User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Death rate steady with pediatric early warning system
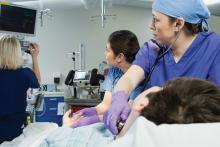
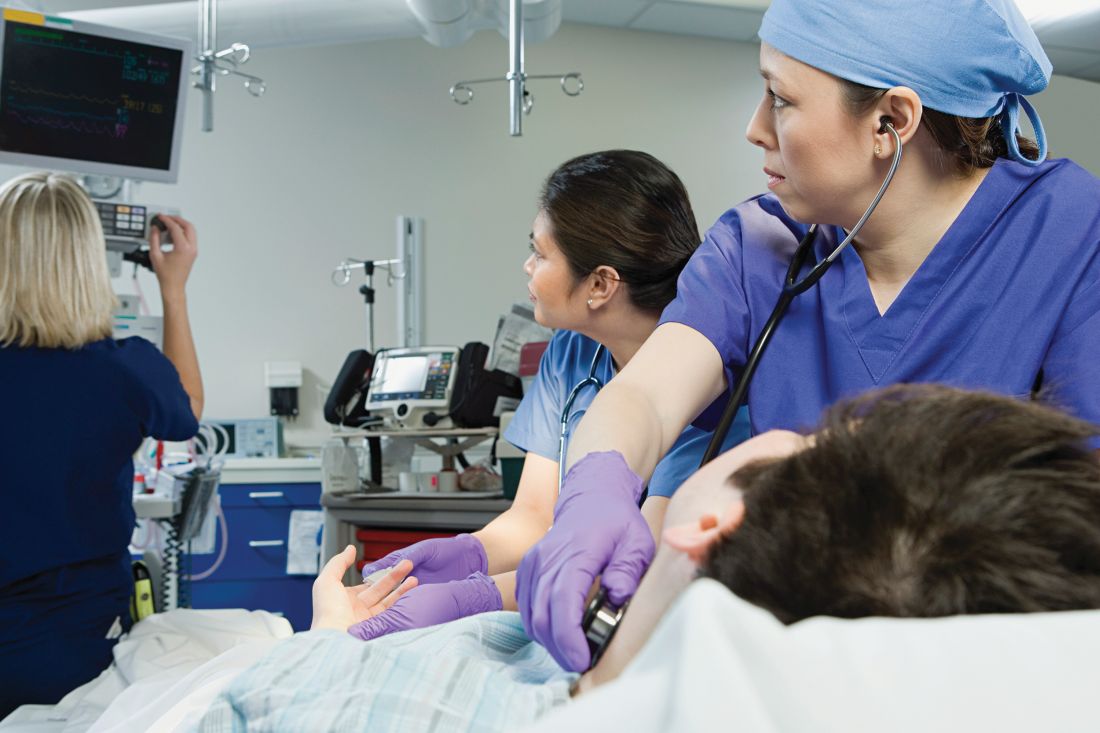
SAN ANTONIO – , but did not reduce the rate of all-cause hospital mortality, according to results of a large, multicenter trial.
Taken together, the findings of the trial do not support the use of the Bedside Pediatric Early Warning System (BedsidePEWS) to reduce hospital mortality, noted investigator Christopher S. Parshuram, MBChB, DPhil, during a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The multicenter randomized cluster study, called the EPOCH trial, included 21 hospitals in seven countries that provided inpatient pediatric care. Ten of the hospitals delivered the BedsidePEWS intervention, while the remaining 11 provided usual care. The study data included 144,539 patient discharges comprising 559,443 patient days. Enrollment began Feb. 28, 2011, and ended on June 21, 2015.
For the BedsidePEWS group, all-cause hospital mortality was 1.93 per 1,000 patient discharges, versus 1.56 per 1,000 patient discharges for usual care (adjusted odds ratio, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.69; P = .96), according to a report on this study that was published in JAMA.
However, the BedsidePEWS group had a significant improvement in the secondary outcome of significant clinical deterioration events, a composite outcome reflecting late ICU admissions.
In the BedsidePEWS group, the rate of significant clinical deterioration events was 0.50 per 1,000 patient-days, compared with 0.84 per 1,000 patient-days at hospitals with usual care (adjusted rate ratio, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.97; P = .03), the investigators wrote.
The goal of the EPOCH trial was to determine whether BedsidePEWS could reduce rates of all-cause hospital mortality and significant clinical deterioration among hospitalized children, according to the researchers.
“The BedsidePEWS versus usual care did improve processes of care and early detection of critical illness, aligned with the notion of providing the right care, right now,” Dr. Parshuram, associate professor of critical care medicine and pediatrics at the University of Toronto, said during his presentation at the meeting. “Certainly more vital signs were documented, and anecdotally there were reports of culture change.
“However, when we looked further, there was no difference in hospital mortality, nor hospital resource utilization,” Dr. Parshuram added.
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research funded the study. Dr. Parshuram is an inventor of BedsidePEWS and owns shares in a company that is commercializing it.
SOURCE: Parshuram et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0948.
SAN ANTONIO – , but did not reduce the rate of all-cause hospital mortality, according to results of a large, multicenter trial.
Taken together, the findings of the trial do not support the use of the Bedside Pediatric Early Warning System (BedsidePEWS) to reduce hospital mortality, noted investigator Christopher S. Parshuram, MBChB, DPhil, during a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The multicenter randomized cluster study, called the EPOCH trial, included 21 hospitals in seven countries that provided inpatient pediatric care. Ten of the hospitals delivered the BedsidePEWS intervention, while the remaining 11 provided usual care. The study data included 144,539 patient discharges comprising 559,443 patient days. Enrollment began Feb. 28, 2011, and ended on June 21, 2015.
For the BedsidePEWS group, all-cause hospital mortality was 1.93 per 1,000 patient discharges, versus 1.56 per 1,000 patient discharges for usual care (adjusted odds ratio, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.69; P = .96), according to a report on this study that was published in JAMA.
However, the BedsidePEWS group had a significant improvement in the secondary outcome of significant clinical deterioration events, a composite outcome reflecting late ICU admissions.
In the BedsidePEWS group, the rate of significant clinical deterioration events was 0.50 per 1,000 patient-days, compared with 0.84 per 1,000 patient-days at hospitals with usual care (adjusted rate ratio, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.97; P = .03), the investigators wrote.
The goal of the EPOCH trial was to determine whether BedsidePEWS could reduce rates of all-cause hospital mortality and significant clinical deterioration among hospitalized children, according to the researchers.
“The BedsidePEWS versus usual care did improve processes of care and early detection of critical illness, aligned with the notion of providing the right care, right now,” Dr. Parshuram, associate professor of critical care medicine and pediatrics at the University of Toronto, said during his presentation at the meeting. “Certainly more vital signs were documented, and anecdotally there were reports of culture change.
“However, when we looked further, there was no difference in hospital mortality, nor hospital resource utilization,” Dr. Parshuram added.
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research funded the study. Dr. Parshuram is an inventor of BedsidePEWS and owns shares in a company that is commercializing it.
SOURCE: Parshuram et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0948.
SAN ANTONIO – , but did not reduce the rate of all-cause hospital mortality, according to results of a large, multicenter trial.
Taken together, the findings of the trial do not support the use of the Bedside Pediatric Early Warning System (BedsidePEWS) to reduce hospital mortality, noted investigator Christopher S. Parshuram, MBChB, DPhil, during a presentation at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The multicenter randomized cluster study, called the EPOCH trial, included 21 hospitals in seven countries that provided inpatient pediatric care. Ten of the hospitals delivered the BedsidePEWS intervention, while the remaining 11 provided usual care. The study data included 144,539 patient discharges comprising 559,443 patient days. Enrollment began Feb. 28, 2011, and ended on June 21, 2015.
For the BedsidePEWS group, all-cause hospital mortality was 1.93 per 1,000 patient discharges, versus 1.56 per 1,000 patient discharges for usual care (adjusted odds ratio, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.69; P = .96), according to a report on this study that was published in JAMA.
However, the BedsidePEWS group had a significant improvement in the secondary outcome of significant clinical deterioration events, a composite outcome reflecting late ICU admissions.
In the BedsidePEWS group, the rate of significant clinical deterioration events was 0.50 per 1,000 patient-days, compared with 0.84 per 1,000 patient-days at hospitals with usual care (adjusted rate ratio, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.97; P = .03), the investigators wrote.
The goal of the EPOCH trial was to determine whether BedsidePEWS could reduce rates of all-cause hospital mortality and significant clinical deterioration among hospitalized children, according to the researchers.
“The BedsidePEWS versus usual care did improve processes of care and early detection of critical illness, aligned with the notion of providing the right care, right now,” Dr. Parshuram, associate professor of critical care medicine and pediatrics at the University of Toronto, said during his presentation at the meeting. “Certainly more vital signs were documented, and anecdotally there were reports of culture change.
“However, when we looked further, there was no difference in hospital mortality, nor hospital resource utilization,” Dr. Parshuram added.
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research funded the study. Dr. Parshuram is an inventor of BedsidePEWS and owns shares in a company that is commercializing it.
SOURCE: Parshuram et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0948.
REPORTING FROM CCC47
Key clinical point: Use of a pediatric early warning system (BedsidePEWS) did not reduce rates of all-cause hospital mortality among hospitalized children, compared with usual care, but did reduce rates of significant clinical deterioration events.
Major finding: For hospitals implementing BedsidePEWS, all-cause hospital mortality was 1.93 per 1,000 patient discharges, versus 1.56 per 1,000 at hospitals with usual care (adjusted odds ratio, 1.01; 95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.69; P = .96).
Study details: A multicenter cluster randomized trial of 144,539 patient discharges from 21 hospitals in seven countries providing pediatric care.
Disclosures: The Canadian Institutes of Health Research funded the study. Dr. Parshuram is an inventor of BedsidePEWS and owns shares in a company that is commercializing it.
Source: Parshuram et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 27. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0948.
Opioid prescriptions got shorter in 2017
Use of opioids was down among enrollees of all types of payers in 2017, while the use of drugs to treat opioid dependence went up for three of the four payer categories, according to pharmacy benefits manager Express Scripts.
The days’ worth of opioids dispensed per person per year was down 16.6% from 2016 to 2017 for enrollees with plans on the health exchanges received managed by Express Scripts. Medicaid patients received 16% fewer days’ worth, patients with commercial plans received 10.3% fewer days’ worth, and Medicare patients received 4.9% fewer days’ worth, Express Scripts said in its 2017 Drug Trend Report, which was based on data for 34.3 million members of pharmacy benefits plans the company administers.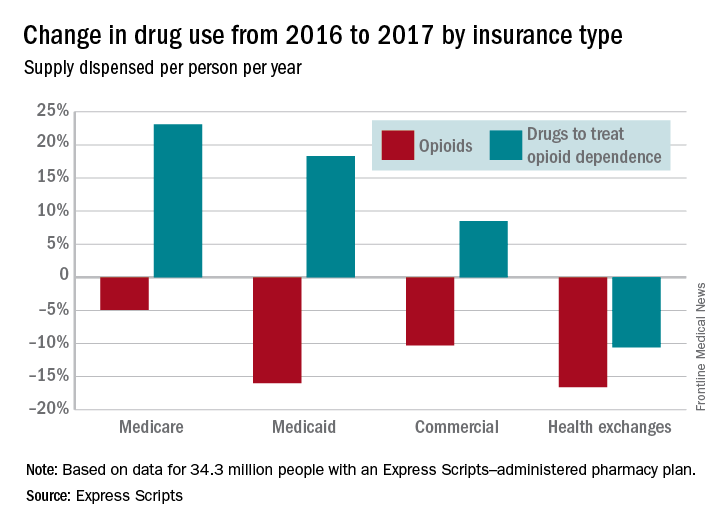
Plans that participated in Express Scripts’ Advanced Opioid Management solution, which was launched in September, experienced “a 60% reduction in the average days’ supply per initial fill, from 18.6 days to just 7.5 days,” according to the report.
Use of opioids was down among enrollees of all types of payers in 2017, while the use of drugs to treat opioid dependence went up for three of the four payer categories, according to pharmacy benefits manager Express Scripts.
The days’ worth of opioids dispensed per person per year was down 16.6% from 2016 to 2017 for enrollees with plans on the health exchanges received managed by Express Scripts. Medicaid patients received 16% fewer days’ worth, patients with commercial plans received 10.3% fewer days’ worth, and Medicare patients received 4.9% fewer days’ worth, Express Scripts said in its 2017 Drug Trend Report, which was based on data for 34.3 million members of pharmacy benefits plans the company administers.
Plans that participated in Express Scripts’ Advanced Opioid Management solution, which was launched in September, experienced “a 60% reduction in the average days’ supply per initial fill, from 18.6 days to just 7.5 days,” according to the report.
Use of opioids was down among enrollees of all types of payers in 2017, while the use of drugs to treat opioid dependence went up for three of the four payer categories, according to pharmacy benefits manager Express Scripts.
The days’ worth of opioids dispensed per person per year was down 16.6% from 2016 to 2017 for enrollees with plans on the health exchanges received managed by Express Scripts. Medicaid patients received 16% fewer days’ worth, patients with commercial plans received 10.3% fewer days’ worth, and Medicare patients received 4.9% fewer days’ worth, Express Scripts said in its 2017 Drug Trend Report, which was based on data for 34.3 million members of pharmacy benefits plans the company administers.
Plans that participated in Express Scripts’ Advanced Opioid Management solution, which was launched in September, experienced “a 60% reduction in the average days’ supply per initial fill, from 18.6 days to just 7.5 days,” according to the report.
Measuring high-value care practices
Because health care in the United States is extremely expensive, it’s driving an increased focus on high-value care (HVC), said Carolyn D. Sy, MD. And, she added, while hospitalists and other physicians are the ones responsible for translating HVC from formalized settings (lectures, modules, etc.) to the bedside, there are few instruments designed to measure the success of HVC practices.
So Dr. Sy, director of the University of Washington Medical Center Hospital Medicine Service in Seattle and her colleagues developed an HVC Rounding Tool, which allows users to empirically assess the discussion of HVC topics at the bedside. They divided 10 HVC topics into three domains (quality, cost, patient values) to create an observational tool and tested its validity.
“It addresses an important educational gap in translating HVC from theoretical knowledge to bedside practice,” she said.
The tool is designed to capture multidisciplinary participation: involvement from faculty, fellows or trainees, nurses, pharmacists, families, and other members of the health care team.
It has multidisciplinary benefits too. “The HVC Rounding Tool provides an opportunity for faculty development through peer observation and feedback on the integration and role modeling of HVC at the bedside,” Dr. Sy said. “It also is an instrument to help assess the educational efficacy of formal HVC curriculum and translation into bedside practice. Lastly, it is a tool that could be used to measure the relationship between HVC behaviors and actual patient outcomes, such as length of stay, readmissions, and cost of hospitalization – a feature with increasing importance given our move towards value-based health care.”
Reference
1. Sy CD et al. The development and validation of a high-value care rounding tool using the Delphi method. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(suppl 2). Accessed Oct 10, 2017.
Because health care in the United States is extremely expensive, it’s driving an increased focus on high-value care (HVC), said Carolyn D. Sy, MD. And, she added, while hospitalists and other physicians are the ones responsible for translating HVC from formalized settings (lectures, modules, etc.) to the bedside, there are few instruments designed to measure the success of HVC practices.
So Dr. Sy, director of the University of Washington Medical Center Hospital Medicine Service in Seattle and her colleagues developed an HVC Rounding Tool, which allows users to empirically assess the discussion of HVC topics at the bedside. They divided 10 HVC topics into three domains (quality, cost, patient values) to create an observational tool and tested its validity.
“It addresses an important educational gap in translating HVC from theoretical knowledge to bedside practice,” she said.
The tool is designed to capture multidisciplinary participation: involvement from faculty, fellows or trainees, nurses, pharmacists, families, and other members of the health care team.
It has multidisciplinary benefits too. “The HVC Rounding Tool provides an opportunity for faculty development through peer observation and feedback on the integration and role modeling of HVC at the bedside,” Dr. Sy said. “It also is an instrument to help assess the educational efficacy of formal HVC curriculum and translation into bedside practice. Lastly, it is a tool that could be used to measure the relationship between HVC behaviors and actual patient outcomes, such as length of stay, readmissions, and cost of hospitalization – a feature with increasing importance given our move towards value-based health care.”
Reference
1. Sy CD et al. The development and validation of a high-value care rounding tool using the Delphi method. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(suppl 2). Accessed Oct 10, 2017.
Because health care in the United States is extremely expensive, it’s driving an increased focus on high-value care (HVC), said Carolyn D. Sy, MD. And, she added, while hospitalists and other physicians are the ones responsible for translating HVC from formalized settings (lectures, modules, etc.) to the bedside, there are few instruments designed to measure the success of HVC practices.
So Dr. Sy, director of the University of Washington Medical Center Hospital Medicine Service in Seattle and her colleagues developed an HVC Rounding Tool, which allows users to empirically assess the discussion of HVC topics at the bedside. They divided 10 HVC topics into three domains (quality, cost, patient values) to create an observational tool and tested its validity.
“It addresses an important educational gap in translating HVC from theoretical knowledge to bedside practice,” she said.
The tool is designed to capture multidisciplinary participation: involvement from faculty, fellows or trainees, nurses, pharmacists, families, and other members of the health care team.
It has multidisciplinary benefits too. “The HVC Rounding Tool provides an opportunity for faculty development through peer observation and feedback on the integration and role modeling of HVC at the bedside,” Dr. Sy said. “It also is an instrument to help assess the educational efficacy of formal HVC curriculum and translation into bedside practice. Lastly, it is a tool that could be used to measure the relationship between HVC behaviors and actual patient outcomes, such as length of stay, readmissions, and cost of hospitalization – a feature with increasing importance given our move towards value-based health care.”
Reference
1. Sy CD et al. The development and validation of a high-value care rounding tool using the Delphi method. J Hosp Med. 2017;12(suppl 2). Accessed Oct 10, 2017.
Haloperidol does not prevent delirium in ICU patients
of 1,789 critically ill adults at 21 ICUs in the Netherlands.
Haloperidol is used routinely in ICUs to both treat and prevent delirium, which strikes up to half of ICU patients and is associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation, longer ICU and hospital stays, and increased mortality. Results of past studies have been mixed, with some showing a benefit for haloperidol in the ICU and others not.
“These findings do not support the use of prophylactic haloperidol in critically ill adults,” said the authors of a new study, led by Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands (JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:680-90).
The subjects were all expected to be in the ICU for at least 2 days, and were not delirious at baseline. The patients were randomly assigned to receive one of two treatments or a placebo three times daily, with 350 receiving 1 mg of haloperidol; 732 receiving 2 mg of haloperidol; and 707 receiving a 0.9% sodium chloride placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol arm was stopped early because of futility.
There was no statistically significant difference in survival at the primary endpoint of 28 days following entrance into the study. At that point, 83.3% of the patients who received 2-mg does of haloperidol and 82.7% of the of the subjects who received the placebo were alive (absolute difference 0.6%, 95% confidence interval –3.4% to 4.6%).
Prophylactic haloperidol had no effect on reducing the incidence of delirium, which was diagnosed in 33.3% of haloperidol subjects and 33.0% of placebo patients. Likewise, there were no significant differences between the groups in the number of delirium-free and coma-free days, duration of mechanical ventilation, and ICU and hospital length of stay. The number of reported adverse events with treatment also did not differ significantly between the groups: 0.3% in the 2-mg haloperidol group versus 0.1% in the placebo arm.
The duration of prophylactic therapy was a median of 2 days, but a subgroup analysis in patients treated for more than 2 days also did not show any benefits with haloperidol.
“The study population included severely ill ICU adults whose brains may have been too seriously affected for haloperidol to exert a prophylactic effect, since in non-ICU adults, prophylactic haloperidol may have beneficial effects. But the subgroup of patients with a low severity of illness score also demonstrated no beneficial effects,” the investigators said.
Subjects were a mean of 66.6 years old; 61.4% were men. Most of the ICU admissions were urgent and for medical or surgical reasons.
This study was supported by ZonMw, the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. van den Boogaard had no disclosures. One author reported grants and consultant and speaker fees from Pfizer, Merck, Astellas, and Gilead, among others.
SOURCE: van den Boogaard M, et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
The study has demonstrated that in critically ill patients currently receiving best-practice nonpharmacological interventions to prevent delirium, the addition of haloperidol does not improve survival nor reduce the incidence of delirium or the harms associated with delirium. The findings challenge the current model that the addition of psychoactive medication to patients who are already receiving multiple interventions may be beneficial. Prophylactic haloperidol is not the solution for the complex problem of delirium in critically ill patients. It may be that no single pharmacological intervention can provide a solution.
Future research is warranted into nonpharmacological interventions. They generally involve either doing less for patients (avoiding excessive sedation, benzodiazepines, nocturnal noise, and stimulation) or ensuring the continued provision of relatively simple therapies (mobilization, maintaining a day-night schedule, and noise reduction). Although some of these interventions may require planning and cooperation of a multidisciplinary team, a strength of ICU care in general, other interventions may be as simple as providing earplugs and eye patches to improve sleep.
Anthony Delaney, MD, PhD, is associate professor of intensive care medicine at the University of Sydney. Naomi Hammond, PhD, is a research fellow and senior lecturer at the University of New South Wales, Sydney. Edward Litton, MD, PhD, is an intensive care specialist in Perth, Australia. They made their comments in a JAMA editorial, and had no disclosures ( JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:659-60 ).
The study has demonstrated that in critically ill patients currently receiving best-practice nonpharmacological interventions to prevent delirium, the addition of haloperidol does not improve survival nor reduce the incidence of delirium or the harms associated with delirium. The findings challenge the current model that the addition of psychoactive medication to patients who are already receiving multiple interventions may be beneficial. Prophylactic haloperidol is not the solution for the complex problem of delirium in critically ill patients. It may be that no single pharmacological intervention can provide a solution.
Future research is warranted into nonpharmacological interventions. They generally involve either doing less for patients (avoiding excessive sedation, benzodiazepines, nocturnal noise, and stimulation) or ensuring the continued provision of relatively simple therapies (mobilization, maintaining a day-night schedule, and noise reduction). Although some of these interventions may require planning and cooperation of a multidisciplinary team, a strength of ICU care in general, other interventions may be as simple as providing earplugs and eye patches to improve sleep.
Anthony Delaney, MD, PhD, is associate professor of intensive care medicine at the University of Sydney. Naomi Hammond, PhD, is a research fellow and senior lecturer at the University of New South Wales, Sydney. Edward Litton, MD, PhD, is an intensive care specialist in Perth, Australia. They made their comments in a JAMA editorial, and had no disclosures ( JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:659-60 ).
The study has demonstrated that in critically ill patients currently receiving best-practice nonpharmacological interventions to prevent delirium, the addition of haloperidol does not improve survival nor reduce the incidence of delirium or the harms associated with delirium. The findings challenge the current model that the addition of psychoactive medication to patients who are already receiving multiple interventions may be beneficial. Prophylactic haloperidol is not the solution for the complex problem of delirium in critically ill patients. It may be that no single pharmacological intervention can provide a solution.
Future research is warranted into nonpharmacological interventions. They generally involve either doing less for patients (avoiding excessive sedation, benzodiazepines, nocturnal noise, and stimulation) or ensuring the continued provision of relatively simple therapies (mobilization, maintaining a day-night schedule, and noise reduction). Although some of these interventions may require planning and cooperation of a multidisciplinary team, a strength of ICU care in general, other interventions may be as simple as providing earplugs and eye patches to improve sleep.
Anthony Delaney, MD, PhD, is associate professor of intensive care medicine at the University of Sydney. Naomi Hammond, PhD, is a research fellow and senior lecturer at the University of New South Wales, Sydney. Edward Litton, MD, PhD, is an intensive care specialist in Perth, Australia. They made their comments in a JAMA editorial, and had no disclosures ( JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:659-60 ).
of 1,789 critically ill adults at 21 ICUs in the Netherlands.
Haloperidol is used routinely in ICUs to both treat and prevent delirium, which strikes up to half of ICU patients and is associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation, longer ICU and hospital stays, and increased mortality. Results of past studies have been mixed, with some showing a benefit for haloperidol in the ICU and others not.
“These findings do not support the use of prophylactic haloperidol in critically ill adults,” said the authors of a new study, led by Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands (JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:680-90).
The subjects were all expected to be in the ICU for at least 2 days, and were not delirious at baseline. The patients were randomly assigned to receive one of two treatments or a placebo three times daily, with 350 receiving 1 mg of haloperidol; 732 receiving 2 mg of haloperidol; and 707 receiving a 0.9% sodium chloride placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol arm was stopped early because of futility.
There was no statistically significant difference in survival at the primary endpoint of 28 days following entrance into the study. At that point, 83.3% of the patients who received 2-mg does of haloperidol and 82.7% of the of the subjects who received the placebo were alive (absolute difference 0.6%, 95% confidence interval –3.4% to 4.6%).
Prophylactic haloperidol had no effect on reducing the incidence of delirium, which was diagnosed in 33.3% of haloperidol subjects and 33.0% of placebo patients. Likewise, there were no significant differences between the groups in the number of delirium-free and coma-free days, duration of mechanical ventilation, and ICU and hospital length of stay. The number of reported adverse events with treatment also did not differ significantly between the groups: 0.3% in the 2-mg haloperidol group versus 0.1% in the placebo arm.
The duration of prophylactic therapy was a median of 2 days, but a subgroup analysis in patients treated for more than 2 days also did not show any benefits with haloperidol.
“The study population included severely ill ICU adults whose brains may have been too seriously affected for haloperidol to exert a prophylactic effect, since in non-ICU adults, prophylactic haloperidol may have beneficial effects. But the subgroup of patients with a low severity of illness score also demonstrated no beneficial effects,” the investigators said.
Subjects were a mean of 66.6 years old; 61.4% were men. Most of the ICU admissions were urgent and for medical or surgical reasons.
This study was supported by ZonMw, the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. van den Boogaard had no disclosures. One author reported grants and consultant and speaker fees from Pfizer, Merck, Astellas, and Gilead, among others.
SOURCE: van den Boogaard M, et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
of 1,789 critically ill adults at 21 ICUs in the Netherlands.
Haloperidol is used routinely in ICUs to both treat and prevent delirium, which strikes up to half of ICU patients and is associated with prolonged mechanical ventilation, longer ICU and hospital stays, and increased mortality. Results of past studies have been mixed, with some showing a benefit for haloperidol in the ICU and others not.
“These findings do not support the use of prophylactic haloperidol in critically ill adults,” said the authors of a new study, led by Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands (JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319[7]:680-90).
The subjects were all expected to be in the ICU for at least 2 days, and were not delirious at baseline. The patients were randomly assigned to receive one of two treatments or a placebo three times daily, with 350 receiving 1 mg of haloperidol; 732 receiving 2 mg of haloperidol; and 707 receiving a 0.9% sodium chloride placebo. The 1-mg haloperidol arm was stopped early because of futility.
There was no statistically significant difference in survival at the primary endpoint of 28 days following entrance into the study. At that point, 83.3% of the patients who received 2-mg does of haloperidol and 82.7% of the of the subjects who received the placebo were alive (absolute difference 0.6%, 95% confidence interval –3.4% to 4.6%).
Prophylactic haloperidol had no effect on reducing the incidence of delirium, which was diagnosed in 33.3% of haloperidol subjects and 33.0% of placebo patients. Likewise, there were no significant differences between the groups in the number of delirium-free and coma-free days, duration of mechanical ventilation, and ICU and hospital length of stay. The number of reported adverse events with treatment also did not differ significantly between the groups: 0.3% in the 2-mg haloperidol group versus 0.1% in the placebo arm.
The duration of prophylactic therapy was a median of 2 days, but a subgroup analysis in patients treated for more than 2 days also did not show any benefits with haloperidol.
“The study population included severely ill ICU adults whose brains may have been too seriously affected for haloperidol to exert a prophylactic effect, since in non-ICU adults, prophylactic haloperidol may have beneficial effects. But the subgroup of patients with a low severity of illness score also demonstrated no beneficial effects,” the investigators said.
Subjects were a mean of 66.6 years old; 61.4% were men. Most of the ICU admissions were urgent and for medical or surgical reasons.
This study was supported by ZonMw, the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. van den Boogaard had no disclosures. One author reported grants and consultant and speaker fees from Pfizer, Merck, Astellas, and Gilead, among others.
SOURCE: van den Boogaard M, et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Prophylactic haloperidol did not prevent delirium or improve survival in a large, placebo-controlled trial at 21 ICUs in the Netherlands.
Major finding: Delirium was diagnosed in 33.3% of haloperidol subjects versus 33.0% of placebo patients.
Study details: The trial enrolled 1,789 critically ill adults.
Disclosures: This work was supported by ZonMw, the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. The lead investigator had no disclosures.
Source: van den Boogaard M et al. JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):680-90.
ALT-70 score outperformed thermal imaging for cellulitis diagnosis
SAN DIEGO – A simple scoring system surpassed thermal imaging for diagnosing lower extremity cellulitis in a head-to-head, single-center comparison in 67 patients.
The ALT-70 score – which tallies points for asymmetry, leukocytosis, tachycardia, and age of at least 70 years – produced a positive predictive value for lower-extremity cellulitis (LEC) of 80.4% and a negative predictive value of 90.9%, compared with values of 75.5% and 57.1%, respectively, for thermal imaging when researchers applied both methods to 67 patients, said David G. Li, a clinical research fellow in the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, where the study was conducted.
The senior author of Mr. Li’s report, Arash Mostaghimi, MD, director of the inpatient consultation service, department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s, was also lead investigator for the team of dermatology researchers – from his center and from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston – who recently devised the ALT-70 scoring system for diagnosing LEC (J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2017 April;76[4]:618-25.e2).
The four-item survey can generate a score of 0-7, with a score of 0-2 suggesting need for additional monitoring, a score of 3-4 initiating a dermatology consult, and a score of 5-7 triggering immediate treatment for cellulitis, Mr. Li said. The 2017 review of ALT-70 showed that among 259 patients, those with a score of 0-2 had an 83% likelihood of having pseudocellulitis, while patients with a score of 5-7 had an 82% likelihood of having true cellulitis.
The current study enrolled 67 patients who had a presumptive diagnosis of LEC while in the emergency department or inpatient wards during a 7-month period. In addition to undergoing blinded assessment by both thermal imaging and by ALT-70 scoring, all patients also underwent blinded assessment by a board-certified dermatologist, who provided the definitive diagnosis. The attending dermatologists determined that 46 of the patients had true LEC and 21 patients did not.
The calculated sensitivity of ALT-70 was 97.8%, compared with 87.0% for thermal imaging. Specificity was 47.6% for ALT-70 and 38.1% for thermal imaging, Mr. Li reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
He also presented an analysis of the results when he combined both methods, with a positive on both assessments required to produce a positive LEC diagnosis. This resulted in a positive predictive value of 86.7%, slightly higher than the 80.4% from ALT-70 alone, but the combination produced a negative predictive value of 68.2%, substantially less than the 90.9% rate with ALT-70 alone. This demonstrated the “marginal benefit” from combining the two methods, he said.
In a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, in which the area under the curve (c-statistic) reflects a diagnostic test’s validity, ALT-70 produced a c-statistic of 0.85, thermal imaging had a c-statistic of 0.63, and when combined, the c-statistic was 0.88.
Mr. Li called for validation of the findings using larger and different patient populations.
He had no reported disclosures.
SOURCE: Li DG et al. AAD 18, Abstract 6744.
SAN DIEGO – A simple scoring system surpassed thermal imaging for diagnosing lower extremity cellulitis in a head-to-head, single-center comparison in 67 patients.
The ALT-70 score – which tallies points for asymmetry, leukocytosis, tachycardia, and age of at least 70 years – produced a positive predictive value for lower-extremity cellulitis (LEC) of 80.4% and a negative predictive value of 90.9%, compared with values of 75.5% and 57.1%, respectively, for thermal imaging when researchers applied both methods to 67 patients, said David G. Li, a clinical research fellow in the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, where the study was conducted.
The senior author of Mr. Li’s report, Arash Mostaghimi, MD, director of the inpatient consultation service, department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s, was also lead investigator for the team of dermatology researchers – from his center and from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston – who recently devised the ALT-70 scoring system for diagnosing LEC (J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2017 April;76[4]:618-25.e2).
The four-item survey can generate a score of 0-7, with a score of 0-2 suggesting need for additional monitoring, a score of 3-4 initiating a dermatology consult, and a score of 5-7 triggering immediate treatment for cellulitis, Mr. Li said. The 2017 review of ALT-70 showed that among 259 patients, those with a score of 0-2 had an 83% likelihood of having pseudocellulitis, while patients with a score of 5-7 had an 82% likelihood of having true cellulitis.
The current study enrolled 67 patients who had a presumptive diagnosis of LEC while in the emergency department or inpatient wards during a 7-month period. In addition to undergoing blinded assessment by both thermal imaging and by ALT-70 scoring, all patients also underwent blinded assessment by a board-certified dermatologist, who provided the definitive diagnosis. The attending dermatologists determined that 46 of the patients had true LEC and 21 patients did not.
The calculated sensitivity of ALT-70 was 97.8%, compared with 87.0% for thermal imaging. Specificity was 47.6% for ALT-70 and 38.1% for thermal imaging, Mr. Li reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
He also presented an analysis of the results when he combined both methods, with a positive on both assessments required to produce a positive LEC diagnosis. This resulted in a positive predictive value of 86.7%, slightly higher than the 80.4% from ALT-70 alone, but the combination produced a negative predictive value of 68.2%, substantially less than the 90.9% rate with ALT-70 alone. This demonstrated the “marginal benefit” from combining the two methods, he said.
In a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, in which the area under the curve (c-statistic) reflects a diagnostic test’s validity, ALT-70 produced a c-statistic of 0.85, thermal imaging had a c-statistic of 0.63, and when combined, the c-statistic was 0.88.
Mr. Li called for validation of the findings using larger and different patient populations.
He had no reported disclosures.
SOURCE: Li DG et al. AAD 18, Abstract 6744.
SAN DIEGO – A simple scoring system surpassed thermal imaging for diagnosing lower extremity cellulitis in a head-to-head, single-center comparison in 67 patients.
The ALT-70 score – which tallies points for asymmetry, leukocytosis, tachycardia, and age of at least 70 years – produced a positive predictive value for lower-extremity cellulitis (LEC) of 80.4% and a negative predictive value of 90.9%, compared with values of 75.5% and 57.1%, respectively, for thermal imaging when researchers applied both methods to 67 patients, said David G. Li, a clinical research fellow in the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, where the study was conducted.
The senior author of Mr. Li’s report, Arash Mostaghimi, MD, director of the inpatient consultation service, department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s, was also lead investigator for the team of dermatology researchers – from his center and from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston – who recently devised the ALT-70 scoring system for diagnosing LEC (J Amer Acad Dermatol. 2017 April;76[4]:618-25.e2).
The four-item survey can generate a score of 0-7, with a score of 0-2 suggesting need for additional monitoring, a score of 3-4 initiating a dermatology consult, and a score of 5-7 triggering immediate treatment for cellulitis, Mr. Li said. The 2017 review of ALT-70 showed that among 259 patients, those with a score of 0-2 had an 83% likelihood of having pseudocellulitis, while patients with a score of 5-7 had an 82% likelihood of having true cellulitis.
The current study enrolled 67 patients who had a presumptive diagnosis of LEC while in the emergency department or inpatient wards during a 7-month period. In addition to undergoing blinded assessment by both thermal imaging and by ALT-70 scoring, all patients also underwent blinded assessment by a board-certified dermatologist, who provided the definitive diagnosis. The attending dermatologists determined that 46 of the patients had true LEC and 21 patients did not.
The calculated sensitivity of ALT-70 was 97.8%, compared with 87.0% for thermal imaging. Specificity was 47.6% for ALT-70 and 38.1% for thermal imaging, Mr. Li reported at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
He also presented an analysis of the results when he combined both methods, with a positive on both assessments required to produce a positive LEC diagnosis. This resulted in a positive predictive value of 86.7%, slightly higher than the 80.4% from ALT-70 alone, but the combination produced a negative predictive value of 68.2%, substantially less than the 90.9% rate with ALT-70 alone. This demonstrated the “marginal benefit” from combining the two methods, he said.
In a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, in which the area under the curve (c-statistic) reflects a diagnostic test’s validity, ALT-70 produced a c-statistic of 0.85, thermal imaging had a c-statistic of 0.63, and when combined, the c-statistic was 0.88.
Mr. Li called for validation of the findings using larger and different patient populations.
He had no reported disclosures.
SOURCE: Li DG et al. AAD 18, Abstract 6744.
REPORTING FROM AAD 18
Key clinical point: The ALT-70 score surpassed thermal imaging for diagnosing lower-extremity cellulitis.
Major finding: Positive and negative predictive values were 80.4% and 90.9% for ALT-70 and 75.5% and 57.1% for thermal imaging.
Study details: A single-center study with 67 patients.
Disclosures: Mr. Li had no disclosures.
Source: Li DG et al. AAD 18, Abstract 6744.
Prehospital antibiotics improved some aspects of sepsis care
SAN ANTONIO – according to results of a randomized trial.
Emergency medical service (EMS) personnel were able to recognize sepsis more quickly, obtain blood cultures, and give antibiotics after the training, reported investigator Prabath Nanayakkara, MD, PhD, FRCP, at the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Critical Care Congress.
At 28 days, 120 patients (8%) in the prehospital antibiotics group had died, compared with 93 patients (8%) in the usual care group (relative risk, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.24), according to the study’s results that were simultaneously published online in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The intervention group received antibiotics a median of 26 minutes prior to emergency department (ED) arrival. In the usual care group, median time to antibiotics after ED arrival was 70 minutes, versus 93 minutes prior to the sepsis recognition training (P = .142), the report further says.
“We do not advise prehospital antibiotics at the moment for patients with suspected sepsis,” Dr. Nanayakkara said, during his presentation at the conference.
Other countries might see different results, he cautioned.
In the Netherlands, ambulances reach the emergency scene within 15 minutes 93% of the time, and the average time from dispatch call to ED arrival is 40 minutes, Dr. Nanayakkara noted in the report.
“In part, due to the relatively short response times in the Netherlands, we don’t know if there are other countries with longer response times that would have other results, and whether they should use antibiotics in their ambulances,” Dr. Nanayakkara said in his presentation.
The study was the first-ever prospective randomized, controlled open-label trial to compare early prehospital antibiotics with standard care.
Before the study was started, EMS personnel at 10 large regional ambulance services serving 34 secondary or tertiary hospitals were trained in recognizing sepsis, the report says.
A total of 2,672 patients with suspected sepsis were included in the intention-to-treat analysis, of whom 1,535 were randomized to receive prehospital antibiotics and 1,137 to usual EMS care, which consisted of fluid resuscitation and supplementary oxygen.
The primary end point of the study was all-cause mortality at 28 days.
The negative mortality results of this trial are “not surprising,” given that the trial’s inclusion criteria allowed individuals with suspected infection but without organ dysfunction, said Jean-Louis Vincent, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Hospital, Brussels, in a related editorial appearing in the Lancet Respiratory Medicine (2018 Jan. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600[17]30446-0).
Recent consensus definitions of sepsis recognize that sepsis is the association of an infection with some degree of organ dysfunction, according to Dr. Vincent.
“After this initial experience, I believe that a randomized, controlled trial could be done to assess the potential benefit of early antibiotic administration in the ambulance for patients with organ dysfunction associated with infection,” Dr. Vincent wrote in his editorial.
Dr. Nanayakkara and his coauthors declared no competing interests related to their study.
SOURCE: Alam N et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Jan;6(1):40-50.
SAN ANTONIO – according to results of a randomized trial.
Emergency medical service (EMS) personnel were able to recognize sepsis more quickly, obtain blood cultures, and give antibiotics after the training, reported investigator Prabath Nanayakkara, MD, PhD, FRCP, at the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Critical Care Congress.
At 28 days, 120 patients (8%) in the prehospital antibiotics group had died, compared with 93 patients (8%) in the usual care group (relative risk, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.24), according to the study’s results that were simultaneously published online in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The intervention group received antibiotics a median of 26 minutes prior to emergency department (ED) arrival. In the usual care group, median time to antibiotics after ED arrival was 70 minutes, versus 93 minutes prior to the sepsis recognition training (P = .142), the report further says.
“We do not advise prehospital antibiotics at the moment for patients with suspected sepsis,” Dr. Nanayakkara said, during his presentation at the conference.
Other countries might see different results, he cautioned.
In the Netherlands, ambulances reach the emergency scene within 15 minutes 93% of the time, and the average time from dispatch call to ED arrival is 40 minutes, Dr. Nanayakkara noted in the report.
“In part, due to the relatively short response times in the Netherlands, we don’t know if there are other countries with longer response times that would have other results, and whether they should use antibiotics in their ambulances,” Dr. Nanayakkara said in his presentation.
The study was the first-ever prospective randomized, controlled open-label trial to compare early prehospital antibiotics with standard care.
Before the study was started, EMS personnel at 10 large regional ambulance services serving 34 secondary or tertiary hospitals were trained in recognizing sepsis, the report says.
A total of 2,672 patients with suspected sepsis were included in the intention-to-treat analysis, of whom 1,535 were randomized to receive prehospital antibiotics and 1,137 to usual EMS care, which consisted of fluid resuscitation and supplementary oxygen.
The primary end point of the study was all-cause mortality at 28 days.
The negative mortality results of this trial are “not surprising,” given that the trial’s inclusion criteria allowed individuals with suspected infection but without organ dysfunction, said Jean-Louis Vincent, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Hospital, Brussels, in a related editorial appearing in the Lancet Respiratory Medicine (2018 Jan. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600[17]30446-0).
Recent consensus definitions of sepsis recognize that sepsis is the association of an infection with some degree of organ dysfunction, according to Dr. Vincent.
“After this initial experience, I believe that a randomized, controlled trial could be done to assess the potential benefit of early antibiotic administration in the ambulance for patients with organ dysfunction associated with infection,” Dr. Vincent wrote in his editorial.
Dr. Nanayakkara and his coauthors declared no competing interests related to their study.
SOURCE: Alam N et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Jan;6(1):40-50.
SAN ANTONIO – according to results of a randomized trial.
Emergency medical service (EMS) personnel were able to recognize sepsis more quickly, obtain blood cultures, and give antibiotics after the training, reported investigator Prabath Nanayakkara, MD, PhD, FRCP, at the Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Critical Care Congress.
At 28 days, 120 patients (8%) in the prehospital antibiotics group had died, compared with 93 patients (8%) in the usual care group (relative risk, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.24), according to the study’s results that were simultaneously published online in Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
The intervention group received antibiotics a median of 26 minutes prior to emergency department (ED) arrival. In the usual care group, median time to antibiotics after ED arrival was 70 minutes, versus 93 minutes prior to the sepsis recognition training (P = .142), the report further says.
“We do not advise prehospital antibiotics at the moment for patients with suspected sepsis,” Dr. Nanayakkara said, during his presentation at the conference.
Other countries might see different results, he cautioned.
In the Netherlands, ambulances reach the emergency scene within 15 minutes 93% of the time, and the average time from dispatch call to ED arrival is 40 minutes, Dr. Nanayakkara noted in the report.
“In part, due to the relatively short response times in the Netherlands, we don’t know if there are other countries with longer response times that would have other results, and whether they should use antibiotics in their ambulances,” Dr. Nanayakkara said in his presentation.
The study was the first-ever prospective randomized, controlled open-label trial to compare early prehospital antibiotics with standard care.
Before the study was started, EMS personnel at 10 large regional ambulance services serving 34 secondary or tertiary hospitals were trained in recognizing sepsis, the report says.
A total of 2,672 patients with suspected sepsis were included in the intention-to-treat analysis, of whom 1,535 were randomized to receive prehospital antibiotics and 1,137 to usual EMS care, which consisted of fluid resuscitation and supplementary oxygen.
The primary end point of the study was all-cause mortality at 28 days.
The negative mortality results of this trial are “not surprising,” given that the trial’s inclusion criteria allowed individuals with suspected infection but without organ dysfunction, said Jean-Louis Vincent, MD, PhD, of Erasmus Hospital, Brussels, in a related editorial appearing in the Lancet Respiratory Medicine (2018 Jan. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600[17]30446-0).
Recent consensus definitions of sepsis recognize that sepsis is the association of an infection with some degree of organ dysfunction, according to Dr. Vincent.
“After this initial experience, I believe that a randomized, controlled trial could be done to assess the potential benefit of early antibiotic administration in the ambulance for patients with organ dysfunction associated with infection,” Dr. Vincent wrote in his editorial.
Dr. Nanayakkara and his coauthors declared no competing interests related to their study.
SOURCE: Alam N et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Jan;6(1):40-50.
REPORTING FROM CCC47
Key clinical point: In patients with suspected sepsis, prehospital antibiotics delivered by EMS personnel improved some aspects of care, but did not reduce mortality.
Major finding: At 28 days, 120 patients (8%) in the prehospital antibiotics group had died, compared with 93 patients (8%) in the usual care group (relative risk, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.74-1.24).
Data source: Intention-to-treat analysis of 2,672 patients in a prospective randomized, controlled open-label trial comparing early prehospital antibiotics to standard care.
Disclosures: The study authors declared no competing interests related to the study.
Source: Alam N et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Jan;6(1):40-50.
Preparing to respond to workplace violence
SAN ANTONIO – , Lewis J. Kaplan, MD, said in a late-breaking session at the Critical Care Congress.
“Workplace violence is not just active shooter – it’s ubiquitous, and we only know a little bit about it,” noted Dr. Kaplan, section chief, surgical critical care, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia. “The facility and everyone in the health care team have a role in being an active participant, rather than a passive one.”
To actively prepare for premeditated events, Dr. Kaplan recommended that clinicians develop partnerships with local law enforcement officials and initiate active training that involves anyone who could come into contact with an active shooter.
There are many steps that can be taken to protect the facility, including visitor screening and management, security that extends to the perimeter of the facility, building design that limits access to specific places in the facility, and deployment of firearm detection canines, Dr. Kaplan said, during the session at the Critical Care Congress, sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In all, Dr. Kaplan listed 19 steps that facilities could take to avert a planned attack, drawing in part on recommendations from the FBI publication, Workplace violence: Issues in response.
“This is a lot, and you don’t need to do all of it,” Dr. Kaplan said. “But you need to have an internally consistent plan for how you will do this at your facility, and it must involve everyone. They all need to be able to be part of your team.”
Recent data on workplace violence
The latest data show that the great majority of workplace violence is perpetrated by individuals outside the organization. According to the IAHSS Foundation 2017 Healthcare Crime Survey, 89% of events involved a customer or patient of the workplace or employees.
In-hospital violence is prevalent, according to 2016 data from Occupational Safety and Health Administration that identified 24,000 workplace assaults in a 3-year span covering 2013-2015, including 33 homicides, 30 assaults, and 74 rapes.
Many in-hospital incidents are marked by failures in communication, patient observation, noncompliance with workplace violence policies or lack of such policies, and perhaps most importantly, an inadequate assessment for the violent potential of the perpetrator, according to Dr. Kaplan.
In a 2017 survey of 150 trauma nurses, 67% said they had been the victim of physical violence at work, though many did not report the incidents, Dr. Kaplan noted. Some reasons nurses gave for not reporting violence included the feeling that it was “just part of the job” in 27% of cases, and concerns about patient satisfaction scores in 10% of the cases.
Active shooter events in the workplace are of particular concern, though they are relatively rare; one recent report identified 160 events that occurred during 2000-2013 in which 1,043 individuals were injured, according to Dr. Kaplan.
Other presentations in the late-breaking session covered issues related to disaster preparedness and the Charlie Gard case.
“We picked these three topics to be in a late-breaker session not only because of the recent events that had happened, but because they have a common thread – it’s not a matter of if it will happen, but when will it happen, and are you ready and how do we prepare,” said session chair Gloria M. Rodriguez Vega, MD.
“One of the things I learned as a fellow was that part of the success in critical care was attention to detail and layers of safety,” said Dr. Rodriguez Vega, an intensivist in Bayamon, Puerto Rico. “I think you can apply that to all these situations.”
Dr. Kaplan had no industry disclosures related to his presentation.
SAN ANTONIO – , Lewis J. Kaplan, MD, said in a late-breaking session at the Critical Care Congress.
“Workplace violence is not just active shooter – it’s ubiquitous, and we only know a little bit about it,” noted Dr. Kaplan, section chief, surgical critical care, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia. “The facility and everyone in the health care team have a role in being an active participant, rather than a passive one.”
To actively prepare for premeditated events, Dr. Kaplan recommended that clinicians develop partnerships with local law enforcement officials and initiate active training that involves anyone who could come into contact with an active shooter.
There are many steps that can be taken to protect the facility, including visitor screening and management, security that extends to the perimeter of the facility, building design that limits access to specific places in the facility, and deployment of firearm detection canines, Dr. Kaplan said, during the session at the Critical Care Congress, sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In all, Dr. Kaplan listed 19 steps that facilities could take to avert a planned attack, drawing in part on recommendations from the FBI publication, Workplace violence: Issues in response.
“This is a lot, and you don’t need to do all of it,” Dr. Kaplan said. “But you need to have an internally consistent plan for how you will do this at your facility, and it must involve everyone. They all need to be able to be part of your team.”
Recent data on workplace violence
The latest data show that the great majority of workplace violence is perpetrated by individuals outside the organization. According to the IAHSS Foundation 2017 Healthcare Crime Survey, 89% of events involved a customer or patient of the workplace or employees.
In-hospital violence is prevalent, according to 2016 data from Occupational Safety and Health Administration that identified 24,000 workplace assaults in a 3-year span covering 2013-2015, including 33 homicides, 30 assaults, and 74 rapes.
Many in-hospital incidents are marked by failures in communication, patient observation, noncompliance with workplace violence policies or lack of such policies, and perhaps most importantly, an inadequate assessment for the violent potential of the perpetrator, according to Dr. Kaplan.
In a 2017 survey of 150 trauma nurses, 67% said they had been the victim of physical violence at work, though many did not report the incidents, Dr. Kaplan noted. Some reasons nurses gave for not reporting violence included the feeling that it was “just part of the job” in 27% of cases, and concerns about patient satisfaction scores in 10% of the cases.
Active shooter events in the workplace are of particular concern, though they are relatively rare; one recent report identified 160 events that occurred during 2000-2013 in which 1,043 individuals were injured, according to Dr. Kaplan.
Other presentations in the late-breaking session covered issues related to disaster preparedness and the Charlie Gard case.
“We picked these three topics to be in a late-breaker session not only because of the recent events that had happened, but because they have a common thread – it’s not a matter of if it will happen, but when will it happen, and are you ready and how do we prepare,” said session chair Gloria M. Rodriguez Vega, MD.
“One of the things I learned as a fellow was that part of the success in critical care was attention to detail and layers of safety,” said Dr. Rodriguez Vega, an intensivist in Bayamon, Puerto Rico. “I think you can apply that to all these situations.”
Dr. Kaplan had no industry disclosures related to his presentation.
SAN ANTONIO – , Lewis J. Kaplan, MD, said in a late-breaking session at the Critical Care Congress.
“Workplace violence is not just active shooter – it’s ubiquitous, and we only know a little bit about it,” noted Dr. Kaplan, section chief, surgical critical care, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia. “The facility and everyone in the health care team have a role in being an active participant, rather than a passive one.”
To actively prepare for premeditated events, Dr. Kaplan recommended that clinicians develop partnerships with local law enforcement officials and initiate active training that involves anyone who could come into contact with an active shooter.
There are many steps that can be taken to protect the facility, including visitor screening and management, security that extends to the perimeter of the facility, building design that limits access to specific places in the facility, and deployment of firearm detection canines, Dr. Kaplan said, during the session at the Critical Care Congress, sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In all, Dr. Kaplan listed 19 steps that facilities could take to avert a planned attack, drawing in part on recommendations from the FBI publication, Workplace violence: Issues in response.
“This is a lot, and you don’t need to do all of it,” Dr. Kaplan said. “But you need to have an internally consistent plan for how you will do this at your facility, and it must involve everyone. They all need to be able to be part of your team.”
Recent data on workplace violence
The latest data show that the great majority of workplace violence is perpetrated by individuals outside the organization. According to the IAHSS Foundation 2017 Healthcare Crime Survey, 89% of events involved a customer or patient of the workplace or employees.
In-hospital violence is prevalent, according to 2016 data from Occupational Safety and Health Administration that identified 24,000 workplace assaults in a 3-year span covering 2013-2015, including 33 homicides, 30 assaults, and 74 rapes.
Many in-hospital incidents are marked by failures in communication, patient observation, noncompliance with workplace violence policies or lack of such policies, and perhaps most importantly, an inadequate assessment for the violent potential of the perpetrator, according to Dr. Kaplan.
In a 2017 survey of 150 trauma nurses, 67% said they had been the victim of physical violence at work, though many did not report the incidents, Dr. Kaplan noted. Some reasons nurses gave for not reporting violence included the feeling that it was “just part of the job” in 27% of cases, and concerns about patient satisfaction scores in 10% of the cases.
Active shooter events in the workplace are of particular concern, though they are relatively rare; one recent report identified 160 events that occurred during 2000-2013 in which 1,043 individuals were injured, according to Dr. Kaplan.
Other presentations in the late-breaking session covered issues related to disaster preparedness and the Charlie Gard case.
“We picked these three topics to be in a late-breaker session not only because of the recent events that had happened, but because they have a common thread – it’s not a matter of if it will happen, but when will it happen, and are you ready and how do we prepare,” said session chair Gloria M. Rodriguez Vega, MD.
“One of the things I learned as a fellow was that part of the success in critical care was attention to detail and layers of safety,” said Dr. Rodriguez Vega, an intensivist in Bayamon, Puerto Rico. “I think you can apply that to all these situations.”
Dr. Kaplan had no industry disclosures related to his presentation.
REPORTING FROM CCC47
Nonopioid analgesics have no major disadvantages vs. opioids for chronic pain
Patients treated with opioids for moderate to severe chronic back pain or knee or hip osteoarthritis pain saw no significant improvement when results were compared with treatment using acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the randomized SPACE study.
These findings may help restructure how physicians treat patients with chronic pain in order to decrease the risk of opioid addiction in a population that is particularly susceptible.
“Long-term opioid therapy became a standard approach to managing chronic musculoskeletal pain despite a lack of high-quality data on benefits and harms,” wrote Erin E. Krebs, MD, MPH, core investigator at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Center for Chronic Disease Outcomes Research, and her colleagues. “Rising rates of opioid overdose deaths have raised questions about prescribing opioids for chronic pain management.”
In the 12-month SPACE (Strategies for Prescribing Analgesics Comparative Effectiveness) trial published March 6 in JAMA, the investigators reported randomizing a total of 240 patients to treatment with immediate-release opioids (morphine, oxycodone, or hydrocodone/acetaminophen) or acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The patients came from the Minneapolis VA system between June 2013 and December 2015. Patients in the opioid group were on average 57 years old, while those in the nonopioid group had an average age of 60 years. Men comprised 87% of all patients, and both groups were predominantly white (86%-88%) with chronic back pain (65%). The investigators excluded patients with physiological opioid dependence from ongoing opioid use.
Patients taking opioids saw no significant improvement in the primary outcome of pain-related function on the seven-item Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) interference scale over those taking nonopioids at the end of the 12-month period (P = .58), according to Dr. Krebs and her fellow investigators.
The main secondary outcome of pain intensity using the four-item BPI severity scale improved significantly more among the nonopioid group, which reported an average score of 3.5, compared with 4.0 in the opioid group (P = .03). However, the small difference of 0.5 is less than the minimal clinically important difference of 1.0, according to the investigators.
Anxiety control was the only secondary outcome measure that was significantly better among patients in the opioid group, which was unsurprising to the investigators. “This finding is consistent with the role of the endogenous opioid system in stress and emotional suffering,” they wrote.
The investigators were uncertain about the significance of this small difference because overall anxiety levels were low, with 9% of patients reporting moderate severity anxiety symptoms at baseline.
Patients in the opioid group took a mean of 1.7 analgesics during the study period, compared with 3.8 in the nonopioid group. In the nonopioid group, the mean number of months that nonopioid analgesics were prescribed ranged from 2.6 for acetaminophen to 5.9 with oral NSAIDs. In this group, tramadol was prescribed to no more than 11% of patients during any particular month and was dispensed for a mean of 0.4 months overall.
Patients in the opioid group took opioids for a mean of 8.1 months, with all other analgesics taken for a mean of 0.4 months or less. The authors noted that in “each 90-day follow-up period, fewer than 15% of patients in the opioid group had a mean dispensed dosage of 50 morphine-equivalent mg/day or more.” Patients could be titrated up to a maximum daily dosage of 100 morphine-equivalent mg/day.
Patients prescribed opioids were significantly more likely to report medication-related symptoms, and while misuse was not significantly higher in the opioid group, the investigators said that “Overall, opioids did not demonstrate any advantage over nonopioid medications that could potentially outweigh their greater risk of harms.”
Further studies will need to include a more diverse population, they noted.
The study was funded by an award from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service. The investigators reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Krebs EE et al. JAMA. 2018 Mar 6;319(9):872-82
Patients treated with opioids for moderate to severe chronic back pain or knee or hip osteoarthritis pain saw no significant improvement when results were compared with treatment using acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the randomized SPACE study.
These findings may help restructure how physicians treat patients with chronic pain in order to decrease the risk of opioid addiction in a population that is particularly susceptible.
“Long-term opioid therapy became a standard approach to managing chronic musculoskeletal pain despite a lack of high-quality data on benefits and harms,” wrote Erin E. Krebs, MD, MPH, core investigator at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Center for Chronic Disease Outcomes Research, and her colleagues. “Rising rates of opioid overdose deaths have raised questions about prescribing opioids for chronic pain management.”
In the 12-month SPACE (Strategies for Prescribing Analgesics Comparative Effectiveness) trial published March 6 in JAMA, the investigators reported randomizing a total of 240 patients to treatment with immediate-release opioids (morphine, oxycodone, or hydrocodone/acetaminophen) or acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The patients came from the Minneapolis VA system between June 2013 and December 2015. Patients in the opioid group were on average 57 years old, while those in the nonopioid group had an average age of 60 years. Men comprised 87% of all patients, and both groups were predominantly white (86%-88%) with chronic back pain (65%). The investigators excluded patients with physiological opioid dependence from ongoing opioid use.
Patients taking opioids saw no significant improvement in the primary outcome of pain-related function on the seven-item Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) interference scale over those taking nonopioids at the end of the 12-month period (P = .58), according to Dr. Krebs and her fellow investigators.
The main secondary outcome of pain intensity using the four-item BPI severity scale improved significantly more among the nonopioid group, which reported an average score of 3.5, compared with 4.0 in the opioid group (P = .03). However, the small difference of 0.5 is less than the minimal clinically important difference of 1.0, according to the investigators.
Anxiety control was the only secondary outcome measure that was significantly better among patients in the opioid group, which was unsurprising to the investigators. “This finding is consistent with the role of the endogenous opioid system in stress and emotional suffering,” they wrote.
The investigators were uncertain about the significance of this small difference because overall anxiety levels were low, with 9% of patients reporting moderate severity anxiety symptoms at baseline.
Patients in the opioid group took a mean of 1.7 analgesics during the study period, compared with 3.8 in the nonopioid group. In the nonopioid group, the mean number of months that nonopioid analgesics were prescribed ranged from 2.6 for acetaminophen to 5.9 with oral NSAIDs. In this group, tramadol was prescribed to no more than 11% of patients during any particular month and was dispensed for a mean of 0.4 months overall.
Patients in the opioid group took opioids for a mean of 8.1 months, with all other analgesics taken for a mean of 0.4 months or less. The authors noted that in “each 90-day follow-up period, fewer than 15% of patients in the opioid group had a mean dispensed dosage of 50 morphine-equivalent mg/day or more.” Patients could be titrated up to a maximum daily dosage of 100 morphine-equivalent mg/day.
Patients prescribed opioids were significantly more likely to report medication-related symptoms, and while misuse was not significantly higher in the opioid group, the investigators said that “Overall, opioids did not demonstrate any advantage over nonopioid medications that could potentially outweigh their greater risk of harms.”
Further studies will need to include a more diverse population, they noted.
The study was funded by an award from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service. The investigators reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Krebs EE et al. JAMA. 2018 Mar 6;319(9):872-82
Patients treated with opioids for moderate to severe chronic back pain or knee or hip osteoarthritis pain saw no significant improvement when results were compared with treatment using acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the randomized SPACE study.
These findings may help restructure how physicians treat patients with chronic pain in order to decrease the risk of opioid addiction in a population that is particularly susceptible.
“Long-term opioid therapy became a standard approach to managing chronic musculoskeletal pain despite a lack of high-quality data on benefits and harms,” wrote Erin E. Krebs, MD, MPH, core investigator at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Center for Chronic Disease Outcomes Research, and her colleagues. “Rising rates of opioid overdose deaths have raised questions about prescribing opioids for chronic pain management.”
In the 12-month SPACE (Strategies for Prescribing Analgesics Comparative Effectiveness) trial published March 6 in JAMA, the investigators reported randomizing a total of 240 patients to treatment with immediate-release opioids (morphine, oxycodone, or hydrocodone/acetaminophen) or acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The patients came from the Minneapolis VA system between June 2013 and December 2015. Patients in the opioid group were on average 57 years old, while those in the nonopioid group had an average age of 60 years. Men comprised 87% of all patients, and both groups were predominantly white (86%-88%) with chronic back pain (65%). The investigators excluded patients with physiological opioid dependence from ongoing opioid use.
Patients taking opioids saw no significant improvement in the primary outcome of pain-related function on the seven-item Brief Pain Inventory (BPI) interference scale over those taking nonopioids at the end of the 12-month period (P = .58), according to Dr. Krebs and her fellow investigators.
The main secondary outcome of pain intensity using the four-item BPI severity scale improved significantly more among the nonopioid group, which reported an average score of 3.5, compared with 4.0 in the opioid group (P = .03). However, the small difference of 0.5 is less than the minimal clinically important difference of 1.0, according to the investigators.
Anxiety control was the only secondary outcome measure that was significantly better among patients in the opioid group, which was unsurprising to the investigators. “This finding is consistent with the role of the endogenous opioid system in stress and emotional suffering,” they wrote.
The investigators were uncertain about the significance of this small difference because overall anxiety levels were low, with 9% of patients reporting moderate severity anxiety symptoms at baseline.
Patients in the opioid group took a mean of 1.7 analgesics during the study period, compared with 3.8 in the nonopioid group. In the nonopioid group, the mean number of months that nonopioid analgesics were prescribed ranged from 2.6 for acetaminophen to 5.9 with oral NSAIDs. In this group, tramadol was prescribed to no more than 11% of patients during any particular month and was dispensed for a mean of 0.4 months overall.
Patients in the opioid group took opioids for a mean of 8.1 months, with all other analgesics taken for a mean of 0.4 months or less. The authors noted that in “each 90-day follow-up period, fewer than 15% of patients in the opioid group had a mean dispensed dosage of 50 morphine-equivalent mg/day or more.” Patients could be titrated up to a maximum daily dosage of 100 morphine-equivalent mg/day.
Patients prescribed opioids were significantly more likely to report medication-related symptoms, and while misuse was not significantly higher in the opioid group, the investigators said that “Overall, opioids did not demonstrate any advantage over nonopioid medications that could potentially outweigh their greater risk of harms.”
Further studies will need to include a more diverse population, they noted.
The study was funded by an award from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service. The investigators reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Krebs EE et al. JAMA. 2018 Mar 6;319(9):872-82
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: Opioids and nonopioid analgesics provided similar improvements in pain-related function for patients with chronic pain.
Major finding: Patients taking opioids did not show significant improvement in pain-related function, compared with those taking nonopioids (P = .58).
Study details: A 12-month, randomized trial of 240 patients with chronic back, knee, or hip pain, gathered from a Veterans Affairs clinic between June 2013 to December 2015.
Disclosures: The study was funded by an award from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Health Services Research and Development Service. The investigators reported no relevant disclosures.
Source: Krebs E et al. JAMA. 2018;319(9):872-82
Opioid deaths in the ED increase nationally
Opioid-related deaths in emergency departments increased by approximately 30% across all regions of the United States between 2016 and 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Analysis of 91 million ED visits from the CDC’s National Syndromic Surveillance Program and Enhanced State Opioid Overdose Surveillance database found significant increases in opioid overdose deaths in 16 states, reaching as high as 109% in Wisconsin and 106% in Delaware, CDC officials said during a press briefing.
“We are currently seeing the highest drug overdose death rate ever recorded in the United States, driven by prescription opioids and by illicit opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl,” said Anne Schuchat, MD, acting CDC director. “In 2016, there were more than 63,000 drug overdose deaths, and more than 42,000 of those deaths involved an opioid.”
Of the 91 million visits, a total of 261,755 were suspected of opioid overdoses across both databases.
The greatest increase was seen in the Midwest region (69.7%), followed by the West (40.3%), Northeast (21.3%), Southwest (20.2%), and Southeast (14%).
Death rates rose across all demographics, regardless of sex or age.
While Delaware recorded some of the highest increases in deaths, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island decreased, although not within statistical significance.
“These decreases may possibly be related to implementation of interventions, including expansion of access to medication-assisted treatment,” said Dr. Schuchat. “The decrease in Kentucky during this period of time may reflect some fluctuations in drug supply.”
In a comparison of urban and rural areas, large and medium metropolitan communities had the sharpest increase, at 45%.
To combat the rise in deaths, the CDC is encouraging an increase in naloxone distribution and training for first responders and community members.
The agency also recommends that local health departments begin using ED data to alert local communities when opioid-related deaths rise.
“This is a very difficult and fast-moving epidemic, and there are no easy solutions,” Dr. Schuchat said. [These data send] “a wake-up call about the need to improve what happens when patients leave the emergency department; all of us working together, government, public health, the medical community, law enforcement, and community members themselves can help fight this epidemic and save lives.”
SOURCE: Vivolo-Kantor AM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 6 Mar 2018. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6709e1.
Opioid-related deaths in emergency departments increased by approximately 30% across all regions of the United States between 2016 and 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Analysis of 91 million ED visits from the CDC’s National Syndromic Surveillance Program and Enhanced State Opioid Overdose Surveillance database found significant increases in opioid overdose deaths in 16 states, reaching as high as 109% in Wisconsin and 106% in Delaware, CDC officials said during a press briefing.
“We are currently seeing the highest drug overdose death rate ever recorded in the United States, driven by prescription opioids and by illicit opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl,” said Anne Schuchat, MD, acting CDC director. “In 2016, there were more than 63,000 drug overdose deaths, and more than 42,000 of those deaths involved an opioid.”
Of the 91 million visits, a total of 261,755 were suspected of opioid overdoses across both databases.
The greatest increase was seen in the Midwest region (69.7%), followed by the West (40.3%), Northeast (21.3%), Southwest (20.2%), and Southeast (14%).
Death rates rose across all demographics, regardless of sex or age.
While Delaware recorded some of the highest increases in deaths, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island decreased, although not within statistical significance.
“These decreases may possibly be related to implementation of interventions, including expansion of access to medication-assisted treatment,” said Dr. Schuchat. “The decrease in Kentucky during this period of time may reflect some fluctuations in drug supply.”
In a comparison of urban and rural areas, large and medium metropolitan communities had the sharpest increase, at 45%.
To combat the rise in deaths, the CDC is encouraging an increase in naloxone distribution and training for first responders and community members.
The agency also recommends that local health departments begin using ED data to alert local communities when opioid-related deaths rise.
“This is a very difficult and fast-moving epidemic, and there are no easy solutions,” Dr. Schuchat said. [These data send] “a wake-up call about the need to improve what happens when patients leave the emergency department; all of us working together, government, public health, the medical community, law enforcement, and community members themselves can help fight this epidemic and save lives.”
SOURCE: Vivolo-Kantor AM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 6 Mar 2018. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6709e1.
Opioid-related deaths in emergency departments increased by approximately 30% across all regions of the United States between 2016 and 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Analysis of 91 million ED visits from the CDC’s National Syndromic Surveillance Program and Enhanced State Opioid Overdose Surveillance database found significant increases in opioid overdose deaths in 16 states, reaching as high as 109% in Wisconsin and 106% in Delaware, CDC officials said during a press briefing.
“We are currently seeing the highest drug overdose death rate ever recorded in the United States, driven by prescription opioids and by illicit opioids such as heroin and illicitly manufactured fentanyl,” said Anne Schuchat, MD, acting CDC director. “In 2016, there were more than 63,000 drug overdose deaths, and more than 42,000 of those deaths involved an opioid.”
Of the 91 million visits, a total of 261,755 were suspected of opioid overdoses across both databases.
The greatest increase was seen in the Midwest region (69.7%), followed by the West (40.3%), Northeast (21.3%), Southwest (20.2%), and Southeast (14%).
Death rates rose across all demographics, regardless of sex or age.
While Delaware recorded some of the highest increases in deaths, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Rhode Island decreased, although not within statistical significance.
“These decreases may possibly be related to implementation of interventions, including expansion of access to medication-assisted treatment,” said Dr. Schuchat. “The decrease in Kentucky during this period of time may reflect some fluctuations in drug supply.”
In a comparison of urban and rural areas, large and medium metropolitan communities had the sharpest increase, at 45%.
To combat the rise in deaths, the CDC is encouraging an increase in naloxone distribution and training for first responders and community members.
The agency also recommends that local health departments begin using ED data to alert local communities when opioid-related deaths rise.
“This is a very difficult and fast-moving epidemic, and there are no easy solutions,” Dr. Schuchat said. [These data send] “a wake-up call about the need to improve what happens when patients leave the emergency department; all of us working together, government, public health, the medical community, law enforcement, and community members themselves can help fight this epidemic and save lives.”
SOURCE: Vivolo-Kantor AM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 6 Mar 2018. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6709e1.
FROM MMWR
PICU, hospital admissions up due to opioid ingestion
Hospitalization and pediatric ICU admission rates for pediatric opioid-related ingestion are increasing, along with hospitalization costs, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“In this study, we demonstrate a significant and steady increase in the diagnosis of opioid ingestion and poisoning across all age groups in U.S. children’s hospitals from 2004 to 2015,” wrote Jason Kane, MD, of the University of Chicago, and his associates. “Not only did the absolute number of opioid-related admissions increase but the rate of both hospital and PICU [pediatric ICU] admissions increased as well.”
Using the Pediatric Health Information System database, the research team performed a retrospective cohort study of children aged 1-17 years who had been admitted to a PICU between Jan. 1, 2004, and Sep. 30, 2015. For statistical analysis, the years were grouped into separate epochs: 2004-2007, 2008-2011, and 2012-2015.
Of the 4,175,624 admissions to 31 different children’s hospitals around the United States, 3,647 (0.09%) were due to opioid-related conditions. Across the three epochs of the study, the number of opioid-related hospitalizations more than doubled from 797 to 1,504 and concurrently increased the rate of hospital admissions from 6.7 per 10,000 in 2004 to 10.9 per 10,000 in 2015 (P less than .001).
Similar to the trends in overall hospital admissions and hospital admission rates, admission to the PICU and PICU admission rates also increased. Of the 3,647 children admitted for opioid-related issues, 1,564 (43%) were subsequently admitted to the PICU. PICU admission rates also increased from 25 to 36 per 10,000 admissions (P less than .001).While the majority of opioid-related hospitalizations are associated with children aged 12-17 years, children under the age of 6 years accounted for one-third of these hospitalizations. Many PICU admissions are severe enough to warrant mechanical ventilator support (37%, P less than .001) and vasopressors (20%, P less than .001).
The opioids ingested prior to hospital admission varied between age groups, with 20% (243 of 1,249) patients aged 1-5 years ingesting methadone, compared with 10% (218 of 2,223) of patients aged 12-17 years. Heroin was much more common in this group, accounting for 4.4% (99 of 2,223) of patient hospitalizations.
In addition to the human cost of pediatric hospital admissions, there is a significant economic cost on the health care system. The median cost for PICU admission was $4,931. Although these costs have been dropping for the better part of a decade ($6,523 in 2004-2007 to $4,552 in 2012-2015, P less than .001), it still represents a substantial problem. In addition, admission rates are increasing, which will only place a heavier burden on the health care system, according to Dr. Kane and his associates.
Perhaps one positive point from this study is that although hospitalizations and intensive care rates have gone up, mortality decreased over time from 2.8% in 2004-2007 to 1.3% in 2012-2015.
A possible limitation of the data in this study is that it provides data from subjects whose data is accessible to the researcher, rather than those strategically selected. In addition, referral bias may reduce the ability to generalize the information to non–tertiary care children’s hospitals.
“The current U.S. opioid crisis is negatively impacting pediatric patients as the rate of hospitalization and PICU care for the ingestion of opioids by children continues to increase over time,” wrote Dr. Kane and his associates. “Current efforts to reduce prescription opioid use in adults have not curtailed the incidence of pediatric opioid ingestion, and additional efforts are needed to reduce preventable opioid exposure in children.”
This study had no external funding. Dr. Allison H. Bartlett has served as a consultant member of the CVS Caremark National Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. All other authors had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCE: Kane JM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Mar 5;141(4):e20173335.
The opioid crisis in the United States is staggering. As of 2016, an estimated 2.4 million Americans were considered to have an opioid use disorder, either from prescription drug misuse or heroin addiction. This number includes 0.6% of adolescents (12- to 17-year-olds) and 1.1% of young adults (18- to 25-year-olds). And 33,000 Americans died from opioid overdose in 2015. Despite the best attempts to control the supply of drugs and increase access to treatment, overdose deaths have doubled in the past 10 years. While the overdose death rate has plateaued among children under the age of 18, and misuse rates have dropped among 12th graders, opioid-related hospitalizations are increasing in preschool-age children and adolescents.
Prior to the work of Kane et al., little was known about critical care resource usage among pediatric patients admitted to pediatric ICUs across the country. They found that hospitalization rates were up, with over one-third of patients requiring mechanical ventilation and about 20% needing vasopressors. Perhaps one of the most important findings is that methadone accounted for nearly 20% of opioids ingested, displaying how adults being treated for their own opioid use disorder can put the children they live with at risk.
As the opioid crisis has worsened and overdoses have increased, the Council of Economic Advisers attempted to measure the societal costs of opioid overdoses using the “value of a statistical life” analytic method. This considers activities other than just lost work productivity and earnings, such as volunteering and raising a family. Using the value of a statistical life method, the Council determined that the true cost to society was nearly $504 billion, which included both fatal and nonfatal overdoses, and is approximately 2.8% of the 2015 U.S. gross domestic product.
Clearly, opioid abuse is both an emotional and financial burden to individual families and society as a whole. Pediatricians must help combat the ongoing opioid crisis in this country by addressing the needs of pediatric patients.
Sheryl A. Ryan, MD, is a pediatrician at Penn State Health Children’s Hospital, Milton S. Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa. She wrote this commentary to the article by Kane et al. (Pediatrics. 2018 Mar. 5;41(4):e20174129). There was no external funding for this commentary, and Dr. Ryan said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
The opioid crisis in the United States is staggering. As of 2016, an estimated 2.4 million Americans were considered to have an opioid use disorder, either from prescription drug misuse or heroin addiction. This number includes 0.6% of adolescents (12- to 17-year-olds) and 1.1% of young adults (18- to 25-year-olds). And 33,000 Americans died from opioid overdose in 2015. Despite the best attempts to control the supply of drugs and increase access to treatment, overdose deaths have doubled in the past 10 years. While the overdose death rate has plateaued among children under the age of 18, and misuse rates have dropped among 12th graders, opioid-related hospitalizations are increasing in preschool-age children and adolescents.
Prior to the work of Kane et al., little was known about critical care resource usage among pediatric patients admitted to pediatric ICUs across the country. They found that hospitalization rates were up, with over one-third of patients requiring mechanical ventilation and about 20% needing vasopressors. Perhaps one of the most important findings is that methadone accounted for nearly 20% of opioids ingested, displaying how adults being treated for their own opioid use disorder can put the children they live with at risk.
As the opioid crisis has worsened and overdoses have increased, the Council of Economic Advisers attempted to measure the societal costs of opioid overdoses using the “value of a statistical life” analytic method. This considers activities other than just lost work productivity and earnings, such as volunteering and raising a family. Using the value of a statistical life method, the Council determined that the true cost to society was nearly $504 billion, which included both fatal and nonfatal overdoses, and is approximately 2.8% of the 2015 U.S. gross domestic product.
Clearly, opioid abuse is both an emotional and financial burden to individual families and society as a whole. Pediatricians must help combat the ongoing opioid crisis in this country by addressing the needs of pediatric patients.
Sheryl A. Ryan, MD, is a pediatrician at Penn State Health Children’s Hospital, Milton S. Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa. She wrote this commentary to the article by Kane et al. (Pediatrics. 2018 Mar. 5;41(4):e20174129). There was no external funding for this commentary, and Dr. Ryan said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
The opioid crisis in the United States is staggering. As of 2016, an estimated 2.4 million Americans were considered to have an opioid use disorder, either from prescription drug misuse or heroin addiction. This number includes 0.6% of adolescents (12- to 17-year-olds) and 1.1% of young adults (18- to 25-year-olds). And 33,000 Americans died from opioid overdose in 2015. Despite the best attempts to control the supply of drugs and increase access to treatment, overdose deaths have doubled in the past 10 years. While the overdose death rate has plateaued among children under the age of 18, and misuse rates have dropped among 12th graders, opioid-related hospitalizations are increasing in preschool-age children and adolescents.
Prior to the work of Kane et al., little was known about critical care resource usage among pediatric patients admitted to pediatric ICUs across the country. They found that hospitalization rates were up, with over one-third of patients requiring mechanical ventilation and about 20% needing vasopressors. Perhaps one of the most important findings is that methadone accounted for nearly 20% of opioids ingested, displaying how adults being treated for their own opioid use disorder can put the children they live with at risk.
As the opioid crisis has worsened and overdoses have increased, the Council of Economic Advisers attempted to measure the societal costs of opioid overdoses using the “value of a statistical life” analytic method. This considers activities other than just lost work productivity and earnings, such as volunteering and raising a family. Using the value of a statistical life method, the Council determined that the true cost to society was nearly $504 billion, which included both fatal and nonfatal overdoses, and is approximately 2.8% of the 2015 U.S. gross domestic product.
Clearly, opioid abuse is both an emotional and financial burden to individual families and society as a whole. Pediatricians must help combat the ongoing opioid crisis in this country by addressing the needs of pediatric patients.
Sheryl A. Ryan, MD, is a pediatrician at Penn State Health Children’s Hospital, Milton S. Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa. She wrote this commentary to the article by Kane et al. (Pediatrics. 2018 Mar. 5;41(4):e20174129). There was no external funding for this commentary, and Dr. Ryan said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
Hospitalization and pediatric ICU admission rates for pediatric opioid-related ingestion are increasing, along with hospitalization costs, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“In this study, we demonstrate a significant and steady increase in the diagnosis of opioid ingestion and poisoning across all age groups in U.S. children’s hospitals from 2004 to 2015,” wrote Jason Kane, MD, of the University of Chicago, and his associates. “Not only did the absolute number of opioid-related admissions increase but the rate of both hospital and PICU [pediatric ICU] admissions increased as well.”
Using the Pediatric Health Information System database, the research team performed a retrospective cohort study of children aged 1-17 years who had been admitted to a PICU between Jan. 1, 2004, and Sep. 30, 2015. For statistical analysis, the years were grouped into separate epochs: 2004-2007, 2008-2011, and 2012-2015.
Of the 4,175,624 admissions to 31 different children’s hospitals around the United States, 3,647 (0.09%) were due to opioid-related conditions. Across the three epochs of the study, the number of opioid-related hospitalizations more than doubled from 797 to 1,504 and concurrently increased the rate of hospital admissions from 6.7 per 10,000 in 2004 to 10.9 per 10,000 in 2015 (P less than .001).
Similar to the trends in overall hospital admissions and hospital admission rates, admission to the PICU and PICU admission rates also increased. Of the 3,647 children admitted for opioid-related issues, 1,564 (43%) were subsequently admitted to the PICU. PICU admission rates also increased from 25 to 36 per 10,000 admissions (P less than .001).While the majority of opioid-related hospitalizations are associated with children aged 12-17 years, children under the age of 6 years accounted for one-third of these hospitalizations. Many PICU admissions are severe enough to warrant mechanical ventilator support (37%, P less than .001) and vasopressors (20%, P less than .001).
The opioids ingested prior to hospital admission varied between age groups, with 20% (243 of 1,249) patients aged 1-5 years ingesting methadone, compared with 10% (218 of 2,223) of patients aged 12-17 years. Heroin was much more common in this group, accounting for 4.4% (99 of 2,223) of patient hospitalizations.
In addition to the human cost of pediatric hospital admissions, there is a significant economic cost on the health care system. The median cost for PICU admission was $4,931. Although these costs have been dropping for the better part of a decade ($6,523 in 2004-2007 to $4,552 in 2012-2015, P less than .001), it still represents a substantial problem. In addition, admission rates are increasing, which will only place a heavier burden on the health care system, according to Dr. Kane and his associates.
Perhaps one positive point from this study is that although hospitalizations and intensive care rates have gone up, mortality decreased over time from 2.8% in 2004-2007 to 1.3% in 2012-2015.
A possible limitation of the data in this study is that it provides data from subjects whose data is accessible to the researcher, rather than those strategically selected. In addition, referral bias may reduce the ability to generalize the information to non–tertiary care children’s hospitals.
“The current U.S. opioid crisis is negatively impacting pediatric patients as the rate of hospitalization and PICU care for the ingestion of opioids by children continues to increase over time,” wrote Dr. Kane and his associates. “Current efforts to reduce prescription opioid use in adults have not curtailed the incidence of pediatric opioid ingestion, and additional efforts are needed to reduce preventable opioid exposure in children.”
This study had no external funding. Dr. Allison H. Bartlett has served as a consultant member of the CVS Caremark National Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. All other authors had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCE: Kane JM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Mar 5;141(4):e20173335.
Hospitalization and pediatric ICU admission rates for pediatric opioid-related ingestion are increasing, along with hospitalization costs, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“In this study, we demonstrate a significant and steady increase in the diagnosis of opioid ingestion and poisoning across all age groups in U.S. children’s hospitals from 2004 to 2015,” wrote Jason Kane, MD, of the University of Chicago, and his associates. “Not only did the absolute number of opioid-related admissions increase but the rate of both hospital and PICU [pediatric ICU] admissions increased as well.”
Using the Pediatric Health Information System database, the research team performed a retrospective cohort study of children aged 1-17 years who had been admitted to a PICU between Jan. 1, 2004, and Sep. 30, 2015. For statistical analysis, the years were grouped into separate epochs: 2004-2007, 2008-2011, and 2012-2015.
Of the 4,175,624 admissions to 31 different children’s hospitals around the United States, 3,647 (0.09%) were due to opioid-related conditions. Across the three epochs of the study, the number of opioid-related hospitalizations more than doubled from 797 to 1,504 and concurrently increased the rate of hospital admissions from 6.7 per 10,000 in 2004 to 10.9 per 10,000 in 2015 (P less than .001).
Similar to the trends in overall hospital admissions and hospital admission rates, admission to the PICU and PICU admission rates also increased. Of the 3,647 children admitted for opioid-related issues, 1,564 (43%) were subsequently admitted to the PICU. PICU admission rates also increased from 25 to 36 per 10,000 admissions (P less than .001).While the majority of opioid-related hospitalizations are associated with children aged 12-17 years, children under the age of 6 years accounted for one-third of these hospitalizations. Many PICU admissions are severe enough to warrant mechanical ventilator support (37%, P less than .001) and vasopressors (20%, P less than .001).
The opioids ingested prior to hospital admission varied between age groups, with 20% (243 of 1,249) patients aged 1-5 years ingesting methadone, compared with 10% (218 of 2,223) of patients aged 12-17 years. Heroin was much more common in this group, accounting for 4.4% (99 of 2,223) of patient hospitalizations.
In addition to the human cost of pediatric hospital admissions, there is a significant economic cost on the health care system. The median cost for PICU admission was $4,931. Although these costs have been dropping for the better part of a decade ($6,523 in 2004-2007 to $4,552 in 2012-2015, P less than .001), it still represents a substantial problem. In addition, admission rates are increasing, which will only place a heavier burden on the health care system, according to Dr. Kane and his associates.
Perhaps one positive point from this study is that although hospitalizations and intensive care rates have gone up, mortality decreased over time from 2.8% in 2004-2007 to 1.3% in 2012-2015.
A possible limitation of the data in this study is that it provides data from subjects whose data is accessible to the researcher, rather than those strategically selected. In addition, referral bias may reduce the ability to generalize the information to non–tertiary care children’s hospitals.
“The current U.S. opioid crisis is negatively impacting pediatric patients as the rate of hospitalization and PICU care for the ingestion of opioids by children continues to increase over time,” wrote Dr. Kane and his associates. “Current efforts to reduce prescription opioid use in adults have not curtailed the incidence of pediatric opioid ingestion, and additional efforts are needed to reduce preventable opioid exposure in children.”
This study had no external funding. Dr. Allison H. Bartlett has served as a consultant member of the CVS Caremark National Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. All other authors had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
SOURCE: Kane JM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Mar 5;141(4):e20173335.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: The rate of hospitalizations and pediatric ICU admissions are up due to opioid ingestion.
Major finding: Over 40% of pediatric patients admitted to hospitals required PICU care.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of children aged 1-17 years who were admitted to a PICU between Jan. 1, 2004, and Sep. 30, 2015.
Disclosures: This study had no external funding. Dr. Allison H. Bartlett has served as a consultant member of the CVS Caremark National Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. All other authors had no relevant financial disclosures to report.
Source: Kane JM et al. Pediatrics. 2018 Mar. 5;141(4):e20173335.