User login
Mobile App Shows Promise in Managing Fibromyalgia Symptoms
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A smartphone app that delivers acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), a type of cognitive behavioral therapy, improves overall well-being and reduces the severity of pain, fatigue, sleep issues, and depression to a greater extent than daily symptom tracking in patients with fibromyalgia.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted the phase 3 PROSPER-FM trial at 25 community sites in the United States to assess the efficacy and safety of digital ACT for patients with fibromyalgia.
- A total of 275 adult patients aged 22-75 years with fibromyalgia were randomly assigned to either the digital ACT group (n = 140) or the active control group (n = 135) for 12 weeks.
- Patients in the digital ACT group received a self-guided, smartphone-delivered program in which they learned and practiced the core ACT skills of acceptance, values, mindfulness, defusion, self as context, and willingness and committed action to build psychological flexibility, while the control group underwent daily symptom tracking and received educational materials.
- The primary endpoint was the response rate on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) at week 12, which is an indicator of patient well-being.
- The secondary endpoints included changes in the Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ-R) total score and pain intensity, pain interference, and sleep interference scores.
TAKEAWAY:
- At week 12, 71% of the patients in the digital ACT group responded with a minimally improved or better change in the PGIC response, compared with only 22% of the patients in the control group (P < .0001).
- The digital ACT group showed a significant reduction in the impact of fibromyalgia, with a between-group effect size of d = 0.65 (P < .0001) at week 12. The FIQ-R total score significantly improved within 3 weeks of using the self-guided digital ACT app.
- The use of digital ACT also demonstrated positive effects on the levels of weekly pain intensity (P = .001) and depression (P < .0001), compared with the control group.
- No serious adverse effects related to the app were reported, and both groups demonstrated high rates of adherence, with most (72%) participants in the digital ACT group completing at least 42 sessions.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results found in the study are essential for professionals who care for patients with fibromyalgia as they present a new viable treatment alternative,” Guilherme Torres Vilarino, PhD, Santa Catarina State University, Florianópolis, Brazil, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
This study was led by R. Michael Gendreau, MD, PhD, Gendreau Consulting, Poway, California. It was published online in The Lancet.
LIMITATIONS:
The study population predominantly consisted of women and White individuals, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to more diverse populations. Additionally, the study was conducted in the United States, and the results may thus not be applicable to other countries with different racial, ethnic, educational, and economic characteristics. The study duration was 12 weeks, and the long-term benefits of digital ACT have not yet been shown.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Swing Therapeutics. Seven authors declared having stock options and/or receiving salary from Swing Therapeutics. Other authors reported having many ties with several sources, including Swing Therapeutics.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinical Controversy: Watch-and-Wait or Surgery in Rectal Cancer Near Complete Responders?
Having an ostomy is a dreaded prospect for many patients with rectal cancer.
To defer, and potentially avoid, this life-altering surgery,
About 80% of these patients who have a complete clinical response — a perfectly healed scar where the tumor used to be and other favorable features — can forgo total mesorectal excision and preserve their rectum.
The success of watch-and-wait among complete responders has led some centers to offer the approach in patients with near-complete responses to neoadjuvant chemoradiation.
But watch-and-wait for near-complete clinical responders “is very controversial,” Alan P. Venook, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
“You sure as hell don’t want to miss a chance to cure a patient,” Dr. Venook said.
A near-complete clinical response essentially means there is no sign of the tumor 8 weeks after total neoadjuvant therapy, but the tumor bed hasn’t completely healed.
The goal of watch-and-wait in this scenario is to give near-complete response lesions time to become complete responses.
But there’s no clear way to predict which tumors will evolve into a clinical complete response.
Recent studies evaluating the conversion rate have reported that anywhere from 39% to about 90% of near-complete responders became complete responders. Some of the variation likely comes down to differences in the clinical stage of patients evaluated in each study as well as the limited number of patients who achieve a near-complete response overall.
Other concerns have emerged that waiting for near-complete responses to become complete leaves extra time for some tumors to metastasize and that tumor regrowth is much higher compared with complete responders.
A recent study found that 13% of near-complete responders who preserved their rectum on watch-and-wait developed distant metastases vs about 5% of long-term complete responders. The study also found that just over half of near-complete responders have tumor regrowth compared with about one in five complete responders.
But even with regrowth, “surgery is still curative,” explained Julio Garcia-Aguilar, MD, PhD, a pioneer of watch-and-wait for rectal cancer.
And overall, around 50%-60% of patients with a near-complete response can avoid surgery and preserve their rectum.
Selecting Patients for Watch-and-Wait
The key to deciding which patients are right for watch-and-wait is to understand how a near-complete clinical response was defined in the OPRA trial, a landmark randomized trial led by Dr. Garcia-Aguilar that helped establish watch-and-wait as an option in rectal cancer.
OPRA defined a near-complete response as no visible tumor but, in the tumor bed, mild erythema, superficial ulceration, minor mucosal abnormality or small nodules, and an irregular mucosa. The criteria also included no palpable tumor with smooth induration or a minor mucosal abnormality on the digital rectal exam.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network mirrored the definition when, for the first time, it recommended watch-and-wait as an option for near-complete response in its 2023 rectal cancer guidelines. The group also added a few MRI requirements.
UCSF offers the watch-and-wait option to some patients with near-complete responses, but each decision is made on a case-by-case basis by a tumor board considering numerous measures of tumor aggressiveness.
Even then, “we have, in many cases, struggled to figure out what the right choices are,” Dr. Venook said.
For those chosen for watch-and-wait, Dr. Venook noted that UCSF has top-notch surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and pathologists who have the resources to follow patients closely.
For community practices without the resources of a major cancer center, watch-and-wait for near-complete response to rectal cancer “is really asking a lot,” Dr. Venook said.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar, a colorectal surgeon at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, explained that after years of studying the issue, he is comfortable with watch-and-wait in near-complete responders as long as it’s done carefully and in patients who will comply with ongoing surveillance.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar explained that, after diagnosing a near-complete response 8 weeks following total neoadjuvant therapy, the patient needs to come back 6 weeks later. At that point, it’s time to assess whether that near-complete response is evolving into a complete response or not evolving into a complete response.
If it’s evolving into a complete response, surveillance continues about every 8 weeks, but if the tumor has stopped responding, “you take [the patient] to the operating room,” Dr. Garcia-Aguilar said.
As for the bigger safety concern — that near clinical complete response tumors will metastasize — Dr. Garcia-Aguilar’s opinion is that micrometastases are probably already there when the rectal cancer is first diagnosed and will manifest themselves “no matter what happens to the primary tumor.”
Because of that, he noted, “I don’t think the risk is very high” when surgery is delayed a few months to give near-complete response patients a chance to keep their rectum.
The way to answer the metastasis question is to do a randomized trial pitting surgery against watch-and-wait in patients with near-clinical complete response rectal cancer.
However, Dr. Garcia-Aguilar doesn’t think that trial will ever happen. Patients won’t allow themselves to be randomized to surgery once they find out they might be able to avoid a permanent ostomy, he said.
Dr. Venook had no disclosures. Dr. Garcia-Aguilar reported personal fees from Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, and Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having an ostomy is a dreaded prospect for many patients with rectal cancer.
To defer, and potentially avoid, this life-altering surgery,
About 80% of these patients who have a complete clinical response — a perfectly healed scar where the tumor used to be and other favorable features — can forgo total mesorectal excision and preserve their rectum.
The success of watch-and-wait among complete responders has led some centers to offer the approach in patients with near-complete responses to neoadjuvant chemoradiation.
But watch-and-wait for near-complete clinical responders “is very controversial,” Alan P. Venook, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
“You sure as hell don’t want to miss a chance to cure a patient,” Dr. Venook said.
A near-complete clinical response essentially means there is no sign of the tumor 8 weeks after total neoadjuvant therapy, but the tumor bed hasn’t completely healed.
The goal of watch-and-wait in this scenario is to give near-complete response lesions time to become complete responses.
But there’s no clear way to predict which tumors will evolve into a clinical complete response.
Recent studies evaluating the conversion rate have reported that anywhere from 39% to about 90% of near-complete responders became complete responders. Some of the variation likely comes down to differences in the clinical stage of patients evaluated in each study as well as the limited number of patients who achieve a near-complete response overall.
Other concerns have emerged that waiting for near-complete responses to become complete leaves extra time for some tumors to metastasize and that tumor regrowth is much higher compared with complete responders.
A recent study found that 13% of near-complete responders who preserved their rectum on watch-and-wait developed distant metastases vs about 5% of long-term complete responders. The study also found that just over half of near-complete responders have tumor regrowth compared with about one in five complete responders.
But even with regrowth, “surgery is still curative,” explained Julio Garcia-Aguilar, MD, PhD, a pioneer of watch-and-wait for rectal cancer.
And overall, around 50%-60% of patients with a near-complete response can avoid surgery and preserve their rectum.
Selecting Patients for Watch-and-Wait
The key to deciding which patients are right for watch-and-wait is to understand how a near-complete clinical response was defined in the OPRA trial, a landmark randomized trial led by Dr. Garcia-Aguilar that helped establish watch-and-wait as an option in rectal cancer.
OPRA defined a near-complete response as no visible tumor but, in the tumor bed, mild erythema, superficial ulceration, minor mucosal abnormality or small nodules, and an irregular mucosa. The criteria also included no palpable tumor with smooth induration or a minor mucosal abnormality on the digital rectal exam.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network mirrored the definition when, for the first time, it recommended watch-and-wait as an option for near-complete response in its 2023 rectal cancer guidelines. The group also added a few MRI requirements.
UCSF offers the watch-and-wait option to some patients with near-complete responses, but each decision is made on a case-by-case basis by a tumor board considering numerous measures of tumor aggressiveness.
Even then, “we have, in many cases, struggled to figure out what the right choices are,” Dr. Venook said.
For those chosen for watch-and-wait, Dr. Venook noted that UCSF has top-notch surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and pathologists who have the resources to follow patients closely.
For community practices without the resources of a major cancer center, watch-and-wait for near-complete response to rectal cancer “is really asking a lot,” Dr. Venook said.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar, a colorectal surgeon at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, explained that after years of studying the issue, he is comfortable with watch-and-wait in near-complete responders as long as it’s done carefully and in patients who will comply with ongoing surveillance.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar explained that, after diagnosing a near-complete response 8 weeks following total neoadjuvant therapy, the patient needs to come back 6 weeks later. At that point, it’s time to assess whether that near-complete response is evolving into a complete response or not evolving into a complete response.
If it’s evolving into a complete response, surveillance continues about every 8 weeks, but if the tumor has stopped responding, “you take [the patient] to the operating room,” Dr. Garcia-Aguilar said.
As for the bigger safety concern — that near clinical complete response tumors will metastasize — Dr. Garcia-Aguilar’s opinion is that micrometastases are probably already there when the rectal cancer is first diagnosed and will manifest themselves “no matter what happens to the primary tumor.”
Because of that, he noted, “I don’t think the risk is very high” when surgery is delayed a few months to give near-complete response patients a chance to keep their rectum.
The way to answer the metastasis question is to do a randomized trial pitting surgery against watch-and-wait in patients with near-clinical complete response rectal cancer.
However, Dr. Garcia-Aguilar doesn’t think that trial will ever happen. Patients won’t allow themselves to be randomized to surgery once they find out they might be able to avoid a permanent ostomy, he said.
Dr. Venook had no disclosures. Dr. Garcia-Aguilar reported personal fees from Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, and Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Having an ostomy is a dreaded prospect for many patients with rectal cancer.
To defer, and potentially avoid, this life-altering surgery,
About 80% of these patients who have a complete clinical response — a perfectly healed scar where the tumor used to be and other favorable features — can forgo total mesorectal excision and preserve their rectum.
The success of watch-and-wait among complete responders has led some centers to offer the approach in patients with near-complete responses to neoadjuvant chemoradiation.
But watch-and-wait for near-complete clinical responders “is very controversial,” Alan P. Venook, MD, a gastrointestinal oncologist at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), told this news organization.
“You sure as hell don’t want to miss a chance to cure a patient,” Dr. Venook said.
A near-complete clinical response essentially means there is no sign of the tumor 8 weeks after total neoadjuvant therapy, but the tumor bed hasn’t completely healed.
The goal of watch-and-wait in this scenario is to give near-complete response lesions time to become complete responses.
But there’s no clear way to predict which tumors will evolve into a clinical complete response.
Recent studies evaluating the conversion rate have reported that anywhere from 39% to about 90% of near-complete responders became complete responders. Some of the variation likely comes down to differences in the clinical stage of patients evaluated in each study as well as the limited number of patients who achieve a near-complete response overall.
Other concerns have emerged that waiting for near-complete responses to become complete leaves extra time for some tumors to metastasize and that tumor regrowth is much higher compared with complete responders.
A recent study found that 13% of near-complete responders who preserved their rectum on watch-and-wait developed distant metastases vs about 5% of long-term complete responders. The study also found that just over half of near-complete responders have tumor regrowth compared with about one in five complete responders.
But even with regrowth, “surgery is still curative,” explained Julio Garcia-Aguilar, MD, PhD, a pioneer of watch-and-wait for rectal cancer.
And overall, around 50%-60% of patients with a near-complete response can avoid surgery and preserve their rectum.
Selecting Patients for Watch-and-Wait
The key to deciding which patients are right for watch-and-wait is to understand how a near-complete clinical response was defined in the OPRA trial, a landmark randomized trial led by Dr. Garcia-Aguilar that helped establish watch-and-wait as an option in rectal cancer.
OPRA defined a near-complete response as no visible tumor but, in the tumor bed, mild erythema, superficial ulceration, minor mucosal abnormality or small nodules, and an irregular mucosa. The criteria also included no palpable tumor with smooth induration or a minor mucosal abnormality on the digital rectal exam.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network mirrored the definition when, for the first time, it recommended watch-and-wait as an option for near-complete response in its 2023 rectal cancer guidelines. The group also added a few MRI requirements.
UCSF offers the watch-and-wait option to some patients with near-complete responses, but each decision is made on a case-by-case basis by a tumor board considering numerous measures of tumor aggressiveness.
Even then, “we have, in many cases, struggled to figure out what the right choices are,” Dr. Venook said.
For those chosen for watch-and-wait, Dr. Venook noted that UCSF has top-notch surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and pathologists who have the resources to follow patients closely.
For community practices without the resources of a major cancer center, watch-and-wait for near-complete response to rectal cancer “is really asking a lot,” Dr. Venook said.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar, a colorectal surgeon at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, explained that after years of studying the issue, he is comfortable with watch-and-wait in near-complete responders as long as it’s done carefully and in patients who will comply with ongoing surveillance.
Dr. Garcia-Aguilar explained that, after diagnosing a near-complete response 8 weeks following total neoadjuvant therapy, the patient needs to come back 6 weeks later. At that point, it’s time to assess whether that near-complete response is evolving into a complete response or not evolving into a complete response.
If it’s evolving into a complete response, surveillance continues about every 8 weeks, but if the tumor has stopped responding, “you take [the patient] to the operating room,” Dr. Garcia-Aguilar said.
As for the bigger safety concern — that near clinical complete response tumors will metastasize — Dr. Garcia-Aguilar’s opinion is that micrometastases are probably already there when the rectal cancer is first diagnosed and will manifest themselves “no matter what happens to the primary tumor.”
Because of that, he noted, “I don’t think the risk is very high” when surgery is delayed a few months to give near-complete response patients a chance to keep their rectum.
The way to answer the metastasis question is to do a randomized trial pitting surgery against watch-and-wait in patients with near-clinical complete response rectal cancer.
However, Dr. Garcia-Aguilar doesn’t think that trial will ever happen. Patients won’t allow themselves to be randomized to surgery once they find out they might be able to avoid a permanent ostomy, he said.
Dr. Venook had no disclosures. Dr. Garcia-Aguilar reported personal fees from Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, and Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Tourniquet: The AED for Bleeding?
This discussion was recorded on July 12, 2024. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi and welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. I recently met an innovative young woman named Hannah Herbst while attending the annual Eagles EMS Conference in Fort Lauderdale, Florida.
Hannah Herbst is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and founder of a company called Golden Hour Medical. She has a background in IT and developed an automated pneumatic tourniquet known as AutoTQ, which we’re going to discuss at length here.
Also joining us is Dr. Peter Antevy, a pediatric emergency physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue as well as Coral Springs Parkland Fire Rescue. Peter is a member of EMS Eagles Global Alliance and is highly involved in high-quality research in prehospital emergency care and is quite well known in Florida and nationally.
Welcome to both of you.
Hannah Herbst: Thank you very much. Very grateful to be here.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, I’ll let you start by explaining what AutoTQ is and then compare that to a standard Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT).
Ms. Herbst: Thank you. Unfortunately, blood loss is a leading cause of preventable death and trauma. When there’s blood loss occurring from an arm or a leg, the easiest way to stop it is by applying a tourniquet, which is this compression type of device that you place above the site of bleeding, and it then applies a high amount of pressure to stop blood flow through the limb.
Currently, tourniquets on the market have failure rates as high as 84%. This became very real to me back in 2018, when I became aware of mass casualty incidents when I was a student. I became interested in how we can reimagine the conventional tourniquet and try to make it something that’s very user-friendly, much like an automated external defibrillator (AED).
My team and I developed AutoTQ, which is an automated tourniquet. which is a leading cause of tourniquet failure and being able to effectively administer treatment to a patient that may bleed out.
Tourniquet Failure Rates
Dr. Glatter: In terms of tourniquet failure, how often do standard tourniquets fail, like the CAT combat-type tourniquet?
Ms. Herbst: Unfortunately, they fail very frequently. There are several studies that have been conducted to evaluate this. Many of them occur immediately after training. They found failure rates between 80% and 90% for the current conventional CAT tourniquet immediately after training, which is very concerning.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of failure, was it the windlass aspect of the tourniquet that failed? Or was it something related to the actual strap? Was that in any way detailed?
Ms. Herbst: There are usually a few different failure points that have been found in the literature. One is placement. Many times, when you’re panicked, you don’t remember exactly how to place it. It should be placed high and tight above the bleed and not over a joint.
The second problem is inadequate tightness. For a CAT tourniquet to be effective, you have to get it extremely tight on that first pull before the windlass is activated, and many times people don’t remember that in the stress of the moment.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of tourniquet application by your medics in the field, certainly the CAT-type device has been in existence for quite a while. Hannah’s proposing a new iteration of how to do this, which is automated and simple. What is your take on such a device? And how did you learn about Hannah’s device?
Peter M. Antevy, MD: We’ve been training on tourniquets ever since the military data showed that there was an extreme benefit in using them. We’ve been doing training for many years, including our police officers. What we’ve noticed is that every time we gather everyone together to show them how to place a tourniquet — and we have to do one-on-one sessions with them — it’s not a device that they can easily put on. These are police officers who had the training last year.
Like Hannah said, most of the time they have a problem unraveling it and understanding how to actually place it. It’s easier on the arm than it is on the leg. You can imagine it would be harder to place it on your own leg, especially if you had an injury. Then, they don’t tighten it well enough, as Hannah just mentioned. In order for a tourniquet to really be placed properly, it’s going to hurt that person. Many people have that tendency not to want to tighten it as much as they can.
Having said that, how I got into all of this is because I’m the medical director for Coral Springs and Parkland, and unfortunately, we had the 2018 Valentine’s Day murders that happened where we lost 17 adults and kids. However, 17 people were saved that day, and the credit goes to our police officers who had tourniquets or chest seals on before those patients were brought out to EMS. Many lives were saved by the tourniquet.
If you look at the Boston Marathon massacre and many other events that have happened, I believe — and I’ve always believed — that tourniquets should be in the glove box of every citizen. It should be in every school room. They should be in buildings along with the AED.
In my town of Davie, we were the first in the country to add an ordinance that required a Stop the Bleed kit in the AED cabinet, and those were required by buildings of certain sizes. In order to get this lifesaving device everywhere, I think it has to be put into local ordinance and supported by states and by the national folks, which they are doing.
Trials Are Underway
Dr. Glatter: In terms of adoption of such a device, it certainly has to go through rigorous testing and maybe some trials. Hannah, where are you at with vetting this in terms of any type of trial? Has it been compared head to head with standard tourniquets?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we’re currently doing large amounts of field testing. We’re doing testing on emergency vehicles and in the surgical setting with different customers. In addition, we’re running pilot studies at different universities and with different organizations, including the military, to make sure that this device is effective. We’re evaluating cognitive offloading of people. We’re hoping to start that study later this year. We’re excited to be doing this in a variety of settings.
We’re also testing the quality of it in different environmental conditions and under different atmospheric pressure. We’re doing everything we can to ensure the device is safe and effective. We’re excited to scale and fill our preorders and be able to develop this and deliver it to many people.
Dr. Glatter: I was wondering if you could describe the actual device. There’s a brain part of it and then, obviously, the strap aspect of it. I was curious about contamination and reusability issues.
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question. One of the limitations of conventional tourniquets on the market is that they are single use, and often, it requires two tourniquets to stop a bleed, both of which have to be disposed of.
With AutoTQ, we have a reusable component and a disposable component. I actually have one here that I can show you. We have a cover on it that says: Stop bleed, slide up and power on. You just pull this cover off and then you have a few simple commands. You have powering the device on. I’ll just click this button: Tighten strap above bleeding, then press inflate. It delivers audible instructions telling you exactly how to use the device. Then, you tighten it above your bleed on the limb, and you press the inflate button. Then it administers air into the cuff and stops the patient’s bleed.
Tourniquet Conversion and Limb Salvage
Dr. Glatter: In terms of ischemia time, how can a device like this make it easier for us to know when to let the tourniquet down and allow some blood flow? Certainly, limb salvage is important, and we don’t want to have necrosis and so forth.
Dr. Antevy: That’s a great question. The limb salvage rate when tourniquets have been used is 85%. When used correctly, you can really improve the outcomes for many patients.
On the flip side of that, there’s something called tourniquet conversion. That’s exactly what you mentioned. It’s making sure that the tourniquet doesn’t stay on for too long of a time. If you can imagine a patient going to an outlying hospital where there’s no trauma center, and then that patient then has to be moved a couple hours to the trauma center, could you potentially have a tourniquet on for too long that then ends up causing the patient a bad outcome? The answer is yes.
I just had someone on my webinar recently describing the appropriate conversion techniques of tourniquets. You don’t find too much of that in the literature, but you really have to ensure that as you’re taking the tourniquet down, the bleeding is actually stopped. It’s not really recommended to take a tourniquet down if the patient was just acutely bleeding.
However, imagine a situation where a tourniquet was put on incorrectly. Let’s say a patient got nervous and they just put it on a patient who didn’t really need it. You really have to understand how to evaluate that wound to be sure that, as you’re taking the tourniquet down slowly, the patient doesn’t rebleed again.
There are two sides of the question, Rob. One is making sure it’s not on inappropriately. The second one is making sure it’s not on for too long, which ends up causing ischemia to that limb.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, does your device collect data on the number of hours or minutes that the tourniquet has been up and then automatically deflate it in some sense to allow for that improvement in limb salvage?
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question, and I really appreciate your answer as well, Dr Antevy. Ischemia time is a very important and critical component of tourniquet use. This is something, when we were designing AutoTQ, that we took into high consideration.
We found, when we evaluated AutoTQ vs a CAT tourniquet in a mannequin model, that AutoTQ can achieve cessation of hemorrhage at around 400 mm Hg of mercury, whereas CAT requires 700-800 mm Hg. Already our ischemia time is slightly extended just based on existing literature with pneumatic tourniquets because it can stop the bleed at a lower pressure, which causes less complications with the patient’s limb.
There are different features that we build out for different customers, so depending on what people want, it is possible to deflate the tourniquet. However, typically, you’re at the hospital within 30 minutes. It’s quick to get them there, and then the physician can treat and take that tourniquet down in a supervised and controlled setting.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of patients with obesity, do you have adjustable straps that will accommodate for that aspect?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we have different cuff sizes to accommodate different limbs.
Will AutoTQ Be Available to the Public?
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of usability in the prehospital setting, where do you think this is going in the next 3-5 years?
Dr. Antevy: I’ll start with the public safety sector of the United States, which is the one that is actually first on scene. Whether you’re talking about police officers or EMS, it would behoove us to have tourniquets everywhere. On all of my ambulances, across all of my agencies that I manage, we have quite a number of tourniquets.
Obviously, cost is a factor, and I know that Hannah has done a great job of making that brain reusable. All we have to do is purchase the straps, which are effectively the same cost, I understand, as a typical tourniquet you would purchase.
Moving forward though, however, I think that this has wide scalability to the public market, whether it be schools, office buildings, the glove box, and so on. It’s really impossible to teach somebody how to do this the right way, if you have to teach them how to put the strap on, tighten it correctly, and so on. If there was an easy way, like Hannah developed, of just putting it on and pushing a button, then I think that the outcomes and the scalability are much further beyond what we can do in EMS. I think there’s great value in both markets.
The ‘AED of Bleeding’: Rechargeable and Reusable
Dr. Glatter: This is the AED of bleeding. You have a device here that has wide-scale interest, certainly from the public and private sector.
Hannah, in terms of battery decay, how would that work out if it was in someone’s garage? Let’s just say someone purchased it and they hadn’t used it in 3 or 4 months. What type of decay are we looking at and can they rely on it?
Ms. Herbst: AutoTQ is rechargeable by a USB-C port, and our battery lasts for a year. Once a year, you’ll get an email reminder that says: “Hey, please charge your AutoTQ and make sure it’s up to the battery level.” We do everything in our power to make sure that our consumers are checking their batteries and that they’re ready to go.
Dr. Glatter: Is it heat and fire resistant? What, in terms of durability, does your device have?
Ms. Herbst: Just like any other medical device, we come with manufacturer recommendations for the upper and lower bounds of temperature and different storage recommendations. All of that is in our instructions for use.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, getting back to logistics. In terms of adoption, do you feel that, in the long term, this device will be something that we’re going to be seeing widely adopted just going forward?
Dr. Antevy: I do, and I’ll tell you why. When you look at AED use in this country, the odds of someone actually getting an AED and using it correctly are still very low. Part of that is because it’s complicated for many people to do. Getting tourniquets everywhere is step No. 1, and I think the federal government and the Stop the Bleed program is really making that happen.
We talked about ordinances, but ease of use, I think, is really the key. You have people who oftentimes have their child in cardiac arrest in front of them, and they won’t put two hands on their chest because they just are afraid of doing it.
When you have a device that’s a tourniquet, that’s a single-button turn on and single-button inflate, I think that would make it much more likely that a person will use that device when they’re passing the scene of an accident, as an example.
We’ve had many non–mass casualty incident events that have had tourniquets. We’ve had some media stories on them, where they’re just happening because someone got into a motor vehicle accident. It doesn’t have to be a school shooting. I think the tourniquets should be everywhere and should be easily used by everybody.
Managing Pain
Dr. Glatter: Regarding sedation, is there a need because of the pain involved with the application? How would you sedate a patient, pediatric or adult, who needs a tourniquet?
Dr. Antevy: We always evaluate people’s pain. If the patient is an extremist, we’re just going to be managing and trying to get them back to life. Once somebody is stabilized and is exhibiting pain of any sort, even, for example, after we intubate somebody, we have to sedate them and provide them pain control because they have a piece of plastic in their trachea.
It’s the same thing here for a tourniquet. These are painful, and we do have the appropriate medications on our vehicles to address that pain. Again, just simply the trauma itself is very painful. Yes, we do address that in EMS, and I would say most public agencies across this country would address pain appropriately.
Training on Tourniquet Use
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, can you talk a little bit about public training types of approaches? How would you train a consumer who purchases this type of device?
Ms. Herbst: A huge part of our mission is making blood loss prevention and control training accessible to a wide variety of people. One way that we’re able to do that is through our online training platform. When you purchase an AutoTQ kit, you plug it into your computer, and it walks you through the process of using it. It lets you practice on your own limb and on your buddy’s limb, just to be able to effectively apply it. We think this will have huge impacts in making sure that people are prepared and ready to stop the bleed with AutoTQ.
Dr. Glatter: Do you recommend people training once a month, in general, just to keep their skills up to use this? In the throes of a trauma and very chaotic situation, people sometimes lose their ability to think clearly and straightly.
Ms. Herbst: One of the studies we’re conducting is a learning curve study to try to figure out how quickly these skills degrade over time. We know that with the windlass tourniquet, it degrades within moments of training. With AutoTQ, we think the learning curve will last much longer. That’s something we’re evaluating, but we recommend people train as often as they can.
Dr. Antevy: Rob, if I can mention that there is a concept of just-in-time training. I think that with having the expectation that people are going to be training frequently, unfortunately, as many of us know, even with the AED as a perfect example, people don’t do that.
Yes. I would agree that you have to train at least once a year, is what I would say. At my office, we have a 2-hour training that goes over all these different items once a year.
The device itself should have the ability to allow you to figure out how to use it just in time, whether via video, or like Hannah’s device, by audio. I think that having both those things would make it more likely that the device be used when needed.
People panic, and if they have a device that can talk to them or walk them through it, they will be much more likely to use it at that time.
Final Takeaways
Dr. Glatter: Any other final thoughts or a few pearls for listeners to take away? Hannah, I’ll start with you.
Ms. Herbst: I’m very grateful for your time, and I’m very excited about the potential for AutoTQ. To me, it’s so exciting to see people preordering the device now. We’ve had people from school bus companies and small sports teams. I think, just like Dr Antevy said, tourniquets aren’t limited to mass casualty situations. Blood loss can happen anywhere and to anyone.
Being able to equip people and serve them to better prepare them for this happening to themselves, their friends, or their family is just the honor of a lifetime. Thank you very much for covering the device and for having me today.
Dr. Glatter: Of course, my pleasure. Peter?
Dr. Antevy: The citizens of this country, and everyone who lives across the world, has started to understand that there are things that we expect from our people, from the community. We expect them to do CPR for cardiac arrest. We expect them to know how to use an EpiPen. We expect them to know how to use an AED, and we also expect them to know how to stop bleeding with a tourniquet.
The American public has gotten to understand that these devices are very important. Having a device that’s easily used, that I can teach you in 10 seconds, that speaks to you — these are all things that make this product have great potential. I do look forward to the studies, not just the cadaver studies, but the real human studies.
I know Hannah is really a phenom and has been doing all these things so that this product can be on the shelves of Walmart and CVS one day. I commend you, Hannah, for everything you’re doing and wishing you the best of luck. We’re here for you.
Dr. Glatter: Same here. Congratulations on your innovative capability and what you’ve done to change the outcomes of bleeding related to penetrating trauma. Thank you so much.
Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. Hannah D. Herbst, BS, is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, was selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and is the founder/CEO of Golden Hour Medical. Peter M. Antevy, MD, is a pediatric emergency medicine physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue and Coral Springs–Parkland Fire Department in Florida. He is also a member of the EMS Eagles Global Alliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This discussion was recorded on July 12, 2024. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi and welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. I recently met an innovative young woman named Hannah Herbst while attending the annual Eagles EMS Conference in Fort Lauderdale, Florida.
Hannah Herbst is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and founder of a company called Golden Hour Medical. She has a background in IT and developed an automated pneumatic tourniquet known as AutoTQ, which we’re going to discuss at length here.
Also joining us is Dr. Peter Antevy, a pediatric emergency physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue as well as Coral Springs Parkland Fire Rescue. Peter is a member of EMS Eagles Global Alliance and is highly involved in high-quality research in prehospital emergency care and is quite well known in Florida and nationally.
Welcome to both of you.
Hannah Herbst: Thank you very much. Very grateful to be here.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, I’ll let you start by explaining what AutoTQ is and then compare that to a standard Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT).
Ms. Herbst: Thank you. Unfortunately, blood loss is a leading cause of preventable death and trauma. When there’s blood loss occurring from an arm or a leg, the easiest way to stop it is by applying a tourniquet, which is this compression type of device that you place above the site of bleeding, and it then applies a high amount of pressure to stop blood flow through the limb.
Currently, tourniquets on the market have failure rates as high as 84%. This became very real to me back in 2018, when I became aware of mass casualty incidents when I was a student. I became interested in how we can reimagine the conventional tourniquet and try to make it something that’s very user-friendly, much like an automated external defibrillator (AED).
My team and I developed AutoTQ, which is an automated tourniquet. which is a leading cause of tourniquet failure and being able to effectively administer treatment to a patient that may bleed out.
Tourniquet Failure Rates
Dr. Glatter: In terms of tourniquet failure, how often do standard tourniquets fail, like the CAT combat-type tourniquet?
Ms. Herbst: Unfortunately, they fail very frequently. There are several studies that have been conducted to evaluate this. Many of them occur immediately after training. They found failure rates between 80% and 90% for the current conventional CAT tourniquet immediately after training, which is very concerning.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of failure, was it the windlass aspect of the tourniquet that failed? Or was it something related to the actual strap? Was that in any way detailed?
Ms. Herbst: There are usually a few different failure points that have been found in the literature. One is placement. Many times, when you’re panicked, you don’t remember exactly how to place it. It should be placed high and tight above the bleed and not over a joint.
The second problem is inadequate tightness. For a CAT tourniquet to be effective, you have to get it extremely tight on that first pull before the windlass is activated, and many times people don’t remember that in the stress of the moment.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of tourniquet application by your medics in the field, certainly the CAT-type device has been in existence for quite a while. Hannah’s proposing a new iteration of how to do this, which is automated and simple. What is your take on such a device? And how did you learn about Hannah’s device?
Peter M. Antevy, MD: We’ve been training on tourniquets ever since the military data showed that there was an extreme benefit in using them. We’ve been doing training for many years, including our police officers. What we’ve noticed is that every time we gather everyone together to show them how to place a tourniquet — and we have to do one-on-one sessions with them — it’s not a device that they can easily put on. These are police officers who had the training last year.
Like Hannah said, most of the time they have a problem unraveling it and understanding how to actually place it. It’s easier on the arm than it is on the leg. You can imagine it would be harder to place it on your own leg, especially if you had an injury. Then, they don’t tighten it well enough, as Hannah just mentioned. In order for a tourniquet to really be placed properly, it’s going to hurt that person. Many people have that tendency not to want to tighten it as much as they can.
Having said that, how I got into all of this is because I’m the medical director for Coral Springs and Parkland, and unfortunately, we had the 2018 Valentine’s Day murders that happened where we lost 17 adults and kids. However, 17 people were saved that day, and the credit goes to our police officers who had tourniquets or chest seals on before those patients were brought out to EMS. Many lives were saved by the tourniquet.
If you look at the Boston Marathon massacre and many other events that have happened, I believe — and I’ve always believed — that tourniquets should be in the glove box of every citizen. It should be in every school room. They should be in buildings along with the AED.
In my town of Davie, we were the first in the country to add an ordinance that required a Stop the Bleed kit in the AED cabinet, and those were required by buildings of certain sizes. In order to get this lifesaving device everywhere, I think it has to be put into local ordinance and supported by states and by the national folks, which they are doing.
Trials Are Underway
Dr. Glatter: In terms of adoption of such a device, it certainly has to go through rigorous testing and maybe some trials. Hannah, where are you at with vetting this in terms of any type of trial? Has it been compared head to head with standard tourniquets?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we’re currently doing large amounts of field testing. We’re doing testing on emergency vehicles and in the surgical setting with different customers. In addition, we’re running pilot studies at different universities and with different organizations, including the military, to make sure that this device is effective. We’re evaluating cognitive offloading of people. We’re hoping to start that study later this year. We’re excited to be doing this in a variety of settings.
We’re also testing the quality of it in different environmental conditions and under different atmospheric pressure. We’re doing everything we can to ensure the device is safe and effective. We’re excited to scale and fill our preorders and be able to develop this and deliver it to many people.
Dr. Glatter: I was wondering if you could describe the actual device. There’s a brain part of it and then, obviously, the strap aspect of it. I was curious about contamination and reusability issues.
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question. One of the limitations of conventional tourniquets on the market is that they are single use, and often, it requires two tourniquets to stop a bleed, both of which have to be disposed of.
With AutoTQ, we have a reusable component and a disposable component. I actually have one here that I can show you. We have a cover on it that says: Stop bleed, slide up and power on. You just pull this cover off and then you have a few simple commands. You have powering the device on. I’ll just click this button: Tighten strap above bleeding, then press inflate. It delivers audible instructions telling you exactly how to use the device. Then, you tighten it above your bleed on the limb, and you press the inflate button. Then it administers air into the cuff and stops the patient’s bleed.
Tourniquet Conversion and Limb Salvage
Dr. Glatter: In terms of ischemia time, how can a device like this make it easier for us to know when to let the tourniquet down and allow some blood flow? Certainly, limb salvage is important, and we don’t want to have necrosis and so forth.
Dr. Antevy: That’s a great question. The limb salvage rate when tourniquets have been used is 85%. When used correctly, you can really improve the outcomes for many patients.
On the flip side of that, there’s something called tourniquet conversion. That’s exactly what you mentioned. It’s making sure that the tourniquet doesn’t stay on for too long of a time. If you can imagine a patient going to an outlying hospital where there’s no trauma center, and then that patient then has to be moved a couple hours to the trauma center, could you potentially have a tourniquet on for too long that then ends up causing the patient a bad outcome? The answer is yes.
I just had someone on my webinar recently describing the appropriate conversion techniques of tourniquets. You don’t find too much of that in the literature, but you really have to ensure that as you’re taking the tourniquet down, the bleeding is actually stopped. It’s not really recommended to take a tourniquet down if the patient was just acutely bleeding.
However, imagine a situation where a tourniquet was put on incorrectly. Let’s say a patient got nervous and they just put it on a patient who didn’t really need it. You really have to understand how to evaluate that wound to be sure that, as you’re taking the tourniquet down slowly, the patient doesn’t rebleed again.
There are two sides of the question, Rob. One is making sure it’s not on inappropriately. The second one is making sure it’s not on for too long, which ends up causing ischemia to that limb.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, does your device collect data on the number of hours or minutes that the tourniquet has been up and then automatically deflate it in some sense to allow for that improvement in limb salvage?
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question, and I really appreciate your answer as well, Dr Antevy. Ischemia time is a very important and critical component of tourniquet use. This is something, when we were designing AutoTQ, that we took into high consideration.
We found, when we evaluated AutoTQ vs a CAT tourniquet in a mannequin model, that AutoTQ can achieve cessation of hemorrhage at around 400 mm Hg of mercury, whereas CAT requires 700-800 mm Hg. Already our ischemia time is slightly extended just based on existing literature with pneumatic tourniquets because it can stop the bleed at a lower pressure, which causes less complications with the patient’s limb.
There are different features that we build out for different customers, so depending on what people want, it is possible to deflate the tourniquet. However, typically, you’re at the hospital within 30 minutes. It’s quick to get them there, and then the physician can treat and take that tourniquet down in a supervised and controlled setting.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of patients with obesity, do you have adjustable straps that will accommodate for that aspect?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we have different cuff sizes to accommodate different limbs.
Will AutoTQ Be Available to the Public?
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of usability in the prehospital setting, where do you think this is going in the next 3-5 years?
Dr. Antevy: I’ll start with the public safety sector of the United States, which is the one that is actually first on scene. Whether you’re talking about police officers or EMS, it would behoove us to have tourniquets everywhere. On all of my ambulances, across all of my agencies that I manage, we have quite a number of tourniquets.
Obviously, cost is a factor, and I know that Hannah has done a great job of making that brain reusable. All we have to do is purchase the straps, which are effectively the same cost, I understand, as a typical tourniquet you would purchase.
Moving forward though, however, I think that this has wide scalability to the public market, whether it be schools, office buildings, the glove box, and so on. It’s really impossible to teach somebody how to do this the right way, if you have to teach them how to put the strap on, tighten it correctly, and so on. If there was an easy way, like Hannah developed, of just putting it on and pushing a button, then I think that the outcomes and the scalability are much further beyond what we can do in EMS. I think there’s great value in both markets.
The ‘AED of Bleeding’: Rechargeable and Reusable
Dr. Glatter: This is the AED of bleeding. You have a device here that has wide-scale interest, certainly from the public and private sector.
Hannah, in terms of battery decay, how would that work out if it was in someone’s garage? Let’s just say someone purchased it and they hadn’t used it in 3 or 4 months. What type of decay are we looking at and can they rely on it?
Ms. Herbst: AutoTQ is rechargeable by a USB-C port, and our battery lasts for a year. Once a year, you’ll get an email reminder that says: “Hey, please charge your AutoTQ and make sure it’s up to the battery level.” We do everything in our power to make sure that our consumers are checking their batteries and that they’re ready to go.
Dr. Glatter: Is it heat and fire resistant? What, in terms of durability, does your device have?
Ms. Herbst: Just like any other medical device, we come with manufacturer recommendations for the upper and lower bounds of temperature and different storage recommendations. All of that is in our instructions for use.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, getting back to logistics. In terms of adoption, do you feel that, in the long term, this device will be something that we’re going to be seeing widely adopted just going forward?
Dr. Antevy: I do, and I’ll tell you why. When you look at AED use in this country, the odds of someone actually getting an AED and using it correctly are still very low. Part of that is because it’s complicated for many people to do. Getting tourniquets everywhere is step No. 1, and I think the federal government and the Stop the Bleed program is really making that happen.
We talked about ordinances, but ease of use, I think, is really the key. You have people who oftentimes have their child in cardiac arrest in front of them, and they won’t put two hands on their chest because they just are afraid of doing it.
When you have a device that’s a tourniquet, that’s a single-button turn on and single-button inflate, I think that would make it much more likely that a person will use that device when they’re passing the scene of an accident, as an example.
We’ve had many non–mass casualty incident events that have had tourniquets. We’ve had some media stories on them, where they’re just happening because someone got into a motor vehicle accident. It doesn’t have to be a school shooting. I think the tourniquets should be everywhere and should be easily used by everybody.
Managing Pain
Dr. Glatter: Regarding sedation, is there a need because of the pain involved with the application? How would you sedate a patient, pediatric or adult, who needs a tourniquet?
Dr. Antevy: We always evaluate people’s pain. If the patient is an extremist, we’re just going to be managing and trying to get them back to life. Once somebody is stabilized and is exhibiting pain of any sort, even, for example, after we intubate somebody, we have to sedate them and provide them pain control because they have a piece of plastic in their trachea.
It’s the same thing here for a tourniquet. These are painful, and we do have the appropriate medications on our vehicles to address that pain. Again, just simply the trauma itself is very painful. Yes, we do address that in EMS, and I would say most public agencies across this country would address pain appropriately.
Training on Tourniquet Use
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, can you talk a little bit about public training types of approaches? How would you train a consumer who purchases this type of device?
Ms. Herbst: A huge part of our mission is making blood loss prevention and control training accessible to a wide variety of people. One way that we’re able to do that is through our online training platform. When you purchase an AutoTQ kit, you plug it into your computer, and it walks you through the process of using it. It lets you practice on your own limb and on your buddy’s limb, just to be able to effectively apply it. We think this will have huge impacts in making sure that people are prepared and ready to stop the bleed with AutoTQ.
Dr. Glatter: Do you recommend people training once a month, in general, just to keep their skills up to use this? In the throes of a trauma and very chaotic situation, people sometimes lose their ability to think clearly and straightly.
Ms. Herbst: One of the studies we’re conducting is a learning curve study to try to figure out how quickly these skills degrade over time. We know that with the windlass tourniquet, it degrades within moments of training. With AutoTQ, we think the learning curve will last much longer. That’s something we’re evaluating, but we recommend people train as often as they can.
Dr. Antevy: Rob, if I can mention that there is a concept of just-in-time training. I think that with having the expectation that people are going to be training frequently, unfortunately, as many of us know, even with the AED as a perfect example, people don’t do that.
Yes. I would agree that you have to train at least once a year, is what I would say. At my office, we have a 2-hour training that goes over all these different items once a year.
The device itself should have the ability to allow you to figure out how to use it just in time, whether via video, or like Hannah’s device, by audio. I think that having both those things would make it more likely that the device be used when needed.
People panic, and if they have a device that can talk to them or walk them through it, they will be much more likely to use it at that time.
Final Takeaways
Dr. Glatter: Any other final thoughts or a few pearls for listeners to take away? Hannah, I’ll start with you.
Ms. Herbst: I’m very grateful for your time, and I’m very excited about the potential for AutoTQ. To me, it’s so exciting to see people preordering the device now. We’ve had people from school bus companies and small sports teams. I think, just like Dr Antevy said, tourniquets aren’t limited to mass casualty situations. Blood loss can happen anywhere and to anyone.
Being able to equip people and serve them to better prepare them for this happening to themselves, their friends, or their family is just the honor of a lifetime. Thank you very much for covering the device and for having me today.
Dr. Glatter: Of course, my pleasure. Peter?
Dr. Antevy: The citizens of this country, and everyone who lives across the world, has started to understand that there are things that we expect from our people, from the community. We expect them to do CPR for cardiac arrest. We expect them to know how to use an EpiPen. We expect them to know how to use an AED, and we also expect them to know how to stop bleeding with a tourniquet.
The American public has gotten to understand that these devices are very important. Having a device that’s easily used, that I can teach you in 10 seconds, that speaks to you — these are all things that make this product have great potential. I do look forward to the studies, not just the cadaver studies, but the real human studies.
I know Hannah is really a phenom and has been doing all these things so that this product can be on the shelves of Walmart and CVS one day. I commend you, Hannah, for everything you’re doing and wishing you the best of luck. We’re here for you.
Dr. Glatter: Same here. Congratulations on your innovative capability and what you’ve done to change the outcomes of bleeding related to penetrating trauma. Thank you so much.
Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. Hannah D. Herbst, BS, is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, was selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and is the founder/CEO of Golden Hour Medical. Peter M. Antevy, MD, is a pediatric emergency medicine physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue and Coral Springs–Parkland Fire Department in Florida. He is also a member of the EMS Eagles Global Alliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This discussion was recorded on July 12, 2024. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi and welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. I recently met an innovative young woman named Hannah Herbst while attending the annual Eagles EMS Conference in Fort Lauderdale, Florida.
Hannah Herbst is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and founder of a company called Golden Hour Medical. She has a background in IT and developed an automated pneumatic tourniquet known as AutoTQ, which we’re going to discuss at length here.
Also joining us is Dr. Peter Antevy, a pediatric emergency physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue as well as Coral Springs Parkland Fire Rescue. Peter is a member of EMS Eagles Global Alliance and is highly involved in high-quality research in prehospital emergency care and is quite well known in Florida and nationally.
Welcome to both of you.
Hannah Herbst: Thank you very much. Very grateful to be here.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, I’ll let you start by explaining what AutoTQ is and then compare that to a standard Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT).
Ms. Herbst: Thank you. Unfortunately, blood loss is a leading cause of preventable death and trauma. When there’s blood loss occurring from an arm or a leg, the easiest way to stop it is by applying a tourniquet, which is this compression type of device that you place above the site of bleeding, and it then applies a high amount of pressure to stop blood flow through the limb.
Currently, tourniquets on the market have failure rates as high as 84%. This became very real to me back in 2018, when I became aware of mass casualty incidents when I was a student. I became interested in how we can reimagine the conventional tourniquet and try to make it something that’s very user-friendly, much like an automated external defibrillator (AED).
My team and I developed AutoTQ, which is an automated tourniquet. which is a leading cause of tourniquet failure and being able to effectively administer treatment to a patient that may bleed out.
Tourniquet Failure Rates
Dr. Glatter: In terms of tourniquet failure, how often do standard tourniquets fail, like the CAT combat-type tourniquet?
Ms. Herbst: Unfortunately, they fail very frequently. There are several studies that have been conducted to evaluate this. Many of them occur immediately after training. They found failure rates between 80% and 90% for the current conventional CAT tourniquet immediately after training, which is very concerning.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of failure, was it the windlass aspect of the tourniquet that failed? Or was it something related to the actual strap? Was that in any way detailed?
Ms. Herbst: There are usually a few different failure points that have been found in the literature. One is placement. Many times, when you’re panicked, you don’t remember exactly how to place it. It should be placed high and tight above the bleed and not over a joint.
The second problem is inadequate tightness. For a CAT tourniquet to be effective, you have to get it extremely tight on that first pull before the windlass is activated, and many times people don’t remember that in the stress of the moment.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of tourniquet application by your medics in the field, certainly the CAT-type device has been in existence for quite a while. Hannah’s proposing a new iteration of how to do this, which is automated and simple. What is your take on such a device? And how did you learn about Hannah’s device?
Peter M. Antevy, MD: We’ve been training on tourniquets ever since the military data showed that there was an extreme benefit in using them. We’ve been doing training for many years, including our police officers. What we’ve noticed is that every time we gather everyone together to show them how to place a tourniquet — and we have to do one-on-one sessions with them — it’s not a device that they can easily put on. These are police officers who had the training last year.
Like Hannah said, most of the time they have a problem unraveling it and understanding how to actually place it. It’s easier on the arm than it is on the leg. You can imagine it would be harder to place it on your own leg, especially if you had an injury. Then, they don’t tighten it well enough, as Hannah just mentioned. In order for a tourniquet to really be placed properly, it’s going to hurt that person. Many people have that tendency not to want to tighten it as much as they can.
Having said that, how I got into all of this is because I’m the medical director for Coral Springs and Parkland, and unfortunately, we had the 2018 Valentine’s Day murders that happened where we lost 17 adults and kids. However, 17 people were saved that day, and the credit goes to our police officers who had tourniquets or chest seals on before those patients were brought out to EMS. Many lives were saved by the tourniquet.
If you look at the Boston Marathon massacre and many other events that have happened, I believe — and I’ve always believed — that tourniquets should be in the glove box of every citizen. It should be in every school room. They should be in buildings along with the AED.
In my town of Davie, we were the first in the country to add an ordinance that required a Stop the Bleed kit in the AED cabinet, and those were required by buildings of certain sizes. In order to get this lifesaving device everywhere, I think it has to be put into local ordinance and supported by states and by the national folks, which they are doing.
Trials Are Underway
Dr. Glatter: In terms of adoption of such a device, it certainly has to go through rigorous testing and maybe some trials. Hannah, where are you at with vetting this in terms of any type of trial? Has it been compared head to head with standard tourniquets?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we’re currently doing large amounts of field testing. We’re doing testing on emergency vehicles and in the surgical setting with different customers. In addition, we’re running pilot studies at different universities and with different organizations, including the military, to make sure that this device is effective. We’re evaluating cognitive offloading of people. We’re hoping to start that study later this year. We’re excited to be doing this in a variety of settings.
We’re also testing the quality of it in different environmental conditions and under different atmospheric pressure. We’re doing everything we can to ensure the device is safe and effective. We’re excited to scale and fill our preorders and be able to develop this and deliver it to many people.
Dr. Glatter: I was wondering if you could describe the actual device. There’s a brain part of it and then, obviously, the strap aspect of it. I was curious about contamination and reusability issues.
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question. One of the limitations of conventional tourniquets on the market is that they are single use, and often, it requires two tourniquets to stop a bleed, both of which have to be disposed of.
With AutoTQ, we have a reusable component and a disposable component. I actually have one here that I can show you. We have a cover on it that says: Stop bleed, slide up and power on. You just pull this cover off and then you have a few simple commands. You have powering the device on. I’ll just click this button: Tighten strap above bleeding, then press inflate. It delivers audible instructions telling you exactly how to use the device. Then, you tighten it above your bleed on the limb, and you press the inflate button. Then it administers air into the cuff and stops the patient’s bleed.
Tourniquet Conversion and Limb Salvage
Dr. Glatter: In terms of ischemia time, how can a device like this make it easier for us to know when to let the tourniquet down and allow some blood flow? Certainly, limb salvage is important, and we don’t want to have necrosis and so forth.
Dr. Antevy: That’s a great question. The limb salvage rate when tourniquets have been used is 85%. When used correctly, you can really improve the outcomes for many patients.
On the flip side of that, there’s something called tourniquet conversion. That’s exactly what you mentioned. It’s making sure that the tourniquet doesn’t stay on for too long of a time. If you can imagine a patient going to an outlying hospital where there’s no trauma center, and then that patient then has to be moved a couple hours to the trauma center, could you potentially have a tourniquet on for too long that then ends up causing the patient a bad outcome? The answer is yes.
I just had someone on my webinar recently describing the appropriate conversion techniques of tourniquets. You don’t find too much of that in the literature, but you really have to ensure that as you’re taking the tourniquet down, the bleeding is actually stopped. It’s not really recommended to take a tourniquet down if the patient was just acutely bleeding.
However, imagine a situation where a tourniquet was put on incorrectly. Let’s say a patient got nervous and they just put it on a patient who didn’t really need it. You really have to understand how to evaluate that wound to be sure that, as you’re taking the tourniquet down slowly, the patient doesn’t rebleed again.
There are two sides of the question, Rob. One is making sure it’s not on inappropriately. The second one is making sure it’s not on for too long, which ends up causing ischemia to that limb.
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, does your device collect data on the number of hours or minutes that the tourniquet has been up and then automatically deflate it in some sense to allow for that improvement in limb salvage?
Ms. Herbst: That’s a great question, and I really appreciate your answer as well, Dr Antevy. Ischemia time is a very important and critical component of tourniquet use. This is something, when we were designing AutoTQ, that we took into high consideration.
We found, when we evaluated AutoTQ vs a CAT tourniquet in a mannequin model, that AutoTQ can achieve cessation of hemorrhage at around 400 mm Hg of mercury, whereas CAT requires 700-800 mm Hg. Already our ischemia time is slightly extended just based on existing literature with pneumatic tourniquets because it can stop the bleed at a lower pressure, which causes less complications with the patient’s limb.
There are different features that we build out for different customers, so depending on what people want, it is possible to deflate the tourniquet. However, typically, you’re at the hospital within 30 minutes. It’s quick to get them there, and then the physician can treat and take that tourniquet down in a supervised and controlled setting.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of patients with obesity, do you have adjustable straps that will accommodate for that aspect?
Ms. Herbst: Yes, we have different cuff sizes to accommodate different limbs.
Will AutoTQ Be Available to the Public?
Dr. Glatter: Peter, in terms of usability in the prehospital setting, where do you think this is going in the next 3-5 years?
Dr. Antevy: I’ll start with the public safety sector of the United States, which is the one that is actually first on scene. Whether you’re talking about police officers or EMS, it would behoove us to have tourniquets everywhere. On all of my ambulances, across all of my agencies that I manage, we have quite a number of tourniquets.
Obviously, cost is a factor, and I know that Hannah has done a great job of making that brain reusable. All we have to do is purchase the straps, which are effectively the same cost, I understand, as a typical tourniquet you would purchase.
Moving forward though, however, I think that this has wide scalability to the public market, whether it be schools, office buildings, the glove box, and so on. It’s really impossible to teach somebody how to do this the right way, if you have to teach them how to put the strap on, tighten it correctly, and so on. If there was an easy way, like Hannah developed, of just putting it on and pushing a button, then I think that the outcomes and the scalability are much further beyond what we can do in EMS. I think there’s great value in both markets.
The ‘AED of Bleeding’: Rechargeable and Reusable
Dr. Glatter: This is the AED of bleeding. You have a device here that has wide-scale interest, certainly from the public and private sector.
Hannah, in terms of battery decay, how would that work out if it was in someone’s garage? Let’s just say someone purchased it and they hadn’t used it in 3 or 4 months. What type of decay are we looking at and can they rely on it?
Ms. Herbst: AutoTQ is rechargeable by a USB-C port, and our battery lasts for a year. Once a year, you’ll get an email reminder that says: “Hey, please charge your AutoTQ and make sure it’s up to the battery level.” We do everything in our power to make sure that our consumers are checking their batteries and that they’re ready to go.
Dr. Glatter: Is it heat and fire resistant? What, in terms of durability, does your device have?
Ms. Herbst: Just like any other medical device, we come with manufacturer recommendations for the upper and lower bounds of temperature and different storage recommendations. All of that is in our instructions for use.
Dr. Glatter: Peter, getting back to logistics. In terms of adoption, do you feel that, in the long term, this device will be something that we’re going to be seeing widely adopted just going forward?
Dr. Antevy: I do, and I’ll tell you why. When you look at AED use in this country, the odds of someone actually getting an AED and using it correctly are still very low. Part of that is because it’s complicated for many people to do. Getting tourniquets everywhere is step No. 1, and I think the federal government and the Stop the Bleed program is really making that happen.
We talked about ordinances, but ease of use, I think, is really the key. You have people who oftentimes have their child in cardiac arrest in front of them, and they won’t put two hands on their chest because they just are afraid of doing it.
When you have a device that’s a tourniquet, that’s a single-button turn on and single-button inflate, I think that would make it much more likely that a person will use that device when they’re passing the scene of an accident, as an example.
We’ve had many non–mass casualty incident events that have had tourniquets. We’ve had some media stories on them, where they’re just happening because someone got into a motor vehicle accident. It doesn’t have to be a school shooting. I think the tourniquets should be everywhere and should be easily used by everybody.
Managing Pain
Dr. Glatter: Regarding sedation, is there a need because of the pain involved with the application? How would you sedate a patient, pediatric or adult, who needs a tourniquet?
Dr. Antevy: We always evaluate people’s pain. If the patient is an extremist, we’re just going to be managing and trying to get them back to life. Once somebody is stabilized and is exhibiting pain of any sort, even, for example, after we intubate somebody, we have to sedate them and provide them pain control because they have a piece of plastic in their trachea.
It’s the same thing here for a tourniquet. These are painful, and we do have the appropriate medications on our vehicles to address that pain. Again, just simply the trauma itself is very painful. Yes, we do address that in EMS, and I would say most public agencies across this country would address pain appropriately.
Training on Tourniquet Use
Dr. Glatter: Hannah, can you talk a little bit about public training types of approaches? How would you train a consumer who purchases this type of device?
Ms. Herbst: A huge part of our mission is making blood loss prevention and control training accessible to a wide variety of people. One way that we’re able to do that is through our online training platform. When you purchase an AutoTQ kit, you plug it into your computer, and it walks you through the process of using it. It lets you practice on your own limb and on your buddy’s limb, just to be able to effectively apply it. We think this will have huge impacts in making sure that people are prepared and ready to stop the bleed with AutoTQ.
Dr. Glatter: Do you recommend people training once a month, in general, just to keep their skills up to use this? In the throes of a trauma and very chaotic situation, people sometimes lose their ability to think clearly and straightly.
Ms. Herbst: One of the studies we’re conducting is a learning curve study to try to figure out how quickly these skills degrade over time. We know that with the windlass tourniquet, it degrades within moments of training. With AutoTQ, we think the learning curve will last much longer. That’s something we’re evaluating, but we recommend people train as often as they can.
Dr. Antevy: Rob, if I can mention that there is a concept of just-in-time training. I think that with having the expectation that people are going to be training frequently, unfortunately, as many of us know, even with the AED as a perfect example, people don’t do that.
Yes. I would agree that you have to train at least once a year, is what I would say. At my office, we have a 2-hour training that goes over all these different items once a year.
The device itself should have the ability to allow you to figure out how to use it just in time, whether via video, or like Hannah’s device, by audio. I think that having both those things would make it more likely that the device be used when needed.
People panic, and if they have a device that can talk to them or walk them through it, they will be much more likely to use it at that time.
Final Takeaways
Dr. Glatter: Any other final thoughts or a few pearls for listeners to take away? Hannah, I’ll start with you.
Ms. Herbst: I’m very grateful for your time, and I’m very excited about the potential for AutoTQ. To me, it’s so exciting to see people preordering the device now. We’ve had people from school bus companies and small sports teams. I think, just like Dr Antevy said, tourniquets aren’t limited to mass casualty situations. Blood loss can happen anywhere and to anyone.
Being able to equip people and serve them to better prepare them for this happening to themselves, their friends, or their family is just the honor of a lifetime. Thank you very much for covering the device and for having me today.
Dr. Glatter: Of course, my pleasure. Peter?
Dr. Antevy: The citizens of this country, and everyone who lives across the world, has started to understand that there are things that we expect from our people, from the community. We expect them to do CPR for cardiac arrest. We expect them to know how to use an EpiPen. We expect them to know how to use an AED, and we also expect them to know how to stop bleeding with a tourniquet.
The American public has gotten to understand that these devices are very important. Having a device that’s easily used, that I can teach you in 10 seconds, that speaks to you — these are all things that make this product have great potential. I do look forward to the studies, not just the cadaver studies, but the real human studies.
I know Hannah is really a phenom and has been doing all these things so that this product can be on the shelves of Walmart and CVS one day. I commend you, Hannah, for everything you’re doing and wishing you the best of luck. We’re here for you.
Dr. Glatter: Same here. Congratulations on your innovative capability and what you’ve done to change the outcomes of bleeding related to penetrating trauma. Thank you so much.
Robert D. Glatter, MD, is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. He is a medical advisor for Medscape and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series. Hannah D. Herbst, BS, is a graduate of Florida Atlantic University, was selected for Forbes 30 Under 30, and is the founder/CEO of Golden Hour Medical. Peter M. Antevy, MD, is a pediatric emergency medicine physician and medical director for Davie Fire Rescue and Coral Springs–Parkland Fire Department in Florida. He is also a member of the EMS Eagles Global Alliance.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regularly Drinking Alcohol After Age 60 Linked to Early Death
That’s according to the findings of a new, large study that was published in JAMA Network Openand build upon numerous other recent studies concluding that any amount of alcohol consumption is linked to significant health risks. That’s a change from decades of public health messaging suggesting that moderate alcohol intake (one or two drinks per day) wasn’t dangerous. Recently, experts have uncovered flaws in how researchers came to those earlier conclusions.
In this latest study, researchers in Spain analyzed health data for more than 135,000 people, all of whom were at least 60 years old, lived in the United Kingdom, and provided their health information to the UK Biobank database. The average age of people at the start of the analysis period was 64.
The researchers compared 12 years of health outcomes for occasional drinkers with those who averaged drinking at least some alcohol on a daily basis. The greatest health risks were seen between occasional drinkers and those whom the researchers labeled “high risk.” Occasional drinkers had less than about two drinks per week. The high-risk group included men who averaged nearly three drinks per day or more, and women who averaged about a drink and a half per day or more. The analysis showed that, compared with occasional drinking, high-risk drinking was linked to a 33% increased risk of early death, a 39% increased risk of dying from cancer, and a 21% increased risk of dying from problems with the heart and blood vessels.
More moderate drinking habits were also linked to an increased risk of early death and dying from cancer, and even just averaging about one drink or less daily was associated with an 11% higher risk of dying from cancer. Low and moderate drinkers were most at risk if they also had health problems or experienced socioeconomic factors like living in less affluent neighborhoods.
The findings also suggested the potential that mostly drinking wine, or drinking mostly with meals, may be lower risk, but the researchers called for further study on those topics since “it may mostly reflect the effect of healthier lifestyles, slower alcohol absorption, or nonalcoholic components of beverages.”
A recent Gallup poll showed that overall, Americans’ attitudes toward the health impacts of alcohol are changing, with 65% of young adults (ages 18-34) saying that drinking can have negative health effects. But just 39% of adults age 55 or older agreed that drinking is bad for a person’s health. The gap in perspectives between younger and older adults about drinking is the largest on record, Gallup reported.
The study investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That’s according to the findings of a new, large study that was published in JAMA Network Openand build upon numerous other recent studies concluding that any amount of alcohol consumption is linked to significant health risks. That’s a change from decades of public health messaging suggesting that moderate alcohol intake (one or two drinks per day) wasn’t dangerous. Recently, experts have uncovered flaws in how researchers came to those earlier conclusions.
In this latest study, researchers in Spain analyzed health data for more than 135,000 people, all of whom were at least 60 years old, lived in the United Kingdom, and provided their health information to the UK Biobank database. The average age of people at the start of the analysis period was 64.
The researchers compared 12 years of health outcomes for occasional drinkers with those who averaged drinking at least some alcohol on a daily basis. The greatest health risks were seen between occasional drinkers and those whom the researchers labeled “high risk.” Occasional drinkers had less than about two drinks per week. The high-risk group included men who averaged nearly three drinks per day or more, and women who averaged about a drink and a half per day or more. The analysis showed that, compared with occasional drinking, high-risk drinking was linked to a 33% increased risk of early death, a 39% increased risk of dying from cancer, and a 21% increased risk of dying from problems with the heart and blood vessels.
More moderate drinking habits were also linked to an increased risk of early death and dying from cancer, and even just averaging about one drink or less daily was associated with an 11% higher risk of dying from cancer. Low and moderate drinkers were most at risk if they also had health problems or experienced socioeconomic factors like living in less affluent neighborhoods.
The findings also suggested the potential that mostly drinking wine, or drinking mostly with meals, may be lower risk, but the researchers called for further study on those topics since “it may mostly reflect the effect of healthier lifestyles, slower alcohol absorption, or nonalcoholic components of beverages.”
A recent Gallup poll showed that overall, Americans’ attitudes toward the health impacts of alcohol are changing, with 65% of young adults (ages 18-34) saying that drinking can have negative health effects. But just 39% of adults age 55 or older agreed that drinking is bad for a person’s health. The gap in perspectives between younger and older adults about drinking is the largest on record, Gallup reported.
The study investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That’s according to the findings of a new, large study that was published in JAMA Network Openand build upon numerous other recent studies concluding that any amount of alcohol consumption is linked to significant health risks. That’s a change from decades of public health messaging suggesting that moderate alcohol intake (one or two drinks per day) wasn’t dangerous. Recently, experts have uncovered flaws in how researchers came to those earlier conclusions.
In this latest study, researchers in Spain analyzed health data for more than 135,000 people, all of whom were at least 60 years old, lived in the United Kingdom, and provided their health information to the UK Biobank database. The average age of people at the start of the analysis period was 64.
The researchers compared 12 years of health outcomes for occasional drinkers with those who averaged drinking at least some alcohol on a daily basis. The greatest health risks were seen between occasional drinkers and those whom the researchers labeled “high risk.” Occasional drinkers had less than about two drinks per week. The high-risk group included men who averaged nearly three drinks per day or more, and women who averaged about a drink and a half per day or more. The analysis showed that, compared with occasional drinking, high-risk drinking was linked to a 33% increased risk of early death, a 39% increased risk of dying from cancer, and a 21% increased risk of dying from problems with the heart and blood vessels.
More moderate drinking habits were also linked to an increased risk of early death and dying from cancer, and even just averaging about one drink or less daily was associated with an 11% higher risk of dying from cancer. Low and moderate drinkers were most at risk if they also had health problems or experienced socioeconomic factors like living in less affluent neighborhoods.
The findings also suggested the potential that mostly drinking wine, or drinking mostly with meals, may be lower risk, but the researchers called for further study on those topics since “it may mostly reflect the effect of healthier lifestyles, slower alcohol absorption, or nonalcoholic components of beverages.”
A recent Gallup poll showed that overall, Americans’ attitudes toward the health impacts of alcohol are changing, with 65% of young adults (ages 18-34) saying that drinking can have negative health effects. But just 39% of adults age 55 or older agreed that drinking is bad for a person’s health. The gap in perspectives between younger and older adults about drinking is the largest on record, Gallup reported.
The study investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Dementia Deemed Highly Preventable: Here’s How
A new report on the preventability of dementia is both exciting and paradigm-shifting. The new study, published in The Lancet by the Lancet Commission on Dementia, estimates that .
This is paradigm-shifting because dementia is often perceived as an inevitable consequence of the aging process, with a major genetic component. But this study suggests that modifying these risk factors can benefit everyone, irrespective of genetic risk, and that it’s important to have a life-course approach. It’s never too early or too late to start to modify these factors.
We’ve known for a long time that many chronic diseases are highly preventable and modifiable. Some that come to mind are type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and even certain forms of cancer. Modifiable risk factors include cigarette smoking, diet, physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. This study suggests that many of the same risk factors and more are relevant to reducing risk for dementia.
Let’s go through the risk factors, many of which are behavioral. These risk factors include lifestyle factors such as lack of physical activity, cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. The cardiovascular or vascular-specific risk factors include not only those behavioral factors but also hypertension, high LDL cholesterol, and diabetes. Cognitive engagement–specific risk factors include social isolation, which is a major risk factor for dementia, as well as untreated hearing or vision loss, which can exacerbate social isolation and depression, and low educational attainment, which can be related to less cognitive engagement.
They also mention traumatic brain injury from an accident or contact sports without head protection as a risk factor, and the environmental risk factor of air pollution or poor air quality.
Two of these risk factors are new since the previous report in 2020: elevated LDL cholesterol and untreated vision loss, both of which are quite treatable. Overall, these findings suggest that a lot can be done to lower dementia risk, but it requires individual behavior modifications as well as a comprehensive approach with involvement of the healthcare system for improved screening, access, and public policy to reduce air pollution.
Some of these risk factors are more relevant to women, especially the social isolation that is so common later in life in women. In the United States, close to two out of three patients with dementia are women.
So, informing our patients about these risk factors and what can be done in terms of behavior modification, increased screening, and treatment for these conditions can go a long way in helping our patients reduce their risk for dementia.
Dr. Manson is professor of medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School, chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and past president, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012. She disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report on the preventability of dementia is both exciting and paradigm-shifting. The new study, published in The Lancet by the Lancet Commission on Dementia, estimates that .
This is paradigm-shifting because dementia is often perceived as an inevitable consequence of the aging process, with a major genetic component. But this study suggests that modifying these risk factors can benefit everyone, irrespective of genetic risk, and that it’s important to have a life-course approach. It’s never too early or too late to start to modify these factors.
We’ve known for a long time that many chronic diseases are highly preventable and modifiable. Some that come to mind are type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and even certain forms of cancer. Modifiable risk factors include cigarette smoking, diet, physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. This study suggests that many of the same risk factors and more are relevant to reducing risk for dementia.
Let’s go through the risk factors, many of which are behavioral. These risk factors include lifestyle factors such as lack of physical activity, cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. The cardiovascular or vascular-specific risk factors include not only those behavioral factors but also hypertension, high LDL cholesterol, and diabetes. Cognitive engagement–specific risk factors include social isolation, which is a major risk factor for dementia, as well as untreated hearing or vision loss, which can exacerbate social isolation and depression, and low educational attainment, which can be related to less cognitive engagement.
They also mention traumatic brain injury from an accident or contact sports without head protection as a risk factor, and the environmental risk factor of air pollution or poor air quality.
Two of these risk factors are new since the previous report in 2020: elevated LDL cholesterol and untreated vision loss, both of which are quite treatable. Overall, these findings suggest that a lot can be done to lower dementia risk, but it requires individual behavior modifications as well as a comprehensive approach with involvement of the healthcare system for improved screening, access, and public policy to reduce air pollution.
Some of these risk factors are more relevant to women, especially the social isolation that is so common later in life in women. In the United States, close to two out of three patients with dementia are women.
So, informing our patients about these risk factors and what can be done in terms of behavior modification, increased screening, and treatment for these conditions can go a long way in helping our patients reduce their risk for dementia.
Dr. Manson is professor of medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School, chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and past president, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012. She disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new report on the preventability of dementia is both exciting and paradigm-shifting. The new study, published in The Lancet by the Lancet Commission on Dementia, estimates that .
This is paradigm-shifting because dementia is often perceived as an inevitable consequence of the aging process, with a major genetic component. But this study suggests that modifying these risk factors can benefit everyone, irrespective of genetic risk, and that it’s important to have a life-course approach. It’s never too early or too late to start to modify these factors.
We’ve known for a long time that many chronic diseases are highly preventable and modifiable. Some that come to mind are type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and even certain forms of cancer. Modifiable risk factors include cigarette smoking, diet, physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. This study suggests that many of the same risk factors and more are relevant to reducing risk for dementia.
Let’s go through the risk factors, many of which are behavioral. These risk factors include lifestyle factors such as lack of physical activity, cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity. The cardiovascular or vascular-specific risk factors include not only those behavioral factors but also hypertension, high LDL cholesterol, and diabetes. Cognitive engagement–specific risk factors include social isolation, which is a major risk factor for dementia, as well as untreated hearing or vision loss, which can exacerbate social isolation and depression, and low educational attainment, which can be related to less cognitive engagement.
They also mention traumatic brain injury from an accident or contact sports without head protection as a risk factor, and the environmental risk factor of air pollution or poor air quality.
Two of these risk factors are new since the previous report in 2020: elevated LDL cholesterol and untreated vision loss, both of which are quite treatable. Overall, these findings suggest that a lot can be done to lower dementia risk, but it requires individual behavior modifications as well as a comprehensive approach with involvement of the healthcare system for improved screening, access, and public policy to reduce air pollution.
Some of these risk factors are more relevant to women, especially the social isolation that is so common later in life in women. In the United States, close to two out of three patients with dementia are women.
So, informing our patients about these risk factors and what can be done in terms of behavior modification, increased screening, and treatment for these conditions can go a long way in helping our patients reduce their risk for dementia.
Dr. Manson is professor of medicine and the Michael and Lee Bell Professor of Women’s Health, Harvard Medical School, chief, Division of Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and past president, North American Menopause Society, 2011-2012. She disclosed receiving study pill donation and infrastructure support from Mars Symbioscience (for the COSMOS trial).
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
One in Ten Chronic Pain Patients May Develop Opioid Use Disorder
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FIT Screening Cuts Colorectal Cancer Mortality by One Third
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- In the United States, annual FIT screening is recommended among average-risk adults to reduce the risk for death from CRC, but evidence on its effectiveness is limited.
- Researchers performed a nested case-control study within two large, demographically diverse health systems with long-standing programs of mailing FITs to promote CRC screening efforts.
- They compared 1103 adults who had died of CRC between 2011 and 2017 (cases) with 9608 matched, randomly selected people who were alive and free of CRC (controls).
- Analyses focused on FIT screening completed within 5 years before CRC diagnosis for cases or the corresponding date for controls.
- The primary outcome measured was CRC death overall and by tumor location; secondary analyses assessed CRC death by race and ethnicity.
TAKEAWAY:
- In regression analysis, completing one or more FIT screenings was associated with a 33% lower risk for CRC death overall.
- There was a 42% lower risk for death from left colon and rectum cancers but no significant reduction in mortality from right colon cancers.
- The benefits of FIT screening were observed across racial and ethnic groups, with significant mortality reductions of 63% in non-Hispanic Asian, 42% in non-Hispanic Black, and 29% in non-Hispanic White individuals.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings support the use of strategies for coordinated and equitable large-scale population-based delivery of FIT screening with follow-up of abnormal screening results to help avert preventable premature CRC deaths,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Chyke A. Doubeni, MD, MPH, Center for Health Equity, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Almost one half of study subjects had completed two or more FITs, but the case-control design was not suitable for assessing the impact of repeated screening. The study was conducted prior to the US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation to start screening at age 45 years, so the findings may not directly apply to adults aged 45-49 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Doubeni reported receiving royalties from UpToDate, and additional authors reported receiving grants outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Colorectal Cancer: New Primary Care Method Predicts Onset Within Next 2 Years
TOPLINE:
Up to 16% of primary care patients are non-compliant with FIT, which is the gold standard for predicting CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- This study was retrospective cohort of 50,387 UK Biobank participants reporting a CRC symptom in primary care at age ≥ 40 years.
- The novel method, called an integrated risk model, used a combination of a polygenic risk score from genetic testing, symptoms, and patient characteristics to identify patients likely to develop CRC in the next 2 years.
- The primary outcome was the risk model’s performance in classifying a CRC case according to a statistical metric, the receiver operating characteristic area under the curve. Values range from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates perfect discriminative power and 0.5 indicates no discriminative power.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort of 50,387 participants was found to have 438 cases of CRC and 49,949 controls without CRC within 2 years of symptom reporting. CRC cases were diagnosed by hospital records, cancer registries, or death records.
- Increased risk of a CRC diagnosis was identified by a combination of six variables: older age at index date of symptom, higher polygenic risk score, which included 201 variants, male sex, previous smoking, rectal bleeding, and change in bowel habit.
- The polygenic risk score alone had good ability to distinguish cases from controls because 1.45% of participants in the highest quintile and 0.42% in the lowest quintile were later diagnosed with CRC.
- The variables were used to calculate an integrated risk model, which estimated the cross-sectional risk (in 80% of the final cohort) of a subsequent CRC diagnosis within 2 years. The highest scoring integrated risk model in this study was found to have a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve value of 0.76 with a 95% CI of 0.71-0.81. (A value of this magnitude indicates moderate discriminative ability to distinguish cases from controls because it falls between 0.7 and 0.8. A higher value [above 0.8] is considered strong and a lower value [< 0.7] is considered weak.)
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded, “The [integrated risk model] developed in this study predicts, with good accuracy, which patients presenting with CRC symptoms in a primary care setting are likely to be diagnosed with CRC within the next 2 years.”
The integrated risk model has “potential to be immediately actionable in the clinical setting … [by] inform[ing] patient triage, improving early diagnostic rates and health outcomes and reducing pressure on diagnostic secondary care services.”
SOURCE:
The corresponding author is Harry D. Green of the University of Exeter, England. The study (2024 Aug 1. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01654-3) appeared in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included an observational design and the inability of the integrated risk model to outperform FIT, which has a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve of 0.95.
DISCLOSURES:
None of the authors reported competing interests. The funding sources included the National Institute for Health and Care Research and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Up to 16% of primary care patients are non-compliant with FIT, which is the gold standard for predicting CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- This study was retrospective cohort of 50,387 UK Biobank participants reporting a CRC symptom in primary care at age ≥ 40 years.
- The novel method, called an integrated risk model, used a combination of a polygenic risk score from genetic testing, symptoms, and patient characteristics to identify patients likely to develop CRC in the next 2 years.
- The primary outcome was the risk model’s performance in classifying a CRC case according to a statistical metric, the receiver operating characteristic area under the curve. Values range from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates perfect discriminative power and 0.5 indicates no discriminative power.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort of 50,387 participants was found to have 438 cases of CRC and 49,949 controls without CRC within 2 years of symptom reporting. CRC cases were diagnosed by hospital records, cancer registries, or death records.
- Increased risk of a CRC diagnosis was identified by a combination of six variables: older age at index date of symptom, higher polygenic risk score, which included 201 variants, male sex, previous smoking, rectal bleeding, and change in bowel habit.
- The polygenic risk score alone had good ability to distinguish cases from controls because 1.45% of participants in the highest quintile and 0.42% in the lowest quintile were later diagnosed with CRC.
- The variables were used to calculate an integrated risk model, which estimated the cross-sectional risk (in 80% of the final cohort) of a subsequent CRC diagnosis within 2 years. The highest scoring integrated risk model in this study was found to have a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve value of 0.76 with a 95% CI of 0.71-0.81. (A value of this magnitude indicates moderate discriminative ability to distinguish cases from controls because it falls between 0.7 and 0.8. A higher value [above 0.8] is considered strong and a lower value [< 0.7] is considered weak.)
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded, “The [integrated risk model] developed in this study predicts, with good accuracy, which patients presenting with CRC symptoms in a primary care setting are likely to be diagnosed with CRC within the next 2 years.”
The integrated risk model has “potential to be immediately actionable in the clinical setting … [by] inform[ing] patient triage, improving early diagnostic rates and health outcomes and reducing pressure on diagnostic secondary care services.”
SOURCE:
The corresponding author is Harry D. Green of the University of Exeter, England. The study (2024 Aug 1. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01654-3) appeared in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included an observational design and the inability of the integrated risk model to outperform FIT, which has a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve of 0.95.
DISCLOSURES:
None of the authors reported competing interests. The funding sources included the National Institute for Health and Care Research and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Up to 16% of primary care patients are non-compliant with FIT, which is the gold standard for predicting CRC.
METHODOLOGY:
- This study was retrospective cohort of 50,387 UK Biobank participants reporting a CRC symptom in primary care at age ≥ 40 years.
- The novel method, called an integrated risk model, used a combination of a polygenic risk score from genetic testing, symptoms, and patient characteristics to identify patients likely to develop CRC in the next 2 years.
- The primary outcome was the risk model’s performance in classifying a CRC case according to a statistical metric, the receiver operating characteristic area under the curve. Values range from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates perfect discriminative power and 0.5 indicates no discriminative power.
TAKEAWAY:
- The cohort of 50,387 participants was found to have 438 cases of CRC and 49,949 controls without CRC within 2 years of symptom reporting. CRC cases were diagnosed by hospital records, cancer registries, or death records.
- Increased risk of a CRC diagnosis was identified by a combination of six variables: older age at index date of symptom, higher polygenic risk score, which included 201 variants, male sex, previous smoking, rectal bleeding, and change in bowel habit.
- The polygenic risk score alone had good ability to distinguish cases from controls because 1.45% of participants in the highest quintile and 0.42% in the lowest quintile were later diagnosed with CRC.
- The variables were used to calculate an integrated risk model, which estimated the cross-sectional risk (in 80% of the final cohort) of a subsequent CRC diagnosis within 2 years. The highest scoring integrated risk model in this study was found to have a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve value of 0.76 with a 95% CI of 0.71-0.81. (A value of this magnitude indicates moderate discriminative ability to distinguish cases from controls because it falls between 0.7 and 0.8. A higher value [above 0.8] is considered strong and a lower value [< 0.7] is considered weak.)
IN PRACTICE:
The authors concluded, “The [integrated risk model] developed in this study predicts, with good accuracy, which patients presenting with CRC symptoms in a primary care setting are likely to be diagnosed with CRC within the next 2 years.”
The integrated risk model has “potential to be immediately actionable in the clinical setting … [by] inform[ing] patient triage, improving early diagnostic rates and health outcomes and reducing pressure on diagnostic secondary care services.”
SOURCE:
The corresponding author is Harry D. Green of the University of Exeter, England. The study (2024 Aug 1. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01654-3) appeared in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included an observational design and the inability of the integrated risk model to outperform FIT, which has a receiver operating characteristic area under the curve of 0.95.
DISCLOSURES:
None of the authors reported competing interests. The funding sources included the National Institute for Health and Care Research and others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stool-Based Methylation Test May Improve CRC Screening
based on a prospective, real-world study.
These findings suggest that the mSDC2 assay could improve the efficacy and resource utilization of existing screening programs, reported co–lead authors Shengbing Zhao, MD and Zixuan He, MD, of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
“Conventional risk-stratification strategies, such as fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and life risk factors, are still criticized for being inferior at identifying early-stage CRC and ACN, and their real-world performance is probably further weakened by the low annual participation rate and compliance of subsequent colonoscopy,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. Recent case studies have reported “high diagnostic performance” using stool-based testing for mSDC2, which is “the most accurate single-targeted gene” for colorectal neoplasia, according to the investigators; however, real-world outcomes have yet to be demonstrated, prompting the present study. The prospective, multicenter, community-based trial compared the diagnostic performance of the mSDC2 test against FIT and Asia-Pacific Colorectal Screening (APCS) scores.
The primary outcome was detection of ACN. Secondary outcomes included detection of CRC, early-stage CRC, ACN, colorectal neoplasia (CN), and clinically relevant serrated polyp (CRSP). Screening strategies were also compared in terms of cost-effectiveness and impact on colonoscopy workload.The final dataset included 10,360 participants aged 45-75 years who underwent screening between 2020 and 2022.
After determining APCS scores, stool samples were analyzed for mSDC2 and FIT markers. Based on risk stratification results, participants were invited to undergo colonoscopy. A total of 3,381 participants completed colonoscopy, with 1914 from the increased-risk population and 1467 from the average-risk population. Participants who tested positive for mSDC2 had significantly higher detection rates for all measured outcomes than those who tested negative (all, P < .05). For example, the detection rate for ACN was 26.6% in mSDC2-positive participants, compared with 9.3% in mSDC2-negative participants, with a relative risk of 2.87 (95% CI, 2.39-3.44). For CRC, the detection rate was 4.2% in mSDC2-positive participants vs 0.1% in mSDC2-negative participants, yielding a relative risk of 29.73 (95% CI, 10.29-85.91). Performance held steady across subgroups.The mSDC2 test demonstrated cost-effectiveness by significantly reducing the number of colonoscopies needed to detect one case of ACN or CRC. Specifically, the number of colonoscopies needed to screen for ACN and CRC was reduced by 56.2% and 81.5%, respectively. Parallel combinations of mSDC2 with APCS or FIT enhanced both diagnostic performance and cost-effectiveness.
“This study further illustrates that the mSDC2 test consistently improves predictive abilities for CN, CRSP, ACN, and CRC, which is not influenced by subgroups of lesion location or risk factors, even under the risk stratification by FIT or APCS,” the investigators wrote. “The excellent diagnostic ability of mSDC2 in premalignant lesions, early-stage CRC, and early-onset CRC indicates a promising value in early detection and prevention of CRC ... the mSDC2 test or a parallel combination of multiple screening methods might be promising to improve real-world CRC screening performance and reduce colonoscopy workload in community practice.”The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Deep Blue Project of Naval Medical University, the Creative Biosciences, and others. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
based on a prospective, real-world study.
These findings suggest that the mSDC2 assay could improve the efficacy and resource utilization of existing screening programs, reported co–lead authors Shengbing Zhao, MD and Zixuan He, MD, of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
“Conventional risk-stratification strategies, such as fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and life risk factors, are still criticized for being inferior at identifying early-stage CRC and ACN, and their real-world performance is probably further weakened by the low annual participation rate and compliance of subsequent colonoscopy,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. Recent case studies have reported “high diagnostic performance” using stool-based testing for mSDC2, which is “the most accurate single-targeted gene” for colorectal neoplasia, according to the investigators; however, real-world outcomes have yet to be demonstrated, prompting the present study. The prospective, multicenter, community-based trial compared the diagnostic performance of the mSDC2 test against FIT and Asia-Pacific Colorectal Screening (APCS) scores.
The primary outcome was detection of ACN. Secondary outcomes included detection of CRC, early-stage CRC, ACN, colorectal neoplasia (CN), and clinically relevant serrated polyp (CRSP). Screening strategies were also compared in terms of cost-effectiveness and impact on colonoscopy workload.The final dataset included 10,360 participants aged 45-75 years who underwent screening between 2020 and 2022.
After determining APCS scores, stool samples were analyzed for mSDC2 and FIT markers. Based on risk stratification results, participants were invited to undergo colonoscopy. A total of 3,381 participants completed colonoscopy, with 1914 from the increased-risk population and 1467 from the average-risk population. Participants who tested positive for mSDC2 had significantly higher detection rates for all measured outcomes than those who tested negative (all, P < .05). For example, the detection rate for ACN was 26.6% in mSDC2-positive participants, compared with 9.3% in mSDC2-negative participants, with a relative risk of 2.87 (95% CI, 2.39-3.44). For CRC, the detection rate was 4.2% in mSDC2-positive participants vs 0.1% in mSDC2-negative participants, yielding a relative risk of 29.73 (95% CI, 10.29-85.91). Performance held steady across subgroups.The mSDC2 test demonstrated cost-effectiveness by significantly reducing the number of colonoscopies needed to detect one case of ACN or CRC. Specifically, the number of colonoscopies needed to screen for ACN and CRC was reduced by 56.2% and 81.5%, respectively. Parallel combinations of mSDC2 with APCS or FIT enhanced both diagnostic performance and cost-effectiveness.
“This study further illustrates that the mSDC2 test consistently improves predictive abilities for CN, CRSP, ACN, and CRC, which is not influenced by subgroups of lesion location or risk factors, even under the risk stratification by FIT or APCS,” the investigators wrote. “The excellent diagnostic ability of mSDC2 in premalignant lesions, early-stage CRC, and early-onset CRC indicates a promising value in early detection and prevention of CRC ... the mSDC2 test or a parallel combination of multiple screening methods might be promising to improve real-world CRC screening performance and reduce colonoscopy workload in community practice.”The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Deep Blue Project of Naval Medical University, the Creative Biosciences, and others. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
based on a prospective, real-world study.
These findings suggest that the mSDC2 assay could improve the efficacy and resource utilization of existing screening programs, reported co–lead authors Shengbing Zhao, MD and Zixuan He, MD, of Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
“Conventional risk-stratification strategies, such as fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and life risk factors, are still criticized for being inferior at identifying early-stage CRC and ACN, and their real-world performance is probably further weakened by the low annual participation rate and compliance of subsequent colonoscopy,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. Recent case studies have reported “high diagnostic performance” using stool-based testing for mSDC2, which is “the most accurate single-targeted gene” for colorectal neoplasia, according to the investigators; however, real-world outcomes have yet to be demonstrated, prompting the present study. The prospective, multicenter, community-based trial compared the diagnostic performance of the mSDC2 test against FIT and Asia-Pacific Colorectal Screening (APCS) scores.
The primary outcome was detection of ACN. Secondary outcomes included detection of CRC, early-stage CRC, ACN, colorectal neoplasia (CN), and clinically relevant serrated polyp (CRSP). Screening strategies were also compared in terms of cost-effectiveness and impact on colonoscopy workload.The final dataset included 10,360 participants aged 45-75 years who underwent screening between 2020 and 2022.
After determining APCS scores, stool samples were analyzed for mSDC2 and FIT markers. Based on risk stratification results, participants were invited to undergo colonoscopy. A total of 3,381 participants completed colonoscopy, with 1914 from the increased-risk population and 1467 from the average-risk population. Participants who tested positive for mSDC2 had significantly higher detection rates for all measured outcomes than those who tested negative (all, P < .05). For example, the detection rate for ACN was 26.6% in mSDC2-positive participants, compared with 9.3% in mSDC2-negative participants, with a relative risk of 2.87 (95% CI, 2.39-3.44). For CRC, the detection rate was 4.2% in mSDC2-positive participants vs 0.1% in mSDC2-negative participants, yielding a relative risk of 29.73 (95% CI, 10.29-85.91). Performance held steady across subgroups.The mSDC2 test demonstrated cost-effectiveness by significantly reducing the number of colonoscopies needed to detect one case of ACN or CRC. Specifically, the number of colonoscopies needed to screen for ACN and CRC was reduced by 56.2% and 81.5%, respectively. Parallel combinations of mSDC2 with APCS or FIT enhanced both diagnostic performance and cost-effectiveness.
“This study further illustrates that the mSDC2 test consistently improves predictive abilities for CN, CRSP, ACN, and CRC, which is not influenced by subgroups of lesion location or risk factors, even under the risk stratification by FIT or APCS,” the investigators wrote. “The excellent diagnostic ability of mSDC2 in premalignant lesions, early-stage CRC, and early-onset CRC indicates a promising value in early detection and prevention of CRC ... the mSDC2 test or a parallel combination of multiple screening methods might be promising to improve real-world CRC screening performance and reduce colonoscopy workload in community practice.”The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Deep Blue Project of Naval Medical University, the Creative Biosciences, and others. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
These Four Factors Account for 18 Years of Life Expectancy
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.
Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.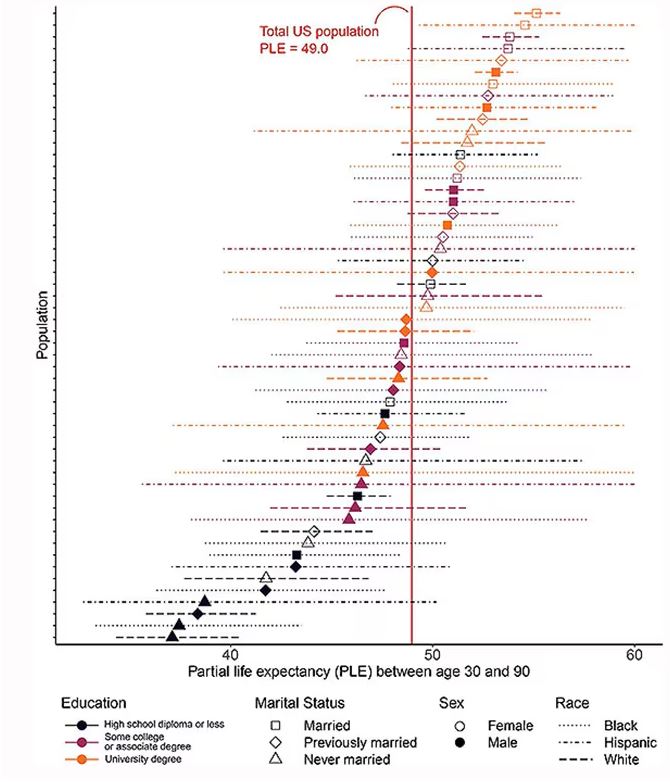
But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.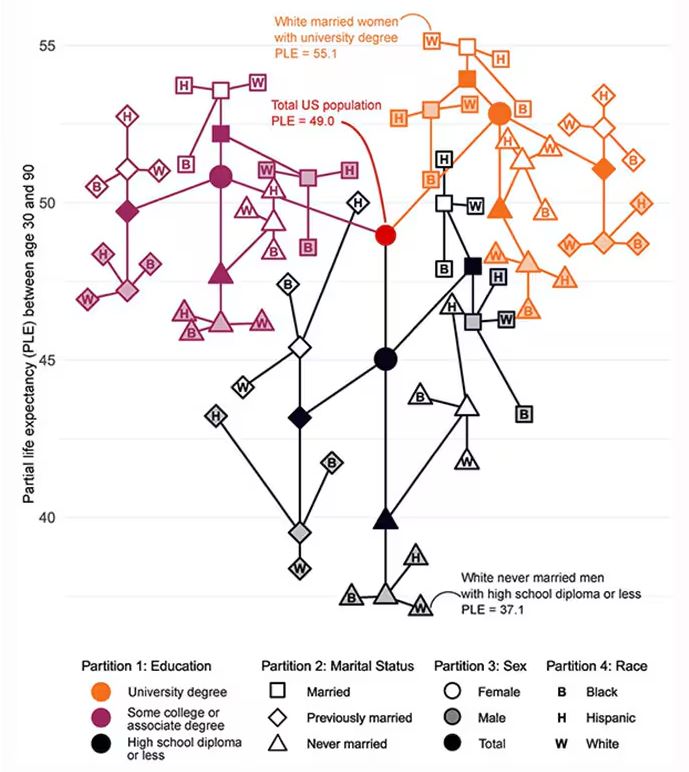
This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.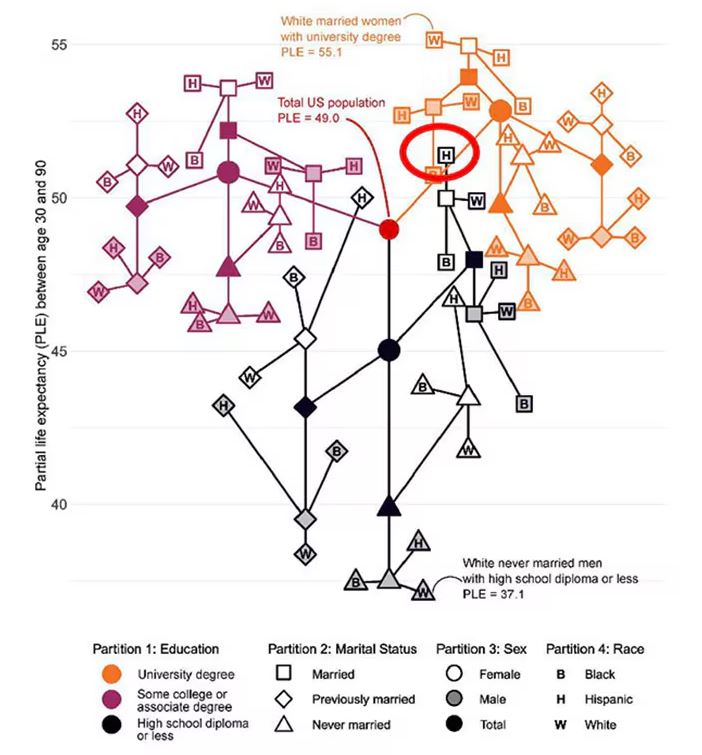
The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.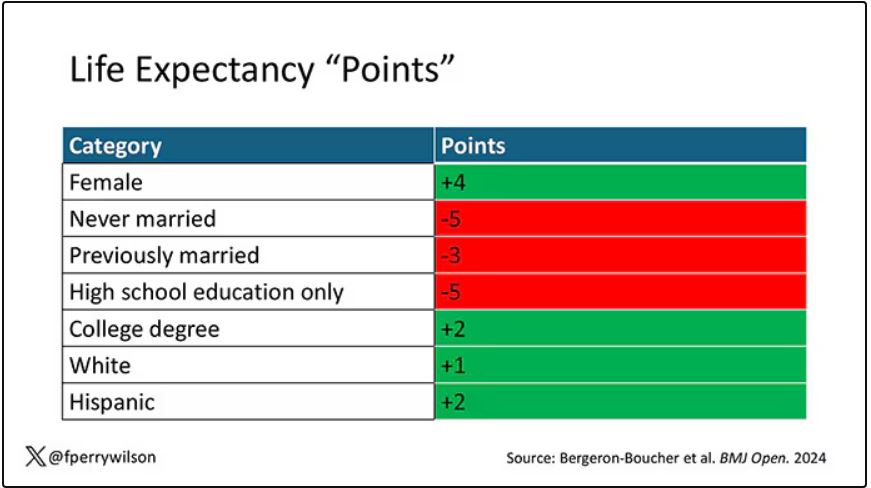
As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.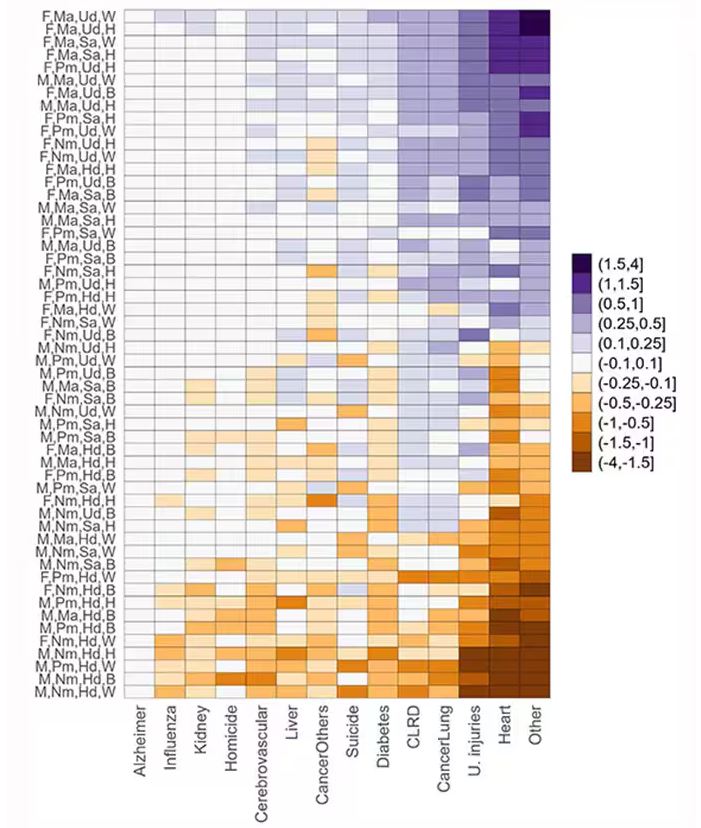
Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall. 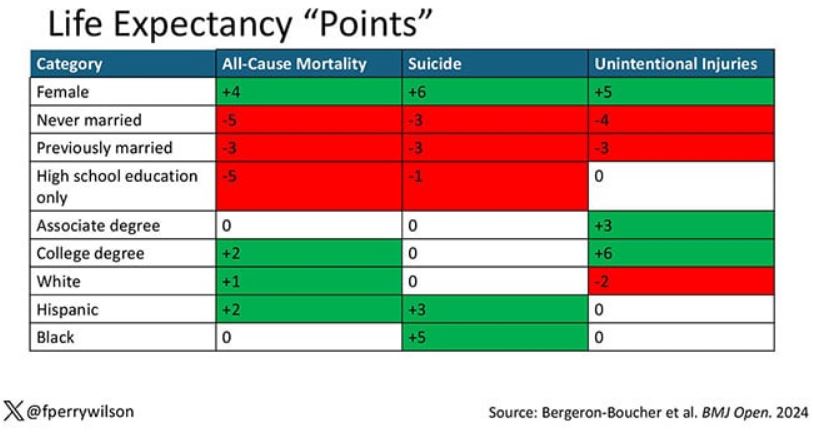
So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.
Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.
But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.
This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.
The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.
As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.
Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall. 
So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Two individuals in the United States are celebrating their 30th birthdays. It’s a good day. They are entering the prime of their lives. One is a married White woman with a university degree. The other is a never-married White man with a high school diploma.
How many more years of life can these two individuals look forward to?
There’s a fairly dramatic difference. The man can expect 37.1 more years of life on average, living to be about 67. The woman can expect to live to age 85. That’s a life-expectancy discrepancy of 18 years based solely on gender, education, and marital status.
I’m using these cases to illustrate the extremes of life expectancy across four key social determinants of health: sex, race, marital status, and education. We all have some sense of how these factors play out in terms of health, but a new study suggests that it’s actually quite a bit more complicated than we thought.
Let me start by acknowledging my own bias here. As a clinical researcher, I sometimes find it hard to appreciate the value of actuarial-type studies that look at life expectancy (or any metric, really) between groups defined by marital status, for example. I’m never quite sure what to do with the conclusion. Married people live longer, the headline says. Okay, but as a doctor, what am I supposed to do about that? Encourage my patients to settle down and commit? Studies showing that women live longer than men or that White people live longer than Black people are also hard for me to incorporate into my practice. These are not easily changeable states.
But studies examining these groups are a reasonable starting point to ask more relevant questions. Why do women live longer than men? Is it behavioral (men take more risks and are less likely to see doctors)? Or is it hormonal (estrogen has a lot of protective effects that testosterone does not)? Or is it something else?
Integrating these social determinants of health into a cohesive story is a bit harder than it might seem, as this study, appearing in BMJ Open, illustrates.
In the context of this study, every person in America can be placed into one of 54 mutually exclusive groups. You can be male or female. You can be Black, White, or Hispanic. You can have a high school diploma or less, an associate degree, or a college degree; and you can be married, previously married, or never married.
Of course, this does not capture the beautiful tapestry that is American life, but let’s give them a pass. They are working with data from the American Community Survey, which contains 8634 people — the statistics would run into trouble with more granular divisions. This survey can be population weighted, so you can scale up the results to reasonably represent the population of the United States.
The survey collected data on the four broad categories of sex, race, education, and marital status and linked those survey results to the Multiple Cause of Death dataset from the CDC. From there, it’s a pretty simple task to rank the 54 categories in order from longest to shortest life expectancy, as you can see here.
But that’s not really the interesting part of this study. Sure, there is a lot of variation; it’s interesting that these four factors explain about 18 years’ difference in life expectancy in this country. What strikes me here, actually, is the lack of an entirely consistent message across this spectrum.
Let me walk you through the second figure in this paper, because this nicely illustrates the surprising heterogeneity that exists here.
This may seem overwhelming, but basically, shapes that are higher up on the Y-axis represent the groups with longer life expectancy.
You can tell, for example, that shapes that are black in color (groups with high school educations or less) are generally lower. But not universally so. This box represents married, Hispanic females who do quite well in terms of life expectancy, even at that lower educational level.
The authors quantify this phenomenon by creating a mortality risk score that integrates these findings. It looks something like this, with 0 being average morality for the United States.
As you can see, you get a bunch of points for being female, but you lose a bunch for not being married. Education plays a large role, with a big hit for those who have a high school diploma or less, and a bonus for those with a college degree. Race plays a relatively more minor role.
This is all very interesting, but as I said at the beginning, this isn’t terribly useful to me as a physician. More important is figuring out why these differences exist. And there are some clues in the study data, particularly when we examine causes of death. This figure ranks those 54 groups again, from the married, White, college-educated females down to the never-married, White, high school–educated males. The boxes show how much more or less likely this group is to die of a given condition than the general population.
Looking at the bottom groups, you can see a dramatically increased risk for death from unintentional injuries, heart disease, and lung cancer. You see an increased risk for suicide as well. In the upper tiers, the only place where risk seems higher than expected is for the category of “other cancers,” reminding us that many types of cancer do not respect definitions of socioeconomic status.
You can even update the risk-scoring system to reflect the risk for different causes of death. You can see here how White people, for example, are at higher risk for death from unintentional injuries relative to other populations, despite having a lower mortality overall. 
So maybe, through cause of death, we get a little closer to the answer of why. But this paper is really just a start. Its primary effect should be to surprise us — that in a country as wealthy as the United States, such dramatic variation exists based on factors that, with the exception of sex, I suppose, are not really biological. Which means that to find the why, we may need to turn from physiology to sociology.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Connecticut. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
