User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Botanical Briefs: Tulipalin A
Cutaneous Manifestations
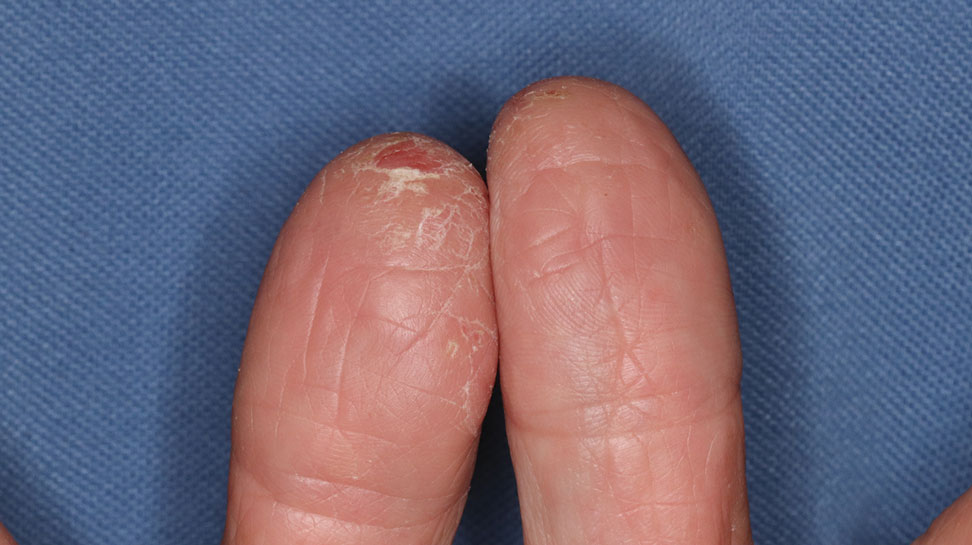
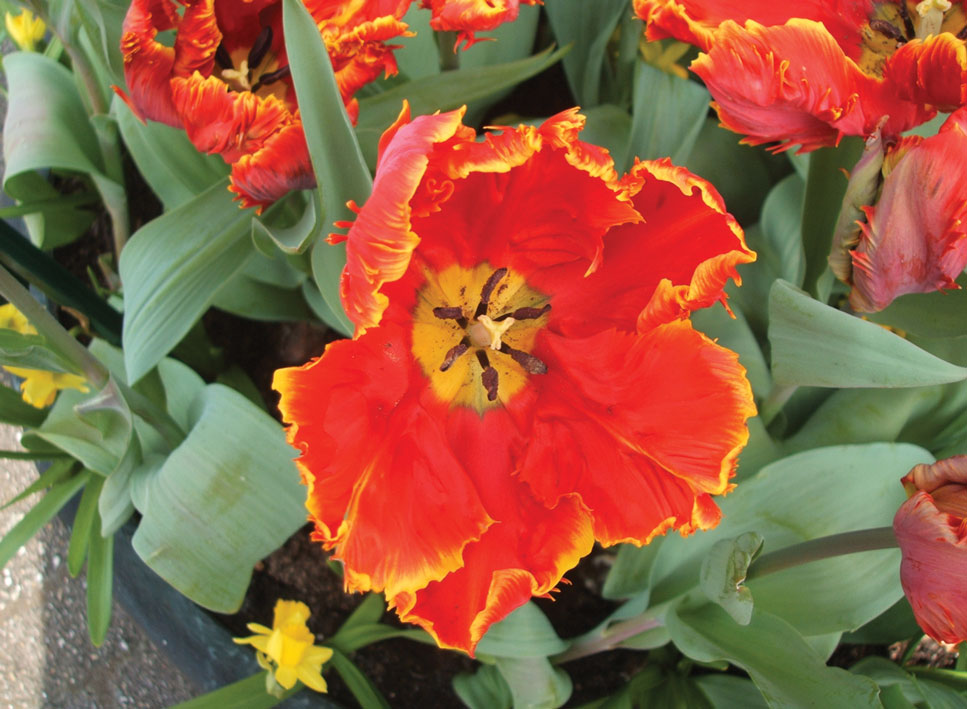
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
Cutaneous Manifestations
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
Cutaneous Manifestations
Contact dermatitis is a common problem for individuals who work in the floral industry. Hand dermatitis has been reported in as many as 26% of floral employees.1Tulipa species have been identified as one of the most common causes of hand dermatitis. Tulipalin A (α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone) is the main sensitizer in tulips (Figure 1) and its precursor tuliposide A also occurs both in tulips and the Peruvian lily (Alstroemeria).

In a 1996 study, 18% (9/51) of tulip workers were found to be allergic to tulipalin A.2 In a more recent study of 164 tulip workers, 48 (29.3%) had clinical evidence of contact dermatitis and subsequently underwent patch testing; 17 (35.4%) showed a positive reaction to either tulipalin A or to tulip-bulb extract.3 Itching was the most common symptom (39 workers [81.3%]) and hand eczema at the tip of the thumb and index finger was the most common finding. In 9 (18.8%) workers, eczema had spread to other body parts including the forearm, face, legs, and abdomen.3
Peruvian lily is widely used in floral arrangements and has become a leading cause of hand dermatitis in florists (Figure 2). Large amounts of free tulipalin A are present in bulb scales of tulips, along with a small amount of tuliposide A. In young developing shoots, the situation is reversed: Both compounds are found in all parts of the plant to some degree, though tulipalin A is the major allergen, and more mature parts of the plant and bulb are most allergenic.

Cultural Considerations
In traditional Kurdish cuisine, raw herbs are part of snacking or are served as a side dish (sawza). Snacks often are consumed raw on the spot. Tulipa montana, Tulipa armena, and possibly other Tulipa species are consumed as a snack.4 Traditionally, Tulipa systola is consumed by the Kurds as an anti-inflammatory medicine and for pain relief. It also has been proposed that T systola has antioxidant properties.5 Cooked tulip also has been consumed in time of famine in Europe, though none of these dietary practices are recommended.4
Clinical Presentation
“Tulip fingers” describes the most common presentation of contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. Erythematous scaling plaques are seen in the periungual skin and first and second fingertips of the dominant hand. Other manifestations include diffuse dry dermatitis of the hand; paronychia; pulpitis; and secondary spread to the face, neck, arms, and genitalia, with eczematous papules and plaques.6 Clinical signs include erythema, vesicles, hyperkeratosis, and exfoliation of the fingertips. The allergen also can cause airborne contact dermatitis and manifest as conjunctivitis, rhinitis, and asthma.2 A considerable number of tulip workers develop paresthesia and tenderness in the fingertips within several hours after working with tulip bulbs, known as “tulip fire.”7
Plant Facts
There are approximately 250 genera of bulbous plants. Tulips are members of the genus Tulipa and family Liliaceae. Tulips often are thought of as native to southwest central Asia and Turkey8; however, Tulipa sylvestris is native to Portugal, Spain, and North Africa.
Etymology and Symbolism—The word tulip is derived from the Turkish word türbent meaning a turban, possibly because the flower is compared to turbans worn by men of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. In Turkish culture, the tulip is a symbol of paradise on earth and can have divine status. In the Netherlands, on the other hand, the tulip represents the briefness of life.
History—By 1562, tulip bulbs had already been introduced to Holland by merchants. However, the first shipment of tulip bulbs was mistaken by the Dutch for onions and were either roasted over a fire or perished when planted in gardens with vegetables. Carolus Clusius—botanist, director of the imperial medical garden in Vienna and recipient of many plants through diplomatic channels—was particularly fond of flower bulbs and contributed to the popularity of the tulip in Europe by sending bulbs and seeds to other European countries.
In the early 17th century, the tulip craze began in France, fueled by a viral disease of tulips that produced variegated color patterns on the petals; entire properties were sold in exchange for a single tulip bulb. The tulip craze drifted from France to Holland in 1634 for 3 years before the tulip market collapsed.
More recently, in 2003 investors started a multimillion-euro tulip fund in the Netherlands to develop new varieties of tulip. Tulip bulbs were used to create money with high percentages over the selling price. With exorbitant pricing and ever-changing ownership of bulbs—bulbs were bought and sold as many as 10 times—the tulip fund collapsed 1 year later and investors lost their money. Bulb speculators then took their profit abroad. In 2006, bulb owners were charged with fraud; the tulip craze often is cited as one of the early major stock market collapses.
Tulips continue to grow in popularity. Today, nearly 6000 cultivars are registered, with 40 new cultivars registered every 5 years.9
Identifying Features
At the base of the erect tulip plant is a cluster of 2 or 3 thick bluish-green leaves. Three petals and 3 sepals make up the solitary bell-shaped flower. Many tulips can propagate only by means of their scaly bulbs. The flowers arise from the tips of stems in different solid colors, except true blue—from pure white to all shades of yellow, red, and a deep purple that is almost black. Solid-color tulips are called “self-colored.” So-called broken tulips are individual flowers with multiple colors, a condition caused by a viral disease transmitted by aphids.10
Tulip Allergen
Tuliposide A is found in many species of the genera Tulipa, Alstroemeria, and Erythronium.6 So far, 7 analogs have been identified: 1-tuliposide A and B; 6-tuliposide A and B; and tuliposides D, E, and F. 6-Tuliposide A and B are the principal tuliposides found in tulip cultivars.11 With trauma and maturation, tuliposides A and B are hydrolyzed to tulipalin A and tulipalin B, respectively.
Tulipalin A and tulipalin B have antimicrobial properties against bacteria and fungi; tulipalin A is mostly an antifungal agent, and tulipalin B has mostly bacteriostatic characteristics.12 The highest concentration of tulipalin A is found in the outer layer of the bulb, followed by (in descending order) the stem, leaves, and petals.13
The prevalence of tulipalin A allergy led the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment to assign tuliposide A and tulipalin A to category B, which is a “solid-based indication for contact allergenic effects”; both chemicals also are considered skin sensitizers, defined by the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals of the United Nations as a substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.14 Patients who are allergic to tulips have cross-sensitivity to Alstroemeria because tuliposide A and its metabolites are found in both plants.15
Symptoms of an allergic response to tulipalin A can be immediate or delayed.14 The most common allergic contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs is type IV hypersensitivity, though type I reactions can occur. Symptoms of a type I reaction including contact urticaria, rhinitis, hoarseness, and dyspnea have been reported.14
The variety of tulip handled also contributes to the severity of dermatitis. Handling bulbs of Rose Copeland variety tulips and cutting the flowers of Preludium tulips have been associated with more severe allergic dermatitis presentations, whereas the Red Emperor tulip was found to have less tuliposide A and thus provoke a weaker patch-test reaction.7
A Word About Garlic—Garlic is in the subfamily Allioideae (formerly Alliaceae) taxonomically related to the tulip family (Liliaceae). Garlic also can cause hand dermatitis in cooks, with a similar clinical appearance as tulip fingers. Gas chromatography has shown that garlic contains predominantly tuliposide B, which has been found to be much less allergenic than tuliposide A.7,16
Prevention of Tulipa Dermatitis
Tuliposide A and its metabolites can be found in storehouses and trucks used to transport tulips, in clothing, and in any other place where dust containing the allergen has settled. The best prevention against contact dermatitis is to avoid the inciting plants. Gloves may prevent contact dermatitis due to tuliposide A, which penetrates vinyl but not nitrile gloves. Barrier creams have been proposed, but data are scant.1
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
- Thiboutot DM, Hamory BH, Marks JG Jr. Dermatoses among floral shop workers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990;22:54-58. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70007-5
- Bruze M, Bjorkner B, Hellstrom AC. Occupational dermatoses in nursery workers. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:100-103.
- Hassan I, Rasool F, Akhtar S, et al. Contact dermatitis caused by tulips: identification of contact sensitizers in tulip works of Kashmir Valley in North India. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:64-69. doi:10.1111/cod.12870
- Pieroni A, Zahir H, Amin HI, et al. Where tulips and crocuses are popular food snacks: Kurdish traditional foraging reveals traces of mobile pastoralism in Southern Iraqi Kurdistan. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2019;15:59. doi:10.1186/s13002-019-0341-0
- Amin HIM, Ibrahim MF, Hussain FHS, et al. Phytochemistry and ethnopharmacology of some medicine plants used in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. Nat Prod Commun. 2016;11:291-296.
- Crawford GH. Botanical dermatology [Plant identification – other families: Liliaceae]. Medscape. Updated June 10, 2021. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1090097-overview#a3
- Gette MT, Marks JE Jr. Tulip fingers. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:203-205.
- Bruynzeel DP. Bulb dermatitis: dermatological problems in the flower bulb industries. Contact Dermatitis. 1997;37:70-77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1997.tb00042.x
- Christenhusz MJ, Govaerts RHA, David J, et al. Tiptoe through the tulips—cultural history, molecular phylogenetics and classification of Tulipa (Liliaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2013;172:280-328. doi:10.1111/boj.12061
- The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. Tulip. Encyclopedia Britannica. Updated July 4, 2022. Accessed August 18, 2022. https://www.britannica.com/plant/tulip
- Hausen BM. Airborne contact dermatitis caused by tulip bulbs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982;7:500-503. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70132-x
- Nomura T, Ogita S, Kato Y. A novel lactone-forming carboxylesterase: molecular identification of a tuliposide A-converting enzyme in tulip. Plant Physiol. 2012;159:565-578. doi:10.1104/pp.112.195388
- Khalid MM, Greenberg MI. Tulip finger. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018; 56:860. doi:10.1080/15563650.2018.1440588
- McCluskey J, Bourgeois M, Harbison R. Tulipalin A induced phytotoxicity. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:181-183. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134187
- Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis to Alstroemeria. Arch Dermatol. 1988;124:914-916.
- Sasseville D. Clinical patterns of phytodermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2009;27:299-308. doi:10.1016/j.det.2009.05.010
Practice Points
- Tulips are a common cause of contact dermatitis among floral workers.
- Tulipalin A is the primary sensitizer in tulips causing allergic contact dermatitis.
- The best preventative for tulip contact dermatitis is avoiding the inciting plants.
Disparities of Cutaneous Malignancies in the US Military
Occupational sun exposure is a well-known risk factor for the development of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). In addition to sun exposure, US military personnel may face other risk factors such as lack of access to adequate sun protection, work in equatorial latitudes, and increased exposure to carcinogens. In one study, fewer than 30% of surveyed soldiers reported regular sunscreen use during deployment and reported the face, neck, and upper extremities were unprotected at least 70% of the time.1 Skin cancer risk factors that are more common in military service members include inadequate sunscreen access, insufficient sun protection, harsh weather conditions, more immediate safety concerns than sun protection, and male gender. A higher incidence of melanoma and NMSC has been correlated with the more common demographics of US veterans such as male sex, older age, and White race.2
Although not uncommon in both civilian and military populations, we present the case of a military service member who developed skin cancer at an early age potentially due to occupational sun exposure. We also provide a review of the literature to examine the risk factors and incidence of melanoma and NMSC in US military personnel and veterans and provide recommendations for skin cancer prevention, screening, and intervention in the military population.
Case Report
A 37-year-old White active-duty male service member in the US Navy (USN) presented with a nonhealing lesion on the nose of 2 years’ duration that had been gradually growing and bleeding for several weeks. He participated in several sea deployments while onboard a naval destroyer over his 10-year military career. He did not routinely use sunscreen during his deployments. His personal and family medical history lacked risk factors for skin cancer other than his skin tone and frequent sun exposure.
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm ulcerated plaque with rolled borders and prominent telangiectases on the mid nasal dorsum. A shave biopsy was performed to confirm the diagnosis of nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery, which required repair with an advancement flap. He currently continues his active-duty service and is preparing for his next overseas deployment.
Literature Review
We conducted a review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms skin cancer, melanoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, or sebaceous carcinoma along with military, Army, Navy, Air Force, or veterans. Studies from January 1984 to April 2020 were included in our qualitative review. All articles were reviewed, and those that did not examine skin cancer and the military population in the United States were excluded. Relevant data, such as results of skin cancer incidence or risk factors or insights about developing skin cancer in this affected population, were extracted from the selected publications.
Several studies showed overall increased age-adjusted incidence rates of melanoma and NMSC among military service personnel compared to age-matched controls in the general population.2 A survey of draft-age men during World War II found a slightly higher percentage of respondents with history of melanoma compared to the control group (83% [74/89] vs 76% [49/65]). Of those who had a history of melanoma, 34% (30/89) served in the tropics compared to 6% (4/65) in the control group.3 A tumor registry review found the age-adjusted melanoma incidence rates per 100,000 person-years for White individuals in the military vs the general population was 33.6 vs 27.5 among those aged 45 to 49 years, 49.8 vs 32.2 among those aged 50 to 54 years, and 178.5 vs 39.2 among those aged 55 to 59 years.4 Among published literature reviews, members of the US Air Force (USAF) had the highest rates of melanoma compared to other military branches, with an incidence rate of 7.6 vs 6.3 among USAF males vs Army males and 9.0 vs 5.5 among USAF females vs Army females.4 These findings were further supported by another study showing a higher incidence rate of melanoma in USAF members compared to Army personnel (17.8 vs 9.5) and a 62% greater melanoma incidence in active-duty military personnel compared to the general population when adjusted for age, race, sex, and year of diagnosis.5 Additionally, a meta-analysis reported a standardized incidence ratio of 1.4 (95% CI, 1.1-1.9) for malignant melanoma and 1.8 (95% CI, 1.3-2.8) for NMSC among military pilots compared to the general population.6 It is important to note that these data are limited to published peer-reviewed studies within PubMed and may not reflect the true skin cancer incidence.
More comprehensive studies are needed to compare NMSC incidence rates in nonpilot military populations compared to the general population. From 2005 to 2014, the average annual NMSC incidence rate in the USAF was 64.4 per 100,000 person-years, with the highest rate at 97.4 per 100,000 person-years in 2007.7 However, this study did not directly compare military service members to the general population. Service in tropical environments among World War II veterans was associated with an increased risk for NMSC. Sixty-six percent of patients with BCC (n=197) and 68% with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)(n=41) were stationed in the Pacific, despite the number and demographics of soldiers deployed to the Pacific and Europe being approximately equal.8 During a 6-month period in 2008, a Combat Dermatology Clinic in Iraq showed 5% (n=129) of visits were for treatment of actinic keratoses (AKs), while 8% of visits (n=205) were related to skin cancer, including BCC, SCC, mycosis fungoides, and melanoma.9 Overall, these studies confirm a higher rate of melanoma in military service members vs the general population and indicate USAF members may be at the greatest risk for developing melanoma and NMSC among the service branches. Further studies are needed to elucidate why this might be the case and should concentrate on demographics, service locations, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, and use of sun-protective measures across each service branch.
Our search yielded no aggregate studies to determine if there is an increased rate of other types of skin cancer in military service members such as Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). Gerall et al10 described a case of MAC in a 43-year-old USAF U-2 pilot with a 15-year history of a slow-growing soft-tissue nodule on the cheek. The patient’s young age differed from the typical age of MAC occurrence (ie, 60–70 years), which led to the possibility that his profession contributed to the development of MAC and the relatively young age of onset.10
Etiology of Disease
The results of our literature review indicated that skin cancers are more prevalent among active-duty military personnel and veterans than in the general population; they also suggest that frequent sun exposure and lack of sun protection may be key etiologic factors. In 2015, only 23% of veterans (n=49) reported receiving skin cancer awareness education from the US Military.1 Among soldiers returning from Iraq and Afghanistan (n=212), only 13% reported routine sunscreen use, and
Exposure to UV radiation at higher altitudes (with corresponding higher UV energy) and altered sleep-wake cycles (with resulting altered immune defenses) may contribute to higher rates of melanoma and NMSC among USAF pilots.11 During a 57-minute flight at 30,000-ft altitude, a pilot is exposed to a UVA dose equivalent to 20 minutes inside a tanning booth.12 Although UVB transmission through plastic and glass windshields was reported to be less than 1%, UVA transmission ranged from 0.4% to 53.5%. The UVA dose for a pilot flying a light aircraft in Las Vegas, Nevada, was reported to be 127 μW/cm2 at ground level vs 242 μW/cm2 at a 30,000-ft altitude.12 Therefore, cosmic radiation exposure for military pilots is higher than for commercial pilots, as they fly at higher altitudes. U-2 pilots are exposed to 20 times the cosmic radiation dose at sea level and 10 times the exposure of commercial pilots.10
It currently is unknown why service in the USAF would increase skin cancer risk compared to service in other branches; however, there are some differences between military branches that require further research, including ethnic demographics, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, duty assignment locations, and the hours the military members are asked to work outside with direct sunlight exposure for each branch of service. Environmental exposures may differ based on the military branch gear requirements; for example, when on the flight line or flight deck, USN aircrews are required to wear cranials (helmets), eyewear (visor or goggles), and long-sleeved shirts. When at sea, USN flight crews wear gloves, headgear, goggles, pants, and long-sleeved shirts to identify their duty onboard. All of these measures offer good sun protection and are carried over to the land-based flight lines in the USN and Marine Corps. Neither the Army nor the USAF commonly utilize these practices. Conversely, the USAF does not allow flight line workers including fuelers, maintainers, and aircrew to wear coveralls due to the risk of being blown off, becoming foreign object debris, and being sucked into jet engines. However, in-flight protective gear such as goggles, gloves, and coveralls are worn.12 Perhaps the USAF may attract, recruit, or commission people with inherently more risk for skin cancer (eg, White individuals). How racial and ethnic factors may affect skin cancer incidence in military branches is an area for future research efforts.
Recommendations
Given the considerable increase in risk factors, efforts are needed to reduce the disparity in skin cancer rates between US military personnel and their civilian counterparts through appropriate prevention, screening, and intervention programs.
Prevention—In wartime settings as well as in training and other peacetime activities, active-duty military members cannot avoid harmful midday sun exposure. Additionally, application and reapplication of sunscreen can be challenging. Sunscreen, broad-spectrum lip balm, and wide-brimmed “boonie” hats can be ordered by supply personnel.13 We recommend that a standard sunscreen supply be available to all active-duty military service members. The long-sleeved, tightly woven fabric of military uniforms also can provide protection from the sun but can be difficult to tolerate for extended periods of time in warm climates. Breathable, lightweight, sun-protective clothing is commercially available and could be incorporated into military uniforms.
All service members should be educated about skin cancer risks while addressing common myths and inaccuracies. Fifty percent (n=50) of surveyed veterans thought discussions of skin cancer prevention and safety during basic training could help prevent skin cancer in service members.14 Suggestions from respondents included education about sun exposure consequences, use of graphic images of skin cancer in teaching, providing protective clothing and sunscreen to active-duty military service members, and discussion about sun protection with physicians during annual physicals. When veterans with a history of skin cancer were surveyed about their personal risk for skin cancer, most believed they were at little risk (average perceived risk response score, 2.2 out of 5 [1=no risk; 5=high risk]).14 The majority explained that they did not seek sun protection after warnings of skin cancer risk because they did not think skin cancer would happen to them,14 though the incidence of NMSC in the United States at the time of these surveys was estimated to be 3.5 million per year.14,15 Another study found that only 13% of veterans knew the back is the most common site of melanoma in men.1 The Army Public Health Center has informational fact sheets available online or in dermatologists’ offices that detail correct sunscreen application techniques and how to reduce sun exposure.16,17 However, military service members reported that they prefer physicians to communicate with them directly about skin cancer risks vs reading brochures in physician offices or gaining information from television, radio, military training, or the Internet (4.4 out 5 rating for communication methods of risks associated with skin cancer [1=ineffective; 5=very effective]).14 However, only 27% of nondermatologist physicians counseled or screened their patients on skin cancer or sunscreen yearly, 49% even less frequently, with 24% never counseling or screening at all. Because not all service members may be able to regularly see a dermatologist, efforts should be focused on increasing primary care physician awareness on counseling and screening.18
Early Detection—Military service members should be educated on how to perform skin self-examinations to alert their providers earlier to concerning lesions. The American Academy of Dermatology publishes infographics regarding the ABCDEs of melanoma and how to perform skin self-examinations.19,20 Although the US Preventive Services Task Force concluded there was insufficient evidence to recommend skin self-examination for all adults, the increased risk that military service members and veterans have requires further studies to examine the utility of self-screening in this population.20 Given the evidence of a higher incidence of melanoma in military service members vs the general population after 45 years of age,4 we recommend starting yearly in-person screenings performed by primary care physicians or dermatologists at this age. Ensuring every service member has routine in-office skin examinations can be difficult given the limited number of active-duty military dermatologists. Civilian dermatologists also could be helpful in this respect.
Teleconsultation, teledermoscopy, or store-and-forward imaging services for concerning lesions could be utilized when in-person consultations with a dermatologist are not feasible or cannot be performed in a timely manner. From 2004 to 2012, 40% of 10,817 teleconsultations were dermatology consultations from deployed or remote environments.21 Teleconsultation can be performed via email through the global military teleconsultation portal.22 These methods can lead to earlier detection of skin cancer rather than delaying evaluation for an in-person consultation.23
Intervention—High-risk patients who have been diagnosed with NMSC or many AKs should consider oral, procedural, or topical chemoprevention to reduce the risk for additional skin cancers as both primary and secondary prevention. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of 386 individuals with a history of 2 or more NMSCs, participants were randomly assigned to receive either 500 mg of nicotinamide twice daily or placebo for 12 months. Compared to the placebo group, the nicotinamide group had a 23% lower rate of new NMSCs and an 11% lower rate of new AKs at 12 months.24 The use of acitretin also has been studied in transplant recipients for the chemoprevention of NMSC. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of renal transplant recipients with more than 10 AKs randomized to receive either 30 mg/d of acitretin or placebo for 6 months, 11% of the acitretin group reported a new NMSC compared to 47% in the placebo group.25 An open-label study of 27 renal transplant recipients treated with methyl-esterified aminolevulinic acid–photodynamic therapy and red light demonstrated an increased mean time to occurrence of an AK, SCC, BCC, keratoacanthoma, or wart from 6.8 months in untreated areas compared to 9.6 months in treated areas.25 In active-duty locations where access to red and blue light sources is unavailable, the use of daylight photodynamic therapy can be considered, as it does not require any special equipment. Topical treatments such as 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod can be used for treatment and chemoprevention of NMSC. In a follow-up study from the Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial, patients who applied 5-fluorouracil cream 5% twice daily to the face and ears for 4 weeks had a 75% risk reduction in developing SCC requiring surgery compared to the control group for the first year after treatment.26,27
Final Thoughts
Focusing on the efforts we propose can help the US Military expand their prevention, screening, and intervention programs for skin cancer in service members. Further research can then be performed to determine which programs have the greatest impact on rates of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel. Given these higher incidences and risk of exposure for skin cancer among service members, the various services may consider mandating sunscreen use as part of the uniform to prevent skin cancer. To maximize effectiveness, these efforts to prevent the development of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel should be adopted nationally.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer incidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rigel DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Mil Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Sanlorenzo M, Vujic I, Posch C, et al. The risk of melanoma in pilots and cabin crew: UV measurements in flying airplanes. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:450-452.
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin cancer in World War II servicemen stationed in the Pacific theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Henning JS, Firoz, BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Gerall CD, Sippel MR, Yracheta JL, et al. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a rare, commonly misdiagnosed malignancy. Mil Med. 2019;184:948-950.
- Wilkison B, Wong E. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Proctor SP, Heaton KJ, Smith KW, et al. The Occupational JP8 Neuroepidemiology Study (OJENES): repeated workday exposure and central nervous system functioning among US Air Force personnel. Neurotoxicology. 2011;32:799-808.
- Soldiers protect themselves from skin cancer. US Army website. Published February 28, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.army.mil/article/17601/soldiers_protect_themselves_from_skin_cancer
- Fisher V, Lee D, McGrath J, et al. Veterans speak up: current warnings on skin cancer miss the target, suggestions for improvement. Mil Med. 2015;180:892-897.
- Rogers HW, Weinstick MA, Harris AR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:283-287.
- Sun safety. Army Public Health Center website. Updated June 6, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/topics/discond/hipss/Pages/Sun-Safety.aspx
- Outdoor ultraviolet radiation hazards and protection. Army Public Health Center website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/PHC%20Resource%20Library/OutdoorUltravioletRadiationHazardsandProtection_FS_24-017-1115.pdf
- Saraiya M, Frank E, Elon L, et al. Personal and clinical skin cancer prevention practices of US women physicians. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:633-642.
- What to look for: ABCDEs of melanoma. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/at-risk/abcdes
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the US military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- Bartling SJ, Rivard SC, Meyerle JH. Melanoma in an active duty marine. Mil Med. 2017;182:2034-2039.
- Day WG, Shirvastava V, Roman JW. Synchronous teledermoscopy in military treatment facilities. Mil Med. 2020;185:1334-1337.
- Chen AC, Martin AJ, Choy B, et al. A phase 3 randomized trial of nicotinamide for skin-cancer chemoprevention. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1618-1626.
- Bavinck JN, Tieben LM, Van der Woude FJ, et al. Prevention of skin cancer and reduction of keratotic skin lesions during acitretin therapy in renal transplant recipients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1933-1938.
- Wulf HC, Pavel S, Stender I, et al. Topical photodynamic therapy for prevention of new skin lesions in renal transplant recipients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006;86:25-28.
- Weinstock MA, Thwin SS, Siegel JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial (VAKCC) Group. Chemoprevention of basal and squamous cell carcinoma with a single course of fluorouracil, 5%, cream: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:167-174.
Occupational sun exposure is a well-known risk factor for the development of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). In addition to sun exposure, US military personnel may face other risk factors such as lack of access to adequate sun protection, work in equatorial latitudes, and increased exposure to carcinogens. In one study, fewer than 30% of surveyed soldiers reported regular sunscreen use during deployment and reported the face, neck, and upper extremities were unprotected at least 70% of the time.1 Skin cancer risk factors that are more common in military service members include inadequate sunscreen access, insufficient sun protection, harsh weather conditions, more immediate safety concerns than sun protection, and male gender. A higher incidence of melanoma and NMSC has been correlated with the more common demographics of US veterans such as male sex, older age, and White race.2
Although not uncommon in both civilian and military populations, we present the case of a military service member who developed skin cancer at an early age potentially due to occupational sun exposure. We also provide a review of the literature to examine the risk factors and incidence of melanoma and NMSC in US military personnel and veterans and provide recommendations for skin cancer prevention, screening, and intervention in the military population.
Case Report
A 37-year-old White active-duty male service member in the US Navy (USN) presented with a nonhealing lesion on the nose of 2 years’ duration that had been gradually growing and bleeding for several weeks. He participated in several sea deployments while onboard a naval destroyer over his 10-year military career. He did not routinely use sunscreen during his deployments. His personal and family medical history lacked risk factors for skin cancer other than his skin tone and frequent sun exposure.
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm ulcerated plaque with rolled borders and prominent telangiectases on the mid nasal dorsum. A shave biopsy was performed to confirm the diagnosis of nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery, which required repair with an advancement flap. He currently continues his active-duty service and is preparing for his next overseas deployment.
Literature Review
We conducted a review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms skin cancer, melanoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, or sebaceous carcinoma along with military, Army, Navy, Air Force, or veterans. Studies from January 1984 to April 2020 were included in our qualitative review. All articles were reviewed, and those that did not examine skin cancer and the military population in the United States were excluded. Relevant data, such as results of skin cancer incidence or risk factors or insights about developing skin cancer in this affected population, were extracted from the selected publications.
Several studies showed overall increased age-adjusted incidence rates of melanoma and NMSC among military service personnel compared to age-matched controls in the general population.2 A survey of draft-age men during World War II found a slightly higher percentage of respondents with history of melanoma compared to the control group (83% [74/89] vs 76% [49/65]). Of those who had a history of melanoma, 34% (30/89) served in the tropics compared to 6% (4/65) in the control group.3 A tumor registry review found the age-adjusted melanoma incidence rates per 100,000 person-years for White individuals in the military vs the general population was 33.6 vs 27.5 among those aged 45 to 49 years, 49.8 vs 32.2 among those aged 50 to 54 years, and 178.5 vs 39.2 among those aged 55 to 59 years.4 Among published literature reviews, members of the US Air Force (USAF) had the highest rates of melanoma compared to other military branches, with an incidence rate of 7.6 vs 6.3 among USAF males vs Army males and 9.0 vs 5.5 among USAF females vs Army females.4 These findings were further supported by another study showing a higher incidence rate of melanoma in USAF members compared to Army personnel (17.8 vs 9.5) and a 62% greater melanoma incidence in active-duty military personnel compared to the general population when adjusted for age, race, sex, and year of diagnosis.5 Additionally, a meta-analysis reported a standardized incidence ratio of 1.4 (95% CI, 1.1-1.9) for malignant melanoma and 1.8 (95% CI, 1.3-2.8) for NMSC among military pilots compared to the general population.6 It is important to note that these data are limited to published peer-reviewed studies within PubMed and may not reflect the true skin cancer incidence.
More comprehensive studies are needed to compare NMSC incidence rates in nonpilot military populations compared to the general population. From 2005 to 2014, the average annual NMSC incidence rate in the USAF was 64.4 per 100,000 person-years, with the highest rate at 97.4 per 100,000 person-years in 2007.7 However, this study did not directly compare military service members to the general population. Service in tropical environments among World War II veterans was associated with an increased risk for NMSC. Sixty-six percent of patients with BCC (n=197) and 68% with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)(n=41) were stationed in the Pacific, despite the number and demographics of soldiers deployed to the Pacific and Europe being approximately equal.8 During a 6-month period in 2008, a Combat Dermatology Clinic in Iraq showed 5% (n=129) of visits were for treatment of actinic keratoses (AKs), while 8% of visits (n=205) were related to skin cancer, including BCC, SCC, mycosis fungoides, and melanoma.9 Overall, these studies confirm a higher rate of melanoma in military service members vs the general population and indicate USAF members may be at the greatest risk for developing melanoma and NMSC among the service branches. Further studies are needed to elucidate why this might be the case and should concentrate on demographics, service locations, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, and use of sun-protective measures across each service branch.
Our search yielded no aggregate studies to determine if there is an increased rate of other types of skin cancer in military service members such as Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). Gerall et al10 described a case of MAC in a 43-year-old USAF U-2 pilot with a 15-year history of a slow-growing soft-tissue nodule on the cheek. The patient’s young age differed from the typical age of MAC occurrence (ie, 60–70 years), which led to the possibility that his profession contributed to the development of MAC and the relatively young age of onset.10
Etiology of Disease
The results of our literature review indicated that skin cancers are more prevalent among active-duty military personnel and veterans than in the general population; they also suggest that frequent sun exposure and lack of sun protection may be key etiologic factors. In 2015, only 23% of veterans (n=49) reported receiving skin cancer awareness education from the US Military.1 Among soldiers returning from Iraq and Afghanistan (n=212), only 13% reported routine sunscreen use, and
Exposure to UV radiation at higher altitudes (with corresponding higher UV energy) and altered sleep-wake cycles (with resulting altered immune defenses) may contribute to higher rates of melanoma and NMSC among USAF pilots.11 During a 57-minute flight at 30,000-ft altitude, a pilot is exposed to a UVA dose equivalent to 20 minutes inside a tanning booth.12 Although UVB transmission through plastic and glass windshields was reported to be less than 1%, UVA transmission ranged from 0.4% to 53.5%. The UVA dose for a pilot flying a light aircraft in Las Vegas, Nevada, was reported to be 127 μW/cm2 at ground level vs 242 μW/cm2 at a 30,000-ft altitude.12 Therefore, cosmic radiation exposure for military pilots is higher than for commercial pilots, as they fly at higher altitudes. U-2 pilots are exposed to 20 times the cosmic radiation dose at sea level and 10 times the exposure of commercial pilots.10
It currently is unknown why service in the USAF would increase skin cancer risk compared to service in other branches; however, there are some differences between military branches that require further research, including ethnic demographics, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, duty assignment locations, and the hours the military members are asked to work outside with direct sunlight exposure for each branch of service. Environmental exposures may differ based on the military branch gear requirements; for example, when on the flight line or flight deck, USN aircrews are required to wear cranials (helmets), eyewear (visor or goggles), and long-sleeved shirts. When at sea, USN flight crews wear gloves, headgear, goggles, pants, and long-sleeved shirts to identify their duty onboard. All of these measures offer good sun protection and are carried over to the land-based flight lines in the USN and Marine Corps. Neither the Army nor the USAF commonly utilize these practices. Conversely, the USAF does not allow flight line workers including fuelers, maintainers, and aircrew to wear coveralls due to the risk of being blown off, becoming foreign object debris, and being sucked into jet engines. However, in-flight protective gear such as goggles, gloves, and coveralls are worn.12 Perhaps the USAF may attract, recruit, or commission people with inherently more risk for skin cancer (eg, White individuals). How racial and ethnic factors may affect skin cancer incidence in military branches is an area for future research efforts.
Recommendations
Given the considerable increase in risk factors, efforts are needed to reduce the disparity in skin cancer rates between US military personnel and their civilian counterparts through appropriate prevention, screening, and intervention programs.
Prevention—In wartime settings as well as in training and other peacetime activities, active-duty military members cannot avoid harmful midday sun exposure. Additionally, application and reapplication of sunscreen can be challenging. Sunscreen, broad-spectrum lip balm, and wide-brimmed “boonie” hats can be ordered by supply personnel.13 We recommend that a standard sunscreen supply be available to all active-duty military service members. The long-sleeved, tightly woven fabric of military uniforms also can provide protection from the sun but can be difficult to tolerate for extended periods of time in warm climates. Breathable, lightweight, sun-protective clothing is commercially available and could be incorporated into military uniforms.
All service members should be educated about skin cancer risks while addressing common myths and inaccuracies. Fifty percent (n=50) of surveyed veterans thought discussions of skin cancer prevention and safety during basic training could help prevent skin cancer in service members.14 Suggestions from respondents included education about sun exposure consequences, use of graphic images of skin cancer in teaching, providing protective clothing and sunscreen to active-duty military service members, and discussion about sun protection with physicians during annual physicals. When veterans with a history of skin cancer were surveyed about their personal risk for skin cancer, most believed they were at little risk (average perceived risk response score, 2.2 out of 5 [1=no risk; 5=high risk]).14 The majority explained that they did not seek sun protection after warnings of skin cancer risk because they did not think skin cancer would happen to them,14 though the incidence of NMSC in the United States at the time of these surveys was estimated to be 3.5 million per year.14,15 Another study found that only 13% of veterans knew the back is the most common site of melanoma in men.1 The Army Public Health Center has informational fact sheets available online or in dermatologists’ offices that detail correct sunscreen application techniques and how to reduce sun exposure.16,17 However, military service members reported that they prefer physicians to communicate with them directly about skin cancer risks vs reading brochures in physician offices or gaining information from television, radio, military training, or the Internet (4.4 out 5 rating for communication methods of risks associated with skin cancer [1=ineffective; 5=very effective]).14 However, only 27% of nondermatologist physicians counseled or screened their patients on skin cancer or sunscreen yearly, 49% even less frequently, with 24% never counseling or screening at all. Because not all service members may be able to regularly see a dermatologist, efforts should be focused on increasing primary care physician awareness on counseling and screening.18
Early Detection—Military service members should be educated on how to perform skin self-examinations to alert their providers earlier to concerning lesions. The American Academy of Dermatology publishes infographics regarding the ABCDEs of melanoma and how to perform skin self-examinations.19,20 Although the US Preventive Services Task Force concluded there was insufficient evidence to recommend skin self-examination for all adults, the increased risk that military service members and veterans have requires further studies to examine the utility of self-screening in this population.20 Given the evidence of a higher incidence of melanoma in military service members vs the general population after 45 years of age,4 we recommend starting yearly in-person screenings performed by primary care physicians or dermatologists at this age. Ensuring every service member has routine in-office skin examinations can be difficult given the limited number of active-duty military dermatologists. Civilian dermatologists also could be helpful in this respect.
Teleconsultation, teledermoscopy, or store-and-forward imaging services for concerning lesions could be utilized when in-person consultations with a dermatologist are not feasible or cannot be performed in a timely manner. From 2004 to 2012, 40% of 10,817 teleconsultations were dermatology consultations from deployed or remote environments.21 Teleconsultation can be performed via email through the global military teleconsultation portal.22 These methods can lead to earlier detection of skin cancer rather than delaying evaluation for an in-person consultation.23
Intervention—High-risk patients who have been diagnosed with NMSC or many AKs should consider oral, procedural, or topical chemoprevention to reduce the risk for additional skin cancers as both primary and secondary prevention. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of 386 individuals with a history of 2 or more NMSCs, participants were randomly assigned to receive either 500 mg of nicotinamide twice daily or placebo for 12 months. Compared to the placebo group, the nicotinamide group had a 23% lower rate of new NMSCs and an 11% lower rate of new AKs at 12 months.24 The use of acitretin also has been studied in transplant recipients for the chemoprevention of NMSC. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of renal transplant recipients with more than 10 AKs randomized to receive either 30 mg/d of acitretin or placebo for 6 months, 11% of the acitretin group reported a new NMSC compared to 47% in the placebo group.25 An open-label study of 27 renal transplant recipients treated with methyl-esterified aminolevulinic acid–photodynamic therapy and red light demonstrated an increased mean time to occurrence of an AK, SCC, BCC, keratoacanthoma, or wart from 6.8 months in untreated areas compared to 9.6 months in treated areas.25 In active-duty locations where access to red and blue light sources is unavailable, the use of daylight photodynamic therapy can be considered, as it does not require any special equipment. Topical treatments such as 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod can be used for treatment and chemoprevention of NMSC. In a follow-up study from the Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial, patients who applied 5-fluorouracil cream 5% twice daily to the face and ears for 4 weeks had a 75% risk reduction in developing SCC requiring surgery compared to the control group for the first year after treatment.26,27
Final Thoughts
Focusing on the efforts we propose can help the US Military expand their prevention, screening, and intervention programs for skin cancer in service members. Further research can then be performed to determine which programs have the greatest impact on rates of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel. Given these higher incidences and risk of exposure for skin cancer among service members, the various services may consider mandating sunscreen use as part of the uniform to prevent skin cancer. To maximize effectiveness, these efforts to prevent the development of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel should be adopted nationally.
Occupational sun exposure is a well-known risk factor for the development of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). In addition to sun exposure, US military personnel may face other risk factors such as lack of access to adequate sun protection, work in equatorial latitudes, and increased exposure to carcinogens. In one study, fewer than 30% of surveyed soldiers reported regular sunscreen use during deployment and reported the face, neck, and upper extremities were unprotected at least 70% of the time.1 Skin cancer risk factors that are more common in military service members include inadequate sunscreen access, insufficient sun protection, harsh weather conditions, more immediate safety concerns than sun protection, and male gender. A higher incidence of melanoma and NMSC has been correlated with the more common demographics of US veterans such as male sex, older age, and White race.2
Although not uncommon in both civilian and military populations, we present the case of a military service member who developed skin cancer at an early age potentially due to occupational sun exposure. We also provide a review of the literature to examine the risk factors and incidence of melanoma and NMSC in US military personnel and veterans and provide recommendations for skin cancer prevention, screening, and intervention in the military population.
Case Report
A 37-year-old White active-duty male service member in the US Navy (USN) presented with a nonhealing lesion on the nose of 2 years’ duration that had been gradually growing and bleeding for several weeks. He participated in several sea deployments while onboard a naval destroyer over his 10-year military career. He did not routinely use sunscreen during his deployments. His personal and family medical history lacked risk factors for skin cancer other than his skin tone and frequent sun exposure.
Physical examination revealed a 1-cm ulcerated plaque with rolled borders and prominent telangiectases on the mid nasal dorsum. A shave biopsy was performed to confirm the diagnosis of nodular basal cell carcinoma (BCC). The patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery, which required repair with an advancement flap. He currently continues his active-duty service and is preparing for his next overseas deployment.
Literature Review
We conducted a review of PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms skin cancer, melanoma, nonmelanoma skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, or sebaceous carcinoma along with military, Army, Navy, Air Force, or veterans. Studies from January 1984 to April 2020 were included in our qualitative review. All articles were reviewed, and those that did not examine skin cancer and the military population in the United States were excluded. Relevant data, such as results of skin cancer incidence or risk factors or insights about developing skin cancer in this affected population, were extracted from the selected publications.
Several studies showed overall increased age-adjusted incidence rates of melanoma and NMSC among military service personnel compared to age-matched controls in the general population.2 A survey of draft-age men during World War II found a slightly higher percentage of respondents with history of melanoma compared to the control group (83% [74/89] vs 76% [49/65]). Of those who had a history of melanoma, 34% (30/89) served in the tropics compared to 6% (4/65) in the control group.3 A tumor registry review found the age-adjusted melanoma incidence rates per 100,000 person-years for White individuals in the military vs the general population was 33.6 vs 27.5 among those aged 45 to 49 years, 49.8 vs 32.2 among those aged 50 to 54 years, and 178.5 vs 39.2 among those aged 55 to 59 years.4 Among published literature reviews, members of the US Air Force (USAF) had the highest rates of melanoma compared to other military branches, with an incidence rate of 7.6 vs 6.3 among USAF males vs Army males and 9.0 vs 5.5 among USAF females vs Army females.4 These findings were further supported by another study showing a higher incidence rate of melanoma in USAF members compared to Army personnel (17.8 vs 9.5) and a 62% greater melanoma incidence in active-duty military personnel compared to the general population when adjusted for age, race, sex, and year of diagnosis.5 Additionally, a meta-analysis reported a standardized incidence ratio of 1.4 (95% CI, 1.1-1.9) for malignant melanoma and 1.8 (95% CI, 1.3-2.8) for NMSC among military pilots compared to the general population.6 It is important to note that these data are limited to published peer-reviewed studies within PubMed and may not reflect the true skin cancer incidence.
More comprehensive studies are needed to compare NMSC incidence rates in nonpilot military populations compared to the general population. From 2005 to 2014, the average annual NMSC incidence rate in the USAF was 64.4 per 100,000 person-years, with the highest rate at 97.4 per 100,000 person-years in 2007.7 However, this study did not directly compare military service members to the general population. Service in tropical environments among World War II veterans was associated with an increased risk for NMSC. Sixty-six percent of patients with BCC (n=197) and 68% with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)(n=41) were stationed in the Pacific, despite the number and demographics of soldiers deployed to the Pacific and Europe being approximately equal.8 During a 6-month period in 2008, a Combat Dermatology Clinic in Iraq showed 5% (n=129) of visits were for treatment of actinic keratoses (AKs), while 8% of visits (n=205) were related to skin cancer, including BCC, SCC, mycosis fungoides, and melanoma.9 Overall, these studies confirm a higher rate of melanoma in military service members vs the general population and indicate USAF members may be at the greatest risk for developing melanoma and NMSC among the service branches. Further studies are needed to elucidate why this might be the case and should concentrate on demographics, service locations, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, and use of sun-protective measures across each service branch.
Our search yielded no aggregate studies to determine if there is an increased rate of other types of skin cancer in military service members such as Merkel cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). Gerall et al10 described a case of MAC in a 43-year-old USAF U-2 pilot with a 15-year history of a slow-growing soft-tissue nodule on the cheek. The patient’s young age differed from the typical age of MAC occurrence (ie, 60–70 years), which led to the possibility that his profession contributed to the development of MAC and the relatively young age of onset.10
Etiology of Disease
The results of our literature review indicated that skin cancers are more prevalent among active-duty military personnel and veterans than in the general population; they also suggest that frequent sun exposure and lack of sun protection may be key etiologic factors. In 2015, only 23% of veterans (n=49) reported receiving skin cancer awareness education from the US Military.1 Among soldiers returning from Iraq and Afghanistan (n=212), only 13% reported routine sunscreen use, and
Exposure to UV radiation at higher altitudes (with corresponding higher UV energy) and altered sleep-wake cycles (with resulting altered immune defenses) may contribute to higher rates of melanoma and NMSC among USAF pilots.11 During a 57-minute flight at 30,000-ft altitude, a pilot is exposed to a UVA dose equivalent to 20 minutes inside a tanning booth.12 Although UVB transmission through plastic and glass windshields was reported to be less than 1%, UVA transmission ranged from 0.4% to 53.5%. The UVA dose for a pilot flying a light aircraft in Las Vegas, Nevada, was reported to be 127 μW/cm2 at ground level vs 242 μW/cm2 at a 30,000-ft altitude.12 Therefore, cosmic radiation exposure for military pilots is higher than for commercial pilots, as they fly at higher altitudes. U-2 pilots are exposed to 20 times the cosmic radiation dose at sea level and 10 times the exposure of commercial pilots.10
It currently is unknown why service in the USAF would increase skin cancer risk compared to service in other branches; however, there are some differences between military branches that require further research, including ethnic demographics, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, duty assignment locations, and the hours the military members are asked to work outside with direct sunlight exposure for each branch of service. Environmental exposures may differ based on the military branch gear requirements; for example, when on the flight line or flight deck, USN aircrews are required to wear cranials (helmets), eyewear (visor or goggles), and long-sleeved shirts. When at sea, USN flight crews wear gloves, headgear, goggles, pants, and long-sleeved shirts to identify their duty onboard. All of these measures offer good sun protection and are carried over to the land-based flight lines in the USN and Marine Corps. Neither the Army nor the USAF commonly utilize these practices. Conversely, the USAF does not allow flight line workers including fuelers, maintainers, and aircrew to wear coveralls due to the risk of being blown off, becoming foreign object debris, and being sucked into jet engines. However, in-flight protective gear such as goggles, gloves, and coveralls are worn.12 Perhaps the USAF may attract, recruit, or commission people with inherently more risk for skin cancer (eg, White individuals). How racial and ethnic factors may affect skin cancer incidence in military branches is an area for future research efforts.
Recommendations
Given the considerable increase in risk factors, efforts are needed to reduce the disparity in skin cancer rates between US military personnel and their civilian counterparts through appropriate prevention, screening, and intervention programs.
Prevention—In wartime settings as well as in training and other peacetime activities, active-duty military members cannot avoid harmful midday sun exposure. Additionally, application and reapplication of sunscreen can be challenging. Sunscreen, broad-spectrum lip balm, and wide-brimmed “boonie” hats can be ordered by supply personnel.13 We recommend that a standard sunscreen supply be available to all active-duty military service members. The long-sleeved, tightly woven fabric of military uniforms also can provide protection from the sun but can be difficult to tolerate for extended periods of time in warm climates. Breathable, lightweight, sun-protective clothing is commercially available and could be incorporated into military uniforms.
All service members should be educated about skin cancer risks while addressing common myths and inaccuracies. Fifty percent (n=50) of surveyed veterans thought discussions of skin cancer prevention and safety during basic training could help prevent skin cancer in service members.14 Suggestions from respondents included education about sun exposure consequences, use of graphic images of skin cancer in teaching, providing protective clothing and sunscreen to active-duty military service members, and discussion about sun protection with physicians during annual physicals. When veterans with a history of skin cancer were surveyed about their personal risk for skin cancer, most believed they were at little risk (average perceived risk response score, 2.2 out of 5 [1=no risk; 5=high risk]).14 The majority explained that they did not seek sun protection after warnings of skin cancer risk because they did not think skin cancer would happen to them,14 though the incidence of NMSC in the United States at the time of these surveys was estimated to be 3.5 million per year.14,15 Another study found that only 13% of veterans knew the back is the most common site of melanoma in men.1 The Army Public Health Center has informational fact sheets available online or in dermatologists’ offices that detail correct sunscreen application techniques and how to reduce sun exposure.16,17 However, military service members reported that they prefer physicians to communicate with them directly about skin cancer risks vs reading brochures in physician offices or gaining information from television, radio, military training, or the Internet (4.4 out 5 rating for communication methods of risks associated with skin cancer [1=ineffective; 5=very effective]).14 However, only 27% of nondermatologist physicians counseled or screened their patients on skin cancer or sunscreen yearly, 49% even less frequently, with 24% never counseling or screening at all. Because not all service members may be able to regularly see a dermatologist, efforts should be focused on increasing primary care physician awareness on counseling and screening.18
Early Detection—Military service members should be educated on how to perform skin self-examinations to alert their providers earlier to concerning lesions. The American Academy of Dermatology publishes infographics regarding the ABCDEs of melanoma and how to perform skin self-examinations.19,20 Although the US Preventive Services Task Force concluded there was insufficient evidence to recommend skin self-examination for all adults, the increased risk that military service members and veterans have requires further studies to examine the utility of self-screening in this population.20 Given the evidence of a higher incidence of melanoma in military service members vs the general population after 45 years of age,4 we recommend starting yearly in-person screenings performed by primary care physicians or dermatologists at this age. Ensuring every service member has routine in-office skin examinations can be difficult given the limited number of active-duty military dermatologists. Civilian dermatologists also could be helpful in this respect.
Teleconsultation, teledermoscopy, or store-and-forward imaging services for concerning lesions could be utilized when in-person consultations with a dermatologist are not feasible or cannot be performed in a timely manner. From 2004 to 2012, 40% of 10,817 teleconsultations were dermatology consultations from deployed or remote environments.21 Teleconsultation can be performed via email through the global military teleconsultation portal.22 These methods can lead to earlier detection of skin cancer rather than delaying evaluation for an in-person consultation.23
Intervention—High-risk patients who have been diagnosed with NMSC or many AKs should consider oral, procedural, or topical chemoprevention to reduce the risk for additional skin cancers as both primary and secondary prevention. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of 386 individuals with a history of 2 or more NMSCs, participants were randomly assigned to receive either 500 mg of nicotinamide twice daily or placebo for 12 months. Compared to the placebo group, the nicotinamide group had a 23% lower rate of new NMSCs and an 11% lower rate of new AKs at 12 months.24 The use of acitretin also has been studied in transplant recipients for the chemoprevention of NMSC. In a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of renal transplant recipients with more than 10 AKs randomized to receive either 30 mg/d of acitretin or placebo for 6 months, 11% of the acitretin group reported a new NMSC compared to 47% in the placebo group.25 An open-label study of 27 renal transplant recipients treated with methyl-esterified aminolevulinic acid–photodynamic therapy and red light demonstrated an increased mean time to occurrence of an AK, SCC, BCC, keratoacanthoma, or wart from 6.8 months in untreated areas compared to 9.6 months in treated areas.25 In active-duty locations where access to red and blue light sources is unavailable, the use of daylight photodynamic therapy can be considered, as it does not require any special equipment. Topical treatments such as 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod can be used for treatment and chemoprevention of NMSC. In a follow-up study from the Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial, patients who applied 5-fluorouracil cream 5% twice daily to the face and ears for 4 weeks had a 75% risk reduction in developing SCC requiring surgery compared to the control group for the first year after treatment.26,27
Final Thoughts
Focusing on the efforts we propose can help the US Military expand their prevention, screening, and intervention programs for skin cancer in service members. Further research can then be performed to determine which programs have the greatest impact on rates of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel. Given these higher incidences and risk of exposure for skin cancer among service members, the various services may consider mandating sunscreen use as part of the uniform to prevent skin cancer. To maximize effectiveness, these efforts to prevent the development of skin cancer among military and veteran personnel should be adopted nationally.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer incidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rigel DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Mil Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Sanlorenzo M, Vujic I, Posch C, et al. The risk of melanoma in pilots and cabin crew: UV measurements in flying airplanes. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:450-452.
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin cancer in World War II servicemen stationed in the Pacific theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Henning JS, Firoz, BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Gerall CD, Sippel MR, Yracheta JL, et al. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a rare, commonly misdiagnosed malignancy. Mil Med. 2019;184:948-950.
- Wilkison B, Wong E. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Proctor SP, Heaton KJ, Smith KW, et al. The Occupational JP8 Neuroepidemiology Study (OJENES): repeated workday exposure and central nervous system functioning among US Air Force personnel. Neurotoxicology. 2011;32:799-808.
- Soldiers protect themselves from skin cancer. US Army website. Published February 28, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.army.mil/article/17601/soldiers_protect_themselves_from_skin_cancer
- Fisher V, Lee D, McGrath J, et al. Veterans speak up: current warnings on skin cancer miss the target, suggestions for improvement. Mil Med. 2015;180:892-897.
- Rogers HW, Weinstick MA, Harris AR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:283-287.
- Sun safety. Army Public Health Center website. Updated June 6, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/topics/discond/hipss/Pages/Sun-Safety.aspx
- Outdoor ultraviolet radiation hazards and protection. Army Public Health Center website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/PHC%20Resource%20Library/OutdoorUltravioletRadiationHazardsandProtection_FS_24-017-1115.pdf
- Saraiya M, Frank E, Elon L, et al. Personal and clinical skin cancer prevention practices of US women physicians. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:633-642.
- What to look for: ABCDEs of melanoma. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/at-risk/abcdes
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the US military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- Bartling SJ, Rivard SC, Meyerle JH. Melanoma in an active duty marine. Mil Med. 2017;182:2034-2039.
- Day WG, Shirvastava V, Roman JW. Synchronous teledermoscopy in military treatment facilities. Mil Med. 2020;185:1334-1337.
- Chen AC, Martin AJ, Choy B, et al. A phase 3 randomized trial of nicotinamide for skin-cancer chemoprevention. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1618-1626.
- Bavinck JN, Tieben LM, Van der Woude FJ, et al. Prevention of skin cancer and reduction of keratotic skin lesions during acitretin therapy in renal transplant recipients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1933-1938.
- Wulf HC, Pavel S, Stender I, et al. Topical photodynamic therapy for prevention of new skin lesions in renal transplant recipients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006;86:25-28.
- Weinstock MA, Thwin SS, Siegel JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial (VAKCC) Group. Chemoprevention of basal and squamous cell carcinoma with a single course of fluorouracil, 5%, cream: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:167-174.
- Powers JG, Patel NA, Powers EM, et al. Skin cancer risk factors and preventative behaviors among United States military veterans deployed to Iraq and Afghanistan. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:2871-2873.
- Riemenschneider K, Liu J, Powers JG. Skin cancer in the military: a systematic review of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer incidence, prevention, and screening among active duty and veteran personnel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1185-1192.
- Brown J, Kopf AW, Rigel DS, et al. Malignant melanoma in World War II veterans. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:661-663.
- Zhou J, Enewold L, Zahm SH, et al. Melanoma incidence rates among whites in the U.S. Military. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011;20:318-323.
- Lea CS, Efird JT, Toland AE, et al. Melanoma incidence rates in active duty military personnel compared with a population-based registry in the United States, 2000-2007. Mil Med. 2014;179:247-253.
- Sanlorenzo M, Vujic I, Posch C, et al. The risk of melanoma in pilots and cabin crew: UV measurements in flying airplanes. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:450-452.
- Lee T, Taubman SB, Williams VF. Incident diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancer, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2005-2014. MSMR. 2016;23:2-6.
- Ramani ML, Bennett RG. High prevalence of skin cancer in World War II servicemen stationed in the Pacific theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:733-737.
- Henning JS, Firoz, BF. Combat dermatology: the prevalence of skin disease in a deployed dermatology clinic in Iraq. J Drugs Dermatol. 2010;9:210-214.
- Gerall CD, Sippel MR, Yracheta JL, et al. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a rare, commonly misdiagnosed malignancy. Mil Med. 2019;184:948-950.
- Wilkison B, Wong E. Skin cancer in military pilots: a special population with special risk factors. Cutis. 2017;100:218-220.
- Proctor SP, Heaton KJ, Smith KW, et al. The Occupational JP8 Neuroepidemiology Study (OJENES): repeated workday exposure and central nervous system functioning among US Air Force personnel. Neurotoxicology. 2011;32:799-808.
- Soldiers protect themselves from skin cancer. US Army website. Published February 28, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.army.mil/article/17601/soldiers_protect_themselves_from_skin_cancer
- Fisher V, Lee D, McGrath J, et al. Veterans speak up: current warnings on skin cancer miss the target, suggestions for improvement. Mil Med. 2015;180:892-897.
- Rogers HW, Weinstick MA, Harris AR, et al. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States, 2006. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:283-287.
- Sun safety. Army Public Health Center website. Updated June 6, 2019. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/topics/discond/hipss/Pages/Sun-Safety.aspx
- Outdoor ultraviolet radiation hazards and protection. Army Public Health Center website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://phc.amedd.army.mil/PHC%20Resource%20Library/OutdoorUltravioletRadiationHazardsandProtection_FS_24-017-1115.pdf
- Saraiya M, Frank E, Elon L, et al. Personal and clinical skin cancer prevention practices of US women physicians. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:633-642.
- What to look for: ABCDEs of melanoma. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/at-risk/abcdes
- Detect skin cancer: how to perform a skin self-exam. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 21, 2022. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/skin-cancer/find/check-skin
- Hwang JS, Lappan CM, Sperling LC, et al. Utilization of telemedicine in the US military in a deployed setting. Mil Med. 2014;179:1347-1353.
- Bartling SJ, Rivard SC, Meyerle JH. Melanoma in an active duty marine. Mil Med. 2017;182:2034-2039.
- Day WG, Shirvastava V, Roman JW. Synchronous teledermoscopy in military treatment facilities. Mil Med. 2020;185:1334-1337.
- Chen AC, Martin AJ, Choy B, et al. A phase 3 randomized trial of nicotinamide for skin-cancer chemoprevention. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1618-1626.
- Bavinck JN, Tieben LM, Van der Woude FJ, et al. Prevention of skin cancer and reduction of keratotic skin lesions during acitretin therapy in renal transplant recipients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1933-1938.
- Wulf HC, Pavel S, Stender I, et al. Topical photodynamic therapy for prevention of new skin lesions in renal transplant recipients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2006;86:25-28.
- Weinstock MA, Thwin SS, Siegel JA, et al; Veterans Affairs Keratinocyte Carcinoma Chemoprevention Trial (VAKCC) Group. Chemoprevention of basal and squamous cell carcinoma with a single course of fluorouracil, 5%, cream: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:167-174.
Practice Points
- Skin cancer is more prevalent among military personnel and veterans, especially those in the US Air Force. Frequent and/or prolonged sun exposure and lack of sun protection may be key factors.
- Future research should compare the prevalence of skin cancer in nonpilot military populations to the general US population; explore racial and ethnic differences by military branch and their influence on skin cancers; analyze each branch’s sun-protective measures, uniform wear and personal protective equipment standards, duty assignment locations, and the hours the military members are asked to work outside with direct sunlight exposure; and explore the effects of appropriate military skin cancer intervention and screening programs.
Association of BRAF V600E Status of Incident Melanoma and Risk for a Second Primary Malignancy: A Population-Based Study
The incidence of cutaneous melanoma in the United States has increased in the last 30 years, with the American Cancer Society estimating that 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed and 7650 melanoma-related deaths will occur in 2022.1 Patients with melanoma have an increased risk for developing a second primary melanoma or other malignancy, such as salivary gland, small intestine, breast, prostate, renal, or thyroid cancer, but most commonly nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 The incidence rate of melanoma among residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 1970 through 2009 has already been described for various age groups4-7; however, the incidence of a second primary malignancy, including melanoma, within these incident cohorts remains unknown.
Mutations in the BRAF oncogene occur in approximately 50% of melanomas.8,9
Although the BRAF mutation event in melanoma is sporadic and should not necessarily affect the development of an unrelated malignancy, we hypothesized that the exposures that may have predisposed a particular individual to a BRAF-mutated melanoma also may have a higher chance of predisposing that individual to the development of another primary malignancy. In this population-based study, we aimed to determine whether the specific melanoma feature of mutant BRAF V600E expression was associated with the development of a second primary malignancy.
Methods
This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center (both in Rochester, Minnesota). The reporting of this study is compliant with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology statement.15
Patient Selection and BRAF Assessment—The Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) links comprehensive health care records for virtually all residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, across different medical providers. The REP provides an index of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, tracks timelines and outcomes of individuals and their medical conditions, and is ideal for population-based studies.
We obtained a list of all residents of Olmsted County aged 18 to 60 years who had a melanoma diagnosed according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, from January 1, 1970, through December 30, 2009; these cohorts have been analyzed previously.4-7 Of the 638 individuals identified, 380 had a melanoma tissue block on file at Mayo Clinic with enough tumor present in available tissue blocks for BRAF assessment. All specimens were reviewed by a board-certified dermatopathologist (J.S.L.) to confirm the diagnosis of melanoma. Tissue blocks were recut, and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were stained for BRAF V600E (Spring Bioscience Corporation). BRAF-stained specimens and the associated hematoxylin and eosin−stained slides were reviewed. Melanocyte cytoplasmic staining for BRAF was graded as negative if no staining was evident. BRAF was graded as positive if focal or partial staining was observed (<50% of tumor or low BRAF expression) or if diffuse staining was evident (>50% of tumor or high BRAF expression).
Using resources of the REP, we confirmed patients’ residency status in Olmsted County at the time of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Patients who denied access to their medical records for research purposes were excluded. We used the complete record of each patient to confirm the date of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Baseline characteristics of patients and their incident melanomas (eg, anatomic site and pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification) were obtained. When only the Clark level was included in the dermatopathology report, the corresponding Breslow thickness was extrapolated from the Clark level,18 and the pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification (7th edition) was determined.
For our study, specific diagnostic codes—International Classification of Diseases, Ninth and Tenth Revisions; Hospital International Classification of Diseases Adaptation19; and Berkson16—were applied across individual records to identify all second primary malignancies using the resources of the REP. The diagnosis date, morphology, and anatomic location of second primary malignancies were confirmed from examination of the clinical records.
Statistical Analysis—Baseline characteristics were compared by BRAF V600E expression using Wilcoxon rank sum and χ2 tests. The rate of developing a second primary malignancy at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident malignant melanoma was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. The duration of follow-up was calculated from the incident melanoma date to the second primary malignancy date or the last follow-up date. Patients with a history of the malignancy of interest, except skin cancers, before the incident melanoma date were excluded because it was not possible to distinguish between recurrence of a prior malignancy and a second primary malignancy. Associations of BRAF V600E expression with the development of a second primary malignancy were evaluated with Cox proportional hazards regression models and summarized with hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs; all associations were adjusted for potential confounders such as age at the incident melanoma, year of the incident melanoma, and sex.
Results
Cumulative Incidence of Second Primary Melanoma—Of 133 patients with positive BRAF V600E expression, we identified 14 (10.5%), 1 (0.8%), and 1 (0.8%) who had 1, 2, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively. Of the 247 patients with negative BRAF V600E expression, we identified 15 (6%), 4 (1.6%), 2 (0.8%), and 1 (0.4%) patients who had 1, 2, 3, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively; BRAF V600E expression was not associated with the number of subsequent melanomas (P=.37; Wilcoxon rank sum test). The cumulative incidences of developing a second primary melanoma (n=38 among the 380 patients studied) at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 5.3%, 7.6%, 8.1%, and 14.6%, respectively.
Cumulative Incidence of All Second Primary Malignancies—Of the 380 patients studied, 60 (16%) had at least 1 malignancy diagnosed before the incident melanoma. Of the remaining 320 patients, 104 later had at least 1 malignancy develop, including a second primary melanoma, at a median (IQR) of 8.0 (2.7–16.2) years after the incident melanoma; the 104 patients with at least 1 subsequent malignancy included 40 with BRAF-positive and 64 with BRAF-negative melanomas. The cumulative incidences of developing at least 1 malignancy of any kind at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 15.0%, 20.5%, 31.2%, and 47.0%, respectively. Table 2 shows the number of patients with at least 1 second primary malignancy after the incident melanoma stratified by BRAF status.
BRAF V600E Expression and Association With Second Primary Malignancy—The eTable shows the associations of mutant BRAF V600E expression status with the development of a new primary malignancy. Malignancies affecting fewer than 10 patients were excluded from the analysis because there were too few events to support the Cox model. Positive BRAF V600E expression was associated with subsequent development of BCCs (HR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.35-3.99; P=.002) and the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.06-2.56; P=.03). However, BRAF V600E status was no longer a significant factor when all second primary malignancies, including second melanomas, were considered (P=.06). Table 3 shows the 5-, 10-, 15-, and 20-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies according to mutant BRAF status.
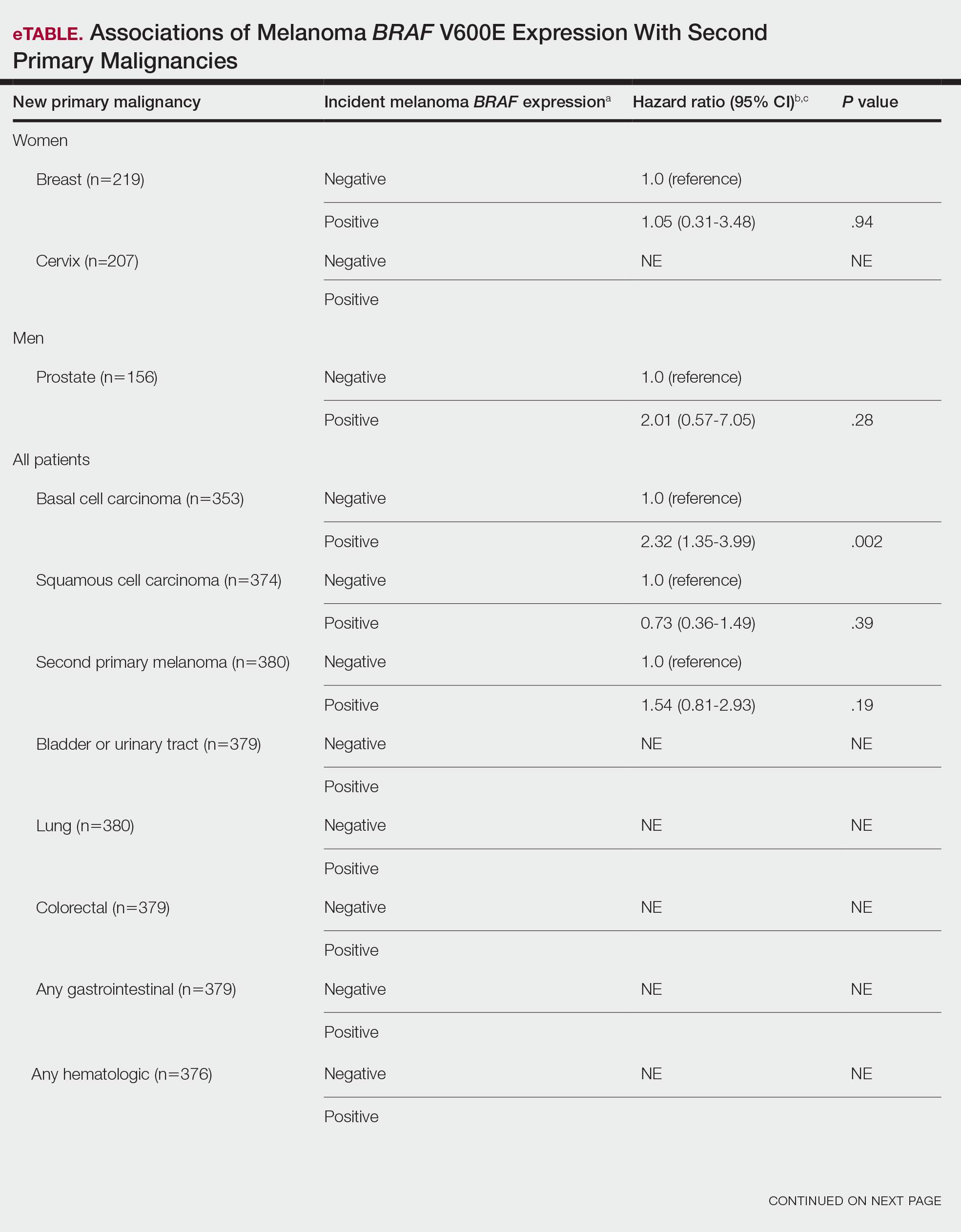
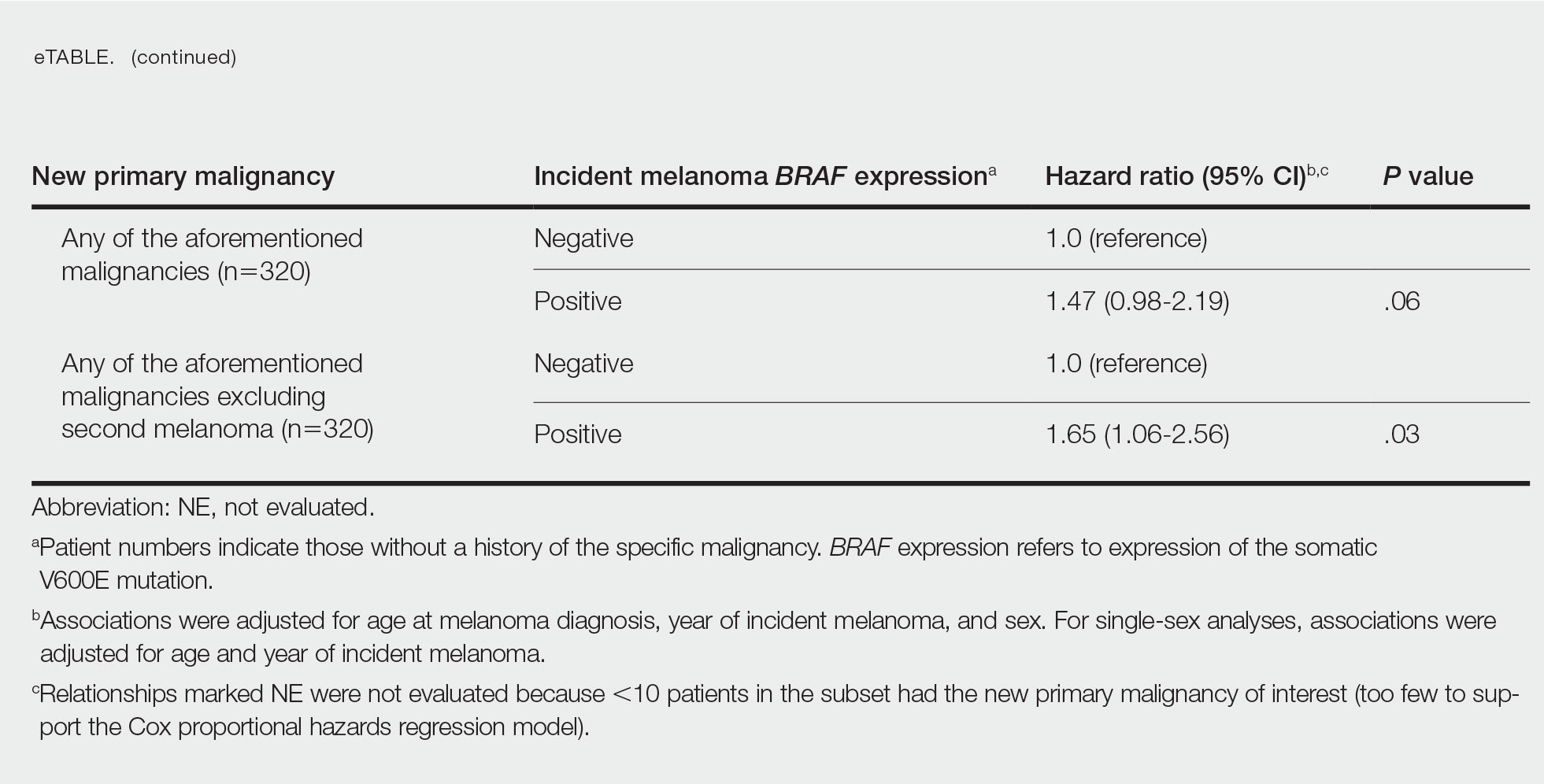
Comment
Association of BRAF V600E Expression With Second Primary Malignancies—BRAF V600E expression of an incident melanoma was associated with the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma; however, this association was not statistically significant when second primary melanomas were included. A possible explanation is that individuals with more than 1 primary melanoma possess additional genetic risk—CDKN2A or CDKN4 gene mutations or MC1R variation—that outweighed the effect of BRAF expression in the statistical analysis.
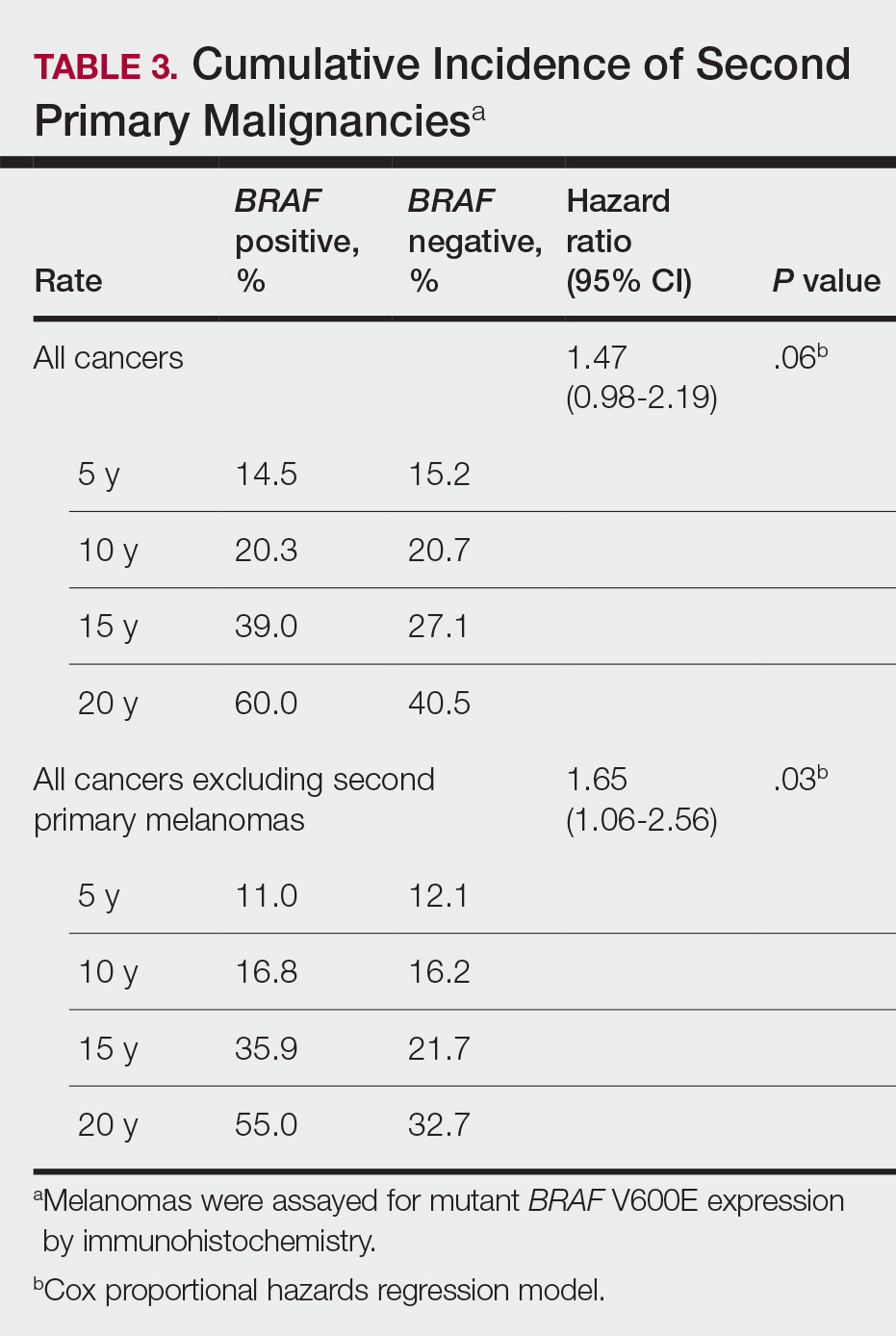
The 5- and 10-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies excluding second primary melanoma were similar between BRAF-positive and BRAF-negative melanoma, but the 15- and 20-year cumulative incidences were greater for the BRAF-positive cohort. This could reflect the association of BRAF expression with BCCs and the increased likelihood of their occurrence with cumulative sun exposure and advancing age. BRAF expression was associated with the development of BCCs, but the reason for this association was unclear. BRAF-mutated melanoma occurs more frequently on sun-protected sites,20 whereas sporadic BCC generally occurs on sun-exposed sites. However, BRAF-mutated melanoma is associated with high levels of ambient UV exposure early in life, particularly birth through 20 years of age,21 and we speculate that such early UV exposure influences the later development of BCCs.
Development of BRAF-Mutated Cancers—It currently is not understood why the same somatic mutation can cause different types of cancer. A recent translational research study showed that in mice models, precursor cells of the pancreas and bile duct responded differently when exposed to PIK3CA and KRAS oncogenes, and tumorigenesis is influenced by specific cooperating genetic events in the tissue microenvironment. Future research investigating these molecular interactions may lead to better understanding of cancer pathogenesis and direct the design of new targeted therapies.22,23
Regarding environmental influences on the development of BRAF-mutated cancers, we found 1 population-based study that identified an association between high iodine content of drinking water and the prevalence of T1799A BRAF papillary thyroid carcinoma in 5 regions in China.24 Another study identified an increased risk for colorectal cancer and nonmelanoma skin cancer in the first-degree relatives of index patients with BRAF V600E colorectal cancer.25 Two studies by institutions in China and Sweden reported the frequency of BRAF mutations in cohorts of patients with melanoma.26,27
Additional studies investigating a possible association between BRAF-mutated melanoma and other cancers with larger numbers of participants than in our study may become more feasible in the future with increased routine genetic testing of biopsied cancers.
Study Limitations—Limitations of this retrospective epidemiologic study include the possibility of ascertainment bias during data collection. We did not account for known risk factors for cancer (eg, excessive sun exposure, smoking).
The main clinical implications from this study are that we do not have enough evidence to recommend BRAF testing for all incident melanomas, and BRAF-mutated melanomas cannot be associated with increased risk for developing other forms of cancer, with the possible exception of BCCs
Conclusion
Physicians should be aware of the risk for a second primary malignancy after an incident melanoma, and we emphasize the importance of long-term cancer surveillance.
Acknowledgment—We thank Ms. Jayne H. Feind (Rochester, Minnesota) for assistance with study coordination.
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. Updated January 12, 2022. Accessed August 15, 2022.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- American Cancer Society. Second Cancers After Melanoma Skin Cancer. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/after-treatment/second-cancers.html
- Spanogle JP, Clarke CA, Aroner S, et al. Risk of second primary malignancies following cutaneous melanoma diagnosis: a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:757-767.
- Olazagasti Lourido JM, Ma JE, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma in the elderly: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1555-1562.
- Reed KB, Brewer JD, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among young adults: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:328-334.
- Lowe GC, Brewer JD, Peters MS, et al. Incidence of melanoma in the pediatric population: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Pediatr Derm. 2015;32:618-620.
- Lowe GC, Saavedra A, Reed KB, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among middle-aged adults: an epidemiologic study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:52-59.
- Ascierto PA, Kirkwood JM, Grob JJ, et al. The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma [editorial]. J Transl Med. 2012;10:85.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:51-65.
- Tiacci E, Trifonov V, Schiavoni G, et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2305-2315.
- Xing M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:245-262.
- Moreau S, Saiag P, Aegerter P, et al. Prognostic value of BRAF(V600) mutations in melanoma patients after resection of metastatic lymph nodes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:4314-4321.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:344-349.
- Rocca WA, Yawn BP, St Sauver JL, et al. History of the Rochester Epidemiology Project: half a century of medical records linkage in a US population. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:1202-1213.
- St. Sauver JL, Grossardt BR, Yawn BP, et al. Data resource profile: the Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) medical records-linkage system. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:1614-1624.
- National Cancer Institute. Staging: melanoma of the skin, vulva, penis and scrotum staging. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/abstract-code-stage/staging.html
- Pakhomov SV, Buntrock JD, Chute CG. Automating the assignment of diagnosis codes to patient encounters using example-based and machine learning techniques. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13:516-525.
- Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2135-2147.
- Thomas NE, Edmiston SN, Alexander A, et al. Number of nevi and early-life ambient UV exposure are associated with BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:991-997.
- German Cancer Research Center. Why identical mutations cause different types of cancer. July 19, 2021. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://www.dkfz.de/en/presse/pressemitteilungen/2021/dkfz-pm-21-41-Why-identical-mutations-cause-different-types-of-cancer.php
- Falcomatà C, Bärthel S, Ulrich A, et al. Genetic screens identify a context-specific PI3K/p27Kip1 node driving extrahepatic biliary cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:3158-3177.
- Guan H, Ji M, Bao R, et al. Association of high iodine intake with the T1799A BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1612-1617.
- Wish TA, Hyde AJ, Parfrey PS, et al. Increased cancer predisposition in family members of colorectal cancer patients harboring the p.V600E BRAF mutation: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:1831-1839.
- Zebary A, Omholt K, Vassilaki I, et al. KIT, NRAS, BRAF and PTEN mutations in a sample of Swedish patients with acral lentiginous melanoma. J Dermatol Sci. 2013;72:284-289.
- Si L, Kong Y, Xu X, et al. Prevalence of BRAF V600E mutation in Chinese melanoma patients: large scale analysis of BRAF and NRAS mutations in a 432-case cohort. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:94-100.
- Safaee Ardekani G, Jafarnejad SM, Khosravi S, et al. Disease progression and patient survival are significantly influenced by BRAF protein expression in primary melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:320-328.
The incidence of cutaneous melanoma in the United States has increased in the last 30 years, with the American Cancer Society estimating that 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed and 7650 melanoma-related deaths will occur in 2022.1 Patients with melanoma have an increased risk for developing a second primary melanoma or other malignancy, such as salivary gland, small intestine, breast, prostate, renal, or thyroid cancer, but most commonly nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 The incidence rate of melanoma among residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 1970 through 2009 has already been described for various age groups4-7; however, the incidence of a second primary malignancy, including melanoma, within these incident cohorts remains unknown.
Mutations in the BRAF oncogene occur in approximately 50% of melanomas.8,9
Although the BRAF mutation event in melanoma is sporadic and should not necessarily affect the development of an unrelated malignancy, we hypothesized that the exposures that may have predisposed a particular individual to a BRAF-mutated melanoma also may have a higher chance of predisposing that individual to the development of another primary malignancy. In this population-based study, we aimed to determine whether the specific melanoma feature of mutant BRAF V600E expression was associated with the development of a second primary malignancy.
Methods
This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center (both in Rochester, Minnesota). The reporting of this study is compliant with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology statement.15
Patient Selection and BRAF Assessment—The Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) links comprehensive health care records for virtually all residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, across different medical providers. The REP provides an index of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, tracks timelines and outcomes of individuals and their medical conditions, and is ideal for population-based studies.
We obtained a list of all residents of Olmsted County aged 18 to 60 years who had a melanoma diagnosed according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, from January 1, 1970, through December 30, 2009; these cohorts have been analyzed previously.4-7 Of the 638 individuals identified, 380 had a melanoma tissue block on file at Mayo Clinic with enough tumor present in available tissue blocks for BRAF assessment. All specimens were reviewed by a board-certified dermatopathologist (J.S.L.) to confirm the diagnosis of melanoma. Tissue blocks were recut, and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were stained for BRAF V600E (Spring Bioscience Corporation). BRAF-stained specimens and the associated hematoxylin and eosin−stained slides were reviewed. Melanocyte cytoplasmic staining for BRAF was graded as negative if no staining was evident. BRAF was graded as positive if focal or partial staining was observed (<50% of tumor or low BRAF expression) or if diffuse staining was evident (>50% of tumor or high BRAF expression).
Using resources of the REP, we confirmed patients’ residency status in Olmsted County at the time of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Patients who denied access to their medical records for research purposes were excluded. We used the complete record of each patient to confirm the date of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Baseline characteristics of patients and their incident melanomas (eg, anatomic site and pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification) were obtained. When only the Clark level was included in the dermatopathology report, the corresponding Breslow thickness was extrapolated from the Clark level,18 and the pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification (7th edition) was determined.
For our study, specific diagnostic codes—International Classification of Diseases, Ninth and Tenth Revisions; Hospital International Classification of Diseases Adaptation19; and Berkson16—were applied across individual records to identify all second primary malignancies using the resources of the REP. The diagnosis date, morphology, and anatomic location of second primary malignancies were confirmed from examination of the clinical records.
Statistical Analysis—Baseline characteristics were compared by BRAF V600E expression using Wilcoxon rank sum and χ2 tests. The rate of developing a second primary malignancy at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident malignant melanoma was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. The duration of follow-up was calculated from the incident melanoma date to the second primary malignancy date or the last follow-up date. Patients with a history of the malignancy of interest, except skin cancers, before the incident melanoma date were excluded because it was not possible to distinguish between recurrence of a prior malignancy and a second primary malignancy. Associations of BRAF V600E expression with the development of a second primary malignancy were evaluated with Cox proportional hazards regression models and summarized with hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs; all associations were adjusted for potential confounders such as age at the incident melanoma, year of the incident melanoma, and sex.
Results

Cumulative Incidence of Second Primary Melanoma—Of 133 patients with positive BRAF V600E expression, we identified 14 (10.5%), 1 (0.8%), and 1 (0.8%) who had 1, 2, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively. Of the 247 patients with negative BRAF V600E expression, we identified 15 (6%), 4 (1.6%), 2 (0.8%), and 1 (0.4%) patients who had 1, 2, 3, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively; BRAF V600E expression was not associated with the number of subsequent melanomas (P=.37; Wilcoxon rank sum test). The cumulative incidences of developing a second primary melanoma (n=38 among the 380 patients studied) at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 5.3%, 7.6%, 8.1%, and 14.6%, respectively.
Cumulative Incidence of All Second Primary Malignancies—Of the 380 patients studied, 60 (16%) had at least 1 malignancy diagnosed before the incident melanoma. Of the remaining 320 patients, 104 later had at least 1 malignancy develop, including a second primary melanoma, at a median (IQR) of 8.0 (2.7–16.2) years after the incident melanoma; the 104 patients with at least 1 subsequent malignancy included 40 with BRAF-positive and 64 with BRAF-negative melanomas. The cumulative incidences of developing at least 1 malignancy of any kind at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 15.0%, 20.5%, 31.2%, and 47.0%, respectively. Table 2 shows the number of patients with at least 1 second primary malignancy after the incident melanoma stratified by BRAF status.

BRAF V600E Expression and Association With Second Primary Malignancy—The eTable shows the associations of mutant BRAF V600E expression status with the development of a new primary malignancy. Malignancies affecting fewer than 10 patients were excluded from the analysis because there were too few events to support the Cox model. Positive BRAF V600E expression was associated with subsequent development of BCCs (HR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.35-3.99; P=.002) and the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.06-2.56; P=.03). However, BRAF V600E status was no longer a significant factor when all second primary malignancies, including second melanomas, were considered (P=.06). Table 3 shows the 5-, 10-, 15-, and 20-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies according to mutant BRAF status.


Comment
Association of BRAF V600E Expression With Second Primary Malignancies—BRAF V600E expression of an incident melanoma was associated with the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma; however, this association was not statistically significant when second primary melanomas were included. A possible explanation is that individuals with more than 1 primary melanoma possess additional genetic risk—CDKN2A or CDKN4 gene mutations or MC1R variation—that outweighed the effect of BRAF expression in the statistical analysis.

The 5- and 10-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies excluding second primary melanoma were similar between BRAF-positive and BRAF-negative melanoma, but the 15- and 20-year cumulative incidences were greater for the BRAF-positive cohort. This could reflect the association of BRAF expression with BCCs and the increased likelihood of their occurrence with cumulative sun exposure and advancing age. BRAF expression was associated with the development of BCCs, but the reason for this association was unclear. BRAF-mutated melanoma occurs more frequently on sun-protected sites,20 whereas sporadic BCC generally occurs on sun-exposed sites. However, BRAF-mutated melanoma is associated with high levels of ambient UV exposure early in life, particularly birth through 20 years of age,21 and we speculate that such early UV exposure influences the later development of BCCs.
Development of BRAF-Mutated Cancers—It currently is not understood why the same somatic mutation can cause different types of cancer. A recent translational research study showed that in mice models, precursor cells of the pancreas and bile duct responded differently when exposed to PIK3CA and KRAS oncogenes, and tumorigenesis is influenced by specific cooperating genetic events in the tissue microenvironment. Future research investigating these molecular interactions may lead to better understanding of cancer pathogenesis and direct the design of new targeted therapies.22,23
Regarding environmental influences on the development of BRAF-mutated cancers, we found 1 population-based study that identified an association between high iodine content of drinking water and the prevalence of T1799A BRAF papillary thyroid carcinoma in 5 regions in China.24 Another study identified an increased risk for colorectal cancer and nonmelanoma skin cancer in the first-degree relatives of index patients with BRAF V600E colorectal cancer.25 Two studies by institutions in China and Sweden reported the frequency of BRAF mutations in cohorts of patients with melanoma.26,27
Additional studies investigating a possible association between BRAF-mutated melanoma and other cancers with larger numbers of participants than in our study may become more feasible in the future with increased routine genetic testing of biopsied cancers.
Study Limitations—Limitations of this retrospective epidemiologic study include the possibility of ascertainment bias during data collection. We did not account for known risk factors for cancer (eg, excessive sun exposure, smoking).
The main clinical implications from this study are that we do not have enough evidence to recommend BRAF testing for all incident melanomas, and BRAF-mutated melanomas cannot be associated with increased risk for developing other forms of cancer, with the possible exception of BCCs
Conclusion
Physicians should be aware of the risk for a second primary malignancy after an incident melanoma, and we emphasize the importance of long-term cancer surveillance.
Acknowledgment—We thank Ms. Jayne H. Feind (Rochester, Minnesota) for assistance with study coordination.
The incidence of cutaneous melanoma in the United States has increased in the last 30 years, with the American Cancer Society estimating that 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed and 7650 melanoma-related deaths will occur in 2022.1 Patients with melanoma have an increased risk for developing a second primary melanoma or other malignancy, such as salivary gland, small intestine, breast, prostate, renal, or thyroid cancer, but most commonly nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 The incidence rate of melanoma among residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 1970 through 2009 has already been described for various age groups4-7; however, the incidence of a second primary malignancy, including melanoma, within these incident cohorts remains unknown.
Mutations in the BRAF oncogene occur in approximately 50% of melanomas.8,9
Although the BRAF mutation event in melanoma is sporadic and should not necessarily affect the development of an unrelated malignancy, we hypothesized that the exposures that may have predisposed a particular individual to a BRAF-mutated melanoma also may have a higher chance of predisposing that individual to the development of another primary malignancy. In this population-based study, we aimed to determine whether the specific melanoma feature of mutant BRAF V600E expression was associated with the development of a second primary malignancy.
Methods
This study was approved by the institutional review boards of the Mayo Clinic and Olmsted Medical Center (both in Rochester, Minnesota). The reporting of this study is compliant with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology statement.15
Patient Selection and BRAF Assessment—The Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) links comprehensive health care records for virtually all residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota, across different medical providers. The REP provides an index of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, tracks timelines and outcomes of individuals and their medical conditions, and is ideal for population-based studies.
We obtained a list of all residents of Olmsted County aged 18 to 60 years who had a melanoma diagnosed according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, from January 1, 1970, through December 30, 2009; these cohorts have been analyzed previously.4-7 Of the 638 individuals identified, 380 had a melanoma tissue block on file at Mayo Clinic with enough tumor present in available tissue blocks for BRAF assessment. All specimens were reviewed by a board-certified dermatopathologist (J.S.L.) to confirm the diagnosis of melanoma. Tissue blocks were recut, and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were stained for BRAF V600E (Spring Bioscience Corporation). BRAF-stained specimens and the associated hematoxylin and eosin−stained slides were reviewed. Melanocyte cytoplasmic staining for BRAF was graded as negative if no staining was evident. BRAF was graded as positive if focal or partial staining was observed (<50% of tumor or low BRAF expression) or if diffuse staining was evident (>50% of tumor or high BRAF expression).
Using resources of the REP, we confirmed patients’ residency status in Olmsted County at the time of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Patients who denied access to their medical records for research purposes were excluded. We used the complete record of each patient to confirm the date of diagnosis of the incident melanoma. Baseline characteristics of patients and their incident melanomas (eg, anatomic site and pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification) were obtained. When only the Clark level was included in the dermatopathology report, the corresponding Breslow thickness was extrapolated from the Clark level,18 and the pathologic stage according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification (7th edition) was determined.
For our study, specific diagnostic codes—International Classification of Diseases, Ninth and Tenth Revisions; Hospital International Classification of Diseases Adaptation19; and Berkson16—were applied across individual records to identify all second primary malignancies using the resources of the REP. The diagnosis date, morphology, and anatomic location of second primary malignancies were confirmed from examination of the clinical records.
Statistical Analysis—Baseline characteristics were compared by BRAF V600E expression using Wilcoxon rank sum and χ2 tests. The rate of developing a second primary malignancy at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident malignant melanoma was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method. The duration of follow-up was calculated from the incident melanoma date to the second primary malignancy date or the last follow-up date. Patients with a history of the malignancy of interest, except skin cancers, before the incident melanoma date were excluded because it was not possible to distinguish between recurrence of a prior malignancy and a second primary malignancy. Associations of BRAF V600E expression with the development of a second primary malignancy were evaluated with Cox proportional hazards regression models and summarized with hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs; all associations were adjusted for potential confounders such as age at the incident melanoma, year of the incident melanoma, and sex.
Results

Cumulative Incidence of Second Primary Melanoma—Of 133 patients with positive BRAF V600E expression, we identified 14 (10.5%), 1 (0.8%), and 1 (0.8%) who had 1, 2, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively. Of the 247 patients with negative BRAF V600E expression, we identified 15 (6%), 4 (1.6%), 2 (0.8%), and 1 (0.4%) patients who had 1, 2, 3, and 4 subsequent melanomas, respectively; BRAF V600E expression was not associated with the number of subsequent melanomas (P=.37; Wilcoxon rank sum test). The cumulative incidences of developing a second primary melanoma (n=38 among the 380 patients studied) at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 5.3%, 7.6%, 8.1%, and 14.6%, respectively.
Cumulative Incidence of All Second Primary Malignancies—Of the 380 patients studied, 60 (16%) had at least 1 malignancy diagnosed before the incident melanoma. Of the remaining 320 patients, 104 later had at least 1 malignancy develop, including a second primary melanoma, at a median (IQR) of 8.0 (2.7–16.2) years after the incident melanoma; the 104 patients with at least 1 subsequent malignancy included 40 with BRAF-positive and 64 with BRAF-negative melanomas. The cumulative incidences of developing at least 1 malignancy of any kind at 5, 10, 15, and 20 years after the incident melanoma were 15.0%, 20.5%, 31.2%, and 47.0%, respectively. Table 2 shows the number of patients with at least 1 second primary malignancy after the incident melanoma stratified by BRAF status.

BRAF V600E Expression and Association With Second Primary Malignancy—The eTable shows the associations of mutant BRAF V600E expression status with the development of a new primary malignancy. Malignancies affecting fewer than 10 patients were excluded from the analysis because there were too few events to support the Cox model. Positive BRAF V600E expression was associated with subsequent development of BCCs (HR, 2.32; 95% CI, 1.35-3.99; P=.002) and the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma (HR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.06-2.56; P=.03). However, BRAF V600E status was no longer a significant factor when all second primary malignancies, including second melanomas, were considered (P=.06). Table 3 shows the 5-, 10-, 15-, and 20-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies according to mutant BRAF status.


Comment
Association of BRAF V600E Expression With Second Primary Malignancies—BRAF V600E expression of an incident melanoma was associated with the development of all combined second primary malignancies excluding melanoma; however, this association was not statistically significant when second primary melanomas were included. A possible explanation is that individuals with more than 1 primary melanoma possess additional genetic risk—CDKN2A or CDKN4 gene mutations or MC1R variation—that outweighed the effect of BRAF expression in the statistical analysis.

The 5- and 10-year cumulative incidences of all second primary malignancies excluding second primary melanoma were similar between BRAF-positive and BRAF-negative melanoma, but the 15- and 20-year cumulative incidences were greater for the BRAF-positive cohort. This could reflect the association of BRAF expression with BCCs and the increased likelihood of their occurrence with cumulative sun exposure and advancing age. BRAF expression was associated with the development of BCCs, but the reason for this association was unclear. BRAF-mutated melanoma occurs more frequently on sun-protected sites,20 whereas sporadic BCC generally occurs on sun-exposed sites. However, BRAF-mutated melanoma is associated with high levels of ambient UV exposure early in life, particularly birth through 20 years of age,21 and we speculate that such early UV exposure influences the later development of BCCs.
Development of BRAF-Mutated Cancers—It currently is not understood why the same somatic mutation can cause different types of cancer. A recent translational research study showed that in mice models, precursor cells of the pancreas and bile duct responded differently when exposed to PIK3CA and KRAS oncogenes, and tumorigenesis is influenced by specific cooperating genetic events in the tissue microenvironment. Future research investigating these molecular interactions may lead to better understanding of cancer pathogenesis and direct the design of new targeted therapies.22,23
Regarding environmental influences on the development of BRAF-mutated cancers, we found 1 population-based study that identified an association between high iodine content of drinking water and the prevalence of T1799A BRAF papillary thyroid carcinoma in 5 regions in China.24 Another study identified an increased risk for colorectal cancer and nonmelanoma skin cancer in the first-degree relatives of index patients with BRAF V600E colorectal cancer.25 Two studies by institutions in China and Sweden reported the frequency of BRAF mutations in cohorts of patients with melanoma.26,27
Additional studies investigating a possible association between BRAF-mutated melanoma and other cancers with larger numbers of participants than in our study may become more feasible in the future with increased routine genetic testing of biopsied cancers.
Study Limitations—Limitations of this retrospective epidemiologic study include the possibility of ascertainment bias during data collection. We did not account for known risk factors for cancer (eg, excessive sun exposure, smoking).
The main clinical implications from this study are that we do not have enough evidence to recommend BRAF testing for all incident melanomas, and BRAF-mutated melanomas cannot be associated with increased risk for developing other forms of cancer, with the possible exception of BCCs
Conclusion
Physicians should be aware of the risk for a second primary malignancy after an incident melanoma, and we emphasize the importance of long-term cancer surveillance.
Acknowledgment—We thank Ms. Jayne H. Feind (Rochester, Minnesota) for assistance with study coordination.
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. Updated January 12, 2022. Accessed August 15, 2022.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- American Cancer Society. Second Cancers After Melanoma Skin Cancer. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/after-treatment/second-cancers.html
- Spanogle JP, Clarke CA, Aroner S, et al. Risk of second primary malignancies following cutaneous melanoma diagnosis: a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:757-767.
- Olazagasti Lourido JM, Ma JE, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma in the elderly: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1555-1562.
- Reed KB, Brewer JD, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among young adults: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:328-334.
- Lowe GC, Brewer JD, Peters MS, et al. Incidence of melanoma in the pediatric population: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Pediatr Derm. 2015;32:618-620.
- Lowe GC, Saavedra A, Reed KB, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among middle-aged adults: an epidemiologic study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:52-59.
- Ascierto PA, Kirkwood JM, Grob JJ, et al. The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma [editorial]. J Transl Med. 2012;10:85.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:51-65.
- Tiacci E, Trifonov V, Schiavoni G, et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2305-2315.
- Xing M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:245-262.
- Moreau S, Saiag P, Aegerter P, et al. Prognostic value of BRAF(V600) mutations in melanoma patients after resection of metastatic lymph nodes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:4314-4321.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:344-349.
- Rocca WA, Yawn BP, St Sauver JL, et al. History of the Rochester Epidemiology Project: half a century of medical records linkage in a US population. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:1202-1213.
- St. Sauver JL, Grossardt BR, Yawn BP, et al. Data resource profile: the Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) medical records-linkage system. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:1614-1624.
- National Cancer Institute. Staging: melanoma of the skin, vulva, penis and scrotum staging. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/abstract-code-stage/staging.html
- Pakhomov SV, Buntrock JD, Chute CG. Automating the assignment of diagnosis codes to patient encounters using example-based and machine learning techniques. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13:516-525.
- Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2135-2147.
- Thomas NE, Edmiston SN, Alexander A, et al. Number of nevi and early-life ambient UV exposure are associated with BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:991-997.
- German Cancer Research Center. Why identical mutations cause different types of cancer. July 19, 2021. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://www.dkfz.de/en/presse/pressemitteilungen/2021/dkfz-pm-21-41-Why-identical-mutations-cause-different-types-of-cancer.php
- Falcomatà C, Bärthel S, Ulrich A, et al. Genetic screens identify a context-specific PI3K/p27Kip1 node driving extrahepatic biliary cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:3158-3177.
- Guan H, Ji M, Bao R, et al. Association of high iodine intake with the T1799A BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1612-1617.
- Wish TA, Hyde AJ, Parfrey PS, et al. Increased cancer predisposition in family members of colorectal cancer patients harboring the p.V600E BRAF mutation: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:1831-1839.
- Zebary A, Omholt K, Vassilaki I, et al. KIT, NRAS, BRAF and PTEN mutations in a sample of Swedish patients with acral lentiginous melanoma. J Dermatol Sci. 2013;72:284-289.
- Si L, Kong Y, Xu X, et al. Prevalence of BRAF V600E mutation in Chinese melanoma patients: large scale analysis of BRAF and NRAS mutations in a 432-case cohort. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:94-100.
- Safaee Ardekani G, Jafarnejad SM, Khosravi S, et al. Disease progression and patient survival are significantly influenced by BRAF protein expression in primary melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:320-328.
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for melanoma skin cancer. Updated January 12, 2022. Accessed August 15, 2022.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
- American Cancer Society. Second Cancers After Melanoma Skin Cancer. Accessed August 19, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/after-treatment/second-cancers.html
- Spanogle JP, Clarke CA, Aroner S, et al. Risk of second primary malignancies following cutaneous melanoma diagnosis: a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:757-767.
- Olazagasti Lourido JM, Ma JE, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma in the elderly: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91:1555-1562.
- Reed KB, Brewer JD, Lohse CM, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among young adults: an epidemiological study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:328-334.
- Lowe GC, Brewer JD, Peters MS, et al. Incidence of melanoma in the pediatric population: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Pediatr Derm. 2015;32:618-620.
- Lowe GC, Saavedra A, Reed KB, et al. Increasing incidence of melanoma among middle-aged adults: an epidemiologic study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:52-59.
- Ascierto PA, Kirkwood JM, Grob JJ, et al. The role of BRAF V600 mutation in melanoma [editorial]. J Transl Med. 2012;10:85.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr. Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:51-65.
- Tiacci E, Trifonov V, Schiavoni G, et al. BRAF mutations in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2305-2315.
- Xing M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:245-262.
- Moreau S, Saiag P, Aegerter P, et al. Prognostic value of BRAF(V600) mutations in melanoma patients after resection of metastatic lymph nodes. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:4314-4321.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:344-349.
- Rocca WA, Yawn BP, St Sauver JL, et al. History of the Rochester Epidemiology Project: half a century of medical records linkage in a US population. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012;87:1202-1213.
- St. Sauver JL, Grossardt BR, Yawn BP, et al. Data resource profile: the Rochester Epidemiology Project (REP) medical records-linkage system. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:1614-1624.
- National Cancer Institute. Staging: melanoma of the skin, vulva, penis and scrotum staging. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/melanoma/abstract-code-stage/staging.html
- Pakhomov SV, Buntrock JD, Chute CG. Automating the assignment of diagnosis codes to patient encounters using example-based and machine learning techniques. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13:516-525.
- Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2135-2147.
- Thomas NE, Edmiston SN, Alexander A, et al. Number of nevi and early-life ambient UV exposure are associated with BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:991-997.
- German Cancer Research Center. Why identical mutations cause different types of cancer. July 19, 2021. Accessed August 15, 2022. https://www.dkfz.de/en/presse/pressemitteilungen/2021/dkfz-pm-21-41-Why-identical-mutations-cause-different-types-of-cancer.php
- Falcomatà C, Bärthel S, Ulrich A, et al. Genetic screens identify a context-specific PI3K/p27Kip1 node driving extrahepatic biliary cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:3158-3177.
- Guan H, Ji M, Bao R, et al. Association of high iodine intake with the T1799A BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1612-1617.
- Wish TA, Hyde AJ, Parfrey PS, et al. Increased cancer predisposition in family members of colorectal cancer patients harboring the p.V600E BRAF mutation: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:1831-1839.
- Zebary A, Omholt K, Vassilaki I, et al. KIT, NRAS, BRAF and PTEN mutations in a sample of Swedish patients with acral lentiginous melanoma. J Dermatol Sci. 2013;72:284-289.
- Si L, Kong Y, Xu X, et al. Prevalence of BRAF V600E mutation in Chinese melanoma patients: large scale analysis of BRAF and NRAS mutations in a 432-case cohort. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:94-100.
- Safaee Ardekani G, Jafarnejad SM, Khosravi S, et al. Disease progression and patient survival are significantly influenced by BRAF protein expression in primary melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:320-328.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware of the long-term risk of second primary malignancies after an incident melanoma.
- BRAF mutations occur in melanomas and several other cancers. Our study found that melanoma BRAF V600E expression is associated with an increased risk for basal cell carcinomas.
Risk Factors Predicting Cellulitis Diagnosis in a Prospective Cohort Undergoing Dermatology Consultation in the Emergency Department
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and skin-associated structures characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and pain of the affected area. Cellulitis most commonly occurs in middle-aged and older adults and frequently affects the lower extremities.1 Serious complications of cellulitis such as bacteremia, metastatic infection, and sepsis are rare, and most cases of cellulitis in patients with normal vital signs and mental status can be managed with outpatient treatment.2
Diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by a number of similarly presenting conditions collectively known as pseudocellulitis, such as venous stasis dermatitis and deep vein thrombosis.1 Misdiagnosis of cellulitis is common, with rates exceeding 30% among hospitalized patients initially diagnosed with cellulitis.3,4 Dermatology or infectious disease assessment is considered the diagnostic gold standard for cellulitis4,5 but is not always readily available, especially in resource-constrained settings.
Most cases of uncomplicated cellulitis can be managed with outpatient treatment, especially because serious complications are rare. Frequent misdiagnosis leads to repeat or unnecessary hospitalization and antibiosis. Exceptions necessitating hospitalization usually are predicated on signs of systemic infection, severe immunocompromised states, or failure of prior outpatient therapy.6 Such presentations can be distinguished by corresponding notable historical or examination factors, such as vital sign abnormalities suggesting systemic infection or history of malignancy leading to an immunocompromised state.
We sought to evaluate factors leading to the diagnosis of cellulitis in a cohort of patients with uncomplicated presentations receiving dermatology consultation to emphasize findings indicative of cellulitis in the absence of clinical or historical factors suggestive of other conditions necessitating hospitalization, such as systemic infection.
Methods
Study Participants—A prospective cohort study of patients presenting to an emergency department (ED) between October 2012 and January 2017 at an urban academic medical center in Boston, Massachusetts, was conducted with approval of study design and procedures by the relevant institutional review board. Patients older than 18 years were eligible for inclusion if given an initial diagnosis of cellulitis by an ED physician. Patients were excluded if incarcerated, pregnant, or unable to provide informed consent. Other exclusion criteria includedinfections overlying temporary or permanent indwelling hardware, animal or human bites, or sites of recent surgery (within the prior 4 weeks); preceding antibiotic treatment for more than 24 hours; or clinical or radiographic evidence of complications requiring alternative management such as osteomyelitis or abscess. Patients presenting with an elevated heart rate (>100 beats per minute) or body temperature (>100.5 °F [38.1 °C]) also were excluded. Eligible patients were enrolled upon providing written informed consent, and no remuneration was offered for participation.
Dermatology Consultation Intervention—A random subset of enrolled patients received dermatology consultation within 24 hours of presentation. Consultation consisted of a patient interview and physical examination with care recommendations to relevant ED and inpatient teams. Consultations confirmed the presence or absence of cellulitis as the primary outcome and also noted the presence of any pseudocellulitis diagnoses either occurring concomitantly with or mimicking cellulitis as a secondary outcome.
Statistical Analysis—Patient characteristics were analyzed to identify factors independently associated with the diagnosis of cellulitis in cases affecting the lower extremities. Factors were recorded with categorical variables reported as counts and percentages and continuous variables as means and standard deviations. Univariate analyses between categorical variables or discretized continuous variables and cellulitis diagnosis were conducted via Fisher exact test to identify a preliminary set of potential risk factors. Continuous variables were discretized at multiple incremental values with the discretization most significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis selected as a preliminary risk factor. Multivariate analyses involved using any objective preliminary factor meeting a significance threshold of P<.1 in univariate comparisons in a multivariate logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis diagnosis with corresponding calculation of odds ratios with confidence intervals and receiver operating characteristic. Factors with confidence intervals that excluded 1 were considered significant independent predictors of cellulitis. Analyses were performed using Python version 3.8 (Python Software Foundation).
Results
Of 1359 patients screened for eligibility, 104 patients with presumed lower extremity cellulitis undergoing dermatology consultation were included in this study (Figure). The mean patient age (SD) was 60.4 (19.2) years, and 63.5% of patients were male. In the study population, 63 (60.6%) patients received a final diagnosis of cellulitis. The most common pseudocellulitis diagnosis identified was venous stasis dermatitis, which occurred in 12 (11.5%) patients with concomitant cellulitis and in 12 (11.5%) patients mimicking cellulitis (Table).
Univariate comparisons revealed a diverse set of historical, examination, and laboratory factors associated with cellulitis diagnosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis was associated with unilateral presentation, recent trauma to the affected site, and history of cellulitis or onychomycosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis also was associated with elevated white blood cell count, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, body mass index, hematocrit, and platelet count; age less than 75 years; and lower serum sodium and serum chloride levels. These were the independent factors included in the multivariate analysis, which consisted of a logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis (eTable).
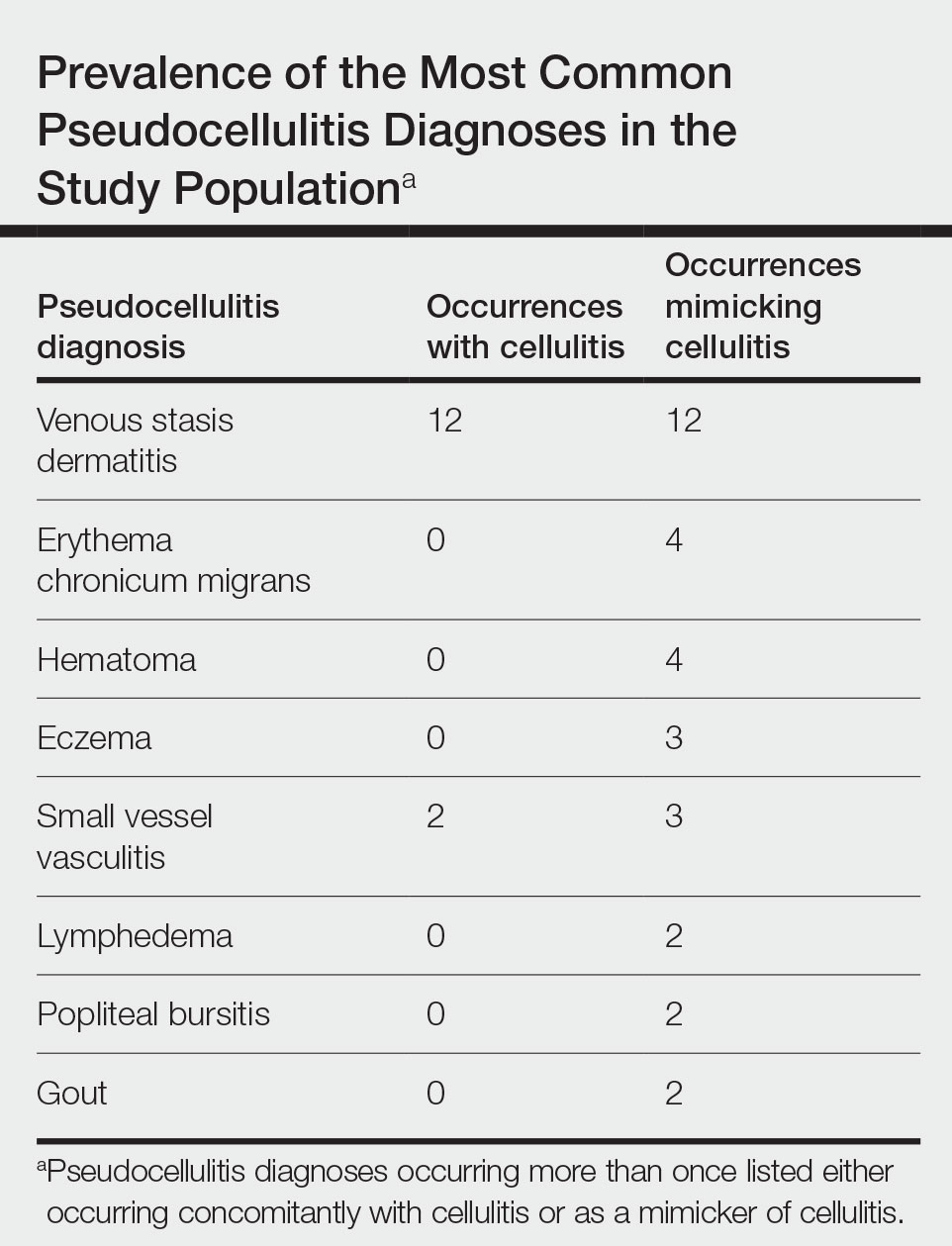
Multivariate logistic regression on all preliminary factors significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis in univariate comparisons demonstrated leukocytosis, which was defined as having a white blood cell count exceeding 11,000/μL, unilateral presentation, history of onychomycosis, and trauma to the affected site as significant independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis; history of cellulitis approached significance (eTable). Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis were the strongest predictors; having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%.

Comment
Importance of Identifying Pseudocellulitis—Successful diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by pseudocellulitis that can present concomitantly with or in lieu of cellulitis itself. Although cellulitis mostly affects the lower extremities in adults, pseudocellulitis also was common in this study population of patients with suspected lower extremity cellulitis, occurring both as a mimicker and concomitantly with cellulitis with substantial frequency. Notably, among patients with both venous stasis dermatitis and cellulitis diagnosed, most patients (n=10/12; 83.3%) had unilateral presentations of cellulitis as evidenced by signs and symptoms more notably affecting one lower extremity than the other. These findings suggest that certain pseudocellulitis diagnoses may predispose patients to cellulitis by disrupting the skin barrier, leading to bacterial infiltration; however, these pseudocellulitis diagnoses typically affect both lower extremities equally,1 and asymmetric involvement suggests the presence of overlying cellulitis. Furthermore, the most common pseudocellulitis entities found, such as venous stasis dermatitis, hematoma, and eczema, do not benefit from antibiotic treatment and require alternative therapy.1 Successful discrimination of these pseudocellulitis entities is critical to bolster proper antibiotic stewardship and discourage unnecessary hospitalization.
Independent Predictors of Cellulitis—Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis each emerged as strong independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis in this study. Having either of these factors furthermore demonstrated high sensitivity and negative predictive value for cellulitis diagnosis. Other notable risk factors were history of onychomycosis, cellulitis, and trauma to the affected site. Prior studies have identified similar historical factors as predisposing patients to cellulitis.7-9 Interestingly, warmth of the affected area on physical examination emerged as strongly associated with cellulitis but was not included in the final predictive model because of its subjective determination. These factors may be especially important in diagnosing cellulitis in patients without concerning vital signs and with concomitant or prior pseudocellulitis.
Study Limitations—This study was limited to patients with uncomplicated presentations to emphasize discrimination of factors associated with cellulitis in the absence of suggestive signs of infection, such as vital sign abnormalities. Signs such as fever and tachypnea have been previously correlated to outpatient treatment failure and necessity for hospitalization.10-12 This study instead focused on patients without concerning vital signs to reduce confounding by such factors in more severe presentations that heighten suspicion for infection and increase likelihood of additional treatment measures. For such patients, suggestive historical factors, such as those discovered in this study, should be considered instead. Interestingly, increased age did not emerge as a significant predictor in this population in contrast to other predictive models that included patients with vital sign abnormalities. Notably, older patients tend to have more variable vital signs, especially in response to physiologic stressors such as infection.13 As such, age may serve as a proxy for vital sign abnormalities to some degree in such predictive models, leading to heightened suspicion for infection in older patients. This study demonstrated that in the absence of concerning vital signs, historical rather than demographic factors are more predictive of cellulitis.
Conclusion
Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis emerged as strong independent predictors of lower extremity cellulitis in patients with uncomplicated presentations. Having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%. Other factors such as history of cellulitis, onychomycosis, and recent trauma to the affected site emerged as additional predictors. These historical, examination, and laboratory characteristics may be especially useful for successful diagnosis of cellulitis in varied practice settings, including outpatient clinics and EDs.
- Raff AB, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: a review. JAMA. 2016;316:325-337.
- Gunderson CG, Cherry BM, Fisher A. Do patients with cellulitis need to be hospitalized? a systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality rates of inpatients with cellulitis. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1553-1560.
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St. John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:147-159.
- Björnsdóttir S, Gottfredsson M, Thórisdóttir AS, et al. Risk factors for acute cellulitis of the lower limb: a prospective case-control study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1416-1422.
- Roujeau JC, Sigurgeirsson B, Korting HC, et al. Chronic dermatomycoses of the foot as risk factors for acute bacterial cellulitis of the leg: a case-control study. Dermatology. 2004;209:301-307.
- McNamara DR, Tleyjeh IM, Berbari EF, et al. A predictive model of recurrent lower extremity cellulitis in a population-based cohort. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:709-715.
- Yadav K, Suh KN, Eagles D, et al. Predictors of oral antibiotic treatment failure for nonpurulent skin and soft tissue infections in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2019;26:51-59.
- Peterson D, McLeod S, Woolfrey K, et al. Predictors of failure of empiric outpatient antibiotic therapy in emergency department patients with uncomplicated cellulitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:526-531.
- Volz KA, Canham L, Kaplan E, et al. Identifying patients with cellulitis who are likely to require inpatient admission after a stay in an ED observation unit. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31:360-364.
- Chester JG, Rudolph JL. Vital signs in older patients: age-related changes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011;12:337-343.
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and skin-associated structures characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and pain of the affected area. Cellulitis most commonly occurs in middle-aged and older adults and frequently affects the lower extremities.1 Serious complications of cellulitis such as bacteremia, metastatic infection, and sepsis are rare, and most cases of cellulitis in patients with normal vital signs and mental status can be managed with outpatient treatment.2
Diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by a number of similarly presenting conditions collectively known as pseudocellulitis, such as venous stasis dermatitis and deep vein thrombosis.1 Misdiagnosis of cellulitis is common, with rates exceeding 30% among hospitalized patients initially diagnosed with cellulitis.3,4 Dermatology or infectious disease assessment is considered the diagnostic gold standard for cellulitis4,5 but is not always readily available, especially in resource-constrained settings.
Most cases of uncomplicated cellulitis can be managed with outpatient treatment, especially because serious complications are rare. Frequent misdiagnosis leads to repeat or unnecessary hospitalization and antibiosis. Exceptions necessitating hospitalization usually are predicated on signs of systemic infection, severe immunocompromised states, or failure of prior outpatient therapy.6 Such presentations can be distinguished by corresponding notable historical or examination factors, such as vital sign abnormalities suggesting systemic infection or history of malignancy leading to an immunocompromised state.
We sought to evaluate factors leading to the diagnosis of cellulitis in a cohort of patients with uncomplicated presentations receiving dermatology consultation to emphasize findings indicative of cellulitis in the absence of clinical or historical factors suggestive of other conditions necessitating hospitalization, such as systemic infection.
Methods
Study Participants—A prospective cohort study of patients presenting to an emergency department (ED) between October 2012 and January 2017 at an urban academic medical center in Boston, Massachusetts, was conducted with approval of study design and procedures by the relevant institutional review board. Patients older than 18 years were eligible for inclusion if given an initial diagnosis of cellulitis by an ED physician. Patients were excluded if incarcerated, pregnant, or unable to provide informed consent. Other exclusion criteria includedinfections overlying temporary or permanent indwelling hardware, animal or human bites, or sites of recent surgery (within the prior 4 weeks); preceding antibiotic treatment for more than 24 hours; or clinical or radiographic evidence of complications requiring alternative management such as osteomyelitis or abscess. Patients presenting with an elevated heart rate (>100 beats per minute) or body temperature (>100.5 °F [38.1 °C]) also were excluded. Eligible patients were enrolled upon providing written informed consent, and no remuneration was offered for participation.
Dermatology Consultation Intervention—A random subset of enrolled patients received dermatology consultation within 24 hours of presentation. Consultation consisted of a patient interview and physical examination with care recommendations to relevant ED and inpatient teams. Consultations confirmed the presence or absence of cellulitis as the primary outcome and also noted the presence of any pseudocellulitis diagnoses either occurring concomitantly with or mimicking cellulitis as a secondary outcome.
Statistical Analysis—Patient characteristics were analyzed to identify factors independently associated with the diagnosis of cellulitis in cases affecting the lower extremities. Factors were recorded with categorical variables reported as counts and percentages and continuous variables as means and standard deviations. Univariate analyses between categorical variables or discretized continuous variables and cellulitis diagnosis were conducted via Fisher exact test to identify a preliminary set of potential risk factors. Continuous variables were discretized at multiple incremental values with the discretization most significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis selected as a preliminary risk factor. Multivariate analyses involved using any objective preliminary factor meeting a significance threshold of P<.1 in univariate comparisons in a multivariate logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis diagnosis with corresponding calculation of odds ratios with confidence intervals and receiver operating characteristic. Factors with confidence intervals that excluded 1 were considered significant independent predictors of cellulitis. Analyses were performed using Python version 3.8 (Python Software Foundation).
Results
Of 1359 patients screened for eligibility, 104 patients with presumed lower extremity cellulitis undergoing dermatology consultation were included in this study (Figure). The mean patient age (SD) was 60.4 (19.2) years, and 63.5% of patients were male. In the study population, 63 (60.6%) patients received a final diagnosis of cellulitis. The most common pseudocellulitis diagnosis identified was venous stasis dermatitis, which occurred in 12 (11.5%) patients with concomitant cellulitis and in 12 (11.5%) patients mimicking cellulitis (Table).

Univariate comparisons revealed a diverse set of historical, examination, and laboratory factors associated with cellulitis diagnosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis was associated with unilateral presentation, recent trauma to the affected site, and history of cellulitis or onychomycosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis also was associated with elevated white blood cell count, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, body mass index, hematocrit, and platelet count; age less than 75 years; and lower serum sodium and serum chloride levels. These were the independent factors included in the multivariate analysis, which consisted of a logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis (eTable).

Multivariate logistic regression on all preliminary factors significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis in univariate comparisons demonstrated leukocytosis, which was defined as having a white blood cell count exceeding 11,000/μL, unilateral presentation, history of onychomycosis, and trauma to the affected site as significant independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis; history of cellulitis approached significance (eTable). Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis were the strongest predictors; having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%.

Comment
Importance of Identifying Pseudocellulitis—Successful diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by pseudocellulitis that can present concomitantly with or in lieu of cellulitis itself. Although cellulitis mostly affects the lower extremities in adults, pseudocellulitis also was common in this study population of patients with suspected lower extremity cellulitis, occurring both as a mimicker and concomitantly with cellulitis with substantial frequency. Notably, among patients with both venous stasis dermatitis and cellulitis diagnosed, most patients (n=10/12; 83.3%) had unilateral presentations of cellulitis as evidenced by signs and symptoms more notably affecting one lower extremity than the other. These findings suggest that certain pseudocellulitis diagnoses may predispose patients to cellulitis by disrupting the skin barrier, leading to bacterial infiltration; however, these pseudocellulitis diagnoses typically affect both lower extremities equally,1 and asymmetric involvement suggests the presence of overlying cellulitis. Furthermore, the most common pseudocellulitis entities found, such as venous stasis dermatitis, hematoma, and eczema, do not benefit from antibiotic treatment and require alternative therapy.1 Successful discrimination of these pseudocellulitis entities is critical to bolster proper antibiotic stewardship and discourage unnecessary hospitalization.
Independent Predictors of Cellulitis—Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis each emerged as strong independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis in this study. Having either of these factors furthermore demonstrated high sensitivity and negative predictive value for cellulitis diagnosis. Other notable risk factors were history of onychomycosis, cellulitis, and trauma to the affected site. Prior studies have identified similar historical factors as predisposing patients to cellulitis.7-9 Interestingly, warmth of the affected area on physical examination emerged as strongly associated with cellulitis but was not included in the final predictive model because of its subjective determination. These factors may be especially important in diagnosing cellulitis in patients without concerning vital signs and with concomitant or prior pseudocellulitis.
Study Limitations—This study was limited to patients with uncomplicated presentations to emphasize discrimination of factors associated with cellulitis in the absence of suggestive signs of infection, such as vital sign abnormalities. Signs such as fever and tachypnea have been previously correlated to outpatient treatment failure and necessity for hospitalization.10-12 This study instead focused on patients without concerning vital signs to reduce confounding by such factors in more severe presentations that heighten suspicion for infection and increase likelihood of additional treatment measures. For such patients, suggestive historical factors, such as those discovered in this study, should be considered instead. Interestingly, increased age did not emerge as a significant predictor in this population in contrast to other predictive models that included patients with vital sign abnormalities. Notably, older patients tend to have more variable vital signs, especially in response to physiologic stressors such as infection.13 As such, age may serve as a proxy for vital sign abnormalities to some degree in such predictive models, leading to heightened suspicion for infection in older patients. This study demonstrated that in the absence of concerning vital signs, historical rather than demographic factors are more predictive of cellulitis.
Conclusion
Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis emerged as strong independent predictors of lower extremity cellulitis in patients with uncomplicated presentations. Having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%. Other factors such as history of cellulitis, onychomycosis, and recent trauma to the affected site emerged as additional predictors. These historical, examination, and laboratory characteristics may be especially useful for successful diagnosis of cellulitis in varied practice settings, including outpatient clinics and EDs.
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and skin-associated structures characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and pain of the affected area. Cellulitis most commonly occurs in middle-aged and older adults and frequently affects the lower extremities.1 Serious complications of cellulitis such as bacteremia, metastatic infection, and sepsis are rare, and most cases of cellulitis in patients with normal vital signs and mental status can be managed with outpatient treatment.2
Diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by a number of similarly presenting conditions collectively known as pseudocellulitis, such as venous stasis dermatitis and deep vein thrombosis.1 Misdiagnosis of cellulitis is common, with rates exceeding 30% among hospitalized patients initially diagnosed with cellulitis.3,4 Dermatology or infectious disease assessment is considered the diagnostic gold standard for cellulitis4,5 but is not always readily available, especially in resource-constrained settings.
Most cases of uncomplicated cellulitis can be managed with outpatient treatment, especially because serious complications are rare. Frequent misdiagnosis leads to repeat or unnecessary hospitalization and antibiosis. Exceptions necessitating hospitalization usually are predicated on signs of systemic infection, severe immunocompromised states, or failure of prior outpatient therapy.6 Such presentations can be distinguished by corresponding notable historical or examination factors, such as vital sign abnormalities suggesting systemic infection or history of malignancy leading to an immunocompromised state.
We sought to evaluate factors leading to the diagnosis of cellulitis in a cohort of patients with uncomplicated presentations receiving dermatology consultation to emphasize findings indicative of cellulitis in the absence of clinical or historical factors suggestive of other conditions necessitating hospitalization, such as systemic infection.
Methods
Study Participants—A prospective cohort study of patients presenting to an emergency department (ED) between October 2012 and January 2017 at an urban academic medical center in Boston, Massachusetts, was conducted with approval of study design and procedures by the relevant institutional review board. Patients older than 18 years were eligible for inclusion if given an initial diagnosis of cellulitis by an ED physician. Patients were excluded if incarcerated, pregnant, or unable to provide informed consent. Other exclusion criteria includedinfections overlying temporary or permanent indwelling hardware, animal or human bites, or sites of recent surgery (within the prior 4 weeks); preceding antibiotic treatment for more than 24 hours; or clinical or radiographic evidence of complications requiring alternative management such as osteomyelitis or abscess. Patients presenting with an elevated heart rate (>100 beats per minute) or body temperature (>100.5 °F [38.1 °C]) also were excluded. Eligible patients were enrolled upon providing written informed consent, and no remuneration was offered for participation.
Dermatology Consultation Intervention—A random subset of enrolled patients received dermatology consultation within 24 hours of presentation. Consultation consisted of a patient interview and physical examination with care recommendations to relevant ED and inpatient teams. Consultations confirmed the presence or absence of cellulitis as the primary outcome and also noted the presence of any pseudocellulitis diagnoses either occurring concomitantly with or mimicking cellulitis as a secondary outcome.
Statistical Analysis—Patient characteristics were analyzed to identify factors independently associated with the diagnosis of cellulitis in cases affecting the lower extremities. Factors were recorded with categorical variables reported as counts and percentages and continuous variables as means and standard deviations. Univariate analyses between categorical variables or discretized continuous variables and cellulitis diagnosis were conducted via Fisher exact test to identify a preliminary set of potential risk factors. Continuous variables were discretized at multiple incremental values with the discretization most significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis selected as a preliminary risk factor. Multivariate analyses involved using any objective preliminary factor meeting a significance threshold of P<.1 in univariate comparisons in a multivariate logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis diagnosis with corresponding calculation of odds ratios with confidence intervals and receiver operating characteristic. Factors with confidence intervals that excluded 1 were considered significant independent predictors of cellulitis. Analyses were performed using Python version 3.8 (Python Software Foundation).
Results
Of 1359 patients screened for eligibility, 104 patients with presumed lower extremity cellulitis undergoing dermatology consultation were included in this study (Figure). The mean patient age (SD) was 60.4 (19.2) years, and 63.5% of patients were male. In the study population, 63 (60.6%) patients received a final diagnosis of cellulitis. The most common pseudocellulitis diagnosis identified was venous stasis dermatitis, which occurred in 12 (11.5%) patients with concomitant cellulitis and in 12 (11.5%) patients mimicking cellulitis (Table).

Univariate comparisons revealed a diverse set of historical, examination, and laboratory factors associated with cellulitis diagnosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis was associated with unilateral presentation, recent trauma to the affected site, and history of cellulitis or onychomycosis. Diagnosis of cellulitis also was associated with elevated white blood cell count, absolute neutrophil count, C-reactive protein, body mass index, hematocrit, and platelet count; age less than 75 years; and lower serum sodium and serum chloride levels. These were the independent factors included in the multivariate analysis, which consisted of a logistic regression model for prediction of cellulitis (eTable).

Multivariate logistic regression on all preliminary factors significantly associated with cellulitis diagnosis in univariate comparisons demonstrated leukocytosis, which was defined as having a white blood cell count exceeding 11,000/μL, unilateral presentation, history of onychomycosis, and trauma to the affected site as significant independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis; history of cellulitis approached significance (eTable). Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis were the strongest predictors; having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%.

Comment
Importance of Identifying Pseudocellulitis—Successful diagnosis of cellulitis can be confounded by pseudocellulitis that can present concomitantly with or in lieu of cellulitis itself. Although cellulitis mostly affects the lower extremities in adults, pseudocellulitis also was common in this study population of patients with suspected lower extremity cellulitis, occurring both as a mimicker and concomitantly with cellulitis with substantial frequency. Notably, among patients with both venous stasis dermatitis and cellulitis diagnosed, most patients (n=10/12; 83.3%) had unilateral presentations of cellulitis as evidenced by signs and symptoms more notably affecting one lower extremity than the other. These findings suggest that certain pseudocellulitis diagnoses may predispose patients to cellulitis by disrupting the skin barrier, leading to bacterial infiltration; however, these pseudocellulitis diagnoses typically affect both lower extremities equally,1 and asymmetric involvement suggests the presence of overlying cellulitis. Furthermore, the most common pseudocellulitis entities found, such as venous stasis dermatitis, hematoma, and eczema, do not benefit from antibiotic treatment and require alternative therapy.1 Successful discrimination of these pseudocellulitis entities is critical to bolster proper antibiotic stewardship and discourage unnecessary hospitalization.
Independent Predictors of Cellulitis—Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis each emerged as strong independent predictors of cellulitis diagnosis in this study. Having either of these factors furthermore demonstrated high sensitivity and negative predictive value for cellulitis diagnosis. Other notable risk factors were history of onychomycosis, cellulitis, and trauma to the affected site. Prior studies have identified similar historical factors as predisposing patients to cellulitis.7-9 Interestingly, warmth of the affected area on physical examination emerged as strongly associated with cellulitis but was not included in the final predictive model because of its subjective determination. These factors may be especially important in diagnosing cellulitis in patients without concerning vital signs and with concomitant or prior pseudocellulitis.
Study Limitations—This study was limited to patients with uncomplicated presentations to emphasize discrimination of factors associated with cellulitis in the absence of suggestive signs of infection, such as vital sign abnormalities. Signs such as fever and tachypnea have been previously correlated to outpatient treatment failure and necessity for hospitalization.10-12 This study instead focused on patients without concerning vital signs to reduce confounding by such factors in more severe presentations that heighten suspicion for infection and increase likelihood of additional treatment measures. For such patients, suggestive historical factors, such as those discovered in this study, should be considered instead. Interestingly, increased age did not emerge as a significant predictor in this population in contrast to other predictive models that included patients with vital sign abnormalities. Notably, older patients tend to have more variable vital signs, especially in response to physiologic stressors such as infection.13 As such, age may serve as a proxy for vital sign abnormalities to some degree in such predictive models, leading to heightened suspicion for infection in older patients. This study demonstrated that in the absence of concerning vital signs, historical rather than demographic factors are more predictive of cellulitis.
Conclusion
Unilateral presentation and leukocytosis emerged as strong independent predictors of lower extremity cellulitis in patients with uncomplicated presentations. Having either of these factors had a sensitivity of 93.7% and a negative predictive value of 76.5%. Other factors such as history of cellulitis, onychomycosis, and recent trauma to the affected site emerged as additional predictors. These historical, examination, and laboratory characteristics may be especially useful for successful diagnosis of cellulitis in varied practice settings, including outpatient clinics and EDs.
- Raff AB, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: a review. JAMA. 2016;316:325-337.
- Gunderson CG, Cherry BM, Fisher A. Do patients with cellulitis need to be hospitalized? a systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality rates of inpatients with cellulitis. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1553-1560.
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St. John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:147-159.
- Björnsdóttir S, Gottfredsson M, Thórisdóttir AS, et al. Risk factors for acute cellulitis of the lower limb: a prospective case-control study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1416-1422.
- Roujeau JC, Sigurgeirsson B, Korting HC, et al. Chronic dermatomycoses of the foot as risk factors for acute bacterial cellulitis of the leg: a case-control study. Dermatology. 2004;209:301-307.
- McNamara DR, Tleyjeh IM, Berbari EF, et al. A predictive model of recurrent lower extremity cellulitis in a population-based cohort. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:709-715.
- Yadav K, Suh KN, Eagles D, et al. Predictors of oral antibiotic treatment failure for nonpurulent skin and soft tissue infections in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2019;26:51-59.
- Peterson D, McLeod S, Woolfrey K, et al. Predictors of failure of empiric outpatient antibiotic therapy in emergency department patients with uncomplicated cellulitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:526-531.
- Volz KA, Canham L, Kaplan E, et al. Identifying patients with cellulitis who are likely to require inpatient admission after a stay in an ED observation unit. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31:360-364.
- Chester JG, Rudolph JL. Vital signs in older patients: age-related changes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011;12:337-343.
- Raff AB, Kroshinsky D. Cellulitis: a review. JAMA. 2016;316:325-337.
- Gunderson CG, Cherry BM, Fisher A. Do patients with cellulitis need to be hospitalized? a systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality rates of inpatients with cellulitis. J Gen Intern Med. 2018;33:1553-1560.
- Ko LN, Garza-Mayers AC, St. John J, et al. Effect of dermatology consultation on outcomes for patients with presumed cellulitis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:529-536.
- David CV, Chira S, Eells SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy in patients admitted to hospitals with cellulitis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:1.
- Hughey LC. The impact dermatologists can have on misdiagnosis of cellulitis and overuse of antibiotics: closing the gap. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1061-1062.
- Stevens DL, Bisno AL, Chambers HF, et al. Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections: 2014 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:147-159.
- Björnsdóttir S, Gottfredsson M, Thórisdóttir AS, et al. Risk factors for acute cellulitis of the lower limb: a prospective case-control study. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1416-1422.
- Roujeau JC, Sigurgeirsson B, Korting HC, et al. Chronic dermatomycoses of the foot as risk factors for acute bacterial cellulitis of the leg: a case-control study. Dermatology. 2004;209:301-307.
- McNamara DR, Tleyjeh IM, Berbari EF, et al. A predictive model of recurrent lower extremity cellulitis in a population-based cohort. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:709-715.
- Yadav K, Suh KN, Eagles D, et al. Predictors of oral antibiotic treatment failure for nonpurulent skin and soft tissue infections in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2019;26:51-59.
- Peterson D, McLeod S, Woolfrey K, et al. Predictors of failure of empiric outpatient antibiotic therapy in emergency department patients with uncomplicated cellulitis. Acad Emerg Med. 2014;21:526-531.
- Volz KA, Canham L, Kaplan E, et al. Identifying patients with cellulitis who are likely to require inpatient admission after a stay in an ED observation unit. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31:360-364.
- Chester JG, Rudolph JL. Vital signs in older patients: age-related changes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011;12:337-343.
Practice Points
- Unilateral involvement and leukocytosis are both highly predictive of lower extremity cellulitis in uncomplicated presentations.
- Historical factors such as history of onychomycosis and trauma to the affected site are more predictive of lower extremity cellulitis than demographic factors such as age in uncomplicated presentations of cellulitis.
Health Literacy in Dermatology Patients: How to Level the Playing Field
Health literacy is a multifaceted construct that encompasses the knowledge of health and health systems, utilization of information related to health, and ability to maintain health.1 Low health literacy impairs health outcomes, disproportionately affecting socioeconomically disadvantaged populations, including racial minorities and the older population. Consistently, it is associated with fewer vaccinations and screenings, higher health care utilization, and poorer ability to take medications or interpret health information.2
With growing utilization of the Internet for health information,3 much patient education now occurs outside the clinic. Differential utilization of the Internet can exacerbate disparities in health outcomes: people with a lower family income more frequently engage in health information and dialogue online.3 Despite opportunities to improve literacy and narrow gaps in care, a lack of awareness, advocacy, and funding limit patient- and community-based initiatives. Herein, we discuss health literacy challenges in dermatology, offer potential solutions, and propose ways that stakeholders can prioritize health literacy advocacy to improve outcomes.
The Importance of Health Literacy in Dermatology
Dermatology patients often face challenges that demand greater health literacy. Active participation in health promotion, protection, and maintenance can remarkably improve outcomes. When patients understand disease pathogenesis and the rationale behind treatment choices, adherence to a treatment regimen might improve.
However, understanding dermatologic diseases and disorders can be challenging. First, many are chronic inflammatory conditions that require intricate treatment regimens. Second, the complexity of those diseases and disorders continues to grow in the era of new research and unprecedented expansion of treatment options.
For chronic conditions that require ongoing complex management, researchers have developed advanced patient tools. For instance, the eczema action plan helps atopic dermatitis patients manage conditions from home.4 However, patients with greater literacy and the ability to participate will better utilize such tools and have fewer uncontrolled flares. Patient tools meant to improve outcomes might, instead, widen gaps in care. Even with nonchronic conditions, such as nonmelanoma skin cancer, continued awareness and the need for preventive care, timely diagnosis, and appropriate intervention remain critical.
Limited Accessibility of Patient Education Materials
Patient education in dermatology occurs through several formats. Because online health resources are more readily available to those with less access to health care, the potential for such resources to narrow health disparities is immense. However, online resources have not adequately taken advantage of the opportunity to make health information openly accessible to its users. The readability of online patient education materials on a large expanse of dermatologic conditions is far too advanced.5 The readability level of some resources is as high as 17th grade (graduate school), which is much higher than the American Medical Association recommendation6 that patient education materials be presented at a 6th-grade level or less. Furthermore, the quality and comprehensiveness of content is highly variable. Rather than serving as an equalizer, the Internet may widen the gap as low health literacy continues to impair the accessibility of health information.
Solutions to Level the Playing Field
What can be done to increase the readability of patient education materials? Leveling the playing field begins with creating materials at an appropriate readability level, including online content, printed handouts, and after-visit summaries in the clinic. Writers of patient education materials should be cognizant of their choice of language and routinely use a free readability checker (https://readabilityformulas.com). Patient education materials should reflect the American Medical Association’s recommended 6th-grade level. Creators should maintain a high standard of quality and comprehensiveness; prior studies note no inverse correlation between readability and quality.5 In the age of multimedia presentation, non–print-based materials can be explored, such as audio or video for online content, podcasts, and webinars. Providers also should take the opportunity to be mindful of health literacy in clinic. Beyond assessing the readability of written resources for a patient, assessing that patient’s health literacy and tailoring one’s language will maximize engagement.
Systemic Change Is Needed
Ultimately, systemic change is needed to address the root causes of health literacy disparity, requiring advocacy for social welfare, public health, and public policy initiatives. In recognizing existing efforts, such as community outreach teams and hospital committees to evaluate health literacy materials, numerous barriers remain. Despite the notable impact of health literacy on health outcomes, there is a lack of advocacy and funds to conduct health literacy–related work.7 Because dermatologists provide holistic care and remain mindful of patients’ health literacy in the clinic, they should continue to advocate for increased awareness, improved funding, and support for local and federal initiatives.
Final Thoughts
With more opportunities to narrow gaps in care, it is more pertinent than ever to acknowledge the impact of health literacy on dermatology outcomes. Leveling the playing field begins with (1) an awareness of health literacy and (2) creating readable and comprehensible patient education content. Greater advocacy from community and professional organizations; increased funding from nonprofit organizations, industry, and federal institutions; and increased involvement by dermatologists in bringing greater attention to health literacy will improve outcomes in dermatology.
- Liu C, Wang D, Liu C, et al. What is the meaning of health literacy? a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Fam Med Community Health. 2020;8:e000351. doi:10.1136/fmch-2020-000351
- Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, et al. Low health literacy and health outcomes: an updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:97-107. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005
- Rice RE. Influences, usage, and outcomes of Internet health information searching: multivariate results from the Pew surveys. Int J Med Inform. 2006;75:8-28. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.07.032
- Brown J, Weitz NW, Liang A, et al. Does an eczema action plan improve atopic dermatitis? a single-site randomized controlled trial. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018;57:1624-1629. doi:10.1177/0009922818795906
- De DR, Shih T, Katta R, et al. Readability, quality, and timeliness of patient online health resources for contact dermatitis and patch testing. Dermatitis. 2022;33:155-160. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000789
- Weiss BD. Health Literacy: A Manual for Clinicians. American Medical Association, American Medical Foundation; 2003.
- Nutbeam D, McGill B, Premkumar P. Improving health literacy in community populations: a review of progress. Health Promot Int. 2018;33:901-911. doi:10.1093/heapro/dax015
Health literacy is a multifaceted construct that encompasses the knowledge of health and health systems, utilization of information related to health, and ability to maintain health.1 Low health literacy impairs health outcomes, disproportionately affecting socioeconomically disadvantaged populations, including racial minorities and the older population. Consistently, it is associated with fewer vaccinations and screenings, higher health care utilization, and poorer ability to take medications or interpret health information.2
With growing utilization of the Internet for health information,3 much patient education now occurs outside the clinic. Differential utilization of the Internet can exacerbate disparities in health outcomes: people with a lower family income more frequently engage in health information and dialogue online.3 Despite opportunities to improve literacy and narrow gaps in care, a lack of awareness, advocacy, and funding limit patient- and community-based initiatives. Herein, we discuss health literacy challenges in dermatology, offer potential solutions, and propose ways that stakeholders can prioritize health literacy advocacy to improve outcomes.
The Importance of Health Literacy in Dermatology
Dermatology patients often face challenges that demand greater health literacy. Active participation in health promotion, protection, and maintenance can remarkably improve outcomes. When patients understand disease pathogenesis and the rationale behind treatment choices, adherence to a treatment regimen might improve.
However, understanding dermatologic diseases and disorders can be challenging. First, many are chronic inflammatory conditions that require intricate treatment regimens. Second, the complexity of those diseases and disorders continues to grow in the era of new research and unprecedented expansion of treatment options.
For chronic conditions that require ongoing complex management, researchers have developed advanced patient tools. For instance, the eczema action plan helps atopic dermatitis patients manage conditions from home.4 However, patients with greater literacy and the ability to participate will better utilize such tools and have fewer uncontrolled flares. Patient tools meant to improve outcomes might, instead, widen gaps in care. Even with nonchronic conditions, such as nonmelanoma skin cancer, continued awareness and the need for preventive care, timely diagnosis, and appropriate intervention remain critical.
Limited Accessibility of Patient Education Materials
Patient education in dermatology occurs through several formats. Because online health resources are more readily available to those with less access to health care, the potential for such resources to narrow health disparities is immense. However, online resources have not adequately taken advantage of the opportunity to make health information openly accessible to its users. The readability of online patient education materials on a large expanse of dermatologic conditions is far too advanced.5 The readability level of some resources is as high as 17th grade (graduate school), which is much higher than the American Medical Association recommendation6 that patient education materials be presented at a 6th-grade level or less. Furthermore, the quality and comprehensiveness of content is highly variable. Rather than serving as an equalizer, the Internet may widen the gap as low health literacy continues to impair the accessibility of health information.
Solutions to Level the Playing Field
What can be done to increase the readability of patient education materials? Leveling the playing field begins with creating materials at an appropriate readability level, including online content, printed handouts, and after-visit summaries in the clinic. Writers of patient education materials should be cognizant of their choice of language and routinely use a free readability checker (https://readabilityformulas.com). Patient education materials should reflect the American Medical Association’s recommended 6th-grade level. Creators should maintain a high standard of quality and comprehensiveness; prior studies note no inverse correlation between readability and quality.5 In the age of multimedia presentation, non–print-based materials can be explored, such as audio or video for online content, podcasts, and webinars. Providers also should take the opportunity to be mindful of health literacy in clinic. Beyond assessing the readability of written resources for a patient, assessing that patient’s health literacy and tailoring one’s language will maximize engagement.
Systemic Change Is Needed
Ultimately, systemic change is needed to address the root causes of health literacy disparity, requiring advocacy for social welfare, public health, and public policy initiatives. In recognizing existing efforts, such as community outreach teams and hospital committees to evaluate health literacy materials, numerous barriers remain. Despite the notable impact of health literacy on health outcomes, there is a lack of advocacy and funds to conduct health literacy–related work.7 Because dermatologists provide holistic care and remain mindful of patients’ health literacy in the clinic, they should continue to advocate for increased awareness, improved funding, and support for local and federal initiatives.
Final Thoughts
With more opportunities to narrow gaps in care, it is more pertinent than ever to acknowledge the impact of health literacy on dermatology outcomes. Leveling the playing field begins with (1) an awareness of health literacy and (2) creating readable and comprehensible patient education content. Greater advocacy from community and professional organizations; increased funding from nonprofit organizations, industry, and federal institutions; and increased involvement by dermatologists in bringing greater attention to health literacy will improve outcomes in dermatology.
Health literacy is a multifaceted construct that encompasses the knowledge of health and health systems, utilization of information related to health, and ability to maintain health.1 Low health literacy impairs health outcomes, disproportionately affecting socioeconomically disadvantaged populations, including racial minorities and the older population. Consistently, it is associated with fewer vaccinations and screenings, higher health care utilization, and poorer ability to take medications or interpret health information.2
With growing utilization of the Internet for health information,3 much patient education now occurs outside the clinic. Differential utilization of the Internet can exacerbate disparities in health outcomes: people with a lower family income more frequently engage in health information and dialogue online.3 Despite opportunities to improve literacy and narrow gaps in care, a lack of awareness, advocacy, and funding limit patient- and community-based initiatives. Herein, we discuss health literacy challenges in dermatology, offer potential solutions, and propose ways that stakeholders can prioritize health literacy advocacy to improve outcomes.
The Importance of Health Literacy in Dermatology
Dermatology patients often face challenges that demand greater health literacy. Active participation in health promotion, protection, and maintenance can remarkably improve outcomes. When patients understand disease pathogenesis and the rationale behind treatment choices, adherence to a treatment regimen might improve.
However, understanding dermatologic diseases and disorders can be challenging. First, many are chronic inflammatory conditions that require intricate treatment regimens. Second, the complexity of those diseases and disorders continues to grow in the era of new research and unprecedented expansion of treatment options.
For chronic conditions that require ongoing complex management, researchers have developed advanced patient tools. For instance, the eczema action plan helps atopic dermatitis patients manage conditions from home.4 However, patients with greater literacy and the ability to participate will better utilize such tools and have fewer uncontrolled flares. Patient tools meant to improve outcomes might, instead, widen gaps in care. Even with nonchronic conditions, such as nonmelanoma skin cancer, continued awareness and the need for preventive care, timely diagnosis, and appropriate intervention remain critical.
Limited Accessibility of Patient Education Materials
Patient education in dermatology occurs through several formats. Because online health resources are more readily available to those with less access to health care, the potential for such resources to narrow health disparities is immense. However, online resources have not adequately taken advantage of the opportunity to make health information openly accessible to its users. The readability of online patient education materials on a large expanse of dermatologic conditions is far too advanced.5 The readability level of some resources is as high as 17th grade (graduate school), which is much higher than the American Medical Association recommendation6 that patient education materials be presented at a 6th-grade level or less. Furthermore, the quality and comprehensiveness of content is highly variable. Rather than serving as an equalizer, the Internet may widen the gap as low health literacy continues to impair the accessibility of health information.
Solutions to Level the Playing Field
What can be done to increase the readability of patient education materials? Leveling the playing field begins with creating materials at an appropriate readability level, including online content, printed handouts, and after-visit summaries in the clinic. Writers of patient education materials should be cognizant of their choice of language and routinely use a free readability checker (https://readabilityformulas.com). Patient education materials should reflect the American Medical Association’s recommended 6th-grade level. Creators should maintain a high standard of quality and comprehensiveness; prior studies note no inverse correlation between readability and quality.5 In the age of multimedia presentation, non–print-based materials can be explored, such as audio or video for online content, podcasts, and webinars. Providers also should take the opportunity to be mindful of health literacy in clinic. Beyond assessing the readability of written resources for a patient, assessing that patient’s health literacy and tailoring one’s language will maximize engagement.
Systemic Change Is Needed
Ultimately, systemic change is needed to address the root causes of health literacy disparity, requiring advocacy for social welfare, public health, and public policy initiatives. In recognizing existing efforts, such as community outreach teams and hospital committees to evaluate health literacy materials, numerous barriers remain. Despite the notable impact of health literacy on health outcomes, there is a lack of advocacy and funds to conduct health literacy–related work.7 Because dermatologists provide holistic care and remain mindful of patients’ health literacy in the clinic, they should continue to advocate for increased awareness, improved funding, and support for local and federal initiatives.
Final Thoughts
With more opportunities to narrow gaps in care, it is more pertinent than ever to acknowledge the impact of health literacy on dermatology outcomes. Leveling the playing field begins with (1) an awareness of health literacy and (2) creating readable and comprehensible patient education content. Greater advocacy from community and professional organizations; increased funding from nonprofit organizations, industry, and federal institutions; and increased involvement by dermatologists in bringing greater attention to health literacy will improve outcomes in dermatology.
- Liu C, Wang D, Liu C, et al. What is the meaning of health literacy? a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Fam Med Community Health. 2020;8:e000351. doi:10.1136/fmch-2020-000351
- Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, et al. Low health literacy and health outcomes: an updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:97-107. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005
- Rice RE. Influences, usage, and outcomes of Internet health information searching: multivariate results from the Pew surveys. Int J Med Inform. 2006;75:8-28. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.07.032
- Brown J, Weitz NW, Liang A, et al. Does an eczema action plan improve atopic dermatitis? a single-site randomized controlled trial. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018;57:1624-1629. doi:10.1177/0009922818795906
- De DR, Shih T, Katta R, et al. Readability, quality, and timeliness of patient online health resources for contact dermatitis and patch testing. Dermatitis. 2022;33:155-160. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000789
- Weiss BD. Health Literacy: A Manual for Clinicians. American Medical Association, American Medical Foundation; 2003.
- Nutbeam D, McGill B, Premkumar P. Improving health literacy in community populations: a review of progress. Health Promot Int. 2018;33:901-911. doi:10.1093/heapro/dax015
- Liu C, Wang D, Liu C, et al. What is the meaning of health literacy? a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Fam Med Community Health. 2020;8:e000351. doi:10.1136/fmch-2020-000351
- Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, et al. Low health literacy and health outcomes: an updated systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:97-107. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005
- Rice RE. Influences, usage, and outcomes of Internet health information searching: multivariate results from the Pew surveys. Int J Med Inform. 2006;75:8-28. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.07.032
- Brown J, Weitz NW, Liang A, et al. Does an eczema action plan improve atopic dermatitis? a single-site randomized controlled trial. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2018;57:1624-1629. doi:10.1177/0009922818795906
- De DR, Shih T, Katta R, et al. Readability, quality, and timeliness of patient online health resources for contact dermatitis and patch testing. Dermatitis. 2022;33:155-160. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000789
- Weiss BD. Health Literacy: A Manual for Clinicians. American Medical Association, American Medical Foundation; 2003.
- Nutbeam D, McGill B, Premkumar P. Improving health literacy in community populations: a review of progress. Health Promot Int. 2018;33:901-911. doi:10.1093/heapro/dax015
Linear Hypopigmentation on the Right Arm
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
The Diagnosis: Chemical Leukoderma
A clinical diagnosis of chemical leukoderma was made. In our patient, the observed linear hypopigmentation likely resulted from the prior treatment for De Quervain tenosynovitis in which an intralesional corticosteroid entered the lymphatic channel causing a linear distribution of chemical leukoderma. The hypopigmentation self-resolved at 6-month follow-up, and the patient was counseled to continue steroid injections if indicated.
Chemical leukoderma is an acquired depigmenting dermatosis that displays vitiligolike patterning. Detailed personal and family history in addition to complete physical examination are crucial given the inability to distinguish chemical leukoderma from vitiligo on histopathology. A set of clinical criteria proposed by Ghosh and Mukhopadhyay1 includes the presence of acquired depigmented macules and patches resembling vitiligo, history of repeat exposure to certain chemical substances, hypopigmentation at the site of exposure, and/ or confettilike white macules. Three of these 4 clinical findings must be present to establish a diagnosis of chemical leukoderma. The extent of disease involvement may be graded as follows: Stage I is defined as leukoderma only at the site of contact to the offending agent. Stage II involvement is characterized by local spread beyond the exposure site via the lymphatic system. Stages IIIA and IIIB leukoderma entail hematogenous spread distant to the site of chemical exposure. Although stage IIIA leukoderma is limited to cutaneous involvement, stage IIIB findings are marked by systemic organ involvement. Stage IV disease is defined by the distant spread of hypopigmented macules and patches that continues following 1 year of strict avoidance of the causative agent.1
The pathogenesis behind chemical leukoderma is not completely understood. Studies have suggested that individuals with certain genetic susceptibilities are predisposed to developing the condition after being exposed to chemicals with melanocytotoxic properties.2,3 It has been proposed that the chemicals accelerate pre-existing cellular stress cascades within melanocytes to levels higher than what healthy cells can tolerate. Genetic factors can increase an individual’s total melanocytic stress or establish a lower cellular threshold for stress than what the immune system can manage.4 These influences culminate in an inflammatory response that results in melanocytic destruction and subsequent cutaneous hypopigmentation.
The most well-known offending chemical agents are phenol and catechol derivatives, such as hydroquinone, which is used in topical bleaching agents to treat diseases of hyperpigmentation, including melasma.2 Potent topical or intralesional corticosteroids also may precipitate chemical leukoderma, most notably in individuals with darker skin tones. Hypomelanosis induced by intralesional steroids frequently occurs weeks to months after administration and commonly is observed in a stellate or linear pattern with an irregular outline.5 Other offending chemical agents include sulfhydryls, mercurials, arsenic, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, imiquimod, chloroquine, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.2,5
Segmental vitiligo is characterized by unilateral hypopigmentation in a linear or blocklike distribution that does not cross the midline. However, onset of segmental vitiligo classically occurs prior to 30 years of age and frequently is related with early leukotrichia.6 Additionally, the hypomelanosis associated with segmental vitiligo more often presents as broad bands or patches that occasionally have a blaschkoid distribution and most commonly appear on the face.5 Lichen striatus is a lichenoid dermatosis that presents as asymptomatic pink or hypopigmented papules that follow the Blaschko lines, often favoring the extremities. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation also may occur as an associated sequela of resolved lichen striatus. Although the disease onset of lichen striatus may occur in adulthood, it typically appears in childhood and is triggered by factors such as trauma, hypersensitivity reactions, viral infections, and medications. Physical injuries such as trauma following surgical procedures also can lead to hypomelanosis; however, our patient denied any relevant surgical history. Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a skin condition presenting as ill-defined, nummular, hypopigmented macules or patches that commonly affects women with darker skin tones with an ethnic background from a tropical location or residing in a tropical environment.5 Lesions frequently appear on the trunk and rarely progress to the proximal extremities, making it an unlikely diagnosis for our patient.
In most cases of chemical leukoderma, spontaneous repigmentation often occurs within 12 months after the elimination of the offending substance; however, hypopigmented lesions may persist or continue to develop at sites distant from the initial site despite discontinuing the causative agent.1 Therapies for vitiligo, such as topical corticosteroids, topical immunosuppressants, narrowband UVB phototherapy, and psoralen plus UVA photochemotherapy, may be utilized for chemical leukoderma that does not self-resolve.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
- Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. Chemical leucoderma: a clinicoaetiological study of 864 cases in the perspective of a developing country [published online September 6, 2008]. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:40-47.
- Ghosh S. Chemical leukoderma: what’s new on etiopathological and clinical aspects? Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:255.
- Boissy RE, Manga P. On the etiology of contact/occupational vitiligo. Pigment Cell Res. 2004;17:208-214.
- Harris J. Chemical-induced vitiligo. Dermatol Clin. 2017; 35:151-161.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, et al. Vitiligo and other disorders of hypopigmentation. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Mosby/Elsevier; 2018:1087-1114.
- Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, et al. New discoveries in the pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:1-13.
A 73-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with hypopigmentation along the right arm. Her medical history was notable for prior treatment with intralesional triamcinolone injections for De Quervain tenosynovitis. Two months after receiving the steroid injections she noted progressive spreading of an asymptomatic white discoloration originating on the right wrist. Physical examination revealed a hypopigmented atrophic patch on the medial aspect of the right wrist (left) with linear hypopigmented patches extending proximally up the forearm (right).
Blue light from cell phones and other devices could be causing wrinkles
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Blue light from screens on smartphones, computers, and other gadgets “may have detrimental effects on a wide range of cells in our body, from skin and fat cells to sensory neurons,” Oregon State University scientist Jadwiga Giebultowicz, PhD, said of the study, which was published in the journal Frontiers in Aging.
“Our study suggests that avoidance of excessive blue light exposure may be a good anti-aging strategy,” Dr. Giebultowicz added.
Ultraviolet rays from the sun harm skin appearance and health. Doctors are continuing to study the damage caused by the screens of devices that most people are exposed to throughout the day. These devices emit blue light.
“Aging occurs in various ways, but on a cellular level, we age when cells stop repairing and producing new healthy cells. And cells that aren’t functioning properly are more likely to self destruct – which has ramifications not only in terms of appearance but for the whole body,” the New York Post wrote. “It’s the reason why the elderly take longer to heal, and their bones and organs begin to deteriorate.”
Dr. Giebultowicz said the study shows that certain substances in the body, called metabolites, are essential indicators of how a cell functions. These metabolites are naturally occurring as the body converts food and drinks into energy. Research indicates that these substances are altered by blue light exposure.
More specifically, researchers found that levels of succinate, or succinic acid, in fruit flies increased under excessive blue light, while glutamate decreased, the newspaper wrote.
Researchers said the insects “make an appropriate analog for humans” because the same signaling devices are shared.
The flies were exposed with more blue light than people usually get. Dr. Giebultowicz said future research is needed on human cells.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM FRONTIERS IN AGING
FDA okays spesolimab, first treatment for generalized pustular psoriasis
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the biologic agent spesolimab (Spevigo) for the treatment of flares in adults with generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), the company that manufactures the drug has announced.
Until this approval, “there were no FDA-approved options to treat patients experiencing a GPP flare,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, principal investigator in the pivotal spesolimab trial, told this news organization. The approval “is a turning point for dermatologists and clinicians who treat patients living with this devastating and debilitating disease,” he said. Treatment with spesolimab “rapidly improves the clinical symptoms of GPP flares and will greatly improve our ability to help our patients manage painful flares,” noted Dr. Lebwohl, dean of clinical therapeutics and professor of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Spesolimab, manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, is a novel, selective monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-36 signaling known to be involved in GPP. It received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
GPP affects an estimated 1 of every 10,000 people in the United States.
Though rare, GPP is a potentially life-threatening disease that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. GPP is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin. Throughout the course of the disease, patients may suffer recurring episodes of widespread eruptions of painful, sterile pustules across all parts of the body.
Spesolimab was evaluated in a global, 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trial that involved 53 adults experiencing a GPP flare. After 1 week, significantly more patients treated with spesolimab than placebo showed no visible pustules (54% vs 6%), according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions, seen in at least 5% of patients treated with spesolimab, were asthenia and fatigue; nausea and vomiting; headache; pruritus and prurigo; hematoma and bruising at the infusion site; and urinary tract infection.
Dr. Lebwohl is a paid consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 9/6/22.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the biologic agent spesolimab (Spevigo) for the treatment of flares in adults with generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), the company that manufactures the drug has announced.
Until this approval, “there were no FDA-approved options to treat patients experiencing a GPP flare,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, principal investigator in the pivotal spesolimab trial, told this news organization. The approval “is a turning point for dermatologists and clinicians who treat patients living with this devastating and debilitating disease,” he said. Treatment with spesolimab “rapidly improves the clinical symptoms of GPP flares and will greatly improve our ability to help our patients manage painful flares,” noted Dr. Lebwohl, dean of clinical therapeutics and professor of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Spesolimab, manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, is a novel, selective monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-36 signaling known to be involved in GPP. It received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
GPP affects an estimated 1 of every 10,000 people in the United States.
Though rare, GPP is a potentially life-threatening disease that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. GPP is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin. Throughout the course of the disease, patients may suffer recurring episodes of widespread eruptions of painful, sterile pustules across all parts of the body.
Spesolimab was evaluated in a global, 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trial that involved 53 adults experiencing a GPP flare. After 1 week, significantly more patients treated with spesolimab than placebo showed no visible pustules (54% vs 6%), according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions, seen in at least 5% of patients treated with spesolimab, were asthenia and fatigue; nausea and vomiting; headache; pruritus and prurigo; hematoma and bruising at the infusion site; and urinary tract infection.
Dr. Lebwohl is a paid consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 9/6/22.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the biologic agent spesolimab (Spevigo) for the treatment of flares in adults with generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), the company that manufactures the drug has announced.
Until this approval, “there were no FDA-approved options to treat patients experiencing a GPP flare,” Mark Lebwohl, MD, principal investigator in the pivotal spesolimab trial, told this news organization. The approval “is a turning point for dermatologists and clinicians who treat patients living with this devastating and debilitating disease,” he said. Treatment with spesolimab “rapidly improves the clinical symptoms of GPP flares and will greatly improve our ability to help our patients manage painful flares,” noted Dr. Lebwohl, dean of clinical therapeutics and professor of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
Spesolimab, manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim, is a novel, selective monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-36 signaling known to be involved in GPP. It received priority review and had orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation.
GPP affects an estimated 1 of every 10,000 people in the United States.
Though rare, GPP is a potentially life-threatening disease that is distinct from plaque psoriasis. GPP is caused by the accumulation of neutrophils in the skin. Throughout the course of the disease, patients may suffer recurring episodes of widespread eruptions of painful, sterile pustules across all parts of the body.
Spesolimab was evaluated in a global, 12-week, placebo-controlled clinical trial that involved 53 adults experiencing a GPP flare. After 1 week, significantly more patients treated with spesolimab than placebo showed no visible pustules (54% vs 6%), according to the company.
The most common adverse reactions, seen in at least 5% of patients treated with spesolimab, were asthenia and fatigue; nausea and vomiting; headache; pruritus and prurigo; hematoma and bruising at the infusion site; and urinary tract infection.
Dr. Lebwohl is a paid consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 9/6/22.
CDC gives final approval to Omicron COVID-19 vaccine boosters
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Sept. 1 approved the use of vaccines designed to target both Omicron and the older variants of the coronavirus, a step that may aid a goal of a widespread immunization campaign before winter arrives in the United States.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 13-1 on two separate questions. One sought the panel’s backing for the use of a single dose of a new version of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 12 and older. The second question dealt with a single dose of the reworked Moderna vaccine for people aged 18 and older.
The federal government wants to speed use of revamped COVID-19 shots, which the Food and Drug Administration on Sept. 1 cleared for use in the United States. Hours later, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, agreed with the panel’s recommendation.
“The updated COVID-19 boosters are formulated to better protect against the most recently circulating COVID-19 variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement. “They can help restore protection that has waned since previous vaccination and were designed to provide broader protection against newer variants. This recommendation followed a comprehensive scientific evaluation and robust scientific discussion. If you are eligible, there is no bad time to get your COVID-19 booster and I strongly encourage you to receive it.”
The FDA vote on Aug. 31 expanded the emergency use authorization EUA for both Moderna and Pfizer’s original COVID-19 vaccines. The new products are also called “updated boosters.” Both contain two mRNA components of SARS-CoV-2 virus, one of the original strain and another that is found in the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of the Omicron variant, the FDA said.
Basically, the FDA cleared the way for these new boosters after it relied heavily on results of certain blood tests that suggested an immune response boost from the new formulas, plus 18 months of mostly safe use of the original versions of the shots.
What neither the FDA nor the CDC has, however, is evidence from studies in humans on how well these new vaccines work or whether they are as safe as the originals. But the FDA did consider clinical evidence for the older shots and results from studies on the new boosters that were done in mice.
ACIP Committee member Pablo Sanchez, MD, of Ohio State University was the sole “no” vote on each question.
“It’s a new vaccine, it’s a new platform. There’s a lot of hesitancy already. We need the human data,” Dr. Sanchez said.
Dr. Sanchez did not doubt that the newer versions of the vaccine would prove safe.
“I personally am in the age group where I’m at high risk and I’m almost sure that I will receive it,” Dr. Sanchez said. “I just feel that this was a bit premature, and I wish that we had seen that data. Having said that, I am comfortable that the vaccine will likely be safe like the others.”
Dr. Sanchez was not alone in raising concerns about backing new COVID-19 shots for which there is not direct clinical evidence from human studies.
Committee member Sarah Long, MD, of Drexel University in Philadelphia, said during the discussion she would “reluctantly” vote in favor of the updated vaccines. She said she believes they will have the potential to reduce hospitalizations and even deaths, even with questions remaining about the data.
Dr. Long joined other committee members in pointing to the approach to updating flu vaccines as a model. In an attempt to keep ahead of influenza, companies seek to defeat new strains through tweaks to their FDA-approved vaccines. There is not much clinical information available about these revised products, Dr. Long said. She compared it to remodeling an existing home.
“It is the same scaffolding, part of the same roof, we’re just putting in some dormers and windows,” with the revisions to the flu vaccine, she said.
Earlier in the day, committee member Jamie Loehr, MD, of Cayuga Family Medicine in Ithaca, N.Y., also used changes to the annual flu shots as the model for advancing COVID-19 shots.
“So after thinking about it, I am comfortable even though we don’t have human data,” he said.
There were several questions during the meeting about why the FDA had not convened a meeting of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (regarding these specific bivalent vaccines). Typically, the FDA committee of advisers considers new vaccines before the agency authorizes their use. In this case, however, the agency acted on its own.
The FDA said the committee considered the new, bivalent COVID-19 boosters in earlier meetings and that was enough outside feedback.
But holding a meeting of advisers on these specific products could have helped build public confidence in these medicines, Dorit Reiss, PhD, of the University of California Hastings College of Law, said during the public comment session of the CDC advisers’ meeting.
“We could wish the vaccines were more effective against infection, but they’re safe and they prevent hospitalization and death,” she said.
The Department of Health and Human Services anticipated the backing of ACIP. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response on Aug. 31 began distributing “millions of doses of the updated booster to tens of thousands of sites nationwide,” Jason Roos, PhD, chief operating officer for HHS Coordination Operations and Response Element, wrote in a blog.
“These boosters will be available at tens of thousands of vaccination sites ... including local pharmacies, their physicians’ offices, and vaccine centers operated by state and local health officials,”Dr. Roos wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Sept. 1 approved the use of vaccines designed to target both Omicron and the older variants of the coronavirus, a step that may aid a goal of a widespread immunization campaign before winter arrives in the United States.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 13-1 on two separate questions. One sought the panel’s backing for the use of a single dose of a new version of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 12 and older. The second question dealt with a single dose of the reworked Moderna vaccine for people aged 18 and older.
The federal government wants to speed use of revamped COVID-19 shots, which the Food and Drug Administration on Sept. 1 cleared for use in the United States. Hours later, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, agreed with the panel’s recommendation.
“The updated COVID-19 boosters are formulated to better protect against the most recently circulating COVID-19 variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement. “They can help restore protection that has waned since previous vaccination and were designed to provide broader protection against newer variants. This recommendation followed a comprehensive scientific evaluation and robust scientific discussion. If you are eligible, there is no bad time to get your COVID-19 booster and I strongly encourage you to receive it.”
The FDA vote on Aug. 31 expanded the emergency use authorization EUA for both Moderna and Pfizer’s original COVID-19 vaccines. The new products are also called “updated boosters.” Both contain two mRNA components of SARS-CoV-2 virus, one of the original strain and another that is found in the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of the Omicron variant, the FDA said.
Basically, the FDA cleared the way for these new boosters after it relied heavily on results of certain blood tests that suggested an immune response boost from the new formulas, plus 18 months of mostly safe use of the original versions of the shots.
What neither the FDA nor the CDC has, however, is evidence from studies in humans on how well these new vaccines work or whether they are as safe as the originals. But the FDA did consider clinical evidence for the older shots and results from studies on the new boosters that were done in mice.
ACIP Committee member Pablo Sanchez, MD, of Ohio State University was the sole “no” vote on each question.
“It’s a new vaccine, it’s a new platform. There’s a lot of hesitancy already. We need the human data,” Dr. Sanchez said.
Dr. Sanchez did not doubt that the newer versions of the vaccine would prove safe.
“I personally am in the age group where I’m at high risk and I’m almost sure that I will receive it,” Dr. Sanchez said. “I just feel that this was a bit premature, and I wish that we had seen that data. Having said that, I am comfortable that the vaccine will likely be safe like the others.”
Dr. Sanchez was not alone in raising concerns about backing new COVID-19 shots for which there is not direct clinical evidence from human studies.
Committee member Sarah Long, MD, of Drexel University in Philadelphia, said during the discussion she would “reluctantly” vote in favor of the updated vaccines. She said she believes they will have the potential to reduce hospitalizations and even deaths, even with questions remaining about the data.
Dr. Long joined other committee members in pointing to the approach to updating flu vaccines as a model. In an attempt to keep ahead of influenza, companies seek to defeat new strains through tweaks to their FDA-approved vaccines. There is not much clinical information available about these revised products, Dr. Long said. She compared it to remodeling an existing home.
“It is the same scaffolding, part of the same roof, we’re just putting in some dormers and windows,” with the revisions to the flu vaccine, she said.
Earlier in the day, committee member Jamie Loehr, MD, of Cayuga Family Medicine in Ithaca, N.Y., also used changes to the annual flu shots as the model for advancing COVID-19 shots.
“So after thinking about it, I am comfortable even though we don’t have human data,” he said.
There were several questions during the meeting about why the FDA had not convened a meeting of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (regarding these specific bivalent vaccines). Typically, the FDA committee of advisers considers new vaccines before the agency authorizes their use. In this case, however, the agency acted on its own.
The FDA said the committee considered the new, bivalent COVID-19 boosters in earlier meetings and that was enough outside feedback.
But holding a meeting of advisers on these specific products could have helped build public confidence in these medicines, Dorit Reiss, PhD, of the University of California Hastings College of Law, said during the public comment session of the CDC advisers’ meeting.
“We could wish the vaccines were more effective against infection, but they’re safe and they prevent hospitalization and death,” she said.
The Department of Health and Human Services anticipated the backing of ACIP. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response on Aug. 31 began distributing “millions of doses of the updated booster to tens of thousands of sites nationwide,” Jason Roos, PhD, chief operating officer for HHS Coordination Operations and Response Element, wrote in a blog.
“These boosters will be available at tens of thousands of vaccination sites ... including local pharmacies, their physicians’ offices, and vaccine centers operated by state and local health officials,”Dr. Roos wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Sept. 1 approved the use of vaccines designed to target both Omicron and the older variants of the coronavirus, a step that may aid a goal of a widespread immunization campaign before winter arrives in the United States.
The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 13-1 on two separate questions. One sought the panel’s backing for the use of a single dose of a new version of the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccines for people aged 12 and older. The second question dealt with a single dose of the reworked Moderna vaccine for people aged 18 and older.
The federal government wants to speed use of revamped COVID-19 shots, which the Food and Drug Administration on Sept. 1 cleared for use in the United States. Hours later, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, agreed with the panel’s recommendation.
“The updated COVID-19 boosters are formulated to better protect against the most recently circulating COVID-19 variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a statement. “They can help restore protection that has waned since previous vaccination and were designed to provide broader protection against newer variants. This recommendation followed a comprehensive scientific evaluation and robust scientific discussion. If you are eligible, there is no bad time to get your COVID-19 booster and I strongly encourage you to receive it.”
The FDA vote on Aug. 31 expanded the emergency use authorization EUA for both Moderna and Pfizer’s original COVID-19 vaccines. The new products are also called “updated boosters.” Both contain two mRNA components of SARS-CoV-2 virus, one of the original strain and another that is found in the BA.4 and BA.5 strains of the Omicron variant, the FDA said.
Basically, the FDA cleared the way for these new boosters after it relied heavily on results of certain blood tests that suggested an immune response boost from the new formulas, plus 18 months of mostly safe use of the original versions of the shots.
What neither the FDA nor the CDC has, however, is evidence from studies in humans on how well these new vaccines work or whether they are as safe as the originals. But the FDA did consider clinical evidence for the older shots and results from studies on the new boosters that were done in mice.
ACIP Committee member Pablo Sanchez, MD, of Ohio State University was the sole “no” vote on each question.
“It’s a new vaccine, it’s a new platform. There’s a lot of hesitancy already. We need the human data,” Dr. Sanchez said.
Dr. Sanchez did not doubt that the newer versions of the vaccine would prove safe.
“I personally am in the age group where I’m at high risk and I’m almost sure that I will receive it,” Dr. Sanchez said. “I just feel that this was a bit premature, and I wish that we had seen that data. Having said that, I am comfortable that the vaccine will likely be safe like the others.”
Dr. Sanchez was not alone in raising concerns about backing new COVID-19 shots for which there is not direct clinical evidence from human studies.
Committee member Sarah Long, MD, of Drexel University in Philadelphia, said during the discussion she would “reluctantly” vote in favor of the updated vaccines. She said she believes they will have the potential to reduce hospitalizations and even deaths, even with questions remaining about the data.
Dr. Long joined other committee members in pointing to the approach to updating flu vaccines as a model. In an attempt to keep ahead of influenza, companies seek to defeat new strains through tweaks to their FDA-approved vaccines. There is not much clinical information available about these revised products, Dr. Long said. She compared it to remodeling an existing home.
“It is the same scaffolding, part of the same roof, we’re just putting in some dormers and windows,” with the revisions to the flu vaccine, she said.
Earlier in the day, committee member Jamie Loehr, MD, of Cayuga Family Medicine in Ithaca, N.Y., also used changes to the annual flu shots as the model for advancing COVID-19 shots.
“So after thinking about it, I am comfortable even though we don’t have human data,” he said.
There were several questions during the meeting about why the FDA had not convened a meeting of its Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (regarding these specific bivalent vaccines). Typically, the FDA committee of advisers considers new vaccines before the agency authorizes their use. In this case, however, the agency acted on its own.
The FDA said the committee considered the new, bivalent COVID-19 boosters in earlier meetings and that was enough outside feedback.
But holding a meeting of advisers on these specific products could have helped build public confidence in these medicines, Dorit Reiss, PhD, of the University of California Hastings College of Law, said during the public comment session of the CDC advisers’ meeting.
“We could wish the vaccines were more effective against infection, but they’re safe and they prevent hospitalization and death,” she said.
The Department of Health and Human Services anticipated the backing of ACIP. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response on Aug. 31 began distributing “millions of doses of the updated booster to tens of thousands of sites nationwide,” Jason Roos, PhD, chief operating officer for HHS Coordination Operations and Response Element, wrote in a blog.
“These boosters will be available at tens of thousands of vaccination sites ... including local pharmacies, their physicians’ offices, and vaccine centers operated by state and local health officials,”Dr. Roos wrote.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Expert shares tips on hair disorders and photoprotection for patients of color
PORTLAND, ORE. – , but sometimes their doctors fall short.
“Many times, you may not have race concordant visits with patients of color,” Janiene Luke, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. She referred to a survey of 200 Black women aged 21-83 years, which found that 28% had visited a physician to discuss hair or scalp issues. Of those, 68% felt like their dermatologists did not understand African American hair.
“I recommend trying the best you can to familiarize yourself with various common cultural hair styling methods and practices in patients of color. It’s important to understand what your patients are engaging in and the types of styles they’re using,” said Dr. Luke, associate professor of dermatology at Loma Linda (Calif.) University. “Approach all patients with cultural humility. We know from studies that patients value dermatologists who take time to listen to their concerns, involve them in the decision-making process, and educate them about their conditions,” she added.
National efforts to educate clinicians on treating skin of color have emerged in recent years, including textbooks, CME courses at dermatology conferences, and the American Academy of Dermatology’s Skin of Color Curriculum, which consists of 15-minute modules that can be viewed online.
At the meeting, Dr. Luke, shared her approach to assessing hair and scalp disorders in skin of color. She begins by taking a thorough history, “because not all things that are associated with hair styling will be the reason why your patient comes in,” she said. “Patients of color can have telogen effluvium and seborrheic dermatitis just like anyone else. I ask about the hair styling practices they use. I also ask how often they wash their hair, because sometimes our recommendations for treatment are not realistic based on their current routine.”
Next, she examines the scalp with her hands – which sometimes surprises patients. “I’ve had so many patients come in and say, ‘the dermatologist never touched my scalp,’ or ‘they never even looked at my hair,’ ” said Dr. Luke, who directs the university’s dermatology residency program. She asks patients to remove any hair extensions or weaves prior to the office visit and to remove wigs prior to the exam itself. The lab tests she customarily orders include CBC, TSH, iron, total iron binding capacity, ferritin, vitamin D, and zinc. If there are signs of androgen excess, she may check testosterone, sex hormone binding globulin, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S). She routinely incorporates a dermoscopy-directed biopsy into the evaluation.
Dr. Luke examines the patient from above, the sides, and the back to assess the pattern/distribution of hair loss. A visible scalp at the vertex indicates a 50% reduction in normal hair density. “I’m looking at the hairline, their part width, and the length of their hair,” she said. “I also look at the eyebrows and eyelashes, because these can be involved in alopecia areata, frontal fibrosing alopecia, or congenital hair shaft disorders.”
On closeup examination, she looks for scarring versus non-scarring types of hair loss, and for the presence or absence of follicular ostia. “I also look at hair changes,” she said. “Is the texture of their hair different? Are there signs of breakage or fragility? It’s been noted in studies that breakage can be an early sign of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.” (For more tips on examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race discordant patient-physician interactions, she recommended a 2021 article in JAMA Dermatology)..
Trichoscopy allows for magnified observation of the hair shafts, hair follicle openings, perifollicular dermis, and blood vessels. Normal trichoscopy findings in skin of color reveal a perifollicular pigment network (honeycomb pattern) and pinpoint white dots that are regularly distributed between follicular units.
Common abnormalities seen on trichoscopy include central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with one or two hairs emerging together, surrounded by a gray halo; lichen planopilaris/frontal fibrosing alopecia, characterized by hair with peripilar casts and absence of vellus hairs; discoid lupus erythematosus, characterized by keratotic plugs; and traction, characterized by hair casts.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, Dr. Luke provides other general advice for optimal skin health, including a balanced (whole food) diet to ensure adequate nutrition. “I tend to find a lot of nutrient deficiencies that contribute to and compound their condition,” she said. Other recommendations include avoiding excess tension on the hair, such as hair styles with tight ponytails, buns, braids, and weaves; avoiding or limiting chemical treatments with hair color, relaxers, and permanents; and avoiding or limiting excessive heat styling with blow dryers, flat irons, and curling irons.
Photoprotection misconceptions
At the meeting, Dr. Luke also discussed three misconceptions of photoprotection in skin of color, drawn from an article on the topic published in 2021.
- Myth No. 1: Endogenous melanin provides complete photoprotection for Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V. Many people with skin of color may believe sunscreen is not needed given the melanin already present in their skin, but research has shown that the epidermis of dark skin has an intrinsic sun protection factor (SPF) of 13.4, compared with an SPF of 3.3 in light skin. “That may not provide them with full protection,” Dr. Luke said. “Many dermatologists are not counseling their skin of color patients about photoprotection.”
- Myth No. 2: Individuals with skin of color have negligible risks associated with skin cancer. Skin cancer prevalence in patients with skin of color is significantly lower compared with those with light skin. However, people with skin of color tend to be diagnosed with cancers at a more advanced stage, and cancers associated with a worse prognosis and poorer survival rate. An analysis of ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma that drew from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program found that Hispanic individuals (odds ratio [OR], 3.6), Black individuals (OR, 4.2), and Asian individuals (OR, 2.4), were more likely than were White individuals to have stage IV melanoma at the time of presentation. “For melanoma in skin of color, UV radiation does not seem to be a major risk factor, as melanoma tends to occur on palmar/plantar and subungual skin as well as mucous membranes,” Dr. Luke said. “For squamous cell carcinoma in skin of color, lesions are more likely to be present in areas that are not sun exposed. The risk factors for this tend to be chronic wounds, nonhealing ulcers, and people with chronic inflammatory conditions.” For basal cell carcinoma, she added, UV radiation seems to play more of a role and tends to occur in sun-exposed areas in patients with lighter Fitzpatrick skin types. Patients are more likely to present with pigmented BCCs.
- Myth No. 3: Broad-spectrum sunscreens provide photoprotection against all wavelengths of light that cause skin damage. To be labeled “broad-spectrum” the Food and Drug Administration requires that sunscreens have a critical wavelength of 370 nm or below, but Dr. Luke noted that broad-spectrum sunscreens do not necessarily protect against visible light (VL) and UV-A1. Research has demonstrated that VL exposure induces both transient and long-term cutaneous pigmentation in a dose-dependent manner.
“This induces free radicals and reactive oxygen species, leading to a cascade of events including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases, and melanogenesis,” she said. “More intense and persistent VL-induced pigmentation occurs in subjects with darker skin. However, there is increasing evidence that antioxidants may help to mitigate these negative effects, so we are starting to see the addition of antioxidants into sunscreens.”
Dr. Luke recommends a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for skin of color patients. Tinted sunscreens, which contain iron oxide pigments, are recommended for the prevention and treatment of pigmentary disorders in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI skin. “What about adding antioxidants to prevent formation of reactive oxygen species?” she asked. “It’s possible but we don’t have a lot of research yet. You also want a sunscreen that’s aesthetically elegant, meaning it doesn’t leave a white cast.”
Dr. Luke reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – , but sometimes their doctors fall short.
“Many times, you may not have race concordant visits with patients of color,” Janiene Luke, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. She referred to a survey of 200 Black women aged 21-83 years, which found that 28% had visited a physician to discuss hair or scalp issues. Of those, 68% felt like their dermatologists did not understand African American hair.
“I recommend trying the best you can to familiarize yourself with various common cultural hair styling methods and practices in patients of color. It’s important to understand what your patients are engaging in and the types of styles they’re using,” said Dr. Luke, associate professor of dermatology at Loma Linda (Calif.) University. “Approach all patients with cultural humility. We know from studies that patients value dermatologists who take time to listen to their concerns, involve them in the decision-making process, and educate them about their conditions,” she added.
National efforts to educate clinicians on treating skin of color have emerged in recent years, including textbooks, CME courses at dermatology conferences, and the American Academy of Dermatology’s Skin of Color Curriculum, which consists of 15-minute modules that can be viewed online.
At the meeting, Dr. Luke, shared her approach to assessing hair and scalp disorders in skin of color. She begins by taking a thorough history, “because not all things that are associated with hair styling will be the reason why your patient comes in,” she said. “Patients of color can have telogen effluvium and seborrheic dermatitis just like anyone else. I ask about the hair styling practices they use. I also ask how often they wash their hair, because sometimes our recommendations for treatment are not realistic based on their current routine.”
Next, she examines the scalp with her hands – which sometimes surprises patients. “I’ve had so many patients come in and say, ‘the dermatologist never touched my scalp,’ or ‘they never even looked at my hair,’ ” said Dr. Luke, who directs the university’s dermatology residency program. She asks patients to remove any hair extensions or weaves prior to the office visit and to remove wigs prior to the exam itself. The lab tests she customarily orders include CBC, TSH, iron, total iron binding capacity, ferritin, vitamin D, and zinc. If there are signs of androgen excess, she may check testosterone, sex hormone binding globulin, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S). She routinely incorporates a dermoscopy-directed biopsy into the evaluation.
Dr. Luke examines the patient from above, the sides, and the back to assess the pattern/distribution of hair loss. A visible scalp at the vertex indicates a 50% reduction in normal hair density. “I’m looking at the hairline, their part width, and the length of their hair,” she said. “I also look at the eyebrows and eyelashes, because these can be involved in alopecia areata, frontal fibrosing alopecia, or congenital hair shaft disorders.”
On closeup examination, she looks for scarring versus non-scarring types of hair loss, and for the presence or absence of follicular ostia. “I also look at hair changes,” she said. “Is the texture of their hair different? Are there signs of breakage or fragility? It’s been noted in studies that breakage can be an early sign of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.” (For more tips on examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race discordant patient-physician interactions, she recommended a 2021 article in JAMA Dermatology)..
Trichoscopy allows for magnified observation of the hair shafts, hair follicle openings, perifollicular dermis, and blood vessels. Normal trichoscopy findings in skin of color reveal a perifollicular pigment network (honeycomb pattern) and pinpoint white dots that are regularly distributed between follicular units.
Common abnormalities seen on trichoscopy include central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with one or two hairs emerging together, surrounded by a gray halo; lichen planopilaris/frontal fibrosing alopecia, characterized by hair with peripilar casts and absence of vellus hairs; discoid lupus erythematosus, characterized by keratotic plugs; and traction, characterized by hair casts.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, Dr. Luke provides other general advice for optimal skin health, including a balanced (whole food) diet to ensure adequate nutrition. “I tend to find a lot of nutrient deficiencies that contribute to and compound their condition,” she said. Other recommendations include avoiding excess tension on the hair, such as hair styles with tight ponytails, buns, braids, and weaves; avoiding or limiting chemical treatments with hair color, relaxers, and permanents; and avoiding or limiting excessive heat styling with blow dryers, flat irons, and curling irons.
Photoprotection misconceptions
At the meeting, Dr. Luke also discussed three misconceptions of photoprotection in skin of color, drawn from an article on the topic published in 2021.
- Myth No. 1: Endogenous melanin provides complete photoprotection for Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V. Many people with skin of color may believe sunscreen is not needed given the melanin already present in their skin, but research has shown that the epidermis of dark skin has an intrinsic sun protection factor (SPF) of 13.4, compared with an SPF of 3.3 in light skin. “That may not provide them with full protection,” Dr. Luke said. “Many dermatologists are not counseling their skin of color patients about photoprotection.”
- Myth No. 2: Individuals with skin of color have negligible risks associated with skin cancer. Skin cancer prevalence in patients with skin of color is significantly lower compared with those with light skin. However, people with skin of color tend to be diagnosed with cancers at a more advanced stage, and cancers associated with a worse prognosis and poorer survival rate. An analysis of ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma that drew from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program found that Hispanic individuals (odds ratio [OR], 3.6), Black individuals (OR, 4.2), and Asian individuals (OR, 2.4), were more likely than were White individuals to have stage IV melanoma at the time of presentation. “For melanoma in skin of color, UV radiation does not seem to be a major risk factor, as melanoma tends to occur on palmar/plantar and subungual skin as well as mucous membranes,” Dr. Luke said. “For squamous cell carcinoma in skin of color, lesions are more likely to be present in areas that are not sun exposed. The risk factors for this tend to be chronic wounds, nonhealing ulcers, and people with chronic inflammatory conditions.” For basal cell carcinoma, she added, UV radiation seems to play more of a role and tends to occur in sun-exposed areas in patients with lighter Fitzpatrick skin types. Patients are more likely to present with pigmented BCCs.
- Myth No. 3: Broad-spectrum sunscreens provide photoprotection against all wavelengths of light that cause skin damage. To be labeled “broad-spectrum” the Food and Drug Administration requires that sunscreens have a critical wavelength of 370 nm or below, but Dr. Luke noted that broad-spectrum sunscreens do not necessarily protect against visible light (VL) and UV-A1. Research has demonstrated that VL exposure induces both transient and long-term cutaneous pigmentation in a dose-dependent manner.
“This induces free radicals and reactive oxygen species, leading to a cascade of events including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases, and melanogenesis,” she said. “More intense and persistent VL-induced pigmentation occurs in subjects with darker skin. However, there is increasing evidence that antioxidants may help to mitigate these negative effects, so we are starting to see the addition of antioxidants into sunscreens.”
Dr. Luke recommends a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for skin of color patients. Tinted sunscreens, which contain iron oxide pigments, are recommended for the prevention and treatment of pigmentary disorders in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI skin. “What about adding antioxidants to prevent formation of reactive oxygen species?” she asked. “It’s possible but we don’t have a lot of research yet. You also want a sunscreen that’s aesthetically elegant, meaning it doesn’t leave a white cast.”
Dr. Luke reported having no relevant disclosures.
PORTLAND, ORE. – , but sometimes their doctors fall short.
“Many times, you may not have race concordant visits with patients of color,” Janiene Luke, MD, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. She referred to a survey of 200 Black women aged 21-83 years, which found that 28% had visited a physician to discuss hair or scalp issues. Of those, 68% felt like their dermatologists did not understand African American hair.
“I recommend trying the best you can to familiarize yourself with various common cultural hair styling methods and practices in patients of color. It’s important to understand what your patients are engaging in and the types of styles they’re using,” said Dr. Luke, associate professor of dermatology at Loma Linda (Calif.) University. “Approach all patients with cultural humility. We know from studies that patients value dermatologists who take time to listen to their concerns, involve them in the decision-making process, and educate them about their conditions,” she added.
National efforts to educate clinicians on treating skin of color have emerged in recent years, including textbooks, CME courses at dermatology conferences, and the American Academy of Dermatology’s Skin of Color Curriculum, which consists of 15-minute modules that can be viewed online.
At the meeting, Dr. Luke, shared her approach to assessing hair and scalp disorders in skin of color. She begins by taking a thorough history, “because not all things that are associated with hair styling will be the reason why your patient comes in,” she said. “Patients of color can have telogen effluvium and seborrheic dermatitis just like anyone else. I ask about the hair styling practices they use. I also ask how often they wash their hair, because sometimes our recommendations for treatment are not realistic based on their current routine.”
Next, she examines the scalp with her hands – which sometimes surprises patients. “I’ve had so many patients come in and say, ‘the dermatologist never touched my scalp,’ or ‘they never even looked at my hair,’ ” said Dr. Luke, who directs the university’s dermatology residency program. She asks patients to remove any hair extensions or weaves prior to the office visit and to remove wigs prior to the exam itself. The lab tests she customarily orders include CBC, TSH, iron, total iron binding capacity, ferritin, vitamin D, and zinc. If there are signs of androgen excess, she may check testosterone, sex hormone binding globulin, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S). She routinely incorporates a dermoscopy-directed biopsy into the evaluation.
Dr. Luke examines the patient from above, the sides, and the back to assess the pattern/distribution of hair loss. A visible scalp at the vertex indicates a 50% reduction in normal hair density. “I’m looking at the hairline, their part width, and the length of their hair,” she said. “I also look at the eyebrows and eyelashes, because these can be involved in alopecia areata, frontal fibrosing alopecia, or congenital hair shaft disorders.”
On closeup examination, she looks for scarring versus non-scarring types of hair loss, and for the presence or absence of follicular ostia. “I also look at hair changes,” she said. “Is the texture of their hair different? Are there signs of breakage or fragility? It’s been noted in studies that breakage can be an early sign of central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.” (For more tips on examining tightly coiled hair among patients with hair loss in race discordant patient-physician interactions, she recommended a 2021 article in JAMA Dermatology)..
Trichoscopy allows for magnified observation of the hair shafts, hair follicle openings, perifollicular dermis, and blood vessels. Normal trichoscopy findings in skin of color reveal a perifollicular pigment network (honeycomb pattern) and pinpoint white dots that are regularly distributed between follicular units.
Common abnormalities seen on trichoscopy include central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA), with one or two hairs emerging together, surrounded by a gray halo; lichen planopilaris/frontal fibrosing alopecia, characterized by hair with peripilar casts and absence of vellus hairs; discoid lupus erythematosus, characterized by keratotic plugs; and traction, characterized by hair casts.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, Dr. Luke provides other general advice for optimal skin health, including a balanced (whole food) diet to ensure adequate nutrition. “I tend to find a lot of nutrient deficiencies that contribute to and compound their condition,” she said. Other recommendations include avoiding excess tension on the hair, such as hair styles with tight ponytails, buns, braids, and weaves; avoiding or limiting chemical treatments with hair color, relaxers, and permanents; and avoiding or limiting excessive heat styling with blow dryers, flat irons, and curling irons.
Photoprotection misconceptions
At the meeting, Dr. Luke also discussed three misconceptions of photoprotection in skin of color, drawn from an article on the topic published in 2021.
- Myth No. 1: Endogenous melanin provides complete photoprotection for Fitzpatrick skin types IV-V. Many people with skin of color may believe sunscreen is not needed given the melanin already present in their skin, but research has shown that the epidermis of dark skin has an intrinsic sun protection factor (SPF) of 13.4, compared with an SPF of 3.3 in light skin. “That may not provide them with full protection,” Dr. Luke said. “Many dermatologists are not counseling their skin of color patients about photoprotection.”
- Myth No. 2: Individuals with skin of color have negligible risks associated with skin cancer. Skin cancer prevalence in patients with skin of color is significantly lower compared with those with light skin. However, people with skin of color tend to be diagnosed with cancers at a more advanced stage, and cancers associated with a worse prognosis and poorer survival rate. An analysis of ethnic differences among patients with cutaneous melanoma that drew from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program found that Hispanic individuals (odds ratio [OR], 3.6), Black individuals (OR, 4.2), and Asian individuals (OR, 2.4), were more likely than were White individuals to have stage IV melanoma at the time of presentation. “For melanoma in skin of color, UV radiation does not seem to be a major risk factor, as melanoma tends to occur on palmar/plantar and subungual skin as well as mucous membranes,” Dr. Luke said. “For squamous cell carcinoma in skin of color, lesions are more likely to be present in areas that are not sun exposed. The risk factors for this tend to be chronic wounds, nonhealing ulcers, and people with chronic inflammatory conditions.” For basal cell carcinoma, she added, UV radiation seems to play more of a role and tends to occur in sun-exposed areas in patients with lighter Fitzpatrick skin types. Patients are more likely to present with pigmented BCCs.
- Myth No. 3: Broad-spectrum sunscreens provide photoprotection against all wavelengths of light that cause skin damage. To be labeled “broad-spectrum” the Food and Drug Administration requires that sunscreens have a critical wavelength of 370 nm or below, but Dr. Luke noted that broad-spectrum sunscreens do not necessarily protect against visible light (VL) and UV-A1. Research has demonstrated that VL exposure induces both transient and long-term cutaneous pigmentation in a dose-dependent manner.
“This induces free radicals and reactive oxygen species, leading to a cascade of events including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases, and melanogenesis,” she said. “More intense and persistent VL-induced pigmentation occurs in subjects with darker skin. However, there is increasing evidence that antioxidants may help to mitigate these negative effects, so we are starting to see the addition of antioxidants into sunscreens.”
Dr. Luke recommends a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher for skin of color patients. Tinted sunscreens, which contain iron oxide pigments, are recommended for the prevention and treatment of pigmentary disorders in patients with Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI skin. “What about adding antioxidants to prevent formation of reactive oxygen species?” she asked. “It’s possible but we don’t have a lot of research yet. You also want a sunscreen that’s aesthetically elegant, meaning it doesn’t leave a white cast.”
Dr. Luke reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT PDA 2022