User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Bigotry and medical injustice
“We cannot teach people to withhold judgment; judgments are embedded in the way we view objects. I do not see a “tree”; I see a pleasant or an ugly tree. It is not possible without great, paralyzing effort to strip these small values we attach to matters. Likewise, it is not possible to hold a situation in one’s head without some element of bias” – Nassim Nicholas Taleb, MBA, PhD, “The Black Swan.”
Each morning I see the hungry ghosts congregate at the end of the alley behind my office waiting for their addiction clinic appointments (Maté G. “In the Realm of Hungry Ghosts, Close Encounters with Addiction” Berkeley, Calif.: North Atlantic Books, 2008). The fast food restaurant and the convenience store won’t let them linger, so there they sit on the curb in the saddest magpie’s row in the world. They have lip, nose, and eyebrow piercings, and lightning bolts tattooed up their cheeks. They all have backpacks, a few even rolling suitcases. They are opioid addicts, and almost all young, White adults. There they sit, once-innocent young girls, now worn and hardened, and vicious-looking young men, all with downcast empty eyes and miserable expressions. They are a frightening group marginalized by their addiction.
Opioid addiction became a national focus of attention with clarion calls for treatment, which resulted in legislative funding for treatment, restrictions on prescribing, and readily available Narcan. Physicians have greatly reduced their prescribing of narcotics and overdose death rates have dropped, but the drug crisis has not gone away, it has only been recently overshadowed by COVID-19.
The most ironic part of the current opioid epidemic and overdose deaths, and the other three bloodborne horsemen of death – endocarditis; hepatitis B, C, and D; and HIV – was that these scourges were affecting the Black community 40 years ago when, in my view, no one seemed to care. There was no addiction counseling, no treatment centers, and law enforcement would visit only with hopes of making a dealer’s arrest. Not until it became a White suburban issue, did this public health problem become recognized as something to act on. This is of course a result of racism, but there is a broader lesson here.
Humans may be naturally bigoted toward any marginalized or minority group. I recall working in the HIV clinic (before it was called HIV) in Dallas in the mid-1980s. The county refused to pay for zidovudine, which was very expensive at the time, and was sued to supply medication for a group marginalized by their sexual orientation. The AIDS epidemic was initially ignored, with the virus spreading to intravenous drug users and eventually to the broader population, which is when effective treatments became a priority.
Physicians and society should pay close attention to the ills of our marginalized communities. Because of isolation from health care, they are the medical canaries in the coal mine for all of us. Medical issues and infectious diseases identified there should be a priority and solutions sought and applied. This not only would benefit the marginalized group and ease their suffering, but would be salutary to society as a whole, because they surely will be coming everyone’s way.
COVID-19 highlights this. The working poor live in close quarters and most rely on crowded public transportation, and so a respiratory illness spreads rapidly in a population that cannot practically physically distance and probably cannot afford face masks, or alcohol hand gel.
As noted above, we have a persistent illegal drug epidemic. We also have a resurgence in venereal disease and tuberculosis, much of it drug resistant, which again is concentrated in our marginalized populations. Meanwhile, we have been cutting spending on public health, while we obviously need more resources devoted to public and community health.
When we step back and look, there are public health issues everywhere. We could eliminate 90% of cervical cancer and most of the oropharyngeal cancer with use of a very effective vaccine, but we struggle to get it paid for and to convince the public of its ultimate good.
Another example is in Ohio, where we raised the age to purchase tobacco to 21, which is laudable. But children of any age can still access tanning beds, which dramatically raises their lifetime risk of melanoma, often using a note from their “parents” that they write for each other on the car hood in the strip mall parking lot. This group of mostly young white women could also be considered a marginalized group despite their disposable income because of their belief in personal invincibility and false impressions of a tan conferring beauty and vitality repeated endlessly in their echo chamber of social media impressions.
Perhaps we should gauge the state of our public health by the health status of the most oppressed group of all, the incarcerated. Is it really possible that we don’t routinely test for and treat hepatitis C in many of our prisons? Is this indifference because the incarcerated are again a largely minority group and hepatitis C is spread by intravenous drug use?
Solutions and interventions for these problems range widely in cost, but all would eventually save the greater society money and alleviate great misery for those affected.
Perhaps we should be talking about the decriminalization of drug use. The drugs are already here and the consequences apparent, including overflowing prisons and out of control gun violence. This is a much thornier discussion, but seems at the root of many of our problems.
Bigotry is insidious and will take a long and continuing active effort to combat. As Dr. Taleb notes in the introductory quote, it requires a constant, tiring, deliberate mental effort to be mindful of one’s biases. As physicians, we have always been careful to try and treat all patients without bias, but this is not enough. We must become more insistent about the funding and application of public health measures.
Recognizing and treating the medical problems of our marginalized populations seems a doable first step while our greater society struggles with mental bias toward marginalized groups. Reducing the health burdens of these groups can only help them in their life struggles and will benefit all.
Someone once told me that the cold wind in the ghetto eventually blows out into the suburbs, and they were right. As physicians and a society, we should be insistent about correcting medical injustices beforehand. Let’s get started.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected]
“We cannot teach people to withhold judgment; judgments are embedded in the way we view objects. I do not see a “tree”; I see a pleasant or an ugly tree. It is not possible without great, paralyzing effort to strip these small values we attach to matters. Likewise, it is not possible to hold a situation in one’s head without some element of bias” – Nassim Nicholas Taleb, MBA, PhD, “The Black Swan.”
Each morning I see the hungry ghosts congregate at the end of the alley behind my office waiting for their addiction clinic appointments (Maté G. “In the Realm of Hungry Ghosts, Close Encounters with Addiction” Berkeley, Calif.: North Atlantic Books, 2008). The fast food restaurant and the convenience store won’t let them linger, so there they sit on the curb in the saddest magpie’s row in the world. They have lip, nose, and eyebrow piercings, and lightning bolts tattooed up their cheeks. They all have backpacks, a few even rolling suitcases. They are opioid addicts, and almost all young, White adults. There they sit, once-innocent young girls, now worn and hardened, and vicious-looking young men, all with downcast empty eyes and miserable expressions. They are a frightening group marginalized by their addiction.
Opioid addiction became a national focus of attention with clarion calls for treatment, which resulted in legislative funding for treatment, restrictions on prescribing, and readily available Narcan. Physicians have greatly reduced their prescribing of narcotics and overdose death rates have dropped, but the drug crisis has not gone away, it has only been recently overshadowed by COVID-19.
The most ironic part of the current opioid epidemic and overdose deaths, and the other three bloodborne horsemen of death – endocarditis; hepatitis B, C, and D; and HIV – was that these scourges were affecting the Black community 40 years ago when, in my view, no one seemed to care. There was no addiction counseling, no treatment centers, and law enforcement would visit only with hopes of making a dealer’s arrest. Not until it became a White suburban issue, did this public health problem become recognized as something to act on. This is of course a result of racism, but there is a broader lesson here.
Humans may be naturally bigoted toward any marginalized or minority group. I recall working in the HIV clinic (before it was called HIV) in Dallas in the mid-1980s. The county refused to pay for zidovudine, which was very expensive at the time, and was sued to supply medication for a group marginalized by their sexual orientation. The AIDS epidemic was initially ignored, with the virus spreading to intravenous drug users and eventually to the broader population, which is when effective treatments became a priority.
Physicians and society should pay close attention to the ills of our marginalized communities. Because of isolation from health care, they are the medical canaries in the coal mine for all of us. Medical issues and infectious diseases identified there should be a priority and solutions sought and applied. This not only would benefit the marginalized group and ease their suffering, but would be salutary to society as a whole, because they surely will be coming everyone’s way.
COVID-19 highlights this. The working poor live in close quarters and most rely on crowded public transportation, and so a respiratory illness spreads rapidly in a population that cannot practically physically distance and probably cannot afford face masks, or alcohol hand gel.
As noted above, we have a persistent illegal drug epidemic. We also have a resurgence in venereal disease and tuberculosis, much of it drug resistant, which again is concentrated in our marginalized populations. Meanwhile, we have been cutting spending on public health, while we obviously need more resources devoted to public and community health.
When we step back and look, there are public health issues everywhere. We could eliminate 90% of cervical cancer and most of the oropharyngeal cancer with use of a very effective vaccine, but we struggle to get it paid for and to convince the public of its ultimate good.
Another example is in Ohio, where we raised the age to purchase tobacco to 21, which is laudable. But children of any age can still access tanning beds, which dramatically raises their lifetime risk of melanoma, often using a note from their “parents” that they write for each other on the car hood in the strip mall parking lot. This group of mostly young white women could also be considered a marginalized group despite their disposable income because of their belief in personal invincibility and false impressions of a tan conferring beauty and vitality repeated endlessly in their echo chamber of social media impressions.
Perhaps we should gauge the state of our public health by the health status of the most oppressed group of all, the incarcerated. Is it really possible that we don’t routinely test for and treat hepatitis C in many of our prisons? Is this indifference because the incarcerated are again a largely minority group and hepatitis C is spread by intravenous drug use?
Solutions and interventions for these problems range widely in cost, but all would eventually save the greater society money and alleviate great misery for those affected.
Perhaps we should be talking about the decriminalization of drug use. The drugs are already here and the consequences apparent, including overflowing prisons and out of control gun violence. This is a much thornier discussion, but seems at the root of many of our problems.
Bigotry is insidious and will take a long and continuing active effort to combat. As Dr. Taleb notes in the introductory quote, it requires a constant, tiring, deliberate mental effort to be mindful of one’s biases. As physicians, we have always been careful to try and treat all patients without bias, but this is not enough. We must become more insistent about the funding and application of public health measures.
Recognizing and treating the medical problems of our marginalized populations seems a doable first step while our greater society struggles with mental bias toward marginalized groups. Reducing the health burdens of these groups can only help them in their life struggles and will benefit all.
Someone once told me that the cold wind in the ghetto eventually blows out into the suburbs, and they were right. As physicians and a society, we should be insistent about correcting medical injustices beforehand. Let’s get started.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected]
“We cannot teach people to withhold judgment; judgments are embedded in the way we view objects. I do not see a “tree”; I see a pleasant or an ugly tree. It is not possible without great, paralyzing effort to strip these small values we attach to matters. Likewise, it is not possible to hold a situation in one’s head without some element of bias” – Nassim Nicholas Taleb, MBA, PhD, “The Black Swan.”
Each morning I see the hungry ghosts congregate at the end of the alley behind my office waiting for their addiction clinic appointments (Maté G. “In the Realm of Hungry Ghosts, Close Encounters with Addiction” Berkeley, Calif.: North Atlantic Books, 2008). The fast food restaurant and the convenience store won’t let them linger, so there they sit on the curb in the saddest magpie’s row in the world. They have lip, nose, and eyebrow piercings, and lightning bolts tattooed up their cheeks. They all have backpacks, a few even rolling suitcases. They are opioid addicts, and almost all young, White adults. There they sit, once-innocent young girls, now worn and hardened, and vicious-looking young men, all with downcast empty eyes and miserable expressions. They are a frightening group marginalized by their addiction.
Opioid addiction became a national focus of attention with clarion calls for treatment, which resulted in legislative funding for treatment, restrictions on prescribing, and readily available Narcan. Physicians have greatly reduced their prescribing of narcotics and overdose death rates have dropped, but the drug crisis has not gone away, it has only been recently overshadowed by COVID-19.
The most ironic part of the current opioid epidemic and overdose deaths, and the other three bloodborne horsemen of death – endocarditis; hepatitis B, C, and D; and HIV – was that these scourges were affecting the Black community 40 years ago when, in my view, no one seemed to care. There was no addiction counseling, no treatment centers, and law enforcement would visit only with hopes of making a dealer’s arrest. Not until it became a White suburban issue, did this public health problem become recognized as something to act on. This is of course a result of racism, but there is a broader lesson here.
Humans may be naturally bigoted toward any marginalized or minority group. I recall working in the HIV clinic (before it was called HIV) in Dallas in the mid-1980s. The county refused to pay for zidovudine, which was very expensive at the time, and was sued to supply medication for a group marginalized by their sexual orientation. The AIDS epidemic was initially ignored, with the virus spreading to intravenous drug users and eventually to the broader population, which is when effective treatments became a priority.
Physicians and society should pay close attention to the ills of our marginalized communities. Because of isolation from health care, they are the medical canaries in the coal mine for all of us. Medical issues and infectious diseases identified there should be a priority and solutions sought and applied. This not only would benefit the marginalized group and ease their suffering, but would be salutary to society as a whole, because they surely will be coming everyone’s way.
COVID-19 highlights this. The working poor live in close quarters and most rely on crowded public transportation, and so a respiratory illness spreads rapidly in a population that cannot practically physically distance and probably cannot afford face masks, or alcohol hand gel.
As noted above, we have a persistent illegal drug epidemic. We also have a resurgence in venereal disease and tuberculosis, much of it drug resistant, which again is concentrated in our marginalized populations. Meanwhile, we have been cutting spending on public health, while we obviously need more resources devoted to public and community health.
When we step back and look, there are public health issues everywhere. We could eliminate 90% of cervical cancer and most of the oropharyngeal cancer with use of a very effective vaccine, but we struggle to get it paid for and to convince the public of its ultimate good.
Another example is in Ohio, where we raised the age to purchase tobacco to 21, which is laudable. But children of any age can still access tanning beds, which dramatically raises their lifetime risk of melanoma, often using a note from their “parents” that they write for each other on the car hood in the strip mall parking lot. This group of mostly young white women could also be considered a marginalized group despite their disposable income because of their belief in personal invincibility and false impressions of a tan conferring beauty and vitality repeated endlessly in their echo chamber of social media impressions.
Perhaps we should gauge the state of our public health by the health status of the most oppressed group of all, the incarcerated. Is it really possible that we don’t routinely test for and treat hepatitis C in many of our prisons? Is this indifference because the incarcerated are again a largely minority group and hepatitis C is spread by intravenous drug use?
Solutions and interventions for these problems range widely in cost, but all would eventually save the greater society money and alleviate great misery for those affected.
Perhaps we should be talking about the decriminalization of drug use. The drugs are already here and the consequences apparent, including overflowing prisons and out of control gun violence. This is a much thornier discussion, but seems at the root of many of our problems.
Bigotry is insidious and will take a long and continuing active effort to combat. As Dr. Taleb notes in the introductory quote, it requires a constant, tiring, deliberate mental effort to be mindful of one’s biases. As physicians, we have always been careful to try and treat all patients without bias, but this is not enough. We must become more insistent about the funding and application of public health measures.
Recognizing and treating the medical problems of our marginalized populations seems a doable first step while our greater society struggles with mental bias toward marginalized groups. Reducing the health burdens of these groups can only help them in their life struggles and will benefit all.
Someone once told me that the cold wind in the ghetto eventually blows out into the suburbs, and they were right. As physicians and a society, we should be insistent about correcting medical injustices beforehand. Let’s get started.
Dr. Coldiron is in private practice but maintains a clinical assistant professorship at the University of Cincinnati. He cares for patients, teaches medical students and residents, and has several active clinical research projects. Dr. Coldiron is the author of more than 80 scientific letters, papers, and several book chapters, and he speaks frequently on a variety of topics. He is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. Write to him at [email protected]
Doctors say their COVID-19 protocol saves lives; others want proof
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 pandemic dictates reconsideration of pemphigus therapy
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM AAD 20
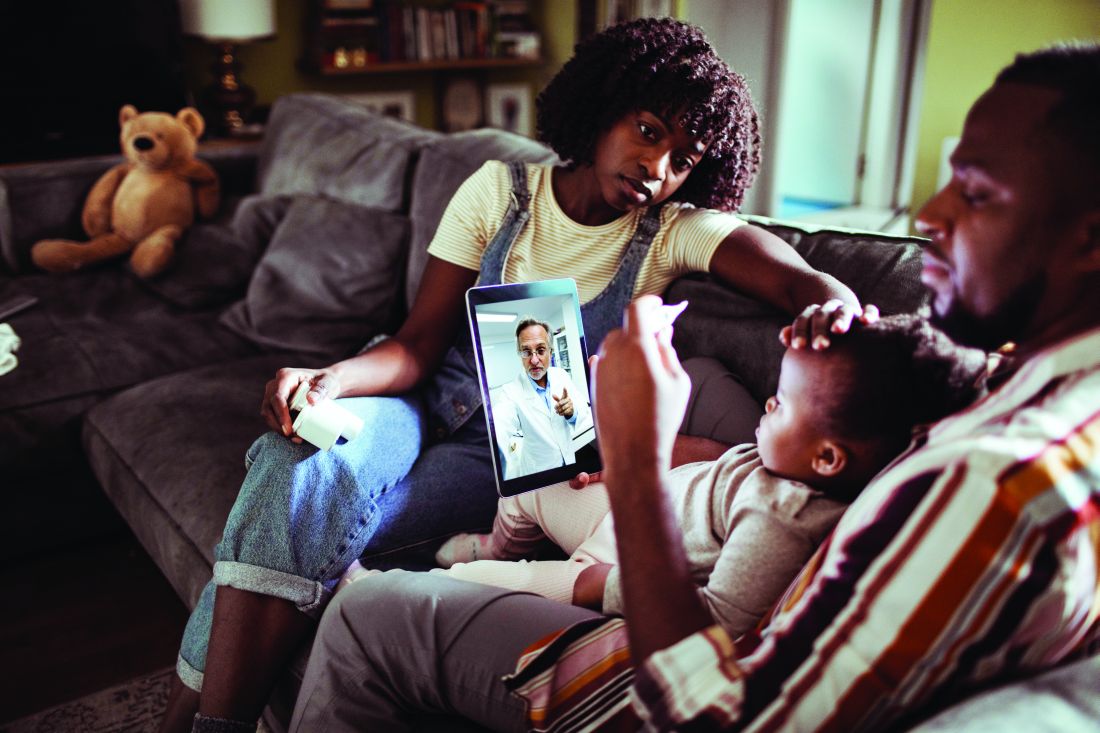
What have we learned from COVID?
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
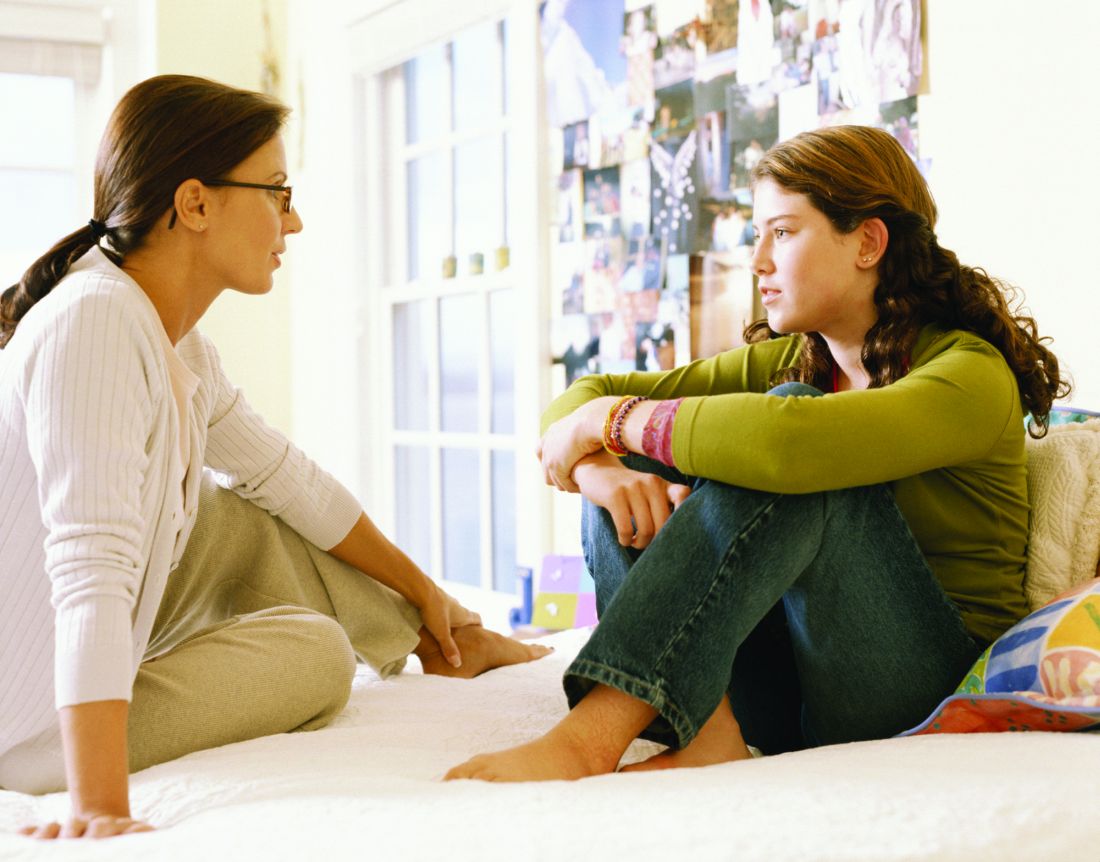
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
In 2015, I proposed virtual care for the division of adolescent medicine, to the administration of our Midwestern children and adolescent hospital; they gladly listened and accepted a copy of the resources I provided. Virtual care was acknowledged to be the future direction of our and other organizations.
Four years later, virtual visits were introduced in the pediatric urgent care, but with little usability as families were slow to adopt this new form of medicine. Fast forward to the COVID-19 crisis in March 2020, and virtual medicine was the only option to meet the needs of patients and to stop the economic consequences. Unfortunately, the expedited rollout at our and many other hospitals may have resulted in limited program development and a lack of shared best practices.
Since March 2020, both patients and medical providers have accepted virtual care, but we now have an opportunity to review some of the limitations to offering virtual care. Work in primary care centers may see limitations using virtual medicine to meet the needs of all patients. Take into consideration the ability to offer confidential care. Confidential care has been a challenge virtually. For example, while completing a virtual visit with a 19-year-old female, it was apparent she was not alone and when asked a benign question the commotion in the background told the real story. The young woman began to laugh and said, “That was my dad running out of the room.” Despite requesting that parents leave the call, they can be heard within earshot of the caller.
On a televisit, written words appear backwards on the video, requiring written questions to be mirror images. When asking questions meant to be confidential, we have used note cards with a question mark. Verbal directions asking the adolescent to give a thumbs up or down to answer the question are required to maintain privacy from others in the room. If the patient responds thumbs up, this leads to additional questions with note cards. Although not ideal, this process gets to the answers, and the adolescent can disclose confidential information without concern about being overheard. Child abuse and neglect professionals have found similar challenges talking to caregivers or children as they are uncertain if others in the home are out of the screen but listening to the questions or prompting responses.
Obtaining vitals may be restricted and picking up hypertension or changes in weight has been limited to face to face visits. To continue to provide virtual care will require screening stations. I foresee a kiosk at the grocery or drugstore with a computer and the ability to obtain vitals or portions of an exam such as heart and lung evaluations. Patients could go at their convenience and the results could be sent to their providers. Technology already exists to use a cell phone to take photos of a toddler’s sore ear drum, and to obtain basic pulse oximetry and ECG, but these have a cost and may be available only to those able to afford these tools.
Billing issues have developed when patients go to a lab on the same day as a virtual visit. Completing a virtual visit for a sore throat thought to be streptococcal pharyngitis should not be finalized without access to a streptococcal throat swab. Until families have home kits to evaluate for strep throat, the families must bring the patient to a clinic or lab to obtain a pharyngeal culture. Furthermore, insurance reimbursement standards will need to be set for ongoing virtual health to become a sustainable option.
Workflows have been disrupted by balancing face to face visits with virtual visits. Unless the virtual visit has been set up for the medical team to access immediately, there are delays accessing the virtual platform, resulting in unnecessary gaps in care. Arranging schedules to separate face to face visits from virtual visits offers more efficiency. Creating a block of virtual visits separated from face-to-face visits or assigning providers to virtual-only schedules may be the best option for an efficient clinic flow. Telemedicine visit templates may need to be created as virtual visits become standard practice.
At present, virtual visits can only be offered to English-speaking patients. The inability to offer translators limits access to a small number of patients. Given COVID-19’s impact on the underserved communities, having a safe resource to reach these patients has been limited, leaving face-to-face visits as their only option. Requiring a face-to-face visit during peak illness has placed patients at risk. They have refused health care as opposed to exposure to the illness in health care settings.
We have innovative opportunities to create a new health care system. Despite the initial struggles with the adoption of virtual care, patients and providers have begun embracing the technology. Best practices and shared resources will be required to have a successful system before brick and mortar organizations can be reduced or insurance companies create their own health care systems which can branch across state lines.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
The article was updated 7/17/2020.
Four-year-old boy presents with itchy rash on face, extremities
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
Contact dermatitis is an eczematous, pruritic eruption caused by direct contact with a substance and an irritant or allergic reaction. While it may not be contagious or life-threatening, contact dermatitis may be tremendously uncomfortable and impactful. Contact dermatitis may occur from exposure to chemicals in soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, metals, plants and topical products, and medications. The hallmark of contact dermatitis is localized eczematous reactions on the portion of the body that has been directly exposed to the reaction-causing substance. – often with oozing and crusting.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type, which occurs when a substance damages the skin’s outer protective layer and does not require prior exposure or sensitization. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can develop after exposure and sensitization, with an external allergen triggering an acute inflammatory response.1 Common causes of ACD include nickel, cobalt, gold, chromium, poison ivy/oak/sumac, cosmetics/personal care products that contain formaldehyde, fragrances, topical medications (anesthetics, antibiotics, corticosteroids), baby wipes, sunscreens, latex materials, protective equipment, soap/cleansers, resins, and acrylics. Among children, nickel sulfate, ammonium persulfate, gold sodium thiosulfate, thimerosal, and toluene-2,5-diamine are the most common sensitizers. Rarely, ACD can be triggered by something that enters the body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
An Id reaction, or autoeczematization, is a generalized acute cutaneous reaction to a variety of stimuli, including infectious and inflammatory skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, stasis dermatitis, or other eczematous dermatitis.3 Id reactions usually are preceded by a preexisting dermatitis. Lesions are, by definition, at a site distant from the primary infection or dermatitis. They often are distributed symmetrically. Papular or papular-vesicular lesions of the extremities and or trunk are common in children.
Our patient had evidence of a localized periocular contact dermatitis reaction that preceded the symmetric papular, eczematous eruption consistent with an id reaction. Our patient was prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5 % ointment for the eyes and triamcinolone 0.1% ointment for the rash on the body, which resulted in significant improvement.
Rosacea is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder that primarily involves the central face. Common clinical features include facial erythema, telangiectasias, and inflammatory papules or pustules. Ocular involvement may occur in the presence or absence of cutaneous manifestations. Patients may report the presence of ocular foreign body sensation, burning, photophobia, blurred vision, redness, and tearing. Ocular disease is usually bilateral and is not proportional to the severity of the skin disease.4 Common skin findings are blepharitis, lid margin telangiectasia, tear abnormalities, meibomian gland inflammation, frequent chalazion, bilateral hordeolum, conjunctivitis, and, rarely, corneal ulcers and vascularization. Our patient initially did have bilateral hordeolum in what may seem to be ocular rosacea. However, given the use of a recent topical antibiotic with subsequent eczematous rash of the eyelids and then resulting distant rash on the body 1week later made the rash likely allergic contact dermatitis with id reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, and usually mild form of dermatitis that occurs in infants and in adults. The severity may vary from minimal, asymptomatic scaliness of the scalp (dandruff) to more widespread involvement. It is usually characterized by well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with greasy-looking, yellowish scales distributed on areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, the external ear, the center of the face, the upper part of the trunk, and the intertriginous areas.
Psoriasis typically affects the outside of the elbows, knees, or scalp, although it can appear on any location. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Ocular involvement is a well known manifestation of psoriasis.5 Psoriatic lesions of the eyelid are rare, even in the erythrodermic variant of the disease. Occasionally, pustular psoriasis may involve the eyelids, with typical psoriatic lesions visible on the skin and lid margin. The reason for the relative sparing of the eyelid skin in patients with psoriasis is unknown. Other manifestations include meibomian gland dysfunction, decreased tear film break-up time, a nonspecific conjunctivitis, and corneal disease secondary to lid disease such as trichiasis.
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome (GCS), also known as papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and infantile papular acrodermatitis, is a self-limited skin disorder that most often occurs in young children. Viral infections are common GCS precipitating factors . GCS typically manifests as a symmetric, papular eruption, often with larger (3- to 10-mm) flat topped papulovesicles. Classic sites of involvement include the cheeks, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the forearms and legs. GCS may be pruritic or asymptomatic, and papules typically resolve spontaneously within 2 months. Occasionally, GCS persists for longer periods. The eyelid lesions and localized pattern, with the absence of larger symmetric papules of the buttocks and legs, was not consistent with papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. They had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Jun; 74(6):1043-54.
2. Pediatr Dermatol 2016 Jul; 33(4):399-404.
3. Evans M & Bronson D. (2019) Id Reaction (Autoeczematization). Retrieved from emedicine.medscape.com/article/1049760-overview.
4. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Dec;15(6):499-502.
5. Clin Dermatol. Mar-Apr 2016;34(2):146-50.
A 4-year-old healthy male with no significant prior medical history presents for evaluation of "itchy bumps" on the face and extremities of 2 weeks' duration.
The child was well until around 2 and a half weeks ago when he presented for evaluation of two lesions on the lower eyelids, diagnosed as hordeolum (a stye). He was prescribed ofloxacin ophthalmic solution.
One week later he developed bilateral itchy red eyes with red, thickened areas on the upper lids, followed several days later by pruritic papules on the ears, wrists, elbows, knees, and ankles. His mother used Vaseline for the eyelids for 1 week with no improvement. Physical exam at the dermatologist's office showed mild erythema, induration, and lichenification of the upper eyelids, and bilateral periocular eczematous patches with overlying scale. Subtle papules were evident on the elbows and feet.
Provide support in uncertain times
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
A sense of safety and stability, both emotional and physical, is crucial in promoting the healthy development of youth. Between the global pandemic, need for social distancing, economic downturn, and increased awareness of racial disparities, for many this sense of stability has been rattled.
School closures have led to a loss of social interaction, challenges to continued academic growth, and, for some students, lack of access to nutrition and increased food insecurity. For students with learning or mental health challenges, closures may have eliminated or significantly reduced desperately needed supports received in school.1 While these trying circumstances have been difficult for many, the transition back to school in the fall also may be challenging because of the uncertainty about what this will look like and possible change in routine. Some students or their families may have anxiety about returning, either because of a history of adverse experiences at school such as bullying, or because of fears about exposure for themselves or others to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The past several months also brought about greater awareness of systemic racial disparities, whether as reflected in health care, education, or the criminal justice system. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, Latinx and African-American individuals in the United States have had a threefold greater chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2 and have a twofold greater risk of death, compared with white people in the same communities.2 Other social determinants of health – economic stability, education, social factors such as incarceration and discrimination, and neighborhood factors including access to healthy food – play a role in this vulnerability.
The pandemic has resulted in a need for social distancing, and as a result, isolation. Children and teens exposed to the news may have anxiety about what they see or hear. Additional pressures in the family can include economic uncertainty, loss of employment for the primary wage earner of the household, or stress related to family members being first responders.
Any one of these factors is a potentially significant stressor, so how do we best support youth to help them survive and hopefully thrive during this time?
- It is important to establish a sense of routine; this can help create a sense of stability and safety. Recognizing that circumstances are not the same as they were 5 or 6 months ago, encouraging structure should not come at the cost of preserving connection.
- Note positive behavior and choices made by children and make sure they know it was observed.
- Many children have experienced increased screen time with the lack of structure of the traditional school day or summer camp and extracurricular activities. Limiting screen time and being mindful of its potential impact on mood is prudent.
- Self-care for parents and guardians is important. This time is stressful for the adults of the household, let alone children who are learning self-regulation skills.
- Listen to children’s or teens’ concerns and share information in developmentally appropriate ways. It is okay to not have all of the answers.
- Balance fostering a sense of gratitude with not invalidating a child’s or teen’s experience. Showing empathy during this time is vital. While there may be other soccer seasons, it is normal to experience grief about the loss of experiences during this time.
- Parents and guardians know their children best, so it is prudent for them to be mindful of concerning changes such as an increase in sadness, anxiety, or irritability that negatively impacts daily functioning such as sleeping, eating, or relationships with family and friends.
- Promote social interactions with appropriate safeguards in place. Unfortunately, the number of SARS-CoV-2 infections is increasing in multiple states, and there is the potential to return to some of the previous restrictions. However, encouraging social interaction while following local guidelines and with cautions such as limiting the number of people present, meeting outside, or considering interacting with others who are similarly social distancing can help foster social connection and development.
- Maintain connection digitally when in-person contact is not an option.3 Social groups, places of worship, and other activities have been agile in developing virtual communities. Communication by voice and/or video is thought to be more powerful than by written communication (text, email) alone.4 However, it is important to consider those who may have limited to no access to electronic methods.
- Encourage open communication with children about diversity and bias, and consider how our interactions with others may affect our children’s perspectives.5
- As providers, it is crucial that we address structural and institutional systems that negatively impact the health, safety, and access to care including our Black, indigenous, and people of color (BIPOC) and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender/transsexual, queer/questioning, intersex, and allied/asexual/aromantic/agender (LGBTQIA) patients.
Dr. Strange is an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at the University of Vermont Medical Center and University of Vermont Robert Larner College of Medicine, both in Burlington. She works with children and adolescents. Dr. Strange has no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Online resources for parents and families
- Child Mind Institute: Coping With the Coronavirus Crisis: Supporting Your Kids.
- American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
- Common Sense Media: Help with determining appropriateness of media for children.
Hotlines
- National Suicide Prevention Hotline: 1-800-273-8255
- GLBT National Hotline: 888-843-4564
- The California Peer-Run Warm Line: 1-855-845-7415
- Trevor Project: 866-488-7386 or text TREVOR to 1-202-304-1200
- Trans Lifeline: 877-565-8860
- Crisis Text Line: Text HOME to 741741
References
1. JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Apr 14. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1456.
2. CDC: COVID-19 in Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups.
3. JAMA. 2020 Mar 23. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4469.
4. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1562.
5. American Psychological Association: Talking with children about discrimination.
Residents, fellows will get minimum 6 weeks leave for caregiving
the American Board of Medical Specialties has announced.
The “ABMS Policy on Parental, Caregiver and Family Leave” announced July 13 was developed after a report from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education’s Council of Review Committee Residents in June 2019.
Richard E. Hawkins, MD, ABMS President and CEO, said in a statement that “the growing shifts in viewpoints regarding work-life balance and parental roles had a great influence in the creation of this policy, which fosters an environment that supports our trainees’ ability to care not only for patients, but also for themselves and their families.”
Specifically, the time can be taken for birth and care of a newborn, adopting a child, or becoming a foster parent; care of a child, spouse, or parent with a serious health condition; or the trainee’s own serious health condition. The policy applies to member boards with training programs of at least 2 years.
Boards must communicate when a leave will require an official extension to avoid disruptions to a physician’s career trajectory, a delay in starting a fellowship, or moving into a salaried position.
Work/life balance was by far the biggest challenge reported in the Medscape Residents Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2019.
Several member boards had already implemented policies that offered more flexibility without unduly delaying board certification; now ABMS is extending that to all boards.
ABMS says member boards may limit the maximum time away in a single year or level of training and directed member boards to “make reasonable testing accommodations” – for example, by allowing candidates to take an exam provided the candidate completes all training requirements by a certain date.
Kristy Rialon, MD, an author of the ACGME report and assistant professor of surgery at Baylor College of Medicine and the Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, noted the significance of the change in a news release.
“By virtue of their ages, residents and fellows – male and female – often find themselves having and raising children, as well as serving as family members’ caregivers,” Dr. Rialon said. “By adopting more realistic and compassionate approaches, the ABMS member boards will significantly improve the quality of life for residents and fellows. This also will support our female physicians, helping to narrow the gender gap in their career advancement by allowing for greater leave flexibility.”
A Medscape survey published July 15 said work-life balance was the No. 1 concern of female physicians, far outpacing pay.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
the American Board of Medical Specialties has announced.
The “ABMS Policy on Parental, Caregiver and Family Leave” announced July 13 was developed after a report from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education’s Council of Review Committee Residents in June 2019.
Richard E. Hawkins, MD, ABMS President and CEO, said in a statement that “the growing shifts in viewpoints regarding work-life balance and parental roles had a great influence in the creation of this policy, which fosters an environment that supports our trainees’ ability to care not only for patients, but also for themselves and their families.”
Specifically, the time can be taken for birth and care of a newborn, adopting a child, or becoming a foster parent; care of a child, spouse, or parent with a serious health condition; or the trainee’s own serious health condition. The policy applies to member boards with training programs of at least 2 years.
Boards must communicate when a leave will require an official extension to avoid disruptions to a physician’s career trajectory, a delay in starting a fellowship, or moving into a salaried position.
Work/life balance was by far the biggest challenge reported in the Medscape Residents Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2019.
Several member boards had already implemented policies that offered more flexibility without unduly delaying board certification; now ABMS is extending that to all boards.
ABMS says member boards may limit the maximum time away in a single year or level of training and directed member boards to “make reasonable testing accommodations” – for example, by allowing candidates to take an exam provided the candidate completes all training requirements by a certain date.
Kristy Rialon, MD, an author of the ACGME report and assistant professor of surgery at Baylor College of Medicine and the Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, noted the significance of the change in a news release.
“By virtue of their ages, residents and fellows – male and female – often find themselves having and raising children, as well as serving as family members’ caregivers,” Dr. Rialon said. “By adopting more realistic and compassionate approaches, the ABMS member boards will significantly improve the quality of life for residents and fellows. This also will support our female physicians, helping to narrow the gender gap in their career advancement by allowing for greater leave flexibility.”
A Medscape survey published July 15 said work-life balance was the No. 1 concern of female physicians, far outpacing pay.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
the American Board of Medical Specialties has announced.
The “ABMS Policy on Parental, Caregiver and Family Leave” announced July 13 was developed after a report from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education’s Council of Review Committee Residents in June 2019.
Richard E. Hawkins, MD, ABMS President and CEO, said in a statement that “the growing shifts in viewpoints regarding work-life balance and parental roles had a great influence in the creation of this policy, which fosters an environment that supports our trainees’ ability to care not only for patients, but also for themselves and their families.”
Specifically, the time can be taken for birth and care of a newborn, adopting a child, or becoming a foster parent; care of a child, spouse, or parent with a serious health condition; or the trainee’s own serious health condition. The policy applies to member boards with training programs of at least 2 years.
Boards must communicate when a leave will require an official extension to avoid disruptions to a physician’s career trajectory, a delay in starting a fellowship, or moving into a salaried position.
Work/life balance was by far the biggest challenge reported in the Medscape Residents Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2019.
Several member boards had already implemented policies that offered more flexibility without unduly delaying board certification; now ABMS is extending that to all boards.
ABMS says member boards may limit the maximum time away in a single year or level of training and directed member boards to “make reasonable testing accommodations” – for example, by allowing candidates to take an exam provided the candidate completes all training requirements by a certain date.
Kristy Rialon, MD, an author of the ACGME report and assistant professor of surgery at Baylor College of Medicine and the Texas Children’s Hospital, both in Houston, noted the significance of the change in a news release.
“By virtue of their ages, residents and fellows – male and female – often find themselves having and raising children, as well as serving as family members’ caregivers,” Dr. Rialon said. “By adopting more realistic and compassionate approaches, the ABMS member boards will significantly improve the quality of life for residents and fellows. This also will support our female physicians, helping to narrow the gender gap in their career advancement by allowing for greater leave flexibility.”
A Medscape survey published July 15 said work-life balance was the No. 1 concern of female physicians, far outpacing pay.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: A primary care perspective
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
With the COVID-19 pandemic, we are experiencing a once-in-a-100-year event. Dr. Steven A. Schulz, who is serving children on the front line in upstate New York, and I outline some of the challenges primary care pediatricians have been facing and solutions that have succeeded.
Reduction in direct patient care and its consequences
Because of the unknowns of COVID-19, many parents have not wanted to bring their children to a medical office because of fear of contracting SARS-CoV-2. At the same time, pediatricians have restricted in-person visits to prevent spread of SARS-CoV-2 and to help flatten the curve of infection. Use of pediatric medical professional services, compared with last year, dropped by 52% in March 2020 and by 58% in April, according to FAIR Health, a nonprofit organization that manages a database of 31 million claims. This is resulting in decreased immunization rates, which increases concern for secondary spikes of other preventable illnesses; for example, data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showed that, from mid-March to mid-April 2020, physicians in the Vaccines for Children program ordered 2.5 million fewer doses of vaccines and 250,000 fewer doses of measles-containing vaccines, compared with the same period in 2019. Fewer children are being seen for well visits, which means opportunities are lost for adequate monitoring of growth, development, physical wellness, and social determinants of health.
This is occurring at a time when families have been experiencing increased stress in terms of finances, social isolation, finding adequate child care, and serving as parent, teacher, and breadwinner. An increase in injuries is occurring because of inadequate parental supervision because many parents have been distracted while working from home. An increase in cases of severe abuse is occurring because schools, child care providers, physicians, and other mandated reporters in the community have decreased interaction with children. Children’s Hospital Colorado in Colorado Springs saw a 118% increase in the number of trauma cases in its ED between January and April 2020. Some of these were accidental injuries caused by falls or bicycle accidents, but there was a 200% increase in nonaccidental trauma, which was associated with a steep fall in calls to the state’s child abuse hotline. Academic gains are being lost, and there has been worry for a prolonged “summer slide” risk, especially for children living in poverty and children with developmental disabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic also is affecting physicians and staff. As frontline personnel, we are at risk to contract the virus, and news media reminds us of severe illness and deaths among health care workers. The pandemic is affecting financial viability; estimated revenue of pediatric offices fell by 45% in March 2020 and 48% in April, compared with the previous year, according to FAIR Health. Nurses and staff have been furloughed. Practices have had to apply for grants and Paycheck Protection Program funds while extending credit lines.
Limited testing capability for SARS-CoV-2
Testing for SARS-CoV-2 has been variably available. There have been problems with false positive and especially false negative results (BMJ. 2020 May 12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1808).The best specimen collection method has yet to be determined. Blood testing for antibody has been touted, but it remains unclear if there is clinical benefit because a positive result offers no guarantee of immunity, and immunity may quickly wane. Perhaps widespread primary care office–based testing will be in place by the fall, with hope for future reliable point of care results.
Evolving knowledge regarding SARS-CoV-2 and MIS-C
It initially was thought that children were relatively spared from serious illness caused by COVID-19. Then reports of cases of newly identified multisystem inflammatory syndrome of children occurred. It has been unclear how children contribute to the spread of COVID-19 illness, although emerging evidence indicates it is lower than adult transmission. What will happen when children return to school and daycare in the fall?
The challenges have led to creative solutions for how to deliver care.
Adapting to telehealth to provide care
At least for the short term, HIPAA regulations have been relaxed to allow for video visits using platforms such as FaceTime, Skype, Zoom, Doximity, and Doxy.me. Some of these platforms are HIPAA compliant and will be long-term solutions; however, electronic medical record portals allowing for video visits are the more secure option, according to HIPAA.
It has been a learning experience to see what can be accomplished with a video visit. Taking a history and visual examination of injuries and rashes has been possible. Addressing mental health concerns through the video exchange generally has been effective.
However, video visits change the provider-patient interpersonal dynamic and offer only visual exam capabilities, compared with an in-person visit. We cannot look in ears, palpate a liver and spleen, touch and examine a joint or bone, or feel a rash. Video visits also are dependent on the quality of patient Internet access, sufficient data plans, and mutual capabilities to address the inevitable technological glitches on the provider’s end as well. Expanding information technology infrastructure ability and added licensure costs have occurred. Practices and health systems have been working with insurance companies to ensure telephone and video visits are reimbursed on a comparable level to in-office visits.
A new type of office visit and developing appropriate safety plans
Patients must be universally screened prior to arrival during appointment scheduling for well and illness visits. Patients aged older than 2 years and caregivers must wear masks on entering the facility. In many practices, patients are scheduled during specific sick or well visit time slots throughout the day. Waiting rooms chairs need to be spaced for 6-foot social distancing, and cars in the parking lot often serve as waiting rooms until staff can meet patients at the door and take them to the exam room. Alternate entrances, car-side exams, and drive-by and/or tent testing facilities often have become part of the new normal everyday practice. Creating virtual visit time blocks in provider’s schedules has allowed for decreased office congestion. Patients often are checked out from their room, as opposed to waiting in a line at a check out desk. Nurse triage protocols also have been adapted and enhanced to meet needs and concerns.
With the need for summer physicals and many regions opening up, a gradual return toward baseline has been evolving, although some of the twists of a “new normal” will stay in place. The new normal has been for providers and staff to wear surgical masks and face shields; sometimes N95 masks, gloves, and gowns have been needed. Cleaning rooms and equipment between patient visits has become a major, new time-consuming task. Acquiring and maintaining adequate supplies has been a challenge.
Summary
The American Academy of Pediatrics, CDC, and state and local health departments have been providing informative and regular updates, webinars, and best practices guidelines. Pediatricians, community organizations, schools, and mental health professionals have been collaborating, overcoming hurdles, and working together to help mitigate the effects of the pandemic on children, their families, and our communities. Continued education, cooperation, and adaptation will be needed in the months ahead. If there is a silver lining to this pandemic experience, it may be that families have grown closer together as they sheltered in place (and we have grown closer to our own families as well). One day perhaps a child who lived through this pandemic might be asked what it was like, and their recollection might be that it was a wonderful time because their parents stayed home all the time, took care of them, taught them their school work, and took lots of long family walks.
Dr. Schulz is pediatric medical director, Rochester (N.Y.) Regional Health. Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. Dr. Schulz and Dr. Pichichero said they have no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
This article was updated 7/16/2020.
How to not miss something
It’s a mad, mad, mad world. In California, we seem bent on swelling our curve. We’d just begun bringing our patients back into the office. We felt safe, back to business. Then air raid sirens again. Retreat to the Underground. Minimize waiting room waiting, convert to telephone and video. Do what we can to protect our patients and people.
As doctors, we’ve gotten proficient at being triage nurses, examining each appointment request, and sorting who should be seen in person and who could be cared for virtually. We do it for every clinic now.
My 11 a.m. patient last Thursday was an 83-year-old Filipino man with at least a 13-year history of hand dermatitis (based on his long electronic medical record). He had plenty of betamethasone refills. There were even photos of his large, brown hands in his chart. Grandpa hands, calloused by tending his garden and scarred from fixing bikes, building sheds, and doing oil changes for any nephew or niece who asked. The most recent uploads showed a bit of fingertip fissuring, some lichenified plaques. Not much different than they looked after planting persimmon trees a decade ago. I called him early that morning to offer a phone appointment. Perhaps I could save him from venturing out.
“I see that you have an appointment with me in a few hours. If you’d like, I might be able to help you by phone instead.” “Oh, thank you, doc,” he replied. “It’s so kind of you to call. But doc, I think maybe it is better if I come in to see you.” “Are you sure?” “Oh, yes. I will be careful.”
He checked in at 10:45. When I walked into the room he was wearing a face mask and a face shield – good job! He also had a cane and U.S. Navy Destroyer hat. And on the bottom left of his plastic shield was a sticker decal of a U.S. Navy Chief Petty Officer, dress blue insignia. His hands looked just like the photos: no purpura, plenty of lentigines. Fissures, calluses, lichenified plaques. I touched them. In the unaffected areas, his skin was remarkably soft. What stories these hands told. “I was 20 years in the Navy, doc,” he said. “I would have stayed longer but my wife, who’s younger, wanted me back home.” He talked about his nine grandchildren, some of whom went on to join the navy too – but as officers, he noted with pride. Now he spends his days caring for his wife; she has dementia. He can’t stay long because she’s in the waiting room and is likely to get confused if alone for too long.
We quickly reviewed good hand care. I ordered clobetasol ointment. He was pleased; that seemed to work years ago and he was glad to have it again.
So, why did he need to come in? Clearly I could have done this remotely. “Thank you so much for seeing me, doc,” as he stood to walk out. “Proper inspections have to be done in person, right?” Yes, I thought. Otherwise, you might miss something.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
It’s a mad, mad, mad world. In California, we seem bent on swelling our curve. We’d just begun bringing our patients back into the office. We felt safe, back to business. Then air raid sirens again. Retreat to the Underground. Minimize waiting room waiting, convert to telephone and video. Do what we can to protect our patients and people.
As doctors, we’ve gotten proficient at being triage nurses, examining each appointment request, and sorting who should be seen in person and who could be cared for virtually. We do it for every clinic now.
My 11 a.m. patient last Thursday was an 83-year-old Filipino man with at least a 13-year history of hand dermatitis (based on his long electronic medical record). He had plenty of betamethasone refills. There were even photos of his large, brown hands in his chart. Grandpa hands, calloused by tending his garden and scarred from fixing bikes, building sheds, and doing oil changes for any nephew or niece who asked. The most recent uploads showed a bit of fingertip fissuring, some lichenified plaques. Not much different than they looked after planting persimmon trees a decade ago. I called him early that morning to offer a phone appointment. Perhaps I could save him from venturing out.
“I see that you have an appointment with me in a few hours. If you’d like, I might be able to help you by phone instead.” “Oh, thank you, doc,” he replied. “It’s so kind of you to call. But doc, I think maybe it is better if I come in to see you.” “Are you sure?” “Oh, yes. I will be careful.”
He checked in at 10:45. When I walked into the room he was wearing a face mask and a face shield – good job! He also had a cane and U.S. Navy Destroyer hat. And on the bottom left of his plastic shield was a sticker decal of a U.S. Navy Chief Petty Officer, dress blue insignia. His hands looked just like the photos: no purpura, plenty of lentigines. Fissures, calluses, lichenified plaques. I touched them. In the unaffected areas, his skin was remarkably soft. What stories these hands told. “I was 20 years in the Navy, doc,” he said. “I would have stayed longer but my wife, who’s younger, wanted me back home.” He talked about his nine grandchildren, some of whom went on to join the navy too – but as officers, he noted with pride. Now he spends his days caring for his wife; she has dementia. He can’t stay long because she’s in the waiting room and is likely to get confused if alone for too long.
We quickly reviewed good hand care. I ordered clobetasol ointment. He was pleased; that seemed to work years ago and he was glad to have it again.
So, why did he need to come in? Clearly I could have done this remotely. “Thank you so much for seeing me, doc,” as he stood to walk out. “Proper inspections have to be done in person, right?” Yes, I thought. Otherwise, you might miss something.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
It’s a mad, mad, mad world. In California, we seem bent on swelling our curve. We’d just begun bringing our patients back into the office. We felt safe, back to business. Then air raid sirens again. Retreat to the Underground. Minimize waiting room waiting, convert to telephone and video. Do what we can to protect our patients and people.
As doctors, we’ve gotten proficient at being triage nurses, examining each appointment request, and sorting who should be seen in person and who could be cared for virtually. We do it for every clinic now.
My 11 a.m. patient last Thursday was an 83-year-old Filipino man with at least a 13-year history of hand dermatitis (based on his long electronic medical record). He had plenty of betamethasone refills. There were even photos of his large, brown hands in his chart. Grandpa hands, calloused by tending his garden and scarred from fixing bikes, building sheds, and doing oil changes for any nephew or niece who asked. The most recent uploads showed a bit of fingertip fissuring, some lichenified plaques. Not much different than they looked after planting persimmon trees a decade ago. I called him early that morning to offer a phone appointment. Perhaps I could save him from venturing out.
“I see that you have an appointment with me in a few hours. If you’d like, I might be able to help you by phone instead.” “Oh, thank you, doc,” he replied. “It’s so kind of you to call. But doc, I think maybe it is better if I come in to see you.” “Are you sure?” “Oh, yes. I will be careful.”
He checked in at 10:45. When I walked into the room he was wearing a face mask and a face shield – good job! He also had a cane and U.S. Navy Destroyer hat. And on the bottom left of his plastic shield was a sticker decal of a U.S. Navy Chief Petty Officer, dress blue insignia. His hands looked just like the photos: no purpura, plenty of lentigines. Fissures, calluses, lichenified plaques. I touched them. In the unaffected areas, his skin was remarkably soft. What stories these hands told. “I was 20 years in the Navy, doc,” he said. “I would have stayed longer but my wife, who’s younger, wanted me back home.” He talked about his nine grandchildren, some of whom went on to join the navy too – but as officers, he noted with pride. Now he spends his days caring for his wife; she has dementia. He can’t stay long because she’s in the waiting room and is likely to get confused if alone for too long.
We quickly reviewed good hand care. I ordered clobetasol ointment. He was pleased; that seemed to work years ago and he was glad to have it again.
So, why did he need to come in? Clearly I could have done this remotely. “Thank you so much for seeing me, doc,” as he stood to walk out. “Proper inspections have to be done in person, right?” Yes, I thought. Otherwise, you might miss something.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
Be wary of ‘for eczema’ claims on labels of popular moisturizers
Be wary of “for eczema” advertising claims contained on the labels of popular skin moisturizers.
Results from a study presented during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology found that .
“Prescription medications are important for managing eczema flares, but a lot of the work in treating eczema is preventative, done by consistently moisturizing the skin at home with drug store products,” co-first study author Catherine L. Ludwig, said in an interview. “Allergic contact dermatitis occurs more commonly in people with eczema. A previous study was done in characterizing the allergenic potential of drug store moisturizers and found that 88% of moisturizers contain at least one common allergen. Many moisturizers are marketed specifically to eczema, but the allergen content of these products are unknown.”
For the current study, Ms. Ludwig, a medical student at the University of Illinois at Chicago and co-first author Alyssa M. Thompson, a medical student at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and their colleagues compiled a list of the top 30 moisturizers “for eczema” sold by Amazon, Target, and Walmart. For each moisturizer they recorded common ingredients and marketing claims related to benefits for atopic dermatitis, including eczema relief, sensitive/gentle skin, hypoallergenic, anti-itch, anti-inflammatory, clinically proven, oatmeal, dermatologist recommended/approved, organic, fragrance-free, for baby, or National Eczema Association approved. To establish allergenic potential, the researchers used MATLAB to compare ingredient lists to compounds listed as common allergens in the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program database (ACDS CAMP). Next, they used the Mann-Whitney U test to evaluate differences in allergen count between products with and without specific marketing claims.
Ms. Ludwig and her associates found that 28 of 30 products analyzed (93%) contained at least one allergen, with an overall average allergen count of 3.60. The three most prevalent allergens were cetyl alcohol (70%), phenoxyethanol (50%), and aloe (33%). “Anti-inflammatory” moisturizers had the greatest average number of allergens (4.00), followed by “anti-itch” (3.71) and “oatmeal” (3.71). Only products claiming to be “hypoallergenic” had significantly lower allergenic ingredient count (an average of 2.45) than those without the claim (P = .011).
“It was validating to see that eczema moisturizer products marketed as ‘hypoallergenic’ truly do have fewer allergenic ingredients than moisturizers without the claim,” Ms. Ludwig said. “However, it was surprising to see that even products marketed to eczema patients, who have a higher prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis, contain an average of 3.6 common allergens. As dermatology providers, we can relay to patients and parents that relying solely on ‘for eczema’ claims is not advisable. Clinicians should acquaint themselves with the top allergens (cetyl alcohol, phenoxyethanol, and aloe) and keep these ingredients, as well as affordability and patient preferences, in mind when making product recommendations.”
The study’s senior author, Vivian Y. Shi, MD, is a stock shareholder of Learn Health and has served as an advisory board member and/or investigator, and/or received research funding from AbbVie, Burt’s Bees, GpSkin, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Skin Actives Scientific, and SUN Pharma, and the Foundation for Atopic Dermatitis, Global Parents for Eczema Research, and the National Eczema Association. The other study authors reported having no financial disclosures.
Be wary of “for eczema” advertising claims contained on the labels of popular skin moisturizers.
Results from a study presented during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology found that .
“Prescription medications are important for managing eczema flares, but a lot of the work in treating eczema is preventative, done by consistently moisturizing the skin at home with drug store products,” co-first study author Catherine L. Ludwig, said in an interview. “Allergic contact dermatitis occurs more commonly in people with eczema. A previous study was done in characterizing the allergenic potential of drug store moisturizers and found that 88% of moisturizers contain at least one common allergen. Many moisturizers are marketed specifically to eczema, but the allergen content of these products are unknown.”
For the current study, Ms. Ludwig, a medical student at the University of Illinois at Chicago and co-first author Alyssa M. Thompson, a medical student at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and their colleagues compiled a list of the top 30 moisturizers “for eczema” sold by Amazon, Target, and Walmart. For each moisturizer they recorded common ingredients and marketing claims related to benefits for atopic dermatitis, including eczema relief, sensitive/gentle skin, hypoallergenic, anti-itch, anti-inflammatory, clinically proven, oatmeal, dermatologist recommended/approved, organic, fragrance-free, for baby, or National Eczema Association approved. To establish allergenic potential, the researchers used MATLAB to compare ingredient lists to compounds listed as common allergens in the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program database (ACDS CAMP). Next, they used the Mann-Whitney U test to evaluate differences in allergen count between products with and without specific marketing claims.
Ms. Ludwig and her associates found that 28 of 30 products analyzed (93%) contained at least one allergen, with an overall average allergen count of 3.60. The three most prevalent allergens were cetyl alcohol (70%), phenoxyethanol (50%), and aloe (33%). “Anti-inflammatory” moisturizers had the greatest average number of allergens (4.00), followed by “anti-itch” (3.71) and “oatmeal” (3.71). Only products claiming to be “hypoallergenic” had significantly lower allergenic ingredient count (an average of 2.45) than those without the claim (P = .011).
“It was validating to see that eczema moisturizer products marketed as ‘hypoallergenic’ truly do have fewer allergenic ingredients than moisturizers without the claim,” Ms. Ludwig said. “However, it was surprising to see that even products marketed to eczema patients, who have a higher prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis, contain an average of 3.6 common allergens. As dermatology providers, we can relay to patients and parents that relying solely on ‘for eczema’ claims is not advisable. Clinicians should acquaint themselves with the top allergens (cetyl alcohol, phenoxyethanol, and aloe) and keep these ingredients, as well as affordability and patient preferences, in mind when making product recommendations.”
The study’s senior author, Vivian Y. Shi, MD, is a stock shareholder of Learn Health and has served as an advisory board member and/or investigator, and/or received research funding from AbbVie, Burt’s Bees, GpSkin, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Skin Actives Scientific, and SUN Pharma, and the Foundation for Atopic Dermatitis, Global Parents for Eczema Research, and the National Eczema Association. The other study authors reported having no financial disclosures.
Be wary of “for eczema” advertising claims contained on the labels of popular skin moisturizers.
Results from a study presented during the virtual annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology found that .
“Prescription medications are important for managing eczema flares, but a lot of the work in treating eczema is preventative, done by consistently moisturizing the skin at home with drug store products,” co-first study author Catherine L. Ludwig, said in an interview. “Allergic contact dermatitis occurs more commonly in people with eczema. A previous study was done in characterizing the allergenic potential of drug store moisturizers and found that 88% of moisturizers contain at least one common allergen. Many moisturizers are marketed specifically to eczema, but the allergen content of these products are unknown.”
For the current study, Ms. Ludwig, a medical student at the University of Illinois at Chicago and co-first author Alyssa M. Thompson, a medical student at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and their colleagues compiled a list of the top 30 moisturizers “for eczema” sold by Amazon, Target, and Walmart. For each moisturizer they recorded common ingredients and marketing claims related to benefits for atopic dermatitis, including eczema relief, sensitive/gentle skin, hypoallergenic, anti-itch, anti-inflammatory, clinically proven, oatmeal, dermatologist recommended/approved, organic, fragrance-free, for baby, or National Eczema Association approved. To establish allergenic potential, the researchers used MATLAB to compare ingredient lists to compounds listed as common allergens in the American Contact Dermatitis Society’s Contact Allergen Management Program database (ACDS CAMP). Next, they used the Mann-Whitney U test to evaluate differences in allergen count between products with and without specific marketing claims.
Ms. Ludwig and her associates found that 28 of 30 products analyzed (93%) contained at least one allergen, with an overall average allergen count of 3.60. The three most prevalent allergens were cetyl alcohol (70%), phenoxyethanol (50%), and aloe (33%). “Anti-inflammatory” moisturizers had the greatest average number of allergens (4.00), followed by “anti-itch” (3.71) and “oatmeal” (3.71). Only products claiming to be “hypoallergenic” had significantly lower allergenic ingredient count (an average of 2.45) than those without the claim (P = .011).
“It was validating to see that eczema moisturizer products marketed as ‘hypoallergenic’ truly do have fewer allergenic ingredients than moisturizers without the claim,” Ms. Ludwig said. “However, it was surprising to see that even products marketed to eczema patients, who have a higher prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis, contain an average of 3.6 common allergens. As dermatology providers, we can relay to patients and parents that relying solely on ‘for eczema’ claims is not advisable. Clinicians should acquaint themselves with the top allergens (cetyl alcohol, phenoxyethanol, and aloe) and keep these ingredients, as well as affordability and patient preferences, in mind when making product recommendations.”
The study’s senior author, Vivian Y. Shi, MD, is a stock shareholder of Learn Health and has served as an advisory board member and/or investigator, and/or received research funding from AbbVie, Burt’s Bees, GpSkin, LEO Pharma, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Skin Actives Scientific, and SUN Pharma, and the Foundation for Atopic Dermatitis, Global Parents for Eczema Research, and the National Eczema Association. The other study authors reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM SPD 2020