User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
Vaccination cuts long COVID risk for rheumatic disease patients
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Children and COVID: Hospitalizations provide a tale of two sources
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.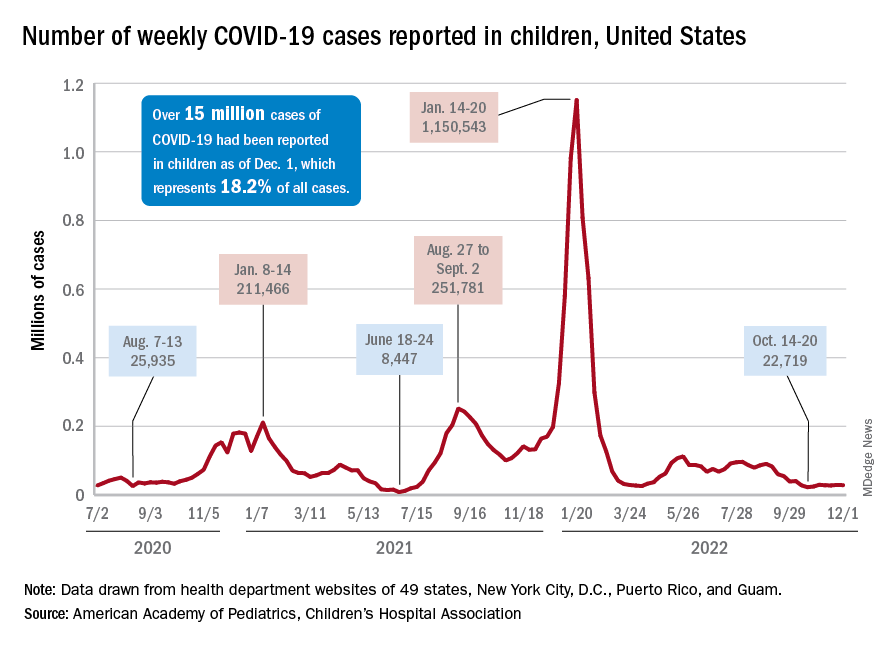
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
Study comparing surgical and N95 masks sparks concern
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Have long COVID? Newest booster vaccines may help you
Yet at 58, the Arizona writer is in no hurry to get the latest vaccine booster. “I just don’t want to risk getting any sicker,” she said.
Ms. Dishner has had two doses of vaccine plus two boosters. Each time, she had what regulators consider to be mild reactions, including a sore arm, slight fever, nausea, and body aches. Still, there’s some evidence that the newest booster, which protects against some of the later variants, could help people like Ms. Dishner in several ways, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and prolific long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis.
“A bivalent booster might actually [help with] your long COVID,” he said.
There may be other benefits. “What vaccines or current vaccine boosters do is reduce your risk of progression to severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “You are avoiding hospital stays or even worse; you’re avoiding potentially fatal outcomes after infection. And that’s really worth it. Who wants to be in the hospital this Christmas holiday?”
Each time people are infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, they have a fresh risk of not only getting severely ill or dying, but of developing long COVID, Dr. Al-Aly and colleagues found in a study published in Nature Medicine. “If you dodged the bullet the first time and did not get long COVID after the first infection, if you get reinfected, you’re trying your luck again,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “I would advise people not to get reinfected, which is another reason to get the booster.”
In a recent review in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine, an international team of researchers looked at 11 studies that sought to find out if vaccines affected long COVID symptoms. Seven of those studies found that people’s symptoms improved after they were vaccinated, and four found that symptoms mostly remained the same. One found symptoms got worse in some patients.
A study of 28,000 people published in the British Medical Journal found more evidence that vaccination may help ease symptoms. “Vaccination may contribute to a reduction in the population health burden of long COVID,” the team at the United Kingdom’s Office for National Statistics concluded. Most studies found vaccination reduced the risk of getting long COVID in the first place.
Vaccines prompt the body to produce antibodies, which stop a microbe from infecting cells. They also prompt the production of immune cells called T cells, which continue to hunt down and attack a pathogen even after infection.
A booster dose could help rev up that immune response in a patient with long COVID, said Stephen J. Thomas, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Upstate Medical Center in Syracuse, N.Y., and the center’s lead principal investigator for Pfizer/BioNTech’s COVID-19 2020 vaccine trial.
Some scientists believe long COVID might be caused when the virus persists in parts of the body where the immune system isn’t particularly active. Although they don’t fully understand the workings of the many and varied long COVID symptoms, they have a good idea about why people with long COVID often do better after receiving a vaccine or booster.
“The theory is that by boosting, the immune system may be able to ‘mop up’ those virus stragglers that have remained behind after your first cleanup attempt,” Dr. Thomas said.
“The vaccine is almost lending a hand or helping your immune response to clear that virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
It could be difficult for long COVID patients to make an informed decision about boosters, given the lack of studies that focus exclusively on the relationship between long COVID and boosters, according to Scott Roberts, MD, associate medical director for infection prevention at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
Dr. Roberts recommended that patients speak with their health care providers and read about the bivalent booster on trusted sites such as those sponsored by the Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Long COVID patients should get the latest boosters, especially as there’s no evidence they are unsafe for them. “The antibody response is appropriately boosted, and there is a decent chance this will help reduce the impact of long COVID as well,” he said. “Waiting will only increase the risk of getting infected and increase the chances of long COVID.”
Only 12% of Americans 5 years and older have received the updated booster, according to the CDC, although it’s recommended for everyone. Just over 80% of Americans have gotten at least one vaccine dose. Dr. Thomas understands why the uptake has been so low: Along with people like Ms. Dishner, who fear more side effects or worse symptoms, there are those who believe that hybrid immunity – vaccination immunity plus natural infection – is superior to vaccination alone and that they don’t need a booster.
Studies show that the bivalent boosters, which protect against older and newer variants, can target even the new, predominant COVID-19 strains. Whether that is enough to convince people in the no-booster camp who lost faith when their vaccinated peers started getting COVID-19 is unclear, although, as Dr. Al-Aly has pointed out, vaccinations help keep people from getting so sick that they wind up in the hospital. And, with most of the population having received at least one dose of vaccine, most of those getting infected will naturally come from among the vaccinated.
Thomas describes the expectation that vaccines would prevent everyone from getting sick as “one of the major fails” of the pandemic.
Counting on a vaccine to confer 100% immunity is “a very high bar,” he said. “I think that’s what people expected, and when they weren’t seeing it, they kind of said: ‘Well, what’s the point? You know, things are getting better. I’d rather take my chances than keep going and getting boosted.’ ”
One point – and it’s a critical one – is that vaccination immunity wanes. Plus new variants arise that can evade at least some of the immunity provided by vaccination. That’s why boosters are built into the COVID vaccination program.
While it’s not clear why some long COVID patients see improvements in their symptoms after being vaccinated or boosted and others do not, Dr. Al-Aly said there’s little evidence vaccines can make long COVID worse. “There are some reports out there that some people with long COVID, when they got a vaccine or booster, their symptoms got worse. You’ll read anecdotes on this side,” he said, adding that efforts to see if this is really happening have been inconclusive.
“The general consensus is that vaccines really save lives,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “Getting vaccinated, even if you are a long COVID patient, is better than not getting vaccinated.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Yet at 58, the Arizona writer is in no hurry to get the latest vaccine booster. “I just don’t want to risk getting any sicker,” she said.
Ms. Dishner has had two doses of vaccine plus two boosters. Each time, she had what regulators consider to be mild reactions, including a sore arm, slight fever, nausea, and body aches. Still, there’s some evidence that the newest booster, which protects against some of the later variants, could help people like Ms. Dishner in several ways, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and prolific long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis.
“A bivalent booster might actually [help with] your long COVID,” he said.
There may be other benefits. “What vaccines or current vaccine boosters do is reduce your risk of progression to severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “You are avoiding hospital stays or even worse; you’re avoiding potentially fatal outcomes after infection. And that’s really worth it. Who wants to be in the hospital this Christmas holiday?”
Each time people are infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, they have a fresh risk of not only getting severely ill or dying, but of developing long COVID, Dr. Al-Aly and colleagues found in a study published in Nature Medicine. “If you dodged the bullet the first time and did not get long COVID after the first infection, if you get reinfected, you’re trying your luck again,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “I would advise people not to get reinfected, which is another reason to get the booster.”
In a recent review in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine, an international team of researchers looked at 11 studies that sought to find out if vaccines affected long COVID symptoms. Seven of those studies found that people’s symptoms improved after they were vaccinated, and four found that symptoms mostly remained the same. One found symptoms got worse in some patients.
A study of 28,000 people published in the British Medical Journal found more evidence that vaccination may help ease symptoms. “Vaccination may contribute to a reduction in the population health burden of long COVID,” the team at the United Kingdom’s Office for National Statistics concluded. Most studies found vaccination reduced the risk of getting long COVID in the first place.
Vaccines prompt the body to produce antibodies, which stop a microbe from infecting cells. They also prompt the production of immune cells called T cells, which continue to hunt down and attack a pathogen even after infection.
A booster dose could help rev up that immune response in a patient with long COVID, said Stephen J. Thomas, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Upstate Medical Center in Syracuse, N.Y., and the center’s lead principal investigator for Pfizer/BioNTech’s COVID-19 2020 vaccine trial.
Some scientists believe long COVID might be caused when the virus persists in parts of the body where the immune system isn’t particularly active. Although they don’t fully understand the workings of the many and varied long COVID symptoms, they have a good idea about why people with long COVID often do better after receiving a vaccine or booster.
“The theory is that by boosting, the immune system may be able to ‘mop up’ those virus stragglers that have remained behind after your first cleanup attempt,” Dr. Thomas said.
“The vaccine is almost lending a hand or helping your immune response to clear that virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
It could be difficult for long COVID patients to make an informed decision about boosters, given the lack of studies that focus exclusively on the relationship between long COVID and boosters, according to Scott Roberts, MD, associate medical director for infection prevention at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
Dr. Roberts recommended that patients speak with their health care providers and read about the bivalent booster on trusted sites such as those sponsored by the Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Long COVID patients should get the latest boosters, especially as there’s no evidence they are unsafe for them. “The antibody response is appropriately boosted, and there is a decent chance this will help reduce the impact of long COVID as well,” he said. “Waiting will only increase the risk of getting infected and increase the chances of long COVID.”
Only 12% of Americans 5 years and older have received the updated booster, according to the CDC, although it’s recommended for everyone. Just over 80% of Americans have gotten at least one vaccine dose. Dr. Thomas understands why the uptake has been so low: Along with people like Ms. Dishner, who fear more side effects or worse symptoms, there are those who believe that hybrid immunity – vaccination immunity plus natural infection – is superior to vaccination alone and that they don’t need a booster.
Studies show that the bivalent boosters, which protect against older and newer variants, can target even the new, predominant COVID-19 strains. Whether that is enough to convince people in the no-booster camp who lost faith when their vaccinated peers started getting COVID-19 is unclear, although, as Dr. Al-Aly has pointed out, vaccinations help keep people from getting so sick that they wind up in the hospital. And, with most of the population having received at least one dose of vaccine, most of those getting infected will naturally come from among the vaccinated.
Thomas describes the expectation that vaccines would prevent everyone from getting sick as “one of the major fails” of the pandemic.
Counting on a vaccine to confer 100% immunity is “a very high bar,” he said. “I think that’s what people expected, and when they weren’t seeing it, they kind of said: ‘Well, what’s the point? You know, things are getting better. I’d rather take my chances than keep going and getting boosted.’ ”
One point – and it’s a critical one – is that vaccination immunity wanes. Plus new variants arise that can evade at least some of the immunity provided by vaccination. That’s why boosters are built into the COVID vaccination program.
While it’s not clear why some long COVID patients see improvements in their symptoms after being vaccinated or boosted and others do not, Dr. Al-Aly said there’s little evidence vaccines can make long COVID worse. “There are some reports out there that some people with long COVID, when they got a vaccine or booster, their symptoms got worse. You’ll read anecdotes on this side,” he said, adding that efforts to see if this is really happening have been inconclusive.
“The general consensus is that vaccines really save lives,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “Getting vaccinated, even if you are a long COVID patient, is better than not getting vaccinated.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Yet at 58, the Arizona writer is in no hurry to get the latest vaccine booster. “I just don’t want to risk getting any sicker,” she said.
Ms. Dishner has had two doses of vaccine plus two boosters. Each time, she had what regulators consider to be mild reactions, including a sore arm, slight fever, nausea, and body aches. Still, there’s some evidence that the newest booster, which protects against some of the later variants, could help people like Ms. Dishner in several ways, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a clinical epidemiologist and prolific long COVID researcher at Washington University in St. Louis.
“A bivalent booster might actually [help with] your long COVID,” he said.
There may be other benefits. “What vaccines or current vaccine boosters do is reduce your risk of progression to severe COVID-19 illness,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “You are avoiding hospital stays or even worse; you’re avoiding potentially fatal outcomes after infection. And that’s really worth it. Who wants to be in the hospital this Christmas holiday?”
Each time people are infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, they have a fresh risk of not only getting severely ill or dying, but of developing long COVID, Dr. Al-Aly and colleagues found in a study published in Nature Medicine. “If you dodged the bullet the first time and did not get long COVID after the first infection, if you get reinfected, you’re trying your luck again,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “I would advise people not to get reinfected, which is another reason to get the booster.”
In a recent review in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine, an international team of researchers looked at 11 studies that sought to find out if vaccines affected long COVID symptoms. Seven of those studies found that people’s symptoms improved after they were vaccinated, and four found that symptoms mostly remained the same. One found symptoms got worse in some patients.
A study of 28,000 people published in the British Medical Journal found more evidence that vaccination may help ease symptoms. “Vaccination may contribute to a reduction in the population health burden of long COVID,” the team at the United Kingdom’s Office for National Statistics concluded. Most studies found vaccination reduced the risk of getting long COVID in the first place.
Vaccines prompt the body to produce antibodies, which stop a microbe from infecting cells. They also prompt the production of immune cells called T cells, which continue to hunt down and attack a pathogen even after infection.
A booster dose could help rev up that immune response in a patient with long COVID, said Stephen J. Thomas, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Upstate Medical Center in Syracuse, N.Y., and the center’s lead principal investigator for Pfizer/BioNTech’s COVID-19 2020 vaccine trial.
Some scientists believe long COVID might be caused when the virus persists in parts of the body where the immune system isn’t particularly active. Although they don’t fully understand the workings of the many and varied long COVID symptoms, they have a good idea about why people with long COVID often do better after receiving a vaccine or booster.
“The theory is that by boosting, the immune system may be able to ‘mop up’ those virus stragglers that have remained behind after your first cleanup attempt,” Dr. Thomas said.
“The vaccine is almost lending a hand or helping your immune response to clear that virus,” Dr. Al-Aly said.
It could be difficult for long COVID patients to make an informed decision about boosters, given the lack of studies that focus exclusively on the relationship between long COVID and boosters, according to Scott Roberts, MD, associate medical director for infection prevention at Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
Dr. Roberts recommended that patients speak with their health care providers and read about the bivalent booster on trusted sites such as those sponsored by the Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Long COVID patients should get the latest boosters, especially as there’s no evidence they are unsafe for them. “The antibody response is appropriately boosted, and there is a decent chance this will help reduce the impact of long COVID as well,” he said. “Waiting will only increase the risk of getting infected and increase the chances of long COVID.”
Only 12% of Americans 5 years and older have received the updated booster, according to the CDC, although it’s recommended for everyone. Just over 80% of Americans have gotten at least one vaccine dose. Dr. Thomas understands why the uptake has been so low: Along with people like Ms. Dishner, who fear more side effects or worse symptoms, there are those who believe that hybrid immunity – vaccination immunity plus natural infection – is superior to vaccination alone and that they don’t need a booster.
Studies show that the bivalent boosters, which protect against older and newer variants, can target even the new, predominant COVID-19 strains. Whether that is enough to convince people in the no-booster camp who lost faith when their vaccinated peers started getting COVID-19 is unclear, although, as Dr. Al-Aly has pointed out, vaccinations help keep people from getting so sick that they wind up in the hospital. And, with most of the population having received at least one dose of vaccine, most of those getting infected will naturally come from among the vaccinated.
Thomas describes the expectation that vaccines would prevent everyone from getting sick as “one of the major fails” of the pandemic.
Counting on a vaccine to confer 100% immunity is “a very high bar,” he said. “I think that’s what people expected, and when they weren’t seeing it, they kind of said: ‘Well, what’s the point? You know, things are getting better. I’d rather take my chances than keep going and getting boosted.’ ”
One point – and it’s a critical one – is that vaccination immunity wanes. Plus new variants arise that can evade at least some of the immunity provided by vaccination. That’s why boosters are built into the COVID vaccination program.
While it’s not clear why some long COVID patients see improvements in their symptoms after being vaccinated or boosted and others do not, Dr. Al-Aly said there’s little evidence vaccines can make long COVID worse. “There are some reports out there that some people with long COVID, when they got a vaccine or booster, their symptoms got worse. You’ll read anecdotes on this side,” he said, adding that efforts to see if this is really happening have been inconclusive.
“The general consensus is that vaccines really save lives,” Dr. Al-Aly said. “Getting vaccinated, even if you are a long COVID patient, is better than not getting vaccinated.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
FDA pulls U.S. authorization for Eli Lilly’s COVID drug bebtelovimab
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
RSV surge stuns parents and strains providers, but doctors offer help
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Buzzy Lancet long COVID paper under investigation for ‘data errors’
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
An editorial that accompanied the paper when it was published in January of last year described it as “the first large cohort study with 6-months’ follow-up” of people hospitalized with COVID-19. The article has received plenty of attention since then.
Titled “6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study,” the paper has been cited nearly 1,600 times, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science. Altmetric finds references to it in multiple documents from the World Health Organization.
According to the expression of concern, dated November 24, a reader found inconsistencies between the data in the article and a later paper describing the same cohort of patients after a year of follow-up. That discovery sparked an investigation that is still ongoing:
- On Jan 8, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study, by Chaolin Huang and colleagues. 1 On Aug 28, 2021, The Lancet published an Article, 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, by Lixue Huang and colleagues. 2 We received an inquiry from a researcher on data inconsistencies between these two Articles, and we sought an explanation from the corresponding author of the two papers. On Nov 7, 2022, Lancet editors were informed that inconsistencies between the 6-month and the 1-year data were due to “some variables in the dataset used for the 6-month paper were mistakenly disrupted in order”. In view of the extent of these data errors, we now issue an Expression of Concern about the 6-month paper 1 while we investigate further, including further statistical and clinical review of the corrected data. We will update this notice as soon as we have further information.
The corresponding author of both papers, Bin Cao of China’s National Center for Respiratory Medicine and the China-Japan Friendship Hospital in Beijing, has not responded to our request for comment.
A profile of Cao published in Lancet Infectious Diseases last March described him as “a leading researcher in pneumonia and influenza” who “has been instrumental in increasing knowledge about COVID-19.” In addition to the follow-up study of hospitalized COVID patients:
- Cao’s seminal papers during the COVID-19 pandemic include the first report of the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, the description of the risk factors for mortality for adult inpatients, and the results of trials testing the use of antiviral drugs, including lopinavir-ritonavir, to treat COVID-19 in China.
We reached out to The Lancet’s press office and Richard Horton, the journal’s editor-in-chief, and received this statement:
- The Lancet Group treats all communications between editors and authors or readers as confidential. Investigations are continuing, and the Expression of Concern will be updated as soon as we have further information to share. More information about our policies is available here:
This year, The Lancet overtook the New England Journal of Medicine as the medical journal with the highest impact factor, in large part due to the papers it published about COVID-19.
We’ve counted retractions for three of those papers, most notably a paper about the use of the drug hydroxychloroquine that claimed to use medical data from a company called Surgisphere. As Retraction Watch readers may remember, the article was retracted after sleuths questioned if the data were real, and the company would not produce it for review.
This article first appeared on Retraction Watch.
Covid vax prevents death in children regardless of variant
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
The vaccine’s effectiveness against infection in the short term has been established, as has the waning effectiveness of the vaccine over time, wrote Juan Manuel Castelli, MD, of the Ministry of Health of Argentina, Buenos Aires, and colleagues, in the British Medical Journal.
However, data on the impact of vaccine effectiveness on mortality in children and adolescents are limited, especially during periods of omicron variant dominance, the researchers said.
In their new study, the researchers reviewed data from 844,460 children and adolescents aged 3-17 years from the National Surveillance System and the Nominalized Federal Vaccination Registry of Argentina, during a time that included a period of omicron dominance.
Argentina began vaccinating adolescents aged 12-17 years against COVID-19 in August 2021 and added children aged 3-11 years in October 2021. Those aged 12-17 years who were considered fully vaccinated received two doses of either Pfizer-BioNTech and/or Moderna vaccines, and fully-vaccinated 3- to 11-year-olds received two doses of Sinopharm vaccine.
The average time from the second vaccine dose to a COVID-19 test was 66 days for those aged 12-17 years and 54 days for 3- to 11-year-olds. The researchers matched COVID-19 cases with uninfected controls, and a total of 139,321 cases were included in the analysis.
Overall, the estimated vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 was 64.2% during a period of delta dominance (61.2% in children aged 3-11 years and 66.8% in adolescents aged 12-17 years).
During a period of omicron dominance, estimated vaccine effectiveness was 19.9% across all ages (15.9% and 26.0% for younger and older age groups, respectively).
Effectiveness of the vaccine decreased over time, regardless of the dominant variant, but the decline was greater during the omicron dominant period, the researchers noted. During the omicron period, effectiveness in children aged 3-11 years decreased from 37.6% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 2.0% at 60 days or longer after vaccination. In adolescents aged 12-17 years, vaccine effectiveness during the omicron period decreased from 55.8% at 15-30 days postvaccination to 12.4% at 60 days or longer after vaccination.
Despite the waning protection against infection, the vaccine’s effectiveness against death from COVID-19 was 66.9% in children aged 3-11 years and 97.6% in adolescents aged 12-17 during the period of omicron dominance, the researchers noted.
The results are consistent with similar studies showing a decreased vaccine effectiveness against infection but a persistent effectiveness against deaths over time, the researchers wrote in the discussion section of their paper.
“Our results suggest that the primary vaccination schedule is effective in preventing mortality in children and adolescents with COVID-19 regardless of the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant,” the researchers said.
Study limitations and strengths
The study was limited by several factors including the incomplete data on symptoms and hospital admissions, the possible impact of unmeasured confounding variables, and the observational design that prevents conclusions of causality, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and access to detailed vaccination records, they said.
Both heterologous and homologous mRNA vaccine schedules showed similar effectiveness in preventing short-term infection and mortality from COVID-19 during periods of differing dominant variants, they noted.
The study findings support the vaccination of children against COVID-19 as an important public health measure to prevent mortality in children and adolescents, they concluded.
Data support value of vaccination, outside experts say
“COVID vaccines may not be as effective over time as the gene variants in the SARS-CoV-2 virus change,” Adrienne G. Randolph, MD, a pediatrician at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, said in an interview. “Therefore, it is essential to assess vaccine effectiveness over time to look at effectiveness against variants and duration of effectiveness.” Dr. Randolph, who was not involved in the study, said she was not surprised by the findings, which she described as consistent with data from the United States. “COVID vaccines are very effective against preventing life-threatening disease, but the effectiveness against less severe illness for COVID vaccines is not as effective against Omicron,” she noted.
The take-home message for clinicians is that it’s important to get children vaccinated against COVID to prevent severe and life-threatening illness, said Dr. Randolph. “Although these cases are uncommon in children, it is not possible to predict which children will be the most severely affected by COVID,” she emphasized.
However, “we need more data on the new COVID booster vaccines in children that are designed to be more effective against Omicron’s newer variants,” Dr. Randolph said in an interview. “We also need more data on COVID vaccine effectiveness in the youngest children, under 5 years of age, and data on vaccinating mothers to prevent COVID in infants,” she said.
Tim Joos, MD, a Seattle-based clinician who practices a combination of internal medicine and pediatrics, agreed that future research should continue to assess how the new COVID boosters are faring against new variants, noting that the current study did not include data from children who received the new bivalent vaccine.
“The methodology of this study uses a test negative case control design which is common for estimating vaccine effectiveness post-release of a vaccine, but is subject to biases,” Dr. Joos explained. “These are not the clean effectiveness numbers of the prospective randomized control trials that we are used to hearing about when a vaccine is first being approved.”
“Nevertheless, the study reinforces the initial manufacturers’ studies that the vaccines are effective at preventing infection in the pediatric population,” Dr. Joos said in an interview. The current study also reinforces the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing “the rare but devastating mortality from COVID-19 in the pediatric population.”
Commenting on other research showing an increasing ratio of COVID deaths among vaccinated individuals compared to total COVID deaths, he noted that this finding is “likely reflecting a denominator effect of rapidly declining COVID deaths overall,” partly from the vaccines and partly from immunity after previous natural infection.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, Dr. Randolph, and Dr. Joos had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Joos serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Pediatric News.
FROM THE BMJ
What is the genetic influence on the severity of COVID-19?
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A striking characteristic of COVID-19 is that the severity of clinical outcomes is remarkably variable. Establishing a prognosis for individuals infected with COVID-19 remains a challenge.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the heterogeneity of individuals who progress toward severe disease or death, along with the fact that individuals directly exposed to the virus do not necessarily become sick, supports the hypothesis that genetic risk or protective factors are at play.
In an interview with this news organization, Mayana Zatz, PhD, head professor of genetics and coordinator of the Human Genome and Stem Cell Study Center at the University of São Paulo, explained: “The first case that caught my eye was the case of my neighbors, a couple. He presented COVID-19 symptoms, but his wife, who took care of him, had absolutely no symptoms. I thought that it was strange, but we received 3,000 emails from people saying, ‘This happened to me, too.’”
Reports in the media about seven pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who died from COVID-19 within days of one another in Brazil also stood out, said the researcher.
, as well as their pathology. Dr. Zatz’s team analyzed the case of a 31-year-old Brazilian MZ twin brother pair who presented simultaneously with severe COVID-19 and the need for oxygen support, despite their age and good health conditions. Curiously, they were admitted and intubated on the same day, but neither of the twins knew about the other’s situation; they found out only when they were extubated.
The study was carried out at the USP with the collaboration of the State University of São Paulo. The authors mapped the genetic profile (by sequencing the genome responsible for coding proteins, or whole-exome sequencing) and the immune cell profile to evaluate innate and adaptive immunity.
The MZ twin brothers shared the same two rare genetic mutations, which may be associated with their increased risk of developing severe COVID-19. However, since these variants were not studied at the protein or functional level, their pathogenicity has yet to be determined. The twins also had [human leukocyte antigen (HLA)] alleles associated with severe COVID-19, which are important candidates for the mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and manifestation.
But one particular oddity stood out to the researchers: One of the brothers required longer hospitalization, and only he reported symptoms of long COVID.
In the authors’ eyes, even though the patients shared genetic mutations potentially associated with the risk of developing severe COVID-19, the differences in clinical progression emphasize that, beyond genetic risk factors, continuous exposure to pathogens over a lifetime and other environmental factors mean that each individual’s immune response is unique, even in twins.
“There is no doubt that genetics contribute to the severity of COVID-19, and environmental factors sometimes give us the opportunity to study the disease, too. Such [is the case with] MZ twins who have genetic similarities, even with changes that take place over a lifetime,” José Eduardo Krieger, MD, PhD, professor of molecular medicine at the University of São Paulo Medical School (FMUSP), told this news organization. “Examining MZ twins is a strategy that may help, but, with n = 2, luck really needs to be on your side to get straight to the problem. You need to combine [these findings] with other studies to solve this conundrum,” said Dr. Krieger, who did not take part in the research.
Large cohorts
Genomic and computer resources allow for the study of large sets of data from thousands of individuals. In each of those sets of data, the signal offered by thousands of markers distributed throughout the genome can be studied. This is the possibility offered by various genomic studies of large cohorts of patients with different clinical manifestations.
“Researchers examine thousands of genetic variants throughout the genome from a large sample of individuals and have the chance, for example, to identify genetic variants that are more prevalent in patients who have presented with severe disease than in those who presented with milder disease,” said Dr. Krieger. “These associations highlight a chromosome region in which one or more genes explain, at least in part, the differences observed.”
Genomewide association studies have identified some genetic variants that indicate severity of COVID-19, with potential impact on the virus entering the cell, the immune response, or the development of cytokine storms.
One of these studies, COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative (COVID-19 HGI), is an international, open-science collaboration for sharing scientific methods and resources with research groups across the world, with the goal of robustly mapping the host genetic determinants of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the severity of the resulting COVID-19 disease. At the start of 2021, the COVID-19 HGI combined genetic data from 49,562 cases and 2 million controls from 46 studies in 19 countries. A total of 853 samples from the BRACOVID study were included in the meta-analysis. The endeavor enabled the identification of 13 genomewide significant loci that are associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe manifestations of COVID-19.
The BRACOVID study, in which Dr. Krieger participates, aims to identify host genetic factors that determine the severity of COVID-19. It is currently the largest project of its kind in Latin America. An article provides the analysis of the first 5,233 participants in the BRACOVID study, who were recruited in São Paulo. Of these participants, 3,533 had been infected with COVID-19 and hospitalized at either the Heart Institute or the Central Institute of the FMUSP General Hospital. The remaining 1,700 made up the control group, which included health care professionals and members of the general population. The controls were recruited through serology assays or PCR tests for SARS-CoV-2.
The researchers discovered a region of chromosome 1 that could play a role in modulating immune response and that could lead to an increase in the likelihood of hospitalization across a wide range of COVID-19 risk factors. This region of chromosome 1 was observed only in Brazilians with a strong European ancestry; however, this finding had not been mentioned in previous studies, suggesting that it could harbor a risk allele specific to the Brazilian population.
The study also confirmed most, but not all, of the regions recorded in the literature, which may be significant in identifying factors determining severity that are specific to a given population.
Including information from the BRACOVID study, other studies have enhanced the knowledge on affected organs. Combined data from 14,000 patients from nine countries evaluated a region of a single chromosome and found that carriers of a certain allele had a higher probability of experiencing various COVID-19 complications, such as severe respiratory failure, venous thromboembolism, and liver damage. The risk was even higher for individuals aged 60 years and over.
Discordant couples
Smaller sample sizes of underrepresented populations also provide relevant data for genomic studies. Dr. Zatz’s team carried out genomic studies on smaller groups, comparing serodiscordant couples (where one was infected and symptomatic while the partner remained asymptomatic and seronegative despite sharing the same bedroom during the infection). Their research found genetic variants related to immune response that were associated with susceptibility to infection and progression to severe COVID-19.
The team also went on to study a group of patients older than 90 years who recovered from COVID-19 with mild symptoms or who remained asymptomatic following a positive test for SARS-CoV-2. They compared these patients with a sample of elderly patients from the same city (São Paulo), sampled before the current pandemic. The researchers identified a genetic variant related to mucin production. “In individuals with mild COVID-19, the degradation of these mucins would be more efficient,” said Dr. Zatz. It is possible for this variant to interfere not only with the production of mucus, but also in its composition, as there is an exchange of amino acids in the protein.
“We continued the study by comparing the extremes, i.e., those in their 90s with mild COVID-19 and younger patients with severe COVID-19, including several who died,” said Dr. Zatz.
More personalized medicine
The specialists agreed that a genetic test to predict COVID-19 severity is still a long way away. The genetic component is too little understood to enable the evaluation of individual risk. It has been possible to identify several important areas but, as Dr. Krieger pointed out, a variant identified in a certain chromosome interval may not be just one gene. There may be various candidate genes, or there may be a regulatory sequence for a distant gene. Furthermore, there are regions with genes that make sense as moderators of COVID-19 severity, because they regulate an inflammatory or immunologic reaction, but evidence is still lacking.
Reaching the molecular mechanism would, in future, allow a medicine to be chosen for a given patient, as already happens with other diseases. It also could enable the discovery of new medicines following as-yet-unexplored lines of research. Dr. Zatz also considers the possibility of genetic therapy.
Even with the knowledge of human genetics, one part of the equation is missing: viral genetics. “Many of the individuals who were resistant to the Delta variant were later affected by Omicron,” she pointed out.
Significance of Brazil
“We have an infinite amount of genomic data worldwide, but the vast majority originates from White Americans of European origin,” said Dr. Krieger. Moreover, genomic associations of COVID-19 severity discovered in the Chinese population were not significant in the European population. Besides underscoring the importance of collaborating with international studies, this situation supports scientists’ interest in carrying out genetic studies within Brazil, he added.
“In the genomic study of the Brazilian population, we found 2 million variants that were not present in the European populations,” said Dr. Zatz.
Dr. Krieger mentioned a technical advantage that Brazil has. “Having been colonized by different ethnic groups and mixed many generations ago, Brazil has a population with a unique genetic structure; the recombinations are different. When preparing the samples, the regions break differently.” This factor could help to separate, in a candidate region, the gene that is significant from those that might not be.
In general, severe COVID-19 would be a complex phenomenon involving several genes and interactions with environmental factors. The Brazilian studies tried to find a factor that was unique to Brazil, but the significance of the differences remained unclear. “We found some signs that were specific to our population,” concluded Dr. Krieger. “But the reason that more people in Brazil died as a result of COVID-19 was not genetic,” he added.
Dr. Zatz and Dr. Krieger reported no conflicts of interest. This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. flu activity already at mid-season levels
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention.
Nationally, 6% of all outpatient visits were because of flu or flu-like illness for the week of Nov. 13-19, up from 5.8% the previous week, the CDC’s Influenza Division said in its weekly FluView report.
Those figures are the highest recorded in November since 2009, but the peak of the 2009-10 flu season occurred even earlier – the week of Oct. 18-24 – and the rate of flu-like illness had already dropped to just over 4.0% by Nov. 15-21 that year and continued to drop thereafter.
Although COVID-19 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are included in the data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, the agency did note that “seasonal influenza activity is elevated across the country” and estimated that “there have been at least 6.2 million illnesses, 53,000 hospitalizations, and 2,900 deaths from flu” during the 2022-23 season.
Total flu deaths include 11 reported in children as of Nov. 19, and children ages 0-4 had a higher proportion of visits for flu like-illness than other age groups.
The agency also said the cumulative hospitalization rate of 11.3 per 100,000 population “is higher than the rate observed in [the corresponding week of] every previous season since 2010-2011.” Adults 65 years and older have the highest cumulative rate, 25.9 per 100,000, for this year, compared with 20.7 for children 0-4; 11.1 for adults 50-64; 10.3 for children 5-17; and 5.6 for adults 18-49 years old, the CDC said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.