User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
New safety data regarding COVID vaccines
from the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM).
The rare condition — more common in men than in women — is characterized by the sudden onset of severe pain in the shoulder, followed by arm paralysis. Its etiopathogenesis is not well understood, but vaccines, in particular the flu vaccine, have been implicated in some cases, the report states.
Six serious cases of the syndrome related to the Comirnaty (Pfizer) vaccine were reported by healthcare professionals and vaccinated individuals or their family and friends since the start of the monitoring program. Four of these cases occurred from September 3 to 16.
All six cases involved patients 19 to 69 years of age — two women and four men — who developed symptoms in the 50 days after vaccination. Half were reported after the first dose and half after the second dose. Four of the patients are currently recovering; the outcomes of the other two are unknown.
In the case of the Spikevax vaccine (Moderna), two cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome were reported after vaccination (plus one that occurred after 50 days, which is currently being managed). The onset of symptoms in these two men — one in his early 30s and one in his early 60s — occurred less than 18 days after vaccination. One occurred after the first dose and one after the second dose. This timing indicates a possible link between the syndrome and the vaccine. Both men are currently in recovery.
This signal of mRNA vaccines is now “officially recognized,” according to the Pfizer and Moderna reports.
It is also considered a “potential signal” in the Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) pharmacovigilance report, released October 8, which describes eight cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome after vaccination.
Safety profile of mRNA COVID vaccines in youth
Between June 15, when children 12 years and older became eligible for vaccination, and August 26, there were 591 reports of potential adverse events — out of 6 million Pfizer doses administered — in 12- to 18-year-old children.
Of the 591 cases, 35.2% were deemed serious. The majority of these were cases of reactogenicity, malaise, or postvaccine discomfort (25%), followed by instances of myocarditis and pericarditis (15.9% and 7.2%, respectively). In eight of 10 cases, one of the first symptom reported was chest pain.
Myocarditis occurred in 39.4% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days) and 54.5% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days). Recorded progress was favorable in nearly nine of 10 cases.
Pericarditis occurred in 53.3% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days), and 40.0% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days).
Three cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) were reported after monitoring ended.
For this age group, “all reported events will continue to be monitored, especially serious events and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children,” report authors conclude.
Data for adverse events after the Moderna vaccine remain limited, but the report stipulates that “the adverse events reported in 12- to 18-year-olds who received an injection do not display any particular pattern, compared with those reported in older subjects, with the exception of a roughly 100-fold lower incidence of reported adverse effects in the 12- to 17-year age group.”
No safety warnings for pregnant women
The pharmacovigilance report — which covered the period from December 27, 2020 to September 9, 2021 — “raises no safety warnings for pregnant or nursing women with any of the COVID-19 vaccines.” In addition, two recent studies — one published in JAMA and one in the New England Journal of Medicine — have shown no link between spontaneous miscarriage and mRNA vaccines.
“Moreover, it should be stressed that current data from the international literature consistently show that maternal SARS COV-2 infection increases the risk for fetal, maternal, and neonatal complications, and that this risk may increase with the arrival of the Alpha and Delta variants,” they write. “It is therefore important to reiterate the current recommendations to vaccinate all pregnant women, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.”
Some adverse effects, such as thromboembolic effects, in utero death, HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome, and uterine contractions, will continue to be monitored.
Questions regarding menstrual disorders
As for gynecological disorders reported after vaccination, questions still remain. “In most of the reported cases, it is difficult to accurately determine whether the vaccine played a role in the occurrence of menstrual/genital bleeding,” the authors of the pharmacovigilance monitoring report state.
“Nonetheless, these cases warrant attention,” they add, and further discussions with the French National Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the French Society of Endocrinology are needed in regard to these potential safety signals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
from the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM).
The rare condition — more common in men than in women — is characterized by the sudden onset of severe pain in the shoulder, followed by arm paralysis. Its etiopathogenesis is not well understood, but vaccines, in particular the flu vaccine, have been implicated in some cases, the report states.
Six serious cases of the syndrome related to the Comirnaty (Pfizer) vaccine were reported by healthcare professionals and vaccinated individuals or their family and friends since the start of the monitoring program. Four of these cases occurred from September 3 to 16.
All six cases involved patients 19 to 69 years of age — two women and four men — who developed symptoms in the 50 days after vaccination. Half were reported after the first dose and half after the second dose. Four of the patients are currently recovering; the outcomes of the other two are unknown.
In the case of the Spikevax vaccine (Moderna), two cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome were reported after vaccination (plus one that occurred after 50 days, which is currently being managed). The onset of symptoms in these two men — one in his early 30s and one in his early 60s — occurred less than 18 days after vaccination. One occurred after the first dose and one after the second dose. This timing indicates a possible link between the syndrome and the vaccine. Both men are currently in recovery.
This signal of mRNA vaccines is now “officially recognized,” according to the Pfizer and Moderna reports.
It is also considered a “potential signal” in the Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) pharmacovigilance report, released October 8, which describes eight cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome after vaccination.
Safety profile of mRNA COVID vaccines in youth
Between June 15, when children 12 years and older became eligible for vaccination, and August 26, there were 591 reports of potential adverse events — out of 6 million Pfizer doses administered — in 12- to 18-year-old children.
Of the 591 cases, 35.2% were deemed serious. The majority of these were cases of reactogenicity, malaise, or postvaccine discomfort (25%), followed by instances of myocarditis and pericarditis (15.9% and 7.2%, respectively). In eight of 10 cases, one of the first symptom reported was chest pain.
Myocarditis occurred in 39.4% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days) and 54.5% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days). Recorded progress was favorable in nearly nine of 10 cases.
Pericarditis occurred in 53.3% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days), and 40.0% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days).
Three cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) were reported after monitoring ended.
For this age group, “all reported events will continue to be monitored, especially serious events and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children,” report authors conclude.
Data for adverse events after the Moderna vaccine remain limited, but the report stipulates that “the adverse events reported in 12- to 18-year-olds who received an injection do not display any particular pattern, compared with those reported in older subjects, with the exception of a roughly 100-fold lower incidence of reported adverse effects in the 12- to 17-year age group.”
No safety warnings for pregnant women
The pharmacovigilance report — which covered the period from December 27, 2020 to September 9, 2021 — “raises no safety warnings for pregnant or nursing women with any of the COVID-19 vaccines.” In addition, two recent studies — one published in JAMA and one in the New England Journal of Medicine — have shown no link between spontaneous miscarriage and mRNA vaccines.
“Moreover, it should be stressed that current data from the international literature consistently show that maternal SARS COV-2 infection increases the risk for fetal, maternal, and neonatal complications, and that this risk may increase with the arrival of the Alpha and Delta variants,” they write. “It is therefore important to reiterate the current recommendations to vaccinate all pregnant women, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.”
Some adverse effects, such as thromboembolic effects, in utero death, HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome, and uterine contractions, will continue to be monitored.
Questions regarding menstrual disorders
As for gynecological disorders reported after vaccination, questions still remain. “In most of the reported cases, it is difficult to accurately determine whether the vaccine played a role in the occurrence of menstrual/genital bleeding,” the authors of the pharmacovigilance monitoring report state.
“Nonetheless, these cases warrant attention,” they add, and further discussions with the French National Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the French Society of Endocrinology are needed in regard to these potential safety signals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
from the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM).
The rare condition — more common in men than in women — is characterized by the sudden onset of severe pain in the shoulder, followed by arm paralysis. Its etiopathogenesis is not well understood, but vaccines, in particular the flu vaccine, have been implicated in some cases, the report states.
Six serious cases of the syndrome related to the Comirnaty (Pfizer) vaccine were reported by healthcare professionals and vaccinated individuals or their family and friends since the start of the monitoring program. Four of these cases occurred from September 3 to 16.
All six cases involved patients 19 to 69 years of age — two women and four men — who developed symptoms in the 50 days after vaccination. Half were reported after the first dose and half after the second dose. Four of the patients are currently recovering; the outcomes of the other two are unknown.
In the case of the Spikevax vaccine (Moderna), two cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome were reported after vaccination (plus one that occurred after 50 days, which is currently being managed). The onset of symptoms in these two men — one in his early 30s and one in his early 60s — occurred less than 18 days after vaccination. One occurred after the first dose and one after the second dose. This timing indicates a possible link between the syndrome and the vaccine. Both men are currently in recovery.
This signal of mRNA vaccines is now “officially recognized,” according to the Pfizer and Moderna reports.
It is also considered a “potential signal” in the Vaxzevria (AstraZeneca) pharmacovigilance report, released October 8, which describes eight cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome after vaccination.
Safety profile of mRNA COVID vaccines in youth
Between June 15, when children 12 years and older became eligible for vaccination, and August 26, there were 591 reports of potential adverse events — out of 6 million Pfizer doses administered — in 12- to 18-year-old children.
Of the 591 cases, 35.2% were deemed serious. The majority of these were cases of reactogenicity, malaise, or postvaccine discomfort (25%), followed by instances of myocarditis and pericarditis (15.9% and 7.2%, respectively). In eight of 10 cases, one of the first symptom reported was chest pain.
Myocarditis occurred in 39.4% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days) and 54.5% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days). Recorded progress was favorable in nearly nine of 10 cases.
Pericarditis occurred in 53.3% of people after the first injection (mean time to onset, 13 days), and 40.0% after the second (mean time to onset, 4 days).
Three cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MISC) were reported after monitoring ended.
For this age group, “all reported events will continue to be monitored, especially serious events and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children,” report authors conclude.
Data for adverse events after the Moderna vaccine remain limited, but the report stipulates that “the adverse events reported in 12- to 18-year-olds who received an injection do not display any particular pattern, compared with those reported in older subjects, with the exception of a roughly 100-fold lower incidence of reported adverse effects in the 12- to 17-year age group.”
No safety warnings for pregnant women
The pharmacovigilance report — which covered the period from December 27, 2020 to September 9, 2021 — “raises no safety warnings for pregnant or nursing women with any of the COVID-19 vaccines.” In addition, two recent studies — one published in JAMA and one in the New England Journal of Medicine — have shown no link between spontaneous miscarriage and mRNA vaccines.
“Moreover, it should be stressed that current data from the international literature consistently show that maternal SARS COV-2 infection increases the risk for fetal, maternal, and neonatal complications, and that this risk may increase with the arrival of the Alpha and Delta variants,” they write. “It is therefore important to reiterate the current recommendations to vaccinate all pregnant women, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.”
Some adverse effects, such as thromboembolic effects, in utero death, HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome, and uterine contractions, will continue to be monitored.
Questions regarding menstrual disorders
As for gynecological disorders reported after vaccination, questions still remain. “In most of the reported cases, it is difficult to accurately determine whether the vaccine played a role in the occurrence of menstrual/genital bleeding,” the authors of the pharmacovigilance monitoring report state.
“Nonetheless, these cases warrant attention,” they add, and further discussions with the French National Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the French Society of Endocrinology are needed in regard to these potential safety signals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Fascinating’ link between Alzheimer’s and COVID-19
The findings could lead to new treatment targets to slow progression and severity of both diseases.
Investigators found that a single genetic variant in the oligoadenylate synthetase 1 (OAS1) gene increases the risk for AD and that related variants in the same gene increase the likelihood of severe COVID-19 outcomes.
“These findings may allow us to identify new drug targets to slow progression of both diseases and reduce their severity,” Dervis Salih, PhD, senior research associate, UK Dementia Research Institute, University College London, said in an interview.
“Our work also suggests new approaches to treat both diseases with the same drugs,” Dr. Salih added.
The study was published online Oct. 7 in Brain.
Shared genetic network
The OAS1 gene is expressed in microglia, a type of immune cell that makes up around 10% of all cells in the brain.
In earlier work, investigators found evidence suggesting a link between the OAS1 gene and AD, but the function of the gene in microglia was unknown.
To further investigate the gene’s link to AD, they sequenced genetic data from 2,547 people – half with AD, and half without.
The genotyping analysis confirmed that the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1131454 within OAS1 is significantly associated with AD.
Given that the same OAS1 locus has recently been linked with severe COVID-19 outcomes, the researchers investigated four variants on the OAS1 gene.
Results indicate that SNPs within OAS1 associated with AD also show linkage to SNP variants associated with critical illness in COVID-19.
The rs1131454 (risk allele A) and rs4766676 (risk allele T) are associated with AD, and rs10735079 (risk allele A) and rs6489867 (risk allele T) are associated with critical illness with COVID-19, the investigators reported. All of these risk alleles dampen expression of OAS1.
“This study also provides strong new evidence that interferon signaling by the innate immune system plays a substantial role in the progression of Alzheimer’s,” said Dr. Salih.
“Identifying this shared genetic network in innate immune cells will allow us with future work to identify new biomarkers to track disease progression and also predict disease risk better for both disorders,” he added.
‘Fascinating’ link
In a statement from the UK nonprofit organization, Science Media Center, Kenneth Baillie, MBChB, with the University of Edinburgh, said this study builds on a discovery he and his colleagues made last year that OAS1 variants are associated with severe COVID-19.
“In the ISARIC4C study, we recently found that this is probably due to a change in the way cell membranes detect viruses, but this mechanism doesn’t explain the fascinating association with Alzheimer’s disease reported in this new work,” Dr. Baillie said.
“It is often the case that the same gene can have different roles in different parts of the body. Importantly, it doesn’t mean that having COVID-19 has any effect on your risk of Alzheimer’s,” he added.
Also weighing in on the new study, Jonathan Schott, MD, professor of neurology, University College London, noted that dementia is the “main preexisting health condition associated with COVID-19 mortality, accounting for about one in four deaths from COVID-19 between March and June 2020.
“While some of this excessive mortality may relate to people with dementia being overrepresented in care homes, which were particularly hard hit by the pandemic, or due to general increased vulnerability to infections, there have been questions as to whether there are common factors that might increase susceptibility both to developing dementia and to dying from COVID-19,” Dr. Schott explained.
This “elegant paper” provides evidence for the latter, “suggesting a common genetic mechanism both for Alzheimer’s disease and for severe COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Schott said.
“The identification of a genetic risk factor and elucidation of inflammatory pathways through which it may increase risk has important implications for our understanding of both diseases, with potential implications for novel treatments,” he added.
The study was funded by the UK Dementia Research Institute. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schott serves as chief medical officer for Alzheimer’s Research UK and is clinical adviser to the UK Dementia Research Institute. Dr. Baillie has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings could lead to new treatment targets to slow progression and severity of both diseases.
Investigators found that a single genetic variant in the oligoadenylate synthetase 1 (OAS1) gene increases the risk for AD and that related variants in the same gene increase the likelihood of severe COVID-19 outcomes.
“These findings may allow us to identify new drug targets to slow progression of both diseases and reduce their severity,” Dervis Salih, PhD, senior research associate, UK Dementia Research Institute, University College London, said in an interview.
“Our work also suggests new approaches to treat both diseases with the same drugs,” Dr. Salih added.
The study was published online Oct. 7 in Brain.
Shared genetic network
The OAS1 gene is expressed in microglia, a type of immune cell that makes up around 10% of all cells in the brain.
In earlier work, investigators found evidence suggesting a link between the OAS1 gene and AD, but the function of the gene in microglia was unknown.
To further investigate the gene’s link to AD, they sequenced genetic data from 2,547 people – half with AD, and half without.
The genotyping analysis confirmed that the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1131454 within OAS1 is significantly associated with AD.
Given that the same OAS1 locus has recently been linked with severe COVID-19 outcomes, the researchers investigated four variants on the OAS1 gene.
Results indicate that SNPs within OAS1 associated with AD also show linkage to SNP variants associated with critical illness in COVID-19.
The rs1131454 (risk allele A) and rs4766676 (risk allele T) are associated with AD, and rs10735079 (risk allele A) and rs6489867 (risk allele T) are associated with critical illness with COVID-19, the investigators reported. All of these risk alleles dampen expression of OAS1.
“This study also provides strong new evidence that interferon signaling by the innate immune system plays a substantial role in the progression of Alzheimer’s,” said Dr. Salih.
“Identifying this shared genetic network in innate immune cells will allow us with future work to identify new biomarkers to track disease progression and also predict disease risk better for both disorders,” he added.
‘Fascinating’ link
In a statement from the UK nonprofit organization, Science Media Center, Kenneth Baillie, MBChB, with the University of Edinburgh, said this study builds on a discovery he and his colleagues made last year that OAS1 variants are associated with severe COVID-19.
“In the ISARIC4C study, we recently found that this is probably due to a change in the way cell membranes detect viruses, but this mechanism doesn’t explain the fascinating association with Alzheimer’s disease reported in this new work,” Dr. Baillie said.
“It is often the case that the same gene can have different roles in different parts of the body. Importantly, it doesn’t mean that having COVID-19 has any effect on your risk of Alzheimer’s,” he added.
Also weighing in on the new study, Jonathan Schott, MD, professor of neurology, University College London, noted that dementia is the “main preexisting health condition associated with COVID-19 mortality, accounting for about one in four deaths from COVID-19 between March and June 2020.
“While some of this excessive mortality may relate to people with dementia being overrepresented in care homes, which were particularly hard hit by the pandemic, or due to general increased vulnerability to infections, there have been questions as to whether there are common factors that might increase susceptibility both to developing dementia and to dying from COVID-19,” Dr. Schott explained.
This “elegant paper” provides evidence for the latter, “suggesting a common genetic mechanism both for Alzheimer’s disease and for severe COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Schott said.
“The identification of a genetic risk factor and elucidation of inflammatory pathways through which it may increase risk has important implications for our understanding of both diseases, with potential implications for novel treatments,” he added.
The study was funded by the UK Dementia Research Institute. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schott serves as chief medical officer for Alzheimer’s Research UK and is clinical adviser to the UK Dementia Research Institute. Dr. Baillie has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings could lead to new treatment targets to slow progression and severity of both diseases.
Investigators found that a single genetic variant in the oligoadenylate synthetase 1 (OAS1) gene increases the risk for AD and that related variants in the same gene increase the likelihood of severe COVID-19 outcomes.
“These findings may allow us to identify new drug targets to slow progression of both diseases and reduce their severity,” Dervis Salih, PhD, senior research associate, UK Dementia Research Institute, University College London, said in an interview.
“Our work also suggests new approaches to treat both diseases with the same drugs,” Dr. Salih added.
The study was published online Oct. 7 in Brain.
Shared genetic network
The OAS1 gene is expressed in microglia, a type of immune cell that makes up around 10% of all cells in the brain.
In earlier work, investigators found evidence suggesting a link between the OAS1 gene and AD, but the function of the gene in microglia was unknown.
To further investigate the gene’s link to AD, they sequenced genetic data from 2,547 people – half with AD, and half without.
The genotyping analysis confirmed that the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1131454 within OAS1 is significantly associated with AD.
Given that the same OAS1 locus has recently been linked with severe COVID-19 outcomes, the researchers investigated four variants on the OAS1 gene.
Results indicate that SNPs within OAS1 associated with AD also show linkage to SNP variants associated with critical illness in COVID-19.
The rs1131454 (risk allele A) and rs4766676 (risk allele T) are associated with AD, and rs10735079 (risk allele A) and rs6489867 (risk allele T) are associated with critical illness with COVID-19, the investigators reported. All of these risk alleles dampen expression of OAS1.
“This study also provides strong new evidence that interferon signaling by the innate immune system plays a substantial role in the progression of Alzheimer’s,” said Dr. Salih.
“Identifying this shared genetic network in innate immune cells will allow us with future work to identify new biomarkers to track disease progression and also predict disease risk better for both disorders,” he added.
‘Fascinating’ link
In a statement from the UK nonprofit organization, Science Media Center, Kenneth Baillie, MBChB, with the University of Edinburgh, said this study builds on a discovery he and his colleagues made last year that OAS1 variants are associated with severe COVID-19.
“In the ISARIC4C study, we recently found that this is probably due to a change in the way cell membranes detect viruses, but this mechanism doesn’t explain the fascinating association with Alzheimer’s disease reported in this new work,” Dr. Baillie said.
“It is often the case that the same gene can have different roles in different parts of the body. Importantly, it doesn’t mean that having COVID-19 has any effect on your risk of Alzheimer’s,” he added.
Also weighing in on the new study, Jonathan Schott, MD, professor of neurology, University College London, noted that dementia is the “main preexisting health condition associated with COVID-19 mortality, accounting for about one in four deaths from COVID-19 between March and June 2020.
“While some of this excessive mortality may relate to people with dementia being overrepresented in care homes, which were particularly hard hit by the pandemic, or due to general increased vulnerability to infections, there have been questions as to whether there are common factors that might increase susceptibility both to developing dementia and to dying from COVID-19,” Dr. Schott explained.
This “elegant paper” provides evidence for the latter, “suggesting a common genetic mechanism both for Alzheimer’s disease and for severe COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Schott said.
“The identification of a genetic risk factor and elucidation of inflammatory pathways through which it may increase risk has important implications for our understanding of both diseases, with potential implications for novel treatments,” he added.
The study was funded by the UK Dementia Research Institute. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Schott serves as chief medical officer for Alzheimer’s Research UK and is clinical adviser to the UK Dementia Research Institute. Dr. Baillie has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even one vaccinated member can cut family’s COVID risk
The chances are reduced even further with each additional vaccinated or otherwise immune family member, according to new data.
Lead author Peter Nordström, MD, PhD, with the unit of geriatric medicine, Umeå (Sweden) University, said in an interview the message is important for public health: “When you vaccinate, you do not just protect yourself but also your relatives.”
The findings were published online on Oct. 11, 2021, in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers analyzed data from 1,789,728 individuals from 814,806 families from nationwide registries in Sweden. All individuals had acquired immunity either from previously being infected with SARS-CoV-2 or by being fully vaccinated (that is, having received two doses of the Moderna, Pfizer, or Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines). Persons were considered for inclusion until May 26, 2021.
Each person with immunity was matched in a 1:1 ratio to a person without immunity from a cohort of individuals with families that had from two to five members. Families with more than five members were excluded because of small sample sizes.
Primarily nonimmune families in which there was one immune family member had a 45%-61% lower risk of contracting COVID-19 (hazard ratio, 0.39-0.55; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.61; P < .001).
The risk reduction increased to 75%-86% when two family members were immune (HR, 0.14-0.25; 95% CI, 0.11-0.27; P < .001).
It increased to 91%-94% when three family members were immune (HR, 0.06-0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.10; P < .001) and to 97% with four immune family members (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.02-0.05; P < .001).
“The results were similar for the outcome of COVID-19 infection that was severe enough to warrant a hospital stay,” the authors wrote. They listed as an example that, in three-member families in which two members were immune, the remaining nonimmune family member had an 80% lower risk for hospitalization (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43; P < .001).
Global implications
Dr. Nordström said the team used the family setting because it was more easily identifiable as a cohort with the national registries and because COVID-19 is spread among people in close contact with each other. The findings have implications for other groups that spend large amounts of time together and for herd immunity, he added.
The findings may be particularly welcome in regions of the world where vaccination rates are very low. The authors noted that most of the global population has not yet been vaccinated and that “it is anticipated that most of the population in low-income countries will be unable to receive a vaccine in 2021, with current vaccination rates suggesting that completely inoculating 70%-85% of the global population may take up to 5 years.”
Jill Foster, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview she agrees that the news could encourage countries that have very low vaccination rates.
This study may help motivate areas with few resources to start small, she said: “Even one is better than zero.”
She added that this news could also help ease the minds of families that have immunocompromised members or in which there are children who are too young to be vaccinated.
With these data, she said, people can see there’s something they can do to help protect a family member.
Dr. Foster said that although it’s intuitive to think that the more vaccinated people there are in a family, the safer people are, “it’s really nice to see the data coming out of such a large dataset.”
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study is that, at the time the study was conducted, the Delta variant was uncommon in Sweden. It is therefore unclear whether the findings regarding immunity are still relevant in Sweden and elsewhere now that the Delta strain is dominant.
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Foster has received grant support from Moderna.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The chances are reduced even further with each additional vaccinated or otherwise immune family member, according to new data.
Lead author Peter Nordström, MD, PhD, with the unit of geriatric medicine, Umeå (Sweden) University, said in an interview the message is important for public health: “When you vaccinate, you do not just protect yourself but also your relatives.”
The findings were published online on Oct. 11, 2021, in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers analyzed data from 1,789,728 individuals from 814,806 families from nationwide registries in Sweden. All individuals had acquired immunity either from previously being infected with SARS-CoV-2 or by being fully vaccinated (that is, having received two doses of the Moderna, Pfizer, or Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines). Persons were considered for inclusion until May 26, 2021.
Each person with immunity was matched in a 1:1 ratio to a person without immunity from a cohort of individuals with families that had from two to five members. Families with more than five members were excluded because of small sample sizes.
Primarily nonimmune families in which there was one immune family member had a 45%-61% lower risk of contracting COVID-19 (hazard ratio, 0.39-0.55; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.61; P < .001).
The risk reduction increased to 75%-86% when two family members were immune (HR, 0.14-0.25; 95% CI, 0.11-0.27; P < .001).
It increased to 91%-94% when three family members were immune (HR, 0.06-0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.10; P < .001) and to 97% with four immune family members (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.02-0.05; P < .001).
“The results were similar for the outcome of COVID-19 infection that was severe enough to warrant a hospital stay,” the authors wrote. They listed as an example that, in three-member families in which two members were immune, the remaining nonimmune family member had an 80% lower risk for hospitalization (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43; P < .001).
Global implications
Dr. Nordström said the team used the family setting because it was more easily identifiable as a cohort with the national registries and because COVID-19 is spread among people in close contact with each other. The findings have implications for other groups that spend large amounts of time together and for herd immunity, he added.
The findings may be particularly welcome in regions of the world where vaccination rates are very low. The authors noted that most of the global population has not yet been vaccinated and that “it is anticipated that most of the population in low-income countries will be unable to receive a vaccine in 2021, with current vaccination rates suggesting that completely inoculating 70%-85% of the global population may take up to 5 years.”
Jill Foster, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview she agrees that the news could encourage countries that have very low vaccination rates.
This study may help motivate areas with few resources to start small, she said: “Even one is better than zero.”
She added that this news could also help ease the minds of families that have immunocompromised members or in which there are children who are too young to be vaccinated.
With these data, she said, people can see there’s something they can do to help protect a family member.
Dr. Foster said that although it’s intuitive to think that the more vaccinated people there are in a family, the safer people are, “it’s really nice to see the data coming out of such a large dataset.”
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study is that, at the time the study was conducted, the Delta variant was uncommon in Sweden. It is therefore unclear whether the findings regarding immunity are still relevant in Sweden and elsewhere now that the Delta strain is dominant.
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Foster has received grant support from Moderna.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The chances are reduced even further with each additional vaccinated or otherwise immune family member, according to new data.
Lead author Peter Nordström, MD, PhD, with the unit of geriatric medicine, Umeå (Sweden) University, said in an interview the message is important for public health: “When you vaccinate, you do not just protect yourself but also your relatives.”
The findings were published online on Oct. 11, 2021, in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researchers analyzed data from 1,789,728 individuals from 814,806 families from nationwide registries in Sweden. All individuals had acquired immunity either from previously being infected with SARS-CoV-2 or by being fully vaccinated (that is, having received two doses of the Moderna, Pfizer, or Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines). Persons were considered for inclusion until May 26, 2021.
Each person with immunity was matched in a 1:1 ratio to a person without immunity from a cohort of individuals with families that had from two to five members. Families with more than five members were excluded because of small sample sizes.
Primarily nonimmune families in which there was one immune family member had a 45%-61% lower risk of contracting COVID-19 (hazard ratio, 0.39-0.55; 95% confidence interval, 0.37-0.61; P < .001).
The risk reduction increased to 75%-86% when two family members were immune (HR, 0.14-0.25; 95% CI, 0.11-0.27; P < .001).
It increased to 91%-94% when three family members were immune (HR, 0.06-0.09; 95% CI, 0.04-0.10; P < .001) and to 97% with four immune family members (HR, 0.03; 95% CI, 0.02-0.05; P < .001).
“The results were similar for the outcome of COVID-19 infection that was severe enough to warrant a hospital stay,” the authors wrote. They listed as an example that, in three-member families in which two members were immune, the remaining nonimmune family member had an 80% lower risk for hospitalization (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43; P < .001).
Global implications
Dr. Nordström said the team used the family setting because it was more easily identifiable as a cohort with the national registries and because COVID-19 is spread among people in close contact with each other. The findings have implications for other groups that spend large amounts of time together and for herd immunity, he added.
The findings may be particularly welcome in regions of the world where vaccination rates are very low. The authors noted that most of the global population has not yet been vaccinated and that “it is anticipated that most of the population in low-income countries will be unable to receive a vaccine in 2021, with current vaccination rates suggesting that completely inoculating 70%-85% of the global population may take up to 5 years.”
Jill Foster, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, said in an interview she agrees that the news could encourage countries that have very low vaccination rates.
This study may help motivate areas with few resources to start small, she said: “Even one is better than zero.”
She added that this news could also help ease the minds of families that have immunocompromised members or in which there are children who are too young to be vaccinated.
With these data, she said, people can see there’s something they can do to help protect a family member.
Dr. Foster said that although it’s intuitive to think that the more vaccinated people there are in a family, the safer people are, “it’s really nice to see the data coming out of such a large dataset.”
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study is that, at the time the study was conducted, the Delta variant was uncommon in Sweden. It is therefore unclear whether the findings regarding immunity are still relevant in Sweden and elsewhere now that the Delta strain is dominant.
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Foster has received grant support from Moderna.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC: Children just as vulnerable to COVID as adults
The study, which focused on 1,000 schools in Arizona’s Maricopa and Pima counties, found that there were 113 COVID-19 outbreaks in schools without mask requirements in the first month of in-person learning. There were 16 outbreaks in schools with mask requirements.
“Masks in schools work to protect our children, to keep them and their school communities safe, and to keep them in school for in-person learning,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at an Oct. 13 White House briefing.
But, she said, more than 95% of schools across the country had remained open through the end of September, despite 1,800 school closures affecting nearly 1 million students.
Protection for children in school is just one piece of the puzzle, Dr. Walensky said – there must also be COVID-safe practices at home to limit transmission. A CDC study published in October found that children had similar infection rates, compared with adults, confirming there is risk to people of all ages.
“For those children not yet eligible for vaccination, the best protection we can provide them is to make sure everyone around them in the household is vaccinated and to make sure they’re wearing a mask in school and during indoor extracurricular activities,” Dr. Walensky said.
Meanwhile, Pfizer’s vaccine for children ages 5-11 may be approved by early November. The Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee will meet Oct. 26 to discuss available data, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet Nov. 2. A decision is expected soon after.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The study, which focused on 1,000 schools in Arizona’s Maricopa and Pima counties, found that there were 113 COVID-19 outbreaks in schools without mask requirements in the first month of in-person learning. There were 16 outbreaks in schools with mask requirements.
“Masks in schools work to protect our children, to keep them and their school communities safe, and to keep them in school for in-person learning,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at an Oct. 13 White House briefing.
But, she said, more than 95% of schools across the country had remained open through the end of September, despite 1,800 school closures affecting nearly 1 million students.
Protection for children in school is just one piece of the puzzle, Dr. Walensky said – there must also be COVID-safe practices at home to limit transmission. A CDC study published in October found that children had similar infection rates, compared with adults, confirming there is risk to people of all ages.
“For those children not yet eligible for vaccination, the best protection we can provide them is to make sure everyone around them in the household is vaccinated and to make sure they’re wearing a mask in school and during indoor extracurricular activities,” Dr. Walensky said.
Meanwhile, Pfizer’s vaccine for children ages 5-11 may be approved by early November. The Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee will meet Oct. 26 to discuss available data, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet Nov. 2. A decision is expected soon after.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The study, which focused on 1,000 schools in Arizona’s Maricopa and Pima counties, found that there were 113 COVID-19 outbreaks in schools without mask requirements in the first month of in-person learning. There were 16 outbreaks in schools with mask requirements.
“Masks in schools work to protect our children, to keep them and their school communities safe, and to keep them in school for in-person learning,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at an Oct. 13 White House briefing.
But, she said, more than 95% of schools across the country had remained open through the end of September, despite 1,800 school closures affecting nearly 1 million students.
Protection for children in school is just one piece of the puzzle, Dr. Walensky said – there must also be COVID-safe practices at home to limit transmission. A CDC study published in October found that children had similar infection rates, compared with adults, confirming there is risk to people of all ages.
“For those children not yet eligible for vaccination, the best protection we can provide them is to make sure everyone around them in the household is vaccinated and to make sure they’re wearing a mask in school and during indoor extracurricular activities,” Dr. Walensky said.
Meanwhile, Pfizer’s vaccine for children ages 5-11 may be approved by early November. The Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee will meet Oct. 26 to discuss available data, and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet Nov. 2. A decision is expected soon after.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
No short-term death risk in elderly after COVID-19 vaccines
and launched an investigation into the safety of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Comirnaty; Pfizer-BioNTech).
Now, the results of that investigation and of a subsequent larger study of nursing home residents in Norway have shown no increased risk for short-term mortality following COVID-19 vaccination in the overall population of elderly patients. The new research also showed clear evidence of a survival benefit compared with the unvaccinated population, Anette Hylen Ranhoff, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Geriatric Medicine Society, held in a hybrid format in Athens, Greece, and online.
“We found no evidence of increased short-term mortality among vaccinated older individuals, and particularly not among the nursing home patients,” said Dr. Ranhoff, a senior researcher at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health and professor at University of Bergen, Norway. “But we think that this [lower] mortality risk was most likely a sort of ‘healthy-vaccinee’ effect, which means that people who were a bit more healthy were vaccinated, and not those who were the very, very most frail.”
“We have more or less the same data in France about events, with very high rates of vaccination,” said session moderator Athanase Benetos MD, PhD, professor and chairman of geriatric medicine at the University Hospital of Nancy in France, who was not involved in the study.
“In my department, a month after the end of the vaccination and at the same time while the pandemic in the city was going up, we had a 90% decrease in mortality from COVID in the nursing homes,” he told Dr. Ranhoff.
Potential risks
Frail elderly patients were not included in clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines, and although previous studies have shown a low incidence of local or systemic reactions to vaccination among older people, “we think that quite mild adverse events following vaccination could trigger and destabilize a frail person,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
As reported Jan. 15, 2021, in BMJ, investigation by the Norwegian Medicines Agency (NOMA) into 13 of the 23 reported cases concluded that common adverse reactions associated with mRNA vaccines could have contributed to the deaths of some of the frail elderly patients
Steinar Madsen, MD, NOMA medical director, told BMJ “we are not alarmed or worried about this, because these are very rare occurrences and they occurred in very frail patients with very serious disease.”
Health authorities investigate
In response to the report and at the request of the Norwegian Public Health Institute and NOMA, Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues investigated the first 100 deaths among nursing-home residents who received the vaccine. The team consisted of three geriatricians and an infectious disease specialist who sees patients in nursing homes.
They looked at each patient’s clinical course before and after vaccination, their health trajectory and life expectancy at the time of vaccination, new symptoms following vaccination, and the time from vaccination to new symptoms and to death.
In addition, the investigators evaluated Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS) scores for each patient. CFS scores range from 1 (very fit) to 9 (terminally ill, with a life expectancy of less than 6 months who are otherwise evidently frail).
The initial investigation found that among 95 evaluable patients, the association between vaccination and death was “probable” in 10, “possible” in 26, and “unlikely” in 59.
The mean time from vaccination to symptoms was 1.4 days in the probable cases, 2.5 days in the possible cases, and 4.7 days in the unlikely cases.
The mean time from vaccination to death was 3.1, 8.3, and 8.2 days, respectively.
In all three categories, the patients had mean CFS scores ranging from 7.6 to 7.9, putting them in the “severely frail” category, defined as people who are completely dependent for personal care but seem stable and not at high risk for dying.
“We have quite many nursing home residents in Norway, 35,000; more than 80% have dementia, and the mean age is 85 years. We know that approximately 45 people die every day in these nursing homes, and their mean age of death is 87.5 years,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
Population-wide study
Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues also looked more broadly into the question of potential vaccine-related mortality in the total population of older people in Norway from the day of vaccination to follow-up at 3 weeks.
They conducted a matched cohort study to investigate the relationship between the mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and overall death among persons aged 65 and older in the general population, and across four groups: patients receiving home-based care, long-term nursing home patients, short-term nursing home patients, and those not receiving health services.
The researchers identified a total of 967,786 residents of Norway aged 65 and over at the start of the country’s vaccination campaign at the end of December, 2020, and they matched vaccinated individuals with unvaccinated persons based on demographic, geographic, and clinical risk group factors.
Dr. Ranhoff showed Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the total population and for each of the health-service states. In all cases there was a clear survival benefit for vaccinated vs. unvaccinated patients. She did not, however, provide specific numbers or hazard ratios for the differences between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in each of the comparisons.
The study was supported by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. Dr. Ranhoff and Dr. Benetos reported no conflicts of interest.
and launched an investigation into the safety of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Comirnaty; Pfizer-BioNTech).
Now, the results of that investigation and of a subsequent larger study of nursing home residents in Norway have shown no increased risk for short-term mortality following COVID-19 vaccination in the overall population of elderly patients. The new research also showed clear evidence of a survival benefit compared with the unvaccinated population, Anette Hylen Ranhoff, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Geriatric Medicine Society, held in a hybrid format in Athens, Greece, and online.
“We found no evidence of increased short-term mortality among vaccinated older individuals, and particularly not among the nursing home patients,” said Dr. Ranhoff, a senior researcher at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health and professor at University of Bergen, Norway. “But we think that this [lower] mortality risk was most likely a sort of ‘healthy-vaccinee’ effect, which means that people who were a bit more healthy were vaccinated, and not those who were the very, very most frail.”
“We have more or less the same data in France about events, with very high rates of vaccination,” said session moderator Athanase Benetos MD, PhD, professor and chairman of geriatric medicine at the University Hospital of Nancy in France, who was not involved in the study.
“In my department, a month after the end of the vaccination and at the same time while the pandemic in the city was going up, we had a 90% decrease in mortality from COVID in the nursing homes,” he told Dr. Ranhoff.
Potential risks
Frail elderly patients were not included in clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines, and although previous studies have shown a low incidence of local or systemic reactions to vaccination among older people, “we think that quite mild adverse events following vaccination could trigger and destabilize a frail person,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
As reported Jan. 15, 2021, in BMJ, investigation by the Norwegian Medicines Agency (NOMA) into 13 of the 23 reported cases concluded that common adverse reactions associated with mRNA vaccines could have contributed to the deaths of some of the frail elderly patients
Steinar Madsen, MD, NOMA medical director, told BMJ “we are not alarmed or worried about this, because these are very rare occurrences and they occurred in very frail patients with very serious disease.”
Health authorities investigate
In response to the report and at the request of the Norwegian Public Health Institute and NOMA, Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues investigated the first 100 deaths among nursing-home residents who received the vaccine. The team consisted of three geriatricians and an infectious disease specialist who sees patients in nursing homes.
They looked at each patient’s clinical course before and after vaccination, their health trajectory and life expectancy at the time of vaccination, new symptoms following vaccination, and the time from vaccination to new symptoms and to death.
In addition, the investigators evaluated Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS) scores for each patient. CFS scores range from 1 (very fit) to 9 (terminally ill, with a life expectancy of less than 6 months who are otherwise evidently frail).
The initial investigation found that among 95 evaluable patients, the association between vaccination and death was “probable” in 10, “possible” in 26, and “unlikely” in 59.
The mean time from vaccination to symptoms was 1.4 days in the probable cases, 2.5 days in the possible cases, and 4.7 days in the unlikely cases.
The mean time from vaccination to death was 3.1, 8.3, and 8.2 days, respectively.
In all three categories, the patients had mean CFS scores ranging from 7.6 to 7.9, putting them in the “severely frail” category, defined as people who are completely dependent for personal care but seem stable and not at high risk for dying.
“We have quite many nursing home residents in Norway, 35,000; more than 80% have dementia, and the mean age is 85 years. We know that approximately 45 people die every day in these nursing homes, and their mean age of death is 87.5 years,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
Population-wide study
Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues also looked more broadly into the question of potential vaccine-related mortality in the total population of older people in Norway from the day of vaccination to follow-up at 3 weeks.
They conducted a matched cohort study to investigate the relationship between the mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and overall death among persons aged 65 and older in the general population, and across four groups: patients receiving home-based care, long-term nursing home patients, short-term nursing home patients, and those not receiving health services.
The researchers identified a total of 967,786 residents of Norway aged 65 and over at the start of the country’s vaccination campaign at the end of December, 2020, and they matched vaccinated individuals with unvaccinated persons based on demographic, geographic, and clinical risk group factors.
Dr. Ranhoff showed Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the total population and for each of the health-service states. In all cases there was a clear survival benefit for vaccinated vs. unvaccinated patients. She did not, however, provide specific numbers or hazard ratios for the differences between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in each of the comparisons.
The study was supported by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. Dr. Ranhoff and Dr. Benetos reported no conflicts of interest.
and launched an investigation into the safety of the BNT162b2 vaccine (Comirnaty; Pfizer-BioNTech).
Now, the results of that investigation and of a subsequent larger study of nursing home residents in Norway have shown no increased risk for short-term mortality following COVID-19 vaccination in the overall population of elderly patients. The new research also showed clear evidence of a survival benefit compared with the unvaccinated population, Anette Hylen Ranhoff, MD, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Geriatric Medicine Society, held in a hybrid format in Athens, Greece, and online.
“We found no evidence of increased short-term mortality among vaccinated older individuals, and particularly not among the nursing home patients,” said Dr. Ranhoff, a senior researcher at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health and professor at University of Bergen, Norway. “But we think that this [lower] mortality risk was most likely a sort of ‘healthy-vaccinee’ effect, which means that people who were a bit more healthy were vaccinated, and not those who were the very, very most frail.”
“We have more or less the same data in France about events, with very high rates of vaccination,” said session moderator Athanase Benetos MD, PhD, professor and chairman of geriatric medicine at the University Hospital of Nancy in France, who was not involved in the study.
“In my department, a month after the end of the vaccination and at the same time while the pandemic in the city was going up, we had a 90% decrease in mortality from COVID in the nursing homes,” he told Dr. Ranhoff.
Potential risks
Frail elderly patients were not included in clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines, and although previous studies have shown a low incidence of local or systemic reactions to vaccination among older people, “we think that quite mild adverse events following vaccination could trigger and destabilize a frail person,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
As reported Jan. 15, 2021, in BMJ, investigation by the Norwegian Medicines Agency (NOMA) into 13 of the 23 reported cases concluded that common adverse reactions associated with mRNA vaccines could have contributed to the deaths of some of the frail elderly patients
Steinar Madsen, MD, NOMA medical director, told BMJ “we are not alarmed or worried about this, because these are very rare occurrences and they occurred in very frail patients with very serious disease.”
Health authorities investigate
In response to the report and at the request of the Norwegian Public Health Institute and NOMA, Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues investigated the first 100 deaths among nursing-home residents who received the vaccine. The team consisted of three geriatricians and an infectious disease specialist who sees patients in nursing homes.
They looked at each patient’s clinical course before and after vaccination, their health trajectory and life expectancy at the time of vaccination, new symptoms following vaccination, and the time from vaccination to new symptoms and to death.
In addition, the investigators evaluated Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS) scores for each patient. CFS scores range from 1 (very fit) to 9 (terminally ill, with a life expectancy of less than 6 months who are otherwise evidently frail).
The initial investigation found that among 95 evaluable patients, the association between vaccination and death was “probable” in 10, “possible” in 26, and “unlikely” in 59.
The mean time from vaccination to symptoms was 1.4 days in the probable cases, 2.5 days in the possible cases, and 4.7 days in the unlikely cases.
The mean time from vaccination to death was 3.1, 8.3, and 8.2 days, respectively.
In all three categories, the patients had mean CFS scores ranging from 7.6 to 7.9, putting them in the “severely frail” category, defined as people who are completely dependent for personal care but seem stable and not at high risk for dying.
“We have quite many nursing home residents in Norway, 35,000; more than 80% have dementia, and the mean age is 85 years. We know that approximately 45 people die every day in these nursing homes, and their mean age of death is 87.5 years,” Dr. Ranhoff said.
Population-wide study
Dr. Ranhoff and colleagues also looked more broadly into the question of potential vaccine-related mortality in the total population of older people in Norway from the day of vaccination to follow-up at 3 weeks.
They conducted a matched cohort study to investigate the relationship between the mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and overall death among persons aged 65 and older in the general population, and across four groups: patients receiving home-based care, long-term nursing home patients, short-term nursing home patients, and those not receiving health services.
The researchers identified a total of 967,786 residents of Norway aged 65 and over at the start of the country’s vaccination campaign at the end of December, 2020, and they matched vaccinated individuals with unvaccinated persons based on demographic, geographic, and clinical risk group factors.
Dr. Ranhoff showed Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the total population and for each of the health-service states. In all cases there was a clear survival benefit for vaccinated vs. unvaccinated patients. She did not, however, provide specific numbers or hazard ratios for the differences between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in each of the comparisons.
The study was supported by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. Dr. Ranhoff and Dr. Benetos reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM EUGMS 2021
What turns wandering thoughts into something worse?
With all the lockdowns and social distancing of the pandemic, millions of people have had a lot of time to themselves. Many may have filled that time with baking, long walks, or video games, but minds wandering during these periods was inevitable. Coincident with these experiences were increases in depression and anxiety, which could be linked to the same brain network that is thought to support a meandering mind, called the default mode network.
Scientists interested in this network wanted to understand how wandering thoughts can lead some people to a state of brooding in which the same negative thoughts resurface repeatedly. To gain some insight into these patterns, they recorded more than 2,000 thoughts spoken aloud by 78 study participants who did nothing but let their minds wander for 10 minutes.
Senior researcher Jessica Andrews-Hanna, PhD, assistant professor of psychology, University of Arizona, Tucson, and colleagues hoped that analyzing these stream-of-consciousness thoughts could yield insights into how people become stuck in negative mental spirals.
They found that most participants thought about the present or future in words that were neither particularly negative nor positive. Almost three-quarters of the thoughts were focused inward on the person or were imaginative.
Negativity breeds negativity
But the investigators found an interesting pattern with regard to negative thoughts. The more negative someone’s thoughts became, the more likely that their next idea would be related to their previous one. In other words, negative thoughts created a chain reaction of more negative thoughts.
, indicating true mental meandering. The pattern suggested that negativity tends to narrow the range of thoughts, whereas positivity tends to expand it during periods in which the mind wanders.
The researchers also found, unsurprisingly, that negative thoughts that were focused on the self and on the past were more likely to result in brooding and that positive thoughts were less likely to arise.
Most study participants were young and educated and may have only said things that they were comfortable allowing the researchers to hear. And because the authors didn’t ask participants about their moods, the investigators could not associate specific patterns of thought with any mental health conditions.
Although the findings, published in Scientific Reports, do not on their own point to solutions for depression or anxiety, they may offer a starting point for future research into how negative trains of thoughts begin – and perhaps how to derail them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With all the lockdowns and social distancing of the pandemic, millions of people have had a lot of time to themselves. Many may have filled that time with baking, long walks, or video games, but minds wandering during these periods was inevitable. Coincident with these experiences were increases in depression and anxiety, which could be linked to the same brain network that is thought to support a meandering mind, called the default mode network.
Scientists interested in this network wanted to understand how wandering thoughts can lead some people to a state of brooding in which the same negative thoughts resurface repeatedly. To gain some insight into these patterns, they recorded more than 2,000 thoughts spoken aloud by 78 study participants who did nothing but let their minds wander for 10 minutes.
Senior researcher Jessica Andrews-Hanna, PhD, assistant professor of psychology, University of Arizona, Tucson, and colleagues hoped that analyzing these stream-of-consciousness thoughts could yield insights into how people become stuck in negative mental spirals.
They found that most participants thought about the present or future in words that were neither particularly negative nor positive. Almost three-quarters of the thoughts were focused inward on the person or were imaginative.
Negativity breeds negativity
But the investigators found an interesting pattern with regard to negative thoughts. The more negative someone’s thoughts became, the more likely that their next idea would be related to their previous one. In other words, negative thoughts created a chain reaction of more negative thoughts.
, indicating true mental meandering. The pattern suggested that negativity tends to narrow the range of thoughts, whereas positivity tends to expand it during periods in which the mind wanders.
The researchers also found, unsurprisingly, that negative thoughts that were focused on the self and on the past were more likely to result in brooding and that positive thoughts were less likely to arise.
Most study participants were young and educated and may have only said things that they were comfortable allowing the researchers to hear. And because the authors didn’t ask participants about their moods, the investigators could not associate specific patterns of thought with any mental health conditions.
Although the findings, published in Scientific Reports, do not on their own point to solutions for depression or anxiety, they may offer a starting point for future research into how negative trains of thoughts begin – and perhaps how to derail them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With all the lockdowns and social distancing of the pandemic, millions of people have had a lot of time to themselves. Many may have filled that time with baking, long walks, or video games, but minds wandering during these periods was inevitable. Coincident with these experiences were increases in depression and anxiety, which could be linked to the same brain network that is thought to support a meandering mind, called the default mode network.
Scientists interested in this network wanted to understand how wandering thoughts can lead some people to a state of brooding in which the same negative thoughts resurface repeatedly. To gain some insight into these patterns, they recorded more than 2,000 thoughts spoken aloud by 78 study participants who did nothing but let their minds wander for 10 minutes.
Senior researcher Jessica Andrews-Hanna, PhD, assistant professor of psychology, University of Arizona, Tucson, and colleagues hoped that analyzing these stream-of-consciousness thoughts could yield insights into how people become stuck in negative mental spirals.
They found that most participants thought about the present or future in words that were neither particularly negative nor positive. Almost three-quarters of the thoughts were focused inward on the person or were imaginative.
Negativity breeds negativity
But the investigators found an interesting pattern with regard to negative thoughts. The more negative someone’s thoughts became, the more likely that their next idea would be related to their previous one. In other words, negative thoughts created a chain reaction of more negative thoughts.
, indicating true mental meandering. The pattern suggested that negativity tends to narrow the range of thoughts, whereas positivity tends to expand it during periods in which the mind wanders.
The researchers also found, unsurprisingly, that negative thoughts that were focused on the self and on the past were more likely to result in brooding and that positive thoughts were less likely to arise.
Most study participants were young and educated and may have only said things that they were comfortable allowing the researchers to hear. And because the authors didn’t ask participants about their moods, the investigators could not associate specific patterns of thought with any mental health conditions.
Although the findings, published in Scientific Reports, do not on their own point to solutions for depression or anxiety, they may offer a starting point for future research into how negative trains of thoughts begin – and perhaps how to derail them.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Omega-3s tame inflammation in elderly COVID-19 patients
results of a small randomized controlled trial suggest.
Results of the study, which included 22 patients with multiple comorbidities, were presented at the European Geriatric Medicine Society annual congress, a hybrid live and online meeting.
The patients, who had a median age of 81 years, were randomized to receive an intravenous infusion of an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) emulsion containing 10 g of fish oil per 100 mL or a saline placebo.
Those who received the intravenous infusion had significant decreases from baseline to end of treatment in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), indicating marked reductions in systemic inflammation.
In contrast, patients randomized to a saline placebo had no significant improvements in NLR, Magnus Bäck, MD, PhD, from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm reported at the meeting.
“Our lipidomic analysis also showed that omega-3 treatment skewed the lipid response, with reduced levels of proinflammatory lipid mediators, and increased levels of proresolving mediators,” according to a late-breaking abstract, which Dr. Bäck presented during the session.
Omega-3 treatment was not significantly associated with reduction in either C-reactive protein (CRP) or the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6, however.
‘Eicosanoid storm’
In a review article published in January 2021 in the open-access journal Frontiers in Physiology, Dr. Bäck and colleagues outlined the rationale for their randomized trial.
“Excessive inflammation has been reported in severe cases with respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications,” they wrote. “In addition to the release of cytokines, referred to as cytokine release syndrome or ‘cytokine storm,’ increased proinflammatory lipid mediators derived from the omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) arachidonic acid may cause an ‘eicosanoid storm,’ which contributes to the uncontrolled systemic inflammation.”
Omega-3 PUFA contains proresolving mediators that can limit inflammatory reactions, suggesting the possibility of an inflammation-resolving benefit in patients with COVID-19 without concerns about immunosuppression, the authors hypothesized.
Trial details
In the trial, COVID-Omega-F, they enrolled patients with a COVID-19 diagnosis requiring hospitalization. Patients with an allergy to fish oil or who had contraindications to intravenous PUFA administration (for example, risk for bleeding, shock, or emboli) were excluded.
Ten patients were randomly assigned to receive infusions of the omega-3 PUFA and 12 were assigned to receive infusions of the placebo, once daily for 5 days. The primary outcome measure was change in inflammatory biomarkers, including white blood cell counts, CRP, cytokines, and lipid mediators.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the two study arms, with a median of about 7 days since the onset of symptoms, and 3.5 days since a diagnosis of COVID-19.
All patients had low lymphocyte responses reflected by a high NLR, a prognostic measure for worse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infections, Dr. Bäck said.
Inflammation was moderate, with a CRP of 65 mg/L in the placebo group and 62 mg/L in the omega-3 group.
Seven patients in each study arm received concomitant corticoid treatment. Two patients in each arm died in hospital, but there were no serious treatment-related adverse events.
Inflammatory markers improve
As noted before, there was a significant decline in NLR from baseline among patients randomized to omega-3 (P = .02) but no corresponding decrease in patients assigned to placebo infusions.
“The significant decrease was largely driven by an increase in the lymphocyte count in the omega-3 treated group (P = .004), whereas lymphocytes did not significantly change,” Dr. Bäck said.
As expected, patients in the omega-3 group had pronounced increases in omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid.
The metabolism of fatty acids also differed markedly between the groups, with a significant decrease in the omega-3 group but not the placebo group in proinflammatory mediators, and an increase in precursors to proresolving mediators, Dr. Bäck noted.
AFib concerns
In a question-and-answer part of the session, a physician who identified herself as “Senya from Russia” questioned the safety of omega-3 treatment in this population, “because recently there was a meta-analysis which showed that omega-3 fatty acids will increase the risk of atrial fibrillation in older adults especially.”
The systematic review and meta-analysis she referred to, published in Circulation and reported on by this news organization, showed that, among 81,210 patients with a mean age of 65 enrolled in seven randomized controlled trials, omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with a 25% increase in risk for atrial fibrillation. This risk appeared to be higher in trials testing doses greater than 1 g/day, according to the paper.
“This was not monitored in this study,” Dr. Bäck replied. “It is true that the meta-analysis showed an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation, so it would be something to monitor in case this trial would be expanded to a larger population.”
The study was supported by the Karolinska Institute. Dr. Bäck disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a small randomized controlled trial suggest.
Results of the study, which included 22 patients with multiple comorbidities, were presented at the European Geriatric Medicine Society annual congress, a hybrid live and online meeting.
The patients, who had a median age of 81 years, were randomized to receive an intravenous infusion of an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) emulsion containing 10 g of fish oil per 100 mL or a saline placebo.
Those who received the intravenous infusion had significant decreases from baseline to end of treatment in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), indicating marked reductions in systemic inflammation.
In contrast, patients randomized to a saline placebo had no significant improvements in NLR, Magnus Bäck, MD, PhD, from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm reported at the meeting.
“Our lipidomic analysis also showed that omega-3 treatment skewed the lipid response, with reduced levels of proinflammatory lipid mediators, and increased levels of proresolving mediators,” according to a late-breaking abstract, which Dr. Bäck presented during the session.
Omega-3 treatment was not significantly associated with reduction in either C-reactive protein (CRP) or the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6, however.
‘Eicosanoid storm’
In a review article published in January 2021 in the open-access journal Frontiers in Physiology, Dr. Bäck and colleagues outlined the rationale for their randomized trial.
“Excessive inflammation has been reported in severe cases with respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications,” they wrote. “In addition to the release of cytokines, referred to as cytokine release syndrome or ‘cytokine storm,’ increased proinflammatory lipid mediators derived from the omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) arachidonic acid may cause an ‘eicosanoid storm,’ which contributes to the uncontrolled systemic inflammation.”
Omega-3 PUFA contains proresolving mediators that can limit inflammatory reactions, suggesting the possibility of an inflammation-resolving benefit in patients with COVID-19 without concerns about immunosuppression, the authors hypothesized.
Trial details
In the trial, COVID-Omega-F, they enrolled patients with a COVID-19 diagnosis requiring hospitalization. Patients with an allergy to fish oil or who had contraindications to intravenous PUFA administration (for example, risk for bleeding, shock, or emboli) were excluded.
Ten patients were randomly assigned to receive infusions of the omega-3 PUFA and 12 were assigned to receive infusions of the placebo, once daily for 5 days. The primary outcome measure was change in inflammatory biomarkers, including white blood cell counts, CRP, cytokines, and lipid mediators.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the two study arms, with a median of about 7 days since the onset of symptoms, and 3.5 days since a diagnosis of COVID-19.
All patients had low lymphocyte responses reflected by a high NLR, a prognostic measure for worse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infections, Dr. Bäck said.
Inflammation was moderate, with a CRP of 65 mg/L in the placebo group and 62 mg/L in the omega-3 group.
Seven patients in each study arm received concomitant corticoid treatment. Two patients in each arm died in hospital, but there were no serious treatment-related adverse events.
Inflammatory markers improve
As noted before, there was a significant decline in NLR from baseline among patients randomized to omega-3 (P = .02) but no corresponding decrease in patients assigned to placebo infusions.
“The significant decrease was largely driven by an increase in the lymphocyte count in the omega-3 treated group (P = .004), whereas lymphocytes did not significantly change,” Dr. Bäck said.
As expected, patients in the omega-3 group had pronounced increases in omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid.
The metabolism of fatty acids also differed markedly between the groups, with a significant decrease in the omega-3 group but not the placebo group in proinflammatory mediators, and an increase in precursors to proresolving mediators, Dr. Bäck noted.
AFib concerns
In a question-and-answer part of the session, a physician who identified herself as “Senya from Russia” questioned the safety of omega-3 treatment in this population, “because recently there was a meta-analysis which showed that omega-3 fatty acids will increase the risk of atrial fibrillation in older adults especially.”
The systematic review and meta-analysis she referred to, published in Circulation and reported on by this news organization, showed that, among 81,210 patients with a mean age of 65 enrolled in seven randomized controlled trials, omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with a 25% increase in risk for atrial fibrillation. This risk appeared to be higher in trials testing doses greater than 1 g/day, according to the paper.
“This was not monitored in this study,” Dr. Bäck replied. “It is true that the meta-analysis showed an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation, so it would be something to monitor in case this trial would be expanded to a larger population.”
The study was supported by the Karolinska Institute. Dr. Bäck disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a small randomized controlled trial suggest.
Results of the study, which included 22 patients with multiple comorbidities, were presented at the European Geriatric Medicine Society annual congress, a hybrid live and online meeting.
The patients, who had a median age of 81 years, were randomized to receive an intravenous infusion of an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) emulsion containing 10 g of fish oil per 100 mL or a saline placebo.
Those who received the intravenous infusion had significant decreases from baseline to end of treatment in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), indicating marked reductions in systemic inflammation.
In contrast, patients randomized to a saline placebo had no significant improvements in NLR, Magnus Bäck, MD, PhD, from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm reported at the meeting.
“Our lipidomic analysis also showed that omega-3 treatment skewed the lipid response, with reduced levels of proinflammatory lipid mediators, and increased levels of proresolving mediators,” according to a late-breaking abstract, which Dr. Bäck presented during the session.
Omega-3 treatment was not significantly associated with reduction in either C-reactive protein (CRP) or the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6, however.
‘Eicosanoid storm’
In a review article published in January 2021 in the open-access journal Frontiers in Physiology, Dr. Bäck and colleagues outlined the rationale for their randomized trial.
“Excessive inflammation has been reported in severe cases with respiratory failure and cardiovascular complications,” they wrote. “In addition to the release of cytokines, referred to as cytokine release syndrome or ‘cytokine storm,’ increased proinflammatory lipid mediators derived from the omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) arachidonic acid may cause an ‘eicosanoid storm,’ which contributes to the uncontrolled systemic inflammation.”
Omega-3 PUFA contains proresolving mediators that can limit inflammatory reactions, suggesting the possibility of an inflammation-resolving benefit in patients with COVID-19 without concerns about immunosuppression, the authors hypothesized.
Trial details
In the trial, COVID-Omega-F, they enrolled patients with a COVID-19 diagnosis requiring hospitalization. Patients with an allergy to fish oil or who had contraindications to intravenous PUFA administration (for example, risk for bleeding, shock, or emboli) were excluded.
Ten patients were randomly assigned to receive infusions of the omega-3 PUFA and 12 were assigned to receive infusions of the placebo, once daily for 5 days. The primary outcome measure was change in inflammatory biomarkers, including white blood cell counts, CRP, cytokines, and lipid mediators.
Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the two study arms, with a median of about 7 days since the onset of symptoms, and 3.5 days since a diagnosis of COVID-19.
All patients had low lymphocyte responses reflected by a high NLR, a prognostic measure for worse outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infections, Dr. Bäck said.
Inflammation was moderate, with a CRP of 65 mg/L in the placebo group and 62 mg/L in the omega-3 group.
Seven patients in each study arm received concomitant corticoid treatment. Two patients in each arm died in hospital, but there were no serious treatment-related adverse events.
Inflammatory markers improve
As noted before, there was a significant decline in NLR from baseline among patients randomized to omega-3 (P = .02) but no corresponding decrease in patients assigned to placebo infusions.
“The significant decrease was largely driven by an increase in the lymphocyte count in the omega-3 treated group (P = .004), whereas lymphocytes did not significantly change,” Dr. Bäck said.
As expected, patients in the omega-3 group had pronounced increases in omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid.
The metabolism of fatty acids also differed markedly between the groups, with a significant decrease in the omega-3 group but not the placebo group in proinflammatory mediators, and an increase in precursors to proresolving mediators, Dr. Bäck noted.
AFib concerns
In a question-and-answer part of the session, a physician who identified herself as “Senya from Russia” questioned the safety of omega-3 treatment in this population, “because recently there was a meta-analysis which showed that omega-3 fatty acids will increase the risk of atrial fibrillation in older adults especially.”
The systematic review and meta-analysis she referred to, published in Circulation and reported on by this news organization, showed that, among 81,210 patients with a mean age of 65 enrolled in seven randomized controlled trials, omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with a 25% increase in risk for atrial fibrillation. This risk appeared to be higher in trials testing doses greater than 1 g/day, according to the paper.
“This was not monitored in this study,” Dr. Bäck replied. “It is true that the meta-analysis showed an increased incidence of atrial fibrillation, so it would be something to monitor in case this trial would be expanded to a larger population.”
The study was supported by the Karolinska Institute. Dr. Bäck disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EUGMS
Pandemic data challenges infection link to Guillain-Barré syndrome
While pediatric cases of various types of infections fell by 45%-95% during the early months of the pandemic, cases of acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP), an inflammatory neuropathy belonging to the clinical spectrum of Guillain-Barré syndrome, only fell by about 32%-37%, a rate that’s similar to the 35.1% decline in overall hospital admissions over that time period, researchers found. There was also no apparent link between the appearance of COVID-19 and the number of reported AIDP cases.
“There was no clear association between respiratory or gastrointestinal infections and rates of AIDP. Further, we found that AIDP did not have the expected dramatic reduction when community-acquired infections decreased during the pandemic,” Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia neurologist Craig A. Press, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Press and colleagues presented their findings in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
According to Dr. Press, the cause of AIDP in most patients is unclear, although infections and vaccinations are often linked to cases. “However, the data supporting this link is often weak. Infections with Campylobacter jejuni [bacteria that causes food poisoning] are known to be associated with AIDP, while rates of AIDP in the general population and in those with influenza are similar.”
For the new multicenter, cross-sectional study, researchers tracked AIDP data from the 47 pediatric hospitals that provide statistics to the Pediatric Health Information System. They focused on the period from January 2017 to September 2020, which included the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States.
“Social distancing, masks, and increased hand hygiene decrease community-acquired infectious rates in a dramatic way,” Dr. Press said. “If these infections were causing AIDP, we hypothesized that the cases of AIDP would drop substantially as a result.”
But this didn’t appear to happen. Researchers found that the numbers of various types of infections declined from April to September 2020: Respiratory infections dipped by 73%-78%, gastrointestinal infections fell by 45%-61%, and influenza infections dipped by 88%-95%. But AIDP cases didn’t fall as precipitously. In fact, their levels were about the same as they were in April 2017, a month when rates of gastrointestinal, respiratory disease and influenza infections were at seasonally low – but not abnormal – ebbs.
“While we must be cautious interpreting the results,” Dr. Press said, “this makes the link between infections as the main driver of pediatric AIDP less likely.”
However, he said, “this study does not exclude the possibility that rare infections cause AIDP – the data supporting that some more rare infections like campylobacter have a connection to AIDP are more robust – or that common infections very rarely lead to AIDP. While we look for triggers causing inflammatory disorders, AIDP maybe an autoinflammatory disorder without a clear trigger.”
Going forward, Dr. Press said, “we hope to look at infectious data in a more granular way to identify if specific viral or bacterial infectious may be associated with this or other inflammatory disorders. We believe that the use of data like this and the natural experiment that COVID-19 provided may help us to explore the impact of infections on disorders thought to be postinfectious.”
No study funding is reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures.
While pediatric cases of various types of infections fell by 45%-95% during the early months of the pandemic, cases of acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP), an inflammatory neuropathy belonging to the clinical spectrum of Guillain-Barré syndrome, only fell by about 32%-37%, a rate that’s similar to the 35.1% decline in overall hospital admissions over that time period, researchers found. There was also no apparent link between the appearance of COVID-19 and the number of reported AIDP cases.
“There was no clear association between respiratory or gastrointestinal infections and rates of AIDP. Further, we found that AIDP did not have the expected dramatic reduction when community-acquired infections decreased during the pandemic,” Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia neurologist Craig A. Press, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Press and colleagues presented their findings in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
According to Dr. Press, the cause of AIDP in most patients is unclear, although infections and vaccinations are often linked to cases. “However, the data supporting this link is often weak. Infections with Campylobacter jejuni [bacteria that causes food poisoning] are known to be associated with AIDP, while rates of AIDP in the general population and in those with influenza are similar.”
For the new multicenter, cross-sectional study, researchers tracked AIDP data from the 47 pediatric hospitals that provide statistics to the Pediatric Health Information System. They focused on the period from January 2017 to September 2020, which included the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States.
“Social distancing, masks, and increased hand hygiene decrease community-acquired infectious rates in a dramatic way,” Dr. Press said. “If these infections were causing AIDP, we hypothesized that the cases of AIDP would drop substantially as a result.”
But this didn’t appear to happen. Researchers found that the numbers of various types of infections declined from April to September 2020: Respiratory infections dipped by 73%-78%, gastrointestinal infections fell by 45%-61%, and influenza infections dipped by 88%-95%. But AIDP cases didn’t fall as precipitously. In fact, their levels were about the same as they were in April 2017, a month when rates of gastrointestinal, respiratory disease and influenza infections were at seasonally low – but not abnormal – ebbs.
“While we must be cautious interpreting the results,” Dr. Press said, “this makes the link between infections as the main driver of pediatric AIDP less likely.”
However, he said, “this study does not exclude the possibility that rare infections cause AIDP – the data supporting that some more rare infections like campylobacter have a connection to AIDP are more robust – or that common infections very rarely lead to AIDP. While we look for triggers causing inflammatory disorders, AIDP maybe an autoinflammatory disorder without a clear trigger.”
Going forward, Dr. Press said, “we hope to look at infectious data in a more granular way to identify if specific viral or bacterial infectious may be associated with this or other inflammatory disorders. We believe that the use of data like this and the natural experiment that COVID-19 provided may help us to explore the impact of infections on disorders thought to be postinfectious.”
No study funding is reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures.
While pediatric cases of various types of infections fell by 45%-95% during the early months of the pandemic, cases of acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP), an inflammatory neuropathy belonging to the clinical spectrum of Guillain-Barré syndrome, only fell by about 32%-37%, a rate that’s similar to the 35.1% decline in overall hospital admissions over that time period, researchers found. There was also no apparent link between the appearance of COVID-19 and the number of reported AIDP cases.
“There was no clear association between respiratory or gastrointestinal infections and rates of AIDP. Further, we found that AIDP did not have the expected dramatic reduction when community-acquired infections decreased during the pandemic,” Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia neurologist Craig A. Press, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Press and colleagues presented their findings in a poster at the 50th annual meeting of the Child Neurology Society.
According to Dr. Press, the cause of AIDP in most patients is unclear, although infections and vaccinations are often linked to cases. “However, the data supporting this link is often weak. Infections with Campylobacter jejuni [bacteria that causes food poisoning] are known to be associated with AIDP, while rates of AIDP in the general population and in those with influenza are similar.”
For the new multicenter, cross-sectional study, researchers tracked AIDP data from the 47 pediatric hospitals that provide statistics to the Pediatric Health Information System. They focused on the period from January 2017 to September 2020, which included the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States.
“Social distancing, masks, and increased hand hygiene decrease community-acquired infectious rates in a dramatic way,” Dr. Press said. “If these infections were causing AIDP, we hypothesized that the cases of AIDP would drop substantially as a result.”
But this didn’t appear to happen. Researchers found that the numbers of various types of infections declined from April to September 2020: Respiratory infections dipped by 73%-78%, gastrointestinal infections fell by 45%-61%, and influenza infections dipped by 88%-95%. But AIDP cases didn’t fall as precipitously. In fact, their levels were about the same as they were in April 2017, a month when rates of gastrointestinal, respiratory disease and influenza infections were at seasonally low – but not abnormal – ebbs.
“While we must be cautious interpreting the results,” Dr. Press said, “this makes the link between infections as the main driver of pediatric AIDP less likely.”
However, he said, “this study does not exclude the possibility that rare infections cause AIDP – the data supporting that some more rare infections like campylobacter have a connection to AIDP are more robust – or that common infections very rarely lead to AIDP. While we look for triggers causing inflammatory disorders, AIDP maybe an autoinflammatory disorder without a clear trigger.”
Going forward, Dr. Press said, “we hope to look at infectious data in a more granular way to identify if specific viral or bacterial infectious may be associated with this or other inflammatory disorders. We believe that the use of data like this and the natural experiment that COVID-19 provided may help us to explore the impact of infections on disorders thought to be postinfectious.”
No study funding is reported, and the authors report no relevant disclosures.
FROM CNS 2021
Children and COVID-19: U.S. adds latest million cases in record time
The United States just passed the 6-million mark in COVID-19 cases among children, with the last million cases taking less time to record than any of the first five, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
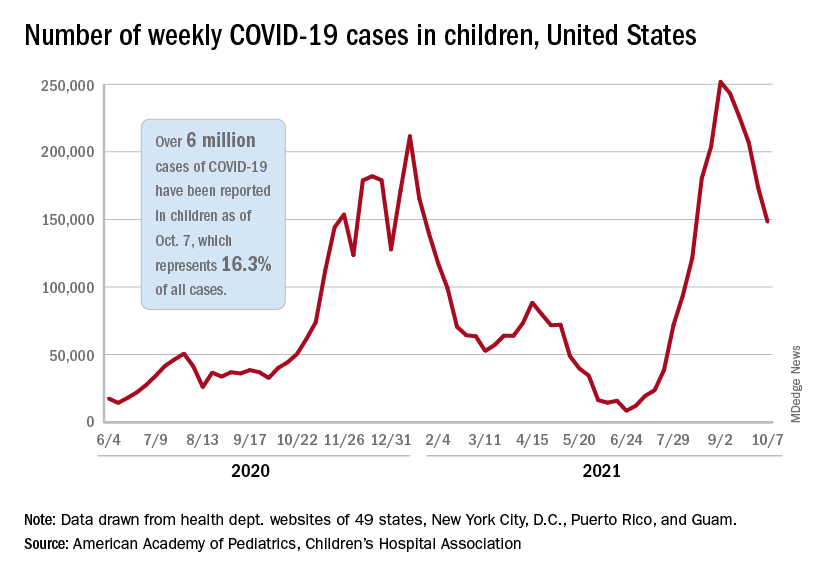
The five-millionth case was reported during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2, and case number 6 million came during the week of Oct. 1-7, just 5 weeks later, compared with the 6 weeks it took to go from 1 million to 2 million last November and December, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
New cases continued to drop, however, and that weekly count was down by 14.6% from the previous week and by 41.1% from the peak of almost 252,000 reached in early September, the two groups said while also noting limitations to the data, such as three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) that are no longer updating their COVID-19 dashboards.
Other metrics show similar drops in recent weeks. Among children aged 0-11 years, emergency department visits involving a COVID-19 diagnosis dropped from 4.1% of all ED visits in late August to 1.4% of ED visits on Oct. 6. ED visits with a COVID-19 diagnosis fell from a peak of 8.5% on Aug. 22 to 1.5% on Oct. 6 for 12- to 15-year-olds and from 8.5% to 1.5% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was down to 0.26 per 100,000 population on Oct. 9 after reaching 0.51 per 100,000 on Sept. 4. Hospitalizations in children totaled just over 64,000 from Aug. 1, 2020, to Oct. 9, 2021, which is just over 2% of all COVID-19–related admissions over that time period, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
That pattern, unfortunately, also applies to vaccinations. “The number of children receiving their first COVID-19 vaccine this week [Sept. 30 to Oct. 6], about 156,000, was the lowest number since vaccines were available,” the AAP said in a separate report on vaccination trends, adding that “the number of children receiving their first dose has steadily declined from 8 weeks ago when 586,000 children received their initial dose the week ending Aug. 11.”
The United States just passed the 6-million mark in COVID-19 cases among children, with the last million cases taking less time to record than any of the first five, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The five-millionth case was reported during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2, and case number 6 million came during the week of Oct. 1-7, just 5 weeks later, compared with the 6 weeks it took to go from 1 million to 2 million last November and December, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
New cases continued to drop, however, and that weekly count was down by 14.6% from the previous week and by 41.1% from the peak of almost 252,000 reached in early September, the two groups said while also noting limitations to the data, such as three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) that are no longer updating their COVID-19 dashboards.
Other metrics show similar drops in recent weeks. Among children aged 0-11 years, emergency department visits involving a COVID-19 diagnosis dropped from 4.1% of all ED visits in late August to 1.4% of ED visits on Oct. 6. ED visits with a COVID-19 diagnosis fell from a peak of 8.5% on Aug. 22 to 1.5% on Oct. 6 for 12- to 15-year-olds and from 8.5% to 1.5% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was down to 0.26 per 100,000 population on Oct. 9 after reaching 0.51 per 100,000 on Sept. 4. Hospitalizations in children totaled just over 64,000 from Aug. 1, 2020, to Oct. 9, 2021, which is just over 2% of all COVID-19–related admissions over that time period, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
That pattern, unfortunately, also applies to vaccinations. “The number of children receiving their first COVID-19 vaccine this week [Sept. 30 to Oct. 6], about 156,000, was the lowest number since vaccines were available,” the AAP said in a separate report on vaccination trends, adding that “the number of children receiving their first dose has steadily declined from 8 weeks ago when 586,000 children received their initial dose the week ending Aug. 11.”
The United States just passed the 6-million mark in COVID-19 cases among children, with the last million cases taking less time to record than any of the first five, according to new data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

The five-millionth case was reported during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2, and case number 6 million came during the week of Oct. 1-7, just 5 weeks later, compared with the 6 weeks it took to go from 1 million to 2 million last November and December, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
New cases continued to drop, however, and that weekly count was down by 14.6% from the previous week and by 41.1% from the peak of almost 252,000 reached in early September, the two groups said while also noting limitations to the data, such as three states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas) that are no longer updating their COVID-19 dashboards.
Other metrics show similar drops in recent weeks. Among children aged 0-11 years, emergency department visits involving a COVID-19 diagnosis dropped from 4.1% of all ED visits in late August to 1.4% of ED visits on Oct. 6. ED visits with a COVID-19 diagnosis fell from a peak of 8.5% on Aug. 22 to 1.5% on Oct. 6 for 12- to 15-year-olds and from 8.5% to 1.5% in those aged 16-17 years, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The rate of new hospital admissions for children aged 0-17 years was down to 0.26 per 100,000 population on Oct. 9 after reaching 0.51 per 100,000 on Sept. 4. Hospitalizations in children totaled just over 64,000 from Aug. 1, 2020, to Oct. 9, 2021, which is just over 2% of all COVID-19–related admissions over that time period, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
That pattern, unfortunately, also applies to vaccinations. “The number of children receiving their first COVID-19 vaccine this week [Sept. 30 to Oct. 6], about 156,000, was the lowest number since vaccines were available,” the AAP said in a separate report on vaccination trends, adding that “the number of children receiving their first dose has steadily declined from 8 weeks ago when 586,000 children received their initial dose the week ending Aug. 11.”
Underrepresented Minority Students Applying to Dermatology Residency in the COVID-19 Era: Challenges and Considerations
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
Practice Points
- Dermatology remains one of the least diverse medical specialties.
- Underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine residency applicants might be negatively affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The implementation of holistic review, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and virtual opportunities might mitigate some of the barriers faced by URM applicants.

