User login
Navigating NAFLD: Unveiling the approach to mitigate the impact of NAFLD
Burden of NAFLD in the U.S.
NAFLD is a manifestation of systemic metabolic abnormalities, including insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, central obesity, and hypertension. In this short review, we summarize data on the burden of NAFLD in the U.S. and its prognostic determinants and review what clinical and public health approaches may be needed to mitigating its impact.
Epidemiology of NAFLD
Worldwide, the prevalence of NAFLD is estimated at 6% to 35%, with biopsy-based studies reporting NASH in 3% to 5%.1 U.S. estimates for the prevalence of NAFLD range from 10% to 46%.2 In our own analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data, transient elastography-detected steatosis was found in 36%, which projected to a minimum of 73 million American adults.3
NAFLD represents a spectrum of disorders ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the latter leading, in some cases, to progressive hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.4 Out of a large number of subjects with NAFLD, the proportions of NASH patients that develop severe liver problems such as end-stage liver disease (ESLD) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are progressively smaller. For example, we recently reported that less than 2,000 liver-related deaths are attributable to NAFLD in the U.S. per annum, which corresponds to a crude case fatality rate of < 0.005% per year.5
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there have been substantial increases in liver-related deaths over the last 2 decades. Mortality from liver disease including hepatobiliary cancers more than doubled from 41,966 deaths (including 15,321 women and 26,645 men) in 2000 to 85,884 deaths (33,000 women and 52,884 men) in 2020. The proportion of deaths specifically attributed to NAFLD among liver-related deaths was miniscule in 2000, accounting for 1.1% in women and 0.7% in men. By 2020, the proportions increased several folds in both sexes (7.4% in women and 2.7% in men).6 Moreover, it is likely that a substantial portion of deaths from chronic liver disease from unknown causes (“cryptogenic”) are likely end-stage NAFLD, making these figures underestimates of the true impact of NAFLD in the U.S.
From a comparative epidemiologic perspective, there are significant racial and ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in NAFLD prevalence, wherein Hispanic persons and individuals experiencing food insecurity – independent of poverty status, education level, race and ethnicity – are disproportionately more affected by NAFLD.7,8 Furthermore, these disparities persist when examining long-term complications of NAFLD, such as developing HCC.
Prognosis in NAFLD: NASH versus fibrosis
Given the enormous prevalence and increasing public health burden of NAFLD, systematic interventions to mitigate its impact are urgently needed. Clearly, patients who already have developed advanced liver disease need to be directed to specialty care so the disease progression may be halted and complications of ESLD may be prevented or managed. On the other hand, in order to mitigate the future impact of ESLD, prompt identification of at-risk patients and proactive interventions to improve liver health are needed.
In the assessment of disease progression, prior data have shown that the presence of NASH and increasing stages of liver fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression. Fibrosis is a component of NASH, while NASH is thought to be a prerequisite for fibrosis. In a prospective, multicenter follow-up study of NAFLD evaluated by liver biopsies (n = 1,773), over a median follow-up of 4 years, 37 (2%) developed hepatic decompensation, while 47 (3%) died from any cause, which included ESLD (n = 12), cardiovascular complications (n = 4), and malignancies (n = 12), including HCC (n = 9).9 It is not entirely surprising that advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis was highly associated with the development of hepatic decompensation. In their multivariable analysis, patients with F3-4 had a 13.8-fold (95% confidence interval [CI]: 4.6, 41.0) increase in the hazard of reaching a MELD score of 15 compared to those with F0-2. In addition, all-cause mortality was 17.2-fold (95% CI: 5.2, 56.6) higher with F3-4 compared to F0-2.
These data have been borne out by a larger body of literature on the topic. In a recent meta-analysis assessing the relation between liver fibrosis and future mortality, which included 17,301 subjects with NAFLD, patients with at least stage 2 fibrosis experience a significantly increased risk of liver-related and overall mortality, a trend that accelerates at higher fibrosis stages.10 These point to liver fibrosis as the singular determinant of long-term prognosis, in comparison, for example, with the diagnosis of NASH. Hagström conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD in Sweden. When fibrosis stage and histological diagnosis of NASH were considered together, NASH did not have an impact on overall mortality (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.83, P = .29) or liver morbidity (HR = 0.62, P = .25).11
On an individual level, factors that affect fibrosis progression are not as well studied. It is commonly believed that demographic factors (e.g., age, sex and race), genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3, TM6SF2), clinical comorbidities (e.g., obesity, DM, and sleep apnea), and environmental factors (e.g., smoking) may accelerate fibrosis and disease outcomes, although prospective data are sparse to estimate the extent these individual variables affect progression.12 Recent guidelines remain silent about whether and how these data may be incorporated in screening for NAFLD in the population.
Assessment of liver fibrosis
The traditional means to detect liver fibrosis is liver histology, which also assesses steatosis, individual components of NASH and, often importantly, other concomitant liver pathology. In reality, however, liver biopsies have several limitations including the risk of complications, patient discomfort, economic costs, and sampling variability. Increasingly, “noninvasive” methods have been used to estimate liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Liver elastography estimates the physical stiffness of the organ, which may be measured by MRI or ultrasound. Among ultrasound-based technologies, vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) is more widely accepted and affordable although it may not be as accurate as MR elastography.13
In general, these elastographic tests are not readily accessible to most physicians outside hepatology specialty practices. Instead, blood test-based markers have been developed and widely recommended as the initial modality to assess liver fibrosis. Figure 1 represents a partial list of blood test-based markers. Traditionally, FIB-4 and NFS have been considered the most widely recommended by society guidelines. The AGA Pathway for evaluation of patients with NAFLD recommends first to apply the FIB-4 score and, in patients considered to be at intermediate risk of fibrosis for advanced fibrosis (stage 3 or 4, FIB-4 = 1.3-2.67), to assess liver stiffness by VCTE.14
More recently, the accumulating natural history data have highlighted the inflection in the risk of future outcomes coinciding with F2 and therapeutic trials that target patients with “at risk NASH,” thus more attention has been paid to the identification of patients with stage 2 (or higher). The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) was developed for this specific purpose. The score has been validated in multiple data sets, in all of which SAFE outperformed FIB-4 and NFS (Figure 1). When the score was applied to assess overall survival in participants of the NHANES, patients with NAFLD deemed to be high risk (SAFE > 100) had significantly lower survival (37% Kaplan-Meier survival at 20 years), compared to those with intermediate (SAFE 0-100, 61% survival) and low (SAFE < 0, 86% survival). In comparison, the 20-year survival of subjects without NAFLD survival was 79%.15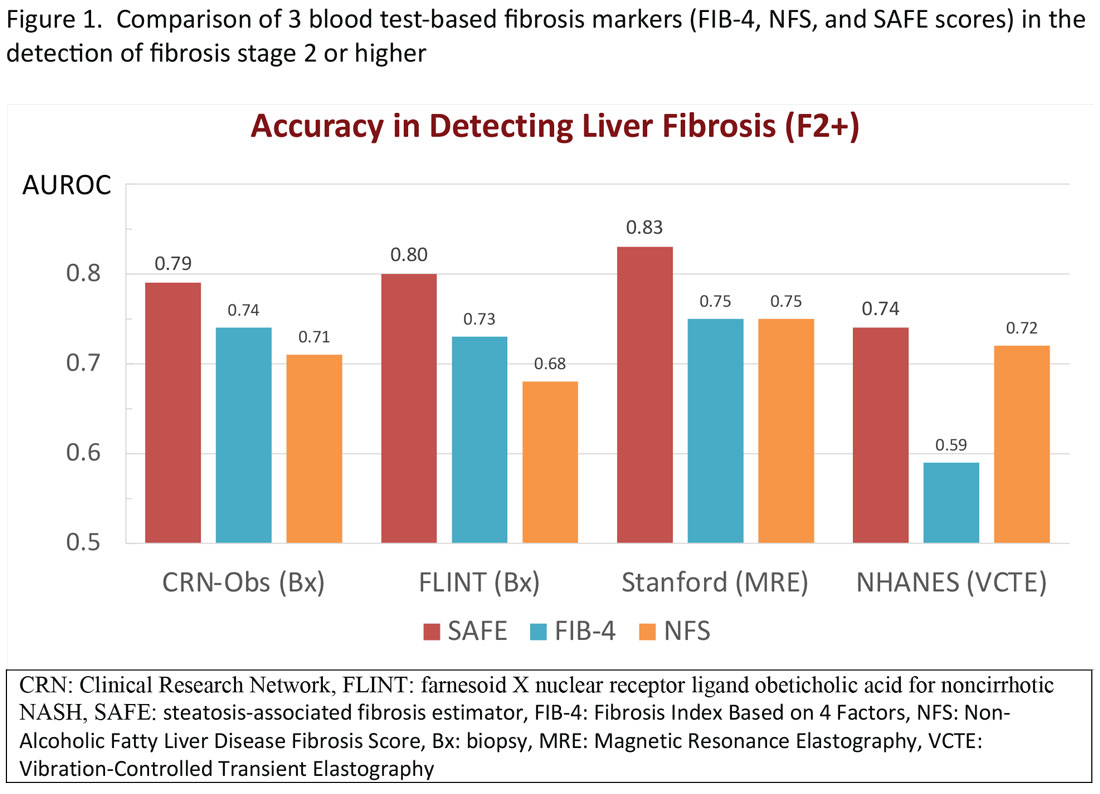
Regardless of the modality for initial stratification, it is widely accepted that mechanical elastography constitutes the next step in prognosticating the patient. In the AGA Pathway, liver stiffness of < 8 kPa is considered low risk, which corresponds in most analysis with lack of stage 2 fibrosis, whereas stiffness of > 12 kPa may be indicative of stage 3 or 4. These recommendations are consistent with those from the latest Baveno Consensus Conference (“Baveno 7”). Figure 2 expands on the so-called “rule of 5” from the consensus document and correlates liver stiffness (by VCTE) with progression of liver fibrosis as well as clinical presentation. For example, liver stiffness < 15 kPa is associated with a low risk of clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH). Similarly, in patients with a normal platelet count (>150,000/mm3) and liver stiffness < 20 kPa, the probability of gastroesophageal varices is sufficiently low that a screening endoscopy may be avoided. On the other hand, liver stiffness > 25 kPa is associated with increasing risk of decompensated cirrhosis and portal hypertension.16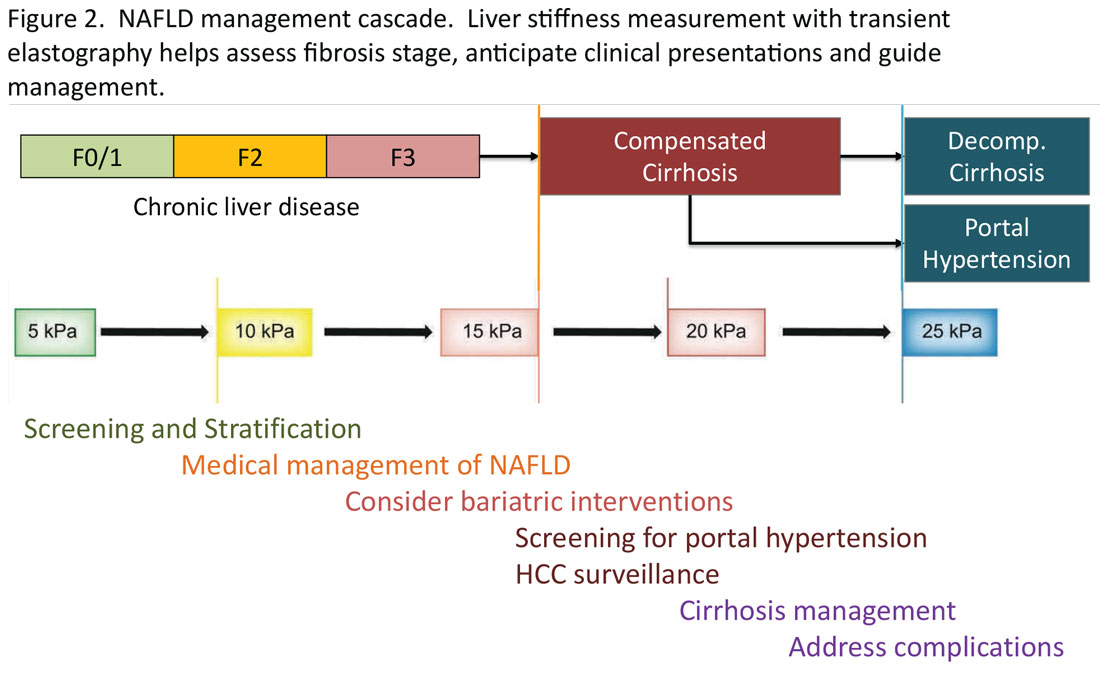
Partnership between primary care and specialty
The insights expressed in Figure 2 can be utilized to guide management decisions. In patients without evidence of liver fibrosis, emphasis may primarily be on screening, stratification and management of metabolic syndrome. For patients with evidence of incipient liver fibrosis, medical management of NAFLD needs to be implemented including lifestyle changes and pharmacological interventions as appropriate. For patients unresponsive to medical therapy, an endoscopic or surgical bariatric procedure should be considered. Management of patients with evidence of cirrhosis includes screening for portal hypertension, surveillance for HCC, medical management of cirrhosis, and finally, in suitable cases, referral for liver transplant evaluation. The reader is referred to the latest treatment guidelines for detailed discussion of these individual management modalities [ref, AGA and AASLD guidelines].14,17
Given the spectrum of management modalities needed to successfully manage patients with NAFLD, it is unrealistic to expect that hepatologists and gastroenterologists are able to manage the large number of patients with NAFLD. In general, clinical activities on the left side of the figure are in the domain of primary care providers, whereas management of patients with progressive liver fibrosis is conducted by the specialist. An important aspect of the overall management of these patients is risk management in terms of the metabolic syndrome, including cardiovascular risk reduction and diabetes management, as appropriate. Many patients with NAFLD are burdened with several comorbidities and likely to benefit from a multidisciplinary team consisting of primary care, endocrinology, preventive cardiology, pharmacy, nutrition/dietetics, social services, and addiction specialists, as well as hepatology and gastroenterology. Prospective, high-quality data to define these teams and their function are yet to be generated.
Conclusion
NAFLD is an important and increasing public health concern in the U.S. Once diagnosed, assessing liver fibrosis and evaluating the presence of the components of metabolic syndrome in these patients, constitute the key components in the care in terms of risk stratification, medical management, and referral decisions. Noninvasive tests have been increasingly utilized including liver stiffness measurements and various blood test-based indicators. For patients in specialty GI/hepatology care, transient elastography is a widely accepted tool, with which standardized recommendations may be made for screening, stratification, and medical and surgical interventions in patients with NAFLD.
Mai Sedki, MD, MPH, is a doctoral candidate at the University of California, San Francisco. W. Ray Kim, MD, is professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology) at Stanford (Calif.) University. Address correspondence to: [email protected]. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Twitter: @SedkiMD and @WRayKimMD.
References
1. Younossi ZM et al. Epidemiology of chronic liver diseases in the USA in the past three decades. Gut. 2020 Mar;69(3):564-8.
2. Lazo M et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Am J Epidemiol. 2013 Jul 1;178(1):38-45.
3. Kim D et al. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57:1357-65.
4. Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002 Apr 18;346:1221-31.
5. Kim D et al. Changing trends in etiology-based annual mortality from chronic liver disease, from 2007 through 2016. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1154-63.e3.
6. FastStats. Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
7. Rich NE et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence, severity, and outcomes in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(2):198-210. e2.
8. Coleman-Jensen A et al. Household food security in the United States in 2020 (ERR-298). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture; Sep 2021.
9. Sanyal AJ et al. Prospective study of outcomes in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 21;385(17):1559-69.
10. Ng CH et al. Mortality outcomes by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Apr;21(4):931-9.e5.
11. Hagström H et al. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2017;67(6):1265-73.
12. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
13. Singh S et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;13(3):440-51.e6.
14. Kanwal F et al. Clinical Care Pathway for the risk stratification and management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2021 Nov;161(5):1657-69.
15. Sripongpun P et al. The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) score: A tool to detect low-risk NAFLD in primary care. .
16. de Franchis R et al. Baveno VII: Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):959-74.
17. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
Burden of NAFLD in the U.S.
NAFLD is a manifestation of systemic metabolic abnormalities, including insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, central obesity, and hypertension. In this short review, we summarize data on the burden of NAFLD in the U.S. and its prognostic determinants and review what clinical and public health approaches may be needed to mitigating its impact.
Epidemiology of NAFLD
Worldwide, the prevalence of NAFLD is estimated at 6% to 35%, with biopsy-based studies reporting NASH in 3% to 5%.1 U.S. estimates for the prevalence of NAFLD range from 10% to 46%.2 In our own analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data, transient elastography-detected steatosis was found in 36%, which projected to a minimum of 73 million American adults.3
NAFLD represents a spectrum of disorders ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the latter leading, in some cases, to progressive hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.4 Out of a large number of subjects with NAFLD, the proportions of NASH patients that develop severe liver problems such as end-stage liver disease (ESLD) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are progressively smaller. For example, we recently reported that less than 2,000 liver-related deaths are attributable to NAFLD in the U.S. per annum, which corresponds to a crude case fatality rate of < 0.005% per year.5
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there have been substantial increases in liver-related deaths over the last 2 decades. Mortality from liver disease including hepatobiliary cancers more than doubled from 41,966 deaths (including 15,321 women and 26,645 men) in 2000 to 85,884 deaths (33,000 women and 52,884 men) in 2020. The proportion of deaths specifically attributed to NAFLD among liver-related deaths was miniscule in 2000, accounting for 1.1% in women and 0.7% in men. By 2020, the proportions increased several folds in both sexes (7.4% in women and 2.7% in men).6 Moreover, it is likely that a substantial portion of deaths from chronic liver disease from unknown causes (“cryptogenic”) are likely end-stage NAFLD, making these figures underestimates of the true impact of NAFLD in the U.S.
From a comparative epidemiologic perspective, there are significant racial and ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in NAFLD prevalence, wherein Hispanic persons and individuals experiencing food insecurity – independent of poverty status, education level, race and ethnicity – are disproportionately more affected by NAFLD.7,8 Furthermore, these disparities persist when examining long-term complications of NAFLD, such as developing HCC.
Prognosis in NAFLD: NASH versus fibrosis
Given the enormous prevalence and increasing public health burden of NAFLD, systematic interventions to mitigate its impact are urgently needed. Clearly, patients who already have developed advanced liver disease need to be directed to specialty care so the disease progression may be halted and complications of ESLD may be prevented or managed. On the other hand, in order to mitigate the future impact of ESLD, prompt identification of at-risk patients and proactive interventions to improve liver health are needed.
In the assessment of disease progression, prior data have shown that the presence of NASH and increasing stages of liver fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression. Fibrosis is a component of NASH, while NASH is thought to be a prerequisite for fibrosis. In a prospective, multicenter follow-up study of NAFLD evaluated by liver biopsies (n = 1,773), over a median follow-up of 4 years, 37 (2%) developed hepatic decompensation, while 47 (3%) died from any cause, which included ESLD (n = 12), cardiovascular complications (n = 4), and malignancies (n = 12), including HCC (n = 9).9 It is not entirely surprising that advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis was highly associated with the development of hepatic decompensation. In their multivariable analysis, patients with F3-4 had a 13.8-fold (95% confidence interval [CI]: 4.6, 41.0) increase in the hazard of reaching a MELD score of 15 compared to those with F0-2. In addition, all-cause mortality was 17.2-fold (95% CI: 5.2, 56.6) higher with F3-4 compared to F0-2.
These data have been borne out by a larger body of literature on the topic. In a recent meta-analysis assessing the relation between liver fibrosis and future mortality, which included 17,301 subjects with NAFLD, patients with at least stage 2 fibrosis experience a significantly increased risk of liver-related and overall mortality, a trend that accelerates at higher fibrosis stages.10 These point to liver fibrosis as the singular determinant of long-term prognosis, in comparison, for example, with the diagnosis of NASH. Hagström conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD in Sweden. When fibrosis stage and histological diagnosis of NASH were considered together, NASH did not have an impact on overall mortality (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.83, P = .29) or liver morbidity (HR = 0.62, P = .25).11
On an individual level, factors that affect fibrosis progression are not as well studied. It is commonly believed that demographic factors (e.g., age, sex and race), genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3, TM6SF2), clinical comorbidities (e.g., obesity, DM, and sleep apnea), and environmental factors (e.g., smoking) may accelerate fibrosis and disease outcomes, although prospective data are sparse to estimate the extent these individual variables affect progression.12 Recent guidelines remain silent about whether and how these data may be incorporated in screening for NAFLD in the population.
Assessment of liver fibrosis
The traditional means to detect liver fibrosis is liver histology, which also assesses steatosis, individual components of NASH and, often importantly, other concomitant liver pathology. In reality, however, liver biopsies have several limitations including the risk of complications, patient discomfort, economic costs, and sampling variability. Increasingly, “noninvasive” methods have been used to estimate liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Liver elastography estimates the physical stiffness of the organ, which may be measured by MRI or ultrasound. Among ultrasound-based technologies, vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) is more widely accepted and affordable although it may not be as accurate as MR elastography.13
In general, these elastographic tests are not readily accessible to most physicians outside hepatology specialty practices. Instead, blood test-based markers have been developed and widely recommended as the initial modality to assess liver fibrosis. Figure 1 represents a partial list of blood test-based markers. Traditionally, FIB-4 and NFS have been considered the most widely recommended by society guidelines. The AGA Pathway for evaluation of patients with NAFLD recommends first to apply the FIB-4 score and, in patients considered to be at intermediate risk of fibrosis for advanced fibrosis (stage 3 or 4, FIB-4 = 1.3-2.67), to assess liver stiffness by VCTE.14
More recently, the accumulating natural history data have highlighted the inflection in the risk of future outcomes coinciding with F2 and therapeutic trials that target patients with “at risk NASH,” thus more attention has been paid to the identification of patients with stage 2 (or higher). The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) was developed for this specific purpose. The score has been validated in multiple data sets, in all of which SAFE outperformed FIB-4 and NFS (Figure 1). When the score was applied to assess overall survival in participants of the NHANES, patients with NAFLD deemed to be high risk (SAFE > 100) had significantly lower survival (37% Kaplan-Meier survival at 20 years), compared to those with intermediate (SAFE 0-100, 61% survival) and low (SAFE < 0, 86% survival). In comparison, the 20-year survival of subjects without NAFLD survival was 79%.15
Regardless of the modality for initial stratification, it is widely accepted that mechanical elastography constitutes the next step in prognosticating the patient. In the AGA Pathway, liver stiffness of < 8 kPa is considered low risk, which corresponds in most analysis with lack of stage 2 fibrosis, whereas stiffness of > 12 kPa may be indicative of stage 3 or 4. These recommendations are consistent with those from the latest Baveno Consensus Conference (“Baveno 7”). Figure 2 expands on the so-called “rule of 5” from the consensus document and correlates liver stiffness (by VCTE) with progression of liver fibrosis as well as clinical presentation. For example, liver stiffness < 15 kPa is associated with a low risk of clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH). Similarly, in patients with a normal platelet count (>150,000/mm3) and liver stiffness < 20 kPa, the probability of gastroesophageal varices is sufficiently low that a screening endoscopy may be avoided. On the other hand, liver stiffness > 25 kPa is associated with increasing risk of decompensated cirrhosis and portal hypertension.16
Partnership between primary care and specialty
The insights expressed in Figure 2 can be utilized to guide management decisions. In patients without evidence of liver fibrosis, emphasis may primarily be on screening, stratification and management of metabolic syndrome. For patients with evidence of incipient liver fibrosis, medical management of NAFLD needs to be implemented including lifestyle changes and pharmacological interventions as appropriate. For patients unresponsive to medical therapy, an endoscopic or surgical bariatric procedure should be considered. Management of patients with evidence of cirrhosis includes screening for portal hypertension, surveillance for HCC, medical management of cirrhosis, and finally, in suitable cases, referral for liver transplant evaluation. The reader is referred to the latest treatment guidelines for detailed discussion of these individual management modalities [ref, AGA and AASLD guidelines].14,17
Given the spectrum of management modalities needed to successfully manage patients with NAFLD, it is unrealistic to expect that hepatologists and gastroenterologists are able to manage the large number of patients with NAFLD. In general, clinical activities on the left side of the figure are in the domain of primary care providers, whereas management of patients with progressive liver fibrosis is conducted by the specialist. An important aspect of the overall management of these patients is risk management in terms of the metabolic syndrome, including cardiovascular risk reduction and diabetes management, as appropriate. Many patients with NAFLD are burdened with several comorbidities and likely to benefit from a multidisciplinary team consisting of primary care, endocrinology, preventive cardiology, pharmacy, nutrition/dietetics, social services, and addiction specialists, as well as hepatology and gastroenterology. Prospective, high-quality data to define these teams and their function are yet to be generated.
Conclusion
NAFLD is an important and increasing public health concern in the U.S. Once diagnosed, assessing liver fibrosis and evaluating the presence of the components of metabolic syndrome in these patients, constitute the key components in the care in terms of risk stratification, medical management, and referral decisions. Noninvasive tests have been increasingly utilized including liver stiffness measurements and various blood test-based indicators. For patients in specialty GI/hepatology care, transient elastography is a widely accepted tool, with which standardized recommendations may be made for screening, stratification, and medical and surgical interventions in patients with NAFLD.
Mai Sedki, MD, MPH, is a doctoral candidate at the University of California, San Francisco. W. Ray Kim, MD, is professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology) at Stanford (Calif.) University. Address correspondence to: [email protected]. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Twitter: @SedkiMD and @WRayKimMD.
References
1. Younossi ZM et al. Epidemiology of chronic liver diseases in the USA in the past three decades. Gut. 2020 Mar;69(3):564-8.
2. Lazo M et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Am J Epidemiol. 2013 Jul 1;178(1):38-45.
3. Kim D et al. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57:1357-65.
4. Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002 Apr 18;346:1221-31.
5. Kim D et al. Changing trends in etiology-based annual mortality from chronic liver disease, from 2007 through 2016. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1154-63.e3.
6. FastStats. Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
7. Rich NE et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence, severity, and outcomes in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(2):198-210. e2.
8. Coleman-Jensen A et al. Household food security in the United States in 2020 (ERR-298). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture; Sep 2021.
9. Sanyal AJ et al. Prospective study of outcomes in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 21;385(17):1559-69.
10. Ng CH et al. Mortality outcomes by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Apr;21(4):931-9.e5.
11. Hagström H et al. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2017;67(6):1265-73.
12. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
13. Singh S et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;13(3):440-51.e6.
14. Kanwal F et al. Clinical Care Pathway for the risk stratification and management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2021 Nov;161(5):1657-69.
15. Sripongpun P et al. The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) score: A tool to detect low-risk NAFLD in primary care. .
16. de Franchis R et al. Baveno VII: Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):959-74.
17. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
Burden of NAFLD in the U.S.
NAFLD is a manifestation of systemic metabolic abnormalities, including insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, central obesity, and hypertension. In this short review, we summarize data on the burden of NAFLD in the U.S. and its prognostic determinants and review what clinical and public health approaches may be needed to mitigating its impact.
Epidemiology of NAFLD
Worldwide, the prevalence of NAFLD is estimated at 6% to 35%, with biopsy-based studies reporting NASH in 3% to 5%.1 U.S. estimates for the prevalence of NAFLD range from 10% to 46%.2 In our own analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data, transient elastography-detected steatosis was found in 36%, which projected to a minimum of 73 million American adults.3
NAFLD represents a spectrum of disorders ranging from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the latter leading, in some cases, to progressive hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.4 Out of a large number of subjects with NAFLD, the proportions of NASH patients that develop severe liver problems such as end-stage liver disease (ESLD) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are progressively smaller. For example, we recently reported that less than 2,000 liver-related deaths are attributable to NAFLD in the U.S. per annum, which corresponds to a crude case fatality rate of < 0.005% per year.5
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there have been substantial increases in liver-related deaths over the last 2 decades. Mortality from liver disease including hepatobiliary cancers more than doubled from 41,966 deaths (including 15,321 women and 26,645 men) in 2000 to 85,884 deaths (33,000 women and 52,884 men) in 2020. The proportion of deaths specifically attributed to NAFLD among liver-related deaths was miniscule in 2000, accounting for 1.1% in women and 0.7% in men. By 2020, the proportions increased several folds in both sexes (7.4% in women and 2.7% in men).6 Moreover, it is likely that a substantial portion of deaths from chronic liver disease from unknown causes (“cryptogenic”) are likely end-stage NAFLD, making these figures underestimates of the true impact of NAFLD in the U.S.
From a comparative epidemiologic perspective, there are significant racial and ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in NAFLD prevalence, wherein Hispanic persons and individuals experiencing food insecurity – independent of poverty status, education level, race and ethnicity – are disproportionately more affected by NAFLD.7,8 Furthermore, these disparities persist when examining long-term complications of NAFLD, such as developing HCC.
Prognosis in NAFLD: NASH versus fibrosis
Given the enormous prevalence and increasing public health burden of NAFLD, systematic interventions to mitigate its impact are urgently needed. Clearly, patients who already have developed advanced liver disease need to be directed to specialty care so the disease progression may be halted and complications of ESLD may be prevented or managed. On the other hand, in order to mitigate the future impact of ESLD, prompt identification of at-risk patients and proactive interventions to improve liver health are needed.
In the assessment of disease progression, prior data have shown that the presence of NASH and increasing stages of liver fibrosis are important predictors of disease progression. Fibrosis is a component of NASH, while NASH is thought to be a prerequisite for fibrosis. In a prospective, multicenter follow-up study of NAFLD evaluated by liver biopsies (n = 1,773), over a median follow-up of 4 years, 37 (2%) developed hepatic decompensation, while 47 (3%) died from any cause, which included ESLD (n = 12), cardiovascular complications (n = 4), and malignancies (n = 12), including HCC (n = 9).9 It is not entirely surprising that advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis was highly associated with the development of hepatic decompensation. In their multivariable analysis, patients with F3-4 had a 13.8-fold (95% confidence interval [CI]: 4.6, 41.0) increase in the hazard of reaching a MELD score of 15 compared to those with F0-2. In addition, all-cause mortality was 17.2-fold (95% CI: 5.2, 56.6) higher with F3-4 compared to F0-2.
These data have been borne out by a larger body of literature on the topic. In a recent meta-analysis assessing the relation between liver fibrosis and future mortality, which included 17,301 subjects with NAFLD, patients with at least stage 2 fibrosis experience a significantly increased risk of liver-related and overall mortality, a trend that accelerates at higher fibrosis stages.10 These point to liver fibrosis as the singular determinant of long-term prognosis, in comparison, for example, with the diagnosis of NASH. Hagström conducted a retrospective cohort study of patients with biopsy-proven NAFLD in Sweden. When fibrosis stage and histological diagnosis of NASH were considered together, NASH did not have an impact on overall mortality (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.83, P = .29) or liver morbidity (HR = 0.62, P = .25).11
On an individual level, factors that affect fibrosis progression are not as well studied. It is commonly believed that demographic factors (e.g., age, sex and race), genetic polymorphisms (e.g., PNPLA3, TM6SF2), clinical comorbidities (e.g., obesity, DM, and sleep apnea), and environmental factors (e.g., smoking) may accelerate fibrosis and disease outcomes, although prospective data are sparse to estimate the extent these individual variables affect progression.12 Recent guidelines remain silent about whether and how these data may be incorporated in screening for NAFLD in the population.
Assessment of liver fibrosis
The traditional means to detect liver fibrosis is liver histology, which also assesses steatosis, individual components of NASH and, often importantly, other concomitant liver pathology. In reality, however, liver biopsies have several limitations including the risk of complications, patient discomfort, economic costs, and sampling variability. Increasingly, “noninvasive” methods have been used to estimate liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Liver elastography estimates the physical stiffness of the organ, which may be measured by MRI or ultrasound. Among ultrasound-based technologies, vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) is more widely accepted and affordable although it may not be as accurate as MR elastography.13
In general, these elastographic tests are not readily accessible to most physicians outside hepatology specialty practices. Instead, blood test-based markers have been developed and widely recommended as the initial modality to assess liver fibrosis. Figure 1 represents a partial list of blood test-based markers. Traditionally, FIB-4 and NFS have been considered the most widely recommended by society guidelines. The AGA Pathway for evaluation of patients with NAFLD recommends first to apply the FIB-4 score and, in patients considered to be at intermediate risk of fibrosis for advanced fibrosis (stage 3 or 4, FIB-4 = 1.3-2.67), to assess liver stiffness by VCTE.14
More recently, the accumulating natural history data have highlighted the inflection in the risk of future outcomes coinciding with F2 and therapeutic trials that target patients with “at risk NASH,” thus more attention has been paid to the identification of patients with stage 2 (or higher). The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) was developed for this specific purpose. The score has been validated in multiple data sets, in all of which SAFE outperformed FIB-4 and NFS (Figure 1). When the score was applied to assess overall survival in participants of the NHANES, patients with NAFLD deemed to be high risk (SAFE > 100) had significantly lower survival (37% Kaplan-Meier survival at 20 years), compared to those with intermediate (SAFE 0-100, 61% survival) and low (SAFE < 0, 86% survival). In comparison, the 20-year survival of subjects without NAFLD survival was 79%.15
Regardless of the modality for initial stratification, it is widely accepted that mechanical elastography constitutes the next step in prognosticating the patient. In the AGA Pathway, liver stiffness of < 8 kPa is considered low risk, which corresponds in most analysis with lack of stage 2 fibrosis, whereas stiffness of > 12 kPa may be indicative of stage 3 or 4. These recommendations are consistent with those from the latest Baveno Consensus Conference (“Baveno 7”). Figure 2 expands on the so-called “rule of 5” from the consensus document and correlates liver stiffness (by VCTE) with progression of liver fibrosis as well as clinical presentation. For example, liver stiffness < 15 kPa is associated with a low risk of clinically significant portal hypertension (CSPH). Similarly, in patients with a normal platelet count (>150,000/mm3) and liver stiffness < 20 kPa, the probability of gastroesophageal varices is sufficiently low that a screening endoscopy may be avoided. On the other hand, liver stiffness > 25 kPa is associated with increasing risk of decompensated cirrhosis and portal hypertension.16
Partnership between primary care and specialty
The insights expressed in Figure 2 can be utilized to guide management decisions. In patients without evidence of liver fibrosis, emphasis may primarily be on screening, stratification and management of metabolic syndrome. For patients with evidence of incipient liver fibrosis, medical management of NAFLD needs to be implemented including lifestyle changes and pharmacological interventions as appropriate. For patients unresponsive to medical therapy, an endoscopic or surgical bariatric procedure should be considered. Management of patients with evidence of cirrhosis includes screening for portal hypertension, surveillance for HCC, medical management of cirrhosis, and finally, in suitable cases, referral for liver transplant evaluation. The reader is referred to the latest treatment guidelines for detailed discussion of these individual management modalities [ref, AGA and AASLD guidelines].14,17
Given the spectrum of management modalities needed to successfully manage patients with NAFLD, it is unrealistic to expect that hepatologists and gastroenterologists are able to manage the large number of patients with NAFLD. In general, clinical activities on the left side of the figure are in the domain of primary care providers, whereas management of patients with progressive liver fibrosis is conducted by the specialist. An important aspect of the overall management of these patients is risk management in terms of the metabolic syndrome, including cardiovascular risk reduction and diabetes management, as appropriate. Many patients with NAFLD are burdened with several comorbidities and likely to benefit from a multidisciplinary team consisting of primary care, endocrinology, preventive cardiology, pharmacy, nutrition/dietetics, social services, and addiction specialists, as well as hepatology and gastroenterology. Prospective, high-quality data to define these teams and their function are yet to be generated.
Conclusion
NAFLD is an important and increasing public health concern in the U.S. Once diagnosed, assessing liver fibrosis and evaluating the presence of the components of metabolic syndrome in these patients, constitute the key components in the care in terms of risk stratification, medical management, and referral decisions. Noninvasive tests have been increasingly utilized including liver stiffness measurements and various blood test-based indicators. For patients in specialty GI/hepatology care, transient elastography is a widely accepted tool, with which standardized recommendations may be made for screening, stratification, and medical and surgical interventions in patients with NAFLD.
Mai Sedki, MD, MPH, is a doctoral candidate at the University of California, San Francisco. W. Ray Kim, MD, is professor of medicine (gastroenterology and hepatology) at Stanford (Calif.) University. Address correspondence to: [email protected]. The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest. Twitter: @SedkiMD and @WRayKimMD.
References
1. Younossi ZM et al. Epidemiology of chronic liver diseases in the USA in the past three decades. Gut. 2020 Mar;69(3):564-8.
2. Lazo M et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Am J Epidemiol. 2013 Jul 1;178(1):38-45.
3. Kim D et al. Association between noninvasive fibrosis markers and mortality among adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States. Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57:1357-65.
4. Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002 Apr 18;346:1221-31.
5. Kim D et al. Changing trends in etiology-based annual mortality from chronic liver disease, from 2007 through 2016. Gastroenterology. 2018;155(4):1154-63.e3.
6. FastStats. Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
7. Rich NE et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence, severity, and outcomes in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(2):198-210. e2.
8. Coleman-Jensen A et al. Household food security in the United States in 2020 (ERR-298). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture; Sep 2021.
9. Sanyal AJ et al. Prospective study of outcomes in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2021 Oct 21;385(17):1559-69.
10. Ng CH et al. Mortality outcomes by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Apr;21(4):931-9.e5.
11. Hagström H et al. Fibrosis stage but not NASH predicts mortality and time to development of severe liver disease in biopsy-proven NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2017;67(6):1265-73.
12. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
13. Singh S et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Mar;13(3):440-51.e6.
14. Kanwal F et al. Clinical Care Pathway for the risk stratification and management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2021 Nov;161(5):1657-69.
15. Sripongpun P et al. The steatosis-associated fibrosis estimator (SAFE) score: A tool to detect low-risk NAFLD in primary care. .
16. de Franchis R et al. Baveno VII: Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):959-74.
17. Rinella ME et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2023 May 1;77(5):1797-835.
Ensuring trustworthy health AI
in health care.
It was a thought-provoking discussion of how to ethically and equitably design and regulate these exciting new technologies to maximize their potential to achieve meaningful improvements in health for our patients while avoiding unintended consequences.
Indeed, one of the vexing challenges in this space is the fact that many AI algorithms and resulting tools are proprietary, impeding the ability to achieve the level of transparency necessary to understand data inputs, outputs, and outcomes, and assess for potential algorithmic bias.
This is an area that remains largely unregulated, with a lack of common standards to guide responsible design, development, and adoption of these tools. This is something that is top of mind for federal regulatory agencies, including the Food and Drug Administration, which in September 2022, announced plans to expand its regulation of AI-powered clinical decision support tools as medical devices.
There are also attempts underway to harmonize standards and reporting for health AI and educate end-users on how to evaluate these technologies to drive their responsible adoption. For example, the Coalition for Health AI, a community of academic health systems, organizations, and expert practitioners of AI and data science, recently released its Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare in April 2023. This is a topic we will surely hear more about in the coming years, and one I encourage you to read about in greater depth as it is truly eye-opening.
In this month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on a new fatty liver disease nomenclature (including several new acronyms) that will be critical to incorporate into your clinical practice moving forward. In a new recurring article reprinted from Gastro Hep Advances, we highlight important Pearls from the Pros from hepatologists Dr. Lawrence Friedman and Dr. Paul Martin on the management of incidental hepatic steatosis. Our August Member Spotlight features Orlando-based gastroenterologist Dr. Mariam Naveed, who shares her passion for medical education and experience starting a new GI fellowship program.
We hope you enjoy these and all the stories featured in our August issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
in health care.
It was a thought-provoking discussion of how to ethically and equitably design and regulate these exciting new technologies to maximize their potential to achieve meaningful improvements in health for our patients while avoiding unintended consequences.
Indeed, one of the vexing challenges in this space is the fact that many AI algorithms and resulting tools are proprietary, impeding the ability to achieve the level of transparency necessary to understand data inputs, outputs, and outcomes, and assess for potential algorithmic bias.
This is an area that remains largely unregulated, with a lack of common standards to guide responsible design, development, and adoption of these tools. This is something that is top of mind for federal regulatory agencies, including the Food and Drug Administration, which in September 2022, announced plans to expand its regulation of AI-powered clinical decision support tools as medical devices.
There are also attempts underway to harmonize standards and reporting for health AI and educate end-users on how to evaluate these technologies to drive their responsible adoption. For example, the Coalition for Health AI, a community of academic health systems, organizations, and expert practitioners of AI and data science, recently released its Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare in April 2023. This is a topic we will surely hear more about in the coming years, and one I encourage you to read about in greater depth as it is truly eye-opening.
In this month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on a new fatty liver disease nomenclature (including several new acronyms) that will be critical to incorporate into your clinical practice moving forward. In a new recurring article reprinted from Gastro Hep Advances, we highlight important Pearls from the Pros from hepatologists Dr. Lawrence Friedman and Dr. Paul Martin on the management of incidental hepatic steatosis. Our August Member Spotlight features Orlando-based gastroenterologist Dr. Mariam Naveed, who shares her passion for medical education and experience starting a new GI fellowship program.
We hope you enjoy these and all the stories featured in our August issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
in health care.
It was a thought-provoking discussion of how to ethically and equitably design and regulate these exciting new technologies to maximize their potential to achieve meaningful improvements in health for our patients while avoiding unintended consequences.
Indeed, one of the vexing challenges in this space is the fact that many AI algorithms and resulting tools are proprietary, impeding the ability to achieve the level of transparency necessary to understand data inputs, outputs, and outcomes, and assess for potential algorithmic bias.
This is an area that remains largely unregulated, with a lack of common standards to guide responsible design, development, and adoption of these tools. This is something that is top of mind for federal regulatory agencies, including the Food and Drug Administration, which in September 2022, announced plans to expand its regulation of AI-powered clinical decision support tools as medical devices.
There are also attempts underway to harmonize standards and reporting for health AI and educate end-users on how to evaluate these technologies to drive their responsible adoption. For example, the Coalition for Health AI, a community of academic health systems, organizations, and expert practitioners of AI and data science, recently released its Blueprint for Trustworthy AI Implementation Guidance and Assurance for Healthcare in April 2023. This is a topic we will surely hear more about in the coming years, and one I encourage you to read about in greater depth as it is truly eye-opening.
In this month’s issue of GI & Hepatology News, we update you on a new fatty liver disease nomenclature (including several new acronyms) that will be critical to incorporate into your clinical practice moving forward. In a new recurring article reprinted from Gastro Hep Advances, we highlight important Pearls from the Pros from hepatologists Dr. Lawrence Friedman and Dr. Paul Martin on the management of incidental hepatic steatosis. Our August Member Spotlight features Orlando-based gastroenterologist Dr. Mariam Naveed, who shares her passion for medical education and experience starting a new GI fellowship program.
We hope you enjoy these and all the stories featured in our August issue.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor-in-Chief
Transitions and growth
Dear friends,
This fall, I will also be starting my first position out of fellowship. I look forward to many opportunities and challenges to come.
This month in In Focus, Dr. Mai Sedki and Dr. W. Ray Kim unpack the nuances of assessing and risk-stratifying patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using non-invasive testing in daily practice. Beyond daily practice, it is important to know where our field is advancing to offer patients more options. In Short Clinical Reviews, Dr. Aileen Bui and Dr. James Buxbaum review how the field of endohepatology is expanding into endoscopic ultrasound–guided liver biopsies, portal pressure measurements, and interventions of gastric varices.
In our Early Career feature, Dr. Corlan Eboh, Dr. Victoria Jaeger, and Dr. Dawn Sears describe how gastroenterologists are uniquely positioned for burnout and what can be done to prevent and treat it, particularly among new and transitioning gastroenterologists. In post-COVID era, practices have experienced an increase in portal messages and other non-face-to-face patient care, which may be contributing burnout.
In our Finance section this month, Dr. Luis Nieto and Dr. Jami Kinnucan review the types of patient encounters and billing options to optimize your compensation for time spent.
In Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. David Ramsey discusses why he joined a private practice and how understanding your own goals and values can guide you to a good fit in different practice models. Lastly, Dr. Dan Kroch describes his unique journey in becoming a third-space endoscopist without an advanced fellowship year and why dedicated training is the future of advanced endoscopic resection and third-space endoscopy.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact: The first endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was first performed by an obstetrician, Dr. William McCune in 1968, and achieved by taping an external accessory channel to a duodenoscope.
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Dear friends,
This fall, I will also be starting my first position out of fellowship. I look forward to many opportunities and challenges to come.
This month in In Focus, Dr. Mai Sedki and Dr. W. Ray Kim unpack the nuances of assessing and risk-stratifying patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using non-invasive testing in daily practice. Beyond daily practice, it is important to know where our field is advancing to offer patients more options. In Short Clinical Reviews, Dr. Aileen Bui and Dr. James Buxbaum review how the field of endohepatology is expanding into endoscopic ultrasound–guided liver biopsies, portal pressure measurements, and interventions of gastric varices.
In our Early Career feature, Dr. Corlan Eboh, Dr. Victoria Jaeger, and Dr. Dawn Sears describe how gastroenterologists are uniquely positioned for burnout and what can be done to prevent and treat it, particularly among new and transitioning gastroenterologists. In post-COVID era, practices have experienced an increase in portal messages and other non-face-to-face patient care, which may be contributing burnout.
In our Finance section this month, Dr. Luis Nieto and Dr. Jami Kinnucan review the types of patient encounters and billing options to optimize your compensation for time spent.
In Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. David Ramsey discusses why he joined a private practice and how understanding your own goals and values can guide you to a good fit in different practice models. Lastly, Dr. Dan Kroch describes his unique journey in becoming a third-space endoscopist without an advanced fellowship year and why dedicated training is the future of advanced endoscopic resection and third-space endoscopy.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact: The first endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was first performed by an obstetrician, Dr. William McCune in 1968, and achieved by taping an external accessory channel to a duodenoscope.
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Dear friends,
This fall, I will also be starting my first position out of fellowship. I look forward to many opportunities and challenges to come.
This month in In Focus, Dr. Mai Sedki and Dr. W. Ray Kim unpack the nuances of assessing and risk-stratifying patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using non-invasive testing in daily practice. Beyond daily practice, it is important to know where our field is advancing to offer patients more options. In Short Clinical Reviews, Dr. Aileen Bui and Dr. James Buxbaum review how the field of endohepatology is expanding into endoscopic ultrasound–guided liver biopsies, portal pressure measurements, and interventions of gastric varices.
In our Early Career feature, Dr. Corlan Eboh, Dr. Victoria Jaeger, and Dr. Dawn Sears describe how gastroenterologists are uniquely positioned for burnout and what can be done to prevent and treat it, particularly among new and transitioning gastroenterologists. In post-COVID era, practices have experienced an increase in portal messages and other non-face-to-face patient care, which may be contributing burnout.
In our Finance section this month, Dr. Luis Nieto and Dr. Jami Kinnucan review the types of patient encounters and billing options to optimize your compensation for time spent.
In Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. David Ramsey discusses why he joined a private practice and how understanding your own goals and values can guide you to a good fit in different practice models. Lastly, Dr. Dan Kroch describes his unique journey in becoming a third-space endoscopist without an advanced fellowship year and why dedicated training is the future of advanced endoscopic resection and third-space endoscopy.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me ([email protected]), or Jillian Schweitzer ([email protected]), managing editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact: The first endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was first performed by an obstetrician, Dr. William McCune in 1968, and achieved by taping an external accessory channel to a duodenoscope.
Yours truly,
Judy A Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Advanced Endoscopy Fellow
Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
UNAIDS targets: Progress reported, but ‘HIV is far from over’
BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA – The year was 1987 and the Grim Reaper (a personification of death), holding a large scythe, rolled a 10-pin bowling ball through a dark, foggy place. In the advertisement on television, the cloaked skeleton aimed the bowling ball at the other end of a lane where a group of people stood in place of pins.
Who would fall next?
In the 1980s, cases of HIV were rising in the community and people in Australia and elsewhere were dying of AIDS. The Australian government opted to use mainstream media to deliver a blunt message through advertising to raise awareness about the health risk and how to manage HIV in the community.
But the campaign also contributed to stigma for those living with the disease and especially those in the gay community who felt ostracized by rising public concern.
In the inner city of Sydney, a few thousand people died of AIDS, Andrew Grulich, MD, PhD, from the Kirby Institute at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and involved in tracking cases, said in an interview. “Sydney was devastated by AIDS, it was truly devastated.”
HIV and AIDS quickly became an even more severe problem for several countries around Australia in Thailand, Papua New Guinea, and beyond. After HIV was first reported in Thailand in 1984, the region had the highest prevalence of HIV in Southeast Asia. Through the 1990s in Papua New Guinea, HIV prevalence rose steeply as well.
By 2010, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) set a target of a 90% reduction in HIV incidence, a 90% reduction in AIDS deaths by 2030, and 95% of people living with HIV and AIDS being aware of their status, on treatment, and having an undetectable viral load.
Since then, significant progress has been made globally with 86% of people knowing their HIV status. However, new infections persist at a rate that has not dropped as fast as possible.
New infections
According to the latest UNAIDS report, regions of North America and western and central Europe showed a 23% decline in new infections from 2010 to 2022, below the target 90% reduction.
Some regions of the United States have seen significant declines in new HIV infections. San Francisco has a 67% drop in new diagnoses. And now, along with the District of Columbia, the four states with the highest HIV rates are New York, Maryland, Georgia, and Florida.
Several countries in eastern and southern Africa are close to achieving their target HIV reduction of 90%.
Mitchell Warren, executive director of AVAC for global health advocacy, access, and equity, said that many of the low- and middle-income countries that are on track to achieve targets are able to do so because of support from the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
“That foreign development assistance is transforming the AIDS response in a number of African countries, and yet at home, in various states and municipalities, not only are we not reaching that effort, we don’t even use those targets,” Mr. Warren pointed out.
“We might see municipalities that are performing well, but at a national level it’s frankly a disgrace by comparison, because we know what’s possible,” Mr. Warren said.
Lowering cases
Today, in the inner city of Sydney, new HIV diagnoses have plummeted by 88%, which puts the area on track to achieve the 90% UNAIDS target ahead of schedule.
Dr. Grulich and his team at the Kirby Institute are tracking new diagnoses by postal code and reported their encouraging findings here this week at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
“This 88% decline is happening in an area where, in the ’80s and ’90s, a few thousand people died of AIDS,” Dr. Grulich told this news organization. “It feels close to miraculous.”
Dr. Grulich attributes some of the success to long-term government leadership that for the most part has been apolitical. HIV has been perceived by the public as an important health issue to be addressed. “We’ve never had a political contest over it,” he added. “We have politicians who are committed to evidence-based policy.”
In inner city Sydney, HIV prevention campaigns are a visible part of community life, Dr. Grulich explained. At public events, it is discussed; at bus stops, posters are on display; and passing trains have messages plastered to the side of them.
That community effort has consistently received government funding for years – albeit linked to key performance indicators – but it has enabled a high level of communication among government, community, clinicians, and researchers.
Another advantage is Australia’s universal health coverage, said Sharon Lewin, PhD, president of the International AIDS Society and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity at the University of Melbourne. “One very clear difference for Australia is a health system that provides free medication and free prevention,” she said. “You can’t underestimate the impact that has on public health.”
Globally, significant progress has been made toward the UN’s 95-95-95 targets, with 86% of people with HIV now knowing their status, 88% of those being on treatment, and 93% of those having an undetectable viral load, “for a total of 75% of all people living with HIV worldwide with undetectable viral load,” Dr. Grulich pointed out.
But Dr. Lewin cautioned that now is not the time to take our eye off the ball, especially with respect to the 39 million or so people living with HIV globally, all of whom need lifelong treatment and care to manage their disease. “We also need to be aware that if we relax the investment, and people stop their treatment, transmission occurs again,” Dr. Lewin warned. “Despite the great news of potentially getting close to eliminating HIV transmission in Australia, HIV is far from over.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA – The year was 1987 and the Grim Reaper (a personification of death), holding a large scythe, rolled a 10-pin bowling ball through a dark, foggy place. In the advertisement on television, the cloaked skeleton aimed the bowling ball at the other end of a lane where a group of people stood in place of pins.
Who would fall next?
In the 1980s, cases of HIV were rising in the community and people in Australia and elsewhere were dying of AIDS. The Australian government opted to use mainstream media to deliver a blunt message through advertising to raise awareness about the health risk and how to manage HIV in the community.
But the campaign also contributed to stigma for those living with the disease and especially those in the gay community who felt ostracized by rising public concern.
In the inner city of Sydney, a few thousand people died of AIDS, Andrew Grulich, MD, PhD, from the Kirby Institute at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and involved in tracking cases, said in an interview. “Sydney was devastated by AIDS, it was truly devastated.”
HIV and AIDS quickly became an even more severe problem for several countries around Australia in Thailand, Papua New Guinea, and beyond. After HIV was first reported in Thailand in 1984, the region had the highest prevalence of HIV in Southeast Asia. Through the 1990s in Papua New Guinea, HIV prevalence rose steeply as well.
By 2010, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) set a target of a 90% reduction in HIV incidence, a 90% reduction in AIDS deaths by 2030, and 95% of people living with HIV and AIDS being aware of their status, on treatment, and having an undetectable viral load.
Since then, significant progress has been made globally with 86% of people knowing their HIV status. However, new infections persist at a rate that has not dropped as fast as possible.
New infections
According to the latest UNAIDS report, regions of North America and western and central Europe showed a 23% decline in new infections from 2010 to 2022, below the target 90% reduction.
Some regions of the United States have seen significant declines in new HIV infections. San Francisco has a 67% drop in new diagnoses. And now, along with the District of Columbia, the four states with the highest HIV rates are New York, Maryland, Georgia, and Florida.
Several countries in eastern and southern Africa are close to achieving their target HIV reduction of 90%.
Mitchell Warren, executive director of AVAC for global health advocacy, access, and equity, said that many of the low- and middle-income countries that are on track to achieve targets are able to do so because of support from the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
“That foreign development assistance is transforming the AIDS response in a number of African countries, and yet at home, in various states and municipalities, not only are we not reaching that effort, we don’t even use those targets,” Mr. Warren pointed out.
“We might see municipalities that are performing well, but at a national level it’s frankly a disgrace by comparison, because we know what’s possible,” Mr. Warren said.
Lowering cases
Today, in the inner city of Sydney, new HIV diagnoses have plummeted by 88%, which puts the area on track to achieve the 90% UNAIDS target ahead of schedule.
Dr. Grulich and his team at the Kirby Institute are tracking new diagnoses by postal code and reported their encouraging findings here this week at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
“This 88% decline is happening in an area where, in the ’80s and ’90s, a few thousand people died of AIDS,” Dr. Grulich told this news organization. “It feels close to miraculous.”
Dr. Grulich attributes some of the success to long-term government leadership that for the most part has been apolitical. HIV has been perceived by the public as an important health issue to be addressed. “We’ve never had a political contest over it,” he added. “We have politicians who are committed to evidence-based policy.”
In inner city Sydney, HIV prevention campaigns are a visible part of community life, Dr. Grulich explained. At public events, it is discussed; at bus stops, posters are on display; and passing trains have messages plastered to the side of them.
That community effort has consistently received government funding for years – albeit linked to key performance indicators – but it has enabled a high level of communication among government, community, clinicians, and researchers.
Another advantage is Australia’s universal health coverage, said Sharon Lewin, PhD, president of the International AIDS Society and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity at the University of Melbourne. “One very clear difference for Australia is a health system that provides free medication and free prevention,” she said. “You can’t underestimate the impact that has on public health.”
Globally, significant progress has been made toward the UN’s 95-95-95 targets, with 86% of people with HIV now knowing their status, 88% of those being on treatment, and 93% of those having an undetectable viral load, “for a total of 75% of all people living with HIV worldwide with undetectable viral load,” Dr. Grulich pointed out.
But Dr. Lewin cautioned that now is not the time to take our eye off the ball, especially with respect to the 39 million or so people living with HIV globally, all of whom need lifelong treatment and care to manage their disease. “We also need to be aware that if we relax the investment, and people stop their treatment, transmission occurs again,” Dr. Lewin warned. “Despite the great news of potentially getting close to eliminating HIV transmission in Australia, HIV is far from over.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BRISBANE, AUSTRALIA – The year was 1987 and the Grim Reaper (a personification of death), holding a large scythe, rolled a 10-pin bowling ball through a dark, foggy place. In the advertisement on television, the cloaked skeleton aimed the bowling ball at the other end of a lane where a group of people stood in place of pins.
Who would fall next?
In the 1980s, cases of HIV were rising in the community and people in Australia and elsewhere were dying of AIDS. The Australian government opted to use mainstream media to deliver a blunt message through advertising to raise awareness about the health risk and how to manage HIV in the community.
But the campaign also contributed to stigma for those living with the disease and especially those in the gay community who felt ostracized by rising public concern.
In the inner city of Sydney, a few thousand people died of AIDS, Andrew Grulich, MD, PhD, from the Kirby Institute at the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and involved in tracking cases, said in an interview. “Sydney was devastated by AIDS, it was truly devastated.”
HIV and AIDS quickly became an even more severe problem for several countries around Australia in Thailand, Papua New Guinea, and beyond. After HIV was first reported in Thailand in 1984, the region had the highest prevalence of HIV in Southeast Asia. Through the 1990s in Papua New Guinea, HIV prevalence rose steeply as well.
By 2010, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) set a target of a 90% reduction in HIV incidence, a 90% reduction in AIDS deaths by 2030, and 95% of people living with HIV and AIDS being aware of their status, on treatment, and having an undetectable viral load.
Since then, significant progress has been made globally with 86% of people knowing their HIV status. However, new infections persist at a rate that has not dropped as fast as possible.
New infections
According to the latest UNAIDS report, regions of North America and western and central Europe showed a 23% decline in new infections from 2010 to 2022, below the target 90% reduction.
Some regions of the United States have seen significant declines in new HIV infections. San Francisco has a 67% drop in new diagnoses. And now, along with the District of Columbia, the four states with the highest HIV rates are New York, Maryland, Georgia, and Florida.
Several countries in eastern and southern Africa are close to achieving their target HIV reduction of 90%.
Mitchell Warren, executive director of AVAC for global health advocacy, access, and equity, said that many of the low- and middle-income countries that are on track to achieve targets are able to do so because of support from the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
“That foreign development assistance is transforming the AIDS response in a number of African countries, and yet at home, in various states and municipalities, not only are we not reaching that effort, we don’t even use those targets,” Mr. Warren pointed out.
“We might see municipalities that are performing well, but at a national level it’s frankly a disgrace by comparison, because we know what’s possible,” Mr. Warren said.
Lowering cases
Today, in the inner city of Sydney, new HIV diagnoses have plummeted by 88%, which puts the area on track to achieve the 90% UNAIDS target ahead of schedule.
Dr. Grulich and his team at the Kirby Institute are tracking new diagnoses by postal code and reported their encouraging findings here this week at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
“This 88% decline is happening in an area where, in the ’80s and ’90s, a few thousand people died of AIDS,” Dr. Grulich told this news organization. “It feels close to miraculous.”
Dr. Grulich attributes some of the success to long-term government leadership that for the most part has been apolitical. HIV has been perceived by the public as an important health issue to be addressed. “We’ve never had a political contest over it,” he added. “We have politicians who are committed to evidence-based policy.”
In inner city Sydney, HIV prevention campaigns are a visible part of community life, Dr. Grulich explained. At public events, it is discussed; at bus stops, posters are on display; and passing trains have messages plastered to the side of them.
That community effort has consistently received government funding for years – albeit linked to key performance indicators – but it has enabled a high level of communication among government, community, clinicians, and researchers.
Another advantage is Australia’s universal health coverage, said Sharon Lewin, PhD, president of the International AIDS Society and director of the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity at the University of Melbourne. “One very clear difference for Australia is a health system that provides free medication and free prevention,” she said. “You can’t underestimate the impact that has on public health.”
Globally, significant progress has been made toward the UN’s 95-95-95 targets, with 86% of people with HIV now knowing their status, 88% of those being on treatment, and 93% of those having an undetectable viral load, “for a total of 75% of all people living with HIV worldwide with undetectable viral load,” Dr. Grulich pointed out.
But Dr. Lewin cautioned that now is not the time to take our eye off the ball, especially with respect to the 39 million or so people living with HIV globally, all of whom need lifelong treatment and care to manage their disease. “We also need to be aware that if we relax the investment, and people stop their treatment, transmission occurs again,” Dr. Lewin warned. “Despite the great news of potentially getting close to eliminating HIV transmission in Australia, HIV is far from over.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reassuring data on stimulants for ADHD in kids and later substance abuse
“Throughout rigorous analyses, and after accounting for more than 70 variables in this longitudinal sample of children with ADHD taking stimulants, we did not find an association with later substance use,” lead investigator Brooke Molina, PhD, director of the youth and family research program at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Protective effect?
Owing to symptoms of impulsivity inherent to ADHD, the disorder itself carries a risk for elevated substance use, the investigators note.
They speculate that this may be why some previous research suggests prescription stimulants reduce the risk of subsequent substance use disorder. However, other studies have found no such protective link.
To shed more light on the issue, the investigators used data from the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD, a multicenter, 14-month randomized clinical trial of medication and behavioral therapy for children with ADHD. However, for the purposes of the present study, investigators focused only on stimulant use in children.
At the time of recruitment, the children were aged 7-9 and had been diagnosed with ADHD between 1994 and 1996.
Investigators assessed the participants prior to randomization, at months 3 and 9, and at the end of treatment. They were then followed for 16 years and were assessed at years 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 until a mean age of 25.
During 12-, 14-, and 16-year follow-up, participants completed a questionnaire on their use of alcohol, marijuana, cigarettes, and several illicit and prescription drugs.
Investigators collected information on participants’ stimulant treatment via the Services for Children and Adolescents Parent Interview until they reached age 18. After that, participants reported their own stimulant treatment.
A total of 579 participants were included in the analysis. Of these, 61% were White, 20% were Black, and 8% were Hispanic.
Decline in stimulant use over time
The analysis showed that stimulant use declined “precipitously” over time – from 60% at the 2- and 3-year assessments to an average of 7% during early adulthood.
The investigators also found that for some participants, substance use increased steadily through adolescence and remained stable through early adulthood. For instance, 36.5% of the adolescents in the total cohort reported smoking tobacco daily, and 29.6% reported using marijuana every week.
In addition, approximately 21% of the participants indulged in heavy drinking at least once a week, and 6% reported “other” substance use, which included sedative misuse, heroin, inhalants, hallucinogens, or other substances taken to “get high.”
After accounting for developmental trends in substance use in the sample through adolescence into early adulthood with several rigorous statistical models, the researchers found no association between current or prior stimulant treatment and cigarette, marijuana, alcohol, or other substance use, with one exception.
While cumulative stimulant treatment was associated with increased heavy drinking, the effect size of this association was small. Each additional year of cumulative stimulant use was estimated to increase participants’ likelihood of any binge drinking/drunkenness vs. none in the past year by 4% (95% confidence interval, 0.01-0.08; P =.03).
When the investigators used a causal analytic method to account for age and other time-varying characteristics, including household income, behavior problems, and parental support, there was no evidence that current (B range, –0.62-0.34) or prior stimulant treatment (B range, –0.06-0.70) or their interaction (B range, –0.49-0.86) was associated with substance use in adulthood.
Dr. Molina noted that although participants were recruited from multiple sites, the sample may not be generalizable because children and parents who present for an intensive treatment study such as this are not necessarily representative of the general ADHD population.
Reassuring findings
In a comment, Julie Schweitzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Davis, said she hopes the study findings will quell the stigma surrounding stimulant use by children with ADHD.
“Parents’ fears that stimulant use will lead to a substance use disorder inhibits them from bringing their children for an ADHD evaluation, thus reducing the likelihood that they will receive timely treatment,” Dr. Schweitzer said.
“While stimulant medication is the first-line treatment most often recommended for most persons with ADHD, by not following through on evaluations, parents also miss the opportunity to learn about nonpharmacological strategies that might also be helpful to help cope with ADHD symptoms and its potential co-occurring challenges,” she added.
Dr. Schweitzer also noted that many parents hope their children will outgrow the symptoms without realizing that by not obtaining an evaluation and treatment for their child, there is an associated cost, including less than optimal academic performance, social relationships, and emotional health.
The Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD was a National Institute of Mental Health cooperative agreement randomized clinical trial, continued under an NIMH contract as a follow-up study and under a National Institute on Drug Abuse contract followed by a data analysis grant. Dr. Molina reported grants from the NIMH and the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Throughout rigorous analyses, and after accounting for more than 70 variables in this longitudinal sample of children with ADHD taking stimulants, we did not find an association with later substance use,” lead investigator Brooke Molina, PhD, director of the youth and family research program at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Protective effect?
Owing to symptoms of impulsivity inherent to ADHD, the disorder itself carries a risk for elevated substance use, the investigators note.
They speculate that this may be why some previous research suggests prescription stimulants reduce the risk of subsequent substance use disorder. However, other studies have found no such protective link.
To shed more light on the issue, the investigators used data from the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD, a multicenter, 14-month randomized clinical trial of medication and behavioral therapy for children with ADHD. However, for the purposes of the present study, investigators focused only on stimulant use in children.
At the time of recruitment, the children were aged 7-9 and had been diagnosed with ADHD between 1994 and 1996.
Investigators assessed the participants prior to randomization, at months 3 and 9, and at the end of treatment. They were then followed for 16 years and were assessed at years 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 until a mean age of 25.
During 12-, 14-, and 16-year follow-up, participants completed a questionnaire on their use of alcohol, marijuana, cigarettes, and several illicit and prescription drugs.
Investigators collected information on participants’ stimulant treatment via the Services for Children and Adolescents Parent Interview until they reached age 18. After that, participants reported their own stimulant treatment.
A total of 579 participants were included in the analysis. Of these, 61% were White, 20% were Black, and 8% were Hispanic.
Decline in stimulant use over time
The analysis showed that stimulant use declined “precipitously” over time – from 60% at the 2- and 3-year assessments to an average of 7% during early adulthood.
The investigators also found that for some participants, substance use increased steadily through adolescence and remained stable through early adulthood. For instance, 36.5% of the adolescents in the total cohort reported smoking tobacco daily, and 29.6% reported using marijuana every week.
In addition, approximately 21% of the participants indulged in heavy drinking at least once a week, and 6% reported “other” substance use, which included sedative misuse, heroin, inhalants, hallucinogens, or other substances taken to “get high.”
After accounting for developmental trends in substance use in the sample through adolescence into early adulthood with several rigorous statistical models, the researchers found no association between current or prior stimulant treatment and cigarette, marijuana, alcohol, or other substance use, with one exception.
While cumulative stimulant treatment was associated with increased heavy drinking, the effect size of this association was small. Each additional year of cumulative stimulant use was estimated to increase participants’ likelihood of any binge drinking/drunkenness vs. none in the past year by 4% (95% confidence interval, 0.01-0.08; P =.03).
When the investigators used a causal analytic method to account for age and other time-varying characteristics, including household income, behavior problems, and parental support, there was no evidence that current (B range, –0.62-0.34) or prior stimulant treatment (B range, –0.06-0.70) or their interaction (B range, –0.49-0.86) was associated with substance use in adulthood.
Dr. Molina noted that although participants were recruited from multiple sites, the sample may not be generalizable because children and parents who present for an intensive treatment study such as this are not necessarily representative of the general ADHD population.
Reassuring findings
In a comment, Julie Schweitzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Davis, said she hopes the study findings will quell the stigma surrounding stimulant use by children with ADHD.
“Parents’ fears that stimulant use will lead to a substance use disorder inhibits them from bringing their children for an ADHD evaluation, thus reducing the likelihood that they will receive timely treatment,” Dr. Schweitzer said.
“While stimulant medication is the first-line treatment most often recommended for most persons with ADHD, by not following through on evaluations, parents also miss the opportunity to learn about nonpharmacological strategies that might also be helpful to help cope with ADHD symptoms and its potential co-occurring challenges,” she added.
Dr. Schweitzer also noted that many parents hope their children will outgrow the symptoms without realizing that by not obtaining an evaluation and treatment for their child, there is an associated cost, including less than optimal academic performance, social relationships, and emotional health.
The Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD was a National Institute of Mental Health cooperative agreement randomized clinical trial, continued under an NIMH contract as a follow-up study and under a National Institute on Drug Abuse contract followed by a data analysis grant. Dr. Molina reported grants from the NIMH and the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Throughout rigorous analyses, and after accounting for more than 70 variables in this longitudinal sample of children with ADHD taking stimulants, we did not find an association with later substance use,” lead investigator Brooke Molina, PhD, director of the youth and family research program at the University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview.
The findings were published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
Protective effect?
Owing to symptoms of impulsivity inherent to ADHD, the disorder itself carries a risk for elevated substance use, the investigators note.
They speculate that this may be why some previous research suggests prescription stimulants reduce the risk of subsequent substance use disorder. However, other studies have found no such protective link.
To shed more light on the issue, the investigators used data from the Multimodal Treatment Study of ADHD, a multicenter, 14-month randomized clinical trial of medication and behavioral therapy for children with ADHD. However, for the purposes of the present study, investigators focused only on stimulant use in children.
At the time of recruitment, the children were aged 7-9 and had been diagnosed with ADHD between 1994 and 1996.
Investigators assessed the participants prior to randomization, at months 3 and 9, and at the end of treatment. They were then followed for 16 years and were assessed at years 2, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 until a mean age of 25.
During 12-, 14-, and 16-year follow-up, participants completed a questionnaire on their use of alcohol, marijuana, cigarettes, and several illicit and prescription drugs.
Investigators collected information on participants’ stimulant treatment via the Services for Children and Adolescents Parent Interview until they reached age 18. After that, participants reported their own stimulant treatment.
A total of 579 participants were included in the analysis. Of these, 61% were White, 20% were Black, and 8% were Hispanic.
Decline in stimulant use over time
The analysis showed that stimulant use declined “precipitously” over time – from 60% at the 2- and 3-year assessments to an average of 7% during early adulthood.
The investigators also found that for some participants, substance use increased steadily through adolescence and remained stable through early adulthood. For instance, 36.5% of the adolescents in the total cohort reported smoking tobacco daily, and 29.6% reported using marijuana every week.
In addition, approximately 21% of the participants indulged in heavy drinking at least once a week, and 6% reported “other” substance use, which included sedative misuse, heroin, inhalants, hallucinogens, or other substances taken to “get high.”
After accounting for developmental trends in substance use in the sample through adolescence into early adulthood with several rigorous statistical models, the researchers found no association between current or prior stimulant treatment and cigarette, marijuana, alcohol, or other substance use, with one exception.
While cumulative stimulant treatment was associated with increased heavy drinking, the effect size of this association was small. Each additional year of cumulative stimulant use was estimated to increase participants’ likelihood of any binge drinking/drunkenness vs. none in the past year by 4% (95% confidence interval, 0.01-0.08; P =.03).
When the investigators used a causal analytic method to account for age and other time-varying characteristics, including household income, behavior problems, and parental support, there was no evidence that current (B range, –0.62-0.34) or prior stimulant treatment (B range, –0.06-0.70) or their interaction (B range, –0.49-0.86) was associated with substance use in adulthood.
Dr. Molina noted that although participants were recruited from multiple sites, the sample may not be generalizable because children and parents who present for an intensive treatment study such as this are not necessarily representative of the general ADHD population.
Reassuring findings
In a comment, Julie Schweitzer, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of California, Davis, said she hopes the study findings will quell the stigma surrounding stimulant use by children with ADHD.
“Parents’ fears that stimulant use will lead to a substance use disorder inhibits them from bringing their children for an ADHD evaluation, thus reducing the likelihood that they will receive timely treatment,” Dr. Schweitzer said.
“While stimulant medication is the first-line treatment most often recommended for most persons with ADHD, by not following through on evaluations, parents also miss the opportunity to learn about nonpharmacological strategies that might also be helpful to help cope with ADHD symptoms and its potential co-occurring challenges,” she added.
Dr. Schweitzer also noted that many parents hope their children will outgrow the symptoms without realizing that by not obtaining an evaluation and treatment for their child, there is an associated cost, including less than optimal academic performance, social relationships, and emotional health.
The Multimodal Treatment Study of Children with ADHD was a National Institute of Mental Health cooperative agreement randomized clinical trial, continued under an NIMH contract as a follow-up study and under a National Institute on Drug Abuse contract followed by a data analysis grant. Dr. Molina reported grants from the NIMH and the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Psilocybin shows early promise for anorexia nervosa
The psychedelic psilocybin may have a role in the treatment of anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder that is notoriously difficult and costly to treat.
Stephanie Knatz Peck, PhD, and colleagues with the eating disorders treatment & research center, University of California San Diego, write that the “robust response” in a subset of women after a single dose of psilocybin is “notable,” given that currently available treatments for adult anorexia result in only modest improvements in symptoms and often focus on weight and nutritional rehabilitation without adequately addressing underlying psychopathology.
However, given this was a small, phase 1, open-label feasibility study, these effects are “preliminary and inconclusive,” they caution.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
Meaningful experience
The 10 women in the study met DSM-5 criteria for AN or partial remission of AN. They were between age 18 and 40 years with a mean body mass index (BMI) of 19.7 kg/m2.
Following the single 25-mg dose of psilocybin, no clinically significant changes were observed in ECG, vital signs, laboratory values, or suicidality.
All adverse events were mild and mirrored typical psilocybin-associated symptoms such as transient headache, nausea, and fatigue.
Psilocybin was associated with reduced levels of anxiety and preoccupations surrounding food, eating, and body shape at the 1-month follow-up.
Weight concerns decreased significantly at the 1-month (P = .036, Cohen’s d = .78) and 3-month (P = .04, d = .78) follow-up, with a medium to large effect.
Shape concerns significantly decreased at 1-month follow-up (P = .036, d = .78) but were no longer significant at 3-month follow-up (P = .081, d = .62).
Four of the 10 women (40%) had clinically significant reductions in eating disorder scores at 3 months, which qualified for remission from eating-disorder psychopathology.
However, the researchers caution that the effects on eating disorder psychopathology were “highly variable.”
On average, changes in BMI were not significant during the 3 months following psilocybin treatment. However, five women had an increase in BMI at 3 months, ranging from 0.4 to 1.2 kg/m2.
Overall, the psilocybin experience was regarded as meaningful by participants; 80% endorsed the experience as one of the top five most meaningful of life; 90% endorsed feeling more positive about life endeavors; and 70% reported experiencing a shift in personal identity and overall quality of life.
The vast majority of women (90%) felt that one dosing session was not enough.
The fact that the treatment was regarded as beneficial by most women and that there were no dropouts are “promising signs of engagement,” given that dropout rates for currently available AN treatments tend to be high, the researchers note.
They urge caution in interpreting the results considering they were based on a small sample size and did not include a placebo group. They note that larger, adequately powered, randomized controlled trials are needed to draw any conclusions about the role of psilocybin for anorexia nervosa.
Encouraging data
The coauthors of a Nature Medicine News & Views commentary say this “encouraging” phase 1 trial “underscores the necessity for more research into classic psychedelics to address the urgent need for effective treatments” for AN.
Outside experts also weighed in on the study in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre.
Alexandra Pike, DPhil, MSc, with University of York, England, noted that this study is “a first step in showing that psilocybin may be a safe treatment for those with anorexia nervosa, but we cannot conclude from this work that it will be effective in this chronic, complex illness.”
Trevor Steward, MD, with University of Melbourne, noted that psilocybin therapy has provided “glimmers of hope in other mental health disorders, notably by providing evidence that it can improve anxiety, cognitive flexibility, and self-acceptance for some people. These are all features of anorexia nervosa and the rationale for exploring psilocybin therapy as an option in the case of anorexia is strong.”
Dr. Steward also noted that the field is only beginning to “scratch the surface in terms of understanding how psilocybin impacts the brain. Dedicated funding to exploring how it specifically acts to target anorexia nervosa symptoms is crucial to advancing this important avenue of research.
“As there are no approved medications available specifically for anorexia nervosa treatment, psilocybin therapy may prove to be a promising option, though additional research is needed to test this,” Dr. Steward said.
The study used an investigational synthetic formulation of psilocybin (COMP360 psilocybin) developed by COMPASS Pathways, which funded the study. Two coauthors have financial and scientific relationships with COMPASS Pathways. The commentary authors and Dr. Steward report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The psychedelic psilocybin may have a role in the treatment of anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder that is notoriously difficult and costly to treat.
Stephanie Knatz Peck, PhD, and colleagues with the eating disorders treatment & research center, University of California San Diego, write that the “robust response” in a subset of women after a single dose of psilocybin is “notable,” given that currently available treatments for adult anorexia result in only modest improvements in symptoms and often focus on weight and nutritional rehabilitation without adequately addressing underlying psychopathology.
However, given this was a small, phase 1, open-label feasibility study, these effects are “preliminary and inconclusive,” they caution.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
Meaningful experience
The 10 women in the study met DSM-5 criteria for AN or partial remission of AN. They were between age 18 and 40 years with a mean body mass index (BMI) of 19.7 kg/m2.
Following the single 25-mg dose of psilocybin, no clinically significant changes were observed in ECG, vital signs, laboratory values, or suicidality.
All adverse events were mild and mirrored typical psilocybin-associated symptoms such as transient headache, nausea, and fatigue.
Psilocybin was associated with reduced levels of anxiety and preoccupations surrounding food, eating, and body shape at the 1-month follow-up.
Weight concerns decreased significantly at the 1-month (P = .036, Cohen’s d = .78) and 3-month (P = .04, d = .78) follow-up, with a medium to large effect.
Shape concerns significantly decreased at 1-month follow-up (P = .036, d = .78) but were no longer significant at 3-month follow-up (P = .081, d = .62).
Four of the 10 women (40%) had clinically significant reductions in eating disorder scores at 3 months, which qualified for remission from eating-disorder psychopathology.
However, the researchers caution that the effects on eating disorder psychopathology were “highly variable.”
On average, changes in BMI were not significant during the 3 months following psilocybin treatment. However, five women had an increase in BMI at 3 months, ranging from 0.4 to 1.2 kg/m2.
Overall, the psilocybin experience was regarded as meaningful by participants; 80% endorsed the experience as one of the top five most meaningful of life; 90% endorsed feeling more positive about life endeavors; and 70% reported experiencing a shift in personal identity and overall quality of life.
The vast majority of women (90%) felt that one dosing session was not enough.
The fact that the treatment was regarded as beneficial by most women and that there were no dropouts are “promising signs of engagement,” given that dropout rates for currently available AN treatments tend to be high, the researchers note.
They urge caution in interpreting the results considering they were based on a small sample size and did not include a placebo group. They note that larger, adequately powered, randomized controlled trials are needed to draw any conclusions about the role of psilocybin for anorexia nervosa.
Encouraging data
The coauthors of a Nature Medicine News & Views commentary say this “encouraging” phase 1 trial “underscores the necessity for more research into classic psychedelics to address the urgent need for effective treatments” for AN.
Outside experts also weighed in on the study in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre.
Alexandra Pike, DPhil, MSc, with University of York, England, noted that this study is “a first step in showing that psilocybin may be a safe treatment for those with anorexia nervosa, but we cannot conclude from this work that it will be effective in this chronic, complex illness.”
Trevor Steward, MD, with University of Melbourne, noted that psilocybin therapy has provided “glimmers of hope in other mental health disorders, notably by providing evidence that it can improve anxiety, cognitive flexibility, and self-acceptance for some people. These are all features of anorexia nervosa and the rationale for exploring psilocybin therapy as an option in the case of anorexia is strong.”
Dr. Steward also noted that the field is only beginning to “scratch the surface in terms of understanding how psilocybin impacts the brain. Dedicated funding to exploring how it specifically acts to target anorexia nervosa symptoms is crucial to advancing this important avenue of research.
“As there are no approved medications available specifically for anorexia nervosa treatment, psilocybin therapy may prove to be a promising option, though additional research is needed to test this,” Dr. Steward said.
The study used an investigational synthetic formulation of psilocybin (COMP360 psilocybin) developed by COMPASS Pathways, which funded the study. Two coauthors have financial and scientific relationships with COMPASS Pathways. The commentary authors and Dr. Steward report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The psychedelic psilocybin may have a role in the treatment of anorexia nervosa (AN), an eating disorder that is notoriously difficult and costly to treat.
Stephanie Knatz Peck, PhD, and colleagues with the eating disorders treatment & research center, University of California San Diego, write that the “robust response” in a subset of women after a single dose of psilocybin is “notable,” given that currently available treatments for adult anorexia result in only modest improvements in symptoms and often focus on weight and nutritional rehabilitation without adequately addressing underlying psychopathology.
However, given this was a small, phase 1, open-label feasibility study, these effects are “preliminary and inconclusive,” they caution.
The study was published online in Nature Medicine.
Meaningful experience
The 10 women in the study met DSM-5 criteria for AN or partial remission of AN. They were between age 18 and 40 years with a mean body mass index (BMI) of 19.7 kg/m2.
Following the single 25-mg dose of psilocybin, no clinically significant changes were observed in ECG, vital signs, laboratory values, or suicidality.
All adverse events were mild and mirrored typical psilocybin-associated symptoms such as transient headache, nausea, and fatigue.
Psilocybin was associated with reduced levels of anxiety and preoccupations surrounding food, eating, and body shape at the 1-month follow-up.
Weight concerns decreased significantly at the 1-month (P = .036, Cohen’s d = .78) and 3-month (P = .04, d = .78) follow-up, with a medium to large effect.
Shape concerns significantly decreased at 1-month follow-up (P = .036, d = .78) but were no longer significant at 3-month follow-up (P = .081, d = .62).
Four of the 10 women (40%) had clinically significant reductions in eating disorder scores at 3 months, which qualified for remission from eating-disorder psychopathology.
However, the researchers caution that the effects on eating disorder psychopathology were “highly variable.”
On average, changes in BMI were not significant during the 3 months following psilocybin treatment. However, five women had an increase in BMI at 3 months, ranging from 0.4 to 1.2 kg/m2.
Overall, the psilocybin experience was regarded as meaningful by participants; 80% endorsed the experience as one of the top five most meaningful of life; 90% endorsed feeling more positive about life endeavors; and 70% reported experiencing a shift in personal identity and overall quality of life.
The vast majority of women (90%) felt that one dosing session was not enough.
The fact that the treatment was regarded as beneficial by most women and that there were no dropouts are “promising signs of engagement,” given that dropout rates for currently available AN treatments tend to be high, the researchers note.
They urge caution in interpreting the results considering they were based on a small sample size and did not include a placebo group. They note that larger, adequately powered, randomized controlled trials are needed to draw any conclusions about the role of psilocybin for anorexia nervosa.
Encouraging data
The coauthors of a Nature Medicine News & Views commentary say this “encouraging” phase 1 trial “underscores the necessity for more research into classic psychedelics to address the urgent need for effective treatments” for AN.
Outside experts also weighed in on the study in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre.
Alexandra Pike, DPhil, MSc, with University of York, England, noted that this study is “a first step in showing that psilocybin may be a safe treatment for those with anorexia nervosa, but we cannot conclude from this work that it will be effective in this chronic, complex illness.”
Trevor Steward, MD, with University of Melbourne, noted that psilocybin therapy has provided “glimmers of hope in other mental health disorders, notably by providing evidence that it can improve anxiety, cognitive flexibility, and self-acceptance for some people. These are all features of anorexia nervosa and the rationale for exploring psilocybin therapy as an option in the case of anorexia is strong.”
Dr. Steward also noted that the field is only beginning to “scratch the surface in terms of understanding how psilocybin impacts the brain. Dedicated funding to exploring how it specifically acts to target anorexia nervosa symptoms is crucial to advancing this important avenue of research.
“As there are no approved medications available specifically for anorexia nervosa treatment, psilocybin therapy may prove to be a promising option, though additional research is needed to test this,” Dr. Steward said.
The study used an investigational synthetic formulation of psilocybin (COMP360 psilocybin) developed by COMPASS Pathways, which funded the study. Two coauthors have financial and scientific relationships with COMPASS Pathways. The commentary authors and Dr. Steward report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
Multiple trials of long COVID treatments advancing, more on the way
Additional clinical trials to test at least seven more treatments are expected to launch in the coming months, officials said.
The trials are part of the NIH’s research effort known as the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative. In December 2020, Congress approved $1.15 billion for the NIH to research and test treatments for long COVID. The new clinical trials are in phase 2 and will test safety and effectiveness.
“The condition affects nearly all body systems and presents with more than 200 symptoms,” said Walter J. Koroshetz, MD, director of the NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and colead of the RECOVER Initiative. How many people have long COVID is uncertain, he told attendees at the briefing. “The answer kind of depends on how you define the problem and also what variant caused it. The incidence was higher in Delta.” Some estimates suggest that 5%-10% of those infected develop long COVID. “I don’t think we have solid numbers, as it’s a moving target,” Dr. Koroshetz said.
Patients with long COVID have grown increasingly frustrated at the lack of effective treatments. Some doctors have turned to off-label use of some drugs to treat them.
The four trials include the following:
- RECOVER-VITAL will focus on a treatment for viral persistence, which can occur if the virus lingers and causes the immune system to not work properly. One treatment will test a longer dose regimen of the antiviral Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir), which is currently used to treat mild to moderate COVID to halt progression to severe COVID.
- RECOVER-NEURO will target treatments for symptoms such as brain fog, memory problems, and attention challenges. Among the potential treatments are a program called BrainHQ, which provides Web-based training, and PASC-Cognitive Recovery (post-acute sequelae of COVID), a Web-based program developed by Mount Sinai Health System in New York. Also being tested is a direct current stimulation program to improve brain activity.
- RECOVER-SLEEP will evaluate treatments for sleep problems, which can include daytime sleepiness and other problems. According to Dr. Koroshetz, melatonin, light therapy, and an educational coaching system are among the treatments that will be studied.
- RECOVER-AUTONOMIC will evaluate treatments to address symptoms linked with problems of the autonomic nervous system. The first trial will target postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), which can include irregular heartbeat, fatigue, and dizziness. A treatment for immune disease and a drug currently used to treat chronic heart failure will be tested.
Timelines
The first trial, on viral persistence, has launched, said Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, a principal investigator at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, the clinical trials data coordinating center for the trials. “We are actively working to launch the second on cognitive dysfunction.” The sleep and autonomic trials will launch in the coming months, she said. Also planned is a trial to study exercise intolerance, which is reported by many with long COVID.
Information on how to join long COVID trials is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional clinical trials to test at least seven more treatments are expected to launch in the coming months, officials said.
The trials are part of the NIH’s research effort known as the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative. In December 2020, Congress approved $1.15 billion for the NIH to research and test treatments for long COVID. The new clinical trials are in phase 2 and will test safety and effectiveness.
“The condition affects nearly all body systems and presents with more than 200 symptoms,” said Walter J. Koroshetz, MD, director of the NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and colead of the RECOVER Initiative. How many people have long COVID is uncertain, he told attendees at the briefing. “The answer kind of depends on how you define the problem and also what variant caused it. The incidence was higher in Delta.” Some estimates suggest that 5%-10% of those infected develop long COVID. “I don’t think we have solid numbers, as it’s a moving target,” Dr. Koroshetz said.
Patients with long COVID have grown increasingly frustrated at the lack of effective treatments. Some doctors have turned to off-label use of some drugs to treat them.
The four trials include the following:
- RECOVER-VITAL will focus on a treatment for viral persistence, which can occur if the virus lingers and causes the immune system to not work properly. One treatment will test a longer dose regimen of the antiviral Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir), which is currently used to treat mild to moderate COVID to halt progression to severe COVID.
- RECOVER-NEURO will target treatments for symptoms such as brain fog, memory problems, and attention challenges. Among the potential treatments are a program called BrainHQ, which provides Web-based training, and PASC-Cognitive Recovery (post-acute sequelae of COVID), a Web-based program developed by Mount Sinai Health System in New York. Also being tested is a direct current stimulation program to improve brain activity.
- RECOVER-SLEEP will evaluate treatments for sleep problems, which can include daytime sleepiness and other problems. According to Dr. Koroshetz, melatonin, light therapy, and an educational coaching system are among the treatments that will be studied.
- RECOVER-AUTONOMIC will evaluate treatments to address symptoms linked with problems of the autonomic nervous system. The first trial will target postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), which can include irregular heartbeat, fatigue, and dizziness. A treatment for immune disease and a drug currently used to treat chronic heart failure will be tested.
Timelines
The first trial, on viral persistence, has launched, said Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, a principal investigator at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, the clinical trials data coordinating center for the trials. “We are actively working to launch the second on cognitive dysfunction.” The sleep and autonomic trials will launch in the coming months, she said. Also planned is a trial to study exercise intolerance, which is reported by many with long COVID.
Information on how to join long COVID trials is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Additional clinical trials to test at least seven more treatments are expected to launch in the coming months, officials said.
The trials are part of the NIH’s research effort known as the Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative. In December 2020, Congress approved $1.15 billion for the NIH to research and test treatments for long COVID. The new clinical trials are in phase 2 and will test safety and effectiveness.
“The condition affects nearly all body systems and presents with more than 200 symptoms,” said Walter J. Koroshetz, MD, director of the NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and colead of the RECOVER Initiative. How many people have long COVID is uncertain, he told attendees at the briefing. “The answer kind of depends on how you define the problem and also what variant caused it. The incidence was higher in Delta.” Some estimates suggest that 5%-10% of those infected develop long COVID. “I don’t think we have solid numbers, as it’s a moving target,” Dr. Koroshetz said.
Patients with long COVID have grown increasingly frustrated at the lack of effective treatments. Some doctors have turned to off-label use of some drugs to treat them.
The four trials include the following:
- RECOVER-VITAL will focus on a treatment for viral persistence, which can occur if the virus lingers and causes the immune system to not work properly. One treatment will test a longer dose regimen of the antiviral Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir and ritonavir), which is currently used to treat mild to moderate COVID to halt progression to severe COVID.
- RECOVER-NEURO will target treatments for symptoms such as brain fog, memory problems, and attention challenges. Among the potential treatments are a program called BrainHQ, which provides Web-based training, and PASC-Cognitive Recovery (post-acute sequelae of COVID), a Web-based program developed by Mount Sinai Health System in New York. Also being tested is a direct current stimulation program to improve brain activity.
- RECOVER-SLEEP will evaluate treatments for sleep problems, which can include daytime sleepiness and other problems. According to Dr. Koroshetz, melatonin, light therapy, and an educational coaching system are among the treatments that will be studied.
- RECOVER-AUTONOMIC will evaluate treatments to address symptoms linked with problems of the autonomic nervous system. The first trial will target postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), which can include irregular heartbeat, fatigue, and dizziness. A treatment for immune disease and a drug currently used to treat chronic heart failure will be tested.
Timelines
The first trial, on viral persistence, has launched, said Kanecia Zimmerman, MD, a principal investigator at the Duke Clinical Research Institute, the clinical trials data coordinating center for the trials. “We are actively working to launch the second on cognitive dysfunction.” The sleep and autonomic trials will launch in the coming months, she said. Also planned is a trial to study exercise intolerance, which is reported by many with long COVID.
Information on how to join long COVID trials is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
RFS failed as endpoint in adjuvant immunotherapy trials
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- FDA approvals in the adjuvant setting for cancer immunotherapy are increasingly based on trials that use RFS as a surrogate endpoint for overall survival, largely because such a design allows for smaller, speedier trials.
- To test the validity of using RFS as a surrogate for overall survival in this setting, investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 15 phase 2 and 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of adjuvant CTLA4 and anti–PD-1/PD-L1 blockers for melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, renal cell cancer, and other tumors.
- The team used weighted regression at the arm and trial levels to assess the efficacy of RFS as a surrogate for overall survival.
- The strength of the association was quantified by weighted coefficients of determination (R2)12Dante MT Stdplz make sure all mentions of R’2’ are superscript, with a strong correlation considered to be R2 of 0.7 or higher.
- If there were strong correlations at both the arm and trial levels, RFS would be considered a robust surrogate endpoint for overall survival; however, if one of the correlations at the arm or trial level was not strong, RFS would not be considered a surrogate endpoint for overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the arm level, moderate and strong associations were observed between 2-year RFS and 3-year overall survival (R2, 0.58) and between 3-year RFS and 5-year overall survival (R2, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.38-.00).
- At the trial level, a moderate association was observed between effect of treatment on RFS and overall survival (R2, 0.63).
- The findings were confirmed in several sensitivity analyses that were based on different trial phases, experimental arms, cancer types, and treatment strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our meta-analysis failed to find a significantly strong association between RFS and OS in RCTs of adjuvant immunotherapy,” the authors concluded. “RFS should not be used as a surrogate endpoint for OS in this clinical context.” Instead, the finding indicates that overall survival is “the ideal primary endpoint” in this setting.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Yuanfang Li, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, was published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
- Correlations were calculated from a relatively limited number of RCTs that involved different types of cancer, and overall survival data were not fully mature in some of the trials.
- The analysis did not include patient-level data.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and others.
- The investigators had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- FDA approvals in the adjuvant setting for cancer immunotherapy are increasingly based on trials that use RFS as a surrogate endpoint for overall survival, largely because such a design allows for smaller, speedier trials.
- To test the validity of using RFS as a surrogate for overall survival in this setting, investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 15 phase 2 and 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of adjuvant CTLA4 and anti–PD-1/PD-L1 blockers for melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, renal cell cancer, and other tumors.
- The team used weighted regression at the arm and trial levels to assess the efficacy of RFS as a surrogate for overall survival.
- The strength of the association was quantified by weighted coefficients of determination (R2)12Dante MT Stdplz make sure all mentions of R’2’ are superscript, with a strong correlation considered to be R2 of 0.7 or higher.
- If there were strong correlations at both the arm and trial levels, RFS would be considered a robust surrogate endpoint for overall survival; however, if one of the correlations at the arm or trial level was not strong, RFS would not be considered a surrogate endpoint for overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the arm level, moderate and strong associations were observed between 2-year RFS and 3-year overall survival (R2, 0.58) and between 3-year RFS and 5-year overall survival (R2, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.38-.00).
- At the trial level, a moderate association was observed between effect of treatment on RFS and overall survival (R2, 0.63).
- The findings were confirmed in several sensitivity analyses that were based on different trial phases, experimental arms, cancer types, and treatment strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our meta-analysis failed to find a significantly strong association between RFS and OS in RCTs of adjuvant immunotherapy,” the authors concluded. “RFS should not be used as a surrogate endpoint for OS in this clinical context.” Instead, the finding indicates that overall survival is “the ideal primary endpoint” in this setting.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Yuanfang Li, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, was published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
- Correlations were calculated from a relatively limited number of RCTs that involved different types of cancer, and overall survival data were not fully mature in some of the trials.
- The analysis did not include patient-level data.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and others.
- The investigators had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- FDA approvals in the adjuvant setting for cancer immunotherapy are increasingly based on trials that use RFS as a surrogate endpoint for overall survival, largely because such a design allows for smaller, speedier trials.
- To test the validity of using RFS as a surrogate for overall survival in this setting, investigators conducted a meta-analysis of 15 phase 2 and 3 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of adjuvant CTLA4 and anti–PD-1/PD-L1 blockers for melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, renal cell cancer, and other tumors.
- The team used weighted regression at the arm and trial levels to assess the efficacy of RFS as a surrogate for overall survival.
- The strength of the association was quantified by weighted coefficients of determination (R2)12Dante MT Stdplz make sure all mentions of R’2’ are superscript, with a strong correlation considered to be R2 of 0.7 or higher.
- If there were strong correlations at both the arm and trial levels, RFS would be considered a robust surrogate endpoint for overall survival; however, if one of the correlations at the arm or trial level was not strong, RFS would not be considered a surrogate endpoint for overall survival.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the arm level, moderate and strong associations were observed between 2-year RFS and 3-year overall survival (R2, 0.58) and between 3-year RFS and 5-year overall survival (R2, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.38-.00).
- At the trial level, a moderate association was observed between effect of treatment on RFS and overall survival (R2, 0.63).
- The findings were confirmed in several sensitivity analyses that were based on different trial phases, experimental arms, cancer types, and treatment strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our meta-analysis failed to find a significantly strong association between RFS and OS in RCTs of adjuvant immunotherapy,” the authors concluded. “RFS should not be used as a surrogate endpoint for OS in this clinical context.” Instead, the finding indicates that overall survival is “the ideal primary endpoint” in this setting.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Yuanfang Li, PhD, of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center in Guangzhou, China, was published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
LIMITATIONS:
- Correlations were calculated from a relatively limited number of RCTs that involved different types of cancer, and overall survival data were not fully mature in some of the trials.
- The analysis did not include patient-level data.
DISCLOSURES:
- The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and others.
- The investigators had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE NATIONAL CANCER INSTITUTE
Foot rash during self-treatment
The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.

The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.

The patient’s toenail thickening appeared consistent with possible onychomycosis—but in addition, there was a marked inflammatory and vesicular eruption consistent with an allergic contact dermatitis.
TTO, also known as melaleuca oil, is a popular product used to treat many disorders including alopecia, seborrheic dermatitis, and onychomycosis.1 Unfortunately, it is a complex compound, and the rate of positive reactions to patch testing ranges from 0.1% to 3.5%.2
There are 2 types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Irritant contact dermatitis results from an irritating or relatively caustic substance causing direct damage and inflammation to the skin. In allergic contact dermatitis, as occurred here, there is sensitization to a substance that causes a type IV delayed cell-mediated immune response. Although radioallergosorbent blood testing will usually show immunoglobulin E antibodies to the inciting substance, patch testing is more specific and will show a reaction to the imputed substance on direct skin application. This usually is performed as a panel of antigens tested at the same time.
The mainstay of treatment is to identify, stop use of, and then avoid the sensitizing substance. Topical steroids (triamcinolone 0.1% ointment or clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily) are helpful in most cases. If the condition is severe or does not respond to initial therapy, systemic steroids (prednisone 40 mg/d for 5 days for most cases or a 2- to 3-week taper for Rhus dermatitis [eg, poison ivy]) are often effective.3
This patient was instructed to stop using TTO and counseled to avoid it in the future. She was told that her nails might fall off due to the inflammation, which might cure her onychomycosis, and that it takes 12 to 18 months to grow new toenails. She was advised to return for evaluation if the new nails developed any abnormalities or if her onychomycosis recurred. Oral terbinafine 250 mg/d for 90 days is usually a safe and effective therapy.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Professor and Chair, Department of Family and Community Medicine, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker, MD School of Medicine, Kalamazoo.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
1. Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N, et al. A review of applications of tea tree oil in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:784-790. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05654.x
2. de Groot AC, Schmidt E. Tea tree oil: contact allergy and chemical composition. Contact Dermatitis. 2016;75:129-143. doi: 10.1111/cod.12591
3. Usatine RP, Riojas M. Diagnosis and management of contact dermatitis. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:249-255.
Fast-acting postpartum depression drug is effective
The Food and Drug Administration is considering approving a postpartum depression medication that can start working rapidly – in as little as 3 days. Promising results for the drug, zuranolone, were published recently in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Approximately 17% of women are affected by postpartum depression (PPD) during pregnancy or after birth, study authors noted. The condition often results in reduced breastfeeding, poor maternal-infant bonding, and hindering behavioral, emotional and brain development of the baby. Severe PPD can lead to suicide of the mother, which accounts for 20% of all postpartum deaths, they wrote.
The study included 196 people who had given birth in the past year, and were between the ages of 18 and 45 years old. Participants had major depression that began in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy or during the first 4 weeks of the postpartum period. Among participants, 22% were Black and 38% were Hispanic.
The average time it took for symptoms to significantly decline was 9 days. Most people who saw improvements had them continue for the entire 45-day follow-up period. The most common side effects were drowsiness, dizziness, and sleepiness.
Currently, PPD treatment includes taking antidepressants, which can take up to 12 weeks to work.
Researchers noted that the limitations of the study were that it only included women with severe PPD, and that women with a history of bipolar or psychotic disorders were excluded. Women in the study were not allowed to breastfeed, so the effect of zuranolone on lactation is unknown, they wrote.
A February news release from drugmaker Biogen indicated the FDA may decide whether to approve the medicine by Aug. 5.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration is considering approving a postpartum depression medication that can start working rapidly – in as little as 3 days. Promising results for the drug, zuranolone, were published recently in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Approximately 17% of women are affected by postpartum depression (PPD) during pregnancy or after birth, study authors noted. The condition often results in reduced breastfeeding, poor maternal-infant bonding, and hindering behavioral, emotional and brain development of the baby. Severe PPD can lead to suicide of the mother, which accounts for 20% of all postpartum deaths, they wrote.
The study included 196 people who had given birth in the past year, and were between the ages of 18 and 45 years old. Participants had major depression that began in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy or during the first 4 weeks of the postpartum period. Among participants, 22% were Black and 38% were Hispanic.
The average time it took for symptoms to significantly decline was 9 days. Most people who saw improvements had them continue for the entire 45-day follow-up period. The most common side effects were drowsiness, dizziness, and sleepiness.
Currently, PPD treatment includes taking antidepressants, which can take up to 12 weeks to work.
Researchers noted that the limitations of the study were that it only included women with severe PPD, and that women with a history of bipolar or psychotic disorders were excluded. Women in the study were not allowed to breastfeed, so the effect of zuranolone on lactation is unknown, they wrote.
A February news release from drugmaker Biogen indicated the FDA may decide whether to approve the medicine by Aug. 5.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Food and Drug Administration is considering approving a postpartum depression medication that can start working rapidly – in as little as 3 days. Promising results for the drug, zuranolone, were published recently in The American Journal of Psychiatry.
Approximately 17% of women are affected by postpartum depression (PPD) during pregnancy or after birth, study authors noted. The condition often results in reduced breastfeeding, poor maternal-infant bonding, and hindering behavioral, emotional and brain development of the baby. Severe PPD can lead to suicide of the mother, which accounts for 20% of all postpartum deaths, they wrote.
The study included 196 people who had given birth in the past year, and were between the ages of 18 and 45 years old. Participants had major depression that began in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy or during the first 4 weeks of the postpartum period. Among participants, 22% were Black and 38% were Hispanic.
The average time it took for symptoms to significantly decline was 9 days. Most people who saw improvements had them continue for the entire 45-day follow-up period. The most common side effects were drowsiness, dizziness, and sleepiness.
Currently, PPD treatment includes taking antidepressants, which can take up to 12 weeks to work.
Researchers noted that the limitations of the study were that it only included women with severe PPD, and that women with a history of bipolar or psychotic disorders were excluded. Women in the study were not allowed to breastfeed, so the effect of zuranolone on lactation is unknown, they wrote.
A February news release from drugmaker Biogen indicated the FDA may decide whether to approve the medicine by Aug. 5.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY