User login
FDA approves Brukinsa for relapsed, refractory MCL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
FDA panel supports Vascepa expanded indication for CVD reduction
Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid, received unanimous backing from a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel for a new indication for reducing cardiovascular event risk.
Icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) received initial agency approval in 2012 for the indication of cutting triglyceride levels once they reached at least 500 mg/dL.
The target patient population for this new, cardiovascular-event protection role will reflect some or all of the types of patients enrolled in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events with Icosapent Ethyl–Intervention Trial), which tested icosapent ethyl in 8,179 patients with either established cardiovascular disease or diabetes and at least one additional cardiovascular disease risk factor. This study provided the bulk of the data considered by the FDA panel.
REDUCE-IT showed that, during a median of 4.9 years, patients who received icosapent ethyl had a statistically significant 25% relative risk reduction in the trial’s primary, composite endpoint (New Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 3;380[1]:11-22).
Icosapent ethyl “appeared effective and safe,” and would be a “useful, new, added agent for treating patients” like those enrolled in the trial, said Kenneth D. Burman, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center and chair of the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee.
The advisory panel members appeared uniformly comfortable with recommending that the FDA add a cardiovascular disease indication based on the REDUCE-IT findings.
But while they agreed that icosapent ethyl should receive some type of indication for cardiovascular event reduction, the committee split over which patients the indication should include. Specifically, they diverged on the issue of primary prevention.
Some said that the patient enrollment that produced a positive result in REDUCE-IT should not be retrospectively subdivided, while others said that combining secondary- and primary-prevention patients in a single large trial inappropriately lumped together patients who would be better considered separately.
Committee members also expressed uncertainty over the appropriate triglyceride level to warrant treatment. The REDUCE-IT trial was designed to enroll patients with triglycerides of 135 mg/dL or greater, but several panel members suggested that, for labeling, the threshold should be at least 150 mg/dL, or even 200 mg/dL.
Safety was another aspect that generated a lot of panel discussion throughout their day-long discussion, with particular focus on a signal of a small but concerning increased rate of incident atrial fibrillation among patients who received icosapent ethyl, as well as a small but nearly significant increase in the rate of serious bleeds.
Further analyses presented during the meeting showed that an increased bleeding rate linked with icosapent ethyl was focused in patients who concurrently received one or more antiplatelet drugs or an anticoagulant.
However, panel members rejected the notion that these safety concerns warranted a boxed warning, agreeing that it could be managed with appropriate labeling information.
Clinician reaction
Clinicians who manage these types of patients viewed the prospect of an expanded indication for icosapent ethyl as an important advance.
The REDUCE-IT results by themselves “were convincing” for patients with established cardiovascular disease without need for a confirmatory trial, Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview. But he remained unconvinced about efficacy for primary-prevention patients, or even for secondary-prevention patients with a triglyceride level below 150 mg/dL.
“Icosapent ethyl will clearly be a mainstay for managing high-risk patients. It gives us another treatment option,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director and principal investigator of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “I do not see the atrial fibrillation or bleeding effects as reasons not to approve this drug. It should be a precaution. Overall, icosapent ethyl is one of the easier drugs for patients to take.”
Dr. Handelsman said it would be unethical to run a confirmatory trial and randomize patients to placebo. “Another trial makes no sense,” he said.
But the data from REDUCE-IT were “not as convincing” for primary-prevention patients, suggesting a need for caution about using icosapent ethyl for patients without established cardiovascular disease, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, an endocrinologist in Fort Lauderdale, Fla., said in an interview.
Cost-effectiveness
An analysis of the cost-effectiveness of icosapent ethyl as used in REDUCE-IT showed that the drug fell into the rare category of being a “dominant” treatment, meaning that it both improved patient outcomes and reduced medical costs. William S. Weintraub, MD, will report findings from this analysis on Nov. 16, 2019, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
The analysis used a wholesale acquisition cost for a 1-day dosage of icosapent ethyl of $4.16, derived from a commercial source for prescription-drug pricing and actual hospitalization costs for the patients in the trial.
Based on the REDUCE-IT outcomes, treatment with icosapent ethyl was linked with a boost in quality-adjusted life-years that extrapolated to an average 0.26 increase during the full lifetime of REDUCE-IT participants, at a cost that averaged $1,284 less per treated patient over their lifetime, according to Dr. Weintraub, director of Outcomes Research at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington.
Although the 0.26 lifetime increase in quality-adjusted life-years may sound modest, “in the cost-effectiveness world, 0.26 is actually significant,” Dr. Weintraub said. He also highlighted how unusual it is to find a patented drug that improves quality of life and longevity while also saving money.
“I know of no other on-patent, branded pharmaceutical that is dominant,” he said.
Off-patent pharmaceuticals, like statins, can be quite inexpensive and may also be dominant, he noted. Being dominant for cost-effectiveness means that icosapent ethyl “provides good value and is worth what we pay for it, well within social thresholds of willingness to pay,” Dr. Weintraub said.
REDUCE-IT was sponsored by Amarin, the company that markets icosapent ethyl (Vascepa). Dr. Burman has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Eisai, and IBSA. Dr. Eckel has received personal fees from Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi/Regeneron, as well as research funding from Endece, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and UniQure. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to and received research funding from Amarin and several other companies. Dr. Jellinger has been a speaker on behalf of Amarin, Amgen, and Regeneron. Dr. Weintraub has received honoraria and research support from Amarin, and honoraria from AstraZeneca.
Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid, received unanimous backing from a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel for a new indication for reducing cardiovascular event risk.
Icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) received initial agency approval in 2012 for the indication of cutting triglyceride levels once they reached at least 500 mg/dL.
The target patient population for this new, cardiovascular-event protection role will reflect some or all of the types of patients enrolled in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events with Icosapent Ethyl–Intervention Trial), which tested icosapent ethyl in 8,179 patients with either established cardiovascular disease or diabetes and at least one additional cardiovascular disease risk factor. This study provided the bulk of the data considered by the FDA panel.
REDUCE-IT showed that, during a median of 4.9 years, patients who received icosapent ethyl had a statistically significant 25% relative risk reduction in the trial’s primary, composite endpoint (New Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 3;380[1]:11-22).
Icosapent ethyl “appeared effective and safe,” and would be a “useful, new, added agent for treating patients” like those enrolled in the trial, said Kenneth D. Burman, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center and chair of the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee.
The advisory panel members appeared uniformly comfortable with recommending that the FDA add a cardiovascular disease indication based on the REDUCE-IT findings.
But while they agreed that icosapent ethyl should receive some type of indication for cardiovascular event reduction, the committee split over which patients the indication should include. Specifically, they diverged on the issue of primary prevention.
Some said that the patient enrollment that produced a positive result in REDUCE-IT should not be retrospectively subdivided, while others said that combining secondary- and primary-prevention patients in a single large trial inappropriately lumped together patients who would be better considered separately.
Committee members also expressed uncertainty over the appropriate triglyceride level to warrant treatment. The REDUCE-IT trial was designed to enroll patients with triglycerides of 135 mg/dL or greater, but several panel members suggested that, for labeling, the threshold should be at least 150 mg/dL, or even 200 mg/dL.
Safety was another aspect that generated a lot of panel discussion throughout their day-long discussion, with particular focus on a signal of a small but concerning increased rate of incident atrial fibrillation among patients who received icosapent ethyl, as well as a small but nearly significant increase in the rate of serious bleeds.
Further analyses presented during the meeting showed that an increased bleeding rate linked with icosapent ethyl was focused in patients who concurrently received one or more antiplatelet drugs or an anticoagulant.
However, panel members rejected the notion that these safety concerns warranted a boxed warning, agreeing that it could be managed with appropriate labeling information.
Clinician reaction
Clinicians who manage these types of patients viewed the prospect of an expanded indication for icosapent ethyl as an important advance.
The REDUCE-IT results by themselves “were convincing” for patients with established cardiovascular disease without need for a confirmatory trial, Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview. But he remained unconvinced about efficacy for primary-prevention patients, or even for secondary-prevention patients with a triglyceride level below 150 mg/dL.
“Icosapent ethyl will clearly be a mainstay for managing high-risk patients. It gives us another treatment option,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director and principal investigator of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “I do not see the atrial fibrillation or bleeding effects as reasons not to approve this drug. It should be a precaution. Overall, icosapent ethyl is one of the easier drugs for patients to take.”
Dr. Handelsman said it would be unethical to run a confirmatory trial and randomize patients to placebo. “Another trial makes no sense,” he said.
But the data from REDUCE-IT were “not as convincing” for primary-prevention patients, suggesting a need for caution about using icosapent ethyl for patients without established cardiovascular disease, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, an endocrinologist in Fort Lauderdale, Fla., said in an interview.
Cost-effectiveness
An analysis of the cost-effectiveness of icosapent ethyl as used in REDUCE-IT showed that the drug fell into the rare category of being a “dominant” treatment, meaning that it both improved patient outcomes and reduced medical costs. William S. Weintraub, MD, will report findings from this analysis on Nov. 16, 2019, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
The analysis used a wholesale acquisition cost for a 1-day dosage of icosapent ethyl of $4.16, derived from a commercial source for prescription-drug pricing and actual hospitalization costs for the patients in the trial.
Based on the REDUCE-IT outcomes, treatment with icosapent ethyl was linked with a boost in quality-adjusted life-years that extrapolated to an average 0.26 increase during the full lifetime of REDUCE-IT participants, at a cost that averaged $1,284 less per treated patient over their lifetime, according to Dr. Weintraub, director of Outcomes Research at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington.
Although the 0.26 lifetime increase in quality-adjusted life-years may sound modest, “in the cost-effectiveness world, 0.26 is actually significant,” Dr. Weintraub said. He also highlighted how unusual it is to find a patented drug that improves quality of life and longevity while also saving money.
“I know of no other on-patent, branded pharmaceutical that is dominant,” he said.
Off-patent pharmaceuticals, like statins, can be quite inexpensive and may also be dominant, he noted. Being dominant for cost-effectiveness means that icosapent ethyl “provides good value and is worth what we pay for it, well within social thresholds of willingness to pay,” Dr. Weintraub said.
REDUCE-IT was sponsored by Amarin, the company that markets icosapent ethyl (Vascepa). Dr. Burman has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Eisai, and IBSA. Dr. Eckel has received personal fees from Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi/Regeneron, as well as research funding from Endece, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and UniQure. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to and received research funding from Amarin and several other companies. Dr. Jellinger has been a speaker on behalf of Amarin, Amgen, and Regeneron. Dr. Weintraub has received honoraria and research support from Amarin, and honoraria from AstraZeneca.
Icosapent ethyl, a highly purified form of the ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid, received unanimous backing from a Food and Drug Administration advisory panel for a new indication for reducing cardiovascular event risk.
Icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) received initial agency approval in 2012 for the indication of cutting triglyceride levels once they reached at least 500 mg/dL.
The target patient population for this new, cardiovascular-event protection role will reflect some or all of the types of patients enrolled in REDUCE-IT (Reduction of Cardiovascular Events with Icosapent Ethyl–Intervention Trial), which tested icosapent ethyl in 8,179 patients with either established cardiovascular disease or diabetes and at least one additional cardiovascular disease risk factor. This study provided the bulk of the data considered by the FDA panel.
REDUCE-IT showed that, during a median of 4.9 years, patients who received icosapent ethyl had a statistically significant 25% relative risk reduction in the trial’s primary, composite endpoint (New Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 3;380[1]:11-22).
Icosapent ethyl “appeared effective and safe,” and would be a “useful, new, added agent for treating patients” like those enrolled in the trial, said Kenneth D. Burman, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology at Medstar Washington (D.C.) Hospital Center and chair of the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee.
The advisory panel members appeared uniformly comfortable with recommending that the FDA add a cardiovascular disease indication based on the REDUCE-IT findings.
But while they agreed that icosapent ethyl should receive some type of indication for cardiovascular event reduction, the committee split over which patients the indication should include. Specifically, they diverged on the issue of primary prevention.
Some said that the patient enrollment that produced a positive result in REDUCE-IT should not be retrospectively subdivided, while others said that combining secondary- and primary-prevention patients in a single large trial inappropriately lumped together patients who would be better considered separately.
Committee members also expressed uncertainty over the appropriate triglyceride level to warrant treatment. The REDUCE-IT trial was designed to enroll patients with triglycerides of 135 mg/dL or greater, but several panel members suggested that, for labeling, the threshold should be at least 150 mg/dL, or even 200 mg/dL.
Safety was another aspect that generated a lot of panel discussion throughout their day-long discussion, with particular focus on a signal of a small but concerning increased rate of incident atrial fibrillation among patients who received icosapent ethyl, as well as a small but nearly significant increase in the rate of serious bleeds.
Further analyses presented during the meeting showed that an increased bleeding rate linked with icosapent ethyl was focused in patients who concurrently received one or more antiplatelet drugs or an anticoagulant.
However, panel members rejected the notion that these safety concerns warranted a boxed warning, agreeing that it could be managed with appropriate labeling information.
Clinician reaction
Clinicians who manage these types of patients viewed the prospect of an expanded indication for icosapent ethyl as an important advance.
The REDUCE-IT results by themselves “were convincing” for patients with established cardiovascular disease without need for a confirmatory trial, Robert H. Eckel, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, said in an interview. But he remained unconvinced about efficacy for primary-prevention patients, or even for secondary-prevention patients with a triglyceride level below 150 mg/dL.
“Icosapent ethyl will clearly be a mainstay for managing high-risk patients. It gives us another treatment option,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and medical director and principal investigator of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “I do not see the atrial fibrillation or bleeding effects as reasons not to approve this drug. It should be a precaution. Overall, icosapent ethyl is one of the easier drugs for patients to take.”
Dr. Handelsman said it would be unethical to run a confirmatory trial and randomize patients to placebo. “Another trial makes no sense,” he said.
But the data from REDUCE-IT were “not as convincing” for primary-prevention patients, suggesting a need for caution about using icosapent ethyl for patients without established cardiovascular disease, Paul S. Jellinger, MD, an endocrinologist in Fort Lauderdale, Fla., said in an interview.
Cost-effectiveness
An analysis of the cost-effectiveness of icosapent ethyl as used in REDUCE-IT showed that the drug fell into the rare category of being a “dominant” treatment, meaning that it both improved patient outcomes and reduced medical costs. William S. Weintraub, MD, will report findings from this analysis on Nov. 16, 2019, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
The analysis used a wholesale acquisition cost for a 1-day dosage of icosapent ethyl of $4.16, derived from a commercial source for prescription-drug pricing and actual hospitalization costs for the patients in the trial.
Based on the REDUCE-IT outcomes, treatment with icosapent ethyl was linked with a boost in quality-adjusted life-years that extrapolated to an average 0.26 increase during the full lifetime of REDUCE-IT participants, at a cost that averaged $1,284 less per treated patient over their lifetime, according to Dr. Weintraub, director of Outcomes Research at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, Washington.
Although the 0.26 lifetime increase in quality-adjusted life-years may sound modest, “in the cost-effectiveness world, 0.26 is actually significant,” Dr. Weintraub said. He also highlighted how unusual it is to find a patented drug that improves quality of life and longevity while also saving money.
“I know of no other on-patent, branded pharmaceutical that is dominant,” he said.
Off-patent pharmaceuticals, like statins, can be quite inexpensive and may also be dominant, he noted. Being dominant for cost-effectiveness means that icosapent ethyl “provides good value and is worth what we pay for it, well within social thresholds of willingness to pay,” Dr. Weintraub said.
REDUCE-IT was sponsored by Amarin, the company that markets icosapent ethyl (Vascepa). Dr. Burman has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Eisai, and IBSA. Dr. Eckel has received personal fees from Kowa Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi/Regeneron, as well as research funding from Endece, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and UniQure. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to and received research funding from Amarin and several other companies. Dr. Jellinger has been a speaker on behalf of Amarin, Amgen, and Regeneron. Dr. Weintraub has received honoraria and research support from Amarin, and honoraria from AstraZeneca.
Vaping-linked lung injury: 2,172 cases, 42 deaths
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has from 49 states (all except Alaska), the District of Columbia, and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). Forty-two deaths have been confirmed in 24 states and the District of Columbia, the CDC reported.
Laboratory test results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples from 29 patients submitted to CDC from 10 states found vitamin E acetate in all of the samples. This is the first time a chemical of concern has been found in biologic samples from patients with EVALI. These findings provide direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury within the lungs.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was identified in 82% of the samples and nicotine was identified in 62% of the samples. Testing continues for other chemicals including plant oils, petroleum distillates like mineral oil, medium-chain triglycerides oil, and terpenes, which are compounds commonly found in or added to THC products. None of these chemicals has been detected in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples tested.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For State and Local Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
REPORTING FROM CDC
CDC releases update of 2013 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report
“You and I are living in a time when some miracle drugs no longer perform miracles and families are being ripped apart by a microscopic enemy. The time for action is now and we can be part of the solution,” said Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in his foreword to the new CDC report on antibiotic resistance.
In this update of the previous 2013 report, The current report uses EHRs and other data sources obtained by the CDC for relevant infections extrapolated to develop national disease incidence. The report focuses on “the top 18 pathogens that require attention now,” advises specific steps be taken to address these pathogens, and puts into perspective the future of antibiotic development, their use and abuse, and the continuing threat of antibiotic resistance.
The CDC categorizes these 18 pathogens as either an urgent, serious, or concerning threat.
Urgent Threats
- Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter, which cause pneumonia and wound, bloodstream, and urinary tract infections; they tend to affect patients in ICUs. Of particular concern, some Acinetobacter are resistant to nearly all antibiotics, with few new drugs in development (8,500 hospital infections in 2017; 700 deaths).
- Candida auris, a drug-resistant fungus that was first identified in 2009 in Asia and has quickly become a cause of severe infections around the world; it is extremely difficult to eradicate from health care settings. It began spreading in the United States in 2015, with 323 cases reported in 2018 (90% resistant to at least one antifungal, and 30% resistant to at least two antifungals).
- Clostridioides difficile, which can cause life-threatening diarrhea, most often in people who have taken antibiotics for other conditions. It is the most common health care–associated infection, and although decreasing in the health care system, it has not decreased in community settings (223,900 hospital infections in 2017, and 12,800 estimated deaths).
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, which most frequently infect patients who require devices such as catheters and those taking long courses of some antibiotics. Of particular concern is the fact that these bacteria contain a transmissible plasmid that can transfer their drug resistance to other pathogens (13,100 hospital infections in 2017, and 1,100 estimated deaths).
- Drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is a sexually transmitted disease that can result in life-threatening ectopic pregnancy, lead to infertility, and can increase the risk of getting and giving HIV; it can also cause cardiovascular and neurological problems. It is resistant to all but one class of antibiotics, and half of all infections are resistant to at least one antibiotic (550,000 drug-resistant infections yearly).
Serious Threats
- Drug-resistant Campylobacter.
- Drug-resistant Candida.
- Extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae.
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci.
- Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Drug-resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella.
- Drug-resistant Salmonella serotype Typhi.
- Drug-resistant Shigella.
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- Drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Drug-resistant Tuberculosis.
Concerning Threats
These comprise erythromycin-resistant group A Streptococcus and clindamycin-resistant group B Streptococcus.
In addition, the CDC has established a Watch List of three pathogens to be wary of: azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus, drug-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium, and drug-resistant Bordetella pertussis.
Because antibiotic resistance is a global phenomenon caused by and affecting everyone, the CDC provided solutions to the problem of antibiotic resistance at every level of society. This “comprehensive and coordinated response implements the U.S. National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria” and includes cooperation with the Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Department of Agriculture, according to the report.
The key components of this response include using data and new technologies to detect and track antibiotic resistance; infection prevention and containment, especially in terms of outbreak response; improving antibiotic use across populations (one successful example being a 16% decrease of outpatient antibiotic prescribing to children during 2011-2017); improvements in the identification and intervention in the environment including water and soil and in sanitation; and a significant investment in vaccines, diagnostics, and novel therapeutics (the CDC provided nearly $110 million to 96 institutions for work in these areas).
The report also details some hope in the development of new antibiotics. As of June 2019, there were 42 new antibiotics in development, including 4 with new drug applications submitted, 17 with the potential to treat serious gram negative bacteria, and 11 that could address the urgent threats of gonorrhea or C. difficile. Overall, a quarter of these new antibiotics represent a novel drug class or use a novel mechanism of action.
Furthermore, 84% of U.S. hospitals report a stewardship program meeting all seven of CDC’s Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship. Proper stewardship is at the core of preventing the development of new antibiotic resistant pathogen strains.
In addition, the CDC noted a 5% overall decline in antibiotic prescribing in outpatient settings during 2011-2016.
“The problem will get worse if we do not act now, but we can make a difference,” according to Dr. Redfield. “Simply, here’s what works. Preventing infections protects everyone. Improving antibiotic use in people and animals slows the threat and helps preserve today’s drugs and those yet to come. Detecting threats and implementing interventions to keep germs from becoming widespread saves lives.”
In response to the release of the report, the AMA issued a supporting statement and cited its collection of educational resources for physicians focused on antibiotic use, resistance, and stewardship.
Similarly, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) stated that hospitals were “a bright spot” in the CDC report and offered tools and resources available to educate and inform health care professionals about best practices in infection prevention and control, as well as antibiotic stewardship.
SOURCE: CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019.
“You and I are living in a time when some miracle drugs no longer perform miracles and families are being ripped apart by a microscopic enemy. The time for action is now and we can be part of the solution,” said Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in his foreword to the new CDC report on antibiotic resistance.
In this update of the previous 2013 report, The current report uses EHRs and other data sources obtained by the CDC for relevant infections extrapolated to develop national disease incidence. The report focuses on “the top 18 pathogens that require attention now,” advises specific steps be taken to address these pathogens, and puts into perspective the future of antibiotic development, their use and abuse, and the continuing threat of antibiotic resistance.
The CDC categorizes these 18 pathogens as either an urgent, serious, or concerning threat.
Urgent Threats
- Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter, which cause pneumonia and wound, bloodstream, and urinary tract infections; they tend to affect patients in ICUs. Of particular concern, some Acinetobacter are resistant to nearly all antibiotics, with few new drugs in development (8,500 hospital infections in 2017; 700 deaths).
- Candida auris, a drug-resistant fungus that was first identified in 2009 in Asia and has quickly become a cause of severe infections around the world; it is extremely difficult to eradicate from health care settings. It began spreading in the United States in 2015, with 323 cases reported in 2018 (90% resistant to at least one antifungal, and 30% resistant to at least two antifungals).
- Clostridioides difficile, which can cause life-threatening diarrhea, most often in people who have taken antibiotics for other conditions. It is the most common health care–associated infection, and although decreasing in the health care system, it has not decreased in community settings (223,900 hospital infections in 2017, and 12,800 estimated deaths).
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, which most frequently infect patients who require devices such as catheters and those taking long courses of some antibiotics. Of particular concern is the fact that these bacteria contain a transmissible plasmid that can transfer their drug resistance to other pathogens (13,100 hospital infections in 2017, and 1,100 estimated deaths).
- Drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is a sexually transmitted disease that can result in life-threatening ectopic pregnancy, lead to infertility, and can increase the risk of getting and giving HIV; it can also cause cardiovascular and neurological problems. It is resistant to all but one class of antibiotics, and half of all infections are resistant to at least one antibiotic (550,000 drug-resistant infections yearly).
Serious Threats
- Drug-resistant Campylobacter.
- Drug-resistant Candida.
- Extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae.
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci.
- Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Drug-resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella.
- Drug-resistant Salmonella serotype Typhi.
- Drug-resistant Shigella.
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- Drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Drug-resistant Tuberculosis.
Concerning Threats
These comprise erythromycin-resistant group A Streptococcus and clindamycin-resistant group B Streptococcus.
In addition, the CDC has established a Watch List of three pathogens to be wary of: azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus, drug-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium, and drug-resistant Bordetella pertussis.
Because antibiotic resistance is a global phenomenon caused by and affecting everyone, the CDC provided solutions to the problem of antibiotic resistance at every level of society. This “comprehensive and coordinated response implements the U.S. National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria” and includes cooperation with the Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Department of Agriculture, according to the report.
The key components of this response include using data and new technologies to detect and track antibiotic resistance; infection prevention and containment, especially in terms of outbreak response; improving antibiotic use across populations (one successful example being a 16% decrease of outpatient antibiotic prescribing to children during 2011-2017); improvements in the identification and intervention in the environment including water and soil and in sanitation; and a significant investment in vaccines, diagnostics, and novel therapeutics (the CDC provided nearly $110 million to 96 institutions for work in these areas).
The report also details some hope in the development of new antibiotics. As of June 2019, there were 42 new antibiotics in development, including 4 with new drug applications submitted, 17 with the potential to treat serious gram negative bacteria, and 11 that could address the urgent threats of gonorrhea or C. difficile. Overall, a quarter of these new antibiotics represent a novel drug class or use a novel mechanism of action.
Furthermore, 84% of U.S. hospitals report a stewardship program meeting all seven of CDC’s Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship. Proper stewardship is at the core of preventing the development of new antibiotic resistant pathogen strains.
In addition, the CDC noted a 5% overall decline in antibiotic prescribing in outpatient settings during 2011-2016.
“The problem will get worse if we do not act now, but we can make a difference,” according to Dr. Redfield. “Simply, here’s what works. Preventing infections protects everyone. Improving antibiotic use in people and animals slows the threat and helps preserve today’s drugs and those yet to come. Detecting threats and implementing interventions to keep germs from becoming widespread saves lives.”
In response to the release of the report, the AMA issued a supporting statement and cited its collection of educational resources for physicians focused on antibiotic use, resistance, and stewardship.
Similarly, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) stated that hospitals were “a bright spot” in the CDC report and offered tools and resources available to educate and inform health care professionals about best practices in infection prevention and control, as well as antibiotic stewardship.
SOURCE: CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019.
“You and I are living in a time when some miracle drugs no longer perform miracles and families are being ripped apart by a microscopic enemy. The time for action is now and we can be part of the solution,” said Robert R. Redfield, MD, director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in his foreword to the new CDC report on antibiotic resistance.
In this update of the previous 2013 report, The current report uses EHRs and other data sources obtained by the CDC for relevant infections extrapolated to develop national disease incidence. The report focuses on “the top 18 pathogens that require attention now,” advises specific steps be taken to address these pathogens, and puts into perspective the future of antibiotic development, their use and abuse, and the continuing threat of antibiotic resistance.
The CDC categorizes these 18 pathogens as either an urgent, serious, or concerning threat.
Urgent Threats
- Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter, which cause pneumonia and wound, bloodstream, and urinary tract infections; they tend to affect patients in ICUs. Of particular concern, some Acinetobacter are resistant to nearly all antibiotics, with few new drugs in development (8,500 hospital infections in 2017; 700 deaths).
- Candida auris, a drug-resistant fungus that was first identified in 2009 in Asia and has quickly become a cause of severe infections around the world; it is extremely difficult to eradicate from health care settings. It began spreading in the United States in 2015, with 323 cases reported in 2018 (90% resistant to at least one antifungal, and 30% resistant to at least two antifungals).
- Clostridioides difficile, which can cause life-threatening diarrhea, most often in people who have taken antibiotics for other conditions. It is the most common health care–associated infection, and although decreasing in the health care system, it has not decreased in community settings (223,900 hospital infections in 2017, and 12,800 estimated deaths).
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, which most frequently infect patients who require devices such as catheters and those taking long courses of some antibiotics. Of particular concern is the fact that these bacteria contain a transmissible plasmid that can transfer their drug resistance to other pathogens (13,100 hospital infections in 2017, and 1,100 estimated deaths).
- Drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is a sexually transmitted disease that can result in life-threatening ectopic pregnancy, lead to infertility, and can increase the risk of getting and giving HIV; it can also cause cardiovascular and neurological problems. It is resistant to all but one class of antibiotics, and half of all infections are resistant to at least one antibiotic (550,000 drug-resistant infections yearly).
Serious Threats
- Drug-resistant Campylobacter.
- Drug-resistant Candida.
- Extended spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae.
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci.
- Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Drug-resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella.
- Drug-resistant Salmonella serotype Typhi.
- Drug-resistant Shigella.
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
- Drug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Drug-resistant Tuberculosis.
Concerning Threats
These comprise erythromycin-resistant group A Streptococcus and clindamycin-resistant group B Streptococcus.
In addition, the CDC has established a Watch List of three pathogens to be wary of: azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus, drug-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium, and drug-resistant Bordetella pertussis.
Because antibiotic resistance is a global phenomenon caused by and affecting everyone, the CDC provided solutions to the problem of antibiotic resistance at every level of society. This “comprehensive and coordinated response implements the U.S. National Action Plan for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria” and includes cooperation with the Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Veterans Affairs, Department of Defense, Department of State, and Department of Agriculture, according to the report.
The key components of this response include using data and new technologies to detect and track antibiotic resistance; infection prevention and containment, especially in terms of outbreak response; improving antibiotic use across populations (one successful example being a 16% decrease of outpatient antibiotic prescribing to children during 2011-2017); improvements in the identification and intervention in the environment including water and soil and in sanitation; and a significant investment in vaccines, diagnostics, and novel therapeutics (the CDC provided nearly $110 million to 96 institutions for work in these areas).
The report also details some hope in the development of new antibiotics. As of June 2019, there were 42 new antibiotics in development, including 4 with new drug applications submitted, 17 with the potential to treat serious gram negative bacteria, and 11 that could address the urgent threats of gonorrhea or C. difficile. Overall, a quarter of these new antibiotics represent a novel drug class or use a novel mechanism of action.
Furthermore, 84% of U.S. hospitals report a stewardship program meeting all seven of CDC’s Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship. Proper stewardship is at the core of preventing the development of new antibiotic resistant pathogen strains.
In addition, the CDC noted a 5% overall decline in antibiotic prescribing in outpatient settings during 2011-2016.
“The problem will get worse if we do not act now, but we can make a difference,” according to Dr. Redfield. “Simply, here’s what works. Preventing infections protects everyone. Improving antibiotic use in people and animals slows the threat and helps preserve today’s drugs and those yet to come. Detecting threats and implementing interventions to keep germs from becoming widespread saves lives.”
In response to the release of the report, the AMA issued a supporting statement and cited its collection of educational resources for physicians focused on antibiotic use, resistance, and stewardship.
Similarly, the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) stated that hospitals were “a bright spot” in the CDC report and offered tools and resources available to educate and inform health care professionals about best practices in infection prevention and control, as well as antibiotic stewardship.
SOURCE: CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States 2019.
FDA still concerned about biotin affecting troponin tests
The
However, not all troponin tests are affected, according to the update. “Since the FDA’s safety communication on this topic in 2017, some lab test developers have been successful at mitigating the biotin interference of their assays, but others have not yet addressed it,” according to the new communication, issued in early November.
Also known as vitamin B7 and appearing in many dietary supplements, including prenatal multivitamins and supplements for hair, skin, and nail growth, biotin can lead to falsely low results on some troponin tests, especially at high levels. The worry is that biotin interference could therefore lead to missed diagnoses. The FDA has provided a list of those tests that have not taken biotin’s effects into account, titled “Biotin Interference with Troponin Lab Tests – Assays Subject to Biotin Interference.”
The daily recommended allowance for biotin, according to the communication, is about 0.3 mg, but it isn’t always clear how much is actually included in supplements – some can contain 20 mg or even as much as 100 mg per pill of biotin. The communication includes recommendations for patients, health care professionals, laboratory personnel, and lab test manufacturers and developers.
The full safety communication can be found on the FDA website, and problems with tests can be reported via the FDA’s MedWatch Voluntary Reporting Form.
The
However, not all troponin tests are affected, according to the update. “Since the FDA’s safety communication on this topic in 2017, some lab test developers have been successful at mitigating the biotin interference of their assays, but others have not yet addressed it,” according to the new communication, issued in early November.
Also known as vitamin B7 and appearing in many dietary supplements, including prenatal multivitamins and supplements for hair, skin, and nail growth, biotin can lead to falsely low results on some troponin tests, especially at high levels. The worry is that biotin interference could therefore lead to missed diagnoses. The FDA has provided a list of those tests that have not taken biotin’s effects into account, titled “Biotin Interference with Troponin Lab Tests – Assays Subject to Biotin Interference.”
The daily recommended allowance for biotin, according to the communication, is about 0.3 mg, but it isn’t always clear how much is actually included in supplements – some can contain 20 mg or even as much as 100 mg per pill of biotin. The communication includes recommendations for patients, health care professionals, laboratory personnel, and lab test manufacturers and developers.
The full safety communication can be found on the FDA website, and problems with tests can be reported via the FDA’s MedWatch Voluntary Reporting Form.
The
However, not all troponin tests are affected, according to the update. “Since the FDA’s safety communication on this topic in 2017, some lab test developers have been successful at mitigating the biotin interference of their assays, but others have not yet addressed it,” according to the new communication, issued in early November.
Also known as vitamin B7 and appearing in many dietary supplements, including prenatal multivitamins and supplements for hair, skin, and nail growth, biotin can lead to falsely low results on some troponin tests, especially at high levels. The worry is that biotin interference could therefore lead to missed diagnoses. The FDA has provided a list of those tests that have not taken biotin’s effects into account, titled “Biotin Interference with Troponin Lab Tests – Assays Subject to Biotin Interference.”
The daily recommended allowance for biotin, according to the communication, is about 0.3 mg, but it isn’t always clear how much is actually included in supplements – some can contain 20 mg or even as much as 100 mg per pill of biotin. The communication includes recommendations for patients, health care professionals, laboratory personnel, and lab test manufacturers and developers.
The full safety communication can be found on the FDA website, and problems with tests can be reported via the FDA’s MedWatch Voluntary Reporting Form.
Fentanyl-related deaths show strong regional pattern
Fentanyl was involved in more overdose deaths than any other drug in 2017, and the death rate in New England was 15 times higher than in regions of the Midwest and West, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
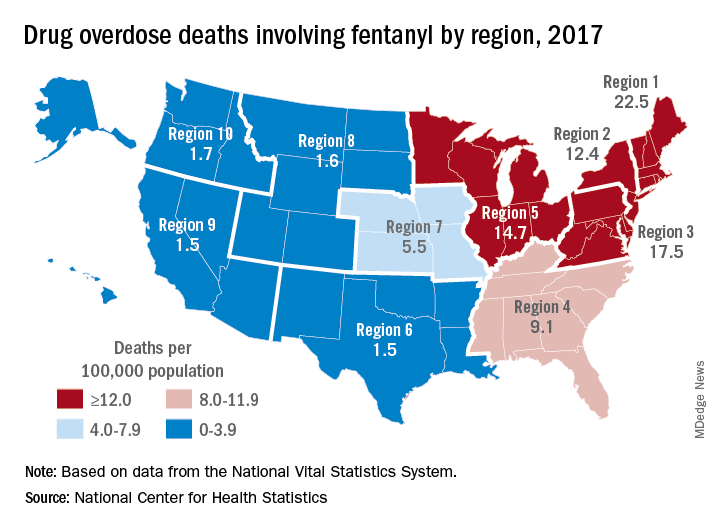
Nationally, fentanyl was involved in 39% of all drug overdose deaths and had an age-adjusted death rate of 8.7/100,000 standard population in 2017. In 2016, when fentanyl also was the most involved drug in the United States, the corresponding figures were 29% and 5.9/100,000, the agency said in a recent report.
Fentanyl was the most involved drug in overdose deaths for 6 of the country’s 10 public health regions in 2017, with a clear pattern of decreasing use from east to west. The highest death rate (22.5/100,000) occurred in Region 1 (New England) and the lowest rates (1.5/100,000) came in Region 6 (Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas) and Region 9 (Arizona, California, Hawaii, and Nevada), the researchers said.
A somewhat similar pattern was seen for heroin, which was second nationally on the list of drugs most frequently involved in overdose deaths (23%), except that New England was somewhat below three other regions in the East and upper Midwest. The highest heroin death rate (8.6/100,000) was seen in Region 2 (New Jersey and New York) and the lowest (2.2) occurred in Region 9, they said, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s mortality files.
The fentanyl pattern was even more closely repeated with cocaine, third in involvement nationally at 21% of overdose deaths in 2017. The high in overdose deaths (9.5/100,000) came in Region 1 again, and the low in Region 9 (1.3), along with Region 7 (Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska) and Region 10 (Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington), the report showed.
The regional pattern of overdose deaths for methamphetamine, which was fourth nationally in involvement (13.3%), basically reversed the other three drugs: highest in the West and lowest in the Northeast. Region 9 had the highest death rate (5.2/100,000) and Region 2 the lowest (0.4), with Region 1 just ahead at 0.6.
Fentanyl was involved in more overdose deaths than any other drug in 2017, and the death rate in New England was 15 times higher than in regions of the Midwest and West, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

Nationally, fentanyl was involved in 39% of all drug overdose deaths and had an age-adjusted death rate of 8.7/100,000 standard population in 2017. In 2016, when fentanyl also was the most involved drug in the United States, the corresponding figures were 29% and 5.9/100,000, the agency said in a recent report.
Fentanyl was the most involved drug in overdose deaths for 6 of the country’s 10 public health regions in 2017, with a clear pattern of decreasing use from east to west. The highest death rate (22.5/100,000) occurred in Region 1 (New England) and the lowest rates (1.5/100,000) came in Region 6 (Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas) and Region 9 (Arizona, California, Hawaii, and Nevada), the researchers said.
A somewhat similar pattern was seen for heroin, which was second nationally on the list of drugs most frequently involved in overdose deaths (23%), except that New England was somewhat below three other regions in the East and upper Midwest. The highest heroin death rate (8.6/100,000) was seen in Region 2 (New Jersey and New York) and the lowest (2.2) occurred in Region 9, they said, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s mortality files.
The fentanyl pattern was even more closely repeated with cocaine, third in involvement nationally at 21% of overdose deaths in 2017. The high in overdose deaths (9.5/100,000) came in Region 1 again, and the low in Region 9 (1.3), along with Region 7 (Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska) and Region 10 (Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington), the report showed.
The regional pattern of overdose deaths for methamphetamine, which was fourth nationally in involvement (13.3%), basically reversed the other three drugs: highest in the West and lowest in the Northeast. Region 9 had the highest death rate (5.2/100,000) and Region 2 the lowest (0.4), with Region 1 just ahead at 0.6.
Fentanyl was involved in more overdose deaths than any other drug in 2017, and the death rate in New England was 15 times higher than in regions of the Midwest and West, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.

Nationally, fentanyl was involved in 39% of all drug overdose deaths and had an age-adjusted death rate of 8.7/100,000 standard population in 2017. In 2016, when fentanyl also was the most involved drug in the United States, the corresponding figures were 29% and 5.9/100,000, the agency said in a recent report.
Fentanyl was the most involved drug in overdose deaths for 6 of the country’s 10 public health regions in 2017, with a clear pattern of decreasing use from east to west. The highest death rate (22.5/100,000) occurred in Region 1 (New England) and the lowest rates (1.5/100,000) came in Region 6 (Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas) and Region 9 (Arizona, California, Hawaii, and Nevada), the researchers said.
A somewhat similar pattern was seen for heroin, which was second nationally on the list of drugs most frequently involved in overdose deaths (23%), except that New England was somewhat below three other regions in the East and upper Midwest. The highest heroin death rate (8.6/100,000) was seen in Region 2 (New Jersey and New York) and the lowest (2.2) occurred in Region 9, they said, based on data from the National Vital Statistics System’s mortality files.
The fentanyl pattern was even more closely repeated with cocaine, third in involvement nationally at 21% of overdose deaths in 2017. The high in overdose deaths (9.5/100,000) came in Region 1 again, and the low in Region 9 (1.3), along with Region 7 (Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska) and Region 10 (Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington), the report showed.
The regional pattern of overdose deaths for methamphetamine, which was fourth nationally in involvement (13.3%), basically reversed the other three drugs: highest in the West and lowest in the Northeast. Region 9 had the highest death rate (5.2/100,000) and Region 2 the lowest (0.4), with Region 1 just ahead at 0.6.
CDC identifies probable culprit in vaping lung injuries
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
found in lung fluid of victims.
In a telebriefing on Friday, Anne Schuchat, MD, the CDC’s principal deputy director, provided an update on recent lab findings and on case and death numbers reported so far to the CDC. The findings and more case information were published in the Mortality and Morbidity Weekly Report.
At the telebriefing, Dr. Schuchat stated that CDC has received 29 samples of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid from EVALI patients from 10 states and that vitamin E acetate was identified in all samples. Vitamin E acetate has already been found in some vaping devices and the discovery of the chemical in the lungs of patients increases the likelihood that this toxin is at least one source of EVALI. These findings are the first to link substances found in vaping products with biological samples from patients hospitalized with EVALI.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) was found in 23 of 28 samples tested and nicotine was found in 16 of 26 samples tested. Other diluents and additives of concern (such as plant oils, medium chain triglyceride oil, petroleum distillates, and diluent terpenes) were not detected in BAL fluid specimens from EVALI patients.
BAL fluid specimens were collected from hospitalized EVALI patients in the course of their treatment, although not for the specific purpose of the CDC investigation, and sent to the CDC by public health laboratories and health departments in California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, Texas, Utah, and Wisconsin for analysis.
Dr. Schuchat stated that, as of Nov. 5, there have been 2,051 cases of EVALI reported to the CDC and 39 EVALI patients have died, with other deaths still under investigation as possibly related to EVALI. She said that the trend in new EVALI cases reported appears to be decreasing, but some states continue to see new cases. She cautioned that the lab findings of vitamin E acetate in BAL fluid do not rule out other possible compounds or ingredients that may contribute to EVALI and said the investigation will continue.
E-cigarette user survey
During the telebriefing, Jennifer Layden, MD, PhD, chief medical officer and state epidemiologist with the Illinois Department of Public Health (IDPH), gave an update on her department’s efforts to investigate vaping behaviors that might have led to EVALI in e-cigarette users and also to obtain more information on sources of vaping devices that could be linked to EVALI. The data were also reported in a MMWR.
The IDPH conducted an online public survey during September 2019 to October 2019 targeting e-cigarette, or vaping, product users in Illinois. The survey was promoted via social media on the IDPH website, local health departments, and other outlets. The survey yielded 4,631 respondents who answered questions about the frequency of vaping, sources of supply, and types of substances used. The investigators were then able to compare vaping-use habits and behaviors with similar information gleaned from EVALI patients.
Among survey respondents, 94% reported using any nicotine-containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products in the past 3 months; 21% used any THC-containing products; and 11% used both THC-containing products and nicotine-containing products. THC-containing product use was highest among survey respondents aged 18-24 years (36%) and decreased with increasing age. Compared with these survey respondents, EVALI patients were more likely to report exclusive use of THC-containing products (adjusted odds ratio, 2.0; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.6), frequent use (more than five times per day) of these products (aOR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.6-6.0), and obtaining these products from informal sources, such as from a dealer, off the street, or from a friend (aOR, 9.2; 95% CI, 2.2-39.4). In addition, “the odds of using Dank Vapes, a class of largely counterfeit THC-containing products, was also higher among EVALI patients” (aOR, 8.5; 95% CI, 3.8-19.0), according to the MMWR.
Recommendations
CDC recommends that people should not buy any type of e-cigarette, or vaping, products, particularly those containing THC, off the street. They should also refrain from modifying or adding any substances to e-cigarette, or vaping, products that are not intended by the manufacturer, including products purchased through retail establishments.
Dr. Layden concluded, “we are in a better place today than we were a few weeks ago in terms of having one very strong culprit of concern based on the lung fluid testing,” but since the specific substances causing lung injury are not yet known, the only way to assure that individuals are not at risk while the investigation continues is to consider refraining from use of all vaping products.
For more information and resources visit For the Public, For Healthcare Providers, and For Health Departments pages, as well as the CDC’s Publications and Resources page.
FDA approves anemia treatment for transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia patients
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first treatment for anemia in adults with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Luspatercept-aamt (Reblozyl) is an erythroid maturation agent that reduced the transfusion burden for patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial of 336 patients. In total, 21% of patients who received luspatercept-aamt achieved at least a 33% reduction in red blood cell transfusions, compared with 4.5% of patients who received placebo, according to the FDA.
Common side effects associated with luspatercept-aamt were headache, bone pain, arthralgia, fatigue, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dizziness. Patients taking the agent should be monitored for thrombosis, the FDA advised.
Celgene, which makes luspatercept-aamt, said the agent would be available about 1 week following the FDA approval.
The FDA is also evaluating luspatercept-aamt as an anemia treatment in adults with very-low– to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions. The agency is expected to take action on that application in April 2020.
Lung cancer on the decline, but still higher among men than women
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2007 to 2016, rates dropped among both sexes in metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, according to Mary Elizabeth O’Neil, MPH, and colleagues. Their report is in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8;68[44];993-8). But lung cancer incidence in 2016 was still 40% higher among men than among women, said Ms. O’Neil, an epidemiologist at the CDC.
Rather than narrowly focusing on the “just stop smoking” message, “a comprehensive approach to lung cancer prevention and control includes such population-based strategies as screening for tobacco dependence, promoting tobacco cessation, implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws, testing all homes for radon and using proven methods to lower high radon levels, and reducing exposure to lung carcinogens such as asbestos.” According to the authors of the report, “increasing the implementation of these strategies, particularly among persons living in nonmetropolitan counties, might help to reduce disparities in the decline of lung cancer incidence.”
The recommendation is based on data extracted from the U.S. Cancer Statistics Database for 2007-2016. The data cover 97% of the population.
In nonmetropolitan counties in 2007, incidence rates among men were 60% higher (99 vs. 61 per 100,000). Although rates decreased in both sexes, they were still elevated compared with women in 2016 (82 vs. 58 per 100,000; 40%).
Over the 10-year period, the rate declined more among men than among women (–2.9% vs. –1.5%) in metropolitan areas. The pattern repeated in nonmetropolitan areas (–2.1% and –0.5%, respectively).
There were different declines in different age groups by region, the authors noted.
Men aged 45-54 years in metropolitan areas experienced the largest decline (–5.2%).
Among women, the largest decline occurred in metropolitan areas among those aged 35-44 years (–5%). In nonmetropolitan areas, women in this age group experienced a 3.6% decline and women aged 65-74 years, a 1.3% decline.
Among persons aged 35-54 years, incidence rates in nonmetropolitan and metropolitan counties did not differ by sex but were higher in nonmetropolitan counties than in metropolitan counties.
There were also overall changes in smoking patterns. According to 2017 data from the National Health Interview Survey data, more adults in metropolitan areas than nonmetropolitan areas smoked (23% versus 13%) but fewer had tried to quit (50% vs. 56%). Successful quitting attempts also were lower (5% vs. 9%).
Although it is a large contributing factor, smoking is not the only risk factor for lung cancer, the authors wrote. About 10%-15% of lung cancer patients have never smoked tobacco. Nonsmoked tobacco products and second-hand exposure to cigarette smoke are risks, as are indoor radon and asbestos exposure.
Clinicians can help improve this scenario by screening at each office visit, the authors said. The recommendation is based on U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidance.
“Lung cancer screening is recommended for adults at high risk for developing lung cancer because of their age and cigarette smoking history. Screening efforts can identify lung cancer in its early stages and provide an important opportunity to promote tobacco smoking cessation.”
However, lack of insurance among residents of nonmetropolitan areas may hamper access to these services, they said. In those regions, “a higher percentage of residents aged less than 65 years report being uninsured compared with those in metropolitan areas.”
SOURCE: O’Neil ME et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8: 68(44);993-8.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2007 to 2016, rates dropped among both sexes in metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, according to Mary Elizabeth O’Neil, MPH, and colleagues. Their report is in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8;68[44];993-8). But lung cancer incidence in 2016 was still 40% higher among men than among women, said Ms. O’Neil, an epidemiologist at the CDC.
Rather than narrowly focusing on the “just stop smoking” message, “a comprehensive approach to lung cancer prevention and control includes such population-based strategies as screening for tobacco dependence, promoting tobacco cessation, implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws, testing all homes for radon and using proven methods to lower high radon levels, and reducing exposure to lung carcinogens such as asbestos.” According to the authors of the report, “increasing the implementation of these strategies, particularly among persons living in nonmetropolitan counties, might help to reduce disparities in the decline of lung cancer incidence.”
The recommendation is based on data extracted from the U.S. Cancer Statistics Database for 2007-2016. The data cover 97% of the population.
In nonmetropolitan counties in 2007, incidence rates among men were 60% higher (99 vs. 61 per 100,000). Although rates decreased in both sexes, they were still elevated compared with women in 2016 (82 vs. 58 per 100,000; 40%).
Over the 10-year period, the rate declined more among men than among women (–2.9% vs. –1.5%) in metropolitan areas. The pattern repeated in nonmetropolitan areas (–2.1% and –0.5%, respectively).
There were different declines in different age groups by region, the authors noted.
Men aged 45-54 years in metropolitan areas experienced the largest decline (–5.2%).
Among women, the largest decline occurred in metropolitan areas among those aged 35-44 years (–5%). In nonmetropolitan areas, women in this age group experienced a 3.6% decline and women aged 65-74 years, a 1.3% decline.
Among persons aged 35-54 years, incidence rates in nonmetropolitan and metropolitan counties did not differ by sex but were higher in nonmetropolitan counties than in metropolitan counties.
There were also overall changes in smoking patterns. According to 2017 data from the National Health Interview Survey data, more adults in metropolitan areas than nonmetropolitan areas smoked (23% versus 13%) but fewer had tried to quit (50% vs. 56%). Successful quitting attempts also were lower (5% vs. 9%).
Although it is a large contributing factor, smoking is not the only risk factor for lung cancer, the authors wrote. About 10%-15% of lung cancer patients have never smoked tobacco. Nonsmoked tobacco products and second-hand exposure to cigarette smoke are risks, as are indoor radon and asbestos exposure.
Clinicians can help improve this scenario by screening at each office visit, the authors said. The recommendation is based on U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidance.
“Lung cancer screening is recommended for adults at high risk for developing lung cancer because of their age and cigarette smoking history. Screening efforts can identify lung cancer in its early stages and provide an important opportunity to promote tobacco smoking cessation.”
However, lack of insurance among residents of nonmetropolitan areas may hamper access to these services, they said. In those regions, “a higher percentage of residents aged less than 65 years report being uninsured compared with those in metropolitan areas.”
SOURCE: O’Neil ME et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8: 68(44);993-8.
according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
From 2007 to 2016, rates dropped among both sexes in metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas, according to Mary Elizabeth O’Neil, MPH, and colleagues. Their report is in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8;68[44];993-8). But lung cancer incidence in 2016 was still 40% higher among men than among women, said Ms. O’Neil, an epidemiologist at the CDC.
Rather than narrowly focusing on the “just stop smoking” message, “a comprehensive approach to lung cancer prevention and control includes such population-based strategies as screening for tobacco dependence, promoting tobacco cessation, implementing comprehensive smoke-free laws, testing all homes for radon and using proven methods to lower high radon levels, and reducing exposure to lung carcinogens such as asbestos.” According to the authors of the report, “increasing the implementation of these strategies, particularly among persons living in nonmetropolitan counties, might help to reduce disparities in the decline of lung cancer incidence.”
The recommendation is based on data extracted from the U.S. Cancer Statistics Database for 2007-2016. The data cover 97% of the population.
In nonmetropolitan counties in 2007, incidence rates among men were 60% higher (99 vs. 61 per 100,000). Although rates decreased in both sexes, they were still elevated compared with women in 2016 (82 vs. 58 per 100,000; 40%).
Over the 10-year period, the rate declined more among men than among women (–2.9% vs. –1.5%) in metropolitan areas. The pattern repeated in nonmetropolitan areas (–2.1% and –0.5%, respectively).
There were different declines in different age groups by region, the authors noted.
Men aged 45-54 years in metropolitan areas experienced the largest decline (–5.2%).
Among women, the largest decline occurred in metropolitan areas among those aged 35-44 years (–5%). In nonmetropolitan areas, women in this age group experienced a 3.6% decline and women aged 65-74 years, a 1.3% decline.
Among persons aged 35-54 years, incidence rates in nonmetropolitan and metropolitan counties did not differ by sex but were higher in nonmetropolitan counties than in metropolitan counties.
There were also overall changes in smoking patterns. According to 2017 data from the National Health Interview Survey data, more adults in metropolitan areas than nonmetropolitan areas smoked (23% versus 13%) but fewer had tried to quit (50% vs. 56%). Successful quitting attempts also were lower (5% vs. 9%).
Although it is a large contributing factor, smoking is not the only risk factor for lung cancer, the authors wrote. About 10%-15% of lung cancer patients have never smoked tobacco. Nonsmoked tobacco products and second-hand exposure to cigarette smoke are risks, as are indoor radon and asbestos exposure.
Clinicians can help improve this scenario by screening at each office visit, the authors said. The recommendation is based on U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidance.
“Lung cancer screening is recommended for adults at high risk for developing lung cancer because of their age and cigarette smoking history. Screening efforts can identify lung cancer in its early stages and provide an important opportunity to promote tobacco smoking cessation.”
However, lack of insurance among residents of nonmetropolitan areas may hamper access to these services, they said. In those regions, “a higher percentage of residents aged less than 65 years report being uninsured compared with those in metropolitan areas.”
SOURCE: O’Neil ME et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Nov 8: 68(44);993-8.
FROM MMWR
FDA approves Ziextenzo for neutropenia-related infection reduction
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar Ziextenzo (pegfilgrastim-bmez) to reduce the incidence of infection in patients with nonmyeloid cancer receiving suppressive anticancer drugs that are associated with febrile neutropenia.
More than 60,000 cancer patients are hospitalized in the United States each year with evidence of neutropenia, resulting in more than 4,000 deaths, according to Ziextenzo maker Sandoz, a Novartis division.
The FDA approval was based on analytical, preclinical, and clinical research, including data from a three-way pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics study that compared pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drug pegfilgrastim (Neulasta) from the United States and the European Union. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic similarity were shown between pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drugs, and there were no clinically significant differences in safety or immunogenicity.
The most common adverse events associated with pegfilgrastim-bmez are bone pain and pain in the extremities, according to the label.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar Ziextenzo (pegfilgrastim-bmez) to reduce the incidence of infection in patients with nonmyeloid cancer receiving suppressive anticancer drugs that are associated with febrile neutropenia.
More than 60,000 cancer patients are hospitalized in the United States each year with evidence of neutropenia, resulting in more than 4,000 deaths, according to Ziextenzo maker Sandoz, a Novartis division.
The FDA approval was based on analytical, preclinical, and clinical research, including data from a three-way pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics study that compared pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drug pegfilgrastim (Neulasta) from the United States and the European Union. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic similarity were shown between pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drugs, and there were no clinically significant differences in safety or immunogenicity.
The most common adverse events associated with pegfilgrastim-bmez are bone pain and pain in the extremities, according to the label.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar Ziextenzo (pegfilgrastim-bmez) to reduce the incidence of infection in patients with nonmyeloid cancer receiving suppressive anticancer drugs that are associated with febrile neutropenia.
More than 60,000 cancer patients are hospitalized in the United States each year with evidence of neutropenia, resulting in more than 4,000 deaths, according to Ziextenzo maker Sandoz, a Novartis division.
The FDA approval was based on analytical, preclinical, and clinical research, including data from a three-way pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics study that compared pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drug pegfilgrastim (Neulasta) from the United States and the European Union. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic similarity were shown between pegfilgrastim-bmez with the reference drugs, and there were no clinically significant differences in safety or immunogenicity.
The most common adverse events associated with pegfilgrastim-bmez are bone pain and pain in the extremities, according to the label.






