User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Double Masking and Decontamination: A Doctor's COVID-19 Routine

This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS: I'm Gary Ferenchick with Hannah Ferenchick, who has agreed to join us to talk about the PPE and decontamination processes she's using. Why don't you introduce yourself?
Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD: I am Hannah Ferenchick. I'm an ER physician and medical intensivist. I split my time between the medical ICU and the emergency department at Detroit Medical Center.
PPE Routine at the Hospital
Dr Gary Ferenchick: You've developed your own PPE and decontamination routines. It's about protecting yourself at work but also about protecting your loved ones by not carrying the virus home. Could you walk us through it? I'll show it on the screen.
Dr Hannah Ferenchick: At work I wear scrubs, and I try to minimize any additional clothing. I don't wear a jacket over my scrubs, and I don't wear any T-shirts under my scrubs. If I'm going to be in a situation that might involve exposure to patient secretions or bodily fluids, then I also wear shoe covers.
Because so many of our patients are infected and we may be called upon at any time to do an aerosol-generating procedure, in the ED we have all taken to wearing N95 masks for our entire shift. I wear a fitted N95 mask. I cover that with a surgical mask.
We are anticipating N95 shortages because our use of the masks has increased exponentially. Every hospital has to think about how to protect their healthcare workers while conserving PPE. We cover the N95 mask with a surgical mask, so that if there is any soiling or droplets reaching the mask, we are able to change the surgical mask and continue to use the same N95.
In addition, eye protection is important. Generally throughout the shift I wear my own goggles. If I'm going to be involved in any procedure with the potential for aerosolization (intubation, performing CPR, bronchoscopy) then I wear a creation of my own, which is a welder's shield.
Many of our providers have chosen to use their own equipment, although we are still able to use hospital-provided equipment. There is probably no difference in effectiveness between these devices.
Cell Phones and Stethoscopes
I carry a personal cell phone at work (which I often use to look things up, use the calculator, and for other purposes), and I'm cognizant that when I touch it, I am potentially transmitting pathogens to my phone or its cover. So I've taken to keeping my phone in a plastic sandwich bag, which I disinfect a couple of times throughout the shift. The phone still works normally.
After my shift, in my "decontamination phase," I remove the phone from the plastic bag and disinfect the phone again.
I try to avoid bringing objects into the vicinity of the patient. That's different from my normal routine—I usually like to write down what the patient has told me—but unfortunately, carrying pen and paper or a clipboard into a patient's room is not feasible at this point. During this time, I've also avoided using my personal stethoscope.
There's also transmission risk associated with shared equipment. We share hospital-provided phones and they must be disinfected. We are each disinfecting our own workspaces: computer, keyboard, mouse, and countertop.
Obviously you are trying to minimize any contact with your mouth or face. You don't want to rub your eyes, touch your nose, or eat anything with your hands while you are at work. The assumption is that you are doing very frequent hand hygiene.
Decontamination Routine
One of our concerns as healthcare providers is the possibility that we could, either asymptomatically or through the objects that we use at work, be bringing the disease home. We want to protect the people who may be at higher risk just because they live with a healthcare provider. These are the decontamination practices I've developed for my own situation, taken from best practices and suggestions from others.
I remove my dirty scrubs and leave them at work, and I change into a clean pair of scrubs or clean clothes. I disinfect any inanimate objects that my hands may have touched during the shift using alcohol, sanitizer wipes, bleach wipes, or hospital-grade chemical wipes.
To keep those objects clean after disinfecting, I place them in clean plastic bags away from other objects (eg, a wallet or purse) that may not be easy to disinfect. Then I store those bags in the trunk of my car for my next shift, so I'm not taking them into my home.
I also change my shoes, leaving my work shoes in the trunk of my car, and wear another pair of shoes into the house.
When I get home, I basically do everything again. I disinfect my phone, I wash my hands, and I shower immediately. At that point, I consider myself sufficiently "disinfected."
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS, is a family physician and professor in the Department of Medicine at Michigan State University in East Lansing, Michigan. His daughter, Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD, is an assistant professor in the Department of Emergency Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, and a medical intensivist and emergency medicine physician at Detroit Medical Center.

This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS: I'm Gary Ferenchick with Hannah Ferenchick, who has agreed to join us to talk about the PPE and decontamination processes she's using. Why don't you introduce yourself?
Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD: I am Hannah Ferenchick. I'm an ER physician and medical intensivist. I split my time between the medical ICU and the emergency department at Detroit Medical Center.
PPE Routine at the Hospital
Dr Gary Ferenchick: You've developed your own PPE and decontamination routines. It's about protecting yourself at work but also about protecting your loved ones by not carrying the virus home. Could you walk us through it? I'll show it on the screen.
Dr Hannah Ferenchick: At work I wear scrubs, and I try to minimize any additional clothing. I don't wear a jacket over my scrubs, and I don't wear any T-shirts under my scrubs. If I'm going to be in a situation that might involve exposure to patient secretions or bodily fluids, then I also wear shoe covers.
Because so many of our patients are infected and we may be called upon at any time to do an aerosol-generating procedure, in the ED we have all taken to wearing N95 masks for our entire shift. I wear a fitted N95 mask. I cover that with a surgical mask.
We are anticipating N95 shortages because our use of the masks has increased exponentially. Every hospital has to think about how to protect their healthcare workers while conserving PPE. We cover the N95 mask with a surgical mask, so that if there is any soiling or droplets reaching the mask, we are able to change the surgical mask and continue to use the same N95.
In addition, eye protection is important. Generally throughout the shift I wear my own goggles. If I'm going to be involved in any procedure with the potential for aerosolization (intubation, performing CPR, bronchoscopy) then I wear a creation of my own, which is a welder's shield.
Many of our providers have chosen to use their own equipment, although we are still able to use hospital-provided equipment. There is probably no difference in effectiveness between these devices.
Cell Phones and Stethoscopes
I carry a personal cell phone at work (which I often use to look things up, use the calculator, and for other purposes), and I'm cognizant that when I touch it, I am potentially transmitting pathogens to my phone or its cover. So I've taken to keeping my phone in a plastic sandwich bag, which I disinfect a couple of times throughout the shift. The phone still works normally.
After my shift, in my "decontamination phase," I remove the phone from the plastic bag and disinfect the phone again.
I try to avoid bringing objects into the vicinity of the patient. That's different from my normal routine—I usually like to write down what the patient has told me—but unfortunately, carrying pen and paper or a clipboard into a patient's room is not feasible at this point. During this time, I've also avoided using my personal stethoscope.
There's also transmission risk associated with shared equipment. We share hospital-provided phones and they must be disinfected. We are each disinfecting our own workspaces: computer, keyboard, mouse, and countertop.
Obviously you are trying to minimize any contact with your mouth or face. You don't want to rub your eyes, touch your nose, or eat anything with your hands while you are at work. The assumption is that you are doing very frequent hand hygiene.
Decontamination Routine
One of our concerns as healthcare providers is the possibility that we could, either asymptomatically or through the objects that we use at work, be bringing the disease home. We want to protect the people who may be at higher risk just because they live with a healthcare provider. These are the decontamination practices I've developed for my own situation, taken from best practices and suggestions from others.
I remove my dirty scrubs and leave them at work, and I change into a clean pair of scrubs or clean clothes. I disinfect any inanimate objects that my hands may have touched during the shift using alcohol, sanitizer wipes, bleach wipes, or hospital-grade chemical wipes.
To keep those objects clean after disinfecting, I place them in clean plastic bags away from other objects (eg, a wallet or purse) that may not be easy to disinfect. Then I store those bags in the trunk of my car for my next shift, so I'm not taking them into my home.
I also change my shoes, leaving my work shoes in the trunk of my car, and wear another pair of shoes into the house.
When I get home, I basically do everything again. I disinfect my phone, I wash my hands, and I shower immediately. At that point, I consider myself sufficiently "disinfected."
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS, is a family physician and professor in the Department of Medicine at Michigan State University in East Lansing, Michigan. His daughter, Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD, is an assistant professor in the Department of Emergency Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, and a medical intensivist and emergency medicine physician at Detroit Medical Center.

This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS: I'm Gary Ferenchick with Hannah Ferenchick, who has agreed to join us to talk about the PPE and decontamination processes she's using. Why don't you introduce yourself?
Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD: I am Hannah Ferenchick. I'm an ER physician and medical intensivist. I split my time between the medical ICU and the emergency department at Detroit Medical Center.
PPE Routine at the Hospital
Dr Gary Ferenchick: You've developed your own PPE and decontamination routines. It's about protecting yourself at work but also about protecting your loved ones by not carrying the virus home. Could you walk us through it? I'll show it on the screen.
Dr Hannah Ferenchick: At work I wear scrubs, and I try to minimize any additional clothing. I don't wear a jacket over my scrubs, and I don't wear any T-shirts under my scrubs. If I'm going to be in a situation that might involve exposure to patient secretions or bodily fluids, then I also wear shoe covers.
Because so many of our patients are infected and we may be called upon at any time to do an aerosol-generating procedure, in the ED we have all taken to wearing N95 masks for our entire shift. I wear a fitted N95 mask. I cover that with a surgical mask.
We are anticipating N95 shortages because our use of the masks has increased exponentially. Every hospital has to think about how to protect their healthcare workers while conserving PPE. We cover the N95 mask with a surgical mask, so that if there is any soiling or droplets reaching the mask, we are able to change the surgical mask and continue to use the same N95.
In addition, eye protection is important. Generally throughout the shift I wear my own goggles. If I'm going to be involved in any procedure with the potential for aerosolization (intubation, performing CPR, bronchoscopy) then I wear a creation of my own, which is a welder's shield.
Many of our providers have chosen to use their own equipment, although we are still able to use hospital-provided equipment. There is probably no difference in effectiveness between these devices.
Cell Phones and Stethoscopes
I carry a personal cell phone at work (which I often use to look things up, use the calculator, and for other purposes), and I'm cognizant that when I touch it, I am potentially transmitting pathogens to my phone or its cover. So I've taken to keeping my phone in a plastic sandwich bag, which I disinfect a couple of times throughout the shift. The phone still works normally.
After my shift, in my "decontamination phase," I remove the phone from the plastic bag and disinfect the phone again.
I try to avoid bringing objects into the vicinity of the patient. That's different from my normal routine—I usually like to write down what the patient has told me—but unfortunately, carrying pen and paper or a clipboard into a patient's room is not feasible at this point. During this time, I've also avoided using my personal stethoscope.
There's also transmission risk associated with shared equipment. We share hospital-provided phones and they must be disinfected. We are each disinfecting our own workspaces: computer, keyboard, mouse, and countertop.
Obviously you are trying to minimize any contact with your mouth or face. You don't want to rub your eyes, touch your nose, or eat anything with your hands while you are at work. The assumption is that you are doing very frequent hand hygiene.
Decontamination Routine
One of our concerns as healthcare providers is the possibility that we could, either asymptomatically or through the objects that we use at work, be bringing the disease home. We want to protect the people who may be at higher risk just because they live with a healthcare provider. These are the decontamination practices I've developed for my own situation, taken from best practices and suggestions from others.
I remove my dirty scrubs and leave them at work, and I change into a clean pair of scrubs or clean clothes. I disinfect any inanimate objects that my hands may have touched during the shift using alcohol, sanitizer wipes, bleach wipes, or hospital-grade chemical wipes.
To keep those objects clean after disinfecting, I place them in clean plastic bags away from other objects (eg, a wallet or purse) that may not be easy to disinfect. Then I store those bags in the trunk of my car for my next shift, so I'm not taking them into my home.
I also change my shoes, leaving my work shoes in the trunk of my car, and wear another pair of shoes into the house.
When I get home, I basically do everything again. I disinfect my phone, I wash my hands, and I shower immediately. At that point, I consider myself sufficiently "disinfected."
Gary S. Ferenchick, MD, MS, is a family physician and professor in the Department of Medicine at Michigan State University in East Lansing, Michigan. His daughter, Hannah R.B. Ferenchick, MD, is an assistant professor in the Department of Emergency Medicine, Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan, and a medical intensivist and emergency medicine physician at Detroit Medical Center.
Signature STEMI sign may be less diagnostic in the COVID-19 age
The signature electrocardiographic sign indicating ST-segment-elevation MI may be a less-consistent indicator of actual STEMI at a time when patients with COVID-19 have come to overwhelm many hospital ICUs.
Many of the 18 such patients identified at six New York City hospitals who showed ST-segment elevation on their 12-lead ECG in the city’s first month of fighting the pandemic turned out to be free of either obstructive coronary artery disease by angiography or of regional wall-motion abnormalities (RWMA) by ECG, according to a letter published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those 10 patients in the 18-case series were said to have noncoronary myocardial injury, perhaps from myocarditis – a prevalent feature of severe COVID-19 – and the remaining 8 patients with obstructive coronary artery disease, RWMA, or both were diagnosed with STEMI. Of the latter patients, six went to the cath lab and five of those underwent percutaneous coronary intervention, Sripal Bangalore, MD, MHA, of New York University, and colleagues reported.
In an interview, Dr. Bangalore framed the case-series report as a caution against substituting fibrinolytic therapy for primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STE while hospitals are unusually burdened by the COVID-19 pandemic and invasive procedures intensify the threat of SARS-CoV-2 exposure to clinicians.
The strategy was recently advanced as an option for highly selected patients in a statement from the American College of Cardiology and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI).
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the main reasons fibrinolytic therapy has been pushed is to reduce the exposure to the cath-lab staff,” Dr. Bangalore observed. “But if you pursue that route, it’s problematic because more than half may not have obstructive disease and fibrinolytic therapy may not help. And if you give them fibrinolytics, you’re potentially increasing their risk of bleeding complications.
“The take-home from these 18 patients is that it’s very difficult to guess who is going to have obstructive disease and who is going to have nonobstructive disease,” Dr. Bangalore said. “Maybe we should assess these patients with not just an ECG but with a quick echo, then make a decision. Our practice so far has been to take these patients to the cath lab.”
The ACC/SCAI statement proposed that “fibrinolysis can be considered an option for the relatively stable STEMI patient with active COVID-19” after careful consideration of possible patient benefit versus the risks of cath-lab personnel exposure to the virus.
Only six patients in the current series, including five in the STEMI group, are reported to have had chest pain at about the time of STE, observed Michael J. Blaha, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
So, he said in an interview, “one of their points is that you have to take ST elevations with a grain of salt in this [COVID-19] era, because there are a lot of people presenting with ST elevations in the absence of chest pain.”
That, and the high prevalence of nonobstructive disease in the series, indeed argues against the use of fibrinolytic therapy in such patients, Dr. Blaha said.
Normally, when there is STE, “the pretest probability of STEMI is so high, and if you can’t make it to the cath lab for some reason, sure, it makes sense to give lytics.” However, he said, “COVID-19 is changing the clinical landscape. Now, with a variety of virus-mediated myocardial injury presentations, including myocarditis, the pretest probability of MI is lower.”
The current report “confirms that, in the COVID era, ST elevations are not diagnostic for MI and must be considered within the totality of clinical evidence, and a conservative approach to going to the cath lab is probably warranted,” Dr. Blaha said in an interview.
However, with the reduced pretest probability of STE for STEMI, he agreed, “I almost don’t see any scenario where I’d be comfortable, based on ECG changes alone, giving lytics at this time.”
Dr. Bangalore pointed out that all of the 18 patients in the series had elevated levels of the fibrin degradation product D-dimer, a biomarker that reflects ongoing hemostatic activation. Levels were higher in the 8 patients who ultimately received a STEMI diagnosis than in the remaining 10 patients.
But COVID-19 patients in general may have elevated D-dimer and “a lot of microthrombi,” he said. “So the question is, are those microthrombi also causal for any of the ECG changes we are also seeing?”
Aside from microthrombi, global hypoxia and myocarditis could be other potential causes of STE in COVID-19 patients in the absence of STEMI, Dr. Bangalore proposed. “At this point we just generally don’t know.”
Dr. Bangalore reported no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Blaha disclosed receiving grants from Amgen and serving on advisory boards for Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The signature electrocardiographic sign indicating ST-segment-elevation MI may be a less-consistent indicator of actual STEMI at a time when patients with COVID-19 have come to overwhelm many hospital ICUs.
Many of the 18 such patients identified at six New York City hospitals who showed ST-segment elevation on their 12-lead ECG in the city’s first month of fighting the pandemic turned out to be free of either obstructive coronary artery disease by angiography or of regional wall-motion abnormalities (RWMA) by ECG, according to a letter published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those 10 patients in the 18-case series were said to have noncoronary myocardial injury, perhaps from myocarditis – a prevalent feature of severe COVID-19 – and the remaining 8 patients with obstructive coronary artery disease, RWMA, or both were diagnosed with STEMI. Of the latter patients, six went to the cath lab and five of those underwent percutaneous coronary intervention, Sripal Bangalore, MD, MHA, of New York University, and colleagues reported.
In an interview, Dr. Bangalore framed the case-series report as a caution against substituting fibrinolytic therapy for primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STE while hospitals are unusually burdened by the COVID-19 pandemic and invasive procedures intensify the threat of SARS-CoV-2 exposure to clinicians.
The strategy was recently advanced as an option for highly selected patients in a statement from the American College of Cardiology and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI).
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the main reasons fibrinolytic therapy has been pushed is to reduce the exposure to the cath-lab staff,” Dr. Bangalore observed. “But if you pursue that route, it’s problematic because more than half may not have obstructive disease and fibrinolytic therapy may not help. And if you give them fibrinolytics, you’re potentially increasing their risk of bleeding complications.
“The take-home from these 18 patients is that it’s very difficult to guess who is going to have obstructive disease and who is going to have nonobstructive disease,” Dr. Bangalore said. “Maybe we should assess these patients with not just an ECG but with a quick echo, then make a decision. Our practice so far has been to take these patients to the cath lab.”
The ACC/SCAI statement proposed that “fibrinolysis can be considered an option for the relatively stable STEMI patient with active COVID-19” after careful consideration of possible patient benefit versus the risks of cath-lab personnel exposure to the virus.
Only six patients in the current series, including five in the STEMI group, are reported to have had chest pain at about the time of STE, observed Michael J. Blaha, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
So, he said in an interview, “one of their points is that you have to take ST elevations with a grain of salt in this [COVID-19] era, because there are a lot of people presenting with ST elevations in the absence of chest pain.”
That, and the high prevalence of nonobstructive disease in the series, indeed argues against the use of fibrinolytic therapy in such patients, Dr. Blaha said.
Normally, when there is STE, “the pretest probability of STEMI is so high, and if you can’t make it to the cath lab for some reason, sure, it makes sense to give lytics.” However, he said, “COVID-19 is changing the clinical landscape. Now, with a variety of virus-mediated myocardial injury presentations, including myocarditis, the pretest probability of MI is lower.”
The current report “confirms that, in the COVID era, ST elevations are not diagnostic for MI and must be considered within the totality of clinical evidence, and a conservative approach to going to the cath lab is probably warranted,” Dr. Blaha said in an interview.
However, with the reduced pretest probability of STE for STEMI, he agreed, “I almost don’t see any scenario where I’d be comfortable, based on ECG changes alone, giving lytics at this time.”
Dr. Bangalore pointed out that all of the 18 patients in the series had elevated levels of the fibrin degradation product D-dimer, a biomarker that reflects ongoing hemostatic activation. Levels were higher in the 8 patients who ultimately received a STEMI diagnosis than in the remaining 10 patients.
But COVID-19 patients in general may have elevated D-dimer and “a lot of microthrombi,” he said. “So the question is, are those microthrombi also causal for any of the ECG changes we are also seeing?”
Aside from microthrombi, global hypoxia and myocarditis could be other potential causes of STE in COVID-19 patients in the absence of STEMI, Dr. Bangalore proposed. “At this point we just generally don’t know.”
Dr. Bangalore reported no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Blaha disclosed receiving grants from Amgen and serving on advisory boards for Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The signature electrocardiographic sign indicating ST-segment-elevation MI may be a less-consistent indicator of actual STEMI at a time when patients with COVID-19 have come to overwhelm many hospital ICUs.
Many of the 18 such patients identified at six New York City hospitals who showed ST-segment elevation on their 12-lead ECG in the city’s first month of fighting the pandemic turned out to be free of either obstructive coronary artery disease by angiography or of regional wall-motion abnormalities (RWMA) by ECG, according to a letter published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Those 10 patients in the 18-case series were said to have noncoronary myocardial injury, perhaps from myocarditis – a prevalent feature of severe COVID-19 – and the remaining 8 patients with obstructive coronary artery disease, RWMA, or both were diagnosed with STEMI. Of the latter patients, six went to the cath lab and five of those underwent percutaneous coronary intervention, Sripal Bangalore, MD, MHA, of New York University, and colleagues reported.
In an interview, Dr. Bangalore framed the case-series report as a caution against substituting fibrinolytic therapy for primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STE while hospitals are unusually burdened by the COVID-19 pandemic and invasive procedures intensify the threat of SARS-CoV-2 exposure to clinicians.
The strategy was recently advanced as an option for highly selected patients in a statement from the American College of Cardiology and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI).
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the main reasons fibrinolytic therapy has been pushed is to reduce the exposure to the cath-lab staff,” Dr. Bangalore observed. “But if you pursue that route, it’s problematic because more than half may not have obstructive disease and fibrinolytic therapy may not help. And if you give them fibrinolytics, you’re potentially increasing their risk of bleeding complications.
“The take-home from these 18 patients is that it’s very difficult to guess who is going to have obstructive disease and who is going to have nonobstructive disease,” Dr. Bangalore said. “Maybe we should assess these patients with not just an ECG but with a quick echo, then make a decision. Our practice so far has been to take these patients to the cath lab.”
The ACC/SCAI statement proposed that “fibrinolysis can be considered an option for the relatively stable STEMI patient with active COVID-19” after careful consideration of possible patient benefit versus the risks of cath-lab personnel exposure to the virus.
Only six patients in the current series, including five in the STEMI group, are reported to have had chest pain at about the time of STE, observed Michael J. Blaha, MD, MPH, of Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
So, he said in an interview, “one of their points is that you have to take ST elevations with a grain of salt in this [COVID-19] era, because there are a lot of people presenting with ST elevations in the absence of chest pain.”
That, and the high prevalence of nonobstructive disease in the series, indeed argues against the use of fibrinolytic therapy in such patients, Dr. Blaha said.
Normally, when there is STE, “the pretest probability of STEMI is so high, and if you can’t make it to the cath lab for some reason, sure, it makes sense to give lytics.” However, he said, “COVID-19 is changing the clinical landscape. Now, with a variety of virus-mediated myocardial injury presentations, including myocarditis, the pretest probability of MI is lower.”
The current report “confirms that, in the COVID era, ST elevations are not diagnostic for MI and must be considered within the totality of clinical evidence, and a conservative approach to going to the cath lab is probably warranted,” Dr. Blaha said in an interview.
However, with the reduced pretest probability of STE for STEMI, he agreed, “I almost don’t see any scenario where I’d be comfortable, based on ECG changes alone, giving lytics at this time.”
Dr. Bangalore pointed out that all of the 18 patients in the series had elevated levels of the fibrin degradation product D-dimer, a biomarker that reflects ongoing hemostatic activation. Levels were higher in the 8 patients who ultimately received a STEMI diagnosis than in the remaining 10 patients.
But COVID-19 patients in general may have elevated D-dimer and “a lot of microthrombi,” he said. “So the question is, are those microthrombi also causal for any of the ECG changes we are also seeing?”
Aside from microthrombi, global hypoxia and myocarditis could be other potential causes of STE in COVID-19 patients in the absence of STEMI, Dr. Bangalore proposed. “At this point we just generally don’t know.”
Dr. Bangalore reported no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are available at nejm.org. Dr. Blaha disclosed receiving grants from Amgen and serving on advisory boards for Amgen and other pharmaceutical companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
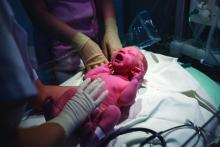
Management of infants born to mothers with COVID-19
Initial guidance for pediatric hospitalists
Clinical question: How should we care for newborns born to mothers with COVID-19?
Background: Around the United States, the SARS-CoV-2 virus is infecting pregnant mothers and causing COVID-19. Current limited data demonstrates that children under the age of 1 year are at risk for severe disease. Clinicians are caring for infants born to mothers with COVID-19 during the pandemic with minimal guidance.
Study design: Clinical practice guidelines.
Synopsis: The American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine and Committee of Infectious Diseases developed guidelines of care for infants born to COVID-19 mothers to help clinicians care for newborns using limited data published before March 30, 2020.
- Neonates should be considered persons under investigation (PUIs) if they are born to mothers with diagnosed COVID-19 or with COVID-19 tests pending at the time of delivery.
- Neonatal clinicians should attend deliveries based on their center’s policies. If clinicians are required to perform stabilization they should use airborne, droplet, and contact personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes, gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and N95 respirator mask or an air-purifying respirator.
- Mother and newborn should be separated to minimize the infant’s risk of postnatal infection.
- Well newborns born at or near term may be admitted to areas physically separated from newborns unaffected by maternal COVID-19. Alternatively, a mother may room-in with her infant with 6 feet of separation between mother and infant. Newborn PUIs should be bathed as soon as possible.
- Newborns requiring intensive care should be admitted to a single negative-pressure room. Alternatively, COVID-19–exposed infants should be grouped with a minimum of 6 feet of separation, or placed in air temperature-controlled isolettes.
- Until the newborn PUI’s virologic status is known, clinical staff caring for the infant should use droplet and contact PPE. This includes gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and a standard surgical mask. Airborne, droplet, and contact precautions should be used for infants requiring CPAP or any form of mechanical ventilation.
- COVID-19–positive mothers who want to breastfeed may feed expressed breast milk using proper breast and hand hygiene or directly breastfeed their infants wearing a mask while practicing proper breast and hand hygiene.
- If testing is available, newborns should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 using molecular arrays. If testing is unavailable, clinicians may monitor newborns clinically. Infants should be tested if they require prolonged intensive care.
- Optimal timing and extent of testing is unknown. Tests should be performed around 24 hours of life and 48 hours of life. If discharge is planned for a well appearing infant before 48 hours of life, the clinician may choose not to do the 48-hour test. A single swab should be taken from the throat followed by the nasopharynx to perform the test.
- Newborns should receive all newborn care, including circumcision if requested.
- Infants who are asymptomatic with positive or pending SARS-CoV-2 tests may be discharged home with plans for frequent outpatient follow-up through 14 days after birth. Infants with negative SARS-CoV-2 testing should be discharged to the care of a noninfected caregiver. If the mother lives in the same household, she must keep a distance of 6 feet as often as possible. When not possible, the mother should wear a mask and practice hand hygiene. The mother may resume caring for her infant normally when she has been afebrile for more than 72 hours (without antipyretics) and has been asymptomatic for 7 days. Alternatively, the mother may resume care if she has two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
- Visitation to infants requiring intensive care should be limited for mothers with COVID-19 until her fever has resolved for more than 72 hours and has improvement of respiratory symptoms and has had two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
Bottom line: Clinicians should protect themselves with contact and droplet PPE at all times until the infant’s viral status is known. Clinicians should use airborne, contact, and droplet PPE when resuscitating the infant and/or when using CPAP/mechanical ventilation. Mothers should be encouraged to feed their infants expressed breast milk while practicing proper hygiene or directly breastfeed while wearing a mask and practicing proper hygiene. Viral testing of every infant born to a mother with COVID-19 should be performed after the infant is 24 hours old. Mothers should resume caring for their infants normally after they have met criteria suggesting they are no longer actively infected.
Article citation: Puopolo KM, Hudak ML, Kimberlin DW, Cummings J. Initial Guidance: Management of Infants born to Mothers with COVID-19. 2020 Apr 2. https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/COVID%2019%20Initial%20Newborn%20Guidance.pdf. Accessed Apr 2, 2020.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Initial guidance for pediatric hospitalists
Initial guidance for pediatric hospitalists
Clinical question: How should we care for newborns born to mothers with COVID-19?
Background: Around the United States, the SARS-CoV-2 virus is infecting pregnant mothers and causing COVID-19. Current limited data demonstrates that children under the age of 1 year are at risk for severe disease. Clinicians are caring for infants born to mothers with COVID-19 during the pandemic with minimal guidance.
Study design: Clinical practice guidelines.
Synopsis: The American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine and Committee of Infectious Diseases developed guidelines of care for infants born to COVID-19 mothers to help clinicians care for newborns using limited data published before March 30, 2020.
- Neonates should be considered persons under investigation (PUIs) if they are born to mothers with diagnosed COVID-19 or with COVID-19 tests pending at the time of delivery.
- Neonatal clinicians should attend deliveries based on their center’s policies. If clinicians are required to perform stabilization they should use airborne, droplet, and contact personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes, gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and N95 respirator mask or an air-purifying respirator.
- Mother and newborn should be separated to minimize the infant’s risk of postnatal infection.
- Well newborns born at or near term may be admitted to areas physically separated from newborns unaffected by maternal COVID-19. Alternatively, a mother may room-in with her infant with 6 feet of separation between mother and infant. Newborn PUIs should be bathed as soon as possible.
- Newborns requiring intensive care should be admitted to a single negative-pressure room. Alternatively, COVID-19–exposed infants should be grouped with a minimum of 6 feet of separation, or placed in air temperature-controlled isolettes.
- Until the newborn PUI’s virologic status is known, clinical staff caring for the infant should use droplet and contact PPE. This includes gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and a standard surgical mask. Airborne, droplet, and contact precautions should be used for infants requiring CPAP or any form of mechanical ventilation.
- COVID-19–positive mothers who want to breastfeed may feed expressed breast milk using proper breast and hand hygiene or directly breastfeed their infants wearing a mask while practicing proper breast and hand hygiene.
- If testing is available, newborns should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 using molecular arrays. If testing is unavailable, clinicians may monitor newborns clinically. Infants should be tested if they require prolonged intensive care.
- Optimal timing and extent of testing is unknown. Tests should be performed around 24 hours of life and 48 hours of life. If discharge is planned for a well appearing infant before 48 hours of life, the clinician may choose not to do the 48-hour test. A single swab should be taken from the throat followed by the nasopharynx to perform the test.
- Newborns should receive all newborn care, including circumcision if requested.
- Infants who are asymptomatic with positive or pending SARS-CoV-2 tests may be discharged home with plans for frequent outpatient follow-up through 14 days after birth. Infants with negative SARS-CoV-2 testing should be discharged to the care of a noninfected caregiver. If the mother lives in the same household, she must keep a distance of 6 feet as often as possible. When not possible, the mother should wear a mask and practice hand hygiene. The mother may resume caring for her infant normally when she has been afebrile for more than 72 hours (without antipyretics) and has been asymptomatic for 7 days. Alternatively, the mother may resume care if she has two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
- Visitation to infants requiring intensive care should be limited for mothers with COVID-19 until her fever has resolved for more than 72 hours and has improvement of respiratory symptoms and has had two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
Bottom line: Clinicians should protect themselves with contact and droplet PPE at all times until the infant’s viral status is known. Clinicians should use airborne, contact, and droplet PPE when resuscitating the infant and/or when using CPAP/mechanical ventilation. Mothers should be encouraged to feed their infants expressed breast milk while practicing proper hygiene or directly breastfeed while wearing a mask and practicing proper hygiene. Viral testing of every infant born to a mother with COVID-19 should be performed after the infant is 24 hours old. Mothers should resume caring for their infants normally after they have met criteria suggesting they are no longer actively infected.
Article citation: Puopolo KM, Hudak ML, Kimberlin DW, Cummings J. Initial Guidance: Management of Infants born to Mothers with COVID-19. 2020 Apr 2. https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/COVID%2019%20Initial%20Newborn%20Guidance.pdf. Accessed Apr 2, 2020.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Clinical question: How should we care for newborns born to mothers with COVID-19?
Background: Around the United States, the SARS-CoV-2 virus is infecting pregnant mothers and causing COVID-19. Current limited data demonstrates that children under the age of 1 year are at risk for severe disease. Clinicians are caring for infants born to mothers with COVID-19 during the pandemic with minimal guidance.
Study design: Clinical practice guidelines.
Synopsis: The American Academy of Pediatrics’ Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine and Committee of Infectious Diseases developed guidelines of care for infants born to COVID-19 mothers to help clinicians care for newborns using limited data published before March 30, 2020.
- Neonates should be considered persons under investigation (PUIs) if they are born to mothers with diagnosed COVID-19 or with COVID-19 tests pending at the time of delivery.
- Neonatal clinicians should attend deliveries based on their center’s policies. If clinicians are required to perform stabilization they should use airborne, droplet, and contact personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes, gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and N95 respirator mask or an air-purifying respirator.
- Mother and newborn should be separated to minimize the infant’s risk of postnatal infection.
- Well newborns born at or near term may be admitted to areas physically separated from newborns unaffected by maternal COVID-19. Alternatively, a mother may room-in with her infant with 6 feet of separation between mother and infant. Newborn PUIs should be bathed as soon as possible.
- Newborns requiring intensive care should be admitted to a single negative-pressure room. Alternatively, COVID-19–exposed infants should be grouped with a minimum of 6 feet of separation, or placed in air temperature-controlled isolettes.
- Until the newborn PUI’s virologic status is known, clinical staff caring for the infant should use droplet and contact PPE. This includes gown, gloves, eye protection (goggles or face shield), and a standard surgical mask. Airborne, droplet, and contact precautions should be used for infants requiring CPAP or any form of mechanical ventilation.
- COVID-19–positive mothers who want to breastfeed may feed expressed breast milk using proper breast and hand hygiene or directly breastfeed their infants wearing a mask while practicing proper breast and hand hygiene.
- If testing is available, newborns should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 using molecular arrays. If testing is unavailable, clinicians may monitor newborns clinically. Infants should be tested if they require prolonged intensive care.
- Optimal timing and extent of testing is unknown. Tests should be performed around 24 hours of life and 48 hours of life. If discharge is planned for a well appearing infant before 48 hours of life, the clinician may choose not to do the 48-hour test. A single swab should be taken from the throat followed by the nasopharynx to perform the test.
- Newborns should receive all newborn care, including circumcision if requested.
- Infants who are asymptomatic with positive or pending SARS-CoV-2 tests may be discharged home with plans for frequent outpatient follow-up through 14 days after birth. Infants with negative SARS-CoV-2 testing should be discharged to the care of a noninfected caregiver. If the mother lives in the same household, she must keep a distance of 6 feet as often as possible. When not possible, the mother should wear a mask and practice hand hygiene. The mother may resume caring for her infant normally when she has been afebrile for more than 72 hours (without antipyretics) and has been asymptomatic for 7 days. Alternatively, the mother may resume care if she has two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
- Visitation to infants requiring intensive care should be limited for mothers with COVID-19 until her fever has resolved for more than 72 hours and has improvement of respiratory symptoms and has had two consecutive negative SARS-CoV-2 nasopharyngeal swabs taken more than 24 hours apart.
Bottom line: Clinicians should protect themselves with contact and droplet PPE at all times until the infant’s viral status is known. Clinicians should use airborne, contact, and droplet PPE when resuscitating the infant and/or when using CPAP/mechanical ventilation. Mothers should be encouraged to feed their infants expressed breast milk while practicing proper hygiene or directly breastfeed while wearing a mask and practicing proper hygiene. Viral testing of every infant born to a mother with COVID-19 should be performed after the infant is 24 hours old. Mothers should resume caring for their infants normally after they have met criteria suggesting they are no longer actively infected.
Article citation: Puopolo KM, Hudak ML, Kimberlin DW, Cummings J. Initial Guidance: Management of Infants born to Mothers with COVID-19. 2020 Apr 2. https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/COVID%2019%20Initial%20Newborn%20Guidance.pdf. Accessed Apr 2, 2020.
Dr. Kumar is a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She is a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and serves as the Pediatrics Editor for The Hospitalist.
Get triage plans in place before COVID-19 surge hits, critical care experts say
, according to authors of recent reports that offer advice on how to prepare for surges in demand.
Even modest numbers of critically ill COVID-19 patients have already rapidly overwhelmed existing hospital capacity in hard-hit areas including Italy, Spain, and New York City, said authors of an expert panel report released in CHEST.
“The ethical burden this places on hospitals, health systems, and society is enormous,” said Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, of the Naval Medical Center in San Diego, lead author of the expert panel report from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
Triage decisions could be especially daunting for resource-intensive therapies such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), as physicians may be forced to decide when and if to offer such support after demand outstrips a hospital’s ability to provide it.
“ECMO requires a lot of specialized capability to initiate on a patient, and then, it requires a lot of specialized capability to maintain and do safely,” said Steven P. Keller, MD, of the division of emergency critical care medicine in the department of emergency medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Those resource requirements can present a challenge to health care systems already overtaxed by COVID-19, according to Dr. Keller, coauthor of a guidance document in Annals of the American Thoracic Society. The guidance suggests a pandemic approach to ECMO response that’s tiered depending on the intensity of the surge over usual hospital volumes.
Mild surges call for a focus on increasing ECMO capacity, while a moderate surge may indicate a need to focus on allocating scarce resources, and a major surge may signal the need to limit or defer use of scarce resources, according to the guidance.
“If your health care system is stretched from a resource standpoint, at what point do you say, ‘we don’t even have the capability to even safely do ECMO, and so, perhaps we should not even be offering the support’?” Dr. Keller said in an interview. “That’s what we tried to get at in the paper – helping institutions think about how to prepare for that pandemic, and then when to make decisions on when it should and should not be offered.”
Critical care guidance for COVID-19
The guidance from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and CHEST offers nine specific actions that authors suggest as part of a framework for communities to establish the infrastructure needed to triage critical care resources and “equitably” meet the needs of the largest number of COVID-19 patients.
“It is the goal of the task force to minimize the need for allocation of scarce resources as much as possible,” the authors stated.
The framework starts with surge planning that includes an inventory of intensive care unit resources such as ventilators, beds, supplies, and staff that could be marshaled to meet a surge in demand, followed by establishing “identification triggers” for triage initiation by a regional authority, should clinical demand reach a crisis stage.
The next step is preparing the triage system, which includes creating a committee at the regional level, identifying members of tertiary triage teams and the support structures they will need, and preparing and distributing training materials.
Agreeing on a triage protocol is important to ensure equitable targeting of resources, and how to allocate limited life-sustaining measures needs to be considered, according to the panel of experts. They also recommend adaptations to the standards of care such as modification of end-of-life care policies, support for health care workers, family, and the public, and consideration of pediatric issues including transport, concentration of care at specific centers, and potential increases in age thresholds to accommodate surges.
Barriers to triage?
When asked about potential barriers to rolling out a triage plan, Dr. Maves said the first is acknowledging the possible need for such a plan: “It is a difficult concept for most in critical care to accept – the idea that we may not be able to provide an individual patient with interventions that we consider routine,” he said.
Beyond acknowledging need, other potential barriers to successful implementation include the limited evidence base to support development of these protocols, as well as the need to address public trust.
“If a triage system is perceived as unjust or biased, or if people think that triage favors or excludes certain groups unfairly, it will undermine any system,” Dr. Maves said. “Making sure the public both understands and has input into system development is critical if we are going to be able to make this work.”
Dr. Maves and coauthors reported that some of the authors of their guidance are United States government employees or military service members, and that their opinions and assertions do not reflect the official views or position of those institutions. Dr. Keller reported no disclosures related to the ECMO guidance.
SOURCES: Maves RC et al. Chest. 2020 Apr 11. pii: S0012-3692(20)30691-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.063; Seethara R and Keller SP. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-233PS.
, according to authors of recent reports that offer advice on how to prepare for surges in demand.
Even modest numbers of critically ill COVID-19 patients have already rapidly overwhelmed existing hospital capacity in hard-hit areas including Italy, Spain, and New York City, said authors of an expert panel report released in CHEST.
“The ethical burden this places on hospitals, health systems, and society is enormous,” said Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, of the Naval Medical Center in San Diego, lead author of the expert panel report from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
Triage decisions could be especially daunting for resource-intensive therapies such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), as physicians may be forced to decide when and if to offer such support after demand outstrips a hospital’s ability to provide it.
“ECMO requires a lot of specialized capability to initiate on a patient, and then, it requires a lot of specialized capability to maintain and do safely,” said Steven P. Keller, MD, of the division of emergency critical care medicine in the department of emergency medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Those resource requirements can present a challenge to health care systems already overtaxed by COVID-19, according to Dr. Keller, coauthor of a guidance document in Annals of the American Thoracic Society. The guidance suggests a pandemic approach to ECMO response that’s tiered depending on the intensity of the surge over usual hospital volumes.
Mild surges call for a focus on increasing ECMO capacity, while a moderate surge may indicate a need to focus on allocating scarce resources, and a major surge may signal the need to limit or defer use of scarce resources, according to the guidance.
“If your health care system is stretched from a resource standpoint, at what point do you say, ‘we don’t even have the capability to even safely do ECMO, and so, perhaps we should not even be offering the support’?” Dr. Keller said in an interview. “That’s what we tried to get at in the paper – helping institutions think about how to prepare for that pandemic, and then when to make decisions on when it should and should not be offered.”
Critical care guidance for COVID-19
The guidance from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and CHEST offers nine specific actions that authors suggest as part of a framework for communities to establish the infrastructure needed to triage critical care resources and “equitably” meet the needs of the largest number of COVID-19 patients.
“It is the goal of the task force to minimize the need for allocation of scarce resources as much as possible,” the authors stated.
The framework starts with surge planning that includes an inventory of intensive care unit resources such as ventilators, beds, supplies, and staff that could be marshaled to meet a surge in demand, followed by establishing “identification triggers” for triage initiation by a regional authority, should clinical demand reach a crisis stage.
The next step is preparing the triage system, which includes creating a committee at the regional level, identifying members of tertiary triage teams and the support structures they will need, and preparing and distributing training materials.
Agreeing on a triage protocol is important to ensure equitable targeting of resources, and how to allocate limited life-sustaining measures needs to be considered, according to the panel of experts. They also recommend adaptations to the standards of care such as modification of end-of-life care policies, support for health care workers, family, and the public, and consideration of pediatric issues including transport, concentration of care at specific centers, and potential increases in age thresholds to accommodate surges.
Barriers to triage?
When asked about potential barriers to rolling out a triage plan, Dr. Maves said the first is acknowledging the possible need for such a plan: “It is a difficult concept for most in critical care to accept – the idea that we may not be able to provide an individual patient with interventions that we consider routine,” he said.
Beyond acknowledging need, other potential barriers to successful implementation include the limited evidence base to support development of these protocols, as well as the need to address public trust.
“If a triage system is perceived as unjust or biased, or if people think that triage favors or excludes certain groups unfairly, it will undermine any system,” Dr. Maves said. “Making sure the public both understands and has input into system development is critical if we are going to be able to make this work.”
Dr. Maves and coauthors reported that some of the authors of their guidance are United States government employees or military service members, and that their opinions and assertions do not reflect the official views or position of those institutions. Dr. Keller reported no disclosures related to the ECMO guidance.
SOURCES: Maves RC et al. Chest. 2020 Apr 11. pii: S0012-3692(20)30691-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.063; Seethara R and Keller SP. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-233PS.
, according to authors of recent reports that offer advice on how to prepare for surges in demand.
Even modest numbers of critically ill COVID-19 patients have already rapidly overwhelmed existing hospital capacity in hard-hit areas including Italy, Spain, and New York City, said authors of an expert panel report released in CHEST.
“The ethical burden this places on hospitals, health systems, and society is enormous,” said Ryan C. Maves, MD, FCCP, of the Naval Medical Center in San Diego, lead author of the expert panel report from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST).
Triage decisions could be especially daunting for resource-intensive therapies such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), as physicians may be forced to decide when and if to offer such support after demand outstrips a hospital’s ability to provide it.
“ECMO requires a lot of specialized capability to initiate on a patient, and then, it requires a lot of specialized capability to maintain and do safely,” said Steven P. Keller, MD, of the division of emergency critical care medicine in the department of emergency medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
Those resource requirements can present a challenge to health care systems already overtaxed by COVID-19, according to Dr. Keller, coauthor of a guidance document in Annals of the American Thoracic Society. The guidance suggests a pandemic approach to ECMO response that’s tiered depending on the intensity of the surge over usual hospital volumes.
Mild surges call for a focus on increasing ECMO capacity, while a moderate surge may indicate a need to focus on allocating scarce resources, and a major surge may signal the need to limit or defer use of scarce resources, according to the guidance.
“If your health care system is stretched from a resource standpoint, at what point do you say, ‘we don’t even have the capability to even safely do ECMO, and so, perhaps we should not even be offering the support’?” Dr. Keller said in an interview. “That’s what we tried to get at in the paper – helping institutions think about how to prepare for that pandemic, and then when to make decisions on when it should and should not be offered.”
Critical care guidance for COVID-19
The guidance from the Task Force for Mass Critical Care and CHEST offers nine specific actions that authors suggest as part of a framework for communities to establish the infrastructure needed to triage critical care resources and “equitably” meet the needs of the largest number of COVID-19 patients.
“It is the goal of the task force to minimize the need for allocation of scarce resources as much as possible,” the authors stated.
The framework starts with surge planning that includes an inventory of intensive care unit resources such as ventilators, beds, supplies, and staff that could be marshaled to meet a surge in demand, followed by establishing “identification triggers” for triage initiation by a regional authority, should clinical demand reach a crisis stage.
The next step is preparing the triage system, which includes creating a committee at the regional level, identifying members of tertiary triage teams and the support structures they will need, and preparing and distributing training materials.
Agreeing on a triage protocol is important to ensure equitable targeting of resources, and how to allocate limited life-sustaining measures needs to be considered, according to the panel of experts. They also recommend adaptations to the standards of care such as modification of end-of-life care policies, support for health care workers, family, and the public, and consideration of pediatric issues including transport, concentration of care at specific centers, and potential increases in age thresholds to accommodate surges.
Barriers to triage?
When asked about potential barriers to rolling out a triage plan, Dr. Maves said the first is acknowledging the possible need for such a plan: “It is a difficult concept for most in critical care to accept – the idea that we may not be able to provide an individual patient with interventions that we consider routine,” he said.
Beyond acknowledging need, other potential barriers to successful implementation include the limited evidence base to support development of these protocols, as well as the need to address public trust.
“If a triage system is perceived as unjust or biased, or if people think that triage favors or excludes certain groups unfairly, it will undermine any system,” Dr. Maves said. “Making sure the public both understands and has input into system development is critical if we are going to be able to make this work.”
Dr. Maves and coauthors reported that some of the authors of their guidance are United States government employees or military service members, and that their opinions and assertions do not reflect the official views or position of those institutions. Dr. Keller reported no disclosures related to the ECMO guidance.
SOURCES: Maves RC et al. Chest. 2020 Apr 11. pii: S0012-3692(20)30691-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.063; Seethara R and Keller SP. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-233PS.
FROM CHEST AND ANNALS OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY
ACEI/ARBs linked with survival in hypertensive, Chinese COVID-19 patients
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension and on treatment with an renin-angiotensin system inhibiting drug had significantly better survival, compared with similar hypertensive patients not on these drugs, in observational, propensity score–matched analyses that drew from a pool of more than 3,430 patients hospitalized at any of nine Chinese hospitals during December 2019–February 2020.
“Among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, inpatient treatment with ACEI [ACE inhibitor]/ARB [angiotensin receptor blocker] was associated with lower risk of all-cause mortality, compared with ACEI/ARB nonusers, during 28 days of follow-up. While study interpretation needs to consider the potential for residual confounders, it is unlikely that inpatient ACEI/ARB would be associated with an increased risk of mortality,” wrote Peng Zhang, MD, a cardiology researcher at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, China, and coauthors in Circulations Research, buttressing recent recommendations from several medical societies to maintain COVID-19 patients on these drugs.
“Our findings in this paper provide evidence supporting continuous use of ACEI/ARB for patients with hypertension infected with SARS-COV-2,” wrote the authors, backing up recent recommendations from cardiology societies that called for not stopping ACEI/ARB prescriptions in patients at risk for contracting or already have COVID-19 infection, including a statement from the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Heart Failure Society of America, and also guidance from the European Society of Cardiology.
The study included 1,128 patients with a history of hypertension, including 188 (17%) who received an ACEI/ARB drug during hospitalization. During 28-day follow-up, 99 died (9%), including 7 deaths among the 188 patients (4%) on an ACEI/ARB drug and 92 deaths among the 940 other hypertensive patients (10%).
The authors ran several analyses to try to adjust for the influence of possible confounders. A mixed-effect Cox model with four adjusted variables showed that treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was tied to a statistically significant 58% lower death rate, compared with patients not receiving these drugs.
The researchers also ran several propensity score–adjusted analyses. One matched 174 of the patients who received an ACEI/ARB drug with 522 who did not, and comparing these two matched arms showed that ACEI/ARB use was linked with a statistically significant 63% cut in mortality, compared with patients not getting these drugs. A second propensity score–matched analysis first excluded the 383 patients who were hypertensive but received no antihypertensive medication during hospitalization. From the remaining 745 patients who received at least one antihypertensive medication, the authors identified 181 patients who received an ACEI/ARB and propensity-score matched them with 181 hypertensive patients on a different medication class, finding that ACEI/ARB use linked with a statistically significant 71% lower rate of all-cause mortality.
Additional analyses also showed that patients with hypertension had a statistically significant, 41% increased rate of all-cause death, compared with patients without hypertension, and another propensity score–matched analysis showed that among hypertensives treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of septic shock.
Although this report was received with caution and some skepticism, it was also acknowledged as a step forward in the creation of an evidence base addressing ACEI/ARB treatment during COVID-19 infection.
“These drugs are lifesaving and should not be discontinued” for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular disease, commented Gian Paolo Rossi, MD, professor and chair of medicine and director of the high blood pressure unit at the University of Padua (Italy). The analysis by Zhang and associates included the largest number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension yet reported to assess the impact of treatment with ACEI/ARB drugs, and adds important evidence in favor of continuing these drugs in patients who develop COVID-19 infection, Dr. Rossi said in an interview. He recently coauthored a review that argued against ACEI/ARB discontinuation in COVID-19 patients based on previously reported evidence (Elife. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57278).
But other researchers take a wary view of the potential impact of ACEI/ARB agents. “If ACEI/ARB therapy increases ACE2 and the virus down-regulates it, and because ACE2 is the viral entry port into cells, why would ACE2-mediated down-regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system lead to amelioration of [COVID-19] disease?” asked Laurence W. Busse, MD, a critical care physician at Emory University, Atlanta. “A number of issues could potentially confound the results, including the definition of COVID-19 and imbalance of antiviral therapy,” added Dr. Busse, who recently coauthored an editorial that posited using angiotensin II (Giapreza), an approved vasopressor drug, as an alternative renin-angiotensin system intervention for COVID-19 patients including both those in shock as well as potentially those not in shock (Crit Care. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02862-1). Despite these caveats, the new Chinese findings reported by Dr. Zhang and associates “are hypothesis generating and worth further exploration.”
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the Zhang study in Circulation Research made similar points. “While the investigators used standard techniques to attempt to reduce bias in this observational study via propensity matching, it is not a randomized study and the residual confounding inherent to this approach renders the conclusions hypothesis generating at best,” wrote Ravi V. Shah, MD, and two coauthors in the editorial (Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317174). They also agreed with the several society statements that have supported continued use of ACEI/ARB drugs in COVID-19 patients. “Withdrawal of these medications in the context of those conditions in which they have proven benefit (e.g., heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction) may actually inflict more harm than good,” they warned. “In the end we must rely on randomized clinical science,” and while this level of evidence is currently lacking, “the study by Zhang and colleagues is a direct step toward that goal.”
Dr. Zhang and coauthors had no commercial disclosures. Dr. Rossi and Dr. Busse had no disclosures. The authors of the Circulation Research editorial reported several disclosures.
SOURCE: Zhang P et al. Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension and on treatment with an renin-angiotensin system inhibiting drug had significantly better survival, compared with similar hypertensive patients not on these drugs, in observational, propensity score–matched analyses that drew from a pool of more than 3,430 patients hospitalized at any of nine Chinese hospitals during December 2019–February 2020.
“Among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, inpatient treatment with ACEI [ACE inhibitor]/ARB [angiotensin receptor blocker] was associated with lower risk of all-cause mortality, compared with ACEI/ARB nonusers, during 28 days of follow-up. While study interpretation needs to consider the potential for residual confounders, it is unlikely that inpatient ACEI/ARB would be associated with an increased risk of mortality,” wrote Peng Zhang, MD, a cardiology researcher at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, China, and coauthors in Circulations Research, buttressing recent recommendations from several medical societies to maintain COVID-19 patients on these drugs.
“Our findings in this paper provide evidence supporting continuous use of ACEI/ARB for patients with hypertension infected with SARS-COV-2,” wrote the authors, backing up recent recommendations from cardiology societies that called for not stopping ACEI/ARB prescriptions in patients at risk for contracting or already have COVID-19 infection, including a statement from the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Heart Failure Society of America, and also guidance from the European Society of Cardiology.
The study included 1,128 patients with a history of hypertension, including 188 (17%) who received an ACEI/ARB drug during hospitalization. During 28-day follow-up, 99 died (9%), including 7 deaths among the 188 patients (4%) on an ACEI/ARB drug and 92 deaths among the 940 other hypertensive patients (10%).
The authors ran several analyses to try to adjust for the influence of possible confounders. A mixed-effect Cox model with four adjusted variables showed that treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was tied to a statistically significant 58% lower death rate, compared with patients not receiving these drugs.
The researchers also ran several propensity score–adjusted analyses. One matched 174 of the patients who received an ACEI/ARB drug with 522 who did not, and comparing these two matched arms showed that ACEI/ARB use was linked with a statistically significant 63% cut in mortality, compared with patients not getting these drugs. A second propensity score–matched analysis first excluded the 383 patients who were hypertensive but received no antihypertensive medication during hospitalization. From the remaining 745 patients who received at least one antihypertensive medication, the authors identified 181 patients who received an ACEI/ARB and propensity-score matched them with 181 hypertensive patients on a different medication class, finding that ACEI/ARB use linked with a statistically significant 71% lower rate of all-cause mortality.
Additional analyses also showed that patients with hypertension had a statistically significant, 41% increased rate of all-cause death, compared with patients without hypertension, and another propensity score–matched analysis showed that among hypertensives treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of septic shock.
Although this report was received with caution and some skepticism, it was also acknowledged as a step forward in the creation of an evidence base addressing ACEI/ARB treatment during COVID-19 infection.
“These drugs are lifesaving and should not be discontinued” for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular disease, commented Gian Paolo Rossi, MD, professor and chair of medicine and director of the high blood pressure unit at the University of Padua (Italy). The analysis by Zhang and associates included the largest number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension yet reported to assess the impact of treatment with ACEI/ARB drugs, and adds important evidence in favor of continuing these drugs in patients who develop COVID-19 infection, Dr. Rossi said in an interview. He recently coauthored a review that argued against ACEI/ARB discontinuation in COVID-19 patients based on previously reported evidence (Elife. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57278).
But other researchers take a wary view of the potential impact of ACEI/ARB agents. “If ACEI/ARB therapy increases ACE2 and the virus down-regulates it, and because ACE2 is the viral entry port into cells, why would ACE2-mediated down-regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system lead to amelioration of [COVID-19] disease?” asked Laurence W. Busse, MD, a critical care physician at Emory University, Atlanta. “A number of issues could potentially confound the results, including the definition of COVID-19 and imbalance of antiviral therapy,” added Dr. Busse, who recently coauthored an editorial that posited using angiotensin II (Giapreza), an approved vasopressor drug, as an alternative renin-angiotensin system intervention for COVID-19 patients including both those in shock as well as potentially those not in shock (Crit Care. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02862-1). Despite these caveats, the new Chinese findings reported by Dr. Zhang and associates “are hypothesis generating and worth further exploration.”
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the Zhang study in Circulation Research made similar points. “While the investigators used standard techniques to attempt to reduce bias in this observational study via propensity matching, it is not a randomized study and the residual confounding inherent to this approach renders the conclusions hypothesis generating at best,” wrote Ravi V. Shah, MD, and two coauthors in the editorial (Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317174). They also agreed with the several society statements that have supported continued use of ACEI/ARB drugs in COVID-19 patients. “Withdrawal of these medications in the context of those conditions in which they have proven benefit (e.g., heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction) may actually inflict more harm than good,” they warned. “In the end we must rely on randomized clinical science,” and while this level of evidence is currently lacking, “the study by Zhang and colleagues is a direct step toward that goal.”
Dr. Zhang and coauthors had no commercial disclosures. Dr. Rossi and Dr. Busse had no disclosures. The authors of the Circulation Research editorial reported several disclosures.
SOURCE: Zhang P et al. Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension and on treatment with an renin-angiotensin system inhibiting drug had significantly better survival, compared with similar hypertensive patients not on these drugs, in observational, propensity score–matched analyses that drew from a pool of more than 3,430 patients hospitalized at any of nine Chinese hospitals during December 2019–February 2020.
“Among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, inpatient treatment with ACEI [ACE inhibitor]/ARB [angiotensin receptor blocker] was associated with lower risk of all-cause mortality, compared with ACEI/ARB nonusers, during 28 days of follow-up. While study interpretation needs to consider the potential for residual confounders, it is unlikely that inpatient ACEI/ARB would be associated with an increased risk of mortality,” wrote Peng Zhang, MD, a cardiology researcher at Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, China, and coauthors in Circulations Research, buttressing recent recommendations from several medical societies to maintain COVID-19 patients on these drugs.
“Our findings in this paper provide evidence supporting continuous use of ACEI/ARB for patients with hypertension infected with SARS-COV-2,” wrote the authors, backing up recent recommendations from cardiology societies that called for not stopping ACEI/ARB prescriptions in patients at risk for contracting or already have COVID-19 infection, including a statement from the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Heart Failure Society of America, and also guidance from the European Society of Cardiology.
The study included 1,128 patients with a history of hypertension, including 188 (17%) who received an ACEI/ARB drug during hospitalization. During 28-day follow-up, 99 died (9%), including 7 deaths among the 188 patients (4%) on an ACEI/ARB drug and 92 deaths among the 940 other hypertensive patients (10%).
The authors ran several analyses to try to adjust for the influence of possible confounders. A mixed-effect Cox model with four adjusted variables showed that treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was tied to a statistically significant 58% lower death rate, compared with patients not receiving these drugs.
The researchers also ran several propensity score–adjusted analyses. One matched 174 of the patients who received an ACEI/ARB drug with 522 who did not, and comparing these two matched arms showed that ACEI/ARB use was linked with a statistically significant 63% cut in mortality, compared with patients not getting these drugs. A second propensity score–matched analysis first excluded the 383 patients who were hypertensive but received no antihypertensive medication during hospitalization. From the remaining 745 patients who received at least one antihypertensive medication, the authors identified 181 patients who received an ACEI/ARB and propensity-score matched them with 181 hypertensive patients on a different medication class, finding that ACEI/ARB use linked with a statistically significant 71% lower rate of all-cause mortality.
Additional analyses also showed that patients with hypertension had a statistically significant, 41% increased rate of all-cause death, compared with patients without hypertension, and another propensity score–matched analysis showed that among hypertensives treatment with an ACEI/ARB drug was linked with a statistically significant 68% reduced rate of septic shock.
Although this report was received with caution and some skepticism, it was also acknowledged as a step forward in the creation of an evidence base addressing ACEI/ARB treatment during COVID-19 infection.
“These drugs are lifesaving and should not be discontinued” for patients with hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular disease, commented Gian Paolo Rossi, MD, professor and chair of medicine and director of the high blood pressure unit at the University of Padua (Italy). The analysis by Zhang and associates included the largest number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with hypertension yet reported to assess the impact of treatment with ACEI/ARB drugs, and adds important evidence in favor of continuing these drugs in patients who develop COVID-19 infection, Dr. Rossi said in an interview. He recently coauthored a review that argued against ACEI/ARB discontinuation in COVID-19 patients based on previously reported evidence (Elife. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57278).
But other researchers take a wary view of the potential impact of ACEI/ARB agents. “If ACEI/ARB therapy increases ACE2 and the virus down-regulates it, and because ACE2 is the viral entry port into cells, why would ACE2-mediated down-regulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system lead to amelioration of [COVID-19] disease?” asked Laurence W. Busse, MD, a critical care physician at Emory University, Atlanta. “A number of issues could potentially confound the results, including the definition of COVID-19 and imbalance of antiviral therapy,” added Dr. Busse, who recently coauthored an editorial that posited using angiotensin II (Giapreza), an approved vasopressor drug, as an alternative renin-angiotensin system intervention for COVID-19 patients including both those in shock as well as potentially those not in shock (Crit Care. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02862-1). Despite these caveats, the new Chinese findings reported by Dr. Zhang and associates “are hypothesis generating and worth further exploration.”
The authors of an editorial that accompanied the Zhang study in Circulation Research made similar points. “While the investigators used standard techniques to attempt to reduce bias in this observational study via propensity matching, it is not a randomized study and the residual confounding inherent to this approach renders the conclusions hypothesis generating at best,” wrote Ravi V. Shah, MD, and two coauthors in the editorial (Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317174). They also agreed with the several society statements that have supported continued use of ACEI/ARB drugs in COVID-19 patients. “Withdrawal of these medications in the context of those conditions in which they have proven benefit (e.g., heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction) may actually inflict more harm than good,” they warned. “In the end we must rely on randomized clinical science,” and while this level of evidence is currently lacking, “the study by Zhang and colleagues is a direct step toward that goal.”
Dr. Zhang and coauthors had no commercial disclosures. Dr. Rossi and Dr. Busse had no disclosures. The authors of the Circulation Research editorial reported several disclosures.
SOURCE: Zhang P et al. Circ Res. 2020 Apr 17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134.
FROM CIRCULATION RESEARCH
Transitions: From editor to president
As I transition out of the role of medical editor for The Hospitalist, and into the role of president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, it is a bittersweet but exciting transition.
In the relatively short time I have served as editor, so much has changed in our hospitalist community! In the last 4 years alone, we have increased:
• Membership from 14,000 to 20,000
• Chapters from 46 to 68
• Special Interest Groups from 8 to 22
• Subscribers to The Hospitalist from 15,000 to 30,000.
This is all a testimony to the engagement of our membership. SHM is clearly no ordinary specialty society; it is full of incredibly intelligent, invested, and talented members, who actively participate in the society for the betterment of their local teams and patients. It is such a privilege to lead this amazing team.
As for The Hospitalist, I would like to warmly welcome Weijen Chang, MD, FACP, SFHM, as the incoming editor. Weijen served as the pediatrics editor for many years and has been extensively involved on The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board for even longer. He also has a broad track record of experience as a hospitalist in many settings; that combined with an inquisitive mind and curious spirit makes him the ideal editor for The Hospitalist. He brings energy and enthusiasm and will serve us very well.
While I will miss being intimately involved with The Hospitalist, I am very much looking forward to serving in the role of SHM president starting in April. During this pivotal year, SHM will transition from our one-and-only CEO, Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, to our newly minted CEO Eric Howell, MD, MHM, who will officially transition in July 2020.
This is a very exciting time in the history of SHM, as we refocus on our mission, vision, values, and core activities. As a membership organization, our primary focus has been, and will always be, serving our member’s needs! As a “Big Tent” organization, we have always supported a broad and diverse set of members, ranging far beyond physician hospitalists, to trainees, medical students, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, practice administrators, and other hospital-based specialists. Being in such a dynamic industry, our diverse members needs are constantly and rapidly changing along with the dramatic transformations in the landscape, including profound shifts in care and reimbursement models that could change the very definition of a hospitalist.
While we continuously scour the landscape and anticipate our members’ needs, we will never lose sight of our core mission, which is to promote exceptional care for hospitalized patients. We will continue to do this by supporting all of our members with tools and materials to help them be the very best they can, for all of our patients. As a humble and servant leader, I am prepared to meet the demands and challenges of the year ahead, with energy and focus, and fulfill the needs of our members, so that together, we can make health care better for those we serve.
Thank you in advance for allowing me the great pleasure of serving this amazing and innovative organization!
Dr. Scheurer is chief quality officer and professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing medical editor of The Hospitalist, and president-elect of SHM.
As I transition out of the role of medical editor for The Hospitalist, and into the role of president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, it is a bittersweet but exciting transition.
In the relatively short time I have served as editor, so much has changed in our hospitalist community! In the last 4 years alone, we have increased:
• Membership from 14,000 to 20,000
• Chapters from 46 to 68
• Special Interest Groups from 8 to 22
• Subscribers to The Hospitalist from 15,000 to 30,000.
This is all a testimony to the engagement of our membership. SHM is clearly no ordinary specialty society; it is full of incredibly intelligent, invested, and talented members, who actively participate in the society for the betterment of their local teams and patients. It is such a privilege to lead this amazing team.
As for The Hospitalist, I would like to warmly welcome Weijen Chang, MD, FACP, SFHM, as the incoming editor. Weijen served as the pediatrics editor for many years and has been extensively involved on The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board for even longer. He also has a broad track record of experience as a hospitalist in many settings; that combined with an inquisitive mind and curious spirit makes him the ideal editor for The Hospitalist. He brings energy and enthusiasm and will serve us very well.
While I will miss being intimately involved with The Hospitalist, I am very much looking forward to serving in the role of SHM president starting in April. During this pivotal year, SHM will transition from our one-and-only CEO, Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, to our newly minted CEO Eric Howell, MD, MHM, who will officially transition in July 2020.
This is a very exciting time in the history of SHM, as we refocus on our mission, vision, values, and core activities. As a membership organization, our primary focus has been, and will always be, serving our member’s needs! As a “Big Tent” organization, we have always supported a broad and diverse set of members, ranging far beyond physician hospitalists, to trainees, medical students, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, practice administrators, and other hospital-based specialists. Being in such a dynamic industry, our diverse members needs are constantly and rapidly changing along with the dramatic transformations in the landscape, including profound shifts in care and reimbursement models that could change the very definition of a hospitalist.
While we continuously scour the landscape and anticipate our members’ needs, we will never lose sight of our core mission, which is to promote exceptional care for hospitalized patients. We will continue to do this by supporting all of our members with tools and materials to help them be the very best they can, for all of our patients. As a humble and servant leader, I am prepared to meet the demands and challenges of the year ahead, with energy and focus, and fulfill the needs of our members, so that together, we can make health care better for those we serve.
Thank you in advance for allowing me the great pleasure of serving this amazing and innovative organization!
Dr. Scheurer is chief quality officer and professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing medical editor of The Hospitalist, and president-elect of SHM.
As I transition out of the role of medical editor for The Hospitalist, and into the role of president of the Society of Hospital Medicine, it is a bittersweet but exciting transition.
In the relatively short time I have served as editor, so much has changed in our hospitalist community! In the last 4 years alone, we have increased:
• Membership from 14,000 to 20,000
• Chapters from 46 to 68
• Special Interest Groups from 8 to 22
• Subscribers to The Hospitalist from 15,000 to 30,000.
This is all a testimony to the engagement of our membership. SHM is clearly no ordinary specialty society; it is full of incredibly intelligent, invested, and talented members, who actively participate in the society for the betterment of their local teams and patients. It is such a privilege to lead this amazing team.
As for The Hospitalist, I would like to warmly welcome Weijen Chang, MD, FACP, SFHM, as the incoming editor. Weijen served as the pediatrics editor for many years and has been extensively involved on The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board for even longer. He also has a broad track record of experience as a hospitalist in many settings; that combined with an inquisitive mind and curious spirit makes him the ideal editor for The Hospitalist. He brings energy and enthusiasm and will serve us very well.
While I will miss being intimately involved with The Hospitalist, I am very much looking forward to serving in the role of SHM president starting in April. During this pivotal year, SHM will transition from our one-and-only CEO, Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM, to our newly minted CEO Eric Howell, MD, MHM, who will officially transition in July 2020.
This is a very exciting time in the history of SHM, as we refocus on our mission, vision, values, and core activities. As a membership organization, our primary focus has been, and will always be, serving our member’s needs! As a “Big Tent” organization, we have always supported a broad and diverse set of members, ranging far beyond physician hospitalists, to trainees, medical students, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, practice administrators, and other hospital-based specialists. Being in such a dynamic industry, our diverse members needs are constantly and rapidly changing along with the dramatic transformations in the landscape, including profound shifts in care and reimbursement models that could change the very definition of a hospitalist.
While we continuously scour the landscape and anticipate our members’ needs, we will never lose sight of our core mission, which is to promote exceptional care for hospitalized patients. We will continue to do this by supporting all of our members with tools and materials to help them be the very best they can, for all of our patients. As a humble and servant leader, I am prepared to meet the demands and challenges of the year ahead, with energy and focus, and fulfill the needs of our members, so that together, we can make health care better for those we serve.
Thank you in advance for allowing me the great pleasure of serving this amazing and innovative organization!
Dr. Scheurer is chief quality officer and professor of medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston. She is the outgoing medical editor of The Hospitalist, and president-elect of SHM.
COVID-19 strikes hard at state-run veterans nursing homes
In early March, 35 residents in the Life Care Center in Kirkland, Washington, died due to complications associated with COVID-19. And that facility thus became the first example of how extremely vulnerable nursing home residents are to COVID-19. Since then, around the US, thousands of nursing home residents have died from complications of the virus. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) nursing homes, while rated high in VA health inspection reports, have not been exempt.
As of April 21, the VA had confirmed > 5,500 coronavirus cases in 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. More than 350 veterans have died of COVID-19, according to VA data. The VA calculates its rates by health care system or VA medical center and does not provide separate data for the community living centers (CLCs).
The VA initiated an isolation strategy on March 10 that suspended most new admissions and barred outsiders from all of its 134 nursing homes. The only exception to the rule was when a patient was expected to die soon. The VA has taken other precautions as well, including extra screening and directing patients to use telehealth where possible.
State-run long-term care facilities for veterans have been hard hit across the country. At the Soldiers’ Home in Holyoke, Massachusetts, which is run by the state of Massachusetts, 5 of 11 veterans who died recently tested positive for COVID-19. At the 4 state-run nursing homes in Alabama, as of April 14, 45 people were confirmed positive and 2 residents had died. The largest outbreak was in the Bill Nichols State Veterans Home in Alexander City. Alabama State Rep. Ed Oliver and Commissioner Kent Davis, of the Alabama Department of Veterans Affairs (ADVA), are looking into how the outbreak started and whether it could have been prevented. “We have reports of lack of hand sanitizers, and those are the things we’re looking at right now,” Rep. Oliver said. The ADVA says residents who test positive are isolated for treatment, and infected employees are prohibited from entering the homes.
States have deployed National Guard troops to facilities following large scale outbreaks and multiple deaths. Pennsylvania deployed 30 National Guard troops to its Southeastern Veterans Center facility in Spring City after at least 10 veterans had died and at least 19 health care workers had tested positive for the virus. The facility is 1 of 6 extended-care facilities run by the Pennsylvania Department of Military and Veterans Affairs. In New Jersey, 40 National Guard troops, 25 New Jersey Department of Health nurses, and 90 VA nurses were deployed to 2 of its veterans facilities amid worsening outbreaks. At the Paramus facility, 155 residents had tested positive and 39 had died, and at the home in Edison, 86 veterans had tested positive and 25 died; 6 more died at a third state facility.
However, reporting remains inconsistent across many states and facilities. Only on April 19 did the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) order nursing home facilities to inform residents and families about COVID-19 cases inside. This followed similar orders in New Jersey, New York, California, Washington, and other states.
“Nursing homes have been ground zero for COVID-19,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in a written statement. “Nursing home reporting to the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] is a critical component of the go-forward national COVID-19 surveillance system and to efforts to reopen America.”
In early March, 35 residents in the Life Care Center in Kirkland, Washington, died due to complications associated with COVID-19. And that facility thus became the first example of how extremely vulnerable nursing home residents are to COVID-19. Since then, around the US, thousands of nursing home residents have died from complications of the virus. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) nursing homes, while rated high in VA health inspection reports, have not been exempt.
As of April 21, the VA had confirmed > 5,500 coronavirus cases in 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. More than 350 veterans have died of COVID-19, according to VA data. The VA calculates its rates by health care system or VA medical center and does not provide separate data for the community living centers (CLCs).
The VA initiated an isolation strategy on March 10 that suspended most new admissions and barred outsiders from all of its 134 nursing homes. The only exception to the rule was when a patient was expected to die soon. The VA has taken other precautions as well, including extra screening and directing patients to use telehealth where possible.
State-run long-term care facilities for veterans have been hard hit across the country. At the Soldiers’ Home in Holyoke, Massachusetts, which is run by the state of Massachusetts, 5 of 11 veterans who died recently tested positive for COVID-19. At the 4 state-run nursing homes in Alabama, as of April 14, 45 people were confirmed positive and 2 residents had died. The largest outbreak was in the Bill Nichols State Veterans Home in Alexander City. Alabama State Rep. Ed Oliver and Commissioner Kent Davis, of the Alabama Department of Veterans Affairs (ADVA), are looking into how the outbreak started and whether it could have been prevented. “We have reports of lack of hand sanitizers, and those are the things we’re looking at right now,” Rep. Oliver said. The ADVA says residents who test positive are isolated for treatment, and infected employees are prohibited from entering the homes.
States have deployed National Guard troops to facilities following large scale outbreaks and multiple deaths. Pennsylvania deployed 30 National Guard troops to its Southeastern Veterans Center facility in Spring City after at least 10 veterans had died and at least 19 health care workers had tested positive for the virus. The facility is 1 of 6 extended-care facilities run by the Pennsylvania Department of Military and Veterans Affairs. In New Jersey, 40 National Guard troops, 25 New Jersey Department of Health nurses, and 90 VA nurses were deployed to 2 of its veterans facilities amid worsening outbreaks. At the Paramus facility, 155 residents had tested positive and 39 had died, and at the home in Edison, 86 veterans had tested positive and 25 died; 6 more died at a third state facility.
However, reporting remains inconsistent across many states and facilities. Only on April 19 did the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) order nursing home facilities to inform residents and families about COVID-19 cases inside. This followed similar orders in New Jersey, New York, California, Washington, and other states.
“Nursing homes have been ground zero for COVID-19,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in a written statement. “Nursing home reporting to the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] is a critical component of the go-forward national COVID-19 surveillance system and to efforts to reopen America.”
In early March, 35 residents in the Life Care Center in Kirkland, Washington, died due to complications associated with COVID-19. And that facility thus became the first example of how extremely vulnerable nursing home residents are to COVID-19. Since then, around the US, thousands of nursing home residents have died from complications of the virus. US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) nursing homes, while rated high in VA health inspection reports, have not been exempt.
As of April 21, the VA had confirmed > 5,500 coronavirus cases in 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. More than 350 veterans have died of COVID-19, according to VA data. The VA calculates its rates by health care system or VA medical center and does not provide separate data for the community living centers (CLCs).
The VA initiated an isolation strategy on March 10 that suspended most new admissions and barred outsiders from all of its 134 nursing homes. The only exception to the rule was when a patient was expected to die soon. The VA has taken other precautions as well, including extra screening and directing patients to use telehealth where possible.
State-run long-term care facilities for veterans have been hard hit across the country. At the Soldiers’ Home in Holyoke, Massachusetts, which is run by the state of Massachusetts, 5 of 11 veterans who died recently tested positive for COVID-19. At the 4 state-run nursing homes in Alabama, as of April 14, 45 people were confirmed positive and 2 residents had died. The largest outbreak was in the Bill Nichols State Veterans Home in Alexander City. Alabama State Rep. Ed Oliver and Commissioner Kent Davis, of the Alabama Department of Veterans Affairs (ADVA), are looking into how the outbreak started and whether it could have been prevented. “We have reports of lack of hand sanitizers, and those are the things we’re looking at right now,” Rep. Oliver said. The ADVA says residents who test positive are isolated for treatment, and infected employees are prohibited from entering the homes.
States have deployed National Guard troops to facilities following large scale outbreaks and multiple deaths. Pennsylvania deployed 30 National Guard troops to its Southeastern Veterans Center facility in Spring City after at least 10 veterans had died and at least 19 health care workers had tested positive for the virus. The facility is 1 of 6 extended-care facilities run by the Pennsylvania Department of Military and Veterans Affairs. In New Jersey, 40 National Guard troops, 25 New Jersey Department of Health nurses, and 90 VA nurses were deployed to 2 of its veterans facilities amid worsening outbreaks. At the Paramus facility, 155 residents had tested positive and 39 had died, and at the home in Edison, 86 veterans had tested positive and 25 died; 6 more died at a third state facility.
However, reporting remains inconsistent across many states and facilities. Only on April 19 did the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) order nursing home facilities to inform residents and families about COVID-19 cases inside. This followed similar orders in New Jersey, New York, California, Washington, and other states.
“Nursing homes have been ground zero for COVID-19,” said CMS Administrator Seema Verma in a written statement. “Nursing home reporting to the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] is a critical component of the go-forward national COVID-19 surveillance system and to efforts to reopen America.”
Mislabeled clopidogrel lot recalled, may contain simvastatin
International Laboratories has initiated a voluntary recall to the consumer level in the United States of a single lot of the antiplatelet clopidogrel because it is mislabeled and may contain simvastatin, a cholesterol-lowering drug, instead of clopidogrel.
The recalled product ― lot number 117099A of clopidogrel tablets (USP 75 mg) packaged in bottles of 30 tablets ― may contain clopidogrel 75 mg tablets or it could contain simvastatin tablets (USP 10 mg), according to a company announcement posted on the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website.
“Missed doses of clopidogrel increases the risk of heart attack and stroke which can be life threatening. Additionally, unintentional consumption of simvastatin could include the common side effects associated with its use and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman,” the company cautions.
To date, the company has not received any reports of harm arising from the problem that prompted the recall.
The recalled product was distributed nationwide and was delivered to distribution centers in Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, California, and Maryland and to retail stores in all US states.
International Laboratories is notifying distributors and customers by letter and is arranging for the return of all recalled products.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Inmar by phone 855-258-7280 (weekdays between 9:00 AM and 5:00 PM EST) or by email at [email protected].
Adverse reactions or quality problems experienced with the use of this product should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch adverse event reporting program.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
International Laboratories has initiated a voluntary recall to the consumer level in the United States of a single lot of the antiplatelet clopidogrel because it is mislabeled and may contain simvastatin, a cholesterol-lowering drug, instead of clopidogrel.
The recalled product ― lot number 117099A of clopidogrel tablets (USP 75 mg) packaged in bottles of 30 tablets ― may contain clopidogrel 75 mg tablets or it could contain simvastatin tablets (USP 10 mg), according to a company announcement posted on the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website.
“Missed doses of clopidogrel increases the risk of heart attack and stroke which can be life threatening. Additionally, unintentional consumption of simvastatin could include the common side effects associated with its use and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman,” the company cautions.
To date, the company has not received any reports of harm arising from the problem that prompted the recall.
The recalled product was distributed nationwide and was delivered to distribution centers in Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, California, and Maryland and to retail stores in all US states.
International Laboratories is notifying distributors and customers by letter and is arranging for the return of all recalled products.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Inmar by phone 855-258-7280 (weekdays between 9:00 AM and 5:00 PM EST) or by email at [email protected].
Adverse reactions or quality problems experienced with the use of this product should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch adverse event reporting program.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
International Laboratories has initiated a voluntary recall to the consumer level in the United States of a single lot of the antiplatelet clopidogrel because it is mislabeled and may contain simvastatin, a cholesterol-lowering drug, instead of clopidogrel.
The recalled product ― lot number 117099A of clopidogrel tablets (USP 75 mg) packaged in bottles of 30 tablets ― may contain clopidogrel 75 mg tablets or it could contain simvastatin tablets (USP 10 mg), according to a company announcement posted on the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website.
“Missed doses of clopidogrel increases the risk of heart attack and stroke which can be life threatening. Additionally, unintentional consumption of simvastatin could include the common side effects associated with its use and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman,” the company cautions.
To date, the company has not received any reports of harm arising from the problem that prompted the recall.
The recalled product was distributed nationwide and was delivered to distribution centers in Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, California, and Maryland and to retail stores in all US states.
International Laboratories is notifying distributors and customers by letter and is arranging for the return of all recalled products.
For questions regarding this recall, contact Inmar by phone 855-258-7280 (weekdays between 9:00 AM and 5:00 PM EST) or by email at [email protected].
Adverse reactions or quality problems experienced with the use of this product should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch adverse event reporting program.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors push back on treating COVID-19 as HAPE
For Luanne Freer, MD, an expert in high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) and founder and director of Everest ER, a nonprofit seasonal clinic at the Mt. Everest base camp in Nepal (elevation, 17,600 ft), a sudden flurry of messages and questions she received about a possible COVID-19/HAPE link was startling.
“That’s why it kind of poked me in the eye,” she said, referencing her extensive experience treating HAPE, which she described as a pressure-related phenomenon. “My goodness, they are so completely different.”
Dr. Freer, an emergency physician, reached out to several pulmonary intensivists with experience treating both HAPE and COVID-19 to gauge their reactions, and within 36 hours, they had drafted their response. In the commentary, published in High Altitude Medicine & Biology, the clinicians note that the comparison between HAPE and COVID-19 is potentially risky.
“As a group of physicians who have in some cases cared for patients with COVID-19 and in all cases cared for patients with HAPE and studied its pathophysiology and management, we feel it important to correct this misconception, as continued amplification of this message could have adverse effects on management of these patients,” they wrote.
The suggestion that COVID-19 lung injury sometimes looks more like HAPE than like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) appeared in a journal review article in late March and was put forth by medical professionals on social media where it gained traction in recent weeks and was amplified in multiple media outlets, including this one.
“With COVID, we don’t understand everything that’s going on, but we know for sure it’s an inflammatory process – not a pressure-related problem,” Dr. Freer said. “I thought ... this could be so dangerous to load the medicines that we use when we’re treating HAPE onto patients with COVID-19.”
The pathophysiological mechanisms in HAPE are different than those in other respiratory syndromes, including those associated with COVID-19, said Andrew M. Luks, MD, of the UW Medicine, Seattle, and the first author on the commentary.
“HAPE is a noncardiogenic form of pulmonary edema, as are ARDS due to bacteria or viral pneumonia, re-expansion pulmonary edema, immersion pulmonary edema, negative pressure pulmonary edema, and neurogenic pulmonary edema,” Dr. Luks, Dr. Freer, and colleagues wrote in the commentary, explaining that all of these entities cause varying degrees of hypoxemia and diffuse bilateral opacities on chest imaging. “Importantly, in all of these cases, edema accumulates in the interstitial and alveolar spaces of the lung as a result of imbalance in Starling forces.”
A difference between these entities, however, is “the mechanism by which that imbalance develops,” they noted.
The excessive and uneven hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction that leads to a marked increase in pulmonary artery pressure, subsequent lung overperfusion, increased pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, and leakage of fluid from the vascular space into the alveolar space as seen in HAPE, is a “fundamentally different phenomenon than what is seen in COVID-19-related ARDS, which involves viral-mediated inflammatory responses as the primary pathophysiological mechanism,” they added.
The authors described several other differences between the conditions, ultimately noting that “understanding the distinction between the pathophysiological mechanisms of these entities is critical for patient management.”
In HAPE, supplemental oxygen alone may be sufficient; in COVID-19, it may improve hypoxemia but won’t resolve the underlying inflammation or injury, they explained, adding that “only good supportive care including mechanical ventilation, quite often for long periods of time, allows some patients to survive until their disease resolves.”
Further, HAPE can be prevented or treated with pulmonary vasodilators such a nifedipine or sildenafil, which decrease pulmonary artery pressure and, as a result lower pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, they said.
Use of such medications for COVID-19 might decrease pulmonary artery pressure and improve right ventricular function in COVID-19, but “by releasing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and increasing perfusion to nonventilated regions of the lung, they could also worsen ventilation-perfusion mismatch” and thereby worsen hypoxemia, they explained, adding that the treatments can also cause or worsen hypotension.
Efforts to share observations and experience are important in medicine, but sometimes, as in this circumstance, “they get out there, spread around – like a brushfire almost – and get [unwarranted] face validity,” Dr. Luks said, noting that in response to information circulating about COVID-19 and HAPE, he has already heard medical professionals floating the idea of treating COVID-19 with treatments used for HAPE.
It’s true that some COVID-19 lung injury cases are behaving differently than typical ARDS, he said, adding that presentation can vary.
“But trying to equate HAPE and COVID-19 is just wrong,” he said. “HAPE and COVID-19 may share several features ...but those are features that are shared by a lot of different forms of respiratory failure.”
In a recent video interview, WebMD’s chief medical officer John Whyte, MD, spoke with a New York City physician trained in critical care and emergency medicine, Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, who raised the need to consider different respiratory protocols for COVID-19, noting that standard protocols were falling short in many cases.
“What we’re seeing ... is something unusual, it’s something that we are not used to,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell of Maimonides Medical Center said in that interview, stressing that the presentation differed from that seen in typical ARDS. “The patterns I was seeing did not make sense.”
Like others, he noted that COVID-19 patients were presenting with illness that clinically looked more like HAPE, but that the pathophysiology is not necessary similar to HAPE.
At around the same time, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues, published a letter to the editor in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine stressing that the ARDS presentation in COVID-19 patients is atypical and requires a patient physiology–driven treatment approach, rather than a standard protocol–driven approach. Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation.
Dr. Luks agreed that “some patients with COVID-19 do not have the same physiologic derangements that we see in a lot of other people with ARDS.”
“[Dr. Gattinoni] is making the point that we need to treat these people differently ... and I think that’s a valid point, and honestly, that’s a point that applied even before COVID-19,” he said. “Most of the things that we see in clinical practice – there’s a lot of heterogeneity between patients, and you have to be prepared to tailor your therapy in light of the differences that you’re picking up from your observations at the bedside and other data that you’re getting on the patient.”
The main concern Dr. Luks and his coauthors wanted to convey, they said, is making sure that the anecdotal experiences and observations of clinicians struggling to find answers don’t spiral out of control without proper vetting, thereby leading to patient harm.
“In this challenging time, we must identify the best means to care for these critically ill patients. That approach should be grounded in sound pulmonary physiology, clinical experience and, when available, evidence from clinical studies,” they concluded.
Dr. Luks and Dr. Freer reported having no financial disclosures.
For Luanne Freer, MD, an expert in high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) and founder and director of Everest ER, a nonprofit seasonal clinic at the Mt. Everest base camp in Nepal (elevation, 17,600 ft), a sudden flurry of messages and questions she received about a possible COVID-19/HAPE link was startling.
“That’s why it kind of poked me in the eye,” she said, referencing her extensive experience treating HAPE, which she described as a pressure-related phenomenon. “My goodness, they are so completely different.”
Dr. Freer, an emergency physician, reached out to several pulmonary intensivists with experience treating both HAPE and COVID-19 to gauge their reactions, and within 36 hours, they had drafted their response. In the commentary, published in High Altitude Medicine & Biology, the clinicians note that the comparison between HAPE and COVID-19 is potentially risky.
“As a group of physicians who have in some cases cared for patients with COVID-19 and in all cases cared for patients with HAPE and studied its pathophysiology and management, we feel it important to correct this misconception, as continued amplification of this message could have adverse effects on management of these patients,” they wrote.
The suggestion that COVID-19 lung injury sometimes looks more like HAPE than like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) appeared in a journal review article in late March and was put forth by medical professionals on social media where it gained traction in recent weeks and was amplified in multiple media outlets, including this one.
“With COVID, we don’t understand everything that’s going on, but we know for sure it’s an inflammatory process – not a pressure-related problem,” Dr. Freer said. “I thought ... this could be so dangerous to load the medicines that we use when we’re treating HAPE onto patients with COVID-19.”
The pathophysiological mechanisms in HAPE are different than those in other respiratory syndromes, including those associated with COVID-19, said Andrew M. Luks, MD, of the UW Medicine, Seattle, and the first author on the commentary.
“HAPE is a noncardiogenic form of pulmonary edema, as are ARDS due to bacteria or viral pneumonia, re-expansion pulmonary edema, immersion pulmonary edema, negative pressure pulmonary edema, and neurogenic pulmonary edema,” Dr. Luks, Dr. Freer, and colleagues wrote in the commentary, explaining that all of these entities cause varying degrees of hypoxemia and diffuse bilateral opacities on chest imaging. “Importantly, in all of these cases, edema accumulates in the interstitial and alveolar spaces of the lung as a result of imbalance in Starling forces.”
A difference between these entities, however, is “the mechanism by which that imbalance develops,” they noted.
The excessive and uneven hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction that leads to a marked increase in pulmonary artery pressure, subsequent lung overperfusion, increased pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, and leakage of fluid from the vascular space into the alveolar space as seen in HAPE, is a “fundamentally different phenomenon than what is seen in COVID-19-related ARDS, which involves viral-mediated inflammatory responses as the primary pathophysiological mechanism,” they added.
The authors described several other differences between the conditions, ultimately noting that “understanding the distinction between the pathophysiological mechanisms of these entities is critical for patient management.”
In HAPE, supplemental oxygen alone may be sufficient; in COVID-19, it may improve hypoxemia but won’t resolve the underlying inflammation or injury, they explained, adding that “only good supportive care including mechanical ventilation, quite often for long periods of time, allows some patients to survive until their disease resolves.”
Further, HAPE can be prevented or treated with pulmonary vasodilators such a nifedipine or sildenafil, which decrease pulmonary artery pressure and, as a result lower pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, they said.
Use of such medications for COVID-19 might decrease pulmonary artery pressure and improve right ventricular function in COVID-19, but “by releasing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and increasing perfusion to nonventilated regions of the lung, they could also worsen ventilation-perfusion mismatch” and thereby worsen hypoxemia, they explained, adding that the treatments can also cause or worsen hypotension.
Efforts to share observations and experience are important in medicine, but sometimes, as in this circumstance, “they get out there, spread around – like a brushfire almost – and get [unwarranted] face validity,” Dr. Luks said, noting that in response to information circulating about COVID-19 and HAPE, he has already heard medical professionals floating the idea of treating COVID-19 with treatments used for HAPE.
It’s true that some COVID-19 lung injury cases are behaving differently than typical ARDS, he said, adding that presentation can vary.
“But trying to equate HAPE and COVID-19 is just wrong,” he said. “HAPE and COVID-19 may share several features ...but those are features that are shared by a lot of different forms of respiratory failure.”
In a recent video interview, WebMD’s chief medical officer John Whyte, MD, spoke with a New York City physician trained in critical care and emergency medicine, Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, who raised the need to consider different respiratory protocols for COVID-19, noting that standard protocols were falling short in many cases.
“What we’re seeing ... is something unusual, it’s something that we are not used to,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell of Maimonides Medical Center said in that interview, stressing that the presentation differed from that seen in typical ARDS. “The patterns I was seeing did not make sense.”
Like others, he noted that COVID-19 patients were presenting with illness that clinically looked more like HAPE, but that the pathophysiology is not necessary similar to HAPE.
At around the same time, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues, published a letter to the editor in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine stressing that the ARDS presentation in COVID-19 patients is atypical and requires a patient physiology–driven treatment approach, rather than a standard protocol–driven approach. Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation.
Dr. Luks agreed that “some patients with COVID-19 do not have the same physiologic derangements that we see in a lot of other people with ARDS.”
“[Dr. Gattinoni] is making the point that we need to treat these people differently ... and I think that’s a valid point, and honestly, that’s a point that applied even before COVID-19,” he said. “Most of the things that we see in clinical practice – there’s a lot of heterogeneity between patients, and you have to be prepared to tailor your therapy in light of the differences that you’re picking up from your observations at the bedside and other data that you’re getting on the patient.”
The main concern Dr. Luks and his coauthors wanted to convey, they said, is making sure that the anecdotal experiences and observations of clinicians struggling to find answers don’t spiral out of control without proper vetting, thereby leading to patient harm.
“In this challenging time, we must identify the best means to care for these critically ill patients. That approach should be grounded in sound pulmonary physiology, clinical experience and, when available, evidence from clinical studies,” they concluded.
Dr. Luks and Dr. Freer reported having no financial disclosures.
For Luanne Freer, MD, an expert in high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) and founder and director of Everest ER, a nonprofit seasonal clinic at the Mt. Everest base camp in Nepal (elevation, 17,600 ft), a sudden flurry of messages and questions she received about a possible COVID-19/HAPE link was startling.
“That’s why it kind of poked me in the eye,” she said, referencing her extensive experience treating HAPE, which she described as a pressure-related phenomenon. “My goodness, they are so completely different.”
Dr. Freer, an emergency physician, reached out to several pulmonary intensivists with experience treating both HAPE and COVID-19 to gauge their reactions, and within 36 hours, they had drafted their response. In the commentary, published in High Altitude Medicine & Biology, the clinicians note that the comparison between HAPE and COVID-19 is potentially risky.
“As a group of physicians who have in some cases cared for patients with COVID-19 and in all cases cared for patients with HAPE and studied its pathophysiology and management, we feel it important to correct this misconception, as continued amplification of this message could have adverse effects on management of these patients,” they wrote.
The suggestion that COVID-19 lung injury sometimes looks more like HAPE than like acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) appeared in a journal review article in late March and was put forth by medical professionals on social media where it gained traction in recent weeks and was amplified in multiple media outlets, including this one.
“With COVID, we don’t understand everything that’s going on, but we know for sure it’s an inflammatory process – not a pressure-related problem,” Dr. Freer said. “I thought ... this could be so dangerous to load the medicines that we use when we’re treating HAPE onto patients with COVID-19.”
The pathophysiological mechanisms in HAPE are different than those in other respiratory syndromes, including those associated with COVID-19, said Andrew M. Luks, MD, of the UW Medicine, Seattle, and the first author on the commentary.
“HAPE is a noncardiogenic form of pulmonary edema, as are ARDS due to bacteria or viral pneumonia, re-expansion pulmonary edema, immersion pulmonary edema, negative pressure pulmonary edema, and neurogenic pulmonary edema,” Dr. Luks, Dr. Freer, and colleagues wrote in the commentary, explaining that all of these entities cause varying degrees of hypoxemia and diffuse bilateral opacities on chest imaging. “Importantly, in all of these cases, edema accumulates in the interstitial and alveolar spaces of the lung as a result of imbalance in Starling forces.”
A difference between these entities, however, is “the mechanism by which that imbalance develops,” they noted.
The excessive and uneven hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction that leads to a marked increase in pulmonary artery pressure, subsequent lung overperfusion, increased pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, and leakage of fluid from the vascular space into the alveolar space as seen in HAPE, is a “fundamentally different phenomenon than what is seen in COVID-19-related ARDS, which involves viral-mediated inflammatory responses as the primary pathophysiological mechanism,” they added.
The authors described several other differences between the conditions, ultimately noting that “understanding the distinction between the pathophysiological mechanisms of these entities is critical for patient management.”
In HAPE, supplemental oxygen alone may be sufficient; in COVID-19, it may improve hypoxemia but won’t resolve the underlying inflammation or injury, they explained, adding that “only good supportive care including mechanical ventilation, quite often for long periods of time, allows some patients to survive until their disease resolves.”
Further, HAPE can be prevented or treated with pulmonary vasodilators such a nifedipine or sildenafil, which decrease pulmonary artery pressure and, as a result lower pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, they said.
Use of such medications for COVID-19 might decrease pulmonary artery pressure and improve right ventricular function in COVID-19, but “by releasing hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and increasing perfusion to nonventilated regions of the lung, they could also worsen ventilation-perfusion mismatch” and thereby worsen hypoxemia, they explained, adding that the treatments can also cause or worsen hypotension.
Efforts to share observations and experience are important in medicine, but sometimes, as in this circumstance, “they get out there, spread around – like a brushfire almost – and get [unwarranted] face validity,” Dr. Luks said, noting that in response to information circulating about COVID-19 and HAPE, he has already heard medical professionals floating the idea of treating COVID-19 with treatments used for HAPE.
It’s true that some COVID-19 lung injury cases are behaving differently than typical ARDS, he said, adding that presentation can vary.
“But trying to equate HAPE and COVID-19 is just wrong,” he said. “HAPE and COVID-19 may share several features ...but those are features that are shared by a lot of different forms of respiratory failure.”
In a recent video interview, WebMD’s chief medical officer John Whyte, MD, spoke with a New York City physician trained in critical care and emergency medicine, Cameron Kyle-Sidell, MD, who raised the need to consider different respiratory protocols for COVID-19, noting that standard protocols were falling short in many cases.
“What we’re seeing ... is something unusual, it’s something that we are not used to,” Dr. Kyle-Sidell of Maimonides Medical Center said in that interview, stressing that the presentation differed from that seen in typical ARDS. “The patterns I was seeing did not make sense.”
Like others, he noted that COVID-19 patients were presenting with illness that clinically looked more like HAPE, but that the pathophysiology is not necessary similar to HAPE.
At around the same time, Luciano Gattinoni, MD, of the Medical University of Göttingen in Germany and colleagues, published a letter to the editor in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine stressing that the ARDS presentation in COVID-19 patients is atypical and requires a patient physiology–driven treatment approach, rather than a standard protocol–driven approach. Dr. Gattinoni and colleagues suggested that instead of high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), physicians should consider the lowest possible PEEP and gentle ventilation.
Dr. Luks agreed that “some patients with COVID-19 do not have the same physiologic derangements that we see in a lot of other people with ARDS.”
“[Dr. Gattinoni] is making the point that we need to treat these people differently ... and I think that’s a valid point, and honestly, that’s a point that applied even before COVID-19,” he said. “Most of the things that we see in clinical practice – there’s a lot of heterogeneity between patients, and you have to be prepared to tailor your therapy in light of the differences that you’re picking up from your observations at the bedside and other data that you’re getting on the patient.”
The main concern Dr. Luks and his coauthors wanted to convey, they said, is making sure that the anecdotal experiences and observations of clinicians struggling to find answers don’t spiral out of control without proper vetting, thereby leading to patient harm.
“In this challenging time, we must identify the best means to care for these critically ill patients. That approach should be grounded in sound pulmonary physiology, clinical experience and, when available, evidence from clinical studies,” they concluded.
Dr. Luks and Dr. Freer reported having no financial disclosures.
ASE issues echocardiography guidance amid COVID-19 pandemic
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) has issued a statement on protecting patients and echocardiography service providers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Given the risk for cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19, echocardiographic services will likely be needed for patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, meaning echo providers will be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, write the statement authors, led by James N. Kirkpatrick, MD, director of the echocardiography laboratory at University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The statement was published online April 6 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors say the statement is intended to help guide the practice of echocardiography in this “challenging time.” It was developed with input from a variety of echocardiography providers and institutions who have experience with the COVID-19, or have been “actively and thoughtfully preparing for it.”
Who, When, Where, and How
The statement covers triaging and decision pathways for handling requests for echocardiography, as well as indications and recommended procedures, in cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
Among the recommendations:
- Only perform transthoracic echocardiograms (TTE), stress echocardiograms, and transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE) if they are expected to provide clinical benefit. Appropriate-use criteria represent the first decision point as to whether an echocardiographic test should be performed.
- Determine which studies are “elective” and reschedule them, performing all others. Identify “nonelective” (urgent/emergent) indications and defer all others.
- Determine the clinical benefit of echocardiography for symptomatic patients whose SARS-CoV-2 status is unknown.
- Cautiously consider the benefit of a TEE examination weighed against the risk for exposure of healthcare personnel to aerosolization in a patient with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
- Postpone or cancel TEEs if an alternative imaging modality can provide the necessary information.
- Note that treadmill or bicycle stress echo tests in patients with COVID-19 may lead to exposure because of deep breathing and/or coughing during exercise. These tests should generally be deferred or converted to a pharmacologic stress echo.
The ASE statement also provides advice on safe imaging protocol and adequate personal protection measures.
“In addition to limiting the number of echocardiography practitioners involved in scanning, consideration should be given to limiting the exposure of staff who may be particularly susceptible to severe complications of COVID-19,” the ASE advises.
Staff who are older than 60 years, who have chronic conditions, are immunocompromised or are pregnant may wish to avoid contact with patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19.
It’s also important to realize the risk for transmission in reading rooms. “Keyboards, monitors, mice, chairs, phones, desktops, and door knobs should be frequently cleaned, and ventilation provided wherever possible,” the ASE advises. When the echo lab reading room is located in a high-traffic area, remote review of images or via webinar might be advisable, they suggest.
Summing up, Kirkland and colleagues say providing echocardiographic service “remains crucial in this difficult time of the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak. Working together, we can continue to provide high-quality care while minimizing risk to ourselves, our patients, and the public at large. Carefully considering ‘Whom to Image’, ‘Where to Image’ and ‘How to Image’ has the potential to reduce the risks of transmission.”
The authors note that the statements and recommendations are primarily based on expert opinion rather than on scientifically verified data and are subject to change as the COVID-19 outbreak continues to evolve and new data emerges.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) has issued a statement on protecting patients and echocardiography service providers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Given the risk for cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19, echocardiographic services will likely be needed for patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, meaning echo providers will be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, write the statement authors, led by James N. Kirkpatrick, MD, director of the echocardiography laboratory at University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The statement was published online April 6 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors say the statement is intended to help guide the practice of echocardiography in this “challenging time.” It was developed with input from a variety of echocardiography providers and institutions who have experience with the COVID-19, or have been “actively and thoughtfully preparing for it.”
Who, When, Where, and How
The statement covers triaging and decision pathways for handling requests for echocardiography, as well as indications and recommended procedures, in cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
Among the recommendations:
- Only perform transthoracic echocardiograms (TTE), stress echocardiograms, and transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE) if they are expected to provide clinical benefit. Appropriate-use criteria represent the first decision point as to whether an echocardiographic test should be performed.
- Determine which studies are “elective” and reschedule them, performing all others. Identify “nonelective” (urgent/emergent) indications and defer all others.
- Determine the clinical benefit of echocardiography for symptomatic patients whose SARS-CoV-2 status is unknown.
- Cautiously consider the benefit of a TEE examination weighed against the risk for exposure of healthcare personnel to aerosolization in a patient with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
- Postpone or cancel TEEs if an alternative imaging modality can provide the necessary information.
- Note that treadmill or bicycle stress echo tests in patients with COVID-19 may lead to exposure because of deep breathing and/or coughing during exercise. These tests should generally be deferred or converted to a pharmacologic stress echo.
The ASE statement also provides advice on safe imaging protocol and adequate personal protection measures.
“In addition to limiting the number of echocardiography practitioners involved in scanning, consideration should be given to limiting the exposure of staff who may be particularly susceptible to severe complications of COVID-19,” the ASE advises.
Staff who are older than 60 years, who have chronic conditions, are immunocompromised or are pregnant may wish to avoid contact with patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19.
It’s also important to realize the risk for transmission in reading rooms. “Keyboards, monitors, mice, chairs, phones, desktops, and door knobs should be frequently cleaned, and ventilation provided wherever possible,” the ASE advises. When the echo lab reading room is located in a high-traffic area, remote review of images or via webinar might be advisable, they suggest.
Summing up, Kirkland and colleagues say providing echocardiographic service “remains crucial in this difficult time of the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak. Working together, we can continue to provide high-quality care while minimizing risk to ourselves, our patients, and the public at large. Carefully considering ‘Whom to Image’, ‘Where to Image’ and ‘How to Image’ has the potential to reduce the risks of transmission.”
The authors note that the statements and recommendations are primarily based on expert opinion rather than on scientifically verified data and are subject to change as the COVID-19 outbreak continues to evolve and new data emerges.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) has issued a statement on protecting patients and echocardiography service providers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Given the risk for cardiovascular complications associated with COVID-19, echocardiographic services will likely be needed for patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, meaning echo providers will be exposed to SARS-CoV-2, write the statement authors, led by James N. Kirkpatrick, MD, director of the echocardiography laboratory at University of Washington Medical Center in Seattle.
The statement was published online April 6 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The authors say the statement is intended to help guide the practice of echocardiography in this “challenging time.” It was developed with input from a variety of echocardiography providers and institutions who have experience with the COVID-19, or have been “actively and thoughtfully preparing for it.”
Who, When, Where, and How
The statement covers triaging and decision pathways for handling requests for echocardiography, as well as indications and recommended procedures, in cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
Among the recommendations:
- Only perform transthoracic echocardiograms (TTE), stress echocardiograms, and transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE) if they are expected to provide clinical benefit. Appropriate-use criteria represent the first decision point as to whether an echocardiographic test should be performed.
- Determine which studies are “elective” and reschedule them, performing all others. Identify “nonelective” (urgent/emergent) indications and defer all others.
- Determine the clinical benefit of echocardiography for symptomatic patients whose SARS-CoV-2 status is unknown.
- Cautiously consider the benefit of a TEE examination weighed against the risk for exposure of healthcare personnel to aerosolization in a patient with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
- Postpone or cancel TEEs if an alternative imaging modality can provide the necessary information.
- Note that treadmill or bicycle stress echo tests in patients with COVID-19 may lead to exposure because of deep breathing and/or coughing during exercise. These tests should generally be deferred or converted to a pharmacologic stress echo.
The ASE statement also provides advice on safe imaging protocol and adequate personal protection measures.
“In addition to limiting the number of echocardiography practitioners involved in scanning, consideration should be given to limiting the exposure of staff who may be particularly susceptible to severe complications of COVID-19,” the ASE advises.
Staff who are older than 60 years, who have chronic conditions, are immunocompromised or are pregnant may wish to avoid contact with patients suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19.
It’s also important to realize the risk for transmission in reading rooms. “Keyboards, monitors, mice, chairs, phones, desktops, and door knobs should be frequently cleaned, and ventilation provided wherever possible,” the ASE advises. When the echo lab reading room is located in a high-traffic area, remote review of images or via webinar might be advisable, they suggest.
Summing up, Kirkland and colleagues say providing echocardiographic service “remains crucial in this difficult time of the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak. Working together, we can continue to provide high-quality care while minimizing risk to ourselves, our patients, and the public at large. Carefully considering ‘Whom to Image’, ‘Where to Image’ and ‘How to Image’ has the potential to reduce the risks of transmission.”
The authors note that the statements and recommendations are primarily based on expert opinion rather than on scientifically verified data and are subject to change as the COVID-19 outbreak continues to evolve and new data emerges.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.