User login
Relapsed MCL: Options for treatment
CHICAGO – according to Kristie A. Blum, MD.
Venetoclax and lenalidomide can also be considered in the relapsed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) setting, Dr. Blum, a professor in the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University in Atlanta, said at the American Society of Hematology Meeting on Hematologic Malignancies.
“I tend to favor BTK inhibitors as my first line of therapy,” she said, later qualifying that this applies when clinical trial enrollment is unavailable.
Ibrutinib
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib is well established as a treatment for MCL and for use in the relapsed setting, she said, noting that pooled data from the phase 2 CYC-1104 trial, the phase 2 MCL 2001 (SPARK) trial, and the phase 3 MCL3001 (RAY) trial showed an overall response (OR) rate of 66% in 370 patients and a complete response (CR) rate of 20%.
The median duration of response (DOR) was 18.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.8 months, and median overall survival (OS) was 25 months (Br J Haematol. 2017 Nov;179[3]:430-8).
Adding rituximab to ibrutinib (R-ibrutinib) improved outcomes, at least in one single center phase 2 trial of 50 relapsed patients with a median of three prior therapies, she said. The OR rate in that study was 88%, and the CR rate was 58% (Br J Haematol. 2018 May;182[3]:404-11).
“What was really impressive to me was that the median duration of response was about 46 months. PFS was 43 months, and patients were on [treatment] as long as 56 cycles,” she said.
Acalabrutinib
The newer BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib also shows benefit in the relapsed MCL setting, Dr. Blum said.
In a recent multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study of 124 patients with a median age of 68 years and a median of two prior therapies, acalabrutinib at a dose of 100 mg twice daily was associated with an OR rate of 81% and a CR rate of 40% (Lancet. 2018 Feb 17;391:659-67).
“Seems a little better than what you’d expect with single agent ibrutinib,” she said, noting that median DOR and PFS have not been reached in that study.
The main toxicities have been “headache and some diarrhea,” but follow-up is currently only about 15 months, she added.
Venetoclax
Another option in this setting is the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor venetoclax, which was shown in a recent phase 1 study of patients with various lymphoma subtypes to have activity in relapsed MCL, Dr. Blum said.
The OR rate in 28 relapsed MCL patients in that study was 75%, and the median PFS was 14 months (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar;35:826-33).
Additionally, an “intriguing combination study of venetoclax and ibrutinib” was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, she noted.
That study included only 23 patients with relapsed MCL, but they were a “pretty high-risk” group with a median age of 68 years, about half having a TP53 abnormality, and 30% having a prior transplant.
The OR and CR rates at 16 weeks by positron emission tomography were 71% and 62%, respectively (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378:1211-23).
“Actually, about 40% achieved [minimal residual disease] negativity, but this was only checked in about half the patients,” she said. “So this is an intriguing combination and hopefully something we’ll see more of in the upcoming years.”
Lenalidomide
In the randomized phase 2 SPRINT study, patients received either single-agent lenolidamine or the investigator’s choice of single-agent rituximab, gemcitabine, fludarabine, chlorambucil, or cytarabine.
The expected OR rate in 170 patients treated with lenalidomide was 40% versus 11% in 84 patients treated with investigator’s choice of treatment, and the respective CR rates were 5% and 0% (Lancet Oncol. 2016 Mar 1;17(3):319-31).
Median DOR was 16 months versus 10.4 months, PFS was 8.7 versus 5.2 months, and median OS was 27.9 versus 21.1 months in the groups, respectively.
Other options
Combination regimens, such as R-CHOP and R-bendamustine, are also options for the treatment of relapsed MCL patients who haven’t received combination therapy in the past, Dr. Blum said. Transplant is another option in some patients.
“I will consider transplants for younger patients if they come to me and they actually hadn’t had one in [their] first CR,” she said.
Dr. Blum is a consultant for Acerta, AstraZeneca, and Molecular Templates and has received research funding from Acerta, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Cephalon, Immunomedics, Janssen, Merck, Millennium, Molecular Templates, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Seattle Genetics.
CHICAGO – according to Kristie A. Blum, MD.
Venetoclax and lenalidomide can also be considered in the relapsed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) setting, Dr. Blum, a professor in the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University in Atlanta, said at the American Society of Hematology Meeting on Hematologic Malignancies.
“I tend to favor BTK inhibitors as my first line of therapy,” she said, later qualifying that this applies when clinical trial enrollment is unavailable.
Ibrutinib
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib is well established as a treatment for MCL and for use in the relapsed setting, she said, noting that pooled data from the phase 2 CYC-1104 trial, the phase 2 MCL 2001 (SPARK) trial, and the phase 3 MCL3001 (RAY) trial showed an overall response (OR) rate of 66% in 370 patients and a complete response (CR) rate of 20%.
The median duration of response (DOR) was 18.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.8 months, and median overall survival (OS) was 25 months (Br J Haematol. 2017 Nov;179[3]:430-8).
Adding rituximab to ibrutinib (R-ibrutinib) improved outcomes, at least in one single center phase 2 trial of 50 relapsed patients with a median of three prior therapies, she said. The OR rate in that study was 88%, and the CR rate was 58% (Br J Haematol. 2018 May;182[3]:404-11).
“What was really impressive to me was that the median duration of response was about 46 months. PFS was 43 months, and patients were on [treatment] as long as 56 cycles,” she said.
Acalabrutinib
The newer BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib also shows benefit in the relapsed MCL setting, Dr. Blum said.
In a recent multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study of 124 patients with a median age of 68 years and a median of two prior therapies, acalabrutinib at a dose of 100 mg twice daily was associated with an OR rate of 81% and a CR rate of 40% (Lancet. 2018 Feb 17;391:659-67).
“Seems a little better than what you’d expect with single agent ibrutinib,” she said, noting that median DOR and PFS have not been reached in that study.
The main toxicities have been “headache and some diarrhea,” but follow-up is currently only about 15 months, she added.
Venetoclax
Another option in this setting is the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor venetoclax, which was shown in a recent phase 1 study of patients with various lymphoma subtypes to have activity in relapsed MCL, Dr. Blum said.
The OR rate in 28 relapsed MCL patients in that study was 75%, and the median PFS was 14 months (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar;35:826-33).
Additionally, an “intriguing combination study of venetoclax and ibrutinib” was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, she noted.
That study included only 23 patients with relapsed MCL, but they were a “pretty high-risk” group with a median age of 68 years, about half having a TP53 abnormality, and 30% having a prior transplant.
The OR and CR rates at 16 weeks by positron emission tomography were 71% and 62%, respectively (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378:1211-23).
“Actually, about 40% achieved [minimal residual disease] negativity, but this was only checked in about half the patients,” she said. “So this is an intriguing combination and hopefully something we’ll see more of in the upcoming years.”
Lenalidomide
In the randomized phase 2 SPRINT study, patients received either single-agent lenolidamine or the investigator’s choice of single-agent rituximab, gemcitabine, fludarabine, chlorambucil, or cytarabine.
The expected OR rate in 170 patients treated with lenalidomide was 40% versus 11% in 84 patients treated with investigator’s choice of treatment, and the respective CR rates were 5% and 0% (Lancet Oncol. 2016 Mar 1;17(3):319-31).
Median DOR was 16 months versus 10.4 months, PFS was 8.7 versus 5.2 months, and median OS was 27.9 versus 21.1 months in the groups, respectively.
Other options
Combination regimens, such as R-CHOP and R-bendamustine, are also options for the treatment of relapsed MCL patients who haven’t received combination therapy in the past, Dr. Blum said. Transplant is another option in some patients.
“I will consider transplants for younger patients if they come to me and they actually hadn’t had one in [their] first CR,” she said.
Dr. Blum is a consultant for Acerta, AstraZeneca, and Molecular Templates and has received research funding from Acerta, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Cephalon, Immunomedics, Janssen, Merck, Millennium, Molecular Templates, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Seattle Genetics.
CHICAGO – according to Kristie A. Blum, MD.
Venetoclax and lenalidomide can also be considered in the relapsed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) setting, Dr. Blum, a professor in the department of hematology and medical oncology at Emory University in Atlanta, said at the American Society of Hematology Meeting on Hematologic Malignancies.
“I tend to favor BTK inhibitors as my first line of therapy,” she said, later qualifying that this applies when clinical trial enrollment is unavailable.
Ibrutinib
The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib is well established as a treatment for MCL and for use in the relapsed setting, she said, noting that pooled data from the phase 2 CYC-1104 trial, the phase 2 MCL 2001 (SPARK) trial, and the phase 3 MCL3001 (RAY) trial showed an overall response (OR) rate of 66% in 370 patients and a complete response (CR) rate of 20%.
The median duration of response (DOR) was 18.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.8 months, and median overall survival (OS) was 25 months (Br J Haematol. 2017 Nov;179[3]:430-8).
Adding rituximab to ibrutinib (R-ibrutinib) improved outcomes, at least in one single center phase 2 trial of 50 relapsed patients with a median of three prior therapies, she said. The OR rate in that study was 88%, and the CR rate was 58% (Br J Haematol. 2018 May;182[3]:404-11).
“What was really impressive to me was that the median duration of response was about 46 months. PFS was 43 months, and patients were on [treatment] as long as 56 cycles,” she said.
Acalabrutinib
The newer BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib also shows benefit in the relapsed MCL setting, Dr. Blum said.
In a recent multicenter, open-label, phase 2 study of 124 patients with a median age of 68 years and a median of two prior therapies, acalabrutinib at a dose of 100 mg twice daily was associated with an OR rate of 81% and a CR rate of 40% (Lancet. 2018 Feb 17;391:659-67).
“Seems a little better than what you’d expect with single agent ibrutinib,” she said, noting that median DOR and PFS have not been reached in that study.
The main toxicities have been “headache and some diarrhea,” but follow-up is currently only about 15 months, she added.
Venetoclax
Another option in this setting is the B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor venetoclax, which was shown in a recent phase 1 study of patients with various lymphoma subtypes to have activity in relapsed MCL, Dr. Blum said.
The OR rate in 28 relapsed MCL patients in that study was 75%, and the median PFS was 14 months (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Mar;35:826-33).
Additionally, an “intriguing combination study of venetoclax and ibrutinib” was recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine, she noted.
That study included only 23 patients with relapsed MCL, but they were a “pretty high-risk” group with a median age of 68 years, about half having a TP53 abnormality, and 30% having a prior transplant.
The OR and CR rates at 16 weeks by positron emission tomography were 71% and 62%, respectively (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378:1211-23).
“Actually, about 40% achieved [minimal residual disease] negativity, but this was only checked in about half the patients,” she said. “So this is an intriguing combination and hopefully something we’ll see more of in the upcoming years.”
Lenalidomide
In the randomized phase 2 SPRINT study, patients received either single-agent lenolidamine or the investigator’s choice of single-agent rituximab, gemcitabine, fludarabine, chlorambucil, or cytarabine.
The expected OR rate in 170 patients treated with lenalidomide was 40% versus 11% in 84 patients treated with investigator’s choice of treatment, and the respective CR rates were 5% and 0% (Lancet Oncol. 2016 Mar 1;17(3):319-31).
Median DOR was 16 months versus 10.4 months, PFS was 8.7 versus 5.2 months, and median OS was 27.9 versus 21.1 months in the groups, respectively.
Other options
Combination regimens, such as R-CHOP and R-bendamustine, are also options for the treatment of relapsed MCL patients who haven’t received combination therapy in the past, Dr. Blum said. Transplant is another option in some patients.
“I will consider transplants for younger patients if they come to me and they actually hadn’t had one in [their] first CR,” she said.
Dr. Blum is a consultant for Acerta, AstraZeneca, and Molecular Templates and has received research funding from Acerta, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Cephalon, Immunomedics, Janssen, Merck, Millennium, Molecular Templates, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, and Seattle Genetics.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM MHM 2018
Resuming DOAC therapy in AF patients after gastrointestinal bleed
Clinical question: For patients who develop a gastrointestinal bleed (GIB) while using direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy for atrial fibrillation (AF), does the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) or recurrent GIB increase after DOAC resumption?
Background: DOACs are increasingly used for stroke prophylaxis in nonvalvular AF and can increase the risk of GIB by 30% compared to warfarin. Although warfarin can be safely resumed within 14 days of GIB cessation, outcomes related to resuming DOAC therapy after hospitalization for GIB are lacking.
Study design: Retrospective analysis of claims data.
Setting: Patients with AF on DOAC therapy admitted for acute GIB in Michigan.
Synopsis: 1,338 adults, median age 79 years, on a DOAC for AF were hospitalized for GIB. After the index hospitalization, patients were followed for resumption of DOAC (defined by new prescription fill), recurrent bleeding, and VTE. 62% of patients resumed DOAC therapy.
Resuming a DOAC within 30 days did not lead to a statistically significant difference in VTE or recurrence of GIB at 90 days or 6 months. However, at 90 days recurrent GIB risk increased with concomitant use of antiplatelet agents (hazard ratio, 3.12; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-5.81; P = .002). Rivaroxaban had higher rates of rebleeding events, compared with the other DOACs (P = .04). History of VTE increased the risk for postdischarge VTE. Key limitations included lack of cerebrovascular accident rates, exclusion of patients who switched from DOAC to warfarin, and uncertainty surrounding the timing of actual DOAC resumption.
Bottom line: DOAC resumption within 30 days of GIB did not increase VTE or recurrent GIB, but concurrent antiplatelet agent use increased recurrent GIB rates.
Citation: Sengupta N et al. Rebleeding vs. thromboembolism after hospitalization for gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on direct oral anticoagulants. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.005.
Dr. Naderi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of Colorado, Denver.
Clinical question: For patients who develop a gastrointestinal bleed (GIB) while using direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy for atrial fibrillation (AF), does the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) or recurrent GIB increase after DOAC resumption?
Background: DOACs are increasingly used for stroke prophylaxis in nonvalvular AF and can increase the risk of GIB by 30% compared to warfarin. Although warfarin can be safely resumed within 14 days of GIB cessation, outcomes related to resuming DOAC therapy after hospitalization for GIB are lacking.
Study design: Retrospective analysis of claims data.
Setting: Patients with AF on DOAC therapy admitted for acute GIB in Michigan.
Synopsis: 1,338 adults, median age 79 years, on a DOAC for AF were hospitalized for GIB. After the index hospitalization, patients were followed for resumption of DOAC (defined by new prescription fill), recurrent bleeding, and VTE. 62% of patients resumed DOAC therapy.
Resuming a DOAC within 30 days did not lead to a statistically significant difference in VTE or recurrence of GIB at 90 days or 6 months. However, at 90 days recurrent GIB risk increased with concomitant use of antiplatelet agents (hazard ratio, 3.12; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-5.81; P = .002). Rivaroxaban had higher rates of rebleeding events, compared with the other DOACs (P = .04). History of VTE increased the risk for postdischarge VTE. Key limitations included lack of cerebrovascular accident rates, exclusion of patients who switched from DOAC to warfarin, and uncertainty surrounding the timing of actual DOAC resumption.
Bottom line: DOAC resumption within 30 days of GIB did not increase VTE or recurrent GIB, but concurrent antiplatelet agent use increased recurrent GIB rates.
Citation: Sengupta N et al. Rebleeding vs. thromboembolism after hospitalization for gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on direct oral anticoagulants. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.005.
Dr. Naderi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of Colorado, Denver.
Clinical question: For patients who develop a gastrointestinal bleed (GIB) while using direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy for atrial fibrillation (AF), does the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) or recurrent GIB increase after DOAC resumption?
Background: DOACs are increasingly used for stroke prophylaxis in nonvalvular AF and can increase the risk of GIB by 30% compared to warfarin. Although warfarin can be safely resumed within 14 days of GIB cessation, outcomes related to resuming DOAC therapy after hospitalization for GIB are lacking.
Study design: Retrospective analysis of claims data.
Setting: Patients with AF on DOAC therapy admitted for acute GIB in Michigan.
Synopsis: 1,338 adults, median age 79 years, on a DOAC for AF were hospitalized for GIB. After the index hospitalization, patients were followed for resumption of DOAC (defined by new prescription fill), recurrent bleeding, and VTE. 62% of patients resumed DOAC therapy.
Resuming a DOAC within 30 days did not lead to a statistically significant difference in VTE or recurrence of GIB at 90 days or 6 months. However, at 90 days recurrent GIB risk increased with concomitant use of antiplatelet agents (hazard ratio, 3.12; 95% confidence interval, 1.55-5.81; P = .002). Rivaroxaban had higher rates of rebleeding events, compared with the other DOACs (P = .04). History of VTE increased the risk for postdischarge VTE. Key limitations included lack of cerebrovascular accident rates, exclusion of patients who switched from DOAC to warfarin, and uncertainty surrounding the timing of actual DOAC resumption.
Bottom line: DOAC resumption within 30 days of GIB did not increase VTE or recurrent GIB, but concurrent antiplatelet agent use increased recurrent GIB rates.
Citation: Sengupta N et al. Rebleeding vs. thromboembolism after hospitalization for gastrointestinal bleeding in patients on direct oral anticoagulants. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.05.005.
Dr. Naderi is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, University of Colorado, Denver.
USPSTF: screen for ‘unhealthy’ alcohol use
Also today, dialysis decisions in elderly patients need to account for comorbidities, chronic liver disease is independently linked to increased risk of falls, and barriers to naloxone remain, despite new access laws.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, dialysis decisions in elderly patients need to account for comorbidities, chronic liver disease is independently linked to increased risk of falls, and barriers to naloxone remain, despite new access laws.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Also today, dialysis decisions in elderly patients need to account for comorbidities, chronic liver disease is independently linked to increased risk of falls, and barriers to naloxone remain, despite new access laws.
Amazon Alexa
Apple Podcasts
Google Podcasts
Spotify
Score can predict thrombosis in ITP
New research suggests a scoring system can predict the risk of thrombosis in patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who are taking anticoagulants.
Researchers tested their Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (TH2) risk assessment score in a small group of ITP patients on anticoagulants, and the score identified all seven patients who developed thrombosis.
The researchers also found that patients’ TH2 scores changed quickly—within a matter of days—which suggests they should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently.
Amaris K. Balitsky, MD, of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, and her colleagues detailed this research in Blood.
About the score
To develop the TH2 score, the researchers conducted a review of the literature and existing tools used to assess the risk of thrombosis and bleeding. The resulting score consists of two thrombosis items and two bleeding items.
The thrombosis items are:
- High thrombotic risk, which includes patients with atrial fibrillation and a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than five; unprovoked, recurrent, or cancer-associated thrombosis; or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- Receipt of ITP therapies known to increase the risk of thrombosis in the previous 14 days or splenectomy in the previous 30 days.
The score’s bleeding items are:
- Platelet count less than 20 x 109/L
- Major bleeding (grade 2 bleeding that does not involve the skin) observed at a clinical encounter.
Each thrombosis item is assigned a score of +1, and each bleeding item is assigned a score of -1. A positive score or score of 0 suggests a net increased risk of thrombosis, and a negative score suggests a net increased risk of bleeding.
Patient population
The researchers tested the TH2 score in patients enrolled in the McMaster ITP Registry from 2010 to 2017.
There were 314 patients enrolled, but only 13 were receiving anticoagulation and had a platelet count less than 50 x 109/L. Six of these patients were receiving anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation and seven for venous thrombosis. Four patients were taking antiplatelet agents as well.
The median follow up was 9 months (interquartile range, 4.5 to 24 months). During that time, there were 41 clinical encounters. Data on treatment decisions and clinical outcomes were available for 32 of these encounters.
Ten of the 13 patients had anticoagulation withheld at some point during their 22 clinical encounters. Major bleeding was present at five of the encounters. At 17 encounters, patients received additional ITP treatments.
Six of the 10 patients who stopped anticoagulation had new thrombotic events, and two of these events were fatal. Three of the patients had thrombotic events even though they resumed anticoagulation.
The remaining three patients (of the 13) did not stop anticoagulation. These patients received additional ITP treatments at six of their 10 clinical encounters.
Major bleeding was present at two of the 10 encounters, and one new thrombotic event occurred in a patient with metastatic squamous cell cancer (despite continued treatment with warfarin).
Testing the score
The TH2 score accurately predicted all seven thrombotic events.
There were four patients who initially had a negative TH2 score, which suggested an increased risk of bleeding.
However, these patients had a positive or 0 score—suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis—when they were assessed again, after their platelet counts increased above 50 x 109/L.
The remaining three patients had initial scores of 0 and subsequent positive scores, both suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis.
The researchers said these findings suggest patients should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently, as ITP treatments are given and platelet counts increase.
“The results of our study suggest that the risk of thrombosis is high in patients with ITP who have a separate indication for anticoagulation, especially after ITP therapies are administered and the severe thrombocytopenia improves,” the researchers wrote. “Early resumption of anticoagulation should be considered in this population.”
The researchers also noted that this study was limited by its retrospective, single-center design and the small number of patients evaluated. Therefore, the TH2 score should be validated in additional, larger studies.
One researcher reported relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Principia Biopharma. The other researchers said they had no competing financial interests.
New research suggests a scoring system can predict the risk of thrombosis in patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who are taking anticoagulants.
Researchers tested their Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (TH2) risk assessment score in a small group of ITP patients on anticoagulants, and the score identified all seven patients who developed thrombosis.
The researchers also found that patients’ TH2 scores changed quickly—within a matter of days—which suggests they should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently.
Amaris K. Balitsky, MD, of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, and her colleagues detailed this research in Blood.
About the score
To develop the TH2 score, the researchers conducted a review of the literature and existing tools used to assess the risk of thrombosis and bleeding. The resulting score consists of two thrombosis items and two bleeding items.
The thrombosis items are:
- High thrombotic risk, which includes patients with atrial fibrillation and a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than five; unprovoked, recurrent, or cancer-associated thrombosis; or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- Receipt of ITP therapies known to increase the risk of thrombosis in the previous 14 days or splenectomy in the previous 30 days.
The score’s bleeding items are:
- Platelet count less than 20 x 109/L
- Major bleeding (grade 2 bleeding that does not involve the skin) observed at a clinical encounter.
Each thrombosis item is assigned a score of +1, and each bleeding item is assigned a score of -1. A positive score or score of 0 suggests a net increased risk of thrombosis, and a negative score suggests a net increased risk of bleeding.
Patient population
The researchers tested the TH2 score in patients enrolled in the McMaster ITP Registry from 2010 to 2017.
There were 314 patients enrolled, but only 13 were receiving anticoagulation and had a platelet count less than 50 x 109/L. Six of these patients were receiving anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation and seven for venous thrombosis. Four patients were taking antiplatelet agents as well.
The median follow up was 9 months (interquartile range, 4.5 to 24 months). During that time, there were 41 clinical encounters. Data on treatment decisions and clinical outcomes were available for 32 of these encounters.
Ten of the 13 patients had anticoagulation withheld at some point during their 22 clinical encounters. Major bleeding was present at five of the encounters. At 17 encounters, patients received additional ITP treatments.
Six of the 10 patients who stopped anticoagulation had new thrombotic events, and two of these events were fatal. Three of the patients had thrombotic events even though they resumed anticoagulation.
The remaining three patients (of the 13) did not stop anticoagulation. These patients received additional ITP treatments at six of their 10 clinical encounters.
Major bleeding was present at two of the 10 encounters, and one new thrombotic event occurred in a patient with metastatic squamous cell cancer (despite continued treatment with warfarin).
Testing the score
The TH2 score accurately predicted all seven thrombotic events.
There were four patients who initially had a negative TH2 score, which suggested an increased risk of bleeding.
However, these patients had a positive or 0 score—suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis—when they were assessed again, after their platelet counts increased above 50 x 109/L.
The remaining three patients had initial scores of 0 and subsequent positive scores, both suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis.
The researchers said these findings suggest patients should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently, as ITP treatments are given and platelet counts increase.
“The results of our study suggest that the risk of thrombosis is high in patients with ITP who have a separate indication for anticoagulation, especially after ITP therapies are administered and the severe thrombocytopenia improves,” the researchers wrote. “Early resumption of anticoagulation should be considered in this population.”
The researchers also noted that this study was limited by its retrospective, single-center design and the small number of patients evaluated. Therefore, the TH2 score should be validated in additional, larger studies.
One researcher reported relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Principia Biopharma. The other researchers said they had no competing financial interests.
New research suggests a scoring system can predict the risk of thrombosis in patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who are taking anticoagulants.
Researchers tested their Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (TH2) risk assessment score in a small group of ITP patients on anticoagulants, and the score identified all seven patients who developed thrombosis.
The researchers also found that patients’ TH2 scores changed quickly—within a matter of days—which suggests they should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently.
Amaris K. Balitsky, MD, of McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, and her colleagues detailed this research in Blood.
About the score
To develop the TH2 score, the researchers conducted a review of the literature and existing tools used to assess the risk of thrombosis and bleeding. The resulting score consists of two thrombosis items and two bleeding items.
The thrombosis items are:
- High thrombotic risk, which includes patients with atrial fibrillation and a CHA2DS2-VASc score greater than five; unprovoked, recurrent, or cancer-associated thrombosis; or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
- Receipt of ITP therapies known to increase the risk of thrombosis in the previous 14 days or splenectomy in the previous 30 days.
The score’s bleeding items are:
- Platelet count less than 20 x 109/L
- Major bleeding (grade 2 bleeding that does not involve the skin) observed at a clinical encounter.
Each thrombosis item is assigned a score of +1, and each bleeding item is assigned a score of -1. A positive score or score of 0 suggests a net increased risk of thrombosis, and a negative score suggests a net increased risk of bleeding.
Patient population
The researchers tested the TH2 score in patients enrolled in the McMaster ITP Registry from 2010 to 2017.
There were 314 patients enrolled, but only 13 were receiving anticoagulation and had a platelet count less than 50 x 109/L. Six of these patients were receiving anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation and seven for venous thrombosis. Four patients were taking antiplatelet agents as well.
The median follow up was 9 months (interquartile range, 4.5 to 24 months). During that time, there were 41 clinical encounters. Data on treatment decisions and clinical outcomes were available for 32 of these encounters.
Ten of the 13 patients had anticoagulation withheld at some point during their 22 clinical encounters. Major bleeding was present at five of the encounters. At 17 encounters, patients received additional ITP treatments.
Six of the 10 patients who stopped anticoagulation had new thrombotic events, and two of these events were fatal. Three of the patients had thrombotic events even though they resumed anticoagulation.
The remaining three patients (of the 13) did not stop anticoagulation. These patients received additional ITP treatments at six of their 10 clinical encounters.
Major bleeding was present at two of the 10 encounters, and one new thrombotic event occurred in a patient with metastatic squamous cell cancer (despite continued treatment with warfarin).
Testing the score
The TH2 score accurately predicted all seven thrombotic events.
There were four patients who initially had a negative TH2 score, which suggested an increased risk of bleeding.
However, these patients had a positive or 0 score—suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis—when they were assessed again, after their platelet counts increased above 50 x 109/L.
The remaining three patients had initial scores of 0 and subsequent positive scores, both suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis.
The researchers said these findings suggest patients should be re-evaluated for thrombosis risk frequently, as ITP treatments are given and platelet counts increase.
“The results of our study suggest that the risk of thrombosis is high in patients with ITP who have a separate indication for anticoagulation, especially after ITP therapies are administered and the severe thrombocytopenia improves,” the researchers wrote. “Early resumption of anticoagulation should be considered in this population.”
The researchers also noted that this study was limited by its retrospective, single-center design and the small number of patients evaluated. Therefore, the TH2 score should be validated in additional, larger studies.
One researcher reported relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Principia Biopharma. The other researchers said they had no competing financial interests.
Health Canada approves two tests for CML patients
Health Canada has approved the use of two tests designed to detect BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)—the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit.
MolecularMD’s MRDx® BCR-ABL Test is approved as an aid to monitor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML patients.
This test is also approved to identify CML patients in the chronic phase being treated with nilotinib who, after sustaining a deep molecular response of MR4.5, may be eligible to stop treatment and be monitored for treatment-free remission.
Asuragen, Inc.’s QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is approved for use in CML patients, regardless of whether they are taking a TKI or how their disease is being managed.
The kit is designed to detect and quantify major breakpoint (e13a2, e14a2) BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts for use in monitoring molecular response.
Both the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit are approved in the United States as well.
The QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is also CE marked for clinical use in the European Union.
Health Canada has approved the use of two tests designed to detect BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)—the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit.
MolecularMD’s MRDx® BCR-ABL Test is approved as an aid to monitor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML patients.
This test is also approved to identify CML patients in the chronic phase being treated with nilotinib who, after sustaining a deep molecular response of MR4.5, may be eligible to stop treatment and be monitored for treatment-free remission.
Asuragen, Inc.’s QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is approved for use in CML patients, regardless of whether they are taking a TKI or how their disease is being managed.
The kit is designed to detect and quantify major breakpoint (e13a2, e14a2) BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts for use in monitoring molecular response.
Both the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit are approved in the United States as well.
The QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is also CE marked for clinical use in the European Union.
Health Canada has approved the use of two tests designed to detect BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)—the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit.
MolecularMD’s MRDx® BCR-ABL Test is approved as an aid to monitor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy in Philadelphia chromosome-positive CML patients.
This test is also approved to identify CML patients in the chronic phase being treated with nilotinib who, after sustaining a deep molecular response of MR4.5, may be eligible to stop treatment and be monitored for treatment-free remission.
Asuragen, Inc.’s QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is approved for use in CML patients, regardless of whether they are taking a TKI or how their disease is being managed.
The kit is designed to detect and quantify major breakpoint (e13a2, e14a2) BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts for use in monitoring molecular response.
Both the MRDx® BCR-ABL Test and the QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit are approved in the United States as well.
The QuantideX qPCR BCR-ABL IS Kit is also CE marked for clinical use in the European Union.
Preoperative anemia management saves blood, money
BOSTON—Results of a pilot program suggest preoperative management of anemia can reduce transfusion rates and cut costs, but the effect on patient outcomes isn’t clear.
For this program, anemic patients received dietary guidance and supplementation prior to surgery.
This increased day-of-surgery hemoglobin levels, reduced intraoperative and postoperative transfusions, and resulted in a cost savings of more than $100,000 over the life of the program.
Christine M. Cahill, BSN, MS, RN, of the University of Rochester and Strong Memorial Hospital in Rochester, New York, presented these results at AABB 2018 (abstract PBM4-ST4-22*).
“Anemia has been thought of as a relatively benign thing our patients live with, traditionally, but what we have been finding lately is that anemia is actually more serious than we once thought and is an independent risk factor for hospitalization, readmission, increased patient length of stay, loss of function, and diminished quality of life,” Cahill said.
She added that anemia also increases the likelihood that a patient will require transfusions.
The pilot program was implemented with this in mind. The program, which ran from February 2016 through September 2017, was designed to test the feasibility of diagnosing anemia during a cardiology consult visit and implementing an anemia management plan.
During the study period, 240 patients presenting for elective cardiac surgery were screened for anemia, and 58 were diagnosed as anemic (hemoglobin <12 g/dL). These patients were referred for anemia workups, which showed that 33 patients had iron-deficiency anemia, and 25 had anemia from other causes.
Preoperative anemia management for the iron-deficient patients included oral iron for seven patients, intravenous (IV) iron with or without folate for 20 patients, and oral folate with or without vitamin B12 for five patients. One iron-deficient patient could not have surgery delayed for anemia management.
Of the iron-replete patients, one received oral iron, 17 received folate with or without B12, and seven patients were not treated for anemia.
One iron-deficient patient had a reaction to the infusion and did not receive a scheduled second dose due to the need for immediate surgery. A second patient scheduled for IV iron and folate broke an arm and therefore missed an IV infusion appointment. No other complications or reactions occurred.
Results
The researchers compared the 58 patients from the pilot program to control subjects—patients who underwent cardiac surgery from March through July 2015, matched by age, sex, and procedures.
The anemia management group received 10 red blood cell (RBC) units intraoperatively, compared to 68 intraoperative RBC units for controls. The total number of postoperative RBC units was 13 and 22, respectively.
The rate of RBC transfusions was 24% in the anemia management group and 60% in controls (P<0.0001). The average RBC units per patient was 0.4 and 2.07, respectively (P<0.0001).
Patients in the anemia management program also had significantly higher day-of-surgery hemoglobin than controls—11.01 and 10.16 g/dL, respectively (P<0.001).
The program provided an average per-patient savings in acquisition costs of $367.40, an average transfusion cost savings of $1,837, and a total cost savings of $106,546 over the life of the program.
The key to success of a similar program is “to make sure you do your homework,” Cahill said.
Specifically, she recommended feasibility studies, evaluation of the potential impact of infusions on the service, work flow analyses, and cost analyses. It’s also important to get high-level administrative support as well as buy-in from surgeons and patients, she added.
Future studies should include assessment of patient outcomes, safety, and length of intensive care unit and hospital stay, Cahill emphasized.
This study was internally funded. Cahill reported no conflicts of interest.
*The data in the presentation differ from the abstract.
BOSTON—Results of a pilot program suggest preoperative management of anemia can reduce transfusion rates and cut costs, but the effect on patient outcomes isn’t clear.
For this program, anemic patients received dietary guidance and supplementation prior to surgery.
This increased day-of-surgery hemoglobin levels, reduced intraoperative and postoperative transfusions, and resulted in a cost savings of more than $100,000 over the life of the program.
Christine M. Cahill, BSN, MS, RN, of the University of Rochester and Strong Memorial Hospital in Rochester, New York, presented these results at AABB 2018 (abstract PBM4-ST4-22*).
“Anemia has been thought of as a relatively benign thing our patients live with, traditionally, but what we have been finding lately is that anemia is actually more serious than we once thought and is an independent risk factor for hospitalization, readmission, increased patient length of stay, loss of function, and diminished quality of life,” Cahill said.
She added that anemia also increases the likelihood that a patient will require transfusions.
The pilot program was implemented with this in mind. The program, which ran from February 2016 through September 2017, was designed to test the feasibility of diagnosing anemia during a cardiology consult visit and implementing an anemia management plan.
During the study period, 240 patients presenting for elective cardiac surgery were screened for anemia, and 58 were diagnosed as anemic (hemoglobin <12 g/dL). These patients were referred for anemia workups, which showed that 33 patients had iron-deficiency anemia, and 25 had anemia from other causes.
Preoperative anemia management for the iron-deficient patients included oral iron for seven patients, intravenous (IV) iron with or without folate for 20 patients, and oral folate with or without vitamin B12 for five patients. One iron-deficient patient could not have surgery delayed for anemia management.
Of the iron-replete patients, one received oral iron, 17 received folate with or without B12, and seven patients were not treated for anemia.
One iron-deficient patient had a reaction to the infusion and did not receive a scheduled second dose due to the need for immediate surgery. A second patient scheduled for IV iron and folate broke an arm and therefore missed an IV infusion appointment. No other complications or reactions occurred.
Results
The researchers compared the 58 patients from the pilot program to control subjects—patients who underwent cardiac surgery from March through July 2015, matched by age, sex, and procedures.
The anemia management group received 10 red blood cell (RBC) units intraoperatively, compared to 68 intraoperative RBC units for controls. The total number of postoperative RBC units was 13 and 22, respectively.
The rate of RBC transfusions was 24% in the anemia management group and 60% in controls (P<0.0001). The average RBC units per patient was 0.4 and 2.07, respectively (P<0.0001).
Patients in the anemia management program also had significantly higher day-of-surgery hemoglobin than controls—11.01 and 10.16 g/dL, respectively (P<0.001).
The program provided an average per-patient savings in acquisition costs of $367.40, an average transfusion cost savings of $1,837, and a total cost savings of $106,546 over the life of the program.
The key to success of a similar program is “to make sure you do your homework,” Cahill said.
Specifically, she recommended feasibility studies, evaluation of the potential impact of infusions on the service, work flow analyses, and cost analyses. It’s also important to get high-level administrative support as well as buy-in from surgeons and patients, she added.
Future studies should include assessment of patient outcomes, safety, and length of intensive care unit and hospital stay, Cahill emphasized.
This study was internally funded. Cahill reported no conflicts of interest.
*The data in the presentation differ from the abstract.
BOSTON—Results of a pilot program suggest preoperative management of anemia can reduce transfusion rates and cut costs, but the effect on patient outcomes isn’t clear.
For this program, anemic patients received dietary guidance and supplementation prior to surgery.
This increased day-of-surgery hemoglobin levels, reduced intraoperative and postoperative transfusions, and resulted in a cost savings of more than $100,000 over the life of the program.
Christine M. Cahill, BSN, MS, RN, of the University of Rochester and Strong Memorial Hospital in Rochester, New York, presented these results at AABB 2018 (abstract PBM4-ST4-22*).
“Anemia has been thought of as a relatively benign thing our patients live with, traditionally, but what we have been finding lately is that anemia is actually more serious than we once thought and is an independent risk factor for hospitalization, readmission, increased patient length of stay, loss of function, and diminished quality of life,” Cahill said.
She added that anemia also increases the likelihood that a patient will require transfusions.
The pilot program was implemented with this in mind. The program, which ran from February 2016 through September 2017, was designed to test the feasibility of diagnosing anemia during a cardiology consult visit and implementing an anemia management plan.
During the study period, 240 patients presenting for elective cardiac surgery were screened for anemia, and 58 were diagnosed as anemic (hemoglobin <12 g/dL). These patients were referred for anemia workups, which showed that 33 patients had iron-deficiency anemia, and 25 had anemia from other causes.
Preoperative anemia management for the iron-deficient patients included oral iron for seven patients, intravenous (IV) iron with or without folate for 20 patients, and oral folate with or without vitamin B12 for five patients. One iron-deficient patient could not have surgery delayed for anemia management.
Of the iron-replete patients, one received oral iron, 17 received folate with or without B12, and seven patients were not treated for anemia.
One iron-deficient patient had a reaction to the infusion and did not receive a scheduled second dose due to the need for immediate surgery. A second patient scheduled for IV iron and folate broke an arm and therefore missed an IV infusion appointment. No other complications or reactions occurred.
Results
The researchers compared the 58 patients from the pilot program to control subjects—patients who underwent cardiac surgery from March through July 2015, matched by age, sex, and procedures.
The anemia management group received 10 red blood cell (RBC) units intraoperatively, compared to 68 intraoperative RBC units for controls. The total number of postoperative RBC units was 13 and 22, respectively.
The rate of RBC transfusions was 24% in the anemia management group and 60% in controls (P<0.0001). The average RBC units per patient was 0.4 and 2.07, respectively (P<0.0001).
Patients in the anemia management program also had significantly higher day-of-surgery hemoglobin than controls—11.01 and 10.16 g/dL, respectively (P<0.001).
The program provided an average per-patient savings in acquisition costs of $367.40, an average transfusion cost savings of $1,837, and a total cost savings of $106,546 over the life of the program.
The key to success of a similar program is “to make sure you do your homework,” Cahill said.
Specifically, she recommended feasibility studies, evaluation of the potential impact of infusions on the service, work flow analyses, and cost analyses. It’s also important to get high-level administrative support as well as buy-in from surgeons and patients, she added.
Future studies should include assessment of patient outcomes, safety, and length of intensive care unit and hospital stay, Cahill emphasized.
This study was internally funded. Cahill reported no conflicts of interest.
*The data in the presentation differ from the abstract.
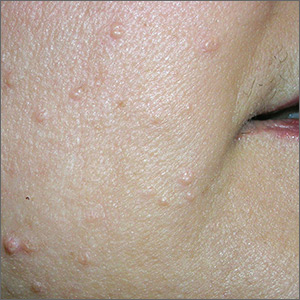
Multiple growths on face
Figure 1
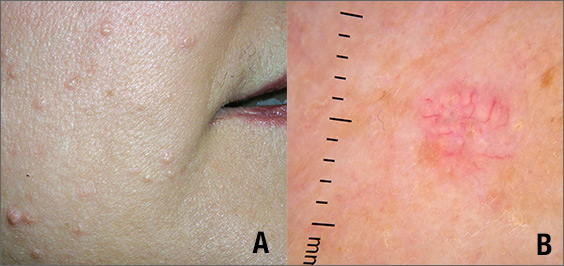
While the differential diagnosis for these lesions (FIGURE 1A) included basal cell carcinoma, the FP had reason to suspect that these papules were actually sebaceous hyperplasia.
The FP saw a pattern of crown-like vessels and popcorn-like structures (FIGURE 1B) when he examined the patient with his dermatoscope. None of the vessels crossed the midline, and the popcorn-like structures were hyperplastic sebaceous glands. The FP photographed the largest lesion with a dermatoscope attached to his smart phone and showed the reassuring pattern to the anxious patient. He explained to her why this was not skin cancer and how hyperplasia of sebaceous glands is often normal for aging facial skin. He also offered her treatment if she thought that the lesions were cosmetically unappealing.
The patient said that she would be grateful to have the largest lesion treated because it did bother her when she looked in the mirror. The FP treated this lesion using electrosurgery with a blunt tipped electrode, on a setting of 2.1, without anesthesia. He warned the patient before he applied the activated electrode to the skin, and the patient tolerated the procedure well. The sebaceous glands melted easily with the current. The result appeared gray and was expected to heal with minimal to no scarring. At a future visit, the patient said that she was happy with the result and asked if additional lesions could be treated with the same electrosurgical approach.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Karnes J, Usatine R. Basal cell carcinoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:989-998.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.
Figure 1

While the differential diagnosis for these lesions (FIGURE 1A) included basal cell carcinoma, the FP had reason to suspect that these papules were actually sebaceous hyperplasia.
The FP saw a pattern of crown-like vessels and popcorn-like structures (FIGURE 1B) when he examined the patient with his dermatoscope. None of the vessels crossed the midline, and the popcorn-like structures were hyperplastic sebaceous glands. The FP photographed the largest lesion with a dermatoscope attached to his smart phone and showed the reassuring pattern to the anxious patient. He explained to her why this was not skin cancer and how hyperplasia of sebaceous glands is often normal for aging facial skin. He also offered her treatment if she thought that the lesions were cosmetically unappealing.
The patient said that she would be grateful to have the largest lesion treated because it did bother her when she looked in the mirror. The FP treated this lesion using electrosurgery with a blunt tipped electrode, on a setting of 2.1, without anesthesia. He warned the patient before he applied the activated electrode to the skin, and the patient tolerated the procedure well. The sebaceous glands melted easily with the current. The result appeared gray and was expected to heal with minimal to no scarring. At a future visit, the patient said that she was happy with the result and asked if additional lesions could be treated with the same electrosurgical approach.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Karnes J, Usatine R. Basal cell carcinoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:989-998.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.
Figure 1

While the differential diagnosis for these lesions (FIGURE 1A) included basal cell carcinoma, the FP had reason to suspect that these papules were actually sebaceous hyperplasia.
The FP saw a pattern of crown-like vessels and popcorn-like structures (FIGURE 1B) when he examined the patient with his dermatoscope. None of the vessels crossed the midline, and the popcorn-like structures were hyperplastic sebaceous glands. The FP photographed the largest lesion with a dermatoscope attached to his smart phone and showed the reassuring pattern to the anxious patient. He explained to her why this was not skin cancer and how hyperplasia of sebaceous glands is often normal for aging facial skin. He also offered her treatment if she thought that the lesions were cosmetically unappealing.
The patient said that she would be grateful to have the largest lesion treated because it did bother her when she looked in the mirror. The FP treated this lesion using electrosurgery with a blunt tipped electrode, on a setting of 2.1, without anesthesia. He warned the patient before he applied the activated electrode to the skin, and the patient tolerated the procedure well. The sebaceous glands melted easily with the current. The result appeared gray and was expected to heal with minimal to no scarring. At a future visit, the patient said that she was happy with the result and asked if additional lesions could be treated with the same electrosurgical approach.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Karnes J, Usatine R. Basal cell carcinoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:989-998.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/.
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com.
ICYMI: Prednisone lowers IRIS risk in patients with HIV
In patients with HIV, treatment with prednisone for 4 weeks after antiretroviral therapy initiation significantly reduced the risk of tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). The results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018 Nov 14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800762).
A total of 240 patients were enrolled in the study, with a median age of 36 years; 60% were men, and 73% had microbiologically confirmed tuberculosis. The median CD4 count of the patients was 49 cells/mcL and the median HIV type 1 RNA viral load was 5.5 log10 copies/mL. A total of 120 patients were assigned to each group, with 18 patients lost to follow-up or withdrawn. Tuberculosis-associated IRIS was diagnosed in 39 patients (32.5%) in the prednisone group and in 56 (46.7%) in the placebo group, yielding a relative IRIS risk of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.96; P = .03), according to the researchers for the PredART (Preventing TB-IRIS in High-Risk Patients: a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Prednisone) study team.
We covered this story before it was published in the journal. Find our coverage from the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections at the link below.
In patients with HIV, treatment with prednisone for 4 weeks after antiretroviral therapy initiation significantly reduced the risk of tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). The results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018 Nov 14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800762).
A total of 240 patients were enrolled in the study, with a median age of 36 years; 60% were men, and 73% had microbiologically confirmed tuberculosis. The median CD4 count of the patients was 49 cells/mcL and the median HIV type 1 RNA viral load was 5.5 log10 copies/mL. A total of 120 patients were assigned to each group, with 18 patients lost to follow-up or withdrawn. Tuberculosis-associated IRIS was diagnosed in 39 patients (32.5%) in the prednisone group and in 56 (46.7%) in the placebo group, yielding a relative IRIS risk of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.96; P = .03), according to the researchers for the PredART (Preventing TB-IRIS in High-Risk Patients: a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Prednisone) study team.
We covered this story before it was published in the journal. Find our coverage from the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections at the link below.
In patients with HIV, treatment with prednisone for 4 weeks after antiretroviral therapy initiation significantly reduced the risk of tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). The results from the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial were published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018 Nov 14. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800762).
A total of 240 patients were enrolled in the study, with a median age of 36 years; 60% were men, and 73% had microbiologically confirmed tuberculosis. The median CD4 count of the patients was 49 cells/mcL and the median HIV type 1 RNA viral load was 5.5 log10 copies/mL. A total of 120 patients were assigned to each group, with 18 patients lost to follow-up or withdrawn. Tuberculosis-associated IRIS was diagnosed in 39 patients (32.5%) in the prednisone group and in 56 (46.7%) in the placebo group, yielding a relative IRIS risk of 0.70 (95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.96; P = .03), according to the researchers for the PredART (Preventing TB-IRIS in High-Risk Patients: a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Prednisone) study team.
We covered this story before it was published in the journal. Find our coverage from the Conference on Retroviruses & Opportunistic Infections at the link below.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Ganglion stimulation boosts cerebral blood flow, improves stroke outcomes
MONTREAL – Stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) using a small, implanted electrode for 5 days in patients who had just had an acute ischemic stroke led to statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in the subset of patients with confirmed cortical involvement in a pivotal, sham-controlled trial.
SPG stimulation started within 24 hours of an acute ischemic stroke “reduced poststroke disability over the entire outcome range and increased the proportion of patients who were alive and independent 3 months after their stroke” in the subgroup with a confirmed cortical infarction (CCI), Jeffrey L. Saver, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Five days of SPG stimulation, done once daily starting within 24 hours of stroke onset, “enhances ipsilateral collateral blood flow” and may also stabilize the blood brain barrier, explained Dr. Saver, professor of neurology and director of the stroke center at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study included a prespecified primary endpoint analysis that focused exclusively on the CCI subgroup, 52% of the total enrolled population.
If the reported data result in Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the system, Dr. Saver said that he anticipated “substantial uptake” of the strategy, which he tested in patients who had not undergone thrombectomy or thrombolysis treatment. In current U.S. practice, there is “a large group of patients with a missed opportunity for recanalization” who would be candidates for treatment with SPG stimulation, a treatment that appeared to provide benefits beyond current standard care, he said in an interview.
Ongoing studies are also testing whether SPG stimulation can benefit acute ischemic stroke patients who have already undergone treatment with thrombectomy or thrombolysis, he added. The same SPG stimulation device is additionally undergoing U.S. testing as a treatment for headache and has regulatory approval in the European Union for treating headache and migraine.
The ImpACT-24B (Implant for Augmentation of Cerebral Blood Flow Trial, Effectiveness and Safety in a 24-Hour Window) trial involved 1,000 patients at 73 centers in 18 countries, including the United States. The investigators enrolled acute ischemic stroke patients 8-24 hours after stroke onset who had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 7-18.
Each patient received an implant of a short, thin metal electrode placed through the soft palate at the rear roof of the mouth, near the SPG. Neurologists primarily performed the implants in a procedure that had a “skin to skin” time of less than 5 minutes. Patients received either electrical stimulation or a sham stimulation through the electrode immediately after placement and then daily for the next 4 days. The investigators titrated the strength of the treatment stimulation in each patient to maximize its strength while maintaining patient comfort. Subsequent analysis of the results showed that the stronger the tolerated stimulation, the bigger the treatment effect in a clear dose-response pattern, Dr. Saver reported.
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement in the modified Rankin scale (mRS) score at 90 days after the index stroke when measured against historical expectations. By this measure, the overall study cohort showed a small, statistically insignificant improvement in actively treated patients, compared with sham-treated patients. However, in the prespecified, coprimary endpoint cohort of patients with a CCI, active treatment resulted in 50% of patients having a better-than-expected 90-day outcome, compared with 40% of controls, a 48% relative improvement in this measure that met the prespecified definition of statistical significance. The results also showed about a 50% relative improvement in each of three secondary outcomes in the CCI cohort: the percentage of patients with a mRS score of 0-2 after 90 days, the percentage with a mRS score of 0-3 after 90 days, and average stroke-related quality of life at 90 days.
Dr. Saver also reported results of a meta-analysis that combined the results he reported from 520 patients with CCI with results from 87 CCI patients enrolled in the preceding pilot study of this treatment strategy, ImpACT-1. The pilot findings were completely consistent and when combined with the current results strengthened the statistical significance of the primary and secondary endpoints.
“There is a compelling story” of efficacy based on the study results, the dose-response relationship, and the meta-analysis results, Dr. Saver said. “I think it’s a very strong case.”
He also reported “no safety concerns” raised in the new study, with no serious adverse effects seen in or experienced by the patients on active treatment.
“The data are compelling” for safety and efficacy, for this novel approach for treating acute ischemic stroke, commented Pooja Khatri, MD, professor of neurology and director of the acute stroke program at the University of Cincinnati.
The study was sponsored by BrainsGate, the company developing the tested device. Dr. Saver has been a consultant to BrainsGate. Dr. Khatri has been a consultant to Biogen, Greenwich, Lumosa, and PTC Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Saver J et al. Int J. Stroke. 2018 Oct;13(2S):28, Abstract 104.
MONTREAL – Stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) using a small, implanted electrode for 5 days in patients who had just had an acute ischemic stroke led to statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in the subset of patients with confirmed cortical involvement in a pivotal, sham-controlled trial.
SPG stimulation started within 24 hours of an acute ischemic stroke “reduced poststroke disability over the entire outcome range and increased the proportion of patients who were alive and independent 3 months after their stroke” in the subgroup with a confirmed cortical infarction (CCI), Jeffrey L. Saver, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Five days of SPG stimulation, done once daily starting within 24 hours of stroke onset, “enhances ipsilateral collateral blood flow” and may also stabilize the blood brain barrier, explained Dr. Saver, professor of neurology and director of the stroke center at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study included a prespecified primary endpoint analysis that focused exclusively on the CCI subgroup, 52% of the total enrolled population.
If the reported data result in Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the system, Dr. Saver said that he anticipated “substantial uptake” of the strategy, which he tested in patients who had not undergone thrombectomy or thrombolysis treatment. In current U.S. practice, there is “a large group of patients with a missed opportunity for recanalization” who would be candidates for treatment with SPG stimulation, a treatment that appeared to provide benefits beyond current standard care, he said in an interview.
Ongoing studies are also testing whether SPG stimulation can benefit acute ischemic stroke patients who have already undergone treatment with thrombectomy or thrombolysis, he added. The same SPG stimulation device is additionally undergoing U.S. testing as a treatment for headache and has regulatory approval in the European Union for treating headache and migraine.
The ImpACT-24B (Implant for Augmentation of Cerebral Blood Flow Trial, Effectiveness and Safety in a 24-Hour Window) trial involved 1,000 patients at 73 centers in 18 countries, including the United States. The investigators enrolled acute ischemic stroke patients 8-24 hours after stroke onset who had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 7-18.
Each patient received an implant of a short, thin metal electrode placed through the soft palate at the rear roof of the mouth, near the SPG. Neurologists primarily performed the implants in a procedure that had a “skin to skin” time of less than 5 minutes. Patients received either electrical stimulation or a sham stimulation through the electrode immediately after placement and then daily for the next 4 days. The investigators titrated the strength of the treatment stimulation in each patient to maximize its strength while maintaining patient comfort. Subsequent analysis of the results showed that the stronger the tolerated stimulation, the bigger the treatment effect in a clear dose-response pattern, Dr. Saver reported.
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement in the modified Rankin scale (mRS) score at 90 days after the index stroke when measured against historical expectations. By this measure, the overall study cohort showed a small, statistically insignificant improvement in actively treated patients, compared with sham-treated patients. However, in the prespecified, coprimary endpoint cohort of patients with a CCI, active treatment resulted in 50% of patients having a better-than-expected 90-day outcome, compared with 40% of controls, a 48% relative improvement in this measure that met the prespecified definition of statistical significance. The results also showed about a 50% relative improvement in each of three secondary outcomes in the CCI cohort: the percentage of patients with a mRS score of 0-2 after 90 days, the percentage with a mRS score of 0-3 after 90 days, and average stroke-related quality of life at 90 days.
Dr. Saver also reported results of a meta-analysis that combined the results he reported from 520 patients with CCI with results from 87 CCI patients enrolled in the preceding pilot study of this treatment strategy, ImpACT-1. The pilot findings were completely consistent and when combined with the current results strengthened the statistical significance of the primary and secondary endpoints.
“There is a compelling story” of efficacy based on the study results, the dose-response relationship, and the meta-analysis results, Dr. Saver said. “I think it’s a very strong case.”
He also reported “no safety concerns” raised in the new study, with no serious adverse effects seen in or experienced by the patients on active treatment.
“The data are compelling” for safety and efficacy, for this novel approach for treating acute ischemic stroke, commented Pooja Khatri, MD, professor of neurology and director of the acute stroke program at the University of Cincinnati.
The study was sponsored by BrainsGate, the company developing the tested device. Dr. Saver has been a consultant to BrainsGate. Dr. Khatri has been a consultant to Biogen, Greenwich, Lumosa, and PTC Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Saver J et al. Int J. Stroke. 2018 Oct;13(2S):28, Abstract 104.
MONTREAL – Stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) using a small, implanted electrode for 5 days in patients who had just had an acute ischemic stroke led to statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in the subset of patients with confirmed cortical involvement in a pivotal, sham-controlled trial.
SPG stimulation started within 24 hours of an acute ischemic stroke “reduced poststroke disability over the entire outcome range and increased the proportion of patients who were alive and independent 3 months after their stroke” in the subgroup with a confirmed cortical infarction (CCI), Jeffrey L. Saver, MD, said at the World Stroke Congress. Five days of SPG stimulation, done once daily starting within 24 hours of stroke onset, “enhances ipsilateral collateral blood flow” and may also stabilize the blood brain barrier, explained Dr. Saver, professor of neurology and director of the stroke center at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study included a prespecified primary endpoint analysis that focused exclusively on the CCI subgroup, 52% of the total enrolled population.
If the reported data result in Food and Drug Administration marketing approval for the system, Dr. Saver said that he anticipated “substantial uptake” of the strategy, which he tested in patients who had not undergone thrombectomy or thrombolysis treatment. In current U.S. practice, there is “a large group of patients with a missed opportunity for recanalization” who would be candidates for treatment with SPG stimulation, a treatment that appeared to provide benefits beyond current standard care, he said in an interview.
Ongoing studies are also testing whether SPG stimulation can benefit acute ischemic stroke patients who have already undergone treatment with thrombectomy or thrombolysis, he added. The same SPG stimulation device is additionally undergoing U.S. testing as a treatment for headache and has regulatory approval in the European Union for treating headache and migraine.
The ImpACT-24B (Implant for Augmentation of Cerebral Blood Flow Trial, Effectiveness and Safety in a 24-Hour Window) trial involved 1,000 patients at 73 centers in 18 countries, including the United States. The investigators enrolled acute ischemic stroke patients 8-24 hours after stroke onset who had a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 7-18.
Each patient received an implant of a short, thin metal electrode placed through the soft palate at the rear roof of the mouth, near the SPG. Neurologists primarily performed the implants in a procedure that had a “skin to skin” time of less than 5 minutes. Patients received either electrical stimulation or a sham stimulation through the electrode immediately after placement and then daily for the next 4 days. The investigators titrated the strength of the treatment stimulation in each patient to maximize its strength while maintaining patient comfort. Subsequent analysis of the results showed that the stronger the tolerated stimulation, the bigger the treatment effect in a clear dose-response pattern, Dr. Saver reported.
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement in the modified Rankin scale (mRS) score at 90 days after the index stroke when measured against historical expectations. By this measure, the overall study cohort showed a small, statistically insignificant improvement in actively treated patients, compared with sham-treated patients. However, in the prespecified, coprimary endpoint cohort of patients with a CCI, active treatment resulted in 50% of patients having a better-than-expected 90-day outcome, compared with 40% of controls, a 48% relative improvement in this measure that met the prespecified definition of statistical significance. The results also showed about a 50% relative improvement in each of three secondary outcomes in the CCI cohort: the percentage of patients with a mRS score of 0-2 after 90 days, the percentage with a mRS score of 0-3 after 90 days, and average stroke-related quality of life at 90 days.
Dr. Saver also reported results of a meta-analysis that combined the results he reported from 520 patients with CCI with results from 87 CCI patients enrolled in the preceding pilot study of this treatment strategy, ImpACT-1. The pilot findings were completely consistent and when combined with the current results strengthened the statistical significance of the primary and secondary endpoints.
“There is a compelling story” of efficacy based on the study results, the dose-response relationship, and the meta-analysis results, Dr. Saver said. “I think it’s a very strong case.”
He also reported “no safety concerns” raised in the new study, with no serious adverse effects seen in or experienced by the patients on active treatment.
“The data are compelling” for safety and efficacy, for this novel approach for treating acute ischemic stroke, commented Pooja Khatri, MD, professor of neurology and director of the acute stroke program at the University of Cincinnati.
The study was sponsored by BrainsGate, the company developing the tested device. Dr. Saver has been a consultant to BrainsGate. Dr. Khatri has been a consultant to Biogen, Greenwich, Lumosa, and PTC Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Saver J et al. Int J. Stroke. 2018 Oct;13(2S):28, Abstract 104.
REPORTING FROM THE WORLD STROKE CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation of acute ischemic stroke patients boosted cerebral blood flow and improved 90-day outcomes in patients with confirmed cortical infarctions.
Major finding: For confirmed cortical infarctions ganglion stimulation led to a 48% higher rate of better-than-expected outcomes, compared with controls.
Study details: ImpACT-24B, a multicenter pivotal trial with 1,000 acute ischemic stroke patients.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by BrainsGate, the company developing the tested device. Dr. Saver has been a consultant to BrainsGate. Dr. Khatri has been a consultant to Biogen, Greenwich, Lumosa, and PTC Therapeutics.
Source: Saver J et al. Int J. Stroke. 2018 Oct;13(2S):28, Abstract 104.
Tofacitinib impresses in first trial for dermatomyositis
CHICAGO – Oral tofacitinib demonstrated strong clinical efficacy and good safety in the first-ever formal study of a Janus kinase inhibitor in patients with active, treatment-resistant dermatomyositis, Julie J. Paik, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based upon the encouraging results of this small, open-label, proof-of-concept study, a larger randomized controlled trial is being planned, according to Dr. Paik, a rheumatologist at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
The study included 10 dermatomyositis patients enrolled at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Clinic. All had previously failed at least two steroid-sparing drugs and/or high-dose steroids. After first going off all steroid-sparing agents and being limited to a maximum of 20 mg/day of prednisone, the participants were placed on 11 mg of open-label, extended-release tofacitinib (Xeljanz XR) once daily. Dr. Paik only reported results in 9 patients because the 10th hadn’t yet reached the 12-week mark.
The primary outcome was the rate of achievement of significant improvement at week 12 as defined using the validated International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies (IMACS) criteria, which require at least a 20% improvement in three of six core set measures coupled with no more than two measures worsening by 25% or more. By this standard, all nine patients met the primary endpoint. Five were rated as showing moderate improvement, and the other four demonstrated minimal improvement, based on the Total Improvement Score of the Myositis Response criteria. The median Total Improvement Score was 40, indicative of at least moderate improvement.
The mean CDASI (Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index) activity score – a key secondary endpoint – improved from 28 at baseline to 9.5 at week 12, which translates to a shift from moderate or severe disease to mild disease.
Levels of the alpha-chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, which are expressed in muscle affected by idiopathic inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis, declined strongly over the course of 12 weeks of treatment to an extent that was just shy of statistical significance.
Myositis antibody titers didn’t change in response to tofacitinib therapy. Of note, six patients were positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1-gamma, and five of the six were moderate responders to JAK inhibitor therapy.
Four patients were on 20 mg/day of prednisone at baseline; three of the four were able to go off steroids altogether over the course of 12 weeks.
The treatment was well tolerated, with no serious adverse events.
Asked if she thought 11 mg/day of tofacitinib was the right dose for this population of refractory dermatomyositis patients, Dr. Paik replied, “We’re not sure we have the right dose. We had one patient who didn’t have as robust a response, and I really wonder, if we gave her a higher dose, it would have made a difference.”
Extended-release tofacitinib at 11 mg/day is the approved dose for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. However, 20 mg/day is approved for patients with ulcerative colitis, and Dr. Paik is lobbying for inclusion of a higher-dose arm in the randomized, controlled trial.
Prior to this formal proof-of-concept study, which was funded by Pfizer, the experience with tofacitinib in refractory dermatomyositis was limited to anecdotal case reports.
Dr. Paik reported having no financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Paik JJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract L02.
CHICAGO – Oral tofacitinib demonstrated strong clinical efficacy and good safety in the first-ever formal study of a Janus kinase inhibitor in patients with active, treatment-resistant dermatomyositis, Julie J. Paik, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based upon the encouraging results of this small, open-label, proof-of-concept study, a larger randomized controlled trial is being planned, according to Dr. Paik, a rheumatologist at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
The study included 10 dermatomyositis patients enrolled at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Clinic. All had previously failed at least two steroid-sparing drugs and/or high-dose steroids. After first going off all steroid-sparing agents and being limited to a maximum of 20 mg/day of prednisone, the participants were placed on 11 mg of open-label, extended-release tofacitinib (Xeljanz XR) once daily. Dr. Paik only reported results in 9 patients because the 10th hadn’t yet reached the 12-week mark.
The primary outcome was the rate of achievement of significant improvement at week 12 as defined using the validated International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies (IMACS) criteria, which require at least a 20% improvement in three of six core set measures coupled with no more than two measures worsening by 25% or more. By this standard, all nine patients met the primary endpoint. Five were rated as showing moderate improvement, and the other four demonstrated minimal improvement, based on the Total Improvement Score of the Myositis Response criteria. The median Total Improvement Score was 40, indicative of at least moderate improvement.
The mean CDASI (Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index) activity score – a key secondary endpoint – improved from 28 at baseline to 9.5 at week 12, which translates to a shift from moderate or severe disease to mild disease.
Levels of the alpha-chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, which are expressed in muscle affected by idiopathic inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis, declined strongly over the course of 12 weeks of treatment to an extent that was just shy of statistical significance.
Myositis antibody titers didn’t change in response to tofacitinib therapy. Of note, six patients were positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1-gamma, and five of the six were moderate responders to JAK inhibitor therapy.
Four patients were on 20 mg/day of prednisone at baseline; three of the four were able to go off steroids altogether over the course of 12 weeks.
The treatment was well tolerated, with no serious adverse events.
Asked if she thought 11 mg/day of tofacitinib was the right dose for this population of refractory dermatomyositis patients, Dr. Paik replied, “We’re not sure we have the right dose. We had one patient who didn’t have as robust a response, and I really wonder, if we gave her a higher dose, it would have made a difference.”
Extended-release tofacitinib at 11 mg/day is the approved dose for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. However, 20 mg/day is approved for patients with ulcerative colitis, and Dr. Paik is lobbying for inclusion of a higher-dose arm in the randomized, controlled trial.
Prior to this formal proof-of-concept study, which was funded by Pfizer, the experience with tofacitinib in refractory dermatomyositis was limited to anecdotal case reports.
Dr. Paik reported having no financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Paik JJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract L02.
CHICAGO – Oral tofacitinib demonstrated strong clinical efficacy and good safety in the first-ever formal study of a Janus kinase inhibitor in patients with active, treatment-resistant dermatomyositis, Julie J. Paik, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
Based upon the encouraging results of this small, open-label, proof-of-concept study, a larger randomized controlled trial is being planned, according to Dr. Paik, a rheumatologist at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore.
The study included 10 dermatomyositis patients enrolled at the Johns Hopkins Myositis Clinic. All had previously failed at least two steroid-sparing drugs and/or high-dose steroids. After first going off all steroid-sparing agents and being limited to a maximum of 20 mg/day of prednisone, the participants were placed on 11 mg of open-label, extended-release tofacitinib (Xeljanz XR) once daily. Dr. Paik only reported results in 9 patients because the 10th hadn’t yet reached the 12-week mark.
The primary outcome was the rate of achievement of significant improvement at week 12 as defined using the validated International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies (IMACS) criteria, which require at least a 20% improvement in three of six core set measures coupled with no more than two measures worsening by 25% or more. By this standard, all nine patients met the primary endpoint. Five were rated as showing moderate improvement, and the other four demonstrated minimal improvement, based on the Total Improvement Score of the Myositis Response criteria. The median Total Improvement Score was 40, indicative of at least moderate improvement.
The mean CDASI (Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index) activity score – a key secondary endpoint – improved from 28 at baseline to 9.5 at week 12, which translates to a shift from moderate or severe disease to mild disease.
Levels of the alpha-chemokines CXCL9 and CXCL10, which are expressed in muscle affected by idiopathic inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis, declined strongly over the course of 12 weeks of treatment to an extent that was just shy of statistical significance.
Myositis antibody titers didn’t change in response to tofacitinib therapy. Of note, six patients were positive for antitranscriptional intermediary factor 1-gamma, and five of the six were moderate responders to JAK inhibitor therapy.
Four patients were on 20 mg/day of prednisone at baseline; three of the four were able to go off steroids altogether over the course of 12 weeks.
The treatment was well tolerated, with no serious adverse events.
Asked if she thought 11 mg/day of tofacitinib was the right dose for this population of refractory dermatomyositis patients, Dr. Paik replied, “We’re not sure we have the right dose. We had one patient who didn’t have as robust a response, and I really wonder, if we gave her a higher dose, it would have made a difference.”
Extended-release tofacitinib at 11 mg/day is the approved dose for rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. However, 20 mg/day is approved for patients with ulcerative colitis, and Dr. Paik is lobbying for inclusion of a higher-dose arm in the randomized, controlled trial.
Prior to this formal proof-of-concept study, which was funded by Pfizer, the experience with tofacitinib in refractory dermatomyositis was limited to anecdotal case reports.
Dr. Paik reported having no financial conflicts.
SOURCE: Paik JJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract L02.
REPORTING FROM THE ACR ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among patients with refractory dermatomyositis, the mean Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index activity score improved from 28 at baseline to 9.5 after 12 weeks on oral tofacitinib.
Study details: This first-in-class, open-label, 12-week study included 10 patients with refractory dermatomyositis placed on extended-release tofacitinib at 11 mg once daily.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, sponsored by Pfizer.
Source: Paik JJ et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(Suppl 10): Abstract L02