User login
Differential diagnosis in MS: What to watch for
SAN DIEGO –
The problem is that MS can vary greatly in its presentation, and many symptoms can mimic other conditions, according to Eoin Flanagan, MBBCh, who discussed the issue during a session at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Mimics and red flags
Dr. Flanagan noted a study that found common themes among MS misdiagnoses. “Many of these conditions are common conditions that we see in our neurology clinic – for example, migraine, fibromyalgia, nonspecific symptoms with an abnormal MRI, or functional neurologic disorder. If you’re teaching medical students or trainees about MS misdiagnosis, it’s important to give this example to show that these are not the zebras that are misdiagnosed, but actually common conditions that we see in our clinics,” said Dr. Flanagan, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Evaluation of MS mimics isn’t always necessary. Much of the time, typical clinical, neurologic, and imaging features provide a clear diagnosis. But some features can be red flags that MS may not be the cause. These can include a cerebrospinal fluid white blood cell count higher than 50, elevated CSF protein with normal white cell counts, low glucose, and negative oligoclonal bands, all of which could signify a range of other conditions.
These and other red flags should prompt a careful look to get the right diagnosis.
Earlier diagnosis = better outcomes
“[Evidence has] shown recently that as the diagnostic criteria have become more sensitive and we diagnose MS earlier, patients have had better outcomes because they’ve been able to initiate treatment earlier,” said Andrew Solomon, MD, who is an associate professor of neurologic sciences and division chief of multiple sclerosis at University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Solomon, Dr. Flanagan, and others are currently writing a review article on differential diagnosis of MS that will update the last review, published in 2008.
“Differential diagnosis has become more complex as we’ve had a broader understanding of disorders that can mimic MS. In the meantime, we still don’t have a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for MS that can help guide us when we first see somebody,” said Dr. Solomon.
Look for patterns and imaging clues
Dr. Flanagan’s talk had several points of emphasis. A key feature is the length of time between when the patient develops the first symptom and maximal symptoms. “If that’s very quick, then that suggests it’s a spinal cord stroke. If it comes down over days to a few weeks, then that suggests inflammation like MS, or like neuromyelitis optica [NMO] or myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease [MOGAD]. As it progresses beyond 21 days, then we’re going to be thinking about a different diagnosis,” said Dr. Flanagan.
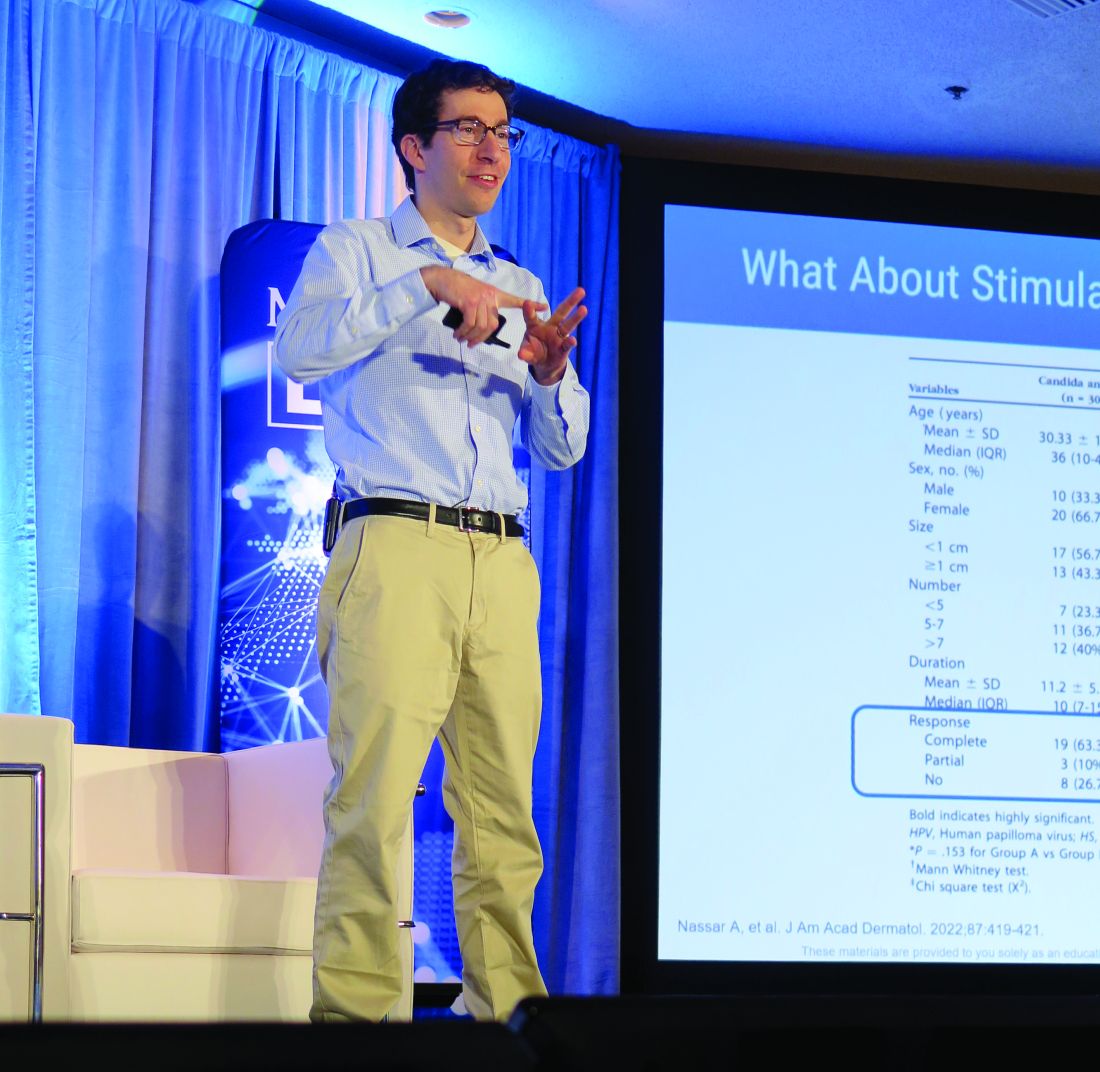
Dr. Flanagan also noted the usefulness of specific features of the spinal cord MRI. Variables like lesion length, location in the center or periphery of the spinal cord, and characteristics of the enhancement pattern may be useful. “The pattern of gadolinium enhancement can be useful in narrowing your differential diagnosis and suggesting the correct diagnosis. For example, the flat pancake-like enhancement on sagittal images can suggest cervical spondylosis, while trident sign on axial images can suggest spinal cord sarcoidosis. Prior studies have shown that education on these patterns can enhance diagnosis.”
Dr. Flanagan suggested that both radiologists and neurologists should be trained to recognize such patterns. “If you educate radiologists or neurologists on these patterns, it can help them with diagnosis.”
Common mistakes
MOGAD and aquaporin 4–positive NMO spectrum disorder (AQP4+NMOSD) can be easily mistaken for MS, but there are some key differences. MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD attacks are more severe than MS attacks, leaving patients more likely to be blind following an optic neuritis attack or wheelchair bound because of myelitis. More than 85% of CSF from patients with MS have oligoclonal bands versus about 15% of CSF from patients with MOGAD or AQP4+NMOSD. There is also a difference in lesion dynamics over time: MOGAD T2 lesions frequently resolve over follow-up while AQP4+NMOSD and MS lesions typically continue and leave a scar and persist. Silent lesions are more likely during surveillance MRI among MS patients, but are rare in MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD, according to Dr. Flanagan. “One caveat to this is that with stronger MS medications we are seeing less silent lesions accumulating as we use those treatments more often.”
Dr. Solomon has been done nonpromotional speaking for EMD Serono. He has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. He has been on an advisory board or consulted for Greenwich Biosciences, TG Therapeutics, Octave Bioscience, and Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Flanagan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Flanagan has served on advisory boards for Alexion, Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, and UCB.
SAN DIEGO –
The problem is that MS can vary greatly in its presentation, and many symptoms can mimic other conditions, according to Eoin Flanagan, MBBCh, who discussed the issue during a session at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Mimics and red flags
Dr. Flanagan noted a study that found common themes among MS misdiagnoses. “Many of these conditions are common conditions that we see in our neurology clinic – for example, migraine, fibromyalgia, nonspecific symptoms with an abnormal MRI, or functional neurologic disorder. If you’re teaching medical students or trainees about MS misdiagnosis, it’s important to give this example to show that these are not the zebras that are misdiagnosed, but actually common conditions that we see in our clinics,” said Dr. Flanagan, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Evaluation of MS mimics isn’t always necessary. Much of the time, typical clinical, neurologic, and imaging features provide a clear diagnosis. But some features can be red flags that MS may not be the cause. These can include a cerebrospinal fluid white blood cell count higher than 50, elevated CSF protein with normal white cell counts, low glucose, and negative oligoclonal bands, all of which could signify a range of other conditions.
These and other red flags should prompt a careful look to get the right diagnosis.
Earlier diagnosis = better outcomes
“[Evidence has] shown recently that as the diagnostic criteria have become more sensitive and we diagnose MS earlier, patients have had better outcomes because they’ve been able to initiate treatment earlier,” said Andrew Solomon, MD, who is an associate professor of neurologic sciences and division chief of multiple sclerosis at University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Solomon, Dr. Flanagan, and others are currently writing a review article on differential diagnosis of MS that will update the last review, published in 2008.
“Differential diagnosis has become more complex as we’ve had a broader understanding of disorders that can mimic MS. In the meantime, we still don’t have a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for MS that can help guide us when we first see somebody,” said Dr. Solomon.
Look for patterns and imaging clues
Dr. Flanagan’s talk had several points of emphasis. A key feature is the length of time between when the patient develops the first symptom and maximal symptoms. “If that’s very quick, then that suggests it’s a spinal cord stroke. If it comes down over days to a few weeks, then that suggests inflammation like MS, or like neuromyelitis optica [NMO] or myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease [MOGAD]. As it progresses beyond 21 days, then we’re going to be thinking about a different diagnosis,” said Dr. Flanagan.
Dr. Flanagan also noted the usefulness of specific features of the spinal cord MRI. Variables like lesion length, location in the center or periphery of the spinal cord, and characteristics of the enhancement pattern may be useful. “The pattern of gadolinium enhancement can be useful in narrowing your differential diagnosis and suggesting the correct diagnosis. For example, the flat pancake-like enhancement on sagittal images can suggest cervical spondylosis, while trident sign on axial images can suggest spinal cord sarcoidosis. Prior studies have shown that education on these patterns can enhance diagnosis.”
Dr. Flanagan suggested that both radiologists and neurologists should be trained to recognize such patterns. “If you educate radiologists or neurologists on these patterns, it can help them with diagnosis.”
Common mistakes
MOGAD and aquaporin 4–positive NMO spectrum disorder (AQP4+NMOSD) can be easily mistaken for MS, but there are some key differences. MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD attacks are more severe than MS attacks, leaving patients more likely to be blind following an optic neuritis attack or wheelchair bound because of myelitis. More than 85% of CSF from patients with MS have oligoclonal bands versus about 15% of CSF from patients with MOGAD or AQP4+NMOSD. There is also a difference in lesion dynamics over time: MOGAD T2 lesions frequently resolve over follow-up while AQP4+NMOSD and MS lesions typically continue and leave a scar and persist. Silent lesions are more likely during surveillance MRI among MS patients, but are rare in MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD, according to Dr. Flanagan. “One caveat to this is that with stronger MS medications we are seeing less silent lesions accumulating as we use those treatments more often.”
Dr. Solomon has been done nonpromotional speaking for EMD Serono. He has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. He has been on an advisory board or consulted for Greenwich Biosciences, TG Therapeutics, Octave Bioscience, and Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Flanagan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Flanagan has served on advisory boards for Alexion, Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, and UCB.
SAN DIEGO –
The problem is that MS can vary greatly in its presentation, and many symptoms can mimic other conditions, according to Eoin Flanagan, MBBCh, who discussed the issue during a session at the annual meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS).
Mimics and red flags
Dr. Flanagan noted a study that found common themes among MS misdiagnoses. “Many of these conditions are common conditions that we see in our neurology clinic – for example, migraine, fibromyalgia, nonspecific symptoms with an abnormal MRI, or functional neurologic disorder. If you’re teaching medical students or trainees about MS misdiagnosis, it’s important to give this example to show that these are not the zebras that are misdiagnosed, but actually common conditions that we see in our clinics,” said Dr. Flanagan, a neurologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Evaluation of MS mimics isn’t always necessary. Much of the time, typical clinical, neurologic, and imaging features provide a clear diagnosis. But some features can be red flags that MS may not be the cause. These can include a cerebrospinal fluid white blood cell count higher than 50, elevated CSF protein with normal white cell counts, low glucose, and negative oligoclonal bands, all of which could signify a range of other conditions.
These and other red flags should prompt a careful look to get the right diagnosis.
Earlier diagnosis = better outcomes
“[Evidence has] shown recently that as the diagnostic criteria have become more sensitive and we diagnose MS earlier, patients have had better outcomes because they’ve been able to initiate treatment earlier,” said Andrew Solomon, MD, who is an associate professor of neurologic sciences and division chief of multiple sclerosis at University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Solomon, Dr. Flanagan, and others are currently writing a review article on differential diagnosis of MS that will update the last review, published in 2008.
“Differential diagnosis has become more complex as we’ve had a broader understanding of disorders that can mimic MS. In the meantime, we still don’t have a highly sensitive and specific biomarker for MS that can help guide us when we first see somebody,” said Dr. Solomon.
Look for patterns and imaging clues
Dr. Flanagan’s talk had several points of emphasis. A key feature is the length of time between when the patient develops the first symptom and maximal symptoms. “If that’s very quick, then that suggests it’s a spinal cord stroke. If it comes down over days to a few weeks, then that suggests inflammation like MS, or like neuromyelitis optica [NMO] or myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease [MOGAD]. As it progresses beyond 21 days, then we’re going to be thinking about a different diagnosis,” said Dr. Flanagan.
Dr. Flanagan also noted the usefulness of specific features of the spinal cord MRI. Variables like lesion length, location in the center or periphery of the spinal cord, and characteristics of the enhancement pattern may be useful. “The pattern of gadolinium enhancement can be useful in narrowing your differential diagnosis and suggesting the correct diagnosis. For example, the flat pancake-like enhancement on sagittal images can suggest cervical spondylosis, while trident sign on axial images can suggest spinal cord sarcoidosis. Prior studies have shown that education on these patterns can enhance diagnosis.”
Dr. Flanagan suggested that both radiologists and neurologists should be trained to recognize such patterns. “If you educate radiologists or neurologists on these patterns, it can help them with diagnosis.”
Common mistakes
MOGAD and aquaporin 4–positive NMO spectrum disorder (AQP4+NMOSD) can be easily mistaken for MS, but there are some key differences. MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD attacks are more severe than MS attacks, leaving patients more likely to be blind following an optic neuritis attack or wheelchair bound because of myelitis. More than 85% of CSF from patients with MS have oligoclonal bands versus about 15% of CSF from patients with MOGAD or AQP4+NMOSD. There is also a difference in lesion dynamics over time: MOGAD T2 lesions frequently resolve over follow-up while AQP4+NMOSD and MS lesions typically continue and leave a scar and persist. Silent lesions are more likely during surveillance MRI among MS patients, but are rare in MOGAD and AQP4+NMOSD, according to Dr. Flanagan. “One caveat to this is that with stronger MS medications we are seeing less silent lesions accumulating as we use those treatments more often.”
Dr. Solomon has been done nonpromotional speaking for EMD Serono. He has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. He has been on an advisory board or consulted for Greenwich Biosciences, TG Therapeutics, Octave Bioscience, and Horizon Therapeutics. Dr. Flanagan has no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Flanagan has served on advisory boards for Alexion, Genentech, Horizon Therapeutics, and UCB.
FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2023
Ketamine plus psychotherapy ‘highly effective’ for PTSD
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of four studies investigating combined use of psychotherapy and ketamine for PTSD, results showed that all the studies showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptom scores.
Overall, the treatment was “highly effective, as seen by the significant improvements in symptoms on multiple measures,” Aaron E. Philipp-Muller, BScH, Centre for Neuroscience Studies, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues write.
Furthermore, the study “demonstrates the potential feasibility of this treatment model and corroborates previous work,” the investigators write.
However, a limitation they note was that only 34 participants were included in the analysis.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Emerging treatment
Ketamine is an “emerging treatment for a number of psychopathologies, such as major depressive disorder and PTSD, with a higher response than other pharmacologic agents,” the researchers write.
It is hypothesized that ketamine rapidly facilitates long-term potentiation, “thereby allowing a patient to disengage from an established pattern of thought more readily,” they write.
However, ketamine has several drawbacks, including the fact that it brings only 1 week of relief for PTSD. Also, because it must be administered intravenously, it is “impractical for long-term weekly administration,” they note.
Pharmacologically enhanced psychotherapy is a potential way to prolong ketamine’s effects. Several prior studies have investigated this model using other psychedelic medications, with encouraging results.
The current investigators decided to review all literature to date on the subject of ketamine plus psychotherapy for the treatment of PTSD.
To be included, the study had to include patients diagnosed with PTSD, an intervention involving ketamine alongside any form of psychotherapy, and assessment of all patients before and after treatment using the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) or the PTSD Checklist (PCL).
Four studies met inclusion criteria. Of these, two were of “moderate” quality and two were of “low” quality, based on the GRADE assessment. The studies encompassed a total of 34 patients with “diverse traumatic experiences” and included several types of ketamine administration protocols, including one used previously for treating depression and another used previously for chronic pain.
The psychotherapy modalities also differed between the studies. In two studies, patients received 12 sessions of trauma interventions using mindfulness-based extinction and reconsolidation therapy; in a third study, patients received 10 weekly sessions of prolonged exposure therapy; and in the fourth study, patients received five daily sessions of exposure therapy.
Across the studies, the psychotherapies were paired differently with ketamine administration, such as the number of ketamine administrations in conjunction with therapy.
Despite the differences in protocols, all the studies of ketamine plus psychotherapy showed a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, with a pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) of –7.26 (95% CI, –12.28 to –2.25; P = .005) for the CAPS and a pooled SMD of –5.17 (95% CI, –7.99 to –2.35; P < .001) for the PCL.
The researchers acknowledge that the sample size was very small “due to the novelty of this research area.” This prompted the inclusion of nonrandomized studies that “lowered the quality of the evidence,” they note.
Nevertheless, “these preliminary findings indicate the potential of ketamine-assisted psychotherapy for PTSD,” the investigators write.
A promising avenue?
In a comment, Dan Iosifescu, MD, professor of psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, called the combination of ketamine and psychotherapy in PTSD “a very promising treatment avenue.”
Dr. Iosifescu, who was not involved with the research, noted that “several PTSD-focused psychotherapies are ultimately very effective but very hard to tolerate for participants.” For example, prolonged exposure therapy has dropout rates as high as 50%.
In addition, ketamine has rapid but not sustained effects in PTSD, he said.
“So in theory, a course of ketamine could help PTSD patients improve rapidly and tolerate the psychotherapy, which could provide sustained benefits,” he added.
However, Dr. Iosifescu cautioned that the data supporting this “is very sparse for now.”
He also noted that the meta-analysis included only “four tiny studies” and had only 34 total participants. In addition, several of the studies had no comparison group and the study designs were all different – “both with respect to the administration of ketamine and to the paired PTSD psychotherapy.”
For this reason, “any conclusions are only a very preliminary suggestion that this may be a fruitful avenue,” he said.
Dr. Iosifescu added that additional studies on this topic are ongoing. The largest one at the Veterans Administration will hopefully include 100 participants and “will provide more reliable evidence for this important topic,” he said.
The study was indirectly supported by the Internal Faculty Grant from the department of psychiatry, Queen’s University. Dr. Iosifescu reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Red wine’s potential benefits for cardiovascular health
In recent weeks, you may have noticed some familiar headlines about red wine and cardiovascular health. Why the sudden return of these stories? Because of an article recently published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Funded in part by a grant from the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), the “Wine Flora Study” was carried out by prominent researchers from institutions in South America, Europe, and the United States: University of São Paulo; State University of Campinas, São Paulo; University of Brasília; University of Verona (Italy); Austrian Institute of Technology, Tulln; and Harvard Medical School, Boston. The team looked into the effects of red wine on gut flora and plasma levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). And what they found was quite interesting.
The study
Previous results have pointed to the beneficial effect that red wine has on the gut microbiome.
The Wine Flora Study involved 42 men (average age, 60 years) with documented coronary artery disease. The trial encompassed two 3-week interventions. In one, the participants consumed 250 mL of red wine per day; the red wine sample had an alcohol content (% v) of 12.75. The Brazilian Wine Institute produced and supplied the red wine: a 2014 Merlot bottled in August 2016 and customized for the study. The second intervention involved alcohol abstention.
Each intervention was preceded by a 2-week washout period. Because certain foods and drinks could interfere with the results, the participants were instructed not to consume alcoholic beverages, fermented foods (yogurt, kombucha, soy lecithin, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented vegetables), synthetic prebiotics (insulin, fructooligosaccharides), fiber, dairy, food polyphenols (grapes, grape juice, cranberries, strawberries), and probiotics.
At each intervention, the gut microbiota was analyzed via 16S ribosomal RNA highthroughput sequencing. This method makes it possible to identify bacterial species. The plasma metabolome of 20 randomly selected participants was evaluated by ultra–high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. In this method, liquid chromatography separates the compounds, and a mass spectrometer is used to analyze them.
One of the metabolites of interest was TMAO, which is produced from the trimethylamine released when gut bacteria process protein-rich foods. TMAO has been identified as playing a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
Results
with a difference in beta diversity and predominance of Parasutterella, Ruminococcaceae, several Bacteroides species, and Prevotella.
Plasma metabolomic analysis revealed significant changes in metabolites after red wine consumption, consistent with improved redox homeostasis, which is involved in the oxidative stress that promotes atherosclerosis.
Plasma TMAO, however, did not differ between red wine intervention and alcohol abstention.
Implications
The researchers concluded that modulation of the gut microbiota may contribute to the putative cardiovascular benefits of moderate red wine consumption. But, as they were careful to point out in the very title of the study, a red wine intervention does not modify plasma TMAO. They also mentioned that the 3-week period may have been too short for the findings to serve as the basis for promoting any meaningful modification. In addition, the team emphasized that these data remain hypothesisgenerating and pave the way for future research.
In an interview with FAPESP, the study’s corresponding author, Protásio Lemos da Luz, MD, PhD, warned about the risks associated with drinking too much alcohol (> 8.5 oz., or 250 mL, of wine daily).
It should be kept in mind that, in Brazil, people do not drink nearly as much wine as they do beer or liquor. Furthermore, the evidence that is available does not provide confirmation of the existence or the extent of the protective health effects associated with light or moderate alcohol intake.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In recent weeks, you may have noticed some familiar headlines about red wine and cardiovascular health. Why the sudden return of these stories? Because of an article recently published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Funded in part by a grant from the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), the “Wine Flora Study” was carried out by prominent researchers from institutions in South America, Europe, and the United States: University of São Paulo; State University of Campinas, São Paulo; University of Brasília; University of Verona (Italy); Austrian Institute of Technology, Tulln; and Harvard Medical School, Boston. The team looked into the effects of red wine on gut flora and plasma levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). And what they found was quite interesting.
The study
Previous results have pointed to the beneficial effect that red wine has on the gut microbiome.
The Wine Flora Study involved 42 men (average age, 60 years) with documented coronary artery disease. The trial encompassed two 3-week interventions. In one, the participants consumed 250 mL of red wine per day; the red wine sample had an alcohol content (% v) of 12.75. The Brazilian Wine Institute produced and supplied the red wine: a 2014 Merlot bottled in August 2016 and customized for the study. The second intervention involved alcohol abstention.
Each intervention was preceded by a 2-week washout period. Because certain foods and drinks could interfere with the results, the participants were instructed not to consume alcoholic beverages, fermented foods (yogurt, kombucha, soy lecithin, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented vegetables), synthetic prebiotics (insulin, fructooligosaccharides), fiber, dairy, food polyphenols (grapes, grape juice, cranberries, strawberries), and probiotics.
At each intervention, the gut microbiota was analyzed via 16S ribosomal RNA highthroughput sequencing. This method makes it possible to identify bacterial species. The plasma metabolome of 20 randomly selected participants was evaluated by ultra–high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. In this method, liquid chromatography separates the compounds, and a mass spectrometer is used to analyze them.
One of the metabolites of interest was TMAO, which is produced from the trimethylamine released when gut bacteria process protein-rich foods. TMAO has been identified as playing a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
Results
with a difference in beta diversity and predominance of Parasutterella, Ruminococcaceae, several Bacteroides species, and Prevotella.
Plasma metabolomic analysis revealed significant changes in metabolites after red wine consumption, consistent with improved redox homeostasis, which is involved in the oxidative stress that promotes atherosclerosis.
Plasma TMAO, however, did not differ between red wine intervention and alcohol abstention.
Implications
The researchers concluded that modulation of the gut microbiota may contribute to the putative cardiovascular benefits of moderate red wine consumption. But, as they were careful to point out in the very title of the study, a red wine intervention does not modify plasma TMAO. They also mentioned that the 3-week period may have been too short for the findings to serve as the basis for promoting any meaningful modification. In addition, the team emphasized that these data remain hypothesisgenerating and pave the way for future research.
In an interview with FAPESP, the study’s corresponding author, Protásio Lemos da Luz, MD, PhD, warned about the risks associated with drinking too much alcohol (> 8.5 oz., or 250 mL, of wine daily).
It should be kept in mind that, in Brazil, people do not drink nearly as much wine as they do beer or liquor. Furthermore, the evidence that is available does not provide confirmation of the existence or the extent of the protective health effects associated with light or moderate alcohol intake.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
In recent weeks, you may have noticed some familiar headlines about red wine and cardiovascular health. Why the sudden return of these stories? Because of an article recently published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Funded in part by a grant from the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), the “Wine Flora Study” was carried out by prominent researchers from institutions in South America, Europe, and the United States: University of São Paulo; State University of Campinas, São Paulo; University of Brasília; University of Verona (Italy); Austrian Institute of Technology, Tulln; and Harvard Medical School, Boston. The team looked into the effects of red wine on gut flora and plasma levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). And what they found was quite interesting.
The study
Previous results have pointed to the beneficial effect that red wine has on the gut microbiome.
The Wine Flora Study involved 42 men (average age, 60 years) with documented coronary artery disease. The trial encompassed two 3-week interventions. In one, the participants consumed 250 mL of red wine per day; the red wine sample had an alcohol content (% v) of 12.75. The Brazilian Wine Institute produced and supplied the red wine: a 2014 Merlot bottled in August 2016 and customized for the study. The second intervention involved alcohol abstention.
Each intervention was preceded by a 2-week washout period. Because certain foods and drinks could interfere with the results, the participants were instructed not to consume alcoholic beverages, fermented foods (yogurt, kombucha, soy lecithin, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented vegetables), synthetic prebiotics (insulin, fructooligosaccharides), fiber, dairy, food polyphenols (grapes, grape juice, cranberries, strawberries), and probiotics.
At each intervention, the gut microbiota was analyzed via 16S ribosomal RNA highthroughput sequencing. This method makes it possible to identify bacterial species. The plasma metabolome of 20 randomly selected participants was evaluated by ultra–high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. In this method, liquid chromatography separates the compounds, and a mass spectrometer is used to analyze them.
One of the metabolites of interest was TMAO, which is produced from the trimethylamine released when gut bacteria process protein-rich foods. TMAO has been identified as playing a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
Results
with a difference in beta diversity and predominance of Parasutterella, Ruminococcaceae, several Bacteroides species, and Prevotella.
Plasma metabolomic analysis revealed significant changes in metabolites after red wine consumption, consistent with improved redox homeostasis, which is involved in the oxidative stress that promotes atherosclerosis.
Plasma TMAO, however, did not differ between red wine intervention and alcohol abstention.
Implications
The researchers concluded that modulation of the gut microbiota may contribute to the putative cardiovascular benefits of moderate red wine consumption. But, as they were careful to point out in the very title of the study, a red wine intervention does not modify plasma TMAO. They also mentioned that the 3-week period may have been too short for the findings to serve as the basis for promoting any meaningful modification. In addition, the team emphasized that these data remain hypothesisgenerating and pave the way for future research.
In an interview with FAPESP, the study’s corresponding author, Protásio Lemos da Luz, MD, PhD, warned about the risks associated with drinking too much alcohol (> 8.5 oz., or 250 mL, of wine daily).
It should be kept in mind that, in Brazil, people do not drink nearly as much wine as they do beer or liquor. Furthermore, the evidence that is available does not provide confirmation of the existence or the extent of the protective health effects associated with light or moderate alcohol intake.
This article was translated from the Medscape Portuguese edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Bacteremia, antibodies link periodontal disease to RA development and activity
a new longitudinal study suggests.
The results suggest that PD involves repeated oral mucosa breakdowns with the release of citrullinated oral bacteria into the bloodstream and that these bacteria activate inflammatory monocytes in the inflamed RA synovium and in the blood of patients with RA. The bacteria also activate anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)–positive B cells, promoting affinity maturation and epitope spreading to citrullinated human antigens, the authors wrote.
“Our study discovered frequent and repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood of patients with periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis,” senior study author Dana E. Orange, MD, associate professor of clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York, said in an interview. “We saw that these bacteria were triggering an inflammatory [monocyte] response that is similar to what we see in the inflamed joints of patients with RA.
“RA patients are less likely to benefit from RA treatment if they have concurrent periodontal disease,” she said.
“RA patients tend to harbor cyclic citrullinated peptide [CCP] autoantibodies. Many groups have noted that CCP antibodies are very highly mutated, a signature of a B-cell/antibody response that has been stimulated over and over again,” Dr. Orange explained. “We found that CCP antibodies also bind the same oral bacteria we detected in the bloodstream. That patients with PD experience frequent, repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood is consistent with the very high level of mutation burden of CCP antibodies.”
Periodontal disease is a large problem among older adults
Periodontal disease ranges from gingivitis with swollen, red gums that may bleed, to periodontitis with gums pulling away from teeth, bone loss, and loose or lost teeth. PD is very prevalent in the United States, with some form of it occurring in 47% of people 30 years of age and older and in 70% of those 65 years and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
PD is more common in people with RA who have detectable ACPAs, and that link implicates oral mucosal inflammation in RA pathogenesis.
Investigating whether PD leads to RA
At Rockefeller University, Dr. Orange and her colleagues followed five female patients with RA who were seropositive for CCP over the course of 1-4 years. Two had severe PD, and three showed no signs of PD. Each week, participants provided finger-stick blood samples for RNA sequencing and B-cell repertoire sequencing, reported changes in their medication and dental work, and completed questionnaires. They also underwent monthly physical exams that evaluated tenderness and swelling in 28 joints, and they provided additional samples during self-reported flares.
At Stanford (Calif.) University, researchers isolated plasmablasts from blood samples collected from 12 donors with anti-CPP+ RA and healthy donors. They also analyzed synovial fluid samples from 65 RA and OA patients.
In addition, University of Colorado researchers collected plasma samples from patients with RA and healthy donors, and they classified the gingival health of participants.
The researchers found that the patients with PD also had repeated flare-ups of oral bacteria in the blood, mainly from the Streptococcaceae family, suggesting that the oral mucosa repeatedly broke down and introduced bacteria into the bloodstream. In the blood, inflammatory immune cells targeted the bacteria and released ACPAs, which have been linked with RA.
“Even without dental procedures, patients with RA and periodontal disease experience repeated episodes of bacteremia,” Dr. Orange said. “While dental procedures are known to be associated with dissemination of oral bacteria into the bloodstream, we didn’t expect to see this happening so frequently and independent of dental procedures. We also had thought that people with oral bacteria in their blood would have symptoms such as fever or malaise, but they were asymptomatic.”
Experts welcome the results
“It is well established that oral health impacts overall health. In particular, the link between periodontal disease and chronic systemic diseases has been explored in many robust studies,” Chi T. Viet, MD, DDS, PhD, oral and maxillofacial surgeon and associate professor at the Loma Linda (Calif.) University School of Dentistry, told this news organization.
“The study ... highlights the importance of early treatment and prevention of oral health issues, as they can have devastating systemic sequelae,” added Dr. Viet, who was not involved in the study.
Devon Charlton, MD, MPH, director of rheumatology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Regional Orthopedics in New Castle, Pa., advised patients and providers to team up to manage RA and PD.
“If the patient and provider aggressively treat periodontal disease and dental health in general, the patient decreases their risk of infection and inflammation, decreases the potential development of RA, and increases their future quality of life,” said Dr. Charlton, also not involved in the study.
However, findings from the study population may be difficult to generalize to other populations, he added.
Dr. Orange and her colleagues suggest further related research, including studies on whether treating PD makes RA easier to treat and whether the treatment of PD in patients whose RA is in clinical remission raises the likelihood of being able to discontinue therapy safely.
The study was supported through grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robertson Foundation, Rockefeller University, the Bernard and Irene Schwartz Foundation, the Iris and Junming Le Foundation, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Dr. Orange reports no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Viet and Dr. Charlton report no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new longitudinal study suggests.
The results suggest that PD involves repeated oral mucosa breakdowns with the release of citrullinated oral bacteria into the bloodstream and that these bacteria activate inflammatory monocytes in the inflamed RA synovium and in the blood of patients with RA. The bacteria also activate anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)–positive B cells, promoting affinity maturation and epitope spreading to citrullinated human antigens, the authors wrote.
“Our study discovered frequent and repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood of patients with periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis,” senior study author Dana E. Orange, MD, associate professor of clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York, said in an interview. “We saw that these bacteria were triggering an inflammatory [monocyte] response that is similar to what we see in the inflamed joints of patients with RA.
“RA patients are less likely to benefit from RA treatment if they have concurrent periodontal disease,” she said.
“RA patients tend to harbor cyclic citrullinated peptide [CCP] autoantibodies. Many groups have noted that CCP antibodies are very highly mutated, a signature of a B-cell/antibody response that has been stimulated over and over again,” Dr. Orange explained. “We found that CCP antibodies also bind the same oral bacteria we detected in the bloodstream. That patients with PD experience frequent, repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood is consistent with the very high level of mutation burden of CCP antibodies.”
Periodontal disease is a large problem among older adults
Periodontal disease ranges from gingivitis with swollen, red gums that may bleed, to periodontitis with gums pulling away from teeth, bone loss, and loose or lost teeth. PD is very prevalent in the United States, with some form of it occurring in 47% of people 30 years of age and older and in 70% of those 65 years and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
PD is more common in people with RA who have detectable ACPAs, and that link implicates oral mucosal inflammation in RA pathogenesis.
Investigating whether PD leads to RA
At Rockefeller University, Dr. Orange and her colleagues followed five female patients with RA who were seropositive for CCP over the course of 1-4 years. Two had severe PD, and three showed no signs of PD. Each week, participants provided finger-stick blood samples for RNA sequencing and B-cell repertoire sequencing, reported changes in their medication and dental work, and completed questionnaires. They also underwent monthly physical exams that evaluated tenderness and swelling in 28 joints, and they provided additional samples during self-reported flares.
At Stanford (Calif.) University, researchers isolated plasmablasts from blood samples collected from 12 donors with anti-CPP+ RA and healthy donors. They also analyzed synovial fluid samples from 65 RA and OA patients.
In addition, University of Colorado researchers collected plasma samples from patients with RA and healthy donors, and they classified the gingival health of participants.
The researchers found that the patients with PD also had repeated flare-ups of oral bacteria in the blood, mainly from the Streptococcaceae family, suggesting that the oral mucosa repeatedly broke down and introduced bacteria into the bloodstream. In the blood, inflammatory immune cells targeted the bacteria and released ACPAs, which have been linked with RA.
“Even without dental procedures, patients with RA and periodontal disease experience repeated episodes of bacteremia,” Dr. Orange said. “While dental procedures are known to be associated with dissemination of oral bacteria into the bloodstream, we didn’t expect to see this happening so frequently and independent of dental procedures. We also had thought that people with oral bacteria in their blood would have symptoms such as fever or malaise, but they were asymptomatic.”
Experts welcome the results
“It is well established that oral health impacts overall health. In particular, the link between periodontal disease and chronic systemic diseases has been explored in many robust studies,” Chi T. Viet, MD, DDS, PhD, oral and maxillofacial surgeon and associate professor at the Loma Linda (Calif.) University School of Dentistry, told this news organization.
“The study ... highlights the importance of early treatment and prevention of oral health issues, as they can have devastating systemic sequelae,” added Dr. Viet, who was not involved in the study.
Devon Charlton, MD, MPH, director of rheumatology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Regional Orthopedics in New Castle, Pa., advised patients and providers to team up to manage RA and PD.
“If the patient and provider aggressively treat periodontal disease and dental health in general, the patient decreases their risk of infection and inflammation, decreases the potential development of RA, and increases their future quality of life,” said Dr. Charlton, also not involved in the study.
However, findings from the study population may be difficult to generalize to other populations, he added.
Dr. Orange and her colleagues suggest further related research, including studies on whether treating PD makes RA easier to treat and whether the treatment of PD in patients whose RA is in clinical remission raises the likelihood of being able to discontinue therapy safely.
The study was supported through grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robertson Foundation, Rockefeller University, the Bernard and Irene Schwartz Foundation, the Iris and Junming Le Foundation, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Dr. Orange reports no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Viet and Dr. Charlton report no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new longitudinal study suggests.
The results suggest that PD involves repeated oral mucosa breakdowns with the release of citrullinated oral bacteria into the bloodstream and that these bacteria activate inflammatory monocytes in the inflamed RA synovium and in the blood of patients with RA. The bacteria also activate anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)–positive B cells, promoting affinity maturation and epitope spreading to citrullinated human antigens, the authors wrote.
“Our study discovered frequent and repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood of patients with periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis,” senior study author Dana E. Orange, MD, associate professor of clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York, said in an interview. “We saw that these bacteria were triggering an inflammatory [monocyte] response that is similar to what we see in the inflamed joints of patients with RA.
“RA patients are less likely to benefit from RA treatment if they have concurrent periodontal disease,” she said.
“RA patients tend to harbor cyclic citrullinated peptide [CCP] autoantibodies. Many groups have noted that CCP antibodies are very highly mutated, a signature of a B-cell/antibody response that has been stimulated over and over again,” Dr. Orange explained. “We found that CCP antibodies also bind the same oral bacteria we detected in the bloodstream. That patients with PD experience frequent, repeated episodes of oral bacteria in the blood is consistent with the very high level of mutation burden of CCP antibodies.”
Periodontal disease is a large problem among older adults
Periodontal disease ranges from gingivitis with swollen, red gums that may bleed, to periodontitis with gums pulling away from teeth, bone loss, and loose or lost teeth. PD is very prevalent in the United States, with some form of it occurring in 47% of people 30 years of age and older and in 70% of those 65 years and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
PD is more common in people with RA who have detectable ACPAs, and that link implicates oral mucosal inflammation in RA pathogenesis.
Investigating whether PD leads to RA
At Rockefeller University, Dr. Orange and her colleagues followed five female patients with RA who were seropositive for CCP over the course of 1-4 years. Two had severe PD, and three showed no signs of PD. Each week, participants provided finger-stick blood samples for RNA sequencing and B-cell repertoire sequencing, reported changes in their medication and dental work, and completed questionnaires. They also underwent monthly physical exams that evaluated tenderness and swelling in 28 joints, and they provided additional samples during self-reported flares.
At Stanford (Calif.) University, researchers isolated plasmablasts from blood samples collected from 12 donors with anti-CPP+ RA and healthy donors. They also analyzed synovial fluid samples from 65 RA and OA patients.
In addition, University of Colorado researchers collected plasma samples from patients with RA and healthy donors, and they classified the gingival health of participants.
The researchers found that the patients with PD also had repeated flare-ups of oral bacteria in the blood, mainly from the Streptococcaceae family, suggesting that the oral mucosa repeatedly broke down and introduced bacteria into the bloodstream. In the blood, inflammatory immune cells targeted the bacteria and released ACPAs, which have been linked with RA.
“Even without dental procedures, patients with RA and periodontal disease experience repeated episodes of bacteremia,” Dr. Orange said. “While dental procedures are known to be associated with dissemination of oral bacteria into the bloodstream, we didn’t expect to see this happening so frequently and independent of dental procedures. We also had thought that people with oral bacteria in their blood would have symptoms such as fever or malaise, but they were asymptomatic.”
Experts welcome the results
“It is well established that oral health impacts overall health. In particular, the link between periodontal disease and chronic systemic diseases has been explored in many robust studies,” Chi T. Viet, MD, DDS, PhD, oral and maxillofacial surgeon and associate professor at the Loma Linda (Calif.) University School of Dentistry, told this news organization.
“The study ... highlights the importance of early treatment and prevention of oral health issues, as they can have devastating systemic sequelae,” added Dr. Viet, who was not involved in the study.
Devon Charlton, MD, MPH, director of rheumatology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Regional Orthopedics in New Castle, Pa., advised patients and providers to team up to manage RA and PD.
“If the patient and provider aggressively treat periodontal disease and dental health in general, the patient decreases their risk of infection and inflammation, decreases the potential development of RA, and increases their future quality of life,” said Dr. Charlton, also not involved in the study.
However, findings from the study population may be difficult to generalize to other populations, he added.
Dr. Orange and her colleagues suggest further related research, including studies on whether treating PD makes RA easier to treat and whether the treatment of PD in patients whose RA is in clinical remission raises the likelihood of being able to discontinue therapy safely.
The study was supported through grant funding from the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robertson Foundation, Rockefeller University, the Bernard and Irene Schwartz Foundation, the Iris and Junming Le Foundation, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. Dr. Orange reports no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors report financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Viet and Dr. Charlton report no relevant financial relationships. All experts commented by email.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
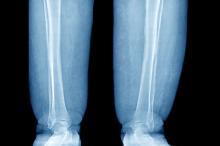
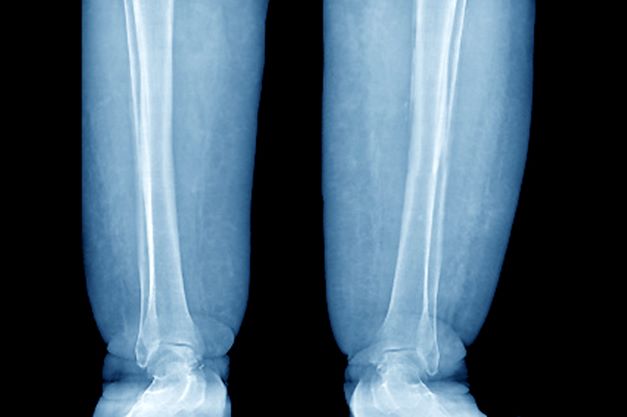
Swelling of the lower extremities
The patient is sent for lymphoscintigraphy, which showed impaired lymphatic drainage of both lower extremities consistent with obesity-induced lymphedema.
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by the abnormal development of the lymphatic system (primary lymphedema) or injury to lymphatic vasculature (secondary lymphedema). Chronic interstitial fluid accumulation may lead to fibrosis, persistent inflammation, and adipose deposition, which often results in massive hypertrophy. Obesity, which affects approximately 40% of the US population, is a rising cause of secondary lymphedema. Obesity-induced lymphedema (OIL) is a result of external compression of the lymphatic system by adipose tissue and increased production of lymph, which results in direct injury to the lymphatic endothelium. As BMI increases, lymphedema worsens and ambulation becomes more difficult, placing patients in an unfavorable cycle of weight gain and lymphatic injury.
The diagnosis of OIL is made by history and physical and is confirmed with diagnostic imaging. The classic presentation of lymphedema is edema of the lower extremities and a positive Stemmer sign. The Stemmer sign is positive if the examiner is unable to grab the dorsal skin between the thumb and index finger. The gold standard for lymphatic imaging is radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy. It involves injecting a tracer protein into the distal extremity, which should be taken up by the lymphatic vasculature and visualized in patients with normal lymphatic function. Lymphoscintigraphy has a high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (100%) for the diagnosis of lymphedema.
The risk for lymphatic dysfunction increases with elevated BMI. A BMI threshold appears to exist between 53 and 59, at which point lower-extremity lymphatic dysfunction begins to occur and is almost universal when BMI exceeds 60. Sixty percent of patients with OIL will develop massive localized lymphedema; the higher the BMI, the greater the risk for massive localized lymphedema. Typical areas of localized lymphedema include the lower extremities, genitals, and abdominal wall. In addition, patients with OIL are at increased risk for infections, such as cellulitis. Other complications of OIL include functional disabilities, psychosocial morbidity, and malignant transformation.
Patients at risk for OIL should be counseled and educated about weight management interventions, such as intensive treatment programs, lifestyle changes, and medications before their BMI reaches 50, a threshold where irreversible lower-extremity lymphedema may occur. Although weight loss may reduce symptoms of OIL, irreversible lymphatic dysfunction also may occur. Individuals at risk for OIL are often referred to a bariatric surgical weight management center.
Lymphedema management consists of compression regimens, physiotherapy, and manual lymphatic drainage. Adipose deposition in the late stages of lymphedema may decrease the response to such manual treatments. Operative procedures are typically used when these treatment options have been inadequate. Patients with chronic advanced lymphedema, in whom lymphatic impairment is accompanied by deposition of fibroadipose tissue, may also require debulking surgery.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The patient is sent for lymphoscintigraphy, which showed impaired lymphatic drainage of both lower extremities consistent with obesity-induced lymphedema.
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by the abnormal development of the lymphatic system (primary lymphedema) or injury to lymphatic vasculature (secondary lymphedema). Chronic interstitial fluid accumulation may lead to fibrosis, persistent inflammation, and adipose deposition, which often results in massive hypertrophy. Obesity, which affects approximately 40% of the US population, is a rising cause of secondary lymphedema. Obesity-induced lymphedema (OIL) is a result of external compression of the lymphatic system by adipose tissue and increased production of lymph, which results in direct injury to the lymphatic endothelium. As BMI increases, lymphedema worsens and ambulation becomes more difficult, placing patients in an unfavorable cycle of weight gain and lymphatic injury.
The diagnosis of OIL is made by history and physical and is confirmed with diagnostic imaging. The classic presentation of lymphedema is edema of the lower extremities and a positive Stemmer sign. The Stemmer sign is positive if the examiner is unable to grab the dorsal skin between the thumb and index finger. The gold standard for lymphatic imaging is radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy. It involves injecting a tracer protein into the distal extremity, which should be taken up by the lymphatic vasculature and visualized in patients with normal lymphatic function. Lymphoscintigraphy has a high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (100%) for the diagnosis of lymphedema.
The risk for lymphatic dysfunction increases with elevated BMI. A BMI threshold appears to exist between 53 and 59, at which point lower-extremity lymphatic dysfunction begins to occur and is almost universal when BMI exceeds 60. Sixty percent of patients with OIL will develop massive localized lymphedema; the higher the BMI, the greater the risk for massive localized lymphedema. Typical areas of localized lymphedema include the lower extremities, genitals, and abdominal wall. In addition, patients with OIL are at increased risk for infections, such as cellulitis. Other complications of OIL include functional disabilities, psychosocial morbidity, and malignant transformation.
Patients at risk for OIL should be counseled and educated about weight management interventions, such as intensive treatment programs, lifestyle changes, and medications before their BMI reaches 50, a threshold where irreversible lower-extremity lymphedema may occur. Although weight loss may reduce symptoms of OIL, irreversible lymphatic dysfunction also may occur. Individuals at risk for OIL are often referred to a bariatric surgical weight management center.
Lymphedema management consists of compression regimens, physiotherapy, and manual lymphatic drainage. Adipose deposition in the late stages of lymphedema may decrease the response to such manual treatments. Operative procedures are typically used when these treatment options have been inadequate. Patients with chronic advanced lymphedema, in whom lymphatic impairment is accompanied by deposition of fibroadipose tissue, may also require debulking surgery.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The patient is sent for lymphoscintigraphy, which showed impaired lymphatic drainage of both lower extremities consistent with obesity-induced lymphedema.
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by the abnormal development of the lymphatic system (primary lymphedema) or injury to lymphatic vasculature (secondary lymphedema). Chronic interstitial fluid accumulation may lead to fibrosis, persistent inflammation, and adipose deposition, which often results in massive hypertrophy. Obesity, which affects approximately 40% of the US population, is a rising cause of secondary lymphedema. Obesity-induced lymphedema (OIL) is a result of external compression of the lymphatic system by adipose tissue and increased production of lymph, which results in direct injury to the lymphatic endothelium. As BMI increases, lymphedema worsens and ambulation becomes more difficult, placing patients in an unfavorable cycle of weight gain and lymphatic injury.
The diagnosis of OIL is made by history and physical and is confirmed with diagnostic imaging. The classic presentation of lymphedema is edema of the lower extremities and a positive Stemmer sign. The Stemmer sign is positive if the examiner is unable to grab the dorsal skin between the thumb and index finger. The gold standard for lymphatic imaging is radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy. It involves injecting a tracer protein into the distal extremity, which should be taken up by the lymphatic vasculature and visualized in patients with normal lymphatic function. Lymphoscintigraphy has a high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (100%) for the diagnosis of lymphedema.
The risk for lymphatic dysfunction increases with elevated BMI. A BMI threshold appears to exist between 53 and 59, at which point lower-extremity lymphatic dysfunction begins to occur and is almost universal when BMI exceeds 60. Sixty percent of patients with OIL will develop massive localized lymphedema; the higher the BMI, the greater the risk for massive localized lymphedema. Typical areas of localized lymphedema include the lower extremities, genitals, and abdominal wall. In addition, patients with OIL are at increased risk for infections, such as cellulitis. Other complications of OIL include functional disabilities, psychosocial morbidity, and malignant transformation.
Patients at risk for OIL should be counseled and educated about weight management interventions, such as intensive treatment programs, lifestyle changes, and medications before their BMI reaches 50, a threshold where irreversible lower-extremity lymphedema may occur. Although weight loss may reduce symptoms of OIL, irreversible lymphatic dysfunction also may occur. Individuals at risk for OIL are often referred to a bariatric surgical weight management center.
Lymphedema management consists of compression regimens, physiotherapy, and manual lymphatic drainage. Adipose deposition in the late stages of lymphedema may decrease the response to such manual treatments. Operative procedures are typically used when these treatment options have been inadequate. Patients with chronic advanced lymphedema, in whom lymphatic impairment is accompanied by deposition of fibroadipose tissue, may also require debulking surgery.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, Pediatric Lead, Obesity Champion, TSPMG, Weight A Minute Clinic, Atlanta, Georgia.
Courtney Whittle, MD, MSW, Diplomate of ABOM, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 52-year-old woman presents with bilateral pain and swelling of the lower extremities. She is 5 ft 6 in tall and weighs 376 lb; her BMI is 60.7. Four years ago, the patient was injured in a car accident, which limited her mobility; at that time her BMI was 39. She complains of difficulty using her legs and has developed periodic infections of the lower limbs, which have been treated at the wound clinic. Past medical history is significant for diabetes and hypertension, managed with metformin and lisinopril. She reports no history of penetrating trauma, lymphadenectomy, recent travel, or radiation. On physical examination, there is pitting edema of the lower extremities and a positive Stemmer sign bilaterally.
Endometriosis: Whole-Body Effects, Treatments and Infertility
How does endometriosis affect the whole body, and how often is it misunderstood for another condition?
Dr. Taylor: Far too often, we think about endometriosis as just a cause of bad menstrual cramps. So many times, we miss the signs and falsely attribute symptoms to other diseases. I cannot tell you the number of people who have seen multiple practitioners for other conditions, when the underlying problem was actually endometriosis.
Endometriosis affects the whole body. It can affect the intestines, the bladder, and body weight, and the brain and mood. Endometriosis causes fatigue and inflammation, and in the long run it can lead to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. When we as physicians do surgery or laparoscopy, we find these little blue and brown lesions in the pelvis, and they certainly do cause pain, but that is not the whole disease.
Endometriosis heightens pain and nerve sensitivity for patients, and we should not dismiss the debilitating effect of these symptoms. Things actually do hurt more. In fact, the pain can spread from beyond the time of the menstrual period and spread to other areas besides the uterus.
We cannot ignore the totality of the effects of the disease and only focus on one part of the problem. More importantly, we cannot be distracted and discount endometriosis or mistake it for another condition. I have seen many patients who went to a gastroenterologist first and may even have had a colonoscopy because of some bowel symptoms, but then we come to find out it was endometriosis irritating the bowels at the time of their period and not another primary disease.
Another example is that the patient may see a urologist and have a cystoscopy to assess bladder pain, especially if the pain comes on around the time of menses. However, that pain is probably due to endometriosis irritating the bladder, not a primary bladder problem.
I have even had patients who were sent to a psychiatrist first because of anxiety that was actually being caused by the endometriosis. It is important to understand that treating the primary problem—endometriosis—should be our focus.
Which effects of this chronic disease can have the most long-term impact?
Dr. Taylor: It is important to understand that endometriosis has long-term effects on the entire body. For example, it affects the brain, increasing anxiety and depression. It causes pain sensitization, fatigue, and body inflammation. Endometriosis can also damage blood vessels or cause atherosclerosis.
A quick diagnosis is crucial because often this disease affects women at the most critical points in their life—either when they are in school, or in the early part of their career, when they need to be able to focus. It is important to get their endometriosis under control early and prevent long-term complications. Unfortunately, the long-term impacts are an aspect we do not focus on enough.
Infertility is another common long-term consequence of endometriosis. The sooner we can diagnose endometriosis, the sooner we can begin treatment and the more likely we can preserve someone's fertility. Our goal is to catch endometriosis early enough, preserve the patient’s fertility, and prevent any damage, so they hopefully will not have trouble getting pregnant or need medical intervention to get pregnant.
What methods do you use to diagnose endometriosis as quickly as possible?
Dr. Taylor: The sooner we can pinpoint the correct diagnosis and begin treatment, the more we can not only relieve patients of pain, but also stop that inflammation and all of these other manifestations of endometriosis so that they are not saddled with this for life.
We used to say you needed a laparoscopy to accurately diagnose endometriosis, and that statement is still true. You cannot see the most common types of endometriosis on an ultrasound or MRI. The endometriosis has to be pretty bad before you see it on an MRI or an ultrasound, and at that point it is often a big cyst in the ovary or a big nodule that is invasive.
However, you can diagnose endometriosis just by listening to your patients. If they have extremely painful menstrual cycles, dysmenorrhea, or painful menstrual cramps that get worse over the years, the problem is most likely endometriosis. You can rule out a few other things, and you can make that empiric clinical diagnosis of endometriosis. You can know with confidence that somebody likely has endometriosis. The treatments are benign. The first-line therapy would be to try a birth control pill. If we had to perform a laparoscopy before beginning endometriosis treatment, I think we would be doing our patients a huge disservice.
In addition to birth control pills, what are the most common therapeutic treatments you use in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Taylor: Birth control pills are still the first-line therapy. We use birth control pills because they are easy, well-tolerated, and inexpensive, but about a third of women will be resistant. Birth control pills are a great option when they work, but they do not always work 100% of the time.
We have a couple of other hormonal treatment options. Rarely, but occasionally, we use something called danazol, which is a mild male hormone. Side effects can be acne or hair growth, but it works well and is inexpensive. We used to give injectable agents, like leuprolide. Leuprolide is a harsh medication with once-a-month injections, and it puts someone in a temporary menopausal state with hot flashes and the possibility of decreased bone mineral density.
Today, we have the new class of GnRH antagonists that are a milder, gentler version of those injectable medications. They are oral, and you do not have to fully suppress estrogen levels all the way down to menopause. Patients can take the GnRH antagonists, stop treatment, and try to get pregnant at their next cycle.
Occasionally, we find that someone does not respond to any medical therapies, so surgery still has an important role. The usual reason for surgery is that you may suppress the active disease with medications, but the old damage is still there causing some pain, which can only be removed with surgery. Surgery is a good way to relieve that pain and it helps improve pregnancy rates for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive.
What does the future look like for endometriosis-related infertility, particularly related to in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
Dr. Taylor: We currently have an IVF trial in the works, in which we are using a hormone-suppressing GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) antagonist, elagolix, which suppresses endometriosis. The medication is administered before IVF. The goal is to determine if this approach leads to a better pregnancy rate in IVF cycles.
We are also working on nonhormonal medications in the laboratory, but these strategies are not yet ready for human clinical trials. These laboratory trials are investigating the basic biology of endometriosis, with the goal of learning what makes endometrial tissue grow in the wrong place, what makes it grow aggressively, and how it signals to other organs to cause damage.
We are looking at some additional nonhormonal medications that may possibly be used in someone trying to conceive, so that we can increase their chances of becoming pregnant. We are testing these medications in mice, but eventually we hope they progress to human clinical trials. The future for endometriosis therapy is nonhormonal treatments that can be used in somebody trying to conceive. That is what we have on the horizon.
Unfortunately for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive, all the classic first-line medications used to treat the condition are reproductive hormones that interfere with the ability to become pregnant. When we stop these medications, many women with endometriosis get pregnant spontaneously always suggest patients with endometriosis wishing to conceive try this approach, unless we know the endometriosis is very extensive. However, IVF is a good way to correct even the worst cases of endometriosis. As long as somebody has not waited until they are in their 40s and they have run out of eggs, IVF will usually correct endometriosis-related infertility.
Overall, how we treat endometriosis has been revolutionized and we have much better options than we had just 5 years ago. In my day-to-day practice, I recognize the importance of talking more openly about endometriosis, understanding the different symptoms, and not dismissing those connections. We should be able to talk about this important medical problem and all of its manifestations. I published a paper in The Lancet at the end of 2021 about the concept of endometriosis as a systemic whole-body disease and its effects. I think open conversations with patients about endometriosis is making a world of difference for the women with this disease.
How does endometriosis affect the whole body, and how often is it misunderstood for another condition?
Dr. Taylor: Far too often, we think about endometriosis as just a cause of bad menstrual cramps. So many times, we miss the signs and falsely attribute symptoms to other diseases. I cannot tell you the number of people who have seen multiple practitioners for other conditions, when the underlying problem was actually endometriosis.
Endometriosis affects the whole body. It can affect the intestines, the bladder, and body weight, and the brain and mood. Endometriosis causes fatigue and inflammation, and in the long run it can lead to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. When we as physicians do surgery or laparoscopy, we find these little blue and brown lesions in the pelvis, and they certainly do cause pain, but that is not the whole disease.
Endometriosis heightens pain and nerve sensitivity for patients, and we should not dismiss the debilitating effect of these symptoms. Things actually do hurt more. In fact, the pain can spread from beyond the time of the menstrual period and spread to other areas besides the uterus.
We cannot ignore the totality of the effects of the disease and only focus on one part of the problem. More importantly, we cannot be distracted and discount endometriosis or mistake it for another condition. I have seen many patients who went to a gastroenterologist first and may even have had a colonoscopy because of some bowel symptoms, but then we come to find out it was endometriosis irritating the bowels at the time of their period and not another primary disease.
Another example is that the patient may see a urologist and have a cystoscopy to assess bladder pain, especially if the pain comes on around the time of menses. However, that pain is probably due to endometriosis irritating the bladder, not a primary bladder problem.
I have even had patients who were sent to a psychiatrist first because of anxiety that was actually being caused by the endometriosis. It is important to understand that treating the primary problem—endometriosis—should be our focus.
Which effects of this chronic disease can have the most long-term impact?
Dr. Taylor: It is important to understand that endometriosis has long-term effects on the entire body. For example, it affects the brain, increasing anxiety and depression. It causes pain sensitization, fatigue, and body inflammation. Endometriosis can also damage blood vessels or cause atherosclerosis.
A quick diagnosis is crucial because often this disease affects women at the most critical points in their life—either when they are in school, or in the early part of their career, when they need to be able to focus. It is important to get their endometriosis under control early and prevent long-term complications. Unfortunately, the long-term impacts are an aspect we do not focus on enough.
Infertility is another common long-term consequence of endometriosis. The sooner we can diagnose endometriosis, the sooner we can begin treatment and the more likely we can preserve someone's fertility. Our goal is to catch endometriosis early enough, preserve the patient’s fertility, and prevent any damage, so they hopefully will not have trouble getting pregnant or need medical intervention to get pregnant.
What methods do you use to diagnose endometriosis as quickly as possible?
Dr. Taylor: The sooner we can pinpoint the correct diagnosis and begin treatment, the more we can not only relieve patients of pain, but also stop that inflammation and all of these other manifestations of endometriosis so that they are not saddled with this for life.
We used to say you needed a laparoscopy to accurately diagnose endometriosis, and that statement is still true. You cannot see the most common types of endometriosis on an ultrasound or MRI. The endometriosis has to be pretty bad before you see it on an MRI or an ultrasound, and at that point it is often a big cyst in the ovary or a big nodule that is invasive.
However, you can diagnose endometriosis just by listening to your patients. If they have extremely painful menstrual cycles, dysmenorrhea, or painful menstrual cramps that get worse over the years, the problem is most likely endometriosis. You can rule out a few other things, and you can make that empiric clinical diagnosis of endometriosis. You can know with confidence that somebody likely has endometriosis. The treatments are benign. The first-line therapy would be to try a birth control pill. If we had to perform a laparoscopy before beginning endometriosis treatment, I think we would be doing our patients a huge disservice.
In addition to birth control pills, what are the most common therapeutic treatments you use in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Taylor: Birth control pills are still the first-line therapy. We use birth control pills because they are easy, well-tolerated, and inexpensive, but about a third of women will be resistant. Birth control pills are a great option when they work, but they do not always work 100% of the time.
We have a couple of other hormonal treatment options. Rarely, but occasionally, we use something called danazol, which is a mild male hormone. Side effects can be acne or hair growth, but it works well and is inexpensive. We used to give injectable agents, like leuprolide. Leuprolide is a harsh medication with once-a-month injections, and it puts someone in a temporary menopausal state with hot flashes and the possibility of decreased bone mineral density.
Today, we have the new class of GnRH antagonists that are a milder, gentler version of those injectable medications. They are oral, and you do not have to fully suppress estrogen levels all the way down to menopause. Patients can take the GnRH antagonists, stop treatment, and try to get pregnant at their next cycle.
Occasionally, we find that someone does not respond to any medical therapies, so surgery still has an important role. The usual reason for surgery is that you may suppress the active disease with medications, but the old damage is still there causing some pain, which can only be removed with surgery. Surgery is a good way to relieve that pain and it helps improve pregnancy rates for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive.
What does the future look like for endometriosis-related infertility, particularly related to in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
Dr. Taylor: We currently have an IVF trial in the works, in which we are using a hormone-suppressing GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) antagonist, elagolix, which suppresses endometriosis. The medication is administered before IVF. The goal is to determine if this approach leads to a better pregnancy rate in IVF cycles.
We are also working on nonhormonal medications in the laboratory, but these strategies are not yet ready for human clinical trials. These laboratory trials are investigating the basic biology of endometriosis, with the goal of learning what makes endometrial tissue grow in the wrong place, what makes it grow aggressively, and how it signals to other organs to cause damage.
We are looking at some additional nonhormonal medications that may possibly be used in someone trying to conceive, so that we can increase their chances of becoming pregnant. We are testing these medications in mice, but eventually we hope they progress to human clinical trials. The future for endometriosis therapy is nonhormonal treatments that can be used in somebody trying to conceive. That is what we have on the horizon.
Unfortunately for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive, all the classic first-line medications used to treat the condition are reproductive hormones that interfere with the ability to become pregnant. When we stop these medications, many women with endometriosis get pregnant spontaneously always suggest patients with endometriosis wishing to conceive try this approach, unless we know the endometriosis is very extensive. However, IVF is a good way to correct even the worst cases of endometriosis. As long as somebody has not waited until they are in their 40s and they have run out of eggs, IVF will usually correct endometriosis-related infertility.
Overall, how we treat endometriosis has been revolutionized and we have much better options than we had just 5 years ago. In my day-to-day practice, I recognize the importance of talking more openly about endometriosis, understanding the different symptoms, and not dismissing those connections. We should be able to talk about this important medical problem and all of its manifestations. I published a paper in The Lancet at the end of 2021 about the concept of endometriosis as a systemic whole-body disease and its effects. I think open conversations with patients about endometriosis is making a world of difference for the women with this disease.
How does endometriosis affect the whole body, and how often is it misunderstood for another condition?
Dr. Taylor: Far too often, we think about endometriosis as just a cause of bad menstrual cramps. So many times, we miss the signs and falsely attribute symptoms to other diseases. I cannot tell you the number of people who have seen multiple practitioners for other conditions, when the underlying problem was actually endometriosis.
Endometriosis affects the whole body. It can affect the intestines, the bladder, and body weight, and the brain and mood. Endometriosis causes fatigue and inflammation, and in the long run it can lead to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease. When we as physicians do surgery or laparoscopy, we find these little blue and brown lesions in the pelvis, and they certainly do cause pain, but that is not the whole disease.
Endometriosis heightens pain and nerve sensitivity for patients, and we should not dismiss the debilitating effect of these symptoms. Things actually do hurt more. In fact, the pain can spread from beyond the time of the menstrual period and spread to other areas besides the uterus.
We cannot ignore the totality of the effects of the disease and only focus on one part of the problem. More importantly, we cannot be distracted and discount endometriosis or mistake it for another condition. I have seen many patients who went to a gastroenterologist first and may even have had a colonoscopy because of some bowel symptoms, but then we come to find out it was endometriosis irritating the bowels at the time of their period and not another primary disease.
Another example is that the patient may see a urologist and have a cystoscopy to assess bladder pain, especially if the pain comes on around the time of menses. However, that pain is probably due to endometriosis irritating the bladder, not a primary bladder problem.
I have even had patients who were sent to a psychiatrist first because of anxiety that was actually being caused by the endometriosis. It is important to understand that treating the primary problem—endometriosis—should be our focus.
Which effects of this chronic disease can have the most long-term impact?
Dr. Taylor: It is important to understand that endometriosis has long-term effects on the entire body. For example, it affects the brain, increasing anxiety and depression. It causes pain sensitization, fatigue, and body inflammation. Endometriosis can also damage blood vessels or cause atherosclerosis.
A quick diagnosis is crucial because often this disease affects women at the most critical points in their life—either when they are in school, or in the early part of their career, when they need to be able to focus. It is important to get their endometriosis under control early and prevent long-term complications. Unfortunately, the long-term impacts are an aspect we do not focus on enough.
Infertility is another common long-term consequence of endometriosis. The sooner we can diagnose endometriosis, the sooner we can begin treatment and the more likely we can preserve someone's fertility. Our goal is to catch endometriosis early enough, preserve the patient’s fertility, and prevent any damage, so they hopefully will not have trouble getting pregnant or need medical intervention to get pregnant.
What methods do you use to diagnose endometriosis as quickly as possible?
Dr. Taylor: The sooner we can pinpoint the correct diagnosis and begin treatment, the more we can not only relieve patients of pain, but also stop that inflammation and all of these other manifestations of endometriosis so that they are not saddled with this for life.
We used to say you needed a laparoscopy to accurately diagnose endometriosis, and that statement is still true. You cannot see the most common types of endometriosis on an ultrasound or MRI. The endometriosis has to be pretty bad before you see it on an MRI or an ultrasound, and at that point it is often a big cyst in the ovary or a big nodule that is invasive.
However, you can diagnose endometriosis just by listening to your patients. If they have extremely painful menstrual cycles, dysmenorrhea, or painful menstrual cramps that get worse over the years, the problem is most likely endometriosis. You can rule out a few other things, and you can make that empiric clinical diagnosis of endometriosis. You can know with confidence that somebody likely has endometriosis. The treatments are benign. The first-line therapy would be to try a birth control pill. If we had to perform a laparoscopy before beginning endometriosis treatment, I think we would be doing our patients a huge disservice.
In addition to birth control pills, what are the most common therapeutic treatments you use in day-to-day practice?
Dr. Taylor: Birth control pills are still the first-line therapy. We use birth control pills because they are easy, well-tolerated, and inexpensive, but about a third of women will be resistant. Birth control pills are a great option when they work, but they do not always work 100% of the time.
We have a couple of other hormonal treatment options. Rarely, but occasionally, we use something called danazol, which is a mild male hormone. Side effects can be acne or hair growth, but it works well and is inexpensive. We used to give injectable agents, like leuprolide. Leuprolide is a harsh medication with once-a-month injections, and it puts someone in a temporary menopausal state with hot flashes and the possibility of decreased bone mineral density.
Today, we have the new class of GnRH antagonists that are a milder, gentler version of those injectable medications. They are oral, and you do not have to fully suppress estrogen levels all the way down to menopause. Patients can take the GnRH antagonists, stop treatment, and try to get pregnant at their next cycle.
Occasionally, we find that someone does not respond to any medical therapies, so surgery still has an important role. The usual reason for surgery is that you may suppress the active disease with medications, but the old damage is still there causing some pain, which can only be removed with surgery. Surgery is a good way to relieve that pain and it helps improve pregnancy rates for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive.
What does the future look like for endometriosis-related infertility, particularly related to in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
Dr. Taylor: We currently have an IVF trial in the works, in which we are using a hormone-suppressing GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) antagonist, elagolix, which suppresses endometriosis. The medication is administered before IVF. The goal is to determine if this approach leads to a better pregnancy rate in IVF cycles.
We are also working on nonhormonal medications in the laboratory, but these strategies are not yet ready for human clinical trials. These laboratory trials are investigating the basic biology of endometriosis, with the goal of learning what makes endometrial tissue grow in the wrong place, what makes it grow aggressively, and how it signals to other organs to cause damage.
We are looking at some additional nonhormonal medications that may possibly be used in someone trying to conceive, so that we can increase their chances of becoming pregnant. We are testing these medications in mice, but eventually we hope they progress to human clinical trials. The future for endometriosis therapy is nonhormonal treatments that can be used in somebody trying to conceive. That is what we have on the horizon.
Unfortunately for people with endometriosis wishing to conceive, all the classic first-line medications used to treat the condition are reproductive hormones that interfere with the ability to become pregnant. When we stop these medications, many women with endometriosis get pregnant spontaneously always suggest patients with endometriosis wishing to conceive try this approach, unless we know the endometriosis is very extensive. However, IVF is a good way to correct even the worst cases of endometriosis. As long as somebody has not waited until they are in their 40s and they have run out of eggs, IVF will usually correct endometriosis-related infertility.
Overall, how we treat endometriosis has been revolutionized and we have much better options than we had just 5 years ago. In my day-to-day practice, I recognize the importance of talking more openly about endometriosis, understanding the different symptoms, and not dismissing those connections. We should be able to talk about this important medical problem and all of its manifestations. I published a paper in The Lancet at the end of 2021 about the concept of endometriosis as a systemic whole-body disease and its effects. I think open conversations with patients about endometriosis is making a world of difference for the women with this disease.
Topical or intralesional cidofovir an option for recalcitrant warts
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU – Combining or those located in areas that are challenging to treat, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA.
“There are 5 million office visits per year in the United States for warts and molluscum, and they’re most common in pediatrics,” Dr. Barbieri, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “In fact, some studies have suggested that one in three children in primary school suffers from warts.”
According to a 2012 Cochrane review of topical therapies for warts, first-line treatments such as salicylic acid, cryotherapy, 5-FU, or Candida antigen injection often have modest efficacy when used alone. For example, the authors found that salicylic acid and cryotherapy cleared warts in about 60%-70% of cases, respectively, but clearance rates were improved by combining the two therapies.
In an earlier literature review and meta-analysis, investigators evaluated the effect of 5-FU plus salicylic acid or salicylic acid alone. The therapeutic effect for common warts across all studies was a 63.4% response rate (complete healing) for 5-FU/SA vversus 23.1% for the 5-FU–free controls, respectively. For plantar warts, the response rate was 63% versus 11%, respectively.
“But what about the person with multiple warts or those in challenging locations where you might worry about destructive treatments hurting the nail fold or causing nail dystrophy?” Dr. Barbieri asked. “Maybe they’ve used salicylic acid or intralesional Candida and they’re still not getting better. What can we do for these patients?”
Emerging research suggests that topical cidofovir can be a valuable option for recalcitrant warts or those in sensitive locations. In a case report of a 10-year-old boy with more than 50 severe verrucous papules on his hands and face that were recalcitrant to multiple conventional therapies, topical 1% cidofovir applied daily for 8 weeks was effective, with no adverse side effects. A young female patient who presented to Dr. Barbieri with multiple warts around the nail matrix of several fingers experienced complete clearance after treatment with topical cidofovir, he said. Other researchers found this approach to be effective for plantar warts as well, in a report of two brothers with severe combined immunodeficiency after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with persistent warts that did not respond to traditional topical treatments.
“Topical cidofovir is typically a painless treatment, which is nice, especially for our pediatric patients who might be afraid of other therapies like or cryotherapy or intralesional injections,” One limitation is that it is “a bit expensive,” Dr. Barbieri said. “To have topical cidofovir compounded is typically $100-$300, depending on the quantity and strength that you ask for.”
Intralesional cidofovir is another treatment option. In a retrospective study of 58 patients, Dr. Barbieri and colleagues evaluated the outcome of intralesional cidofovir treatment of warts in immunocompromised and nonimmunocompromised patients. Rates of improvement ranged from 98.3% to 100%, while resolution rates ranged from 75.9% to 97.6%.
“Most of the patients had warts for more than 5 years and almost half of them had recalcitrant warts,” Dr. Barbieri said. “These were mostly adult patients, but I think this is a treatment that can work in younger populations as well. About 10%-15% had HIV or cancer or diabetes or were transplant recipients, but despite these challenges and despite these recalcitrant warts, about 100% had improvement.”
He pointed out that cidofovir is available as a 75 mg/mL vial that comes with a 5 mL single-use vial. He dilutes this with normal saline to create a 15 mg/mL solution.
“If you want to be efficient you can try to schedule multiple patients together on the same day as a single vial is sufficient to treat about 25 patients,” assuming about 1 mL is injected per patient, he said. “The challenge with intralesional cidofovir is that it’s painful beyond just the needle part of the injection. Sometimes a nerve block can be helpful. But this can be an effective treatment for patients with recalcitrant warts or those with comorbidities.”
Other intralesional therapies to try for recalcitrant warts, he said, include bleomycin (1 U/mL solution, 1-2 mL per treatment, spaced every 2-4 weeks), and 5-FU (a 4:1 mixture of 5-FU [50 mg/mL] and 2% lidocaine).
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPELIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Too many screenings, too little time, not enough payment
Pediatricians have long charted the vitals of children and adolescents – height, weight, blood pressure – to ensure that kids are healthy and developing as they should. This is the core of the profession. But today the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that pediatricians also perform maternal depression screenings, childhood depression screenings, autism screenings, and suicide risk screenings once children become 12 years old in addition to other screenings. Specific screening tools might include the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (MCHAT) for autism screening, the PHQ2 and PHQ9 (part of the longer Patient Health Questionnaire) for depression screening, and the Suicide Behavior Questionnaire Revised (SBQ-R) for suicide screening.
The AAP’s list of recommended screenings – which are developed by various research groups and endorsed by AAP – includes approximately 30 screenings in all, which vary somewhat depending on age. Seven screenings are mental and behavioral health assessments that would, depending on the screening results, require other expertise to address.
“We all want to keep [children] healthy. We actually do want to do these screenings, because they can be very helpful,” said Herschel Lessin, MD, of the Children’s Medical Group in Hopewell Junction, N.Y. Dr. Lessin’s concern is that he may not have anywhere to refer children and their families if he conducts a screening that flags something concerning such as a deeply depressed teenager. Sometimes first appointments with mental health professionals are not available for months.
“Sure – they want us to screen for depression, they want us to screen for anxiety. OK, you get a positive. What do you do? Well, guess what – there are no resources for children and mental health in this country,” Dr. Lessin said.
In Dr. Lessin’s view, economic realities prevent pediatricians from performing detailed psychological screenings anyway – no matter how useful or evidence based they might be, even if mental health support was abundant. He estimates that his practice conducts 20-25 visits a day, around 20 minutes each, of which maybe a dozen are well-child visits, just to keep the doors open. If he thoroughly screened every child or adolescent in the manner recommended by the AAP, Dr. Lessin said, he could do a fraction of that volume and would have to close his doors as a result.
Beside the time burden, insurers reimburse developmental and psychological screenings at low rates, Dr. Lessin said, even with claims that accurately itemize every screening delivered.
“Insurance companies refuse to pay adequately for any of this stuff. They expect me to do it for free, or do it for pennies,” Dr. Lessin said. He said that the natural result of such an arrangement is that some pediatricians stop taking insurance and only work with families that can afford their rates, further entrenching unequal health care by catering to wealthy families who can afford to pay for longer visits. Other pediatricians just don’t do all of the recommended screenings.
“I don’t want it to sound like I’m whining about being paid. They don’t adequately resource what they expect us to do, which is to be society’s social worker,” Dr. Lessin said.
Practical advice for interpreting and prioritizing screenings
Other pediatricians called for screening developers to include guidance for pediatricians about how to counsel families when a screening turns up a concerning result.
“What can we do as pediatricians in that moment to help that family?” asked Karalyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire in Cheshire, Conn.
Sometimes the path forward is clear, as with an autism screening; in those cases, Dr. Kinsella said, Connecticut requires referral for a full autism evaluation from birth to age 3. But for other situations, such as an anxiety screening, it is less clear how to proceed.
Dr. Kinsella said that in her experience in-person appointments with a mental health professional, compared with telehealth, work best for her patients. This enables the teenager to find a good fit with a therapist, which can take time when first appointments are so elusive. Any support for pediatricians to bridge the gap until therapy is established is welcome.
“It would be great if it came along with some training – just a brief training – of some ways we can help families before they get into a therapist, or before it gets to the point that they need therapy,” Dr. Kinsella said.
Dr. Kinsella stressed that pediatricians need to use their own judgment when interpreting screening results. Sometimes the MCHAT will miss cases of autism, for example, or the PHQ9 will flag a teenager for depression who is actually just fidgety and having some trouble sleeping.
In her view, the existence of such screens – which might also include screenings for drug abuse, toxic stress, or food insecurity, along with autism, anxiety, and maternal or child depression – is a good development, despite their imperfections and the difficulties of getting help in a timely manner.
“Twenty years ago we really didn’t have any screens,” Dr. Kinsella said.
But it may be that there are now too many recommended screens in pediatrics, even if they all individually have value.
“In the adult world, screenings haven’t mushroomed as in pediatrics” said Dr. Timothy J. Joos, MD, MPH, who practices combined internal medicine and pediatrics at Neighborcare Health in Seattle. Recommended adult health screenings are largely driven by the work of the United States Preventive Services Task Force, which requires a high level of evidence before a screening is recommended. The pediatrics screening world, in Dr. Joos’s view, is populated by a more diffuse set of actors and has therefore inevitably resulted in a profusion of recommended screenings.
Although its main focus is adults, Dr. Joos noted that the USPSTF has evaluated many of the pediatric screenings currently endorsed by AAP. Sometimes there is strong evidence for these screenings, such as universal screening for depression and anxiety in older children. But Dr. Joos noted that per the USPSTF, many of the screenings now recommended by AAP on asymptomatic children for autism, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or anemia don’t have strong evidence on a population level.
“In many cases, we have a good screen, but it just lacks the research,” Dr. Joos said. Nonetheless, every screening is recommended with “equal weight,” Dr. Joos said, calling for AAP to offer a more prioritized approach to screening rather than an “all comers” approach.
“If you don’t set priorities, you don’t have priorities,” Dr. Joos said, which leads to untenable expectations for what can be accomplished during short visits.
AAP responds
Susan Kressly, MD, who chairs AAP’s Section on Administration and Practice and is a consultant based in Sanibel, Fla., said that we know that using targeting screenings will miss a significant proportion of patients whom you could better assist and care for; for example, if you just go by your gut feeling about whether kids are using drugs or alcohol and just screen those kids. Every screening endorsed by AAP has some degree of evidence for use at a population level rather than case by case, Dr. Kressly noted.
This doesn’t mean that every single screening must be done at each and every recommended interval, she emphasized.
“The first priority is what’s important to the patient and the family. While we understand that screening is at a population health level, there should be some intelligent use and prioritization of these screening tools,” Dr. Kressly said. As examples, Dr. Kressly noted that there is no need to keep administering autism screenings in families whose children already receive autism services, or to ask a teenager questions about anxiety they had answered 6 weeks earlier.
The screenings should be seen as a tool for enhancing relationships with children and their families, not as a series of endless tasks, Dr. Kressly concluded.
Dr. Lessin’s priority is that pediatricians get more support – time, money, training, adequately resourced mental health care – to carry out their expanded role.
“Pediatricians are pretty nice. We want to do the right thing, but everything blocks us from doing it,” Dr. Lessin said.
Dr. Joos, Dr. Kinsella, and Dr. Lessin are on the MDedge Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Pediatricians have long charted the vitals of children and adolescents – height, weight, blood pressure – to ensure that kids are healthy and developing as they should. This is the core of the profession. But today the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that pediatricians also perform maternal depression screenings, childhood depression screenings, autism screenings, and suicide risk screenings once children become 12 years old in addition to other screenings. Specific screening tools might include the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (MCHAT) for autism screening, the PHQ2 and PHQ9 (part of the longer Patient Health Questionnaire) for depression screening, and the Suicide Behavior Questionnaire Revised (SBQ-R) for suicide screening.
The AAP’s list of recommended screenings – which are developed by various research groups and endorsed by AAP – includes approximately 30 screenings in all, which vary somewhat depending on age. Seven screenings are mental and behavioral health assessments that would, depending on the screening results, require other expertise to address.
“We all want to keep [children] healthy. We actually do want to do these screenings, because they can be very helpful,” said Herschel Lessin, MD, of the Children’s Medical Group in Hopewell Junction, N.Y. Dr. Lessin’s concern is that he may not have anywhere to refer children and their families if he conducts a screening that flags something concerning such as a deeply depressed teenager. Sometimes first appointments with mental health professionals are not available for months.
“Sure – they want us to screen for depression, they want us to screen for anxiety. OK, you get a positive. What do you do? Well, guess what – there are no resources for children and mental health in this country,” Dr. Lessin said.
In Dr. Lessin’s view, economic realities prevent pediatricians from performing detailed psychological screenings anyway – no matter how useful or evidence based they might be, even if mental health support was abundant. He estimates that his practice conducts 20-25 visits a day, around 20 minutes each, of which maybe a dozen are well-child visits, just to keep the doors open. If he thoroughly screened every child or adolescent in the manner recommended by the AAP, Dr. Lessin said, he could do a fraction of that volume and would have to close his doors as a result.
Beside the time burden, insurers reimburse developmental and psychological screenings at low rates, Dr. Lessin said, even with claims that accurately itemize every screening delivered.
“Insurance companies refuse to pay adequately for any of this stuff. They expect me to do it for free, or do it for pennies,” Dr. Lessin said. He said that the natural result of such an arrangement is that some pediatricians stop taking insurance and only work with families that can afford their rates, further entrenching unequal health care by catering to wealthy families who can afford to pay for longer visits. Other pediatricians just don’t do all of the recommended screenings.
“I don’t want it to sound like I’m whining about being paid. They don’t adequately resource what they expect us to do, which is to be society’s social worker,” Dr. Lessin said.
Practical advice for interpreting and prioritizing screenings
Other pediatricians called for screening developers to include guidance for pediatricians about how to counsel families when a screening turns up a concerning result.
“What can we do as pediatricians in that moment to help that family?” asked Karalyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire in Cheshire, Conn.
Sometimes the path forward is clear, as with an autism screening; in those cases, Dr. Kinsella said, Connecticut requires referral for a full autism evaluation from birth to age 3. But for other situations, such as an anxiety screening, it is less clear how to proceed.
Dr. Kinsella said that in her experience in-person appointments with a mental health professional, compared with telehealth, work best for her patients. This enables the teenager to find a good fit with a therapist, which can take time when first appointments are so elusive. Any support for pediatricians to bridge the gap until therapy is established is welcome.
“It would be great if it came along with some training – just a brief training – of some ways we can help families before they get into a therapist, or before it gets to the point that they need therapy,” Dr. Kinsella said.
Dr. Kinsella stressed that pediatricians need to use their own judgment when interpreting screening results. Sometimes the MCHAT will miss cases of autism, for example, or the PHQ9 will flag a teenager for depression who is actually just fidgety and having some trouble sleeping.
In her view, the existence of such screens – which might also include screenings for drug abuse, toxic stress, or food insecurity, along with autism, anxiety, and maternal or child depression – is a good development, despite their imperfections and the difficulties of getting help in a timely manner.
“Twenty years ago we really didn’t have any screens,” Dr. Kinsella said.
But it may be that there are now too many recommended screens in pediatrics, even if they all individually have value.
“In the adult world, screenings haven’t mushroomed as in pediatrics” said Dr. Timothy J. Joos, MD, MPH, who practices combined internal medicine and pediatrics at Neighborcare Health in Seattle. Recommended adult health screenings are largely driven by the work of the United States Preventive Services Task Force, which requires a high level of evidence before a screening is recommended. The pediatrics screening world, in Dr. Joos’s view, is populated by a more diffuse set of actors and has therefore inevitably resulted in a profusion of recommended screenings.
Although its main focus is adults, Dr. Joos noted that the USPSTF has evaluated many of the pediatric screenings currently endorsed by AAP. Sometimes there is strong evidence for these screenings, such as universal screening for depression and anxiety in older children. But Dr. Joos noted that per the USPSTF, many of the screenings now recommended by AAP on asymptomatic children for autism, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or anemia don’t have strong evidence on a population level.
“In many cases, we have a good screen, but it just lacks the research,” Dr. Joos said. Nonetheless, every screening is recommended with “equal weight,” Dr. Joos said, calling for AAP to offer a more prioritized approach to screening rather than an “all comers” approach.
“If you don’t set priorities, you don’t have priorities,” Dr. Joos said, which leads to untenable expectations for what can be accomplished during short visits.
AAP responds
Susan Kressly, MD, who chairs AAP’s Section on Administration and Practice and is a consultant based in Sanibel, Fla., said that we know that using targeting screenings will miss a significant proportion of patients whom you could better assist and care for; for example, if you just go by your gut feeling about whether kids are using drugs or alcohol and just screen those kids. Every screening endorsed by AAP has some degree of evidence for use at a population level rather than case by case, Dr. Kressly noted.
This doesn’t mean that every single screening must be done at each and every recommended interval, she emphasized.
“The first priority is what’s important to the patient and the family. While we understand that screening is at a population health level, there should be some intelligent use and prioritization of these screening tools,” Dr. Kressly said. As examples, Dr. Kressly noted that there is no need to keep administering autism screenings in families whose children already receive autism services, or to ask a teenager questions about anxiety they had answered 6 weeks earlier.
The screenings should be seen as a tool for enhancing relationships with children and their families, not as a series of endless tasks, Dr. Kressly concluded.
Dr. Lessin’s priority is that pediatricians get more support – time, money, training, adequately resourced mental health care – to carry out their expanded role.
“Pediatricians are pretty nice. We want to do the right thing, but everything blocks us from doing it,” Dr. Lessin said.
Dr. Joos, Dr. Kinsella, and Dr. Lessin are on the MDedge Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Pediatricians have long charted the vitals of children and adolescents – height, weight, blood pressure – to ensure that kids are healthy and developing as they should. This is the core of the profession. But today the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that pediatricians also perform maternal depression screenings, childhood depression screenings, autism screenings, and suicide risk screenings once children become 12 years old in addition to other screenings. Specific screening tools might include the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (MCHAT) for autism screening, the PHQ2 and PHQ9 (part of the longer Patient Health Questionnaire) for depression screening, and the Suicide Behavior Questionnaire Revised (SBQ-R) for suicide screening.
The AAP’s list of recommended screenings – which are developed by various research groups and endorsed by AAP – includes approximately 30 screenings in all, which vary somewhat depending on age. Seven screenings are mental and behavioral health assessments that would, depending on the screening results, require other expertise to address.
“We all want to keep [children] healthy. We actually do want to do these screenings, because they can be very helpful,” said Herschel Lessin, MD, of the Children’s Medical Group in Hopewell Junction, N.Y. Dr. Lessin’s concern is that he may not have anywhere to refer children and their families if he conducts a screening that flags something concerning such as a deeply depressed teenager. Sometimes first appointments with mental health professionals are not available for months.
“Sure – they want us to screen for depression, they want us to screen for anxiety. OK, you get a positive. What do you do? Well, guess what – there are no resources for children and mental health in this country,” Dr. Lessin said.
In Dr. Lessin’s view, economic realities prevent pediatricians from performing detailed psychological screenings anyway – no matter how useful or evidence based they might be, even if mental health support was abundant. He estimates that his practice conducts 20-25 visits a day, around 20 minutes each, of which maybe a dozen are well-child visits, just to keep the doors open. If he thoroughly screened every child or adolescent in the manner recommended by the AAP, Dr. Lessin said, he could do a fraction of that volume and would have to close his doors as a result.
Beside the time burden, insurers reimburse developmental and psychological screenings at low rates, Dr. Lessin said, even with claims that accurately itemize every screening delivered.
“Insurance companies refuse to pay adequately for any of this stuff. They expect me to do it for free, or do it for pennies,” Dr. Lessin said. He said that the natural result of such an arrangement is that some pediatricians stop taking insurance and only work with families that can afford their rates, further entrenching unequal health care by catering to wealthy families who can afford to pay for longer visits. Other pediatricians just don’t do all of the recommended screenings.
“I don’t want it to sound like I’m whining about being paid. They don’t adequately resource what they expect us to do, which is to be society’s social worker,” Dr. Lessin said.
Practical advice for interpreting and prioritizing screenings
Other pediatricians called for screening developers to include guidance for pediatricians about how to counsel families when a screening turns up a concerning result.
“What can we do as pediatricians in that moment to help that family?” asked Karalyn Kinsella, MD, of Pediatric Associates of Cheshire in Cheshire, Conn.
Sometimes the path forward is clear, as with an autism screening; in those cases, Dr. Kinsella said, Connecticut requires referral for a full autism evaluation from birth to age 3. But for other situations, such as an anxiety screening, it is less clear how to proceed.
Dr. Kinsella said that in her experience in-person appointments with a mental health professional, compared with telehealth, work best for her patients. This enables the teenager to find a good fit with a therapist, which can take time when first appointments are so elusive. Any support for pediatricians to bridge the gap until therapy is established is welcome.
“It would be great if it came along with some training – just a brief training – of some ways we can help families before they get into a therapist, or before it gets to the point that they need therapy,” Dr. Kinsella said.
Dr. Kinsella stressed that pediatricians need to use their own judgment when interpreting screening results. Sometimes the MCHAT will miss cases of autism, for example, or the PHQ9 will flag a teenager for depression who is actually just fidgety and having some trouble sleeping.
In her view, the existence of such screens – which might also include screenings for drug abuse, toxic stress, or food insecurity, along with autism, anxiety, and maternal or child depression – is a good development, despite their imperfections and the difficulties of getting help in a timely manner.
“Twenty years ago we really didn’t have any screens,” Dr. Kinsella said.
But it may be that there are now too many recommended screens in pediatrics, even if they all individually have value.
“In the adult world, screenings haven’t mushroomed as in pediatrics” said Dr. Timothy J. Joos, MD, MPH, who practices combined internal medicine and pediatrics at Neighborcare Health in Seattle. Recommended adult health screenings are largely driven by the work of the United States Preventive Services Task Force, which requires a high level of evidence before a screening is recommended. The pediatrics screening world, in Dr. Joos’s view, is populated by a more diffuse set of actors and has therefore inevitably resulted in a profusion of recommended screenings.
Although its main focus is adults, Dr. Joos noted that the USPSTF has evaluated many of the pediatric screenings currently endorsed by AAP. Sometimes there is strong evidence for these screenings, such as universal screening for depression and anxiety in older children. But Dr. Joos noted that per the USPSTF, many of the screenings now recommended by AAP on asymptomatic children for autism, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or anemia don’t have strong evidence on a population level.
“In many cases, we have a good screen, but it just lacks the research,” Dr. Joos said. Nonetheless, every screening is recommended with “equal weight,” Dr. Joos said, calling for AAP to offer a more prioritized approach to screening rather than an “all comers” approach.
“If you don’t set priorities, you don’t have priorities,” Dr. Joos said, which leads to untenable expectations for what can be accomplished during short visits.
AAP responds
Susan Kressly, MD, who chairs AAP’s Section on Administration and Practice and is a consultant based in Sanibel, Fla., said that we know that using targeting screenings will miss a significant proportion of patients whom you could better assist and care for; for example, if you just go by your gut feeling about whether kids are using drugs or alcohol and just screen those kids. Every screening endorsed by AAP has some degree of evidence for use at a population level rather than case by case, Dr. Kressly noted.
This doesn’t mean that every single screening must be done at each and every recommended interval, she emphasized.
“The first priority is what’s important to the patient and the family. While we understand that screening is at a population health level, there should be some intelligent use and prioritization of these screening tools,” Dr. Kressly said. As examples, Dr. Kressly noted that there is no need to keep administering autism screenings in families whose children already receive autism services, or to ask a teenager questions about anxiety they had answered 6 weeks earlier.
The screenings should be seen as a tool for enhancing relationships with children and their families, not as a series of endless tasks, Dr. Kressly concluded.
Dr. Lessin’s priority is that pediatricians get more support – time, money, training, adequately resourced mental health care – to carry out their expanded role.
“Pediatricians are pretty nice. We want to do the right thing, but everything blocks us from doing it,” Dr. Lessin said.
Dr. Joos, Dr. Kinsella, and Dr. Lessin are on the MDedge Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
New AHA statement urges focus on CV risk before pregnancy
Increased public health and research efforts to optimize prepregnancy cardiovascular health are needed, particularly among those in under-represented racial and ethnic groups, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
“We have released this statement at this time because there is a maternal health crisis in the U.S. with rising maternal morbidity and mortality rates, which are the highest among high-income countries,” chair of the scientific statement writing group, Sadiya S. Khan, MD, told this news organization.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death during pregnancy and the postpartum period and represents 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, the statement reports.
“While there is a lot of emphasis in trying to reduce cardiovascular risk during the period of actual pregnancy, much of that risk has often already developed and the women have been living with it for some time, so interventions during pregnancy may be too late,” Dr. Khan, assistant professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, said.
“We wanted to try and emphasize the importance of starting to reduce cardiovascular risk earlier before pregnancy. In terms of improving cardiovascular health, this should have benefits both for the mother and the child,” she added.
The statement, “Optimizing Prepregnancy Cardiovascular Health to Improve Outcomes in Pregnant and Postpartum Individuals and Offspring” was published online in a “Go Red For Women” spotlight issue of the AHA publication Circulation.
Currently, nearly one in five births are complicated by such an adverse pregnancy outcome, and there is a strong association between these complications and risk for subsequent cardiovascular disease.
Prepregnancy window
Over the past decade, rates of adverse pregnancy outcomes have increased significantly in the United States, with a near doubling in rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and there are persistent disparities, with Black individuals significantly more likely to experience adverse pregnancy outcomes, the statement notes.
Emerging data suggest that these complications have, at least in part, prepregnancy origins. Thus, the prepregnancy period may be a critical window during which interventions have a great potential for benefit in both women and their offspring, it says.
The authors suggest a life-course approach to measure, modify, and monitor prepregnancy cardiovascular health, with all clinicians who interact with pregnancy-capable individuals emphasizing optimization of cardiovascular health beginning early in childhood.
“Leveraging these opportunities to target cardiovascular health has the potential to improve health across the life course and for subsequent generations,” they add.
Critical research gap
Despite the evidence linking an individual’s prepregnancy health to their offspring’s health, there are no large trials to test whether improving overall cardiovascular health before pregnancy will reduce pregnancy complications, pregnancy-related cardiovascular death, or cardiovascular risk for offspring. The statement authors suggest that such a trial should be considered.
“This would be a big undertaking, but it could be feasible and could be really impactful,” Dr. Khan said. “Of course it would be challenging to recruit women who are planning a pregnancy and to follow them to see if they do get pregnant and consider interventions and outcomes, but given the importance of the need, we think this is something that should be invested in.”
She pointed out that the main way to improve the cardiovascular health of this cohort would be through behavioral counseling on physical activity and diet. “We need to develop strategies tailored to this age group – young women and those who may already have young children – and often the last thing they are thinking about is themselves and their own health.”
She explained that while it is presumed that controlling cardiovascular risk factors will be beneficial, the bigger question is how that can be achieved. “Behavioral interventions are difficult to achieve and often have low adherence, so the focus of the trials should be on strategies on how to deliver behavioral counseling to achieve better cardiovascular health in this population.”
Dr. Khan stressed that any approaches to improving prepregnancy cardiovascular health must address the current racial disparities that are present. “We must make sure that our policies are successful not just in improving cardiovascular health but to ensure it is done equitably. We must find ways to ensure all individuals can access care.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Increased public health and research efforts to optimize prepregnancy cardiovascular health are needed, particularly among those in under-represented racial and ethnic groups, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
“We have released this statement at this time because there is a maternal health crisis in the U.S. with rising maternal morbidity and mortality rates, which are the highest among high-income countries,” chair of the scientific statement writing group, Sadiya S. Khan, MD, told this news organization.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death during pregnancy and the postpartum period and represents 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, the statement reports.
“While there is a lot of emphasis in trying to reduce cardiovascular risk during the period of actual pregnancy, much of that risk has often already developed and the women have been living with it for some time, so interventions during pregnancy may be too late,” Dr. Khan, assistant professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, said.
“We wanted to try and emphasize the importance of starting to reduce cardiovascular risk earlier before pregnancy. In terms of improving cardiovascular health, this should have benefits both for the mother and the child,” she added.
The statement, “Optimizing Prepregnancy Cardiovascular Health to Improve Outcomes in Pregnant and Postpartum Individuals and Offspring” was published online in a “Go Red For Women” spotlight issue of the AHA publication Circulation.
Currently, nearly one in five births are complicated by such an adverse pregnancy outcome, and there is a strong association between these complications and risk for subsequent cardiovascular disease.
Prepregnancy window
Over the past decade, rates of adverse pregnancy outcomes have increased significantly in the United States, with a near doubling in rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and there are persistent disparities, with Black individuals significantly more likely to experience adverse pregnancy outcomes, the statement notes.
Emerging data suggest that these complications have, at least in part, prepregnancy origins. Thus, the prepregnancy period may be a critical window during which interventions have a great potential for benefit in both women and their offspring, it says.
The authors suggest a life-course approach to measure, modify, and monitor prepregnancy cardiovascular health, with all clinicians who interact with pregnancy-capable individuals emphasizing optimization of cardiovascular health beginning early in childhood.
“Leveraging these opportunities to target cardiovascular health has the potential to improve health across the life course and for subsequent generations,” they add.
Critical research gap
Despite the evidence linking an individual’s prepregnancy health to their offspring’s health, there are no large trials to test whether improving overall cardiovascular health before pregnancy will reduce pregnancy complications, pregnancy-related cardiovascular death, or cardiovascular risk for offspring. The statement authors suggest that such a trial should be considered.
“This would be a big undertaking, but it could be feasible and could be really impactful,” Dr. Khan said. “Of course it would be challenging to recruit women who are planning a pregnancy and to follow them to see if they do get pregnant and consider interventions and outcomes, but given the importance of the need, we think this is something that should be invested in.”
She pointed out that the main way to improve the cardiovascular health of this cohort would be through behavioral counseling on physical activity and diet. “We need to develop strategies tailored to this age group – young women and those who may already have young children – and often the last thing they are thinking about is themselves and their own health.”
She explained that while it is presumed that controlling cardiovascular risk factors will be beneficial, the bigger question is how that can be achieved. “Behavioral interventions are difficult to achieve and often have low adherence, so the focus of the trials should be on strategies on how to deliver behavioral counseling to achieve better cardiovascular health in this population.”
Dr. Khan stressed that any approaches to improving prepregnancy cardiovascular health must address the current racial disparities that are present. “We must make sure that our policies are successful not just in improving cardiovascular health but to ensure it is done equitably. We must find ways to ensure all individuals can access care.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Increased public health and research efforts to optimize prepregnancy cardiovascular health are needed, particularly among those in under-represented racial and ethnic groups, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
“We have released this statement at this time because there is a maternal health crisis in the U.S. with rising maternal morbidity and mortality rates, which are the highest among high-income countries,” chair of the scientific statement writing group, Sadiya S. Khan, MD, told this news organization.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death during pregnancy and the postpartum period and represents 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, the statement reports.
“While there is a lot of emphasis in trying to reduce cardiovascular risk during the period of actual pregnancy, much of that risk has often already developed and the women have been living with it for some time, so interventions during pregnancy may be too late,” Dr. Khan, assistant professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago, said.
“We wanted to try and emphasize the importance of starting to reduce cardiovascular risk earlier before pregnancy. In terms of improving cardiovascular health, this should have benefits both for the mother and the child,” she added.
The statement, “Optimizing Prepregnancy Cardiovascular Health to Improve Outcomes in Pregnant and Postpartum Individuals and Offspring” was published online in a “Go Red For Women” spotlight issue of the AHA publication Circulation.
Currently, nearly one in five births are complicated by such an adverse pregnancy outcome, and there is a strong association between these complications and risk for subsequent cardiovascular disease.
Prepregnancy window
Over the past decade, rates of adverse pregnancy outcomes have increased significantly in the United States, with a near doubling in rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and there are persistent disparities, with Black individuals significantly more likely to experience adverse pregnancy outcomes, the statement notes.
Emerging data suggest that these complications have, at least in part, prepregnancy origins. Thus, the prepregnancy period may be a critical window during which interventions have a great potential for benefit in both women and their offspring, it says.
The authors suggest a life-course approach to measure, modify, and monitor prepregnancy cardiovascular health, with all clinicians who interact with pregnancy-capable individuals emphasizing optimization of cardiovascular health beginning early in childhood.
“Leveraging these opportunities to target cardiovascular health has the potential to improve health across the life course and for subsequent generations,” they add.
Critical research gap
Despite the evidence linking an individual’s prepregnancy health to their offspring’s health, there are no large trials to test whether improving overall cardiovascular health before pregnancy will reduce pregnancy complications, pregnancy-related cardiovascular death, or cardiovascular risk for offspring. The statement authors suggest that such a trial should be considered.
“This would be a big undertaking, but it could be feasible and could be really impactful,” Dr. Khan said. “Of course it would be challenging to recruit women who are planning a pregnancy and to follow them to see if they do get pregnant and consider interventions and outcomes, but given the importance of the need, we think this is something that should be invested in.”
She pointed out that the main way to improve the cardiovascular health of this cohort would be through behavioral counseling on physical activity and diet. “We need to develop strategies tailored to this age group – young women and those who may already have young children – and often the last thing they are thinking about is themselves and their own health.”
She explained that while it is presumed that controlling cardiovascular risk factors will be beneficial, the bigger question is how that can be achieved. “Behavioral interventions are difficult to achieve and often have low adherence, so the focus of the trials should be on strategies on how to deliver behavioral counseling to achieve better cardiovascular health in this population.”
Dr. Khan stressed that any approaches to improving prepregnancy cardiovascular health must address the current racial disparities that are present. “We must make sure that our policies are successful not just in improving cardiovascular health but to ensure it is done equitably. We must find ways to ensure all individuals can access care.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
‘Forever chemicals’ disrupt biological processes in children: Study
Exposure to “forever chemicals” widely used in consumer products disrupts important biological processes in children and young adults, a new study says.
That could leave children vulnerable to numerous diseases later in life, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, the study said.
Another important finding was that the disruption appeared to be caused by a mixture of PFAS, rather than a single chemical of that type.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down easily over time and persist in water, soil, and the body. They’re used in numerous consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, cosmetics, and water-repellent clothing.
PFAS have previously been linked to a host of health issues, including decreased birth weights and immune system problems. To the study authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate which biological processes are altered by exposure to multiple PFAS, said a news release from the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Researchers studied blood samples from 312 children from the Study of Latino Adolescents at Risk and 137 children from the Southern California Children’s Health Study. All the children had a mixture of common PFAS in their blood, including PFOS, PFHxS, PFHpS, PFOA, and PFNA.
“While current interventions have focused on phasing out the use of individual PFAS, such as PFOS and PFOA, this research shows why the focus should be on reducing exposure to all PFAS chemicals,” said Leda Chatzi, MD, a professor of population and public health sciences at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Dr. Chatzi is also one of the study authors.
In October 2021, the Biden administration announced a plan to reduce the amount of PFAS released into the air, drinking and ground water, and food supply chain.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Exposure to “forever chemicals” widely used in consumer products disrupts important biological processes in children and young adults, a new study says.
That could leave children vulnerable to numerous diseases later in life, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, the study said.
Another important finding was that the disruption appeared to be caused by a mixture of PFAS, rather than a single chemical of that type.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down easily over time and persist in water, soil, and the body. They’re used in numerous consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, cosmetics, and water-repellent clothing.
PFAS have previously been linked to a host of health issues, including decreased birth weights and immune system problems. To the study authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate which biological processes are altered by exposure to multiple PFAS, said a news release from the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Researchers studied blood samples from 312 children from the Study of Latino Adolescents at Risk and 137 children from the Southern California Children’s Health Study. All the children had a mixture of common PFAS in their blood, including PFOS, PFHxS, PFHpS, PFOA, and PFNA.
“While current interventions have focused on phasing out the use of individual PFAS, such as PFOS and PFOA, this research shows why the focus should be on reducing exposure to all PFAS chemicals,” said Leda Chatzi, MD, a professor of population and public health sciences at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Dr. Chatzi is also one of the study authors.
In October 2021, the Biden administration announced a plan to reduce the amount of PFAS released into the air, drinking and ground water, and food supply chain.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Exposure to “forever chemicals” widely used in consumer products disrupts important biological processes in children and young adults, a new study says.
That could leave children vulnerable to numerous diseases later in life, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, the study said.
Another important finding was that the disruption appeared to be caused by a mixture of PFAS, rather than a single chemical of that type.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down easily over time and persist in water, soil, and the body. They’re used in numerous consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, cosmetics, and water-repellent clothing.
PFAS have previously been linked to a host of health issues, including decreased birth weights and immune system problems. To the study authors’ knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate which biological processes are altered by exposure to multiple PFAS, said a news release from the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Researchers studied blood samples from 312 children from the Study of Latino Adolescents at Risk and 137 children from the Southern California Children’s Health Study. All the children had a mixture of common PFAS in their blood, including PFOS, PFHxS, PFHpS, PFOA, and PFNA.
“While current interventions have focused on phasing out the use of individual PFAS, such as PFOS and PFOA, this research shows why the focus should be on reducing exposure to all PFAS chemicals,” said Leda Chatzi, MD, a professor of population and public health sciences at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Dr. Chatzi is also one of the study authors.
In October 2021, the Biden administration announced a plan to reduce the amount of PFAS released into the air, drinking and ground water, and food supply chain.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH PERSPECTIVES