User login
Screening for lung cancer in never-smokers is ‘feasible’
“Lung cancer in never-smokers is a global rising threat,” said lead researcher Pan-Chyr Yang, MD, PhD, chair professor at the National Taiwan University Hospital and academician of Academia Sinica, Taiwan.
In Taiwan, more than half of the cases of lung cancer occur in never-smokers; among female lung cancer patients, 93% are never-smokers.
The incidence of lung cancer – in particular, adenocarcinoma – is increasing in Taiwan, even though the prevalence of smoking has fallen dramatically in men in recent years and has remained low in women.
At the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021, Dr. Yang presented new results that suggest “LDCT screening for never-smokers with high risk may be feasible.”
The Taiwan Lung Cancer Screening in Never-Smoker Trial (TALENT) recruited over 12,000 individuals aged 55-70 years who had never smoked or had done so more than 15 years previously and had risk factors such as a family history of the disease or passive smoke exposure, or who had regularly been exposed to frying food.
Participants underwent LDCT after chest x-ray, followed by biopsy if necessary.
These procedures detected largely invasive lung cancer in 2.6% of participants. Tumors were of stage 0-I in 95% of cases.
The lung cancer detection rate of 2.6% in TALENT in never-smokers is higher than has been found in large studies of smokers, including the 1.1% rate recorded in the NLST study and the 0.9% seen in the NELSON study.
The key factor associated with increased prevalence of lung cancer was a first-degree family history of the disease, Dr. Yang reported.
Notably, having a sister with lung cancer increased the risk for the disease by 78%. Having an affected brother doubled the risk. An increase in the number of first-degree relatives with lung cancer also significantly increased the risk.
More research needed
The TALENT study “provides new, very original evidence on lung cancer risks, and therefore lung cancer screening eligibility could be redefined in Asia, or at least in East Asia,” said the discussant for the paper, Ugo Pastorino, MD, director of thoracic surgery at IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori Foundation, Milan.
However, he said that “more research is needed on lung cancer biology in nonsmokers.”
There is currently no follow-up or mortality data, and given the proportion of patients who underwent invasive procedures, it could be that more than 40% of those procedures were carried out in individuals with benign disease, he cautioned.
On Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said that although family history “emerges” from the study as a potential risk factor for lung cancer, “this analysis would be much more insightful with genomic analyses of these cancers.”
Devika Das, MD, clinical assistant professor of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the study is “interesting,” given the rise of adenocarcinoma among never-smokers.
She agreed that further details and long-term outcomes are needed and said the key learning point was the need for a “robust” study of the biology of lung cancer in this population.
Lillian Leigh, an Australian lawyer and a lung cancer patient advocate, said the study “provides new evidence” on lung cancer risks.
“As an Asian never-smoker living with lung cancer, the TALENT trial results give me hope,” she said.
Details of TALENT findings
The TALENT study recruited individuals aged 55-70 years at 17 medical centers between February 2015 and July 2019.
Participants were required to be never-smokers or to have a smoking history of less than 10 pack-years and to have quit the habit more than 15 years previously.
They also had to have one of the following risk factors:
- Family history of lung cancer in up to third-degree relatives, in which case younger patients could be recruited.
- Environmental (passive) tobacco smoking history.
- Chronic lung disease, namely, or .
- A cooking index ≥110, defined as 2/7 × the number of days of frying per week × the number of years cooking.
- Cooking without ventilation.
The participants underwent chest x-ray. If the x-ray proved negative, the team performed standard LDCT, examined blood and urine samples for lung cancer biomarkers, and administered standard questionnaires.
Participants who were found on LDCT to have solid or part-solid nodules greater than 6 mm in diameter or pure ground-glass nodules greater than 5 mm in diameter underwent biopsy or standard follow-up.
Individuals whose initial chest x-ray was positive underwent standard contrast-enhanced chest CT prior to biopsy or standard follow-up.
Of 13,207 individuals initially screened, 12,011 were enrolled. Of those, 73.8% were women. The mean age was 61.2 years, and 93.3% were never-smokers.
Among the participants, 46.4% had a first-degree family history of lung cancer; 3.0% had a second-degree family history; and 0.5% had a third-degree family history.
Environmental tobacco exposure was recorded in 83.2% of patients. Chronic lung disease was present in 9.8%; 36.7% had a cooking index ≥110; and 1.8 cooked without ventilation.
Dr. Yang said LDCT results were positive for 17.4% of patients, and 3.4% underwent invasive procedures.
Overall, lung cancer was detected in 313 participants (2.6%). Invasive lung cancer was detected in 255 (2.1%). Of those, 17.9% had multiple primary lung cancers.
Strikingly, 96.5% of the confirmed lung cancer cases were stage 0-I. The majority were stage IA, “which is higher than in other studies that have focused on heavy smokers,” Dr. Yang said. More than half of cases (58.5%) were invasive adenocarcinomas.
The prevalence of lung cancer was significantly higher among people who had a family history of the disease, at 3.2%, vs. 2.0% in those without, at a relative risk of 1.61 (P < .001).
The prevalence was higher still in individuals who had a first-degree family history of lung cancer, at 3.3%, giving a relative risk of 1.69 in comparison with those who did not have a family history (P < .001). The findings were nonsignificant for second- and third-degree relatives.
The relative risk increased even further when the first-degree relative who had a history of lung cancer was a sister, at 1.78 (P < .001), or a brother, at 2.00 (P < .001).
The relative risk was slightly lower if the patient’s relative was the mother, at 1.43 (P = .010), and was nonsignificant if the relative was the father (P = .077).
The risk for lung cancer also increased with an increase in the number of first-degree relatives with the disease, rising from 3.1% with one relative to 4.0% with two relatives, 6.7% with three relatives, and 9.1% with at least four relatives (P < .001). A similar pattern was seen for invasive lung cancer.
The other risk factors included in the study, such as environmental tobacco exposure, chronic lung disease, and cooking index, were not significantly associated with the prevalence of lung cancer.
No funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Yang has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Merck, Eli Lilly, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and ONO Pharma and has served on the advisory board of OBI Pharma, CHO Pharma, and Lin BioScience. Dr. Pastorino has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Lung cancer in never-smokers is a global rising threat,” said lead researcher Pan-Chyr Yang, MD, PhD, chair professor at the National Taiwan University Hospital and academician of Academia Sinica, Taiwan.
In Taiwan, more than half of the cases of lung cancer occur in never-smokers; among female lung cancer patients, 93% are never-smokers.
The incidence of lung cancer – in particular, adenocarcinoma – is increasing in Taiwan, even though the prevalence of smoking has fallen dramatically in men in recent years and has remained low in women.
At the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021, Dr. Yang presented new results that suggest “LDCT screening for never-smokers with high risk may be feasible.”
The Taiwan Lung Cancer Screening in Never-Smoker Trial (TALENT) recruited over 12,000 individuals aged 55-70 years who had never smoked or had done so more than 15 years previously and had risk factors such as a family history of the disease or passive smoke exposure, or who had regularly been exposed to frying food.
Participants underwent LDCT after chest x-ray, followed by biopsy if necessary.
These procedures detected largely invasive lung cancer in 2.6% of participants. Tumors were of stage 0-I in 95% of cases.
The lung cancer detection rate of 2.6% in TALENT in never-smokers is higher than has been found in large studies of smokers, including the 1.1% rate recorded in the NLST study and the 0.9% seen in the NELSON study.
The key factor associated with increased prevalence of lung cancer was a first-degree family history of the disease, Dr. Yang reported.
Notably, having a sister with lung cancer increased the risk for the disease by 78%. Having an affected brother doubled the risk. An increase in the number of first-degree relatives with lung cancer also significantly increased the risk.
More research needed
The TALENT study “provides new, very original evidence on lung cancer risks, and therefore lung cancer screening eligibility could be redefined in Asia, or at least in East Asia,” said the discussant for the paper, Ugo Pastorino, MD, director of thoracic surgery at IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori Foundation, Milan.
However, he said that “more research is needed on lung cancer biology in nonsmokers.”
There is currently no follow-up or mortality data, and given the proportion of patients who underwent invasive procedures, it could be that more than 40% of those procedures were carried out in individuals with benign disease, he cautioned.
On Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said that although family history “emerges” from the study as a potential risk factor for lung cancer, “this analysis would be much more insightful with genomic analyses of these cancers.”
Devika Das, MD, clinical assistant professor of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the study is “interesting,” given the rise of adenocarcinoma among never-smokers.
She agreed that further details and long-term outcomes are needed and said the key learning point was the need for a “robust” study of the biology of lung cancer in this population.
Lillian Leigh, an Australian lawyer and a lung cancer patient advocate, said the study “provides new evidence” on lung cancer risks.
“As an Asian never-smoker living with lung cancer, the TALENT trial results give me hope,” she said.
Details of TALENT findings
The TALENT study recruited individuals aged 55-70 years at 17 medical centers between February 2015 and July 2019.
Participants were required to be never-smokers or to have a smoking history of less than 10 pack-years and to have quit the habit more than 15 years previously.
They also had to have one of the following risk factors:
- Family history of lung cancer in up to third-degree relatives, in which case younger patients could be recruited.
- Environmental (passive) tobacco smoking history.
- Chronic lung disease, namely, or .
- A cooking index ≥110, defined as 2/7 × the number of days of frying per week × the number of years cooking.
- Cooking without ventilation.
The participants underwent chest x-ray. If the x-ray proved negative, the team performed standard LDCT, examined blood and urine samples for lung cancer biomarkers, and administered standard questionnaires.
Participants who were found on LDCT to have solid or part-solid nodules greater than 6 mm in diameter or pure ground-glass nodules greater than 5 mm in diameter underwent biopsy or standard follow-up.
Individuals whose initial chest x-ray was positive underwent standard contrast-enhanced chest CT prior to biopsy or standard follow-up.
Of 13,207 individuals initially screened, 12,011 were enrolled. Of those, 73.8% were women. The mean age was 61.2 years, and 93.3% were never-smokers.
Among the participants, 46.4% had a first-degree family history of lung cancer; 3.0% had a second-degree family history; and 0.5% had a third-degree family history.
Environmental tobacco exposure was recorded in 83.2% of patients. Chronic lung disease was present in 9.8%; 36.7% had a cooking index ≥110; and 1.8 cooked without ventilation.
Dr. Yang said LDCT results were positive for 17.4% of patients, and 3.4% underwent invasive procedures.
Overall, lung cancer was detected in 313 participants (2.6%). Invasive lung cancer was detected in 255 (2.1%). Of those, 17.9% had multiple primary lung cancers.
Strikingly, 96.5% of the confirmed lung cancer cases were stage 0-I. The majority were stage IA, “which is higher than in other studies that have focused on heavy smokers,” Dr. Yang said. More than half of cases (58.5%) were invasive adenocarcinomas.
The prevalence of lung cancer was significantly higher among people who had a family history of the disease, at 3.2%, vs. 2.0% in those without, at a relative risk of 1.61 (P < .001).
The prevalence was higher still in individuals who had a first-degree family history of lung cancer, at 3.3%, giving a relative risk of 1.69 in comparison with those who did not have a family history (P < .001). The findings were nonsignificant for second- and third-degree relatives.
The relative risk increased even further when the first-degree relative who had a history of lung cancer was a sister, at 1.78 (P < .001), or a brother, at 2.00 (P < .001).
The relative risk was slightly lower if the patient’s relative was the mother, at 1.43 (P = .010), and was nonsignificant if the relative was the father (P = .077).
The risk for lung cancer also increased with an increase in the number of first-degree relatives with the disease, rising from 3.1% with one relative to 4.0% with two relatives, 6.7% with three relatives, and 9.1% with at least four relatives (P < .001). A similar pattern was seen for invasive lung cancer.
The other risk factors included in the study, such as environmental tobacco exposure, chronic lung disease, and cooking index, were not significantly associated with the prevalence of lung cancer.
No funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Yang has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Merck, Eli Lilly, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and ONO Pharma and has served on the advisory board of OBI Pharma, CHO Pharma, and Lin BioScience. Dr. Pastorino has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Lung cancer in never-smokers is a global rising threat,” said lead researcher Pan-Chyr Yang, MD, PhD, chair professor at the National Taiwan University Hospital and academician of Academia Sinica, Taiwan.
In Taiwan, more than half of the cases of lung cancer occur in never-smokers; among female lung cancer patients, 93% are never-smokers.
The incidence of lung cancer – in particular, adenocarcinoma – is increasing in Taiwan, even though the prevalence of smoking has fallen dramatically in men in recent years and has remained low in women.
At the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021, Dr. Yang presented new results that suggest “LDCT screening for never-smokers with high risk may be feasible.”
The Taiwan Lung Cancer Screening in Never-Smoker Trial (TALENT) recruited over 12,000 individuals aged 55-70 years who had never smoked or had done so more than 15 years previously and had risk factors such as a family history of the disease or passive smoke exposure, or who had regularly been exposed to frying food.
Participants underwent LDCT after chest x-ray, followed by biopsy if necessary.
These procedures detected largely invasive lung cancer in 2.6% of participants. Tumors were of stage 0-I in 95% of cases.
The lung cancer detection rate of 2.6% in TALENT in never-smokers is higher than has been found in large studies of smokers, including the 1.1% rate recorded in the NLST study and the 0.9% seen in the NELSON study.
The key factor associated with increased prevalence of lung cancer was a first-degree family history of the disease, Dr. Yang reported.
Notably, having a sister with lung cancer increased the risk for the disease by 78%. Having an affected brother doubled the risk. An increase in the number of first-degree relatives with lung cancer also significantly increased the risk.
More research needed
The TALENT study “provides new, very original evidence on lung cancer risks, and therefore lung cancer screening eligibility could be redefined in Asia, or at least in East Asia,” said the discussant for the paper, Ugo Pastorino, MD, director of thoracic surgery at IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori Foundation, Milan.
However, he said that “more research is needed on lung cancer biology in nonsmokers.”
There is currently no follow-up or mortality data, and given the proportion of patients who underwent invasive procedures, it could be that more than 40% of those procedures were carried out in individuals with benign disease, he cautioned.
On Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said that although family history “emerges” from the study as a potential risk factor for lung cancer, “this analysis would be much more insightful with genomic analyses of these cancers.”
Devika Das, MD, clinical assistant professor of hematology and oncology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, said that the study is “interesting,” given the rise of adenocarcinoma among never-smokers.
She agreed that further details and long-term outcomes are needed and said the key learning point was the need for a “robust” study of the biology of lung cancer in this population.
Lillian Leigh, an Australian lawyer and a lung cancer patient advocate, said the study “provides new evidence” on lung cancer risks.
“As an Asian never-smoker living with lung cancer, the TALENT trial results give me hope,” she said.
Details of TALENT findings
The TALENT study recruited individuals aged 55-70 years at 17 medical centers between February 2015 and July 2019.
Participants were required to be never-smokers or to have a smoking history of less than 10 pack-years and to have quit the habit more than 15 years previously.
They also had to have one of the following risk factors:
- Family history of lung cancer in up to third-degree relatives, in which case younger patients could be recruited.
- Environmental (passive) tobacco smoking history.
- Chronic lung disease, namely, or .
- A cooking index ≥110, defined as 2/7 × the number of days of frying per week × the number of years cooking.
- Cooking without ventilation.
The participants underwent chest x-ray. If the x-ray proved negative, the team performed standard LDCT, examined blood and urine samples for lung cancer biomarkers, and administered standard questionnaires.
Participants who were found on LDCT to have solid or part-solid nodules greater than 6 mm in diameter or pure ground-glass nodules greater than 5 mm in diameter underwent biopsy or standard follow-up.
Individuals whose initial chest x-ray was positive underwent standard contrast-enhanced chest CT prior to biopsy or standard follow-up.
Of 13,207 individuals initially screened, 12,011 were enrolled. Of those, 73.8% were women. The mean age was 61.2 years, and 93.3% were never-smokers.
Among the participants, 46.4% had a first-degree family history of lung cancer; 3.0% had a second-degree family history; and 0.5% had a third-degree family history.
Environmental tobacco exposure was recorded in 83.2% of patients. Chronic lung disease was present in 9.8%; 36.7% had a cooking index ≥110; and 1.8 cooked without ventilation.
Dr. Yang said LDCT results were positive for 17.4% of patients, and 3.4% underwent invasive procedures.
Overall, lung cancer was detected in 313 participants (2.6%). Invasive lung cancer was detected in 255 (2.1%). Of those, 17.9% had multiple primary lung cancers.
Strikingly, 96.5% of the confirmed lung cancer cases were stage 0-I. The majority were stage IA, “which is higher than in other studies that have focused on heavy smokers,” Dr. Yang said. More than half of cases (58.5%) were invasive adenocarcinomas.
The prevalence of lung cancer was significantly higher among people who had a family history of the disease, at 3.2%, vs. 2.0% in those without, at a relative risk of 1.61 (P < .001).
The prevalence was higher still in individuals who had a first-degree family history of lung cancer, at 3.3%, giving a relative risk of 1.69 in comparison with those who did not have a family history (P < .001). The findings were nonsignificant for second- and third-degree relatives.
The relative risk increased even further when the first-degree relative who had a history of lung cancer was a sister, at 1.78 (P < .001), or a brother, at 2.00 (P < .001).
The relative risk was slightly lower if the patient’s relative was the mother, at 1.43 (P = .010), and was nonsignificant if the relative was the father (P = .077).
The risk for lung cancer also increased with an increase in the number of first-degree relatives with the disease, rising from 3.1% with one relative to 4.0% with two relatives, 6.7% with three relatives, and 9.1% with at least four relatives (P < .001). A similar pattern was seen for invasive lung cancer.
The other risk factors included in the study, such as environmental tobacco exposure, chronic lung disease, and cooking index, were not significantly associated with the prevalence of lung cancer.
No funding for the study has been disclosed. Dr. Yang has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Merck, Eli Lilly, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and ONO Pharma and has served on the advisory board of OBI Pharma, CHO Pharma, and Lin BioScience. Dr. Pastorino has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA grants MET inhibitor tepotinib accelerated approval for NSCLC
Tepotinib is the first once-daily oral MET inhibitor approved for this patient population, and the approval applies to both treatment-naive and previously treated patients with NSCLC.
The approval was supported by results from the ongoing phase 2 VISION trial. Tepotinib produced an overall response rate of 43% in both treatment-naive patients (n = 69) and previously treated patients (n = 83) in this trial. The median duration of response was 10.8 months and 11.1 months, respectively.
Results of the primary analysis were published in The New England Journal of Medicine last year.
Study subjects received the recommended dose of 450 mg taken as two 225-mg tablets once daily with food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Adverse reactions occurring in at least 20% of patients included edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea. Interstitial lung disease, hepatotoxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity also have been reported with tepotinib.
Continued approval of tepotinib “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” the FDA stated in an approval announcement.
EMD Serono, the drug’s maker, also announced the approval in a press statement, calling tepotinib “an important and welcome new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring these genetic mutations.”
“METex14 skipping occurs in approximately 3% to 4% of NSCLC cases, and patients with this aggressive lung cancer are often elderly and face a poor clinical prognosis,” Paul K. Paik, MD, the VISION primary investigator and clinical director of the thoracic oncology service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said in the statement.
“There is a pressing need for targeted treatments that have the potential to generate durable antitumor activity and improve the lives of patients with this challenging disease,” he added.
Andrea Ferris, president and chief executive officer of the nonprofit LUNGevity Foundation, further noted the “powerful progress” made in recent years with respect to understanding genetic mutations in NSCLC.
“The availability of a new precision medicine for NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations advances patient access to targeted treatment and underscores the importance of routine comprehensive biomarker testing for patients with this challenging cancer,” she said in the statement.
Tepotinib was approved in Japan in March 2020. The drug previously received breakthrough therapy designation and orphan drug designation from the FDA. A marketing authorization application for tepotinib was validated by the European Medicines Agency in November 2020 for a similar indication, EMD Serono reported, adding that applications “have also been submitted in Australia, Switzerland, and Canada under the FDA’s Project Orbis initiative, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among international partners.”
Other phase 2 studies of tepotinib are ongoing. The INSIGHT 2 study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with osimertinib in MET amplified, advanced, or metastatic NSCLC with activating EGFR mutations that has progressed following first-line treatment with osimertinib. The PERSPECTIVE study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with cetuximab in patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type left-sided metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR antibody targeting therapy due to MET amplification.
For more details on tepotinib, see the full prescribing information.
Tepotinib is the first once-daily oral MET inhibitor approved for this patient population, and the approval applies to both treatment-naive and previously treated patients with NSCLC.
The approval was supported by results from the ongoing phase 2 VISION trial. Tepotinib produced an overall response rate of 43% in both treatment-naive patients (n = 69) and previously treated patients (n = 83) in this trial. The median duration of response was 10.8 months and 11.1 months, respectively.
Results of the primary analysis were published in The New England Journal of Medicine last year.
Study subjects received the recommended dose of 450 mg taken as two 225-mg tablets once daily with food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Adverse reactions occurring in at least 20% of patients included edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea. Interstitial lung disease, hepatotoxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity also have been reported with tepotinib.
Continued approval of tepotinib “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” the FDA stated in an approval announcement.
EMD Serono, the drug’s maker, also announced the approval in a press statement, calling tepotinib “an important and welcome new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring these genetic mutations.”
“METex14 skipping occurs in approximately 3% to 4% of NSCLC cases, and patients with this aggressive lung cancer are often elderly and face a poor clinical prognosis,” Paul K. Paik, MD, the VISION primary investigator and clinical director of the thoracic oncology service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said in the statement.
“There is a pressing need for targeted treatments that have the potential to generate durable antitumor activity and improve the lives of patients with this challenging disease,” he added.
Andrea Ferris, president and chief executive officer of the nonprofit LUNGevity Foundation, further noted the “powerful progress” made in recent years with respect to understanding genetic mutations in NSCLC.
“The availability of a new precision medicine for NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations advances patient access to targeted treatment and underscores the importance of routine comprehensive biomarker testing for patients with this challenging cancer,” she said in the statement.
Tepotinib was approved in Japan in March 2020. The drug previously received breakthrough therapy designation and orphan drug designation from the FDA. A marketing authorization application for tepotinib was validated by the European Medicines Agency in November 2020 for a similar indication, EMD Serono reported, adding that applications “have also been submitted in Australia, Switzerland, and Canada under the FDA’s Project Orbis initiative, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among international partners.”
Other phase 2 studies of tepotinib are ongoing. The INSIGHT 2 study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with osimertinib in MET amplified, advanced, or metastatic NSCLC with activating EGFR mutations that has progressed following first-line treatment with osimertinib. The PERSPECTIVE study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with cetuximab in patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type left-sided metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR antibody targeting therapy due to MET amplification.
For more details on tepotinib, see the full prescribing information.
Tepotinib is the first once-daily oral MET inhibitor approved for this patient population, and the approval applies to both treatment-naive and previously treated patients with NSCLC.
The approval was supported by results from the ongoing phase 2 VISION trial. Tepotinib produced an overall response rate of 43% in both treatment-naive patients (n = 69) and previously treated patients (n = 83) in this trial. The median duration of response was 10.8 months and 11.1 months, respectively.
Results of the primary analysis were published in The New England Journal of Medicine last year.
Study subjects received the recommended dose of 450 mg taken as two 225-mg tablets once daily with food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Adverse reactions occurring in at least 20% of patients included edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, and dyspnea. Interstitial lung disease, hepatotoxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity also have been reported with tepotinib.
Continued approval of tepotinib “may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials,” the FDA stated in an approval announcement.
EMD Serono, the drug’s maker, also announced the approval in a press statement, calling tepotinib “an important and welcome new therapeutic option for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring these genetic mutations.”
“METex14 skipping occurs in approximately 3% to 4% of NSCLC cases, and patients with this aggressive lung cancer are often elderly and face a poor clinical prognosis,” Paul K. Paik, MD, the VISION primary investigator and clinical director of the thoracic oncology service at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, said in the statement.
“There is a pressing need for targeted treatments that have the potential to generate durable antitumor activity and improve the lives of patients with this challenging disease,” he added.
Andrea Ferris, president and chief executive officer of the nonprofit LUNGevity Foundation, further noted the “powerful progress” made in recent years with respect to understanding genetic mutations in NSCLC.
“The availability of a new precision medicine for NSCLC with METex14 skipping alterations advances patient access to targeted treatment and underscores the importance of routine comprehensive biomarker testing for patients with this challenging cancer,” she said in the statement.
Tepotinib was approved in Japan in March 2020. The drug previously received breakthrough therapy designation and orphan drug designation from the FDA. A marketing authorization application for tepotinib was validated by the European Medicines Agency in November 2020 for a similar indication, EMD Serono reported, adding that applications “have also been submitted in Australia, Switzerland, and Canada under the FDA’s Project Orbis initiative, which provides a framework for concurrent submission and review of oncology medicines among international partners.”
Other phase 2 studies of tepotinib are ongoing. The INSIGHT 2 study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with osimertinib in MET amplified, advanced, or metastatic NSCLC with activating EGFR mutations that has progressed following first-line treatment with osimertinib. The PERSPECTIVE study is designed to test tepotinib in combination with cetuximab in patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type left-sided metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-EGFR antibody targeting therapy due to MET amplification.
For more details on tepotinib, see the full prescribing information.
‘Astonishing’ 4-year survival in NSCLC with pembro plus chemo
The results are from a 4-year follow-up of 160 patients with previously untreated stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) taking part in the KEYNOTE-189 trial of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed–platinum chemotherapy versus chemotherapy plus placebo.
After a median follow-up of 46.3 months, the median overall survival (OS) in the intention-to-treat population was 22.0 months with the combination versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.60).
A similar pattern was seen for progression-free survival (PFS), with patients receiving the combination having a longer median PFS, at 9.0 months versus 4.9 months with chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50).
“Stellar data,” Riyaz Shah, MD, PhD, consultant medical oncologist, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust, Royal Tunbridge Wells, England, exclaimed on Twitter.
He described the results for the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression subgroups as “astonishing” and singled out the performance of the combination therapy in patients with very low (<1%) tumor PD-L1 expression, showing more than 23% of patients were alive at 3 years versus just over 5% in the group given chemotherapy alone.
Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, Leslye M. Heisler associate professor for lung cancer excellence, Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, said the outcomes with the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were “terrific.”
Sandip P. Patel, MD, medical oncologist, associate professor of medicine, University of California, San Diego, agreed that these long-term results were “very impressive.” However, he noted the “full effect” of chemotherapy plus immunotherapy has not “fully been captured in our overall cancer mortality statistics in the U.S. yet.”
The new results were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021.
Previous results from KEYNOTE-189 had already demonstrated that, after a median follow-up of 10.5 months, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy significantly improves both OS and PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone.
The latest results show that the combination “continued to provide overall survival and progression-free survival benefit” in extended follow-up, said study presenter Jhanelle Elaine Gray, MD, chair, department of thoracic oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
The 3-year OS rate with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone was 31.3% versus 17.4%, and the estimated 3-year PFS was 11.8% versus 1.3%.
Substantial improvements were even seen in patients with tumors that had a low level of PD-L1 expression (measured as the PD-L1 tumor proportion score [TPS]).
Dr. Gray highlighted the finding that the survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was seen regardless of PD-L1 expression in the tumor, with a hazard ratio versus chemotherapy alone of 0.71 in patients with a TPS ≥ 50%, 0.66 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.52 in patients with a TPS less than 1%. A similar pattern was seen with PFS, with a hazard ratio of 0.36 in patients with a TPS of at least 50%, 0.54 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.68 in patients with a TPS less than 1%.
In addition, overall response rate and duration of response were also improved with combination therapy, regardless of tumor PD-L1 expression.
Among 56 patients who completed 35 cycles of pembrolizumab, the objective response rate was 87.5% (with 10.7% having a complete response and 76.8% a partial response).
At the data cutoff, 45 patients were alive, 28 did not have progressive disease, and seven had started a second course of pembrolizumab.
The side effect profile of the combination was “manageable,” Dr. Gray reported.
The combination arm was associated with more grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events than the chemotherapy alone arm, at 52.1% versus 42.1%, and more grade 3-5 immune-related adverse events and infusion reactions, at 27.7% versus 13.4%.
Events leading to treatment discontinuation were also more common with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy than chemotherapy, at 27.4% versus 9.9%.
The combination of pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed-platinum has already become “a standard-of-care therapy for patients with newly diagnosed metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC,” Dr. Gray commented.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Gray disclosed relationships with Array, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results are from a 4-year follow-up of 160 patients with previously untreated stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) taking part in the KEYNOTE-189 trial of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed–platinum chemotherapy versus chemotherapy plus placebo.
After a median follow-up of 46.3 months, the median overall survival (OS) in the intention-to-treat population was 22.0 months with the combination versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.60).
A similar pattern was seen for progression-free survival (PFS), with patients receiving the combination having a longer median PFS, at 9.0 months versus 4.9 months with chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50).
“Stellar data,” Riyaz Shah, MD, PhD, consultant medical oncologist, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust, Royal Tunbridge Wells, England, exclaimed on Twitter.
He described the results for the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression subgroups as “astonishing” and singled out the performance of the combination therapy in patients with very low (<1%) tumor PD-L1 expression, showing more than 23% of patients were alive at 3 years versus just over 5% in the group given chemotherapy alone.
Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, Leslye M. Heisler associate professor for lung cancer excellence, Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, said the outcomes with the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were “terrific.”
Sandip P. Patel, MD, medical oncologist, associate professor of medicine, University of California, San Diego, agreed that these long-term results were “very impressive.” However, he noted the “full effect” of chemotherapy plus immunotherapy has not “fully been captured in our overall cancer mortality statistics in the U.S. yet.”
The new results were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021.
Previous results from KEYNOTE-189 had already demonstrated that, after a median follow-up of 10.5 months, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy significantly improves both OS and PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone.
The latest results show that the combination “continued to provide overall survival and progression-free survival benefit” in extended follow-up, said study presenter Jhanelle Elaine Gray, MD, chair, department of thoracic oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
The 3-year OS rate with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone was 31.3% versus 17.4%, and the estimated 3-year PFS was 11.8% versus 1.3%.
Substantial improvements were even seen in patients with tumors that had a low level of PD-L1 expression (measured as the PD-L1 tumor proportion score [TPS]).
Dr. Gray highlighted the finding that the survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was seen regardless of PD-L1 expression in the tumor, with a hazard ratio versus chemotherapy alone of 0.71 in patients with a TPS ≥ 50%, 0.66 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.52 in patients with a TPS less than 1%. A similar pattern was seen with PFS, with a hazard ratio of 0.36 in patients with a TPS of at least 50%, 0.54 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.68 in patients with a TPS less than 1%.
In addition, overall response rate and duration of response were also improved with combination therapy, regardless of tumor PD-L1 expression.
Among 56 patients who completed 35 cycles of pembrolizumab, the objective response rate was 87.5% (with 10.7% having a complete response and 76.8% a partial response).
At the data cutoff, 45 patients were alive, 28 did not have progressive disease, and seven had started a second course of pembrolizumab.
The side effect profile of the combination was “manageable,” Dr. Gray reported.
The combination arm was associated with more grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events than the chemotherapy alone arm, at 52.1% versus 42.1%, and more grade 3-5 immune-related adverse events and infusion reactions, at 27.7% versus 13.4%.
Events leading to treatment discontinuation were also more common with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy than chemotherapy, at 27.4% versus 9.9%.
The combination of pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed-platinum has already become “a standard-of-care therapy for patients with newly diagnosed metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC,” Dr. Gray commented.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Gray disclosed relationships with Array, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results are from a 4-year follow-up of 160 patients with previously untreated stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) taking part in the KEYNOTE-189 trial of immunotherapy with pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed–platinum chemotherapy versus chemotherapy plus placebo.
After a median follow-up of 46.3 months, the median overall survival (OS) in the intention-to-treat population was 22.0 months with the combination versus 10.6 months with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio, 0.60).
A similar pattern was seen for progression-free survival (PFS), with patients receiving the combination having a longer median PFS, at 9.0 months versus 4.9 months with chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.50).
“Stellar data,” Riyaz Shah, MD, PhD, consultant medical oncologist, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust, Royal Tunbridge Wells, England, exclaimed on Twitter.
He described the results for the programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression subgroups as “astonishing” and singled out the performance of the combination therapy in patients with very low (<1%) tumor PD-L1 expression, showing more than 23% of patients were alive at 3 years versus just over 5% in the group given chemotherapy alone.
Charu Aggarwal, MD, MPH, Leslye M. Heisler associate professor for lung cancer excellence, Penn Medicine, Philadelphia, said the outcomes with the combination of chemotherapy and immunotherapy were “terrific.”
Sandip P. Patel, MD, medical oncologist, associate professor of medicine, University of California, San Diego, agreed that these long-term results were “very impressive.” However, he noted the “full effect” of chemotherapy plus immunotherapy has not “fully been captured in our overall cancer mortality statistics in the U.S. yet.”
The new results were presented at the 2020 World Conference on Lung Cancer, which was rescheduled for January 2021.
Previous results from KEYNOTE-189 had already demonstrated that, after a median follow-up of 10.5 months, adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy significantly improves both OS and PFS, compared with chemotherapy alone.
The latest results show that the combination “continued to provide overall survival and progression-free survival benefit” in extended follow-up, said study presenter Jhanelle Elaine Gray, MD, chair, department of thoracic oncology, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa.
The 3-year OS rate with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone was 31.3% versus 17.4%, and the estimated 3-year PFS was 11.8% versus 1.3%.
Substantial improvements were even seen in patients with tumors that had a low level of PD-L1 expression (measured as the PD-L1 tumor proportion score [TPS]).
Dr. Gray highlighted the finding that the survival benefit with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was seen regardless of PD-L1 expression in the tumor, with a hazard ratio versus chemotherapy alone of 0.71 in patients with a TPS ≥ 50%, 0.66 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.52 in patients with a TPS less than 1%. A similar pattern was seen with PFS, with a hazard ratio of 0.36 in patients with a TPS of at least 50%, 0.54 in those with a TPS of 1%-49%, and 0.68 in patients with a TPS less than 1%.
In addition, overall response rate and duration of response were also improved with combination therapy, regardless of tumor PD-L1 expression.
Among 56 patients who completed 35 cycles of pembrolizumab, the objective response rate was 87.5% (with 10.7% having a complete response and 76.8% a partial response).
At the data cutoff, 45 patients were alive, 28 did not have progressive disease, and seven had started a second course of pembrolizumab.
The side effect profile of the combination was “manageable,” Dr. Gray reported.
The combination arm was associated with more grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events than the chemotherapy alone arm, at 52.1% versus 42.1%, and more grade 3-5 immune-related adverse events and infusion reactions, at 27.7% versus 13.4%.
Events leading to treatment discontinuation were also more common with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy than chemotherapy, at 27.4% versus 9.9%.
The combination of pembrolizumab plus pemetrexed-platinum has already become “a standard-of-care therapy for patients with newly diagnosed metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC,” Dr. Gray commented.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Gray disclosed relationships with Array, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, and Merck.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
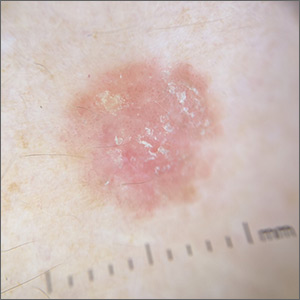
Scaly lesion on forearm
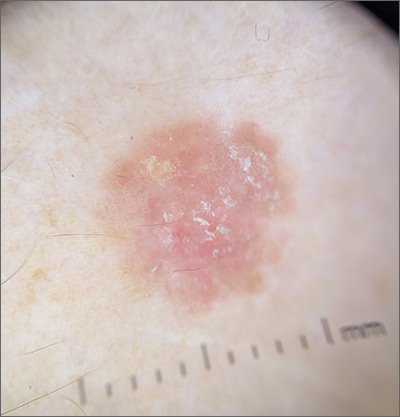
The suspicion raised by the dermoscopy results led to a shave biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ, also known as Bowen disease.
Bowen disease typically manifests as a scaly erythematous patch, often on sun-exposed skin. If untreated, these lesions have the potential to develop into invasive SCCs. Generally, the lesions are preceded by the formation of actinic keratosis (AK). In a 2009 trial performed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, up to 65% of SCCs were found to have previously been diagnosed as AK lesions.1
The selection of treatments includes excision, electrodessication and curettage, cryotherapy, and topical options such as fluorouracil bid for 4 weeks or imiquimod qd for 9 weeks.
After the physician outlined the treatment options, this patient opted for an elliptical excision. At the patient’s next follow-up appointment, she was found to have multiple AKs on her face; they were treated with cryotherapy. Patients with a diagnosis of precancerous or cancerous skin lesions are at high risk for additional AKs and skin cancer, so they should be counseled regarding the use of sun protective measures and the importance of annual screening for new lesions.
Image courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and text courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the veterans affairs topical tretinoin chemoprevention trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24284.

The suspicion raised by the dermoscopy results led to a shave biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ, also known as Bowen disease.
Bowen disease typically manifests as a scaly erythematous patch, often on sun-exposed skin. If untreated, these lesions have the potential to develop into invasive SCCs. Generally, the lesions are preceded by the formation of actinic keratosis (AK). In a 2009 trial performed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, up to 65% of SCCs were found to have previously been diagnosed as AK lesions.1
The selection of treatments includes excision, electrodessication and curettage, cryotherapy, and topical options such as fluorouracil bid for 4 weeks or imiquimod qd for 9 weeks.
After the physician outlined the treatment options, this patient opted for an elliptical excision. At the patient’s next follow-up appointment, she was found to have multiple AKs on her face; they were treated with cryotherapy. Patients with a diagnosis of precancerous or cancerous skin lesions are at high risk for additional AKs and skin cancer, so they should be counseled regarding the use of sun protective measures and the importance of annual screening for new lesions.
Image courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and text courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The suspicion raised by the dermoscopy results led to a shave biopsy, which confirmed the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ, also known as Bowen disease.
Bowen disease typically manifests as a scaly erythematous patch, often on sun-exposed skin. If untreated, these lesions have the potential to develop into invasive SCCs. Generally, the lesions are preceded by the formation of actinic keratosis (AK). In a 2009 trial performed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, up to 65% of SCCs were found to have previously been diagnosed as AK lesions.1
The selection of treatments includes excision, electrodessication and curettage, cryotherapy, and topical options such as fluorouracil bid for 4 weeks or imiquimod qd for 9 weeks.
After the physician outlined the treatment options, this patient opted for an elliptical excision. At the patient’s next follow-up appointment, she was found to have multiple AKs on her face; they were treated with cryotherapy. Patients with a diagnosis of precancerous or cancerous skin lesions are at high risk for additional AKs and skin cancer, so they should be counseled regarding the use of sun protective measures and the importance of annual screening for new lesions.
Image courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and text courtesy of Carlos Cano, MD, and Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
1. Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the veterans affairs topical tretinoin chemoprevention trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24284.
1. Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the veterans affairs topical tretinoin chemoprevention trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24284.
PURE: High refined-grain intake boosts death, CVD events
That’s one finding from an assessment of a more than 137,000 people in 21 countries that documented a clear link between a high level of consumption of refined grains and a significantly increased risk for death from any cause or major cardiovascular disease (CVD) event during a median follow-up of 9.5 years.
The results showed that people who reported eating at least 350 g (seven servings) of refined grain daily had a significant 29% increased risk of either death or a major CVD event (MI, stroke, or heart failure), compared with those who consumed less than one serving per day (fewer than 50 g) of refined grain after adjustment for multiple potential confounders, according to a report from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study published in the BMJ on Feb. 3, 2021.
The analysis also showed no significant association between levels of whole grains or white rice in the diet and CVD events. Rice was considered a separate grain in the analysis because nearly two-thirds of the PURE study population reside in Asia, where rice is a staple food.
The findings show that “reduction in the quantity of refined grains and sugar, and improvement in the quality of carbohydrates is essential for better health outcomes, although we do not suggest complete elimination of refined grains,” said Mahshid Dehghan, PhD, lead investigator for this report and a researcher in nutrition epidemiology at the Population Health Research Institute of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
‘Widely applicable’ results from large, diverse study
Although prior evidence had already shown the CVD risk from eating larger amounts of refined grains, “our findings are robust and more widely applicable because our large study recorded over 9,000 deaths and 3,500 major CVD events across a broad range of refined grain intake, and in a variety of different settings and cultures with varying dietary patterns,” Dr. Dehghan said in an interview.
“This is an important paper, with the strength of data from diverse countries. The associations are robust,” commented Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, professor and dean of the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, Boston, who was not involved in the new report.
“The public and the public health community think about added sugar in food as harmful, but starch has gotten a free pass,” he said in an interview. Recently revised U.S. dietary guidelines recommend that refined grains constitute less than half of a person’s carbohydrate consumption, but that limitation remains set too high, Dr. Mozaffarian cautioned. A much safer daily consumption limit would cap refined grains to no more than one serving a day.
The data for the current PURE analysis came from more than 148,000 people aged 35-70 years at entry in 21 geographically and economically diverse countries. Excluding patients with known CVD at baseline left a cohort of 137,130 people.
The results showed no significant association between the quantity of whole grains consumed and the main outcome, nor a link between higher amounts of white rice consumption and the main outcome.
“Our findings suggest that intake of up to 350 g of cooked rice daily may not pose a significant health risk,” said Dr. Dehghan.
Refined grains produce a glucose surge
Dr. Dehghan and associates speculated that possible explanations for their findings are that “varieties of rice such as long-grain rice and especially parboiled white rice may have both a definite glycemic advantage and an overall nutritional advantage over refined wheat products. Also, depending on the culture and the nature of the rice eaten, rice may be displacing less desirable foods.”
In contrast, refined grains undergo “rapid action by digestive enzymes and quick absorption from the small intestines [that] could lead to an increase in postprandial blood glucose concentrations. The rise in glucose concentrations increases the insulin concentrations, which leads to hypoglycemia, lipolysis, and the stimulation of hunger and food intake,” the authors wrote.
“It’s similar to eating sugar, or candy,” noted Dr. Mozaffarian, as refined grain “is 100% glucose.” Whole grains differ by entering the gut packaged in cell structures that slow digestion and avoid delivering sugar in an unnaturally rapid way.
“We are providing new evidence, and we hope that dietary guidelines in North America encourage individuals to lower their refined grain and sugar intake,” Dr. Dehghan said.
PURE has received partial funding with unrestricted grants from several drug companies. Dr. Dehghan had no disclosures. Dr. Mozaffarian has been an adviser to or has received personal fees from several food companies, but had no relevant disclosures.
That’s one finding from an assessment of a more than 137,000 people in 21 countries that documented a clear link between a high level of consumption of refined grains and a significantly increased risk for death from any cause or major cardiovascular disease (CVD) event during a median follow-up of 9.5 years.
The results showed that people who reported eating at least 350 g (seven servings) of refined grain daily had a significant 29% increased risk of either death or a major CVD event (MI, stroke, or heart failure), compared with those who consumed less than one serving per day (fewer than 50 g) of refined grain after adjustment for multiple potential confounders, according to a report from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study published in the BMJ on Feb. 3, 2021.
The analysis also showed no significant association between levels of whole grains or white rice in the diet and CVD events. Rice was considered a separate grain in the analysis because nearly two-thirds of the PURE study population reside in Asia, where rice is a staple food.
The findings show that “reduction in the quantity of refined grains and sugar, and improvement in the quality of carbohydrates is essential for better health outcomes, although we do not suggest complete elimination of refined grains,” said Mahshid Dehghan, PhD, lead investigator for this report and a researcher in nutrition epidemiology at the Population Health Research Institute of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
‘Widely applicable’ results from large, diverse study
Although prior evidence had already shown the CVD risk from eating larger amounts of refined grains, “our findings are robust and more widely applicable because our large study recorded over 9,000 deaths and 3,500 major CVD events across a broad range of refined grain intake, and in a variety of different settings and cultures with varying dietary patterns,” Dr. Dehghan said in an interview.
“This is an important paper, with the strength of data from diverse countries. The associations are robust,” commented Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, professor and dean of the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, Boston, who was not involved in the new report.
“The public and the public health community think about added sugar in food as harmful, but starch has gotten a free pass,” he said in an interview. Recently revised U.S. dietary guidelines recommend that refined grains constitute less than half of a person’s carbohydrate consumption, but that limitation remains set too high, Dr. Mozaffarian cautioned. A much safer daily consumption limit would cap refined grains to no more than one serving a day.
The data for the current PURE analysis came from more than 148,000 people aged 35-70 years at entry in 21 geographically and economically diverse countries. Excluding patients with known CVD at baseline left a cohort of 137,130 people.
The results showed no significant association between the quantity of whole grains consumed and the main outcome, nor a link between higher amounts of white rice consumption and the main outcome.
“Our findings suggest that intake of up to 350 g of cooked rice daily may not pose a significant health risk,” said Dr. Dehghan.
Refined grains produce a glucose surge
Dr. Dehghan and associates speculated that possible explanations for their findings are that “varieties of rice such as long-grain rice and especially parboiled white rice may have both a definite glycemic advantage and an overall nutritional advantage over refined wheat products. Also, depending on the culture and the nature of the rice eaten, rice may be displacing less desirable foods.”
In contrast, refined grains undergo “rapid action by digestive enzymes and quick absorption from the small intestines [that] could lead to an increase in postprandial blood glucose concentrations. The rise in glucose concentrations increases the insulin concentrations, which leads to hypoglycemia, lipolysis, and the stimulation of hunger and food intake,” the authors wrote.
“It’s similar to eating sugar, or candy,” noted Dr. Mozaffarian, as refined grain “is 100% glucose.” Whole grains differ by entering the gut packaged in cell structures that slow digestion and avoid delivering sugar in an unnaturally rapid way.
“We are providing new evidence, and we hope that dietary guidelines in North America encourage individuals to lower their refined grain and sugar intake,” Dr. Dehghan said.
PURE has received partial funding with unrestricted grants from several drug companies. Dr. Dehghan had no disclosures. Dr. Mozaffarian has been an adviser to or has received personal fees from several food companies, but had no relevant disclosures.
That’s one finding from an assessment of a more than 137,000 people in 21 countries that documented a clear link between a high level of consumption of refined grains and a significantly increased risk for death from any cause or major cardiovascular disease (CVD) event during a median follow-up of 9.5 years.
The results showed that people who reported eating at least 350 g (seven servings) of refined grain daily had a significant 29% increased risk of either death or a major CVD event (MI, stroke, or heart failure), compared with those who consumed less than one serving per day (fewer than 50 g) of refined grain after adjustment for multiple potential confounders, according to a report from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study published in the BMJ on Feb. 3, 2021.
The analysis also showed no significant association between levels of whole grains or white rice in the diet and CVD events. Rice was considered a separate grain in the analysis because nearly two-thirds of the PURE study population reside in Asia, where rice is a staple food.
The findings show that “reduction in the quantity of refined grains and sugar, and improvement in the quality of carbohydrates is essential for better health outcomes, although we do not suggest complete elimination of refined grains,” said Mahshid Dehghan, PhD, lead investigator for this report and a researcher in nutrition epidemiology at the Population Health Research Institute of McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont.
‘Widely applicable’ results from large, diverse study
Although prior evidence had already shown the CVD risk from eating larger amounts of refined grains, “our findings are robust and more widely applicable because our large study recorded over 9,000 deaths and 3,500 major CVD events across a broad range of refined grain intake, and in a variety of different settings and cultures with varying dietary patterns,” Dr. Dehghan said in an interview.
“This is an important paper, with the strength of data from diverse countries. The associations are robust,” commented Dariush Mozaffarian, MD, DrPH, professor and dean of the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, Boston, who was not involved in the new report.
“The public and the public health community think about added sugar in food as harmful, but starch has gotten a free pass,” he said in an interview. Recently revised U.S. dietary guidelines recommend that refined grains constitute less than half of a person’s carbohydrate consumption, but that limitation remains set too high, Dr. Mozaffarian cautioned. A much safer daily consumption limit would cap refined grains to no more than one serving a day.
The data for the current PURE analysis came from more than 148,000 people aged 35-70 years at entry in 21 geographically and economically diverse countries. Excluding patients with known CVD at baseline left a cohort of 137,130 people.
The results showed no significant association between the quantity of whole grains consumed and the main outcome, nor a link between higher amounts of white rice consumption and the main outcome.
“Our findings suggest that intake of up to 350 g of cooked rice daily may not pose a significant health risk,” said Dr. Dehghan.
Refined grains produce a glucose surge
Dr. Dehghan and associates speculated that possible explanations for their findings are that “varieties of rice such as long-grain rice and especially parboiled white rice may have both a definite glycemic advantage and an overall nutritional advantage over refined wheat products. Also, depending on the culture and the nature of the rice eaten, rice may be displacing less desirable foods.”
In contrast, refined grains undergo “rapid action by digestive enzymes and quick absorption from the small intestines [that] could lead to an increase in postprandial blood glucose concentrations. The rise in glucose concentrations increases the insulin concentrations, which leads to hypoglycemia, lipolysis, and the stimulation of hunger and food intake,” the authors wrote.
“It’s similar to eating sugar, or candy,” noted Dr. Mozaffarian, as refined grain “is 100% glucose.” Whole grains differ by entering the gut packaged in cell structures that slow digestion and avoid delivering sugar in an unnaturally rapid way.
“We are providing new evidence, and we hope that dietary guidelines in North America encourage individuals to lower their refined grain and sugar intake,” Dr. Dehghan said.
PURE has received partial funding with unrestricted grants from several drug companies. Dr. Dehghan had no disclosures. Dr. Mozaffarian has been an adviser to or has received personal fees from several food companies, but had no relevant disclosures.
A minimally invasive modification for fascia lata mid-urethral sling
mid-urethral sling
mid-urethral sling
mid-urethral sling
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children continue to drop
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.
Despite a drop in the number of weekly COVID-19 cases, children made up a larger share of cases for the fourth consecutive week, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

Just over 140,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children were reported for the week of Jan. 22-28, down from 165,000 the week before and down from the record high of 211,000 2 weeks earlier, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Since the beginning of January, however, the proportion of weekly cases occurring in children has risen from 12.9% to 15.1%, based on data collected by the AAP/CHA from the health department websites of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, 2.81 million children have been infected by the coronavirus, representing 12.8% of the total for all ages, which is almost 22 million. The cumulative rate since the start of the pandemic passed 3,700 cases per 100,000 children after increasing by 5.2% over the previous week, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Cumulative hospitalizations in children just passed 11,000 in the 24 states (and New York City) that are reporting data for children, which represents 1.8% of COVID-19–related admissions for all ages, a proportion that has not changed since mid-November. Ten more deaths in children were reported during Jan. 22-28, bringing the total to 215 in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are tracking mortality.
In the 10 states that are reporting data on testing, rates of positive results in children range from 7.1% in Indiana, in which children make up the largest proportion of total tests performed (18.1%) to 28.4% in Iowa, where children make up the smallest proportion of tests (6.0%), the AAP and CHA said.
COVID-19 in pregnancy tied to hypertension, preeclampsia
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having COVID-19 during pregnancy is linked to a significantly increased risk for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia compared with not having COVID-19 while pregnant, according to findings from a retrospective study presented Jan. 28 at the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine 2021 Annual Pregnancy Meeting.
“This was not entirely surprising given that inflammation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of both hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and COVID-19 infection and thus may serve to exacerbate each other,” Nigel Madden, MD, a resident physician in the ob.gyn. department at Columbia University, New York. , told this news organization after she presented the results.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy occur in 10%-15% of all pregnancies and are the leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide, Dr. Madden told attendees of the meeting. Although it’s not clear what causes hypertensive diseases in pregnancy generally, “it is possible that the acute inflammatory state of the COVID infection may incite or exacerbate hypertensive disease of pregnancy,” Dr. Madden said.
The researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of 1,715 patients who had a singleton pregnancy and who underwent routine nasal polymerase chain reaction testing at admission to one institution’s labor and delivery department between March and June 2020. The researchers excluded patients who had a history of chronic hypertension.
Overall, 10% of the patients tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 167), and 90% tested negative (n = 1,548). There were several differences at baseline between the groups. Those who tested positive tended to be younger, with an average age of 28, compared with an average age of 31 years for the group that tested negative. The group that tested negative also had a higher proportion of mothers aged 35 and older (P < .01). There were also significant differences in the racial makeup of the groups. Half of those in the COVID-positive group reported “other” for their race. The biggest baseline disparity between the groups was with regard to insurance type: 73% of those who tested positive for COVID-19 used Medicaid; only 36% of patients in the COVID-negative group used Medicaid. Those with private insurance were more likely to test negative (43%) than positive (25%) (P < .01).
The researchers defined gestational hypertension as having a systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg on two occasions at least 4 hours apart. A preeclampsia diagnosis required elevated blood pressure (using the same definition as for hypertension) as well as proteinuria, characterized by a protein/creatine ratio greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL or greater than or equal to 300 mg of protein on a 24-hour urine collection. Preeclampsia with severe features required prespecified laboratory abnormalities, pulmonary edema, or symptoms of headache, vision changes, chest pain, shortness of breath, or right upper quadrant pain.
More than twice as many patients with COVID had a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (18%) as those who tested negative (8%). The patients who were COVID positive were significantly more likely than those who tested negative to have gestational hypertension and preeclampsia without severe features. Rates of preeclampsia with severe features were not significantly different between the groups.
The severity of hypertensive disease did not differ between the groups. Limitations of the study included its retrospective design, the small number of COVID-positive patients, and the fact that it was conducted at a single institution in New York. However, the study population was diverse, and it was conducted during the height of infections at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This was a study of great clinical significance,” said Kim Boggess, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, while moderating the session. “I would argue that you guys in New York are the best poised to answer some of the questions that need to be answered as it relates to the effect of coronavirus infection in pregnancy.”
Dr. Boggess asked whether the study examined associations related to the severity of COVID-19. Only 10 of the patients were symptomatic, Dr. Madden said, and only one of those patients developed preeclampsia with severe features.
Michelle Y. Owens, MD, professor and chief of maternal fetal medicine at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, who also moderated the session, said in an interview that the findings call for physicians to remain vigilant about evaluating patients who test positive for COVID-19 for hypertensive disease and disorders.
“Additionally, these women should be educated about hypertensive disorders and the common symptoms to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment when indicated,” Dr. Owens said. “I believe this is of particular interest in those women who are not severely affected by COVID, as these changes may occur while they are undergoing quarantine or being monitored remotely. This amplifies the need for remote assessment or home monitoring of maternal blood pressures.”
Dr. Madden, Dr. Boggess, and Dr. Owens have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves intramuscular administration for peginterferon beta-1a in MS
“The new IM administration offers people living with relapsing MS the well-characterized efficacy and safety of Plegridy with the potential for significantly reduced injection site reactions,” Biogen said in a news release announcing the FDA action.
Plegridy is a pegylated version of interferon beta-1a, which prolongs the circulation time of the molecule in the body by increasing its size. The process extends the drug’s half-life, allowing for a less-frequent dosing schedule.
Peginterferon beta-1a administered subcutaneously was first approved by the FDA in 2014 based on data showing it significantly reduces MS relapses, disability progression, and brain lesions.
The FDA approved IM administration for peginterferon beta-1a based on data evaluating bioequivalence and adverse reactions associated with IM administration compared with subcutaneous (SC) administration in healthy volunteers.
Bioequivalence of the IM and SC dosing regimens was confirmed and volunteers receiving the drug through IM administration experienced fewer injection site reactions relative to those receiving SC administration (14.4% vs. 32.1%), the company said.
The overall safety profiles of IM and SC administration were generally similar, with no new safety signals.
The European Commission allowed marketing authorization for IM administration of peginterferon beta-1a in December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The new IM administration offers people living with relapsing MS the well-characterized efficacy and safety of Plegridy with the potential for significantly reduced injection site reactions,” Biogen said in a news release announcing the FDA action.
Plegridy is a pegylated version of interferon beta-1a, which prolongs the circulation time of the molecule in the body by increasing its size. The process extends the drug’s half-life, allowing for a less-frequent dosing schedule.
Peginterferon beta-1a administered subcutaneously was first approved by the FDA in 2014 based on data showing it significantly reduces MS relapses, disability progression, and brain lesions.
The FDA approved IM administration for peginterferon beta-1a based on data evaluating bioequivalence and adverse reactions associated with IM administration compared with subcutaneous (SC) administration in healthy volunteers.
Bioequivalence of the IM and SC dosing regimens was confirmed and volunteers receiving the drug through IM administration experienced fewer injection site reactions relative to those receiving SC administration (14.4% vs. 32.1%), the company said.
The overall safety profiles of IM and SC administration were generally similar, with no new safety signals.
The European Commission allowed marketing authorization for IM administration of peginterferon beta-1a in December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The new IM administration offers people living with relapsing MS the well-characterized efficacy and safety of Plegridy with the potential for significantly reduced injection site reactions,” Biogen said in a news release announcing the FDA action.
Plegridy is a pegylated version of interferon beta-1a, which prolongs the circulation time of the molecule in the body by increasing its size. The process extends the drug’s half-life, allowing for a less-frequent dosing schedule.
Peginterferon beta-1a administered subcutaneously was first approved by the FDA in 2014 based on data showing it significantly reduces MS relapses, disability progression, and brain lesions.
The FDA approved IM administration for peginterferon beta-1a based on data evaluating bioequivalence and adverse reactions associated with IM administration compared with subcutaneous (SC) administration in healthy volunteers.
Bioequivalence of the IM and SC dosing regimens was confirmed and volunteers receiving the drug through IM administration experienced fewer injection site reactions relative to those receiving SC administration (14.4% vs. 32.1%), the company said.
The overall safety profiles of IM and SC administration were generally similar, with no new safety signals.
The European Commission allowed marketing authorization for IM administration of peginterferon beta-1a in December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe Refractory Hailey-Hailey Disease Treated With Electron Beam Radiotherapy and Low-Level Laser Therapy
To the Editor:
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), or familial benign chronic pemphigus, is a genetic disorder caused by an autosomal-dominant mutation in ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1, which disrupts intracellular calcium signaling and blocks synthesis of junctional proteins required for cell-cell adhesion.1,2 As a result, patients develop acantholysis of the suprabasilar epidermis resulting in chronic flaccid blisters and erosions, particularly in intertriginous areas.3 Patients often report associated itching, pain, and burning, and they frequently present with secondary polymicrobial infections.4 Although HHD is genetic, patients may present without a family history due to variable expressivity and sporadic germline mutations.5 Therapeutic options are numerous, and patients may attempt many treatments before a benefit is observed.4 Local disease improvement was noted in a case series of 3 patients treated with electron beam radiotherapy with no disease recurrence in treated sites at 38, 33, and 9 months’ follow-up.6 Herein, we present a case of HHD refractory to numerous prior therapies that was successfully treated with electron beam radiotherapy, highlighting the potential role for palliative radiotherapy in select refractory cases of HHD.
A 35-year-old woman with a 7-year of history of HHD presented with severe recalcitrant disease including extensive erosive patches and plaques in the intertriginous areas of the bilateral axillae, groin, and inframammary folds (Figure 1). The skin eruptions first appeared at 28 years of age after her last pregnancy and continued as painful blistering that worsened with each menstrual cycle. Initially the affected desquamated skin would heal between menstrual cycles, but large areas of desquamation remained unhealed in the groin and inframammary regions throughout her full menstrual cycles by the time of referral. Family history included 4 family members with HHD: 2 aunts, an uncle, and a cousin on the paternal side of her family. Over a 7-year period, treatment with clobetasol cream, clindamycin gel, tacrolimus ointment, doxycycline, dapsone, cyclosporine, methotrexate, etanercept, isotretinoin, and prednisone (15 mg every other day) all failed. Most recently, axillary abobotulinumtoxinA injections were attempted but failed. She had been prednisone dependent for more than 1 year. Due to the ongoing refractory disease, she was referred to radiation oncology to discuss radiotherapy treatment options.
At the time of presentation to the radiation oncology clinic, she continued to have extensive involvement of the intertriginous areas as well as involvement of the right neck at sites of skin chafing from clothing. Consistent with the limited available evidence, a dose of 20 Gy in 10 fractions was first prescribed to the axillae to assess response in the event of radiosensitivity, resulting in brisk desquamation. The conventional fractionation of 2 Gy per fraction allowed for assessment of response/tolerance and the opportunity to stop the treatment in the unlikely event of a severe skin reaction. Her skin tolerated treatment well with slight dryness and mild irritation that was less severe than the typical HHD flares. Concurrently with the axillary radiotherapy, we delivered a trial of low-level laser therapy to areas of severe disease in both inguinal regions in the hope that it could be used instead of radiotherapy to avoid any associated risks of radiation. Low-level laser therapy was administered with a light-emitting diode cluster probe at 2.5 Hz for 1 minute to 2 sites in each inguinal area daily for a total of 10 treatments. Unfortunately, this therapy temporarily exacerbated exudation present in the skin before it resolved to its pretreatment state with no improvement.
One month after treatment she had total resolution of the erosive patches and plaques with mild residual hyperpigmentation in the axillae, establishing that radiation therapy was reasonably effective. To lower the total radiation dose and decrease the risk of radiation-induced malignancy, we treated the bilateral groin and the inframammary region with a treatment schedule of 8 Gy in 2 fractions at a higher dose of 4 Gy per fraction instead of 2 Gy. At 12 days posttreatment, she had a dramatic response in the groin and a mixed response in the inframammary region, with a focus that had not yet regressed. Given the dramatic response in the treated sites, the patient requested treatment to the right side of the neck. Thus, we treated this area with a similar 8 Gy in 2 fractions, and an additional 6 Gy in 2 fractions boost was added to the slow responding focus in the inframammary fold for a total of 14 Gy in 4 fractions. The patient tolerated all treatments well with mild grade 1 skin irritation that was unlike the blistering of the typical HHD flares. Two months following completion of the first course of radiotherapy to the axillae and 2 weeks from the most recent course, she tapered off her prednisone regimen (15 mg every other day) but had a relapse of disease with her subsequent menstrual cycles that presented as a blistering skin reaction in the inframammary region, which healed in response to restarting steroids. This flare was less severe than those prior to radiotherapy. At 10 months posttreatment, the patient was free of disease in the neck and axillae (Figure 2). She continued to have relapses in the inframammary region with menstrual cycles and noted new disease in the popliteal regions; however, the relapses were less severe, and her skin had improved more with radiation than any of the prior therapies.
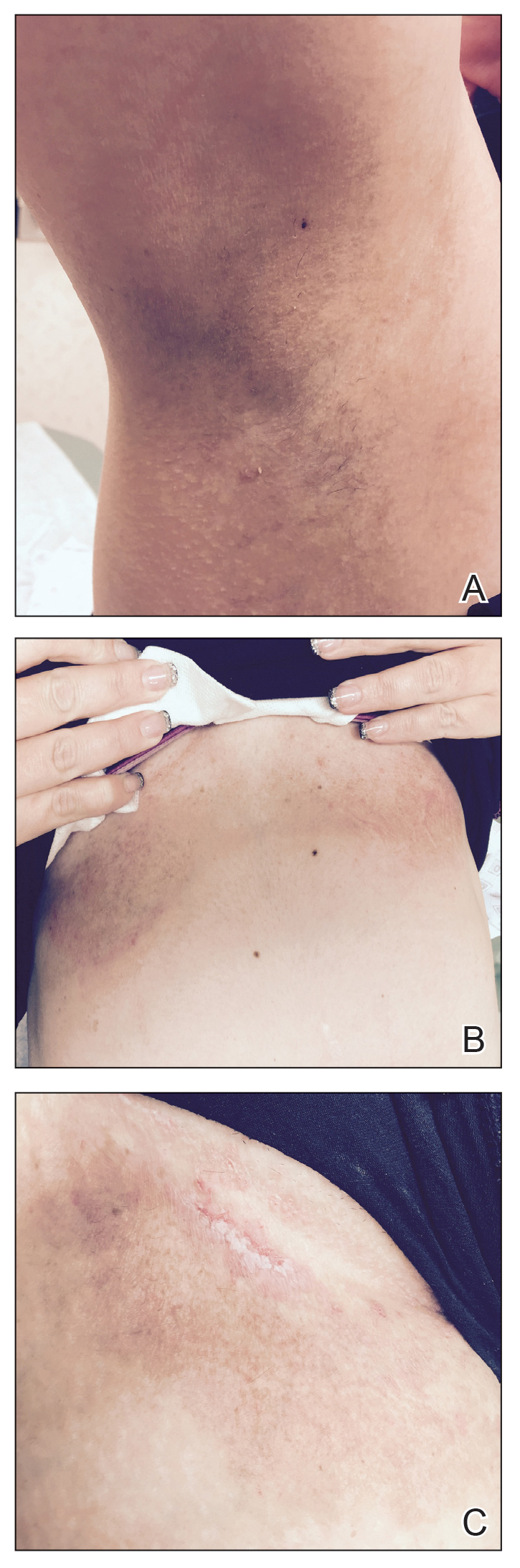
Our experience with low-level laser therapy indicated that it should be completely avoided in HHD. Our patient’s treatment with radiotherapy demonstrated excellent short-term responses in areas of pemphigus but later proved to be a mixed response with further follow-up including a mild posttreatment flare of the inframammary region that responded to steroids and new popliteal region involvement. As summarized in the Table, earlier reports of radiotherapy for the treatment of HHD have yielded varied results.6-8 The mixed response seen in our patient suggests that response to radiotherapy may be site specific, related to underlying inflammation from microbial overgrowth, or a function of the disease severity.
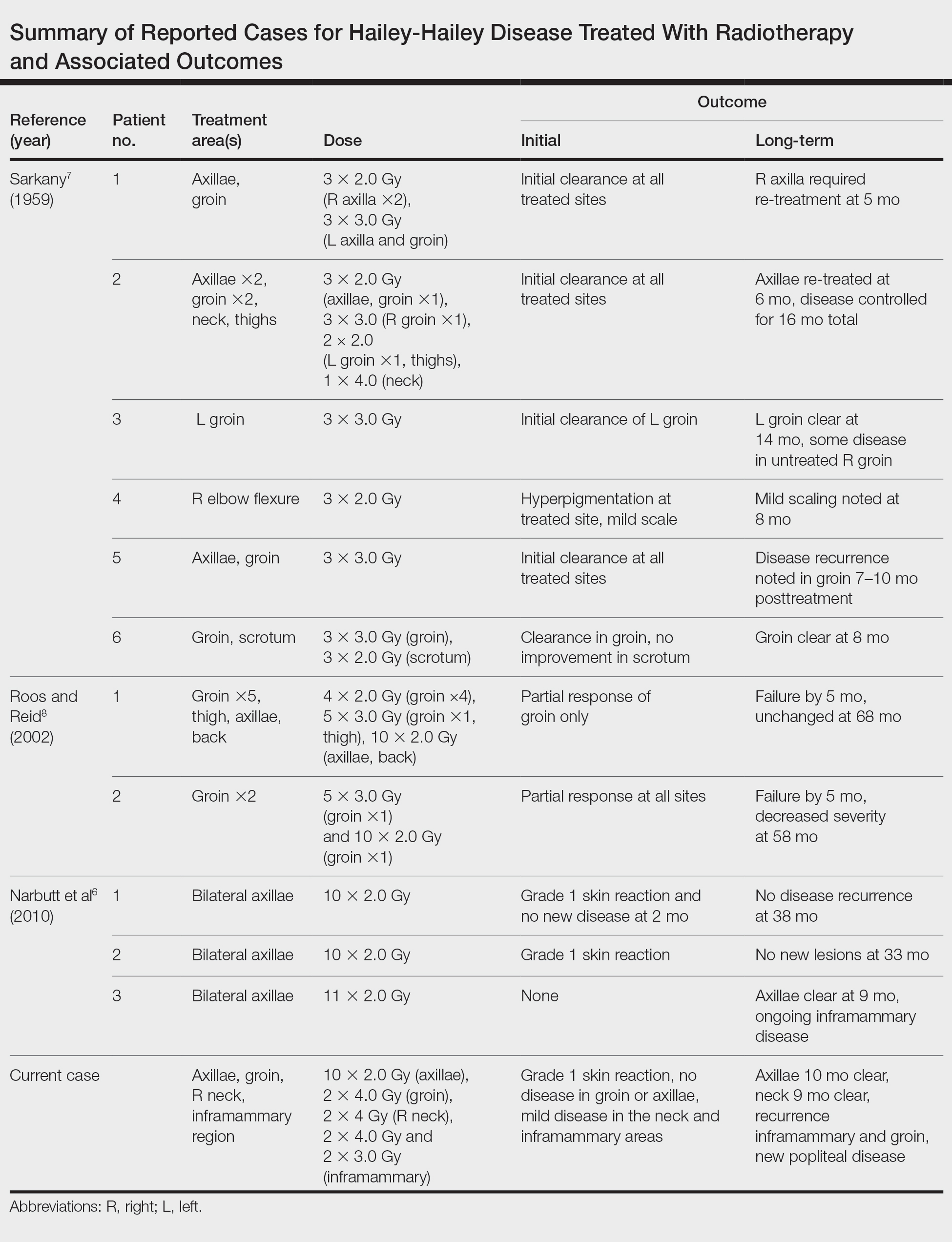
Although the number of reports on radiotherapy in HHD is small, there have been several reports of Darier disease, another acantholytic autosomal-dominant genodermatosis affecting the ATP2A2 gene, successfully treated incidentally with radiation.9,10 Total skin electron beam therapy also has been employed in the treatment of Darier disease; this patient experienced a severe flare after a relatively low treatment dose that required intensive care monitoring, possibly highlighting the potential radiosensitivity of patients with underlying genodermatoses and cautioning against radiotherapy dose escalation.11 In light of the mixed responses seen, radiation therapy should be used sparingly for severe relapsing cases that have failed a plethora of prior treatments. The risk of second cancer induction is especially of concern when using radiotherapy in a benign disease.12 We observed excellent initial responses in our patient, both with conventionally fractionated radiotherapy and hypofractionation. The risk of second malignancy induction is a linear function of radiotherapy dose.12 Thus, utilization of hypofractionated regimens such as 4 Gy times 2 fractions seems most prudent. It remains unclear if further dose de-escalation may yield a similar response, as seen in studies utilizing radiotherapy for other benign disease.13,14 Overall, given our mixed results with short follow-up, we conclude that the consideration of radiotherapy should be limited to patients with severe recalcitrant HHD.
- Dhitavat J, Fairclough RJ, Hovnanian A, et al. Calcium pumps and keratinocytes: lessons from Darier’s disease and Hailey-Hailey disease. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:821-828.
- Hu Z, Bonifas JM, Beech J, et al. Mutations in ATP2C1, encoding a calcium pump, cause Hailey-Hailey disease. Nat Genet. 2000;24:61-65.
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282.
- Chiaravalloti A, Payette M. Hailey-Hailey disease and review of management. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1254-1257.
- Zhang F, Yan X, Jiang D, et al. Eight novel mutations of ATP2C1 identified in 17 Chinese families with Hailey-Hailey disease. Dermatology. 2007;215:277-283.
- Narbutt J, Chrusciel A, Rychter A, et al. Persistent improvement of previously recalcitrant Hailey-Hailey disease with electron beam radiotherapy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:179-182.
- Sarkany I. Grenz-ray treatment of familial benign chronic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 1959;71:247-252.
- Roos DE, Reid CM. Benign familial pemphigus: little benefit from superficial radiotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:305-308.
- Podgornii A, Ciammella P, Ramundo D, et al. Efficacy of the radiotherapy on Darier’s disease: an indirect evidence. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2013;2013:907802.
- Mac Manus MP, Cavalleri G, Ball DL, et al. Exacerbation, then clearance, of mutation-proven Darier’s disease of the skin after radiotherapy for bronchial carcinoma: a case of radiation-induced epidermal differentiation? Radiat Res. 2001;156:724-730.
- Kittridge A, Wahlgren C, Fuhrer R, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant Darier’s disease with electron beam therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:302-304.
- Preston DL, Shimizu Y, Pierce DA, et al. Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. report 13: solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950-1997. Radiat Res. 2003;160:381-407.
- Fröhlich D, Baaske D, Glatzel M. Radiotherapy of hidradenitis suppurativa—still valid today? [in German]. Strahlenther Onkol. 2000;176:286-289.
- Heyd R, Tselis N, Ackermann H, et al. Radiation therapy for painful heel spurs: results of a prospective randomized study. Strahlenther Onkol. 2007;183:3-9.
To the Editor:
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), or familial benign chronic pemphigus, is a genetic disorder caused by an autosomal-dominant mutation in ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1, which disrupts intracellular calcium signaling and blocks synthesis of junctional proteins required for cell-cell adhesion.1,2 As a result, patients develop acantholysis of the suprabasilar epidermis resulting in chronic flaccid blisters and erosions, particularly in intertriginous areas.3 Patients often report associated itching, pain, and burning, and they frequently present with secondary polymicrobial infections.4 Although HHD is genetic, patients may present without a family history due to variable expressivity and sporadic germline mutations.5 Therapeutic options are numerous, and patients may attempt many treatments before a benefit is observed.4 Local disease improvement was noted in a case series of 3 patients treated with electron beam radiotherapy with no disease recurrence in treated sites at 38, 33, and 9 months’ follow-up.6 Herein, we present a case of HHD refractory to numerous prior therapies that was successfully treated with electron beam radiotherapy, highlighting the potential role for palliative radiotherapy in select refractory cases of HHD.
A 35-year-old woman with a 7-year of history of HHD presented with severe recalcitrant disease including extensive erosive patches and plaques in the intertriginous areas of the bilateral axillae, groin, and inframammary folds (Figure 1). The skin eruptions first appeared at 28 years of age after her last pregnancy and continued as painful blistering that worsened with each menstrual cycle. Initially the affected desquamated skin would heal between menstrual cycles, but large areas of desquamation remained unhealed in the groin and inframammary regions throughout her full menstrual cycles by the time of referral. Family history included 4 family members with HHD: 2 aunts, an uncle, and a cousin on the paternal side of her family. Over a 7-year period, treatment with clobetasol cream, clindamycin gel, tacrolimus ointment, doxycycline, dapsone, cyclosporine, methotrexate, etanercept, isotretinoin, and prednisone (15 mg every other day) all failed. Most recently, axillary abobotulinumtoxinA injections were attempted but failed. She had been prednisone dependent for more than 1 year. Due to the ongoing refractory disease, she was referred to radiation oncology to discuss radiotherapy treatment options.

At the time of presentation to the radiation oncology clinic, she continued to have extensive involvement of the intertriginous areas as well as involvement of the right neck at sites of skin chafing from clothing. Consistent with the limited available evidence, a dose of 20 Gy in 10 fractions was first prescribed to the axillae to assess response in the event of radiosensitivity, resulting in brisk desquamation. The conventional fractionation of 2 Gy per fraction allowed for assessment of response/tolerance and the opportunity to stop the treatment in the unlikely event of a severe skin reaction. Her skin tolerated treatment well with slight dryness and mild irritation that was less severe than the typical HHD flares. Concurrently with the axillary radiotherapy, we delivered a trial of low-level laser therapy to areas of severe disease in both inguinal regions in the hope that it could be used instead of radiotherapy to avoid any associated risks of radiation. Low-level laser therapy was administered with a light-emitting diode cluster probe at 2.5 Hz for 1 minute to 2 sites in each inguinal area daily for a total of 10 treatments. Unfortunately, this therapy temporarily exacerbated exudation present in the skin before it resolved to its pretreatment state with no improvement.
One month after treatment she had total resolution of the erosive patches and plaques with mild residual hyperpigmentation in the axillae, establishing that radiation therapy was reasonably effective. To lower the total radiation dose and decrease the risk of radiation-induced malignancy, we treated the bilateral groin and the inframammary region with a treatment schedule of 8 Gy in 2 fractions at a higher dose of 4 Gy per fraction instead of 2 Gy. At 12 days posttreatment, she had a dramatic response in the groin and a mixed response in the inframammary region, with a focus that had not yet regressed. Given the dramatic response in the treated sites, the patient requested treatment to the right side of the neck. Thus, we treated this area with a similar 8 Gy in 2 fractions, and an additional 6 Gy in 2 fractions boost was added to the slow responding focus in the inframammary fold for a total of 14 Gy in 4 fractions. The patient tolerated all treatments well with mild grade 1 skin irritation that was unlike the blistering of the typical HHD flares. Two months following completion of the first course of radiotherapy to the axillae and 2 weeks from the most recent course, she tapered off her prednisone regimen (15 mg every other day) but had a relapse of disease with her subsequent menstrual cycles that presented as a blistering skin reaction in the inframammary region, which healed in response to restarting steroids. This flare was less severe than those prior to radiotherapy. At 10 months posttreatment, the patient was free of disease in the neck and axillae (Figure 2). She continued to have relapses in the inframammary region with menstrual cycles and noted new disease in the popliteal regions; however, the relapses were less severe, and her skin had improved more with radiation than any of the prior therapies.

Our experience with low-level laser therapy indicated that it should be completely avoided in HHD. Our patient’s treatment with radiotherapy demonstrated excellent short-term responses in areas of pemphigus but later proved to be a mixed response with further follow-up including a mild posttreatment flare of the inframammary region that responded to steroids and new popliteal region involvement. As summarized in the Table, earlier reports of radiotherapy for the treatment of HHD have yielded varied results.6-8 The mixed response seen in our patient suggests that response to radiotherapy may be site specific, related to underlying inflammation from microbial overgrowth, or a function of the disease severity.

Although the number of reports on radiotherapy in HHD is small, there have been several reports of Darier disease, another acantholytic autosomal-dominant genodermatosis affecting the ATP2A2 gene, successfully treated incidentally with radiation.9,10 Total skin electron beam therapy also has been employed in the treatment of Darier disease; this patient experienced a severe flare after a relatively low treatment dose that required intensive care monitoring, possibly highlighting the potential radiosensitivity of patients with underlying genodermatoses and cautioning against radiotherapy dose escalation.11 In light of the mixed responses seen, radiation therapy should be used sparingly for severe relapsing cases that have failed a plethora of prior treatments. The risk of second cancer induction is especially of concern when using radiotherapy in a benign disease.12 We observed excellent initial responses in our patient, both with conventionally fractionated radiotherapy and hypofractionation. The risk of second malignancy induction is a linear function of radiotherapy dose.12 Thus, utilization of hypofractionated regimens such as 4 Gy times 2 fractions seems most prudent. It remains unclear if further dose de-escalation may yield a similar response, as seen in studies utilizing radiotherapy for other benign disease.13,14 Overall, given our mixed results with short follow-up, we conclude that the consideration of radiotherapy should be limited to patients with severe recalcitrant HHD.
To the Editor:
Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), or familial benign chronic pemphigus, is a genetic disorder caused by an autosomal-dominant mutation in ATPase secretory pathway Ca2+ transporting 1 gene, ATP2C1, which disrupts intracellular calcium signaling and blocks synthesis of junctional proteins required for cell-cell adhesion.1,2 As a result, patients develop acantholysis of the suprabasilar epidermis resulting in chronic flaccid blisters and erosions, particularly in intertriginous areas.3 Patients often report associated itching, pain, and burning, and they frequently present with secondary polymicrobial infections.4 Although HHD is genetic, patients may present without a family history due to variable expressivity and sporadic germline mutations.5 Therapeutic options are numerous, and patients may attempt many treatments before a benefit is observed.4 Local disease improvement was noted in a case series of 3 patients treated with electron beam radiotherapy with no disease recurrence in treated sites at 38, 33, and 9 months’ follow-up.6 Herein, we present a case of HHD refractory to numerous prior therapies that was successfully treated with electron beam radiotherapy, highlighting the potential role for palliative radiotherapy in select refractory cases of HHD.
A 35-year-old woman with a 7-year of history of HHD presented with severe recalcitrant disease including extensive erosive patches and plaques in the intertriginous areas of the bilateral axillae, groin, and inframammary folds (Figure 1). The skin eruptions first appeared at 28 years of age after her last pregnancy and continued as painful blistering that worsened with each menstrual cycle. Initially the affected desquamated skin would heal between menstrual cycles, but large areas of desquamation remained unhealed in the groin and inframammary regions throughout her full menstrual cycles by the time of referral. Family history included 4 family members with HHD: 2 aunts, an uncle, and a cousin on the paternal side of her family. Over a 7-year period, treatment with clobetasol cream, clindamycin gel, tacrolimus ointment, doxycycline, dapsone, cyclosporine, methotrexate, etanercept, isotretinoin, and prednisone (15 mg every other day) all failed. Most recently, axillary abobotulinumtoxinA injections were attempted but failed. She had been prednisone dependent for more than 1 year. Due to the ongoing refractory disease, she was referred to radiation oncology to discuss radiotherapy treatment options.

At the time of presentation to the radiation oncology clinic, she continued to have extensive involvement of the intertriginous areas as well as involvement of the right neck at sites of skin chafing from clothing. Consistent with the limited available evidence, a dose of 20 Gy in 10 fractions was first prescribed to the axillae to assess response in the event of radiosensitivity, resulting in brisk desquamation. The conventional fractionation of 2 Gy per fraction allowed for assessment of response/tolerance and the opportunity to stop the treatment in the unlikely event of a severe skin reaction. Her skin tolerated treatment well with slight dryness and mild irritation that was less severe than the typical HHD flares. Concurrently with the axillary radiotherapy, we delivered a trial of low-level laser therapy to areas of severe disease in both inguinal regions in the hope that it could be used instead of radiotherapy to avoid any associated risks of radiation. Low-level laser therapy was administered with a light-emitting diode cluster probe at 2.5 Hz for 1 minute to 2 sites in each inguinal area daily for a total of 10 treatments. Unfortunately, this therapy temporarily exacerbated exudation present in the skin before it resolved to its pretreatment state with no improvement.
One month after treatment she had total resolution of the erosive patches and plaques with mild residual hyperpigmentation in the axillae, establishing that radiation therapy was reasonably effective. To lower the total radiation dose and decrease the risk of radiation-induced malignancy, we treated the bilateral groin and the inframammary region with a treatment schedule of 8 Gy in 2 fractions at a higher dose of 4 Gy per fraction instead of 2 Gy. At 12 days posttreatment, she had a dramatic response in the groin and a mixed response in the inframammary region, with a focus that had not yet regressed. Given the dramatic response in the treated sites, the patient requested treatment to the right side of the neck. Thus, we treated this area with a similar 8 Gy in 2 fractions, and an additional 6 Gy in 2 fractions boost was added to the slow responding focus in the inframammary fold for a total of 14 Gy in 4 fractions. The patient tolerated all treatments well with mild grade 1 skin irritation that was unlike the blistering of the typical HHD flares. Two months following completion of the first course of radiotherapy to the axillae and 2 weeks from the most recent course, she tapered off her prednisone regimen (15 mg every other day) but had a relapse of disease with her subsequent menstrual cycles that presented as a blistering skin reaction in the inframammary region, which healed in response to restarting steroids. This flare was less severe than those prior to radiotherapy. At 10 months posttreatment, the patient was free of disease in the neck and axillae (Figure 2). She continued to have relapses in the inframammary region with menstrual cycles and noted new disease in the popliteal regions; however, the relapses were less severe, and her skin had improved more with radiation than any of the prior therapies.

Our experience with low-level laser therapy indicated that it should be completely avoided in HHD. Our patient’s treatment with radiotherapy demonstrated excellent short-term responses in areas of pemphigus but later proved to be a mixed response with further follow-up including a mild posttreatment flare of the inframammary region that responded to steroids and new popliteal region involvement. As summarized in the Table, earlier reports of radiotherapy for the treatment of HHD have yielded varied results.6-8 The mixed response seen in our patient suggests that response to radiotherapy may be site specific, related to underlying inflammation from microbial overgrowth, or a function of the disease severity.

Although the number of reports on radiotherapy in HHD is small, there have been several reports of Darier disease, another acantholytic autosomal-dominant genodermatosis affecting the ATP2A2 gene, successfully treated incidentally with radiation.9,10 Total skin electron beam therapy also has been employed in the treatment of Darier disease; this patient experienced a severe flare after a relatively low treatment dose that required intensive care monitoring, possibly highlighting the potential radiosensitivity of patients with underlying genodermatoses and cautioning against radiotherapy dose escalation.11 In light of the mixed responses seen, radiation therapy should be used sparingly for severe relapsing cases that have failed a plethora of prior treatments. The risk of second cancer induction is especially of concern when using radiotherapy in a benign disease.12 We observed excellent initial responses in our patient, both with conventionally fractionated radiotherapy and hypofractionation. The risk of second malignancy induction is a linear function of radiotherapy dose.12 Thus, utilization of hypofractionated regimens such as 4 Gy times 2 fractions seems most prudent. It remains unclear if further dose de-escalation may yield a similar response, as seen in studies utilizing radiotherapy for other benign disease.13,14 Overall, given our mixed results with short follow-up, we conclude that the consideration of radiotherapy should be limited to patients with severe recalcitrant HHD.
- Dhitavat J, Fairclough RJ, Hovnanian A, et al. Calcium pumps and keratinocytes: lessons from Darier’s disease and Hailey-Hailey disease. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:821-828.
- Hu Z, Bonifas JM, Beech J, et al. Mutations in ATP2C1, encoding a calcium pump, cause Hailey-Hailey disease. Nat Genet. 2000;24:61-65.
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282.
- Chiaravalloti A, Payette M. Hailey-Hailey disease and review of management. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1254-1257.
- Zhang F, Yan X, Jiang D, et al. Eight novel mutations of ATP2C1 identified in 17 Chinese families with Hailey-Hailey disease. Dermatology. 2007;215:277-283.
- Narbutt J, Chrusciel A, Rychter A, et al. Persistent improvement of previously recalcitrant Hailey-Hailey disease with electron beam radiotherapy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:179-182.
- Sarkany I. Grenz-ray treatment of familial benign chronic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 1959;71:247-252.
- Roos DE, Reid CM. Benign familial pemphigus: little benefit from superficial radiotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:305-308.
- Podgornii A, Ciammella P, Ramundo D, et al. Efficacy of the radiotherapy on Darier’s disease: an indirect evidence. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2013;2013:907802.
- Mac Manus MP, Cavalleri G, Ball DL, et al. Exacerbation, then clearance, of mutation-proven Darier’s disease of the skin after radiotherapy for bronchial carcinoma: a case of radiation-induced epidermal differentiation? Radiat Res. 2001;156:724-730.
- Kittridge A, Wahlgren C, Fuhrer R, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant Darier’s disease with electron beam therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:302-304.
- Preston DL, Shimizu Y, Pierce DA, et al. Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. report 13: solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950-1997. Radiat Res. 2003;160:381-407.
- Fröhlich D, Baaske D, Glatzel M. Radiotherapy of hidradenitis suppurativa—still valid today? [in German]. Strahlenther Onkol. 2000;176:286-289.
- Heyd R, Tselis N, Ackermann H, et al. Radiation therapy for painful heel spurs: results of a prospective randomized study. Strahlenther Onkol. 2007;183:3-9.
- Dhitavat J, Fairclough RJ, Hovnanian A, et al. Calcium pumps and keratinocytes: lessons from Darier’s disease and Hailey-Hailey disease. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:821-828.
- Hu Z, Bonifas JM, Beech J, et al. Mutations in ATP2C1, encoding a calcium pump, cause Hailey-Hailey disease. Nat Genet. 2000;24:61-65.
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282.
- Chiaravalloti A, Payette M. Hailey-Hailey disease and review of management. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:1254-1257.
- Zhang F, Yan X, Jiang D, et al. Eight novel mutations of ATP2C1 identified in 17 Chinese families with Hailey-Hailey disease. Dermatology. 2007;215:277-283.
- Narbutt J, Chrusciel A, Rychter A, et al. Persistent improvement of previously recalcitrant Hailey-Hailey disease with electron beam radiotherapy. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:179-182.
- Sarkany I. Grenz-ray treatment of familial benign chronic pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 1959;71:247-252.
- Roos DE, Reid CM. Benign familial pemphigus: little benefit from superficial radiotherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2002;43:305-308.
- Podgornii A, Ciammella P, Ramundo D, et al. Efficacy of the radiotherapy on Darier’s disease: an indirect evidence. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2013;2013:907802.
- Mac Manus MP, Cavalleri G, Ball DL, et al. Exacerbation, then clearance, of mutation-proven Darier’s disease of the skin after radiotherapy for bronchial carcinoma: a case of radiation-induced epidermal differentiation? Radiat Res. 2001;156:724-730.
- Kittridge A, Wahlgren C, Fuhrer R, et al. Treatment of recalcitrant Darier’s disease with electron beam therapy. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:302-304.
- Preston DL, Shimizu Y, Pierce DA, et al. Studies of mortality of atomic bomb survivors. report 13: solid cancer and noncancer disease mortality: 1950-1997. Radiat Res. 2003;160:381-407.
- Fröhlich D, Baaske D, Glatzel M. Radiotherapy of hidradenitis suppurativa—still valid today? [in German]. Strahlenther Onkol. 2000;176:286-289.
- Heyd R, Tselis N, Ackermann H, et al. Radiation therapy for painful heel spurs: results of a prospective randomized study. Strahlenther Onkol. 2007;183:3-9.
Practice Points
- Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) is a rare blistering dermatosis characterized by recurrent erythematous plaques with a predilection for the intertriginous areas.
- Electron beam radiotherapy is a potential treatment option for local control in patients with recalcitrant HHD.