User login
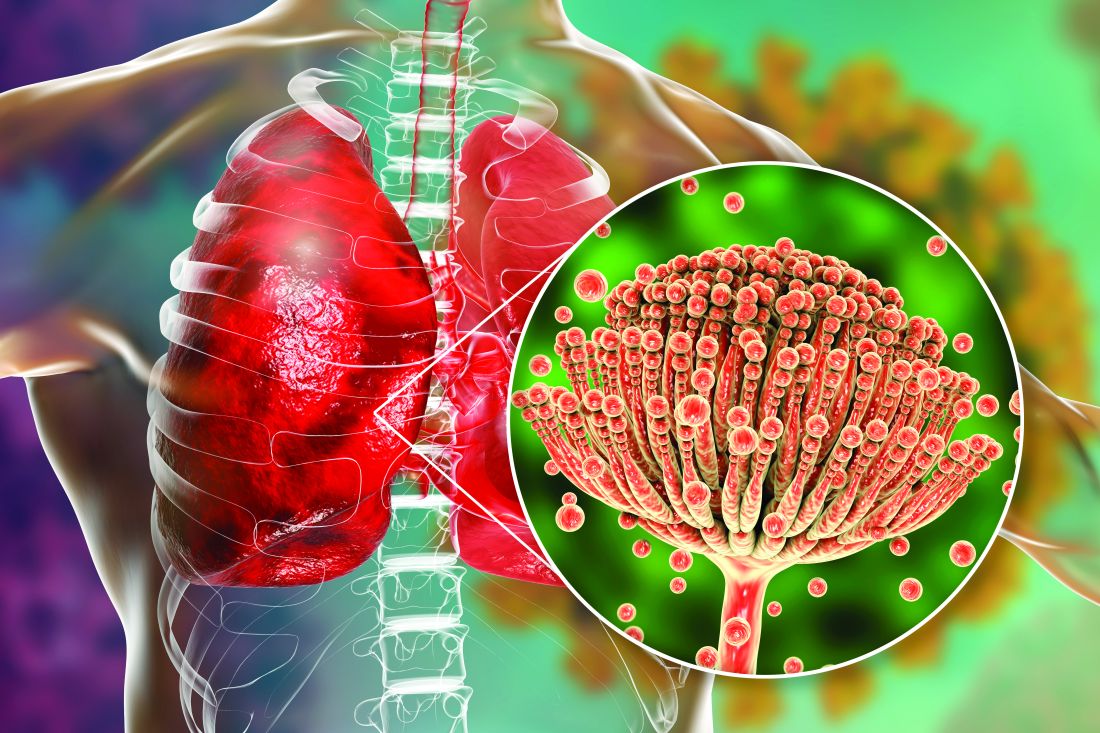
Rise of the fungi: Pandemic tied to increasing fungal infections
COVID-19 has lifted the lid on the risks of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with severe respiratory viral illness – even previously immunocompetent individuals – and highlighted the importance of vigilant investigation to achieve early diagnoses, leading experts say.
Most fungi are not under surveillance in the United States, leaving experts without a national picture of the true burden of infection through the pandemic. However, a collection of published case series, cohort studies, and reviews from Europe, the United States, and throughout the world – mainly pre-Omicron – show that fungal disease has affected a significant portion of critically ill patients with COVID-19, with concerning excess mortality, these experts say.
COVID-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) has been the predominant fungal coinfection in the United States and internationally. But COVID-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – the infection that surged in India in early 2021 – has also affected some patients in the United States, published data show. So have Pneumocystitis pneumonia, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, and Candida infections (which mainly affect the bloodstream and abdomen), say the experts who were interviewed.
“We had predicted [a rise in] aspergillosis, but we saw more than we thought we’d see. Most fungal infections became more common with COVID-19,” said George Thompson, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Davis, and cochair of the University of Alabama–based Mycoses Study Group Education Committee, a group of experts in medical mycology. Pneumocystitis, for instance, “has historically been associated with AIDS or different types of leukemia or lymphoma, and is not an infection we’ve typically seen in our otherwise healthy ICU patients,” he noted. “But we did see more of it [with COVID-19].”
More recently, with fewer patients during the Omicron phase in intensive care units with acute respiratory failure, the profile of fungal disease secondary to COVID-19 has changed. Increasing proportions of patients have traditional risk factors for aspergillosis, such as hematologic malignancies and longer-term, pre-COVID use of systemic corticosteroids – a change that makes the contribution of the viral illness harder to distinguish.
Moving forward, the lessons of the COVID era – the fungal risks to patients with serious viral infections and the persistence needed to diagnose aspergillosis and other pulmonary fungal infections using bronchoscopy and imperfect noninvasive tests – should be taken to heart, experts say.
“Fungal diseases are not rare. They’re just not diagnosed because no one thinks to look for them,” said Dr. Thompson, a contributor to a recently released World Health Organization report naming a “fungal priority pathogens” list.
“We’re going to continue to see [secondary fungal infections] with other respiratory viruses,” he said. And overall, given environmental and other changes, “we’re going to see more and more fungal disease in the patients we take care of.”
CAPA not a surprise
CAPA is “not an unfamiliar story” in the world of fungal disease, given a history of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA), said Kieren A. Marr, MD, MBA, adjunct professor of medicine and past director of the transplant and oncology infectious diseases program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who has long researched invasive fungal disease.
European researchers, she said, have led the way in describing a high incidence of IAPA in patients admitted to ICUs with influenza. In a retrospective multicenter cohort study reported in 2018 by the Dutch-Belgian Mycosis Study group, for instance, almost 20% of 432 influenza patients admitted to the ICU, including patients who were otherwise healthy and not immunocompromised, had the diagnosis a median of 3 days after ICU admission. (Across other cohort studies, rates of IAPA have ranged from 7% to 30%.)
Mortality was significant: 51% of patients with influenza and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis died within 90 days, compared with 28% of patients with influenza and no invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Reports from Europe early in the pandemic indicated that CAPA was a similarly serious problem, prompting establishment at Johns Hopkins University of an aggressive screening program utilizing biomarker-based testing of blood and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Of 396 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients admitted to Johns Hopkins University hospitals between March and August 2020, 39 met the institution’s criteria for CAPA, Dr. Marr and her colleagues reported this year in what might be the largest U.S. cohort study of CAPA published to date.
“We now know definitively that people with severe influenza and with severe COVID also have high risks for both invasive and airway disease caused by airborne fungi, most commonly aspergilliosis,” Dr. Marr said.
More recent unpublished analyses of patients from the start of the pandemic to June 2021 show persistent risk, said Nitipong Permpalung, MD, MPH, assistant professor in transplant and oncology infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University and lead author of the cohort study. Among 832 patients with COVID-19 who were mechanically ventilated in Johns Hopkins University hospitals, 11.8% had CAPA, he said. (Also, 3.2% had invasive candidiasis, and 1.1% had other invasive fungal infections.)
Other sources said in interviews that these CAPA prevalence rates generally mirror reports from Europe, though some investigators in Europe have reported CAPA rates more toward 15%.
(The Mycoses Study Group recently collected data from its consortium of U.S. medical centers on the prevalence of CAPA, with funding support from the CDC, but at press time the data had not yet been released. Dr. Thompson said he suspected the prevalence will be lower than earlier papers have suggested, “but still will reflect a significant burden of disease.”)
Patients in the published Johns Hopkins University study who had CAPA were more likely than those with COVID-19 but no CAPA to have underlying pulmonary disease, liver disease, coagulopathy, solid tumors, multiple myeloma, and COVID-19–directed corticosteroids. And they had uniformly worse outcomes with regards to severity of illness and length of intubation.
How much of CAPA is driven by the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself and how much is a consequence of COVID-19 treatments is a topic of active discussion and research. Martin Hoenigl, MD, of the University of Graz, Austria, a leading researcher in medical mycology, said research shows corticosteroids and anti–IL-6 treatments, such as tocilizumab, used to treat COVID-19–driven acute respiratory failure clearly have contributed to CAPA. But he contends that “a number of other mechanisms” are involved as well.
“The immunologic mechanisms are definitely different in these patients with viral illness than in other ICU patients [who develop aspergilliosis]. It’s not just the corticosteroids. The more we learn, we see the virus plays a role as well, suppressing the interferon pathway,” for example, said Dr. Hoenigl, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases and the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Center of Excellence at the university. The earliest reports of CAPA came “when ICUs weren’t using dexamethasone or tocilizumab,” he noted.
In a paper published recently in Lancet Respiratory Medicine that Dr. Hoenigl and others point to, Belgian researchers reported a “three-level breach” in innate antifungal immunity in both IAPA and CAPA, affecting the integrity of the epithelial barrier, the capacity to phagocytose and kill Aspergillus spores, and the ability to destroy Aspergillus hyphae, which is mainly mediated by neutrophils.
The researchers ran a host of genetic and protein analyses on lung samples (most collected via BAL) of 169 patients with influenza or COVID-19, with and without aspergillosis. They found that patients with CAPA had significantly lower neutrophil cell fractions than patients with COVID-19 only, and patients with IAPA or CAPA had reduced type II IFN signaling and increased concentrations of fibrosis-associated growth factors in the lower respiratory tracts (Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Aug 24).
Tom Chiller, MD, MPH, chief of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Mycotic Disease Branch, said he’s watching such research with interest. For now, he said, it’s important to also consider that “data on COVID show that almost all patients going into the ICUs with pneumonia and COVID are getting broad-spectrum antibiotics” in addition to corticosteroids.
By wiping out good bacteria, the antibiotics could be “creating a perfect niche for fungi to grow,” he said.
Diagnostic challenges
Aspergillus that has invaded the lung tissue in patients with COVID-19 appears to grow there for some time – around 8-10 days, much longer than in IAPA – before becoming angioinvasive, said Dr. Hoenigl. Such a pathophysiology “implicates that we should try to diagnose it while it’s in the lung tissue, using the BAL fluid, and not yet in the blood,” he said.
Some multicenter studies, including one from Europe on Aspergillus test profiles in critically ill COVID-19 patients, have shown mortality rates of close to 90% in patients with CAPA who have positive serum biomarkers, despite appropriate antifungal therapy. “If diagnosed while confined to the lung, however, mortality rates are more like 40%-50% with antifungal therapy,” Dr. Hoenigl said. (Cohort studies published thus far have fairly consistently reported mortality rates in patients with CAPA greater than 40%, he said.)
Bronchoscopy isn’t always pragmatic or possible, however, and is variably used. Some patients with severe COVID-19 may be too unstable for any invasive procedure, said Dr. Permpalung.
Dr. Permpalung looks for CAPA using serum (1-3) beta-D-glucan (BDG, a generic fungal test not specific to Aspergillus), serum galactomannan (GM, specific for Aspergillus), and respiratory cultures (sputum or endotracheal aspirate if intubated) as initial screening tests in the ICU. If there are concerns for CAPA – based on these tests and/or the clinical picture – “a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion is required to determine if patients would benefit from a bronchoscopy or if we should just start them on empiric antifungal therapy.”
Unfortunately, the sensitivity of serum GM is relatively low in CAPA – lower than with classic invasive aspergillosis in the nonviral setting, sources said. BDG, on the other hand, can be falsely positive in the setting of antimicrobials and within the ICU. And the utility of imaging for CAPA is limited. Both the clinical picture and radiological findings of CAPA have resembled those of severe COVID – with the caveat of cavitary lung lesions visible on imaging.
“Cavities or nodules are a highly suspicious finding that could indicate possible fungal infection,” said pulmonologist Amir A. Zeki, MD, MAS, professor of medicine at the University of California, Davis, and codirector of the UC Davis Asthma Network Clinic, who has cared for patients with CAPA.
Cavitation has been described in only a proportion of patients with CAPA, however. So in patients not doing well, “your suspicion has to be raised if you’re not seeing cavities,” he said.
Early in the pandemic, when patients worsened or failed to progress on mechanical ventilation, clinicians at the University of California, Davis, quickly learned not to pin blame too quickly on COVID-19 alone. This remains good advice today, Dr. Zeki said.
“If you have a patient who’s not doing well on a ventilator, not getting better [over weeks], has to be reintubated, has infiltrates or lung nodules that are evolving, or certainly, if they have a cavity, you have to suspect fungal infection,” said Dr. Zeki, who also practices at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego. “Think about it for those patients who just aren’t moving forward and are continuing to struggle. Have a high index of suspicion, and consult with your infectious disease colleagues.”
Empiric treatment is warranted in some cases if a patient is doing poorly and suspicion for fungal infection is high based on clinical, radiographic, and/or laboratory evidence, he said.
The CDC’s Dr. Chiller said that screening and diagnostic algorithms currently vary from institution to institution, and that diagnostic challenges likely dissuade clinicians from thinking about fungi. “Clinicians often don’t want to deal with fungi – they’re difficult to diagnose, the treatments are limited and can be toxic. But fungi get pushed back until it’s too late,” he said.
“Fungal diagnostics is an area we all need a lot more help with,” and new diagnostics are in the pipeline, he said. In the meantime, he said, “there are tools out there, and we just need to use them more, and improve how they’re used.”
While reported CAPA thus far has typically occurred in the setting of ICU care and mechanical ventilation, it’s not always the case, Dr. Permpalung said. Lung and other solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients with COVID-19 are developing CAPA and other invasive secondary invasive fungal infections despite not being intubated, he said.
Of 276 SOT recipients with COVID-19 who required inpatient treatment at Johns Hopkins University hospitals from the beginning of the pandemic to March 2022, 23 patients developed invasive fungal infections (13 CAPA). Only a fraction – 38 of the 276 – had been intubated, he said.
Mucormycosis resistance
After CAPA, candidiasis and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – most frequently, rhino-orbital-cerebral disease or pulmonary disease – have been the leading reported fungal coinfections in COVID-19, said Dr. Hoenigl, who described the incidence, timeline, risk factors, and pathogenesis of these infections in a review published this year in Nature Microbiology. .
In India, where there has long been high exposure to Mucorales spores and a greater burden of invasive fungal disease, the rate of mucormycosis doubled in 2021, with rhino-orbital-cerebral disease reported almost exclusively, he said. Pulmonary disease has occurred almost exclusively in the ICU setting and has been present in about 50% of cases outside of India, including Europe and the United States.
A preprint meta-analysis of CAM cases posted by the Lancet in July 2022, in which investigators analyzed individual data of 556 reported cases of COVID-19–associated CAM, shows diabetes and history of corticosteroid use present in most patients, and an overall mortality rate of 44.4%, most of which stems from cases of pulmonary or disseminated disease. Thirteen of the 556 reported cases were from the United States.
An important take-away from the analysis, Dr. Hoenigl said, is that Aspergillus coinfection was seen in 7% of patients and was associated with higher mortality. “It’s important to consider that coinfections [of Aspergillus and Mucorales] can exist,” Dr. Hoenigl said, noting that like CAPA, pulmonary CAM is likely underdiagnosed and underreported.
As with CAPA, the clinical and radiological features of pulmonary CAM largely overlap with those associated with COVID-19, and bronchoscopy plays a central role in definitive diagnosis. In the United States, a Mucorales PCR test for blood and BAL fluid is commercially available and used at some centers, Dr. Hoenigl said.
“Mucormycosis is always difficult to treat ... a lot of the treatments don’t work particularly well,” said Dr. Thompson. “With aspergillosis, we have better treatment options.”
Dr. Thompson worries, however, about treatment resistance becoming widespread. Resistance to azole antifungal agents “is already pretty widespread in northern Europe, particularly in the Netherlands and part of the U.K.” because of injudicious use of antifungals in agriculture, he said. “We’ve started to see a few cases [of azole-resistant aspergillosis in the United States] and know it will be more widespread soon.”
Treatment resistance is a focus of the new WHO fungal priority pathogens list – the first such report from the organization. Of the 19 fungi on the list, 4 were ranked as critical: Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida auris, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida albicans. Like Dr. Thompson, Dr. Hoenigl contributed to the WHO report.
Dr. Hoenigl reported grant/research support from Astellas, Merck, F2G, Gilread, Pfizer, and Scynexis. Dr. Marr disclosed employment and equity in Pearl Diagnostics and Sfunga Therapeutics. Dr. Thompson, Dr. Permpalung, and Dr. Zeki reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
COVID-19 has lifted the lid on the risks of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with severe respiratory viral illness – even previously immunocompetent individuals – and highlighted the importance of vigilant investigation to achieve early diagnoses, leading experts say.
Most fungi are not under surveillance in the United States, leaving experts without a national picture of the true burden of infection through the pandemic. However, a collection of published case series, cohort studies, and reviews from Europe, the United States, and throughout the world – mainly pre-Omicron – show that fungal disease has affected a significant portion of critically ill patients with COVID-19, with concerning excess mortality, these experts say.
COVID-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) has been the predominant fungal coinfection in the United States and internationally. But COVID-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – the infection that surged in India in early 2021 – has also affected some patients in the United States, published data show. So have Pneumocystitis pneumonia, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, and Candida infections (which mainly affect the bloodstream and abdomen), say the experts who were interviewed.
“We had predicted [a rise in] aspergillosis, but we saw more than we thought we’d see. Most fungal infections became more common with COVID-19,” said George Thompson, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Davis, and cochair of the University of Alabama–based Mycoses Study Group Education Committee, a group of experts in medical mycology. Pneumocystitis, for instance, “has historically been associated with AIDS or different types of leukemia or lymphoma, and is not an infection we’ve typically seen in our otherwise healthy ICU patients,” he noted. “But we did see more of it [with COVID-19].”
More recently, with fewer patients during the Omicron phase in intensive care units with acute respiratory failure, the profile of fungal disease secondary to COVID-19 has changed. Increasing proportions of patients have traditional risk factors for aspergillosis, such as hematologic malignancies and longer-term, pre-COVID use of systemic corticosteroids – a change that makes the contribution of the viral illness harder to distinguish.
Moving forward, the lessons of the COVID era – the fungal risks to patients with serious viral infections and the persistence needed to diagnose aspergillosis and other pulmonary fungal infections using bronchoscopy and imperfect noninvasive tests – should be taken to heart, experts say.
“Fungal diseases are not rare. They’re just not diagnosed because no one thinks to look for them,” said Dr. Thompson, a contributor to a recently released World Health Organization report naming a “fungal priority pathogens” list.
“We’re going to continue to see [secondary fungal infections] with other respiratory viruses,” he said. And overall, given environmental and other changes, “we’re going to see more and more fungal disease in the patients we take care of.”
CAPA not a surprise
CAPA is “not an unfamiliar story” in the world of fungal disease, given a history of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA), said Kieren A. Marr, MD, MBA, adjunct professor of medicine and past director of the transplant and oncology infectious diseases program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who has long researched invasive fungal disease.
European researchers, she said, have led the way in describing a high incidence of IAPA in patients admitted to ICUs with influenza. In a retrospective multicenter cohort study reported in 2018 by the Dutch-Belgian Mycosis Study group, for instance, almost 20% of 432 influenza patients admitted to the ICU, including patients who were otherwise healthy and not immunocompromised, had the diagnosis a median of 3 days after ICU admission. (Across other cohort studies, rates of IAPA have ranged from 7% to 30%.)
Mortality was significant: 51% of patients with influenza and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis died within 90 days, compared with 28% of patients with influenza and no invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Reports from Europe early in the pandemic indicated that CAPA was a similarly serious problem, prompting establishment at Johns Hopkins University of an aggressive screening program utilizing biomarker-based testing of blood and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Of 396 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients admitted to Johns Hopkins University hospitals between March and August 2020, 39 met the institution’s criteria for CAPA, Dr. Marr and her colleagues reported this year in what might be the largest U.S. cohort study of CAPA published to date.
“We now know definitively that people with severe influenza and with severe COVID also have high risks for both invasive and airway disease caused by airborne fungi, most commonly aspergilliosis,” Dr. Marr said.
More recent unpublished analyses of patients from the start of the pandemic to June 2021 show persistent risk, said Nitipong Permpalung, MD, MPH, assistant professor in transplant and oncology infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University and lead author of the cohort study. Among 832 patients with COVID-19 who were mechanically ventilated in Johns Hopkins University hospitals, 11.8% had CAPA, he said. (Also, 3.2% had invasive candidiasis, and 1.1% had other invasive fungal infections.)
Other sources said in interviews that these CAPA prevalence rates generally mirror reports from Europe, though some investigators in Europe have reported CAPA rates more toward 15%.
(The Mycoses Study Group recently collected data from its consortium of U.S. medical centers on the prevalence of CAPA, with funding support from the CDC, but at press time the data had not yet been released. Dr. Thompson said he suspected the prevalence will be lower than earlier papers have suggested, “but still will reflect a significant burden of disease.”)
Patients in the published Johns Hopkins University study who had CAPA were more likely than those with COVID-19 but no CAPA to have underlying pulmonary disease, liver disease, coagulopathy, solid tumors, multiple myeloma, and COVID-19–directed corticosteroids. And they had uniformly worse outcomes with regards to severity of illness and length of intubation.
How much of CAPA is driven by the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself and how much is a consequence of COVID-19 treatments is a topic of active discussion and research. Martin Hoenigl, MD, of the University of Graz, Austria, a leading researcher in medical mycology, said research shows corticosteroids and anti–IL-6 treatments, such as tocilizumab, used to treat COVID-19–driven acute respiratory failure clearly have contributed to CAPA. But he contends that “a number of other mechanisms” are involved as well.
“The immunologic mechanisms are definitely different in these patients with viral illness than in other ICU patients [who develop aspergilliosis]. It’s not just the corticosteroids. The more we learn, we see the virus plays a role as well, suppressing the interferon pathway,” for example, said Dr. Hoenigl, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases and the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Center of Excellence at the university. The earliest reports of CAPA came “when ICUs weren’t using dexamethasone or tocilizumab,” he noted.
In a paper published recently in Lancet Respiratory Medicine that Dr. Hoenigl and others point to, Belgian researchers reported a “three-level breach” in innate antifungal immunity in both IAPA and CAPA, affecting the integrity of the epithelial barrier, the capacity to phagocytose and kill Aspergillus spores, and the ability to destroy Aspergillus hyphae, which is mainly mediated by neutrophils.
The researchers ran a host of genetic and protein analyses on lung samples (most collected via BAL) of 169 patients with influenza or COVID-19, with and without aspergillosis. They found that patients with CAPA had significantly lower neutrophil cell fractions than patients with COVID-19 only, and patients with IAPA or CAPA had reduced type II IFN signaling and increased concentrations of fibrosis-associated growth factors in the lower respiratory tracts (Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Aug 24).
Tom Chiller, MD, MPH, chief of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Mycotic Disease Branch, said he’s watching such research with interest. For now, he said, it’s important to also consider that “data on COVID show that almost all patients going into the ICUs with pneumonia and COVID are getting broad-spectrum antibiotics” in addition to corticosteroids.
By wiping out good bacteria, the antibiotics could be “creating a perfect niche for fungi to grow,” he said.
Diagnostic challenges
Aspergillus that has invaded the lung tissue in patients with COVID-19 appears to grow there for some time – around 8-10 days, much longer than in IAPA – before becoming angioinvasive, said Dr. Hoenigl. Such a pathophysiology “implicates that we should try to diagnose it while it’s in the lung tissue, using the BAL fluid, and not yet in the blood,” he said.
Some multicenter studies, including one from Europe on Aspergillus test profiles in critically ill COVID-19 patients, have shown mortality rates of close to 90% in patients with CAPA who have positive serum biomarkers, despite appropriate antifungal therapy. “If diagnosed while confined to the lung, however, mortality rates are more like 40%-50% with antifungal therapy,” Dr. Hoenigl said. (Cohort studies published thus far have fairly consistently reported mortality rates in patients with CAPA greater than 40%, he said.)
Bronchoscopy isn’t always pragmatic or possible, however, and is variably used. Some patients with severe COVID-19 may be too unstable for any invasive procedure, said Dr. Permpalung.
Dr. Permpalung looks for CAPA using serum (1-3) beta-D-glucan (BDG, a generic fungal test not specific to Aspergillus), serum galactomannan (GM, specific for Aspergillus), and respiratory cultures (sputum or endotracheal aspirate if intubated) as initial screening tests in the ICU. If there are concerns for CAPA – based on these tests and/or the clinical picture – “a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion is required to determine if patients would benefit from a bronchoscopy or if we should just start them on empiric antifungal therapy.”
Unfortunately, the sensitivity of serum GM is relatively low in CAPA – lower than with classic invasive aspergillosis in the nonviral setting, sources said. BDG, on the other hand, can be falsely positive in the setting of antimicrobials and within the ICU. And the utility of imaging for CAPA is limited. Both the clinical picture and radiological findings of CAPA have resembled those of severe COVID – with the caveat of cavitary lung lesions visible on imaging.
“Cavities or nodules are a highly suspicious finding that could indicate possible fungal infection,” said pulmonologist Amir A. Zeki, MD, MAS, professor of medicine at the University of California, Davis, and codirector of the UC Davis Asthma Network Clinic, who has cared for patients with CAPA.
Cavitation has been described in only a proportion of patients with CAPA, however. So in patients not doing well, “your suspicion has to be raised if you’re not seeing cavities,” he said.
Early in the pandemic, when patients worsened or failed to progress on mechanical ventilation, clinicians at the University of California, Davis, quickly learned not to pin blame too quickly on COVID-19 alone. This remains good advice today, Dr. Zeki said.
“If you have a patient who’s not doing well on a ventilator, not getting better [over weeks], has to be reintubated, has infiltrates or lung nodules that are evolving, or certainly, if they have a cavity, you have to suspect fungal infection,” said Dr. Zeki, who also practices at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego. “Think about it for those patients who just aren’t moving forward and are continuing to struggle. Have a high index of suspicion, and consult with your infectious disease colleagues.”
Empiric treatment is warranted in some cases if a patient is doing poorly and suspicion for fungal infection is high based on clinical, radiographic, and/or laboratory evidence, he said.
The CDC’s Dr. Chiller said that screening and diagnostic algorithms currently vary from institution to institution, and that diagnostic challenges likely dissuade clinicians from thinking about fungi. “Clinicians often don’t want to deal with fungi – they’re difficult to diagnose, the treatments are limited and can be toxic. But fungi get pushed back until it’s too late,” he said.
“Fungal diagnostics is an area we all need a lot more help with,” and new diagnostics are in the pipeline, he said. In the meantime, he said, “there are tools out there, and we just need to use them more, and improve how they’re used.”
While reported CAPA thus far has typically occurred in the setting of ICU care and mechanical ventilation, it’s not always the case, Dr. Permpalung said. Lung and other solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients with COVID-19 are developing CAPA and other invasive secondary invasive fungal infections despite not being intubated, he said.
Of 276 SOT recipients with COVID-19 who required inpatient treatment at Johns Hopkins University hospitals from the beginning of the pandemic to March 2022, 23 patients developed invasive fungal infections (13 CAPA). Only a fraction – 38 of the 276 – had been intubated, he said.
Mucormycosis resistance
After CAPA, candidiasis and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – most frequently, rhino-orbital-cerebral disease or pulmonary disease – have been the leading reported fungal coinfections in COVID-19, said Dr. Hoenigl, who described the incidence, timeline, risk factors, and pathogenesis of these infections in a review published this year in Nature Microbiology. .
In India, where there has long been high exposure to Mucorales spores and a greater burden of invasive fungal disease, the rate of mucormycosis doubled in 2021, with rhino-orbital-cerebral disease reported almost exclusively, he said. Pulmonary disease has occurred almost exclusively in the ICU setting and has been present in about 50% of cases outside of India, including Europe and the United States.
A preprint meta-analysis of CAM cases posted by the Lancet in July 2022, in which investigators analyzed individual data of 556 reported cases of COVID-19–associated CAM, shows diabetes and history of corticosteroid use present in most patients, and an overall mortality rate of 44.4%, most of which stems from cases of pulmonary or disseminated disease. Thirteen of the 556 reported cases were from the United States.
An important take-away from the analysis, Dr. Hoenigl said, is that Aspergillus coinfection was seen in 7% of patients and was associated with higher mortality. “It’s important to consider that coinfections [of Aspergillus and Mucorales] can exist,” Dr. Hoenigl said, noting that like CAPA, pulmonary CAM is likely underdiagnosed and underreported.
As with CAPA, the clinical and radiological features of pulmonary CAM largely overlap with those associated with COVID-19, and bronchoscopy plays a central role in definitive diagnosis. In the United States, a Mucorales PCR test for blood and BAL fluid is commercially available and used at some centers, Dr. Hoenigl said.
“Mucormycosis is always difficult to treat ... a lot of the treatments don’t work particularly well,” said Dr. Thompson. “With aspergillosis, we have better treatment options.”
Dr. Thompson worries, however, about treatment resistance becoming widespread. Resistance to azole antifungal agents “is already pretty widespread in northern Europe, particularly in the Netherlands and part of the U.K.” because of injudicious use of antifungals in agriculture, he said. “We’ve started to see a few cases [of azole-resistant aspergillosis in the United States] and know it will be more widespread soon.”
Treatment resistance is a focus of the new WHO fungal priority pathogens list – the first such report from the organization. Of the 19 fungi on the list, 4 were ranked as critical: Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida auris, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida albicans. Like Dr. Thompson, Dr. Hoenigl contributed to the WHO report.
Dr. Hoenigl reported grant/research support from Astellas, Merck, F2G, Gilread, Pfizer, and Scynexis. Dr. Marr disclosed employment and equity in Pearl Diagnostics and Sfunga Therapeutics. Dr. Thompson, Dr. Permpalung, and Dr. Zeki reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
COVID-19 has lifted the lid on the risks of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with severe respiratory viral illness – even previously immunocompetent individuals – and highlighted the importance of vigilant investigation to achieve early diagnoses, leading experts say.
Most fungi are not under surveillance in the United States, leaving experts without a national picture of the true burden of infection through the pandemic. However, a collection of published case series, cohort studies, and reviews from Europe, the United States, and throughout the world – mainly pre-Omicron – show that fungal disease has affected a significant portion of critically ill patients with COVID-19, with concerning excess mortality, these experts say.
COVID-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) has been the predominant fungal coinfection in the United States and internationally. But COVID-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – the infection that surged in India in early 2021 – has also affected some patients in the United States, published data show. So have Pneumocystitis pneumonia, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, and Candida infections (which mainly affect the bloodstream and abdomen), say the experts who were interviewed.
“We had predicted [a rise in] aspergillosis, but we saw more than we thought we’d see. Most fungal infections became more common with COVID-19,” said George Thompson, MD, professor of clinical medicine at the University of California, Davis, and cochair of the University of Alabama–based Mycoses Study Group Education Committee, a group of experts in medical mycology. Pneumocystitis, for instance, “has historically been associated with AIDS or different types of leukemia or lymphoma, and is not an infection we’ve typically seen in our otherwise healthy ICU patients,” he noted. “But we did see more of it [with COVID-19].”
More recently, with fewer patients during the Omicron phase in intensive care units with acute respiratory failure, the profile of fungal disease secondary to COVID-19 has changed. Increasing proportions of patients have traditional risk factors for aspergillosis, such as hematologic malignancies and longer-term, pre-COVID use of systemic corticosteroids – a change that makes the contribution of the viral illness harder to distinguish.
Moving forward, the lessons of the COVID era – the fungal risks to patients with serious viral infections and the persistence needed to diagnose aspergillosis and other pulmonary fungal infections using bronchoscopy and imperfect noninvasive tests – should be taken to heart, experts say.
“Fungal diseases are not rare. They’re just not diagnosed because no one thinks to look for them,” said Dr. Thompson, a contributor to a recently released World Health Organization report naming a “fungal priority pathogens” list.
“We’re going to continue to see [secondary fungal infections] with other respiratory viruses,” he said. And overall, given environmental and other changes, “we’re going to see more and more fungal disease in the patients we take care of.”
CAPA not a surprise
CAPA is “not an unfamiliar story” in the world of fungal disease, given a history of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA), said Kieren A. Marr, MD, MBA, adjunct professor of medicine and past director of the transplant and oncology infectious diseases program at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who has long researched invasive fungal disease.
European researchers, she said, have led the way in describing a high incidence of IAPA in patients admitted to ICUs with influenza. In a retrospective multicenter cohort study reported in 2018 by the Dutch-Belgian Mycosis Study group, for instance, almost 20% of 432 influenza patients admitted to the ICU, including patients who were otherwise healthy and not immunocompromised, had the diagnosis a median of 3 days after ICU admission. (Across other cohort studies, rates of IAPA have ranged from 7% to 30%.)
Mortality was significant: 51% of patients with influenza and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis died within 90 days, compared with 28% of patients with influenza and no invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Reports from Europe early in the pandemic indicated that CAPA was a similarly serious problem, prompting establishment at Johns Hopkins University of an aggressive screening program utilizing biomarker-based testing of blood and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Of 396 mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients admitted to Johns Hopkins University hospitals between March and August 2020, 39 met the institution’s criteria for CAPA, Dr. Marr and her colleagues reported this year in what might be the largest U.S. cohort study of CAPA published to date.
“We now know definitively that people with severe influenza and with severe COVID also have high risks for both invasive and airway disease caused by airborne fungi, most commonly aspergilliosis,” Dr. Marr said.
More recent unpublished analyses of patients from the start of the pandemic to June 2021 show persistent risk, said Nitipong Permpalung, MD, MPH, assistant professor in transplant and oncology infectious diseases at Johns Hopkins University and lead author of the cohort study. Among 832 patients with COVID-19 who were mechanically ventilated in Johns Hopkins University hospitals, 11.8% had CAPA, he said. (Also, 3.2% had invasive candidiasis, and 1.1% had other invasive fungal infections.)
Other sources said in interviews that these CAPA prevalence rates generally mirror reports from Europe, though some investigators in Europe have reported CAPA rates more toward 15%.
(The Mycoses Study Group recently collected data from its consortium of U.S. medical centers on the prevalence of CAPA, with funding support from the CDC, but at press time the data had not yet been released. Dr. Thompson said he suspected the prevalence will be lower than earlier papers have suggested, “but still will reflect a significant burden of disease.”)
Patients in the published Johns Hopkins University study who had CAPA were more likely than those with COVID-19 but no CAPA to have underlying pulmonary disease, liver disease, coagulopathy, solid tumors, multiple myeloma, and COVID-19–directed corticosteroids. And they had uniformly worse outcomes with regards to severity of illness and length of intubation.
How much of CAPA is driven by the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself and how much is a consequence of COVID-19 treatments is a topic of active discussion and research. Martin Hoenigl, MD, of the University of Graz, Austria, a leading researcher in medical mycology, said research shows corticosteroids and anti–IL-6 treatments, such as tocilizumab, used to treat COVID-19–driven acute respiratory failure clearly have contributed to CAPA. But he contends that “a number of other mechanisms” are involved as well.
“The immunologic mechanisms are definitely different in these patients with viral illness than in other ICU patients [who develop aspergilliosis]. It’s not just the corticosteroids. The more we learn, we see the virus plays a role as well, suppressing the interferon pathway,” for example, said Dr. Hoenigl, associate professor in the division of infectious diseases and the European Confederation of Medical Mycology (ECMM) Center of Excellence at the university. The earliest reports of CAPA came “when ICUs weren’t using dexamethasone or tocilizumab,” he noted.
In a paper published recently in Lancet Respiratory Medicine that Dr. Hoenigl and others point to, Belgian researchers reported a “three-level breach” in innate antifungal immunity in both IAPA and CAPA, affecting the integrity of the epithelial barrier, the capacity to phagocytose and kill Aspergillus spores, and the ability to destroy Aspergillus hyphae, which is mainly mediated by neutrophils.
The researchers ran a host of genetic and protein analyses on lung samples (most collected via BAL) of 169 patients with influenza or COVID-19, with and without aspergillosis. They found that patients with CAPA had significantly lower neutrophil cell fractions than patients with COVID-19 only, and patients with IAPA or CAPA had reduced type II IFN signaling and increased concentrations of fibrosis-associated growth factors in the lower respiratory tracts (Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Aug 24).
Tom Chiller, MD, MPH, chief of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Mycotic Disease Branch, said he’s watching such research with interest. For now, he said, it’s important to also consider that “data on COVID show that almost all patients going into the ICUs with pneumonia and COVID are getting broad-spectrum antibiotics” in addition to corticosteroids.
By wiping out good bacteria, the antibiotics could be “creating a perfect niche for fungi to grow,” he said.
Diagnostic challenges
Aspergillus that has invaded the lung tissue in patients with COVID-19 appears to grow there for some time – around 8-10 days, much longer than in IAPA – before becoming angioinvasive, said Dr. Hoenigl. Such a pathophysiology “implicates that we should try to diagnose it while it’s in the lung tissue, using the BAL fluid, and not yet in the blood,” he said.
Some multicenter studies, including one from Europe on Aspergillus test profiles in critically ill COVID-19 patients, have shown mortality rates of close to 90% in patients with CAPA who have positive serum biomarkers, despite appropriate antifungal therapy. “If diagnosed while confined to the lung, however, mortality rates are more like 40%-50% with antifungal therapy,” Dr. Hoenigl said. (Cohort studies published thus far have fairly consistently reported mortality rates in patients with CAPA greater than 40%, he said.)
Bronchoscopy isn’t always pragmatic or possible, however, and is variably used. Some patients with severe COVID-19 may be too unstable for any invasive procedure, said Dr. Permpalung.
Dr. Permpalung looks for CAPA using serum (1-3) beta-D-glucan (BDG, a generic fungal test not specific to Aspergillus), serum galactomannan (GM, specific for Aspergillus), and respiratory cultures (sputum or endotracheal aspirate if intubated) as initial screening tests in the ICU. If there are concerns for CAPA – based on these tests and/or the clinical picture – “a thoughtful risk-benefit discussion is required to determine if patients would benefit from a bronchoscopy or if we should just start them on empiric antifungal therapy.”
Unfortunately, the sensitivity of serum GM is relatively low in CAPA – lower than with classic invasive aspergillosis in the nonviral setting, sources said. BDG, on the other hand, can be falsely positive in the setting of antimicrobials and within the ICU. And the utility of imaging for CAPA is limited. Both the clinical picture and radiological findings of CAPA have resembled those of severe COVID – with the caveat of cavitary lung lesions visible on imaging.
“Cavities or nodules are a highly suspicious finding that could indicate possible fungal infection,” said pulmonologist Amir A. Zeki, MD, MAS, professor of medicine at the University of California, Davis, and codirector of the UC Davis Asthma Network Clinic, who has cared for patients with CAPA.
Cavitation has been described in only a proportion of patients with CAPA, however. So in patients not doing well, “your suspicion has to be raised if you’re not seeing cavities,” he said.
Early in the pandemic, when patients worsened or failed to progress on mechanical ventilation, clinicians at the University of California, Davis, quickly learned not to pin blame too quickly on COVID-19 alone. This remains good advice today, Dr. Zeki said.
“If you have a patient who’s not doing well on a ventilator, not getting better [over weeks], has to be reintubated, has infiltrates or lung nodules that are evolving, or certainly, if they have a cavity, you have to suspect fungal infection,” said Dr. Zeki, who also practices at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in San Diego. “Think about it for those patients who just aren’t moving forward and are continuing to struggle. Have a high index of suspicion, and consult with your infectious disease colleagues.”
Empiric treatment is warranted in some cases if a patient is doing poorly and suspicion for fungal infection is high based on clinical, radiographic, and/or laboratory evidence, he said.
The CDC’s Dr. Chiller said that screening and diagnostic algorithms currently vary from institution to institution, and that diagnostic challenges likely dissuade clinicians from thinking about fungi. “Clinicians often don’t want to deal with fungi – they’re difficult to diagnose, the treatments are limited and can be toxic. But fungi get pushed back until it’s too late,” he said.
“Fungal diagnostics is an area we all need a lot more help with,” and new diagnostics are in the pipeline, he said. In the meantime, he said, “there are tools out there, and we just need to use them more, and improve how they’re used.”
While reported CAPA thus far has typically occurred in the setting of ICU care and mechanical ventilation, it’s not always the case, Dr. Permpalung said. Lung and other solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients with COVID-19 are developing CAPA and other invasive secondary invasive fungal infections despite not being intubated, he said.
Of 276 SOT recipients with COVID-19 who required inpatient treatment at Johns Hopkins University hospitals from the beginning of the pandemic to March 2022, 23 patients developed invasive fungal infections (13 CAPA). Only a fraction – 38 of the 276 – had been intubated, he said.
Mucormycosis resistance
After CAPA, candidiasis and COVID-19-associated mucormycosis (CAM) – most frequently, rhino-orbital-cerebral disease or pulmonary disease – have been the leading reported fungal coinfections in COVID-19, said Dr. Hoenigl, who described the incidence, timeline, risk factors, and pathogenesis of these infections in a review published this year in Nature Microbiology. .
In India, where there has long been high exposure to Mucorales spores and a greater burden of invasive fungal disease, the rate of mucormycosis doubled in 2021, with rhino-orbital-cerebral disease reported almost exclusively, he said. Pulmonary disease has occurred almost exclusively in the ICU setting and has been present in about 50% of cases outside of India, including Europe and the United States.
A preprint meta-analysis of CAM cases posted by the Lancet in July 2022, in which investigators analyzed individual data of 556 reported cases of COVID-19–associated CAM, shows diabetes and history of corticosteroid use present in most patients, and an overall mortality rate of 44.4%, most of which stems from cases of pulmonary or disseminated disease. Thirteen of the 556 reported cases were from the United States.
An important take-away from the analysis, Dr. Hoenigl said, is that Aspergillus coinfection was seen in 7% of patients and was associated with higher mortality. “It’s important to consider that coinfections [of Aspergillus and Mucorales] can exist,” Dr. Hoenigl said, noting that like CAPA, pulmonary CAM is likely underdiagnosed and underreported.
As with CAPA, the clinical and radiological features of pulmonary CAM largely overlap with those associated with COVID-19, and bronchoscopy plays a central role in definitive diagnosis. In the United States, a Mucorales PCR test for blood and BAL fluid is commercially available and used at some centers, Dr. Hoenigl said.
“Mucormycosis is always difficult to treat ... a lot of the treatments don’t work particularly well,” said Dr. Thompson. “With aspergillosis, we have better treatment options.”
Dr. Thompson worries, however, about treatment resistance becoming widespread. Resistance to azole antifungal agents “is already pretty widespread in northern Europe, particularly in the Netherlands and part of the U.K.” because of injudicious use of antifungals in agriculture, he said. “We’ve started to see a few cases [of azole-resistant aspergillosis in the United States] and know it will be more widespread soon.”
Treatment resistance is a focus of the new WHO fungal priority pathogens list – the first such report from the organization. Of the 19 fungi on the list, 4 were ranked as critical: Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida auris, Aspergillus fumigatus, and Candida albicans. Like Dr. Thompson, Dr. Hoenigl contributed to the WHO report.
Dr. Hoenigl reported grant/research support from Astellas, Merck, F2G, Gilread, Pfizer, and Scynexis. Dr. Marr disclosed employment and equity in Pearl Diagnostics and Sfunga Therapeutics. Dr. Thompson, Dr. Permpalung, and Dr. Zeki reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
They trusted their prenatal test. They didn’t know the industry is an unregulated ‘Wild West.’
Amanda wanted to warn someone. In June 2021, her daughter – the one she and her husband had tried for 3 years to conceive – had died after only 28 hours. With an underdeveloped nose, she had battled for every breath.
Nobody knew why. Later, an autopsy report revealed their daughter had an extra 13th chromosome. The condition is nearly always fatal.
“But didn’t we test for that?” Amanda recalled asking herself. “That was kind of where the light bulb clicked.”
Through her doctor, Amanda had gotten a popular prenatal screening from a lab company. It had come back “negative.”
For three major conditions, including the one her baby had, the report gave the impression of near certainty. The likelihood that she would be born without them was “greater than 99%.”
As she recovered from a cesarean section, Amanda found herself facing a long maternity leave without a child. She shut the door to the empty nursery and began spending what seemed like endless hours of that hazy summer learning about the test.
It’s a simple blood draw designed to check for an array of genetic anomalies. But Amanda, a science researcher, read academic articles showing there was a higher risk of inaccurate results than she had realized. (She asked to be identified by only her first name to protect her privacy.)
On Reddit, she found other women reporting problems with the tests, too. She thought Labcorp, the company that made her test, would want to know about the screening that failed her. Maybe by alerting them, she could help other families. Maybe it would help her understand what happened.
“I was trying to gain answers,” said Amanda, now 32. She tried calling Labcorp’s customer service line, but she said she was passed along from one person to another. “It was just a circle,” she remembered.
She phoned Labcorp a second time. The call ended when an employee hung up on her.
Amanda was baffled. Why didn’t the company seem interested in her experience? Why, she wondered, wouldn’t it want to collect this data? Why wasn’t there someone who could answer her questions about how often this happens, and why?
If she had taken any number of other common commercial tests – including certain tests for COVID-19 or, say, pregnancy – the company would have been required to inform the U.S. Food and Drug Administration about reports of so-called adverse events.
But the test Amanda had falls into a regulatory void. No federal agency checks to make sure these prenatal screenings work the way they claim before they’re sold to health care providers. The FDA doesn’t ensure that marketing claims are backed up by evidence before screenings reach patients. And companies aren’t required to publicly report instances of when the tests get it wrong – sometimes catastrophically.
The broader lab testing industry and its lobbyists have successfully fought for years to keep it this way, cowing regulators into staying on the sidelines.
Worried about a growing variety of tests escaping scrutiny, the FDA was on the cusp of stepping in 6 years ago. But then it backed down.
Peter Lurie, then a top agency official, was at the meetings where the FDA tabled its plans. Not pushing harder, he told ProPublica, “remains one of my greatest regrets.”
The risk of false positives from prenatal screenings, in particular, has been known for years.
In 2014, the New England Center for Investigative Reporting detailed how some companies gave a misleading impression of the precision of the prenatal screenings. Women often didn’t understand they needed diagnostic testing to confirm the results. Some had gotten abortions based on false positive results, the story said. Earlier this year, the New York Times reported how companies sell optional extra screenings that are “usually wrong” when they predict a disorder.
Despite these stories and calls for reform by patient advocates, the government has done little to improve oversight of prenatal screenings. ProPublica set out to examine the forces that led to this inertia and left patients like Amanda feeling misled. Interviews with more than three dozen women revealed ongoing confusion about the screenings – and anger when their reliability proved to be overblown.
“This is a Wild West scenario where everybody is on their own,” said Lawrence Gostin, a Georgetown University, Washington, law professor specializing in bioethics.
The stakes for families are increasing. Upward of half of all pregnant people now receive one of these prenatal screenings. And with many states banning abortions or limiting them to early in pregnancies, the need for fast, accurate information has become more urgent.
The FDA itself acknowledges the problem. In correspondence with ProPublica, a spokesperson cited an “outdated policy” regarding the lack of vetting of many lab tests that the agency has “spent the better part of the last 2 decades trying to address.”
The screening industry, meanwhile, continues to expand, proving lucrative for those who lead it. The chief executive of Natera, which claims about 40% of the market share of prenatal screenings, received a $23 million compensation package last year, the highest of any executive at a publicly traded lab company.
Testing companies told ProPublica that, even without the FDA, there is significant oversight. Labs must abide by state regulations, and another federal agency, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, is charged with monitoring quality standards. It does not, however, check whether the tests the labs perform are clinically valid.
Companies also said the screenings offer important guidance to expectant families. Echoing others in the field, Labcorp said in a statement that the screenings, when used properly, “provide vital information about the presence of increased risk, but do not provide a definitive diagnosis.” (It declined to discuss the specifics of Amanda’s experience.)
Natera pointed out that its materials tell patients that “this test does not make a final diagnosis.” It reports results as “high-risk” or “low-risk,” not positive or negative.
Companies have stressed that, ultimately, it’s the responsibility of health care providers, who order the tests, to inform patients about the limits of screenings.
For all that, the statistical nuances of the test aren’t easy to parse for patients and even some doctors and nurses. For example, the test for trisomy 13, which doomed Amanda’s baby, is actually less likely to correctly predict the condition than other tests in the standard bundle of screenings offered to every patient.
When ProPublica asked readers to share their experiences with noninvasive prenatal screening tests, often referred to as NIPTs or NIPS, more than a thousand responded. Many said the tests had given them peace of mind. Some said they had provided an early warning about problems.
But others had more questions than answers. None more so than Amanda.
“What are these tests?” she wondered. “And how did mine end up in the margin of error?”
‘They started using it on humans, and then they went back and said: “Was our test accurate?” ’
Scientists have long tried to find ways to help parents and doctors understand what’s happening inside the womb. Amniocentesis was first used to reveal genetic anomalies in the late 1960s. But it didn’t become more popular until it began to be paired with ultrasound to precisely guide the procedure.
In the 1980s, doctors started using chorionic villus sampling, or CVS, an analysis of placental tissue that offers a diagnosis earlier in pregnancy. But, like amniocentesis, it is an invasive test that involves some risk to the fetus, though experts say it’s exceptionally low.
A breakthrough came in the late 1990s, when a scientist recognized that free-floating placental DNA could be detected in the mother’s blood. This meant that the fetus’s chromosomes could be examined by collecting a blood sample as soon as 9 weeks into pregnancy. This also provides an early opportunity to learn the likely fetal sex – a particularly popular feature.
Champions of the new science celebrated the arrival of a simple technique for patients that was particularly precise, at least for some conditions. Many favored it over other noninvasive options. But the industry that developed around NIPT has been marred by controversy from the beginning.
Dr. Ronald Wapner, director of reproductive genetics at Columbia University, described that time as “very chaotic.”
The tests had not been appropriately evaluated in clinical practice, said Dr. Wapner, whose research has sometimes been funded by testing companies. Because of this, he said, the industry “had very incomplete data on how well it worked.”
That didn’t stop the excitement. The chief executive of Sequenom, a biotechnology company that planned to release the first NIPT for Down syndrome, championed the company as the “Google of Molecular Diagnostics.” Its stock price soared.
Then, about 2 months before an expected launch in 2009, Sequenom killed the plan. The company’s research director, it turned out, had manipulated testing data and made misleading claims about how well the screening worked.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and Federal Bureau of Investigation opened investigations. Top executives were fired, and the research director pleaded guilty to conspiracy to commit securities fraud. Sequenom still managed to commercialize the test in 2011. (Labcorp, which later acquired Sequenom, said it uses a different kind of test.)
Other companies soon debuted their own tests. Still, there was little data on their clinical performance, researchers said.
As Megan Allyse, a bioethicist at the Mayo Clinic, put it, the companies “launched the test, they started using it on humans, and then they went back and said, ‘Was our test accurate?’ ” She also questioned the lack of attention to the ethics of how tests are presented to patients.
Despite missteps by the industry, the FDA didn’t scrutinize the screenings because they were considered lab-developed tests, which means they are created by the same laboratory that conducts them.
In 1976, Congress revamped oversight over medical devices. Since then, the FDA has effectively exempted such “home-brew” tests from key regulatory requirements. The idea was that when, say, a hospital lab wanted to create a simple test for its own patients, it was spared the time, money, and hassle of getting approval from Washington bureaucrats.
Today, lab-developed tests are vastly more numerous and complex. Because they aren’t registered with the federal government, nobody knows how many exist.
The distinction between tests the FDA actively regulates and those they don’t can seem nonsensical. It isn’t based on the complexity of the tests, or how people use them. It’s simply a matter of where the test is made.
The prenatal genetic screening industry took off almost immediately, powered by an army of aggressive sales representatives.
“At the very beginning, obstetricians in practice were being just completely inundated with visits from the sales reps,” said Dr. John Williams, director of reproductive health at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The push left many ob.gyns. and patients thinking the screenings were accurate enough to substitute for diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis or CVS.
In some cases, sales tactics escalated into lawbreaking.
Former Sequenom executives who exited during the fraud scandal created a new company that became Progenity, which also offered prenatal screening. Shortly after the company went public in 2020, it finalized a $49 million settlement with federal and state governments, where it admitted to falsifying insurance claims and giving kickbacks to physicians and their staff. According to a legal filing, one sales rep spent $65,658 on meals and alcohol for physicians in 1 year.
Now called Biora Therapeutics, the company said in a statement it no longer does any laboratory testing, including prenatal screenings.
Industry revenue continues to grow, but some testing companies are still fighting to make a profit, and competition to survive is fierce. “There’s a multibillion-dollar market, and they all want a piece of it,” said a former Progenity sales rep who quit in disgust after 5 months in 2016.
The rep, who requested anonymity because she continues to work in the field, said she still sees competitors from NIPT companies visiting medical practices “every week, buying breakfast or dinner, or taking them out for happy hour.”
Over time, companies pointed to new peer-reviewed studies, research the industry itself funded, to earn the confidence of doctors and other stakeholders. They showed that two tests – for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 – often performed better than other screening methods.
This research was valid, said Dr. Mary Norton, a perinatologist and clinical geneticist at the University of California, San Francisco, Medical Center’s prenatal diagnostic center. Considered a leading researcher in the field, she was an author of many of these key industry-funded studies.
But, she said, when research findings were presented publicly, the companies sometimes downplayed “inconvenient truths,” such as the exclusion of inconclusive results from accuracy estimates. Crucial caveats were also glossed over by some companies when they translated research into promotional copy aimed at health care providers and patients. Those materials didn’t always mention the many factors that can limit the performance of the screenings, including high body weight, the rarity of the condition tested, and younger maternal age.
Testing companies said they try to help patients understand the screenings through online resources and other materials. Some offer genetic counseling services.
The younger a person is, the lower the test’s positive predictive value – that is, the probability that a positive screening result will turn out to be correct – will be for some conditions. For instance, because Down syndrome is less prevalent in younger people’s pregnancies, a positive screening test is more likely to be a false positive for them.
Kristina was 30 years old in 2016, when her Progenity test came back positive for Down syndrome. She and her husband, who asked not to be fully named to protect their privacy, said they didn’t plan to carry a pregnancy with this condition to term.
But waiting to get an amniocentesis, and then waiting for the results, took 5 agonizing weeks, she said. It showed her son did not have Down syndrome.
Kristina, who lives in Texas, is still troubled by what she describes as a traumatic experience.
“I researched both late-term abortion providers and cemeteries,” she said. They even picked out a burial place, near their house.
She bought a blue baby blanket she intended to bury the baby’s tiny body in. She still has it. Her son, now 5, sleeps with it every night.
‘I can’t believe I didn’t say more’
As lab-developed tests became a bigger business, moving well past their home-brew origins, regulators looked for a way to assert oversight. In 2014, after years of study and debate, the time seemed right.
The FDA released plans proposing to regulate the tests, prioritizing those used to make major medical decisions. The agency has pointed to NIPTs as 1 of 20 concerning tests.
But, over the next 2 years, a coalition of power players urged the FDA to back off. Professional associations issued statements and hosted webinars devoted to the issue. Some created polished websites featuring sample letters to send to Washington.
Academic medical centers and pathology departments joined the fight, too. Scientists from 23 of them put it bluntly in a letter to the Office of Management and Budget: “FDA regulation of LDTs would be contrary to the public health,” it said, using a common acronym for the tests.
“Critical testing would be unavailable in the ‘lag time’ between development of new tests and FDA authorizing them,” the authors of the letter wrote, “and subsequent improvements on existing tests would slow significantly under the rigid, inflexible, and duplicative FDA regulatory scheme.”
This could delay essential care for patients. What’s more, opponents argued, existing lab reviews by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services are sufficiently rigorous. Some have suggested modernizing the CMS review process to improve oversight.
An FDA spokesperson told ProPublica that the agency encountered “continued, negative feedback,” including a 25-page paper written by two legal heavyweights hired by the American Clinical Laboratory Association: Paul Clement, President George W. Bush’s former solicitor general, and Laurence Tribe, law professor at Harvard University.
Mr. Clement has reportedly commanded rates of $1,350 per hour. He and Mr. Tribe did not respond to ProPublica’s queries about their work.
Their brief argued that the FDA “lacked legal authority” to regulate lab-developed tests because they are properly seen as the practice of medicine: a service, rather than a product.
However, as lawyers representing the American Association of Bioanalysts countered, the FDA would vet tests before they reach the market, not control how doctors use them. The government proposal, they wrote, is “similar to imposing requirements to screen blood or label drugs.”
After the election of President Donald Trump, but before he took office, a handful of FDA officials discussed their battered proposal. It had represented a breakthrough in the decades of excruciating back-and-forth with industry. But now, with an incoming administration bent on deregulation, their efforts seemed futile.
The regulators feared anything they enacted would be undone by Congress – and, under the Congressional Review Act, they might not be able to reissue anything “substantially similar” in the future. So the FDA published a white paper instead, summarizing the issue “for further public discussion.”
After the meeting where officials made this call, Mr. Lurie, then the FDA’s associate commissioner, recalled a colleague approaching him: “I can’t believe you didn’t say more.”
“And I was like, ‘Yeah, actually, I can’t believe I didn’t say more either,’ ” Mr. Lurie later told ProPublica. (After leaving the agency, Mr. Lurie went on to lead the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a consumer advocacy nonprofit, which has pushed the FDA to finally assert oversight over lab-developed tests.)
Nancy Stade, an attorney and senior policy official who left the FDA in 2015, said the agency often moves slowly as it seeks to get buy-in from industry and professional groups. In her work on regulatory policy, she saw it happen with lab-developed tests.
The agency is “always testing the waters,” she said, “and always coming out with something a little bit softer.”
In 2020, the influential American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, representing doctors who handle pregnancies, gave the screening industry another huge boost.
In a bulletin updating their advice on the tests, the two groups described growing research on the performance of some of the standard tests and said people have the right to information about their pregnancies, so the tests should be offered to all patients. Previously, they recommended this only for those facing higher risk of genetic anomalies.
The bulletin said the coauthors had disclosed no conflicts of interest. But two of the four coauthors, including Mary Norton, had disclosed in prior publications that test-makers had provided funding for their research. A company had provided a third coauthor with laboratory services needed to run tests, according to that researcher, a connection she also disclosed in past papers.
ACOG, in a statement to ProPublica, said the organization “identified no conflicts because research funding is provided to academic institutions with institutional review boards, not to individual investigators.” Two of the three researchers responded to questions from ProPublica and said they maintained independence over their work.
One test-maker, Illumina, celebrated the ACOG guidance in a tweet, saying it “recognizes the superior performance of #NIPT and the benefit it provides expectant families.” Natera’s share prices doubled in 5 months. UnitedHealthcare, the nation’s largest private insurer and long a target of industry lobbying, told ProPublica it changed its stance to cover screenings for all patients, regardless of risk, because of the recommendation.
In a recent shareholder report, Natera stated that prenatal genetic and carrier screenings “represent the significant majority of our revenues,” which totaled $625.5 million in 2021. The company expects more growth to come.
“The NIPT market is still very underpenetrated, compared to the 4 to 5 million pregnancies in the U.S.,” Natera’s chief executive said on a 2021 earnings call, “so there’s a long way to go.”
But even Dr. Norton, who coauthored the ACOG recommendation and favors NIPTs for patients 40 and over, has concerns about screenings becoming widespread among those who are younger. In most cases, she prefers other screening methods that catch the nongenetic problems younger moms are more likely to face. Negative results from an NIPT, she said, can be “falsely reassuring.”
In the years after the FDA set aside its regulatory proposal, the agency has assisted members of Congress on a proposed legislative solution. That effort, dubbed the VALID Act, aims to end any debate over the agency’s authority over lab-developed tests. An FDA press officer said the legislation would ensure the prenatal screening tests and others are “accurate and reliable.”
But, as in the past, intense lobbying followed the proposal. The VALID Act was a rider to a funding reauthorization bill, but in September the House and Senate agreed to remove it. Advocates now hope to attach it to proposed end-of-year legislation.
Meanwhile, earlier this year, 4 months after the New York Times story on the usefulness of some screenings, the FDA took a step toward more public awareness about prenatal genetic screening. It issued its first safety communication on them, noting the potential for false results.
It cautioned patients about making “critical health care decisions based on results from these screening tests alone.”
Cara Tenenbaum, a former FDA policy advisor, was pleased to see the statement. Still, she said, it was long overdue.
“This has been known – known, or should have been known – for 10 years,” she said.
‘It had me so messed up’
With the demise of Roe v. Wade, restrictive and ever-changing abortion laws can pressure people to act quickly with limited information, heightening the stakes of prenatal screening.
Julia, a mom from Mississippi’s Gulf Coast, knows what it’s like to face harrowing consequences while navigating state-imposed time limits – and doing so with little guidance. Last fall, she was pregnant with her fourth child when, she said, a nurse practitioner suggested prenatal genetic screening.
At 33, Julia had no risk factors. Her previous pregnancies hadn’t been screened with an NIPT. But with three sons and 18 nephews, she and her husband were curious about the baby’s sex. And the screening seemed like it had no downside.
Julia figured it would only be offered if it was reliable, so her nurse practitioner ordered her both the basic bundle of screenings and the extra tests. (The medical practice didn’t respond to interview requests. Julia is a family nickname that’s used here to protect her privacy.)
The screenings showed the baby was a girl – but the extra tests also detected trisomy 16, a condition caused by an extra chromosome that is so rare, the nurse didn’t know what it was, Julia recalled.
The nurse borrowed Julia’s phone, using it to search online and read aloud what she found. Julia was stunned to hear trisomy 16 was incompatible with life.
“I was utterly devastated,” she said. “I made it out of my doctor’s office but completely broke down in the car.”
But ACOG does not recommend the trisomy 16 screening, saying “its accuracy with regard to detection and the false-positive rate is not established.” Julia wasn’t informed of this, she said, and she’s not sure if her health care providers knew it either.
The lab report recommended diagnostic testing to confirm the results, but time was short. She had her amniocentesis at 17 weeks. It could take up to 4 more weeks to receive results.
That would be too late for a legal abortion in Mississippi. So she made an appointment for one in Florida, where the cutoff was 24 weeks. (It’s now 15 weeks in Florida, while Mississippi went from 15 weeks for legal procedures to a ban on nearly all abortions.)
The wait was excruciating. Julia was driving twice a week to New Orleans for specialized care. With work and child care, it was too hard. She quit the teaching job she loved.
One winter night, she felt the fetus move for the first time – ordinarily a milestone, but now, facing a fatal prognosis, she didn’t want to get attached. “It had me so messed up,” she said.
On the way to the amniocentesis, Julia and her husband chose a name. Drawing from a language conjured by J.R.R. Tolkien in the fantasy novels they love, it means “hope.”
More than halfway through her pregnancy, the amnio results arrived. The prenatal screening had given a false positive. The baby would be fine. In May, Julia gave birth to a healthy daughter.
Julia and her husband are upset about the needless anguish brought on by the screening. “They like to have it both ways,” said Julia’s husband. “They say they are 99% accurate, but when there’s a false positive, they say, ‘Well, we’re not diagnostic.’ ”
Believing the prenatal screening was likely accurate, they had seriously considered canceling the amniocentesis, saving their limited funds for an abortion in Florida, hundreds of miles away.
Their dilemma points to a longtime concern: ending pregnancies based on false positives. The FDA cited it as a risk as far back as 2015. Now, those with positive results are facing an even tighter time crunch. They must consider whether waiting for a definitive test, and possibly traveling to another state for an abortion later in pregnancy, is worth it.
In their promotional material, some companies not only sidestep the variability of the standard tests, they fail to distinguish them from the least reliable ones – those for exceptionally rare conditions. They tout the extra screenings as “premium,” “plus,” or “advanced” options.
“Going to greater lengths for the answers that matter most,” says a brochure aimed at health care providers from test-maker Illumina. Elsewhere it states that the “expanded” panel of tests provides “confident results” and “the additional insights you need.”
But the companies themselves know the accuracy of some of their tests has yet to be established in the research. Natera acknowledged in a recent shareholder report that many insurers won’t pay for screenings for missing chromosomal fragments, known as microdeletions, in part because there isn’t enough published data behind them.
The company, responding to ProPublica, stressed the quality of the data over the quantity, saying the research so far has been favorable. “Natera’s microdeletion testing was thoroughly validated with results published in peer-reviewed publications,” it said in a statement.
Natera pointed to a recent study that looked at DiGeorge syndrome, one of several chromosomal anomalies it checks for with its microdeletion screenings. Researchers found the positive predictive value (PPV) of the test to be 52.6%, meaning that nearly half of positive results are false positives. (For many patients, PPVs for more common conditions can exceed 90%.)
Natera said the performance of the diGeorge syndrome test “is excellent and not considered a low PPV,” because of the condition being extremely rare.
Companies also play up the danger of diagnostic tests like amnio. They “can cause miscarriages,” warns the marketing from Labcorp, which made Amanda’s screening, while its test “does not cause miscarriages.” But medical experts emphasize that diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis, are more accurate and, in fact, carry little risk to the pregnancy.
Labcorp, in a statement, said the company “acknowledges the well-documented risk associated with amniocentesis and CVS in our literature. It is the patient’s prerogative to decide which risks they are willing or unwilling to take.”
Marketing claims also sometimes skate over the nuances in the guidance from the leading professional societies. On a webpage targeting health care providers, for example, a Labcorp chart said groups such as ACOG “endorse and/or recognize” prenatal screenings as an option for all pregnancies. But the chart listed screenings ACOG does not recommend, including trisomy 16.
When asked about it, Labcorp said in a statement that ACOG “endorses NIPS for all pregnancies.” In fact, the guidance is not so sweeping. It says only that the basic bundle of tests should be offered to all, alongside other screening options. It explicitly advises providers to not offer patients the extra tests.
Soon after ProPublica’s query, the Labcorp webpage was updated to remove any mention of the professional societies.
Patients say they often don’t know where to turn for informed and unbiased information. That’s why the r/NIPT Reddit page became such a robust community. Facing difficult news, Julia turned to it for counsel from other prospective parents. Kristina in Texas found the same community. Amanda, too.
‘The margin of error is a human life’
On a warm and cloudy day this past June, on what would have been their daughter’s first birthday, Amanda and her husband visited her grave. They brought a unicorn balloon and vanilla cake, which they ate nearby on the grass. Her husband read a poem.
To them, their baby had been perfect. She had fingers and toes. A thatch of dark hair. While in intensive care, peering up at her parents, she grabbed for her mother’s hand.
Had her condition been known, they would’ve spared her futile medical interventions, as doctors tried to save her life. Their family priest would have been able to baptize her. As it was, they never got to hold their child while she was alive.
These days, when Amanda and her husband say grace before dinner, they give thanks for the 28 hours of their daughter’s life.
They’re also thinking about making comfort boxes the hospital could give to other parents who lose a child. It might include books on grief. Softer tissues. Something that says, as Amanda puts it, “This is to help you get through.”
Amid their grief, they had a prayer answered: Amanda is pregnant again.
It’s frightening to go through this again. She barely sleeps the night before visiting the doctor. It feels like she never stopped being pregnant. It will feel that way, she said, until she brings a baby home – one who lives past the first 2 nights.
Amanda planned to get another genetic screening test. At first she couldn’t bear it, wasn’t sure she could trust it. “The margin of error is a human life,” Amanda said.
The 10-week appointment passed. Then the 12-week appointment. After her 13th week, she took the plunge. The test she was given was from Labcorp.
Around this time, more than a year after Amanda had desperately tried to alert the company about what had happened to her and her first baby, she finally heard back. Labcorp’s vice president of genetic counseling and services reached out – after ProPublica contacted the company and shared Amanda’s story.
The executive would only speak to Amanda without a reporter present.
Amanda said that during the call, the executive told her that prenatal genetic tests are evolving, and doctors should be clear about what the screenings can and cannot do. By the end of the conversation, the executive offered Amanda her cell number.
Amanda said she appreciated the call. “I feel better. I feel like I got something.”
The same day, her screening results came back. They were negative.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Amanda wanted to warn someone. In June 2021, her daughter – the one she and her husband had tried for 3 years to conceive – had died after only 28 hours. With an underdeveloped nose, she had battled for every breath.
Nobody knew why. Later, an autopsy report revealed their daughter had an extra 13th chromosome. The condition is nearly always fatal.
“But didn’t we test for that?” Amanda recalled asking herself. “That was kind of where the light bulb clicked.”
Through her doctor, Amanda had gotten a popular prenatal screening from a lab company. It had come back “negative.”
For three major conditions, including the one her baby had, the report gave the impression of near certainty. The likelihood that she would be born without them was “greater than 99%.”
As she recovered from a cesarean section, Amanda found herself facing a long maternity leave without a child. She shut the door to the empty nursery and began spending what seemed like endless hours of that hazy summer learning about the test.
It’s a simple blood draw designed to check for an array of genetic anomalies. But Amanda, a science researcher, read academic articles showing there was a higher risk of inaccurate results than she had realized. (She asked to be identified by only her first name to protect her privacy.)
On Reddit, she found other women reporting problems with the tests, too. She thought Labcorp, the company that made her test, would want to know about the screening that failed her. Maybe by alerting them, she could help other families. Maybe it would help her understand what happened.
“I was trying to gain answers,” said Amanda, now 32. She tried calling Labcorp’s customer service line, but she said she was passed along from one person to another. “It was just a circle,” she remembered.
She phoned Labcorp a second time. The call ended when an employee hung up on her.
Amanda was baffled. Why didn’t the company seem interested in her experience? Why, she wondered, wouldn’t it want to collect this data? Why wasn’t there someone who could answer her questions about how often this happens, and why?
If she had taken any number of other common commercial tests – including certain tests for COVID-19 or, say, pregnancy – the company would have been required to inform the U.S. Food and Drug Administration about reports of so-called adverse events.
But the test Amanda had falls into a regulatory void. No federal agency checks to make sure these prenatal screenings work the way they claim before they’re sold to health care providers. The FDA doesn’t ensure that marketing claims are backed up by evidence before screenings reach patients. And companies aren’t required to publicly report instances of when the tests get it wrong – sometimes catastrophically.
The broader lab testing industry and its lobbyists have successfully fought for years to keep it this way, cowing regulators into staying on the sidelines.
Worried about a growing variety of tests escaping scrutiny, the FDA was on the cusp of stepping in 6 years ago. But then it backed down.
Peter Lurie, then a top agency official, was at the meetings where the FDA tabled its plans. Not pushing harder, he told ProPublica, “remains one of my greatest regrets.”
The risk of false positives from prenatal screenings, in particular, has been known for years.
In 2014, the New England Center for Investigative Reporting detailed how some companies gave a misleading impression of the precision of the prenatal screenings. Women often didn’t understand they needed diagnostic testing to confirm the results. Some had gotten abortions based on false positive results, the story said. Earlier this year, the New York Times reported how companies sell optional extra screenings that are “usually wrong” when they predict a disorder.
Despite these stories and calls for reform by patient advocates, the government has done little to improve oversight of prenatal screenings. ProPublica set out to examine the forces that led to this inertia and left patients like Amanda feeling misled. Interviews with more than three dozen women revealed ongoing confusion about the screenings – and anger when their reliability proved to be overblown.
“This is a Wild West scenario where everybody is on their own,” said Lawrence Gostin, a Georgetown University, Washington, law professor specializing in bioethics.
The stakes for families are increasing. Upward of half of all pregnant people now receive one of these prenatal screenings. And with many states banning abortions or limiting them to early in pregnancies, the need for fast, accurate information has become more urgent.
The FDA itself acknowledges the problem. In correspondence with ProPublica, a spokesperson cited an “outdated policy” regarding the lack of vetting of many lab tests that the agency has “spent the better part of the last 2 decades trying to address.”
The screening industry, meanwhile, continues to expand, proving lucrative for those who lead it. The chief executive of Natera, which claims about 40% of the market share of prenatal screenings, received a $23 million compensation package last year, the highest of any executive at a publicly traded lab company.
Testing companies told ProPublica that, even without the FDA, there is significant oversight. Labs must abide by state regulations, and another federal agency, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, is charged with monitoring quality standards. It does not, however, check whether the tests the labs perform are clinically valid.
Companies also said the screenings offer important guidance to expectant families. Echoing others in the field, Labcorp said in a statement that the screenings, when used properly, “provide vital information about the presence of increased risk, but do not provide a definitive diagnosis.” (It declined to discuss the specifics of Amanda’s experience.)
Natera pointed out that its materials tell patients that “this test does not make a final diagnosis.” It reports results as “high-risk” or “low-risk,” not positive or negative.
Companies have stressed that, ultimately, it’s the responsibility of health care providers, who order the tests, to inform patients about the limits of screenings.
For all that, the statistical nuances of the test aren’t easy to parse for patients and even some doctors and nurses. For example, the test for trisomy 13, which doomed Amanda’s baby, is actually less likely to correctly predict the condition than other tests in the standard bundle of screenings offered to every patient.
When ProPublica asked readers to share their experiences with noninvasive prenatal screening tests, often referred to as NIPTs or NIPS, more than a thousand responded. Many said the tests had given them peace of mind. Some said they had provided an early warning about problems.
But others had more questions than answers. None more so than Amanda.
“What are these tests?” she wondered. “And how did mine end up in the margin of error?”
‘They started using it on humans, and then they went back and said: “Was our test accurate?” ’
Scientists have long tried to find ways to help parents and doctors understand what’s happening inside the womb. Amniocentesis was first used to reveal genetic anomalies in the late 1960s. But it didn’t become more popular until it began to be paired with ultrasound to precisely guide the procedure.
In the 1980s, doctors started using chorionic villus sampling, or CVS, an analysis of placental tissue that offers a diagnosis earlier in pregnancy. But, like amniocentesis, it is an invasive test that involves some risk to the fetus, though experts say it’s exceptionally low.
A breakthrough came in the late 1990s, when a scientist recognized that free-floating placental DNA could be detected in the mother’s blood. This meant that the fetus’s chromosomes could be examined by collecting a blood sample as soon as 9 weeks into pregnancy. This also provides an early opportunity to learn the likely fetal sex – a particularly popular feature.
Champions of the new science celebrated the arrival of a simple technique for patients that was particularly precise, at least for some conditions. Many favored it over other noninvasive options. But the industry that developed around NIPT has been marred by controversy from the beginning.
Dr. Ronald Wapner, director of reproductive genetics at Columbia University, described that time as “very chaotic.”
The tests had not been appropriately evaluated in clinical practice, said Dr. Wapner, whose research has sometimes been funded by testing companies. Because of this, he said, the industry “had very incomplete data on how well it worked.”
That didn’t stop the excitement. The chief executive of Sequenom, a biotechnology company that planned to release the first NIPT for Down syndrome, championed the company as the “Google of Molecular Diagnostics.” Its stock price soared.
Then, about 2 months before an expected launch in 2009, Sequenom killed the plan. The company’s research director, it turned out, had manipulated testing data and made misleading claims about how well the screening worked.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and Federal Bureau of Investigation opened investigations. Top executives were fired, and the research director pleaded guilty to conspiracy to commit securities fraud. Sequenom still managed to commercialize the test in 2011. (Labcorp, which later acquired Sequenom, said it uses a different kind of test.)
Other companies soon debuted their own tests. Still, there was little data on their clinical performance, researchers said.
As Megan Allyse, a bioethicist at the Mayo Clinic, put it, the companies “launched the test, they started using it on humans, and then they went back and said, ‘Was our test accurate?’ ” She also questioned the lack of attention to the ethics of how tests are presented to patients.
Despite missteps by the industry, the FDA didn’t scrutinize the screenings because they were considered lab-developed tests, which means they are created by the same laboratory that conducts them.
In 1976, Congress revamped oversight over medical devices. Since then, the FDA has effectively exempted such “home-brew” tests from key regulatory requirements. The idea was that when, say, a hospital lab wanted to create a simple test for its own patients, it was spared the time, money, and hassle of getting approval from Washington bureaucrats.
Today, lab-developed tests are vastly more numerous and complex. Because they aren’t registered with the federal government, nobody knows how many exist.
The distinction between tests the FDA actively regulates and those they don’t can seem nonsensical. It isn’t based on the complexity of the tests, or how people use them. It’s simply a matter of where the test is made.
The prenatal genetic screening industry took off almost immediately, powered by an army of aggressive sales representatives.
“At the very beginning, obstetricians in practice were being just completely inundated with visits from the sales reps,” said Dr. John Williams, director of reproductive health at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The push left many ob.gyns. and patients thinking the screenings were accurate enough to substitute for diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis or CVS.
In some cases, sales tactics escalated into lawbreaking.
Former Sequenom executives who exited during the fraud scandal created a new company that became Progenity, which also offered prenatal screening. Shortly after the company went public in 2020, it finalized a $49 million settlement with federal and state governments, where it admitted to falsifying insurance claims and giving kickbacks to physicians and their staff. According to a legal filing, one sales rep spent $65,658 on meals and alcohol for physicians in 1 year.
Now called Biora Therapeutics, the company said in a statement it no longer does any laboratory testing, including prenatal screenings.
Industry revenue continues to grow, but some testing companies are still fighting to make a profit, and competition to survive is fierce. “There’s a multibillion-dollar market, and they all want a piece of it,” said a former Progenity sales rep who quit in disgust after 5 months in 2016.
The rep, who requested anonymity because she continues to work in the field, said she still sees competitors from NIPT companies visiting medical practices “every week, buying breakfast or dinner, or taking them out for happy hour.”
Over time, companies pointed to new peer-reviewed studies, research the industry itself funded, to earn the confidence of doctors and other stakeholders. They showed that two tests – for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 – often performed better than other screening methods.
This research was valid, said Dr. Mary Norton, a perinatologist and clinical geneticist at the University of California, San Francisco, Medical Center’s prenatal diagnostic center. Considered a leading researcher in the field, she was an author of many of these key industry-funded studies.
But, she said, when research findings were presented publicly, the companies sometimes downplayed “inconvenient truths,” such as the exclusion of inconclusive results from accuracy estimates. Crucial caveats were also glossed over by some companies when they translated research into promotional copy aimed at health care providers and patients. Those materials didn’t always mention the many factors that can limit the performance of the screenings, including high body weight, the rarity of the condition tested, and younger maternal age.
Testing companies said they try to help patients understand the screenings through online resources and other materials. Some offer genetic counseling services.
The younger a person is, the lower the test’s positive predictive value – that is, the probability that a positive screening result will turn out to be correct – will be for some conditions. For instance, because Down syndrome is less prevalent in younger people’s pregnancies, a positive screening test is more likely to be a false positive for them.
Kristina was 30 years old in 2016, when her Progenity test came back positive for Down syndrome. She and her husband, who asked not to be fully named to protect their privacy, said they didn’t plan to carry a pregnancy with this condition to term.
But waiting to get an amniocentesis, and then waiting for the results, took 5 agonizing weeks, she said. It showed her son did not have Down syndrome.
Kristina, who lives in Texas, is still troubled by what she describes as a traumatic experience.
“I researched both late-term abortion providers and cemeteries,” she said. They even picked out a burial place, near their house.
She bought a blue baby blanket she intended to bury the baby’s tiny body in. She still has it. Her son, now 5, sleeps with it every night.
‘I can’t believe I didn’t say more’
As lab-developed tests became a bigger business, moving well past their home-brew origins, regulators looked for a way to assert oversight. In 2014, after years of study and debate, the time seemed right.
The FDA released plans proposing to regulate the tests, prioritizing those used to make major medical decisions. The agency has pointed to NIPTs as 1 of 20 concerning tests.
But, over the next 2 years, a coalition of power players urged the FDA to back off. Professional associations issued statements and hosted webinars devoted to the issue. Some created polished websites featuring sample letters to send to Washington.
Academic medical centers and pathology departments joined the fight, too. Scientists from 23 of them put it bluntly in a letter to the Office of Management and Budget: “FDA regulation of LDTs would be contrary to the public health,” it said, using a common acronym for the tests.
“Critical testing would be unavailable in the ‘lag time’ between development of new tests and FDA authorizing them,” the authors of the letter wrote, “and subsequent improvements on existing tests would slow significantly under the rigid, inflexible, and duplicative FDA regulatory scheme.”
This could delay essential care for patients. What’s more, opponents argued, existing lab reviews by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services are sufficiently rigorous. Some have suggested modernizing the CMS review process to improve oversight.
An FDA spokesperson told ProPublica that the agency encountered “continued, negative feedback,” including a 25-page paper written by two legal heavyweights hired by the American Clinical Laboratory Association: Paul Clement, President George W. Bush’s former solicitor general, and Laurence Tribe, law professor at Harvard University.
Mr. Clement has reportedly commanded rates of $1,350 per hour. He and Mr. Tribe did not respond to ProPublica’s queries about their work.
Their brief argued that the FDA “lacked legal authority” to regulate lab-developed tests because they are properly seen as the practice of medicine: a service, rather than a product.
However, as lawyers representing the American Association of Bioanalysts countered, the FDA would vet tests before they reach the market, not control how doctors use them. The government proposal, they wrote, is “similar to imposing requirements to screen blood or label drugs.”
After the election of President Donald Trump, but before he took office, a handful of FDA officials discussed their battered proposal. It had represented a breakthrough in the decades of excruciating back-and-forth with industry. But now, with an incoming administration bent on deregulation, their efforts seemed futile.
The regulators feared anything they enacted would be undone by Congress – and, under the Congressional Review Act, they might not be able to reissue anything “substantially similar” in the future. So the FDA published a white paper instead, summarizing the issue “for further public discussion.”
After the meeting where officials made this call, Mr. Lurie, then the FDA’s associate commissioner, recalled a colleague approaching him: “I can’t believe you didn’t say more.”
“And I was like, ‘Yeah, actually, I can’t believe I didn’t say more either,’ ” Mr. Lurie later told ProPublica. (After leaving the agency, Mr. Lurie went on to lead the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a consumer advocacy nonprofit, which has pushed the FDA to finally assert oversight over lab-developed tests.)
Nancy Stade, an attorney and senior policy official who left the FDA in 2015, said the agency often moves slowly as it seeks to get buy-in from industry and professional groups. In her work on regulatory policy, she saw it happen with lab-developed tests.
The agency is “always testing the waters,” she said, “and always coming out with something a little bit softer.”
In 2020, the influential American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, representing doctors who handle pregnancies, gave the screening industry another huge boost.
In a bulletin updating their advice on the tests, the two groups described growing research on the performance of some of the standard tests and said people have the right to information about their pregnancies, so the tests should be offered to all patients. Previously, they recommended this only for those facing higher risk of genetic anomalies.
The bulletin said the coauthors had disclosed no conflicts of interest. But two of the four coauthors, including Mary Norton, had disclosed in prior publications that test-makers had provided funding for their research. A company had provided a third coauthor with laboratory services needed to run tests, according to that researcher, a connection she also disclosed in past papers.
ACOG, in a statement to ProPublica, said the organization “identified no conflicts because research funding is provided to academic institutions with institutional review boards, not to individual investigators.” Two of the three researchers responded to questions from ProPublica and said they maintained independence over their work.
One test-maker, Illumina, celebrated the ACOG guidance in a tweet, saying it “recognizes the superior performance of #NIPT and the benefit it provides expectant families.” Natera’s share prices doubled in 5 months. UnitedHealthcare, the nation’s largest private insurer and long a target of industry lobbying, told ProPublica it changed its stance to cover screenings for all patients, regardless of risk, because of the recommendation.
In a recent shareholder report, Natera stated that prenatal genetic and carrier screenings “represent the significant majority of our revenues,” which totaled $625.5 million in 2021. The company expects more growth to come.
“The NIPT market is still very underpenetrated, compared to the 4 to 5 million pregnancies in the U.S.,” Natera’s chief executive said on a 2021 earnings call, “so there’s a long way to go.”
But even Dr. Norton, who coauthored the ACOG recommendation and favors NIPTs for patients 40 and over, has concerns about screenings becoming widespread among those who are younger. In most cases, she prefers other screening methods that catch the nongenetic problems younger moms are more likely to face. Negative results from an NIPT, she said, can be “falsely reassuring.”
In the years after the FDA set aside its regulatory proposal, the agency has assisted members of Congress on a proposed legislative solution. That effort, dubbed the VALID Act, aims to end any debate over the agency’s authority over lab-developed tests. An FDA press officer said the legislation would ensure the prenatal screening tests and others are “accurate and reliable.”
But, as in the past, intense lobbying followed the proposal. The VALID Act was a rider to a funding reauthorization bill, but in September the House and Senate agreed to remove it. Advocates now hope to attach it to proposed end-of-year legislation.
Meanwhile, earlier this year, 4 months after the New York Times story on the usefulness of some screenings, the FDA took a step toward more public awareness about prenatal genetic screening. It issued its first safety communication on them, noting the potential for false results.
It cautioned patients about making “critical health care decisions based on results from these screening tests alone.”
Cara Tenenbaum, a former FDA policy advisor, was pleased to see the statement. Still, she said, it was long overdue.
“This has been known – known, or should have been known – for 10 years,” she said.
‘It had me so messed up’
With the demise of Roe v. Wade, restrictive and ever-changing abortion laws can pressure people to act quickly with limited information, heightening the stakes of prenatal screening.
Julia, a mom from Mississippi’s Gulf Coast, knows what it’s like to face harrowing consequences while navigating state-imposed time limits – and doing so with little guidance. Last fall, she was pregnant with her fourth child when, she said, a nurse practitioner suggested prenatal genetic screening.
At 33, Julia had no risk factors. Her previous pregnancies hadn’t been screened with an NIPT. But with three sons and 18 nephews, she and her husband were curious about the baby’s sex. And the screening seemed like it had no downside.
Julia figured it would only be offered if it was reliable, so her nurse practitioner ordered her both the basic bundle of screenings and the extra tests. (The medical practice didn’t respond to interview requests. Julia is a family nickname that’s used here to protect her privacy.)
The screenings showed the baby was a girl – but the extra tests also detected trisomy 16, a condition caused by an extra chromosome that is so rare, the nurse didn’t know what it was, Julia recalled.
The nurse borrowed Julia’s phone, using it to search online and read aloud what she found. Julia was stunned to hear trisomy 16 was incompatible with life.
“I was utterly devastated,” she said. “I made it out of my doctor’s office but completely broke down in the car.”
But ACOG does not recommend the trisomy 16 screening, saying “its accuracy with regard to detection and the false-positive rate is not established.” Julia wasn’t informed of this, she said, and she’s not sure if her health care providers knew it either.
The lab report recommended diagnostic testing to confirm the results, but time was short. She had her amniocentesis at 17 weeks. It could take up to 4 more weeks to receive results.
That would be too late for a legal abortion in Mississippi. So she made an appointment for one in Florida, where the cutoff was 24 weeks. (It’s now 15 weeks in Florida, while Mississippi went from 15 weeks for legal procedures to a ban on nearly all abortions.)
The wait was excruciating. Julia was driving twice a week to New Orleans for specialized care. With work and child care, it was too hard. She quit the teaching job she loved.
One winter night, she felt the fetus move for the first time – ordinarily a milestone, but now, facing a fatal prognosis, she didn’t want to get attached. “It had me so messed up,” she said.
On the way to the amniocentesis, Julia and her husband chose a name. Drawing from a language conjured by J.R.R. Tolkien in the fantasy novels they love, it means “hope.”
More than halfway through her pregnancy, the amnio results arrived. The prenatal screening had given a false positive. The baby would be fine. In May, Julia gave birth to a healthy daughter.
Julia and her husband are upset about the needless anguish brought on by the screening. “They like to have it both ways,” said Julia’s husband. “They say they are 99% accurate, but when there’s a false positive, they say, ‘Well, we’re not diagnostic.’ ”
Believing the prenatal screening was likely accurate, they had seriously considered canceling the amniocentesis, saving their limited funds for an abortion in Florida, hundreds of miles away.
Their dilemma points to a longtime concern: ending pregnancies based on false positives. The FDA cited it as a risk as far back as 2015. Now, those with positive results are facing an even tighter time crunch. They must consider whether waiting for a definitive test, and possibly traveling to another state for an abortion later in pregnancy, is worth it.
In their promotional material, some companies not only sidestep the variability of the standard tests, they fail to distinguish them from the least reliable ones – those for exceptionally rare conditions. They tout the extra screenings as “premium,” “plus,” or “advanced” options.
“Going to greater lengths for the answers that matter most,” says a brochure aimed at health care providers from test-maker Illumina. Elsewhere it states that the “expanded” panel of tests provides “confident results” and “the additional insights you need.”
But the companies themselves know the accuracy of some of their tests has yet to be established in the research. Natera acknowledged in a recent shareholder report that many insurers won’t pay for screenings for missing chromosomal fragments, known as microdeletions, in part because there isn’t enough published data behind them.
The company, responding to ProPublica, stressed the quality of the data over the quantity, saying the research so far has been favorable. “Natera’s microdeletion testing was thoroughly validated with results published in peer-reviewed publications,” it said in a statement.
Natera pointed to a recent study that looked at DiGeorge syndrome, one of several chromosomal anomalies it checks for with its microdeletion screenings. Researchers found the positive predictive value (PPV) of the test to be 52.6%, meaning that nearly half of positive results are false positives. (For many patients, PPVs for more common conditions can exceed 90%.)
Natera said the performance of the diGeorge syndrome test “is excellent and not considered a low PPV,” because of the condition being extremely rare.
Companies also play up the danger of diagnostic tests like amnio. They “can cause miscarriages,” warns the marketing from Labcorp, which made Amanda’s screening, while its test “does not cause miscarriages.” But medical experts emphasize that diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis, are more accurate and, in fact, carry little risk to the pregnancy.
Labcorp, in a statement, said the company “acknowledges the well-documented risk associated with amniocentesis and CVS in our literature. It is the patient’s prerogative to decide which risks they are willing or unwilling to take.”
Marketing claims also sometimes skate over the nuances in the guidance from the leading professional societies. On a webpage targeting health care providers, for example, a Labcorp chart said groups such as ACOG “endorse and/or recognize” prenatal screenings as an option for all pregnancies. But the chart listed screenings ACOG does not recommend, including trisomy 16.
When asked about it, Labcorp said in a statement that ACOG “endorses NIPS for all pregnancies.” In fact, the guidance is not so sweeping. It says only that the basic bundle of tests should be offered to all, alongside other screening options. It explicitly advises providers to not offer patients the extra tests.
Soon after ProPublica’s query, the Labcorp webpage was updated to remove any mention of the professional societies.
Patients say they often don’t know where to turn for informed and unbiased information. That’s why the r/NIPT Reddit page became such a robust community. Facing difficult news, Julia turned to it for counsel from other prospective parents. Kristina in Texas found the same community. Amanda, too.
‘The margin of error is a human life’
On a warm and cloudy day this past June, on what would have been their daughter’s first birthday, Amanda and her husband visited her grave. They brought a unicorn balloon and vanilla cake, which they ate nearby on the grass. Her husband read a poem.
To them, their baby had been perfect. She had fingers and toes. A thatch of dark hair. While in intensive care, peering up at her parents, she grabbed for her mother’s hand.
Had her condition been known, they would’ve spared her futile medical interventions, as doctors tried to save her life. Their family priest would have been able to baptize her. As it was, they never got to hold their child while she was alive.
These days, when Amanda and her husband say grace before dinner, they give thanks for the 28 hours of their daughter’s life.
They’re also thinking about making comfort boxes the hospital could give to other parents who lose a child. It might include books on grief. Softer tissues. Something that says, as Amanda puts it, “This is to help you get through.”
Amid their grief, they had a prayer answered: Amanda is pregnant again.
It’s frightening to go through this again. She barely sleeps the night before visiting the doctor. It feels like she never stopped being pregnant. It will feel that way, she said, until she brings a baby home – one who lives past the first 2 nights.
Amanda planned to get another genetic screening test. At first she couldn’t bear it, wasn’t sure she could trust it. “The margin of error is a human life,” Amanda said.
The 10-week appointment passed. Then the 12-week appointment. After her 13th week, she took the plunge. The test she was given was from Labcorp.
Around this time, more than a year after Amanda had desperately tried to alert the company about what had happened to her and her first baby, she finally heard back. Labcorp’s vice president of genetic counseling and services reached out – after ProPublica contacted the company and shared Amanda’s story.
The executive would only speak to Amanda without a reporter present.
Amanda said that during the call, the executive told her that prenatal genetic tests are evolving, and doctors should be clear about what the screenings can and cannot do. By the end of the conversation, the executive offered Amanda her cell number.
Amanda said she appreciated the call. “I feel better. I feel like I got something.”
The same day, her screening results came back. They were negative.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Amanda wanted to warn someone. In June 2021, her daughter – the one she and her husband had tried for 3 years to conceive – had died after only 28 hours. With an underdeveloped nose, she had battled for every breath.
Nobody knew why. Later, an autopsy report revealed their daughter had an extra 13th chromosome. The condition is nearly always fatal.
“But didn’t we test for that?” Amanda recalled asking herself. “That was kind of where the light bulb clicked.”
Through her doctor, Amanda had gotten a popular prenatal screening from a lab company. It had come back “negative.”
For three major conditions, including the one her baby had, the report gave the impression of near certainty. The likelihood that she would be born without them was “greater than 99%.”
As she recovered from a cesarean section, Amanda found herself facing a long maternity leave without a child. She shut the door to the empty nursery and began spending what seemed like endless hours of that hazy summer learning about the test.
It’s a simple blood draw designed to check for an array of genetic anomalies. But Amanda, a science researcher, read academic articles showing there was a higher risk of inaccurate results than she had realized. (She asked to be identified by only her first name to protect her privacy.)
On Reddit, she found other women reporting problems with the tests, too. She thought Labcorp, the company that made her test, would want to know about the screening that failed her. Maybe by alerting them, she could help other families. Maybe it would help her understand what happened.
“I was trying to gain answers,” said Amanda, now 32. She tried calling Labcorp’s customer service line, but she said she was passed along from one person to another. “It was just a circle,” she remembered.
She phoned Labcorp a second time. The call ended when an employee hung up on her.
Amanda was baffled. Why didn’t the company seem interested in her experience? Why, she wondered, wouldn’t it want to collect this data? Why wasn’t there someone who could answer her questions about how often this happens, and why?
If she had taken any number of other common commercial tests – including certain tests for COVID-19 or, say, pregnancy – the company would have been required to inform the U.S. Food and Drug Administration about reports of so-called adverse events.
But the test Amanda had falls into a regulatory void. No federal agency checks to make sure these prenatal screenings work the way they claim before they’re sold to health care providers. The FDA doesn’t ensure that marketing claims are backed up by evidence before screenings reach patients. And companies aren’t required to publicly report instances of when the tests get it wrong – sometimes catastrophically.
The broader lab testing industry and its lobbyists have successfully fought for years to keep it this way, cowing regulators into staying on the sidelines.
Worried about a growing variety of tests escaping scrutiny, the FDA was on the cusp of stepping in 6 years ago. But then it backed down.
Peter Lurie, then a top agency official, was at the meetings where the FDA tabled its plans. Not pushing harder, he told ProPublica, “remains one of my greatest regrets.”
The risk of false positives from prenatal screenings, in particular, has been known for years.
In 2014, the New England Center for Investigative Reporting detailed how some companies gave a misleading impression of the precision of the prenatal screenings. Women often didn’t understand they needed diagnostic testing to confirm the results. Some had gotten abortions based on false positive results, the story said. Earlier this year, the New York Times reported how companies sell optional extra screenings that are “usually wrong” when they predict a disorder.
Despite these stories and calls for reform by patient advocates, the government has done little to improve oversight of prenatal screenings. ProPublica set out to examine the forces that led to this inertia and left patients like Amanda feeling misled. Interviews with more than three dozen women revealed ongoing confusion about the screenings – and anger when their reliability proved to be overblown.
“This is a Wild West scenario where everybody is on their own,” said Lawrence Gostin, a Georgetown University, Washington, law professor specializing in bioethics.
The stakes for families are increasing. Upward of half of all pregnant people now receive one of these prenatal screenings. And with many states banning abortions or limiting them to early in pregnancies, the need for fast, accurate information has become more urgent.
The FDA itself acknowledges the problem. In correspondence with ProPublica, a spokesperson cited an “outdated policy” regarding the lack of vetting of many lab tests that the agency has “spent the better part of the last 2 decades trying to address.”
The screening industry, meanwhile, continues to expand, proving lucrative for those who lead it. The chief executive of Natera, which claims about 40% of the market share of prenatal screenings, received a $23 million compensation package last year, the highest of any executive at a publicly traded lab company.
Testing companies told ProPublica that, even without the FDA, there is significant oversight. Labs must abide by state regulations, and another federal agency, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, is charged with monitoring quality standards. It does not, however, check whether the tests the labs perform are clinically valid.
Companies also said the screenings offer important guidance to expectant families. Echoing others in the field, Labcorp said in a statement that the screenings, when used properly, “provide vital information about the presence of increased risk, but do not provide a definitive diagnosis.” (It declined to discuss the specifics of Amanda’s experience.)
Natera pointed out that its materials tell patients that “this test does not make a final diagnosis.” It reports results as “high-risk” or “low-risk,” not positive or negative.
Companies have stressed that, ultimately, it’s the responsibility of health care providers, who order the tests, to inform patients about the limits of screenings.
For all that, the statistical nuances of the test aren’t easy to parse for patients and even some doctors and nurses. For example, the test for trisomy 13, which doomed Amanda’s baby, is actually less likely to correctly predict the condition than other tests in the standard bundle of screenings offered to every patient.
When ProPublica asked readers to share their experiences with noninvasive prenatal screening tests, often referred to as NIPTs or NIPS, more than a thousand responded. Many said the tests had given them peace of mind. Some said they had provided an early warning about problems.
But others had more questions than answers. None more so than Amanda.
“What are these tests?” she wondered. “And how did mine end up in the margin of error?”
‘They started using it on humans, and then they went back and said: “Was our test accurate?” ’
Scientists have long tried to find ways to help parents and doctors understand what’s happening inside the womb. Amniocentesis was first used to reveal genetic anomalies in the late 1960s. But it didn’t become more popular until it began to be paired with ultrasound to precisely guide the procedure.
In the 1980s, doctors started using chorionic villus sampling, or CVS, an analysis of placental tissue that offers a diagnosis earlier in pregnancy. But, like amniocentesis, it is an invasive test that involves some risk to the fetus, though experts say it’s exceptionally low.
A breakthrough came in the late 1990s, when a scientist recognized that free-floating placental DNA could be detected in the mother’s blood. This meant that the fetus’s chromosomes could be examined by collecting a blood sample as soon as 9 weeks into pregnancy. This also provides an early opportunity to learn the likely fetal sex – a particularly popular feature.
Champions of the new science celebrated the arrival of a simple technique for patients that was particularly precise, at least for some conditions. Many favored it over other noninvasive options. But the industry that developed around NIPT has been marred by controversy from the beginning.
Dr. Ronald Wapner, director of reproductive genetics at Columbia University, described that time as “very chaotic.”
The tests had not been appropriately evaluated in clinical practice, said Dr. Wapner, whose research has sometimes been funded by testing companies. Because of this, he said, the industry “had very incomplete data on how well it worked.”
That didn’t stop the excitement. The chief executive of Sequenom, a biotechnology company that planned to release the first NIPT for Down syndrome, championed the company as the “Google of Molecular Diagnostics.” Its stock price soared.
Then, about 2 months before an expected launch in 2009, Sequenom killed the plan. The company’s research director, it turned out, had manipulated testing data and made misleading claims about how well the screening worked.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and Federal Bureau of Investigation opened investigations. Top executives were fired, and the research director pleaded guilty to conspiracy to commit securities fraud. Sequenom still managed to commercialize the test in 2011. (Labcorp, which later acquired Sequenom, said it uses a different kind of test.)
Other companies soon debuted their own tests. Still, there was little data on their clinical performance, researchers said.
As Megan Allyse, a bioethicist at the Mayo Clinic, put it, the companies “launched the test, they started using it on humans, and then they went back and said, ‘Was our test accurate?’ ” She also questioned the lack of attention to the ethics of how tests are presented to patients.
Despite missteps by the industry, the FDA didn’t scrutinize the screenings because they were considered lab-developed tests, which means they are created by the same laboratory that conducts them.
In 1976, Congress revamped oversight over medical devices. Since then, the FDA has effectively exempted such “home-brew” tests from key regulatory requirements. The idea was that when, say, a hospital lab wanted to create a simple test for its own patients, it was spared the time, money, and hassle of getting approval from Washington bureaucrats.
Today, lab-developed tests are vastly more numerous and complex. Because they aren’t registered with the federal government, nobody knows how many exist.
The distinction between tests the FDA actively regulates and those they don’t can seem nonsensical. It isn’t based on the complexity of the tests, or how people use them. It’s simply a matter of where the test is made.
The prenatal genetic screening industry took off almost immediately, powered by an army of aggressive sales representatives.
“At the very beginning, obstetricians in practice were being just completely inundated with visits from the sales reps,” said Dr. John Williams, director of reproductive health at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. The push left many ob.gyns. and patients thinking the screenings were accurate enough to substitute for diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis or CVS.
In some cases, sales tactics escalated into lawbreaking.
Former Sequenom executives who exited during the fraud scandal created a new company that became Progenity, which also offered prenatal screening. Shortly after the company went public in 2020, it finalized a $49 million settlement with federal and state governments, where it admitted to falsifying insurance claims and giving kickbacks to physicians and their staff. According to a legal filing, one sales rep spent $65,658 on meals and alcohol for physicians in 1 year.
Now called Biora Therapeutics, the company said in a statement it no longer does any laboratory testing, including prenatal screenings.
Industry revenue continues to grow, but some testing companies are still fighting to make a profit, and competition to survive is fierce. “There’s a multibillion-dollar market, and they all want a piece of it,” said a former Progenity sales rep who quit in disgust after 5 months in 2016.
The rep, who requested anonymity because she continues to work in the field, said she still sees competitors from NIPT companies visiting medical practices “every week, buying breakfast or dinner, or taking them out for happy hour.”
Over time, companies pointed to new peer-reviewed studies, research the industry itself funded, to earn the confidence of doctors and other stakeholders. They showed that two tests – for Down syndrome and trisomy 18 – often performed better than other screening methods.
This research was valid, said Dr. Mary Norton, a perinatologist and clinical geneticist at the University of California, San Francisco, Medical Center’s prenatal diagnostic center. Considered a leading researcher in the field, she was an author of many of these key industry-funded studies.
But, she said, when research findings were presented publicly, the companies sometimes downplayed “inconvenient truths,” such as the exclusion of inconclusive results from accuracy estimates. Crucial caveats were also glossed over by some companies when they translated research into promotional copy aimed at health care providers and patients. Those materials didn’t always mention the many factors that can limit the performance of the screenings, including high body weight, the rarity of the condition tested, and younger maternal age.
Testing companies said they try to help patients understand the screenings through online resources and other materials. Some offer genetic counseling services.
The younger a person is, the lower the test’s positive predictive value – that is, the probability that a positive screening result will turn out to be correct – will be for some conditions. For instance, because Down syndrome is less prevalent in younger people’s pregnancies, a positive screening test is more likely to be a false positive for them.
Kristina was 30 years old in 2016, when her Progenity test came back positive for Down syndrome. She and her husband, who asked not to be fully named to protect their privacy, said they didn’t plan to carry a pregnancy with this condition to term.
But waiting to get an amniocentesis, and then waiting for the results, took 5 agonizing weeks, she said. It showed her son did not have Down syndrome.
Kristina, who lives in Texas, is still troubled by what she describes as a traumatic experience.
“I researched both late-term abortion providers and cemeteries,” she said. They even picked out a burial place, near their house.
She bought a blue baby blanket she intended to bury the baby’s tiny body in. She still has it. Her son, now 5, sleeps with it every night.
‘I can’t believe I didn’t say more’
As lab-developed tests became a bigger business, moving well past their home-brew origins, regulators looked for a way to assert oversight. In 2014, after years of study and debate, the time seemed right.
The FDA released plans proposing to regulate the tests, prioritizing those used to make major medical decisions. The agency has pointed to NIPTs as 1 of 20 concerning tests.
But, over the next 2 years, a coalition of power players urged the FDA to back off. Professional associations issued statements and hosted webinars devoted to the issue. Some created polished websites featuring sample letters to send to Washington.
Academic medical centers and pathology departments joined the fight, too. Scientists from 23 of them put it bluntly in a letter to the Office of Management and Budget: “FDA regulation of LDTs would be contrary to the public health,” it said, using a common acronym for the tests.
“Critical testing would be unavailable in the ‘lag time’ between development of new tests and FDA authorizing them,” the authors of the letter wrote, “and subsequent improvements on existing tests would slow significantly under the rigid, inflexible, and duplicative FDA regulatory scheme.”
This could delay essential care for patients. What’s more, opponents argued, existing lab reviews by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services are sufficiently rigorous. Some have suggested modernizing the CMS review process to improve oversight.
An FDA spokesperson told ProPublica that the agency encountered “continued, negative feedback,” including a 25-page paper written by two legal heavyweights hired by the American Clinical Laboratory Association: Paul Clement, President George W. Bush’s former solicitor general, and Laurence Tribe, law professor at Harvard University.
Mr. Clement has reportedly commanded rates of $1,350 per hour. He and Mr. Tribe did not respond to ProPublica’s queries about their work.
Their brief argued that the FDA “lacked legal authority” to regulate lab-developed tests because they are properly seen as the practice of medicine: a service, rather than a product.
However, as lawyers representing the American Association of Bioanalysts countered, the FDA would vet tests before they reach the market, not control how doctors use them. The government proposal, they wrote, is “similar to imposing requirements to screen blood or label drugs.”
After the election of President Donald Trump, but before he took office, a handful of FDA officials discussed their battered proposal. It had represented a breakthrough in the decades of excruciating back-and-forth with industry. But now, with an incoming administration bent on deregulation, their efforts seemed futile.
The regulators feared anything they enacted would be undone by Congress – and, under the Congressional Review Act, they might not be able to reissue anything “substantially similar” in the future. So the FDA published a white paper instead, summarizing the issue “for further public discussion.”
After the meeting where officials made this call, Mr. Lurie, then the FDA’s associate commissioner, recalled a colleague approaching him: “I can’t believe you didn’t say more.”
“And I was like, ‘Yeah, actually, I can’t believe I didn’t say more either,’ ” Mr. Lurie later told ProPublica. (After leaving the agency, Mr. Lurie went on to lead the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a consumer advocacy nonprofit, which has pushed the FDA to finally assert oversight over lab-developed tests.)
Nancy Stade, an attorney and senior policy official who left the FDA in 2015, said the agency often moves slowly as it seeks to get buy-in from industry and professional groups. In her work on regulatory policy, she saw it happen with lab-developed tests.
The agency is “always testing the waters,” she said, “and always coming out with something a little bit softer.”
In 2020, the influential American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, representing doctors who handle pregnancies, gave the screening industry another huge boost.
In a bulletin updating their advice on the tests, the two groups described growing research on the performance of some of the standard tests and said people have the right to information about their pregnancies, so the tests should be offered to all patients. Previously, they recommended this only for those facing higher risk of genetic anomalies.
The bulletin said the coauthors had disclosed no conflicts of interest. But two of the four coauthors, including Mary Norton, had disclosed in prior publications that test-makers had provided funding for their research. A company had provided a third coauthor with laboratory services needed to run tests, according to that researcher, a connection she also disclosed in past papers.
ACOG, in a statement to ProPublica, said the organization “identified no conflicts because research funding is provided to academic institutions with institutional review boards, not to individual investigators.” Two of the three researchers responded to questions from ProPublica and said they maintained independence over their work.
One test-maker, Illumina, celebrated the ACOG guidance in a tweet, saying it “recognizes the superior performance of #NIPT and the benefit it provides expectant families.” Natera’s share prices doubled in 5 months. UnitedHealthcare, the nation’s largest private insurer and long a target of industry lobbying, told ProPublica it changed its stance to cover screenings for all patients, regardless of risk, because of the recommendation.
In a recent shareholder report, Natera stated that prenatal genetic and carrier screenings “represent the significant majority of our revenues,” which totaled $625.5 million in 2021. The company expects more growth to come.
“The NIPT market is still very underpenetrated, compared to the 4 to 5 million pregnancies in the U.S.,” Natera’s chief executive said on a 2021 earnings call, “so there’s a long way to go.”
But even Dr. Norton, who coauthored the ACOG recommendation and favors NIPTs for patients 40 and over, has concerns about screenings becoming widespread among those who are younger. In most cases, she prefers other screening methods that catch the nongenetic problems younger moms are more likely to face. Negative results from an NIPT, she said, can be “falsely reassuring.”
In the years after the FDA set aside its regulatory proposal, the agency has assisted members of Congress on a proposed legislative solution. That effort, dubbed the VALID Act, aims to end any debate over the agency’s authority over lab-developed tests. An FDA press officer said the legislation would ensure the prenatal screening tests and others are “accurate and reliable.”
But, as in the past, intense lobbying followed the proposal. The VALID Act was a rider to a funding reauthorization bill, but in September the House and Senate agreed to remove it. Advocates now hope to attach it to proposed end-of-year legislation.
Meanwhile, earlier this year, 4 months after the New York Times story on the usefulness of some screenings, the FDA took a step toward more public awareness about prenatal genetic screening. It issued its first safety communication on them, noting the potential for false results.
It cautioned patients about making “critical health care decisions based on results from these screening tests alone.”
Cara Tenenbaum, a former FDA policy advisor, was pleased to see the statement. Still, she said, it was long overdue.
“This has been known – known, or should have been known – for 10 years,” she said.
‘It had me so messed up’
With the demise of Roe v. Wade, restrictive and ever-changing abortion laws can pressure people to act quickly with limited information, heightening the stakes of prenatal screening.
Julia, a mom from Mississippi’s Gulf Coast, knows what it’s like to face harrowing consequences while navigating state-imposed time limits – and doing so with little guidance. Last fall, she was pregnant with her fourth child when, she said, a nurse practitioner suggested prenatal genetic screening.
At 33, Julia had no risk factors. Her previous pregnancies hadn’t been screened with an NIPT. But with three sons and 18 nephews, she and her husband were curious about the baby’s sex. And the screening seemed like it had no downside.
Julia figured it would only be offered if it was reliable, so her nurse practitioner ordered her both the basic bundle of screenings and the extra tests. (The medical practice didn’t respond to interview requests. Julia is a family nickname that’s used here to protect her privacy.)
The screenings showed the baby was a girl – but the extra tests also detected trisomy 16, a condition caused by an extra chromosome that is so rare, the nurse didn’t know what it was, Julia recalled.
The nurse borrowed Julia’s phone, using it to search online and read aloud what she found. Julia was stunned to hear trisomy 16 was incompatible with life.
“I was utterly devastated,” she said. “I made it out of my doctor’s office but completely broke down in the car.”
But ACOG does not recommend the trisomy 16 screening, saying “its accuracy with regard to detection and the false-positive rate is not established.” Julia wasn’t informed of this, she said, and she’s not sure if her health care providers knew it either.
The lab report recommended diagnostic testing to confirm the results, but time was short. She had her amniocentesis at 17 weeks. It could take up to 4 more weeks to receive results.
That would be too late for a legal abortion in Mississippi. So she made an appointment for one in Florida, where the cutoff was 24 weeks. (It’s now 15 weeks in Florida, while Mississippi went from 15 weeks for legal procedures to a ban on nearly all abortions.)
The wait was excruciating. Julia was driving twice a week to New Orleans for specialized care. With work and child care, it was too hard. She quit the teaching job she loved.
One winter night, she felt the fetus move for the first time – ordinarily a milestone, but now, facing a fatal prognosis, she didn’t want to get attached. “It had me so messed up,” she said.
On the way to the amniocentesis, Julia and her husband chose a name. Drawing from a language conjured by J.R.R. Tolkien in the fantasy novels they love, it means “hope.”
More than halfway through her pregnancy, the amnio results arrived. The prenatal screening had given a false positive. The baby would be fine. In May, Julia gave birth to a healthy daughter.
Julia and her husband are upset about the needless anguish brought on by the screening. “They like to have it both ways,” said Julia’s husband. “They say they are 99% accurate, but when there’s a false positive, they say, ‘Well, we’re not diagnostic.’ ”
Believing the prenatal screening was likely accurate, they had seriously considered canceling the amniocentesis, saving their limited funds for an abortion in Florida, hundreds of miles away.
Their dilemma points to a longtime concern: ending pregnancies based on false positives. The FDA cited it as a risk as far back as 2015. Now, those with positive results are facing an even tighter time crunch. They must consider whether waiting for a definitive test, and possibly traveling to another state for an abortion later in pregnancy, is worth it.
In their promotional material, some companies not only sidestep the variability of the standard tests, they fail to distinguish them from the least reliable ones – those for exceptionally rare conditions. They tout the extra screenings as “premium,” “plus,” or “advanced” options.
“Going to greater lengths for the answers that matter most,” says a brochure aimed at health care providers from test-maker Illumina. Elsewhere it states that the “expanded” panel of tests provides “confident results” and “the additional insights you need.”
But the companies themselves know the accuracy of some of their tests has yet to be established in the research. Natera acknowledged in a recent shareholder report that many insurers won’t pay for screenings for missing chromosomal fragments, known as microdeletions, in part because there isn’t enough published data behind them.
The company, responding to ProPublica, stressed the quality of the data over the quantity, saying the research so far has been favorable. “Natera’s microdeletion testing was thoroughly validated with results published in peer-reviewed publications,” it said in a statement.
Natera pointed to a recent study that looked at DiGeorge syndrome, one of several chromosomal anomalies it checks for with its microdeletion screenings. Researchers found the positive predictive value (PPV) of the test to be 52.6%, meaning that nearly half of positive results are false positives. (For many patients, PPVs for more common conditions can exceed 90%.)
Natera said the performance of the diGeorge syndrome test “is excellent and not considered a low PPV,” because of the condition being extremely rare.
Companies also play up the danger of diagnostic tests like amnio. They “can cause miscarriages,” warns the marketing from Labcorp, which made Amanda’s screening, while its test “does not cause miscarriages.” But medical experts emphasize that diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis, are more accurate and, in fact, carry little risk to the pregnancy.
Labcorp, in a statement, said the company “acknowledges the well-documented risk associated with amniocentesis and CVS in our literature. It is the patient’s prerogative to decide which risks they are willing or unwilling to take.”
Marketing claims also sometimes skate over the nuances in the guidance from the leading professional societies. On a webpage targeting health care providers, for example, a Labcorp chart said groups such as ACOG “endorse and/or recognize” prenatal screenings as an option for all pregnancies. But the chart listed screenings ACOG does not recommend, including trisomy 16.
When asked about it, Labcorp said in a statement that ACOG “endorses NIPS for all pregnancies.” In fact, the guidance is not so sweeping. It says only that the basic bundle of tests should be offered to all, alongside other screening options. It explicitly advises providers to not offer patients the extra tests.
Soon after ProPublica’s query, the Labcorp webpage was updated to remove any mention of the professional societies.
Patients say they often don’t know where to turn for informed and unbiased information. That’s why the r/NIPT Reddit page became such a robust community. Facing difficult news, Julia turned to it for counsel from other prospective parents. Kristina in Texas found the same community. Amanda, too.
‘The margin of error is a human life’
On a warm and cloudy day this past June, on what would have been their daughter’s first birthday, Amanda and her husband visited her grave. They brought a unicorn balloon and vanilla cake, which they ate nearby on the grass. Her husband read a poem.
To them, their baby had been perfect. She had fingers and toes. A thatch of dark hair. While in intensive care, peering up at her parents, she grabbed for her mother’s hand.
Had her condition been known, they would’ve spared her futile medical interventions, as doctors tried to save her life. Their family priest would have been able to baptize her. As it was, they never got to hold their child while she was alive.
These days, when Amanda and her husband say grace before dinner, they give thanks for the 28 hours of their daughter’s life.
They’re also thinking about making comfort boxes the hospital could give to other parents who lose a child. It might include books on grief. Softer tissues. Something that says, as Amanda puts it, “This is to help you get through.”
Amid their grief, they had a prayer answered: Amanda is pregnant again.
It’s frightening to go through this again. She barely sleeps the night before visiting the doctor. It feels like she never stopped being pregnant. It will feel that way, she said, until she brings a baby home – one who lives past the first 2 nights.
Amanda planned to get another genetic screening test. At first she couldn’t bear it, wasn’t sure she could trust it. “The margin of error is a human life,” Amanda said.
The 10-week appointment passed. Then the 12-week appointment. After her 13th week, she took the plunge. The test she was given was from Labcorp.
Around this time, more than a year after Amanda had desperately tried to alert the company about what had happened to her and her first baby, she finally heard back. Labcorp’s vice president of genetic counseling and services reached out – after ProPublica contacted the company and shared Amanda’s story.
The executive would only speak to Amanda without a reporter present.
Amanda said that during the call, the executive told her that prenatal genetic tests are evolving, and doctors should be clear about what the screenings can and cannot do. By the end of the conversation, the executive offered Amanda her cell number.
Amanda said she appreciated the call. “I feel better. I feel like I got something.”
The same day, her screening results came back. They were negative.
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Know the right resuscitation for right-sided heart failure
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
Paxlovid has been free so far. Next year, sticker shock awaits
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Mind the geriatrician gap
These should be the best of times for geriatric medicine.
The baby boom has become a senior surge, bringing in a rapidly growing pool of aging patients for geriatricians to treat. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, more than 56 million adults aged 65 and older live in the United States. They account for about 17% of the nation’s population. That number is expected to hit 73 million by 2030 and 86 million by 2050.
The American Geriatrics Society estimates that 30% of older people require the attention of geriatricians. These clinicians excel in managing complex cases – patients with multiple comorbidities, such as coronary artery disease, dementia, and osteoporosis, who are taking a half dozen, and often more, medications.
. In the 2010s, geriatricians called for “25,000 [such specialists] by 2025.” As of 2021, 7123 certified geriatricians were practicing in the United States, according to the American Board of Medical Specialties.
The Health Resources and Services Administration, a federal agency that addresses medical workforce shortages, estimates that there will be 6,230 geriatricians by 2025, or approximately 1 for every 3,000 older adults requiring geriatric care. HRSA projects a shortage of 27,000 geriatricians by 2025.
The specialty has faced an uphill battle to attract fellows. This year, only 43% of the nation’s 177 geriatrics fellowship slots were filled, according to November’s National Resident Match Program report. Family medicine–based geriatrics achieved only a 32% fill rate, while internal medicine–based programs saw a rate of 45%.
“Our numbers are shrinking so we need another approach to make sure older adults get the care they need and deserve,” said G. Michael Harper, MD, president of the 6,000-member AGS.
But Dr. Harper, who practices at the University of California, San Francisco, and the San Francisco VA Medical Center, added a positive note: “We may be struggling to increase the number of board-certified geriatricians, but the field itself has made a lot of progress in terms of improving clinical care through advancements in science and in the ways we deliver care.”
Dr. Harper cited the Hospital Elder Life Program, a hospital model developed at the Harvard-affiliated Marcus Institute for Aging Research, which uses an interprofessional team and trained volunteers to prevent delirium and functional decline. HELP has been adopted by more than 200 hospitals worldwide and has been successful at returning older adults to their homes or previous living situations with maintained or improved ability to function, he said.
Mark Supiano, MD, professor and chief of geriatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said the specialty has been in shortage mode since ABMS recognized it in 1988. He was in the initial cohort of fellowship-trained geriatricians, sitting for the first certifying exam in geriatrics offered that year.
“Back then, the demographic imperative of the aging of our society was on the horizon. We’re living it now. I knew enough to recognize it was coming and saw an opportunity,” Dr. Supiano said in an interview. “There was so much then that we didn’t know about how to understand aging or how to care for older adults that there really was such a knowledge gap.”
Dr. Supiano is an associate editor of Hazzard’s Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology (McGraw-Hill Education), which has more than doubled in pages and word count during his career.
Unfavorable finances
Katherine Thompson, MD, director of the geriatrics fellowship program at the University of Chicago and codirector of UChicago’s Successful Aging and Frailty Evaluation Clinic, said money is a major reason for the struggle. “I think probably the biggest driver is financial,” she said. “A lot of people are graduating medical school with really astronomical amounts of medical school loans.”
Geriatricians, like other doctors, carry a large debt – $200,000, on average, not counting undergraduate debt, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
But the typical geriatrician earns less than an internist or family medicine doctor who doesn’t undergo the additional year of training, Dr. Thompson said. “There’s not a lot of financial motivation to do this fellowship,” she said.
The jobs website Zippia reports that geriatricians earned roughly $165,000 per year on average in 2022. The average annual incomes in 2022 were $191,000 for pediatricians, $215,000 for family physicians, and $223,000 for internists, according to the site.
In other words, Dr. Harper said, “geriatrics is one of the few professions where you can actually do additional training and make less money.”
The reason for the pay issue is simple: Geriatricians treat patients covered by Medicare, whose reimbursement schedules lag behind those of commercial insurers. The Kaiser Family Foundation reported in 2020 that private insurance paid 143% of Medicare rates on average for physician services.
Dr. Harper said overall compensation for geriatricians has “not gained a lot of traction,” but they can earn comfortable livings.
Still, representation of the specialty on the American Medical Association’s Relative Value Scale Update Committee has led to approval by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services of billing codes that pay geriatricians “for what they do. Examples include chronic care management, advance care planning, and dementia evaluation,” he said.
But the geriatrician gap goes beyond money.
Ageism, too, may play a role in residents not choosing geriatrics.
“Our culture is ageist. It definitely focuses on youth and looks at aging as being loss rather than just a change in what works well and what doesn’t work well,” said Mary Tinetti, MD, a geriatrician and researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “Ageism happens among physicians, just because they’re part of the broader society.”
Time for a new goal?
Dr. Tinetti said she’s optimistic that new ideas about geriatricians teaching other primary care clinicians about the tenets of geriatric medicine, which offer a wholistic approach to comorbidities, such as diabetes, atrial fibrillation, dementia, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and polypharmacy problems faced by this population, especially those 85 and older.
She has called on her profession to abandon the goal of increasing the numbers of board-certified geriatricians – whom she refers to as big “G” geriatricians. She instead wants to develop a “small, elite workforce” that discovers and tests geriatrics principles through research, teaches these principles to all healthcare professions and to the public, and disseminates and implements the policies.
“We need a cadre of geriatricians who train all other clinicians in the care of older adults,” Dr. Tinetti said. “The goal is not more geriatricians but rather the preparation of all clinicians in the care of older adults.”
Dr. Thompson said geriatricians are teaching primary care specialists, nurses, social workers, and other health care providers the principles of age-friendly care. AGS has for the past 20 years led a program called the Geriatrics for Specialists Initiative to increase geriatrics knowledge and expertise of surgical and medical specialists.
Some specialties have taken the cue and have added geriatrics-related hyphens through additional training: geriatric-emergency, geriatric-general surgery, geriatric-hospitalists, and more.
HRSA runs programs to encourage physicians to train as geriatricians and geriatrics faculty, and it encourages the geriatrics interdisciplinary team approach.
Richard Olague, director of public affairs for HRSA, said his agency has invested over $160 million over the past 4 years in the education and training of geriatricians and other health care professionals who care for the elderly through its Geriatrics Workforce Enhancement Program and Geriatrics Academic Career Awards Program. In the academic year 2020-2021, the two programs trained 109 geriatricians; 456 other geriatric/gerontology providers and students; 44,450 other healthcare workforce professionals and students; and served 17,666 patients and 5,409 caregivers.
Dr. Harper, like his fellow geriatricians, tells young doctors that geriatrics is a fulfilling specialty.
“I get to care for the whole person and sometimes their families, too, and in the process form rich and meaningful relationships. And while I’m rarely in the position to cure, I always have the ability to care,” he said. “Sometimes that can mean being an advocate trying to make sure my patients receive the care they need, and other times it might mean protecting them from burdensome care that is unlikely to lead to any meaningful benefit. There is great reward in all of that.”
Dr. Supiano said geriatric patients are being helped by the Age-Friendly Health System initiative of the John A. Hartford Foundation and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement in partnership with the American Hospital Association and the Catholic Health Association of the United States. This is sort of a seal of approval for facilities committed to age-friendly care.
“When you go to your hospital, if they don’t have this age-friendly health system banner on the front door ... you either ask why that is not there, or you vote with your feet and go to another health system that is age friendly,” he said. “Geriatricians are eternal optimists.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
These should be the best of times for geriatric medicine.
The baby boom has become a senior surge, bringing in a rapidly growing pool of aging patients for geriatricians to treat. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, more than 56 million adults aged 65 and older live in the United States. They account for about 17% of the nation’s population. That number is expected to hit 73 million by 2030 and 86 million by 2050.
The American Geriatrics Society estimates that 30% of older people require the attention of geriatricians. These clinicians excel in managing complex cases – patients with multiple comorbidities, such as coronary artery disease, dementia, and osteoporosis, who are taking a half dozen, and often more, medications.
. In the 2010s, geriatricians called for “25,000 [such specialists] by 2025.” As of 2021, 7123 certified geriatricians were practicing in the United States, according to the American Board of Medical Specialties.
The Health Resources and Services Administration, a federal agency that addresses medical workforce shortages, estimates that there will be 6,230 geriatricians by 2025, or approximately 1 for every 3,000 older adults requiring geriatric care. HRSA projects a shortage of 27,000 geriatricians by 2025.
The specialty has faced an uphill battle to attract fellows. This year, only 43% of the nation’s 177 geriatrics fellowship slots were filled, according to November’s National Resident Match Program report. Family medicine–based geriatrics achieved only a 32% fill rate, while internal medicine–based programs saw a rate of 45%.
“Our numbers are shrinking so we need another approach to make sure older adults get the care they need and deserve,” said G. Michael Harper, MD, president of the 6,000-member AGS.
But Dr. Harper, who practices at the University of California, San Francisco, and the San Francisco VA Medical Center, added a positive note: “We may be struggling to increase the number of board-certified geriatricians, but the field itself has made a lot of progress in terms of improving clinical care through advancements in science and in the ways we deliver care.”
Dr. Harper cited the Hospital Elder Life Program, a hospital model developed at the Harvard-affiliated Marcus Institute for Aging Research, which uses an interprofessional team and trained volunteers to prevent delirium and functional decline. HELP has been adopted by more than 200 hospitals worldwide and has been successful at returning older adults to their homes or previous living situations with maintained or improved ability to function, he said.
Mark Supiano, MD, professor and chief of geriatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said the specialty has been in shortage mode since ABMS recognized it in 1988. He was in the initial cohort of fellowship-trained geriatricians, sitting for the first certifying exam in geriatrics offered that year.
“Back then, the demographic imperative of the aging of our society was on the horizon. We’re living it now. I knew enough to recognize it was coming and saw an opportunity,” Dr. Supiano said in an interview. “There was so much then that we didn’t know about how to understand aging or how to care for older adults that there really was such a knowledge gap.”
Dr. Supiano is an associate editor of Hazzard’s Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology (McGraw-Hill Education), which has more than doubled in pages and word count during his career.
Unfavorable finances
Katherine Thompson, MD, director of the geriatrics fellowship program at the University of Chicago and codirector of UChicago’s Successful Aging and Frailty Evaluation Clinic, said money is a major reason for the struggle. “I think probably the biggest driver is financial,” she said. “A lot of people are graduating medical school with really astronomical amounts of medical school loans.”
Geriatricians, like other doctors, carry a large debt – $200,000, on average, not counting undergraduate debt, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
But the typical geriatrician earns less than an internist or family medicine doctor who doesn’t undergo the additional year of training, Dr. Thompson said. “There’s not a lot of financial motivation to do this fellowship,” she said.
The jobs website Zippia reports that geriatricians earned roughly $165,000 per year on average in 2022. The average annual incomes in 2022 were $191,000 for pediatricians, $215,000 for family physicians, and $223,000 for internists, according to the site.
In other words, Dr. Harper said, “geriatrics is one of the few professions where you can actually do additional training and make less money.”
The reason for the pay issue is simple: Geriatricians treat patients covered by Medicare, whose reimbursement schedules lag behind those of commercial insurers. The Kaiser Family Foundation reported in 2020 that private insurance paid 143% of Medicare rates on average for physician services.
Dr. Harper said overall compensation for geriatricians has “not gained a lot of traction,” but they can earn comfortable livings.
Still, representation of the specialty on the American Medical Association’s Relative Value Scale Update Committee has led to approval by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services of billing codes that pay geriatricians “for what they do. Examples include chronic care management, advance care planning, and dementia evaluation,” he said.
But the geriatrician gap goes beyond money.
Ageism, too, may play a role in residents not choosing geriatrics.
“Our culture is ageist. It definitely focuses on youth and looks at aging as being loss rather than just a change in what works well and what doesn’t work well,” said Mary Tinetti, MD, a geriatrician and researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “Ageism happens among physicians, just because they’re part of the broader society.”
Time for a new goal?
Dr. Tinetti said she’s optimistic that new ideas about geriatricians teaching other primary care clinicians about the tenets of geriatric medicine, which offer a wholistic approach to comorbidities, such as diabetes, atrial fibrillation, dementia, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and polypharmacy problems faced by this population, especially those 85 and older.
She has called on her profession to abandon the goal of increasing the numbers of board-certified geriatricians – whom she refers to as big “G” geriatricians. She instead wants to develop a “small, elite workforce” that discovers and tests geriatrics principles through research, teaches these principles to all healthcare professions and to the public, and disseminates and implements the policies.
“We need a cadre of geriatricians who train all other clinicians in the care of older adults,” Dr. Tinetti said. “The goal is not more geriatricians but rather the preparation of all clinicians in the care of older adults.”
Dr. Thompson said geriatricians are teaching primary care specialists, nurses, social workers, and other health care providers the principles of age-friendly care. AGS has for the past 20 years led a program called the Geriatrics for Specialists Initiative to increase geriatrics knowledge and expertise of surgical and medical specialists.
Some specialties have taken the cue and have added geriatrics-related hyphens through additional training: geriatric-emergency, geriatric-general surgery, geriatric-hospitalists, and more.
HRSA runs programs to encourage physicians to train as geriatricians and geriatrics faculty, and it encourages the geriatrics interdisciplinary team approach.
Richard Olague, director of public affairs for HRSA, said his agency has invested over $160 million over the past 4 years in the education and training of geriatricians and other health care professionals who care for the elderly through its Geriatrics Workforce Enhancement Program and Geriatrics Academic Career Awards Program. In the academic year 2020-2021, the two programs trained 109 geriatricians; 456 other geriatric/gerontology providers and students; 44,450 other healthcare workforce professionals and students; and served 17,666 patients and 5,409 caregivers.
Dr. Harper, like his fellow geriatricians, tells young doctors that geriatrics is a fulfilling specialty.
“I get to care for the whole person and sometimes their families, too, and in the process form rich and meaningful relationships. And while I’m rarely in the position to cure, I always have the ability to care,” he said. “Sometimes that can mean being an advocate trying to make sure my patients receive the care they need, and other times it might mean protecting them from burdensome care that is unlikely to lead to any meaningful benefit. There is great reward in all of that.”
Dr. Supiano said geriatric patients are being helped by the Age-Friendly Health System initiative of the John A. Hartford Foundation and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement in partnership with the American Hospital Association and the Catholic Health Association of the United States. This is sort of a seal of approval for facilities committed to age-friendly care.
“When you go to your hospital, if they don’t have this age-friendly health system banner on the front door ... you either ask why that is not there, or you vote with your feet and go to another health system that is age friendly,” he said. “Geriatricians are eternal optimists.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
These should be the best of times for geriatric medicine.
The baby boom has become a senior surge, bringing in a rapidly growing pool of aging patients for geriatricians to treat. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, more than 56 million adults aged 65 and older live in the United States. They account for about 17% of the nation’s population. That number is expected to hit 73 million by 2030 and 86 million by 2050.
The American Geriatrics Society estimates that 30% of older people require the attention of geriatricians. These clinicians excel in managing complex cases – patients with multiple comorbidities, such as coronary artery disease, dementia, and osteoporosis, who are taking a half dozen, and often more, medications.
. In the 2010s, geriatricians called for “25,000 [such specialists] by 2025.” As of 2021, 7123 certified geriatricians were practicing in the United States, according to the American Board of Medical Specialties.
The Health Resources and Services Administration, a federal agency that addresses medical workforce shortages, estimates that there will be 6,230 geriatricians by 2025, or approximately 1 for every 3,000 older adults requiring geriatric care. HRSA projects a shortage of 27,000 geriatricians by 2025.
The specialty has faced an uphill battle to attract fellows. This year, only 43% of the nation’s 177 geriatrics fellowship slots were filled, according to November’s National Resident Match Program report. Family medicine–based geriatrics achieved only a 32% fill rate, while internal medicine–based programs saw a rate of 45%.
“Our numbers are shrinking so we need another approach to make sure older adults get the care they need and deserve,” said G. Michael Harper, MD, president of the 6,000-member AGS.
But Dr. Harper, who practices at the University of California, San Francisco, and the San Francisco VA Medical Center, added a positive note: “We may be struggling to increase the number of board-certified geriatricians, but the field itself has made a lot of progress in terms of improving clinical care through advancements in science and in the ways we deliver care.”
Dr. Harper cited the Hospital Elder Life Program, a hospital model developed at the Harvard-affiliated Marcus Institute for Aging Research, which uses an interprofessional team and trained volunteers to prevent delirium and functional decline. HELP has been adopted by more than 200 hospitals worldwide and has been successful at returning older adults to their homes or previous living situations with maintained or improved ability to function, he said.
Mark Supiano, MD, professor and chief of geriatrics at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said the specialty has been in shortage mode since ABMS recognized it in 1988. He was in the initial cohort of fellowship-trained geriatricians, sitting for the first certifying exam in geriatrics offered that year.
“Back then, the demographic imperative of the aging of our society was on the horizon. We’re living it now. I knew enough to recognize it was coming and saw an opportunity,” Dr. Supiano said in an interview. “There was so much then that we didn’t know about how to understand aging or how to care for older adults that there really was such a knowledge gap.”
Dr. Supiano is an associate editor of Hazzard’s Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology (McGraw-Hill Education), which has more than doubled in pages and word count during his career.
Unfavorable finances
Katherine Thompson, MD, director of the geriatrics fellowship program at the University of Chicago and codirector of UChicago’s Successful Aging and Frailty Evaluation Clinic, said money is a major reason for the struggle. “I think probably the biggest driver is financial,” she said. “A lot of people are graduating medical school with really astronomical amounts of medical school loans.”
Geriatricians, like other doctors, carry a large debt – $200,000, on average, not counting undergraduate debt, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
But the typical geriatrician earns less than an internist or family medicine doctor who doesn’t undergo the additional year of training, Dr. Thompson said. “There’s not a lot of financial motivation to do this fellowship,” she said.
The jobs website Zippia reports that geriatricians earned roughly $165,000 per year on average in 2022. The average annual incomes in 2022 were $191,000 for pediatricians, $215,000 for family physicians, and $223,000 for internists, according to the site.
In other words, Dr. Harper said, “geriatrics is one of the few professions where you can actually do additional training and make less money.”
The reason for the pay issue is simple: Geriatricians treat patients covered by Medicare, whose reimbursement schedules lag behind those of commercial insurers. The Kaiser Family Foundation reported in 2020 that private insurance paid 143% of Medicare rates on average for physician services.
Dr. Harper said overall compensation for geriatricians has “not gained a lot of traction,” but they can earn comfortable livings.
Still, representation of the specialty on the American Medical Association’s Relative Value Scale Update Committee has led to approval by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services of billing codes that pay geriatricians “for what they do. Examples include chronic care management, advance care planning, and dementia evaluation,” he said.
But the geriatrician gap goes beyond money.
Ageism, too, may play a role in residents not choosing geriatrics.
“Our culture is ageist. It definitely focuses on youth and looks at aging as being loss rather than just a change in what works well and what doesn’t work well,” said Mary Tinetti, MD, a geriatrician and researcher at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. “Ageism happens among physicians, just because they’re part of the broader society.”
Time for a new goal?
Dr. Tinetti said she’s optimistic that new ideas about geriatricians teaching other primary care clinicians about the tenets of geriatric medicine, which offer a wholistic approach to comorbidities, such as diabetes, atrial fibrillation, dementia, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and polypharmacy problems faced by this population, especially those 85 and older.
She has called on her profession to abandon the goal of increasing the numbers of board-certified geriatricians – whom she refers to as big “G” geriatricians. She instead wants to develop a “small, elite workforce” that discovers and tests geriatrics principles through research, teaches these principles to all healthcare professions and to the public, and disseminates and implements the policies.
“We need a cadre of geriatricians who train all other clinicians in the care of older adults,” Dr. Tinetti said. “The goal is not more geriatricians but rather the preparation of all clinicians in the care of older adults.”
Dr. Thompson said geriatricians are teaching primary care specialists, nurses, social workers, and other health care providers the principles of age-friendly care. AGS has for the past 20 years led a program called the Geriatrics for Specialists Initiative to increase geriatrics knowledge and expertise of surgical and medical specialists.
Some specialties have taken the cue and have added geriatrics-related hyphens through additional training: geriatric-emergency, geriatric-general surgery, geriatric-hospitalists, and more.
HRSA runs programs to encourage physicians to train as geriatricians and geriatrics faculty, and it encourages the geriatrics interdisciplinary team approach.
Richard Olague, director of public affairs for HRSA, said his agency has invested over $160 million over the past 4 years in the education and training of geriatricians and other health care professionals who care for the elderly through its Geriatrics Workforce Enhancement Program and Geriatrics Academic Career Awards Program. In the academic year 2020-2021, the two programs trained 109 geriatricians; 456 other geriatric/gerontology providers and students; 44,450 other healthcare workforce professionals and students; and served 17,666 patients and 5,409 caregivers.
Dr. Harper, like his fellow geriatricians, tells young doctors that geriatrics is a fulfilling specialty.
“I get to care for the whole person and sometimes their families, too, and in the process form rich and meaningful relationships. And while I’m rarely in the position to cure, I always have the ability to care,” he said. “Sometimes that can mean being an advocate trying to make sure my patients receive the care they need, and other times it might mean protecting them from burdensome care that is unlikely to lead to any meaningful benefit. There is great reward in all of that.”
Dr. Supiano said geriatric patients are being helped by the Age-Friendly Health System initiative of the John A. Hartford Foundation and the Institute for Healthcare Improvement in partnership with the American Hospital Association and the Catholic Health Association of the United States. This is sort of a seal of approval for facilities committed to age-friendly care.
“When you go to your hospital, if they don’t have this age-friendly health system banner on the front door ... you either ask why that is not there, or you vote with your feet and go to another health system that is age friendly,” he said. “Geriatricians are eternal optimists.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Advanced practice providers – an evolving role in pulmonary medicine
The integration of advanced practice providers (APPs) into pulmonology practice is in flux and deepening across numerous settings, from outpatient clinics to intensive care and inpatient pulmonary consult services – and as it evolves, so are issues of training.
Some institutions are developing pulmonary fellowship programs for APPs. This is a good indication that team-based pulmonology may be moving toward a time in the future when nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) join pulmonologists in practice after having undergone formal education in the subspecialty, rather than learning solely on the job from dedicated mentors.
Neither NPs nor PAs, who comprise almost all of the APP workforce in pulmonology, currently have a pulmonary tract for training. “Weight falls on the employer’s shoulders to train and educate their APPs,” said Corinne R. Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of APP and clinical services at Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants and founder and president of the Association of Pulmonary Advanced Practice Providers, which launched in 2018.
The role that an APP plays and their scope of practice is determined not only by state policies and regulations – and by their prior experience, knowledge and motivation – but by “how much work a practice puts into [education and training],” she said.
An estimated 3,000-8,000 APPs are working in pulmonology, according to an analysis done by a marketing agency that has worked for the American College of Chest Physicians, Ms. Young said.
A 2021 APAPP survey of its several hundred members at the time showed them working in hospital systems (41%), private practice (28%), university systems (10%), and other health care systems (21%). They indicated practicing in pulmonary medicine, sleep medicine, or critical care – or some combination of these areas – and the vast majority (82%) indicated they were seeing both new and established patients in their roles.
“Nobody knows exactly how many of us are out there,” Ms. Young said. “But CHEST and APAPP are making great efforts to be beacons to APPs working in this realm and to bring them together to have a voice.”
The APAPP also wants to “close the education gap” and to “eventually develop a certification program to vet our knowledge in this area,” she said. “Right now, the closest we can get to vetting our knowledge is to become an FCCP through CHEST.”
Earning trust, seeking training
Omar Hussain, DO, has been practicing with an NP for over a decade in his role as an intensivist and knows what it’s like to train, supervise, and grow together. He and his private practice colleagues have a contract with Advocate Condell Hospital in Libertyville, Ill., to cover its ICU, and they hired their NP primarily to help care for shorter-stay, non–critically ill patients in the ICU (for example, patients receiving postoperative monitoring).
The NP has been invaluable. “We literally sit next to each other and in the mornings we make a game plan of which patients she will tackle first and which ones I’ll see first,” Dr. Hussain said. “When we’re called by the nurse for an ICU evaluation [on the floor], we’ll decide in real time who goes.”
The NP ensures that all guidelines and quality measures are followed in the ICU and, with a Monday-Friday schedule, she provides valuable continuity when there are handoffs from one intensivist to another, said Dr. Hussain, who serves as cochair of the joint CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee, which deals with issues of physician-APP collaboration.
After working collaboratively for some time, Dr. Hussain and his partners decided to teach the NP how to intubate. It was a thoughtful and deliberate process, and “we used the same kind of mindset we’d used when we’ve supervised residents at other institutions,” he said.
Dr. Hussain and his partners have been fortunate in having such a long-term relationship with an APP. Their NP had worked as a nurse in the ICU before training as an adult gerontology–acute care NP and joining Dr. Hussain’s practice, so she was also “well known to us,” he added.
Rachel Adney, CPNP-PC, a certified pediatric NP in the division of pediatric pulmonology at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health, is an APP who actively sought advanced training. She joined Stanford in 2011 to provide ambulatory care, primarily, and having years of prior experience in asthma management and education, she fast became known as “the asthma person.”
After a physician colleague one day objected to her caring for a patient without asthma, Ms. Adney, the first APP in the division, approached John D. Mark, MD, program director of the pediatric fellowship program at Stanford, and inquired about training “so I could have more breadth and depth across the whole pulmonary milieu.”
Together they designed a “mini pediatric pulmonary fellowship” for Ms. Adney, incorporating elements of the first year of Stanford’s pediatric fellowship program as well as training materials from the University of Arizona’s Pediatric Pulmonary Center, Tucson, one of six federally funded PCCs that train various health care providers to care for pediatric patients with chronic pulmonary conditions. (Dr. Mark had previously been an educator at the center while serving on the University of Arizona faculty.)
Her curriculum consisted of 1,000 total hours of training, including 125 hours of didactic learning and 400 hours of both inpatient and outpatient clinical training in areas such as cystic fibrosis, sleep medicine, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), neuromuscular disorders, and general pulmonary medicine. “Rachel rotated through clinics, first as an observer, then as a trainee ... and she attended lectures that my fellows attended,” said Dr. Mark, who has long been a preceptor for APPs. “She became like a 1-year fellow in my division.”
Today, Ms. Adney sees patients independently in four outreach clinics along California’s central coast. “She sees very complicated pediatric pulmonary patients now” overall, and has become integral to Stanford’s interdisciplinary CRIB program (cardiac and respiratory care for infants with BPD), Dr. Mark said. “She follows these patients at Stanford along with the whole CRIB group, then sees them on her own for follow-up.”
As a result of her training, Ms. Adney said, “knowing that I have the knowledge and experience to take on more complex patients, my colleagues now trust me and are confident in my skills. They feel comfortable sending [patients] to me much earlier. ... And they know that if there’s something I need help with I will go to them instantly.”
Pulmonology “really spoke to my heart,” she said, recalling her pre-Stanford journey as an in-hospital medical-surgical nurse, and then, after her NP training, as a outpatient primary care PNP. “For the most part, it’s like putting a puzzle together, and being able to really impact the quality of life these patients have,” said Ms. Adney, who serves on the APAPP’s pediatric subcommittee.
It’s clear, Dr. Mark said, that “things are changing around the country” with increasing institutional interest in developing formal APP specialty training programs. “There’s no way [for an APP] to walk into a specialty and play an active role without additional training,” and institutions are frustrated with turnover and the loss of APPs who decide after 6-9 months of on-the-job training that they’re not interested in the field.
Stanford Medicine Children’s Health, in fact, has launched an internal Pediatric APP Fellowship Program that is training its first cohort of six newly graduated NPs and PAs in two clinical tracks, including a medical/surgical track that incorporates rotations in pulmonary medicine, said Raji Koppolu, CPNP-PC/AC, manager of advanced practice professional development for Stanford Medicine Children’s Health.
APP fellowship programs have been in existence since 2007 in a variety of clinical settings, she said, but more institutions are developing them as a way of recruiting and retaining APPs in areas of high need and of equipping them for successful transitions to their APP roles. Various national bodies accredit APP fellowship programs.
Most pulmonary fellowship programs, Ms. Young said, are also internal programs providing postgraduate education to their own newly hired APPs or recent NP/PA graduates. This limits their reach, but “it’s a step in the right direction toward standardizing education for pulmonary APPs.”
Defining APP competencies
In interventional pulmonology, training may soon be guided by newly defined “core clinical competencies” for APPs. The soon-to-be published and distributed competencies – the first such national APP competencies in pulmonology – were developed by an APP Leadership Council within the American Association of Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology and cover the most common disease processes and practices in IP, from COPD and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction to pleural effusion and lung cancer screening.
Rebecca Priebe, ACNP-BC, who cochairs the AABIP’s APP chapter, organized the effort several years ago, bringing together a group of APPs and physician experts in advanced bronchoscopy and IP (some but not all of whom have worked with APPs), after fielding questions from pulmonologists at AABIP meetings about what to look for in an AAP and how to train them.
Physicians and institutions who are hiring and training APPs for IP can use any or all of the 11 core competencies to personalize and evaluate the training process for each APP’s needs, she said. “Someone looking to hire an APP for pleural disease, for instance, can pull up the content on plural effusion.”
APP interest in interventional pulmonology is growing rapidly, Ms. Priebe said, noting growth in the AABIP’s APP chapter from about 7-8 APPs 5 years ago to at least 60 currently.
Ms. Priebe was hired by Henry Ford Health in Detroit about 5 years ago to help establish and run an inpatient IP consult service, and more recently, she helped establish their inpatient pleural disease service and a bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program.
For the inpatient IP service, after several months of side-by-side training with an IP fellow and attending physicians, she began independently evaluating new patients, writing notes, and making recommendations.
For patients with pleural disease, she performs ultrasound examinations, chest tube insertions, and bedside thoracentesis independently. And for the bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program, she evaluates patients for candidate status, participates in valve placement, and sees patients independently through a year of follow-up.
“Physician colleagues often aren’t sure what an APP’s education and scope of practice is,” said Ms. Priebe, who was an ICU nurse before training as an acute care NP and then worked first with a private practice inpatient service and then with the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, where she established and grew an APP-run program managing lung transplant patients and a step-down ICU unit.
“It’s a matter of knowing [your state’s policies], treating them like a fellow you would train, and then using them to the fullest extent of their education and training. If they’re given an opportunity to learn a subspecialty skill set, they can be an asset to any pulmonary program.”
‘We’re here to support,’ not replace
In her own practice, Ms. Young is one of seven APPs who work with nine physicians on a full range of inpatient care, outpatient care, critical care, sleep medicine, and procedures. Many new patients are seen first by the APP, who does the workup and orders tests, and by the physician on a follow-up visit. Most patients needing routine management of asthma and COPD are seen by the physician every third or fourth visit, she said.
Ms. Young also directs a 24-hour in-house APP service recently established by the practice, and she participates in research. In a practice across town, she noted, APPs see mainly established patients and do not practice as autonomously as the state permits. “Part of that difference may [stem from] the lack of a standard of education and variable amounts of work the practice puts into their APPs.”
The American Medical Association’s #StopScopeCreep social media messaging feels divisive and “sheds a negative light on APPs working in any area,” Ms. Young said. “One of the biggest things we want to convey [at APAPP] is that we’re not here for [physicians’] jobs.”
“We’re here to support those who are practicing, to support underserved populations, and to help bridge gaps” created by an aging pulmonologist workforce and real and projected physician shortages, Ms. Young said, referring to a 2016 report from the Health Resources and Services Administration and a 2017 report from Merritt Hawkins indicating that 73% of U.S. pulmonologists (the largest percentage of all subspecialties) were at least 55 years old.
Dr. Hussain said he has “seen scope creep” first-hand in his hospitals, in the form of noncollaborative practices and tasks performed by APPs without adequate training – most likely often stemming from poor decisions and oversight by physicians. But when constructed thoughtfully, APP-physician teams are “serving great needs” in many types of care, he said, from follow-up care and management of chronic conditions to inpatient rounding. “My [colleagues] are having great success,” he said.
He is watching with interest – and some concern – pending reimbursement changes from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services that will make time the only defining feature of the “substantive” portion of a split/shared visit involving physicians and APPs in a facility setting. Medical decision-making will no longer be applicable.
For time-based services like critical care, time alone is currently the metric. (And in the nonfacility setting, physician-APP teams may still apply “incident to” billing practices). But in the facility setting, said Amy M. Ahasic, MD, MPH, a pulmonologist in Norwalk, Conn., who coauthored a 2022 commentary on the issue, the change (now planned for 2024) could be problematic for employed physicians whose contracts are based on productivity, and could create tension and possibly lead to reduced use of APPs rather than supporting collaborative care.
“The team model has been evolving so well over the past 10-15 years,” said Dr. Ahasic, who serves on the CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Reimbursement Workgroup and cochairs the CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee with Dr. Hussain. “It’s good for patient safety to have more [providers] involved ... and because APP salaries are lower health systems could do it and be able to have better care and better coverage.”
The pulmonology culture, said Dr. Hussain, has been increasingly embracing APPs and “it’s collegial.” Pulmonologists are “coming to CHEST meetings with their APPs. They’re learning the same things we’re learning, to manage the same patients we manage.”
The article sources reported that they had no relevant financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
The integration of advanced practice providers (APPs) into pulmonology practice is in flux and deepening across numerous settings, from outpatient clinics to intensive care and inpatient pulmonary consult services – and as it evolves, so are issues of training.
Some institutions are developing pulmonary fellowship programs for APPs. This is a good indication that team-based pulmonology may be moving toward a time in the future when nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) join pulmonologists in practice after having undergone formal education in the subspecialty, rather than learning solely on the job from dedicated mentors.
Neither NPs nor PAs, who comprise almost all of the APP workforce in pulmonology, currently have a pulmonary tract for training. “Weight falls on the employer’s shoulders to train and educate their APPs,” said Corinne R. Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of APP and clinical services at Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants and founder and president of the Association of Pulmonary Advanced Practice Providers, which launched in 2018.
The role that an APP plays and their scope of practice is determined not only by state policies and regulations – and by their prior experience, knowledge and motivation – but by “how much work a practice puts into [education and training],” she said.
An estimated 3,000-8,000 APPs are working in pulmonology, according to an analysis done by a marketing agency that has worked for the American College of Chest Physicians, Ms. Young said.
A 2021 APAPP survey of its several hundred members at the time showed them working in hospital systems (41%), private practice (28%), university systems (10%), and other health care systems (21%). They indicated practicing in pulmonary medicine, sleep medicine, or critical care – or some combination of these areas – and the vast majority (82%) indicated they were seeing both new and established patients in their roles.
“Nobody knows exactly how many of us are out there,” Ms. Young said. “But CHEST and APAPP are making great efforts to be beacons to APPs working in this realm and to bring them together to have a voice.”
The APAPP also wants to “close the education gap” and to “eventually develop a certification program to vet our knowledge in this area,” she said. “Right now, the closest we can get to vetting our knowledge is to become an FCCP through CHEST.”
Earning trust, seeking training
Omar Hussain, DO, has been practicing with an NP for over a decade in his role as an intensivist and knows what it’s like to train, supervise, and grow together. He and his private practice colleagues have a contract with Advocate Condell Hospital in Libertyville, Ill., to cover its ICU, and they hired their NP primarily to help care for shorter-stay, non–critically ill patients in the ICU (for example, patients receiving postoperative monitoring).
The NP has been invaluable. “We literally sit next to each other and in the mornings we make a game plan of which patients she will tackle first and which ones I’ll see first,” Dr. Hussain said. “When we’re called by the nurse for an ICU evaluation [on the floor], we’ll decide in real time who goes.”
The NP ensures that all guidelines and quality measures are followed in the ICU and, with a Monday-Friday schedule, she provides valuable continuity when there are handoffs from one intensivist to another, said Dr. Hussain, who serves as cochair of the joint CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee, which deals with issues of physician-APP collaboration.
After working collaboratively for some time, Dr. Hussain and his partners decided to teach the NP how to intubate. It was a thoughtful and deliberate process, and “we used the same kind of mindset we’d used when we’ve supervised residents at other institutions,” he said.
Dr. Hussain and his partners have been fortunate in having such a long-term relationship with an APP. Their NP had worked as a nurse in the ICU before training as an adult gerontology–acute care NP and joining Dr. Hussain’s practice, so she was also “well known to us,” he added.
Rachel Adney, CPNP-PC, a certified pediatric NP in the division of pediatric pulmonology at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health, is an APP who actively sought advanced training. She joined Stanford in 2011 to provide ambulatory care, primarily, and having years of prior experience in asthma management and education, she fast became known as “the asthma person.”
After a physician colleague one day objected to her caring for a patient without asthma, Ms. Adney, the first APP in the division, approached John D. Mark, MD, program director of the pediatric fellowship program at Stanford, and inquired about training “so I could have more breadth and depth across the whole pulmonary milieu.”
Together they designed a “mini pediatric pulmonary fellowship” for Ms. Adney, incorporating elements of the first year of Stanford’s pediatric fellowship program as well as training materials from the University of Arizona’s Pediatric Pulmonary Center, Tucson, one of six federally funded PCCs that train various health care providers to care for pediatric patients with chronic pulmonary conditions. (Dr. Mark had previously been an educator at the center while serving on the University of Arizona faculty.)
Her curriculum consisted of 1,000 total hours of training, including 125 hours of didactic learning and 400 hours of both inpatient and outpatient clinical training in areas such as cystic fibrosis, sleep medicine, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), neuromuscular disorders, and general pulmonary medicine. “Rachel rotated through clinics, first as an observer, then as a trainee ... and she attended lectures that my fellows attended,” said Dr. Mark, who has long been a preceptor for APPs. “She became like a 1-year fellow in my division.”
Today, Ms. Adney sees patients independently in four outreach clinics along California’s central coast. “She sees very complicated pediatric pulmonary patients now” overall, and has become integral to Stanford’s interdisciplinary CRIB program (cardiac and respiratory care for infants with BPD), Dr. Mark said. “She follows these patients at Stanford along with the whole CRIB group, then sees them on her own for follow-up.”
As a result of her training, Ms. Adney said, “knowing that I have the knowledge and experience to take on more complex patients, my colleagues now trust me and are confident in my skills. They feel comfortable sending [patients] to me much earlier. ... And they know that if there’s something I need help with I will go to them instantly.”
Pulmonology “really spoke to my heart,” she said, recalling her pre-Stanford journey as an in-hospital medical-surgical nurse, and then, after her NP training, as a outpatient primary care PNP. “For the most part, it’s like putting a puzzle together, and being able to really impact the quality of life these patients have,” said Ms. Adney, who serves on the APAPP’s pediatric subcommittee.
It’s clear, Dr. Mark said, that “things are changing around the country” with increasing institutional interest in developing formal APP specialty training programs. “There’s no way [for an APP] to walk into a specialty and play an active role without additional training,” and institutions are frustrated with turnover and the loss of APPs who decide after 6-9 months of on-the-job training that they’re not interested in the field.
Stanford Medicine Children’s Health, in fact, has launched an internal Pediatric APP Fellowship Program that is training its first cohort of six newly graduated NPs and PAs in two clinical tracks, including a medical/surgical track that incorporates rotations in pulmonary medicine, said Raji Koppolu, CPNP-PC/AC, manager of advanced practice professional development for Stanford Medicine Children’s Health.
APP fellowship programs have been in existence since 2007 in a variety of clinical settings, she said, but more institutions are developing them as a way of recruiting and retaining APPs in areas of high need and of equipping them for successful transitions to their APP roles. Various national bodies accredit APP fellowship programs.
Most pulmonary fellowship programs, Ms. Young said, are also internal programs providing postgraduate education to their own newly hired APPs or recent NP/PA graduates. This limits their reach, but “it’s a step in the right direction toward standardizing education for pulmonary APPs.”
Defining APP competencies
In interventional pulmonology, training may soon be guided by newly defined “core clinical competencies” for APPs. The soon-to-be published and distributed competencies – the first such national APP competencies in pulmonology – were developed by an APP Leadership Council within the American Association of Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology and cover the most common disease processes and practices in IP, from COPD and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction to pleural effusion and lung cancer screening.
Rebecca Priebe, ACNP-BC, who cochairs the AABIP’s APP chapter, organized the effort several years ago, bringing together a group of APPs and physician experts in advanced bronchoscopy and IP (some but not all of whom have worked with APPs), after fielding questions from pulmonologists at AABIP meetings about what to look for in an AAP and how to train them.
Physicians and institutions who are hiring and training APPs for IP can use any or all of the 11 core competencies to personalize and evaluate the training process for each APP’s needs, she said. “Someone looking to hire an APP for pleural disease, for instance, can pull up the content on plural effusion.”
APP interest in interventional pulmonology is growing rapidly, Ms. Priebe said, noting growth in the AABIP’s APP chapter from about 7-8 APPs 5 years ago to at least 60 currently.
Ms. Priebe was hired by Henry Ford Health in Detroit about 5 years ago to help establish and run an inpatient IP consult service, and more recently, she helped establish their inpatient pleural disease service and a bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program.
For the inpatient IP service, after several months of side-by-side training with an IP fellow and attending physicians, she began independently evaluating new patients, writing notes, and making recommendations.
For patients with pleural disease, she performs ultrasound examinations, chest tube insertions, and bedside thoracentesis independently. And for the bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program, she evaluates patients for candidate status, participates in valve placement, and sees patients independently through a year of follow-up.
“Physician colleagues often aren’t sure what an APP’s education and scope of practice is,” said Ms. Priebe, who was an ICU nurse before training as an acute care NP and then worked first with a private practice inpatient service and then with the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, where she established and grew an APP-run program managing lung transplant patients and a step-down ICU unit.
“It’s a matter of knowing [your state’s policies], treating them like a fellow you would train, and then using them to the fullest extent of their education and training. If they’re given an opportunity to learn a subspecialty skill set, they can be an asset to any pulmonary program.”
‘We’re here to support,’ not replace
In her own practice, Ms. Young is one of seven APPs who work with nine physicians on a full range of inpatient care, outpatient care, critical care, sleep medicine, and procedures. Many new patients are seen first by the APP, who does the workup and orders tests, and by the physician on a follow-up visit. Most patients needing routine management of asthma and COPD are seen by the physician every third or fourth visit, she said.
Ms. Young also directs a 24-hour in-house APP service recently established by the practice, and she participates in research. In a practice across town, she noted, APPs see mainly established patients and do not practice as autonomously as the state permits. “Part of that difference may [stem from] the lack of a standard of education and variable amounts of work the practice puts into their APPs.”
The American Medical Association’s #StopScopeCreep social media messaging feels divisive and “sheds a negative light on APPs working in any area,” Ms. Young said. “One of the biggest things we want to convey [at APAPP] is that we’re not here for [physicians’] jobs.”
“We’re here to support those who are practicing, to support underserved populations, and to help bridge gaps” created by an aging pulmonologist workforce and real and projected physician shortages, Ms. Young said, referring to a 2016 report from the Health Resources and Services Administration and a 2017 report from Merritt Hawkins indicating that 73% of U.S. pulmonologists (the largest percentage of all subspecialties) were at least 55 years old.
Dr. Hussain said he has “seen scope creep” first-hand in his hospitals, in the form of noncollaborative practices and tasks performed by APPs without adequate training – most likely often stemming from poor decisions and oversight by physicians. But when constructed thoughtfully, APP-physician teams are “serving great needs” in many types of care, he said, from follow-up care and management of chronic conditions to inpatient rounding. “My [colleagues] are having great success,” he said.
He is watching with interest – and some concern – pending reimbursement changes from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services that will make time the only defining feature of the “substantive” portion of a split/shared visit involving physicians and APPs in a facility setting. Medical decision-making will no longer be applicable.
For time-based services like critical care, time alone is currently the metric. (And in the nonfacility setting, physician-APP teams may still apply “incident to” billing practices). But in the facility setting, said Amy M. Ahasic, MD, MPH, a pulmonologist in Norwalk, Conn., who coauthored a 2022 commentary on the issue, the change (now planned for 2024) could be problematic for employed physicians whose contracts are based on productivity, and could create tension and possibly lead to reduced use of APPs rather than supporting collaborative care.
“The team model has been evolving so well over the past 10-15 years,” said Dr. Ahasic, who serves on the CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Reimbursement Workgroup and cochairs the CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee with Dr. Hussain. “It’s good for patient safety to have more [providers] involved ... and because APP salaries are lower health systems could do it and be able to have better care and better coverage.”
The pulmonology culture, said Dr. Hussain, has been increasingly embracing APPs and “it’s collegial.” Pulmonologists are “coming to CHEST meetings with their APPs. They’re learning the same things we’re learning, to manage the same patients we manage.”
The article sources reported that they had no relevant financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
The integration of advanced practice providers (APPs) into pulmonology practice is in flux and deepening across numerous settings, from outpatient clinics to intensive care and inpatient pulmonary consult services – and as it evolves, so are issues of training.
Some institutions are developing pulmonary fellowship programs for APPs. This is a good indication that team-based pulmonology may be moving toward a time in the future when nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) join pulmonologists in practice after having undergone formal education in the subspecialty, rather than learning solely on the job from dedicated mentors.
Neither NPs nor PAs, who comprise almost all of the APP workforce in pulmonology, currently have a pulmonary tract for training. “Weight falls on the employer’s shoulders to train and educate their APPs,” said Corinne R. Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, director of APP and clinical services at Colorado Springs Pulmonary Consultants and founder and president of the Association of Pulmonary Advanced Practice Providers, which launched in 2018.
The role that an APP plays and their scope of practice is determined not only by state policies and regulations – and by their prior experience, knowledge and motivation – but by “how much work a practice puts into [education and training],” she said.
An estimated 3,000-8,000 APPs are working in pulmonology, according to an analysis done by a marketing agency that has worked for the American College of Chest Physicians, Ms. Young said.
A 2021 APAPP survey of its several hundred members at the time showed them working in hospital systems (41%), private practice (28%), university systems (10%), and other health care systems (21%). They indicated practicing in pulmonary medicine, sleep medicine, or critical care – or some combination of these areas – and the vast majority (82%) indicated they were seeing both new and established patients in their roles.
“Nobody knows exactly how many of us are out there,” Ms. Young said. “But CHEST and APAPP are making great efforts to be beacons to APPs working in this realm and to bring them together to have a voice.”
The APAPP also wants to “close the education gap” and to “eventually develop a certification program to vet our knowledge in this area,” she said. “Right now, the closest we can get to vetting our knowledge is to become an FCCP through CHEST.”
Earning trust, seeking training
Omar Hussain, DO, has been practicing with an NP for over a decade in his role as an intensivist and knows what it’s like to train, supervise, and grow together. He and his private practice colleagues have a contract with Advocate Condell Hospital in Libertyville, Ill., to cover its ICU, and they hired their NP primarily to help care for shorter-stay, non–critically ill patients in the ICU (for example, patients receiving postoperative monitoring).
The NP has been invaluable. “We literally sit next to each other and in the mornings we make a game plan of which patients she will tackle first and which ones I’ll see first,” Dr. Hussain said. “When we’re called by the nurse for an ICU evaluation [on the floor], we’ll decide in real time who goes.”
The NP ensures that all guidelines and quality measures are followed in the ICU and, with a Monday-Friday schedule, she provides valuable continuity when there are handoffs from one intensivist to another, said Dr. Hussain, who serves as cochair of the joint CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee, which deals with issues of physician-APP collaboration.
After working collaboratively for some time, Dr. Hussain and his partners decided to teach the NP how to intubate. It was a thoughtful and deliberate process, and “we used the same kind of mindset we’d used when we’ve supervised residents at other institutions,” he said.
Dr. Hussain and his partners have been fortunate in having such a long-term relationship with an APP. Their NP had worked as a nurse in the ICU before training as an adult gerontology–acute care NP and joining Dr. Hussain’s practice, so she was also “well known to us,” he added.
Rachel Adney, CPNP-PC, a certified pediatric NP in the division of pediatric pulmonology at Stanford (Calif.) Medicine Children’s Health, is an APP who actively sought advanced training. She joined Stanford in 2011 to provide ambulatory care, primarily, and having years of prior experience in asthma management and education, she fast became known as “the asthma person.”
After a physician colleague one day objected to her caring for a patient without asthma, Ms. Adney, the first APP in the division, approached John D. Mark, MD, program director of the pediatric fellowship program at Stanford, and inquired about training “so I could have more breadth and depth across the whole pulmonary milieu.”
Together they designed a “mini pediatric pulmonary fellowship” for Ms. Adney, incorporating elements of the first year of Stanford’s pediatric fellowship program as well as training materials from the University of Arizona’s Pediatric Pulmonary Center, Tucson, one of six federally funded PCCs that train various health care providers to care for pediatric patients with chronic pulmonary conditions. (Dr. Mark had previously been an educator at the center while serving on the University of Arizona faculty.)
Her curriculum consisted of 1,000 total hours of training, including 125 hours of didactic learning and 400 hours of both inpatient and outpatient clinical training in areas such as cystic fibrosis, sleep medicine, bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), neuromuscular disorders, and general pulmonary medicine. “Rachel rotated through clinics, first as an observer, then as a trainee ... and she attended lectures that my fellows attended,” said Dr. Mark, who has long been a preceptor for APPs. “She became like a 1-year fellow in my division.”
Today, Ms. Adney sees patients independently in four outreach clinics along California’s central coast. “She sees very complicated pediatric pulmonary patients now” overall, and has become integral to Stanford’s interdisciplinary CRIB program (cardiac and respiratory care for infants with BPD), Dr. Mark said. “She follows these patients at Stanford along with the whole CRIB group, then sees them on her own for follow-up.”
As a result of her training, Ms. Adney said, “knowing that I have the knowledge and experience to take on more complex patients, my colleagues now trust me and are confident in my skills. They feel comfortable sending [patients] to me much earlier. ... And they know that if there’s something I need help with I will go to them instantly.”
Pulmonology “really spoke to my heart,” she said, recalling her pre-Stanford journey as an in-hospital medical-surgical nurse, and then, after her NP training, as a outpatient primary care PNP. “For the most part, it’s like putting a puzzle together, and being able to really impact the quality of life these patients have,” said Ms. Adney, who serves on the APAPP’s pediatric subcommittee.
It’s clear, Dr. Mark said, that “things are changing around the country” with increasing institutional interest in developing formal APP specialty training programs. “There’s no way [for an APP] to walk into a specialty and play an active role without additional training,” and institutions are frustrated with turnover and the loss of APPs who decide after 6-9 months of on-the-job training that they’re not interested in the field.
Stanford Medicine Children’s Health, in fact, has launched an internal Pediatric APP Fellowship Program that is training its first cohort of six newly graduated NPs and PAs in two clinical tracks, including a medical/surgical track that incorporates rotations in pulmonary medicine, said Raji Koppolu, CPNP-PC/AC, manager of advanced practice professional development for Stanford Medicine Children’s Health.
APP fellowship programs have been in existence since 2007 in a variety of clinical settings, she said, but more institutions are developing them as a way of recruiting and retaining APPs in areas of high need and of equipping them for successful transitions to their APP roles. Various national bodies accredit APP fellowship programs.
Most pulmonary fellowship programs, Ms. Young said, are also internal programs providing postgraduate education to their own newly hired APPs or recent NP/PA graduates. This limits their reach, but “it’s a step in the right direction toward standardizing education for pulmonary APPs.”
Defining APP competencies
In interventional pulmonology, training may soon be guided by newly defined “core clinical competencies” for APPs. The soon-to-be published and distributed competencies – the first such national APP competencies in pulmonology – were developed by an APP Leadership Council within the American Association of Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology and cover the most common disease processes and practices in IP, from COPD and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction to pleural effusion and lung cancer screening.
Rebecca Priebe, ACNP-BC, who cochairs the AABIP’s APP chapter, organized the effort several years ago, bringing together a group of APPs and physician experts in advanced bronchoscopy and IP (some but not all of whom have worked with APPs), after fielding questions from pulmonologists at AABIP meetings about what to look for in an AAP and how to train them.
Physicians and institutions who are hiring and training APPs for IP can use any or all of the 11 core competencies to personalize and evaluate the training process for each APP’s needs, she said. “Someone looking to hire an APP for pleural disease, for instance, can pull up the content on plural effusion.”
APP interest in interventional pulmonology is growing rapidly, Ms. Priebe said, noting growth in the AABIP’s APP chapter from about 7-8 APPs 5 years ago to at least 60 currently.
Ms. Priebe was hired by Henry Ford Health in Detroit about 5 years ago to help establish and run an inpatient IP consult service, and more recently, she helped establish their inpatient pleural disease service and a bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program.
For the inpatient IP service, after several months of side-by-side training with an IP fellow and attending physicians, she began independently evaluating new patients, writing notes, and making recommendations.
For patients with pleural disease, she performs ultrasound examinations, chest tube insertions, and bedside thoracentesis independently. And for the bronchoscopic lung volume reduction program, she evaluates patients for candidate status, participates in valve placement, and sees patients independently through a year of follow-up.
“Physician colleagues often aren’t sure what an APP’s education and scope of practice is,” said Ms. Priebe, who was an ICU nurse before training as an acute care NP and then worked first with a private practice inpatient service and then with the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, where she established and grew an APP-run program managing lung transplant patients and a step-down ICU unit.
“It’s a matter of knowing [your state’s policies], treating them like a fellow you would train, and then using them to the fullest extent of their education and training. If they’re given an opportunity to learn a subspecialty skill set, they can be an asset to any pulmonary program.”
‘We’re here to support,’ not replace
In her own practice, Ms. Young is one of seven APPs who work with nine physicians on a full range of inpatient care, outpatient care, critical care, sleep medicine, and procedures. Many new patients are seen first by the APP, who does the workup and orders tests, and by the physician on a follow-up visit. Most patients needing routine management of asthma and COPD are seen by the physician every third or fourth visit, she said.
Ms. Young also directs a 24-hour in-house APP service recently established by the practice, and she participates in research. In a practice across town, she noted, APPs see mainly established patients and do not practice as autonomously as the state permits. “Part of that difference may [stem from] the lack of a standard of education and variable amounts of work the practice puts into their APPs.”
The American Medical Association’s #StopScopeCreep social media messaging feels divisive and “sheds a negative light on APPs working in any area,” Ms. Young said. “One of the biggest things we want to convey [at APAPP] is that we’re not here for [physicians’] jobs.”
“We’re here to support those who are practicing, to support underserved populations, and to help bridge gaps” created by an aging pulmonologist workforce and real and projected physician shortages, Ms. Young said, referring to a 2016 report from the Health Resources and Services Administration and a 2017 report from Merritt Hawkins indicating that 73% of U.S. pulmonologists (the largest percentage of all subspecialties) were at least 55 years old.
Dr. Hussain said he has “seen scope creep” first-hand in his hospitals, in the form of noncollaborative practices and tasks performed by APPs without adequate training – most likely often stemming from poor decisions and oversight by physicians. But when constructed thoughtfully, APP-physician teams are “serving great needs” in many types of care, he said, from follow-up care and management of chronic conditions to inpatient rounding. “My [colleagues] are having great success,” he said.
He is watching with interest – and some concern – pending reimbursement changes from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services that will make time the only defining feature of the “substantive” portion of a split/shared visit involving physicians and APPs in a facility setting. Medical decision-making will no longer be applicable.
For time-based services like critical care, time alone is currently the metric. (And in the nonfacility setting, physician-APP teams may still apply “incident to” billing practices). But in the facility setting, said Amy M. Ahasic, MD, MPH, a pulmonologist in Norwalk, Conn., who coauthored a 2022 commentary on the issue, the change (now planned for 2024) could be problematic for employed physicians whose contracts are based on productivity, and could create tension and possibly lead to reduced use of APPs rather than supporting collaborative care.
“The team model has been evolving so well over the past 10-15 years,” said Dr. Ahasic, who serves on the CHEST Health Policy and Advocacy Reimbursement Workgroup and cochairs the CHEST/American Thoracic Society clinical practice committee with Dr. Hussain. “It’s good for patient safety to have more [providers] involved ... and because APP salaries are lower health systems could do it and be able to have better care and better coverage.”
The pulmonology culture, said Dr. Hussain, has been increasingly embracing APPs and “it’s collegial.” Pulmonologists are “coming to CHEST meetings with their APPs. They’re learning the same things we’re learning, to manage the same patients we manage.”
The article sources reported that they had no relevant financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Everyone wins when losers get paid
Bribery really is the solution to all of life’s problems
Breaking news: The United States has a bit of an obesity epidemic. Okay, maybe not so breaking news. But it’s a problem we’ve been struggling with for a very long time. Part of the issue is that there really is no secret to weight loss. Pretty much anything can work if you’re committed. The millions of diets floating around are testament to this idea.
The problem of losing weight is amplified if you don’t rake in the big bucks. Lower-income individuals often can’t afford healthy superfoods, and they’re often too busy to spend time at classes, exercising, or following programs. A group of researchers at New York University has offered up an alternate solution to encourage weight loss in low-income people: Pay them.
Specifically, pay them for losing weight. A reward, if you will. The researchers recruited several hundred lower-income people and split them into three groups. All participants received a free 1-year membership to a gym and weight-loss program, as well as food journals and fitness devices, but one group received payment (on average, about $300 overall) for attending meetings, exercising a certain amount every week, or weighing themselves twice a week. About 40% of people in this group lost 5% of their body weight after 6 months, twice as many as in the group that did not receive payment for performing these tasks.
The big winners, however, were those in the third group. They also received the free stuff, but the researchers offered them a more simple and direct bribe: Lose 5% of your weight over 6 months and we’ll pay you. The reward? About $450 on average, and it worked very well, with half this group losing the weight after 6 months. That said, after a year something like a fifth of this group put the weight back on, bringing them in line with the group that was paid to perform tasks. Still, both groups outperformed the control group, which received no money.
The takeaway from this research is pretty obvious. Pay people a fair price to do something, and they’ll do it. This is a lesson that has absolutely no relevance in the modern world. Nope, none whatsoever. We all receive completely fair wages. We all have plenty of money to pay for things. Everything is fine.
More green space, less medicine
Have you heard of the 3-30-300 rule? Proposed by urban forester Cecil Konijnendijk, it’s become the rule of thumb for urban planners and other foresters into getting more green space in populated areas. A recent study has found that people who lived within this 3-30-300 rule had better mental health and less medication use.
If you’re not an urban forester, however, you may not know what the 3-30-300 rule is. But it’s pretty simple, people should be able to see at least three trees from their home, have 30% tree canopy in their neighborhood, and have 300 Spartans to defend against the Persian army.
We may have made that last one up. It’s actually have a green space or park within 300 meters of your home.
In the new study, only 4.7% of people surveyed lived in an area that followed all three rules. About 62% of the surveyed lived with a green space at least 300 meters away, 43% had at least three trees within 15 meters from their home, and a rather pitiful 9% had adequate tree canopy coverage in their neighborhood.
Greater adherence to the 3-30-300 rule was associated with fewer visits to the psychologist, with 8.3% of the participants reporting a psychologist visit in the last year. The data come from a sample of a little over 3,000 Barcelona residents aged 15-97 who were randomly selected to participate in the Barcelona Public Health Agency Survey.
“There is an urgent need to provide citizens with more green space,” said Mark Nieuwenhuijsen, lead author of the study. “We may need to tear out asphalt and plant more trees, which would not only improve health, but also reduce heat island effects and contribute to carbon capture.”
The main goal and message is that more green space is good for everyone. So if you’re feeling a little overwhelmed, take a breather and sit somewhere green. Or call those 300 Spartans and get them to start knocking some buildings down.
Said the toilet to the engineer: Do you hear what I hear?
A mythical hero’s journey took Dorothy along the yellow brick road to find the Wizard of Oz. Huckleberry Finn used a raft to float down the Mississippi River. Luke Skywalker did most of his traveling between planets. For the rest of us, the journey may be just a bit shorter.
Also a bit less heroic. Unless, of course, you’re prepping for a colonoscopy. Yup, we’re headed to the toilet, but not just any toilet. This toilet was the subject of a presentation at the annual meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, titled “The feces thesis: Using machine learning to detect diarrhea,” and that presentation was the hero’s journey of Maia Gatlin, PhD, a research engineer at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
She and her team attached a noninvasive microphone sensor to a toilet, and now they can identify bowel diseases without collecting any identifiable information.
The audio sample of an excretion event is “transformed into a spectrogram, which essentially captures the sound in an image. Different events produce different features in the audio and the spectrogram. For example, urination creates a consistent tone, while defecation may have a singular tone. In contrast, diarrhea is more random,” they explained in the written statement.
They used a machine learning algorithm to classify each spectrogram based on its features. “The algorithm’s performance was tested against data with and without background noises to make sure it was learning the right sound features, regardless of the sensor’s environment,” Dr. Gatlin and associates wrote.
Their goal is to use the toilet sensor in areas where cholera is common to prevent the spread of disease. After that, who knows? “Perhaps someday, our algorithm can be used with existing in-home smart devices to monitor one’s own bowel movements and health!” she suggested.
That would be a heroic toilet indeed.
Bribery really is the solution to all of life’s problems
Breaking news: The United States has a bit of an obesity epidemic. Okay, maybe not so breaking news. But it’s a problem we’ve been struggling with for a very long time. Part of the issue is that there really is no secret to weight loss. Pretty much anything can work if you’re committed. The millions of diets floating around are testament to this idea.
The problem of losing weight is amplified if you don’t rake in the big bucks. Lower-income individuals often can’t afford healthy superfoods, and they’re often too busy to spend time at classes, exercising, or following programs. A group of researchers at New York University has offered up an alternate solution to encourage weight loss in low-income people: Pay them.
Specifically, pay them for losing weight. A reward, if you will. The researchers recruited several hundred lower-income people and split them into three groups. All participants received a free 1-year membership to a gym and weight-loss program, as well as food journals and fitness devices, but one group received payment (on average, about $300 overall) for attending meetings, exercising a certain amount every week, or weighing themselves twice a week. About 40% of people in this group lost 5% of their body weight after 6 months, twice as many as in the group that did not receive payment for performing these tasks.
The big winners, however, were those in the third group. They also received the free stuff, but the researchers offered them a more simple and direct bribe: Lose 5% of your weight over 6 months and we’ll pay you. The reward? About $450 on average, and it worked very well, with half this group losing the weight after 6 months. That said, after a year something like a fifth of this group put the weight back on, bringing them in line with the group that was paid to perform tasks. Still, both groups outperformed the control group, which received no money.
The takeaway from this research is pretty obvious. Pay people a fair price to do something, and they’ll do it. This is a lesson that has absolutely no relevance in the modern world. Nope, none whatsoever. We all receive completely fair wages. We all have plenty of money to pay for things. Everything is fine.
More green space, less medicine
Have you heard of the 3-30-300 rule? Proposed by urban forester Cecil Konijnendijk, it’s become the rule of thumb for urban planners and other foresters into getting more green space in populated areas. A recent study has found that people who lived within this 3-30-300 rule had better mental health and less medication use.
If you’re not an urban forester, however, you may not know what the 3-30-300 rule is. But it’s pretty simple, people should be able to see at least three trees from their home, have 30% tree canopy in their neighborhood, and have 300 Spartans to defend against the Persian army.
We may have made that last one up. It’s actually have a green space or park within 300 meters of your home.
In the new study, only 4.7% of people surveyed lived in an area that followed all three rules. About 62% of the surveyed lived with a green space at least 300 meters away, 43% had at least three trees within 15 meters from their home, and a rather pitiful 9% had adequate tree canopy coverage in their neighborhood.
Greater adherence to the 3-30-300 rule was associated with fewer visits to the psychologist, with 8.3% of the participants reporting a psychologist visit in the last year. The data come from a sample of a little over 3,000 Barcelona residents aged 15-97 who were randomly selected to participate in the Barcelona Public Health Agency Survey.
“There is an urgent need to provide citizens with more green space,” said Mark Nieuwenhuijsen, lead author of the study. “We may need to tear out asphalt and plant more trees, which would not only improve health, but also reduce heat island effects and contribute to carbon capture.”
The main goal and message is that more green space is good for everyone. So if you’re feeling a little overwhelmed, take a breather and sit somewhere green. Or call those 300 Spartans and get them to start knocking some buildings down.
Said the toilet to the engineer: Do you hear what I hear?
A mythical hero’s journey took Dorothy along the yellow brick road to find the Wizard of Oz. Huckleberry Finn used a raft to float down the Mississippi River. Luke Skywalker did most of his traveling between planets. For the rest of us, the journey may be just a bit shorter.
Also a bit less heroic. Unless, of course, you’re prepping for a colonoscopy. Yup, we’re headed to the toilet, but not just any toilet. This toilet was the subject of a presentation at the annual meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, titled “The feces thesis: Using machine learning to detect diarrhea,” and that presentation was the hero’s journey of Maia Gatlin, PhD, a research engineer at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
She and her team attached a noninvasive microphone sensor to a toilet, and now they can identify bowel diseases without collecting any identifiable information.
The audio sample of an excretion event is “transformed into a spectrogram, which essentially captures the sound in an image. Different events produce different features in the audio and the spectrogram. For example, urination creates a consistent tone, while defecation may have a singular tone. In contrast, diarrhea is more random,” they explained in the written statement.
They used a machine learning algorithm to classify each spectrogram based on its features. “The algorithm’s performance was tested against data with and without background noises to make sure it was learning the right sound features, regardless of the sensor’s environment,” Dr. Gatlin and associates wrote.
Their goal is to use the toilet sensor in areas where cholera is common to prevent the spread of disease. After that, who knows? “Perhaps someday, our algorithm can be used with existing in-home smart devices to monitor one’s own bowel movements and health!” she suggested.
That would be a heroic toilet indeed.
Bribery really is the solution to all of life’s problems
Breaking news: The United States has a bit of an obesity epidemic. Okay, maybe not so breaking news. But it’s a problem we’ve been struggling with for a very long time. Part of the issue is that there really is no secret to weight loss. Pretty much anything can work if you’re committed. The millions of diets floating around are testament to this idea.
The problem of losing weight is amplified if you don’t rake in the big bucks. Lower-income individuals often can’t afford healthy superfoods, and they’re often too busy to spend time at classes, exercising, or following programs. A group of researchers at New York University has offered up an alternate solution to encourage weight loss in low-income people: Pay them.
Specifically, pay them for losing weight. A reward, if you will. The researchers recruited several hundred lower-income people and split them into three groups. All participants received a free 1-year membership to a gym and weight-loss program, as well as food journals and fitness devices, but one group received payment (on average, about $300 overall) for attending meetings, exercising a certain amount every week, or weighing themselves twice a week. About 40% of people in this group lost 5% of their body weight after 6 months, twice as many as in the group that did not receive payment for performing these tasks.
The big winners, however, were those in the third group. They also received the free stuff, but the researchers offered them a more simple and direct bribe: Lose 5% of your weight over 6 months and we’ll pay you. The reward? About $450 on average, and it worked very well, with half this group losing the weight after 6 months. That said, after a year something like a fifth of this group put the weight back on, bringing them in line with the group that was paid to perform tasks. Still, both groups outperformed the control group, which received no money.
The takeaway from this research is pretty obvious. Pay people a fair price to do something, and they’ll do it. This is a lesson that has absolutely no relevance in the modern world. Nope, none whatsoever. We all receive completely fair wages. We all have plenty of money to pay for things. Everything is fine.
More green space, less medicine
Have you heard of the 3-30-300 rule? Proposed by urban forester Cecil Konijnendijk, it’s become the rule of thumb for urban planners and other foresters into getting more green space in populated areas. A recent study has found that people who lived within this 3-30-300 rule had better mental health and less medication use.
If you’re not an urban forester, however, you may not know what the 3-30-300 rule is. But it’s pretty simple, people should be able to see at least three trees from their home, have 30% tree canopy in their neighborhood, and have 300 Spartans to defend against the Persian army.
We may have made that last one up. It’s actually have a green space or park within 300 meters of your home.
In the new study, only 4.7% of people surveyed lived in an area that followed all three rules. About 62% of the surveyed lived with a green space at least 300 meters away, 43% had at least three trees within 15 meters from their home, and a rather pitiful 9% had adequate tree canopy coverage in their neighborhood.
Greater adherence to the 3-30-300 rule was associated with fewer visits to the psychologist, with 8.3% of the participants reporting a psychologist visit in the last year. The data come from a sample of a little over 3,000 Barcelona residents aged 15-97 who were randomly selected to participate in the Barcelona Public Health Agency Survey.
“There is an urgent need to provide citizens with more green space,” said Mark Nieuwenhuijsen, lead author of the study. “We may need to tear out asphalt and plant more trees, which would not only improve health, but also reduce heat island effects and contribute to carbon capture.”
The main goal and message is that more green space is good for everyone. So if you’re feeling a little overwhelmed, take a breather and sit somewhere green. Or call those 300 Spartans and get them to start knocking some buildings down.
Said the toilet to the engineer: Do you hear what I hear?
A mythical hero’s journey took Dorothy along the yellow brick road to find the Wizard of Oz. Huckleberry Finn used a raft to float down the Mississippi River. Luke Skywalker did most of his traveling between planets. For the rest of us, the journey may be just a bit shorter.
Also a bit less heroic. Unless, of course, you’re prepping for a colonoscopy. Yup, we’re headed to the toilet, but not just any toilet. This toilet was the subject of a presentation at the annual meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, titled “The feces thesis: Using machine learning to detect diarrhea,” and that presentation was the hero’s journey of Maia Gatlin, PhD, a research engineer at the Georgia Institute of Technology.
She and her team attached a noninvasive microphone sensor to a toilet, and now they can identify bowel diseases without collecting any identifiable information.
The audio sample of an excretion event is “transformed into a spectrogram, which essentially captures the sound in an image. Different events produce different features in the audio and the spectrogram. For example, urination creates a consistent tone, while defecation may have a singular tone. In contrast, diarrhea is more random,” they explained in the written statement.
They used a machine learning algorithm to classify each spectrogram based on its features. “The algorithm’s performance was tested against data with and without background noises to make sure it was learning the right sound features, regardless of the sensor’s environment,” Dr. Gatlin and associates wrote.
Their goal is to use the toilet sensor in areas where cholera is common to prevent the spread of disease. After that, who knows? “Perhaps someday, our algorithm can be used with existing in-home smart devices to monitor one’s own bowel movements and health!” she suggested.
That would be a heroic toilet indeed.
‘Slugging’: A TikTok skin trend that has some merit
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ohio measles outbreak sickens nearly 60 children
None of the children had been fully vaccinated against measles, and 23 of them have been hospitalized, local officials report.
“Measles can be very serious, especially for children under age 5,” Columbus Public Health spokesperson Kelli Newman told CNN.
Nearly all of the infected children are under age 5, with 12 of them being under 1 year old.
“Many children are hospitalized for dehydration,” Ms. Newman told CNN in an email. “Other serious complications also can include pneumonia and neurological conditions such as encephalitis. There’s no way of knowing which children will become so sick they have to be hospitalized. The safest way to protect children from measles is to make sure they are vaccinated with MMR.”
Of the 59 infected children, 56 were unvaccinated and three had been partially vaccinated. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is recommended for children beginning at 12 months old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and American Academy of Pediatrics. Two doses are needed to be considered fully vaccinated, and the second dose is usually given between 4 and 6 years old.
Measles “is one of the most infectious agents known to man,” the academy says.
It is so contagious that if one person has it, up to 9 out of 10 people around that person will also become infected if they are not protected, the CDC explains. Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, or death.
Last month, the World Health Organization and CDC warned that 40 million children worldwide missed their measles vaccinations in 2021, partly due to pandemic disruptions. The American Academy of Pediatrics also notes that many parents choose not to vaccinate their children due to misinformation.
Infants are at heightened risk because they are too young to be vaccinated.
The academy offered several tips for protecting unvaccinated infants during a measles outbreak:
- Limit your baby’s exposure to crowds, other children, and people with cold symptoms.
- Disinfect objects and surfaces at home regularly, because the measles virus can live on surfaces or suspended in the air for 2 hours.
- If possible, feed your baby breast milk, because it has antibodies to prevent and fight infections.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
None of the children had been fully vaccinated against measles, and 23 of them have been hospitalized, local officials report.
“Measles can be very serious, especially for children under age 5,” Columbus Public Health spokesperson Kelli Newman told CNN.
Nearly all of the infected children are under age 5, with 12 of them being under 1 year old.
“Many children are hospitalized for dehydration,” Ms. Newman told CNN in an email. “Other serious complications also can include pneumonia and neurological conditions such as encephalitis. There’s no way of knowing which children will become so sick they have to be hospitalized. The safest way to protect children from measles is to make sure they are vaccinated with MMR.”
Of the 59 infected children, 56 were unvaccinated and three had been partially vaccinated. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is recommended for children beginning at 12 months old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and American Academy of Pediatrics. Two doses are needed to be considered fully vaccinated, and the second dose is usually given between 4 and 6 years old.
Measles “is one of the most infectious agents known to man,” the academy says.
It is so contagious that if one person has it, up to 9 out of 10 people around that person will also become infected if they are not protected, the CDC explains. Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, or death.
Last month, the World Health Organization and CDC warned that 40 million children worldwide missed their measles vaccinations in 2021, partly due to pandemic disruptions. The American Academy of Pediatrics also notes that many parents choose not to vaccinate their children due to misinformation.
Infants are at heightened risk because they are too young to be vaccinated.
The academy offered several tips for protecting unvaccinated infants during a measles outbreak:
- Limit your baby’s exposure to crowds, other children, and people with cold symptoms.
- Disinfect objects and surfaces at home regularly, because the measles virus can live on surfaces or suspended in the air for 2 hours.
- If possible, feed your baby breast milk, because it has antibodies to prevent and fight infections.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
None of the children had been fully vaccinated against measles, and 23 of them have been hospitalized, local officials report.
“Measles can be very serious, especially for children under age 5,” Columbus Public Health spokesperson Kelli Newman told CNN.
Nearly all of the infected children are under age 5, with 12 of them being under 1 year old.
“Many children are hospitalized for dehydration,” Ms. Newman told CNN in an email. “Other serious complications also can include pneumonia and neurological conditions such as encephalitis. There’s no way of knowing which children will become so sick they have to be hospitalized. The safest way to protect children from measles is to make sure they are vaccinated with MMR.”
Of the 59 infected children, 56 were unvaccinated and three had been partially vaccinated. The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is recommended for children beginning at 12 months old, according to the Centers for Disease Control and American Academy of Pediatrics. Two doses are needed to be considered fully vaccinated, and the second dose is usually given between 4 and 6 years old.
Measles “is one of the most infectious agents known to man,” the academy says.
It is so contagious that if one person has it, up to 9 out of 10 people around that person will also become infected if they are not protected, the CDC explains. Measles infection causes a rash and a fever that can spike beyond 104° F. Sometimes, the illness can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, or death.
Last month, the World Health Organization and CDC warned that 40 million children worldwide missed their measles vaccinations in 2021, partly due to pandemic disruptions. The American Academy of Pediatrics also notes that many parents choose not to vaccinate their children due to misinformation.
Infants are at heightened risk because they are too young to be vaccinated.
The academy offered several tips for protecting unvaccinated infants during a measles outbreak:
- Limit your baby’s exposure to crowds, other children, and people with cold symptoms.
- Disinfect objects and surfaces at home regularly, because the measles virus can live on surfaces or suspended in the air for 2 hours.
- If possible, feed your baby breast milk, because it has antibodies to prevent and fight infections.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Tackling oral health in primary care: A task that’s worth the time
Tooth decay can be easy to overlook – particularly for pediatricians and family physicians, who may be neglecting a crucial aspect of childhood health.
Left untreated, it can lead to serious and even fatal medical problems. The incorporation of preventive oral health care services like the application of fluoride varnish into primary care may be helping protect kids’ smiles and improving their overall physical well-being, according to doctors and a recent government report.
‘We don’t deal with that in pediatrics’
Physicians historically were not trained to examine teeth. That was the dentist’s job.
But dental caries is one of the most common chronic diseases in children, and many children do not regularly see a dentist.
“I stumbled across the statistic that oral health problems in children are five times as common as asthma,” said Susan A. Fisher-Owens, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “And I said to myself, ‘Well, that can’t be. We don’t deal with that in pediatrics.’ And then I realized, ‘Oh my goodness, we don’t deal with that in pediatrics!’ ”
Children should see a dentist, of course. Physicians should refer families to a dentist by age 1 for routine care, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. The sooner kids are seen, the more likely they are to stay healthy and avoid the need for costlier care, she said.
But the receipt of dental care has gaps.
“About half of all American children do not receive regular dental care because of social, economic, and geographic obstacles,” according to a 2021 fact sheet from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings is improving children’s oral health.”
Many children do not start to see a dentist when they are supposed to, acknowledged Kami Hoss, DDS, MS, founder of a large dental practice in California and the author of a new book, “If Your Mouth Could Talk,” that examines links between oral health and physical disease.
Although the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry says every child should see a pediatric dentist by the time their first baby teeth come in, usually at around 6 months or no later than age 1 year, that does not always happen.
Indeed, only about 16% of children adhere to that guidance, Dr. Hoss said, “which means 84% of parents rely on their pediatricians for oral health advice.”
At older ages, oral health problems like gum disease are linked to almost every chronic disease, Dr. Hoss said.
“We love to bridge the gap, to build bridges between medicine and dentistry,” he said. “After all, your mouth is part of your body.”
A 2021 NIDCR report similarly describes the stakes: “Although caries is largely preventable, if untreated it can lead to pain, inflammation, and the spread of infection to bone and soft tissue. Children may suffer from difficulty eating, poor nutrition, delayed physical development, and poor self-image and socialization. Even academic performance can be affected.”
In November, the World Health Organization published a report showing that about 45% of the world’s population – 3.5 billion people – have oral diseases, including 2.5 billion people with untreated dental caries.
Oral health care is often neglected in public health research, and often entails high out-of-pocket costs for families, the organization notes.
‘Strep tooth’
Dental cavities are caused by bacteria – mainly Streptococcus mutans – that eat sugars or carbohydrates in the mouth. That process causes acid, which can erode teeth. In that way, the development of caries is a fully preventable infectious disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
“I think if people looked at this disease as ‘strep tooth,’ it would get a lot more people interested,” she said.
Bacteria that cause caries can spread from caregiver to child, such as when a parent tries to clean a dropped pacifier in their own mouth, or from child to child.
Caries can be prevented with proper diet and oral hygiene: toothbrushing and then applying fluoride to strengthen teeth or restrengthen teeth that have been weakened by the disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
The biggest risk factor for having cavities in adult teeth is having them in primary teeth, she said. “There is a common misconception that it doesn’t matter what happens with baby teeth. They’ll fall out,” she said. “But actually it does because it puts you on a trajectory of having cavities in the adult teeth and worse outcomes with other adult conditions, such as diabetes.”
At the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics in Anaheim in October, Dr. Fisher-Owens and Jean Calvo, DDS, MPH, also with the University of California, San Francisco, trained colleagues to apply fluoride varnish to primary teeth – so-called baby teeth – in the doctor’s office. This session is a regular feature at these conferences.
Since 2014, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has recommended that primary care clinicians apply fluoride varnish to the primary teeth of all infants and children.
Many pediatricians may not do this regularly, however.
Researchers recently reported that, despite insurance coverage, less than 5% of well-child visits for privately insured young children between 2016 and 2018 included the service.
Nevertheless, the practice may be helping, according to the NIDCR report.
Since 2000, untreated tooth decay in primary teeth among children younger than 12 years has fallen from 23% to 15%, according to the report. For children aged 2-5 years, untreated tooth decay decreased from at least 19% to 10%. For children aged 6-11 years, the prevalence of dental cavities in permanent teeth fell from 25% to 18%, the report states.
“Fluoridated water, toothpastes, and varnish – as well as dental sealants – can work together to dramatically reduce the incidence of caries,” according to the NIDCR. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings has been another important advancement. The delivery of preventive oral health services, such as fluoride varnish, during well-child visits in medical offices is showing promise in reducing dental caries among preschool-age children.”
Integrating oral health care with medical primary care has met challenges, however, including “resistance by providers, lack of training, and the need for insurance reimbursement for services,” the report notes.
Clinicians can already bill for the application of fluoride varnish using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 99188, and additional oral health care procedures may be on the horizon.
The American Medical Association this fall established a new Category III CPT code for the application of silver diamine fluoride to dental cavities.
Silver diamine fluoride is a newer product that was approved as a desensitizing agent by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014. It has antimicrobial and remineralizing properties, and researchers have found that it can stop the progression of early tooth decay and is more effective than fluoride varnish in preventing cavities.
Several dental groups supported the creation of this new code, which is expected to be made available by electronic health records vendors in July.
Some dentists have reservations, however. The Academy of General Dentistry in October expressed concerns that allowing “nondental health care workers to administer silver diamine fluoride is a temporary solution to a growing oral health crisis.”
Silver diamine fluoride may stop about 80% of cavities. Although the CPT code for silver diamine fluoride has been established, whether insurers will reimburse health care professionals for the service is another matter, said Richard Niederman, DMD, professor and chair of epidemiology and health promotion at New York University College of Dentistry.
Fatal consequences
Disparities in oral health in children may be greater than with almost any other disease process. The rate of caries in children who are poor is about twice that for children who are not poor, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. Disparities by race or ethnicity compound these differences.
In 2007, 12-year-old Deamonte Driver died after bacteria from a dental abscess spread to his brain. He had needed a tooth extraction, but his family lacked insurance and had had trouble finding dentists that accepted Medicaid near where they lived in Maryland.
After two emergency brain surgeries, 2 weeks in a hospital, and another 6 weeks in a hospital for rehabilitation, Deamonte died from the infection. The case sparked calls to fix the dental health system.
Physicians may notice more oral health problems in their patients, including dental abscesses, once they start looking for them, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
She recalled one instance where a child with an underlying seizure disorder was hospitalized at an academic center because they appeared to be having more seizures.
“They eventually discharged the kid because they looked at all of the things related to seizures. None of them were there,” she said.
When Dr. Fisher-Owens saw the child for a discharge exam, she looked in the mouth and saw a whopping dental abscess.
“I realized that this kid wasn’t seizing but was actually rigoring in pain,” she said. No one else on the medical team had seen the true problem despite multiple examinations. The child started antibiotics, was referred to a dentist to have the abscess drained, and had a good outcome.
Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, adjunct clinical professor of pediatrics and community health at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., had noticed that many of her poorer patients had oral health problems, but many pediatric dentists were not able or willing to see them to provide treatment.
“Taking it one step further, you really want to prevent early childhood caries,” Dr. Boulter said. She started speaking up about oral health at pediatric meetings and became an early adopter of preventive interventions, including the use of fluoride varnish.
“Fluoride varnish is a sticky substance that has a very high concentration of fluoride in it,and it’s a very powerful reducer of oral childhood caries, by maybe 35%,” Dr. Boulter said.
Applying the varnish is fairly simple, but it had never been part of the well-child exam. Dr. Boulter started using it around 2005.
Initially, convincing other pediatricians to adopt this procedure – when visits are already time-constrained – was not always easy, she said.
Now that fluoride varnish is recommended for all children and is part of Bright Futures recommendations and is covered in the Affordable Care Act, “it became more the norm,” Dr. Boulter said. But there is room for improvement.
“There is still not a high enough percentage of pediatricians and family physicians who actually have incorporated application of fluoride varnish into their practice,” she said.
Brush, book, bed
Clinicians can take other steps to counsel parents about protecting their child’s teeth, like making sure that their teeth get brushed before bed, encouraging kids to drink tap water, especially if it’s fluoridated, and avoiding juice. The AAP has a program called Brush, Book, Bed to promote oral health, along with reading and good sleep habits.
Dr. Hoss noted that parents, and even dentists, may have misconceptions about optimal oral hygiene. “For example, you’re supposed to brush your teeth before breakfast, not after breakfast. But I’ve seen dentists even tell their patients, brush after breakfast,” he said.
In addition, people should brush gently but thoroughly using high-quality toothbrushes with soft bristles – “not scrubbing the teeth away with a coarse toothbrush,” he said.
Dr. Niederman has studied ways to prevent caries in underserved communities and is co-CEO of CariedAway, an organization that brings free cavity-prevention programs to schools.
In an average classroom of 24 students, about 6 children would be expected to have untreated tooth decay, Dr. Niederman said. And about 10% of the children with untreated tooth decay experience a toothache. So in two classrooms, at least one child would be expected to be experiencing pain, while the other students with caries might feel a lesser degree of discomfort. “That reduces presenteeism in the classroom and certainly presenteeism for the kid with a toothache,” Dr. Niederman said.
In communities with less access to dental care, including rural areas, the number of students with tooth decay might be double.
The new WHO report shows that the prevalence of caries in permanent teeth in various countries has remained at roughly 30%, regardless of a country’s income level, and despite efforts to bolster the dental workforce, said Dr. Niederman.
“The dental system is similar globally and focused on drilling and filling rather than prevention,” he said.
A 2019 Lancet series on oral health called for radical change in dental care, Dr. Niederman noted. “One of those radical changes would be primary care physicians or their offices participating in outreach programs to deliver care in schools,” he said.
Dr. Fisher-Owens is on a data and safety monitoring board for research by Colgate. Dr. Boulter serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News. Dr. Hoss is the author of “If Your Mouth Could Talk” and the founder and CEO of SuperMouth, which markets children’s oral care products. Dr. Niederman’s research has used toothbrushes, toothpaste, and fluoride varnish donated by Colgate; silver diamine fluoride provided by Elevate Oral Health; and glass ionomer provided by GC America.
Tooth decay can be easy to overlook – particularly for pediatricians and family physicians, who may be neglecting a crucial aspect of childhood health.
Left untreated, it can lead to serious and even fatal medical problems. The incorporation of preventive oral health care services like the application of fluoride varnish into primary care may be helping protect kids’ smiles and improving their overall physical well-being, according to doctors and a recent government report.
‘We don’t deal with that in pediatrics’
Physicians historically were not trained to examine teeth. That was the dentist’s job.
But dental caries is one of the most common chronic diseases in children, and many children do not regularly see a dentist.
“I stumbled across the statistic that oral health problems in children are five times as common as asthma,” said Susan A. Fisher-Owens, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “And I said to myself, ‘Well, that can’t be. We don’t deal with that in pediatrics.’ And then I realized, ‘Oh my goodness, we don’t deal with that in pediatrics!’ ”
Children should see a dentist, of course. Physicians should refer families to a dentist by age 1 for routine care, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. The sooner kids are seen, the more likely they are to stay healthy and avoid the need for costlier care, she said.
But the receipt of dental care has gaps.
“About half of all American children do not receive regular dental care because of social, economic, and geographic obstacles,” according to a 2021 fact sheet from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings is improving children’s oral health.”
Many children do not start to see a dentist when they are supposed to, acknowledged Kami Hoss, DDS, MS, founder of a large dental practice in California and the author of a new book, “If Your Mouth Could Talk,” that examines links between oral health and physical disease.
Although the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry says every child should see a pediatric dentist by the time their first baby teeth come in, usually at around 6 months or no later than age 1 year, that does not always happen.
Indeed, only about 16% of children adhere to that guidance, Dr. Hoss said, “which means 84% of parents rely on their pediatricians for oral health advice.”
At older ages, oral health problems like gum disease are linked to almost every chronic disease, Dr. Hoss said.
“We love to bridge the gap, to build bridges between medicine and dentistry,” he said. “After all, your mouth is part of your body.”
A 2021 NIDCR report similarly describes the stakes: “Although caries is largely preventable, if untreated it can lead to pain, inflammation, and the spread of infection to bone and soft tissue. Children may suffer from difficulty eating, poor nutrition, delayed physical development, and poor self-image and socialization. Even academic performance can be affected.”
In November, the World Health Organization published a report showing that about 45% of the world’s population – 3.5 billion people – have oral diseases, including 2.5 billion people with untreated dental caries.
Oral health care is often neglected in public health research, and often entails high out-of-pocket costs for families, the organization notes.
‘Strep tooth’
Dental cavities are caused by bacteria – mainly Streptococcus mutans – that eat sugars or carbohydrates in the mouth. That process causes acid, which can erode teeth. In that way, the development of caries is a fully preventable infectious disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
“I think if people looked at this disease as ‘strep tooth,’ it would get a lot more people interested,” she said.
Bacteria that cause caries can spread from caregiver to child, such as when a parent tries to clean a dropped pacifier in their own mouth, or from child to child.
Caries can be prevented with proper diet and oral hygiene: toothbrushing and then applying fluoride to strengthen teeth or restrengthen teeth that have been weakened by the disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
The biggest risk factor for having cavities in adult teeth is having them in primary teeth, she said. “There is a common misconception that it doesn’t matter what happens with baby teeth. They’ll fall out,” she said. “But actually it does because it puts you on a trajectory of having cavities in the adult teeth and worse outcomes with other adult conditions, such as diabetes.”
At the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics in Anaheim in October, Dr. Fisher-Owens and Jean Calvo, DDS, MPH, also with the University of California, San Francisco, trained colleagues to apply fluoride varnish to primary teeth – so-called baby teeth – in the doctor’s office. This session is a regular feature at these conferences.
Since 2014, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has recommended that primary care clinicians apply fluoride varnish to the primary teeth of all infants and children.
Many pediatricians may not do this regularly, however.
Researchers recently reported that, despite insurance coverage, less than 5% of well-child visits for privately insured young children between 2016 and 2018 included the service.
Nevertheless, the practice may be helping, according to the NIDCR report.
Since 2000, untreated tooth decay in primary teeth among children younger than 12 years has fallen from 23% to 15%, according to the report. For children aged 2-5 years, untreated tooth decay decreased from at least 19% to 10%. For children aged 6-11 years, the prevalence of dental cavities in permanent teeth fell from 25% to 18%, the report states.
“Fluoridated water, toothpastes, and varnish – as well as dental sealants – can work together to dramatically reduce the incidence of caries,” according to the NIDCR. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings has been another important advancement. The delivery of preventive oral health services, such as fluoride varnish, during well-child visits in medical offices is showing promise in reducing dental caries among preschool-age children.”
Integrating oral health care with medical primary care has met challenges, however, including “resistance by providers, lack of training, and the need for insurance reimbursement for services,” the report notes.
Clinicians can already bill for the application of fluoride varnish using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 99188, and additional oral health care procedures may be on the horizon.
The American Medical Association this fall established a new Category III CPT code for the application of silver diamine fluoride to dental cavities.
Silver diamine fluoride is a newer product that was approved as a desensitizing agent by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014. It has antimicrobial and remineralizing properties, and researchers have found that it can stop the progression of early tooth decay and is more effective than fluoride varnish in preventing cavities.
Several dental groups supported the creation of this new code, which is expected to be made available by electronic health records vendors in July.
Some dentists have reservations, however. The Academy of General Dentistry in October expressed concerns that allowing “nondental health care workers to administer silver diamine fluoride is a temporary solution to a growing oral health crisis.”
Silver diamine fluoride may stop about 80% of cavities. Although the CPT code for silver diamine fluoride has been established, whether insurers will reimburse health care professionals for the service is another matter, said Richard Niederman, DMD, professor and chair of epidemiology and health promotion at New York University College of Dentistry.
Fatal consequences
Disparities in oral health in children may be greater than with almost any other disease process. The rate of caries in children who are poor is about twice that for children who are not poor, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. Disparities by race or ethnicity compound these differences.
In 2007, 12-year-old Deamonte Driver died after bacteria from a dental abscess spread to his brain. He had needed a tooth extraction, but his family lacked insurance and had had trouble finding dentists that accepted Medicaid near where they lived in Maryland.
After two emergency brain surgeries, 2 weeks in a hospital, and another 6 weeks in a hospital for rehabilitation, Deamonte died from the infection. The case sparked calls to fix the dental health system.
Physicians may notice more oral health problems in their patients, including dental abscesses, once they start looking for them, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
She recalled one instance where a child with an underlying seizure disorder was hospitalized at an academic center because they appeared to be having more seizures.
“They eventually discharged the kid because they looked at all of the things related to seizures. None of them were there,” she said.
When Dr. Fisher-Owens saw the child for a discharge exam, she looked in the mouth and saw a whopping dental abscess.
“I realized that this kid wasn’t seizing but was actually rigoring in pain,” she said. No one else on the medical team had seen the true problem despite multiple examinations. The child started antibiotics, was referred to a dentist to have the abscess drained, and had a good outcome.
Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, adjunct clinical professor of pediatrics and community health at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., had noticed that many of her poorer patients had oral health problems, but many pediatric dentists were not able or willing to see them to provide treatment.
“Taking it one step further, you really want to prevent early childhood caries,” Dr. Boulter said. She started speaking up about oral health at pediatric meetings and became an early adopter of preventive interventions, including the use of fluoride varnish.
“Fluoride varnish is a sticky substance that has a very high concentration of fluoride in it,and it’s a very powerful reducer of oral childhood caries, by maybe 35%,” Dr. Boulter said.
Applying the varnish is fairly simple, but it had never been part of the well-child exam. Dr. Boulter started using it around 2005.
Initially, convincing other pediatricians to adopt this procedure – when visits are already time-constrained – was not always easy, she said.
Now that fluoride varnish is recommended for all children and is part of Bright Futures recommendations and is covered in the Affordable Care Act, “it became more the norm,” Dr. Boulter said. But there is room for improvement.
“There is still not a high enough percentage of pediatricians and family physicians who actually have incorporated application of fluoride varnish into their practice,” she said.
Brush, book, bed
Clinicians can take other steps to counsel parents about protecting their child’s teeth, like making sure that their teeth get brushed before bed, encouraging kids to drink tap water, especially if it’s fluoridated, and avoiding juice. The AAP has a program called Brush, Book, Bed to promote oral health, along with reading and good sleep habits.
Dr. Hoss noted that parents, and even dentists, may have misconceptions about optimal oral hygiene. “For example, you’re supposed to brush your teeth before breakfast, not after breakfast. But I’ve seen dentists even tell their patients, brush after breakfast,” he said.
In addition, people should brush gently but thoroughly using high-quality toothbrushes with soft bristles – “not scrubbing the teeth away with a coarse toothbrush,” he said.
Dr. Niederman has studied ways to prevent caries in underserved communities and is co-CEO of CariedAway, an organization that brings free cavity-prevention programs to schools.
In an average classroom of 24 students, about 6 children would be expected to have untreated tooth decay, Dr. Niederman said. And about 10% of the children with untreated tooth decay experience a toothache. So in two classrooms, at least one child would be expected to be experiencing pain, while the other students with caries might feel a lesser degree of discomfort. “That reduces presenteeism in the classroom and certainly presenteeism for the kid with a toothache,” Dr. Niederman said.
In communities with less access to dental care, including rural areas, the number of students with tooth decay might be double.
The new WHO report shows that the prevalence of caries in permanent teeth in various countries has remained at roughly 30%, regardless of a country’s income level, and despite efforts to bolster the dental workforce, said Dr. Niederman.
“The dental system is similar globally and focused on drilling and filling rather than prevention,” he said.
A 2019 Lancet series on oral health called for radical change in dental care, Dr. Niederman noted. “One of those radical changes would be primary care physicians or their offices participating in outreach programs to deliver care in schools,” he said.
Dr. Fisher-Owens is on a data and safety monitoring board for research by Colgate. Dr. Boulter serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News. Dr. Hoss is the author of “If Your Mouth Could Talk” and the founder and CEO of SuperMouth, which markets children’s oral care products. Dr. Niederman’s research has used toothbrushes, toothpaste, and fluoride varnish donated by Colgate; silver diamine fluoride provided by Elevate Oral Health; and glass ionomer provided by GC America.
Tooth decay can be easy to overlook – particularly for pediatricians and family physicians, who may be neglecting a crucial aspect of childhood health.
Left untreated, it can lead to serious and even fatal medical problems. The incorporation of preventive oral health care services like the application of fluoride varnish into primary care may be helping protect kids’ smiles and improving their overall physical well-being, according to doctors and a recent government report.
‘We don’t deal with that in pediatrics’
Physicians historically were not trained to examine teeth. That was the dentist’s job.
But dental caries is one of the most common chronic diseases in children, and many children do not regularly see a dentist.
“I stumbled across the statistic that oral health problems in children are five times as common as asthma,” said Susan A. Fisher-Owens, MD, MPH, professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “And I said to myself, ‘Well, that can’t be. We don’t deal with that in pediatrics.’ And then I realized, ‘Oh my goodness, we don’t deal with that in pediatrics!’ ”
Children should see a dentist, of course. Physicians should refer families to a dentist by age 1 for routine care, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. The sooner kids are seen, the more likely they are to stay healthy and avoid the need for costlier care, she said.
But the receipt of dental care has gaps.
“About half of all American children do not receive regular dental care because of social, economic, and geographic obstacles,” according to a 2021 fact sheet from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings is improving children’s oral health.”
Many children do not start to see a dentist when they are supposed to, acknowledged Kami Hoss, DDS, MS, founder of a large dental practice in California and the author of a new book, “If Your Mouth Could Talk,” that examines links between oral health and physical disease.
Although the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry says every child should see a pediatric dentist by the time their first baby teeth come in, usually at around 6 months or no later than age 1 year, that does not always happen.
Indeed, only about 16% of children adhere to that guidance, Dr. Hoss said, “which means 84% of parents rely on their pediatricians for oral health advice.”
At older ages, oral health problems like gum disease are linked to almost every chronic disease, Dr. Hoss said.
“We love to bridge the gap, to build bridges between medicine and dentistry,” he said. “After all, your mouth is part of your body.”
A 2021 NIDCR report similarly describes the stakes: “Although caries is largely preventable, if untreated it can lead to pain, inflammation, and the spread of infection to bone and soft tissue. Children may suffer from difficulty eating, poor nutrition, delayed physical development, and poor self-image and socialization. Even academic performance can be affected.”
In November, the World Health Organization published a report showing that about 45% of the world’s population – 3.5 billion people – have oral diseases, including 2.5 billion people with untreated dental caries.
Oral health care is often neglected in public health research, and often entails high out-of-pocket costs for families, the organization notes.
‘Strep tooth’
Dental cavities are caused by bacteria – mainly Streptococcus mutans – that eat sugars or carbohydrates in the mouth. That process causes acid, which can erode teeth. In that way, the development of caries is a fully preventable infectious disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
“I think if people looked at this disease as ‘strep tooth,’ it would get a lot more people interested,” she said.
Bacteria that cause caries can spread from caregiver to child, such as when a parent tries to clean a dropped pacifier in their own mouth, or from child to child.
Caries can be prevented with proper diet and oral hygiene: toothbrushing and then applying fluoride to strengthen teeth or restrengthen teeth that have been weakened by the disease process, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
The biggest risk factor for having cavities in adult teeth is having them in primary teeth, she said. “There is a common misconception that it doesn’t matter what happens with baby teeth. They’ll fall out,” she said. “But actually it does because it puts you on a trajectory of having cavities in the adult teeth and worse outcomes with other adult conditions, such as diabetes.”
At the 2022 annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics in Anaheim in October, Dr. Fisher-Owens and Jean Calvo, DDS, MPH, also with the University of California, San Francisco, trained colleagues to apply fluoride varnish to primary teeth – so-called baby teeth – in the doctor’s office. This session is a regular feature at these conferences.
Since 2014, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has recommended that primary care clinicians apply fluoride varnish to the primary teeth of all infants and children.
Many pediatricians may not do this regularly, however.
Researchers recently reported that, despite insurance coverage, less than 5% of well-child visits for privately insured young children between 2016 and 2018 included the service.
Nevertheless, the practice may be helping, according to the NIDCR report.
Since 2000, untreated tooth decay in primary teeth among children younger than 12 years has fallen from 23% to 15%, according to the report. For children aged 2-5 years, untreated tooth decay decreased from at least 19% to 10%. For children aged 6-11 years, the prevalence of dental cavities in permanent teeth fell from 25% to 18%, the report states.
“Fluoridated water, toothpastes, and varnish – as well as dental sealants – can work together to dramatically reduce the incidence of caries,” according to the NIDCR. “Integrating dental care within family and pediatric medical care settings has been another important advancement. The delivery of preventive oral health services, such as fluoride varnish, during well-child visits in medical offices is showing promise in reducing dental caries among preschool-age children.”
Integrating oral health care with medical primary care has met challenges, however, including “resistance by providers, lack of training, and the need for insurance reimbursement for services,” the report notes.
Clinicians can already bill for the application of fluoride varnish using Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 99188, and additional oral health care procedures may be on the horizon.
The American Medical Association this fall established a new Category III CPT code for the application of silver diamine fluoride to dental cavities.
Silver diamine fluoride is a newer product that was approved as a desensitizing agent by the Food and Drug Administration in 2014. It has antimicrobial and remineralizing properties, and researchers have found that it can stop the progression of early tooth decay and is more effective than fluoride varnish in preventing cavities.
Several dental groups supported the creation of this new code, which is expected to be made available by electronic health records vendors in July.
Some dentists have reservations, however. The Academy of General Dentistry in October expressed concerns that allowing “nondental health care workers to administer silver diamine fluoride is a temporary solution to a growing oral health crisis.”
Silver diamine fluoride may stop about 80% of cavities. Although the CPT code for silver diamine fluoride has been established, whether insurers will reimburse health care professionals for the service is another matter, said Richard Niederman, DMD, professor and chair of epidemiology and health promotion at New York University College of Dentistry.
Fatal consequences
Disparities in oral health in children may be greater than with almost any other disease process. The rate of caries in children who are poor is about twice that for children who are not poor, Dr. Fisher-Owens said. Disparities by race or ethnicity compound these differences.
In 2007, 12-year-old Deamonte Driver died after bacteria from a dental abscess spread to his brain. He had needed a tooth extraction, but his family lacked insurance and had had trouble finding dentists that accepted Medicaid near where they lived in Maryland.
After two emergency brain surgeries, 2 weeks in a hospital, and another 6 weeks in a hospital for rehabilitation, Deamonte died from the infection. The case sparked calls to fix the dental health system.
Physicians may notice more oral health problems in their patients, including dental abscesses, once they start looking for them, Dr. Fisher-Owens said.
She recalled one instance where a child with an underlying seizure disorder was hospitalized at an academic center because they appeared to be having more seizures.
“They eventually discharged the kid because they looked at all of the things related to seizures. None of them were there,” she said.
When Dr. Fisher-Owens saw the child for a discharge exam, she looked in the mouth and saw a whopping dental abscess.
“I realized that this kid wasn’t seizing but was actually rigoring in pain,” she said. No one else on the medical team had seen the true problem despite multiple examinations. The child started antibiotics, was referred to a dentist to have the abscess drained, and had a good outcome.
Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, adjunct clinical professor of pediatrics and community health at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., had noticed that many of her poorer patients had oral health problems, but many pediatric dentists were not able or willing to see them to provide treatment.
“Taking it one step further, you really want to prevent early childhood caries,” Dr. Boulter said. She started speaking up about oral health at pediatric meetings and became an early adopter of preventive interventions, including the use of fluoride varnish.
“Fluoride varnish is a sticky substance that has a very high concentration of fluoride in it,and it’s a very powerful reducer of oral childhood caries, by maybe 35%,” Dr. Boulter said.
Applying the varnish is fairly simple, but it had never been part of the well-child exam. Dr. Boulter started using it around 2005.
Initially, convincing other pediatricians to adopt this procedure – when visits are already time-constrained – was not always easy, she said.
Now that fluoride varnish is recommended for all children and is part of Bright Futures recommendations and is covered in the Affordable Care Act, “it became more the norm,” Dr. Boulter said. But there is room for improvement.
“There is still not a high enough percentage of pediatricians and family physicians who actually have incorporated application of fluoride varnish into their practice,” she said.
Brush, book, bed
Clinicians can take other steps to counsel parents about protecting their child’s teeth, like making sure that their teeth get brushed before bed, encouraging kids to drink tap water, especially if it’s fluoridated, and avoiding juice. The AAP has a program called Brush, Book, Bed to promote oral health, along with reading and good sleep habits.
Dr. Hoss noted that parents, and even dentists, may have misconceptions about optimal oral hygiene. “For example, you’re supposed to brush your teeth before breakfast, not after breakfast. But I’ve seen dentists even tell their patients, brush after breakfast,” he said.
In addition, people should brush gently but thoroughly using high-quality toothbrushes with soft bristles – “not scrubbing the teeth away with a coarse toothbrush,” he said.
Dr. Niederman has studied ways to prevent caries in underserved communities and is co-CEO of CariedAway, an organization that brings free cavity-prevention programs to schools.
In an average classroom of 24 students, about 6 children would be expected to have untreated tooth decay, Dr. Niederman said. And about 10% of the children with untreated tooth decay experience a toothache. So in two classrooms, at least one child would be expected to be experiencing pain, while the other students with caries might feel a lesser degree of discomfort. “That reduces presenteeism in the classroom and certainly presenteeism for the kid with a toothache,” Dr. Niederman said.
In communities with less access to dental care, including rural areas, the number of students with tooth decay might be double.
The new WHO report shows that the prevalence of caries in permanent teeth in various countries has remained at roughly 30%, regardless of a country’s income level, and despite efforts to bolster the dental workforce, said Dr. Niederman.
“The dental system is similar globally and focused on drilling and filling rather than prevention,” he said.
A 2019 Lancet series on oral health called for radical change in dental care, Dr. Niederman noted. “One of those radical changes would be primary care physicians or their offices participating in outreach programs to deliver care in schools,” he said.
Dr. Fisher-Owens is on a data and safety monitoring board for research by Colgate. Dr. Boulter serves on the editorial advisory board of Pediatric News. Dr. Hoss is the author of “If Your Mouth Could Talk” and the founder and CEO of SuperMouth, which markets children’s oral care products. Dr. Niederman’s research has used toothbrushes, toothpaste, and fluoride varnish donated by Colgate; silver diamine fluoride provided by Elevate Oral Health; and glass ionomer provided by GC America.