User login
Holy smoke: Air pollution link to bone damage confirmed
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution appears to contribute independently to bone damage in postmenopausal women, new data suggest.
The findings come from a new analysis of data from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and location-specific air particulate information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
“Our findings confirm that poor air quality may be a risk factor for bone loss, independent of socioeconomic or demographic factors, and expands previous findings to postmenopausal women. Indeed, to our knowledge, this is the first study of the impact of criteria air pollutants on bone health in postmenopausal women,” Diddier Prada, MD, PhD, Columbia University, New York, and colleagues wrote.
The results are also the first to show that “nitrogen oxides contribute the most to bone damage and that the lumbar spine is one of the most susceptible sites,” they added.
Public health policies should aim to reduce air pollution in general, they wrote, and reducing nitrogen oxides, in particular, will reduce bone damage in postmenopausal women, prevent bone fractures, and reduce the health cost burden associated with osteoporosis in this population.
The findings were recently published in eClinicalMedicine.
Asked to comment, Giovanni Adami, MD, PhD, said in an interview that the study “adds to the body of literature on air pollution and bone health. The study confirms and provides further evidence linking air pollution exposure and osteoporosis.”
Dr. Adami, of the University of Verona (Italy), who also studies this topic, said that these new findings align with those from his group and others.
“The scientific literature in the field is clearly pointing toward a negative effect of chronic pollution exposure on bone health.”
He pointed to one study from his group that found chronic exposure to ultrafine particulate matter is associated with low BMD, and consequently, bone fragility, and another study that showed acute exposure to high levels of pollutants could actually cause fractures.
As for what might be done clinically, Dr. Adami said: “It is difficult to extrapolate direct and immediate recommendations for patients.
“However, it might be acceptable to say that patients at risk of osteoporosis, such as older women or those with prior bone fractures, should avoid chronic exposure to air pollution, perhaps using masks when walking in traffic or using air filters for indoor ventilation.”
Dr. Adami also said that this evidence so far might spur the future inclusion of chronic exposure to air pollution in fracture risk assessment tools, although this isn’t likely to come about in the near future.
Particulates linked to whole-body, hip, lumbar, and femoral neck BMD
The prospective observational study included 9,041 WHI participants seen over 32,663 visits who were an average of 63 years old at baseline. More than 70% were White, and just under half were college graduates.
With geocoded address data used to estimate particulate matter concentrations, mean levels of particulate matter of 10 mcm or less, nitrogen oxide nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide over 1, 3, and 5 years were all negatively associated with whole-body, total hip, femoral neck, and lumbar spine BMD.
In the multivariate analysis, the highest correlations were found between nitrogen oxide and nitrogen dioxide. For example, lumbar spine BMD decreased by 0.026 g/cm2 per year per 10% increase in 3-year mean nitrogen dioxide concentration.
“Our findings show that both particulate matter and gases may adversely impact BMD and that nitrogen oxides may play a critical role in bone damage and osteoporosis risk,” Dr. Prada and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Adami added: “We need more data to understand the precise magnitude of effect of air pollution on fractures, which might depend on levels of exposure but also on genetics and lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Adami reported receiving fees from Amgen, Eli Lilly, UCB, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, and Theramex.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
Rheumatology fellows learn about career opportunities
SAN FRANCISCO – Various career paths open to newly board-certified rheumatologists – and some of the pros and cons for each – were explored at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations.
CSRO’s annual Fellows Conference aims to helps rheumatology fellows-in-training transition into future roles as practicing physicians, said Christopher Sonntag, MD, a 2nd-year rheumatology fellow at Roger Williams Medical Center, Providence, R.I., and the Fellow-At-Large representative on CSRO’s Board of Directors. He will launch his own career at Washington Regional Medical Center in Fayetteville, Ark., close to where he grew up, when his fellowship winds up in June.
“I started going to CSRO meetings in 2019, when I was still a resident,” said Dr. Sonntag, who fell in love with rheumatology in medical school. “This conference is a great opportunity for fellows. They can learn a lot of critical issues and skills that we just don’t get enough information about in our training, basic things we ought to know about: how insurance works, medical benefits, and the like.”
Job seekers in a specialty in short supply like rheumatology have some competitive advantages, but that varies by locality in a volatile health care market. “The job I ended up taking was not one where they were initially looking to hire another rheumatologist,” Dr. Sonntag told this news organization. The Fayetteville hospital already had two busy rheumatologists, but after Dr. Sonntag had unsatisfying interviews at six other groups, he called them back and they decided to go ahead and hire him. He said the position provides an acceptable work-life balance, as well as opportunities to teach. He hopes eventually to create a rheumatology fellowship program.
Models and Career Paths
Decisions about one’s career path are very important, said CSRO’s president, Gary Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist at Pacific Arthritis in Los Angeles. “We want your choice to work for you,” he told attendees. “We need you to be happy [in your jobs] for the next 30 years. You are the future.”
Dr. Feldman cited a recent Medscape salary survey of 13,000 full-time physicians from 29 specialties, which ranked rheumatologists 22nd in average annual income at $289,000. Total income may not be the first consideration in pursuing rheumatology as a career, Dr. Feldman noted. The same Medscape survey revealed that 60% of rheumatologists believe they are fairly compensated. “Something else is going on, something to do with work/life balance, which is complicated,” he said.
Other contributors to their career fulfillment may include the in-depth, long-term therapeutic relationships rheumatologists develop with their patients who have chronic, incurable illnesses; the ability with new treatments to make such a difference in managing their pain and discomfort; and engagement with giving good medical care that is centered on the patient’s experience.
“We have drugs that work to make our patients feel better. Patients come to us with no idea what’s going on, and we can turn their lives around,” Dr. Sonntag noted.
Other important career-oriented questions to ask, Dr. Feldman said, include:
What is important to you?
Who are you going to be working alongside?
How much autonomy, agency, security, or risk are you comfortable with?
What is your best balance between being a physician and an entrepreneur?
Finding your niche
Presenter Aaron Broadwell, MD, a rheumatologist in a private specialty practice of five physicians and five advanced practice providers in Shreveport, La., discussed the prospects for a career in private practice at the Fellows Conference. Private practice is not dead as a career choice, he observed, “despite what I continue to hear.” Data show that 70% of rheumatologists currently are in employed positions, but he sees signs of a movement back toward private practice.
Other basic career paths outlined by Dr. Broadwell include:
- Academic medicine, which offers opportunities to teach future physicians (although it’s also possible for rheumatologists practicing outside of academia to teach as well).
- Hospital employment, which has a higher starting salary but also a greater emphasis on RVUs (relative value units) and productivity, with less job security than it used to enjoy.
- Military/Veterans Administration positions, which may have antiquated office systems and salary caps.
- Other paths, including corporate medical director positions with pharmaceutical companies and insurance companies.
Newer options include concierge and direct specialty care models where physician-operated practices partner with their patients to provide specialty care services under a flat or periodic membership fee, and joining one of the large, multistate, rheumatology care management groups like United Rheumatology, LLC, and American Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates.
Private practice medical groups are both single specialty and multispecialty, both large and small – as well as solo rheumatology practices, Dr. Broadwell said. “People launch solo private practices all the time. It is good for some doctors. It has the highest risk and the highest potential reward.”
Becoming profitable in solo practice may take a year or two, while the doctor remains responsible 24/7, including the need to arrange for vacation and sick leave coverage. Solo practitioners need to be up to date on billing, coding, revenue cycles, bundled payments and the like, and eventually need to hire and supervise a team the doctor can trust.
What can young rheumatologists do to learn more of the nuances of these approaches? Dr. Broadwell recommended joining their state rheumatology society as well as the American College of Rheumatology. “The National Organization of Rheumatology Management is a phenomenal source of information, not just for your office manager but also for you,” he said. He also recommended linking up with colleagues through social media outlets such as the Rheumatology Private Practice Group on Facebook.
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – Various career paths open to newly board-certified rheumatologists – and some of the pros and cons for each – were explored at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations.
CSRO’s annual Fellows Conference aims to helps rheumatology fellows-in-training transition into future roles as practicing physicians, said Christopher Sonntag, MD, a 2nd-year rheumatology fellow at Roger Williams Medical Center, Providence, R.I., and the Fellow-At-Large representative on CSRO’s Board of Directors. He will launch his own career at Washington Regional Medical Center in Fayetteville, Ark., close to where he grew up, when his fellowship winds up in June.
“I started going to CSRO meetings in 2019, when I was still a resident,” said Dr. Sonntag, who fell in love with rheumatology in medical school. “This conference is a great opportunity for fellows. They can learn a lot of critical issues and skills that we just don’t get enough information about in our training, basic things we ought to know about: how insurance works, medical benefits, and the like.”
Job seekers in a specialty in short supply like rheumatology have some competitive advantages, but that varies by locality in a volatile health care market. “The job I ended up taking was not one where they were initially looking to hire another rheumatologist,” Dr. Sonntag told this news organization. The Fayetteville hospital already had two busy rheumatologists, but after Dr. Sonntag had unsatisfying interviews at six other groups, he called them back and they decided to go ahead and hire him. He said the position provides an acceptable work-life balance, as well as opportunities to teach. He hopes eventually to create a rheumatology fellowship program.
Models and Career Paths
Decisions about one’s career path are very important, said CSRO’s president, Gary Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist at Pacific Arthritis in Los Angeles. “We want your choice to work for you,” he told attendees. “We need you to be happy [in your jobs] for the next 30 years. You are the future.”
Dr. Feldman cited a recent Medscape salary survey of 13,000 full-time physicians from 29 specialties, which ranked rheumatologists 22nd in average annual income at $289,000. Total income may not be the first consideration in pursuing rheumatology as a career, Dr. Feldman noted. The same Medscape survey revealed that 60% of rheumatologists believe they are fairly compensated. “Something else is going on, something to do with work/life balance, which is complicated,” he said.
Other contributors to their career fulfillment may include the in-depth, long-term therapeutic relationships rheumatologists develop with their patients who have chronic, incurable illnesses; the ability with new treatments to make such a difference in managing their pain and discomfort; and engagement with giving good medical care that is centered on the patient’s experience.
“We have drugs that work to make our patients feel better. Patients come to us with no idea what’s going on, and we can turn their lives around,” Dr. Sonntag noted.
Other important career-oriented questions to ask, Dr. Feldman said, include:
What is important to you?
Who are you going to be working alongside?
How much autonomy, agency, security, or risk are you comfortable with?
What is your best balance between being a physician and an entrepreneur?
Finding your niche
Presenter Aaron Broadwell, MD, a rheumatologist in a private specialty practice of five physicians and five advanced practice providers in Shreveport, La., discussed the prospects for a career in private practice at the Fellows Conference. Private practice is not dead as a career choice, he observed, “despite what I continue to hear.” Data show that 70% of rheumatologists currently are in employed positions, but he sees signs of a movement back toward private practice.
Other basic career paths outlined by Dr. Broadwell include:
- Academic medicine, which offers opportunities to teach future physicians (although it’s also possible for rheumatologists practicing outside of academia to teach as well).
- Hospital employment, which has a higher starting salary but also a greater emphasis on RVUs (relative value units) and productivity, with less job security than it used to enjoy.
- Military/Veterans Administration positions, which may have antiquated office systems and salary caps.
- Other paths, including corporate medical director positions with pharmaceutical companies and insurance companies.
Newer options include concierge and direct specialty care models where physician-operated practices partner with their patients to provide specialty care services under a flat or periodic membership fee, and joining one of the large, multistate, rheumatology care management groups like United Rheumatology, LLC, and American Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates.
Private practice medical groups are both single specialty and multispecialty, both large and small – as well as solo rheumatology practices, Dr. Broadwell said. “People launch solo private practices all the time. It is good for some doctors. It has the highest risk and the highest potential reward.”
Becoming profitable in solo practice may take a year or two, while the doctor remains responsible 24/7, including the need to arrange for vacation and sick leave coverage. Solo practitioners need to be up to date on billing, coding, revenue cycles, bundled payments and the like, and eventually need to hire and supervise a team the doctor can trust.
What can young rheumatologists do to learn more of the nuances of these approaches? Dr. Broadwell recommended joining their state rheumatology society as well as the American College of Rheumatology. “The National Organization of Rheumatology Management is a phenomenal source of information, not just for your office manager but also for you,” he said. He also recommended linking up with colleagues through social media outlets such as the Rheumatology Private Practice Group on Facebook.
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – Various career paths open to newly board-certified rheumatologists – and some of the pros and cons for each – were explored at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations.
CSRO’s annual Fellows Conference aims to helps rheumatology fellows-in-training transition into future roles as practicing physicians, said Christopher Sonntag, MD, a 2nd-year rheumatology fellow at Roger Williams Medical Center, Providence, R.I., and the Fellow-At-Large representative on CSRO’s Board of Directors. He will launch his own career at Washington Regional Medical Center in Fayetteville, Ark., close to where he grew up, when his fellowship winds up in June.
“I started going to CSRO meetings in 2019, when I was still a resident,” said Dr. Sonntag, who fell in love with rheumatology in medical school. “This conference is a great opportunity for fellows. They can learn a lot of critical issues and skills that we just don’t get enough information about in our training, basic things we ought to know about: how insurance works, medical benefits, and the like.”
Job seekers in a specialty in short supply like rheumatology have some competitive advantages, but that varies by locality in a volatile health care market. “The job I ended up taking was not one where they were initially looking to hire another rheumatologist,” Dr. Sonntag told this news organization. The Fayetteville hospital already had two busy rheumatologists, but after Dr. Sonntag had unsatisfying interviews at six other groups, he called them back and they decided to go ahead and hire him. He said the position provides an acceptable work-life balance, as well as opportunities to teach. He hopes eventually to create a rheumatology fellowship program.
Models and Career Paths
Decisions about one’s career path are very important, said CSRO’s president, Gary Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist at Pacific Arthritis in Los Angeles. “We want your choice to work for you,” he told attendees. “We need you to be happy [in your jobs] for the next 30 years. You are the future.”
Dr. Feldman cited a recent Medscape salary survey of 13,000 full-time physicians from 29 specialties, which ranked rheumatologists 22nd in average annual income at $289,000. Total income may not be the first consideration in pursuing rheumatology as a career, Dr. Feldman noted. The same Medscape survey revealed that 60% of rheumatologists believe they are fairly compensated. “Something else is going on, something to do with work/life balance, which is complicated,” he said.
Other contributors to their career fulfillment may include the in-depth, long-term therapeutic relationships rheumatologists develop with their patients who have chronic, incurable illnesses; the ability with new treatments to make such a difference in managing their pain and discomfort; and engagement with giving good medical care that is centered on the patient’s experience.
“We have drugs that work to make our patients feel better. Patients come to us with no idea what’s going on, and we can turn their lives around,” Dr. Sonntag noted.
Other important career-oriented questions to ask, Dr. Feldman said, include:
What is important to you?
Who are you going to be working alongside?
How much autonomy, agency, security, or risk are you comfortable with?
What is your best balance between being a physician and an entrepreneur?
Finding your niche
Presenter Aaron Broadwell, MD, a rheumatologist in a private specialty practice of five physicians and five advanced practice providers in Shreveport, La., discussed the prospects for a career in private practice at the Fellows Conference. Private practice is not dead as a career choice, he observed, “despite what I continue to hear.” Data show that 70% of rheumatologists currently are in employed positions, but he sees signs of a movement back toward private practice.
Other basic career paths outlined by Dr. Broadwell include:
- Academic medicine, which offers opportunities to teach future physicians (although it’s also possible for rheumatologists practicing outside of academia to teach as well).
- Hospital employment, which has a higher starting salary but also a greater emphasis on RVUs (relative value units) and productivity, with less job security than it used to enjoy.
- Military/Veterans Administration positions, which may have antiquated office systems and salary caps.
- Other paths, including corporate medical director positions with pharmaceutical companies and insurance companies.
Newer options include concierge and direct specialty care models where physician-operated practices partner with their patients to provide specialty care services under a flat or periodic membership fee, and joining one of the large, multistate, rheumatology care management groups like United Rheumatology, LLC, and American Arthritis and Rheumatology Associates.
Private practice medical groups are both single specialty and multispecialty, both large and small – as well as solo rheumatology practices, Dr. Broadwell said. “People launch solo private practices all the time. It is good for some doctors. It has the highest risk and the highest potential reward.”
Becoming profitable in solo practice may take a year or two, while the doctor remains responsible 24/7, including the need to arrange for vacation and sick leave coverage. Solo practitioners need to be up to date on billing, coding, revenue cycles, bundled payments and the like, and eventually need to hire and supervise a team the doctor can trust.
What can young rheumatologists do to learn more of the nuances of these approaches? Dr. Broadwell recommended joining their state rheumatology society as well as the American College of Rheumatology. “The National Organization of Rheumatology Management is a phenomenal source of information, not just for your office manager but also for you,” he said. He also recommended linking up with colleagues through social media outlets such as the Rheumatology Private Practice Group on Facebook.
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT CSRO 2023
Ozempic: The latest weight loss craze and how over-prescribing is harming patients
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Social media and mainstream media websites are full of stories on the new wonder weight loss drug: Ozempic. Even Hollywood stars are talking about it.
Recently, the zealous prescribing of this diabetes medication fueled a 6-month shortage making it difficult for anyone to get it. Part of the problem stems from digital access to these medications where a patient can get a prescription online or via a telemedicine platform. Additionally, certain weight loss programs contributed to promoting the weight loss benefits.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist, with the generic name semaglutide, that lowers hemoglobin A1c in patients with diabetes and lowers the risk of cardiovascular events. Semaglutide is also sold as Wegovy, which is indicated for weight loss. Both Ozempic and Wegovy are sold in multiple doses, but the target dose for Wegovy is higher.
Weight loss with Wegovy is, on average, higher than that seen with Ozempic. However, it is often more difficult to get Wegovy covered by health insurance companies.
As doctors, we must be stewards of the medications we are prescribing. Clearly, the Internet should not be driving our prescribing habits. Prescribing Ozempic for weight loss can make it more difficult for patients with diabetes to receive it, and we should consider other options until it is more available and/or receives FDA approval for treating obesity.
Most of us have seen our patients with diabetes having difficulty getting a prescription for Ozempic filled, either because it is on back-order or because of a lack of coverage. Insurance companies have no incentive to lower the cost when it is in such high demand at its current rate. For these patients, lowering their A1c can be life-saving and prevent complications of diabetes, such as kidney failure and heart disease. In our current environment, we should reserve prescribing Ozempic for our patients with diabetes who need it more. Wegovy is available and can be prescribed for patients wishing to lose weight.
Many patients are looking for a magic cure. Neither medication is that. Patients need to start with making lifestyle changes first. In primary care, advising on and helping patients implement those are often our most difficult tasks. However, no medication is going to work unless the patient makes adjustments to their diet and amount and type of movement they are doing. In patients who have a hard time changing their diet, lowering carbohydrate intake may be a good first step. Exercising, or being more active if a patient is unable to formally exercise, is an important therapy.
As we all know, metformin is the usual preferred method for the treatment of type 2 diabetes unless contraindicated in a given patient. There are many oral diabetes medications available, and which of these and how these are prescribed need to be tailored to the individual patient. Ozempic can be used when a patient is failing on metformin, or other oral meds, or if they would rather do a weekly injection rather than remembering to take daily pills, for example.
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the United States. According to the CDC, more than 40% of the U.S. population is obese. Additionally, millions of children between the ages of 2 and 19 are now considered obese, and the medical complications for these individuals ares yet to be seen. Plus, many of us are seeing higher frequencies of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic medical conditions in adolescents in our daily practices.
Our war against obesity is a fight for future lives and having more tools available is definitely a help. Like with patients with diabetes, all treatment regimens should start off with lifestyle modifications. Fad diets rarely result in long-term weight loss.
There are several medications now available to help with weight loss, Wegovy being just one of them. Patients often come to us with their own personal preferences, and it is our job to guide them on the best course to take. Some people may prefer a weekly injection. There are oral medications available, such as Contrave and Phentermine, and the best one should be decided upon by the patient and doctor after a discussion of the risks.
Let’s stop prescribing Ozempic for weight loss because nonphysicians say we should. Leave it for our patients with diabetes, those whose lives may depend on taking it. If we didn’t have other medications available, it would be a very different story. But, we do, and we need to resist the pressure others place on us and do the right thing for all of our patients.
*This article was updated on 3/23/2023.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. She has no conflicts related to this piece. You can contact her at [email protected].
Fat Necrosis of the Breast Mimicking Breast Cancer in a Male Patient Following Wax Hair Removal
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
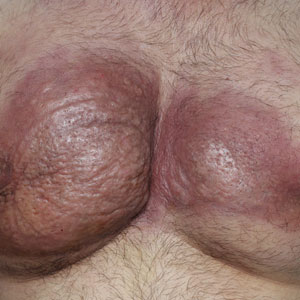
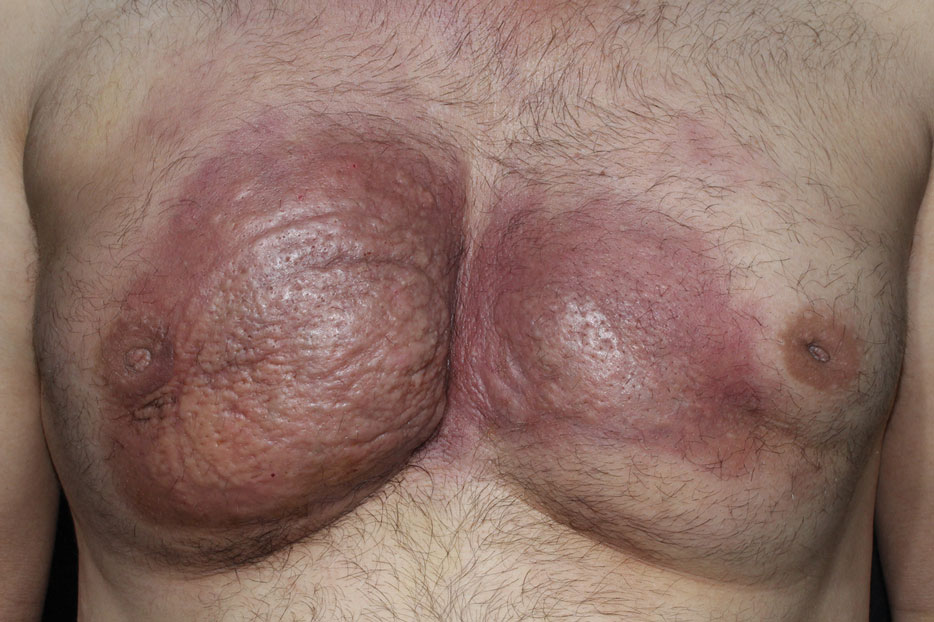
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.
Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
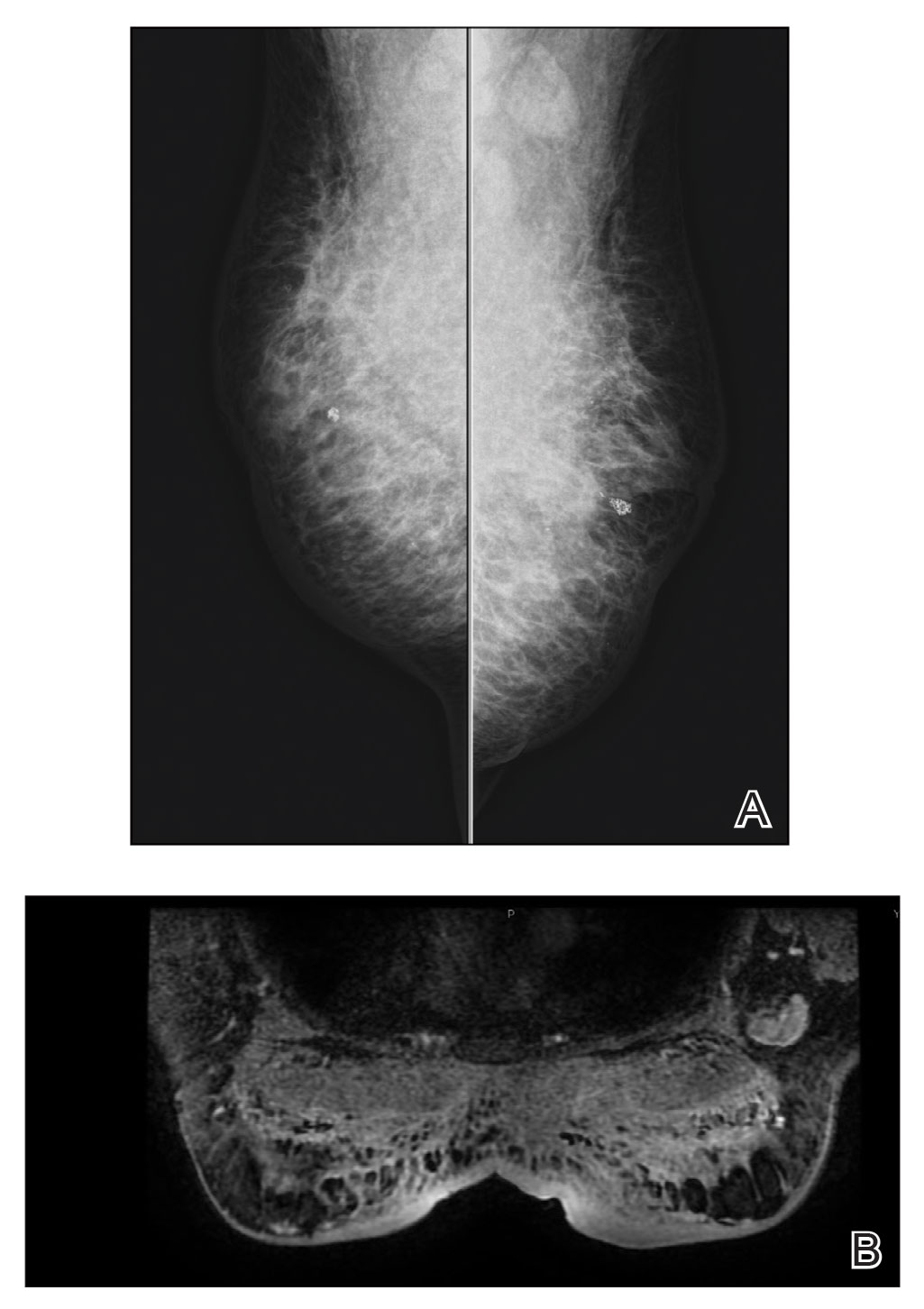
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).
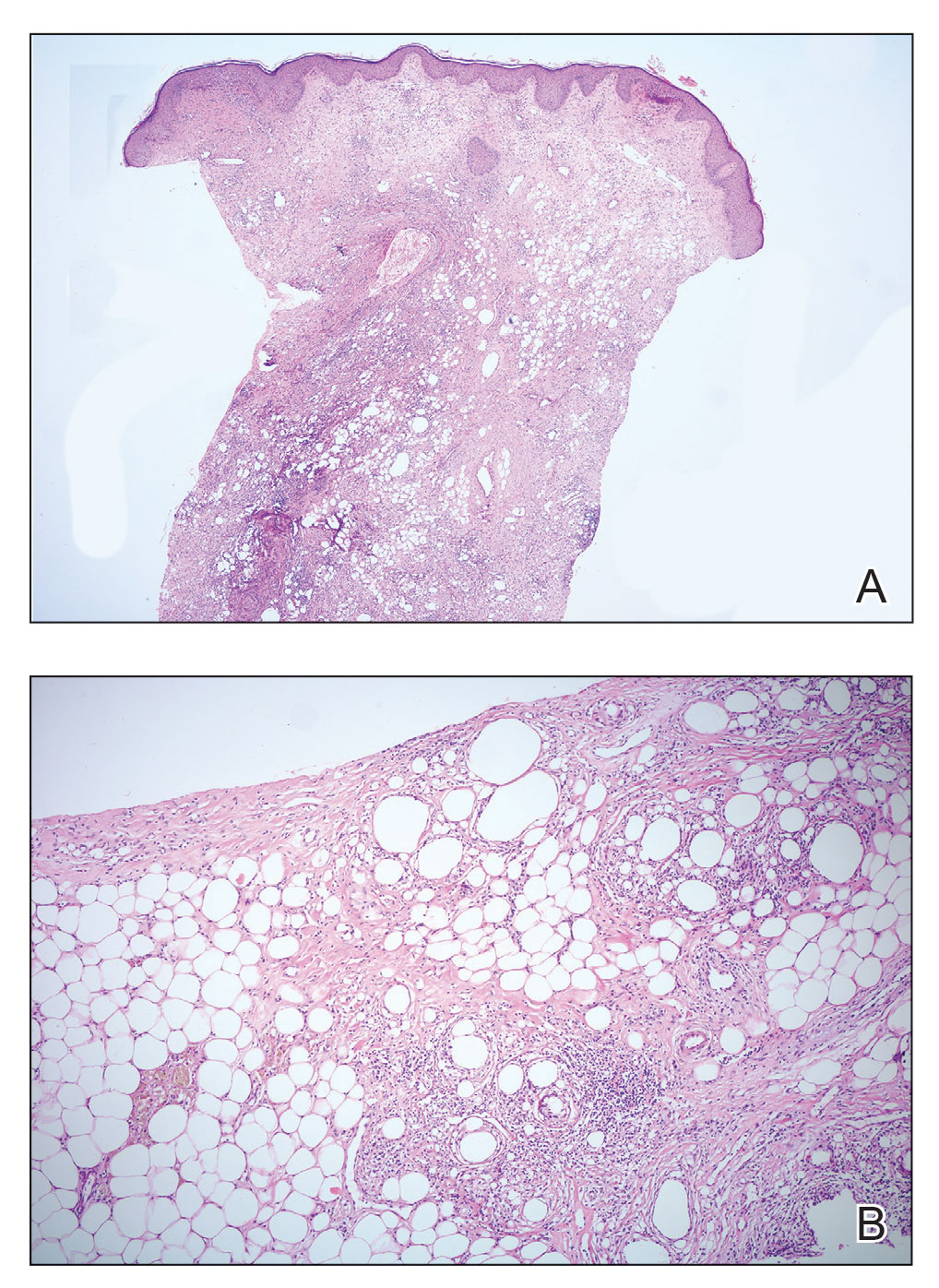
Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.
Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
To the Editor:
Fat necrosis of the breast is a benign inflammatory disease of adipose tissue commonly observed after trauma in the female breast during the perimenopausal period.1 Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, first described by Silverstone2 in 1949; the condition usually presents with unilateral, painful or asymptomatic, firm nodules, which in rare cases are observed as skin retraction and thickening, ecchymosis, erythematous plaque–like cellulitis, local depression, and/or discoloration of the breast skin.3-5
Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the male breast may need to be confirmed via biopsy in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings because the condition can mimic breast cancer.1 We report a case of bilateral fat necrosis of the breast mimicking breast cancer following wax hair removal.
A 42-year-old man presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of redness, swelling, and hardness of the skin of both breasts of 3 weeks’ duration. The patient had a history of wax hair removal of the entire anterior aspect of the body. He reported an erythematous, edematous, warm plaque that developed on the breasts 2 days after waxing. The plaque did not respond to antibiotics. The swelling and induration progressed over the 2 weeks after the patient was waxed. The patient had no family history of breast cancer. He had a standing diagnosis of gynecomastia. He denied any history of fat or filler injection in the affected area.
Dermatologic examination revealed erythematous, edematous, indurated, asymptomatic plaques with a peau d’orange appearance on the bilateral pectoral and presternal region. Minimal retraction of the right areola was noted (Figure 1). The bilateral axillary lymph nodes were palpable.

Laboratory results including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (108 mm/h [reference range, 2–20 mm/h]), C-reactive protein (9.2 mg/dL [reference range, >0.5 mg/dL]), and ferritin levels (645
Mammography of both breasts revealed a Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) score of 4 with a suspicious abnormality (ie, diffuse edema of the breast, multiple calcifications in a nonspecific pattern, oil cysts with calcifications, and bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a thick and irregular cortex)(Figure 2A). Ultrasonography of both breasts revealed an inflammatory breast. Magnetic resonance imaging showed similar findings with diffuse edema and a heterogeneous appearance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse contrast enhancement in both breasts extending to the pectoral muscles and axillary regions, consistent with inflammatory changes (Figure 2B).

Because of difficulty differentiating inflammation and an infiltrating tumor, histopathologic examination was recommended by radiology. Results from a 5-mm punch biopsy from the right breast yielded the following differential diagnoses: cellulitis, panniculitis, inflammatory breast cancer, subcutaneous fat necrosis, and paraffinoma. Histopathologic examination of the skin revealed a normal epidermis and a dense inflammatory cell infiltrate comprising lymphocytes and monocytes in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Marked fibrosis also was noted in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Lipophagic fat necrosis accompanied by a variable inflammatory cell infiltrate consisted of histiocytes and neutrophils (Figure 3A). Pankeratin immunostaining was negative. Fat necrosis was present in a biopsy specimen obtained from the right breast; no signs of malignancy were present (Figure 3B). Fine-needle aspiration of the axillary lymph nodes was benign. Given these histopathologic findings, malignancy was excluded from the differential diagnosis. Paraffinoma also was ruled out because the patient insistently denied any history of fat or filler injection.

Based on the clinical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings, as well as the history of minor trauma due to wax hair removal, a diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast was made. Intervention was not recommended by the plastic surgeons who subsequently evaluated the patient, because the additional trauma may aggravate the lesion. He was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At 6-month follow-up, there was marked reduction in the erythema and edema but no notable improvement of the induration. A potent topical steroid was added to the treatment, but only slight regression of the induration was observed.
The normal male breast is comprised of fat and a few secretory ducts.6 Gynecomastia and breast cancer are the 2 most common conditions of the male breast; fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. In a study of 236 male patients with breast disease, only 5 had fat necrosis.7
Fat necrosis of the breast can be observed with various clinical and radiological presentations. Subcutaneous nodules, skin retraction and thickening, local skin depression, and ecchymosis are the more common presentations of fat necrosis.3-5 In our case, the first symptoms of disease were similar to those seen in cellulitis. The presentation of fat necrosis–like cellulitis has been described only rarely in the medical literature. Haikin et al5 reported a case of fat necrosis of the leg in a child that presented with cellulitis followed by induration, which did not respond to antibiotics, as was the case with our patient.5
Blunt trauma, breast reduction surgery, and breast augmentation surgery can cause fat necrosis of the breast1,4; in some cases, the cause cannot be determined.8 The only pertinent history in our patient was wax hair removal. Fat necrosis was an unexpected complication, but hair removal can be considered minor trauma; however, this is not commonly reported in the literature following hair removal with wax. In a study that reviewed diseases of the male breast, the investigators observed that all male patients with fat necrosis had pseudogynecomastia (adipomastia).7 Although our patient’s entire anterior trunk was epilated, only the breast was affected. This situation might be explained by underlying gynecomastia because fat necrosis is common in areas of the body where subcutaneous fat tissue is dense.
Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy, such as in our case. Diagnosis of fat necrosis of the breast should be a diagnosis of exclusion; therefore, histopathologic confirmation of the lesion is imperative.9
In conclusion, fat necrosis of the male breast is rare. The condition can present as cellulitis. Hair removal with wax might be a cause of fat necrosis. Because breast cancer and fat necrosis can exhibit clinical and radiologic similarities, the diagnosis of fat necrosis should be confirmed by histopathologic analysis in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
- Tan PH, Lai LM, Carrington EV, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast—a review. Breast. 2006;15:313-318. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2005.07.003
- Silverstone M. Fat necrosis of the breast with report of a case in a male. Br J Surg. 1949;37:49-52. doi:10.1002/bjs.18003714508
- Akyol M, Kayali A, Yildirim N. Traumatic fat necrosis of male breast. Clin Imaging. 2013;37:954-956. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.05.009
- Crawford EA, King JJ, Fox EJ, et al. Symptomatic fat necrosis and lipoatrophy of the posterior pelvis following trauma. Orthopedics. 2009;32:444. doi:10.3928/01477447-20090511-25
- Haikin Herzberger E, Aviner S, Cherniavsky E. Posttraumatic fat necrosis presented as cellulitis of the leg. Case Rep Pediatr. 2012;2012:672397. doi:10.1155/2012/672397
- Michels LG, Gold RH, Arndt RD. Radiography of gynecomastia and other disorders of the male breast. Radiology. 1977;122:117-122. doi:10.1148/122.1.117
- Günhan-Bilgen I, Bozkaya H, Ustün E, et al. Male breast disease: clinical, mammographic, and ultrasonographic features. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:246-255. doi:10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00483-1
- Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004;33:106-126. doi:10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.01.001
- Pullyblank AM, Davies JD, Basten J, et al. Fat necrosis of the female breast—Hadfield re-visited. Breast. 2001;10:388-391. doi:10.1054/brst.2000.0287
Practice Points
- Fat necrosis of the breast can be mistaken—both clinically and radiologically—for malignancy; therefore, diagnosis should be confirmed by histopathology in conjunction with clinical and radiologic findings.
- Fat necrosis of the male breast is rare, and hair removal with wax may be a rare cause of the disease.
NSCLC- The Basics
Marathon running does not increase arthritis risk: Survey
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Runners who had undergone knee or hip surgery or had a previous hip or knee injury that prevented running were most likely to have arthritis, researchers found. Family history of arthritis, higher body mass index (BMI), and older age were also associated with increased risk of the condition.
The study was presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2023 Annual Meeting.
It has generally been thought that running may increase risk of osteoarthritis because it puts more load on joints than walking or standing, noted Grace Hsiao-Wei Lo, MD, an assistant professor of immunology, allergy, and rheumatology at the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who was not involved with the work. Research in this area has yielded mixed results: A 2017 analysis of multiple studies found that competitive runners did have higher rates of arthritis than recreational runners, while another study conducted by Dr. Lo found that runners did not have an increased risk of knee osteoarthritis, compared with nonrunners. A 2018 study showed that marathon runners had lower instances of arthritis, compared with the general population.
In this new study, researchers surveyed 3,804 runners who participated in the 2019 or 2021 Chicago Marathon about their running history, average mileage per week, and average running pace. The survey also asked about known risk factors for osteoarthritis, including BMI, family history of arthritis, and past knee and hip injuries that prevented running.
Runners, on average, were about 44 years old and ran 27.9 miles per week. The largest proportion of respondents had completed 2-5 marathons (37.3%), around 21% of respondents had finished 6-10 marathons, and 17% were running their first marathon. Study participants had an average of 15 years of running experience, 1,892 reported a previous hip or knee injury, and 413 had undergone knee or hip surgery. Overall, 36.4% reported experiencing hip or knee pain in the past year, and 7.3% had been diagnosed with arthritis.
Researchers found that there was no association between the risk of osteoarthritis and weekly mileage, years spent running, number of marathons completed, or running pace. Respondents who had undergone knee or hip surgery had the highest risk of osteoarthritis (odds ratio, 5.85; P < .0001), followed by those with a history of knee or hip injuries that prevented running (OR, 5.04; P < .0001). Other identified risk factors were family history of arthritis (OR, 3.47; P < .0001), BMI (OR, 1.10; P < .0001), and older age (OR, 1.08; P < .0001).
The news should be encouraging for runners, said Matthew Hartwell, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the research. If someone does not have injuries or surgeries that keep them from running, “you can still continue to run,” he said. “There may not necessarily be this dose-response relationship where the more you run, the more you break down your knee or your hip.”
Still, 24.2% of runners reported that their physician had advised them to reduce their mileage or stop running altogether. Most runners (94.2%) said they planned to run another marathon.
“The results of this study are consistent with the experiences of many lifelong runners and observations of sports medicine professionals that osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of distance running,” said Brett Toresdahl, MD, a sports medicine physician at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, who was not involved with the study.
Still, he emphasized that more research is necessary to understand whether running contributes to the risk of developing osteoarthritis. The participants in the study were current marathoners, he noted, so it is likely they have healthy joints that can tolerate running longer distances. “If there is a subset of people who have joints that are negatively affected by running, they wouldn’t likely be registering for a marathon,” he said in an email interview.
Dr. Lo added that comparing these marathoners to a group who did not run would help assess whether running can be harmful to joints. “To be fair, this is a challenging subject to study,” she said. “Osteoarthritis has a long natural history, and so it is difficult to evaluate this kind of question over many years of running and many years of evaluation of arthritis.”
While the research does not answer the question of whether running can lead to osteoarthritis, it helps show the need for long-term research on how running affects joints over time as well as one’s general health, Dr. Toresdahl noted. “I would not be surprised if future longitudinal research will come to the same conclusion that running for the majority of patients is a net benefit for overall health and at least net neutral for joint health when done in moderation,” he said.
Dr. Hartwell, Dr. Lo, and Dr. Toresdahl report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAOS 2023
Match Day: Record number of residencies offered
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.
NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Increased cancer in military pilots and ground crew: Pentagon
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Military aircrew and ground crew were overall more likely to be diagnosed with cancer, but less likely to die from cancer compared to the U.S. population,” the report concludes.
The study involved 156,050 aircrew and 737,891 ground crew. Participants were followed between 1992 and 2017. Both groups were predominantly male and non-Hispanic.
Data on cancer incidence and mortality for these two groups were compared with data from groups of similar age in the general population through use of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database of the National Cancer Institute.
For aircrew, the study found an 87% higher rate of melanoma, a 39% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 16% higher rate of prostate cancer, and a 24% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
A higher rate of melanoma and prostate cancer among aircrew has been reported previously, but the increased rate of thyroid cancer is a new finding, the authors note.
The uptick in melanoma has also been reported in studies of civilian pilots and cabin crew. It has been attributed to exposure to hazardous ultraviolet and cosmic radiation.
For ground crew members, the analysis found a 19% higher rate of cancers of the brain and nervous system, a 15% higher rate of thyroid cancer, a 9% higher rate of melanoma and of kidney and renal pelvis cancers, and a 3% higher rate of cancer for all sites combined.
There is little to compare these findings with: This is the first time that cancer risk has been evaluated in such a large population of military ground crew.
Lower rates of cancer mortality
In contrast to the increase in cancer incidence, the report found a decrease in cancer mortality.
When compared with a demographically similar U.S. population, the mortality rate among aircrew was 56% lower for all cancer sites; for ground crew, the mortality rate was 35% lower.
However, the report authors emphasize that “it is important to note that the military study population was relatively young.”
The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer incidence analysis was 41 years for aircrew and 26 years for ground crew. The median age at the end of follow-up for the cancer mortality analysis was 48 years for aircrew and 41 years for ground crew.
“Results may have differed if additional older former Service members had been included in the study, since cancer risk and mortality rates increase with age,” the authors comment.
Other studies have found an increase in deaths from melanoma as well as an increase in the incidence of melanoma. A meta-analysis published in 2019 in the British Journal of Dermatology found that airline pilots and cabin crew have about twice the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers than the general population. Pilots are also more likely to die from melanoma.
Further study underway
The findings on military air and ground crew come from phase 1 of a study that was required by Congress in the 2021 defense bill. Because the investigators found an increase in the incidence of cancer, phase 2 of the study is now necessary.
The report authors explain that phase 2 will consist of identifying the carcinogenic toxicants or hazardous materials associated with military flight operations; identifying operating environments that could be associated with increased amounts of ionizing and nonionizing radiation; identifying specific duties, dates of service, and types of aircraft flown that could have increased the risk for cancer; identifying duty locations associated with a higher incidence of cancers; identifying potential exposures through military service that are not related to aviation; and determining the appropriate age to begin screening military aircrew and ground crew for cancers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New rheumatologists need insurance awareness to give best care
SAN FRANCISCO – New rheumatologists face a wide range of significant challenges brought on by the increasing complexity of insurance billing and rapid changes to managed care practices, especially techniques of utilization management and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), speakers said at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO).
“We are seeing the impact of the environment eroding the patient-doctor relationship,” CSRO President Gary Feldman, MD, told participants.
Michael Saitta, MD, MBA, a rheumatologist in Fayetteville, Ark., said fellows should learn more about health insurance to take better care of their patients and their practice. “Your training includes a variable level of discourse on the health insurance market,” he said. Health insurance today is a mess. Costs have exploded. “Is anybody really happy with the current system?”
Although the health care system is sometimes compared to a dumpster fire, he said, a plate of spaghetti, with its multiple interconnected pathways, might be a better metaphor for understanding all that’s happening in the health care system and, more importantly, how it might be fixed.
Madelaine Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist in private practice in New Orleans and CSRO’s vice president of advocacy and government affairs, is a frequent advocate in Congress, state legislatures, and elsewhere regarding the utilization management techniques used by managed care and PBMs and how these are negatively affecting the ability of rheumatology patients to get the treatments they need. Such techniques include the following:
- Prior authorizations imposed by the health plan before a medication can be dispensed.
- Step therapy, which requires the patient to fail as many as three or four payer-preferred drugs before trying the one recommended by the rheumatologist.
- Nonmedical switching, in which a patient is forced to change medications for a nonmedical reason related to the PBM’s formulary.
- Accumulator adjustment programs, which increase the patient’s out-of-pocket and deductible commitments.
“There is very little transparency in how the money flows with PBMs,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. “In reality, PBMs are able to make profits by the perverse incentive of putting higher-priced drugs on their formularies, thus increasing the amount of rebates paid to them, without sharing any of the benefit with patients.”
PBMs have resisted disclosing this information, saying it would inhibit competition and cause drug prices to go up. The key thing to understand, she said, is that there is huge competition today to get preferred formulary placement. “Consequently, treatment choice for patients is not based on doctor-patient shared decision-making but on the highest rebate promised to the PBM,” she said.
“A rheumatology fellow recently told me that his patients will sometimes blame him for the lack of choice and high prices of the medications,” she noted. What she has started to do with patients, after discussing all the available drugs appropriate to their condition, is to ask: “What is your insurance? The reason I’m asking is that we can come up with a game plan, but the entity that will determine what you will receive is the insurance company.”
What does Dr. Madelaine Feldman want fellows to take away from the CSRO conference? “I hope to arouse their anger, initially, which then works its way into a passion to change the system. We’re all so busy. Sometimes it takes lighting a fire under people,” she said.
CSRO has an online action center to facilitate sending letters to legislators, as well as a map tool for looking up any active legislation in their state. “Spread the word to your peers. Use your voice to help pass PBM reforms. Tell other fellows to come to the next CSRO fellows meeting,” she said.
“We got into this space because a few community rheumatologists were angry over decisions about how drug infusions would be paid for,” she said. “A group went to Washington, to Congress and Medicare, and changed the policy,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. A few passionate people really can make a difference. “Join the action. We’re always looking for rheumatologists and their patients to testify on these issues.”
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – New rheumatologists face a wide range of significant challenges brought on by the increasing complexity of insurance billing and rapid changes to managed care practices, especially techniques of utilization management and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), speakers said at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO).
“We are seeing the impact of the environment eroding the patient-doctor relationship,” CSRO President Gary Feldman, MD, told participants.
Michael Saitta, MD, MBA, a rheumatologist in Fayetteville, Ark., said fellows should learn more about health insurance to take better care of their patients and their practice. “Your training includes a variable level of discourse on the health insurance market,” he said. Health insurance today is a mess. Costs have exploded. “Is anybody really happy with the current system?”
Although the health care system is sometimes compared to a dumpster fire, he said, a plate of spaghetti, with its multiple interconnected pathways, might be a better metaphor for understanding all that’s happening in the health care system and, more importantly, how it might be fixed.
Madelaine Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist in private practice in New Orleans and CSRO’s vice president of advocacy and government affairs, is a frequent advocate in Congress, state legislatures, and elsewhere regarding the utilization management techniques used by managed care and PBMs and how these are negatively affecting the ability of rheumatology patients to get the treatments they need. Such techniques include the following:
- Prior authorizations imposed by the health plan before a medication can be dispensed.
- Step therapy, which requires the patient to fail as many as three or four payer-preferred drugs before trying the one recommended by the rheumatologist.
- Nonmedical switching, in which a patient is forced to change medications for a nonmedical reason related to the PBM’s formulary.
- Accumulator adjustment programs, which increase the patient’s out-of-pocket and deductible commitments.
“There is very little transparency in how the money flows with PBMs,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. “In reality, PBMs are able to make profits by the perverse incentive of putting higher-priced drugs on their formularies, thus increasing the amount of rebates paid to them, without sharing any of the benefit with patients.”
PBMs have resisted disclosing this information, saying it would inhibit competition and cause drug prices to go up. The key thing to understand, she said, is that there is huge competition today to get preferred formulary placement. “Consequently, treatment choice for patients is not based on doctor-patient shared decision-making but on the highest rebate promised to the PBM,” she said.
“A rheumatology fellow recently told me that his patients will sometimes blame him for the lack of choice and high prices of the medications,” she noted. What she has started to do with patients, after discussing all the available drugs appropriate to their condition, is to ask: “What is your insurance? The reason I’m asking is that we can come up with a game plan, but the entity that will determine what you will receive is the insurance company.”
What does Dr. Madelaine Feldman want fellows to take away from the CSRO conference? “I hope to arouse their anger, initially, which then works its way into a passion to change the system. We’re all so busy. Sometimes it takes lighting a fire under people,” she said.
CSRO has an online action center to facilitate sending letters to legislators, as well as a map tool for looking up any active legislation in their state. “Spread the word to your peers. Use your voice to help pass PBM reforms. Tell other fellows to come to the next CSRO fellows meeting,” she said.
“We got into this space because a few community rheumatologists were angry over decisions about how drug infusions would be paid for,” she said. “A group went to Washington, to Congress and Medicare, and changed the policy,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. A few passionate people really can make a difference. “Join the action. We’re always looking for rheumatologists and their patients to testify on these issues.”
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN FRANCISCO – New rheumatologists face a wide range of significant challenges brought on by the increasing complexity of insurance billing and rapid changes to managed care practices, especially techniques of utilization management and pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs), speakers said at the 2023 Fellows Conference of the Coalition for State Rheumatology Organizations (CSRO).
“We are seeing the impact of the environment eroding the patient-doctor relationship,” CSRO President Gary Feldman, MD, told participants.
Michael Saitta, MD, MBA, a rheumatologist in Fayetteville, Ark., said fellows should learn more about health insurance to take better care of their patients and their practice. “Your training includes a variable level of discourse on the health insurance market,” he said. Health insurance today is a mess. Costs have exploded. “Is anybody really happy with the current system?”
Although the health care system is sometimes compared to a dumpster fire, he said, a plate of spaghetti, with its multiple interconnected pathways, might be a better metaphor for understanding all that’s happening in the health care system and, more importantly, how it might be fixed.
Madelaine Feldman, MD, a rheumatologist in private practice in New Orleans and CSRO’s vice president of advocacy and government affairs, is a frequent advocate in Congress, state legislatures, and elsewhere regarding the utilization management techniques used by managed care and PBMs and how these are negatively affecting the ability of rheumatology patients to get the treatments they need. Such techniques include the following:
- Prior authorizations imposed by the health plan before a medication can be dispensed.
- Step therapy, which requires the patient to fail as many as three or four payer-preferred drugs before trying the one recommended by the rheumatologist.
- Nonmedical switching, in which a patient is forced to change medications for a nonmedical reason related to the PBM’s formulary.
- Accumulator adjustment programs, which increase the patient’s out-of-pocket and deductible commitments.
“There is very little transparency in how the money flows with PBMs,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. “In reality, PBMs are able to make profits by the perverse incentive of putting higher-priced drugs on their formularies, thus increasing the amount of rebates paid to them, without sharing any of the benefit with patients.”
PBMs have resisted disclosing this information, saying it would inhibit competition and cause drug prices to go up. The key thing to understand, she said, is that there is huge competition today to get preferred formulary placement. “Consequently, treatment choice for patients is not based on doctor-patient shared decision-making but on the highest rebate promised to the PBM,” she said.
“A rheumatology fellow recently told me that his patients will sometimes blame him for the lack of choice and high prices of the medications,” she noted. What she has started to do with patients, after discussing all the available drugs appropriate to their condition, is to ask: “What is your insurance? The reason I’m asking is that we can come up with a game plan, but the entity that will determine what you will receive is the insurance company.”
What does Dr. Madelaine Feldman want fellows to take away from the CSRO conference? “I hope to arouse their anger, initially, which then works its way into a passion to change the system. We’re all so busy. Sometimes it takes lighting a fire under people,” she said.
CSRO has an online action center to facilitate sending letters to legislators, as well as a map tool for looking up any active legislation in their state. “Spread the word to your peers. Use your voice to help pass PBM reforms. Tell other fellows to come to the next CSRO fellows meeting,” she said.
“We got into this space because a few community rheumatologists were angry over decisions about how drug infusions would be paid for,” she said. “A group went to Washington, to Congress and Medicare, and changed the policy,” Dr. Madelaine Feldman said. A few passionate people really can make a difference. “Join the action. We’re always looking for rheumatologists and their patients to testify on these issues.”
No relevant financial relationships were reported by the conference speakers.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Guidelines: Don’t delay total joint arthroplasty for additional nonoperative therapies
Patients with moderate to severe osteoarthritis (OA) or osteonecrosis (ON) eligible for total joint arthroplasty (TJA) who have failed one or more nonoperative therapies should proceed directly to surgery, according to new guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons.
“One of the reasons for creating this guideline was that many patients have been subjected to delays for surgery after completing nonoperative therapy, despite persistent moderate to severe pain, loss of function, and moderate to severe radiographic OA or ON,” said coauthors Susan M. Goodman, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and Charles Hannon, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Washington University in St. Louis, in an email interview with this news organization. “This guideline supports surgery being performed in an expeditious fashion after the decision has been made to proceed with surgery by both the physician and patient through a shared decision-making process,” they said.
The guidelines also state that obesity by itself should not be a reason to delay TJA. “We could not find a rationale for a strict cut off for weight/body mass index (BMI). Our literature review revealed that though many adverse events were, in fact, increased in patients with morbid obesity, there is also an increase in adverse events for those who had bariatric surgery prior to their arthroplasty,” they added, noting that patients need to be made aware of the increased risk for adverse events in patients with obesity. Though the guidelines do not pose any BMI cutoffs, they state that weight loss should be “strongly encouraged.” These new recommendations are conditional, and all had a “low” to “very low” certainty of evidence; however, there was high consensus on the recommendations from the expert panel.
The guidelines also recommended:
- Delaying TJA to achieve smoking and nicotine cessation or reduction.
- Delaying TJA to improve glycemic control in patients with diabetes, although the group did not recommend any specific measure or threshold.
- Not delaying TJA in patients with a severe deformity, bone loss, or a neuropathic joint.
The new guidelines formalize what many surgeons have already been doing for the past few years, said Arjun Saxena, MD, MBA, an orthopedic surgeon in Philadelphia who was not involved with the guidelines. “A lot of total joint programs have really focused on patient optimization, including smoking cessation, glycemic control, and weight loss prior to surgery,” he said.
Most importantly, the guidelines put an emphasis on how the decision to proceed with TJA should be a shared decision between a physician and patient, he added. Some insurance companies with prior authorization policies may require a patient to try additional nonoperative therapies before approving surgery, creating barriers to care, he said. “Hopefully [these new recommendations] will help third parties understand that joint replacement is a big decision – most doctors aren’t going to recommend that unless it’s necessary or something that is going to help patients,” he said. “I understand that there is a certain need for preauthorization, but just having strict guidelines isn’t appropriate. You really need to look at the whole picture,” he added.
The full manuscript has been submitted for review and is expected to be jointly published in American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons journals later this year.
Dr. Saxena consults for the orthopedic implant company Corin.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with moderate to severe osteoarthritis (OA) or osteonecrosis (ON) eligible for total joint arthroplasty (TJA) who have failed one or more nonoperative therapies should proceed directly to surgery, according to new guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons.
“One of the reasons for creating this guideline was that many patients have been subjected to delays for surgery after completing nonoperative therapy, despite persistent moderate to severe pain, loss of function, and moderate to severe radiographic OA or ON,” said coauthors Susan M. Goodman, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and Charles Hannon, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Washington University in St. Louis, in an email interview with this news organization. “This guideline supports surgery being performed in an expeditious fashion after the decision has been made to proceed with surgery by both the physician and patient through a shared decision-making process,” they said.
The guidelines also state that obesity by itself should not be a reason to delay TJA. “We could not find a rationale for a strict cut off for weight/body mass index (BMI). Our literature review revealed that though many adverse events were, in fact, increased in patients with morbid obesity, there is also an increase in adverse events for those who had bariatric surgery prior to their arthroplasty,” they added, noting that patients need to be made aware of the increased risk for adverse events in patients with obesity. Though the guidelines do not pose any BMI cutoffs, they state that weight loss should be “strongly encouraged.” These new recommendations are conditional, and all had a “low” to “very low” certainty of evidence; however, there was high consensus on the recommendations from the expert panel.
The guidelines also recommended:
- Delaying TJA to achieve smoking and nicotine cessation or reduction.
- Delaying TJA to improve glycemic control in patients with diabetes, although the group did not recommend any specific measure or threshold.
- Not delaying TJA in patients with a severe deformity, bone loss, or a neuropathic joint.
The new guidelines formalize what many surgeons have already been doing for the past few years, said Arjun Saxena, MD, MBA, an orthopedic surgeon in Philadelphia who was not involved with the guidelines. “A lot of total joint programs have really focused on patient optimization, including smoking cessation, glycemic control, and weight loss prior to surgery,” he said.
Most importantly, the guidelines put an emphasis on how the decision to proceed with TJA should be a shared decision between a physician and patient, he added. Some insurance companies with prior authorization policies may require a patient to try additional nonoperative therapies before approving surgery, creating barriers to care, he said. “Hopefully [these new recommendations] will help third parties understand that joint replacement is a big decision – most doctors aren’t going to recommend that unless it’s necessary or something that is going to help patients,” he said. “I understand that there is a certain need for preauthorization, but just having strict guidelines isn’t appropriate. You really need to look at the whole picture,” he added.
The full manuscript has been submitted for review and is expected to be jointly published in American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons journals later this year.
Dr. Saxena consults for the orthopedic implant company Corin.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with moderate to severe osteoarthritis (OA) or osteonecrosis (ON) eligible for total joint arthroplasty (TJA) who have failed one or more nonoperative therapies should proceed directly to surgery, according to new guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons.
“One of the reasons for creating this guideline was that many patients have been subjected to delays for surgery after completing nonoperative therapy, despite persistent moderate to severe pain, loss of function, and moderate to severe radiographic OA or ON,” said coauthors Susan M. Goodman, MD, a rheumatologist at Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, and Charles Hannon, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Washington University in St. Louis, in an email interview with this news organization. “This guideline supports surgery being performed in an expeditious fashion after the decision has been made to proceed with surgery by both the physician and patient through a shared decision-making process,” they said.
The guidelines also state that obesity by itself should not be a reason to delay TJA. “We could not find a rationale for a strict cut off for weight/body mass index (BMI). Our literature review revealed that though many adverse events were, in fact, increased in patients with morbid obesity, there is also an increase in adverse events for those who had bariatric surgery prior to their arthroplasty,” they added, noting that patients need to be made aware of the increased risk for adverse events in patients with obesity. Though the guidelines do not pose any BMI cutoffs, they state that weight loss should be “strongly encouraged.” These new recommendations are conditional, and all had a “low” to “very low” certainty of evidence; however, there was high consensus on the recommendations from the expert panel.
The guidelines also recommended:
- Delaying TJA to achieve smoking and nicotine cessation or reduction.
- Delaying TJA to improve glycemic control in patients with diabetes, although the group did not recommend any specific measure or threshold.
- Not delaying TJA in patients with a severe deformity, bone loss, or a neuropathic joint.
The new guidelines formalize what many surgeons have already been doing for the past few years, said Arjun Saxena, MD, MBA, an orthopedic surgeon in Philadelphia who was not involved with the guidelines. “A lot of total joint programs have really focused on patient optimization, including smoking cessation, glycemic control, and weight loss prior to surgery,” he said.
Most importantly, the guidelines put an emphasis on how the decision to proceed with TJA should be a shared decision between a physician and patient, he added. Some insurance companies with prior authorization policies may require a patient to try additional nonoperative therapies before approving surgery, creating barriers to care, he said. “Hopefully [these new recommendations] will help third parties understand that joint replacement is a big decision – most doctors aren’t going to recommend that unless it’s necessary or something that is going to help patients,” he said. “I understand that there is a certain need for preauthorization, but just having strict guidelines isn’t appropriate. You really need to look at the whole picture,” he added.
The full manuscript has been submitted for review and is expected to be jointly published in American College of Rheumatology and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons journals later this year.
Dr. Saxena consults for the orthopedic implant company Corin.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.