User login
Children and COVID: New cases increase for third straight week
There were almost 142,000 new cases reported during the week of Nov. 12-18, marking an increase of 16% over the previous week and the 15th straight week with a weekly total over 100,000, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said.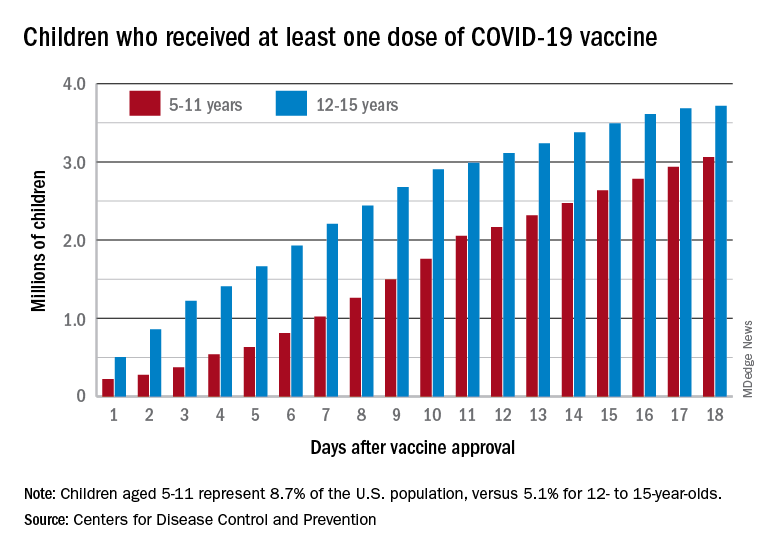
Regional data show that the Midwest has experienced the largest share of this latest surge, followed by the Northeast. Cases increased in the South during the week of Nov. 12-18 after holding steady over the previous 2 weeks, while new cases in the West dropped in the last week. At the state level, Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont again reported the largest percent increases, with Michigan, Minnesota, and New Mexico also above average, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show similar trends for both emergency department visits and hospital admissions, as both have risen in November after declines that began in late August and early September.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 6.77 million since the pandemic began, based on the AAP/CHA accounting of state cases, although Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer, suggesting the actual number is higher. The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 5.96 million, but there are age discrepancies between the CDC and the AAP/CHA’s state-based data.
The vaccine gap is closing
Vaccinations among the recently eligible 5- to 11-year-olds have steadily increased following a somewhat slow start. The initial pace was behind that of the 12- to 15-years-olds through the first postapproval week but has since closed the gap, based on data from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The tally of children who received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine among the 5- to 11-year-olds was behind the older group by almost 1.2 million on day 7 after the CDC’s Nov. 2 approval, but by day 18 the deficit was down to about 650,000, the CDC reported.
Altogether, just over 3 million children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, which is 10.7% of that age group’s total population. Among children aged 12-17, the proportions are 60.7% with at least one dose and 51.1% at full vaccination. Children aged 5-11, who make up 8.7% of the total U.S. population, represented 42.8% of all vaccinations initiated over the 2 weeks ending Nov. 21, compared with 4.2% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
There were almost 142,000 new cases reported during the week of Nov. 12-18, marking an increase of 16% over the previous week and the 15th straight week with a weekly total over 100,000, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said.
Regional data show that the Midwest has experienced the largest share of this latest surge, followed by the Northeast. Cases increased in the South during the week of Nov. 12-18 after holding steady over the previous 2 weeks, while new cases in the West dropped in the last week. At the state level, Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont again reported the largest percent increases, with Michigan, Minnesota, and New Mexico also above average, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show similar trends for both emergency department visits and hospital admissions, as both have risen in November after declines that began in late August and early September.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 6.77 million since the pandemic began, based on the AAP/CHA accounting of state cases, although Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer, suggesting the actual number is higher. The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 5.96 million, but there are age discrepancies between the CDC and the AAP/CHA’s state-based data.
The vaccine gap is closing
Vaccinations among the recently eligible 5- to 11-year-olds have steadily increased following a somewhat slow start. The initial pace was behind that of the 12- to 15-years-olds through the first postapproval week but has since closed the gap, based on data from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The tally of children who received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine among the 5- to 11-year-olds was behind the older group by almost 1.2 million on day 7 after the CDC’s Nov. 2 approval, but by day 18 the deficit was down to about 650,000, the CDC reported.
Altogether, just over 3 million children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, which is 10.7% of that age group’s total population. Among children aged 12-17, the proportions are 60.7% with at least one dose and 51.1% at full vaccination. Children aged 5-11, who make up 8.7% of the total U.S. population, represented 42.8% of all vaccinations initiated over the 2 weeks ending Nov. 21, compared with 4.2% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
There were almost 142,000 new cases reported during the week of Nov. 12-18, marking an increase of 16% over the previous week and the 15th straight week with a weekly total over 100,000, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said.
Regional data show that the Midwest has experienced the largest share of this latest surge, followed by the Northeast. Cases increased in the South during the week of Nov. 12-18 after holding steady over the previous 2 weeks, while new cases in the West dropped in the last week. At the state level, Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont again reported the largest percent increases, with Michigan, Minnesota, and New Mexico also above average, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention show similar trends for both emergency department visits and hospital admissions, as both have risen in November after declines that began in late August and early September.
The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 6.77 million since the pandemic began, based on the AAP/CHA accounting of state cases, although Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer, suggesting the actual number is higher. The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 5.96 million, but there are age discrepancies between the CDC and the AAP/CHA’s state-based data.
The vaccine gap is closing
Vaccinations among the recently eligible 5- to 11-year-olds have steadily increased following a somewhat slow start. The initial pace was behind that of the 12- to 15-years-olds through the first postapproval week but has since closed the gap, based on data from the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The tally of children who received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine among the 5- to 11-year-olds was behind the older group by almost 1.2 million on day 7 after the CDC’s Nov. 2 approval, but by day 18 the deficit was down to about 650,000, the CDC reported.
Altogether, just over 3 million children aged 5-11 have received at least one dose, which is 10.7% of that age group’s total population. Among children aged 12-17, the proportions are 60.7% with at least one dose and 51.1% at full vaccination. Children aged 5-11, who make up 8.7% of the total U.S. population, represented 42.8% of all vaccinations initiated over the 2 weeks ending Nov. 21, compared with 4.2% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said.
CDC: All adults should be eligible for Pfizer, Moderna boosters
on its vaccine recommendations.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, recommended that all adults be eligible for a third dose of a Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccine, at least 6 months after their second dose.
They also strengthened a recommendation that everyone over the age of 50 should get a third dose, whether or not they have an underlying health condition that may increase their risk from a COVID-19 infection.
The committee voted 11 to 0 in favor of both policies.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must now sign off on both policies, which she is expected to do.
More than 70 million adults are now eligible for booster shots in the United States, but only about 31 million people have received one. About half of those who have been boosted are over the age of 65.
In a recent survey, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that about 4 in 10 younger adults said they were unsure if they qualified for a booster.
Under the current policy, boosters are recommended for everyone age 65 and older. But people who are younger than age 65 are eligible for boosters if they have an underlying health condition or live or work in a high-risk situation—something individuals have to determine on their own. Experts said that shading of the policy had created confusion that was holding people back.
Nirav Shah, MD, JD, president of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, noted that public health officials have been swamped with calls from people who are trying to figure out if they are eligible to get a booster dose.
He said that in a call the evening of Nov. 18 with state health departments, “There was not a single state that voiced opposition to this move,” he told the ACIP.
Dr. Shah said that the current guidelines were well intentioned, but “in pursuit of precision, they create confusion.”
“Our concern is that eligible individuals are not receiving boosters right now as a result of this confusion,” he said.
The committee based its decision on the results of a new study of boosters in Pfizer vaccine recipients, as well as reassuring safety information that’s being collected through the CDC and FDA’s monitoring systems.
Pfizer presented the early results from a study of 10,000 people who had all received two doses of its vaccine. Half of the study participants received a third shot, or booster. The other half got a placebo.
The study is ongoing, but so far, six of the people in the booster group have gotten a COVID-19 infection with symptoms compared to 123 people who got COVID-19 in the placebo group, making boosters 95% effective at keeping people from getting sick. Most people in the study had gotten their original doses about 10 months earlier. They’ve been followed for about 10 weeks since their booster. Importantly, there were no study participants hospitalized for COVID-19 infections in either the placebo or booster group, indicating that the first two doses were still very effective at preventing severe outcomes from infection.
The majority of side effects after a third Pfizer dose were mild and temporary. Side effects like sore arms, swelling, fever, headache, and fatigue were more common in the booster group — affecting about 1 in 4 people who got a third shot. Vaccination side effects were less common after boosters than have been seen after the second dose of the vaccine.
Some cases of myocarditis and pericarditis have been reported after people received vaccine boosters, but the risk for this heart inflammation appears to be extremely low, about two cases for every million doses given. There were 54 cases of myocarditis reported so far to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS. So far, only 12 have met the case definition and are considered related to vaccination. Most of the reported cases are still being studied.
on its vaccine recommendations.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, recommended that all adults be eligible for a third dose of a Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccine, at least 6 months after their second dose.
They also strengthened a recommendation that everyone over the age of 50 should get a third dose, whether or not they have an underlying health condition that may increase their risk from a COVID-19 infection.
The committee voted 11 to 0 in favor of both policies.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must now sign off on both policies, which she is expected to do.
More than 70 million adults are now eligible for booster shots in the United States, but only about 31 million people have received one. About half of those who have been boosted are over the age of 65.
In a recent survey, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that about 4 in 10 younger adults said they were unsure if they qualified for a booster.
Under the current policy, boosters are recommended for everyone age 65 and older. But people who are younger than age 65 are eligible for boosters if they have an underlying health condition or live or work in a high-risk situation—something individuals have to determine on their own. Experts said that shading of the policy had created confusion that was holding people back.
Nirav Shah, MD, JD, president of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, noted that public health officials have been swamped with calls from people who are trying to figure out if they are eligible to get a booster dose.
He said that in a call the evening of Nov. 18 with state health departments, “There was not a single state that voiced opposition to this move,” he told the ACIP.
Dr. Shah said that the current guidelines were well intentioned, but “in pursuit of precision, they create confusion.”
“Our concern is that eligible individuals are not receiving boosters right now as a result of this confusion,” he said.
The committee based its decision on the results of a new study of boosters in Pfizer vaccine recipients, as well as reassuring safety information that’s being collected through the CDC and FDA’s monitoring systems.
Pfizer presented the early results from a study of 10,000 people who had all received two doses of its vaccine. Half of the study participants received a third shot, or booster. The other half got a placebo.
The study is ongoing, but so far, six of the people in the booster group have gotten a COVID-19 infection with symptoms compared to 123 people who got COVID-19 in the placebo group, making boosters 95% effective at keeping people from getting sick. Most people in the study had gotten their original doses about 10 months earlier. They’ve been followed for about 10 weeks since their booster. Importantly, there were no study participants hospitalized for COVID-19 infections in either the placebo or booster group, indicating that the first two doses were still very effective at preventing severe outcomes from infection.
The majority of side effects after a third Pfizer dose were mild and temporary. Side effects like sore arms, swelling, fever, headache, and fatigue were more common in the booster group — affecting about 1 in 4 people who got a third shot. Vaccination side effects were less common after boosters than have been seen after the second dose of the vaccine.
Some cases of myocarditis and pericarditis have been reported after people received vaccine boosters, but the risk for this heart inflammation appears to be extremely low, about two cases for every million doses given. There were 54 cases of myocarditis reported so far to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS. So far, only 12 have met the case definition and are considered related to vaccination. Most of the reported cases are still being studied.
on its vaccine recommendations.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, or ACIP, recommended that all adults be eligible for a third dose of a Pfizer or Moderna mRNA vaccine, at least 6 months after their second dose.
They also strengthened a recommendation that everyone over the age of 50 should get a third dose, whether or not they have an underlying health condition that may increase their risk from a COVID-19 infection.
The committee voted 11 to 0 in favor of both policies.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, must now sign off on both policies, which she is expected to do.
More than 70 million adults are now eligible for booster shots in the United States, but only about 31 million people have received one. About half of those who have been boosted are over the age of 65.
In a recent survey, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that about 4 in 10 younger adults said they were unsure if they qualified for a booster.
Under the current policy, boosters are recommended for everyone age 65 and older. But people who are younger than age 65 are eligible for boosters if they have an underlying health condition or live or work in a high-risk situation—something individuals have to determine on their own. Experts said that shading of the policy had created confusion that was holding people back.
Nirav Shah, MD, JD, president of the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials, noted that public health officials have been swamped with calls from people who are trying to figure out if they are eligible to get a booster dose.
He said that in a call the evening of Nov. 18 with state health departments, “There was not a single state that voiced opposition to this move,” he told the ACIP.
Dr. Shah said that the current guidelines were well intentioned, but “in pursuit of precision, they create confusion.”
“Our concern is that eligible individuals are not receiving boosters right now as a result of this confusion,” he said.
The committee based its decision on the results of a new study of boosters in Pfizer vaccine recipients, as well as reassuring safety information that’s being collected through the CDC and FDA’s monitoring systems.
Pfizer presented the early results from a study of 10,000 people who had all received two doses of its vaccine. Half of the study participants received a third shot, or booster. The other half got a placebo.
The study is ongoing, but so far, six of the people in the booster group have gotten a COVID-19 infection with symptoms compared to 123 people who got COVID-19 in the placebo group, making boosters 95% effective at keeping people from getting sick. Most people in the study had gotten their original doses about 10 months earlier. They’ve been followed for about 10 weeks since their booster. Importantly, there were no study participants hospitalized for COVID-19 infections in either the placebo or booster group, indicating that the first two doses were still very effective at preventing severe outcomes from infection.
The majority of side effects after a third Pfizer dose were mild and temporary. Side effects like sore arms, swelling, fever, headache, and fatigue were more common in the booster group — affecting about 1 in 4 people who got a third shot. Vaccination side effects were less common after boosters than have been seen after the second dose of the vaccine.
Some cases of myocarditis and pericarditis have been reported after people received vaccine boosters, but the risk for this heart inflammation appears to be extremely low, about two cases for every million doses given. There were 54 cases of myocarditis reported so far to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, or VAERS. So far, only 12 have met the case definition and are considered related to vaccination. Most of the reported cases are still being studied.
CDC: Thirty percent of hospital workers in U.S. still unvaccinated
, according to a new survey by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The snapshot in time – Jan. 20, 2021 to Sept. 15, 2021 – is based on voluntary weekly reports from hospitals. Only about 48% of the 5,085 hospitals in the U.S. Health and Human Services department’s Unified Hospital Data Surveillance System reported data on vaccination coverage during the period, and, after validation checks, the study included reports from 2,086 facilities, or just 41% of all hospitals, covering 3.35 million workers.
Overall, the number who were fully vaccinated rose from 36.1% in Jan. 2021 to 60.2% in April 2021, and then crept slowly up to 70% by Sept. 15, the CDC researchers reported in the American Journal of Infection Control.
The slowdown among hospital workers seems to mirror the same decline as in the general population.
Arjun Srinivasan, MD, associate director for health care–associated infection prevention programs at the CDC, said the decline in part may be the result of misinformation.
Health care personnel “are not fully immune from vaccine misinformation,” he said, adding that such misinformation “is contributing to decreased vaccine uptake among non–health care personnel.”
“The take-home message is that there is a lot of work to do in health care settings in order to get all of our health care personnel vaccinated,” Dr. Srinivasan told this news organization. “We need them to be vaccinated to protect themselves. It is also really important that we as health care personnel get vaccinated to protect our patients.”
Vaccine mandates
The analysis shows that workers were more likely to be vaccinated if they worked at a children’s hospital (77%), lived in metropolitan counties (71%), or worked in a hospital with lower cumulative admissions of COVID-19 patients, or lower cumulative COVID-19 cases.
The odds of being fully vaccinated were lower if the surrounding community had lower vaccination coverage. Workers in non-metropolitan counties (63.3%) and in rural counties (65.1%) were also less likely to be fully vaccinated, as well as those who were in critical access hospitals (64%) or long-term acute care hospitals (68.8%).
Surveys have shown that health care personnel who are vaccine-hesitant cited concerns they had about vaccine efficacy, adverse effects, the speed of vaccine development, and lack of full Food and Drug Administration approval, the study authors noted. In addition, many reported low trust in the government.
A Medscape survey this past April found that 25% of health care workers said they did not plan to be fully vaccinated. Some 40% of the 9,349 workers who responded said that employers should never require a COVID-19 vaccine for clinicians.
But the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is attempting to require all health care facilities that receive Medicare or Medicaid payment to vaccinate workers. All eligible staff must receive the first dose of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine or a one-dose vaccine by Dec. 6, and a second dose by Jan. 4, 2022. The policy allows exemptions based on recognized medical conditions or religious beliefs.
Some hospitals and health systems and various states and cities have already begun implementing vaccine mandates. Northwell Health in New York, for instance, lost 1,400 workers (evenly split between clinical and nonclinical staff), or 2% of its 77,000 employees, as a result of the state’s mandate.
Northwell’s workforce is now considered 100% vaccinated, a hospital spokesman said in an interview. In addition, “we have allowed for team members who changed their minds and presented proof of vaccination to return,” said the spokesman, adding that “a couple of hundred employees have done just that.”
Ten states sued the Biden administration recently, aiming to stop the health care worker vaccine mandate. Other challenges to vaccine mandates have generally been unsuccessful. The U.S. Supreme Court, for example, in October declined to hear a challenge to Maine’s mandate for health care workers, even though it did not allow religious exemptions, according to the Washington Post.
“The courts seem to agree that health care personnel are different, and could be subject to these mandates,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new survey by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The snapshot in time – Jan. 20, 2021 to Sept. 15, 2021 – is based on voluntary weekly reports from hospitals. Only about 48% of the 5,085 hospitals in the U.S. Health and Human Services department’s Unified Hospital Data Surveillance System reported data on vaccination coverage during the period, and, after validation checks, the study included reports from 2,086 facilities, or just 41% of all hospitals, covering 3.35 million workers.
Overall, the number who were fully vaccinated rose from 36.1% in Jan. 2021 to 60.2% in April 2021, and then crept slowly up to 70% by Sept. 15, the CDC researchers reported in the American Journal of Infection Control.
The slowdown among hospital workers seems to mirror the same decline as in the general population.
Arjun Srinivasan, MD, associate director for health care–associated infection prevention programs at the CDC, said the decline in part may be the result of misinformation.
Health care personnel “are not fully immune from vaccine misinformation,” he said, adding that such misinformation “is contributing to decreased vaccine uptake among non–health care personnel.”
“The take-home message is that there is a lot of work to do in health care settings in order to get all of our health care personnel vaccinated,” Dr. Srinivasan told this news organization. “We need them to be vaccinated to protect themselves. It is also really important that we as health care personnel get vaccinated to protect our patients.”
Vaccine mandates
The analysis shows that workers were more likely to be vaccinated if they worked at a children’s hospital (77%), lived in metropolitan counties (71%), or worked in a hospital with lower cumulative admissions of COVID-19 patients, or lower cumulative COVID-19 cases.
The odds of being fully vaccinated were lower if the surrounding community had lower vaccination coverage. Workers in non-metropolitan counties (63.3%) and in rural counties (65.1%) were also less likely to be fully vaccinated, as well as those who were in critical access hospitals (64%) or long-term acute care hospitals (68.8%).
Surveys have shown that health care personnel who are vaccine-hesitant cited concerns they had about vaccine efficacy, adverse effects, the speed of vaccine development, and lack of full Food and Drug Administration approval, the study authors noted. In addition, many reported low trust in the government.
A Medscape survey this past April found that 25% of health care workers said they did not plan to be fully vaccinated. Some 40% of the 9,349 workers who responded said that employers should never require a COVID-19 vaccine for clinicians.
But the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is attempting to require all health care facilities that receive Medicare or Medicaid payment to vaccinate workers. All eligible staff must receive the first dose of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine or a one-dose vaccine by Dec. 6, and a second dose by Jan. 4, 2022. The policy allows exemptions based on recognized medical conditions or religious beliefs.
Some hospitals and health systems and various states and cities have already begun implementing vaccine mandates. Northwell Health in New York, for instance, lost 1,400 workers (evenly split between clinical and nonclinical staff), or 2% of its 77,000 employees, as a result of the state’s mandate.
Northwell’s workforce is now considered 100% vaccinated, a hospital spokesman said in an interview. In addition, “we have allowed for team members who changed their minds and presented proof of vaccination to return,” said the spokesman, adding that “a couple of hundred employees have done just that.”
Ten states sued the Biden administration recently, aiming to stop the health care worker vaccine mandate. Other challenges to vaccine mandates have generally been unsuccessful. The U.S. Supreme Court, for example, in October declined to hear a challenge to Maine’s mandate for health care workers, even though it did not allow religious exemptions, according to the Washington Post.
“The courts seem to agree that health care personnel are different, and could be subject to these mandates,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new survey by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The snapshot in time – Jan. 20, 2021 to Sept. 15, 2021 – is based on voluntary weekly reports from hospitals. Only about 48% of the 5,085 hospitals in the U.S. Health and Human Services department’s Unified Hospital Data Surveillance System reported data on vaccination coverage during the period, and, after validation checks, the study included reports from 2,086 facilities, or just 41% of all hospitals, covering 3.35 million workers.
Overall, the number who were fully vaccinated rose from 36.1% in Jan. 2021 to 60.2% in April 2021, and then crept slowly up to 70% by Sept. 15, the CDC researchers reported in the American Journal of Infection Control.
The slowdown among hospital workers seems to mirror the same decline as in the general population.
Arjun Srinivasan, MD, associate director for health care–associated infection prevention programs at the CDC, said the decline in part may be the result of misinformation.
Health care personnel “are not fully immune from vaccine misinformation,” he said, adding that such misinformation “is contributing to decreased vaccine uptake among non–health care personnel.”
“The take-home message is that there is a lot of work to do in health care settings in order to get all of our health care personnel vaccinated,” Dr. Srinivasan told this news organization. “We need them to be vaccinated to protect themselves. It is also really important that we as health care personnel get vaccinated to protect our patients.”
Vaccine mandates
The analysis shows that workers were more likely to be vaccinated if they worked at a children’s hospital (77%), lived in metropolitan counties (71%), or worked in a hospital with lower cumulative admissions of COVID-19 patients, or lower cumulative COVID-19 cases.
The odds of being fully vaccinated were lower if the surrounding community had lower vaccination coverage. Workers in non-metropolitan counties (63.3%) and in rural counties (65.1%) were also less likely to be fully vaccinated, as well as those who were in critical access hospitals (64%) or long-term acute care hospitals (68.8%).
Surveys have shown that health care personnel who are vaccine-hesitant cited concerns they had about vaccine efficacy, adverse effects, the speed of vaccine development, and lack of full Food and Drug Administration approval, the study authors noted. In addition, many reported low trust in the government.
A Medscape survey this past April found that 25% of health care workers said they did not plan to be fully vaccinated. Some 40% of the 9,349 workers who responded said that employers should never require a COVID-19 vaccine for clinicians.
But the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services is attempting to require all health care facilities that receive Medicare or Medicaid payment to vaccinate workers. All eligible staff must receive the first dose of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine or a one-dose vaccine by Dec. 6, and a second dose by Jan. 4, 2022. The policy allows exemptions based on recognized medical conditions or religious beliefs.
Some hospitals and health systems and various states and cities have already begun implementing vaccine mandates. Northwell Health in New York, for instance, lost 1,400 workers (evenly split between clinical and nonclinical staff), or 2% of its 77,000 employees, as a result of the state’s mandate.
Northwell’s workforce is now considered 100% vaccinated, a hospital spokesman said in an interview. In addition, “we have allowed for team members who changed their minds and presented proof of vaccination to return,” said the spokesman, adding that “a couple of hundred employees have done just that.”
Ten states sued the Biden administration recently, aiming to stop the health care worker vaccine mandate. Other challenges to vaccine mandates have generally been unsuccessful. The U.S. Supreme Court, for example, in October declined to hear a challenge to Maine’s mandate for health care workers, even though it did not allow religious exemptions, according to the Washington Post.
“The courts seem to agree that health care personnel are different, and could be subject to these mandates,” said Dr. Srinivasan.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Youngest vaccinees off to a slower start

Specific figures for children aged 5-11 years are not yet available, but CDC data show that 1.55 million children under the age of 12 years had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Nov. 15, of whom almost 204,000 already had been vaccinated before Nov. 2. For children aged 12-15, the first 2 weeks after approval on May 12 produced almost 2.1 million vaccine initiations, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
That dataset reveals several other noteworthy differences between the two age groups in the 10 days after approval:
- There were over 7,000 vaccine initiations on the first day in the 12-15 group; the younger group had 32.
- The older children reached 100,000 per day in 3 days; the younger children took 8 days.
- The older group topped 200,000 vaccinations per day on six different days; the younger group didn’t get above 175,000.
Children under 12 made up 27.5% of vaccine initiations in all age groups during the 2 weeks from Nov. 2 to Nov. 15, versus 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.2% for 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said, while also reporting that 3.6% of children under age 12 had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, compared with 57.8% of those aged 12-15 and 64.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds.
Meanwhile, the first full week of November marked the second consecutive increase in the number of weekly child COVID cases, with 122,000 reported for Nov. 5-11. The number of new cases has now surpassed 100,000 for 14 consecutive weeks, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That report, which covers state health departments, has not included current information from Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas since the summer.
Regionally, the increases over the past 2 weeks were spread out among the East, the Midwest, and the West, while the decline that had been going on for several weeks in the South has largely come to a halt. The states with the highest percent increases over those 2 weeks are all in New England: Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, the AAP and CHA noted. In a separate report, the AAP said that Vermont has the second-highest child vaccination rate (81%) in the country, just behind Massachusetts (82%).

Specific figures for children aged 5-11 years are not yet available, but CDC data show that 1.55 million children under the age of 12 years had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Nov. 15, of whom almost 204,000 already had been vaccinated before Nov. 2. For children aged 12-15, the first 2 weeks after approval on May 12 produced almost 2.1 million vaccine initiations, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
That dataset reveals several other noteworthy differences between the two age groups in the 10 days after approval:
- There were over 7,000 vaccine initiations on the first day in the 12-15 group; the younger group had 32.
- The older children reached 100,000 per day in 3 days; the younger children took 8 days.
- The older group topped 200,000 vaccinations per day on six different days; the younger group didn’t get above 175,000.
Children under 12 made up 27.5% of vaccine initiations in all age groups during the 2 weeks from Nov. 2 to Nov. 15, versus 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.2% for 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said, while also reporting that 3.6% of children under age 12 had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, compared with 57.8% of those aged 12-15 and 64.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds.
Meanwhile, the first full week of November marked the second consecutive increase in the number of weekly child COVID cases, with 122,000 reported for Nov. 5-11. The number of new cases has now surpassed 100,000 for 14 consecutive weeks, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That report, which covers state health departments, has not included current information from Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas since the summer.
Regionally, the increases over the past 2 weeks were spread out among the East, the Midwest, and the West, while the decline that had been going on for several weeks in the South has largely come to a halt. The states with the highest percent increases over those 2 weeks are all in New England: Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, the AAP and CHA noted. In a separate report, the AAP said that Vermont has the second-highest child vaccination rate (81%) in the country, just behind Massachusetts (82%).

Specific figures for children aged 5-11 years are not yet available, but CDC data show that 1.55 million children under the age of 12 years had received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine as of Nov. 15, of whom almost 204,000 already had been vaccinated before Nov. 2. For children aged 12-15, the first 2 weeks after approval on May 12 produced almost 2.1 million vaccine initiations, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
That dataset reveals several other noteworthy differences between the two age groups in the 10 days after approval:
- There were over 7,000 vaccine initiations on the first day in the 12-15 group; the younger group had 32.
- The older children reached 100,000 per day in 3 days; the younger children took 8 days.
- The older group topped 200,000 vaccinations per day on six different days; the younger group didn’t get above 175,000.
Children under 12 made up 27.5% of vaccine initiations in all age groups during the 2 weeks from Nov. 2 to Nov. 15, versus 3.4% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.2% for 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said, while also reporting that 3.6% of children under age 12 had received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, compared with 57.8% of those aged 12-15 and 64.4% of 16- to 17-year-olds.
Meanwhile, the first full week of November marked the second consecutive increase in the number of weekly child COVID cases, with 122,000 reported for Nov. 5-11. The number of new cases has now surpassed 100,000 for 14 consecutive weeks, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report. That report, which covers state health departments, has not included current information from Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas since the summer.
Regionally, the increases over the past 2 weeks were spread out among the East, the Midwest, and the West, while the decline that had been going on for several weeks in the South has largely come to a halt. The states with the highest percent increases over those 2 weeks are all in New England: Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont, the AAP and CHA noted. In a separate report, the AAP said that Vermont has the second-highest child vaccination rate (81%) in the country, just behind Massachusetts (82%).
Children and COVID: New cases up again after dropping for 8 weeks
As children aged 5-11 years began to receive the first officially approved doses of COVID-19 vaccine, new pediatric cases increased after 8 consecutive weeks of declines, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Weekly cases peaked at almost 252,000 in early September and then dropped for 8 straight weeks before this latest rise, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report, which is based on data reported by 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.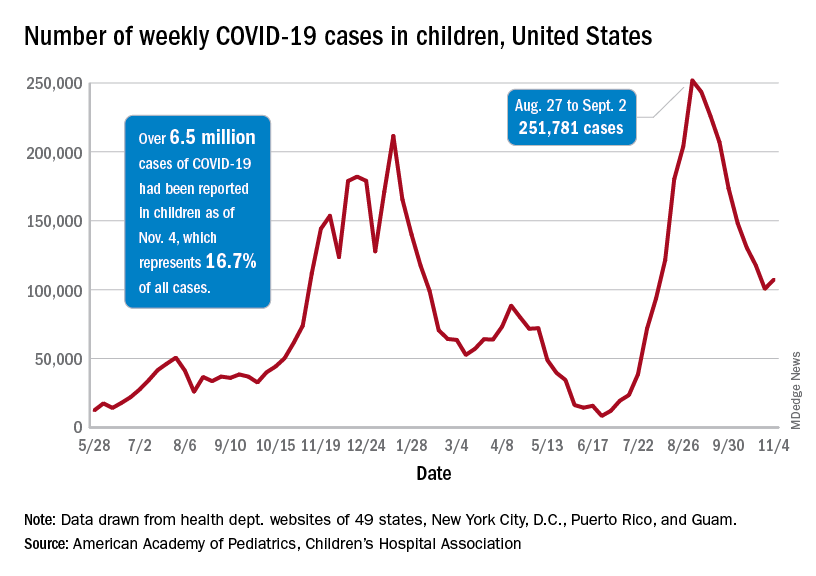
The end of that 8-week drop, unfortunately, allowed another streak to continue: New cases have been above 100,000 for 13 consecutive weeks, the AAP and CHA noted.
The cumulative COVID count in children as of Nov. 4 was 6.5 million, the AAP/CHA said, although that figure does not fully cover Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas, which stopped public reporting over the summer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, with input from all states and territories, puts the total through Nov. 8 at almost 5.7 million cases in children under 18 years of age, while most states define a child as someone aged 0-19 years.
As for the newest group of vaccinees, the CDC said that “updated vaccination data for 5-11 year-olds will be added to COVID Data Tracker later this week,” meaning the week of Nov. 7-13. Currently available data, however, show that almost 157,000 children under age 12 initiated vaccination in the 14 days ending Nov. 8, which was more than those aged 12-15 and 16-17 years combined (127,000).
Among those older groups, the CDC reports that 57.1% of 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose and 47.9% are fully vaccinated, while 64.0% of those aged 16-17 have gotten at least one dose and 55.2% are fully vaccinated. Altogether, about 13.9 million children under age 18 have gotten at least one dose and almost 11.6 million are fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
As children aged 5-11 years began to receive the first officially approved doses of COVID-19 vaccine, new pediatric cases increased after 8 consecutive weeks of declines, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Weekly cases peaked at almost 252,000 in early September and then dropped for 8 straight weeks before this latest rise, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report, which is based on data reported by 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The end of that 8-week drop, unfortunately, allowed another streak to continue: New cases have been above 100,000 for 13 consecutive weeks, the AAP and CHA noted.
The cumulative COVID count in children as of Nov. 4 was 6.5 million, the AAP/CHA said, although that figure does not fully cover Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas, which stopped public reporting over the summer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, with input from all states and territories, puts the total through Nov. 8 at almost 5.7 million cases in children under 18 years of age, while most states define a child as someone aged 0-19 years.
As for the newest group of vaccinees, the CDC said that “updated vaccination data for 5-11 year-olds will be added to COVID Data Tracker later this week,” meaning the week of Nov. 7-13. Currently available data, however, show that almost 157,000 children under age 12 initiated vaccination in the 14 days ending Nov. 8, which was more than those aged 12-15 and 16-17 years combined (127,000).
Among those older groups, the CDC reports that 57.1% of 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose and 47.9% are fully vaccinated, while 64.0% of those aged 16-17 have gotten at least one dose and 55.2% are fully vaccinated. Altogether, about 13.9 million children under age 18 have gotten at least one dose and almost 11.6 million are fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
As children aged 5-11 years began to receive the first officially approved doses of COVID-19 vaccine, new pediatric cases increased after 8 consecutive weeks of declines, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
Weekly cases peaked at almost 252,000 in early September and then dropped for 8 straight weeks before this latest rise, the AAP and the CHA said in their weekly COVID report, which is based on data reported by 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The end of that 8-week drop, unfortunately, allowed another streak to continue: New cases have been above 100,000 for 13 consecutive weeks, the AAP and CHA noted.
The cumulative COVID count in children as of Nov. 4 was 6.5 million, the AAP/CHA said, although that figure does not fully cover Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas, which stopped public reporting over the summer. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, with input from all states and territories, puts the total through Nov. 8 at almost 5.7 million cases in children under 18 years of age, while most states define a child as someone aged 0-19 years.
As for the newest group of vaccinees, the CDC said that “updated vaccination data for 5-11 year-olds will be added to COVID Data Tracker later this week,” meaning the week of Nov. 7-13. Currently available data, however, show that almost 157,000 children under age 12 initiated vaccination in the 14 days ending Nov. 8, which was more than those aged 12-15 and 16-17 years combined (127,000).
Among those older groups, the CDC reports that 57.1% of 12- to 15-year-olds have received at least one dose and 47.9% are fully vaccinated, while 64.0% of those aged 16-17 have gotten at least one dose and 55.2% are fully vaccinated. Altogether, about 13.9 million children under age 18 have gotten at least one dose and almost 11.6 million are fully vaccinated, according to the CDC.
CDC endorses Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for young kids
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.
– meaning the shots are now available for immediate use.
The Nov. 2 decision came mere hours after experts that advise the CDC on vaccinations strongly recommended the vaccine for this age group.
“Together, with science leading the charge, we have taken another important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus that causes COVID-19. We know millions of parents are eager to get their children vaccinated and with this decision, we now have recommended that about 28 million children receive a COVID-19 vaccine. As a mom, I encourage parents with questions to talk to their pediatrician, school nurse, or local pharmacist to learn more about the vaccine and the importance of getting their children vaccinated,” Dr. Walensky said in a prepared statement.
President Joe Biden applauded Dr. Walensky’s endorsement: “Today, we have reached a turning point in our battle against COVID-19: authorization of a safe, effective vaccine for children age 5 to 11. It will allow parents to end months of anxious worrying about their kids, and reduce the extent to which children spread the virus to others. It is a major step forward for our nation in our fight to defeat the virus,” he said in a statement.
The 14 members of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously earlier in the day to recommend the vaccine for kids.
“I feel like I have a responsibility to make this vaccine available to children and their parents,” said committee member Beth Bell, MD, MPH, a clinical professor at the University of Washington in Seattle. Bell noted that all evidence the committee had reviewed pointed to a vaccine that was safe and effective for younger children.
“If I had a grandchild, I would certainly get that grandchild vaccinated as soon as possible,” she said.
Their recommendations follow the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s emergency authorization of Pfizer-BioNTech’s vaccine for this same age group last week.
“I’m voting for this because I think it could have a huge positive impact on [kids’] health and their social and emotional wellbeing,” said Grace Lee, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Stanford University School of Medicine, who chairs the CDC’s ACIP.
She noted that, though masks are available to reduce the risk for kids, they aren’t perfect and transmission still occurs.
“Vaccines are really the only consistent and reliable way to provide that protection,” Lee said.
The vaccine for children is two doses given 3 weeks apart. Each dose is 10 micrograms, which is one-third of the dose used in adults and teens.
To avoid confusion, the smaller dose for kids will come in bottles with orange labels and orange tops. The vaccine for adults is packaged in purple.
The CDC also addressed the question of kids who are close to age 12 when they get their first dose.
In general, pediatricians allow for a 4-day grace period around birthdays to determine which dose is needed. That will be the same with the COVID-19 vaccine.
For kids who are 11 when they start the series, they should get another 10-microgram dose after they turn 12 a few weeks later.
COVID-19 cases in this age group have climbed sharply over the summer and into the fall as schools have fully reopened, sometimes without the benefit of masks.
In the first week of October, roughly 10% of all COVID-19 cases recorded in the United States were among children ages 5 through 11. Since the start of pandemic, about 1.9 million children in this age group have been infected, though that’s almost certainly an undercount. More than 8,300 have been hospitalized, and 94 children have died.
Children of color have been disproportionately impacted. More than two-thirds of hospitalized children have been black or Hispanic.
Weighing benefits and risks
In clinical trials that included more than 4,600 children, the most common adverse events were pain and swelling at the injection site. They could also have side effects like fevers, fatigue, headache, chills, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes.
These kinds of side effects appear to be less common in children ages 5 to 11 than they have been in teens and adults, and they were temporary.
No cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were seen in the studies, but myocarditis is a very rare side effect, and the studies were too small to pick up these cases.
Still, doctors say they’re watching for it. In general, the greatest risk for myocarditis after vaccination has been seen in younger males between the ages of 12 and 30.
Even without COVID-19 or vaccines in the mix, doctors expect to see as many as two cases of myocarditis for every million people over the course of a week. The risk for myocarditis jumps up to about 11 cases for every million doses of mRNA vaccine given to men ages 25 to 30. It’s between 37 and 69 cases per million doses in boys between the ages of 12 and 24.
Still, experts say the possibility of this rare risk shouldn’t deter parents from vaccinating younger children.
Here’s why: The risk for myocarditis is higher after COVID-19 infection than after vaccination. Younger children have a lower risk for myocarditis than teens and young adults, suggesting that this side effect may be less frequent in this age group, although that remains to be seen.
Additionally, the smaller dose authorized for children is expected to minimize the risk for myocarditis even further.
The CDC says parents should call their doctor if a child develops pain in their chest, has trouble breathing, or feels like they have a beating or fluttering heart after vaccination.
What about benefits?
Models looking at the impact of vaccines in this age group predict that, nationally, cases would drop by about 8% if children are vaccinated.
The models also suggested that vaccination of kids this age would slow — but not stop — the emergence of new variants.
For every million doses, the CDC’s modeling predicts that more than 56,000 COVID-19 infections would be prevented in this age group, along with dozens of hospitalizations, and post-COVID conditions like multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
CDC experts estimate that just 10 kids would need to be vaccinated over 6 months to prevent a single case of COVID-19.
The CDC pointed out that vaccinating kids may help slow transmission of the virus and would give parents and other caregivers greater confidence in participating in school and extracurricular activities.
CDC experts said they would use a variety of systems, including hospital networks, the open Vaccines and Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) database, the cell-phone based V-SAFE app, and insurance claims databases to keep an eye out for any rare adverse events related to the vaccines in children.
This article, a version of which first appeared on Medscape.com, was updated on Nov. 3, 2021.
Children and COVID: A look at the pace of vaccination
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?
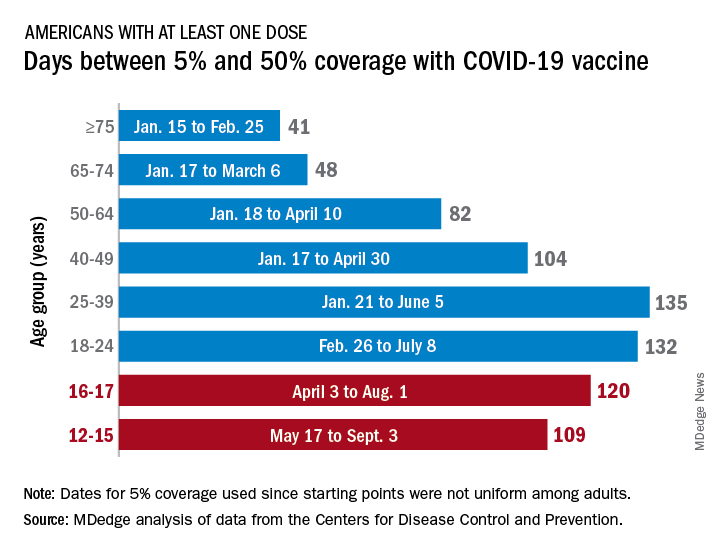
Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?

Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
With children aged 5-11 years about to enter the battle-of-the-COVID-vaccine phase of the war on COVID, there are many questions. MDedge takes a look at one: How long will it take to get 5- to 11-year-olds vaccinated?

Previous experience may provide some guidance. The vaccine was approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for the closest group in age, 12- to 15-year-olds, on May 12, 2021, and according to data from the CDC.
(Use of the 5% figure acknowledges the uneven start after approval – the vaccine became available to different age groups at different times, even though it had been approved for all adults aged 18 years and older.)
The 16- to 17-year-olds, despite being a smaller group of less than 7.6 million individuals, took 120 days to go from 5% to 50% coverage. For those aged 18-24 years, the corresponding time was 132 days, while the 24- to 36-year-olds took longer than any other age group, 135 days, to reach the 50%-with-at-least-one-dose milestone. The time, in turn, decreased for each group as age increased, with those aged 75 and older taking just 41 days to get at least one dose in 50% of individuals, the CDC data show.
That trend also applies to full vaccination, for the most part. The oldest group, 75 and older, had the shortest time to 50% being fully vaccinated at 69 days, and the 25- to 39-year-olds had the longest time at 206 days, with the length rising as age decreased and dropping for groups younger than 25-39. Except for the 12- to 15-year-olds. It has been 160 days (as of Nov. 2) since the 5% mark was reached on May 17, but only 47.4% of the group is fully vaccinated, making it unlikely that the 50% mark will be reached earlier than the 169 days it took the 16- to 17-year-olds.
So where does that put the 5- to 11-year-olds?
The White House said on Nov. 1 that vaccinations could start the first week of November, pending approval from the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, which meets on Nov. 2. “This is an important step forward in our nation’s fight against the virus,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator, said in a briefing. “As we await the CDC decision, we are not waiting on the operations and logistics. In fact, we’ve been preparing for weeks.”
Availability, of course, is not the only factor involved. In a survey conducted Oct. 14-24, the Kaiser Family Foundation found that only 27% of parents of children aged 5-11 years are planning to have them vaccinated against COVID-19 “right away” once the vaccine is available, and that 33% would “wait and see” how the vaccine works.
“Parents of 5-11 year-olds cite a range of concerns when it comes to vaccinating their children for COVID-19, with safety issues topping off the list,” and “two-thirds say they are concerned the vaccine may negatively impact their child’s fertility in the future,” Kaiser said.
COVID-19 vaccines provide 5 times the protection of natural immunity, CDC study says
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published recently in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The research team concluded that vaccination can provide a higher, stronger, and more consistent level of immunity against COVID-19 hospitalization than infection alone for at least six months.
“We now have additional evidence that reaffirms the importance of COVID-19 vaccines, even if you have had prior infection,” Rochelle Walensky, MD, director of the CDC, said in a statement.
“This study adds more to the body of knowledge demonstrating the protection of vaccines against severe disease from COVID-19,” she said. “The best way to stop COVID-19, including the emergence of variants, is with widespread COVID-19 vaccination and with disease prevention actions such as mask wearing, washing hands often, physical distancing and staying home when sick.”
Researchers looked at data from the VISION Network, which included more than 201,000 hospitalizations for COVID-like illness at 187 hospitals across nine states between Jan. 1 to Sept. 2. Among those, more than 94,000 had rapid testing for the coronavirus, and 7,300 had a lab-confirmed test for COVID-19.
The research team found that unvaccinated people with a prior infection within 3 to 6 months were about 5-1/2 times more likely to have laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated within 3 to 6 months with the Pfizer or Moderna shots. They found similar results when looking at the months that the Delta variant was the dominant strain of the coronavirus.
Protection from the Moderna vaccine “appeared to be higher” than for the Pfizer vaccine, the study authors wrote. The boost in protection also “trended higher” among older adults, as compared to those under age 65.
Importantly, the research team noted, these estimates may change over time as immunity wanes. Future studies should consider infection-induced and vaccine-induced immunity as time passes during the pandemic, they wrote.
Additional research is also needed for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, they wrote. Those who have received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are currently recommended to receive a booster shot at least two months after the first shot.
Overall, “all eligible persons should be vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible, including unvaccinated persons previously infected,” the research team concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA panel votes to approve Pfizer’s vaccine for children
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Seventeen of the 18 members of the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) on Oct. 26 voted to recommend the 10-microgram shot for kids, which is one-third the dose given to adults.
One member, Michael Kurilla, MD, director of the division of clinical innovation at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., abstained from voting.
If the FDA follows the recommendation, as it typically does, and issues an Emergency Use Authorization for the vaccine, the shots could be available within days.
After the FDA’s final decision, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet to make specific recommendations for its use. The CDC committee must stick closely to the conditions for use spelled out in the EUA, so their recommendations are likely to be similar to those made by the FDA. Their next meeting is scheduled for Nov. 2 and 3.
In the end, some on the panel felt uneasy with their decision.
“I voted yes primarily because I wanted to make sure that children who really need this vaccine, the Black and brown children of our country, get the vaccine,” said James Hildreth, MD, PhD, president and CEO of Meharry Medical College in Nashville.
“But to be honest, the best way to protect the health of some children will be to do nothing because they will be just fine,” he said.
Others said they were surprised by how difficult the decision had been.
“This is a much tougher one than we had expected going into it,” said committee member Eric Rubin, MD, editor and chief of the New England Journal of Medicine, during the FDA advisory committee’s meeting.
Ahead of the vote, the committee heard presentations outlining the expected benefits of vaccinating children along with potential risks.
“Children have been greatly impacted by the pandemic,” said Fiona Havers, MD, a medical officer with the CDC in Atlanta who reviewed the epidemiology of COVID-19 in kids.
In the second year of the pandemic, as more seniors have been vaccinated against the virus, COVID cases have largely shifted from older to younger age groups.
So far, there have been more than 1.9 million COVID-19 cases in children ages 5 through 11 in the United States.. Cases in kids saw a big jump in July and August with summer travel, schools reopening, and the dominance of the Delta variant.
And those are just the cases reported to the CDC. Regular testing of anonymous blood samples collected at sites across the United States indicates that 6 times as many kids have had COVID than what is reflected in official counts.
Last winter, blood sample testing showed about 13% of children had antibodies against the virus, suggesting they’d been infected. By this summer, that number had risen to 42%.
That figure clearly made an impression on many members of the committee who asked the FDA’s vaccine reviewers if they had tried to account for immunity from past infections in their modeling. They had not.
Some felt that even with a highly effective vaccine — new data presented by Pfizer showed the children’s dose was 90% effective at preventing symptomatic infections in kids — caution was warranted as much is still unknown about myocarditis, a rare side effect of the mRNA vaccines.
Myocarditis has been more common in younger age groups. It usually goes away over time but requires hospital care. It’s not known if myocarditis could have lingering effects for those who experience it.
There were no cases of myocarditis seen in Pfizer’s studies of the vaccine in children, and no other serious events were seen. Vaccine side effects reported in the Pfizer studies were mostly mild and included fatigue, headache, and pain at the injection site.
“We think we have optimized the immune response and minimized our reactions,” said William Gruber, MD, senior vice president vaccine research and clinical development at Pfizer.
But the studies didn’t include enough participants to pick up rare, but serious adverse events like myocarditis.
“We’re worried about a side effect that we can’t measure yet, but it’s probably real, and we see a benefit that isn’t the same as it is in older age groups,” said Dr. Rubin.
Benefits vs. risks
FDA modeled the benefits and risks for children under a variety of scenarios. The benefits of the vaccines to children very much depend on the amount of transmission in the community.
When transmission is high, the benefits to children — in terms of infections, hospitalizations, ICU admissions — clearly outweigh its risks.
But when COVID-19 rates are low in the community, as they were in June, FDA analysts predicted the vaccines might send more children to the hospital for myocarditis than the virus would.
The FDA noted that kids who are hospitalized for myocarditis tend not to be as ill as children with COVID-19, however.
“If the trends continue the way they are going, the emergency for children is not what we might think it would be. That was my concern,” Dr. Hildreth said.
But others warned against complacency.
“Thinking that this is going to be the end of the wave permanently may be a little overly optimistic,” said committee chairman Arnold Monto, MD, a professor of public health and epidemiology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The majority of COVID-19 cases in children are mild. Only about 1% of kids are hospitalized for their infections, according to CDC data. But the rates of hospitalizations in kids are about 3 times higher for people of color — including Blacks, Hispanics, and Native Americans, as compared to Whites and Asian Americans.
Since the start of the pandemic, 94 children ages 5 to 11 have died, making it the eighth leading cause of death for kids this age last year.
More than 5,200 children have developed a delayed complication from their infections called Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C).
MIS-C can be severe and require hospital care and can lead to myocarditis. Children ages 5 to 11 are the age group at greatest risk for this complication.
Kids can also get long COVID. There’s not a lot of data on how often this happens, though it appears to be less frequent in children than in adults.
But a survey in the United Kingdom found that 7%-8% of kids have symptoms from their infections that last longer than 12 weeks, Dr. Havers said. Symptoms that can linger for kids include fatigue, cough, muscle and joint pain, headaches, and insomnia.
More than 1 million children have been impacted by school closures so far this year, and quarantines have had lasting impacts on learning, social development, and mental health.
Even though kids aren’t usually COVID superspreaders, they can still pass the infection on to others.
“What is clear is that secondary transmission from children, both to other children and to adults, does occur,” Dr. Havers said.
For that reason, they can continue the spread of the virus and give it opportunities to mutate and become more dangerous.
Safety monitoring to continue
Some committee members referenced thousands of letters they had received within the past few days urging them to vote against the vaccine.
Jay Portnoy, MD, a professor of pediatrics at Children’s Mercy Hospital in Kansas City, Mo., said he had personally received about 4,000 emails.
“But I feel like I need to also represent the consumers, the parents that I see every day in the clinic who are terrified of sending their children to school because they’re not protected against COVID,” he said, explaining his vote to recommend authorization.
“Our kids are going to be dealing with this virus for many years to come. It’s going to come repeatedly. Getting this vaccine is just the first step that they can take to protect themselves from having bad outcomes,” Dr. Portnoy said.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, reminded members of the committee that there were several government surveillance systems in place to catch any potential safety issues in near real time.
“I really appreciate very much the concern here. The safety monitoring of this vaccine will continue,” Dr. Marks said. “I do view this as one of our greatest responsibilities.”
“I really am so grateful that we had this discussion and voted to approve,” said Capt. Amanda Cohn, MD, chief medical officer at the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
“I think the benefits in this age group really are super important even if they are lower than for other age groups.”
This article was updated 10/27/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves first nasal spray for dry eye
The first nasal spray to treat dry eye disease has won approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Sprayed twice daily into the nostrils, 0.03-mg varenicline solution (Tyrvaya) improves signs and symptoms of dry eye disease. It provides an alternative to the immunomodulators currently available as prescription treatments, according to Marian Macsai, MD, chief medical officer for the drug’s maker, Oyster Point Pharma.
“We’re super excited to bring a new treatment for dry eye disease to patients and eye care practitioners,” she told this news organization.
The company plans to make the drug available to wholesalers in November in cartons containing two multidose nasal spray bottles. Each bottle supplies treatment for 15 days. Samples will be made available to eye care practitioners.
The company is working with payers on reimbursement codes and will supply the drug for $10 or less to patients who are not insured, said Dr. Macsai.
Varenicline can be prescribed for anyone with dry eye disease who has not gotten relief from artificial tears or who needs to use artificial tears “more than three or four times a day,” she said.
“In our pivotal trials, we enrolled patients with mild, moderate, and severe disease,” said Dr. Macsai. “And in each subgroup, we reached statistical significance. So with this new route of administration and a new mechanism of action, I’m hopeful that this will provide relief to many of the dry eye patients out there that are currently suffering.”
The causes of dry eye disease are multifactorial, and it can prove difficult to treat. Varenicline appears to work by stimulating the trigeminal nerve, causing natural tears to form.
Marketed as the oral drug Chantix by Pfizer, varenicline is prescribed to reduce cigarette cravings. Administered as a nasal spray for dry eye, much less of it enters the bloodstream, according to Michael Raizman, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at Tufts University, Boston, who was an investigator in the phase 3 ONSET-2 trial of the drug.
The spray acts in as little as 14 days, rather than the 3-6 months required for prescription immunomodulators, and it doesn’t irritate the eyes, he said.
In the ONSET-2 trial, basal tear production and symptoms were assessed. Schirmer test scores increased by10 mm or more for 47% of the patients treated with varenicline vs. 28% of patients treated with placebo.
The mean change from baseline in Eye Dryness Score at week 4 was –10.3 mm for varenicline-treated patients, compared with –7.4 mm for vehicle-treated patients. The difference was not statistically significant. However, that test was disrupted by COVID-19 precautions, Dr. Macsai said. The phase 2b ONSET-1 trial showed a statistically significant advantage in Eye Dryness Score for patients treated with varenicline in comparison with those treated with placebo.
Almost everyone who took varenicline sneezed, but only about 12% experienced any ocular adverse events, which was similar to the placebo group. No one reported burning or stinging in the eyes.
A few patients coughed or felt throat or nose irritation. In the group that received 1.2 mg/mL, eight people discontinued the drug because of adverse reactions, compared with five in the group that received 0.6 mg/mL and four in the placebo group.
“This approval is exciting for the ophthalmic community, as it gives us a new therapeutic agent that can be used alone or in combination with existing therapies to treat individuals who fall under the umbrella term ‘dry eye,’ “ said Anat Galor, MD, MSPH, clinical spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology and associate professor at University of Miami.
Some idea of what to expect from Tyrvaya comes from TrueTear, a device made by Allergan that caused tearing by electrically stimulating the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the nasal passage. It provided benefit to some patients who had not gotten relief through medication, but was expensive and was eventually discontinued, Dr. Galor said.
A new device, the iTear100, from Olympic Ophthalmics, stimulates the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the side of the nose. It received FDA clearance last year.
ONSET-2 was funded by Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Macsai is an employee of Oyster Point. Dr. Raizman is a consultant to Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Galor reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first nasal spray to treat dry eye disease has won approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Sprayed twice daily into the nostrils, 0.03-mg varenicline solution (Tyrvaya) improves signs and symptoms of dry eye disease. It provides an alternative to the immunomodulators currently available as prescription treatments, according to Marian Macsai, MD, chief medical officer for the drug’s maker, Oyster Point Pharma.
“We’re super excited to bring a new treatment for dry eye disease to patients and eye care practitioners,” she told this news organization.
The company plans to make the drug available to wholesalers in November in cartons containing two multidose nasal spray bottles. Each bottle supplies treatment for 15 days. Samples will be made available to eye care practitioners.
The company is working with payers on reimbursement codes and will supply the drug for $10 or less to patients who are not insured, said Dr. Macsai.
Varenicline can be prescribed for anyone with dry eye disease who has not gotten relief from artificial tears or who needs to use artificial tears “more than three or four times a day,” she said.
“In our pivotal trials, we enrolled patients with mild, moderate, and severe disease,” said Dr. Macsai. “And in each subgroup, we reached statistical significance. So with this new route of administration and a new mechanism of action, I’m hopeful that this will provide relief to many of the dry eye patients out there that are currently suffering.”
The causes of dry eye disease are multifactorial, and it can prove difficult to treat. Varenicline appears to work by stimulating the trigeminal nerve, causing natural tears to form.
Marketed as the oral drug Chantix by Pfizer, varenicline is prescribed to reduce cigarette cravings. Administered as a nasal spray for dry eye, much less of it enters the bloodstream, according to Michael Raizman, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at Tufts University, Boston, who was an investigator in the phase 3 ONSET-2 trial of the drug.
The spray acts in as little as 14 days, rather than the 3-6 months required for prescription immunomodulators, and it doesn’t irritate the eyes, he said.
In the ONSET-2 trial, basal tear production and symptoms were assessed. Schirmer test scores increased by10 mm or more for 47% of the patients treated with varenicline vs. 28% of patients treated with placebo.
The mean change from baseline in Eye Dryness Score at week 4 was –10.3 mm for varenicline-treated patients, compared with –7.4 mm for vehicle-treated patients. The difference was not statistically significant. However, that test was disrupted by COVID-19 precautions, Dr. Macsai said. The phase 2b ONSET-1 trial showed a statistically significant advantage in Eye Dryness Score for patients treated with varenicline in comparison with those treated with placebo.
Almost everyone who took varenicline sneezed, but only about 12% experienced any ocular adverse events, which was similar to the placebo group. No one reported burning or stinging in the eyes.
A few patients coughed or felt throat or nose irritation. In the group that received 1.2 mg/mL, eight people discontinued the drug because of adverse reactions, compared with five in the group that received 0.6 mg/mL and four in the placebo group.
“This approval is exciting for the ophthalmic community, as it gives us a new therapeutic agent that can be used alone or in combination with existing therapies to treat individuals who fall under the umbrella term ‘dry eye,’ “ said Anat Galor, MD, MSPH, clinical spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology and associate professor at University of Miami.
Some idea of what to expect from Tyrvaya comes from TrueTear, a device made by Allergan that caused tearing by electrically stimulating the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the nasal passage. It provided benefit to some patients who had not gotten relief through medication, but was expensive and was eventually discontinued, Dr. Galor said.
A new device, the iTear100, from Olympic Ophthalmics, stimulates the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the side of the nose. It received FDA clearance last year.
ONSET-2 was funded by Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Macsai is an employee of Oyster Point. Dr. Raizman is a consultant to Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Galor reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first nasal spray to treat dry eye disease has won approval from the Food and Drug Administration.
Sprayed twice daily into the nostrils, 0.03-mg varenicline solution (Tyrvaya) improves signs and symptoms of dry eye disease. It provides an alternative to the immunomodulators currently available as prescription treatments, according to Marian Macsai, MD, chief medical officer for the drug’s maker, Oyster Point Pharma.
“We’re super excited to bring a new treatment for dry eye disease to patients and eye care practitioners,” she told this news organization.
The company plans to make the drug available to wholesalers in November in cartons containing two multidose nasal spray bottles. Each bottle supplies treatment for 15 days. Samples will be made available to eye care practitioners.
The company is working with payers on reimbursement codes and will supply the drug for $10 or less to patients who are not insured, said Dr. Macsai.
Varenicline can be prescribed for anyone with dry eye disease who has not gotten relief from artificial tears or who needs to use artificial tears “more than three or four times a day,” she said.
“In our pivotal trials, we enrolled patients with mild, moderate, and severe disease,” said Dr. Macsai. “And in each subgroup, we reached statistical significance. So with this new route of administration and a new mechanism of action, I’m hopeful that this will provide relief to many of the dry eye patients out there that are currently suffering.”
The causes of dry eye disease are multifactorial, and it can prove difficult to treat. Varenicline appears to work by stimulating the trigeminal nerve, causing natural tears to form.
Marketed as the oral drug Chantix by Pfizer, varenicline is prescribed to reduce cigarette cravings. Administered as a nasal spray for dry eye, much less of it enters the bloodstream, according to Michael Raizman, MD, an associate professor of ophthalmology at Tufts University, Boston, who was an investigator in the phase 3 ONSET-2 trial of the drug.
The spray acts in as little as 14 days, rather than the 3-6 months required for prescription immunomodulators, and it doesn’t irritate the eyes, he said.
In the ONSET-2 trial, basal tear production and symptoms were assessed. Schirmer test scores increased by10 mm or more for 47% of the patients treated with varenicline vs. 28% of patients treated with placebo.
The mean change from baseline in Eye Dryness Score at week 4 was –10.3 mm for varenicline-treated patients, compared with –7.4 mm for vehicle-treated patients. The difference was not statistically significant. However, that test was disrupted by COVID-19 precautions, Dr. Macsai said. The phase 2b ONSET-1 trial showed a statistically significant advantage in Eye Dryness Score for patients treated with varenicline in comparison with those treated with placebo.
Almost everyone who took varenicline sneezed, but only about 12% experienced any ocular adverse events, which was similar to the placebo group. No one reported burning or stinging in the eyes.
A few patients coughed or felt throat or nose irritation. In the group that received 1.2 mg/mL, eight people discontinued the drug because of adverse reactions, compared with five in the group that received 0.6 mg/mL and four in the placebo group.
“This approval is exciting for the ophthalmic community, as it gives us a new therapeutic agent that can be used alone or in combination with existing therapies to treat individuals who fall under the umbrella term ‘dry eye,’ “ said Anat Galor, MD, MSPH, clinical spokesperson for the American Academy of Ophthalmology and associate professor at University of Miami.
Some idea of what to expect from Tyrvaya comes from TrueTear, a device made by Allergan that caused tearing by electrically stimulating the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the nasal passage. It provided benefit to some patients who had not gotten relief through medication, but was expensive and was eventually discontinued, Dr. Galor said.
A new device, the iTear100, from Olympic Ophthalmics, stimulates the anterior ethmoidal nerve through the side of the nose. It received FDA clearance last year.
ONSET-2 was funded by Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Macsai is an employee of Oyster Point. Dr. Raizman is a consultant to Oyster Point Pharma. Dr. Galor reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.