User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


Walking the Line: Balancing Autonomy and Safety at End-of-Life
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Background
The goal of hospice and palliative care is to provide comfort and dignity for individuals by honoring autonomy and patient preferences at endof- life. These standards can be difficult to balance when concerns around decision-making capacity and safety arise. The Veteran’s Health Administration has numerous resources to support interdisciplinary teams. We present a case study highlighting conflict between these ethical principles
Case Presentation
Veteran is a 66-year-old male with metastatic neuroendocrine cancer to brain and co-occurring polysubstance use disorder. Veteran agreed to VA inpatient hospice due to functional decline and limited social support at home. Day passes were initially allowed but later restricted due to multiple safety concerns surrounding mental status, smoking on campus and unauthorized passes. Behaviors escalated and veteran removed secure care monitor, left the unit without notifying staff, and erratically drove off campus prompting local police involvement.
Discussion
Patient demonstrated a preference to attend Alcoholics Anonymous meetings in person, to use his vehicle and to live at home. Given the complexity of this case, we turned to the National Center for Ethics in Health Care for input. This included guidance about legal and ethical limitations and recommendations for ongoing assessment and documentation of decisionmaking capacity and use of a surrogate.
Results
As veteran’s mental status declined, veteran no longer demonstrated the capacity to understand the safety risks of driving or living at home. His sister served as his health care agent and was opposed to home discharge due to safety concerns. The interdisciplinary team attempted to focus on respecting veteran’s dignity and autonomy as veteran approached end-oflife. Conflicts arose between the ethical pillars of autonomy, non-maleficence, community safety, and legal risks to institution. Lessons learned included the importance of daily safety huddles, ensuring secure care system functions properly, performing ongoing capacity assessments, and improving pre-admission screening.
Conclusions
Balancing autonomy and patient prefpreferences in VA hospice care demands continuous evaluation and adjustment of care plans. Legal and institutional ethics can be consulted to assist providers in formulating optimal plans and to guide use of ethical pillars within the VA framework.
Successful Targeted Therapy with Alectinib in ALK-Positive Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Background
Pancreatic cancer has one of the highest mortality rates due to its typical late-stage diagnosis and subsequent limited surgical options. However, recent advances in molecular profiling offer hope for targeted therapies. We present a case of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma which progressed despite surgery and chemotherapy yet showed a positive respond to Alectinib.
Case Description
A 79-year-old male with medical history of tobacco use and ulcerative colitis presented to the clinic with 15lb unintentional weight loss over the past few months in 04/2021. Computed tomography (CT) showed dilated common bile duct due to 2.2 x 1.9 x 1.7 cm mass with no metastatic disease. Biopsy was consistent with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and patient completed 6 cycles of dose-reduced neoadjuvant gemcitabine and paclitaxel in late 2021 due to his severe neuropathy and ECOG. Subsequent CT and PET-CT showed stable disease prior to undergoing pylorus-sparing pancreatoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy with portal vein resection in 05/2022 with surgical pathology grading yPT4N2cM0. The follow- up PET scan in 09/2022 revealed new pulmonary and liver metastases, along with increased uptake in the pancreatic region, suggesting recurrent disease. Next generation sequencing (NGS) identified an ELM4-ALK chromosomal rearrangement on the surgical pathology. Given the patient’s cancer progression and concerns about chemotherapy tolerance, Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor more commonly used in lung cancer, was considered as a treatment option. Patient began Alectinib 10/2022 with no significant side effects and PET scan on 03/2023 and 06/2023 showing resolution of his lung nodules and liver lesions. Patient remained on Alectinib until he transitioned to hospice after an ischemic stroke in 03/2024.
Discussion
Pancreatic cancer urgently requires novel therapies as about 25% of patients harbor actionable molecular alterations that have led to the success of targeted therapies. ALK fusion genes are identified in multiple cancers, but the prevalence is only 0.16% in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Alectinib provided an extended progression free survival compared with standard chemotherapy in our patient. ALK inhibitors may demonstrate a remarkable response in metastatic pancreatic cancer even in poor candidates for standard chemotherapy highlighting the emphasis of NGS and targeted therapy options for pancreatic cancer to improve survival.
Lung Cancer Exposome in U.S. Military Veterans: Study of Environment and Epigenetic Factors on Risk and Survival
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Background
The Exposome—the comprehensive accumulation of environmental exposures from birth to death—provides a framework for linking external risk factors to cancer biology. In U.S. veterans, the exposome includes both military-specific exposures (e.g., asbestos, Agent Orange, burn pits) and postservice socioeconomic and environmental factors. These cumulative exposures may drive tumor development and progression via epigenetic mechanisms, though their impact on lung cancer outcomes remain poorly characterized.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of 71 lung cancer subjects (NSCLC and SCLC) from the Jesse Brown VA Medical Center (IRB# 1586320). We assessed the Area Deprivation Index (ADI), Environmental Burden Index (EBI), and occupational exposure in relation to DNA methylation of CDO1, TAC1, SOX17, and HOXA7. Geospatial data were mapped to US census tracts, and standard statistical analysis were conducted.
Results
NSCLC patients exhibited significantly higher methylation levels across all genes. High EBI exposure was associated with lower SOX17 methylation (p = 0.064) and worse overall survival (p = 0.046). In NSCLC patients, occupational exposure predicted a 7.7-fold increased hazard of death (p = 0.027). SOX17 and TAC1 methylation were independently associated with reduced survival (p = 0.037 and 0.0058, respectively). While ADI did not independently predict survival, it correlated with late-stage presentation and reduced HOXA7 methylation.
Conclusions
Exposome factors such as environmental burden and occupational exposure are biologically embedded in lung cancer cell through gene-specific methylation and significantly impact survival. We posit that integrating exposomic and molecular data could enhance lung precision oncology approaches for high-risk veteran populations.
Access to Germline Genetic Testing through Clinical Pathways in Veterans With Prostate Cancer
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
Background
Germline genetic testing (GGT) is essential in prostate cancer care, informing clinical decisions. The Veterans Affairs National Oncology Program (VA NOP) recommends GGT for patients with specific risk factors in non-metastatic prostate cancer and all patients with metastatic disease. Understanding GGT access helps evaluate care quality and guide improvements. Since 2021, VA NOP has implemented pathway health factor (HF) templates to standardize cancer care documentation, including GGT status, enabling data extraction from the Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) rather than requiring manual review of clinical notes. This work aims to evaluate Veterans’ access to GGT in prostate cancer care by leveraging pathway HF templates, and to assess the feasibility of using structured electronic health record (EHR) data to monitor adherence to GGT recommendations.
Methods
Process delivery diagrams (PDDs) were used to map data flow from prostate cancer clinical pathways to the VA CDW. We identified and categorized HFs related to prostate cancer GGT through the computerized patient record system (CPRS). Descriptive statistics were used to summarize access, ordering, and consent rates.
Results
We identified 5,744 Veterans with at least one prostate cancer GGT-relevant HF entered between 02/01/2021 and 12/31/2024. Of these, 5,125 (89.2%) had access to GGT, with 4,569 (89.2%) consenting to or having GGT ordered, while 556 (10.8%) declined testing. Among the 619 (10.8%) Veterans without GGT access, providers reported plans to discuss GGT in the future for 528 (85.3%) patients, while 91 (14.7%) were off pathway.
Conclusions
NOP-developed HF templates enabled extraction of GGT information from structured EHR data, eliminating manual extraction from clinical notes. We observed high GGT utilization among Veterans with pathway-entered HFs. However, low overall HF utilization may introduce selection bias. Future work includes developing a Natural Language Processing pipeline using large language models to automatically extract GGT information from clinical notes, with HF data serving as ground truth.
VA Ann Arbor Immunotherapy Stewardship Program
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
Purpose
To compare vial utilization and spending between fixed and weight-based dosing of pembrolizumab in Veterans. Promote and assess pembrolizumab extended interval dosing.
Background
FDA approved pembrolizumab label change from weight-based to fixed dosing without evidence of fixed-dosing’s superiority. Retrospective studies demonstrate equivalent outcomes for 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks (Q3W), 200 mg Q3W, 4 mg/kg every 6 weeks (Q6W), and 400 mg Q6W.
Methods
In July 2024 VAAAHS (VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System) initiated an immunotherapy stewardship quality improvement program to deprescribe unnecessary pembrolizumab units and promote extended-interval dosing. Specific interventions included order template modification and targeted outreach to key stakeholders.
Data Analysis
All pembrolizumab doses administered at VAAAHS between July 1, 2024 (launch) and March 31, 2025 (data cutoff) were extracted from EHR. Drug utilization, spending, and healthcare contact hours averted were compared to a fixed-dosing counterfactual.
Results
Sixty-three Veterans received 286 total pembrolizumab doses, of which 107 (37.4%) were Q6W and 179 (62.6%) were Q3W. In total, 741 vials were utilized, against expectation of 786 (5.7% reduction), reflecting approximately $182,000 in savings (annualized, $243,000) and 86.5% of the theoretical maximum savings were captured. Q6W’s share of all doses rose from 27.3% in July 2024 to 53.8% in March 2025. Amongst monotherapy, Q6W’s share rose from 60.0% in July 2024 to 86.7% in March 2025. Q6W adoption saved 381 Veteran-healthcare contact hours, not including travel time.
Conclusions
Stewardship efforts reduced unnecessary pembrolizumab utilization and spending while saving Veterans and VAAAHS providers’ time. Continued provider reinforcement, preparation for Oracle/ Cerner implementation, VISN expansion, refinement of pembrolizumab dose-banding, and development of dose bands for other immunotherapies are underway.
Significance
National implementation would improve Veteran convenience and quality of life, enable reductions in drug and resource costs, and enhance clinic throughput.
From Screening to Support: Enhancing Cancer Care Through eScreener Technology
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Background
Addressing cancer-related distress is a critical component of comprehensive oncology care. In alignment with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, which advocate for routine distress screening as a standard of care, our institution aimed to enhance a previously underutilized paper-based screening process by implementing a more efficient and accessible solution.
Objective
To improve screening rates and streamline the identification of psychosocial needs of Veterans who have cancer.
Population
This initiative was conducted in an outpatient Hematology/Oncology clinic at a Midwest Federal Healthcare Center.
Methods
The Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) quality improvement model was used to guide the implementation of the electronic screener. The eScreener was integrated into routine clinical workflow and staff received training to facilitate implementation. Veterans self-identified their needs through the screener, which included a range of practical, family/social, physical, religious or emotional concerns. Clinical staff then review the responses, assessed the identified needs, and entered appropriate referrals into the electronic health record. A dedicated certified nursing assistant (CNA) was incorporated into the workflow to support implementation efforts. As part of their role, the CNA was tasked with ensuring that all Veterans completed the distress screener either electronically or on paper during their visit
Results
Between January 2025 and March 2025, a total of 180 distress screens were completed using the newly implement method. During the same period in the previous year, only 60 screens were completed, representing a 200% increase. The new process enabled timely referrals based on identified needs, resulting in 39 referrals to physicians, 32 to psychologists, 10 to social work, 7 to dieticians, 6 to nurses, and 1 to pastoral care. These outcomes reflect a significant improvement in both accessibility and patient engagement.
Conclusions
The implementation of an electronic cancer distress screener, along with a dedicated staff member resulted in a substantial increase in screening completion rates and multidisciplinary referrals. These preliminary finds suggest that digital tools can significantly enhance psychosocial assessment, improve coordination, and support the delivery of timely, patient-centered oncology care.
Case Presentation: First Ever VA "Bloodless" Autologous Stem Cell Transplant Was a Success
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
Background
Autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) is an important part of the treatment paradigm for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and remains the standard of care for newly diagnosed patients. Blood product transfusion support in the form of platelets and packed red blood cells (pRBCs) is part of the standard of practice as supportive measures during the severely pancytopenic period. Some MM patients, such as those of Jehovah’s Witness (JW) faith, may have religious beliefs or preferences that preclude acceptance of such blood products. Some transplant centers have developed protocols to allow safe “bloodless” ASCT that allows these patients to receive this important treatment while adhering to their beliefs or preferences.
Case Presentation
A 61-year-old veteran of JW faith with newly diagnosed IgG Kappa Multiple Myeloma was referred to the Tennessee Valley Healthcare System (TVHS) Stem Cell Transplant program for consideration of “bloodless” ASCT. With the assistance and expertise of the academic affiliate, Vanderbilt University Medical Center’s established bloodless ASCT protocol, this same protocol was established at TVHS to optimize the patient’s care pretransplant (use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, intravenous iron, B12 supplementation) as well as post-transplant (use of antifibrinolytics, close inpatient monitoring). Both Ethics and Legal consultation was obtained, and guidance was provided to create a life sustaining treatment (LST) note in the veteran’s electronic health record that captured the veteran’s blood product preference. Once all protocols and guidance were in place, the TVHS SCT/CT program proceeded to treat the veteran with a myeloablative melphalan ASCT. The patient tolerated the procedure exceptionally well with minimal complications. He achieved full engraftment on day +14 after ASCT as expected and was discharged from the inpatient setting. He was monitored in the outpatient setting until day +30 without further complications.
Conclusions
The TVHS SCT/CT performed the first ever bloodless autologous stem cell transplant within the VA. This pioneering effort to establish such protocols to provide care to all veterans whatever their personal or religious preferences is a testament to commitment of VA to provide care for all veterans and the willingness to innovate to do so.
ACES Act to Study Cancer in Aviators Is Now Law
A bipartisan bill establishing research directives aimed at revealing cancer risks among military aviators and aircrews recently became law.
Spearheaded by Sen. Mark Kelly (D-AZ) and Sen. Tom Cotton (R-AR), as well as Rep. August Pfluger (R-TX-11) and Rep. Jimmy Panetta (D-CA-19), all of whom are veterans, the Aviator Cancer Examination Study (ACES) Act was signed into law on August 14. The ACES Act will address cancer rates among Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps aircrew members by directing the Secretary of the US Department of Veterans Affairs to study cancer incidence and mortality rates among these populations.
Military aviators and aircrews face a 15% to 24% higher rate of cancer compared with the general US population, including a 75% higher rate of melanoma, 31% higher rate of thyroid cancer, 20% higher rate of prostate cancer, and 11% higher rate of female breast cancer, with potential links to non-Hodgkin lymphoma and testicular cancer. These individuals are also diagnosed earlier in life, at the median age of 55 years compared with 67 years. However, further investigation is still needed to understand why.
“By better understanding the correlation between aviator service and cancer, we can better assist our military and provide more adequate care for our veterans,” Kelly said.
Some reasons for the higher rates of cancer in aviators seem clear, such as the association between dioxin exposure and cancer. In a study of cancer incidence and mortality in Air Force veterans of the Vietnam War, incidence of melanoma and prostate cancer was increased among White veterans who sprayed herbicides during Operation Ranch Hand. The risk of cancer at any site, prostate cancer, and melanoma was increased in the highest dioxin exposure category among veterans who spent ≤ 2 years in Southeast Asia.
However, some links between these veterans and increased cancer rates are less clear. In a review of 28 studies (including 18 studies in military settings), slight evidence was found for associations between jet fuel exposure and various outcomes including cancer. Cosmic ionizing radiation (CIR) exposure is another possible cause. Several epidemiological studies have documented elevated incidence and mortality for several cancers in flight crews, but a link between them and CIR exposure has not been established.
Certain occupations have been associated with increased risk of testicular germ cell tumors, including aircraft maintenance, military pilots, fighter pilots, and aircrews. Those associations led to hypotheses that job-related chemical exposures (eg, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, solvents, paints, hydrocarbons in degreasing/lubricating agents, lubricating oils) may increase risk. A study of young active-duty Air Force servicemen found that pilots and men with aircraft maintenance jobs had elevated tenosynovial giant cell tumor risk, but indicates that further research is needed to “elucidate specific occupational exposures underlying these associations.”
“As a former Navy pilot, there are certain risks that we know and accept come with our service, but we know far less about the health risks that are affecting many aviators and aircrews years later,” Kelly said in a statement. “Veteran aviators and aircrews deserve answers about the correlation between their job and cancer risks so we can reduce those risks for future pilots. Getting this across the finish line has been a bipartisan effort from the start, and I’m proud to see this bill become law so we can deliver real answers and accountability for those who served.”
“The ACES Act is now the law of the land,” Cotton added. “We owe it to past, present, and future aviators in the armed forces to study the prevalence of cancer among this group of veterans.”
The ACES Act complements Kelly’s bipartisan Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act, which requires Veterans Health Administration facilities to share cancer data with state cancer registries, thereby guaranteeing their inclusion in the national registries. Key provisions of the Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act were included in the first government funding package of fiscal year 2024.
A bipartisan bill establishing research directives aimed at revealing cancer risks among military aviators and aircrews recently became law.
Spearheaded by Sen. Mark Kelly (D-AZ) and Sen. Tom Cotton (R-AR), as well as Rep. August Pfluger (R-TX-11) and Rep. Jimmy Panetta (D-CA-19), all of whom are veterans, the Aviator Cancer Examination Study (ACES) Act was signed into law on August 14. The ACES Act will address cancer rates among Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps aircrew members by directing the Secretary of the US Department of Veterans Affairs to study cancer incidence and mortality rates among these populations.
Military aviators and aircrews face a 15% to 24% higher rate of cancer compared with the general US population, including a 75% higher rate of melanoma, 31% higher rate of thyroid cancer, 20% higher rate of prostate cancer, and 11% higher rate of female breast cancer, with potential links to non-Hodgkin lymphoma and testicular cancer. These individuals are also diagnosed earlier in life, at the median age of 55 years compared with 67 years. However, further investigation is still needed to understand why.
“By better understanding the correlation between aviator service and cancer, we can better assist our military and provide more adequate care for our veterans,” Kelly said.
Some reasons for the higher rates of cancer in aviators seem clear, such as the association between dioxin exposure and cancer. In a study of cancer incidence and mortality in Air Force veterans of the Vietnam War, incidence of melanoma and prostate cancer was increased among White veterans who sprayed herbicides during Operation Ranch Hand. The risk of cancer at any site, prostate cancer, and melanoma was increased in the highest dioxin exposure category among veterans who spent ≤ 2 years in Southeast Asia.
However, some links between these veterans and increased cancer rates are less clear. In a review of 28 studies (including 18 studies in military settings), slight evidence was found for associations between jet fuel exposure and various outcomes including cancer. Cosmic ionizing radiation (CIR) exposure is another possible cause. Several epidemiological studies have documented elevated incidence and mortality for several cancers in flight crews, but a link between them and CIR exposure has not been established.
Certain occupations have been associated with increased risk of testicular germ cell tumors, including aircraft maintenance, military pilots, fighter pilots, and aircrews. Those associations led to hypotheses that job-related chemical exposures (eg, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, solvents, paints, hydrocarbons in degreasing/lubricating agents, lubricating oils) may increase risk. A study of young active-duty Air Force servicemen found that pilots and men with aircraft maintenance jobs had elevated tenosynovial giant cell tumor risk, but indicates that further research is needed to “elucidate specific occupational exposures underlying these associations.”
“As a former Navy pilot, there are certain risks that we know and accept come with our service, but we know far less about the health risks that are affecting many aviators and aircrews years later,” Kelly said in a statement. “Veteran aviators and aircrews deserve answers about the correlation between their job and cancer risks so we can reduce those risks for future pilots. Getting this across the finish line has been a bipartisan effort from the start, and I’m proud to see this bill become law so we can deliver real answers and accountability for those who served.”
“The ACES Act is now the law of the land,” Cotton added. “We owe it to past, present, and future aviators in the armed forces to study the prevalence of cancer among this group of veterans.”
The ACES Act complements Kelly’s bipartisan Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act, which requires Veterans Health Administration facilities to share cancer data with state cancer registries, thereby guaranteeing their inclusion in the national registries. Key provisions of the Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act were included in the first government funding package of fiscal year 2024.
A bipartisan bill establishing research directives aimed at revealing cancer risks among military aviators and aircrews recently became law.
Spearheaded by Sen. Mark Kelly (D-AZ) and Sen. Tom Cotton (R-AR), as well as Rep. August Pfluger (R-TX-11) and Rep. Jimmy Panetta (D-CA-19), all of whom are veterans, the Aviator Cancer Examination Study (ACES) Act was signed into law on August 14. The ACES Act will address cancer rates among Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps aircrew members by directing the Secretary of the US Department of Veterans Affairs to study cancer incidence and mortality rates among these populations.
Military aviators and aircrews face a 15% to 24% higher rate of cancer compared with the general US population, including a 75% higher rate of melanoma, 31% higher rate of thyroid cancer, 20% higher rate of prostate cancer, and 11% higher rate of female breast cancer, with potential links to non-Hodgkin lymphoma and testicular cancer. These individuals are also diagnosed earlier in life, at the median age of 55 years compared with 67 years. However, further investigation is still needed to understand why.
“By better understanding the correlation between aviator service and cancer, we can better assist our military and provide more adequate care for our veterans,” Kelly said.
Some reasons for the higher rates of cancer in aviators seem clear, such as the association between dioxin exposure and cancer. In a study of cancer incidence and mortality in Air Force veterans of the Vietnam War, incidence of melanoma and prostate cancer was increased among White veterans who sprayed herbicides during Operation Ranch Hand. The risk of cancer at any site, prostate cancer, and melanoma was increased in the highest dioxin exposure category among veterans who spent ≤ 2 years in Southeast Asia.
However, some links between these veterans and increased cancer rates are less clear. In a review of 28 studies (including 18 studies in military settings), slight evidence was found for associations between jet fuel exposure and various outcomes including cancer. Cosmic ionizing radiation (CIR) exposure is another possible cause. Several epidemiological studies have documented elevated incidence and mortality for several cancers in flight crews, but a link between them and CIR exposure has not been established.
Certain occupations have been associated with increased risk of testicular germ cell tumors, including aircraft maintenance, military pilots, fighter pilots, and aircrews. Those associations led to hypotheses that job-related chemical exposures (eg, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, solvents, paints, hydrocarbons in degreasing/lubricating agents, lubricating oils) may increase risk. A study of young active-duty Air Force servicemen found that pilots and men with aircraft maintenance jobs had elevated tenosynovial giant cell tumor risk, but indicates that further research is needed to “elucidate specific occupational exposures underlying these associations.”
“As a former Navy pilot, there are certain risks that we know and accept come with our service, but we know far less about the health risks that are affecting many aviators and aircrews years later,” Kelly said in a statement. “Veteran aviators and aircrews deserve answers about the correlation between their job and cancer risks so we can reduce those risks for future pilots. Getting this across the finish line has been a bipartisan effort from the start, and I’m proud to see this bill become law so we can deliver real answers and accountability for those who served.”
“The ACES Act is now the law of the land,” Cotton added. “We owe it to past, present, and future aviators in the armed forces to study the prevalence of cancer among this group of veterans.”
The ACES Act complements Kelly’s bipartisan Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act, which requires Veterans Health Administration facilities to share cancer data with state cancer registries, thereby guaranteeing their inclusion in the national registries. Key provisions of the Counting Veterans’ Cancer Act were included in the first government funding package of fiscal year 2024.
Agent Orange Exposure and Genetic Factors Independently Raise Risk for Multiple Lymphoma Types
TOPLINE: A large-scale case-control study using the Million Veteran Program (MVP) found The study found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange (AO) exposure for several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
METHODOLOGY:
A case-control study included 255,155 US veterans enrolled in the MVP with available genotype, Agent Orange exposure information, and lymphoid malignant neoplasm diagnosis from January 1, 1965, through June T1, 2024.
Analysis focused on non-Hispanic White veterans (median age 67 years; 92.5% male) due to ancestry distribution requirements for genome-wide association studies data availability.
Researchers excluded 628 samples across all lymphoid malignant neoplasm groups and 61,343 control samples due to unavailability of AO exposure information.
Investigators analyzed risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, and multiple myeloma as primary outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
Agent Orange exposure was associated with increased risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (odds ratio [OR], 1.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.40-1.84), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03-1.53), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.39-2.11), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.35-1.86).
Polygenic risk scores showed significant associations with all subtypes: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (OR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.70-1.93), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.02-1.21), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.21-1.47), marginal zone lymphoma (OR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.04-1.32), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.31-1.52).
No significant polygenic risk score and AO exposure interactions were observed in the development of any lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
The researchers found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange exposure on several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
IN PRACTICE:
"Our study addressed the public health concerns surrounding AO exposure and lymphoid malignant neoplasms, finding that both AO exposure and polygenic risk are independently associated with disease, suggesting potentially distinct and additive pathways that merit further investigation,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Xueyi Teng, PhD, Department of Biological Chemistry, School of Medicine, University of California in Irvine, and Helen Ma, MD, Tibor Rubin Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Long Beach. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, while this represents the largest study of Agent Orange exposure and genetic risk in lymphoid malignant neoplasm development, the power to find interaction associations in specific subtypes might be limited. Self-reported AO exposure may have introduced survival bias, especially in aggressive subtypes, as patients with aggressive tumors might have died before joining the MVP. Additionally, approximately half of the patients were diagnosed with lymphoid malignant neoplasm before self-reporting AO exposure in the survey, potentially introducing recall bias.
DISCLOSURES: Xueyi Teng, PhD, reported receiving grants from the George E. Hewitt Foundation for Medical Research Postdoc Fellowship during the conduct of the study. The research was supported by grant MVPOOO and Veterans Affairs Career Development Award 1IK2CX002437-O1A1. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: A large-scale case-control study using the Million Veteran Program (MVP) found The study found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange (AO) exposure for several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
METHODOLOGY:
A case-control study included 255,155 US veterans enrolled in the MVP with available genotype, Agent Orange exposure information, and lymphoid malignant neoplasm diagnosis from January 1, 1965, through June T1, 2024.
Analysis focused on non-Hispanic White veterans (median age 67 years; 92.5% male) due to ancestry distribution requirements for genome-wide association studies data availability.
Researchers excluded 628 samples across all lymphoid malignant neoplasm groups and 61,343 control samples due to unavailability of AO exposure information.
Investigators analyzed risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, and multiple myeloma as primary outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
Agent Orange exposure was associated with increased risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (odds ratio [OR], 1.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.40-1.84), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03-1.53), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.39-2.11), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.35-1.86).
Polygenic risk scores showed significant associations with all subtypes: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (OR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.70-1.93), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.02-1.21), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.21-1.47), marginal zone lymphoma (OR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.04-1.32), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.31-1.52).
No significant polygenic risk score and AO exposure interactions were observed in the development of any lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
The researchers found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange exposure on several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
IN PRACTICE:
"Our study addressed the public health concerns surrounding AO exposure and lymphoid malignant neoplasms, finding that both AO exposure and polygenic risk are independently associated with disease, suggesting potentially distinct and additive pathways that merit further investigation,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Xueyi Teng, PhD, Department of Biological Chemistry, School of Medicine, University of California in Irvine, and Helen Ma, MD, Tibor Rubin Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Long Beach. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, while this represents the largest study of Agent Orange exposure and genetic risk in lymphoid malignant neoplasm development, the power to find interaction associations in specific subtypes might be limited. Self-reported AO exposure may have introduced survival bias, especially in aggressive subtypes, as patients with aggressive tumors might have died before joining the MVP. Additionally, approximately half of the patients were diagnosed with lymphoid malignant neoplasm before self-reporting AO exposure in the survey, potentially introducing recall bias.
DISCLOSURES: Xueyi Teng, PhD, reported receiving grants from the George E. Hewitt Foundation for Medical Research Postdoc Fellowship during the conduct of the study. The research was supported by grant MVPOOO and Veterans Affairs Career Development Award 1IK2CX002437-O1A1. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: A large-scale case-control study using the Million Veteran Program (MVP) found The study found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange (AO) exposure for several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
METHODOLOGY:
A case-control study included 255,155 US veterans enrolled in the MVP with available genotype, Agent Orange exposure information, and lymphoid malignant neoplasm diagnosis from January 1, 1965, through June T1, 2024.
Analysis focused on non-Hispanic White veterans (median age 67 years; 92.5% male) due to ancestry distribution requirements for genome-wide association studies data availability.
Researchers excluded 628 samples across all lymphoid malignant neoplasm groups and 61,343 control samples due to unavailability of AO exposure information.
Investigators analyzed risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, and multiple myeloma as primary outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
Agent Orange exposure was associated with increased risk for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (odds ratio [OR], 1.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.40-1.84), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.03-1.53), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.39-2.11), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.35-1.86).
Polygenic risk scores showed significant associations with all subtypes: chronic lymphocytic leukemia (OR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.70-1.93), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.02-1.21), follicular lymphoma (OR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.21-1.47), marginal zone lymphoma (OR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.04-1.32), and multiple myeloma (OR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.31-1.52).
No significant polygenic risk score and AO exposure interactions were observed in the development of any lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
The researchers found independent associations of both genetic predisposition and Agent Orange exposure on several lymphoid malignant neoplasm subtypes.
IN PRACTICE:
"Our study addressed the public health concerns surrounding AO exposure and lymphoid malignant neoplasms, finding that both AO exposure and polygenic risk are independently associated with disease, suggesting potentially distinct and additive pathways that merit further investigation,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE: The study was led by Xueyi Teng, PhD, Department of Biological Chemistry, School of Medicine, University of California in Irvine, and Helen Ma, MD, Tibor Rubin Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Long Beach. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS: According to the authors, while this represents the largest study of Agent Orange exposure and genetic risk in lymphoid malignant neoplasm development, the power to find interaction associations in specific subtypes might be limited. Self-reported AO exposure may have introduced survival bias, especially in aggressive subtypes, as patients with aggressive tumors might have died before joining the MVP. Additionally, approximately half of the patients were diagnosed with lymphoid malignant neoplasm before self-reporting AO exposure in the survey, potentially introducing recall bias.
DISCLOSURES: Xueyi Teng, PhD, reported receiving grants from the George E. Hewitt Foundation for Medical Research Postdoc Fellowship during the conduct of the study. The research was supported by grant MVPOOO and Veterans Affairs Career Development Award 1IK2CX002437-O1A1. No other disclosures were reported.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
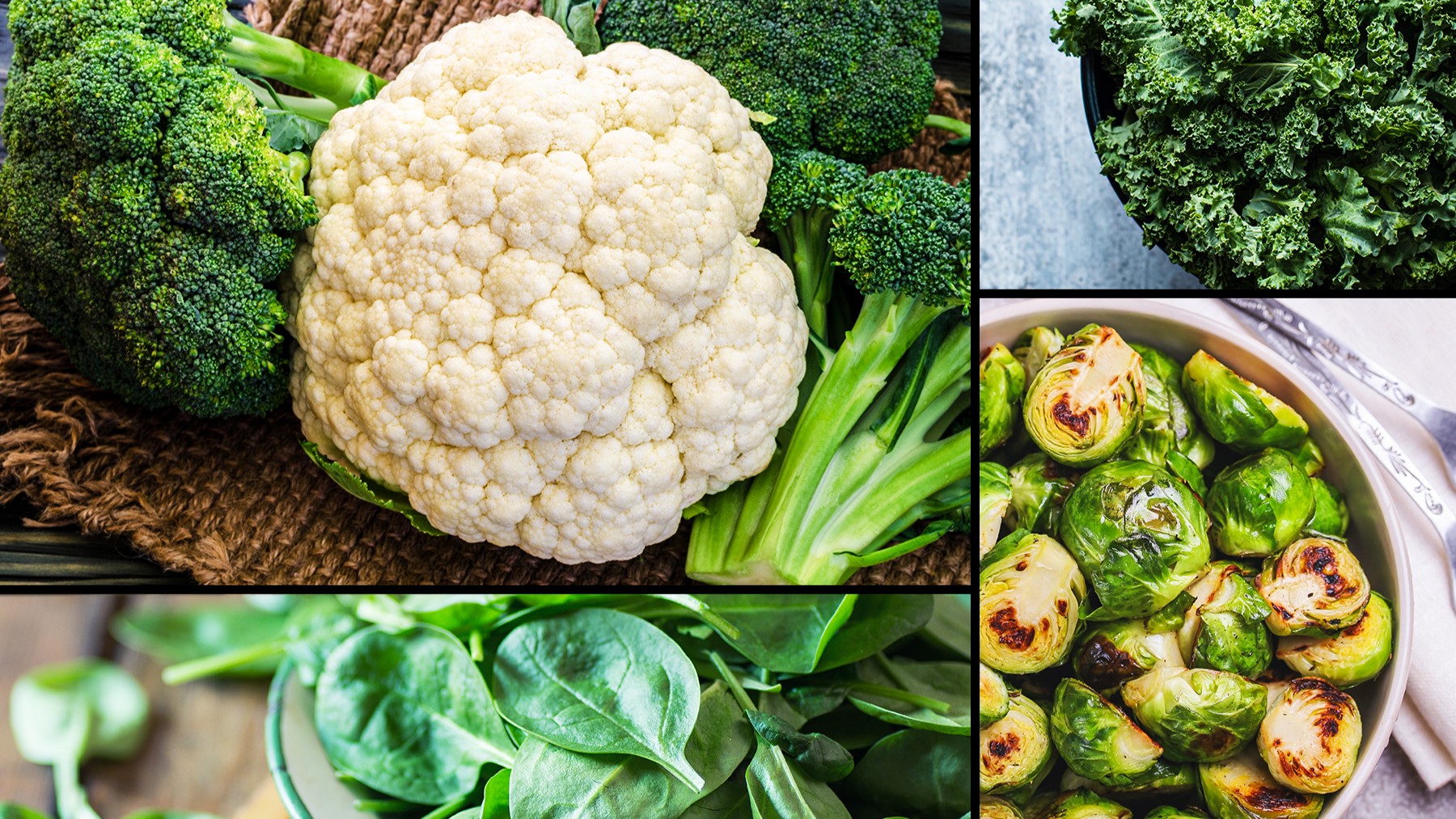
Eating More Cruciferous Vegetables May Cut Colon Cancer Risk
TOPLINE:
A higher consumption of cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower was associated with a notably reduced risk for colon cancer (CC), with an optimal intake of 40-60 g/d providing a risk reduction of 20% to 26%.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous meta-analyses have studied the association between the intake of cruciferous vegetables and the risk for CC; however, the quantitative dose-response relationship remained uncharacterized, limiting insights for dietary guidance.
- Researchers performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 studies (seven cohort and 10 case-control studies) to analyze the dose-response association between the consumption of cruciferous vegetables and CC risk.
- Studies were included if they enrolled adults without CC at baseline (cohort studies) or adults with diagnosed cases who were matched with control individuals (case-control studies), quantified the dietary intake of cruciferous vegetables through standardized questionnaires, and included comparator groups with lower or no intake of such vegetables.
- The studies included 639,539 participants, of whom 97,595 had CC. Incident cases of CC were confirmed via medical records, pathology, registries, or validated self-report.
TAKEAWAY:
- A pooled analysis revealed that people who consumed the largest amounts of cruciferous vegetables had a 20% lower risk for CC than those who consumed the lowest amounts.
- A dose-response analysis showed that risk reduction was near maximal at an intake of 40-60 g/d (odds ratio, 0.74-0.8), with benefits plateauing beyond this range.
- The peak protective effect per gram occurred at an intake of 20-40 g/d of cruciferous vegetables and fell after 60 g/d.
IN PRACTICE:
“The pathophysiology of CC has been linked to dietary factors, specifically inadequate intake of vegetables and dietary fiber, as well as excessive alcohol and caffeine use. These empirical findings lend credence to our results, suggesting a potential chemopreventive role of CV [cruciferous vegetables] against CC development,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Bo Lai, Department of Interventional Radiology, The Second Clinical Medical School of Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, Yakeshi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The inclusion of both case-control and cohort studies and variations in the assessment of cruciferous vegetable intake across studies may have introduced methodological heterogeneity and measurement error, respectively. This study did not measure factors such as pesticide exposure and genetic susceptibility. The predominance of studies from North America and Asia — regions with an elevated incidence of CC — may have limited generalizability to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received no financial support. The authors declared having no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher consumption of cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower was associated with a notably reduced risk for colon cancer (CC), with an optimal intake of 40-60 g/d providing a risk reduction of 20% to 26%.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous meta-analyses have studied the association between the intake of cruciferous vegetables and the risk for CC; however, the quantitative dose-response relationship remained uncharacterized, limiting insights for dietary guidance.
- Researchers performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 studies (seven cohort and 10 case-control studies) to analyze the dose-response association between the consumption of cruciferous vegetables and CC risk.
- Studies were included if they enrolled adults without CC at baseline (cohort studies) or adults with diagnosed cases who were matched with control individuals (case-control studies), quantified the dietary intake of cruciferous vegetables through standardized questionnaires, and included comparator groups with lower or no intake of such vegetables.
- The studies included 639,539 participants, of whom 97,595 had CC. Incident cases of CC were confirmed via medical records, pathology, registries, or validated self-report.
TAKEAWAY:
- A pooled analysis revealed that people who consumed the largest amounts of cruciferous vegetables had a 20% lower risk for CC than those who consumed the lowest amounts.
- A dose-response analysis showed that risk reduction was near maximal at an intake of 40-60 g/d (odds ratio, 0.74-0.8), with benefits plateauing beyond this range.
- The peak protective effect per gram occurred at an intake of 20-40 g/d of cruciferous vegetables and fell after 60 g/d.
IN PRACTICE:
“The pathophysiology of CC has been linked to dietary factors, specifically inadequate intake of vegetables and dietary fiber, as well as excessive alcohol and caffeine use. These empirical findings lend credence to our results, suggesting a potential chemopreventive role of CV [cruciferous vegetables] against CC development,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Bo Lai, Department of Interventional Radiology, The Second Clinical Medical School of Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, Yakeshi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The inclusion of both case-control and cohort studies and variations in the assessment of cruciferous vegetable intake across studies may have introduced methodological heterogeneity and measurement error, respectively. This study did not measure factors such as pesticide exposure and genetic susceptibility. The predominance of studies from North America and Asia — regions with an elevated incidence of CC — may have limited generalizability to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received no financial support. The authors declared having no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A higher consumption of cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower was associated with a notably reduced risk for colon cancer (CC), with an optimal intake of 40-60 g/d providing a risk reduction of 20% to 26%.
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous meta-analyses have studied the association between the intake of cruciferous vegetables and the risk for CC; however, the quantitative dose-response relationship remained uncharacterized, limiting insights for dietary guidance.
- Researchers performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of 17 studies (seven cohort and 10 case-control studies) to analyze the dose-response association between the consumption of cruciferous vegetables and CC risk.
- Studies were included if they enrolled adults without CC at baseline (cohort studies) or adults with diagnosed cases who were matched with control individuals (case-control studies), quantified the dietary intake of cruciferous vegetables through standardized questionnaires, and included comparator groups with lower or no intake of such vegetables.
- The studies included 639,539 participants, of whom 97,595 had CC. Incident cases of CC were confirmed via medical records, pathology, registries, or validated self-report.
TAKEAWAY:
- A pooled analysis revealed that people who consumed the largest amounts of cruciferous vegetables had a 20% lower risk for CC than those who consumed the lowest amounts.
- A dose-response analysis showed that risk reduction was near maximal at an intake of 40-60 g/d (odds ratio, 0.74-0.8), with benefits plateauing beyond this range.
- The peak protective effect per gram occurred at an intake of 20-40 g/d of cruciferous vegetables and fell after 60 g/d.
IN PRACTICE:
“The pathophysiology of CC has been linked to dietary factors, specifically inadequate intake of vegetables and dietary fiber, as well as excessive alcohol and caffeine use. These empirical findings lend credence to our results, suggesting a potential chemopreventive role of CV [cruciferous vegetables] against CC development,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Bo Lai, Department of Interventional Radiology, The Second Clinical Medical School of Inner Mongolia University for the Nationalities, Yakeshi, China, was published online in BMC Gastroenterology.
LIMITATIONS:
The inclusion of both case-control and cohort studies and variations in the assessment of cruciferous vegetable intake across studies may have introduced methodological heterogeneity and measurement error, respectively. This study did not measure factors such as pesticide exposure and genetic susceptibility. The predominance of studies from North America and Asia — regions with an elevated incidence of CC — may have limited generalizability to other populations.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received no financial support. The authors declared having no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.