User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Empagliflozin cut PA pressures in heart failure patients
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
Elevated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure is “perhaps the best predictor of bad outcomes in patients with heart failure, including hospitalization and death,” and new evidence clearly showed that the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin cuts this metric in patients by a clinically significant amount, Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, said at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The evidence he collected from a total of 65 heart failure patients with either reduced or preserved ejection fraction is the first documentation from a randomized, controlled study to show a direct effect by a SGLT2 inhibitor on pulmonary artery (PA) pressures.
Other key findings were that the drop in PA diastolic pressure with empagliflozin treatment compared with placebo became discernible early (within the first 4 weeks on treatment), that the pressure-lowering effect steadily grew over time, and that it showed no link to the intensity of loop diuretic treatment, which held steady during 12 weeks on treatment and 13 weeks of overall monitoring.
The study’s primary endpoint was the change from baseline in PA diastolic pressure after 12 weeks on treatment. The 31 patients who completed the full 12-week course had an average drop in their PA diastolic pressure of about 1.5 mm Hg, compared with 28 patients who completed 12 weeks on placebo. Average PA diastolic pressure at baseline was about 21 mm Hg in both treatment arms, and on treatment this fell by more than 0.5 mm Hg among those who received empagliflozin and rose by close to 1 mm Hg among control patients.
“There appears to be a direct effect of empagliflozin on pulmonary artery pressure that’s not been previously demonstrated” by an SGLT2 inhibitor, Dr. Kosiborod said. “I think this is one mechanism of action” for this drug class. “If you control pulmonary artery filling pressures you can prevent hospitalizations and deaths.”
Small reductions matter
“Small pressure differences are particularly important for pulmonary hypertension,” commented Lynne W. Stevenson, MD, professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tenn., and the report’s designated discussant.
“In the Vanderbilt heart failure database, patients with a pulmonary artery mean pressure of 20-24 mm Hg had 30% higher mortality than patients with lower pressures,” Dr. Stevenson noted. “This has led to a new definition of pulmonary hypertension, a mean pulmonary artery pressure above at or above 20 mm Hg.”
In Dr. Kosiborod’s study, patients began with an average PA mean pressure of about 30 mm Hg, and empagliflozin treatment led to a reduction in this metric with about the same magnitude as its effect on PA diastolic pressure. Empagliflozin also produced a similar reduction in average PA systolic pressure.
A study built on ambulatory PA monitoring
The results “also provide more proof for the concept of ambulatory hemodynamic monitoring” in patients with heart failure to monitor their status, she added. The study enrolled only patients who had already received a CardioMEMS implant as part of their routine care. This device allows for frequent, noninvasive monitoring of PA pressures. Researchers collected PA pressure data from patients twice daily for the entire 13-week study.
The EMBRACE HF (Empagliflozin Impact on Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure) study enrolled patients with established heart failure, a CardioMEMS implant, and New York Heart Association class II-IV symptoms at any of eight U.S. centers. Patients averaged about 65 years old, and slightly more than half had class III disease, which denotes marked limitation of physical activity.
Despite the brief treatment period, patients who received empagliflozin showed other evidence of benefit including a trend toward improved quality of life scores, reduced levels of two different forms of brain natriuretic peptide, and significant weight loss, compared with controls, that averaged 2.4 kg.
The mechanism by which empagliflozin and other drugs in its class might lower PA filling pressures is unclear, but Dr. Kosiborod stressed that the consistent level of loop diuretic use during the study seems to rule out a diuretic effect from the SGLT2 inhibitor as having a role. A pulmonary vasculature effect is “much more likely,” perhaps mediated through modified endothelial function and vasodilation, he suggested.
EMBRACE HF was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that markets empagliflozin (Jardiance) along with Eli Lilly. Dr. Kosiborod has received research support and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, and he has received honoraria from several other companies. Dr. Stevenson had no disclosures.
FROM HFSA 2020
Remdesivir effective, well-tolerated in final trial report
Drug beats placebo across multiple endpoints in COVID-19 patients
In May 2020, remdesivir received Food and Drug Administration approval for emergency treatment of severe COVID-19 on the basis of a preliminary report on this trial. In August 2020, the FDA expanded the indication to include all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients with suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 infection irrespective of severity.
“Our findings were consistent with the findings of the preliminary report: a 10-day course of remdesivir was superior to placebo in the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” reported a team of investigators led by John H. Beigel, MD, of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The drug’s broadened indication was not based on the ACTT-1 trial, according to Dr. Beigel. “Other data have demonstrated that remdesivir shortens recovery in patients with lower acuity. In our study, evidence of pneumonia was an enrollment requirement,” he explained in an interview.
In the newly published final ACTT-1 data, the median time to recovery was 10 days for those on active therapy versus 15 days for those randomized to placebo. With a rate ratio of 1.29 (P less than .001), this translated to a recovery that was about one third faster.
In this final report, remdesivir’s significant advantage over placebo regarding the trial’s primary endpoint was reinforced by efficacy on multiple secondary endpoints.
This benefits on multiple secondary endpoints included a 50% greater odds ratio (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.9) of significant clinical improvement by day 15 after adjustment for baseline severity, a shorter initial length of hospital stay (12 vs. 17 days) and fewer days on oxygen supplementation (13 vs. 21 days) for the subgroup of patients on oxygen at enrollment.
Although the numerically lower mortality in the remdesivir arm (6.75 vs. 11.9%) did not reach statistical significance, Dr. Beigel said, “mortality was moving in the same direction as the other key endpoints.”
According to the study investigators, the types of rates of adverse events on remdesivir, which inhibits viral replication, “were generally similar in the remdesivir and placebo groups.”
In ACTT-1, 1,062 patients were randomized to remdesivir (200 mg loading dose followed by 100 mg daily for up to 9 days) or placebo. Patients were enrolled at study sites in North America, Europe, and Asia.
The data of ACTT-1 confirm a benefit from remdesivir in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe disease, but Dr. Beigel said he agrees with the current FDA indication that supports treatment in any hospitalized COVID-19 patient.
“We saw bigger benefits in patients with more severe infections. The benefits are not as large in patients with mild disease, but I think remdesivir should be considered in any hospitalized patient,” Dr. Beigel said.
This point of view is shared.
“I would give this drug to anyone in the hospital infected with COVID-19 assuming there was an ample supply and no need for rationing,” said Donna E. Sweet, MD, professor of internal medicine, University of Kansas, Wichita. She noted that this study has implications for hospital and hospital staff, as well as for patients.
“This type of reduction in recovery time means a reduction in potential exposures to hospital staff, a reduced need for PPE [personal protective equipment], and it will free up beds in the ICU [intensive care unit],” said Dr. Sweet, who also serves as an editorial advisory board member for Internal Medicine News.
An infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota also considers remdesivir to have an important role for conserving resources that deserves emphasis.
The reduction in time to recovery “is of benefit to the health system by maintaining hospital bed capacity,” said David R. Boulware, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
According to his reading of the available data, including those from ACTT-1, the benefit appears to be greatest in those with a moderate degree of illness, which he defined as “sick enough to be hospitalized and require oxygen, yet not severely sick [and] requiring a ventilator or [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].”
This does not preclude a benefit in those with more severe or milder disease, but patients with mild disease “are likely to recover regardless – or despite – whatever therapy they receive,” he said.
Dr. Beigel, the principal investigator of this trial, reports no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Beigel JH et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.
Drug beats placebo across multiple endpoints in COVID-19 patients
Drug beats placebo across multiple endpoints in COVID-19 patients
In May 2020, remdesivir received Food and Drug Administration approval for emergency treatment of severe COVID-19 on the basis of a preliminary report on this trial. In August 2020, the FDA expanded the indication to include all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients with suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 infection irrespective of severity.
“Our findings were consistent with the findings of the preliminary report: a 10-day course of remdesivir was superior to placebo in the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” reported a team of investigators led by John H. Beigel, MD, of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The drug’s broadened indication was not based on the ACTT-1 trial, according to Dr. Beigel. “Other data have demonstrated that remdesivir shortens recovery in patients with lower acuity. In our study, evidence of pneumonia was an enrollment requirement,” he explained in an interview.
In the newly published final ACTT-1 data, the median time to recovery was 10 days for those on active therapy versus 15 days for those randomized to placebo. With a rate ratio of 1.29 (P less than .001), this translated to a recovery that was about one third faster.
In this final report, remdesivir’s significant advantage over placebo regarding the trial’s primary endpoint was reinforced by efficacy on multiple secondary endpoints.
This benefits on multiple secondary endpoints included a 50% greater odds ratio (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.9) of significant clinical improvement by day 15 after adjustment for baseline severity, a shorter initial length of hospital stay (12 vs. 17 days) and fewer days on oxygen supplementation (13 vs. 21 days) for the subgroup of patients on oxygen at enrollment.
Although the numerically lower mortality in the remdesivir arm (6.75 vs. 11.9%) did not reach statistical significance, Dr. Beigel said, “mortality was moving in the same direction as the other key endpoints.”
According to the study investigators, the types of rates of adverse events on remdesivir, which inhibits viral replication, “were generally similar in the remdesivir and placebo groups.”
In ACTT-1, 1,062 patients were randomized to remdesivir (200 mg loading dose followed by 100 mg daily for up to 9 days) or placebo. Patients were enrolled at study sites in North America, Europe, and Asia.
The data of ACTT-1 confirm a benefit from remdesivir in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe disease, but Dr. Beigel said he agrees with the current FDA indication that supports treatment in any hospitalized COVID-19 patient.
“We saw bigger benefits in patients with more severe infections. The benefits are not as large in patients with mild disease, but I think remdesivir should be considered in any hospitalized patient,” Dr. Beigel said.
This point of view is shared.
“I would give this drug to anyone in the hospital infected with COVID-19 assuming there was an ample supply and no need for rationing,” said Donna E. Sweet, MD, professor of internal medicine, University of Kansas, Wichita. She noted that this study has implications for hospital and hospital staff, as well as for patients.
“This type of reduction in recovery time means a reduction in potential exposures to hospital staff, a reduced need for PPE [personal protective equipment], and it will free up beds in the ICU [intensive care unit],” said Dr. Sweet, who also serves as an editorial advisory board member for Internal Medicine News.
An infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota also considers remdesivir to have an important role for conserving resources that deserves emphasis.
The reduction in time to recovery “is of benefit to the health system by maintaining hospital bed capacity,” said David R. Boulware, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
According to his reading of the available data, including those from ACTT-1, the benefit appears to be greatest in those with a moderate degree of illness, which he defined as “sick enough to be hospitalized and require oxygen, yet not severely sick [and] requiring a ventilator or [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].”
This does not preclude a benefit in those with more severe or milder disease, but patients with mild disease “are likely to recover regardless – or despite – whatever therapy they receive,” he said.
Dr. Beigel, the principal investigator of this trial, reports no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Beigel JH et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.
In May 2020, remdesivir received Food and Drug Administration approval for emergency treatment of severe COVID-19 on the basis of a preliminary report on this trial. In August 2020, the FDA expanded the indication to include all hospitalized adult and pediatric patients with suspected or laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 infection irrespective of severity.
“Our findings were consistent with the findings of the preliminary report: a 10-day course of remdesivir was superior to placebo in the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19,” reported a team of investigators led by John H. Beigel, MD, of the Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The drug’s broadened indication was not based on the ACTT-1 trial, according to Dr. Beigel. “Other data have demonstrated that remdesivir shortens recovery in patients with lower acuity. In our study, evidence of pneumonia was an enrollment requirement,” he explained in an interview.
In the newly published final ACTT-1 data, the median time to recovery was 10 days for those on active therapy versus 15 days for those randomized to placebo. With a rate ratio of 1.29 (P less than .001), this translated to a recovery that was about one third faster.
In this final report, remdesivir’s significant advantage over placebo regarding the trial’s primary endpoint was reinforced by efficacy on multiple secondary endpoints.
This benefits on multiple secondary endpoints included a 50% greater odds ratio (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.9) of significant clinical improvement by day 15 after adjustment for baseline severity, a shorter initial length of hospital stay (12 vs. 17 days) and fewer days on oxygen supplementation (13 vs. 21 days) for the subgroup of patients on oxygen at enrollment.
Although the numerically lower mortality in the remdesivir arm (6.75 vs. 11.9%) did not reach statistical significance, Dr. Beigel said, “mortality was moving in the same direction as the other key endpoints.”
According to the study investigators, the types of rates of adverse events on remdesivir, which inhibits viral replication, “were generally similar in the remdesivir and placebo groups.”
In ACTT-1, 1,062 patients were randomized to remdesivir (200 mg loading dose followed by 100 mg daily for up to 9 days) or placebo. Patients were enrolled at study sites in North America, Europe, and Asia.
The data of ACTT-1 confirm a benefit from remdesivir in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with severe disease, but Dr. Beigel said he agrees with the current FDA indication that supports treatment in any hospitalized COVID-19 patient.
“We saw bigger benefits in patients with more severe infections. The benefits are not as large in patients with mild disease, but I think remdesivir should be considered in any hospitalized patient,” Dr. Beigel said.
This point of view is shared.
“I would give this drug to anyone in the hospital infected with COVID-19 assuming there was an ample supply and no need for rationing,” said Donna E. Sweet, MD, professor of internal medicine, University of Kansas, Wichita. She noted that this study has implications for hospital and hospital staff, as well as for patients.
“This type of reduction in recovery time means a reduction in potential exposures to hospital staff, a reduced need for PPE [personal protective equipment], and it will free up beds in the ICU [intensive care unit],” said Dr. Sweet, who also serves as an editorial advisory board member for Internal Medicine News.
An infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota also considers remdesivir to have an important role for conserving resources that deserves emphasis.
The reduction in time to recovery “is of benefit to the health system by maintaining hospital bed capacity,” said David R. Boulware, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
According to his reading of the available data, including those from ACTT-1, the benefit appears to be greatest in those with a moderate degree of illness, which he defined as “sick enough to be hospitalized and require oxygen, yet not severely sick [and] requiring a ventilator or [extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].”
This does not preclude a benefit in those with more severe or milder disease, but patients with mild disease “are likely to recover regardless – or despite – whatever therapy they receive,” he said.
Dr. Beigel, the principal investigator of this trial, reports no potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Beigel JH et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Oct 8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.
The socioeconomic revolving door of 30-day heart failure readmissions
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving even top-notch hospital care for heart failure (HF) are, once discharged to home, at higher short-term risk of another HF hospitalization if home is in a socioeconomically deprived neighborhood. That helps explain why Blacks in the United States have a much higher 30-day HF readmission risk than Whites, a disparity that only worsens with the level of neighborhood deprivation, a new analysis suggests.
Some systemic and entrenched socioeconomic inequities that health care providers have little sway over, and which disproportionately affect Black individuals, are independent and robust predictors of worsened HF outcomes, Alanna A. Morris, MD, MSc, Emory University, Atlanta, said during her presentation at the virtual annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
In a retrospective cohort study, Blacks had a 45% higher risk of 30-day readmission than Whites (P < .001) independent of cardiovascular risk factors, clinical history, comorbidities, type and location of hospital, and type of third-party payer coverage. The analysis included more than 30,000 patients with at least one HF hospitalization at centers in a major metropolitan health system.
The racial disparity widened with worsening socioeconomic deprivation of patients’ residential neighborhoods, that is, with rising quartiles of neighborhood scores on the Social Deprivation Index (SDI).
The SDI, based on U.S. census data, incorporates seven socioeconomic criteria, including household income, education level, employment, and prevalence of rented housing and households that are without a car, single parent, or overcrowded.
There was a 4–percentage point gap in adjusted 30-day readmission rate between Blacks and Whites in the lowest quartile that widened to more than 8 points by the third quartile; the disparity in both the second and fourth quartiles was the same, at about 5.5 percentage points.
A remaining question, Dr. Morris said in an interview, is why the outcomes disparity between Blacks and Whites peaks in the third SDI quartile but drops a bit in the fourth quartile representing the most severe neighborhood deprivation.
“Our hypothesis is that when you look at patients who are the poorest, who live in the most deprived neighborhoods, race may be less of a factor,” she said. Socioeconomic deprivation may have similar consequences for everyone “regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or other demographic characteristics if you live in a neighborhood that’s highly deprived.”
Based on the current study, “it does appear that increased heart failure incident rates are related to living in deprived neighborhoods, and it raises important clinical and public health concerns that must be addressed,” Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, Tulane University, New Orleans, said as invited discussant after the presentation from Dr. Morris.
“These findings could serve as an aid to policy makers, going forward, in terms of allocating resources for primary health care,” he said. “And it’s important looking at these data and other [data] that we target heart failure patients who reside in deprived neighborhoods before, during, and [after] hospitalization.”
Dr. Morris agreed that policy makers are in a better position to attack the racial disparity in HF readmission rates identified in the study. “This is not a problem that can be fixed within the health care system.”
If the reported interpretation is correct, it could add a twist to the public health care debate in the United States, observed session moderator Mandeep R. Mehra, MD, Brigham and Woman’s Hospital in Boston.
That debate, he noted, has often focused on insurability, access to coverage, and the merits or shortcomings of a single-payer system. Yet the study suggests outcomes disparities stemming from neighborhood deprivation will not be corrected by improved access to health insurance, a conclusion he finds “startling,” Dr. Mehra said in an interview.
Some proposed explanations for the disparities by race blame unequal access to health care and or variable health insurance coverage, Dr. Morris observed in an interview. But “that may not fully explain the increased risk that we see.”
Black patients followed at Emory University’s advanced HF clinic still have a higher risk of rehospitalization than Whites. “These are patients who have insurance, who are followed by advanced heart failure providers, who are on equal amounts of guideline-recommended medical therapy – and you still see about a 50% higher risk of rehospitalization,” Dr. Morris said, citing data that isn’t part of the current analysis.
“We can say that these patients are certainly able to access care, because they are able to access our emergency room and be taken care of within the hospital setting,” he said. The study controlled for whether health coverage was by private insurance, Medicare, or Medicaid.
Instead, the current analysis points to socioeconomic and environmental factors as a major source of the disparity in 30-day readmissions, Dr. Morris said.
“When patients are discharged from our healthcare systems, they still go back into environments where they don’t have the same resources as patients who live in higher-SDI neighborhoods,” she explained.
For example, “we tell them to eat low-sodium [foods], exercise, eat fresh fruits and vegetables, take their medicines, but the reality is that certain neighborhoods within the United States – and this is much more true for Blacks – make it very difficult to follow those self-care recommendations.”
The analysis included 16,147 Black patients and 14,483 White patients hospitalized with HF within the Emory Healthcare system at least once from 2010-2018, Dr. Morris reported. Compared with Whites, Blacks were younger (63.5 vs 69.1 years) and less likely to be 65 or older (48.9% vs. 66.5%); more likely to be women (53.5% vs. 42.2%), more likely to reside in deprived census tracts and to have diabetes, hypertension, or chronic kidney disease; and had higher comorbidity scores.
In all, 20.6% of Black and 13.5% of White patients were readmitted for HF within 30 days of discharge, for an unadjusted risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI, 1.44-1.61).
The RR hardly budged, 1.45 (95% CI, 1.37-1.54, P < .001), after adjustment for age, sex, type of insurance, type of HF, vital signs and laboratory values, medical history (diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease), Charlson Comorbidity Index, discharging medical specialty, and hospital location.
The excess in 30-day HF readmissions for Black, compared with White patients climbed from the first to the third neighborhood SDI quartile, the disparity peaking at 8.2 absolute percentage points.
A major criticism of the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program component of the Affordable Care Act, Dr. Morris said in a Q&A discussion after her presentation, is that it can hold hospitals “responsible for structural inequalities that exist beyond the health care system,” including neighborhood deprivation.
“But public policy makers have to realize that there are certain patients we take care of who don’t have the resources to carry out the therapeutic lifestyle changes that will allow them to live healthy.”
The HRRP’s 30-day HF readmission metric that steers reimbursement “is penalizing health care systems across the United States” with its premise that hospital performance can be measured by 30-day HF readmission rates, Dr. Morris said in an interview.
“The reality is that some of these patients are going to a postdischarge environment that is inherently high risk, and that many of them are going to come back to us within 30 days,” she said. “We would like to make sure that we don’t put excess penalties on health care systems that take care of disproportionate numbers of African Americans in neighborhoods that have fewer resources.”
Dr. Morris and Dr. Ferdinand have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mehra discloses consulting or serving on an advisory board for Abbott, Medtronic, Janssen, Leviticus, NupulseCV, FineHeart, Portola, Bayer, the Baim Institute for Clinical Research, and Mesoblast.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
More data on impact of corticosteroids on COVID-19 mortality in patients with COPD
, a study of almost 1 million individuals in the United Kingdom has shown.
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma who used ICS on a regular basis were more likely to die from COVID-19 than COPD or asthma patients who were prescribed non-ICS therapies, reported co-lead author Anna Schultze, PhD, of London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and colleagues.
Of note, the increased risk of death among ICS users likely stemmed from greater severity of preexisting chronic respiratory conditions, instead of directly from ICS usage, which has little apparent impact on COVID-19 mortality, the investigators wrote in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
These findings conflict with a hypothesis proposed early in the pandemic: that ICS may protect individuals from SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes with COVID-19.
According to Megan Conroy, MD, of the department of internal medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, this hypothesis was based on some unexpected epidemiological findings.
“In general, we tend to think people with underlying lung disease – like COPD or asthma – to be at higher risk for severe forms of lower respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Conroy said. “Somewhat surprisingly, early data in the pandemic showed patients with COPD and asthma [were] underrepresented [among patients with COVID] when compared to the prevalence of these diseases in the population.”
This raised the possibility of an incidental protective effect from regular ICS therapy, which “had some strong theoretic pathophysiologic basis,” Dr. Conroy said, referring to research that demonstrated ICS-mediated downregulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
Dr. Schultze and colleagues noted that investigators for two ongoing randomized controlled trials (NCT04331054, NCT04330586) are studying ICS as an intervention for COVID-19; but neither trial includes individuals already taking ICS for chronic respiratory disease.
The present observational study therefore aimed to assess mortality risk within this population. Data were drawn from electronic health records and a U.K. national mortality database, with follow-up ranging from March 1 to May 6, 2020. Eligibility required a relevant prescription within 4 months of first follow-up. In the COPD group, patients were prescribed a long-acting beta agonist plus a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LABA–LAMA), LABA alone, LABA plus ICS, LABA–LAMA plus ICS, or ICS alone (if prescribed LABA within 4 months).
In the asthma group, patients received low/medium-dose ICS, high-dose ICS, or a short-acting beta agonist (SABA) alone. Patients with COPD were at least 35 years of age, while those with asthma were 18 years or older. Hazard ratios were adjusted for a variety of covariates, including respiratory disease–exacerbation history, age, sex, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes, and others.
These eligibility criteria returned 148,557 patients with COPD and 818,490 with asthma.
Patients with COPD who were prescribed ICS plus LABA-LAMA or ICS plus LABA had an increased risk of COVID-19-related death, compared with those who did not receive ICS (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.76). Separate analyses of patients who received a triple combination (LABA–LAMA plus ICS) versus those who took a dual combination (LABA plus ICS) showed that triple-combination therapy was significantly associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.12-1.83), while dual-combination therapy was less so (aHR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.96-1.74). Non–COVID-19–related mortality was significantly increased for all COPD patients who were prescribed ICS, with or without adjustment for covariates.
Asthma patients prescribed high-dose ICS instead of SABA alone had a slightly greater risk of COVID-19–related death, based on an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.55 (95% CI, 1.10-2.18). Those with asthma who received low/medium–dose ICS demonstrated a slight trend toward increased mortality risk, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.85-1.54). ICS usage in the asthma group was not linked with a significant increase in non–COVID-19–related death.
“In summary, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect of regular ICS use among people with COPD and asthma on COVID-19–related mortality,” the investigators concluded.
In agreement with the investigators, Dr. Conroy said that the increased mortality rate among ICS users should not be misconstrued as a medication-related risk.
“While the study found that those with COPD or asthma taking ICS and high-dose ICS were at an increased risk of death, this could easily be explained by the likelihood that those are the patients who are more likely to have more severe underlying lung disease,” Dr. Conroy said. “While this observational study did attempt to control for exacerbation history, the ability to do so by electronic health records data is certainly imperfect.”
With this in mind, patients with chronic respiratory disease should be encouraged to adhere to their usual treatment regimen, Dr. Conroy added.
“There isn’t evidence to increase or decrease medications just because of the pandemic,” she said. “A patient with asthma or COPD should continue to take the medications that are needed to achieve good control of their lung disease.”
The study was funded by the U.K. Medical Research Council. The investigators reported additional relationships with the Wellcome Trust, the Good Thinking Foundation, the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, and others. Dr. Conroy reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Schultze A et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1016/ S2213-2600(20)30415-X.
, a study of almost 1 million individuals in the United Kingdom has shown.
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma who used ICS on a regular basis were more likely to die from COVID-19 than COPD or asthma patients who were prescribed non-ICS therapies, reported co-lead author Anna Schultze, PhD, of London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and colleagues.
Of note, the increased risk of death among ICS users likely stemmed from greater severity of preexisting chronic respiratory conditions, instead of directly from ICS usage, which has little apparent impact on COVID-19 mortality, the investigators wrote in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
These findings conflict with a hypothesis proposed early in the pandemic: that ICS may protect individuals from SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes with COVID-19.
According to Megan Conroy, MD, of the department of internal medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, this hypothesis was based on some unexpected epidemiological findings.
“In general, we tend to think people with underlying lung disease – like COPD or asthma – to be at higher risk for severe forms of lower respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Conroy said. “Somewhat surprisingly, early data in the pandemic showed patients with COPD and asthma [were] underrepresented [among patients with COVID] when compared to the prevalence of these diseases in the population.”
This raised the possibility of an incidental protective effect from regular ICS therapy, which “had some strong theoretic pathophysiologic basis,” Dr. Conroy said, referring to research that demonstrated ICS-mediated downregulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
Dr. Schultze and colleagues noted that investigators for two ongoing randomized controlled trials (NCT04331054, NCT04330586) are studying ICS as an intervention for COVID-19; but neither trial includes individuals already taking ICS for chronic respiratory disease.
The present observational study therefore aimed to assess mortality risk within this population. Data were drawn from electronic health records and a U.K. national mortality database, with follow-up ranging from March 1 to May 6, 2020. Eligibility required a relevant prescription within 4 months of first follow-up. In the COPD group, patients were prescribed a long-acting beta agonist plus a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LABA–LAMA), LABA alone, LABA plus ICS, LABA–LAMA plus ICS, or ICS alone (if prescribed LABA within 4 months).
In the asthma group, patients received low/medium-dose ICS, high-dose ICS, or a short-acting beta agonist (SABA) alone. Patients with COPD were at least 35 years of age, while those with asthma were 18 years or older. Hazard ratios were adjusted for a variety of covariates, including respiratory disease–exacerbation history, age, sex, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes, and others.
These eligibility criteria returned 148,557 patients with COPD and 818,490 with asthma.
Patients with COPD who were prescribed ICS plus LABA-LAMA or ICS plus LABA had an increased risk of COVID-19-related death, compared with those who did not receive ICS (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.76). Separate analyses of patients who received a triple combination (LABA–LAMA plus ICS) versus those who took a dual combination (LABA plus ICS) showed that triple-combination therapy was significantly associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.12-1.83), while dual-combination therapy was less so (aHR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.96-1.74). Non–COVID-19–related mortality was significantly increased for all COPD patients who were prescribed ICS, with or without adjustment for covariates.
Asthma patients prescribed high-dose ICS instead of SABA alone had a slightly greater risk of COVID-19–related death, based on an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.55 (95% CI, 1.10-2.18). Those with asthma who received low/medium–dose ICS demonstrated a slight trend toward increased mortality risk, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.85-1.54). ICS usage in the asthma group was not linked with a significant increase in non–COVID-19–related death.
“In summary, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect of regular ICS use among people with COPD and asthma on COVID-19–related mortality,” the investigators concluded.
In agreement with the investigators, Dr. Conroy said that the increased mortality rate among ICS users should not be misconstrued as a medication-related risk.
“While the study found that those with COPD or asthma taking ICS and high-dose ICS were at an increased risk of death, this could easily be explained by the likelihood that those are the patients who are more likely to have more severe underlying lung disease,” Dr. Conroy said. “While this observational study did attempt to control for exacerbation history, the ability to do so by electronic health records data is certainly imperfect.”
With this in mind, patients with chronic respiratory disease should be encouraged to adhere to their usual treatment regimen, Dr. Conroy added.
“There isn’t evidence to increase or decrease medications just because of the pandemic,” she said. “A patient with asthma or COPD should continue to take the medications that are needed to achieve good control of their lung disease.”
The study was funded by the U.K. Medical Research Council. The investigators reported additional relationships with the Wellcome Trust, the Good Thinking Foundation, the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, and others. Dr. Conroy reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Schultze A et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1016/ S2213-2600(20)30415-X.
, a study of almost 1 million individuals in the United Kingdom has shown.
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma who used ICS on a regular basis were more likely to die from COVID-19 than COPD or asthma patients who were prescribed non-ICS therapies, reported co-lead author Anna Schultze, PhD, of London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and colleagues.
Of note, the increased risk of death among ICS users likely stemmed from greater severity of preexisting chronic respiratory conditions, instead of directly from ICS usage, which has little apparent impact on COVID-19 mortality, the investigators wrote in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
These findings conflict with a hypothesis proposed early in the pandemic: that ICS may protect individuals from SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes with COVID-19.
According to Megan Conroy, MD, of the department of internal medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, this hypothesis was based on some unexpected epidemiological findings.
“In general, we tend to think people with underlying lung disease – like COPD or asthma – to be at higher risk for severe forms of lower respiratory tract infections,” Dr. Conroy said. “Somewhat surprisingly, early data in the pandemic showed patients with COPD and asthma [were] underrepresented [among patients with COVID] when compared to the prevalence of these diseases in the population.”
This raised the possibility of an incidental protective effect from regular ICS therapy, which “had some strong theoretic pathophysiologic basis,” Dr. Conroy said, referring to research that demonstrated ICS-mediated downregulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2.
Dr. Schultze and colleagues noted that investigators for two ongoing randomized controlled trials (NCT04331054, NCT04330586) are studying ICS as an intervention for COVID-19; but neither trial includes individuals already taking ICS for chronic respiratory disease.
The present observational study therefore aimed to assess mortality risk within this population. Data were drawn from electronic health records and a U.K. national mortality database, with follow-up ranging from March 1 to May 6, 2020. Eligibility required a relevant prescription within 4 months of first follow-up. In the COPD group, patients were prescribed a long-acting beta agonist plus a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LABA–LAMA), LABA alone, LABA plus ICS, LABA–LAMA plus ICS, or ICS alone (if prescribed LABA within 4 months).
In the asthma group, patients received low/medium-dose ICS, high-dose ICS, or a short-acting beta agonist (SABA) alone. Patients with COPD were at least 35 years of age, while those with asthma were 18 years or older. Hazard ratios were adjusted for a variety of covariates, including respiratory disease–exacerbation history, age, sex, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes, and others.
These eligibility criteria returned 148,557 patients with COPD and 818,490 with asthma.
Patients with COPD who were prescribed ICS plus LABA-LAMA or ICS plus LABA had an increased risk of COVID-19-related death, compared with those who did not receive ICS (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.76). Separate analyses of patients who received a triple combination (LABA–LAMA plus ICS) versus those who took a dual combination (LABA plus ICS) showed that triple-combination therapy was significantly associated with increased COVID-19-related mortality (aHR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.12-1.83), while dual-combination therapy was less so (aHR, 1.29; 95% CI, 0.96-1.74). Non–COVID-19–related mortality was significantly increased for all COPD patients who were prescribed ICS, with or without adjustment for covariates.
Asthma patients prescribed high-dose ICS instead of SABA alone had a slightly greater risk of COVID-19–related death, based on an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.55 (95% CI, 1.10-2.18). Those with asthma who received low/medium–dose ICS demonstrated a slight trend toward increased mortality risk, but this was not significant (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 0.85-1.54). ICS usage in the asthma group was not linked with a significant increase in non–COVID-19–related death.
“In summary, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect of regular ICS use among people with COPD and asthma on COVID-19–related mortality,” the investigators concluded.
In agreement with the investigators, Dr. Conroy said that the increased mortality rate among ICS users should not be misconstrued as a medication-related risk.
“While the study found that those with COPD or asthma taking ICS and high-dose ICS were at an increased risk of death, this could easily be explained by the likelihood that those are the patients who are more likely to have more severe underlying lung disease,” Dr. Conroy said. “While this observational study did attempt to control for exacerbation history, the ability to do so by electronic health records data is certainly imperfect.”
With this in mind, patients with chronic respiratory disease should be encouraged to adhere to their usual treatment regimen, Dr. Conroy added.
“There isn’t evidence to increase or decrease medications just because of the pandemic,” she said. “A patient with asthma or COPD should continue to take the medications that are needed to achieve good control of their lung disease.”
The study was funded by the U.K. Medical Research Council. The investigators reported additional relationships with the Wellcome Trust, the Good Thinking Foundation, the Laura and John Arnold Foundation, and others. Dr. Conroy reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Schultze A et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Sep 24. doi: 10.1016/ S2213-2600(20)30415-X.
FROM LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
Hospital medicine, it’s time to vote
Whether physicians or advanced practice practitioners, we are the backbone of our nation’s network of acute care facilities, and on a daily basis, we see just about everything. We have valuable insight into how to improve our nation’s health care system, especially now, as our nation continues to battle COVID-19.
Our role, squarely on the front lines during this pandemic, has given us an important perspective that needs to be heard. We spend our days managing patients with complexity, coordinating with specialists and subspecialists, and advocating – at local, state, and national levels – so that our patients can more easily transition to their lives out of the hospital.
Our current polarized political climate makes it seem that individual voices will not make a difference. It is easy to feel frustrated and powerless. However, those in our specialty are actually in a perfect position to have an educated and influential say in how we move forward, not only about the immediate health crises, but also regarding future health care issues. That voice begins with voting.
Historically, physicians have had surprisingly low rates of voting. For example, a 2007 study found significantly lower rates of voting among physicians, compared with the general public.1 While physician voter turnout may have improved in the past decade, given the substantial changes in health care and the increasing amount of physician engagement in the public sphere, our participation should be greater still. Elected officials listen to, and follow up with, constituents who make their voices heard. Each of us can ensure that the health care policy priorities of our fast-growing specialty are addressed by mobilizing to the voting booth.
Candidates we elect shape our health care system for the future, directly impacting us and our patients. Cost, coverage, access to health care, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services inpatient fee schedules, the ongoing pandemic response, surprise billing, use of telehealth, observation status, and the three-midnight rule are just a few of the issues most important to hospital medicine.
Therefore, we, the SHM Public Policy Committee, urge all of our colleagues, regardless of political sway, to make your voice heard this and every election henceforth. The first step is to register to vote, if you have not done so already.2 Next, exercise that privilege. Given the pandemic, this is not as simple a process as it has been in the past. Take the time to plan your approach to early voting, mail-in voting, or election day voting. Check your County Supervisor of Elections’ website for further information, including how to register, view candidate profiles, check your precinct, and request a mail-in ballot.
In addition to casting your vote, we encourage you to share your opinions and engage in dialogue about health care issues. Clinical fact can dispel rumor and misinformation, and daily experiences can personalize our patients’ health care stories and the impact laws and rules have on our ability to practice. We are part of a trusted profession and have a unique perspective; others need and want to hear it. They can only do that if we are part of the process. Arming yourself with information and voting are the first steps on the path of advocacy. Interpersonal advocacy can also be done on social media. For example, SHM has an active grassroots advocacy network on Twitter. Tag @SHMadvocacy in your tweets to share your thoughts with their network.
Finally, as advocates for our patients in health care, we can also help ensure their safety during this election, in particular regarding COVID-19. Some patients may not wish to engage us in politics, and we must respect their decision. Others may seek our counsel and we should provide it in an unbiased fashion. We can ask our patients if they have considered a safe voting plan, help patients review the alternatives to voting in person if desired, and inform those who wish to physically cast a vote on Election Day of how to mitigate the risk of in-person voting.
Every election is important and health care is front and center for a multitude of reasons. We who practice hospital medicine are integral to our communities and need to be more politically involved. This is our chance to share our voice through our vote, not just this year, but in future elections as well.
Ann Sheehy, MD, SFHM, is division chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. Other members of the SHM PPC include Marta Almli, MD; John Biebelhausen, MD; Robert Burke, MD, MS, FHM; George Cheely, MD; Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM; Jennifer Cowart, MD, FHM; Suparna Dutta, MD, MS, MPH; Bradley Flansbaum, DO, MPH, MHM; Alain Folefack, MD; Rick Hilger MD SFHM; Melinda Johnson, MD; Sevan Karadolian, MD; Joshua D. Lenchus, DO, FACP, SFHM; Steve Phillipson, MD; Dahlia Rizk, DO; Kendall Rogers, MD, SFHM; Brett Stauffer, MD, MHS; Amit Vashist, MD, SFHM; Robert Zipper, MD, SFHM.
References
1. Grande D et al. Do doctors vote? J Gen Int Med. 2007 May;22(5):585-9.
2. How to register to vote, confirm or change your registration and get a voter registration card. https://www.usa.gov/voter-registration/.
Whether physicians or advanced practice practitioners, we are the backbone of our nation’s network of acute care facilities, and on a daily basis, we see just about everything. We have valuable insight into how to improve our nation’s health care system, especially now, as our nation continues to battle COVID-19.
Our role, squarely on the front lines during this pandemic, has given us an important perspective that needs to be heard. We spend our days managing patients with complexity, coordinating with specialists and subspecialists, and advocating – at local, state, and national levels – so that our patients can more easily transition to their lives out of the hospital.
Our current polarized political climate makes it seem that individual voices will not make a difference. It is easy to feel frustrated and powerless. However, those in our specialty are actually in a perfect position to have an educated and influential say in how we move forward, not only about the immediate health crises, but also regarding future health care issues. That voice begins with voting.
Historically, physicians have had surprisingly low rates of voting. For example, a 2007 study found significantly lower rates of voting among physicians, compared with the general public.1 While physician voter turnout may have improved in the past decade, given the substantial changes in health care and the increasing amount of physician engagement in the public sphere, our participation should be greater still. Elected officials listen to, and follow up with, constituents who make their voices heard. Each of us can ensure that the health care policy priorities of our fast-growing specialty are addressed by mobilizing to the voting booth.
Candidates we elect shape our health care system for the future, directly impacting us and our patients. Cost, coverage, access to health care, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services inpatient fee schedules, the ongoing pandemic response, surprise billing, use of telehealth, observation status, and the three-midnight rule are just a few of the issues most important to hospital medicine.
Therefore, we, the SHM Public Policy Committee, urge all of our colleagues, regardless of political sway, to make your voice heard this and every election henceforth. The first step is to register to vote, if you have not done so already.2 Next, exercise that privilege. Given the pandemic, this is not as simple a process as it has been in the past. Take the time to plan your approach to early voting, mail-in voting, or election day voting. Check your County Supervisor of Elections’ website for further information, including how to register, view candidate profiles, check your precinct, and request a mail-in ballot.
In addition to casting your vote, we encourage you to share your opinions and engage in dialogue about health care issues. Clinical fact can dispel rumor and misinformation, and daily experiences can personalize our patients’ health care stories and the impact laws and rules have on our ability to practice. We are part of a trusted profession and have a unique perspective; others need and want to hear it. They can only do that if we are part of the process. Arming yourself with information and voting are the first steps on the path of advocacy. Interpersonal advocacy can also be done on social media. For example, SHM has an active grassroots advocacy network on Twitter. Tag @SHMadvocacy in your tweets to share your thoughts with their network.
Finally, as advocates for our patients in health care, we can also help ensure their safety during this election, in particular regarding COVID-19. Some patients may not wish to engage us in politics, and we must respect their decision. Others may seek our counsel and we should provide it in an unbiased fashion. We can ask our patients if they have considered a safe voting plan, help patients review the alternatives to voting in person if desired, and inform those who wish to physically cast a vote on Election Day of how to mitigate the risk of in-person voting.
Every election is important and health care is front and center for a multitude of reasons. We who practice hospital medicine are integral to our communities and need to be more politically involved. This is our chance to share our voice through our vote, not just this year, but in future elections as well.
Ann Sheehy, MD, SFHM, is division chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. Other members of the SHM PPC include Marta Almli, MD; John Biebelhausen, MD; Robert Burke, MD, MS, FHM; George Cheely, MD; Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM; Jennifer Cowart, MD, FHM; Suparna Dutta, MD, MS, MPH; Bradley Flansbaum, DO, MPH, MHM; Alain Folefack, MD; Rick Hilger MD SFHM; Melinda Johnson, MD; Sevan Karadolian, MD; Joshua D. Lenchus, DO, FACP, SFHM; Steve Phillipson, MD; Dahlia Rizk, DO; Kendall Rogers, MD, SFHM; Brett Stauffer, MD, MHS; Amit Vashist, MD, SFHM; Robert Zipper, MD, SFHM.
References
1. Grande D et al. Do doctors vote? J Gen Int Med. 2007 May;22(5):585-9.
2. How to register to vote, confirm or change your registration and get a voter registration card. https://www.usa.gov/voter-registration/.
Whether physicians or advanced practice practitioners, we are the backbone of our nation’s network of acute care facilities, and on a daily basis, we see just about everything. We have valuable insight into how to improve our nation’s health care system, especially now, as our nation continues to battle COVID-19.
Our role, squarely on the front lines during this pandemic, has given us an important perspective that needs to be heard. We spend our days managing patients with complexity, coordinating with specialists and subspecialists, and advocating – at local, state, and national levels – so that our patients can more easily transition to their lives out of the hospital.
Our current polarized political climate makes it seem that individual voices will not make a difference. It is easy to feel frustrated and powerless. However, those in our specialty are actually in a perfect position to have an educated and influential say in how we move forward, not only about the immediate health crises, but also regarding future health care issues. That voice begins with voting.
Historically, physicians have had surprisingly low rates of voting. For example, a 2007 study found significantly lower rates of voting among physicians, compared with the general public.1 While physician voter turnout may have improved in the past decade, given the substantial changes in health care and the increasing amount of physician engagement in the public sphere, our participation should be greater still. Elected officials listen to, and follow up with, constituents who make their voices heard. Each of us can ensure that the health care policy priorities of our fast-growing specialty are addressed by mobilizing to the voting booth.
Candidates we elect shape our health care system for the future, directly impacting us and our patients. Cost, coverage, access to health care, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services inpatient fee schedules, the ongoing pandemic response, surprise billing, use of telehealth, observation status, and the three-midnight rule are just a few of the issues most important to hospital medicine.
Therefore, we, the SHM Public Policy Committee, urge all of our colleagues, regardless of political sway, to make your voice heard this and every election henceforth. The first step is to register to vote, if you have not done so already.2 Next, exercise that privilege. Given the pandemic, this is not as simple a process as it has been in the past. Take the time to plan your approach to early voting, mail-in voting, or election day voting. Check your County Supervisor of Elections’ website for further information, including how to register, view candidate profiles, check your precinct, and request a mail-in ballot.
In addition to casting your vote, we encourage you to share your opinions and engage in dialogue about health care issues. Clinical fact can dispel rumor and misinformation, and daily experiences can personalize our patients’ health care stories and the impact laws and rules have on our ability to practice. We are part of a trusted profession and have a unique perspective; others need and want to hear it. They can only do that if we are part of the process. Arming yourself with information and voting are the first steps on the path of advocacy. Interpersonal advocacy can also be done on social media. For example, SHM has an active grassroots advocacy network on Twitter. Tag @SHMadvocacy in your tweets to share your thoughts with their network.
Finally, as advocates for our patients in health care, we can also help ensure their safety during this election, in particular regarding COVID-19. Some patients may not wish to engage us in politics, and we must respect their decision. Others may seek our counsel and we should provide it in an unbiased fashion. We can ask our patients if they have considered a safe voting plan, help patients review the alternatives to voting in person if desired, and inform those who wish to physically cast a vote on Election Day of how to mitigate the risk of in-person voting.
Every election is important and health care is front and center for a multitude of reasons. We who practice hospital medicine are integral to our communities and need to be more politically involved. This is our chance to share our voice through our vote, not just this year, but in future elections as well.
Ann Sheehy, MD, SFHM, is division chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and chair of the SHM Public Policy Committee. Other members of the SHM PPC include Marta Almli, MD; John Biebelhausen, MD; Robert Burke, MD, MS, FHM; George Cheely, MD; Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM; Jennifer Cowart, MD, FHM; Suparna Dutta, MD, MS, MPH; Bradley Flansbaum, DO, MPH, MHM; Alain Folefack, MD; Rick Hilger MD SFHM; Melinda Johnson, MD; Sevan Karadolian, MD; Joshua D. Lenchus, DO, FACP, SFHM; Steve Phillipson, MD; Dahlia Rizk, DO; Kendall Rogers, MD, SFHM; Brett Stauffer, MD, MHS; Amit Vashist, MD, SFHM; Robert Zipper, MD, SFHM.
References
1. Grande D et al. Do doctors vote? J Gen Int Med. 2007 May;22(5):585-9.
2. How to register to vote, confirm or change your registration and get a voter registration card. https://www.usa.gov/voter-registration/.
COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy ‘somewhat understandable,’ expert says
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
“I worry that vaccines are going to be sold like magic powder that we sprinkle across the land and make the virus go away,” Paul Offit, MD, said at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference. “That’s not true.”
according to Dr. Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center and an attending physician in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“I think we can get a vaccine that’s 75%-80% effective at preventing mild to moderate disease, but that means one of every four people can still get moderate to severe disease,” Dr. Offit continued.
And that’s if there is high uptake of the vaccine, which may not be the case. Recent polls have suggested there is considerable concern about the pending vaccines.
“It’s somewhat understandable,” Dr. Offitt acknowledged, especially given the “frightening” language used to describe vaccine development. Terms such as “warp speed” may suggest that haste might trump safety considerations. Before COVID-19, the fastest vaccine ever developed was for mumps, he said, with the virus isolated in 1963 and a commercial product available in 1967.
Addressing hesitancy in clinics
In a wide-ranging livestream plenary presentation, Dr. Offit, coinventor of a rotavirus vaccine, shed light on SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development and his impressions of vaccine hesitancy among patients and families. He also offered advice for how to reassure those skeptical of the safety and efficacy of any SARS-COV-2 vaccine, given the accelerated development process.
With more than 180 different vaccines in various stages of investigation, Dr. Offit called the effort to develop COVID-19 vaccines “unprecedented.” Part of that is a result of governments relieving pharmaceutical companies of much of the typical financial risk – which often climbs to hundreds of millions of dollars – by underwriting the costs of vaccine development to battle the pandemic-inducing virus, he said.
But this very swiftness is also stoking antivaccine sentiment. Dr. Offit, part of vaccine advisory groups for the National Institutes of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration, cited recent research reporting nearly half of American adults definitely or probably would not get a COVID-19 vaccine if it were available today.
“One way you convince skeptics is with data presented in a clear, compassionate, and compelling way,” he said.
“The other group is vaccine cynics, who are basically conspiracy theorists who believe pharmaceutical companies control the world, the government, the medical establishment. I think there’s no talking them down from this.”
Numerous strategies are being used in COVID-19 vaccine development, he noted, including messenger RNA, DNA, viral vectors, purified protein, and whole killed virus. Dr. Offit believes any candidates approved for distribution will likely be in the range of 75% effective at preventing mild to moderate symptoms.
But clinicians should be ready to face immediate questions of safety. “Even if this vaccination is given to 20,000 [trial participants] safely, that’s not 20 million,” Dr. Offit said. “Anyone could reasonably ask questions about if it causes rare, serious side effects.
“The good news is, there are systems in place,” such as adverse event reporting systems, to identify rare events, even those that occur in one in a million vaccine recipients. Reminding patients of that continued surveillance can be reassuring.
Another reassuring point is that COVID-19 vaccine trial participants have included people from many diverse populations, he said. But children, notably absent so far, should be added to trials immediately, Dr. Offit contends.
“This is going to be important when you consider strategies to get children universally back into school,” he said, which is a “critical issue” from both learning and wellness standpoints. “It breaks my heart that we’ve been unable to do this when other countries have.”
Transparency will be paramount
While presenting data transparently to patients is key in helping them accept COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Offit said, he also believes “telling stories” can be just as effective, if not more so. When the varicella vaccine was approved in 1995, he said, the “uptake the first few years was pretty miserable” until public service messaging emphasized that some children die from chickenpox.
“Fear works,” he said. “You always worry about pushback of something being oversold, but hopefully we’re scared enough about this virus” to convince people that vaccination is wise. “I do think personal stories carry weight on both sides,” Dr. Offit said.
Mark Sawyer, MD, of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego, California, said Offit’s presentation offered important takeaways for clinicians about how to broach the topic of COVID-19 vaccination with patients and families.
“We need to communicate clearly and transparently to patients about what we do and don’t know” about the vaccines, Dr. Sawyer said in an interview. “We will know if they have common side effects, but we will not know about very rare side effects until we have used the vaccines for a while.
“We will know how well the vaccine works over the short-term, but we won’t know over the long term,” added Dr. Sawyer, a member of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases.
“We can reassure the community that SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are being evaluated in trials in the same way and with the same thoroughness as other vaccines have been,” he said. “That should give people confidence that shortcuts are not being taken with regard to safety and effectiveness evaluations.”
Dr. Offit and Dr. Sawyer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 and the superspreaders: Teens
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Although cases of COVID-19 in children is reported to be low, we are seeing a surge in Wisconsin with a 27.6% positivity rate reported on Sept. 27. Numerous other states across the country are reporting similar jumps of 10% or more.
According to the Wisconsin Department of Health Services as of Sept. 20, 2020, there were 10,644 cumulative cases in persons aged less than 18 years. This rise in cases is consistent with a return to school and sports. This cumulative case load amounts to 836.7/100, 000 cases. This population may not experience the level of illness seen in the older populations with hospitalization rates of only 3% under the age of 9 years and 13% of those age 10- 19-years, yet exposing older family and members of the community is driving the death rates. The combined influenza and COVID-19 season may greatly impact hospitalization rates of young and old. Additionally, we may see a surge in pediatric cancer rates and autoimmune diseases secondary to these trends.
I believe the overall number of adolescents with COVID-19 is underreported. Teens admit to a lack of understanding of symptoms. Many do not realize they have COVID-19 until someone points out the symptoms they describe such as a loss of taste or smell are COVID-19 symptoms. Others report they do not report symptoms to prevent quarantine. Additionally, others endorse ridicule from peers if they have tested positive and contract tracing identifies others potentially exposed and forced to sit out of sports because of quarantine. They have been bullied into amnesia when contract tracers call to prevent identifying others at school or in the community. All these behaviors proliferate the spread of disease within the community and will continue to drive both exposures and death rates.
Teens in high schools require increased education of the symptoms of COVID-19, promotion of the flu vaccine, and knowledge of the impact they can have on preventing the spread of viruses.
Ms. Thew is the medical director of the department of adolescent medicine at Children’s Wisconsin in Milwaukee. She is a member of the Pediatric News editorial advisory board. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Reference
COVID-19: Wisconsin Cases, Wisconsin Department of Health Services. Accessed 2020 Sep 27.
Pediatric fractures shift during pandemic
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric fractures dropped by 2.5-fold during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, but more breaks happened at home and on bicycles, and younger kids were more affected, new research indicates.
The study of 1,745 patients also found that those with distal radius torus fractures were more likely to receive a Velcro splint during the pandemic. Experts said this key trend points toward widespread shifts to streamline treatment, which should persist after the pandemic.
“We expected to see a drop in fracture volume, but what was a bit unexpected was the proportional rise in at-home injuries, which we weren’t immediately aware of,” said senior author Apurva Shah, MD, MBA, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“As time went on, it became more apparent that trampoline and bicycle injuries were on the rise, but at the beginning of the pandemic, we didn’t intuitively expect that,” he added.
“Whenever there’s a major shift in how the world is working, we want to understand how that impacts child safety,” Dr. Shah said in an interview. “The message to get out to parents is that it’s obviously difficult to supervise kids while working from home” during the pandemic “and that supervision obviously is not always working as well as intended.”
Joshua T. Bram, a medical student, presented the study at the virtual American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2020 National Conference.
Dr. Bram, Dr. Shah, and colleagues compared patients with acute fractures who presented at CHOP between March and April 2020 with those who presented during the same months in 2018 and 2019.
Overall, the number of patients with pediatric fractures who presented to CHOP fell to an average of just under 10 per day, compared with more than 22 per day in prior years (P < .001). In addition, the age of the patients fell from an average of 9.4 years to 7.5 years (P < .001), with fewer adolescents affected in 2020.
“I think when you cancel a 14-year-old’s baseball season” because of the pandemic, “unfortunately, that lost outdoor time might be substituted with time on a screen,” he explained. “But canceling a 6-year-old’s soccer season might mean substituting that with more time outside on bikes or on a trampoline.”
As noted, because of the pandemic, a higher proportion of pediatric fractures occurred at home (57.8% vs. 32.5%; P < .001) or on bicycles (18.3% vs. 8.2%; P < .001), but there were fewer organized sports–related (7.2% vs. 26.0%; P < .001) or playground-related injuries (5.2% vs. 9.0%; P < .001).
In the study period this year, the researchers saw no increase in the amount of time between injury and presentation. However, data suggest that, in more recent months, “kids are presenting with fractures late, with sometimes great consequences,” Dr. Shah said.
“What has changed is that a lot of adults have lost their jobs, and as a consequence, a lot of children have lost their access to private insurance,” he said. “But fracture is really a major injury, and this is a reminder for pediatricians and primary care physicians to recognize that families are going through these changes and that delays in care can really be detrimental to children.”
Velcro splints more common
A potential upside to shifts seen during the pandemic, Dr. Shah said, is the finding that distal radius torus fractures were more likely to be treated with a Velcro splint than in previous years (44.2% vs. 25.9%; P = .010).
“This is hitting on something important – that sometimes it’s crisis that forces us as physicians to evolve,” he said. “This is something I think is here to stay.
“Although research had already been there suggesting a close equivalent between splints and casting, culturally, a lot of surgeons hadn’t made that shift when historically the gold standard had been casting,” Dr. Shah added. “But with the pandemic, the shift to minimize contact with the health care system to keep families safe in their COVID bubble helped [usage of] splints take off.
“I suspect – and we’ll only know when we’re on the other side of this – when physicians see good results in splints in their own patients, they’re going to adopt those strategies more permanently,” he said.
Benjamin Shore, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital, agreed with Dr. Shah’s prediction that fracture care will be more streamlined after the pandemic. Dr. Shore, who wasn’t involved in the study, said not only are more orthopedic providers treating patients with Velcro splints and bivalve casts, but they are also monitoring patients via telehealth.
“All of these are great examples of innovation, and one of the unique parts of the pandemic is it created a lot of rapid change across healthcare because it caused us to scrutinize the ways we practice and make a change,” Dr. Shore said in an interview.
“It wasn’t a very fancy study, but it’s very important in terms of demonstrating a change in practice,” Dr. Shore said. “The research here basically validated what many of us are seeing and hopefully will help us in future pandemics – which hopefully won’t happen – to tell families what to be proactive about.”
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore agreed that, because fewer fractures are occurring in kids during the pandemic, there is an opportunity to redeploy orthopedic providers to other clinical areas on the basis of volume and need.
Dr. Shah and Dr. Shore have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
One measure of child COVID-19 may be trending downward
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
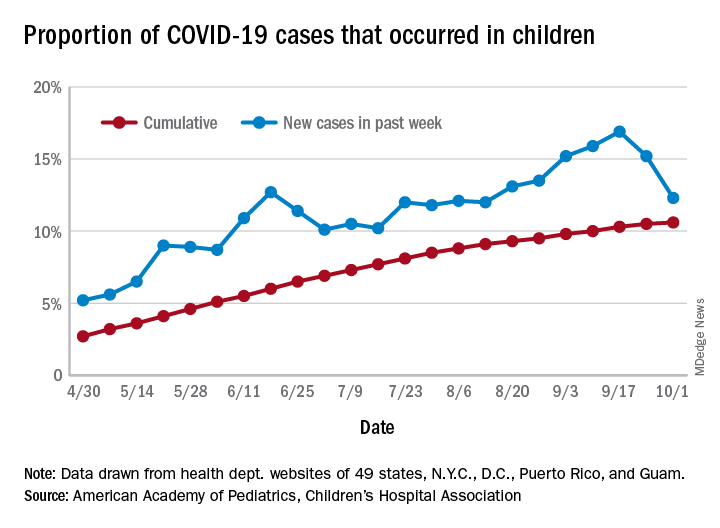
COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
After increasing for several weeks, the proportion of new COVID-19 cases occurring in children has dropped for the second week in a row, according to data in a new report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

COVID-19 cases in children accounted for 12.3% of all new cases in the United States for the week ending Oct. 1, down from 15.2% the previous week. That measure had reached its highest point, 16.9%, just one week earlier (Sept. 17), the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
based on data from the health departments of 49 states (New York does not provide ages on its website), as well as the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The child COVID-19 rate for the United States was 874 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 1, and that figure has doubled since the end of July. At the state level, the highest rates can be found in Tennessee (2,031.4 per 100,000), North Dakota (2,029.6), and South Carolina (2,002.6), with the lowest rates in Vermont (168.9), Maine (229.1), and New Hampshire (268.3), the AAP/CHA report shows.
The children of Wyoming make up the largest share, 22.4%, of any state’s COVID-19 cases, followed by North Dakota and Tennessee, both at 18.3%. New Jersey is lower than any other state at 3.9%, although New York City is a slightly lower 3.6%, the AAP and CHA said.
“The data are limited because the states differ in how they report the data, and it is unknown how many children have been infected but not tested. It is unclear how much of the increase in child cases is due to increased testing capacity,” the AAP said in an earlier statement.
CMS gives hospitals 14 weeks to start daily COVID, flu reports
The federal government is giving hospitals 14 weeks to comply with daily reporting requirements for COVID-19.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will send letters on October 7 to all 6,200 hospitals that receive reimbursement from the two federal health programs informing them of how well they are doing now, said CMS Administrator Seema Verma on a press call.
Verma would not give an estimate on how many hospitals are currently not compliant. But Deborah Birx, MD, a member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, said on the call that 86% of hospitals are currently reporting daily.
Federal officials on the call also announced that hospitals would have the option to begin reporting certain data on influenza starting October 19, but that it would become mandatory a few weeks later.
The reporting is important “to really ensure that we’re triangulating all data to understand where this epidemic is, how it’s moving through different populations, and ensuring that we’re meeting the needs of specific hospitals and communities,” Birx said.
The federal government began a new hospital reporting system in April but did not require hospitals to participate until it quietly issued guidance in mid-July informing facilities that they should no longer report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The move perplexed many public health experts and epidemiologists, who expressed concern that asking hospitals to use a new data system during a pandemic could result in delays and lost information. The new HHS data collection site, HHS Protect, is being managed by a private contractor, not the CDC, which also raised alarms.
The final CMS rule issued in August went into effect immediately, without any chance for comment or revision. CMS said at the time that the pandemic was reason enough to skip over the normal bureaucratic process.
Hospitals were not pleased. But Verma claimed that since then CMS had been working with hospital organizations on enforcement.
“We’re going to do everything we can to facilitate reporting, including an enforcement timeline that will provide hospitals ample opportunity to come into compliance,” she said.
Hospitals that do not comply will get a notice every 3 weeks. Three weeks after the second notice, they’ll get weekly notices for a month, and a final termination notice at 14 weeks.
The Federation of American Hospitals (FAH), however, said their members were still not happy. “It is both inappropriate and frankly overkill for CMS to tie compliance with reporting to Medicare conditions of participation,” said FAH President and CEO Chip Kahn in a statement. He called the CMS proposal “sledgehammer enforcement,” and said that the continuing data request might weaken hospitals’ response to the pandemic because it would divert time and money away from patient care.
Rick Pollack, president and CEO of the American Hospital Association called the CMS rule an “overly heavy-handed approach that could jeopardize access to hospital care for all Americans.” He noted in a statement that barring hospitals from Medicare and Medicaid could harm beneficiaries and the effort to provide COVID care.
Pollack also noted that AHA has “observed errors in data processing and confusion about exactly what was being requested at the hospital, state, contractor, and federal level, and has worked diligently with the federal agencies to identify and correct those problems.”
The document that lays out U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Protect reporting requirements were updated again on October 6 to add influenza data. The hospitals must report on total patients with laboratory-confirmed flu; previous day’s flu admissions; total ICU patients with lab-confirmed flu; total inpatients with either flu or COVID-19; and the previous day’s deaths for flu and COVID.
CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said on the press call that the new data will give the agency crucial hospital-level information and perhaps better estimates of the flu burden. Flu trends have been tracked using the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET), which will not be replaced, Redfield said. But that network only tracks hospitalizations in 14 states and does not provide information in “nearly real-time,” he said.
Having the new data “will give us a true situational awareness of severe respiratory illness, provide local hospitalization trends, and help direct resources such as antiretrovirals to address potential increased impact of flu and COVID cocirculation,” Redfield said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government is giving hospitals 14 weeks to comply with daily reporting requirements for COVID-19.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will send letters on October 7 to all 6,200 hospitals that receive reimbursement from the two federal health programs informing them of how well they are doing now, said CMS Administrator Seema Verma on a press call.
Verma would not give an estimate on how many hospitals are currently not compliant. But Deborah Birx, MD, a member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, said on the call that 86% of hospitals are currently reporting daily.
Federal officials on the call also announced that hospitals would have the option to begin reporting certain data on influenza starting October 19, but that it would become mandatory a few weeks later.
The reporting is important “to really ensure that we’re triangulating all data to understand where this epidemic is, how it’s moving through different populations, and ensuring that we’re meeting the needs of specific hospitals and communities,” Birx said.
The federal government began a new hospital reporting system in April but did not require hospitals to participate until it quietly issued guidance in mid-July informing facilities that they should no longer report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The move perplexed many public health experts and epidemiologists, who expressed concern that asking hospitals to use a new data system during a pandemic could result in delays and lost information. The new HHS data collection site, HHS Protect, is being managed by a private contractor, not the CDC, which also raised alarms.
The final CMS rule issued in August went into effect immediately, without any chance for comment or revision. CMS said at the time that the pandemic was reason enough to skip over the normal bureaucratic process.
Hospitals were not pleased. But Verma claimed that since then CMS had been working with hospital organizations on enforcement.
“We’re going to do everything we can to facilitate reporting, including an enforcement timeline that will provide hospitals ample opportunity to come into compliance,” she said.
Hospitals that do not comply will get a notice every 3 weeks. Three weeks after the second notice, they’ll get weekly notices for a month, and a final termination notice at 14 weeks.
The Federation of American Hospitals (FAH), however, said their members were still not happy. “It is both inappropriate and frankly overkill for CMS to tie compliance with reporting to Medicare conditions of participation,” said FAH President and CEO Chip Kahn in a statement. He called the CMS proposal “sledgehammer enforcement,” and said that the continuing data request might weaken hospitals’ response to the pandemic because it would divert time and money away from patient care.
Rick Pollack, president and CEO of the American Hospital Association called the CMS rule an “overly heavy-handed approach that could jeopardize access to hospital care for all Americans.” He noted in a statement that barring hospitals from Medicare and Medicaid could harm beneficiaries and the effort to provide COVID care.
Pollack also noted that AHA has “observed errors in data processing and confusion about exactly what was being requested at the hospital, state, contractor, and federal level, and has worked diligently with the federal agencies to identify and correct those problems.”
The document that lays out U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Protect reporting requirements were updated again on October 6 to add influenza data. The hospitals must report on total patients with laboratory-confirmed flu; previous day’s flu admissions; total ICU patients with lab-confirmed flu; total inpatients with either flu or COVID-19; and the previous day’s deaths for flu and COVID.
CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said on the press call that the new data will give the agency crucial hospital-level information and perhaps better estimates of the flu burden. Flu trends have been tracked using the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET), which will not be replaced, Redfield said. But that network only tracks hospitalizations in 14 states and does not provide information in “nearly real-time,” he said.
Having the new data “will give us a true situational awareness of severe respiratory illness, provide local hospitalization trends, and help direct resources such as antiretrovirals to address potential increased impact of flu and COVID cocirculation,” Redfield said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government is giving hospitals 14 weeks to comply with daily reporting requirements for COVID-19.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will send letters on October 7 to all 6,200 hospitals that receive reimbursement from the two federal health programs informing them of how well they are doing now, said CMS Administrator Seema Verma on a press call.
Verma would not give an estimate on how many hospitals are currently not compliant. But Deborah Birx, MD, a member of the White House Coronavirus Task Force, said on the call that 86% of hospitals are currently reporting daily.
Federal officials on the call also announced that hospitals would have the option to begin reporting certain data on influenza starting October 19, but that it would become mandatory a few weeks later.
The reporting is important “to really ensure that we’re triangulating all data to understand where this epidemic is, how it’s moving through different populations, and ensuring that we’re meeting the needs of specific hospitals and communities,” Birx said.
The federal government began a new hospital reporting system in April but did not require hospitals to participate until it quietly issued guidance in mid-July informing facilities that they should no longer report to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The move perplexed many public health experts and epidemiologists, who expressed concern that asking hospitals to use a new data system during a pandemic could result in delays and lost information. The new HHS data collection site, HHS Protect, is being managed by a private contractor, not the CDC, which also raised alarms.
The final CMS rule issued in August went into effect immediately, without any chance for comment or revision. CMS said at the time that the pandemic was reason enough to skip over the normal bureaucratic process.
Hospitals were not pleased. But Verma claimed that since then CMS had been working with hospital organizations on enforcement.
“We’re going to do everything we can to facilitate reporting, including an enforcement timeline that will provide hospitals ample opportunity to come into compliance,” she said.
Hospitals that do not comply will get a notice every 3 weeks. Three weeks after the second notice, they’ll get weekly notices for a month, and a final termination notice at 14 weeks.
The Federation of American Hospitals (FAH), however, said their members were still not happy. “It is both inappropriate and frankly overkill for CMS to tie compliance with reporting to Medicare conditions of participation,” said FAH President and CEO Chip Kahn in a statement. He called the CMS proposal “sledgehammer enforcement,” and said that the continuing data request might weaken hospitals’ response to the pandemic because it would divert time and money away from patient care.
Rick Pollack, president and CEO of the American Hospital Association called the CMS rule an “overly heavy-handed approach that could jeopardize access to hospital care for all Americans.” He noted in a statement that barring hospitals from Medicare and Medicaid could harm beneficiaries and the effort to provide COVID care.
Pollack also noted that AHA has “observed errors in data processing and confusion about exactly what was being requested at the hospital, state, contractor, and federal level, and has worked diligently with the federal agencies to identify and correct those problems.”
The document that lays out U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Protect reporting requirements were updated again on October 6 to add influenza data. The hospitals must report on total patients with laboratory-confirmed flu; previous day’s flu admissions; total ICU patients with lab-confirmed flu; total inpatients with either flu or COVID-19; and the previous day’s deaths for flu and COVID.
CDC Director Robert Redfield, MD, said on the press call that the new data will give the agency crucial hospital-level information and perhaps better estimates of the flu burden. Flu trends have been tracked using the CDC’s Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET), which will not be replaced, Redfield said. But that network only tracks hospitalizations in 14 states and does not provide information in “nearly real-time,” he said.
Having the new data “will give us a true situational awareness of severe respiratory illness, provide local hospitalization trends, and help direct resources such as antiretrovirals to address potential increased impact of flu and COVID cocirculation,” Redfield said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.










