User login
Children and COVID: Weekly cases resume their climb
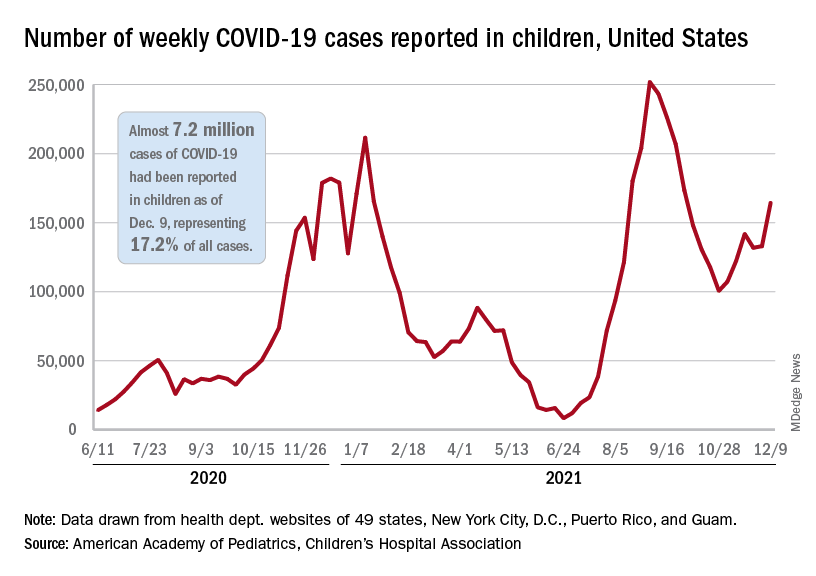
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
After a brief lull in activity, weekly COVID-19 cases in children returned to the upward trend that began in early November, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New COVID-19 cases were up by 23.5% for the week of Dec. 3-9, after a 2-week period that saw a drop and then just a slight increase, the AAP and CHA said in their latest weekly COVID report. There were 164,000 new cases from Dec. 3 to Dec. 9 in 46 states (Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer of 2021 and New York has never reported by age), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The increase occurred across all four regions of the country, but the largest share came in the Midwest, with over 65,000 new cases, followed by the West (just over 35,000), the Northeast (just under 35,000), and the South (close to 28,000), the AAP/CHA data show.
The 7.2 million cumulative cases in children as of Dec. 9 represent 17.2% of all cases reported in the United States since the start of the pandemic, with available state reports showing that proportion ranges from 12.3% in Florida to 26.1% in Vermont. Alaska has the highest incidence of COVID at 19,000 cases per 100,000 children, and Hawaii has the lowest (5,300 per 100,000) among the states currently reporting, the AAP and CHA said.
State reporting on vaccinations shows that 37% of children aged 5-11 years in Massachusetts have received at least one dose, the highest of any state, while West Virginia is lowest at just 4%. The highest vaccination rate for children aged 12-17 goes to Massachusetts at 84%, with Wyoming lowest at 37%, the AAP said in a separate report.
Nationally, new vaccinations fell by a third during the week of Dec. 7-13, compared with the previous week, with the largest decline (34.7%) coming from the 5- to 11-year-olds, who still represented the majority (almost 84%) of the 430,000 new child vaccinations received, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker. Corresponding declines for the last week were 27.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 22.7% for those aged 16-17.
Altogether, 21.2 million children aged 5-17 had received at least one dose and 16.0 million were fully vaccinated as of Dec. 13. By age group, 19.2% of children aged 5-11 years have gotten at least one dose and 9.6% are fully vaccinated, compared with 62.1% and 52.3%, respectively, among children aged 12-17, the CDC said.
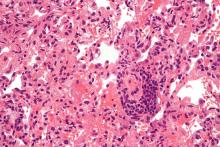
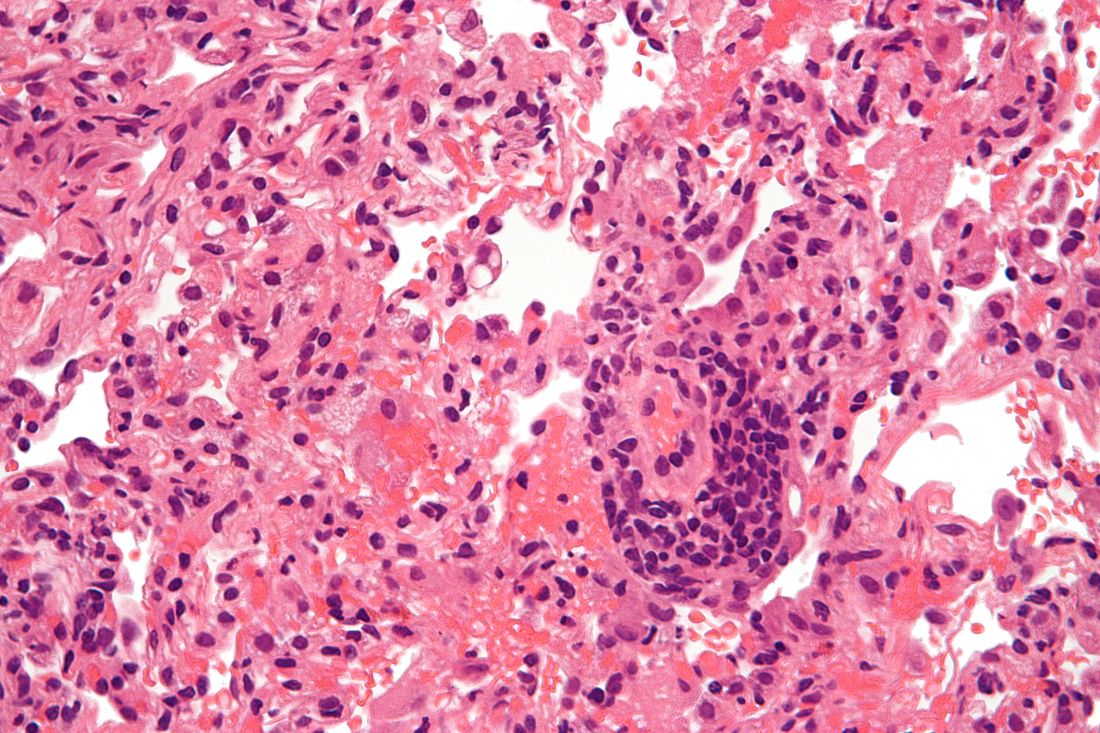
Epilepsy linked to 1.5-fold higher COVID-19 mortality in hospital
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
according to a new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society. While the findings are preliminary and not yet adjusted for various confounders, the authors say they are a warning sign that patients with epilepsy may face higher risks.
“These findings suggest that epilepsy may be a pre-existing condition that places patients at increased risk for death if hospitalized with a COVID-19 infection. It may offer neurologists guidance when counseling patients on critical preventative measures such as masking, social distancing, and most importantly, vaccination,” lead author Claire Ufongene, a student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview.
According to Ms. Ufongene, there’s sparse data about COVID-19 outcomes in patients with epilepsy, although she highlighted a 2021 meta-analysis of 13 studies that found a higher risk of severity (odds ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-2.59, P = .010) and mortality (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.14-2.56, P = .010).
For the new study, researchers retrospectively tracked identified 334 patients with epilepsy and COVID-19 and 9,499 other patients with COVID-19 from March 15, 2020, to May 17, 2021. All were treated at hospitals within the New York–based Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The groups of patients with and without epilepsy were similar in some ways: 45% and 46%, respectively, were female (P = .674), and their ages were similar (average, 62 years and 65 years, respectively; P = .02). Racial makeup was also similar (non-Hispanic groups made up 27.8% of those with epilepsy and 24.5% of those without; the difference was not statistically significant).
“In addition, more of those with epilepsy were English speaking [83.2% vs. 77.9%] and had Medicaid insurance [50.9% vs. 38.9%], while fewer of those with epilepsy had private insurance [16.2% vs. 25.5%] or were Spanish speaking [14.0% vs. 9.3%],” study coauthor Nathalie Jette, MD, MSc, a neurologist at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, said in an interview.
In terms of outcomes, patients with epilepsy were much more likely to need ventilator support (37.7% vs. 14.3%; P < .001), to be admitted to the ICU (39.2% vs. 17.7%; P < .001), and to die in the hospital (29.6% vs. 19.9%; P < .001).
“Most patients we follow in our practices with epilepsy who experienced COVID-19 in general have had symptoms similar to the general population,” Dr. Jette said. “There are rare instances where COVID-19 can result in an exacerbation of seizures in some with pre-existing epilepsy. This is not surprising as infections in particular can decrease the seizure threshold and result in breakthrough seizures in people living with epilepsy.”
Loss of seizure control
How might epilepsy be related to worse outcomes in COVID-19? Andrew Wilner, MD, a neurologist and internist at University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, who’s familiar with the study findings, said COVID-19 itself may not worsen epilepsy. “Evidence to suggest that COVID-19 directly affects the central nervous system is extremely limited. As such, one would not expect that a COVID-19 infection would cause epilepsy or exacerbate epilepsy,” he said. “However, patients with epilepsy who suffer from infections may be predisposed to decreased seizure control. Consequently, it would not be surprising if patients with epilepsy who also had COVID-19 had loss of seizure control and even status epilepticus, which could adversely affect their hospital course. However, there are no data on this potential phenomenon.”
Dr. Wilner suspected that comorbidities explain the higher mortality in patients with epilepsy. “The findings are probably most useful in that they call attention to the fact that epilepsy patients are more vulnerable to a host of comorbidities and resultant poorer outcomes due to any acute illness.”
As for treatment, Dr. Wilner urged colleagues to make sure that hospitalized patients with epilepsy “continue to receive their antiepileptic medications, which they may no longer be able to take orally. They may need to be switched temporarily to an intravenous formulation.”
In an interview, Selim Benbadis, MD, a neurologist from the University of South Florida, Tampa, suggested that antiseizure medications may play a role in the COVID-19 disease course because they can reduce the efficacy of other medications, although he noted that drug treatments for COVID-19 were limited early on. He recommended that neurologists “avoid old enzyme-inducing seizure medications, as is generally recommended.”
No study funding is reported. The study authors and Dr. Benbadis reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wilner is a medical adviser for the epilepsy disease management program for CVS/Health.
FROM AES 2021
Treatment of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients
An opportunity for impact
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.
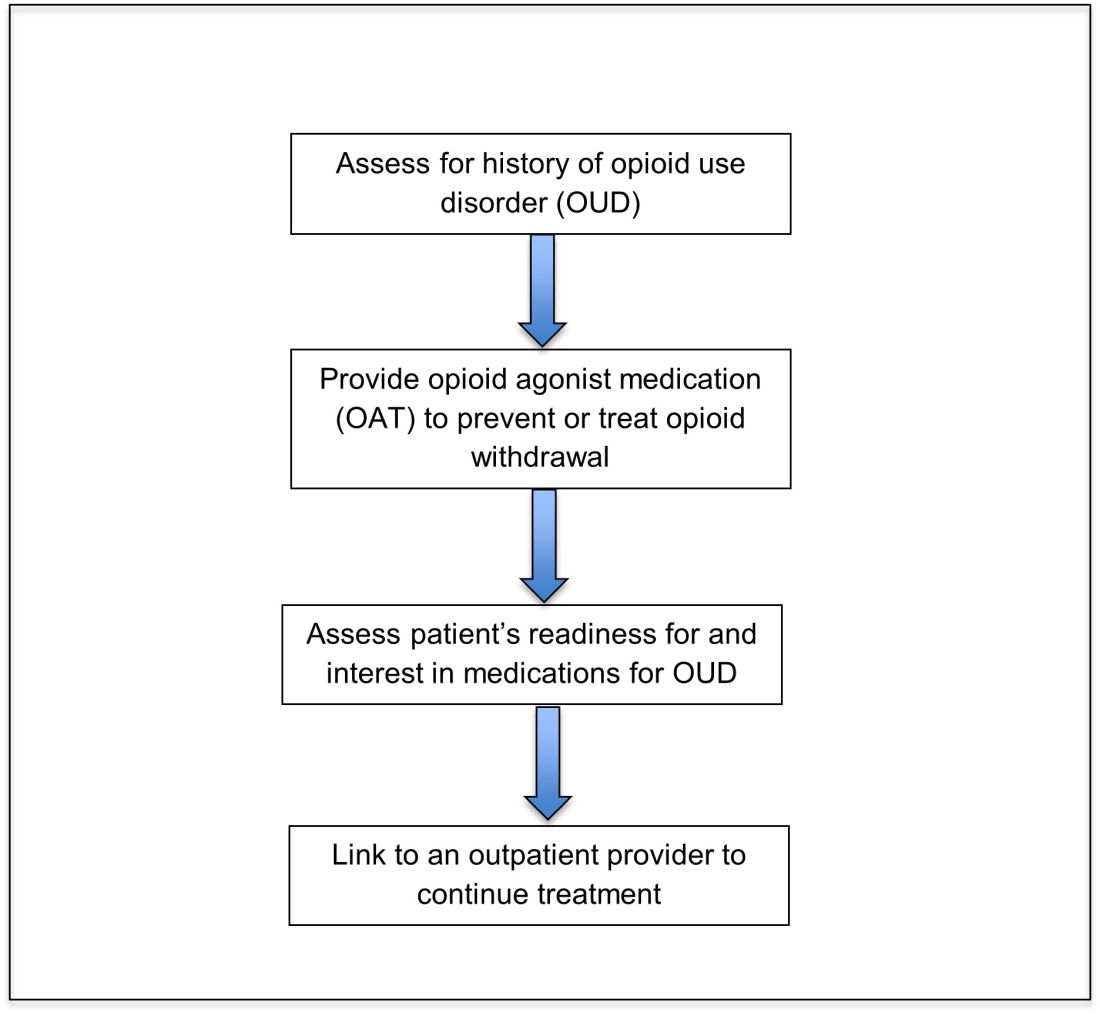
Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
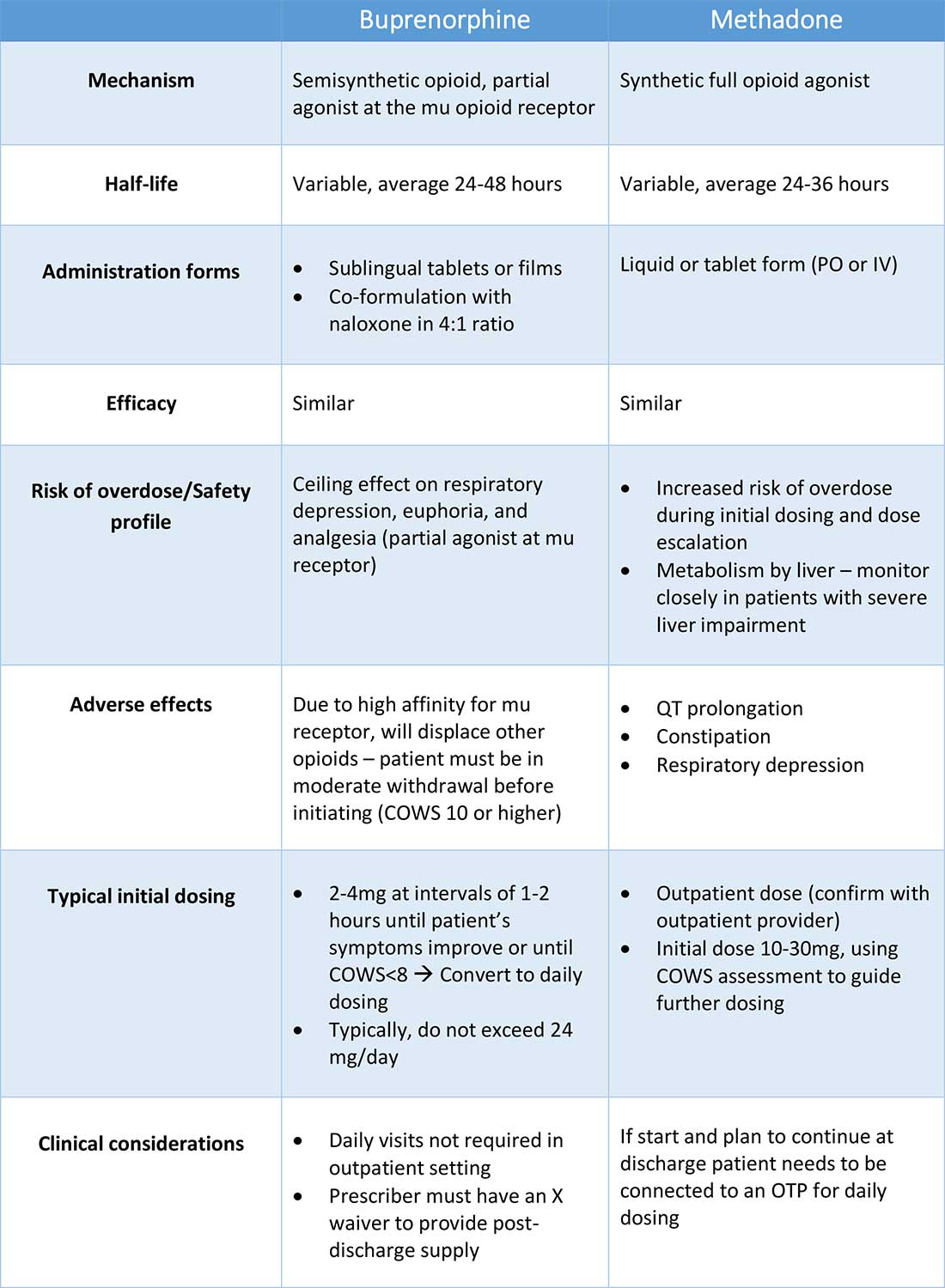
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.
Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
An opportunity for impact
An opportunity for impact
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.

Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.

Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
Case
A 35-year-old woman with opioid use disorder (OUD) presents with fever, left arm redness, and swelling. She is admitted to the hospital for cellulitis treatment. On the day after admission she becomes agitated and develops nausea, diarrhea, and generalized pain. Opioid withdrawal is suspected. How should her opioid use be addressed while in the hospital?
Brief overview of the issue
Since 1999, there have been more than 800,000 deaths related to drug overdose in the United States, and in 2019 more than 70% of drug overdose deaths involved an opioid.1,2 Although effective treatments for OUD exist, less than 20% of those with OUD are engaged in treatment.3
In America, 4%-11% of hospitalized patients have OUD. Hospitalized patients with OUD often experience stigma surrounding their disease, and many inpatient clinicians lack knowledge regarding the care of patients with OUD. As a result, withdrawal symptoms may go untreated, which can erode trust in the medical system and contribute to patients’ leaving the hospital before their primary medical issue is fully addressed. Therefore, it is essential that inpatient clinicians be familiar with the management of this complex and vulnerable patient population. Initiating treatment for OUD in the hospital setting is feasible and effective, and can lead to increased engagement in OUD treatment even after the hospital stay.
Overview of the data
Assessing patients with suspected OUD
Assessment for OUD starts with an in-depth opioid use history including frequency, amount, and method of administration. Clinicians should gather information regarding use of other substances or nonprescribed medications, and take thorough psychiatric and social histories. A formal diagnosis of OUD can be made using the Fifth Edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic criteria.
Recognizing and managing opioid withdrawal
OUD in hospitalized patients often becomes apparent when patients develop signs and symptoms of withdrawal. Decreasing physical discomfort related to withdrawal can allow inpatient clinicians to address the condition for which the patient was hospitalized, help to strengthen the patient-clinician relationship, and provide an opportunity to discuss long-term OUD treatment.
Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal include anxiety, restlessness, irritability, generalized pain, rhinorrhea, yawning, lacrimation, piloerection, anorexia, and nausea. Withdrawal can last days to weeks, depending on the half-life of the opioid that was used. Opioids with shorter half-lives, such as heroin or oxycodone, cause withdrawal with earlier onset and shorter duration than do opioids with longer half-lives, such as methadone. The degree of withdrawal can be quantified with validated tools, such as the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS).
Treatment of opioid withdrawal should generally include the use of an opioid agonist such as methadone or buprenorphine. A 2017 Cochrane meta-analysis found methadone or buprenorphine to be more effective than clonidine in alleviating symptoms of withdrawal and in retaining patients in treatment.4 Clonidine, an alpha2-adrenergic agonist that binds to receptors in the locus coeruleus, does not alleviate opioid cravings, but may be used as an adjunctive treatment for associated autonomic withdrawal symptoms. Other adjunctive medications include analgesics, antiemetics, antidiarrheals, and antihistamines.

Opioid agonist treatment for opioid use disorder
Opioid agonist treatment (OAT) with methadone or buprenorphine is associated with decreased mortality, opioid use, and infectious complications, but remains underutilized.5 Hospitalized patients with OUD are frequently managed with a rapid opioid detoxification and then discharged without continued OUD treatment. Detoxification alone can lead to a relapse rate as high as 90%.6 Patients are at increased risk for overdose after withdrawal due to loss of tolerance. Inpatient clinicians can close this OUD treatment gap by familiarizing themselves with OAT and offering to initiate OAT for maintenance treatment in interested patients. In one study, patients started on buprenorphine while hospitalized were more likely to be engaged in treatment and less likely to report drug use at follow-up, compared to patients who were referred without starting the medication.7
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial agonist at the mu opioid receptor that can be ordered in the inpatient setting by any clinician. In the outpatient setting only DATA 2000 waivered clinicians can prescribe buprenorphine.8 Buprenorphine is most commonly coformulated with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is available in sublingual films or tablets. The naloxone component is not bioavailable when taken sublingually but becomes bioavailable if the drug is injected intravenously, leading to acute withdrawal.
Buprenorphine has a higher affinity for the mu opioid receptor than most opioids. If administered while other opioids are still present, it will displace the other opioid from the receptor but only partially stimulate the receptor, which can cause precipitated withdrawal. Buprenorphine initiation can start when the COWS score reflects moderate withdrawal. Many institutions use a threshold of 8-12 on the COWS scale. Typical dosing is 2-4 mg of buprenorphine at intervals of 1-2 hours as needed until the COWS score is less than 8, up to a maximum of 16 mg on day 1. The total dose from day 1 may be given as a daily dose beginning on day 2, up to a maximum total daily dose of 24 mg.
In recent years, a method of initiating buprenorphine called “micro-dosing” has gained traction. Very small doses of buprenorphine are given while a patient is receiving other opioids, thereby reducing the risk of precipitated withdrawal. This method can be helpful for patients who cannot tolerate withdrawal or who have recently taken long-acting opioids such as methadone. Such protocols should be utilized only at centers where consultation with an addiction specialist or experienced clinician is possible.
Despite evidence of buprenorphine’s efficacy, there are barriers to prescribing it. Physicians and advanced practitioners must be granted a waiver from the Drug Enforcement Administration to prescribe buprenorphine to outpatients. As of 2017, less than 10% of primary care physicians had obtained waivers.9 However, inpatient clinicians without a waiver can order buprenorphine and initiate treatment. Best practice is to do so with a specific plan for continuation at discharge. We encourage inpatient clinicians to obtain a waiver, so that a prescription can be given at discharge to bridge the patient to a first appointment with a community clinician who can continue treatment. As of April 27, 2021, providers treating fewer than 30 patients with OUD at one time may obtain a waiver without additional training.10
Methadone
Methadone is a full agonist at the mu opioid receptor. In the hospital setting, methadone can be ordered by any clinician to prevent and treat withdrawal. Commonly, doses of 10 mg can be given using the COWS score to guide the need for additional dosing. The patient can be reassessed every 1-2 hours to ensure that symptoms are improving, and that there is no sign of oversedation before giving additional methadone. For most patients, withdrawal can be managed with 20-40 mg of methadone daily.
In contrast to buprenorphine, methadone will not precipitate withdrawal and can be initiated even when patients are not yet showing withdrawal symptoms. Outpatient methadone treatment for OUD is federally regulated and can be delivered only in opioid treatment programs (OTPs).
Choosing methadone or buprenorphine in the inpatient setting
The choice between buprenorphine and methadone should take into consideration several factors, including patient preference, treatment history, and available outpatient treatment programs, which may vary widely by geographic region. Some patients benefit from the higher level of support and counseling available at OTPs. Methadone is available at all OTPs, and the availability of buprenorphine in this setting is increasing. Other patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of buprenorphine treatment in an outpatient office setting.
Some patients have prior negative experiences with OAT. These can include prior precipitated withdrawal with buprenorphine induction, or negative experiences with the structure of OTPs. Clinicians are encouraged to provide counseling if patients have a history of precipitated withdrawal to assure them that this can be avoided with proper dosing. Clinicians should be familiar with available treatment options in their community and can refer to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website to locate OTPs and buprenorphine prescribers.

Polypharmacy and safety
If combined with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other sedating agents, methadone or buprenorphine can increase risk of overdose. However, OUD treatment should not be withheld because of other substance use. Clinicians initiating treatment should counsel patients on the risk of concomitant substance use and provide overdose prevention education.
A brief note on naltrexone
Naltrexone, an opioid antagonist, is used more commonly in outpatient addiction treatment than in the inpatient setting, but inpatient clinicians should be aware of its use. It is available in oral and long-acting injectable formulations. Its utility in the inpatient setting may be limited as safe administration requires 7-10 days of opioid abstinence.
Discharge planning
Patients with OUD or who are started on OAT during a hospitalization should be linked to continued outpatient treatment. Before discharge it is best to ensure vaccinations for HAV, HBV, pneumococcus, and tetanus are up to date, and perform screening for HIV, hepatitis C, tuberculosis, and sexually transmitted infections if appropriate. All patients with OUD should be prescribed or provided with take-home naloxone for overdose reversal. Patients can also be referred to syringe service programs for additional harm reduction counseling and services.
Application of the data to our patient
For our patient, either methadone or buprenorphine could be used to treat her withdrawal. The COWS score should be used to assess withdrawal severity, and to guide appropriate timing of medication initiation. If she wishes to continue OAT after discharge, she should be linked to a clinician who can engage her in ongoing medical care. Prior to discharge she should also receive relevant vaccines and screening for infectious diseases as outlined above, as well as take-home naloxone (or a prescription).
Bottom line
Inpatient clinicians can play a pivotal role in patients’ lives by ensuring that patients with OUD receive OAT and are connected to outpatient care at discharge.
Dr. Linker is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Ms. Hirt, Mr. Fine, and Mr. Villasanivis are medical students at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Wang is assistant professor in the division of general internal medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Dr. Herscher is assistant professor in the division of hospital medicine, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
References
1. Wide-ranging online data for epidemiologic research (WONDER). Atlanta, GA: CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2020. Available at http://wonder.cdc.gov.
2. Mattson CL et al. Trends and geographic patterns in drug and synthetic opioid overdose deaths – United States, 2013-2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:202-7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7006a4.
3. Wakeman SE et al. Comparative effectiveness of different treatment pathways for opioid use disorder. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920622. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20622.
4. Gowing L et al. Buprenorphine for managing opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb;2017(2):CD002025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002025.pub5.
5. Sordo L et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: Systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017 Apr 26;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550.
6. Smyth BP et al. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir Med J. 2010 Jun;103(6):176-9. Available at www.drugsandalcohol.ie/13405.
7. Liebschutz JM. Buprenorphine treatment for hospitalized, opioid-dependent patients: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014 Aug;174(8):1369-76. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.2556.
8. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (Aug 20, 2020) Statutes, Regulations, and Guidelines.
9. McBain RK et al. Growth and distribution of buprenorphine-waivered providers in the United States, 2007-2017. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(7):504-6. doi: 10.7326/M19-2403.
10. HHS releases new buprenorphine practice guidelines, expanding access to treatment for opioid use disorder. Apr 27, 2021.
11. Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Additional reading
Winetsky D. Expanding treatment opportunities for hospitalized patients with opioid use disorders. J Hosp Med. 2018 Jan;13(1):62-4. doi: 10.12788/jhm.2861.
Donroe JH. Caring for patients with opioid use disorder in the hospital. Can Med Assoc J. 2016 Dec 6;188(17-18):1232-9. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.160290.
Herscher M et al. Diagnosis and management of opioid use disorder in hospitalized patients. Med Clin North Am. 2020 Jul;104(4):695-708. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.03.003.
Key points
- Most patients with OUD are not engaged in evidence-based treatment. Clinicians have an opportunity to utilize the inpatient stay as a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
- Buprenorphine and methadone are effective opioid agonist medications used to treat OUD, and clinicians with the appropriate knowledge base can initiate either during the inpatient encounter, and link the patient to OUD treatment after the hospital stay.
Quiz
Caring for hospitalized patients with OUD
Most patients with OUD are not engaged in effective treatment. Hospitalization can be a ‘reachable moment’ to engage patients with OUD in evidence-based treatment.
1. Which is an effective and evidence-based medication for treating opioid withdrawal and OUD?
a) Naltrexone.
b) Buprenorphine.
c) Opioid detoxification.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Buprenorphine is effective for alleviating symptoms of withdrawal as well as for the long-term treatment of OUD. While naltrexone is also used to treat OUD, it is not useful for treating withdrawal. Clonidine can be a useful adjunctive medication for treating withdrawal but is not a long-term treatment for OUD. Nonpharmacologic detoxification is not an effective treatment for OUD and is associated with high relapse rates.
2. What scale can be used during a hospital stay to monitor patients with OUD at risk of opioid withdrawal, and to aid in buprenorphine initiation?
a) CIWA score.
b) PADUA score.
c) COWS score.
d) 4T score.
Explanation: COWS is the “clinical opiate withdrawal scale.” The COWS score should be calculated by a trained provider, and includes objective parameters (such as pulse) and subjective symptoms (such as GI upset, bone/joint aches.) It is recommended that agonist therapy be started when the COWS score is consistent with moderate withdrawal.
3. How can clinicians reliably find out if there are outpatient resources/clinics for patients with OUD in their area?
a) No way to find this out without personal knowledge.
b) Hospital providers and patients can visit www.samhsa.gov/find-help/national-helpline or call 1-800-662-HELP (4357) to find options for treatment for substance use disorders in their areas.
c) Dial “0” on any phone and ask.
d) Ask around at your hospital.
Explanation: The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that is engaged in public health efforts to reduce the impact of substance abuse and mental illness on local communities. The agency’s website has helpful information about resources for substance use treatment.
4. Patients with OUD should be prescribed and given training about what medication that can be lifesaving when given during an opioid overdose?
a) Aspirin.
b) Naloxone.
c) Naltrexone.
d) Clonidine.
Explanation: Naloxone can be life-saving in the setting of an overdose. Best practice is to provide naloxone and training to patients with OUD.
5. When patients take buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids, there is concern for the development of which reaction:
a) Precipitated withdrawal.
b) Opioid overdose.
c) Allergic reaction.
d) Intoxication.
Explanation: Administering buprenorphine soon after taking other opioids can cause precipitated withdrawal, as buprenorphine binds with higher affinity to the mu receptor than many opioids. Precipitated withdrawal causes severe discomfort and can be dangerous for patients.
D-dimer thresholds rule out PE in meta-analysis
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
In a patient suspected to have a PE, “diagnosis is made radiographically, usually with CT pulmonary angiogram, or V/Q scan,” Suman Pal, MD, of the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, said in an interview.
“Validated clinical decision tools such as Wells’ score or Geneva score may be used to identify patients at low pretest probability of PE who may initially get a D-dimer level check, followed by imaging only if D-dimer level is elevated,” explained Dr. Pal, who was not involved with the new research, which was published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
According to the authors of the new paper, while current diagnostic strategies in patients with suspected PE include use of a validated clinical decision rule (CDR) and D-dimer testing to rule out PE without imaging tests, the effectiveness of D-dimer tests in older patients, inpatients, cancer patients, and other high-risk groups has not been well-studied.
Lead author of the paper, Milou A.M. Stals, MD, and colleagues said their goal was to evaluate the safety and efficiency of the Wells rule and revised Geneva score in combination with D-dimer tests, and also the YEARS algorithm for D-dimer thresholds, in their paper.
Dr. Stals, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, and the coinvestigators conducted an international systemic review and individual patient data meta-analysis that included 16 studies and 20,553 patients, with all studies having been published between Jan. 1, 1995, and Jan. 1, 2021. Their primary outcomes were the safety and efficiency of each of these three strategies.
In the review, the researchers defined safety as the 3-month incidence of venous thromboembolism after PE was ruled out without imaging at baseline. They defined efficiency as the proportion patients for whom PE was ruled out based on D-dimer thresholds without imaging.
Overall, efficiency was highest in the subset of patients aged younger than 40 years, ranging from 47% to 68% in this group. Efficiency was lowest in patients aged 80 years and older (6.0%-23%), and in patients with cancer (9.6%-26%).
The efficiency was higher when D-dimer thresholds based on pretest probability were used, compared with when fixed or age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds were used.
The key finding was the significant variability in performance of the diagnostic strategies, the researchers said.
“The predicted failure rate was generally highest for strategies incorporating adapted D-dimer thresholds. However, at the same time, predicted overall efficiency was substantially higher with these strategies versus strategies with a fixed D-dimer threshold as well,” they said. Given that the benefits of each of the three diagnostic strategies depends on their correct application, the researchers recommended that an individual hospitalist choose one strategy for their institution.
“Whether clinicians should rely on the Wells rule, the YEARS algorithm, or the revised Geneva score becomes a matter of local preference and experience,” Dr. Stals and colleagues wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including between-study differences in scoring predictors and D-dimer assays. Another limitation was that differential verification biases for classifying fatal events and PE may have contributed to overestimation of failure rates of the adapted D-dimer thresholds.
Strengths of the study included its large sample size and original data on pretest probability, and that data support the use of any of the three strategies for ruling out PE in the identified subgroups without the need for imaging tests, the authors wrote.
“Pending the results of ongoing diagnostic randomized trials, physicians and guideline committees should balance the interlink between safety and efficiency of available diagnostic strategies,” they concluded.
Adapted D-dimer benefits some patients
“Clearly, increasing the D-dimer cutoff will lower the number of patients who require radiographic imaging (improved specificity), but this comes with a risk for missing PE (lower sensitivity). Is this risk worth taking?” Daniel J. Brotman, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, asked in an editorial accompanying the new study.
Dr. Brotman was not surprised by the study findings.
“Conditions that predispose to thrombosis through activated hemostasis – such as advanced age, cancer, inflammation, prolonged hospitalization, and trauma – drive D-dimer levels higher independent of the presence or absence of radiographically apparent thrombosis,” he said. However, these patients are unlikely to have normal D-dimer levels regardless of the cutoff used.
Adapted D-dimer cutoffs may benefit some patients, including those with contraindications or limited access to imaging, said Dr. Brotman. D-dimer may be used for risk stratification regardless of PE, since patients with marginally elevated D-dimers have better prognoses than those with higher D-dimer elevations, even if a small PE is missed.
Dr. Brotman wrote that increasing D-dimer cutoffs for high-risk patients in the subgroups analyzed may spare some patients radiographic testing, but doing so carries an increased risk for diagnostic failure. Overall, “the important work by Stals and colleagues offers reassurance that modifying D-dimer thresholds according to age or pretest probability is safe enough for widespread practice, even in high-risk groups.”
Focus on single strategy ‘based on local needs’
“Several validated clinical decision tools, along with age or pretest probability adjusted D-dimer threshold are currently in use as diagnostic strategies for ruling out pulmonary embolism,” Dr. Pal said in an interview.
The current study is important because of limited data on the performance of these strategies in specific subgroups of patients whose risk of PE may differ from the overall patient population, he noted.
“Different diagnostic strategies for PE have a variable performance in patients with differences of age, active cancer, and history of VTE,” said Dr. Pal. “However, in this study, no clear preference for one strategy over others could be established for these subgroups, and clinicians should continue to follow institution-specific guidance.
“A single strategy should be adopted at each institution based on local needs and used as the standard of care until further data are available,” he said.
“The use of D-dimer to rule out PE, either with fixed threshold or age-adjusted thresholds, can be confounded in clinical settings by other comorbid conditions such as sepsis, recent surgery, and more recently, COVID-19,” he said.
“Since the findings of this study do not show a clear benefit of one diagnostic strategy over others in the analyzed subgroups of patients, further prospective head-to-head comparison among the subgroups of interest would be helpful to guide clinical decision making,” Dr. Pal added.
YEARS-specific study supports D-dimer safety and value
A recent paper published in JAMA supported the results of the meta-analysis. In that study, Yonathan Freund, MD, of Sorbonne Université, Paris, and colleagues focused on the YEARS strategy combined with age-adjusted D-dimer thresholds as a way to rule out PE in PERC-positive ED patients.
The authors of this paper randomized 18 EDs to either a protocol of intervention followed by control, or control followed by intervention. The study population included 726 patients in the intervention group and 688 in the control group.
The intervention strategy to rule out PE consisted of assessing the YEARS criteria and D-dimer testing. PE was ruled out in patients with no YEARS criteria and a D-dimer level below 1,000 ng/mL and in patients with one or more YEARS criteria and D-dimers below an age-adjusted threshold (defined as age times 10 ng/mL in patients aged 50 years and older).
The control strategy consisted of D-dimer testing for all patients with the threshold at age-adjusted levels; D-dimers about these levels prompted chest imaging.
Overall, the risk of a missed VTE at 3 months was noninferior between the groups (0.15% in the intervention group and 0.80% in the controls).
“The intervention was associated with a statistically significant reduction in chest imaging use,” the researchers wrote.
This study’s findings were limited by randomization at the center level, rather than the patient level, and the use of imaging on some patients despite negative D-dimer tests, the researchers wrote. However, their findings support those of previous studies and especially support the safety of the intervention, in an emergency medicine setting, as no PEs occurred in patients with a YEARS score of zero who underwent the intervention.
Downsides to applying algorithms to every patient explained
In an editorial accompanying the JAMA study, Marcel Levi, MD, and Nick van Es, MD, of Amsterdam University Medical Center, emphasized the challenges of diagnosing PE given that many patients present with nonspecific clinical manifestations and without typical signs and symptoms. High-resolution CT pulmonary angiography allows for a fast and easy diagnosis in an emergency setting. However, efforts are ongoing to develop alternative strategies that avoid unnecessary scanning for potential PE patients, many of whom have alternative diagnoses such as pulmonary infections, cardiac conditions, pleural disease, or musculoskeletal problems.
On review of the JAMA study using the YEARS rule with adjusted D-dimer thresholds, the editorialists noted that the data were robust and indicated a 10% reduction in chest imaging. They also emphasized the potential to overwhelm busy clinicians with more algorithms.
“Blindly applying algorithms to every patient may be less appropriate or even undesirable in specific situations in which deviation from the rules on clinical grounds is indicated,” but a complex imaging approach may be time consuming and challenging in the acute setting, and a simple algorithm may be safe and efficient in many cases, they wrote. “From a patient perspective, a negative diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary embolism does not diminish the physician’s obligation to consider other diagnoses that explain the symptoms, for which chest CT scans may still be needed and helpful.”
The Annals of Internal Medicine study was supported by the Dutch Research Council. The JAMA study was supported by the French Health Ministry. Dr. Stals, Dr. Freund, Dr. Pal, Dr. Levi, and Dr. van Es had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Lung transplantation in the era of COVID-19: New issues and paradigms
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Data is sparse thus far, but there is concern in lung transplant medicine about the long-term risk of chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) and a potentially shortened longevity of transplanted lungs in recipients who become ill with COVID-19.
“My fear is that we’re potentially sitting on this iceberg worth of people who, come 6 months or a year from [the acute phase of] their COVID illness, will in fact have earlier and progressive, chronic rejection,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, MBBS, MPH, associate professor of medicine in transplant infectious disease at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
Lower respiratory viral infections have long been concerning for lung transplant recipients given their propensity to cause scarring, a decline in lung function, and a heightened risk of allograft rejection. Time will tell whether lung transplant recipients who survive COVID-19 follow a similar path, or one that is worse, he said.
Short-term data
Outcomes beyond hospitalization and acute illness for lung transplant recipients affected by COVID-19 have been reported in the literature by only a few lung transplant programs. These reports – as well as anecdotal experiences being informally shared among transplant programs – have raised the specter of more severe dysfunction following the acute phase and more early CLAD, said Tathagat Narula, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Medical School, Rochester, Minn., and a consultant in lung transplantation at the Mayo Clinic’s Jacksonville program.
“The available data cover only 3-6 months out. We don’t know what will happen in the next 6 months and beyond,” Dr. Narula said in an interview.
The risks of COVID-19 in already-transplanted patients and issues relating to the inadequate antibody responses to vaccination are just some of the challenges of lung transplant medicine in the era of SARS-CoV-2. “COVID-19,” said Dr. Narula, “has completely changed the way we practice lung transplant medicine – the way we’re looking both at our recipients and our donors.”
Potential donors are being evaluated with lower respiratory SARS-CoV-2 testing and an abundance of caution. And patients with severe COVID-19 affecting their own lungs are roundly expected to drive up lung transplant volume in the near future. “The whole paradigm has changed,” Dr. Narula said.
Post-acute trajectories
A chart review study published in October by the lung transplant team at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, covered 44 consecutive survivors at a median follow-up of 4.5 months from hospital discharge or acute illness (the survival rate was 83.3%). Patients had significantly impaired functional status, and 18 of the 44 (40.9%) had a significant and persistent loss of forced vital capacity or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (>10% from pre–COVID-19 baseline).
Three patients met the criteria for new CLAD after COVID-19 infection, with all three classified as restrictive allograft syndrome (RAS) phenotype.
Moreover, the majority of COVID-19 survivors who had CT chest scans (22 of 28) showed persistent parenchymal opacities – a finding that, regardless of symptomatology, suggests persistent allograft injury, said Amit Banga, MD, associate professor of medicine and medical director of the ex vivo lung perfusion program in UT Southwestern’s lung transplant program.
“The implication is that there may be long-term consequences of COVID-19, perhaps related to some degree of ongoing inflammation and damage,” said Dr. Banga, a coauthor of the postinfection outcomes paper.
The UT Southwestern lung transplant program, which normally performs 60-80 transplants a year, began routine CT scanning 4-5 months into the pandemic, after “stumbling into a few patients who had no symptoms indicative of COVID pneumonia and no changes on an x-ray but significant involvement on a CT,” he said.
Without routine scanning in the general population of COVID-19 patients, Dr. Banga noted, “we’re limited in convincingly saying that COVID is uniquely doing this to lung transplant recipients.” Nor can they conclude that SARS-CoV-2 is unique from other respiratory viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in this regard. (The program has added CT scanning to its protocol for lung transplant recipients afflicted with other respiratory viruses to learn more.)
However, in the big picture, COVID-19 has proven to be far worse for lung transplant recipients than illness with other respiratory viruses, including RSV. “Patients have more frequent and greater loss of lung function, and worse debility from the acute illness,” Dr. Banga said.
“The cornerstones of treatment of both these viruses are very similar, but both the in-hospital course and the postdischarge outcomes are significantly different.”
In an initial paper published in September 2021, Dr. Banga and colleagues compared their first 25 lung transplant patients testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 with a historical cohort of 36 patients with RSV treated during 2016-2018.
Patients with COVID-19 had significantly worse morbidity and mortality, including worse postinfection lung function loss, functional decline, and 3-month survival.
More time, he said, will shed light on the risks of CLAD and the long-term potential for recovery of lung function. Currently, at UT Southwestern, it appears that patients who survive acute illness and the “first 3-6 months after COVID-19, when we’re seeing all the postinfection morbidity, may [enter] a period of stability,” Dr. Banga said.
Overall, he said, patients in their initial cohort are “holding steady” without unusual morbidity, readmissions, or “other setbacks to their allografts.”
At the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, which normally performs 40-50 lung transplants a year, transplant physicians have similarly observed significant declines in lung function beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. “Anecdotally, we’re seeing that some patients are beginning to recover some of their lung function, while others have not,” said Dr. Narula. “And we don’t have predictors as to who will progress to CLAD. It’s a big knowledge gap.”
Dr. Narula noted that patients with restrictive allograft syndrome, such as those reported by the UT Southwestern team, “have scarring of the lung and a much worse prognosis than the obstructive type of chronic rejection.” Whether there’s a role for antifibrotic therapy is a question worthy of research.
In UT Southwestern’s analysis, persistently lower absolute lymphocyte counts (< 600/dL) and higher ferritin levels (>150 ng/mL) at the time of hospital discharge were independently associated with significant lung function loss. This finding, reported in their October paper, has helped guide their management practices, Dr. Banga said.
“Persistently elevated ferritin may indicate ongoing inflammation at the allograft level,” he said. “We now send [such patients] home on a longer course of oral corticosteroids.”
At the front end of care for infected lung transplant recipients, Dr. Banga said that his team and physicians at other lung transplant programs are holding the cell-cycle inhibitor component of patients’ maintenance immunosuppression therapy (commonly mycophenolate or azathioprine) once infection is diagnosed to maximize chances of a better outcome.
“There may be variation on how long [the regimens are adjusted],” he said. “We changed our duration from 4 weeks to 2 due to patients developing a rebound worsening in the third and fourth week of acute illness.”
There is significant variation from institution to institution in how viral infections are managed in lung transplant recipients, he and Dr. Narula said. “Our numbers are so small in lung transplant, and we don’t have standardized protocols – it’s one of the biggest challenges in our field,” said Dr. Narula.
Vaccination issues, evaluation of donors
Whether or not immunosuppression regimens should be adjusted prior to vaccination is a controversial question, but is “an absolutely valid one” and is currently being studied in at least one National Institutes of Health–funded trial involving solid organ transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe.
“Some have jumped to the conclusion [based on some earlier data] that they should reduce immunosuppression regimens for everyone at the time of vaccination ... but I don’t know the answer yet,” he said. “Balancing staying rejection free with potentially gaining more immune response is complicated ... and it may depend on where the pandemic is going in your area and other factors.”
Reductions aside, Dr. Wolfe tells lung transplant recipients that, based on his approximation of a number of different studies in solid organ transplant recipients, approximately 40%-50% of patients who are immunized with two doses of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines will develop meaningful antibody levels – and that this rises to 50%-60% after a third dose.
It is difficult to glean from available studies the level of vaccine response for lung transplant recipients specifically. But given that their level of maintenance immunosuppression is higher than for recipients of other donor organs, “as a broad sweep, lung transplant recipients tend to be lower in the pecking order of response,” he said.
Still, “there’s a lot to gain,” he said, pointing to a recent study from the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2021 Nov 5. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7044e3) showing that effectiveness of mRNA vaccination against COVID-19–associated hospitalization was 77% among immunocompromised adults (compared with 90% in immunocompetent adults).
“This is good vindication to keep vaccinating,” he said, “and perhaps speaks to how difficult it is to assess the vaccine response [through measurement of antibody only].”
Neither Duke University’s transplant program, which performed 100-120 lung transplants a year pre-COVID, nor the programs at UT Southwestern or the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville require that solid organ transplant candidates be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in order to receive transplants, as some other transplant programs have done. (When asked about the issue, Dr. Banga and Dr. Narula each said that they have had no or little trouble convincing patients awaiting lung transplants of the need for COVID-19 vaccination.)
In an August statement, the American Society of Transplantation recommended vaccination for all solid organ transplant recipients, preferably prior to transplantation, and said that it “support[s] the development of institutional policies regarding pretransplant vaccination.”
The Society is not tracking centers’ vaccination policies. But Kaiser Health News reported in October that a growing number of transplant programs, such as UCHealth in Denver and UW Medicine in Seattle, have decided to either bar patients who refuse to be vaccinated from receiving transplants or give them lower priority on waitlists.
Potential lung donors, meanwhile, must be evaluated with lower respiratory COVID-19 testing, with results available prior to transplantation, according to policy developed by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and effective in May 2021. The policy followed three published cases of donor-derived COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients, said Dr. Wolfe, who wrote about use of COVID-positive donors in an editorial published in October.
In each case, the donor had a negative COVID-19 nasopharyngeal swab at the time of organ procurement but was later found to have the virus on bronchoalveolar lavage, he said.
(The use of other organs from COVID-positive donors is appearing thus far to be safe, Dr. Wolfe noted. In the editorial, he references 13 cases of solid organ transplantation from SARS-CoV-2–infected donors into noninfected recipients; none of the 13 transplant recipients developed COVID-19).
Some questions remain, such as how many lower respiratory tests should be run, and how donors should be evaluated in cases of discordant results. Dr. Banga shared the case of a donor with one positive lower respiratory test result followed by two negative results. After internal debate, and consideration of potential false positives and other issues, the team at UT Southwestern decided to decline the donor, Dr. Banga said.
Other programs are likely making similar, appropriately cautious decisions, said Dr. Wolfe. “There’s no way in real-time donor evaluation to know whether the positive test is active virus that could infect the recipient and replicate ... or whether it’s [picking up] inactive or dead fragments of virus that was there several weeks ago. Our tests don’t differentiate that.”
Transplants in COVID-19 patients
Decision-making about lung transplant candidacy among patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome is complex and in need of a new paradigm.
“Some of these patients have the potential to recover, and they’re going to recover way later than what we’re used to,” said Dr. Banga. “We can’t extrapolate for COVID ARDS what we’ve learned for any other virus-related ARDS.”
Dr. Narula also has recently seen at least one COVID-19 patient on ECMO and under evaluation for transplantation recover. “We do not want to transplant too early,” he said, noting that there is consensus that lung transplant should be pursued only when the damage is deemed irreversible clinically and radiologically in the best judgment of the team. Still, “for many of these patients the only exit route will be lung transplants. For the next 12-24 months, a significant proportion of our lung transplant patients will have had post-COVID–related lung damage.”
As of October 2021, 233 lung transplants had been performed in the United States in recipients whose primary diagnosis was reported as COVID related, said Anne Paschke, media relations specialist with the United Network for Organ Sharing.
Dr. Banga, Dr. Wolfe, and Dr. Narula reported that they have no relevant disclosures.
Oral step-down therapy for infective endocarditis
Background: The standard of care for IE has been a prolonged course of IV antibiotics. Recent literature has suggested that oral antibiotics might be a safe and effective step-down therapy for IE.
Study design: Systematic review.
Setting: Literature review in October 2019, with update in February 2020, consisting of 21 observational studies and 3 randomized controlled trials.
Synopsis: Three RCTs and 21 observational studies were reviewed, with a focus on the effectiveness of antibiotics administered orally for part of the therapeutic course for IE patients. Patients included in the study had left- or right-sided IE. Pathogens included viridians streptococci, staphylococci, and enterococci, with a minority of patients infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment regimens included beta-lactams, linezolid, fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or clindamycin, with or without rifampin.
In studies wherein IV antibiotics alone were compared with IV antibiotics with oral step-down therapy, there was no difference in clinical cure rate. Those given oral step-down therapy had a statistically significant lower mortality rate than patients who received only IV therapy.
Limitations include inconclusive data regarding duration of IV lead-in therapy, with the variance before conversion to oral antibiotics amongst the studies ranging from 0 to 24 days. The limited number of patients with MRSA infections makes it difficult to draw conclusions regarding this particular pathogen.
Bottom line: Highly orally bioavailable antibiotics should be considered for patients with IE who have cleared bacteremia and achieved clinical stability with IV regimens.
Citation: Spellberg B et al. Evaluation of a paradigm shift from intravenous antibiotics to oral step-down therapy for the treatment of infective endocarditis: a narrative review. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(5):769-77. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0555.
Dr. Yoo is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: The standard of care for IE has been a prolonged course of IV antibiotics. Recent literature has suggested that oral antibiotics might be a safe and effective step-down therapy for IE.
Study design: Systematic review.
Setting: Literature review in October 2019, with update in February 2020, consisting of 21 observational studies and 3 randomized controlled trials.
Synopsis: Three RCTs and 21 observational studies were reviewed, with a focus on the effectiveness of antibiotics administered orally for part of the therapeutic course for IE patients. Patients included in the study had left- or right-sided IE. Pathogens included viridians streptococci, staphylococci, and enterococci, with a minority of patients infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment regimens included beta-lactams, linezolid, fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or clindamycin, with or without rifampin.
In studies wherein IV antibiotics alone were compared with IV antibiotics with oral step-down therapy, there was no difference in clinical cure rate. Those given oral step-down therapy had a statistically significant lower mortality rate than patients who received only IV therapy.
Limitations include inconclusive data regarding duration of IV lead-in therapy, with the variance before conversion to oral antibiotics amongst the studies ranging from 0 to 24 days. The limited number of patients with MRSA infections makes it difficult to draw conclusions regarding this particular pathogen.
Bottom line: Highly orally bioavailable antibiotics should be considered for patients with IE who have cleared bacteremia and achieved clinical stability with IV regimens.
Citation: Spellberg B et al. Evaluation of a paradigm shift from intravenous antibiotics to oral step-down therapy for the treatment of infective endocarditis: a narrative review. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(5):769-77. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0555.
Dr. Yoo is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: The standard of care for IE has been a prolonged course of IV antibiotics. Recent literature has suggested that oral antibiotics might be a safe and effective step-down therapy for IE.
Study design: Systematic review.
Setting: Literature review in October 2019, with update in February 2020, consisting of 21 observational studies and 3 randomized controlled trials.
Synopsis: Three RCTs and 21 observational studies were reviewed, with a focus on the effectiveness of antibiotics administered orally for part of the therapeutic course for IE patients. Patients included in the study had left- or right-sided IE. Pathogens included viridians streptococci, staphylococci, and enterococci, with a minority of patients infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment regimens included beta-lactams, linezolid, fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or clindamycin, with or without rifampin.
In studies wherein IV antibiotics alone were compared with IV antibiotics with oral step-down therapy, there was no difference in clinical cure rate. Those given oral step-down therapy had a statistically significant lower mortality rate than patients who received only IV therapy.
Limitations include inconclusive data regarding duration of IV lead-in therapy, with the variance before conversion to oral antibiotics amongst the studies ranging from 0 to 24 days. The limited number of patients with MRSA infections makes it difficult to draw conclusions regarding this particular pathogen.
Bottom line: Highly orally bioavailable antibiotics should be considered for patients with IE who have cleared bacteremia and achieved clinical stability with IV regimens.
Citation: Spellberg B et al. Evaluation of a paradigm shift from intravenous antibiotics to oral step-down therapy for the treatment of infective endocarditis: a narrative review. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(5):769-77. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0555.
Dr. Yoo is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Anticoagulant choice in antiphospholipid syndrome–associated thrombosis
Background: DOACs have largely replaced VKAs as first-line therapy for venous thromboembolism in patients with adequate renal function. However, there is concern in APS that DOACs may have higher rates of recurrent thrombosis than VKAs when treating thromboembolism.
Study design: Randomized noninferiority trial.
Setting: Six teaching hospitals in Spain.
Synopsis: Of adults with thrombotic APS, 190 were randomized to receive rivaroxaban or warfarin. Primary outcomes were thrombotic events and major bleeding. Follow-up after 3 years demonstrated new thromboses in 11 patients (11.6%) in the DOAC group and 6 patients (6.3%) in the VKA group (P = .29). Major bleeding occurred in six patients (6.3%) in the DOAC group and seven patients (7.4%) in the VKA group (P = .77). By contrast, stroke occurred in nine patients in the DOAC group while the VKA group had zero events, yielding a significant relative RR of 19.00 (95% CI, 1.12-321.90) for the DOAC group.
The DOAC arm was not proven to be noninferior with respect to the primary outcome of thrombotic events. The higher risk of stroke in this group suggests the need for caution in using DOACs in this population.
Bottom line: DOACs have a higher risk of stroke than VKAs in patients with APS without a significant difference in rate of a major bleed.
Citation: Ordi-Ros J et. al. Rivaroxaban versus vitamin K antagonist in antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):685-94. doi: 10.7326/M19-0291.
Dr. Portnoy is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: DOACs have largely replaced VKAs as first-line therapy for venous thromboembolism in patients with adequate renal function. However, there is concern in APS that DOACs may have higher rates of recurrent thrombosis than VKAs when treating thromboembolism.
Study design: Randomized noninferiority trial.
Setting: Six teaching hospitals in Spain.
Synopsis: Of adults with thrombotic APS, 190 were randomized to receive rivaroxaban or warfarin. Primary outcomes were thrombotic events and major bleeding. Follow-up after 3 years demonstrated new thromboses in 11 patients (11.6%) in the DOAC group and 6 patients (6.3%) in the VKA group (P = .29). Major bleeding occurred in six patients (6.3%) in the DOAC group and seven patients (7.4%) in the VKA group (P = .77). By contrast, stroke occurred in nine patients in the DOAC group while the VKA group had zero events, yielding a significant relative RR of 19.00 (95% CI, 1.12-321.90) for the DOAC group.
The DOAC arm was not proven to be noninferior with respect to the primary outcome of thrombotic events. The higher risk of stroke in this group suggests the need for caution in using DOACs in this population.
Bottom line: DOACs have a higher risk of stroke than VKAs in patients with APS without a significant difference in rate of a major bleed.
Citation: Ordi-Ros J et. al. Rivaroxaban versus vitamin K antagonist in antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):685-94. doi: 10.7326/M19-0291.
Dr. Portnoy is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: DOACs have largely replaced VKAs as first-line therapy for venous thromboembolism in patients with adequate renal function. However, there is concern in APS that DOACs may have higher rates of recurrent thrombosis than VKAs when treating thromboembolism.
Study design: Randomized noninferiority trial.
Setting: Six teaching hospitals in Spain.
Synopsis: Of adults with thrombotic APS, 190 were randomized to receive rivaroxaban or warfarin. Primary outcomes were thrombotic events and major bleeding. Follow-up after 3 years demonstrated new thromboses in 11 patients (11.6%) in the DOAC group and 6 patients (6.3%) in the VKA group (P = .29). Major bleeding occurred in six patients (6.3%) in the DOAC group and seven patients (7.4%) in the VKA group (P = .77). By contrast, stroke occurred in nine patients in the DOAC group while the VKA group had zero events, yielding a significant relative RR of 19.00 (95% CI, 1.12-321.90) for the DOAC group.
The DOAC arm was not proven to be noninferior with respect to the primary outcome of thrombotic events. The higher risk of stroke in this group suggests the need for caution in using DOACs in this population.
Bottom line: DOACs have a higher risk of stroke than VKAs in patients with APS without a significant difference in rate of a major bleed.
Citation: Ordi-Ros J et. al. Rivaroxaban versus vitamin K antagonist in antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):685-94. doi: 10.7326/M19-0291.
Dr. Portnoy is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Chronically interrupted: The importance of communication with patient and family during the COVID-19 pandemic
Case narrative
A 35-year-old woman has worsening alcoholic cirrhosis and repeated admissions for ascites, hepato-renal syndrome, and alcoholic hepatitis. Upon recognition of her grave prognosis, we proceeded with a shared-management approach involving medicine, gastroenterology, social work, chaplaincy, and palliative care. When the team spoke with the patient’s health care proxy (HCP), family, and friends for collateral information and involvement in goals of care conversation, we realized that none were aware of her months-long decline and poor prognosis for recovery to hospital discharge.
Although several factors contributed to the disconnect between the patient and her support system, the obstacles were greatly exacerbated by profound changes in hospital protocol because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Physicians feel underprepared and challenged by prognostication and discussion of end of life during normal times; we believe COVID-19 has limited this essential physician role and led to tragic delays in effective communication and end of life planning.
Closing the loop
For patients with complex medical issues or those reaching end of life, effective communication within the health care system is critical. While inpatient teams often drive the plan, they care for their patients during a snapshot in time; contrarily, primary care providers and specialists often have established longitudinal relationships with their patients. Ergo, clinicians should communicate directly, and ideally with both patients and families, to achieve patient-centered and goal-concordant care.
For medically complex patients, PCPs tend to prefer verbal hand-offs. Timely and reliable communication between inpatient and outpatient providers has also been shown to prevent medical adverse events.1 Despite this, direct communication occurs infrequently.2 Given that hospitalists serve as primary inpatient providers for most general admissions, it is their responsibility to communicate with outpatient providers.
A multidisciplinary team redesigned the process by which PCPs were contacted following patient discharge. The transmission of information should ideally occur prior to discharge.3 Deficits in communication are extremely common and may negatively impact patient care, patient satisfaction, and patient safety.
Changes during the COVID-19 era
During the pandemic, patients have only one visitor per day, restricted visiting hours, and limited interactions with clinicians per implemented policies. Along with the increased burdens from personal protective equipment, remote hospital providers (social workers, case managers), and increased bureaucratic duties, COVID-19 has elucidated limitations in medical capacity and revealed the difficulties that clinicians face in communicating with patients and families, especially about serious illness.
Tasks include facilitating virtual goodbyes between dying patients and families, conducting family meetings via teleconference, and discussing patient care with specialists through virtual technologies.4 While these tasks are arguably more important during a global disaster, COVID-19 paradoxically restricts physical presence and severely hinders communication.5 Clinicians should continue to utilize core skills like building rapport, assessing patient/family perspectives and agenda, and using empathy.6 Patients tend to more frequently value functional outcomes while clinicians tend to default to treatment modalities.7 Additionally, goals of care and end of life discussions are associated with improved quality of life, fewer aggressive medical interventions near death, and even increased survival.
Given the limited resources and difficulties in communication during the pandemic, clinicians should place greater emphasis on values-based shared decision-making. Internet-based solutions are essential and widely used, and videoconferencing has been initiated at the institutional scale at many hospitals. Many clinicians with little experience are broadly implementing these technologies.7 Despite these technological innovations, issues still arise in how to communicate effectively in the hospital setting, and we must acknowledge that strategies require devices, Internet access, and technological literacy, highlighting disparities in access to quality health care.6 Conversations during the pandemic will require listening, empathy, responsive action, and the acknowledgment of the social determinants of health.7
Improving communication and transition of care
Multiple steps will be warranted to implement the safe transition process and improve communication. High-quality patient care encompasses careful review of medications, communication between inpatient and outpatient providers, and close follow-up at discharge. These steps serve to increase our reliance on patient compliance and the exchange of information about global progression of disease.
The quantitative and qualitative steps of transition of care should overcome disconnect between teams, specifically deficit areas regarding postdischarge communication, monitoring, and understanding of prognosis around the relevance to this era of COVID-19.
Dr. Haddad is a resident physician in the psychiatry residency program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. Dr. Halporn is clinic director, Division of Adult Palliative Care, in the department of psychosocial oncology and palliative care, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Barkoudah is associate director of the Hospital Medicine Unit at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
References
1. Goldman L et al. Passing the clinical baton: 6 principles to guide the hospitalist. Am J Med. 2001;111(9B):36S-39S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00968-8.
2. Kripalani S et al. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians. JAMA. 2007 Feb 28;297(8):831-41. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.8.831.
3. Scotten M et al. Minding the gap: Interprofessional communication during inpatient and post discharge chasm care. Patient Educ Couns. 2015 Jul;98(7):895-900. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2015.03.009.
4. Back A et al. Communication skills in the age of COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 2;172(11):759-60. doi: 10.7326/M20-1376.
5. Hart JL et al. Family-centered care during the COVID-19 era. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020 Aug;60(2):e93-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.04.017.
6. Rubinelli S et al. Implications of the current COVID-19 pandemic for communication in healthcare. Patient Educ Couns. 2020 Jun;103(6):1067-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2020.04.021.
7. Simpson N et al. Don’t forget shared decision-making in the COVID-19 crisis. Intern Med J. 2020 Jun;50(6):761-3. doi: 10.1111/imj.14862.
Case narrative
A 35-year-old woman has worsening alcoholic cirrhosis and repeated admissions for ascites, hepato-renal syndrome, and alcoholic hepatitis. Upon recognition of her grave prognosis, we proceeded with a shared-management approach involving medicine, gastroenterology, social work, chaplaincy, and palliative care. When the team spoke with the patient’s health care proxy (HCP), family, and friends for collateral information and involvement in goals of care conversation, we realized that none were aware of her months-long decline and poor prognosis for recovery to hospital discharge.
Although several factors contributed to the disconnect between the patient and her support system, the obstacles were greatly exacerbated by profound changes in hospital protocol because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Physicians feel underprepared and challenged by prognostication and discussion of end of life during normal times; we believe COVID-19 has limited this essential physician role and led to tragic delays in effective communication and end of life planning.
Closing the loop
For patients with complex medical issues or those reaching end of life, effective communication within the health care system is critical. While inpatient teams often drive the plan, they care for their patients during a snapshot in time; contrarily, primary care providers and specialists often have established longitudinal relationships with their patients. Ergo, clinicians should communicate directly, and ideally with both patients and families, to achieve patient-centered and goal-concordant care.
For medically complex patients, PCPs tend to prefer verbal hand-offs. Timely and reliable communication between inpatient and outpatient providers has also been shown to prevent medical adverse events.1 Despite this, direct communication occurs infrequently.2 Given that hospitalists serve as primary inpatient providers for most general admissions, it is their responsibility to communicate with outpatient providers.
A multidisciplinary team redesigned the process by which PCPs were contacted following patient discharge. The transmission of information should ideally occur prior to discharge.3 Deficits in communication are extremely common and may negatively impact patient care, patient satisfaction, and patient safety.
Changes during the COVID-19 era
During the pandemic, patients have only one visitor per day, restricted visiting hours, and limited interactions with clinicians per implemented policies. Along with the increased burdens from personal protective equipment, remote hospital providers (social workers, case managers), and increased bureaucratic duties, COVID-19 has elucidated limitations in medical capacity and revealed the difficulties that clinicians face in communicating with patients and families, especially about serious illness.
Tasks include facilitating virtual goodbyes between dying patients and families, conducting family meetings via teleconference, and discussing patient care with specialists through virtual technologies.4 While these tasks are arguably more important during a global disaster, COVID-19 paradoxically restricts physical presence and severely hinders communication.5 Clinicians should continue to utilize core skills like building rapport, assessing patient/family perspectives and agenda, and using empathy.6 Patients tend to more frequently value functional outcomes while clinicians tend to default to treatment modalities.7 Additionally, goals of care and end of life discussions are associated with improved quality of life, fewer aggressive medical interventions near death, and even increased survival.
Given the limited resources and difficulties in communication during the pandemic, clinicians should place greater emphasis on values-based shared decision-making. Internet-based solutions are essential and widely used, and videoconferencing has been initiated at the institutional scale at many hospitals. Many clinicians with little experience are broadly implementing these technologies.7 Despite these technological innovations, issues still arise in how to communicate effectively in the hospital setting, and we must acknowledge that strategies require devices, Internet access, and technological literacy, highlighting disparities in access to quality health care.6 Conversations during the pandemic will require listening, empathy, responsive action, and the acknowledgment of the social determinants of health.7
Improving communication and transition of care
Multiple steps will be warranted to implement the safe transition process and improve communication. High-quality patient care encompasses careful review of medications, communication between inpatient and outpatient providers, and close follow-up at discharge. These steps serve to increase our reliance on patient compliance and the exchange of information about global progression of disease.
The quantitative and qualitative steps of transition of care should overcome disconnect between teams, specifically deficit areas regarding postdischarge communication, monitoring, and understanding of prognosis around the relevance to this era of COVID-19.
Dr. Haddad is a resident physician in the psychiatry residency program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. Dr. Halporn is clinic director, Division of Adult Palliative Care, in the department of psychosocial oncology and palliative care, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Barkoudah is associate director of the Hospital Medicine Unit at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
References
1. Goldman L et al. Passing the clinical baton: 6 principles to guide the hospitalist. Am J Med. 2001;111(9B):36S-39S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00968-8.
2. Kripalani S et al. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians. JAMA. 2007 Feb 28;297(8):831-41. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.8.831.
3. Scotten M et al. Minding the gap: Interprofessional communication during inpatient and post discharge chasm care. Patient Educ Couns. 2015 Jul;98(7):895-900. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2015.03.009.
4. Back A et al. Communication skills in the age of COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 2;172(11):759-60. doi: 10.7326/M20-1376.
5. Hart JL et al. Family-centered care during the COVID-19 era. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020 Aug;60(2):e93-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.04.017.
6. Rubinelli S et al. Implications of the current COVID-19 pandemic for communication in healthcare. Patient Educ Couns. 2020 Jun;103(6):1067-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2020.04.021.
7. Simpson N et al. Don’t forget shared decision-making in the COVID-19 crisis. Intern Med J. 2020 Jun;50(6):761-3. doi: 10.1111/imj.14862.
Case narrative
A 35-year-old woman has worsening alcoholic cirrhosis and repeated admissions for ascites, hepato-renal syndrome, and alcoholic hepatitis. Upon recognition of her grave prognosis, we proceeded with a shared-management approach involving medicine, gastroenterology, social work, chaplaincy, and palliative care. When the team spoke with the patient’s health care proxy (HCP), family, and friends for collateral information and involvement in goals of care conversation, we realized that none were aware of her months-long decline and poor prognosis for recovery to hospital discharge.
Although several factors contributed to the disconnect between the patient and her support system, the obstacles were greatly exacerbated by profound changes in hospital protocol because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Physicians feel underprepared and challenged by prognostication and discussion of end of life during normal times; we believe COVID-19 has limited this essential physician role and led to tragic delays in effective communication and end of life planning.
Closing the loop
For patients with complex medical issues or those reaching end of life, effective communication within the health care system is critical. While inpatient teams often drive the plan, they care for their patients during a snapshot in time; contrarily, primary care providers and specialists often have established longitudinal relationships with their patients. Ergo, clinicians should communicate directly, and ideally with both patients and families, to achieve patient-centered and goal-concordant care.
For medically complex patients, PCPs tend to prefer verbal hand-offs. Timely and reliable communication between inpatient and outpatient providers has also been shown to prevent medical adverse events.1 Despite this, direct communication occurs infrequently.2 Given that hospitalists serve as primary inpatient providers for most general admissions, it is their responsibility to communicate with outpatient providers.
A multidisciplinary team redesigned the process by which PCPs were contacted following patient discharge. The transmission of information should ideally occur prior to discharge.3 Deficits in communication are extremely common and may negatively impact patient care, patient satisfaction, and patient safety.
Changes during the COVID-19 era
During the pandemic, patients have only one visitor per day, restricted visiting hours, and limited interactions with clinicians per implemented policies. Along with the increased burdens from personal protective equipment, remote hospital providers (social workers, case managers), and increased bureaucratic duties, COVID-19 has elucidated limitations in medical capacity and revealed the difficulties that clinicians face in communicating with patients and families, especially about serious illness.
Tasks include facilitating virtual goodbyes between dying patients and families, conducting family meetings via teleconference, and discussing patient care with specialists through virtual technologies.4 While these tasks are arguably more important during a global disaster, COVID-19 paradoxically restricts physical presence and severely hinders communication.5 Clinicians should continue to utilize core skills like building rapport, assessing patient/family perspectives and agenda, and using empathy.6 Patients tend to more frequently value functional outcomes while clinicians tend to default to treatment modalities.7 Additionally, goals of care and end of life discussions are associated with improved quality of life, fewer aggressive medical interventions near death, and even increased survival.
Given the limited resources and difficulties in communication during the pandemic, clinicians should place greater emphasis on values-based shared decision-making. Internet-based solutions are essential and widely used, and videoconferencing has been initiated at the institutional scale at many hospitals. Many clinicians with little experience are broadly implementing these technologies.7 Despite these technological innovations, issues still arise in how to communicate effectively in the hospital setting, and we must acknowledge that strategies require devices, Internet access, and technological literacy, highlighting disparities in access to quality health care.6 Conversations during the pandemic will require listening, empathy, responsive action, and the acknowledgment of the social determinants of health.7
Improving communication and transition of care
Multiple steps will be warranted to implement the safe transition process and improve communication. High-quality patient care encompasses careful review of medications, communication between inpatient and outpatient providers, and close follow-up at discharge. These steps serve to increase our reliance on patient compliance and the exchange of information about global progression of disease.
The quantitative and qualitative steps of transition of care should overcome disconnect between teams, specifically deficit areas regarding postdischarge communication, monitoring, and understanding of prognosis around the relevance to this era of COVID-19.
Dr. Haddad is a resident physician in the psychiatry residency program at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. Dr. Halporn is clinic director, Division of Adult Palliative Care, in the department of psychosocial oncology and palliative care, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Barkoudah is associate director of the Hospital Medicine Unit at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
References
1. Goldman L et al. Passing the clinical baton: 6 principles to guide the hospitalist. Am J Med. 2001;111(9B):36S-39S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00968-8.
2. Kripalani S et al. Deficits in communication and information transfer between hospital-based and primary care physicians. JAMA. 2007 Feb 28;297(8):831-41. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.8.831.
3. Scotten M et al. Minding the gap: Interprofessional communication during inpatient and post discharge chasm care. Patient Educ Couns. 2015 Jul;98(7):895-900. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2015.03.009.
4. Back A et al. Communication skills in the age of COVID-19. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 2;172(11):759-60. doi: 10.7326/M20-1376.
5. Hart JL et al. Family-centered care during the COVID-19 era. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2020 Aug;60(2):e93-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.04.017.
6. Rubinelli S et al. Implications of the current COVID-19 pandemic for communication in healthcare. Patient Educ Couns. 2020 Jun;103(6):1067-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2020.04.021.
7. Simpson N et al. Don’t forget shared decision-making in the COVID-19 crisis. Intern Med J. 2020 Jun;50(6):761-3. doi: 10.1111/imj.14862.
Apixaban a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
Background: Over 6 million Americans are prescribed anticoagulation; however, available anticoagulation options for patients with concomitant renal impairment are limited. Until recently, warfarin was the only recommended option because of a lack of data to support the use of alternative agents in such patients. This study evaluates the safety and effectiveness of apixaban, compared with warfarin, in patients with severe renal dysfunction.
Study design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Seven hospitals in Michigan between January 2013 and December 2015 and including adult patients with CrCl less than 25 cc/min who were newly initiated on apixaban or warfarin.
Synopsis: Patients in the apixaban group (n=128) had a higher rate of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stent placement, and hyperlipidemia, while the warfarin group (n=733) had a higher rate of prior venous thromboembolism. The primary outcome was time to first bleeding or thrombotic event. Apixaban was associated with a lower risk of thrombotic or bleeding events, compared with warfarin (HR, 0.47). Post-hoc analysis controlling for patient differences showed similar results. There was no statistical difference in the severity of events or overall mortality. Further subgroup analysis showed that 5 mg B.I.D. dosing was not associated with higher risk of bleeding than 2.5 mg B.I.D.
The main limitation is the retrospective observational design, which may have introduced confounding variables that were not accounted for in the analyses. The study also did not account for patient nonadherence to medication.
Bottom line: Apixaban is a reasonable alternative to warfarin in patients with severe renal impairment.
Citation: Hanni C et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs. warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020;4(11): 2366-71. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000972.
Dr. Narayan is a hospitalist in the Division of Hospital Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New York.
New data on rare myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Adolescents and adults younger than age 21 who develop myocarditis after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination frequently have abnormal findings on cardiac MRI (cMRI) but most have a mild clinical course with rapid resolution of symptoms, a new study concludes.
“This study supports what we’ve been seeing. People identified and treated early and appropriately for the rare complication of COVID-19 vaccine-related myocarditis typically experienced only mild cases and short recovery times,” American Heart Association President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a podcast.
“Overwhelmingly, the data continue to indicate [that] the benefits of COVID-19 vaccine far outweigh any very rare risks of adverse events from the vaccine, including myocarditis,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
The study was published online Dec. 6 in Circulation.
Using data from 26 pediatric medical centers across the United States and Canada, the researchers reviewed the medical records of 139 patients younger than 21 with suspected myocarditis within 1 month of receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
They made the following key observations:
- Most patients were male (90.6%), White (66.2%) and with a median age of 15.8 years.
- Suspected myocarditis occurred in 136 patients (97.8%) following mRNA vaccine, with 131 (94.2%) following the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; 128 cases (91.4%) occurred after the second dose.
- Symptoms started a median of 2 days (range 0 to 22 days) following vaccination administration.
- Chest pain was the most common symptom (99.3%), with fever present in 30.9% of patients and shortness of breath in 27.3%.
- Patients were treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (81.3%), intravenous immunoglobulin (21.6%), glucocorticoids (21.6%), colchicine (7.9%) or no anti-inflammatory therapies (8.6%).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) were admitted to the intensive care unit; 2 received inotropic/vasoactive support; none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or died.
- Median time spent in the hospital was 2 days.
- A total of 111 patients had elevated troponin I (8.12 ng/mL) and 28 had elevated troponin T (0.61 ng/mL).
- More than two-thirds (69.8%) had abnormal electrocardiograms and/or arrhythmias (7 with nonsustained ventricular tachycardia).
- Twenty-six patients (18.7%) had left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 55% on echocardiogram; LVEF had returned to normal in the 25 who returned for follow-up.
- 75 of 97 patients (77.3%) who underwent cMRI at a median of 5 days from symptom onset had abnormal findings; 74 (76.3%) had late gadolinium enhancement, 54 (55.7%) had myocardial edema, and 49 (50.5%) met Lake Louise criteria for myocarditis.
“These data suggest that most cases of suspected COVID-19 vaccine–related myocarditis in people younger than 21 are mild and resolve quickly,” corresponding author Dongngan Truong, MD, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“We were very happy to see that type of recovery. However, we are awaiting further studies to better understand the long-term outcomes of patients who have had COVID-19 vaccination-related myocarditis. We also need to study the risk factors and mechanisms for this rare complication,” Dr. Truong added.
Dr. Lloyd-Jones said these findings support the AHA’s position that COVID-19 vaccines are “safe, highly effective, and fundamental to saving lives, protecting our families and communities against COVID-19, and ending the pandemic.”
The study received no funding. Dr. Truong consults for Pfizer on vaccine-associated myocarditis. A complete list of author disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.