User login
Children bearing the brunt of declining flu activity
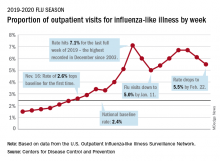
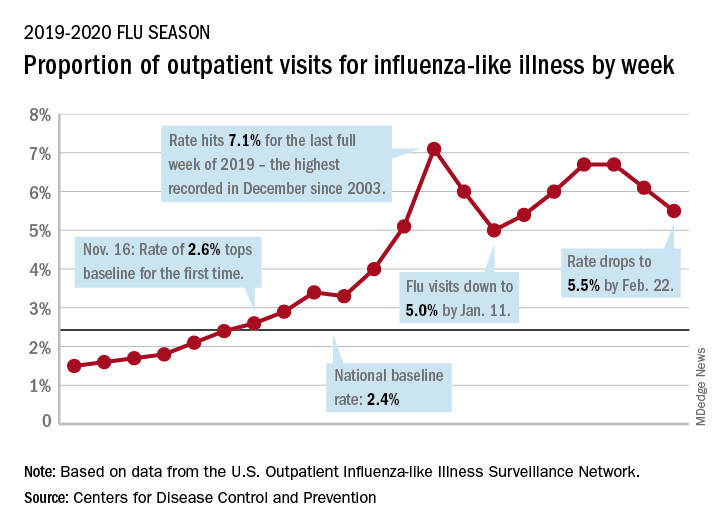
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
National flu activity decreased for the second consecutive week, but pediatric mortality is heading in the opposite direction, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Influenza-like illness (ILI) represented 5.5% of all visits to outpatient health care providers during the week ending Feb. 22, compared with 6.1% the previous week, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 28. The ILI visit rate had reached 6.6% in early February after dropping to 5.0% in mid-January, following a rise to a season-high 7.1% in the last week of December.
Another measure of ILI activity, the percentage of laboratory specimens testing positive, also declined for the second week in a row. The rate was 26.4% for the week ending Feb. 22, which is down from the season high of 30.3% reached 2 weeks before, the influenza division said.
ILI-related deaths among children, however, are not dropping. The total for 2019-2020 is now up to 125, and that “number is higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, except for the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC noted.
Hospitalization rates, which have been fairly typical in the general population, also are elevated for young adults and school-aged children, the agency said, and “rates among children 0-4 years old are now the highest CDC has on record at this point in the season, surpassing rates reported during the second wave of the 2009 H1N1 pandemic.”
FDA approves neratinib in combination for metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer
The Food and Drug Administration has approved neratinib (NERLYNX) in combination with capecitabine for use in adults with advanced or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who have received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The recommended dose for neratinib in this population is 240 mg once daily with food on days 1-21 of a 21-day cycle. Neratinib should be given with capecitabine at 750 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1-14 until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The full prescribing information for neratinib is available from the FDA website.
The FDA’s new approval of neratinib is based on results from the NALA trial (NCT01808573). The trial enrolled 621 patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who had received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The patients were randomized to neratinib plus capecitabine or lapatinib plus capecitabine and received treatment until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The objective response rate was 32.8% in the neratinib arm and 26.7% in the lapatinib arm. The median duration of response was 8.5 months and 5.6 months, respectively.
The median progression-free survival was 5.6 months in the neratinib arm and 5.5 months in the lapatinib arm (hazard ratio 0.76; P = .0059). The median overall survival was 21 months and 18.7 months, respectively (HR 0.88; P = .2086).
The most common grade 3/4 adverse events in the neratinib arm were diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and decreased appetite.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved neratinib (NERLYNX) in combination with capecitabine for use in adults with advanced or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who have received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The recommended dose for neratinib in this population is 240 mg once daily with food on days 1-21 of a 21-day cycle. Neratinib should be given with capecitabine at 750 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1-14 until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The full prescribing information for neratinib is available from the FDA website.
The FDA’s new approval of neratinib is based on results from the NALA trial (NCT01808573). The trial enrolled 621 patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who had received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The patients were randomized to neratinib plus capecitabine or lapatinib plus capecitabine and received treatment until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The objective response rate was 32.8% in the neratinib arm and 26.7% in the lapatinib arm. The median duration of response was 8.5 months and 5.6 months, respectively.
The median progression-free survival was 5.6 months in the neratinib arm and 5.5 months in the lapatinib arm (hazard ratio 0.76; P = .0059). The median overall survival was 21 months and 18.7 months, respectively (HR 0.88; P = .2086).
The most common grade 3/4 adverse events in the neratinib arm were diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and decreased appetite.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved neratinib (NERLYNX) in combination with capecitabine for use in adults with advanced or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who have received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The recommended dose for neratinib in this population is 240 mg once daily with food on days 1-21 of a 21-day cycle. Neratinib should be given with capecitabine at 750 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1-14 until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The full prescribing information for neratinib is available from the FDA website.
The FDA’s new approval of neratinib is based on results from the NALA trial (NCT01808573). The trial enrolled 621 patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer who had received at least two prior anti-HER2 based regimens in the metastatic setting.
The patients were randomized to neratinib plus capecitabine or lapatinib plus capecitabine and received treatment until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The objective response rate was 32.8% in the neratinib arm and 26.7% in the lapatinib arm. The median duration of response was 8.5 months and 5.6 months, respectively.
The median progression-free survival was 5.6 months in the neratinib arm and 5.5 months in the lapatinib arm (hazard ratio 0.76; P = .0059). The median overall survival was 21 months and 18.7 months, respectively (HR 0.88; P = .2086).
The most common grade 3/4 adverse events in the neratinib arm were diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and decreased appetite.
ACIP advocates pre-exposure Ebola vaccination for high-risk groups
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Vaccination against the Ebola virus is recommended for first responders, health care personnel, and laboratory workers deemed at high risk of exposure, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The committee voted unanimously to recommended pre-exposure vaccination with the rVSVdeltaG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine for adults aged 18 years and older who are at potential risk of exposure to the Ebola species Zaire ebolavirus because they fall into any of the following three categories:
- They are responding to an outbreak of Ebola virus disease.
- They are working as health care personnel at a federally designated Ebola Treatment Center in the United States.
- The are working in laboratories or are other staff members at biosafety-level 4 facilities in the United States.
Mary Choi, MD, of the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID) presented data on the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine and the work group considerations in recommending vaccination in the three target populations.
In clinical trials, the most commonly reported adverse events associated with the vaccine were arthritis and arthralgia, Dr. Choi said, but the duration of those cases was limited to months and did not persist long term.
Pre-exposure vaccination for health care personnel, laboratory workers, and support staff would provide an additional layer of protection, she explained, in addition to existing safeguards such as personal protective equipment and engineering controls at the facility. The work group’s research showed that most of the target population believed that the desirable effects of that protection outweigh potentially undesirable effects, Dr. Choi noted.
Some committee members expressed concerns about vaccination of pregnant women. But the recommendations are presented as “population based, not shared decision making,” said Sharon E. Frey, MD, of Saint Louis University in St. Louis, Missouri.
Several members noted that pregnant women should not be automatically included or excluded from vaccination if they fall into a high-risk population. And the committee agreed that additional guidance in the policy note will help assess risk and that organizations will determine the risk for their employees and whether to offer the vaccine.
The FDA approved the currently available U.S. vaccine for Ebola in 2019. Merck manufactures that vaccine.
The ACIP members had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
FDA okays first generic of ProAir HFA
Generic albuterol sulfate inhalation, from Perrigo Pharmaceutical, is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in people aged 4 years or older who have reversible obstructive airway disease, as well as for the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“Approval of the first generic drug product for one of the most commonly used rescue inhalers in the US is part of our long-standing commitment to advance patient access to lower-cost, high-quality generic drug products that are as safe and effective as their brand name counterparts, and to expand opportunities to bring generic copies of complex drugs to the market,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
Metered-dose inhalers are hard to duplicate because of the complexities of their formulation or mode of delivery. “As a result, too many complex drugs lack generic competition even after patents and exclusivities no longer block generic approval,” he explained.
“Supporting development and approval of generic copies of these complex medicines so that these products can get to patients has been a major focus of our efforts to improve competition and access and to lower drug prices. Getting more generic copies of complex drugs to the market is a key priority for how we’ll help bring new savings to consumers,” Hahn added.
In the United States, more than 26 million people suffer from asthma; about 7 million of these people are children.
Perrigo said it will immediately launch a limited quantity of generic albuterol sulfate and, in collaboration with its development and manufacturing partner, Catalent Pharma Solutions, is ramping up production to meet future demand.
The company “anticipates that we will be in a position to provide a steady supply of this product by the fourth quarter of 2020,” Perrigo Executive Vice President and Rx Pharmaceuticals President Sharon Kochan said in a statement.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Generic albuterol sulfate inhalation, from Perrigo Pharmaceutical, is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in people aged 4 years or older who have reversible obstructive airway disease, as well as for the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“Approval of the first generic drug product for one of the most commonly used rescue inhalers in the US is part of our long-standing commitment to advance patient access to lower-cost, high-quality generic drug products that are as safe and effective as their brand name counterparts, and to expand opportunities to bring generic copies of complex drugs to the market,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
Metered-dose inhalers are hard to duplicate because of the complexities of their formulation or mode of delivery. “As a result, too many complex drugs lack generic competition even after patents and exclusivities no longer block generic approval,” he explained.
“Supporting development and approval of generic copies of these complex medicines so that these products can get to patients has been a major focus of our efforts to improve competition and access and to lower drug prices. Getting more generic copies of complex drugs to the market is a key priority for how we’ll help bring new savings to consumers,” Hahn added.
In the United States, more than 26 million people suffer from asthma; about 7 million of these people are children.
Perrigo said it will immediately launch a limited quantity of generic albuterol sulfate and, in collaboration with its development and manufacturing partner, Catalent Pharma Solutions, is ramping up production to meet future demand.
The company “anticipates that we will be in a position to provide a steady supply of this product by the fourth quarter of 2020,” Perrigo Executive Vice President and Rx Pharmaceuticals President Sharon Kochan said in a statement.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Generic albuterol sulfate inhalation, from Perrigo Pharmaceutical, is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in people aged 4 years or older who have reversible obstructive airway disease, as well as for the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“Approval of the first generic drug product for one of the most commonly used rescue inhalers in the US is part of our long-standing commitment to advance patient access to lower-cost, high-quality generic drug products that are as safe and effective as their brand name counterparts, and to expand opportunities to bring generic copies of complex drugs to the market,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
Metered-dose inhalers are hard to duplicate because of the complexities of their formulation or mode of delivery. “As a result, too many complex drugs lack generic competition even after patents and exclusivities no longer block generic approval,” he explained.
“Supporting development and approval of generic copies of these complex medicines so that these products can get to patients has been a major focus of our efforts to improve competition and access and to lower drug prices. Getting more generic copies of complex drugs to the market is a key priority for how we’ll help bring new savings to consumers,” Hahn added.
In the United States, more than 26 million people suffer from asthma; about 7 million of these people are children.
Perrigo said it will immediately launch a limited quantity of generic albuterol sulfate and, in collaboration with its development and manufacturing partner, Catalent Pharma Solutions, is ramping up production to meet future demand.
The company “anticipates that we will be in a position to provide a steady supply of this product by the fourth quarter of 2020,” Perrigo Executive Vice President and Rx Pharmaceuticals President Sharon Kochan said in a statement.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC expects eventual community spread of coronavirus in U.S.
“We have for many weeks been saying that, while we hope this is not going to be severe, we are planning as if it is,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the CDC, said during a Feb. 25, 2020, telebriefing with reporters. “The data over the last week and the spread in other countries has certainly raised our level of concern and raised our level expectation that we are going to have community spread here.”
Dr. Messonnier noted that the coronavirus is now showing signs of community spread without a known source of exposure in a number of countries, including in Hong Kong, Iran, Italy, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand. This has now raised the belief that there will be more widespread outbreaks in the United States.
“What we still don’t know is what that will look like,” she said. “As many of you know, we can have community spread in the United States and have it be reasonably mild. We can have community spread in the U.S. and have it be very severe. That is what we don’t completely know yet and we certainly also don’t exactly know when it is going to happen.”
She reiterated the number of actions being taken to slow the potential spread in the United States, including detecting, tracking, and isolating all cases, as well as restricting travel into the United States and issuing travel advisories for countries where coronavirus outbreaks are known.
“We are doing this with the goal of slowing the introduction of this new virus into the U.S. and buying us more time to prepare,” Dr. Messonnier said, noting the containment strategies have been largely successful, though it will be more difficult as more countries experience community spread of the virus.
Dr. Messonnier also reiterated that at this time there are no vaccines and no medicines to treat the coronavirus. She stressed the need to adhere to nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs), as they will be “the most important tools in our response to this virus.”
She said the NPIs will vary based on the severity of the outbreak in any given local community and include personal protective measures that individuals can take every day (many of which mirror the recommendations for preventing the spread of the seasonal flu virus), community NPIs that involve social distancing measures designed to keep people away from others, and environmental NPIs such as surface cleaning measures.
CDC’s latest warning comes as parent agency the Department of Health & Human Services is seeking $2.5 billion in funds from Congress to address the coronavirus outbreak.
During a separate press conference on the same day, HHS Secretary Alex Azar noted that there are five major priorities related to those funds, which would be used in the current year, including expansion of surveillance work within the influenza surveillance network; supporting public health preparedness and response for state and local governments; support the development of therapeutics and the development of vaccines; and the purchase of personal protective equipment for national stockpiles.
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health, added during the press conference that vaccine work is in progress and could be ready for phase 1 testing within a month and a half. If all goes well, it would still be at least 12 - 18 months following the completion of a phase 2 trial before it could be produced for mass consumption.
“It is certainly conceivable that this issue with this coronavirus will go well beyond this season into next season,” Dr. Fauci said. “So a vaccine may not solve the problems of the next couple of months, but it certainly would be an important tool that we would have and we will keep you posted on that.”
He also mentioned that NIAID is looking at a number of candidates for therapeutic treatment of coronavirus. He highlighted Gilead’s remdesivir, a nucleotide analog, as one which undergoing two trials – a randomized controlled trial in China and a copy of that trial in Nebraska among patients with the coronavirus who were taken from the Diamond Princess cruise line in Japan.
“I am optimistic that we will at least get an answer if we do have do have a therapy that really is a gamechanger because then we could do something from the standpoint of intervention for those who are sick,” Dr. Fauci said.
UPDATE: This story was updated 2/25 at 4:51 p.m. ET
“We have for many weeks been saying that, while we hope this is not going to be severe, we are planning as if it is,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the CDC, said during a Feb. 25, 2020, telebriefing with reporters. “The data over the last week and the spread in other countries has certainly raised our level of concern and raised our level expectation that we are going to have community spread here.”
Dr. Messonnier noted that the coronavirus is now showing signs of community spread without a known source of exposure in a number of countries, including in Hong Kong, Iran, Italy, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand. This has now raised the belief that there will be more widespread outbreaks in the United States.
“What we still don’t know is what that will look like,” she said. “As many of you know, we can have community spread in the United States and have it be reasonably mild. We can have community spread in the U.S. and have it be very severe. That is what we don’t completely know yet and we certainly also don’t exactly know when it is going to happen.”
She reiterated the number of actions being taken to slow the potential spread in the United States, including detecting, tracking, and isolating all cases, as well as restricting travel into the United States and issuing travel advisories for countries where coronavirus outbreaks are known.
“We are doing this with the goal of slowing the introduction of this new virus into the U.S. and buying us more time to prepare,” Dr. Messonnier said, noting the containment strategies have been largely successful, though it will be more difficult as more countries experience community spread of the virus.
Dr. Messonnier also reiterated that at this time there are no vaccines and no medicines to treat the coronavirus. She stressed the need to adhere to nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs), as they will be “the most important tools in our response to this virus.”
She said the NPIs will vary based on the severity of the outbreak in any given local community and include personal protective measures that individuals can take every day (many of which mirror the recommendations for preventing the spread of the seasonal flu virus), community NPIs that involve social distancing measures designed to keep people away from others, and environmental NPIs such as surface cleaning measures.
CDC’s latest warning comes as parent agency the Department of Health & Human Services is seeking $2.5 billion in funds from Congress to address the coronavirus outbreak.
During a separate press conference on the same day, HHS Secretary Alex Azar noted that there are five major priorities related to those funds, which would be used in the current year, including expansion of surveillance work within the influenza surveillance network; supporting public health preparedness and response for state and local governments; support the development of therapeutics and the development of vaccines; and the purchase of personal protective equipment for national stockpiles.
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health, added during the press conference that vaccine work is in progress and could be ready for phase 1 testing within a month and a half. If all goes well, it would still be at least 12 - 18 months following the completion of a phase 2 trial before it could be produced for mass consumption.
“It is certainly conceivable that this issue with this coronavirus will go well beyond this season into next season,” Dr. Fauci said. “So a vaccine may not solve the problems of the next couple of months, but it certainly would be an important tool that we would have and we will keep you posted on that.”
He also mentioned that NIAID is looking at a number of candidates for therapeutic treatment of coronavirus. He highlighted Gilead’s remdesivir, a nucleotide analog, as one which undergoing two trials – a randomized controlled trial in China and a copy of that trial in Nebraska among patients with the coronavirus who were taken from the Diamond Princess cruise line in Japan.
“I am optimistic that we will at least get an answer if we do have do have a therapy that really is a gamechanger because then we could do something from the standpoint of intervention for those who are sick,” Dr. Fauci said.
UPDATE: This story was updated 2/25 at 4:51 p.m. ET
“We have for many weeks been saying that, while we hope this is not going to be severe, we are planning as if it is,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases at the CDC, said during a Feb. 25, 2020, telebriefing with reporters. “The data over the last week and the spread in other countries has certainly raised our level of concern and raised our level expectation that we are going to have community spread here.”
Dr. Messonnier noted that the coronavirus is now showing signs of community spread without a known source of exposure in a number of countries, including in Hong Kong, Iran, Italy, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand. This has now raised the belief that there will be more widespread outbreaks in the United States.
“What we still don’t know is what that will look like,” she said. “As many of you know, we can have community spread in the United States and have it be reasonably mild. We can have community spread in the U.S. and have it be very severe. That is what we don’t completely know yet and we certainly also don’t exactly know when it is going to happen.”
She reiterated the number of actions being taken to slow the potential spread in the United States, including detecting, tracking, and isolating all cases, as well as restricting travel into the United States and issuing travel advisories for countries where coronavirus outbreaks are known.
“We are doing this with the goal of slowing the introduction of this new virus into the U.S. and buying us more time to prepare,” Dr. Messonnier said, noting the containment strategies have been largely successful, though it will be more difficult as more countries experience community spread of the virus.
Dr. Messonnier also reiterated that at this time there are no vaccines and no medicines to treat the coronavirus. She stressed the need to adhere to nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs), as they will be “the most important tools in our response to this virus.”
She said the NPIs will vary based on the severity of the outbreak in any given local community and include personal protective measures that individuals can take every day (many of which mirror the recommendations for preventing the spread of the seasonal flu virus), community NPIs that involve social distancing measures designed to keep people away from others, and environmental NPIs such as surface cleaning measures.
CDC’s latest warning comes as parent agency the Department of Health & Human Services is seeking $2.5 billion in funds from Congress to address the coronavirus outbreak.
During a separate press conference on the same day, HHS Secretary Alex Azar noted that there are five major priorities related to those funds, which would be used in the current year, including expansion of surveillance work within the influenza surveillance network; supporting public health preparedness and response for state and local governments; support the development of therapeutics and the development of vaccines; and the purchase of personal protective equipment for national stockpiles.
Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health, added during the press conference that vaccine work is in progress and could be ready for phase 1 testing within a month and a half. If all goes well, it would still be at least 12 - 18 months following the completion of a phase 2 trial before it could be produced for mass consumption.
“It is certainly conceivable that this issue with this coronavirus will go well beyond this season into next season,” Dr. Fauci said. “So a vaccine may not solve the problems of the next couple of months, but it certainly would be an important tool that we would have and we will keep you posted on that.”
He also mentioned that NIAID is looking at a number of candidates for therapeutic treatment of coronavirus. He highlighted Gilead’s remdesivir, a nucleotide analog, as one which undergoing two trials – a randomized controlled trial in China and a copy of that trial in Nebraska among patients with the coronavirus who were taken from the Diamond Princess cruise line in Japan.
“I am optimistic that we will at least get an answer if we do have do have a therapy that really is a gamechanger because then we could do something from the standpoint of intervention for those who are sick,” Dr. Fauci said.
UPDATE: This story was updated 2/25 at 4:51 p.m. ET
China’s health authorities release large coronavirus case series
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention has released the largest case series to date for novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), and a summary of key findings appears in JAMA.
- The virus, which spread from a single city to a whole country in only 30 days, has so far has caused over 72,314 cases as of Feb. 11, 2020, and 1,023 fatalities (2.3%) overall.
- The age distribution shows that most of the cases (87%) occurred in patients aged 30-79 years, while 10% were in patients 29 years and younger and 3% at 80 years and older.
- Following the SARS outbreak in 2002-2003, the Chinese government adjusted its epidemic response protocol. For example, according to the summary, while there were 300 cases and 5 deaths with SARS before the Chinese government reported it to the World Health Organization, there were only 27 cases and no deaths with COVID-19 before it was reported to that agency.
- A major goal, the authors wrote, is to buy enough time for scientific research, hopefully before the disease has become too widespread.
The summary argues that, while some measures the Chinese government has taken could be seen as extreme, the overall benefits and lives saved outweigh the potential infringement on civil liberties. It also suggests that countries need to work together in situations like this because disease pathogens do not respect geopolitical borders.
SOURCE: Wu Z, McGoogan JM. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention has released the largest case series to date for novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), and a summary of key findings appears in JAMA.
- The virus, which spread from a single city to a whole country in only 30 days, has so far has caused over 72,314 cases as of Feb. 11, 2020, and 1,023 fatalities (2.3%) overall.
- The age distribution shows that most of the cases (87%) occurred in patients aged 30-79 years, while 10% were in patients 29 years and younger and 3% at 80 years and older.
- Following the SARS outbreak in 2002-2003, the Chinese government adjusted its epidemic response protocol. For example, according to the summary, while there were 300 cases and 5 deaths with SARS before the Chinese government reported it to the World Health Organization, there were only 27 cases and no deaths with COVID-19 before it was reported to that agency.
- A major goal, the authors wrote, is to buy enough time for scientific research, hopefully before the disease has become too widespread.
The summary argues that, while some measures the Chinese government has taken could be seen as extreme, the overall benefits and lives saved outweigh the potential infringement on civil liberties. It also suggests that countries need to work together in situations like this because disease pathogens do not respect geopolitical borders.
SOURCE: Wu Z, McGoogan JM. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention has released the largest case series to date for novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), and a summary of key findings appears in JAMA.
- The virus, which spread from a single city to a whole country in only 30 days, has so far has caused over 72,314 cases as of Feb. 11, 2020, and 1,023 fatalities (2.3%) overall.
- The age distribution shows that most of the cases (87%) occurred in patients aged 30-79 years, while 10% were in patients 29 years and younger and 3% at 80 years and older.
- Following the SARS outbreak in 2002-2003, the Chinese government adjusted its epidemic response protocol. For example, according to the summary, while there were 300 cases and 5 deaths with SARS before the Chinese government reported it to the World Health Organization, there were only 27 cases and no deaths with COVID-19 before it was reported to that agency.
- A major goal, the authors wrote, is to buy enough time for scientific research, hopefully before the disease has become too widespread.
The summary argues that, while some measures the Chinese government has taken could be seen as extreme, the overall benefits and lives saved outweigh the potential infringement on civil liberties. It also suggests that countries need to work together in situations like this because disease pathogens do not respect geopolitical borders.
SOURCE: Wu Z, McGoogan JM. JAMA. 2020 Feb 24. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648.
FROM JAMA
FDA, FTC uniting to promote biosimilars
The Food and Drug Administration is collaborating with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to expand the biosimilars market.
The two agencies signed a joint statement on Feb. 3, 2020, outlining four sets of goals aimed at creating meaningful competition from biosimilars against their reference biologic products.
“Competition is key for helping American patients have access to affordable medicines,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “Strengthening efforts to curtail and discourage anticompetitive behavior is key for facilitating robust competition for patients in the biologics marketplace, including through biosimilars, bringing down the costs of these crucial products for patients.”
“We appreciate and applaud the FDA and FTC in recognizing that biosimilar development and approval has not been as robust as many stakeholders had hoped,” said Colin Edgerton, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “We continue to see anticompetitive activities that prevent manufacturers from developing biosimilar products. We hope that a greater focus on these practices will pave the way for more biosimilars to be developed.”
The statement highlighted four goals. First is that the agencies will coordinate to promote greater competition in the biologic market, including the development of materials to educate the market about biosimilars. The FDA and FTC also will be sponsoring a public workshop on March 9 to discuss competition for biologics.
“This workshop is the first step,” Dr. Edgerton said. “ACR will continue to work with other organizations and patient groups to help educate providers and patients on the scientific rigor that is required in developing and approving biosimilars. Additionally, we look forward to working with the FDA and FTC to continue this conversation on ways to encourage more development of biosimilar products and greater education for the providers and patients.”
The second goal has the FDA and FTC working together “to deter behavior that impedes access to samples needed for the development of biologics, including biosimilars,” the joint statement notes.
Third, the agencies will crack down on “false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars, within their respective authorities,” according to the joint statement.
“FDA and FTC, as authorized by their respective statutes, will work together to address false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars,” the statement continues. “In particular, if a communication makes a false or misleading comparison between a reference product and a biosimilar in a manner that misrepresents the safety or efficacy of biosimilars, deceives consumers, or deters competition, FDA and FTC intend to take appropriate action within their respective authorities. FDA intends to take appropriate action to address such communications where those communications have the potential to impact public health.”
Finally, the FTC committed to review patent settlement agreements involving biologics, including biosimilars, for antitrust violations.
Dr. Edgerton highlighted why this agreement between the two agencies is so important.
“Biologics are life-changing treatments for many of our patients,” he said. “Due to the high cost of discovery and development, the cost of biologics has resulted in delayed access and financial hardships for so many. It has always been our hope that biosimilars would offer the same life-changing treatment for patients at a lower price point. A robust biosimilars market is imperative to allow greater access to these treatments that can help patients to have a better quality of life.”
Separately, the FDA issued a draft guidance document for comment on manufacturers seeking licensure of biosimilar products that do not cover all the approved uses of the reference product, as well as how to add uses over time that were not part of the initial license of the biosimilar product. The draft guidance covers licensure of products, labeling of biosimilars with fewer indications than the reference product, supplemental applications for indications not on the initial biosimilar application but covered by the reference product, and the timing of applications.
The FDA notes in the draft guidance that this is needed to cover situations such as when some indications on the reference product are covered by exclusivity, although it does encourage a biosimilar manufacturer to seek licensure for all indications that the reference product does have.
The Food and Drug Administration is collaborating with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to expand the biosimilars market.
The two agencies signed a joint statement on Feb. 3, 2020, outlining four sets of goals aimed at creating meaningful competition from biosimilars against their reference biologic products.
“Competition is key for helping American patients have access to affordable medicines,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “Strengthening efforts to curtail and discourage anticompetitive behavior is key for facilitating robust competition for patients in the biologics marketplace, including through biosimilars, bringing down the costs of these crucial products for patients.”
“We appreciate and applaud the FDA and FTC in recognizing that biosimilar development and approval has not been as robust as many stakeholders had hoped,” said Colin Edgerton, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “We continue to see anticompetitive activities that prevent manufacturers from developing biosimilar products. We hope that a greater focus on these practices will pave the way for more biosimilars to be developed.”
The statement highlighted four goals. First is that the agencies will coordinate to promote greater competition in the biologic market, including the development of materials to educate the market about biosimilars. The FDA and FTC also will be sponsoring a public workshop on March 9 to discuss competition for biologics.
“This workshop is the first step,” Dr. Edgerton said. “ACR will continue to work with other organizations and patient groups to help educate providers and patients on the scientific rigor that is required in developing and approving biosimilars. Additionally, we look forward to working with the FDA and FTC to continue this conversation on ways to encourage more development of biosimilar products and greater education for the providers and patients.”
The second goal has the FDA and FTC working together “to deter behavior that impedes access to samples needed for the development of biologics, including biosimilars,” the joint statement notes.
Third, the agencies will crack down on “false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars, within their respective authorities,” according to the joint statement.
“FDA and FTC, as authorized by their respective statutes, will work together to address false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars,” the statement continues. “In particular, if a communication makes a false or misleading comparison between a reference product and a biosimilar in a manner that misrepresents the safety or efficacy of biosimilars, deceives consumers, or deters competition, FDA and FTC intend to take appropriate action within their respective authorities. FDA intends to take appropriate action to address such communications where those communications have the potential to impact public health.”
Finally, the FTC committed to review patent settlement agreements involving biologics, including biosimilars, for antitrust violations.
Dr. Edgerton highlighted why this agreement between the two agencies is so important.
“Biologics are life-changing treatments for many of our patients,” he said. “Due to the high cost of discovery and development, the cost of biologics has resulted in delayed access and financial hardships for so many. It has always been our hope that biosimilars would offer the same life-changing treatment for patients at a lower price point. A robust biosimilars market is imperative to allow greater access to these treatments that can help patients to have a better quality of life.”
Separately, the FDA issued a draft guidance document for comment on manufacturers seeking licensure of biosimilar products that do not cover all the approved uses of the reference product, as well as how to add uses over time that were not part of the initial license of the biosimilar product. The draft guidance covers licensure of products, labeling of biosimilars with fewer indications than the reference product, supplemental applications for indications not on the initial biosimilar application but covered by the reference product, and the timing of applications.
The FDA notes in the draft guidance that this is needed to cover situations such as when some indications on the reference product are covered by exclusivity, although it does encourage a biosimilar manufacturer to seek licensure for all indications that the reference product does have.
The Food and Drug Administration is collaborating with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to expand the biosimilars market.
The two agencies signed a joint statement on Feb. 3, 2020, outlining four sets of goals aimed at creating meaningful competition from biosimilars against their reference biologic products.
“Competition is key for helping American patients have access to affordable medicines,” FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, MD, said in a statement. “Strengthening efforts to curtail and discourage anticompetitive behavior is key for facilitating robust competition for patients in the biologics marketplace, including through biosimilars, bringing down the costs of these crucial products for patients.”
“We appreciate and applaud the FDA and FTC in recognizing that biosimilar development and approval has not been as robust as many stakeholders had hoped,” said Colin Edgerton, MD, chair of the American College of Rheumatology’s Committee on Rheumatologic Care. “We continue to see anticompetitive activities that prevent manufacturers from developing biosimilar products. We hope that a greater focus on these practices will pave the way for more biosimilars to be developed.”
The statement highlighted four goals. First is that the agencies will coordinate to promote greater competition in the biologic market, including the development of materials to educate the market about biosimilars. The FDA and FTC also will be sponsoring a public workshop on March 9 to discuss competition for biologics.
“This workshop is the first step,” Dr. Edgerton said. “ACR will continue to work with other organizations and patient groups to help educate providers and patients on the scientific rigor that is required in developing and approving biosimilars. Additionally, we look forward to working with the FDA and FTC to continue this conversation on ways to encourage more development of biosimilar products and greater education for the providers and patients.”
The second goal has the FDA and FTC working together “to deter behavior that impedes access to samples needed for the development of biologics, including biosimilars,” the joint statement notes.
Third, the agencies will crack down on “false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars, within their respective authorities,” according to the joint statement.
“FDA and FTC, as authorized by their respective statutes, will work together to address false or misleading communications about biologics, including biosimilars,” the statement continues. “In particular, if a communication makes a false or misleading comparison between a reference product and a biosimilar in a manner that misrepresents the safety or efficacy of biosimilars, deceives consumers, or deters competition, FDA and FTC intend to take appropriate action within their respective authorities. FDA intends to take appropriate action to address such communications where those communications have the potential to impact public health.”
Finally, the FTC committed to review patent settlement agreements involving biologics, including biosimilars, for antitrust violations.
Dr. Edgerton highlighted why this agreement between the two agencies is so important.
“Biologics are life-changing treatments for many of our patients,” he said. “Due to the high cost of discovery and development, the cost of biologics has resulted in delayed access and financial hardships for so many. It has always been our hope that biosimilars would offer the same life-changing treatment for patients at a lower price point. A robust biosimilars market is imperative to allow greater access to these treatments that can help patients to have a better quality of life.”
Separately, the FDA issued a draft guidance document for comment on manufacturers seeking licensure of biosimilar products that do not cover all the approved uses of the reference product, as well as how to add uses over time that were not part of the initial license of the biosimilar product. The draft guidance covers licensure of products, labeling of biosimilars with fewer indications than the reference product, supplemental applications for indications not on the initial biosimilar application but covered by the reference product, and the timing of applications.
The FDA notes in the draft guidance that this is needed to cover situations such as when some indications on the reference product are covered by exclusivity, although it does encourage a biosimilar manufacturer to seek licensure for all indications that the reference product does have.
Vitamin E acetate found in more vapers’ lung fluid
Analysis of additional lung fluid samples confirms the presence of vitamin E acetate in patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, according to a report on 51 patients in 16 states.
The average age of the patients was 23 years; 69% were male.
The report extends previous work by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to test for harmful substances in bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid obtained from patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) as part of a strategy to understand and manage the recent outbreak of EVALI cases in the United States, wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the Division of Laboratory Sciences at the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, and colleagues.
“CDC was addressing a serious outbreak of lung injury that was sometimes lethal; but after the first 10 weeks of the outbreak investigation, the cause was still unknown,” Dr. Blount said in an interview. “Possible theories could not be evaluated unless the laboratory could develop tests that could confidently connect exposure to lung injury. Detection of toxicants in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid from patients with EVALI can provide direct information on exposure within the lung.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers examined the BAL of 51 cases of EVALI from 16 states. They analyzed the samples for multiple toxicants, including vitamin E acetate, plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, coconut oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes.
Overall, 77% of the patients reported using products containing THC, 67% reported using products containing nicotine, and 51% reported using both types.
Researchers found vitamin E acetate in 48 of the 51 patients (94%); no vitamin E acetate was found in the BAL of healthy controls. Coconut oil and limonene were found in one patient each, but none of the other toxicants was found in the samples from the patients or controls.
In addition, 47 of the 50 patients for whom data were available either had detectable tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or its metabolites in their BAL fluid samples, or they reported vaping THC products within 90 days before they became ill. Nicotine or its metabolites were found in 30 of 47 patients (64%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential role of vitamin E acetate as a marker for exposure to other toxicants, the uncertainty of the role of aerosolized constituents formed when vitamin E acetate is heated, and the lack of data on the timing and burden of toxicant exposure, the investigators noted.
As for the next steps in research, “additional studies are needed to examine the respiratory effects of inhaling aerosolized vitamin E acetate and provide information on whether vitamin E acetate in isolation causes lung injury,” Dr. Blount explained. Analysis of the aerosol and gases generated by case-associated product fluids is ongoing.
“When CDC developed the BAL study for this response, we considered several possible toxicants in this investigation to find a possible cause of the outbreak,” Dr. Blount noted. “To accomplish the study, CDC’s Environmental Health Laboratory developed 12 analytical methods and validated them in less than 3 weeks because of the urgent nature of the emergency.”
Dr. Blount said he would advise clinicians to “continue to reference CDC guidance on treating suspected or EVALI patients.” In December, the CDC published updated guidance for clinicians on hospitalized EVALI patients. “Following this guidance and other recommendations could reduce EVALI-associated morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Blount said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and Ohio State University Pelotonia Intramural Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Analysis of additional lung fluid samples confirms the presence of vitamin E acetate in patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, according to a report on 51 patients in 16 states.
The average age of the patients was 23 years; 69% were male.
The report extends previous work by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to test for harmful substances in bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid obtained from patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) as part of a strategy to understand and manage the recent outbreak of EVALI cases in the United States, wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the Division of Laboratory Sciences at the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, and colleagues.
“CDC was addressing a serious outbreak of lung injury that was sometimes lethal; but after the first 10 weeks of the outbreak investigation, the cause was still unknown,” Dr. Blount said in an interview. “Possible theories could not be evaluated unless the laboratory could develop tests that could confidently connect exposure to lung injury. Detection of toxicants in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid from patients with EVALI can provide direct information on exposure within the lung.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers examined the BAL of 51 cases of EVALI from 16 states. They analyzed the samples for multiple toxicants, including vitamin E acetate, plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, coconut oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes.
Overall, 77% of the patients reported using products containing THC, 67% reported using products containing nicotine, and 51% reported using both types.
Researchers found vitamin E acetate in 48 of the 51 patients (94%); no vitamin E acetate was found in the BAL of healthy controls. Coconut oil and limonene were found in one patient each, but none of the other toxicants was found in the samples from the patients or controls.
In addition, 47 of the 50 patients for whom data were available either had detectable tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or its metabolites in their BAL fluid samples, or they reported vaping THC products within 90 days before they became ill. Nicotine or its metabolites were found in 30 of 47 patients (64%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential role of vitamin E acetate as a marker for exposure to other toxicants, the uncertainty of the role of aerosolized constituents formed when vitamin E acetate is heated, and the lack of data on the timing and burden of toxicant exposure, the investigators noted.
As for the next steps in research, “additional studies are needed to examine the respiratory effects of inhaling aerosolized vitamin E acetate and provide information on whether vitamin E acetate in isolation causes lung injury,” Dr. Blount explained. Analysis of the aerosol and gases generated by case-associated product fluids is ongoing.
“When CDC developed the BAL study for this response, we considered several possible toxicants in this investigation to find a possible cause of the outbreak,” Dr. Blount noted. “To accomplish the study, CDC’s Environmental Health Laboratory developed 12 analytical methods and validated them in less than 3 weeks because of the urgent nature of the emergency.”
Dr. Blount said he would advise clinicians to “continue to reference CDC guidance on treating suspected or EVALI patients.” In December, the CDC published updated guidance for clinicians on hospitalized EVALI patients. “Following this guidance and other recommendations could reduce EVALI-associated morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Blount said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and Ohio State University Pelotonia Intramural Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
Analysis of additional lung fluid samples confirms the presence of vitamin E acetate in patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury, according to a report on 51 patients in 16 states.
The average age of the patients was 23 years; 69% were male.
The report extends previous work by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to test for harmful substances in bronchoalveolar-lavage (BAL) fluid obtained from patients with electronic-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI) as part of a strategy to understand and manage the recent outbreak of EVALI cases in the United States, wrote Benjamin C. Blount, PhD, of the Division of Laboratory Sciences at the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, and colleagues.
“CDC was addressing a serious outbreak of lung injury that was sometimes lethal; but after the first 10 weeks of the outbreak investigation, the cause was still unknown,” Dr. Blount said in an interview. “Possible theories could not be evaluated unless the laboratory could develop tests that could confidently connect exposure to lung injury. Detection of toxicants in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid from patients with EVALI can provide direct information on exposure within the lung.”
In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the researchers examined the BAL of 51 cases of EVALI from 16 states. They analyzed the samples for multiple toxicants, including vitamin E acetate, plant oils, medium-chain triglyceride oil, coconut oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes.
Overall, 77% of the patients reported using products containing THC, 67% reported using products containing nicotine, and 51% reported using both types.
Researchers found vitamin E acetate in 48 of the 51 patients (94%); no vitamin E acetate was found in the BAL of healthy controls. Coconut oil and limonene were found in one patient each, but none of the other toxicants was found in the samples from the patients or controls.
In addition, 47 of the 50 patients for whom data were available either had detectable tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or its metabolites in their BAL fluid samples, or they reported vaping THC products within 90 days before they became ill. Nicotine or its metabolites were found in 30 of 47 patients (64%).
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential role of vitamin E acetate as a marker for exposure to other toxicants, the uncertainty of the role of aerosolized constituents formed when vitamin E acetate is heated, and the lack of data on the timing and burden of toxicant exposure, the investigators noted.
As for the next steps in research, “additional studies are needed to examine the respiratory effects of inhaling aerosolized vitamin E acetate and provide information on whether vitamin E acetate in isolation causes lung injury,” Dr. Blount explained. Analysis of the aerosol and gases generated by case-associated product fluids is ongoing.
“When CDC developed the BAL study for this response, we considered several possible toxicants in this investigation to find a possible cause of the outbreak,” Dr. Blount noted. “To accomplish the study, CDC’s Environmental Health Laboratory developed 12 analytical methods and validated them in less than 3 weeks because of the urgent nature of the emergency.”
Dr. Blount said he would advise clinicians to “continue to reference CDC guidance on treating suspected or EVALI patients.” In December, the CDC published updated guidance for clinicians on hospitalized EVALI patients. “Following this guidance and other recommendations could reduce EVALI-associated morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Blount said.
The study was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute, the FDA Center for Tobacco Products, and Ohio State University Pelotonia Intramural Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Blount BC et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916433.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Drop in flu activity suggests season may have peaked
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.
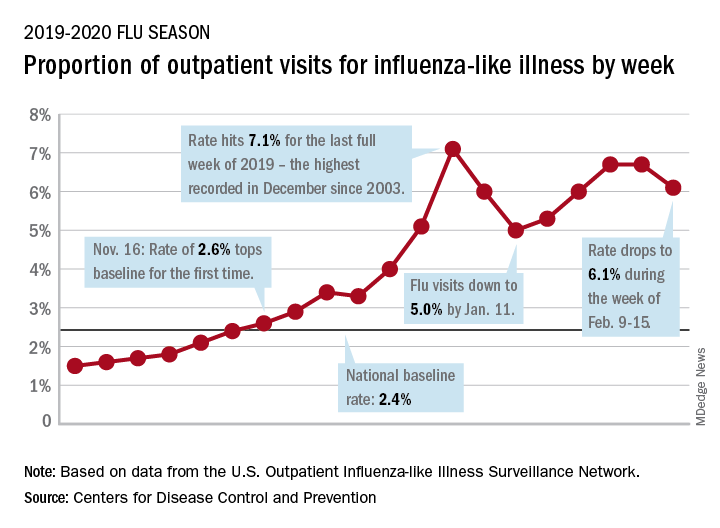
The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.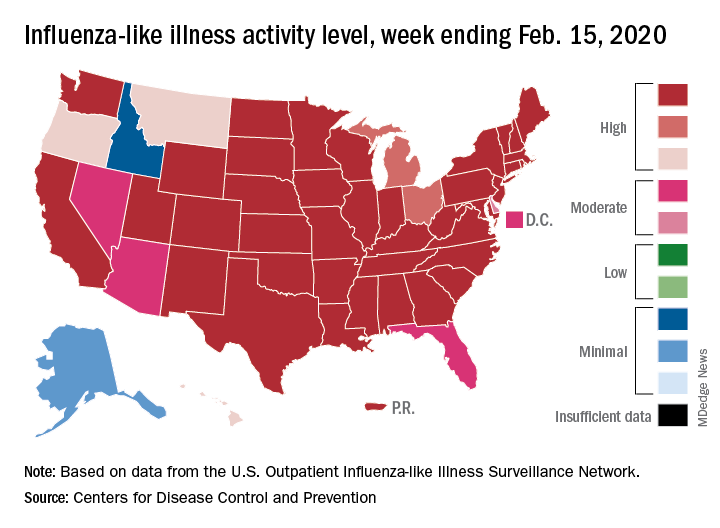
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.

The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
Influenza activity dropped during the week ending Feb. 15, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That decline, along with revised data from the 2 previous weeks, suggests that the 2019-2020 season has peaked for the second time. The rate of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) came in at 6.1% for the week ending Feb. 15, after two straight weeks at 6.7%, the CDC’s influenza division reported Feb. 21.

The rates for those 2 earlier weeks had previously been reported at 6.8% (Feb. 8) and 6.6% (Feb. 1), which means that there have now been 2 consecutive weeks without an increase in national ILI activity.
State-level activity was down slightly as well. For the week ending Feb. 15, there were 39 states and Puerto Rico at the highest level of activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, compared with 41 states and Puerto Rico the week before. The number of states in the “high” range, which includes levels 8 and 9, went from 44 to 45, however, CDC data show.
Laboratory measures also dropped a bit. For the week, 29.6% of respiratory specimens tested positive for influenza, compared with 30.3% the previous week. The predominance of influenza A continued to increase, as type A went from 59.4% to 63.5% of positive specimens and type B dropped from 40.6% to 36.5%, the influenza division said.
In a separate report, the CDC announced interim flu vaccine effectiveness estimates.For the 2019-2020 season so far, “flu vaccines are reducing doctor’s visits for flu illness by almost half (45%). This is consistent with estimates of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) from previous flu seasons that ranged from 40% to 60% when flu vaccine viruses were similar to circulating influenza viruses,” the CDC said.
Although VE among children aged 6 months to 17 years is even higher, at 55%, this season “has been especially bad for children. Flu hospitalization rates among children are higher than at this time in other recent seasons, including the 2017-18 season,” the CDC noted.
The number of pediatric flu deaths for 2019-2020 – now up to 105 – is “higher for the same time period than in every season since reporting began in 2004-05, with the exception of the 2009 pandemic,” the CDC added.
Interim VE estimates for other age groups are 25% for adults aged 18-49 and 43% for those 50 years and older. “The lower VE point estimates observed among adults 18-49 years appear to be associated with a trend suggesting lower VE in this age group against A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the CDC said.
FROM THE CDC
Prescription osteoarthritis relief gets OTC approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved formerly prescription-only Voltaren Arthritis Pain (diclofenac sodium topical gel, 1%) for nonprescription use via a process known as a prescription to over-the-counter (Rx-to-OTC) switch, according to a news release from the agency.
“As a result of the Rx-to-OTC switch process, many products sold over the counter today use ingredients or dosage strengths that were available only by prescription 30 years ago,” Karen Mahoney, MD, acting deputy director of the Office of Nonprescription Drugs in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in the release.
This switch to nonprescription status is usually initiated by the manufacturer, who must provide data that demonstrates the drug in question is both safe and effective as self-medication in accordance with the proposed labeling and that consumers can use it safely and effectively without the supervision of a health care professional.
This particular therapy is a topical NSAID gel and was first approved by the FDA in 2007 with the indication for relief of osteoarthritis pain. It can take 7 days to have an effect, but if patients find it takes longer than that or they need to use it for more than 21 days, they should seek medical attention. The gel can cause severe allergic reactions, especially in people allergic to aspirin; patients who experience such reactions are advised to stop use and seek immediate medical care. Other concerns include potential for liver damage with extended use; the possibility of severe stomach bleeds; and risk of heart attack, heart failure, and stroke.
The gel will no longer be available in prescription form.
Full prescribing information can be found on the FDA website, as can the full news release regarding this approval.