User login
Safe to stop immunotherapy at 2 years in stable lung cancer
A new review of clinical trial data suggests that it is safe to stop immunotherapy after 2 years if the patient is progression free. There was no difference in overall survival between such patients and those who carried on with immunotherapy for another 2 years, so for 4 years in total.
“For patients who are progression free on immunotherapy for NSCLC, it is reasonable to stop therapy at 2 years, rather than continuing indefinitely,” said the investigators, led by medical oncologist Lova Sun, MD, a lung and head and neck cancer specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The lack of statistically significant overall survival advantage for” indefinite treatment “on adjusted analysis provides reassurance to patients and clinicians who wish to discontinue immunotherapy at 2 years,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology to coincide with a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Dr. Sun and colleagues commented that there have been a number of trials that have shown durable benefits persisting long after immunotherapy was stopped at 2 years, but clinicians seem to have been spooked into preferring indefinite treatment by a trial that showed worse survival with nivolumab when it was stopped at 1 year in responders versus ongoing treatment.
In an accompanying editorial, Jack West, MD, a medical oncologist and lung cancer specialist at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., noted that given the “clear limitations in retrospective clinical data, we may want to wait for prospective randomized clinical trial data, but this will be a difficult study to complete, and results will take many years to become available.
“In the meantime, the perfect should not be the enemy of the good. These data may provide reassurance to us and patients that discontinuing treatment at 2 years can confer the same overall survival as extended treatment with lower risk of toxic effects, less time in treatment for patients, and considerably lower costs for our health care system,” he said.
Study details
For their review, Dr. Sun and colleagues included patients with advanced NSCLC called from 280 cancer clinics from across the United States.
The investigators compared overall survival in 113 advanced NSCLC patients treated with up-front immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) for 700-760 days (that is, stopping within 2 years) with survival in 593 patients treated beyond 760 days (the indefinite therapy group).
Patients were diagnosed from 2016 to 2020 at a median age of 69 years and were about evenly split between the sexes. The team noted that although all the patients were progression free at 2 years, only about one in five discontinued ICIs, highlighting “a strong bias toward potential overtreatment [vs.] possible undertreatment,” as Dr. West put it in the editorial.
Approximately half of the patients in both groups were treated initially with immunotherapy alone and the rest in combination with chemotherapy.
The 2-year overall survival from the 760-day mark was 79% in the fixed-duration group versus 81% with indefinite treatment, with no difference on either univariate (hazard ratio, 1.26; P = .36) or multivariable (HR, 1.33; P = .29) analysis adjusting for smoking history, PD-L1 status, histology, and other covariates.
Eleven patients in the fixed-duration cohort (10%) subsequently had progression and were rechallenged with an ICI; all but one with the same ICI used frontline.
Median progression-free survival after rechallenge was 8.1 months, demonstrating that patients can still benefit from ICIs even after discontinuation, the investigators said.
The groups were well balanced except that patients in the fixed-duration group were more likely to be treated at an academic center and have a history of smoking, with a trend toward being more likely to have squamous cell carcinoma. “Even after adjusting for these covariates, there was no overall survival benefit for indefinite-duration therapy,” the team said.
There was no funding for the work. The investigators have numerous pharmaceutical industry ties, including Dr. Sun, who is a consultant for Regeneron, Genmab, Seagen, and Bayer, and disclosed funding from BluePrint Research, Seagen Research, and IO Biotech Research. Dr. West reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review of clinical trial data suggests that it is safe to stop immunotherapy after 2 years if the patient is progression free. There was no difference in overall survival between such patients and those who carried on with immunotherapy for another 2 years, so for 4 years in total.
“For patients who are progression free on immunotherapy for NSCLC, it is reasonable to stop therapy at 2 years, rather than continuing indefinitely,” said the investigators, led by medical oncologist Lova Sun, MD, a lung and head and neck cancer specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The lack of statistically significant overall survival advantage for” indefinite treatment “on adjusted analysis provides reassurance to patients and clinicians who wish to discontinue immunotherapy at 2 years,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology to coincide with a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Dr. Sun and colleagues commented that there have been a number of trials that have shown durable benefits persisting long after immunotherapy was stopped at 2 years, but clinicians seem to have been spooked into preferring indefinite treatment by a trial that showed worse survival with nivolumab when it was stopped at 1 year in responders versus ongoing treatment.
In an accompanying editorial, Jack West, MD, a medical oncologist and lung cancer specialist at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., noted that given the “clear limitations in retrospective clinical data, we may want to wait for prospective randomized clinical trial data, but this will be a difficult study to complete, and results will take many years to become available.
“In the meantime, the perfect should not be the enemy of the good. These data may provide reassurance to us and patients that discontinuing treatment at 2 years can confer the same overall survival as extended treatment with lower risk of toxic effects, less time in treatment for patients, and considerably lower costs for our health care system,” he said.
Study details
For their review, Dr. Sun and colleagues included patients with advanced NSCLC called from 280 cancer clinics from across the United States.
The investigators compared overall survival in 113 advanced NSCLC patients treated with up-front immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) for 700-760 days (that is, stopping within 2 years) with survival in 593 patients treated beyond 760 days (the indefinite therapy group).
Patients were diagnosed from 2016 to 2020 at a median age of 69 years and were about evenly split between the sexes. The team noted that although all the patients were progression free at 2 years, only about one in five discontinued ICIs, highlighting “a strong bias toward potential overtreatment [vs.] possible undertreatment,” as Dr. West put it in the editorial.
Approximately half of the patients in both groups were treated initially with immunotherapy alone and the rest in combination with chemotherapy.
The 2-year overall survival from the 760-day mark was 79% in the fixed-duration group versus 81% with indefinite treatment, with no difference on either univariate (hazard ratio, 1.26; P = .36) or multivariable (HR, 1.33; P = .29) analysis adjusting for smoking history, PD-L1 status, histology, and other covariates.
Eleven patients in the fixed-duration cohort (10%) subsequently had progression and were rechallenged with an ICI; all but one with the same ICI used frontline.
Median progression-free survival after rechallenge was 8.1 months, demonstrating that patients can still benefit from ICIs even after discontinuation, the investigators said.
The groups were well balanced except that patients in the fixed-duration group were more likely to be treated at an academic center and have a history of smoking, with a trend toward being more likely to have squamous cell carcinoma. “Even after adjusting for these covariates, there was no overall survival benefit for indefinite-duration therapy,” the team said.
There was no funding for the work. The investigators have numerous pharmaceutical industry ties, including Dr. Sun, who is a consultant for Regeneron, Genmab, Seagen, and Bayer, and disclosed funding from BluePrint Research, Seagen Research, and IO Biotech Research. Dr. West reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new review of clinical trial data suggests that it is safe to stop immunotherapy after 2 years if the patient is progression free. There was no difference in overall survival between such patients and those who carried on with immunotherapy for another 2 years, so for 4 years in total.
“For patients who are progression free on immunotherapy for NSCLC, it is reasonable to stop therapy at 2 years, rather than continuing indefinitely,” said the investigators, led by medical oncologist Lova Sun, MD, a lung and head and neck cancer specialist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The lack of statistically significant overall survival advantage for” indefinite treatment “on adjusted analysis provides reassurance to patients and clinicians who wish to discontinue immunotherapy at 2 years,” they added.
The study was published online in JAMA Oncology to coincide with a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Dr. Sun and colleagues commented that there have been a number of trials that have shown durable benefits persisting long after immunotherapy was stopped at 2 years, but clinicians seem to have been spooked into preferring indefinite treatment by a trial that showed worse survival with nivolumab when it was stopped at 1 year in responders versus ongoing treatment.
In an accompanying editorial, Jack West, MD, a medical oncologist and lung cancer specialist at City of Hope, Duarte, Calif., noted that given the “clear limitations in retrospective clinical data, we may want to wait for prospective randomized clinical trial data, but this will be a difficult study to complete, and results will take many years to become available.
“In the meantime, the perfect should not be the enemy of the good. These data may provide reassurance to us and patients that discontinuing treatment at 2 years can confer the same overall survival as extended treatment with lower risk of toxic effects, less time in treatment for patients, and considerably lower costs for our health care system,” he said.
Study details
For their review, Dr. Sun and colleagues included patients with advanced NSCLC called from 280 cancer clinics from across the United States.
The investigators compared overall survival in 113 advanced NSCLC patients treated with up-front immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) for 700-760 days (that is, stopping within 2 years) with survival in 593 patients treated beyond 760 days (the indefinite therapy group).
Patients were diagnosed from 2016 to 2020 at a median age of 69 years and were about evenly split between the sexes. The team noted that although all the patients were progression free at 2 years, only about one in five discontinued ICIs, highlighting “a strong bias toward potential overtreatment [vs.] possible undertreatment,” as Dr. West put it in the editorial.
Approximately half of the patients in both groups were treated initially with immunotherapy alone and the rest in combination with chemotherapy.
The 2-year overall survival from the 760-day mark was 79% in the fixed-duration group versus 81% with indefinite treatment, with no difference on either univariate (hazard ratio, 1.26; P = .36) or multivariable (HR, 1.33; P = .29) analysis adjusting for smoking history, PD-L1 status, histology, and other covariates.
Eleven patients in the fixed-duration cohort (10%) subsequently had progression and were rechallenged with an ICI; all but one with the same ICI used frontline.
Median progression-free survival after rechallenge was 8.1 months, demonstrating that patients can still benefit from ICIs even after discontinuation, the investigators said.
The groups were well balanced except that patients in the fixed-duration group were more likely to be treated at an academic center and have a history of smoking, with a trend toward being more likely to have squamous cell carcinoma. “Even after adjusting for these covariates, there was no overall survival benefit for indefinite-duration therapy,” the team said.
There was no funding for the work. The investigators have numerous pharmaceutical industry ties, including Dr. Sun, who is a consultant for Regeneron, Genmab, Seagen, and Bayer, and disclosed funding from BluePrint Research, Seagen Research, and IO Biotech Research. Dr. West reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Merck, and Regeneron.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Therapeutic hypothermia to treat neonatal encephalopathy improves childhood outcomes
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for moderate and severe neonatal encephalopathy has been shown to reduce the risk of newborn death, major neurodevelopmental disability, developmental delay, and cerebral palsy.1 It is estimated that 8 newborns with moderate or severe neonatal encephalopathy need to be treated with TH to prevent 1 case of cerebral palsy.1 The key elements of TH include:
- initiate hypothermia within 6 hoursof birth
- cool the newborn to a core temperature of 33.5˚ C to 34.5˚ C (92.3˚ F to 94.1˚ F) for 72 hours
- obtain brain ultrasonography to assess for intracranial hemorrhage
- obtain sequential MRI studies to assess brain structure and function
- initiate EEG monitoring for seizure activity.
During hypothermia the newborn is sedated, and oral feedings are reduced. During TH, important physiological goals are to maintain normal oxygenation, blood pressure, fluid balance, and glucose levels.1,2
TH: The basics
Most of the major published randomized clinical trials used the following inclusion criteria to initiate TH2:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 35 weeks
- neonate is within 6 hours of birth
- an Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation at birth or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or the presence of seizures
- absence of recognizable congenital abnormalities at birth.
However, in some institutions, expert neonatologists have developed more liberal criteria for the initiation of TH, to be considered on a case-by-case basis. These more inclusive criteria, which will result in more newborns being treated with TH, include3:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 34 weeks
- neonate is within 12 hours of birth
- a sentinel event at birth or Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1 or postnatal cardiopulmonary failure
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or concern for the presence of seizures.
Birth at a gestational age ≤ 34 weeks is a contraindication to TH. Relative contraindications to initiation of TH include: birth weight < 1,750 g, severe congenital anomaly, major genetic disorders, known severe metabolic disorders, major intracranial hemorrhage, severe septicemia, and uncorrectable coagulopathy.3 Adverse outcomes of TH include thrombocytopenia, cardiac arrythmia, and fat necrosis.4
Diagnosing neonatal encephalopathy
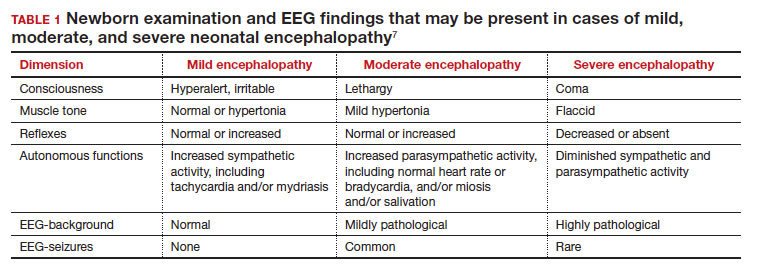
Neonatal encephalopathy is a clinical diagnosis, defined as abnormal neurologic function in the first few days of life in an infant born at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation. It is divided into 3 categories: mild (Stage 1), moderate (Stage 2), and severe (Stage 3).5,6 Institutions vary in the criteria used to differentiate mild from moderate neonatal encephalopathy, the two most frequent forms of encephalopathy. Newborns with mild encephalopathy are not routinely treated with TH because TH has not been shown to be helpful in this setting. Institutions with liberal criteria for diagnosing moderate encephalopathy will initiate TH in more cases. Involvement of a pediatric neurologist in the diagnosis of moderate encephalopathy may help confirm the diagnosis made by the primary neonatologist and provide an independent, second opinion about whether the newborn should be diagnosed with mild or moderate encephalopathy, a clinically important distinction. Physical examination and EEG findings associated with cases of mild, moderate, and severe encephalopathy are presented in TABLE 1.7
Continue: Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy...
Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy
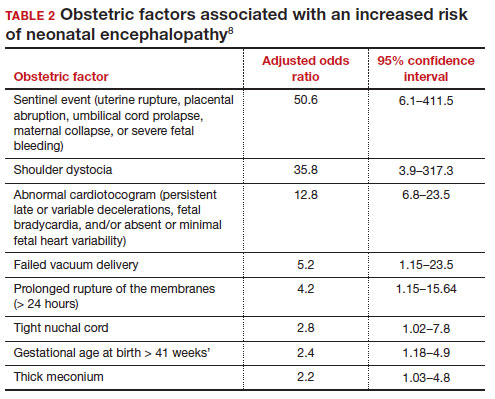
In a retrospective case-control study that included 405 newborns at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestational age with neonatal encephalopathy thought to be due to hypoxia, 8 obstetric factors were identified as being associated with an increased risk of neonatal encephalopathy, including (TABLE 2)8:
1. an obstetric sentinel event (uterine rupture, placental abruption, umbilical cord prolapse, maternal collapse, or severe fetal bleeding)
2. shoulder dystocia
3. abnormal cardiotocogram (persistent late or variable decelerations, fetal bradycardia, and/or absent or minimal fetal heart variability)
4. failed vacuum delivery
5. prolonged rupture of the membranes (> 24 hours)
6. tight nuchal cord
7. gestational age at birth > 41 weeks
8. thick meconium.
Similar findings have been reported by other investigators analyzing the obstetric risk factors for neonatal encephalopathy.7,9
Genetic causes of neonatal seizures and neonatal encephalopathy
Many neonatologists practice with the belief that for a newborn with encephalopathy in the setting of a sentinel labor event, a low Apgar score at 5 minutes, an umbilical cord artery pH < 7.00, and/or an elevated lactate level, the diagnosis of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is warranted. However, there are many causes of neonatal encephalopathy not related to intrapartum events. For example, neonatal encephalopathy and seizures may be caused by infectious, vascular, metabolic, medications, or congenital problems.10
There are genetic disorders that can be associated with both neonatal seizures and encephalopathy, suggesting that in some cases the primary cause of the encephalopathy is a genetic problem, not management of labor. Mutations in the potassium channel and sodium channel genes are well recognized causes of neonatal seizures.11,12 Cerebral palsy, a childhood outcome that may follow neonatal encephalopathy, also has numerous etiologies, including genetic causes. Among 1,345 children with cerebral palsy referred for exome sequencing, investigators reported that a genetic abnormality was identified in 33% of the cases.13 Mutations in 86 genes were identified in multiple children. Similar results have been reported in other cohorts.14-16 Maintaining an open mind about the causes of a case of neonatal encephalopathy and not jumping to a conclusion before completing an evaluation is an optimal approach.
Parent’s evolving emotional and intellectual reaction to the initiation of TH
Initiation of TH for a newborn with encephalopathy catalyzes parents to wonder, “How did my baby develop an encephalopathy?”, “Did my obstetrician’s management of labor and delivery contribute to the outcome?” and “What is the prognosis for my baby?” These are difficult questions with high emotional valence for both patients and clinicians. Obstetricians and neonatologists should collaborate to provide consistent responses to these questions.
The presence of a low umbilical cord artery pH and high lactate in combination with a low Apgar score at 5 minutes may lead the neonatologist to diagnose hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the medical record. The diagnosis of brain hypoxia and ischemia in a newborn may be interpreted by parents as meaning that labor events caused or contributed to the encephalopathy. During the 72 hours of TH, the newborn is sedated and separated from the parents, causing additional emotional stress and uncertainty. When a baby is transferred from a community hospital to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at a tertiary center, the parents may be geographically separated from their baby during a critical period of time, adding to their anxiety. At some point during the care process most newborns treated with TH will have an EEG, brain ultrasound, and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These data will be discussed with the parent(s) and may cause confusion and additional stress.
The optimal approach to communicating with parents whose newborn is treated with TH continues to evolve. Best practices may include17-20:
- in-person, regular multidisciplinary family meetings with the parents, including neonatologists, obstetricians, social service specialists and mental health experts when possible
- providing emotional support to parents, recognizing the psychological trauma of the clinical events
- encouraging parents to have physical contact with the newborn during TH
- elevating the role of the parents in the care process by having them participate in care events such as diapering the newborn
- ensuring that clinicians do not blame other clinicians for the clinical outcome
- communicating the results and interpretation of advanced physiological monitoring and imaging studies, with an emphasis on clarity, recognizing the limitations of the studies
- providing educational materials for parents about TH, early intervention programs, and support resources.
Coordinated and consistent communication with the parents is often difficult to facilitate due to many factors, including the unique perspectives and vocabularies of clinicians from different specialties and the difficulty of coordinating communications with all those involved over multiple shifts and sites of care. In terms of vocabulary, neonatologists are comfortable with making a diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in a newborn, but obstetricians would prefer that neonatologists use the more generic diagnosis of encephalopathy, holding judgment on the cause until additional data are available. In terms of coordinating communication over multiple shifts and sites of care, interactions between an obstetrician and their patient typically occurs in the postpartum unit, while interactions between neonatologists and parents occur in the NICU.
Parents of a baby with neonatal encephalopathy undergoing TH may have numerous traumatic experiences during the care process. For weeks or months after birth, they may recall or dream about the absence of sounds from their newborn at birth, the resuscitation events including chest compressions and intubation, the shivering of the baby during TH, and the jarring pivot from the expectation of holding and bonding with a healthy newborn to the reality of a sick newborn requiring intensive care. Obstetricians are also traumatized by these events and support from peers and mental health experts may help them recognize, explore, and adapt to the trauma. Neonatologists believe that TH can help improve the childhood outcomes of newborns with encephalopathy, a goal endorsed by all clinicians and family members. ●
- Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, et al. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;CD003311.
- Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Papile E, Baley JE, Benitz W, et al. Hypothermia and neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2014;133:1146-1150.
- Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonates. Recommendations of the neonatal encephalopathy task force. 2016. https://www.rmf.harvard. edu/-/media/Files/_Global/KC/PDFs/Guide lines/crico_neonates.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2023.
- Zhang W, Ma J, Danzeng Q, et al. Safety of moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;74:51-61.
- Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976;33:696-705.
- Thompson CM, Puterman AS, Linley LL, et al. The value of a scoring system for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in predicting neurodevelopmental outcome. Acta Pediatr. 1997;86:757-761.
- Lundgren C, Brudin L, Wanby AS, et al. Ante- and intrapartum risk factors for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:1595-1601.
- Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Wusthoff CJ, et al. Antepartum and intrapartum factors preceding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e952-e959.
- Lorain P, Bower A, Gottardi E, et al. Risk factors for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in cases of severe acidosis: a case-control study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:471-478.
- Russ JB, Simmons R, Glass HC. Neonatal encephalopathy: beyond hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neo Reviews. 2021;22:e148-e162.
- Allen NM, Mannion M, Conroy J, et al. The variable phenotypes of KCNQ-related epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:e99-e105.
- Zibro J, Shellhaas RA. Neonatal seizures: diagnosis, etiologies and management. Semin Neurol. 2020;40:246-256.
- Moreno-De-Luca A, Millan F, Peacreta DR, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in patients with cerebral palsy. JAMA. 2021;325:467-475.
- Srivastava S, Lewis SA, Cohen JS, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray in cerebral palsy. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurology. 2022;79:1287-1295.
- Gonzalez-Mantilla PJ, Hu Y, Myers SM, et al. Diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in cerebral palsy and implications for genetic testing guidelines. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- van Eyk C, MacLennon SC, MacLennan AH. All patients with cerebral palsy diagnosis merit genomic sequencing. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- Craig AK, James C, Bainter J, et al. Parental perceptions of neonatal therapeutic hypothermia; emotional and healing experiences. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:2889-2896. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1563592.
- Sagaser A, Pilon B, Goeller A, et al. Parent experience of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and hypothermia: a call for trauma informed care. Am J Perinatol. Epub March 4, 2022.
- Cascio A, Ferrand A, Racine E, et al. Discussing brain magnetic resonance imaging results for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia: a challenge for clinicians and parents. E Neurological Sci. 2022;29:100424.
- Thyagarajan B, Baral V, Gunda R, et al. Parental perceptions of hypothermia treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:2527-2533.
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for moderate and severe neonatal encephalopathy has been shown to reduce the risk of newborn death, major neurodevelopmental disability, developmental delay, and cerebral palsy.1 It is estimated that 8 newborns with moderate or severe neonatal encephalopathy need to be treated with TH to prevent 1 case of cerebral palsy.1 The key elements of TH include:
- initiate hypothermia within 6 hoursof birth
- cool the newborn to a core temperature of 33.5˚ C to 34.5˚ C (92.3˚ F to 94.1˚ F) for 72 hours
- obtain brain ultrasonography to assess for intracranial hemorrhage
- obtain sequential MRI studies to assess brain structure and function
- initiate EEG monitoring for seizure activity.
During hypothermia the newborn is sedated, and oral feedings are reduced. During TH, important physiological goals are to maintain normal oxygenation, blood pressure, fluid balance, and glucose levels.1,2
TH: The basics
Most of the major published randomized clinical trials used the following inclusion criteria to initiate TH2:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 35 weeks
- neonate is within 6 hours of birth
- an Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation at birth or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or the presence of seizures
- absence of recognizable congenital abnormalities at birth.
However, in some institutions, expert neonatologists have developed more liberal criteria for the initiation of TH, to be considered on a case-by-case basis. These more inclusive criteria, which will result in more newborns being treated with TH, include3:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 34 weeks
- neonate is within 12 hours of birth
- a sentinel event at birth or Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1 or postnatal cardiopulmonary failure
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or concern for the presence of seizures.
Birth at a gestational age ≤ 34 weeks is a contraindication to TH. Relative contraindications to initiation of TH include: birth weight < 1,750 g, severe congenital anomaly, major genetic disorders, known severe metabolic disorders, major intracranial hemorrhage, severe septicemia, and uncorrectable coagulopathy.3 Adverse outcomes of TH include thrombocytopenia, cardiac arrythmia, and fat necrosis.4
Diagnosing neonatal encephalopathy
Neonatal encephalopathy is a clinical diagnosis, defined as abnormal neurologic function in the first few days of life in an infant born at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation. It is divided into 3 categories: mild (Stage 1), moderate (Stage 2), and severe (Stage 3).5,6 Institutions vary in the criteria used to differentiate mild from moderate neonatal encephalopathy, the two most frequent forms of encephalopathy. Newborns with mild encephalopathy are not routinely treated with TH because TH has not been shown to be helpful in this setting. Institutions with liberal criteria for diagnosing moderate encephalopathy will initiate TH in more cases. Involvement of a pediatric neurologist in the diagnosis of moderate encephalopathy may help confirm the diagnosis made by the primary neonatologist and provide an independent, second opinion about whether the newborn should be diagnosed with mild or moderate encephalopathy, a clinically important distinction. Physical examination and EEG findings associated with cases of mild, moderate, and severe encephalopathy are presented in TABLE 1.7

Continue: Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy...
Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy
In a retrospective case-control study that included 405 newborns at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestational age with neonatal encephalopathy thought to be due to hypoxia, 8 obstetric factors were identified as being associated with an increased risk of neonatal encephalopathy, including (TABLE 2)8:
1. an obstetric sentinel event (uterine rupture, placental abruption, umbilical cord prolapse, maternal collapse, or severe fetal bleeding)
2. shoulder dystocia
3. abnormal cardiotocogram (persistent late or variable decelerations, fetal bradycardia, and/or absent or minimal fetal heart variability)
4. failed vacuum delivery
5. prolonged rupture of the membranes (> 24 hours)
6. tight nuchal cord
7. gestational age at birth > 41 weeks
8. thick meconium.

Similar findings have been reported by other investigators analyzing the obstetric risk factors for neonatal encephalopathy.7,9
Genetic causes of neonatal seizures and neonatal encephalopathy
Many neonatologists practice with the belief that for a newborn with encephalopathy in the setting of a sentinel labor event, a low Apgar score at 5 minutes, an umbilical cord artery pH < 7.00, and/or an elevated lactate level, the diagnosis of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is warranted. However, there are many causes of neonatal encephalopathy not related to intrapartum events. For example, neonatal encephalopathy and seizures may be caused by infectious, vascular, metabolic, medications, or congenital problems.10
There are genetic disorders that can be associated with both neonatal seizures and encephalopathy, suggesting that in some cases the primary cause of the encephalopathy is a genetic problem, not management of labor. Mutations in the potassium channel and sodium channel genes are well recognized causes of neonatal seizures.11,12 Cerebral palsy, a childhood outcome that may follow neonatal encephalopathy, also has numerous etiologies, including genetic causes. Among 1,345 children with cerebral palsy referred for exome sequencing, investigators reported that a genetic abnormality was identified in 33% of the cases.13 Mutations in 86 genes were identified in multiple children. Similar results have been reported in other cohorts.14-16 Maintaining an open mind about the causes of a case of neonatal encephalopathy and not jumping to a conclusion before completing an evaluation is an optimal approach.
Parent’s evolving emotional and intellectual reaction to the initiation of TH
Initiation of TH for a newborn with encephalopathy catalyzes parents to wonder, “How did my baby develop an encephalopathy?”, “Did my obstetrician’s management of labor and delivery contribute to the outcome?” and “What is the prognosis for my baby?” These are difficult questions with high emotional valence for both patients and clinicians. Obstetricians and neonatologists should collaborate to provide consistent responses to these questions.
The presence of a low umbilical cord artery pH and high lactate in combination with a low Apgar score at 5 minutes may lead the neonatologist to diagnose hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the medical record. The diagnosis of brain hypoxia and ischemia in a newborn may be interpreted by parents as meaning that labor events caused or contributed to the encephalopathy. During the 72 hours of TH, the newborn is sedated and separated from the parents, causing additional emotional stress and uncertainty. When a baby is transferred from a community hospital to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at a tertiary center, the parents may be geographically separated from their baby during a critical period of time, adding to their anxiety. At some point during the care process most newborns treated with TH will have an EEG, brain ultrasound, and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These data will be discussed with the parent(s) and may cause confusion and additional stress.
The optimal approach to communicating with parents whose newborn is treated with TH continues to evolve. Best practices may include17-20:
- in-person, regular multidisciplinary family meetings with the parents, including neonatologists, obstetricians, social service specialists and mental health experts when possible
- providing emotional support to parents, recognizing the psychological trauma of the clinical events
- encouraging parents to have physical contact with the newborn during TH
- elevating the role of the parents in the care process by having them participate in care events such as diapering the newborn
- ensuring that clinicians do not blame other clinicians for the clinical outcome
- communicating the results and interpretation of advanced physiological monitoring and imaging studies, with an emphasis on clarity, recognizing the limitations of the studies
- providing educational materials for parents about TH, early intervention programs, and support resources.
Coordinated and consistent communication with the parents is often difficult to facilitate due to many factors, including the unique perspectives and vocabularies of clinicians from different specialties and the difficulty of coordinating communications with all those involved over multiple shifts and sites of care. In terms of vocabulary, neonatologists are comfortable with making a diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in a newborn, but obstetricians would prefer that neonatologists use the more generic diagnosis of encephalopathy, holding judgment on the cause until additional data are available. In terms of coordinating communication over multiple shifts and sites of care, interactions between an obstetrician and their patient typically occurs in the postpartum unit, while interactions between neonatologists and parents occur in the NICU.
Parents of a baby with neonatal encephalopathy undergoing TH may have numerous traumatic experiences during the care process. For weeks or months after birth, they may recall or dream about the absence of sounds from their newborn at birth, the resuscitation events including chest compressions and intubation, the shivering of the baby during TH, and the jarring pivot from the expectation of holding and bonding with a healthy newborn to the reality of a sick newborn requiring intensive care. Obstetricians are also traumatized by these events and support from peers and mental health experts may help them recognize, explore, and adapt to the trauma. Neonatologists believe that TH can help improve the childhood outcomes of newborns with encephalopathy, a goal endorsed by all clinicians and family members. ●
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for moderate and severe neonatal encephalopathy has been shown to reduce the risk of newborn death, major neurodevelopmental disability, developmental delay, and cerebral palsy.1 It is estimated that 8 newborns with moderate or severe neonatal encephalopathy need to be treated with TH to prevent 1 case of cerebral palsy.1 The key elements of TH include:
- initiate hypothermia within 6 hoursof birth
- cool the newborn to a core temperature of 33.5˚ C to 34.5˚ C (92.3˚ F to 94.1˚ F) for 72 hours
- obtain brain ultrasonography to assess for intracranial hemorrhage
- obtain sequential MRI studies to assess brain structure and function
- initiate EEG monitoring for seizure activity.
During hypothermia the newborn is sedated, and oral feedings are reduced. During TH, important physiological goals are to maintain normal oxygenation, blood pressure, fluid balance, and glucose levels.1,2
TH: The basics
Most of the major published randomized clinical trials used the following inclusion criteria to initiate TH2:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 35 weeks
- neonate is within 6 hours of birth
- an Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation at birth or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or the presence of seizures
- absence of recognizable congenital abnormalities at birth.
However, in some institutions, expert neonatologists have developed more liberal criteria for the initiation of TH, to be considered on a case-by-case basis. These more inclusive criteria, which will result in more newborns being treated with TH, include3:
- gestational age at birth of ≥ 34 weeks
- neonate is within 12 hours of birth
- a sentinel event at birth or Apgar score ≤ 5 at 10 minutes of life or prolonged resuscitation or umbilical artery cord pH < 7.1 or neonatal blood gas within 60 minutes of life < 7.1 or postnatal cardiopulmonary failure
- moderate to severe encephalopathy or concern for the presence of seizures.
Birth at a gestational age ≤ 34 weeks is a contraindication to TH. Relative contraindications to initiation of TH include: birth weight < 1,750 g, severe congenital anomaly, major genetic disorders, known severe metabolic disorders, major intracranial hemorrhage, severe septicemia, and uncorrectable coagulopathy.3 Adverse outcomes of TH include thrombocytopenia, cardiac arrythmia, and fat necrosis.4
Diagnosing neonatal encephalopathy
Neonatal encephalopathy is a clinical diagnosis, defined as abnormal neurologic function in the first few days of life in an infant born at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation. It is divided into 3 categories: mild (Stage 1), moderate (Stage 2), and severe (Stage 3).5,6 Institutions vary in the criteria used to differentiate mild from moderate neonatal encephalopathy, the two most frequent forms of encephalopathy. Newborns with mild encephalopathy are not routinely treated with TH because TH has not been shown to be helpful in this setting. Institutions with liberal criteria for diagnosing moderate encephalopathy will initiate TH in more cases. Involvement of a pediatric neurologist in the diagnosis of moderate encephalopathy may help confirm the diagnosis made by the primary neonatologist and provide an independent, second opinion about whether the newborn should be diagnosed with mild or moderate encephalopathy, a clinically important distinction. Physical examination and EEG findings associated with cases of mild, moderate, and severe encephalopathy are presented in TABLE 1.7

Continue: Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy...
Obstetric factors that may be associated with neonatal encephalopathy
In a retrospective case-control study that included 405 newborns at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestational age with neonatal encephalopathy thought to be due to hypoxia, 8 obstetric factors were identified as being associated with an increased risk of neonatal encephalopathy, including (TABLE 2)8:
1. an obstetric sentinel event (uterine rupture, placental abruption, umbilical cord prolapse, maternal collapse, or severe fetal bleeding)
2. shoulder dystocia
3. abnormal cardiotocogram (persistent late or variable decelerations, fetal bradycardia, and/or absent or minimal fetal heart variability)
4. failed vacuum delivery
5. prolonged rupture of the membranes (> 24 hours)
6. tight nuchal cord
7. gestational age at birth > 41 weeks
8. thick meconium.

Similar findings have been reported by other investigators analyzing the obstetric risk factors for neonatal encephalopathy.7,9
Genetic causes of neonatal seizures and neonatal encephalopathy
Many neonatologists practice with the belief that for a newborn with encephalopathy in the setting of a sentinel labor event, a low Apgar score at 5 minutes, an umbilical cord artery pH < 7.00, and/or an elevated lactate level, the diagnosis of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy is warranted. However, there are many causes of neonatal encephalopathy not related to intrapartum events. For example, neonatal encephalopathy and seizures may be caused by infectious, vascular, metabolic, medications, or congenital problems.10
There are genetic disorders that can be associated with both neonatal seizures and encephalopathy, suggesting that in some cases the primary cause of the encephalopathy is a genetic problem, not management of labor. Mutations in the potassium channel and sodium channel genes are well recognized causes of neonatal seizures.11,12 Cerebral palsy, a childhood outcome that may follow neonatal encephalopathy, also has numerous etiologies, including genetic causes. Among 1,345 children with cerebral palsy referred for exome sequencing, investigators reported that a genetic abnormality was identified in 33% of the cases.13 Mutations in 86 genes were identified in multiple children. Similar results have been reported in other cohorts.14-16 Maintaining an open mind about the causes of a case of neonatal encephalopathy and not jumping to a conclusion before completing an evaluation is an optimal approach.
Parent’s evolving emotional and intellectual reaction to the initiation of TH
Initiation of TH for a newborn with encephalopathy catalyzes parents to wonder, “How did my baby develop an encephalopathy?”, “Did my obstetrician’s management of labor and delivery contribute to the outcome?” and “What is the prognosis for my baby?” These are difficult questions with high emotional valence for both patients and clinicians. Obstetricians and neonatologists should collaborate to provide consistent responses to these questions.
The presence of a low umbilical cord artery pH and high lactate in combination with a low Apgar score at 5 minutes may lead the neonatologist to diagnose hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the medical record. The diagnosis of brain hypoxia and ischemia in a newborn may be interpreted by parents as meaning that labor events caused or contributed to the encephalopathy. During the 72 hours of TH, the newborn is sedated and separated from the parents, causing additional emotional stress and uncertainty. When a baby is transferred from a community hospital to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at a tertiary center, the parents may be geographically separated from their baby during a critical period of time, adding to their anxiety. At some point during the care process most newborns treated with TH will have an EEG, brain ultrasound, and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These data will be discussed with the parent(s) and may cause confusion and additional stress.
The optimal approach to communicating with parents whose newborn is treated with TH continues to evolve. Best practices may include17-20:
- in-person, regular multidisciplinary family meetings with the parents, including neonatologists, obstetricians, social service specialists and mental health experts when possible
- providing emotional support to parents, recognizing the psychological trauma of the clinical events
- encouraging parents to have physical contact with the newborn during TH
- elevating the role of the parents in the care process by having them participate in care events such as diapering the newborn
- ensuring that clinicians do not blame other clinicians for the clinical outcome
- communicating the results and interpretation of advanced physiological monitoring and imaging studies, with an emphasis on clarity, recognizing the limitations of the studies
- providing educational materials for parents about TH, early intervention programs, and support resources.
Coordinated and consistent communication with the parents is often difficult to facilitate due to many factors, including the unique perspectives and vocabularies of clinicians from different specialties and the difficulty of coordinating communications with all those involved over multiple shifts and sites of care. In terms of vocabulary, neonatologists are comfortable with making a diagnosis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in a newborn, but obstetricians would prefer that neonatologists use the more generic diagnosis of encephalopathy, holding judgment on the cause until additional data are available. In terms of coordinating communication over multiple shifts and sites of care, interactions between an obstetrician and their patient typically occurs in the postpartum unit, while interactions between neonatologists and parents occur in the NICU.
Parents of a baby with neonatal encephalopathy undergoing TH may have numerous traumatic experiences during the care process. For weeks or months after birth, they may recall or dream about the absence of sounds from their newborn at birth, the resuscitation events including chest compressions and intubation, the shivering of the baby during TH, and the jarring pivot from the expectation of holding and bonding with a healthy newborn to the reality of a sick newborn requiring intensive care. Obstetricians are also traumatized by these events and support from peers and mental health experts may help them recognize, explore, and adapt to the trauma. Neonatologists believe that TH can help improve the childhood outcomes of newborns with encephalopathy, a goal endorsed by all clinicians and family members. ●
- Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, et al. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;CD003311.
- Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Papile E, Baley JE, Benitz W, et al. Hypothermia and neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2014;133:1146-1150.
- Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonates. Recommendations of the neonatal encephalopathy task force. 2016. https://www.rmf.harvard. edu/-/media/Files/_Global/KC/PDFs/Guide lines/crico_neonates.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2023.
- Zhang W, Ma J, Danzeng Q, et al. Safety of moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;74:51-61.
- Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976;33:696-705.
- Thompson CM, Puterman AS, Linley LL, et al. The value of a scoring system for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in predicting neurodevelopmental outcome. Acta Pediatr. 1997;86:757-761.
- Lundgren C, Brudin L, Wanby AS, et al. Ante- and intrapartum risk factors for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:1595-1601.
- Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Wusthoff CJ, et al. Antepartum and intrapartum factors preceding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e952-e959.
- Lorain P, Bower A, Gottardi E, et al. Risk factors for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in cases of severe acidosis: a case-control study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:471-478.
- Russ JB, Simmons R, Glass HC. Neonatal encephalopathy: beyond hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neo Reviews. 2021;22:e148-e162.
- Allen NM, Mannion M, Conroy J, et al. The variable phenotypes of KCNQ-related epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:e99-e105.
- Zibro J, Shellhaas RA. Neonatal seizures: diagnosis, etiologies and management. Semin Neurol. 2020;40:246-256.
- Moreno-De-Luca A, Millan F, Peacreta DR, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in patients with cerebral palsy. JAMA. 2021;325:467-475.
- Srivastava S, Lewis SA, Cohen JS, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray in cerebral palsy. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurology. 2022;79:1287-1295.
- Gonzalez-Mantilla PJ, Hu Y, Myers SM, et al. Diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in cerebral palsy and implications for genetic testing guidelines. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- van Eyk C, MacLennon SC, MacLennan AH. All patients with cerebral palsy diagnosis merit genomic sequencing. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- Craig AK, James C, Bainter J, et al. Parental perceptions of neonatal therapeutic hypothermia; emotional and healing experiences. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:2889-2896. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1563592.
- Sagaser A, Pilon B, Goeller A, et al. Parent experience of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and hypothermia: a call for trauma informed care. Am J Perinatol. Epub March 4, 2022.
- Cascio A, Ferrand A, Racine E, et al. Discussing brain magnetic resonance imaging results for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia: a challenge for clinicians and parents. E Neurological Sci. 2022;29:100424.
- Thyagarajan B, Baral V, Gunda R, et al. Parental perceptions of hypothermia treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:2527-2533.
- Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, et al. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;CD003311.
- Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Papile E, Baley JE, Benitz W, et al. Hypothermia and neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2014;133:1146-1150.
- Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonates. Recommendations of the neonatal encephalopathy task force. 2016. https://www.rmf.harvard. edu/-/media/Files/_Global/KC/PDFs/Guide lines/crico_neonates.pdf. Accessed May 25, 2023.
- Zhang W, Ma J, Danzeng Q, et al. Safety of moderate hypothermia for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;74:51-61.
- Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976;33:696-705.
- Thompson CM, Puterman AS, Linley LL, et al. The value of a scoring system for hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in predicting neurodevelopmental outcome. Acta Pediatr. 1997;86:757-761.
- Lundgren C, Brudin L, Wanby AS, et al. Ante- and intrapartum risk factors for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:1595-1601.
- Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J, Wusthoff CJ, et al. Antepartum and intrapartum factors preceding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2013;132:e952-e959.
- Lorain P, Bower A, Gottardi E, et al. Risk factors for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in cases of severe acidosis: a case-control study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2022;101:471-478.
- Russ JB, Simmons R, Glass HC. Neonatal encephalopathy: beyond hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neo Reviews. 2021;22:e148-e162.
- Allen NM, Mannion M, Conroy J, et al. The variable phenotypes of KCNQ-related epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:e99-e105.
- Zibro J, Shellhaas RA. Neonatal seizures: diagnosis, etiologies and management. Semin Neurol. 2020;40:246-256.
- Moreno-De-Luca A, Millan F, Peacreta DR, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in patients with cerebral palsy. JAMA. 2021;325:467-475.
- Srivastava S, Lewis SA, Cohen JS, et al. Molecular diagnostic yield of exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray in cerebral palsy. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurology. 2022;79:1287-1295.
- Gonzalez-Mantilla PJ, Hu Y, Myers SM, et al. Diagnostic yield of exome sequencing in cerebral palsy and implications for genetic testing guidelines. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- van Eyk C, MacLennon SC, MacLennan AH. All patients with cerebral palsy diagnosis merit genomic sequencing. JAMA Pediatr. Epub March 6, 2023.
- Craig AK, James C, Bainter J, et al. Parental perceptions of neonatal therapeutic hypothermia; emotional and healing experiences. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:2889-2896. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1563592.
- Sagaser A, Pilon B, Goeller A, et al. Parent experience of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and hypothermia: a call for trauma informed care. Am J Perinatol. Epub March 4, 2022.
- Cascio A, Ferrand A, Racine E, et al. Discussing brain magnetic resonance imaging results for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia: a challenge for clinicians and parents. E Neurological Sci. 2022;29:100424.
- Thyagarajan B, Baral V, Gunda R, et al. Parental perceptions of hypothermia treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:2527-2533.
Can cffDNA technology be used to determine the underlying cause of pregnancy loss to better inform future pregnancy planning?
Hartwig TJ, Ambye L, Gruhn JR, et al. Cell-free fetal DNA for genetic evaluation in Copenhagen Pregnancy Loss Study (COPL): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2023;401:762-771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02610-1.
Expert Commentary
A devastating outcome for women, pregnancy loss is directly proportional to maternal age, estimated to occur in approximately 15% of clinically recognized pregnancies and 30% of preclinical pregnancies.1 Approximately 80% of pregnancy losses occur in the first trimester.2 The frequency of clinically recognized early pregnancy loss for women aged 20–30 years is 9% to 17%, and these rates increase sharply, from 20% at age 35 years to 40% at age 40 years, and 80% at age 45 years. Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), defined as the spontaneous loss of 2 or more clinically recognized pregnancies, affects less than 5% of women.3 Genetic testing using chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) has identified aneuploidy in about 55% of cases of miscarriage.4
Following ASRM guidelines for the evaluation of RPL, which consists of analyzing parental chromosomal abnormalities, congenital and acquired uterine anomalies, endocrine imbalances, and autoimmune factors (including antiphospholipid syndrome), no explainable cause is determined in 50% of cases.3 Recently, it has been shown that more than 90% of patients with RPL will have a probable or definitive cause identified when CMA testing on miscarriage tissue with the ASRM evaluation guidelines.5
Details of the study
In this prospective cohort study from Denmark, the authors analyzed maternal serum for cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) to determine the ploidy status of the pregnancy loss. One thousand women older than age 18 were included (those who demonstrated an ultrasound-confirmed intrauterine pregnancy loss prior to 22 weeks’ gestation). Maternal blood was obtained while pregnancy tissue was in situ or within 24 hours of passage of products of conception (POC), then analyzed by genome-wide sequencing of cffDNA.
For the first 333 recruited women (validation phase), direct sequencing of the POC was performed for sensitivity and specificity. Following the elimination of inconclusive samples, 302 of the 333 cases demonstrated a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 93%. In the subsequent evaluation of 667 women, researchers analyzed maternal serum from the gestational age of fetuses ranging from 35 days to 149 days.
Results. In total, nearly 90% of cases yielded conclusive results, with 50% euploid, 46% aneuploid, and 4% multiple aneuploidies. Earlier gestational ages (less than 7 weeks) had a no-call rate (ie, inconclusive) of approximately 50% (only based on 16 patients), with results typically obtained in maternal serum following passage of POC; in pregnancies at gestational ages past 7 weeks, the no-call rate was about 10%. In general, the longer the time after the pregnancy tissue passed, the higher likelihood of a no-call result.
Applying the technology of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based CMA can improve identification of fetal and/or maternal sources as causes of pregnancy loss with accuracy, but it does require collection of POC. Of note, samples were deficient in this study, the authors cite, in one-third of the cases. Given this limitation of collection, the authors argue for use of the noninvasive method of cffDNA, obtained from maternal serum.
Study strengths and weaknesses
Several weaknesses of this study are highlighted. Of the validation cohort, one-third of pregnancy tissue could not be analyzed due to insufficient collection. Only 73% of cases allowed for DNA isolation from fetal tissue or chorionic villi; in 27% of cases samples were labeled “unknown tissue.” In those cases classified as unknown, 70% were further determined to be maternal. When all female and monosomy cases were excluded in an effort to assuredly reduce the risk of contamination with maternal DNA, sensitivity of the cffDNA testing process declined to 78%. Another limitation was the required short window for maternal blood sampling (within 24 hours) and its impact on the no-call rate.
The authors note an association with later-life morbidity in patients with a history of pregnancy loss and RPL (including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and mental health disorders), thereby arguing for cffDNA-based testing versus no causal testing; however, no treatment has been proven to be effective at reducing pregnancy loss. ●
The best management course for unexplained RPL is uncertain. Despite its use for a euploid miscarriage or parental chromosomal structural rearrangement, in vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic testing remains an unproven modality.6,7 Given that approximately 70% of human conceptions never achieve viability, and 50% fail spontaneously before being detected,8 the authors’ findings demonstrate peripheral maternal blood can provide a reasonably high sensitivity and specificity for fetal ploidy status when compared with direct sequencing of pregnancy tissue. As fetal aneuploidy offers a higher percentage of subsequent successful pregnancy outcomes, cffDNA may offer reassurance, or direct further testing, following a pregnancy loss. As an application of their results, evaluation may be deferred for an aneuploid miscarriage.
—MARK P. TROLICE, MD, MBA
- Brown S. Miscarriage and its associations. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26:391-400. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087105.
- Wang X, Chen C , Wang L, et al. Conception, early pregnancy loss, and time to clinical pregnancy: a population-based prospective study. Fertil Steril. 2003;79:577-584.
- Evaluation and treatment of recurrent pregnancy loss: a committee opinion. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;98: 1103-1111.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/tacg.s320778.
- Popescu F, Jaslow FC, Kutteh WH. Recurrent pregnancy loss evaluation combined with 24-chromosome microarray of miscarriage tissue provides a probable or definite cause of pregnancy loss in over 90% of patients. Hum Reprod. 2018;33:579-587. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dey021.
- Dahdouh EM, Balayla J, Garcia-Velasco JA, et al. PGT-A for recurrent pregnancy loss: evidence is growing but the issue is not resolved. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:2805-2806. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deab194.
- Iews M, Tan J, Taskin O, et al. Does preimplantation genetic diagnosis improve reproductive outcome in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss owing to structural chromosomal rearrangement? A systematic review. Reproductive Bio Medicine Online. 2018;36:677-685. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.rbmo.2018.03.005.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/TACG.S320778.
Hartwig TJ, Ambye L, Gruhn JR, et al. Cell-free fetal DNA for genetic evaluation in Copenhagen Pregnancy Loss Study (COPL): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2023;401:762-771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02610-1.
Expert Commentary
A devastating outcome for women, pregnancy loss is directly proportional to maternal age, estimated to occur in approximately 15% of clinically recognized pregnancies and 30% of preclinical pregnancies.1 Approximately 80% of pregnancy losses occur in the first trimester.2 The frequency of clinically recognized early pregnancy loss for women aged 20–30 years is 9% to 17%, and these rates increase sharply, from 20% at age 35 years to 40% at age 40 years, and 80% at age 45 years. Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), defined as the spontaneous loss of 2 or more clinically recognized pregnancies, affects less than 5% of women.3 Genetic testing using chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) has identified aneuploidy in about 55% of cases of miscarriage.4
Following ASRM guidelines for the evaluation of RPL, which consists of analyzing parental chromosomal abnormalities, congenital and acquired uterine anomalies, endocrine imbalances, and autoimmune factors (including antiphospholipid syndrome), no explainable cause is determined in 50% of cases.3 Recently, it has been shown that more than 90% of patients with RPL will have a probable or definitive cause identified when CMA testing on miscarriage tissue with the ASRM evaluation guidelines.5
Details of the study
In this prospective cohort study from Denmark, the authors analyzed maternal serum for cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) to determine the ploidy status of the pregnancy loss. One thousand women older than age 18 were included (those who demonstrated an ultrasound-confirmed intrauterine pregnancy loss prior to 22 weeks’ gestation). Maternal blood was obtained while pregnancy tissue was in situ or within 24 hours of passage of products of conception (POC), then analyzed by genome-wide sequencing of cffDNA.
For the first 333 recruited women (validation phase), direct sequencing of the POC was performed for sensitivity and specificity. Following the elimination of inconclusive samples, 302 of the 333 cases demonstrated a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 93%. In the subsequent evaluation of 667 women, researchers analyzed maternal serum from the gestational age of fetuses ranging from 35 days to 149 days.
Results. In total, nearly 90% of cases yielded conclusive results, with 50% euploid, 46% aneuploid, and 4% multiple aneuploidies. Earlier gestational ages (less than 7 weeks) had a no-call rate (ie, inconclusive) of approximately 50% (only based on 16 patients), with results typically obtained in maternal serum following passage of POC; in pregnancies at gestational ages past 7 weeks, the no-call rate was about 10%. In general, the longer the time after the pregnancy tissue passed, the higher likelihood of a no-call result.
Applying the technology of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based CMA can improve identification of fetal and/or maternal sources as causes of pregnancy loss with accuracy, but it does require collection of POC. Of note, samples were deficient in this study, the authors cite, in one-third of the cases. Given this limitation of collection, the authors argue for use of the noninvasive method of cffDNA, obtained from maternal serum.
Study strengths and weaknesses
Several weaknesses of this study are highlighted. Of the validation cohort, one-third of pregnancy tissue could not be analyzed due to insufficient collection. Only 73% of cases allowed for DNA isolation from fetal tissue or chorionic villi; in 27% of cases samples were labeled “unknown tissue.” In those cases classified as unknown, 70% were further determined to be maternal. When all female and monosomy cases were excluded in an effort to assuredly reduce the risk of contamination with maternal DNA, sensitivity of the cffDNA testing process declined to 78%. Another limitation was the required short window for maternal blood sampling (within 24 hours) and its impact on the no-call rate.
The authors note an association with later-life morbidity in patients with a history of pregnancy loss and RPL (including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and mental health disorders), thereby arguing for cffDNA-based testing versus no causal testing; however, no treatment has been proven to be effective at reducing pregnancy loss. ●
The best management course for unexplained RPL is uncertain. Despite its use for a euploid miscarriage or parental chromosomal structural rearrangement, in vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic testing remains an unproven modality.6,7 Given that approximately 70% of human conceptions never achieve viability, and 50% fail spontaneously before being detected,8 the authors’ findings demonstrate peripheral maternal blood can provide a reasonably high sensitivity and specificity for fetal ploidy status when compared with direct sequencing of pregnancy tissue. As fetal aneuploidy offers a higher percentage of subsequent successful pregnancy outcomes, cffDNA may offer reassurance, or direct further testing, following a pregnancy loss. As an application of their results, evaluation may be deferred for an aneuploid miscarriage.
—MARK P. TROLICE, MD, MBA
Hartwig TJ, Ambye L, Gruhn JR, et al. Cell-free fetal DNA for genetic evaluation in Copenhagen Pregnancy Loss Study (COPL): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2023;401:762-771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02610-1.
Expert Commentary
A devastating outcome for women, pregnancy loss is directly proportional to maternal age, estimated to occur in approximately 15% of clinically recognized pregnancies and 30% of preclinical pregnancies.1 Approximately 80% of pregnancy losses occur in the first trimester.2 The frequency of clinically recognized early pregnancy loss for women aged 20–30 years is 9% to 17%, and these rates increase sharply, from 20% at age 35 years to 40% at age 40 years, and 80% at age 45 years. Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), defined as the spontaneous loss of 2 or more clinically recognized pregnancies, affects less than 5% of women.3 Genetic testing using chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) has identified aneuploidy in about 55% of cases of miscarriage.4
Following ASRM guidelines for the evaluation of RPL, which consists of analyzing parental chromosomal abnormalities, congenital and acquired uterine anomalies, endocrine imbalances, and autoimmune factors (including antiphospholipid syndrome), no explainable cause is determined in 50% of cases.3 Recently, it has been shown that more than 90% of patients with RPL will have a probable or definitive cause identified when CMA testing on miscarriage tissue with the ASRM evaluation guidelines.5
Details of the study
In this prospective cohort study from Denmark, the authors analyzed maternal serum for cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) to determine the ploidy status of the pregnancy loss. One thousand women older than age 18 were included (those who demonstrated an ultrasound-confirmed intrauterine pregnancy loss prior to 22 weeks’ gestation). Maternal blood was obtained while pregnancy tissue was in situ or within 24 hours of passage of products of conception (POC), then analyzed by genome-wide sequencing of cffDNA.
For the first 333 recruited women (validation phase), direct sequencing of the POC was performed for sensitivity and specificity. Following the elimination of inconclusive samples, 302 of the 333 cases demonstrated a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 93%. In the subsequent evaluation of 667 women, researchers analyzed maternal serum from the gestational age of fetuses ranging from 35 days to 149 days.
Results. In total, nearly 90% of cases yielded conclusive results, with 50% euploid, 46% aneuploid, and 4% multiple aneuploidies. Earlier gestational ages (less than 7 weeks) had a no-call rate (ie, inconclusive) of approximately 50% (only based on 16 patients), with results typically obtained in maternal serum following passage of POC; in pregnancies at gestational ages past 7 weeks, the no-call rate was about 10%. In general, the longer the time after the pregnancy tissue passed, the higher likelihood of a no-call result.
Applying the technology of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based CMA can improve identification of fetal and/or maternal sources as causes of pregnancy loss with accuracy, but it does require collection of POC. Of note, samples were deficient in this study, the authors cite, in one-third of the cases. Given this limitation of collection, the authors argue for use of the noninvasive method of cffDNA, obtained from maternal serum.
Study strengths and weaknesses
Several weaknesses of this study are highlighted. Of the validation cohort, one-third of pregnancy tissue could not be analyzed due to insufficient collection. Only 73% of cases allowed for DNA isolation from fetal tissue or chorionic villi; in 27% of cases samples were labeled “unknown tissue.” In those cases classified as unknown, 70% were further determined to be maternal. When all female and monosomy cases were excluded in an effort to assuredly reduce the risk of contamination with maternal DNA, sensitivity of the cffDNA testing process declined to 78%. Another limitation was the required short window for maternal blood sampling (within 24 hours) and its impact on the no-call rate.
The authors note an association with later-life morbidity in patients with a history of pregnancy loss and RPL (including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and mental health disorders), thereby arguing for cffDNA-based testing versus no causal testing; however, no treatment has been proven to be effective at reducing pregnancy loss. ●
The best management course for unexplained RPL is uncertain. Despite its use for a euploid miscarriage or parental chromosomal structural rearrangement, in vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic testing remains an unproven modality.6,7 Given that approximately 70% of human conceptions never achieve viability, and 50% fail spontaneously before being detected,8 the authors’ findings demonstrate peripheral maternal blood can provide a reasonably high sensitivity and specificity for fetal ploidy status when compared with direct sequencing of pregnancy tissue. As fetal aneuploidy offers a higher percentage of subsequent successful pregnancy outcomes, cffDNA may offer reassurance, or direct further testing, following a pregnancy loss. As an application of their results, evaluation may be deferred for an aneuploid miscarriage.
—MARK P. TROLICE, MD, MBA
- Brown S. Miscarriage and its associations. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26:391-400. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087105.
- Wang X, Chen C , Wang L, et al. Conception, early pregnancy loss, and time to clinical pregnancy: a population-based prospective study. Fertil Steril. 2003;79:577-584.
- Evaluation and treatment of recurrent pregnancy loss: a committee opinion. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;98: 1103-1111.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/tacg.s320778.
- Popescu F, Jaslow FC, Kutteh WH. Recurrent pregnancy loss evaluation combined with 24-chromosome microarray of miscarriage tissue provides a probable or definite cause of pregnancy loss in over 90% of patients. Hum Reprod. 2018;33:579-587. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dey021.
- Dahdouh EM, Balayla J, Garcia-Velasco JA, et al. PGT-A for recurrent pregnancy loss: evidence is growing but the issue is not resolved. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:2805-2806. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deab194.
- Iews M, Tan J, Taskin O, et al. Does preimplantation genetic diagnosis improve reproductive outcome in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss owing to structural chromosomal rearrangement? A systematic review. Reproductive Bio Medicine Online. 2018;36:677-685. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.rbmo.2018.03.005.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/TACG.S320778.
- Brown S. Miscarriage and its associations. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26:391-400. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087105.
- Wang X, Chen C , Wang L, et al. Conception, early pregnancy loss, and time to clinical pregnancy: a population-based prospective study. Fertil Steril. 2003;79:577-584.
- Evaluation and treatment of recurrent pregnancy loss: a committee opinion. Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Fertil Steril. 2012;98: 1103-1111.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/tacg.s320778.
- Popescu F, Jaslow FC, Kutteh WH. Recurrent pregnancy loss evaluation combined with 24-chromosome microarray of miscarriage tissue provides a probable or definite cause of pregnancy loss in over 90% of patients. Hum Reprod. 2018;33:579-587. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dey021.
- Dahdouh EM, Balayla J, Garcia-Velasco JA, et al. PGT-A for recurrent pregnancy loss: evidence is growing but the issue is not resolved. Hum Reprod. 2021;36:2805-2806. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deab194.
- Iews M, Tan J, Taskin O, et al. Does preimplantation genetic diagnosis improve reproductive outcome in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss owing to structural chromosomal rearrangement? A systematic review. Reproductive Bio Medicine Online. 2018;36:677-685. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.rbmo.2018.03.005.
- Papas RS, Kutteh WH. Genetic testing for aneuploidy in patients who have had multiple miscarriages: a review of current literature. Appl Clin Genet. 2021;14:321-329. https://doi.org/10.2147/TACG.S320778.
Studies reveal nuances in efficacy, MACE risk between JAKi and TNFi
Milan – Clinical trial and registry data comparisons between patients with rheumatoid arthritis who take Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) such as tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) continue to contribute to a better understanding of their efficacy and cardiovascular safety profile, based on presentations given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Tofacitinib vs. TNFi efficacy with or without history of atherosclerotic CVD
The efficacy of tofacitinib appears to be at least as good as TNFi, regardless of the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and baseline cardiovascular risk, according to a post hoc analysis of the ORAL Surveillance study presented by Maya Buch, MD, PhD, of NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre and University of Manchester, England. ORAL Surveillance was a randomized, open-label, postmarketing safety study sponsored by Pfizer. The study enrolled patients aged 50 or older, with one or more additional CV risk factors, and with active disease despite methotrexate treatment. The cohort included patients treated with the tofacitinib at two different doses (5 mg or 10 mg daily) or TNFi.
Given that a prior “post hoc analysis showed differences in the risk of major adverse CV events (MACE) with tofacitinib versus TNFi, depending on the personal history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Buch and coauthors aimed to further characterize the benefit/risk profile of tofacitinib by evaluating its efficacy, compared with TNFi, in patients with a history of ASCVD and baseline CV risk. Out of the 4,362 patients, 640 (14.7%) had a positive history of ASCVD, while 3,722 (85.3%) did not. For the latter group, the 10-year risk of ASCVD was calculated at baseline, which was high (≥ 20%) in 22.5% and intermediate (≥ 7.5% to < 20%) in 39.4%.
The analysis demonstrated that in patients without a history of ASCVD, the odds of achieving either remission (Clinical Disease Activity Index [CDAI] ≤ 2.8) or low disease activity (CDAI ≤ 10) were greater with tofacitinib vs. TNFi. With a history of ASCVD, the likelihood of achieving remission or low disease activity (LDA) was not statistically different between tofacitinib and TNFi. Patients with high or intermediate CV risk scores tended to be more likely to reach remission or LDA with tofacitinib vs. TNFi.
Dr. Buch emphasized that selecting the right therapy for each patient requires careful consideration of potential benefits and risks by the rheumatologist, taking into account individual patient history. “Stratification by baseline risk of CV events may help ensure appropriate and effective use of tofacitinib in patients with RA,” she concluded.
Kim Lauper, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Geneva University Hospitals, who was not involved in the study, commented on the importance of this data: “These findings are important because we currently lack information on how the presence of CV comorbidities can impact the efficacy of RA drugs.”
A real-world perspective
MACE occurred at similar rates between JAKi and TNFi, as well as for biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) with other modes of action (OMA) vs. TNFi, in the JAK-Pot study, an international collaboration of RA registries, reported Romain Aymon, of Geneva University Hospitals. But a subanalysis of JAK-Pot in patients resembling the population in the ORAL Surveillance trial found that the incidence of MACE was higher in each treatment group, compared with the overall population. However, no significant difference was found between JAKi vs. TNFi and OMA vs. TNFi.
Mr. Aymon said that the analysis is still ongoing, with additional registries being included.
Dr. Lauper, who is the principal investigator of the study presented by Mr. Aymon, noted that “the absence of a difference in MACE risk in the population resembling the ORAL Surveillance study is in contrast with the results from the ORAL Surveillance itself. This may be due to differences in the populations, with the ORAL Surveillance study having a more selected set of patients.”
The Dutch perspective
In line with the findings from the JAK-Pot study, a retrospective inception cohort study conducted on a Dutch RA population also revealed no difference in the incidence of cardiovascular events between JAKi starters and bDMARD starters, according to Merel Opdam, MSc, of Sint Maartenskliniek in Ubbergen, the Netherlands, who reported the findings at the meeting. Two subanalyses of the cohort study, funded by Pfizer, also did not show any difference between tofacitinib and baricitinib (Olumiant), compared with DMARDs, or in patients above 65 years of age. The analysis was conducted on 15,191 patients with RA who were initiating treatment with a JAKi or a new bDMARD, selected from IQVIA’s Dutch Real-World Data Longitudinal Prescription database, which covers approximately 63% of outpatient prescriptions in the Netherlands.
“Not all DMARDs have similar effects on cardiovascular outcomes, and observational studies can contribute to understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with JAKi,” Ms. Opdam said.
“Real-world data holds significant importance as it provides insights into a broader spectrum of patients and reflects the actual clinical practice where treatment decisions are tailored to individual patient needs,” commented Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin, and Charité University Medicine Berlin. She said that registries have a pivotal role in this regard.
Dr. Buch reports serving on a speakers bureau for AbbVie; serving as a consultant to AbbVie, CESAS Medical, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, and Pfizer; and receiving grant/research support from Gilead, Pfizer, and UCB. Mr. Aymon and Ms. Opdam report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Milan – Clinical trial and registry data comparisons between patients with rheumatoid arthritis who take Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) such as tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) continue to contribute to a better understanding of their efficacy and cardiovascular safety profile, based on presentations given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Tofacitinib vs. TNFi efficacy with or without history of atherosclerotic CVD
The efficacy of tofacitinib appears to be at least as good as TNFi, regardless of the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and baseline cardiovascular risk, according to a post hoc analysis of the ORAL Surveillance study presented by Maya Buch, MD, PhD, of NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre and University of Manchester, England. ORAL Surveillance was a randomized, open-label, postmarketing safety study sponsored by Pfizer. The study enrolled patients aged 50 or older, with one or more additional CV risk factors, and with active disease despite methotrexate treatment. The cohort included patients treated with the tofacitinib at two different doses (5 mg or 10 mg daily) or TNFi.
Given that a prior “post hoc analysis showed differences in the risk of major adverse CV events (MACE) with tofacitinib versus TNFi, depending on the personal history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Buch and coauthors aimed to further characterize the benefit/risk profile of tofacitinib by evaluating its efficacy, compared with TNFi, in patients with a history of ASCVD and baseline CV risk. Out of the 4,362 patients, 640 (14.7%) had a positive history of ASCVD, while 3,722 (85.3%) did not. For the latter group, the 10-year risk of ASCVD was calculated at baseline, which was high (≥ 20%) in 22.5% and intermediate (≥ 7.5% to < 20%) in 39.4%.
The analysis demonstrated that in patients without a history of ASCVD, the odds of achieving either remission (Clinical Disease Activity Index [CDAI] ≤ 2.8) or low disease activity (CDAI ≤ 10) were greater with tofacitinib vs. TNFi. With a history of ASCVD, the likelihood of achieving remission or low disease activity (LDA) was not statistically different between tofacitinib and TNFi. Patients with high or intermediate CV risk scores tended to be more likely to reach remission or LDA with tofacitinib vs. TNFi.
Dr. Buch emphasized that selecting the right therapy for each patient requires careful consideration of potential benefits and risks by the rheumatologist, taking into account individual patient history. “Stratification by baseline risk of CV events may help ensure appropriate and effective use of tofacitinib in patients with RA,” she concluded.
Kim Lauper, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Geneva University Hospitals, who was not involved in the study, commented on the importance of this data: “These findings are important because we currently lack information on how the presence of CV comorbidities can impact the efficacy of RA drugs.”
A real-world perspective
MACE occurred at similar rates between JAKi and TNFi, as well as for biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) with other modes of action (OMA) vs. TNFi, in the JAK-Pot study, an international collaboration of RA registries, reported Romain Aymon, of Geneva University Hospitals. But a subanalysis of JAK-Pot in patients resembling the population in the ORAL Surveillance trial found that the incidence of MACE was higher in each treatment group, compared with the overall population. However, no significant difference was found between JAKi vs. TNFi and OMA vs. TNFi.
Mr. Aymon said that the analysis is still ongoing, with additional registries being included.
Dr. Lauper, who is the principal investigator of the study presented by Mr. Aymon, noted that “the absence of a difference in MACE risk in the population resembling the ORAL Surveillance study is in contrast with the results from the ORAL Surveillance itself. This may be due to differences in the populations, with the ORAL Surveillance study having a more selected set of patients.”
The Dutch perspective
In line with the findings from the JAK-Pot study, a retrospective inception cohort study conducted on a Dutch RA population also revealed no difference in the incidence of cardiovascular events between JAKi starters and bDMARD starters, according to Merel Opdam, MSc, of Sint Maartenskliniek in Ubbergen, the Netherlands, who reported the findings at the meeting. Two subanalyses of the cohort study, funded by Pfizer, also did not show any difference between tofacitinib and baricitinib (Olumiant), compared with DMARDs, or in patients above 65 years of age. The analysis was conducted on 15,191 patients with RA who were initiating treatment with a JAKi or a new bDMARD, selected from IQVIA’s Dutch Real-World Data Longitudinal Prescription database, which covers approximately 63% of outpatient prescriptions in the Netherlands.
“Not all DMARDs have similar effects on cardiovascular outcomes, and observational studies can contribute to understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with JAKi,” Ms. Opdam said.
“Real-world data holds significant importance as it provides insights into a broader spectrum of patients and reflects the actual clinical practice where treatment decisions are tailored to individual patient needs,” commented Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin, and Charité University Medicine Berlin. She said that registries have a pivotal role in this regard.
Dr. Buch reports serving on a speakers bureau for AbbVie; serving as a consultant to AbbVie, CESAS Medical, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, and Pfizer; and receiving grant/research support from Gilead, Pfizer, and UCB. Mr. Aymon and Ms. Opdam report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Milan – Clinical trial and registry data comparisons between patients with rheumatoid arthritis who take Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) such as tofacitinib (Xeljanz) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) continue to contribute to a better understanding of their efficacy and cardiovascular safety profile, based on presentations given at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Tofacitinib vs. TNFi efficacy with or without history of atherosclerotic CVD
The efficacy of tofacitinib appears to be at least as good as TNFi, regardless of the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and baseline cardiovascular risk, according to a post hoc analysis of the ORAL Surveillance study presented by Maya Buch, MD, PhD, of NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre and University of Manchester, England. ORAL Surveillance was a randomized, open-label, postmarketing safety study sponsored by Pfizer. The study enrolled patients aged 50 or older, with one or more additional CV risk factors, and with active disease despite methotrexate treatment. The cohort included patients treated with the tofacitinib at two different doses (5 mg or 10 mg daily) or TNFi.
Given that a prior “post hoc analysis showed differences in the risk of major adverse CV events (MACE) with tofacitinib versus TNFi, depending on the personal history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Buch and coauthors aimed to further characterize the benefit/risk profile of tofacitinib by evaluating its efficacy, compared with TNFi, in patients with a history of ASCVD and baseline CV risk. Out of the 4,362 patients, 640 (14.7%) had a positive history of ASCVD, while 3,722 (85.3%) did not. For the latter group, the 10-year risk of ASCVD was calculated at baseline, which was high (≥ 20%) in 22.5% and intermediate (≥ 7.5% to < 20%) in 39.4%.
The analysis demonstrated that in patients without a history of ASCVD, the odds of achieving either remission (Clinical Disease Activity Index [CDAI] ≤ 2.8) or low disease activity (CDAI ≤ 10) were greater with tofacitinib vs. TNFi. With a history of ASCVD, the likelihood of achieving remission or low disease activity (LDA) was not statistically different between tofacitinib and TNFi. Patients with high or intermediate CV risk scores tended to be more likely to reach remission or LDA with tofacitinib vs. TNFi.
Dr. Buch emphasized that selecting the right therapy for each patient requires careful consideration of potential benefits and risks by the rheumatologist, taking into account individual patient history. “Stratification by baseline risk of CV events may help ensure appropriate and effective use of tofacitinib in patients with RA,” she concluded.
Kim Lauper, MD, of the division of rheumatology at Geneva University Hospitals, who was not involved in the study, commented on the importance of this data: “These findings are important because we currently lack information on how the presence of CV comorbidities can impact the efficacy of RA drugs.”
A real-world perspective
MACE occurred at similar rates between JAKi and TNFi, as well as for biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) with other modes of action (OMA) vs. TNFi, in the JAK-Pot study, an international collaboration of RA registries, reported Romain Aymon, of Geneva University Hospitals. But a subanalysis of JAK-Pot in patients resembling the population in the ORAL Surveillance trial found that the incidence of MACE was higher in each treatment group, compared with the overall population. However, no significant difference was found between JAKi vs. TNFi and OMA vs. TNFi.
Mr. Aymon said that the analysis is still ongoing, with additional registries being included.
Dr. Lauper, who is the principal investigator of the study presented by Mr. Aymon, noted that “the absence of a difference in MACE risk in the population resembling the ORAL Surveillance study is in contrast with the results from the ORAL Surveillance itself. This may be due to differences in the populations, with the ORAL Surveillance study having a more selected set of patients.”
The Dutch perspective
In line with the findings from the JAK-Pot study, a retrospective inception cohort study conducted on a Dutch RA population also revealed no difference in the incidence of cardiovascular events between JAKi starters and bDMARD starters, according to Merel Opdam, MSc, of Sint Maartenskliniek in Ubbergen, the Netherlands, who reported the findings at the meeting. Two subanalyses of the cohort study, funded by Pfizer, also did not show any difference between tofacitinib and baricitinib (Olumiant), compared with DMARDs, or in patients above 65 years of age. The analysis was conducted on 15,191 patients with RA who were initiating treatment with a JAKi or a new bDMARD, selected from IQVIA’s Dutch Real-World Data Longitudinal Prescription database, which covers approximately 63% of outpatient prescriptions in the Netherlands.
“Not all DMARDs have similar effects on cardiovascular outcomes, and observational studies can contribute to understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with JAKi,” Ms. Opdam said.
“Real-world data holds significant importance as it provides insights into a broader spectrum of patients and reflects the actual clinical practice where treatment decisions are tailored to individual patient needs,” commented Anja Strangfeld, MD, PhD, of the German Rheumatism Research Center Berlin, and Charité University Medicine Berlin. She said that registries have a pivotal role in this regard.
Dr. Buch reports serving on a speakers bureau for AbbVie; serving as a consultant to AbbVie, CESAS Medical, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, and Pfizer; and receiving grant/research support from Gilead, Pfizer, and UCB. Mr. Aymon and Ms. Opdam report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EULAR 2023
AGA update outlines best scenarios for EUS vascular interventions
, according to a practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
The AGA Institute’s Clinical Practice Update on interventional EUS, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , makes the case for broader adoption of two clinically available interventions – EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices and EUS-guided portosystemic pressure gradient measurement – while listing key research questions that remain to be answered. The update also describes current evidence for several emerging EUS interventions.
The update’s authors, led by Marvin Ryou, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, advised, when available, EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices over conventional direct endoscopic injection with cyanoacrylate glue, noting that EUS guidance “enhances the precision of injection,” expands treatment options to include placement of hemostatic coils, and uses Doppler to provide real-time feedback on hemostasis.
Available evidence suggests that EUS-guided gastric variceal therapy is “safe, with excellent acute hemostasis and low re-bleeding rates, and likely superiority over traditional direct endoscopic glue injection,” Dr. Ryou and colleagues wrote in their update.
Nonetheless, they cautioned, “the development of a consensus technique would be helpful,” better training of technicians is needed, and large, multicenter studies comparing EUS with standard interventional radiology approaches are still needed.
EUS-guided direct measurement of the portosystemic pressure gradient (PPG) may offer improved clinical efficiency over a percutaneous endovascular approach, Dr. Ryou and colleagues determined, notably when there is concern for a pre-sinusoidal cause of portal hypertension. The EUS intervention allows for the “concurrent ability to perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy and EUS as a one-stop shop during which PPG, liver biopsy, and endoscopic features of portal hypertension … can all be evaluated, obtained, and potentially treated during a single procedure.” The authors updated guidance on four emerging interventions for which evidence remains limited: EUS-guided injection therapy of rectal varices, EUS-guided splenic artery embolization, EUS-guided injection therapy in patients with splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, and EUS-guided portal vein sampling.
While the last of these interventions appears safe, the authors cautioned, it should be performed only as part of a research protocol. The authors described an experimental intervention tested in animal models using a EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in which a self-expanding metal stent was deployed via EUS to bridge the hepatic and portal vein and decompress a hypertensive portal system.
The authors cautioned that the guidance was not the product of a formal systematic review, but represented a summary of practical advice gleaned from a literature review to provide practical advice. As a general rule, they said, EUS-guided vascular interventions should be considered when the vascular target occurs in or near the gastrointestinal wall, “which may confer an advantage to an endoscopic rather than percutaneous access,” and when the intervention has “a clinical efficacy and safety profile comparable, if not superior, to current alternatives.” All the interventions described in the clinical practice update satisfy the first condition, but not the second.
Dr. Ryou and two of his three coauthors disclosed financial relationships, including consulting fees and research support, from device manufacturers.
, according to a practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
The AGA Institute’s Clinical Practice Update on interventional EUS, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , makes the case for broader adoption of two clinically available interventions – EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices and EUS-guided portosystemic pressure gradient measurement – while listing key research questions that remain to be answered. The update also describes current evidence for several emerging EUS interventions.
The update’s authors, led by Marvin Ryou, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, advised, when available, EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices over conventional direct endoscopic injection with cyanoacrylate glue, noting that EUS guidance “enhances the precision of injection,” expands treatment options to include placement of hemostatic coils, and uses Doppler to provide real-time feedback on hemostasis.
Available evidence suggests that EUS-guided gastric variceal therapy is “safe, with excellent acute hemostasis and low re-bleeding rates, and likely superiority over traditional direct endoscopic glue injection,” Dr. Ryou and colleagues wrote in their update.
Nonetheless, they cautioned, “the development of a consensus technique would be helpful,” better training of technicians is needed, and large, multicenter studies comparing EUS with standard interventional radiology approaches are still needed.
EUS-guided direct measurement of the portosystemic pressure gradient (PPG) may offer improved clinical efficiency over a percutaneous endovascular approach, Dr. Ryou and colleagues determined, notably when there is concern for a pre-sinusoidal cause of portal hypertension. The EUS intervention allows for the “concurrent ability to perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy and EUS as a one-stop shop during which PPG, liver biopsy, and endoscopic features of portal hypertension … can all be evaluated, obtained, and potentially treated during a single procedure.” The authors updated guidance on four emerging interventions for which evidence remains limited: EUS-guided injection therapy of rectal varices, EUS-guided splenic artery embolization, EUS-guided injection therapy in patients with splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, and EUS-guided portal vein sampling.
While the last of these interventions appears safe, the authors cautioned, it should be performed only as part of a research protocol. The authors described an experimental intervention tested in animal models using a EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in which a self-expanding metal stent was deployed via EUS to bridge the hepatic and portal vein and decompress a hypertensive portal system.
The authors cautioned that the guidance was not the product of a formal systematic review, but represented a summary of practical advice gleaned from a literature review to provide practical advice. As a general rule, they said, EUS-guided vascular interventions should be considered when the vascular target occurs in or near the gastrointestinal wall, “which may confer an advantage to an endoscopic rather than percutaneous access,” and when the intervention has “a clinical efficacy and safety profile comparable, if not superior, to current alternatives.” All the interventions described in the clinical practice update satisfy the first condition, but not the second.
Dr. Ryou and two of his three coauthors disclosed financial relationships, including consulting fees and research support, from device manufacturers.
, according to a practice update from the American Gastroenterological Association.
The AGA Institute’s Clinical Practice Update on interventional EUS, published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology , makes the case for broader adoption of two clinically available interventions – EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices and EUS-guided portosystemic pressure gradient measurement – while listing key research questions that remain to be answered. The update also describes current evidence for several emerging EUS interventions.
The update’s authors, led by Marvin Ryou, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, advised, when available, EUS-guided coil injection therapy of gastric varices over conventional direct endoscopic injection with cyanoacrylate glue, noting that EUS guidance “enhances the precision of injection,” expands treatment options to include placement of hemostatic coils, and uses Doppler to provide real-time feedback on hemostasis.
Available evidence suggests that EUS-guided gastric variceal therapy is “safe, with excellent acute hemostasis and low re-bleeding rates, and likely superiority over traditional direct endoscopic glue injection,” Dr. Ryou and colleagues wrote in their update.
Nonetheless, they cautioned, “the development of a consensus technique would be helpful,” better training of technicians is needed, and large, multicenter studies comparing EUS with standard interventional radiology approaches are still needed.
EUS-guided direct measurement of the portosystemic pressure gradient (PPG) may offer improved clinical efficiency over a percutaneous endovascular approach, Dr. Ryou and colleagues determined, notably when there is concern for a pre-sinusoidal cause of portal hypertension. The EUS intervention allows for the “concurrent ability to perform esophagogastroduodenoscopy and EUS as a one-stop shop during which PPG, liver biopsy, and endoscopic features of portal hypertension … can all be evaluated, obtained, and potentially treated during a single procedure.” The authors updated guidance on four emerging interventions for which evidence remains limited: EUS-guided injection therapy of rectal varices, EUS-guided splenic artery embolization, EUS-guided injection therapy in patients with splenic artery pseudoaneurysms, and EUS-guided portal vein sampling.
While the last of these interventions appears safe, the authors cautioned, it should be performed only as part of a research protocol. The authors described an experimental intervention tested in animal models using a EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in which a self-expanding metal stent was deployed via EUS to bridge the hepatic and portal vein and decompress a hypertensive portal system.
The authors cautioned that the guidance was not the product of a formal systematic review, but represented a summary of practical advice gleaned from a literature review to provide practical advice. As a general rule, they said, EUS-guided vascular interventions should be considered when the vascular target occurs in or near the gastrointestinal wall, “which may confer an advantage to an endoscopic rather than percutaneous access,” and when the intervention has “a clinical efficacy and safety profile comparable, if not superior, to current alternatives.” All the interventions described in the clinical practice update satisfy the first condition, but not the second.
Dr. Ryou and two of his three coauthors disclosed financial relationships, including consulting fees and research support, from device manufacturers.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Molecular mechanisms may predict major depressive disorder
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
“Given the multifaceted nature of MDD, the multiple small but dynamic genetic alterations in biomolecular pathways, which are modulated by epigenetic modifications, could contribute to a better understanding of the underlying aetiology and pathophysiology of this disorder,” wrote Cyrus Su Hui Ho, MD, of National University Health System, Singapore, and colleagues. However, studies of biomarkers in psychiatry are limited, and the predictive potential of microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) has not been examined, they said.
In a study published in Comprehensive Psychiatry, the researchers identified 60 adults with depression and 60 healthy controls. Depression severity was assessed with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. Other demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the patients and controls; 10 patients were unmedicated.
The researchers used QUIAGEN Ingenuity Pathway Analysis to identify the specific depression-related biological pathways affected by various miRNAs.
A total of six miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, miR-190a-5p, miR-33a-3p, miR-3690, and miR-6895-3p) were down-regulated in unmedicated depressed patients, compared with healthy controls.
In a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis, a combination panel with three miRNAs (miR-542-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) in whole blood yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.67. This combination correctly classified 66.7% of MDD patients and 63.3% of healthy controls.
The ability of individual miRNAs to differentiate between MDD patients and controls in the current study was limited, the researchers wrote in their discussion. “However, when three miRNAs (miR-542b-3p, miR-181b-3p, and miR-3690) were combined as a panel, the AUC was enhanced to an almost acceptable degree (AUC of 0.67, approaching 0.7) and might have value in complementing clinical diagnoses,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the small sample size and the use of medications by most MDD patients, which resulted in an especially small number of unmedicated patients, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of study population from a single center, and the inability to explain the link between blood and brain miRNA expression, they said.
However, the study is the first clinical trial in Singapore to examine the role of miRNA in depression and to identify miRNAs as potential biomarkers for MDD, they said.
Additional studies are needed to explore miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis, disease prognosis, and treatment response in MDD, they concluded.
The study was supported by the National University Health System Seed Fund. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM COMPREHENSIVE PSYCHIATRY
First-line or BiV backup? Conduction system pacing for CRT in heart failure
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pacing as a device therapy for heart failure (HF) is headed for what is probably its next big advance.
After decades of biventricular (BiV) pacemaker success in resynchronizing the ventricles and improving clinical outcomes, relatively new conduction-system pacing (CSP) techniques that avoid the pitfalls of right-ventricular (RV) pacing using BiV lead systems have been supplanting traditional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in selected patients at some major centers. In fact, they are solidly ensconced in a new guideline document addressing indications for CSP and BiV pacing in HF.
But , an alternative when BiV pacing isn’t appropriate or can’t be engaged.
That’s mainly because the limited, mostly observational evidence supporting CSP in the document can’t measure up to the clinical experience and plethora of large, randomized trials behind BiV-CRT.
But that shortfall is headed for change. Several new comparative studies, including a small, randomized trial, have added significantly to evidence suggesting that CSP is at least as effective as traditional CRT for procedural, functional safety, and clinical outcomes.
The new studies “are inherently prone to bias, but their results are really good,” observed Juan C. Diaz, MD. They show improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and symptoms with CSP that are “outstanding compared to what we have been doing for the last 20 years,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Diaz, Clínica Las Vegas, Medellin, Colombia, is an investigator with the observational SYNCHRONY, which is among the new CSP studies formally presented at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society. He is also lead author on its same-day publication in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
Dr. Diaz said that CSP, which sustains pacing via the native conduction system, makes more “physiologic sense” than BiV pacing and represents “a step forward” for HF device therapy.
SYNCHRONY compared LBB-area with BiV pacing as the initial strategy for achieving cardiac resynchronization in patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy.
CSP is “a long way” from replacing conventional CRT, he said. But the new studies at the HRS sessions should help extend His-bundle and LBB-area pacing to more patients, he added, given the significant long-term “drawbacks” of BiV pacing. These include inevitable RV pacing, multiple leads, and the risks associated with chronic transvenous leads.
Zachary Goldberger, MD, University of Wisconsin–Madison, went a bit further in support of CSP as invited discussant for the SYNCHRONY presentation.
Given that it improved LVEF, heart failure class, HF hospitalizations (HFH), and mortality in that study and others, Dr. Goldberger said, CSP could potentially “become the dominant mode of resynchronization going forward.”
Other experts at the meeting saw CSP’s potential more as one of several pacing techniques that could be brought to bear for patients with CRT indications.
“Conduction system pacing is going to be a huge complement to biventricular pacing,” to which about 30% of patients have a “less than optimal response,” said Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, chief of clinical electrophysiology, Geisinger Heart Institute, Danville, Pa.
“I don’t think it needs to replace biventricular pacing, because biventricular pacing is a well-established, incredibly powerful therapy,” he told this news organization. But CSP is likely to provide “a good alternative option” in patients with poor responses to BiV-CRT.
It may, however, render some current BiV-pacing alternatives “obsolete,” Dr. Vijayaraman observed. “At our center, at least for the last 5 years, no patient has needed epicardial surgical left ventricular lead placement” because CSP was a better backup option.
Dr. Vijayaraman presented two of the meeting’s CSP vs. BiV pacing comparisons. In one, the 100-patient randomized HOT-CRT trial, contractile function improved significantly on CSP, which could be either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing.
He also presented an observational study of LBB-area pacing at 15 centers in Asia, Europe, and North America and led the authors of its simultaneous publication in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“I think left-bundle conduction system pacing is the future, for sure,” Jagmeet P. Singh, MD, DPhil, told this news organization. Still, it doesn’t always work and when it does, it “doesn’t work equally in all patients,” he said.
“Conduction system pacing certainly makes a lot of sense,” especially in patients with left-bundle-branch block (LBBB), and “maybe not as a primary approach but certainly as a secondary approach,” said Dr. Singh, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, who is not a coauthor on any of the three studies.
He acknowledged that CSP may work well as a first-line option in patients with LBBB at some experienced centers. For those without LBBB or who have an intraventricular conduction delay, who represent 45%-50% of current CRT cases, Dr. Singh observed, “there’s still more evidence” that BiV-CRT is a more appropriate initial approach.
Standard CRT may fail, however, even in some patients who otherwise meet guideline-based indications. “We don’t really understand all the mechanisms for nonresponse in conventional biventricular pacing,” observed Niraj Varma, MD, PhD, Cleveland Clinic, also not involved with any of the three studies.
In some groups, including “patients with larger ventricles,” for example, BiV-CRT doesn’t always narrow the electrocardiographic QRS complex or preexcite delayed left ventricular (LV) activation, hallmarks of successful CRT, he said in an interview.
“I think we need to understand why this occurs in both situations,” but in such cases, CSP alone or as an adjunct to direct LV pacing may be successful. “Sometimes we need both an LV lead and the conduction-system pacing lead.”
Narrower, more efficient use of CSP as a BiV-CRT alternative may also boost its chances for success, Dr. Varma added. “I think we need to refine patient selection.”
HOT-CRT: Randomized CSP vs. BiV pacing trial
Conducted at three centers in a single health system, the His-optimized cardiac resynchronization therapy study (HOT-CRT) randomly assigned 100 patients with primary or secondary CRT indications to either to CSP – by either His-bundle or LBB-area pacing – or to standard BiV-CRT as the first-line resynchronization method.
Treatment crossovers, allowed for either pacing modality in the event of implantation failure, occurred in two patients and nine patients initially assigned to CSP and BiV pacing, respectively (4% vs. 18%), Dr. Vijayaraman reported.
Historically in trials, BiV pacing has elevated LVEF by about 7%, he said. The mean 12-point increase observed with CSP “is huge, in that sense.” HOT-CRT enrolled a predominantly male and White population at centers highly experienced in both CSP and BiV pacing, limiting its broad relevance to practice, as pointed out by both Dr. Vijayaraman and his presentation’s invited discussant, Yong-Mei Cha, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. Dr. Cha, who is director of cardiac device services at her center, also highlighted the greater rate of crossover from BiV pacing to CSP, 18% vs. 4% in the other direction. “This is a very encouraging result,” because the implant-failure rate for LBB-area pacing may drop once more operators become “familiar and skilled with conduction-system pacing.” Overall, the study supports CSP as “a very good alternative for heart failure patients when BiV pacing fails.”
International comparison of CSP and BiV pacing
In Dr. Vijayaraman’s other study, the observational comparison of LBB-area pacing and BiV-CRT, the CSP technique emerged as a “reasonable alternative to biventricular pacing, not only for improvement in LV function but also to reduce adverse clinical outcomes.”
Indeed, in the international study of 1,778 mostly male patients with primary or secondary CRT indications who received LBB-area or BiV pacing (797 and 981 patients, respectively), those on CSP saw a significant drop in risk for the primary endpoint, death or HFH.
Mean LVEF improved from 27% to 41% in the LBB-area pacing group and 27% to 37% with BiV pacing (P < .001 for both changes) over a follow-up averaging 33 months. The difference in improvement between CSP and BiV pacing was significant at P < .001.
In adjusted analysis, the risk for death or HFH was greater for BiV-pacing patients, a difference driven by HFH events.
- Death or HF: hazard ratio, 1.49 (95% confidence interval, 1.21-1.84; P < .001).
- Death: HR, 1.14 (95% CI, 0.88-1.48; P = .313).
- HFH: HR, 1.49 (95% CI, 1.16-1.92; P = .002)
The analysis has all the “inherent biases” of an observational study. The risk for patient-selection bias, however, was somewhat mitigated by consistent practice patterns at participating centers, Dr. Vijayaraman told this news organization.
For example, he said, operators at six of the institutions were most likely to use CSP as the first-line approach, and the same number of centers usually went with BiV pacing.
SYNCHRONY: First-line LBB-area pacing vs. BiV-CRT
Outcomes using the two approaches were similar in the prospective, international, observational study of 371 patients with ischemic or nonischemic cardiomyopathy and standard CRT indications. Allocation of 128 patients to LBB-area pacing and 243 to BiV-CRT was based on patient and operator preferences, reported Jorge Romero Jr, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, at the HRS sessions.
Risk for the death-HFH primary endpoint dropped 38% for those initially treated with LBB-area pacing, compared with BiV pacing, primarily because of a lower HFH risk:
- Death or HFH: HR, 0.62 (95% CI, 0.41-0.93; P = .02).
- Death: HR, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.25-1.32; P = .19).
- HFH: HR, 0.61 (95% CI, 0.34-0.93; P = .02)
Patients in the CSP group were also more likely to improve by at least one NYHA (New York Heart Association) class (80.4% vs. 67.9%; P < .001), consistent with their greater absolute change in LVEF (8.0 vs. 3.9 points; P < .01).
The findings “suggest that LBBAP [left-bundle branch area pacing] is an excellent alternative to BiV pacing,” with a comparable safety profile, write Jayanthi N. Koneru, MBBS, and Kenneth A. Ellenbogen, MD, in an editorial accompanying the published SYNCHRONY report.
“The differences in improvement of LVEF are encouraging for both groups,” but were superior for LBB-area pacing, continue Dr. Koneru and Dr. Ellenbogen, both with Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond. “Whether these results would have regressed to the mean over a longer period of follow-up or diverge further with LBB-area pacing continuing to be superior is unknown.”
Years for an answer?
A large randomized comparison of CSP and BiV-CRT, called Left vs. Left, is currently in early stages, Sana M. Al-Khatib, MD, MHS, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said in a media presentation on two of the presented studies. It has a planned enrollment of more than 2,100 patients on optimal meds with an LVEF of 50% or lower and either a QRS duration of at least 130 ms or an anticipated burden of RV pacing exceeding 40%.
The trial, she said, “will take years to give an answer, but it is actually designed to address the question of whether a composite endpoint of time to death or heart failure hospitalization can be improved with conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing.”
Dr. Al-Khatib is a coauthor on the new guideline covering both CSP and BiV-CRT in HF, as are Dr. Cha, Dr. Varma, Dr. Singh, Dr. Vijayaraman, and Dr. Goldberger; Dr. Ellenbogen is one of the reviewers.
Dr. Diaz discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or teaching from Bayer Healthcare, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. Dr. Vijayaraman discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking, teaching, or consulting for Abbott, Medtronic, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and receiving research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Varma discloses receiving honoraria or fees for speaking or consulting as an independent contractor for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Impulse Dynamics USA, Cardiologs, Abbott, Pacemate, Implicity, and EP Solutions. Dr. Singh discloses receiving fees for consulting from EBR Systems, Merit Medical Systems, New Century Health, Biotronik, Abbott, Medtronic, MicroPort Scientific, Cardiologs, Sanofi, CVRx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Octagos, Implicity, Orchestra Biomed, Rhythm Management Group, and Biosense Webster; and receiving honoraria or fees for speaking and teaching from Medscape. Dr. Cha had no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Romero discloses receiving research grants from Biosense Webster; and speaking or receiving honoraria or fees for consulting, speaking, or teaching, or serving on a board for Sanofi, Boston Scientific, and AtriCure. Dr. Koneru discloses consulting for Medtronic and receiving honoraria from Abbott. Dr. Ellenbogen discloses consulting or lecturing for or receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Abbott. Dr. Goldberger discloses receiving royalty income from and serving as an independent contractor for Elsevier. Dr. Al-Khatib discloses receiving research grants from Medtronic and Boston Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEART RHYTHM 2023
Dapagliflozin matches non–loop diuretic for congestion in AHF: DAPA-RESIST
suggests a new randomized trial. The drugs were given to the study’s loop diuretic–resistant patients on top of furosemide.
Changes in volume status and measures of pulmonary congestion and risk for serious adverse events were similar for those assigned to take dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or metolazone, a quinazoline diuretic. Those on dapagliflozin zone ultimately received a larger cumulative furosemide dose in the 61-patient trial, called DAPA-RESIST.
“The next steps are to assess whether a strategy of using SGLT2 inhibitors up front in patients with HF reduces the incidence of diuretic resistance, and to test further combinations of diuretics such as thiazide or thiazide-like diuretics, compared with acetazolamide, when used in addition to an IV loop diuretic and SGLT2 inhibitors together,” Ross T. Campbell, MBChB, PhD, University of Glasgow and Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, also in Glasgow, said in an interview.
Dr. Campbell presented the findings at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology and is senior author on its simultaneous publication in the European Heart Journal.
The multicenter trial randomly assigned 61 patients with AHF to receive dapagliflozin at a fixed dose of 10 mg once daily or metolazone 5 mg or 10 mg (starting dosage at physician discretion) once daily for 3 days of treatment on an open-label basis.
Patients had entered the trial on furosemide at a mean daily dosage of 260 mg in the dapagliflozin group and 229 mg for those assigned metolazone; dosages for the loop diuretic in the trial weren’t prespecified.
Their median age was 79 and 54% were women; 44% had HF with reduced ejection fraction. Their mean glomerular filtration rate was below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in 26%, 90% had chronic kidney disease, 98% had peripheral edema, and 46% had diabetes.
The mean cumulative furosemide dose was significantly higher among the dapagliflozin group’s 31 patients, 976 mg versus 704 mg for the 30 on acetazolamide (P < .05), 96 hours after the start of randomized therapy. However, patients on dapagliflozin experienced a lesser increase in creatinine (P < .05) and in blood urea (P < .01), a greater change in serum sodium (P < .05), and a smaller reduction in serum potassium (P < .01).
Although the trial wasn’t powered for those outcomes, Dr. Campbell said, “less biochemical upset could be associated with better outcomes in terms of less medium- to long-term renal impairment, and in the short-term length of stay.”
The mean decrease in weight at 96 hours, the primary endpoint, reached 3 kg on dapagliflozin, compared with 3.6 kg with metolazone (P = .082), a difference that fell short of significance.
Loop diuretic efficiency, that is weight change in kg per 40 mg furosemide, “was smaller with dapagliflozin than with metolazone at each time point after randomization, although the difference was only significant at 24 hours,” the published report states.
Changes in pulmonary congestion (by lung ultrasound) and fluid volume were similar between the groups.
“This trial further adds to the evidence base and safety profile for using SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with acute heart failure,” and “gives further confidence to clinicians that this class can be started in ‘sicker’ patients with HF who also have diuretic resistance,” Dr. Campbell said.
Asked during his presentation’s question and answer whether dapagliflozin might have shown a greater effect had the dosage been higher, Dr. Campbell explained that the drug was investigational when the trial started. Adding a higher-dose dapagliflozin arm, he said, would have made for an excessively complex study. But “that’s a great research question for another trial.”
DAPA-RESIST was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Campbell disclosed receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca for speaking and from Bayer for serving on an advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new randomized trial. The drugs were given to the study’s loop diuretic–resistant patients on top of furosemide.
Changes in volume status and measures of pulmonary congestion and risk for serious adverse events were similar for those assigned to take dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or metolazone, a quinazoline diuretic. Those on dapagliflozin zone ultimately received a larger cumulative furosemide dose in the 61-patient trial, called DAPA-RESIST.
“The next steps are to assess whether a strategy of using SGLT2 inhibitors up front in patients with HF reduces the incidence of diuretic resistance, and to test further combinations of diuretics such as thiazide or thiazide-like diuretics, compared with acetazolamide, when used in addition to an IV loop diuretic and SGLT2 inhibitors together,” Ross T. Campbell, MBChB, PhD, University of Glasgow and Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, also in Glasgow, said in an interview.
Dr. Campbell presented the findings at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology and is senior author on its simultaneous publication in the European Heart Journal.
The multicenter trial randomly assigned 61 patients with AHF to receive dapagliflozin at a fixed dose of 10 mg once daily or metolazone 5 mg or 10 mg (starting dosage at physician discretion) once daily for 3 days of treatment on an open-label basis.
Patients had entered the trial on furosemide at a mean daily dosage of 260 mg in the dapagliflozin group and 229 mg for those assigned metolazone; dosages for the loop diuretic in the trial weren’t prespecified.
Their median age was 79 and 54% were women; 44% had HF with reduced ejection fraction. Their mean glomerular filtration rate was below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in 26%, 90% had chronic kidney disease, 98% had peripheral edema, and 46% had diabetes.
The mean cumulative furosemide dose was significantly higher among the dapagliflozin group’s 31 patients, 976 mg versus 704 mg for the 30 on acetazolamide (P < .05), 96 hours after the start of randomized therapy. However, patients on dapagliflozin experienced a lesser increase in creatinine (P < .05) and in blood urea (P < .01), a greater change in serum sodium (P < .05), and a smaller reduction in serum potassium (P < .01).
Although the trial wasn’t powered for those outcomes, Dr. Campbell said, “less biochemical upset could be associated with better outcomes in terms of less medium- to long-term renal impairment, and in the short-term length of stay.”
The mean decrease in weight at 96 hours, the primary endpoint, reached 3 kg on dapagliflozin, compared with 3.6 kg with metolazone (P = .082), a difference that fell short of significance.
Loop diuretic efficiency, that is weight change in kg per 40 mg furosemide, “was smaller with dapagliflozin than with metolazone at each time point after randomization, although the difference was only significant at 24 hours,” the published report states.
Changes in pulmonary congestion (by lung ultrasound) and fluid volume were similar between the groups.
“This trial further adds to the evidence base and safety profile for using SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with acute heart failure,” and “gives further confidence to clinicians that this class can be started in ‘sicker’ patients with HF who also have diuretic resistance,” Dr. Campbell said.
Asked during his presentation’s question and answer whether dapagliflozin might have shown a greater effect had the dosage been higher, Dr. Campbell explained that the drug was investigational when the trial started. Adding a higher-dose dapagliflozin arm, he said, would have made for an excessively complex study. But “that’s a great research question for another trial.”
DAPA-RESIST was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Campbell disclosed receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca for speaking and from Bayer for serving on an advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new randomized trial. The drugs were given to the study’s loop diuretic–resistant patients on top of furosemide.
Changes in volume status and measures of pulmonary congestion and risk for serious adverse events were similar for those assigned to take dapagliflozin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or metolazone, a quinazoline diuretic. Those on dapagliflozin zone ultimately received a larger cumulative furosemide dose in the 61-patient trial, called DAPA-RESIST.
“The next steps are to assess whether a strategy of using SGLT2 inhibitors up front in patients with HF reduces the incidence of diuretic resistance, and to test further combinations of diuretics such as thiazide or thiazide-like diuretics, compared with acetazolamide, when used in addition to an IV loop diuretic and SGLT2 inhibitors together,” Ross T. Campbell, MBChB, PhD, University of Glasgow and Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, also in Glasgow, said in an interview.
Dr. Campbell presented the findings at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology and is senior author on its simultaneous publication in the European Heart Journal.
The multicenter trial randomly assigned 61 patients with AHF to receive dapagliflozin at a fixed dose of 10 mg once daily or metolazone 5 mg or 10 mg (starting dosage at physician discretion) once daily for 3 days of treatment on an open-label basis.
Patients had entered the trial on furosemide at a mean daily dosage of 260 mg in the dapagliflozin group and 229 mg for those assigned metolazone; dosages for the loop diuretic in the trial weren’t prespecified.
Their median age was 79 and 54% were women; 44% had HF with reduced ejection fraction. Their mean glomerular filtration rate was below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in 26%, 90% had chronic kidney disease, 98% had peripheral edema, and 46% had diabetes.
The mean cumulative furosemide dose was significantly higher among the dapagliflozin group’s 31 patients, 976 mg versus 704 mg for the 30 on acetazolamide (P < .05), 96 hours after the start of randomized therapy. However, patients on dapagliflozin experienced a lesser increase in creatinine (P < .05) and in blood urea (P < .01), a greater change in serum sodium (P < .05), and a smaller reduction in serum potassium (P < .01).
Although the trial wasn’t powered for those outcomes, Dr. Campbell said, “less biochemical upset could be associated with better outcomes in terms of less medium- to long-term renal impairment, and in the short-term length of stay.”
The mean decrease in weight at 96 hours, the primary endpoint, reached 3 kg on dapagliflozin, compared with 3.6 kg with metolazone (P = .082), a difference that fell short of significance.
Loop diuretic efficiency, that is weight change in kg per 40 mg furosemide, “was smaller with dapagliflozin than with metolazone at each time point after randomization, although the difference was only significant at 24 hours,” the published report states.
Changes in pulmonary congestion (by lung ultrasound) and fluid volume were similar between the groups.
“This trial further adds to the evidence base and safety profile for using SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with acute heart failure,” and “gives further confidence to clinicians that this class can be started in ‘sicker’ patients with HF who also have diuretic resistance,” Dr. Campbell said.
Asked during his presentation’s question and answer whether dapagliflozin might have shown a greater effect had the dosage been higher, Dr. Campbell explained that the drug was investigational when the trial started. Adding a higher-dose dapagliflozin arm, he said, would have made for an excessively complex study. But “that’s a great research question for another trial.”
DAPA-RESIST was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Campbell disclosed receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca for speaking and from Bayer for serving on an advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HFA-ESC 2023
Gout linked to smaller brain volume, higher likelihood of neurodegenerative diseases
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
Patients with gout may have smaller brain volumes and higher brain iron markers than people without gout, and also be more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease, probable essential tremor, and dementia, researchers in the United Kingdom report.
“We were surprised about the regions of the brain affected by gout, several of which are important for motor function. The other intriguing finding was that the risk of dementia amongst gout patients was strongly time-dependent: highest in the first 3 years after their gout diagnosis,” lead study author Anya Topiwala, BMBCh, DPhil, said in an interview.
“Our combination of traditional and genetic approaches increases the confidence that gout is causing the brain findings,” said Dr. Topiwala, a clinical research fellow and consultant psychiatrist in the Nuffield Department of Population Health at the University of Oxford, England.
“We suggest that clinicians be vigilant for cognitive and motor problems after gout diagnosis, particularly in the early stages,” she added.
Links between gout and neurodegenerative diseases debated in earlier studies
Gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, affects around 1%-4% of people, the authors wrote, with monosodium urate crystal deposits causing acute flares of pain and swelling in joints and periarticular tissues.
Whether and how gout may affect the brain has been debated in the literature. Gout and hyperuricemia have been linked with elevated stroke risk; and although observational studies have linked hyperuricemia with lower dementia risk, especially Alzheimer’s disease, Mendelian randomization studies have had conflicting results in Alzheimer’s disease.
A novel approach that analyzes brain structure and genetics
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues combined observational and Mendelian randomization techniques to explore relationships between gout and neurodegenerative diseases. They analyzed data from over 303,000 volunteer participants between 40 and 69 years of age recruited between 2006 and 2010 to contribute their detailed genetic and health information to the U.K. Biobank, a large-scale biomedical database and research resource.
Patients with gout tended to be older and male. At baseline, all participants’ serum urate levels were measured, and 30.8% of patients with gout reported that they currently used urate-lowering therapy.
MRI shows brain changes in patients with gout
In what the authors said is the first investigation of neuroimaging markers in patients with gout, they compared differences in gray matter volumes found in the 1,165 participants with gout and the 32,202 controls without gout who had MRI data.
They found no marked sex differences in associations. Urate was inversely linked with global brain volume and with gray and white matter volumes, and gout appeared to age global gray matter by 2 years.
Patients with gout and higher urate showed significant differences in regional gray matter volumes, especially in the cerebellum, pons, and midbrain, as well as subcortical differences in the nucleus accumbens, putamen, and caudate. They also showed significant differences in white matter tract microstructure in the fornix.
Patients with gout were more likely to develop dementia (average hazard ratio [HR] over study = 1.60), especially in the first 3 years after gout diagnosis (HR = 7.40). They were also at higher risk for vascular dementia (average HR = 2.41), compared with all-cause dementia, but not for Alzheimer’s disease (average HR = 1.62).
In asymptomatic participants though, urate and dementia were inversely linked (HR = 0.85), with no time dependence.
Gout was linked with higher incidence of Parkinson’s disease (HR = 1.43) and probable essential tremor (HR = 6.75). In asymptomatic participants, urate and Parkinson’s disease (HR = 0.89), but not probable essential tremor, were inversely linked.
Genetic analyses reinforce MRI results
Using Mendelian randomization estimates, the authors found that genetic links generally reflected their observational findings. Both genetically predicted gout and serum urate were significantly linked with regional gray matter volumes, including cerebellar, midbrain, pons, and brainstem.
They also found significant links with higher magnetic susceptibility in the putamen and caudate, markers of higher iron. But while genetically predicted gout was significantly linked with global gray matter volume, urate was not.
In males, but not in females, urate was positively linked with alcohol intake and lower socioeconomic status.
Dr. Topiwala acknowledged several limitations to the study, writing that “the results from the volunteer participants may not apply to other populations; the cross-sectional serum urate measurements may not reflect chronic exposure; and Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor may have been diagnostically confounded.”
A novel approach that suggests further related research
Asked to comment on the study, Puja Khanna, MD, MPH, a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, called its novel use of neuroimaging interesting.
Dr. Khanna, who was not involved in the study, said she would like to know more about the role that horizontal pleiotropy – one genetic variant having independent effects on multiple traits – plays in this disease process, and about the impact of the antioxidative properties of urate in maintaining neuroprotection.
“[The] U.K. Biobank is an excellent database to look at questions of association,” John D. FitzGerald, MD, PhD, MPH, MBA, professor and clinical chief of rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“This is a fairly rigorous study,” added Dr. FitzGerald, also not involved in the study. “While it has lots of strengths,” including its large sample size and Mendelian randomization, it also has “abundant weaknesses,” he added. “It is largely cross-sectional, with single urate measurement and single brain MRI.”
“Causation is the big question,” Dr. FitzGerald noted. “Does treating gout (or urate) help prevent dementia or neurodegenerative decline?”
Early diagnosis benefits patients
Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald joined the authors in advising doctors to monitor their gout patients for cognitive and motor symptoms of neurodegenerative disease.
“It is clearly important to pay close attention to the neurologic exam and history in gout, especially because it is a disease of the aging population,” Dr. Khanna advised. “Addressing dementia when gout is diagnosed can lead to prompt mitigation strategies that can hugely impact patients.”
Dr. Topiwala and her colleagues would like to investigate why the dementia risk was time-dependent. “Is this because of the acute inflammatory response in gout, or could it just be that patients with gout visit their doctors more frequently, so any cognitive problems are picked up sooner?” she asked.
The authors, and Dr. Khanna and Dr. FitzGerald, report no relevant financial relationships. The Wellcome Trust; the U.K. Medical Research Council; the European Commission Horizon 2020 research and innovation program; the British Heart Foundation; the U.S. National Institutes of Health; the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; and the National Institute for Health and Care Research funded the study.
FROM NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
ER+/HER2– breast cancer: Is first or second line CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy better?
That was the conclusion of the phase 3 SONIA study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The benefit from first line therapy is not maintained and almost completely disappears when patients in the control arm cross over to receive CDK4/6 inhibition in second line,” said Gabe Sonke, MD, PhD, during his presentation at the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors have shown benefit in both the first-and second-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke, who is a medical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam. He added that most guidelines suggest use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the first line, but there hasn’t been a direct comparison between use in the first and second line.
“Many patients do very well on endocrine therapy alone [in the first line]. Combination treatment leads to a higher risk of the emergence of resistant patterns such as ESR1 mutations, and CDK4/6 inhibitors also come with added costs and toxicities. Given the absence of comparative data between first line and second line, we designed the SONIA trial,” said Dr. Sonke.
Study methods and results
The researchers recruited 1,050 pre- and postmenopausal women who were randomized to a nonsteroidal AI in the first line followed by second-line CDK4/6i plus the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant, or a nonsteroidal AI plus a CDK4/6i in the first line and fulvestrant in the second line. The most commonly used CDK4/6i was palbociclib at 91%, followed by ribociclib at 8%, and abemaciclib at 1%.
After a median follow-up of 37.3 months, the median duration of CDK4/6i exposure was 24.6 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 8.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group.
The median PFS during first-line therapy was 24.7 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 16.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .0001), which was consistent with the results seen in CDK4/6i pivotal trials in the first-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke. However, PFS after two lines of therapy was not significantly different between the groups (31.0 months vs. 26.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.87; P =.10).
The safety profile was similar to what had been seen in previous trials with respect to adverse events like bone marrow and liver function abnormalities and fatigue, but there were 42% more grade 3 or higher adverse events in the first-line CDK4/6i group than in the second-line CDK4/6i group. Dr. Sonke estimated that the increase in costs related to adverse events amounted to about $200,000 per patient receiving CDK4/6i as first line.
There were no significant differences between the two groups in quality of life measurement.
Subgroup analyses of patient categories including prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy or endocrine therapy, de novo metastatic disease, visceral disease, bone-only disease, and treatment with palbociclib or ribociclib showed no difference in outcome for first- versus second-line CDK4/6i treatment.
Are CDK4/6i costs and side effects worth it?
The findings challenge the need for using CDK4/6 inhibitors as first-line treatment in this population, according to Dr. Sonke, who also raised the following related questions.
“If you were a patient, would you consider a treatment that offers no improvement in quality of life and does not improve overall survival? As a doctor or nurse, would you recommend such a treatment to your patient that nearly doubles the incidence of side effects? And if you were responsible for covering the costs of this treatment, whether as an individual or health care insurance, would you consider it worth $200,000?”
For many patients, particularly in the first line setting where resistance mechanisms are less prevalent, endocrine therapy alone remains an excellent option,” said Dr. Sonke during his presentation.
During the discussion portion of the session, Daniel Stover, MD, who is an associate professor of translational therapeutics at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, pointed out that the lack of differences in the subanalyses leaves little guidance for physicians.
“We really have a limited signal on who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitors. I think one of the most important outcomes of this study is the focus on the patient, as there were substantially fewer adverse events and of course we need to think about financial toxicity as well,” he said. “I think one of the things that is perhaps most exciting to think about is who are the very good risk patients who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitor [therapy]? I think for the majority of patients, endocrine therapy plus CDK4/6 inhibitor is still the appropriate treatment, but I would argue we need additional biomarkers, be it RNA-based biomarkers, novel PET imaging, or perhaps [circulating tumor] DNA dynamics.”
Do cost savings and reduced side effects outweigh first-line PFS benefit?
During the question-and-answer session, William Sikov, MD, spoke up from the audience in support of Dr. Sonke’s conclusions.
“Clearly there are still patients who benefit from that approach, but I think that we have reached an inflection point: I posit that the question has now changed. [We should not ask] why a certain patient should not receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor, but why a certain patient should receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor in the first-line setting,” said Dr. Sikov, who is professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Sonke agreed that first-line CDK4/6i is appropriate for some patients, and later echoed the need for biomarkers, but he said that researchers have so far had little luck in identifying any.
“Of course, it’s a shared decision-making between the patient and a doctor, but I think the baseline would be for all of us to consider first line single-agent endocrine therapy,” he said.
Session comoderator Michael Danso, MD, praised the trial but questioned whether the strategy would be adopted in places like the United States, where cost savings is not a major emphasis.
“Progression-free survival is so significant in the first line setting that I can’t imagine that many oncologists in the U.S. will adopt this approach. The other thing is that this was [almost] all palbociclib, so the question remains, would having a different cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor result in the same results? I think the jury’s still out,” said Dr. Danso, who is the research director at Virginia Oncology Associates, Norfolk.
The study was funded by the Dutch government and Dutch Health Insurers. Dr. Sonke has consulted for or advised Biovica, Novartis, and Seagen. He has received research support through his institution from Agendia, AstraZeneca/Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, and Seagen. Dr. Sikov has been a speaker for Lilly. Dr. Danso has received honoraria from Amgen and has consulted or advised Immunomedics, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seagen.
That was the conclusion of the phase 3 SONIA study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The benefit from first line therapy is not maintained and almost completely disappears when patients in the control arm cross over to receive CDK4/6 inhibition in second line,” said Gabe Sonke, MD, PhD, during his presentation at the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors have shown benefit in both the first-and second-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke, who is a medical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam. He added that most guidelines suggest use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the first line, but there hasn’t been a direct comparison between use in the first and second line.
“Many patients do very well on endocrine therapy alone [in the first line]. Combination treatment leads to a higher risk of the emergence of resistant patterns such as ESR1 mutations, and CDK4/6 inhibitors also come with added costs and toxicities. Given the absence of comparative data between first line and second line, we designed the SONIA trial,” said Dr. Sonke.
Study methods and results
The researchers recruited 1,050 pre- and postmenopausal women who were randomized to a nonsteroidal AI in the first line followed by second-line CDK4/6i plus the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant, or a nonsteroidal AI plus a CDK4/6i in the first line and fulvestrant in the second line. The most commonly used CDK4/6i was palbociclib at 91%, followed by ribociclib at 8%, and abemaciclib at 1%.
After a median follow-up of 37.3 months, the median duration of CDK4/6i exposure was 24.6 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 8.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group.
The median PFS during first-line therapy was 24.7 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 16.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .0001), which was consistent with the results seen in CDK4/6i pivotal trials in the first-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke. However, PFS after two lines of therapy was not significantly different between the groups (31.0 months vs. 26.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.87; P =.10).
The safety profile was similar to what had been seen in previous trials with respect to adverse events like bone marrow and liver function abnormalities and fatigue, but there were 42% more grade 3 or higher adverse events in the first-line CDK4/6i group than in the second-line CDK4/6i group. Dr. Sonke estimated that the increase in costs related to adverse events amounted to about $200,000 per patient receiving CDK4/6i as first line.
There were no significant differences between the two groups in quality of life measurement.
Subgroup analyses of patient categories including prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy or endocrine therapy, de novo metastatic disease, visceral disease, bone-only disease, and treatment with palbociclib or ribociclib showed no difference in outcome for first- versus second-line CDK4/6i treatment.
Are CDK4/6i costs and side effects worth it?
The findings challenge the need for using CDK4/6 inhibitors as first-line treatment in this population, according to Dr. Sonke, who also raised the following related questions.
“If you were a patient, would you consider a treatment that offers no improvement in quality of life and does not improve overall survival? As a doctor or nurse, would you recommend such a treatment to your patient that nearly doubles the incidence of side effects? And if you were responsible for covering the costs of this treatment, whether as an individual or health care insurance, would you consider it worth $200,000?”
For many patients, particularly in the first line setting where resistance mechanisms are less prevalent, endocrine therapy alone remains an excellent option,” said Dr. Sonke during his presentation.
During the discussion portion of the session, Daniel Stover, MD, who is an associate professor of translational therapeutics at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, pointed out that the lack of differences in the subanalyses leaves little guidance for physicians.
“We really have a limited signal on who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitors. I think one of the most important outcomes of this study is the focus on the patient, as there were substantially fewer adverse events and of course we need to think about financial toxicity as well,” he said. “I think one of the things that is perhaps most exciting to think about is who are the very good risk patients who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitor [therapy]? I think for the majority of patients, endocrine therapy plus CDK4/6 inhibitor is still the appropriate treatment, but I would argue we need additional biomarkers, be it RNA-based biomarkers, novel PET imaging, or perhaps [circulating tumor] DNA dynamics.”
Do cost savings and reduced side effects outweigh first-line PFS benefit?
During the question-and-answer session, William Sikov, MD, spoke up from the audience in support of Dr. Sonke’s conclusions.
“Clearly there are still patients who benefit from that approach, but I think that we have reached an inflection point: I posit that the question has now changed. [We should not ask] why a certain patient should not receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor, but why a certain patient should receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor in the first-line setting,” said Dr. Sikov, who is professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Sonke agreed that first-line CDK4/6i is appropriate for some patients, and later echoed the need for biomarkers, but he said that researchers have so far had little luck in identifying any.
“Of course, it’s a shared decision-making between the patient and a doctor, but I think the baseline would be for all of us to consider first line single-agent endocrine therapy,” he said.
Session comoderator Michael Danso, MD, praised the trial but questioned whether the strategy would be adopted in places like the United States, where cost savings is not a major emphasis.
“Progression-free survival is so significant in the first line setting that I can’t imagine that many oncologists in the U.S. will adopt this approach. The other thing is that this was [almost] all palbociclib, so the question remains, would having a different cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor result in the same results? I think the jury’s still out,” said Dr. Danso, who is the research director at Virginia Oncology Associates, Norfolk.
The study was funded by the Dutch government and Dutch Health Insurers. Dr. Sonke has consulted for or advised Biovica, Novartis, and Seagen. He has received research support through his institution from Agendia, AstraZeneca/Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, and Seagen. Dr. Sikov has been a speaker for Lilly. Dr. Danso has received honoraria from Amgen and has consulted or advised Immunomedics, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seagen.
That was the conclusion of the phase 3 SONIA study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The benefit from first line therapy is not maintained and almost completely disappears when patients in the control arm cross over to receive CDK4/6 inhibition in second line,” said Gabe Sonke, MD, PhD, during his presentation at the meeting.
CDK4/6 inhibitors have shown benefit in both the first-and second-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke, who is a medical oncologist at the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam. He added that most guidelines suggest use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the first line, but there hasn’t been a direct comparison between use in the first and second line.
“Many patients do very well on endocrine therapy alone [in the first line]. Combination treatment leads to a higher risk of the emergence of resistant patterns such as ESR1 mutations, and CDK4/6 inhibitors also come with added costs and toxicities. Given the absence of comparative data between first line and second line, we designed the SONIA trial,” said Dr. Sonke.
Study methods and results
The researchers recruited 1,050 pre- and postmenopausal women who were randomized to a nonsteroidal AI in the first line followed by second-line CDK4/6i plus the estrogen receptor antagonist fulvestrant, or a nonsteroidal AI plus a CDK4/6i in the first line and fulvestrant in the second line. The most commonly used CDK4/6i was palbociclib at 91%, followed by ribociclib at 8%, and abemaciclib at 1%.
After a median follow-up of 37.3 months, the median duration of CDK4/6i exposure was 24.6 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 8.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group.
The median PFS during first-line therapy was 24.7 months in the first-line CDK4/6i group and 16.1 months in the second-line CDK4/6i group (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .0001), which was consistent with the results seen in CDK4/6i pivotal trials in the first-line setting, according to Dr. Sonke. However, PFS after two lines of therapy was not significantly different between the groups (31.0 months vs. 26.8 months, respectively; HR, 0.87; P =.10).
The safety profile was similar to what had been seen in previous trials with respect to adverse events like bone marrow and liver function abnormalities and fatigue, but there were 42% more grade 3 or higher adverse events in the first-line CDK4/6i group than in the second-line CDK4/6i group. Dr. Sonke estimated that the increase in costs related to adverse events amounted to about $200,000 per patient receiving CDK4/6i as first line.
There were no significant differences between the two groups in quality of life measurement.
Subgroup analyses of patient categories including prior adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy or endocrine therapy, de novo metastatic disease, visceral disease, bone-only disease, and treatment with palbociclib or ribociclib showed no difference in outcome for first- versus second-line CDK4/6i treatment.
Are CDK4/6i costs and side effects worth it?
The findings challenge the need for using CDK4/6 inhibitors as first-line treatment in this population, according to Dr. Sonke, who also raised the following related questions.
“If you were a patient, would you consider a treatment that offers no improvement in quality of life and does not improve overall survival? As a doctor or nurse, would you recommend such a treatment to your patient that nearly doubles the incidence of side effects? And if you were responsible for covering the costs of this treatment, whether as an individual or health care insurance, would you consider it worth $200,000?”
For many patients, particularly in the first line setting where resistance mechanisms are less prevalent, endocrine therapy alone remains an excellent option,” said Dr. Sonke during his presentation.
During the discussion portion of the session, Daniel Stover, MD, who is an associate professor of translational therapeutics at Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, pointed out that the lack of differences in the subanalyses leaves little guidance for physicians.
“We really have a limited signal on who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitors. I think one of the most important outcomes of this study is the focus on the patient, as there were substantially fewer adverse events and of course we need to think about financial toxicity as well,” he said. “I think one of the things that is perhaps most exciting to think about is who are the very good risk patients who can delay CDK4/6 inhibitor [therapy]? I think for the majority of patients, endocrine therapy plus CDK4/6 inhibitor is still the appropriate treatment, but I would argue we need additional biomarkers, be it RNA-based biomarkers, novel PET imaging, or perhaps [circulating tumor] DNA dynamics.”
Do cost savings and reduced side effects outweigh first-line PFS benefit?
During the question-and-answer session, William Sikov, MD, spoke up from the audience in support of Dr. Sonke’s conclusions.
“Clearly there are still patients who benefit from that approach, but I think that we have reached an inflection point: I posit that the question has now changed. [We should not ask] why a certain patient should not receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor, but why a certain patient should receive a CDK4/6 inhibitor in the first-line setting,” said Dr. Sikov, who is professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I.
Dr. Sonke agreed that first-line CDK4/6i is appropriate for some patients, and later echoed the need for biomarkers, but he said that researchers have so far had little luck in identifying any.
“Of course, it’s a shared decision-making between the patient and a doctor, but I think the baseline would be for all of us to consider first line single-agent endocrine therapy,” he said.
Session comoderator Michael Danso, MD, praised the trial but questioned whether the strategy would be adopted in places like the United States, where cost savings is not a major emphasis.
“Progression-free survival is so significant in the first line setting that I can’t imagine that many oncologists in the U.S. will adopt this approach. The other thing is that this was [almost] all palbociclib, so the question remains, would having a different cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor result in the same results? I think the jury’s still out,” said Dr. Danso, who is the research director at Virginia Oncology Associates, Norfolk.
The study was funded by the Dutch government and Dutch Health Insurers. Dr. Sonke has consulted for or advised Biovica, Novartis, and Seagen. He has received research support through his institution from Agendia, AstraZeneca/Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, and Seagen. Dr. Sikov has been a speaker for Lilly. Dr. Danso has received honoraria from Amgen and has consulted or advised Immunomedics, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seagen.
AT ASCO 2023