingdom, and Germany each reported this variant, as have Italy and the Netherlands. Over the weekend, the first North American cases were identified in Canada.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, announced over the weekend that this newest variant was likely already in the United States, telling ABC’s This Week its appearance here was “inevitable.”
Similar to previous variants, this new strain likely started circulating in the United States before scientists could do genetic tests to confirm its presence.
The World Health Organization named Omicron a “variant of concern” on Nov. 26, even though much remains unknown about how well it spreads, how severe it can be, and how it may resist vaccines. In the meantime, the United States enacted travel bans from multiple South African countries.
It remains to be seen if Omicron will follow the pattern of the Delta variant, which was first identified in the United States in May and became the dominant strain by July. It’s also possible it will follow the path taken by the Mu variant. Mu emerged in March and April to much concern, only to fizzle out by September because it was unable to compete with the Delta variant.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
He or she was fully vaccinated against COVID-19 and experienced only “mild symptoms that are improving,” officials with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
The patient, who was not named in the CDC’s announcement of the first U.S. case of the Omicron variant Dec. 1, is self-quarantining.
“All close contacts have been contacted and have tested negative,” officials said.
The announcement comes as no surprise to many as the Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa, has been reported in countries around the world in recent days. Hong Kong, the United Kingdom, and Germany each reported this variant, as have Italy and the Netherlands. Over the weekend, the first North American cases were identified in Canada.
Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, announced over the weekend that this newest variant was likely already in the United States, telling ABC’s This Week its appearance here was “inevitable.”
Similar to previous variants, this new strain likely started circulating in the United States before scientists could do genetic tests to confirm its presence.
The World Health Organization named Omicron a “variant of concern” on Nov. 26, even though much remains unknown about how well it spreads, how severe it can be, and how it may resist vaccines. In the meantime, the United States enacted travel bans from multiple South African countries.
It remains to be seen if Omicron will follow the pattern of the Delta variant, which was first identified in the United States in May and became the dominant strain by July. It’s also possible it will follow the path taken by the Mu variant. Mu emerged in March and April to much concern, only to fizzle out by September because it was unable to compete with the Delta variant.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Moderna warns of material drop in vaccine efficacy against Omicron
“There is no world, I think, where [the effectiveness] is the same level … we had with Delta,” Stephane Bancel told the Financial Times .
“I think it’s going to be a material drop,” he said. “I just don’t know how much, because we need to wait for the data. But all the scientists I’ve talked to … are like, ‘This is not going to be good.’”
Vaccine companies are now studying whether the new Omicron variant could evade the current shots. Some data is expected in about 2 weeks.
Mr. Bancel said that if a new vaccine is needed, it could take several months to produce at scale. He estimated that Moderna could make billions of vaccine doses in 2022.
“[Moderna] and Pfizer cannot get a billion doses next week. The math doesn’t work,” he said. “But could we get the billion doses out by the summer? Sure.”
The news caused some panic on Nov. 30, prompting financial markets to fall sharply, according to Reuters. But the markets recovered after European officials gave a more reassuring outlook.
“Even if the new variant becomes more widespread, the vaccines we have will continue to provide protection,” Emer Cooke, executive director of the European Medicines Agency, told the European Parliament.
Mr. Cooke said the agency could approve new vaccines that target the Omicron variant within 3 to 4 months, if needed. Moderna and Pfizer have announced they are beginning to tailor a shot to address the Omicron variant in case the data shows they are necessary.
Also on Nov. 30, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control announced that 42 Omicron cases had been identified in 10 European Union countries, according to Reuters.
The cases were mild or had no symptoms, although they were found in younger people who may have mild or no symptoms anyway.
“For the assessment of whether [Omicron] escapes immunity, we still have to wait until investigations in the laboratories with [blood samples] from people who have recovered have been carried out,” Andrea Ammon, MD, chair of the agency, said during an online conference.
The University of Oxford, which developed a COVID-19 vaccine with AstraZeneca, said Nov. 30 that there’s no evidence that vaccines won’t prevent severe disease from the Omicron variant, according to Reuters.
“Despite the appearance of new variants over the past year, vaccines have continued to provide very high levels of protection against severe disease and there is no evidence so far that Omicron is any different,” the university said in a statement. “However, we have the necessary tools and processes in place for rapid development of an updated COVID-19 vaccine if it should be necessary.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“There is no world, I think, where [the effectiveness] is the same level … we had with Delta,” Stephane Bancel told the Financial Times .
“I think it’s going to be a material drop,” he said. “I just don’t know how much, because we need to wait for the data. But all the scientists I’ve talked to … are like, ‘This is not going to be good.’”
Vaccine companies are now studying whether the new Omicron variant could evade the current shots. Some data is expected in about 2 weeks.
Mr. Bancel said that if a new vaccine is needed, it could take several months to produce at scale. He estimated that Moderna could make billions of vaccine doses in 2022.
“[Moderna] and Pfizer cannot get a billion doses next week. The math doesn’t work,” he said. “But could we get the billion doses out by the summer? Sure.”
The news caused some panic on Nov. 30, prompting financial markets to fall sharply, according to Reuters. But the markets recovered after European officials gave a more reassuring outlook.
“Even if the new variant becomes more widespread, the vaccines we have will continue to provide protection,” Emer Cooke, executive director of the European Medicines Agency, told the European Parliament.
Mr. Cooke said the agency could approve new vaccines that target the Omicron variant within 3 to 4 months, if needed. Moderna and Pfizer have announced they are beginning to tailor a shot to address the Omicron variant in case the data shows they are necessary.
Also on Nov. 30, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control announced that 42 Omicron cases had been identified in 10 European Union countries, according to Reuters.
The cases were mild or had no symptoms, although they were found in younger people who may have mild or no symptoms anyway.
“For the assessment of whether [Omicron] escapes immunity, we still have to wait until investigations in the laboratories with [blood samples] from people who have recovered have been carried out,” Andrea Ammon, MD, chair of the agency, said during an online conference.
The University of Oxford, which developed a COVID-19 vaccine with AstraZeneca, said Nov. 30 that there’s no evidence that vaccines won’t prevent severe disease from the Omicron variant, according to Reuters.
“Despite the appearance of new variants over the past year, vaccines have continued to provide very high levels of protection against severe disease and there is no evidence so far that Omicron is any different,” the university said in a statement. “However, we have the necessary tools and processes in place for rapid development of an updated COVID-19 vaccine if it should be necessary.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“There is no world, I think, where [the effectiveness] is the same level … we had with Delta,” Stephane Bancel told the Financial Times .
“I think it’s going to be a material drop,” he said. “I just don’t know how much, because we need to wait for the data. But all the scientists I’ve talked to … are like, ‘This is not going to be good.’”
Vaccine companies are now studying whether the new Omicron variant could evade the current shots. Some data is expected in about 2 weeks.
Mr. Bancel said that if a new vaccine is needed, it could take several months to produce at scale. He estimated that Moderna could make billions of vaccine doses in 2022.
“[Moderna] and Pfizer cannot get a billion doses next week. The math doesn’t work,” he said. “But could we get the billion doses out by the summer? Sure.”
The news caused some panic on Nov. 30, prompting financial markets to fall sharply, according to Reuters. But the markets recovered after European officials gave a more reassuring outlook.
“Even if the new variant becomes more widespread, the vaccines we have will continue to provide protection,” Emer Cooke, executive director of the European Medicines Agency, told the European Parliament.
Mr. Cooke said the agency could approve new vaccines that target the Omicron variant within 3 to 4 months, if needed. Moderna and Pfizer have announced they are beginning to tailor a shot to address the Omicron variant in case the data shows they are necessary.
Also on Nov. 30, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control announced that 42 Omicron cases had been identified in 10 European Union countries, according to Reuters.
The cases were mild or had no symptoms, although they were found in younger people who may have mild or no symptoms anyway.
“For the assessment of whether [Omicron] escapes immunity, we still have to wait until investigations in the laboratories with [blood samples] from people who have recovered have been carried out,” Andrea Ammon, MD, chair of the agency, said during an online conference.
The University of Oxford, which developed a COVID-19 vaccine with AstraZeneca, said Nov. 30 that there’s no evidence that vaccines won’t prevent severe disease from the Omicron variant, according to Reuters.
“Despite the appearance of new variants over the past year, vaccines have continued to provide very high levels of protection against severe disease and there is no evidence so far that Omicron is any different,” the university said in a statement. “However, we have the necessary tools and processes in place for rapid development of an updated COVID-19 vaccine if it should be necessary.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: New cases, vaccinations both decline
States reported 131,828 new pediatric cases for the week of Nov. 19-25, a decline of 7.1% over the previous week but still enough to surpass 100,000 for the 16th consecutive week. The weekly count had risen for 3 straight weeks since the last decrease in late October, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said Nov. 30 in their weekly COVID report.
The AAP/CHA analysis, based on data from state and territorial health departments, puts the total number of cases in children at 6.9 million since the pandemic began, representing 17.0% of cases in Americans of all ages. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which uses an age limit of 18 years to define a child, unlike some states, reports numbers of 6.1 million and 15.5%.
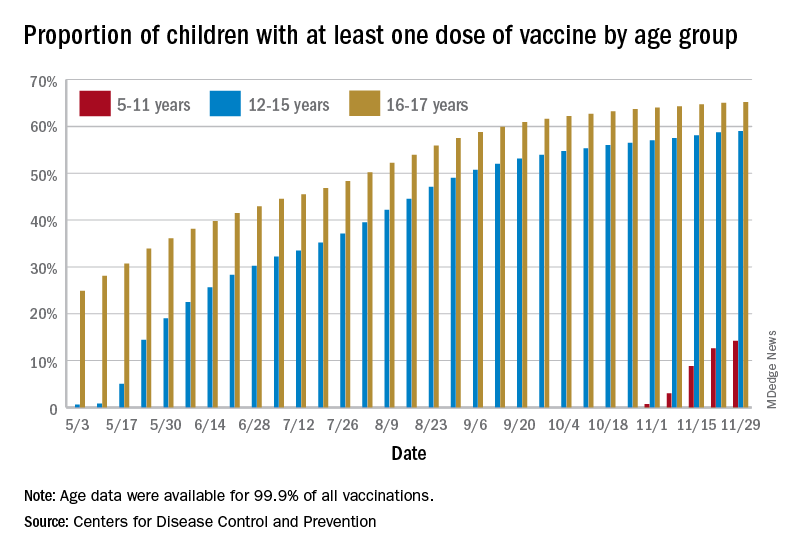
New vaccinations among the youngest eligible children, those aged 5-11 years, were down for the second week in a row after reaching almost 1.7 million during the first full week after approval on Nov. 2. Since then, the vaccination counts have been 1.2 million (Nov. 16-22) and 333,000 (Nov. 23-29), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. A similar drop in the last week – from 127,000 to just 50,000 – also was seen for those aged 12-17 years.
Altogether, 14.2% of children aged 5-11, almost 4.1 million individuals, have received at least one dose of the vaccine, compared with 59.0% (10 million) of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 65.2% (5.5 million) of those aged 16-17. Just under 1% of the youngest group has been fully vaccinated, versus 49.0% and 55.8% for the older children, the CDC said.
It has been reported that Pfizer and BioNTech, which produce the only COVID vaccine approved for children, are planning to apply to the Food and Drug Administration during the first week of December for authorization for a booster dose for 16- and 17-year-olds.

States reported 131,828 new pediatric cases for the week of Nov. 19-25, a decline of 7.1% over the previous week but still enough to surpass 100,000 for the 16th consecutive week. The weekly count had risen for 3 straight weeks since the last decrease in late October, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said Nov. 30 in their weekly COVID report.
The AAP/CHA analysis, based on data from state and territorial health departments, puts the total number of cases in children at 6.9 million since the pandemic began, representing 17.0% of cases in Americans of all ages. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which uses an age limit of 18 years to define a child, unlike some states, reports numbers of 6.1 million and 15.5%.
New vaccinations among the youngest eligible children, those aged 5-11 years, were down for the second week in a row after reaching almost 1.7 million during the first full week after approval on Nov. 2. Since then, the vaccination counts have been 1.2 million (Nov. 16-22) and 333,000 (Nov. 23-29), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. A similar drop in the last week – from 127,000 to just 50,000 – also was seen for those aged 12-17 years.
Altogether, 14.2% of children aged 5-11, almost 4.1 million individuals, have received at least one dose of the vaccine, compared with 59.0% (10 million) of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 65.2% (5.5 million) of those aged 16-17. Just under 1% of the youngest group has been fully vaccinated, versus 49.0% and 55.8% for the older children, the CDC said.
It has been reported that Pfizer and BioNTech, which produce the only COVID vaccine approved for children, are planning to apply to the Food and Drug Administration during the first week of December for authorization for a booster dose for 16- and 17-year-olds.

States reported 131,828 new pediatric cases for the week of Nov. 19-25, a decline of 7.1% over the previous week but still enough to surpass 100,000 for the 16th consecutive week. The weekly count had risen for 3 straight weeks since the last decrease in late October, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said Nov. 30 in their weekly COVID report.
The AAP/CHA analysis, based on data from state and territorial health departments, puts the total number of cases in children at 6.9 million since the pandemic began, representing 17.0% of cases in Americans of all ages. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which uses an age limit of 18 years to define a child, unlike some states, reports numbers of 6.1 million and 15.5%.
New vaccinations among the youngest eligible children, those aged 5-11 years, were down for the second week in a row after reaching almost 1.7 million during the first full week after approval on Nov. 2. Since then, the vaccination counts have been 1.2 million (Nov. 16-22) and 333,000 (Nov. 23-29), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. A similar drop in the last week – from 127,000 to just 50,000 – also was seen for those aged 12-17 years.
Altogether, 14.2% of children aged 5-11, almost 4.1 million individuals, have received at least one dose of the vaccine, compared with 59.0% (10 million) of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 65.2% (5.5 million) of those aged 16-17. Just under 1% of the youngest group has been fully vaccinated, versus 49.0% and 55.8% for the older children, the CDC said.
It has been reported that Pfizer and BioNTech, which produce the only COVID vaccine approved for children, are planning to apply to the Food and Drug Administration during the first week of December for authorization for a booster dose for 16- and 17-year-olds.
Fauci: Omicron ‘very different from other variants’
The newly detected Omicron COVID-19 variant may be highly infectious and less responsive to available vaccines than other variants, but it is too early to know how it compares to the Delta variant, top infectious disease official Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said Nov. 30.
Dr. Fauci, speaking at a White House COVID-19 briefing, said there’s a “very unusual constellation of changes” across the COVID-19 genome that indicates it is unlike any variant we have seen so far.
“This mutational profile is very different from other variants of interest and concern, and although some mutations are also found in Delta, this is not Delta,” Dr. Fauci said. “These mutations have been associated with increased transmissibility and immune evasion.”
Omicron is the fifth designated COVID-19 variant of concern.
Detected first in South Africa, Omicron has been found in 20 countries so far. There are no known cases yet in the United States, but it has been detected in Canada.
Omicron has more than 30 mutations to the spike protein, the part of the virus that binds to human cells, Dr. Fauci said.
Cross-protection from boosters
Though the mutations suggest there is increased transmission of this variant, he said it is too soon to know how this compares to the Delta variant. And although the vaccines may not be as effective against Omicron, Dr. Fauci said there will likely be some protection.
“Remember, as with other variants, although partial immune escape may occur, vaccines, particularly boosters, give a level of antibodies that even with variants like Delta give you a degree of cross-protection, particularly against severe disease,” he said.
“When we say that although these mutations suggest a diminution of protection and a degree of immune evasion, we still, from experience with Delta, can make a reasonable conclusion that you would not eliminate all protection against this particular variant,” Dr. Fauci said.
So far, there is no reason to believe Omicron will cause more severe illness than other variants of concern.
“Although some preliminary information from South Africa suggests no unusual symptoms associated with variant, we do not know, and it is too early to tell,” Dr. Fauci said.
He recommended that people continue to wear masks, wash hands, and avoid crowded indoor venues. Most importantly, he recommended that everyone get their vaccines and boosters.
“One thing has become clear over the last 20 months: We can’t predict the future, but we can be prepared for it,” CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, said at the briefing. “We have far more tools to fight the variant today than we did at this time last year.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
The newly detected Omicron COVID-19 variant may be highly infectious and less responsive to available vaccines than other variants, but it is too early to know how it compares to the Delta variant, top infectious disease official Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said Nov. 30.
Dr. Fauci, speaking at a White House COVID-19 briefing, said there’s a “very unusual constellation of changes” across the COVID-19 genome that indicates it is unlike any variant we have seen so far.
“This mutational profile is very different from other variants of interest and concern, and although some mutations are also found in Delta, this is not Delta,” Dr. Fauci said. “These mutations have been associated with increased transmissibility and immune evasion.”
Omicron is the fifth designated COVID-19 variant of concern.
Detected first in South Africa, Omicron has been found in 20 countries so far. There are no known cases yet in the United States, but it has been detected in Canada.
Omicron has more than 30 mutations to the spike protein, the part of the virus that binds to human cells, Dr. Fauci said.
Cross-protection from boosters
Though the mutations suggest there is increased transmission of this variant, he said it is too soon to know how this compares to the Delta variant. And although the vaccines may not be as effective against Omicron, Dr. Fauci said there will likely be some protection.
“Remember, as with other variants, although partial immune escape may occur, vaccines, particularly boosters, give a level of antibodies that even with variants like Delta give you a degree of cross-protection, particularly against severe disease,” he said.
“When we say that although these mutations suggest a diminution of protection and a degree of immune evasion, we still, from experience with Delta, can make a reasonable conclusion that you would not eliminate all protection against this particular variant,” Dr. Fauci said.
So far, there is no reason to believe Omicron will cause more severe illness than other variants of concern.
“Although some preliminary information from South Africa suggests no unusual symptoms associated with variant, we do not know, and it is too early to tell,” Dr. Fauci said.
He recommended that people continue to wear masks, wash hands, and avoid crowded indoor venues. Most importantly, he recommended that everyone get their vaccines and boosters.
“One thing has become clear over the last 20 months: We can’t predict the future, but we can be prepared for it,” CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, said at the briefing. “We have far more tools to fight the variant today than we did at this time last year.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
The newly detected Omicron COVID-19 variant may be highly infectious and less responsive to available vaccines than other variants, but it is too early to know how it compares to the Delta variant, top infectious disease official Anthony S. Fauci, MD, said Nov. 30.
Dr. Fauci, speaking at a White House COVID-19 briefing, said there’s a “very unusual constellation of changes” across the COVID-19 genome that indicates it is unlike any variant we have seen so far.
“This mutational profile is very different from other variants of interest and concern, and although some mutations are also found in Delta, this is not Delta,” Dr. Fauci said. “These mutations have been associated with increased transmissibility and immune evasion.”
Omicron is the fifth designated COVID-19 variant of concern.
Detected first in South Africa, Omicron has been found in 20 countries so far. There are no known cases yet in the United States, but it has been detected in Canada.
Omicron has more than 30 mutations to the spike protein, the part of the virus that binds to human cells, Dr. Fauci said.
Cross-protection from boosters
Though the mutations suggest there is increased transmission of this variant, he said it is too soon to know how this compares to the Delta variant. And although the vaccines may not be as effective against Omicron, Dr. Fauci said there will likely be some protection.
“Remember, as with other variants, although partial immune escape may occur, vaccines, particularly boosters, give a level of antibodies that even with variants like Delta give you a degree of cross-protection, particularly against severe disease,” he said.
“When we say that although these mutations suggest a diminution of protection and a degree of immune evasion, we still, from experience with Delta, can make a reasonable conclusion that you would not eliminate all protection against this particular variant,” Dr. Fauci said.
So far, there is no reason to believe Omicron will cause more severe illness than other variants of concern.
“Although some preliminary information from South Africa suggests no unusual symptoms associated with variant, we do not know, and it is too early to tell,” Dr. Fauci said.
He recommended that people continue to wear masks, wash hands, and avoid crowded indoor venues. Most importantly, he recommended that everyone get their vaccines and boosters.
“One thing has become clear over the last 20 months: We can’t predict the future, but we can be prepared for it,” CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, said at the briefing. “We have far more tools to fight the variant today than we did at this time last year.”
A version of this story first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel backs first pill for COVID-19 by a small margin
, according to a panel of experts that advises the Food and Drug Administration on its regulatory decisions for these types of drugs.
The FDA’s Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted to authorize the drug molnupiravir, voting 13 to 10 to support emergency use, which requires a medication to meet a lower standard of evidence than does full approval.
The FDA is not bound by the committee’s vote but typically follows its advice.
If authorized by the agency, molnupiravir would be the first antiviral agent available as a pill to treat COVID-19. Other therapies to treat the infection are available — monoclonal antibodies and the drug remdesivir — but they are given by infusion.
The United Kingdom has already authorized the use of Merck’s drug.
“This was clearly a difficult decision,” said committee member Michael Green, MD, a pediatric infectious disease expert at the University of Pittsburg School of Medicine.
Green said he voted yes, and that the drug’s ability to prevent deaths in the study weighed heavily on his decision. He said given uncertainties around the drug both the company and FDA should keep a close eye on patients taking the drug going forward.
“Should an alternative oral agent become available that had a better safety profile and equal or better efficacy profile, the agency might reconsider its authorization,” he said.
Others didn’t agree that the drug should be allowed onto the market.
“I voted no,” said Jennifer Le, PharmD, a professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California. Dr. Le said the modest benefit of the medication didn’t outweigh all the potential safety issues. “I think I just need more efficacy and safety data,” she said.
Initial results from the first half of people enrolled in the clinical trial found the pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 50% in patients at higher risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
But later results, released just days before the meeting, showed that the drug’s effectiveness had dropped to about 30%.
In the updated analysis, 48 patients out of the 709 who were taking the drug were hospitalized or died within 29 days compared to 68 out of 699 who randomly got the placebo. There was one death in the group that got molnupiravir compared to nine in the placebo group. Nearly all those deaths occurred during the first phase of the study.
On Nov. 30 Merck explained that the drug’s efficacy appeared to fall, in part, because the placebo group had experienced fewer hospitalizations and deaths than expected during the second half of the study, making the drug look less beneficial by comparison.
The company said it wasn’t sure why patients in the placebo group had fared so much better in later trial enrollments.
“The efficacy of this product is not overwhelmingly good,” said committee member David Hardy, MD, an infectious disease expert at Charles Drew University School of Medicine in Los Angeles. “And I think that makes all of us a little uncomfortable about whether this is an advanced therapeutic because it’s an oral medication rather than an intravenous medication,” he said during the panel’s deliberations.
“I think we have to be very careful about how we’re going to allow people to use this,” Dr. Hardy said.
Many who voted for authorization thought use of the drug should be restricted to unvaccinated people who were at high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes, the same population enrolled in the clinical trial. People in the trial were considered at higher risk if they were over age 60, had cancer, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, were obese, or had heart disease or diabetes.
There are some significant limitations of the study that may affect how the drug is used. Vaccinated people couldn’t enroll in the study, so it’s not known if the medication would have any benefit for them. Nearly two-thirds of the U.S. population is fully vaccinated. The study found no additional benefit of the medication compared to the placebo in people who had detectable antibodies, presumably from a prior infection.
Animal studies found that the drug — which kills the virus by forcing it to make errors as it copies its genetic material inside cells — could disrupt bone formation. For that reason, the manufacturer and the FDA agreed that it should not be used in anyone younger than age 18.
Animal studies also indicated that the drug could cause birth defects. For that reason, the company said the drug shouldn’t be given to women who are pregnant or breastfeeding and said doctors should make sure women of childbearing age aren’t pregnant before taking the medication.
Some members of the panel felt that pregnant women and their doctors should be given the choice of whether or not to use the drug, given that pregnant women are at high risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes and infused therapies may not be available in all settings.
Other members of the committee said they were uncomfortable authorizing the drug given its potential to mutate the virus.
The drug, which forces the virus to mutate as it copies its RNA, eventually causes the virus to make so many errors in its genetic material that it can no longer make more of itself and the immune system clears it out of the body.
But it takes a few days to work — the drug is designed to be taken for 5 consecutive days -- and studies of the viral loads of patients taking the drug show that through the first 2 days, viral loads remain detectable as these mutations occur.
Studies by the FDA show some of those mutations in the spike protein are the same ones that have helped the virus become more transmissible and escape the protection of vaccines.
So the question is whether someone taking the medication could develop a dangerous mutation and then infect someone else, sparking the spread of a new variant.
Nicholas Kartsonis, MD, a vice president at Merck, said that the company was still analyzing data.
“Even if the probability is very low — 1 in 10,000 or 1 in 100,000 -- that this drug would induce an escape mutant for which the vaccines we have would not cover, that would be catastrophic for the whole world, actually,” said committee member James Hildreth, MD, an immunologist and president of Meharry Medical College, Nashville. “Do you have sufficient data on the likelihood of that happening?” he asked Dr. Kartsonis of Merck.
“So we don’t,” Dr. Kartsonis said.
He said, in theory, the risk of mutation with molnupiravir is the same as seen with the use of vaccines or monoclonal antibody therapies. Dr. Hildreth wasn’t satisfied with that answer.
“With all respect, the mechanism of your drug is to drive [genetic mutations], so it’s not the same as the vaccine. It’s not the same as monoclonal antibodies,” he said.
Dr. Hildreth later said he didn’t feel comfortable voting for authorization given the uncertainties around escape mutants. He voted no.
“It was an easy vote for me,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a panel of experts that advises the Food and Drug Administration on its regulatory decisions for these types of drugs.
The FDA’s Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted to authorize the drug molnupiravir, voting 13 to 10 to support emergency use, which requires a medication to meet a lower standard of evidence than does full approval.
The FDA is not bound by the committee’s vote but typically follows its advice.
If authorized by the agency, molnupiravir would be the first antiviral agent available as a pill to treat COVID-19. Other therapies to treat the infection are available — monoclonal antibodies and the drug remdesivir — but they are given by infusion.
The United Kingdom has already authorized the use of Merck’s drug.
“This was clearly a difficult decision,” said committee member Michael Green, MD, a pediatric infectious disease expert at the University of Pittsburg School of Medicine.
Green said he voted yes, and that the drug’s ability to prevent deaths in the study weighed heavily on his decision. He said given uncertainties around the drug both the company and FDA should keep a close eye on patients taking the drug going forward.
“Should an alternative oral agent become available that had a better safety profile and equal or better efficacy profile, the agency might reconsider its authorization,” he said.
Others didn’t agree that the drug should be allowed onto the market.
“I voted no,” said Jennifer Le, PharmD, a professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California. Dr. Le said the modest benefit of the medication didn’t outweigh all the potential safety issues. “I think I just need more efficacy and safety data,” she said.
Initial results from the first half of people enrolled in the clinical trial found the pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 50% in patients at higher risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
But later results, released just days before the meeting, showed that the drug’s effectiveness had dropped to about 30%.
In the updated analysis, 48 patients out of the 709 who were taking the drug were hospitalized or died within 29 days compared to 68 out of 699 who randomly got the placebo. There was one death in the group that got molnupiravir compared to nine in the placebo group. Nearly all those deaths occurred during the first phase of the study.
On Nov. 30 Merck explained that the drug’s efficacy appeared to fall, in part, because the placebo group had experienced fewer hospitalizations and deaths than expected during the second half of the study, making the drug look less beneficial by comparison.
The company said it wasn’t sure why patients in the placebo group had fared so much better in later trial enrollments.
“The efficacy of this product is not overwhelmingly good,” said committee member David Hardy, MD, an infectious disease expert at Charles Drew University School of Medicine in Los Angeles. “And I think that makes all of us a little uncomfortable about whether this is an advanced therapeutic because it’s an oral medication rather than an intravenous medication,” he said during the panel’s deliberations.
“I think we have to be very careful about how we’re going to allow people to use this,” Dr. Hardy said.
Many who voted for authorization thought use of the drug should be restricted to unvaccinated people who were at high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes, the same population enrolled in the clinical trial. People in the trial were considered at higher risk if they were over age 60, had cancer, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, were obese, or had heart disease or diabetes.
There are some significant limitations of the study that may affect how the drug is used. Vaccinated people couldn’t enroll in the study, so it’s not known if the medication would have any benefit for them. Nearly two-thirds of the U.S. population is fully vaccinated. The study found no additional benefit of the medication compared to the placebo in people who had detectable antibodies, presumably from a prior infection.
Animal studies found that the drug — which kills the virus by forcing it to make errors as it copies its genetic material inside cells — could disrupt bone formation. For that reason, the manufacturer and the FDA agreed that it should not be used in anyone younger than age 18.
Animal studies also indicated that the drug could cause birth defects. For that reason, the company said the drug shouldn’t be given to women who are pregnant or breastfeeding and said doctors should make sure women of childbearing age aren’t pregnant before taking the medication.
Some members of the panel felt that pregnant women and their doctors should be given the choice of whether or not to use the drug, given that pregnant women are at high risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes and infused therapies may not be available in all settings.
Other members of the committee said they were uncomfortable authorizing the drug given its potential to mutate the virus.
The drug, which forces the virus to mutate as it copies its RNA, eventually causes the virus to make so many errors in its genetic material that it can no longer make more of itself and the immune system clears it out of the body.
But it takes a few days to work — the drug is designed to be taken for 5 consecutive days -- and studies of the viral loads of patients taking the drug show that through the first 2 days, viral loads remain detectable as these mutations occur.
Studies by the FDA show some of those mutations in the spike protein are the same ones that have helped the virus become more transmissible and escape the protection of vaccines.
So the question is whether someone taking the medication could develop a dangerous mutation and then infect someone else, sparking the spread of a new variant.
Nicholas Kartsonis, MD, a vice president at Merck, said that the company was still analyzing data.
“Even if the probability is very low — 1 in 10,000 or 1 in 100,000 -- that this drug would induce an escape mutant for which the vaccines we have would not cover, that would be catastrophic for the whole world, actually,” said committee member James Hildreth, MD, an immunologist and president of Meharry Medical College, Nashville. “Do you have sufficient data on the likelihood of that happening?” he asked Dr. Kartsonis of Merck.
“So we don’t,” Dr. Kartsonis said.
He said, in theory, the risk of mutation with molnupiravir is the same as seen with the use of vaccines or monoclonal antibody therapies. Dr. Hildreth wasn’t satisfied with that answer.
“With all respect, the mechanism of your drug is to drive [genetic mutations], so it’s not the same as the vaccine. It’s not the same as monoclonal antibodies,” he said.
Dr. Hildreth later said he didn’t feel comfortable voting for authorization given the uncertainties around escape mutants. He voted no.
“It was an easy vote for me,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a panel of experts that advises the Food and Drug Administration on its regulatory decisions for these types of drugs.
The FDA’s Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted to authorize the drug molnupiravir, voting 13 to 10 to support emergency use, which requires a medication to meet a lower standard of evidence than does full approval.
The FDA is not bound by the committee’s vote but typically follows its advice.
If authorized by the agency, molnupiravir would be the first antiviral agent available as a pill to treat COVID-19. Other therapies to treat the infection are available — monoclonal antibodies and the drug remdesivir — but they are given by infusion.
The United Kingdom has already authorized the use of Merck’s drug.
“This was clearly a difficult decision,” said committee member Michael Green, MD, a pediatric infectious disease expert at the University of Pittsburg School of Medicine.
Green said he voted yes, and that the drug’s ability to prevent deaths in the study weighed heavily on his decision. He said given uncertainties around the drug both the company and FDA should keep a close eye on patients taking the drug going forward.
“Should an alternative oral agent become available that had a better safety profile and equal or better efficacy profile, the agency might reconsider its authorization,” he said.
Others didn’t agree that the drug should be allowed onto the market.
“I voted no,” said Jennifer Le, PharmD, a professor of clinical pharmacy at the University of California. Dr. Le said the modest benefit of the medication didn’t outweigh all the potential safety issues. “I think I just need more efficacy and safety data,” she said.
Initial results from the first half of people enrolled in the clinical trial found the pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 50% in patients at higher risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
But later results, released just days before the meeting, showed that the drug’s effectiveness had dropped to about 30%.
In the updated analysis, 48 patients out of the 709 who were taking the drug were hospitalized or died within 29 days compared to 68 out of 699 who randomly got the placebo. There was one death in the group that got molnupiravir compared to nine in the placebo group. Nearly all those deaths occurred during the first phase of the study.
On Nov. 30 Merck explained that the drug’s efficacy appeared to fall, in part, because the placebo group had experienced fewer hospitalizations and deaths than expected during the second half of the study, making the drug look less beneficial by comparison.
The company said it wasn’t sure why patients in the placebo group had fared so much better in later trial enrollments.
“The efficacy of this product is not overwhelmingly good,” said committee member David Hardy, MD, an infectious disease expert at Charles Drew University School of Medicine in Los Angeles. “And I think that makes all of us a little uncomfortable about whether this is an advanced therapeutic because it’s an oral medication rather than an intravenous medication,” he said during the panel’s deliberations.
“I think we have to be very careful about how we’re going to allow people to use this,” Dr. Hardy said.
Many who voted for authorization thought use of the drug should be restricted to unvaccinated people who were at high risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes, the same population enrolled in the clinical trial. People in the trial were considered at higher risk if they were over age 60, had cancer, chronic kidney disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, were obese, or had heart disease or diabetes.
There are some significant limitations of the study that may affect how the drug is used. Vaccinated people couldn’t enroll in the study, so it’s not known if the medication would have any benefit for them. Nearly two-thirds of the U.S. population is fully vaccinated. The study found no additional benefit of the medication compared to the placebo in people who had detectable antibodies, presumably from a prior infection.
Animal studies found that the drug — which kills the virus by forcing it to make errors as it copies its genetic material inside cells — could disrupt bone formation. For that reason, the manufacturer and the FDA agreed that it should not be used in anyone younger than age 18.
Animal studies also indicated that the drug could cause birth defects. For that reason, the company said the drug shouldn’t be given to women who are pregnant or breastfeeding and said doctors should make sure women of childbearing age aren’t pregnant before taking the medication.
Some members of the panel felt that pregnant women and their doctors should be given the choice of whether or not to use the drug, given that pregnant women are at high risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes and infused therapies may not be available in all settings.
Other members of the committee said they were uncomfortable authorizing the drug given its potential to mutate the virus.
The drug, which forces the virus to mutate as it copies its RNA, eventually causes the virus to make so many errors in its genetic material that it can no longer make more of itself and the immune system clears it out of the body.
But it takes a few days to work — the drug is designed to be taken for 5 consecutive days -- and studies of the viral loads of patients taking the drug show that through the first 2 days, viral loads remain detectable as these mutations occur.
Studies by the FDA show some of those mutations in the spike protein are the same ones that have helped the virus become more transmissible and escape the protection of vaccines.
So the question is whether someone taking the medication could develop a dangerous mutation and then infect someone else, sparking the spread of a new variant.
Nicholas Kartsonis, MD, a vice president at Merck, said that the company was still analyzing data.
“Even if the probability is very low — 1 in 10,000 or 1 in 100,000 -- that this drug would induce an escape mutant for which the vaccines we have would not cover, that would be catastrophic for the whole world, actually,” said committee member James Hildreth, MD, an immunologist and president of Meharry Medical College, Nashville. “Do you have sufficient data on the likelihood of that happening?” he asked Dr. Kartsonis of Merck.
“So we don’t,” Dr. Kartsonis said.
He said, in theory, the risk of mutation with molnupiravir is the same as seen with the use of vaccines or monoclonal antibody therapies. Dr. Hildreth wasn’t satisfied with that answer.
“With all respect, the mechanism of your drug is to drive [genetic mutations], so it’s not the same as the vaccine. It’s not the same as monoclonal antibodies,” he said.
Dr. Hildreth later said he didn’t feel comfortable voting for authorization given the uncertainties around escape mutants. He voted no.
“It was an easy vote for me,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We physicians must pull together as a knowledge community
The COVID-19 pandemic is a biosocial phenomenon. Patients and doctors alike find themselves assigned to groups designated as responsible and wise, or selfish and irrational, based strictly upon their personal assessments of medical risk. This trend in our culture is represented by threats of disciplinary action issued by medical regulators against physicians who are perceived to be undermining the public health message by spreading “misinformation.”
Our review of the literature reveals many references to “misinformation” but no definition narrow and precise enough to be interpreted consistently in a disciplinary environment. More pressing, this ambiguous word’s use is correlated with negative meaning and innuendo, often discrediting valuable information a priori without actual data points.
The most basic definition available is Merriam Webster’s: “incorrect or misleading information.” This definition includes no point of reference against which competing scientific claims can be measured.
Claudia E. Haupt, PhD, a political scientist and law professor, articulates a useful framework for understanding the relationship between medicine and state regulators. In the Yale Law Journal, Dr. Haupt wrote: “Knowledge communities have specialized expertise and are closest to those affected; they must have the freedom to work things out for themselves. The professions as knowledge communities have a fundamental interest in not having the state (or anyone else, for that matter) corrupt or distort what amounts to the state of the art in their respective fields.”
Injecting the artificial term “misinformation” into the science information ecosystem obfuscates and impedes the very ability of this vital knowledge community to perform its raison d’être. , rather than attending to healing or promoting progress.
Time has certainly shown us that science is anything but settled on all things COVID. If the scientific community accepts disrespect as the response of choice to difference of opinion and practice, we lose the trust in one another as colleagues; we need to keep scientific inquiry and exploration alive. Curiosity, equanimity, and tolerance are key components of the professional attitude as we deftly maneuver against the virus together.
In the face of deadly disease, it is especially imperative that intelligent, thoughtful, highly respected scientists, researchers, and physicians have room to safely share their knowledge and clinical experience. The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons has published a statement on scientific integrity that can be used as a measuring stick for claims about misinformation in medicine. We call on physicians to pull together as a knowledge community. Kindness and respect for patients starts with kindness and respect for one another as colleagues.
Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The COVID-19 pandemic is a biosocial phenomenon. Patients and doctors alike find themselves assigned to groups designated as responsible and wise, or selfish and irrational, based strictly upon their personal assessments of medical risk. This trend in our culture is represented by threats of disciplinary action issued by medical regulators against physicians who are perceived to be undermining the public health message by spreading “misinformation.”
Our review of the literature reveals many references to “misinformation” but no definition narrow and precise enough to be interpreted consistently in a disciplinary environment. More pressing, this ambiguous word’s use is correlated with negative meaning and innuendo, often discrediting valuable information a priori without actual data points.
The most basic definition available is Merriam Webster’s: “incorrect or misleading information.” This definition includes no point of reference against which competing scientific claims can be measured.
Claudia E. Haupt, PhD, a political scientist and law professor, articulates a useful framework for understanding the relationship between medicine and state regulators. In the Yale Law Journal, Dr. Haupt wrote: “Knowledge communities have specialized expertise and are closest to those affected; they must have the freedom to work things out for themselves. The professions as knowledge communities have a fundamental interest in not having the state (or anyone else, for that matter) corrupt or distort what amounts to the state of the art in their respective fields.”
Injecting the artificial term “misinformation” into the science information ecosystem obfuscates and impedes the very ability of this vital knowledge community to perform its raison d’être. , rather than attending to healing or promoting progress.
Time has certainly shown us that science is anything but settled on all things COVID. If the scientific community accepts disrespect as the response of choice to difference of opinion and practice, we lose the trust in one another as colleagues; we need to keep scientific inquiry and exploration alive. Curiosity, equanimity, and tolerance are key components of the professional attitude as we deftly maneuver against the virus together.
In the face of deadly disease, it is especially imperative that intelligent, thoughtful, highly respected scientists, researchers, and physicians have room to safely share their knowledge and clinical experience. The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons has published a statement on scientific integrity that can be used as a measuring stick for claims about misinformation in medicine. We call on physicians to pull together as a knowledge community. Kindness and respect for patients starts with kindness and respect for one another as colleagues.
Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
The COVID-19 pandemic is a biosocial phenomenon. Patients and doctors alike find themselves assigned to groups designated as responsible and wise, or selfish and irrational, based strictly upon their personal assessments of medical risk. This trend in our culture is represented by threats of disciplinary action issued by medical regulators against physicians who are perceived to be undermining the public health message by spreading “misinformation.”
Our review of the literature reveals many references to “misinformation” but no definition narrow and precise enough to be interpreted consistently in a disciplinary environment. More pressing, this ambiguous word’s use is correlated with negative meaning and innuendo, often discrediting valuable information a priori without actual data points.
The most basic definition available is Merriam Webster’s: “incorrect or misleading information.” This definition includes no point of reference against which competing scientific claims can be measured.
Claudia E. Haupt, PhD, a political scientist and law professor, articulates a useful framework for understanding the relationship between medicine and state regulators. In the Yale Law Journal, Dr. Haupt wrote: “Knowledge communities have specialized expertise and are closest to those affected; they must have the freedom to work things out for themselves. The professions as knowledge communities have a fundamental interest in not having the state (or anyone else, for that matter) corrupt or distort what amounts to the state of the art in their respective fields.”
Injecting the artificial term “misinformation” into the science information ecosystem obfuscates and impedes the very ability of this vital knowledge community to perform its raison d’être. , rather than attending to healing or promoting progress.
Time has certainly shown us that science is anything but settled on all things COVID. If the scientific community accepts disrespect as the response of choice to difference of opinion and practice, we lose the trust in one another as colleagues; we need to keep scientific inquiry and exploration alive. Curiosity, equanimity, and tolerance are key components of the professional attitude as we deftly maneuver against the virus together.
In the face of deadly disease, it is especially imperative that intelligent, thoughtful, highly respected scientists, researchers, and physicians have room to safely share their knowledge and clinical experience. The Association of American Physicians and Surgeons has published a statement on scientific integrity that can be used as a measuring stick for claims about misinformation in medicine. We call on physicians to pull together as a knowledge community. Kindness and respect for patients starts with kindness and respect for one another as colleagues.
Dr. Kohanski is in private practice in Somerset, N.J., and is a diplomate of the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. She disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emmons is part-time clinical associate professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and is a past chair of the Ethics Committee for the Vermont District Branch of the American Psychiatric Association. He is in private practice in Moretown, Vt., and disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Merck’s COVID-19 pill may be less effective than first hoped
According to an analysis by scientists at the Food and Drug Administration, the experimental pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death from COVID-19 by about 30%, compared to a placebo, and the pill showed no benefit for people with antibodies against COVID-19 from prior infection.
The updated analysis showed 48 hospitalizations or deaths among study participants who were randomly assigned to take the antiviral drug, compared to 68 among those who took a placebo.
Those results come from the full set of 1,433 patients who were randomized in the clinical trial, which just became available last week.
Initial results from the first 775 patients enrolled in the clinical trial, which were issued in a company news release in October, had said the drug cut the risk of hospitalization or death for patients at high risk of severe disease by about 50%.
Merck has been producing millions of doses of molnupiravir, which is the first antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 infections. The United Kingdom’s drug regulator authorized use of the medication in early November. The company said it expected to distribute the medication globally by the end of 2021.
In October, two Indian drug companies halted late-stage clinical trials of a generic version of molnupiravir after the studies failed to find any benefit to patients with moderate COVID-19. Trials in patients with milder symptoms are still ongoing.
On Nov. 27, the New England Journal of Medicine postponed its planned early release of the molnupiravir study results, citing “new information.”
The medication is designed to be given as four pills taken every 12 hours for 5 days. It’s most effective when taken within the first few days of new symptoms, something that requires convenient and affordable testing.
The new results seem to put molnupiravir far below the effectiveness of existing treatments.
The infused monoclonal antibody cocktail REGEN-COV, which the FDA has already authorized for emergency use, is about 85% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in patients who are at risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes, and it appears to be just as effective in people who already have antibodies against COVID-19, which is why it is being given to both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the FDA said.
In early November, Pfizer said its experimental antiviral pill Paxlovid cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 89%.
In briefing documents posted ahead of an advisory committee meeting Nov. 30, the FDA highlights other potential safety issues with the Merck drug, which works by causing the virus to make mistakes as it copies itself, eventually causing the virus to mutate itself to death.
The agency has asked the advisory committee to weigh in on the right patient population for the drug: Should pregnant women get it? Could the drug harm a developing fetus?
Should vaccinated people with breakthrough infections get it? Would it work for them? People with reduced immune function are more likely to get a breakthrough infection. They’re also more likely to shed virus for a longer period of time, making them perfect incubators for variants. What could happen if we give this type of patient a drug that increases mutations?
And what about mutations caused by the medication? Could they increase the potential for more variants? The agency concluded the risk of this happening was low.
In animal studies, the drug impacted bone formation. For this reason, the agency has agreed with the drug company that molnupiravir should not be given to anyone under the age of 18.
Aside from these concerns, the FDA says there were no major safety issues among people who took part in the clinical trial, though they acknowledge that number is small.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
According to an analysis by scientists at the Food and Drug Administration, the experimental pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death from COVID-19 by about 30%, compared to a placebo, and the pill showed no benefit for people with antibodies against COVID-19 from prior infection.
The updated analysis showed 48 hospitalizations or deaths among study participants who were randomly assigned to take the antiviral drug, compared to 68 among those who took a placebo.
Those results come from the full set of 1,433 patients who were randomized in the clinical trial, which just became available last week.
Initial results from the first 775 patients enrolled in the clinical trial, which were issued in a company news release in October, had said the drug cut the risk of hospitalization or death for patients at high risk of severe disease by about 50%.
Merck has been producing millions of doses of molnupiravir, which is the first antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 infections. The United Kingdom’s drug regulator authorized use of the medication in early November. The company said it expected to distribute the medication globally by the end of 2021.
In October, two Indian drug companies halted late-stage clinical trials of a generic version of molnupiravir after the studies failed to find any benefit to patients with moderate COVID-19. Trials in patients with milder symptoms are still ongoing.
On Nov. 27, the New England Journal of Medicine postponed its planned early release of the molnupiravir study results, citing “new information.”
The medication is designed to be given as four pills taken every 12 hours for 5 days. It’s most effective when taken within the first few days of new symptoms, something that requires convenient and affordable testing.
The new results seem to put molnupiravir far below the effectiveness of existing treatments.
The infused monoclonal antibody cocktail REGEN-COV, which the FDA has already authorized for emergency use, is about 85% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in patients who are at risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes, and it appears to be just as effective in people who already have antibodies against COVID-19, which is why it is being given to both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the FDA said.
In early November, Pfizer said its experimental antiviral pill Paxlovid cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 89%.
In briefing documents posted ahead of an advisory committee meeting Nov. 30, the FDA highlights other potential safety issues with the Merck drug, which works by causing the virus to make mistakes as it copies itself, eventually causing the virus to mutate itself to death.
The agency has asked the advisory committee to weigh in on the right patient population for the drug: Should pregnant women get it? Could the drug harm a developing fetus?
Should vaccinated people with breakthrough infections get it? Would it work for them? People with reduced immune function are more likely to get a breakthrough infection. They’re also more likely to shed virus for a longer period of time, making them perfect incubators for variants. What could happen if we give this type of patient a drug that increases mutations?
And what about mutations caused by the medication? Could they increase the potential for more variants? The agency concluded the risk of this happening was low.
In animal studies, the drug impacted bone formation. For this reason, the agency has agreed with the drug company that molnupiravir should not be given to anyone under the age of 18.
Aside from these concerns, the FDA says there were no major safety issues among people who took part in the clinical trial, though they acknowledge that number is small.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
According to an analysis by scientists at the Food and Drug Administration, the experimental pill cut the risk of hospitalization or death from COVID-19 by about 30%, compared to a placebo, and the pill showed no benefit for people with antibodies against COVID-19 from prior infection.
The updated analysis showed 48 hospitalizations or deaths among study participants who were randomly assigned to take the antiviral drug, compared to 68 among those who took a placebo.
Those results come from the full set of 1,433 patients who were randomized in the clinical trial, which just became available last week.
Initial results from the first 775 patients enrolled in the clinical trial, which were issued in a company news release in October, had said the drug cut the risk of hospitalization or death for patients at high risk of severe disease by about 50%.
Merck has been producing millions of doses of molnupiravir, which is the first antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 infections. The United Kingdom’s drug regulator authorized use of the medication in early November. The company said it expected to distribute the medication globally by the end of 2021.
In October, two Indian drug companies halted late-stage clinical trials of a generic version of molnupiravir after the studies failed to find any benefit to patients with moderate COVID-19. Trials in patients with milder symptoms are still ongoing.
On Nov. 27, the New England Journal of Medicine postponed its planned early release of the molnupiravir study results, citing “new information.”
The medication is designed to be given as four pills taken every 12 hours for 5 days. It’s most effective when taken within the first few days of new symptoms, something that requires convenient and affordable testing.
The new results seem to put molnupiravir far below the effectiveness of existing treatments.
The infused monoclonal antibody cocktail REGEN-COV, which the FDA has already authorized for emergency use, is about 85% effective at preventing hospitalization or death in patients who are at risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes, and it appears to be just as effective in people who already have antibodies against COVID-19, which is why it is being given to both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients, the FDA said.
In early November, Pfizer said its experimental antiviral pill Paxlovid cut the risk of hospitalization or death by 89%.
In briefing documents posted ahead of an advisory committee meeting Nov. 30, the FDA highlights other potential safety issues with the Merck drug, which works by causing the virus to make mistakes as it copies itself, eventually causing the virus to mutate itself to death.
The agency has asked the advisory committee to weigh in on the right patient population for the drug: Should pregnant women get it? Could the drug harm a developing fetus?
Should vaccinated people with breakthrough infections get it? Would it work for them? People with reduced immune function are more likely to get a breakthrough infection. They’re also more likely to shed virus for a longer period of time, making them perfect incubators for variants. What could happen if we give this type of patient a drug that increases mutations?
And what about mutations caused by the medication? Could they increase the potential for more variants? The agency concluded the risk of this happening was low.
In animal studies, the drug impacted bone formation. For this reason, the agency has agreed with the drug company that molnupiravir should not be given to anyone under the age of 18.
Aside from these concerns, the FDA says there were no major safety issues among people who took part in the clinical trial, though they acknowledge that number is small.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Multiple Lesions With Recurrent Bleeding
The Diagnosis: Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS), also known as Gorlin syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder that increases the risk for developing various carcinomas and affects multiple organ systems. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is estimated at 1 per 40,000 to 60,000 individuals with no sexual predilection.1,2 Pathogenesis of NBCCS occurs through molecular alterations in the dormant hedgehog signaling pathway, causing constitutive signaling activity and a loss of function in the tumor suppressor patched 1 gene, PTCH1. As a result, the inhibition of smoothened oncogenes is released, Gli proteins are activated, and the hedgehog signaling pathway is no longer quiescent.2 Additional loss of function in the suppressor of fused homolog protein, a negative regulator of the hedgehog pathway, allows for further tumor proliferation. The crucial role these genes play in the hedgehog signaling pathway and their mutation association with NBCCS allows for molecular confirmation in the diagnosis of NBCCS. Allelic losses at the PTCH1 gene site are thought to occur in approximately 70% of NBCCS patients.2
Diagnosis of NBCCS is based on genetic testing to examine pathogenic gene variants, notably in the PTCH1 gene, and identification of characteristic clinical findings.2 Diagnosis of NBCCS requires either 2 minor suggestive criteria and 1 major suggestive criterion, 2 major suggestive criteria and 1 minor suggestive criterion, or 1 major suggestive criterion with molecular confirmation. The presence of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) before 20 years of age or an excessive numbers of BCCs, keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KOTs), palmar or plantar pitting, and first-degree relatives with NBCCS are classified as major suggestive criteria.2 Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients typically have BCCs that crust, ulcerate, or bleed. Minor suggestive criteria for NBCCS are rib abnormalities, skeletal malformations, macrocephaly, cleft lip or palate, and desmoplastic medulloblastoma.2-4 Suppressor of fused homolog protein mutations may increase the risk for desmoplastic medulloblastoma in NBCCS patients. Our patient had 4 of the major suggestive criteria, including a history of KOTs, multiple BCCs, first-degree relatives with NBCCS, and palmar or plantar pitting (bottom quiz image), while having 1 minor suggestive criterion of frontal bossing.
Patients with NBCCS have high phenotypic variability, as their skin carcinomas do not have the classic features of pearly surfaces or corkscrew telangiectasia that typically are associated with BCCs.1 Basal cell carcinomas in NBCCS-affected individuals usually are indistinguishable from sporadic lesions that arise in sun-exposed areas, making NBCCS difficult to diagnose. These sporadic lesions often are misdiagnosed as psoriatic or eczematous lesions, and additional subsequent examination is required. The findings of multiple papules and plaques spanning the body as well as lesions with rolled borders and ulcerated bases, indicative of BCCs, aid dermatologists in distinguishing benign lesions from those of NBCCS.1
Additional differential diagnoses are required to distinguish NBCCS from other similar inherited skin disorders that are characterized by BCCs. The presence of multiple incidental BCCs early in life remains a histopathologic clue for NBCCS diagnosis, as opposed to Rombo syndrome, in which BCCs often develop in adulthood.2,4 In addition, although both Bazex syndrome and Muir-Torre syndrome are characterized by the early onset of BCCs, the lack of skeletal abnormalities and palmar and plantar pitting distinguish these entities from NBCCS.2,4 Furthermore, though psoriasis also can present on the scalp, clinical presentation often includes well-demarcated and symmetric plaques that are erythematous and silvery, all of which were not present in our patient and typically are not seen in NBCCS.5
The recommended treatment of NBCCS is vismodegib, a specific oncogene inhibitor. This medication suppresses the hedgehog signaling pathway by inhibiting smoothened oncogenes and downstream target molecules, thereby decreasing tumor proliferation.6 In doing so, vismodegib inhibits the development of new BCCs while reducing the burden of present ones. Additionally, vismodegib appears to effectively treat KOTs. If successful, this medication may be able to suppress KOTs in patients with NBCCS and thus facilitate surgery.6 Additional hedgehog inhibitors include patidegib, sonidegib, and itraconazole. Patidegib gel 2% currently is in phase 3 clinical trials for evaluation of efficacy and safety in treatment of NBCCS. Sonidegib is approved for the treatment of locally advanced BCCs in the United States and the European Union and for both locally advanced BCCs and metastatic BCCs in Switzerland and Australia.7 Further research is needed before recommending antifungal itraconazole for NBCCS clinical use.8 Other medications for localized areas include topical application of 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod.2
- Sangehra R, Grewal P. Gorlin syndrome presentation and the importance of differential diagnosis of skin cancer: a case report. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21:222-224.
- Bresler S, Padwa B, Granter S. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). Head Neck Pathol. 2016;10:119-124.
- Fujii K, Miyashita T. Gorlin syndrome (nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome): update and literature review. Pediatr Int. 2014;56:667-674.
- Evans G, Farndon P. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. GeneReviews [Internet]. University of Washington; 1993-2020.
- Kim WB, Jerome D, Yeung J. Diagnosis and management of psoriasis. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:278-285.
- Booms P, Harth M, Sader R, et al. Vismodegib hedgehog-signaling inhibition and treatment of basal cell carcinomas as well as keratocystic odontogenic tumors in Gorlin syndrome. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5:14-19.
- Gutzmer R, Soloon J. Hedgehog pathway inhibition for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Target Oncol. 2019;14:253-267.
- Leavitt E, Lask G, Martin S. Sonic hedgehog pathway inhibition in the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:84.
The Diagnosis: Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS), also known as Gorlin syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder that increases the risk for developing various carcinomas and affects multiple organ systems. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is estimated at 1 per 40,000 to 60,000 individuals with no sexual predilection.1,2 Pathogenesis of NBCCS occurs through molecular alterations in the dormant hedgehog signaling pathway, causing constitutive signaling activity and a loss of function in the tumor suppressor patched 1 gene, PTCH1. As a result, the inhibition of smoothened oncogenes is released, Gli proteins are activated, and the hedgehog signaling pathway is no longer quiescent.2 Additional loss of function in the suppressor of fused homolog protein, a negative regulator of the hedgehog pathway, allows for further tumor proliferation. The crucial role these genes play in the hedgehog signaling pathway and their mutation association with NBCCS allows for molecular confirmation in the diagnosis of NBCCS. Allelic losses at the PTCH1 gene site are thought to occur in approximately 70% of NBCCS patients.2
Diagnosis of NBCCS is based on genetic testing to examine pathogenic gene variants, notably in the PTCH1 gene, and identification of characteristic clinical findings.2 Diagnosis of NBCCS requires either 2 minor suggestive criteria and 1 major suggestive criterion, 2 major suggestive criteria and 1 minor suggestive criterion, or 1 major suggestive criterion with molecular confirmation. The presence of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) before 20 years of age or an excessive numbers of BCCs, keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KOTs), palmar or plantar pitting, and first-degree relatives with NBCCS are classified as major suggestive criteria.2 Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients typically have BCCs that crust, ulcerate, or bleed. Minor suggestive criteria for NBCCS are rib abnormalities, skeletal malformations, macrocephaly, cleft lip or palate, and desmoplastic medulloblastoma.2-4 Suppressor of fused homolog protein mutations may increase the risk for desmoplastic medulloblastoma in NBCCS patients. Our patient had 4 of the major suggestive criteria, including a history of KOTs, multiple BCCs, first-degree relatives with NBCCS, and palmar or plantar pitting (bottom quiz image), while having 1 minor suggestive criterion of frontal bossing.
Patients with NBCCS have high phenotypic variability, as their skin carcinomas do not have the classic features of pearly surfaces or corkscrew telangiectasia that typically are associated with BCCs.1 Basal cell carcinomas in NBCCS-affected individuals usually are indistinguishable from sporadic lesions that arise in sun-exposed areas, making NBCCS difficult to diagnose. These sporadic lesions often are misdiagnosed as psoriatic or eczematous lesions, and additional subsequent examination is required. The findings of multiple papules and plaques spanning the body as well as lesions with rolled borders and ulcerated bases, indicative of BCCs, aid dermatologists in distinguishing benign lesions from those of NBCCS.1
Additional differential diagnoses are required to distinguish NBCCS from other similar inherited skin disorders that are characterized by BCCs. The presence of multiple incidental BCCs early in life remains a histopathologic clue for NBCCS diagnosis, as opposed to Rombo syndrome, in which BCCs often develop in adulthood.2,4 In addition, although both Bazex syndrome and Muir-Torre syndrome are characterized by the early onset of BCCs, the lack of skeletal abnormalities and palmar and plantar pitting distinguish these entities from NBCCS.2,4 Furthermore, though psoriasis also can present on the scalp, clinical presentation often includes well-demarcated and symmetric plaques that are erythematous and silvery, all of which were not present in our patient and typically are not seen in NBCCS.5
The recommended treatment of NBCCS is vismodegib, a specific oncogene inhibitor. This medication suppresses the hedgehog signaling pathway by inhibiting smoothened oncogenes and downstream target molecules, thereby decreasing tumor proliferation.6 In doing so, vismodegib inhibits the development of new BCCs while reducing the burden of present ones. Additionally, vismodegib appears to effectively treat KOTs. If successful, this medication may be able to suppress KOTs in patients with NBCCS and thus facilitate surgery.6 Additional hedgehog inhibitors include patidegib, sonidegib, and itraconazole. Patidegib gel 2% currently is in phase 3 clinical trials for evaluation of efficacy and safety in treatment of NBCCS. Sonidegib is approved for the treatment of locally advanced BCCs in the United States and the European Union and for both locally advanced BCCs and metastatic BCCs in Switzerland and Australia.7 Further research is needed before recommending antifungal itraconazole for NBCCS clinical use.8 Other medications for localized areas include topical application of 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod.2
The Diagnosis: Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS), also known as Gorlin syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder that increases the risk for developing various carcinomas and affects multiple organ systems. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is estimated at 1 per 40,000 to 60,000 individuals with no sexual predilection.1,2 Pathogenesis of NBCCS occurs through molecular alterations in the dormant hedgehog signaling pathway, causing constitutive signaling activity and a loss of function in the tumor suppressor patched 1 gene, PTCH1. As a result, the inhibition of smoothened oncogenes is released, Gli proteins are activated, and the hedgehog signaling pathway is no longer quiescent.2 Additional loss of function in the suppressor of fused homolog protein, a negative regulator of the hedgehog pathway, allows for further tumor proliferation. The crucial role these genes play in the hedgehog signaling pathway and their mutation association with NBCCS allows for molecular confirmation in the diagnosis of NBCCS. Allelic losses at the PTCH1 gene site are thought to occur in approximately 70% of NBCCS patients.2
Diagnosis of NBCCS is based on genetic testing to examine pathogenic gene variants, notably in the PTCH1 gene, and identification of characteristic clinical findings.2 Diagnosis of NBCCS requires either 2 minor suggestive criteria and 1 major suggestive criterion, 2 major suggestive criteria and 1 minor suggestive criterion, or 1 major suggestive criterion with molecular confirmation. The presence of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) before 20 years of age or an excessive numbers of BCCs, keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KOTs), palmar or plantar pitting, and first-degree relatives with NBCCS are classified as major suggestive criteria.2 Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients typically have BCCs that crust, ulcerate, or bleed. Minor suggestive criteria for NBCCS are rib abnormalities, skeletal malformations, macrocephaly, cleft lip or palate, and desmoplastic medulloblastoma.2-4 Suppressor of fused homolog protein mutations may increase the risk for desmoplastic medulloblastoma in NBCCS patients. Our patient had 4 of the major suggestive criteria, including a history of KOTs, multiple BCCs, first-degree relatives with NBCCS, and palmar or plantar pitting (bottom quiz image), while having 1 minor suggestive criterion of frontal bossing.
Patients with NBCCS have high phenotypic variability, as their skin carcinomas do not have the classic features of pearly surfaces or corkscrew telangiectasia that typically are associated with BCCs.1 Basal cell carcinomas in NBCCS-affected individuals usually are indistinguishable from sporadic lesions that arise in sun-exposed areas, making NBCCS difficult to diagnose. These sporadic lesions often are misdiagnosed as psoriatic or eczematous lesions, and additional subsequent examination is required. The findings of multiple papules and plaques spanning the body as well as lesions with rolled borders and ulcerated bases, indicative of BCCs, aid dermatologists in distinguishing benign lesions from those of NBCCS.1
Additional differential diagnoses are required to distinguish NBCCS from other similar inherited skin disorders that are characterized by BCCs. The presence of multiple incidental BCCs early in life remains a histopathologic clue for NBCCS diagnosis, as opposed to Rombo syndrome, in which BCCs often develop in adulthood.2,4 In addition, although both Bazex syndrome and Muir-Torre syndrome are characterized by the early onset of BCCs, the lack of skeletal abnormalities and palmar and plantar pitting distinguish these entities from NBCCS.2,4 Furthermore, though psoriasis also can present on the scalp, clinical presentation often includes well-demarcated and symmetric plaques that are erythematous and silvery, all of which were not present in our patient and typically are not seen in NBCCS.5
The recommended treatment of NBCCS is vismodegib, a specific oncogene inhibitor. This medication suppresses the hedgehog signaling pathway by inhibiting smoothened oncogenes and downstream target molecules, thereby decreasing tumor proliferation.6 In doing so, vismodegib inhibits the development of new BCCs while reducing the burden of present ones. Additionally, vismodegib appears to effectively treat KOTs. If successful, this medication may be able to suppress KOTs in patients with NBCCS and thus facilitate surgery.6 Additional hedgehog inhibitors include patidegib, sonidegib, and itraconazole. Patidegib gel 2% currently is in phase 3 clinical trials for evaluation of efficacy and safety in treatment of NBCCS. Sonidegib is approved for the treatment of locally advanced BCCs in the United States and the European Union and for both locally advanced BCCs and metastatic BCCs in Switzerland and Australia.7 Further research is needed before recommending antifungal itraconazole for NBCCS clinical use.8 Other medications for localized areas include topical application of 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod.2
- Sangehra R, Grewal P. Gorlin syndrome presentation and the importance of differential diagnosis of skin cancer: a case report. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21:222-224.
- Bresler S, Padwa B, Granter S. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). Head Neck Pathol. 2016;10:119-124.
- Fujii K, Miyashita T. Gorlin syndrome (nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome): update and literature review. Pediatr Int. 2014;56:667-674.
- Evans G, Farndon P. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. GeneReviews [Internet]. University of Washington; 1993-2020.
- Kim WB, Jerome D, Yeung J. Diagnosis and management of psoriasis. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:278-285.
- Booms P, Harth M, Sader R, et al. Vismodegib hedgehog-signaling inhibition and treatment of basal cell carcinomas as well as keratocystic odontogenic tumors in Gorlin syndrome. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5:14-19.
- Gutzmer R, Soloon J. Hedgehog pathway inhibition for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Target Oncol. 2019;14:253-267.
- Leavitt E, Lask G, Martin S. Sonic hedgehog pathway inhibition in the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:84.
- Sangehra R, Grewal P. Gorlin syndrome presentation and the importance of differential diagnosis of skin cancer: a case report. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21:222-224.
- Bresler S, Padwa B, Granter S. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). Head Neck Pathol. 2016;10:119-124.
- Fujii K, Miyashita T. Gorlin syndrome (nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome): update and literature review. Pediatr Int. 2014;56:667-674.
- Evans G, Farndon P. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. GeneReviews [Internet]. University of Washington; 1993-2020.
- Kim WB, Jerome D, Yeung J. Diagnosis and management of psoriasis. Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:278-285.
- Booms P, Harth M, Sader R, et al. Vismodegib hedgehog-signaling inhibition and treatment of basal cell carcinomas as well as keratocystic odontogenic tumors in Gorlin syndrome. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5:14-19.
- Gutzmer R, Soloon J. Hedgehog pathway inhibition for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Target Oncol. 2019;14:253-267.
- Leavitt E, Lask G, Martin S. Sonic hedgehog pathway inhibition in the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:84.

A 63-year-old man with frontal bossing and a history of jaw cysts presented with numerous lesions on the scalp, trunk, and legs with recurrent bleeding. Both of his siblings had similar findings. Many lesions had been present for at least 40 years. Physical examination revealed a large, irregular, atrophic, hyperpigmented plaque on the central scalp with multiple translucent hyperpigmented papules at the periphery (top). Similar papules and plaques were present at the temples, around the waist, and on the distal lower extremities, leading to surgical excision of the largest leg lesions. In addition, there were many pinpoint pits on both palms (bottom). A biopsy was submitted for review, which confirmed basal cell carcinomas on the scalp.