User login
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
Choosing your first job out of residency can be overwhelming. The things you need to consider go way beyond the job itself: things like geography, work/life balance, and practice focus (eg, skin cancer, cosmetics, medical dermatology, pediatrics) are all relatively independent factors from the specific practice you join. About 1 in 6 dermatologists change practices every year, with even higher rates for new graduates.1
Drawing from my 20 years of experience as a dermatologist (10 in academia and 10 in 3 different private group practice settings—one that was independently owned and 2 with private equity owners, of which I am one), I have seen firsthand what matters and what does not when it comes to joining a group practice, both in my own career and in watching the careers of many young dermatologists. I will do my best to summarize that experience into useful advice.
Important Factors to Consider When Choosing a Practice
As a second- or third-year resident, you likely are excited but nervous about leaping into practice. To approach it with confidence, allow me to outline certain factors that apply to all dermatology practices that you may consider joining as you start your career and beyond.
- Every Practice Owner Has to Prioritize Profit. Independent owners need to build the value of their main asset, academics need to fund research and teaching, and private equity owners need to drive returns for their investors. In other words, there are lots of negative situations in academic and independently owned groups, although private equity gets all the bad press.2-5 Nothing inherently makes one type of practice setting better; it depends on the specific organization. Owners do care about other things beyond just profit (eg, providing quality care, performing cutting-edge research), but when the rubber meets the road, if a practice is providing amazing quality care but losing money doing so, in a short time it won’t be providing any care at all.
- There Is No Free Money. Your long-term compensation will 100% be determined by how much revenue you generate minus the overhead. There is no magic fund to boost your pay long term, no matter how badly the practice needs or wants you. Be clear and even blunt: ask how the practice is going to profit from you. Ask how they plan to make back any signing bonus or guaranteed salary. If they are paying you a higher percentage of collections, ask them how they are able to pay more than competitors. If they say it is because they are more efficient with lower overhead, make sure that increased efficiency does not translate into less support.
- Percent of Collections Is Irrelevant. OK, perhaps not completely irrelevant, but it is one of the least important aspects in determining how much you will make or how happy you will be. Percent of collections is the percentage of the money that the practice actually collects that is paid out to you as compensation. For example, if your percentage of collections is 40%, that means that if the practice collects $1,000,000 for the care you deliver, you will be compensated $400,000. Read on to find out why it is not as important as it seems.
- Don’t Get Too Hung Up on the Details of the Contract. I have seen so many young dermatologists spend enormous amounts of time and money on attorneys and negotiating the fine points of the contract, but not a single one has ever said later that because of all that negotiation they were protected or treated well when things got contentious. What it comes down to is that, if the practice wants to treat you well, they will. If they want to treat you badly, no contract on earth can protect you from all the ways they can do so. And if you leave, no matter what the contract says, they can do whatever they want unless you are willing to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to fight them in court. So review the contract with an attorney and know what it says, but don’t sweat every period and clause. It isn’t worth it.
- Your Day-to-Day Is Everything. The practice you join may be the best-run practice in the world in every way, except that the office you happen to be going to work in is the one office in the practice that has 2 providers who are jerks and everyone dreads coming to work every morning. There are so many other examples of ways one location can be a disaster even in a great practice—and unfortunately, even great locations can change. The best you can do is to make sure you know where you will be working and with whom. Go and visit the actual office and spend a day shadowing to feel what the vibe is.
What Really Matters
If factors like the percentage of collections you keep are not the big things, what are? The good and bad news is that there isn’t a single answer to this question. Rather, the fundamental question is whether the practice’s plan to maximize profit includes having satisfied, motivated, and engaged long-term providers. Obviously every group practice says this is fundamental to them, but often it isn’t true. Your real job is to find out whether or not it is. The second fundamental question is whether or not the leadership and members of a group practice are competent. It doesn’t matter if they want and intend to do everything right; if the practice is not competent at getting it done, your life practicing dermatology there is not going to be good.
As a dermatologist who has practiced for 20 years in multiple settings, here are some of the questions I would ask when assessing a practice setting I might consider joining. The practice should be able to easily answer all of these questions. If they won’t, can’t, or don’t—or if they answer but don’t give you clear, concrete responses—it is a huge red flag. It could be that they know you won’t like the answers or it could be that they don’t know the answers, but either reason indicates a big problem.
- How do the contracted rates compare to other practices? Pick 5 to 10 Current Procedural Terminology codes you expect to bill the most and ask the practice to tell you the contracted rates for each of those codes with their top 5 payers. Get the same information from all the practices you are considering joining and compare them. The variation between 2 practices in the same market can be as high as 30%. That means that for doing the same work at Practice A you could collect $800,000 and at Practice B in the same market you could collect more than $1,000,000. Getting 45% of your collection from Practice A is a losing proposition compared to getting 40% at Practice B.
- What is the collection rate? If the practice has great contracted rates but terrible revenue cycle management operations, the rates don’t matter. For example, maybe their contracted rate for a given code is $150, compared to another practice whose contracted rate is $125. But if their collection rate is only 60% and the other practice has a collection rate of 80%, they are only getting $90 while the practice with the lower contracted rate is getting $100.
- What billing and coding support does the practice offer? Are you expected to know and keep up with all the procedure codes, modifiers, etc, and use them correctly yourself or do they have professional coders who review every visit? Do they appeal every denied claim? Will you get reports on what charges get denied and why so that you can adjust your practices to avoid further denials?
- How do they train and assign medical assistants (MAs)? The single biggest determinant of your day-to-day productivity and happiness will be your MAs. Having 3 experienced, efficient MAs will allow you to see 50 patients per day with less effort and more fun than seeing 30 patients per day with 2 inexperienced, inefficient MAs. Seeing 50 patients per day at 40% of collections leads to you earning a lot more than seeing 30 per day at 50% of collections. Beyond the basic question of how many MAs you will have, also ask: Will you be expected to train them yourself, or does the practice have a formal training program? Who assesses how well they are performing? Will you have the same MAs every day? When more senior providers have MAs call off sick or leave the practice, will your MAs be pulled to cover their clinics? If that happens, will you be compensated in some way? Get the answers in writing.
- What is the “feel” of the office you will be working in? Ideally you will go and spend a day seeing patients in the office with one of the existing providers to get a sense of whether it’s a place you will be excited to come to every morning. Do you like the other providers? Is there someone who could act as a mentor for you? Does the staff seem happy? Will the physical layout and square footage accommodate the way you imagine practicing? Are the sociodemographics of the patients a fit for what you want?
- Who will be the office manager responsible for your personal practice? Some practices have an on-site manager for every location; others have district or regional managers who are split between multiple practices. Some have both. All can work, but having a competent, supportive office manager with whom you get along with whom and who “gets it” is crucial. You should ask about office manager turnover (high rates are bad, of course) and should ask to meet and interview the office manager who will be the boots on the ground for the practice in your location.
- How much demand for services is there and how are new patients scheduled? If the new hire gets all the hair loss, acne, and eczema cases and the established providers get all the skin cancer/Medicare patients, you are not going to have a balanced patient mix, and you are not going to meet productivity goals because you won’t be doing enough procedures. If there is not enough demand to fill your schedule, what kind of marketing support does the practice offer and what other approaches might they take? If you want to do cosmetics, how are they going to help you grow in that area? Are there other providers who don’t do cosmetics and will refer to you? Is there already someone in the practice who all the referrals go to? Is your percentage of collections based on total collections or on collections after the cost of injectables is deducted?
- What educational support does the practice offer? Do they have an annual meeting for networking and continuing medical education (CME)? If so, will you be expected to use your CME budget to pay to attend? Are there restrictions on what you can use your CME budget for? Is your CME budget considered part of your percentage of collections? Are there experts in the practice you can go to if you have a challenging case or difficult situation?
- Are physician associates and nurse practitioners a big part of the practice? Will you have the opportunity to increase your compensation by supervising them? If so, what is expected of supervising physicians and how are they compensated (flat fee vs percentage of collections vs another model)?
- What does the noncompete say? Obviously the shorter the time period and the smaller the distance, the better. For most practices, a noncompete is nonnegotiable. But there are some nuances to consider: Is the restricted distance from any location that the practice has in the market, or from any location(s) in which you personally have practiced, or from the primary location(s) in which you have practiced? If it is from the primary location(s), get details on how this term is defined: How much do you have to be at a location before it is considered primary? If you stop going to a location, after what period of time is it no longer considered a primary location? Additional questions to ask about noncompetes include: Is there a nonsolicitation clause for employees or patients? Will the practice include a buy-out clause in which you can pay them a set amount to waive the noncompete? Will they make the noncompete time dependent? In other words, if it is a terrible fit and you want to leave in the first year, there is very little justification for them to enforce a noncompete—but unless it is in your contract that they won’t enforce it if you leave before a certain amount of time, they will enforce it.
- Is there a path to having equity in the practice? In academia, this obviously is not a possibility. In independent practices it generally is referred to as an ownership stake or becoming a partner, and in private-equity groups it is literally referred to as “equity,” but they mean essentially the same thing for our purposes. It benefits the practice if you have equity because it gives you a reason to work to help increase the value of the practice. It benefits you to have equity because it means you have more input into decisions that will affect you (and the influence is proportional to how much equity you have) and the equity is an asset that can become very valuable.
The primary advice I have when it comes to being promised an opportunity to become an owner/partner in an independent group is to get the timing and conditions under which you can become an owner in the contract and strongly advocate for a clause that states that if you are not offered the opportunity as defined in the contract that you will be compensated. Also consider what happens if the current owner(s) sell the practice before you become an owner.
In private-equity groups, ask how many of the current providers have equity and ask how the equity is currently divided (what percentage is held by the private equity group, what percentage is held by the CEO and other executives, and what percentage is held by providers). The more equity held by the executive leadership and providers the better, as that means more people are on the same team of trying to increase the value of the practice. Find out how and when you will be able to buy in and try to get this in the contract or at least in writing. Also ask for a guarantee that your equity will not decrease in value. There are instances in which the practice loses value over time due to mismanagement, and the legal structure typically prioritizes the equity of the private-equity owners over the equity of providers. This is called an equity waterfall. Equity that providers were told was worth millions can literally be worth nothing.
One Key Thing You Need to Know
More important than the formal interviews and meetings that will provide you with answers to the questions outlined here, you need to know if you can trust the answers and you need to know the overall culture of the organization. Are they truly pro-provider, and do they believe that engaged and supported providers are the best route to long-term profit maximization? Or do they see providers primarily as replaceable adversaries who need to be placated and managed in order to minimize overhead? The only way to find out is to talk to providers already working there.
If you ask the practice for contact information for providers you can talk to, they likely will put you in touch with those who they know are going to talk about the practice in the best possible light. Be aware that providers may speak positively about a practice for a few different reasons other than that they are actually happy. Maybe the provider has an ownership stake in the practice and will benefit financially if you join. Keep in mind that, if a friend or colleague introduced you to the practice, they are almost certainly getting a substantial referral bonus if you join, so they may not be unbiased; however, if they are an actual friend, the last thing they want is for you to join and be unhappy in the practice because they didn’t tell the truth.
To learn about the experiences of others in your situation who have joined the practice, go to the website and look through the list of providers. Ideally, look for people who are in their first 3 years out of residency who have been there long enough to know the ins and outs but who still are considered newbies and almost certainly don’t have a meaningful ownership stake or strong allegiance to the practice. If it is a geographically widespread practice, focus on people in the region you will be in, but also talk to at least one person from a distant site.
Next, go to the American Academy of Dermatology’s website to find the email addresses for the providers you want to contact in the member directory. Send them an email explaining that you are thinking about joining the practice and that you would like to have an off-the-record phone conversation with them about their experiences. If they decline or don’t respond, it could be a red flag that likely means they don’t think they can speak positively about the practice. If they do agree to speak with you, you can reiterate at that time that the conversation is off the record and that you won’t relay your discussion to anyone at the practice.
Here is a sample email you can use to reach out to providers from a practice you are considering joining:
Subject: Advice on Joining [Practice Name]
Dear Dr. [Name],
I’m a dermatology resident considering joining [Practice Name] and came across your profile. Would you be willing to have a brief (5 to 10 minutes), off-the-record call about your experience? I’d value your perspective and won’t share our conversation with the practice. Thank you!
Best, [Your Name]
Start the conversation with open-ended questions and see where it goes. Some things to ask might be, are you glad you joined the practice? Was there anything that surprised you after you joined? Is there anything you wish you would have asked or known before you joined? I would recommend not asking specifically about their compensation, as it likely will be different from what you are being offered due to variations in location and current market situations.
Final Thoughts
There is no perfect dermatology practice, but the approach outlined here—rooted in first principles and real-world experience—will help you find one that is right for you. Ask tough questions, talk to other providers, and trust your instincts.
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
- Cwalina TB, Mazmudar RS, Bordeaux JS, et al. Dermatologist workforce mobility: recent trends and characteristics. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:323-325. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.5862
- Oscherwitz ME, Godinich BM, Patel RH, et al. Effects of private equity on dermatologic quality of patient care. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:E100-E102. doi:10.1111/jdv.20191
- Walsh S, Seaton E. Private equity in dermatology: a cloud on the horizon of quality care? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2025;39:9-10. doi:10.1111/jdv.20272
- Konda S, Patel S, Francis J. Private equity: the bad and the ugly. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:597-610. doi:10.1016/j.det.2023.04.004
- Novice T, Portney D, Eshaq M. Dermatology resident perspectives on practice ownership structures and private equity-backed group practices. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:296-302. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.008
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
What Dermatology Residents Need to Know About Joining Group Practices
PRACTICE POINTS
- Finding the right fit in the first position out of dermatology residency can be difficult and feel overwhelming.
- Leaving one practice and joining another is especially common in the first 10 years after residency.
- Asking the right questions can increase the probability of finding the right practice for you and receiving fair compensation.
Dermatology Boards Demystified: Conquer the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams
Dermatology Boards Demystified: Conquer the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams
Dermatology trainees are no strangers to standardized examinations that assess basic science and medical knowledge, from the Medical College Admission Test and the National Board of Medical Examiners Subject Examinations to the United States Medical Licensing Examination series (I know, cue the collective flashbacks!). As a dermatology resident, you will complete a series of 6 examinations, culminating with the final APPLIED Exam, which assesses a trainee's ability to apply therapeutic knowledge and clinical reasoning in scenarios relevant to the practice of general dermatology.1 This article features high-yield tips and study resources alongside test-day strategies to help you perform at your best.
The Path to Board Certification for Dermatology Trainees
After years of dedicated study in medical school, navigating the demanding match process, and completing your intern year, you have finally made it to dermatology! With the USMLE Step 3 out of the way, you are now officially able to trade in electrocardiograms for Kodachromes and dermoscopy. As a dermatology trainee, you will complete the American Board of Dermatology (ABD) Certification Pathway—a staged evaluation beginning with a BASIC Exam for first-year residents, which covers dermatology fundamentals and is proctored at your home institution.1 This exam is solely for informational purposes, and ultimately no minimum score is required for certification purposes. Subsequently, second- and third-year residents sit for 4 CORE Exam modules assessing advanced knowledge of the major clinical areas of the specialty: medical dermatology, surgical dermatology, pediatric dermatology, and dermatopathology. These exams consist of 75 to 100 multiple-choice questions per each 2-hour module and are administered either online in a private setting, via a secure online proctoring system, or at an approved testing center. The APPLIED Exam is the final component of the pathway and prioritizes clinical acumen and judgement. This 8-hour, 200-question exam is offered exclusively in person at approved testing centers to residents who have passed all 4 compulsory CORE modules and completed residency training. There is a 20-minute break between sections 1 and 2, a 60-minute break between sections 2 and 3, and a 20-minute break between sections 3 and 4.1 Following successful completion of the ABD Certification Pathway, dermatologists maintain board certification through quarterly CertLink questions, which you must complete at least 3 quarters of each year, and regular completion of focused practice improvement modules every 5 years. Additionally, one must maintain a full and unrestricted medical license in the United States or Canada and pay an annual fee of $150.
High-Yield Study Resources and Exam Preparation Strategies
Growing up, I was taught that proper preparation prevents poor performance. This principle holds particularly true when approaching the ABD Certification Pathway. Before diving into high-yield study resources and comprehensive exam preparation strategies, here are some big-picture essentials you need to know:
- Your residency program covers the fee for the BASIC Exam, but the CORE and APPLIED Exams are out-of-pocket expenses. As of 2026, you should plan to budget $2450 ($200 for 4 CORE module attempts and $2250 for the APPLIED Exam) for all 5 exams.2
- Testing center space is limited for each test date. While the ABD offers CORE Exams 3 times annually in 2-week windows (Winter [February], Summer [July], and Fall [October/November]), the APPLIED Exam is only given once per year. For the best chance of getting your preferred date, be sure to register as early as possible (especially if you live and train in a city with limited testing sites).
- After you have successfully passed your first CORE Exam module, you may take up to 3 in one sitting. When taking multiple modules consecutively on the same day, a 15-minute break is configured between each module.
Study Resources
When it comes to studying, there are more resources available than you will have time to explore; therefore, it is crucial to prioritize the ones that best match your learning style. Whether you retain information through visuals, audio, reading comprehension, practice questions, or spaced repetition, there are complimentary and paid high-yield tools designed to support how you learn and make the most of your valuable time outside of clinical responsibilities (Table). Furthermore, there are numerous discipline-specific textbooks and resources encompassing dermatopathology, dermoscopy, trichology, pediatric dermatology, surgical dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, and skin of color.11-13 As a trainee, you also have access to the American Academy of Dermatology’s Learning Center (https://learning.aad.org/Catalogue/AAD-Learning-Center) featuring the Question of the Week series, Board Prep Plus question bank, Dialogues in Dermatology podcast, and continuing medical education articles. Additionally, board review sessions occur at many local, regional, and national dermatology conferences annually.
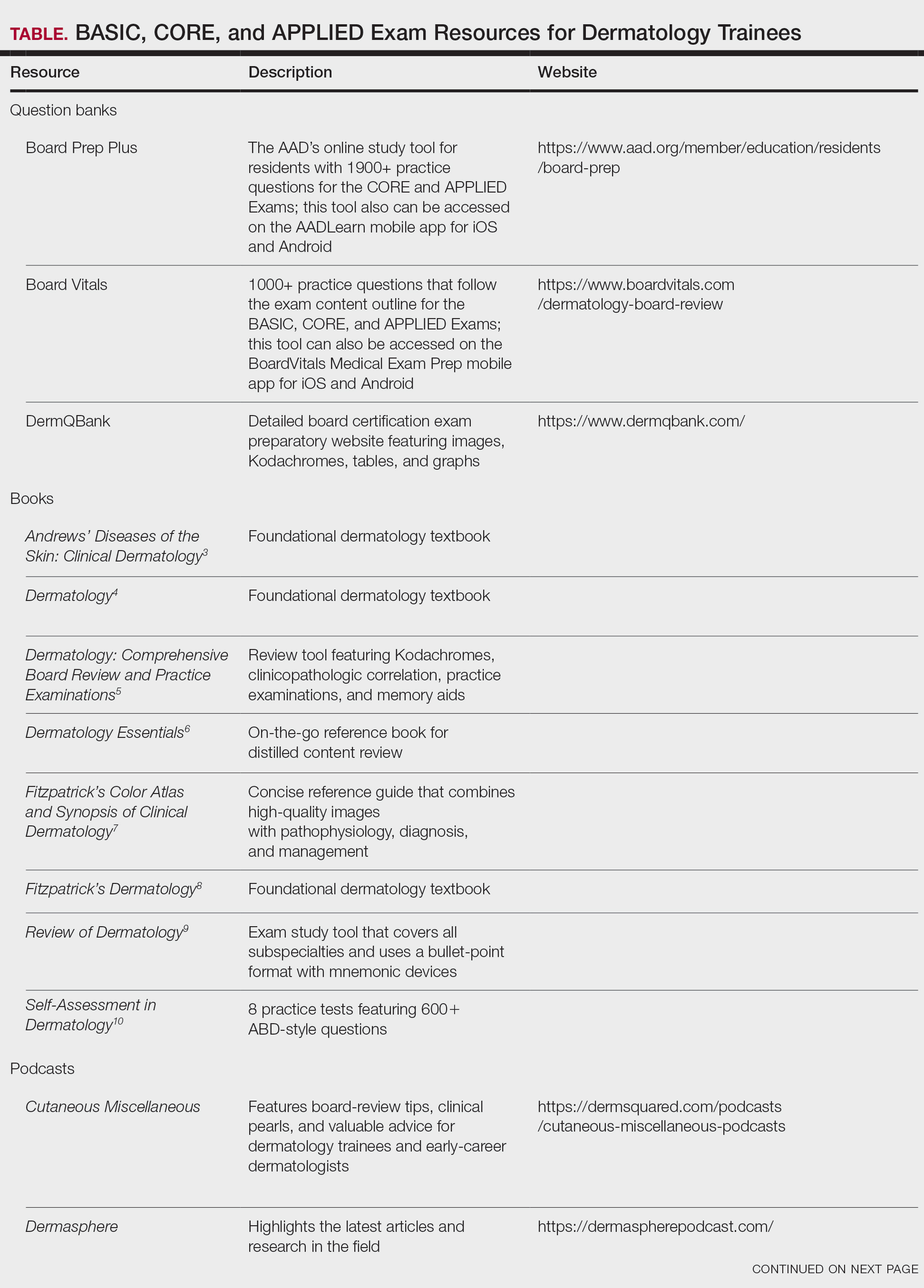
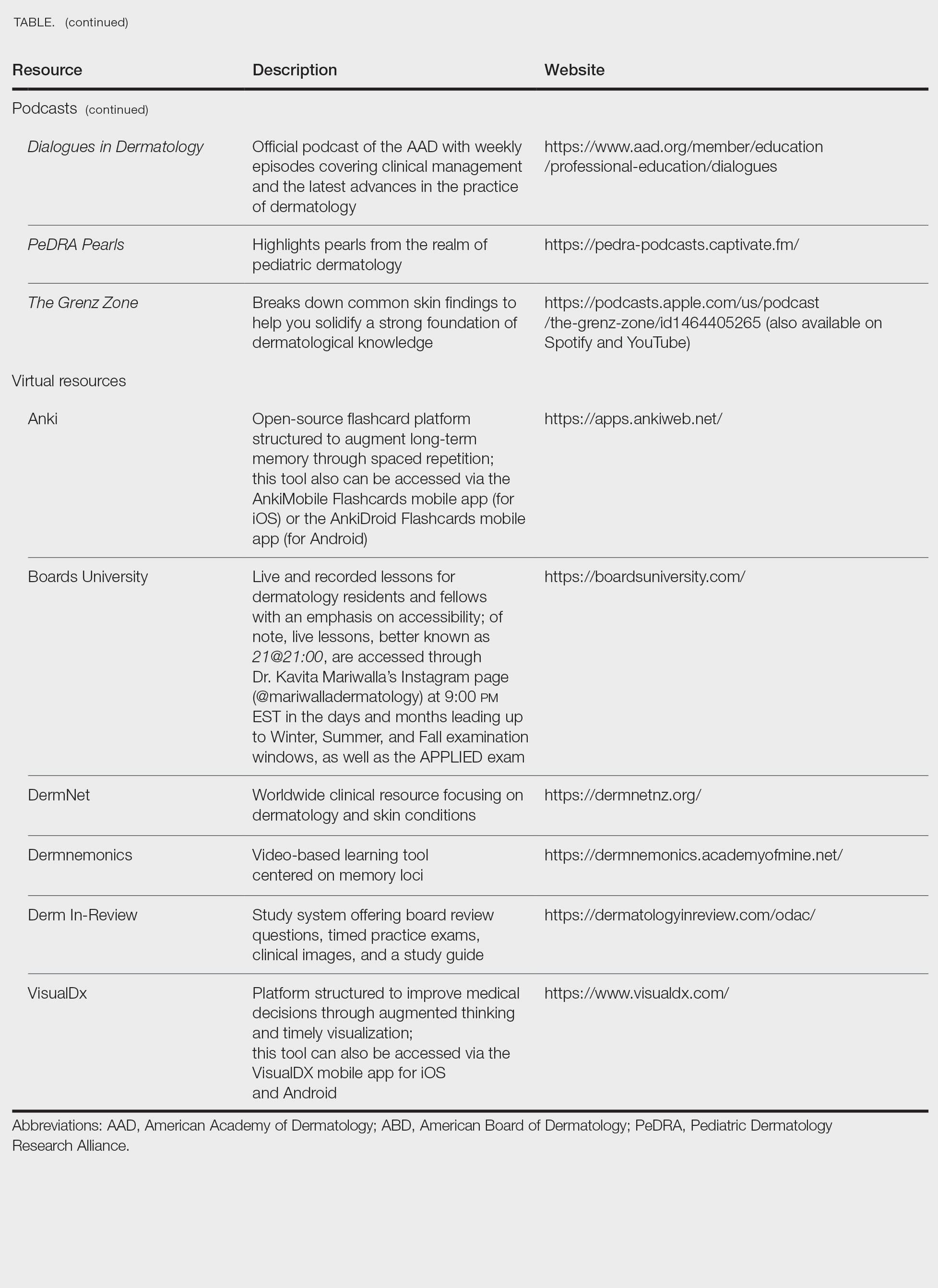
Exam Preparation Strategy
A comprehensive preparation strategy should begin during your first year of residency and appropriately intensify in the months leading up to the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams. Ultimately, active learning is ongoing, and your daily clinical work combined with program-sanctioned didactics, journal reading, and conference attendance comprise your framework. I often found it helpful to spend 30 to 60 minutes after clinic each evening reviewing high-yield or interesting cases from the day, as our patients are our greatest teachers. To reinforce key concepts, I used a combination of premade Anki decks14 and custom flashcards for topics that required rote memorization and spaced repetition. Podcasts such as Cutaneous Miscellaneous, The Grenz Zone, and Dermasphere became valuable learning tools that I incorporated into my commutes and long runs. I also enjoyed listening to the Derm In-Review audio study guide.19 Early in residency, I also created a digital notebook on OneNote (https://onenote.cloud.microsoft/en-us/)—organized by postgraduate year and subject—to consolidate notes and procedural pearls. As a fellow, I still use this note-taking system to organize notes from laser and energy-based device trainings and catalogue high-yield conference takeaways. Finally, task management applications can further help you achieve your study goals by organizing assignments, setting deadlines, and breaking larger objectives into manageable steps, making it easier to stay focused and on track.
Test Day Strategies
After sitting for many standardized examinations on the journey to dermatology residency, I am certain that you have cultivated your own reliable test day rituals and strategies; however, if you are looking for additional ones to add to your toolbox, here are a few that helped me stay calm, focused, and in the zone throughout my time in residency.
The Day Before the Test
- Secure your test-day snacks and preferred form of hydration. I am a fan of cheese sticks for protein and fruit for vitamins and antioxidants. Additionally, I always bring something salty and something sweet (usually chocolate or sour gummy snacks) just in case I happen to get a specific craving on test day.
- Make sure you have valid forms of identification in accordance with the test center policy.16
- Confirm your exam location and time. Testing center details can be found on the Pearson Vue portal,16 which is easily accessed via the “ABD Tools” tab on the official ABD website (https://www.abderm.org/). Additionally, the exam location, time, and directions to the test center are located in your Pearson Vue confirmation email.
- Trust that you are prepared. Try your best to avoid last-minute cramming and prioritize a good night’s sleep.
The Day of the Test
- Center yourself before the exam. I prefer to start my morning with a run to clear my mind; however, you can also consider other mindfulness exercises such as deep breathing or positive grounding affirmations.
- Arrive early and dress in layers. You never know if the testing location will run warm or cold.
- Pace yourself, trust your gut instincts, and do not be afraid to mark and move on if you get stuck on a particular question. Ultimately, make sure you answer every question, as you will not have points deducted for guessing.
- Make sure to plan something you are excited about for after the exam! That may mean celebrating with co-residents, spending time with loved ones, or just relaxing on the couch and finally catching up on that show you have been meaning to watch for weeks but have not had time for because you have been focused on studying (yes, we all have that one show).
Final Thoughts
While this article is not comprehensive of all ABD Certification Pathway preparation materials and resources, I hope that you will find it helpful along your residency journey. Starting dermatology residency can feel like drinking from a firehose: there is an overwhelming volume of new information, unfamiliar terminology, and a demanding workflow that varies considerably from that of intern year.17 As a resident, it is vital to prioritize your mental health and well-being, as the journey is a marathon rather than a sprint.18
Never forget that you have already come this far; trust in your journey and remember what is meant for you will not miss you. Juggling 6 exams during residency alongside clinical and personal responsibilities is no small feat. With a strong study plan and smart test-day strategies, I have no doubt you will become a board-certified dermatologist!
- ABD certification pathway info center. Accessed October 1, 2025. https://www.abderm.org/residents-and-fellows/abd-certification-pathway/abd-certification-pathway-info-center
- American Board of Dermatology. General exam information. Accessed January 13, 2026. https://www.abderm.org/exams/general-exam-information
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al, eds. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Nelson KC, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology: Comprehensive Board Review and Practice Examinations. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology Essentials. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2023.
- Saavedra AP, Kang S, Amagai M, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2023.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Alikhan A, Hocker TL, eds. Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017.
- Leventhal JS, Levy LL. Self-Assessment in Dermatology: Questions and Answers. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Association of Academic Cosmetic Dermatology. Resources for dermatology residents. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://theaacd.org/resident-resources/
- Mukosera GT, Ibraheim MK, Lee MP, et al. From scope to screen: a collection of online dermatopathology resources for residents and fellows. JAAD Int. 2023;12:12-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.12.007
- Shabeeb N. Dermatology resident education for skin of color. Cutis. 2020;106:E18-E20. doi:10.12788/cutis.0099
- Azhar AF. Review of 3 comprehensive Anki flash card decks for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2023;112:E10-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0813
- ODAC Dermatology. Derm In-Review. Accessed October 22, 2025. https://dermatologyinreview.com/odac/
- American Board of Dermatology (ABD) certification testing with Pearson VUE. Accessed October 19, 2025. https://www.pearsonvue.com/us/en/abd.html
- Lim YH. Transitioning from an intern to a dermatology resident. Cutis. 2022;110:E14-E16. doi:10.12788/cutis.0638
- Lim YH. Prioritizing mental health in residency. Cutis. 2022;109:E36-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0551
Dermatology trainees are no strangers to standardized examinations that assess basic science and medical knowledge, from the Medical College Admission Test and the National Board of Medical Examiners Subject Examinations to the United States Medical Licensing Examination series (I know, cue the collective flashbacks!). As a dermatology resident, you will complete a series of 6 examinations, culminating with the final APPLIED Exam, which assesses a trainee's ability to apply therapeutic knowledge and clinical reasoning in scenarios relevant to the practice of general dermatology.1 This article features high-yield tips and study resources alongside test-day strategies to help you perform at your best.
The Path to Board Certification for Dermatology Trainees
After years of dedicated study in medical school, navigating the demanding match process, and completing your intern year, you have finally made it to dermatology! With the USMLE Step 3 out of the way, you are now officially able to trade in electrocardiograms for Kodachromes and dermoscopy. As a dermatology trainee, you will complete the American Board of Dermatology (ABD) Certification Pathway—a staged evaluation beginning with a BASIC Exam for first-year residents, which covers dermatology fundamentals and is proctored at your home institution.1 This exam is solely for informational purposes, and ultimately no minimum score is required for certification purposes. Subsequently, second- and third-year residents sit for 4 CORE Exam modules assessing advanced knowledge of the major clinical areas of the specialty: medical dermatology, surgical dermatology, pediatric dermatology, and dermatopathology. These exams consist of 75 to 100 multiple-choice questions per each 2-hour module and are administered either online in a private setting, via a secure online proctoring system, or at an approved testing center. The APPLIED Exam is the final component of the pathway and prioritizes clinical acumen and judgement. This 8-hour, 200-question exam is offered exclusively in person at approved testing centers to residents who have passed all 4 compulsory CORE modules and completed residency training. There is a 20-minute break between sections 1 and 2, a 60-minute break between sections 2 and 3, and a 20-minute break between sections 3 and 4.1 Following successful completion of the ABD Certification Pathway, dermatologists maintain board certification through quarterly CertLink questions, which you must complete at least 3 quarters of each year, and regular completion of focused practice improvement modules every 5 years. Additionally, one must maintain a full and unrestricted medical license in the United States or Canada and pay an annual fee of $150.
High-Yield Study Resources and Exam Preparation Strategies
Growing up, I was taught that proper preparation prevents poor performance. This principle holds particularly true when approaching the ABD Certification Pathway. Before diving into high-yield study resources and comprehensive exam preparation strategies, here are some big-picture essentials you need to know:
- Your residency program covers the fee for the BASIC Exam, but the CORE and APPLIED Exams are out-of-pocket expenses. As of 2026, you should plan to budget $2450 ($200 for 4 CORE module attempts and $2250 for the APPLIED Exam) for all 5 exams.2
- Testing center space is limited for each test date. While the ABD offers CORE Exams 3 times annually in 2-week windows (Winter [February], Summer [July], and Fall [October/November]), the APPLIED Exam is only given once per year. For the best chance of getting your preferred date, be sure to register as early as possible (especially if you live and train in a city with limited testing sites).
- After you have successfully passed your first CORE Exam module, you may take up to 3 in one sitting. When taking multiple modules consecutively on the same day, a 15-minute break is configured between each module.
Study Resources
When it comes to studying, there are more resources available than you will have time to explore; therefore, it is crucial to prioritize the ones that best match your learning style. Whether you retain information through visuals, audio, reading comprehension, practice questions, or spaced repetition, there are complimentary and paid high-yield tools designed to support how you learn and make the most of your valuable time outside of clinical responsibilities (Table). Furthermore, there are numerous discipline-specific textbooks and resources encompassing dermatopathology, dermoscopy, trichology, pediatric dermatology, surgical dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, and skin of color.11-13 As a trainee, you also have access to the American Academy of Dermatology’s Learning Center (https://learning.aad.org/Catalogue/AAD-Learning-Center) featuring the Question of the Week series, Board Prep Plus question bank, Dialogues in Dermatology podcast, and continuing medical education articles. Additionally, board review sessions occur at many local, regional, and national dermatology conferences annually.


Exam Preparation Strategy
A comprehensive preparation strategy should begin during your first year of residency and appropriately intensify in the months leading up to the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams. Ultimately, active learning is ongoing, and your daily clinical work combined with program-sanctioned didactics, journal reading, and conference attendance comprise your framework. I often found it helpful to spend 30 to 60 minutes after clinic each evening reviewing high-yield or interesting cases from the day, as our patients are our greatest teachers. To reinforce key concepts, I used a combination of premade Anki decks14 and custom flashcards for topics that required rote memorization and spaced repetition. Podcasts such as Cutaneous Miscellaneous, The Grenz Zone, and Dermasphere became valuable learning tools that I incorporated into my commutes and long runs. I also enjoyed listening to the Derm In-Review audio study guide.19 Early in residency, I also created a digital notebook on OneNote (https://onenote.cloud.microsoft/en-us/)—organized by postgraduate year and subject—to consolidate notes and procedural pearls. As a fellow, I still use this note-taking system to organize notes from laser and energy-based device trainings and catalogue high-yield conference takeaways. Finally, task management applications can further help you achieve your study goals by organizing assignments, setting deadlines, and breaking larger objectives into manageable steps, making it easier to stay focused and on track.
Test Day Strategies
After sitting for many standardized examinations on the journey to dermatology residency, I am certain that you have cultivated your own reliable test day rituals and strategies; however, if you are looking for additional ones to add to your toolbox, here are a few that helped me stay calm, focused, and in the zone throughout my time in residency.
The Day Before the Test
- Secure your test-day snacks and preferred form of hydration. I am a fan of cheese sticks for protein and fruit for vitamins and antioxidants. Additionally, I always bring something salty and something sweet (usually chocolate or sour gummy snacks) just in case I happen to get a specific craving on test day.
- Make sure you have valid forms of identification in accordance with the test center policy.16
- Confirm your exam location and time. Testing center details can be found on the Pearson Vue portal,16 which is easily accessed via the “ABD Tools” tab on the official ABD website (https://www.abderm.org/). Additionally, the exam location, time, and directions to the test center are located in your Pearson Vue confirmation email.
- Trust that you are prepared. Try your best to avoid last-minute cramming and prioritize a good night’s sleep.
The Day of the Test
- Center yourself before the exam. I prefer to start my morning with a run to clear my mind; however, you can also consider other mindfulness exercises such as deep breathing or positive grounding affirmations.
- Arrive early and dress in layers. You never know if the testing location will run warm or cold.
- Pace yourself, trust your gut instincts, and do not be afraid to mark and move on if you get stuck on a particular question. Ultimately, make sure you answer every question, as you will not have points deducted for guessing.
- Make sure to plan something you are excited about for after the exam! That may mean celebrating with co-residents, spending time with loved ones, or just relaxing on the couch and finally catching up on that show you have been meaning to watch for weeks but have not had time for because you have been focused on studying (yes, we all have that one show).
Final Thoughts
While this article is not comprehensive of all ABD Certification Pathway preparation materials and resources, I hope that you will find it helpful along your residency journey. Starting dermatology residency can feel like drinking from a firehose: there is an overwhelming volume of new information, unfamiliar terminology, and a demanding workflow that varies considerably from that of intern year.17 As a resident, it is vital to prioritize your mental health and well-being, as the journey is a marathon rather than a sprint.18
Never forget that you have already come this far; trust in your journey and remember what is meant for you will not miss you. Juggling 6 exams during residency alongside clinical and personal responsibilities is no small feat. With a strong study plan and smart test-day strategies, I have no doubt you will become a board-certified dermatologist!
Dermatology trainees are no strangers to standardized examinations that assess basic science and medical knowledge, from the Medical College Admission Test and the National Board of Medical Examiners Subject Examinations to the United States Medical Licensing Examination series (I know, cue the collective flashbacks!). As a dermatology resident, you will complete a series of 6 examinations, culminating with the final APPLIED Exam, which assesses a trainee's ability to apply therapeutic knowledge and clinical reasoning in scenarios relevant to the practice of general dermatology.1 This article features high-yield tips and study resources alongside test-day strategies to help you perform at your best.
The Path to Board Certification for Dermatology Trainees
After years of dedicated study in medical school, navigating the demanding match process, and completing your intern year, you have finally made it to dermatology! With the USMLE Step 3 out of the way, you are now officially able to trade in electrocardiograms for Kodachromes and dermoscopy. As a dermatology trainee, you will complete the American Board of Dermatology (ABD) Certification Pathway—a staged evaluation beginning with a BASIC Exam for first-year residents, which covers dermatology fundamentals and is proctored at your home institution.1 This exam is solely for informational purposes, and ultimately no minimum score is required for certification purposes. Subsequently, second- and third-year residents sit for 4 CORE Exam modules assessing advanced knowledge of the major clinical areas of the specialty: medical dermatology, surgical dermatology, pediatric dermatology, and dermatopathology. These exams consist of 75 to 100 multiple-choice questions per each 2-hour module and are administered either online in a private setting, via a secure online proctoring system, or at an approved testing center. The APPLIED Exam is the final component of the pathway and prioritizes clinical acumen and judgement. This 8-hour, 200-question exam is offered exclusively in person at approved testing centers to residents who have passed all 4 compulsory CORE modules and completed residency training. There is a 20-minute break between sections 1 and 2, a 60-minute break between sections 2 and 3, and a 20-minute break between sections 3 and 4.1 Following successful completion of the ABD Certification Pathway, dermatologists maintain board certification through quarterly CertLink questions, which you must complete at least 3 quarters of each year, and regular completion of focused practice improvement modules every 5 years. Additionally, one must maintain a full and unrestricted medical license in the United States or Canada and pay an annual fee of $150.
High-Yield Study Resources and Exam Preparation Strategies
Growing up, I was taught that proper preparation prevents poor performance. This principle holds particularly true when approaching the ABD Certification Pathway. Before diving into high-yield study resources and comprehensive exam preparation strategies, here are some big-picture essentials you need to know:
- Your residency program covers the fee for the BASIC Exam, but the CORE and APPLIED Exams are out-of-pocket expenses. As of 2026, you should plan to budget $2450 ($200 for 4 CORE module attempts and $2250 for the APPLIED Exam) for all 5 exams.2
- Testing center space is limited for each test date. While the ABD offers CORE Exams 3 times annually in 2-week windows (Winter [February], Summer [July], and Fall [October/November]), the APPLIED Exam is only given once per year. For the best chance of getting your preferred date, be sure to register as early as possible (especially if you live and train in a city with limited testing sites).
- After you have successfully passed your first CORE Exam module, you may take up to 3 in one sitting. When taking multiple modules consecutively on the same day, a 15-minute break is configured between each module.
Study Resources
When it comes to studying, there are more resources available than you will have time to explore; therefore, it is crucial to prioritize the ones that best match your learning style. Whether you retain information through visuals, audio, reading comprehension, practice questions, or spaced repetition, there are complimentary and paid high-yield tools designed to support how you learn and make the most of your valuable time outside of clinical responsibilities (Table). Furthermore, there are numerous discipline-specific textbooks and resources encompassing dermatopathology, dermoscopy, trichology, pediatric dermatology, surgical dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, and skin of color.11-13 As a trainee, you also have access to the American Academy of Dermatology’s Learning Center (https://learning.aad.org/Catalogue/AAD-Learning-Center) featuring the Question of the Week series, Board Prep Plus question bank, Dialogues in Dermatology podcast, and continuing medical education articles. Additionally, board review sessions occur at many local, regional, and national dermatology conferences annually.


Exam Preparation Strategy
A comprehensive preparation strategy should begin during your first year of residency and appropriately intensify in the months leading up to the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams. Ultimately, active learning is ongoing, and your daily clinical work combined with program-sanctioned didactics, journal reading, and conference attendance comprise your framework. I often found it helpful to spend 30 to 60 minutes after clinic each evening reviewing high-yield or interesting cases from the day, as our patients are our greatest teachers. To reinforce key concepts, I used a combination of premade Anki decks14 and custom flashcards for topics that required rote memorization and spaced repetition. Podcasts such as Cutaneous Miscellaneous, The Grenz Zone, and Dermasphere became valuable learning tools that I incorporated into my commutes and long runs. I also enjoyed listening to the Derm In-Review audio study guide.19 Early in residency, I also created a digital notebook on OneNote (https://onenote.cloud.microsoft/en-us/)—organized by postgraduate year and subject—to consolidate notes and procedural pearls. As a fellow, I still use this note-taking system to organize notes from laser and energy-based device trainings and catalogue high-yield conference takeaways. Finally, task management applications can further help you achieve your study goals by organizing assignments, setting deadlines, and breaking larger objectives into manageable steps, making it easier to stay focused and on track.
Test Day Strategies
After sitting for many standardized examinations on the journey to dermatology residency, I am certain that you have cultivated your own reliable test day rituals and strategies; however, if you are looking for additional ones to add to your toolbox, here are a few that helped me stay calm, focused, and in the zone throughout my time in residency.
The Day Before the Test
- Secure your test-day snacks and preferred form of hydration. I am a fan of cheese sticks for protein and fruit for vitamins and antioxidants. Additionally, I always bring something salty and something sweet (usually chocolate or sour gummy snacks) just in case I happen to get a specific craving on test day.
- Make sure you have valid forms of identification in accordance with the test center policy.16
- Confirm your exam location and time. Testing center details can be found on the Pearson Vue portal,16 which is easily accessed via the “ABD Tools” tab on the official ABD website (https://www.abderm.org/). Additionally, the exam location, time, and directions to the test center are located in your Pearson Vue confirmation email.
- Trust that you are prepared. Try your best to avoid last-minute cramming and prioritize a good night’s sleep.
The Day of the Test
- Center yourself before the exam. I prefer to start my morning with a run to clear my mind; however, you can also consider other mindfulness exercises such as deep breathing or positive grounding affirmations.
- Arrive early and dress in layers. You never know if the testing location will run warm or cold.
- Pace yourself, trust your gut instincts, and do not be afraid to mark and move on if you get stuck on a particular question. Ultimately, make sure you answer every question, as you will not have points deducted for guessing.
- Make sure to plan something you are excited about for after the exam! That may mean celebrating with co-residents, spending time with loved ones, or just relaxing on the couch and finally catching up on that show you have been meaning to watch for weeks but have not had time for because you have been focused on studying (yes, we all have that one show).
Final Thoughts
While this article is not comprehensive of all ABD Certification Pathway preparation materials and resources, I hope that you will find it helpful along your residency journey. Starting dermatology residency can feel like drinking from a firehose: there is an overwhelming volume of new information, unfamiliar terminology, and a demanding workflow that varies considerably from that of intern year.17 As a resident, it is vital to prioritize your mental health and well-being, as the journey is a marathon rather than a sprint.18
Never forget that you have already come this far; trust in your journey and remember what is meant for you will not miss you. Juggling 6 exams during residency alongside clinical and personal responsibilities is no small feat. With a strong study plan and smart test-day strategies, I have no doubt you will become a board-certified dermatologist!
- ABD certification pathway info center. Accessed October 1, 2025. https://www.abderm.org/residents-and-fellows/abd-certification-pathway/abd-certification-pathway-info-center
- American Board of Dermatology. General exam information. Accessed January 13, 2026. https://www.abderm.org/exams/general-exam-information
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al, eds. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Nelson KC, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology: Comprehensive Board Review and Practice Examinations. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology Essentials. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2023.
- Saavedra AP, Kang S, Amagai M, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2023.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Alikhan A, Hocker TL, eds. Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017.
- Leventhal JS, Levy LL. Self-Assessment in Dermatology: Questions and Answers. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Association of Academic Cosmetic Dermatology. Resources for dermatology residents. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://theaacd.org/resident-resources/
- Mukosera GT, Ibraheim MK, Lee MP, et al. From scope to screen: a collection of online dermatopathology resources for residents and fellows. JAAD Int. 2023;12:12-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.12.007
- Shabeeb N. Dermatology resident education for skin of color. Cutis. 2020;106:E18-E20. doi:10.12788/cutis.0099
- Azhar AF. Review of 3 comprehensive Anki flash card decks for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2023;112:E10-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0813
- ODAC Dermatology. Derm In-Review. Accessed October 22, 2025. https://dermatologyinreview.com/odac/
- American Board of Dermatology (ABD) certification testing with Pearson VUE. Accessed October 19, 2025. https://www.pearsonvue.com/us/en/abd.html
- Lim YH. Transitioning from an intern to a dermatology resident. Cutis. 2022;110:E14-E16. doi:10.12788/cutis.0638
- Lim YH. Prioritizing mental health in residency. Cutis. 2022;109:E36-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0551
- ABD certification pathway info center. Accessed October 1, 2025. https://www.abderm.org/residents-and-fellows/abd-certification-pathway/abd-certification-pathway-info-center
- American Board of Dermatology. General exam information. Accessed January 13, 2026. https://www.abderm.org/exams/general-exam-information
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al, eds. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018.
- Nelson KC, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology: Comprehensive Board Review and Practice Examinations. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2019.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology Essentials. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2023.
- Saavedra AP, Kang S, Amagai M, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2023.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw Hill; 2019.
- Alikhan A, Hocker TL, eds. Review of Dermatology. Elsevier; 2017.
- Leventhal JS, Levy LL. Self-Assessment in Dermatology: Questions and Answers. 2nd ed. Elsevier; 2024.
- Association of Academic Cosmetic Dermatology. Resources for dermatology residents. Accessed October 15, 2025. https://theaacd.org/resident-resources/
- Mukosera GT, Ibraheim MK, Lee MP, et al. From scope to screen: a collection of online dermatopathology resources for residents and fellows. JAAD Int. 2023;12:12-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2022.12.007
- Shabeeb N. Dermatology resident education for skin of color. Cutis. 2020;106:E18-E20. doi:10.12788/cutis.0099
- Azhar AF. Review of 3 comprehensive Anki flash card decks for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2023;112:E10-E12. doi:10.12788/cutis.0813
- ODAC Dermatology. Derm In-Review. Accessed October 22, 2025. https://dermatologyinreview.com/odac/
- American Board of Dermatology (ABD) certification testing with Pearson VUE. Accessed October 19, 2025. https://www.pearsonvue.com/us/en/abd.html
- Lim YH. Transitioning from an intern to a dermatology resident. Cutis. 2022;110:E14-E16. doi:10.12788/cutis.0638
- Lim YH. Prioritizing mental health in residency. Cutis. 2022;109:E36-E38. doi:10.12788/cutis.0551
Dermatology Boards Demystified: Conquer the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams
Dermatology Boards Demystified: Conquer the BASIC, CORE, and APPLIED Exams
Practice Points
- To become a board-certified dermatologist, one must complete the American Board of Dermatology Certification Pathway—a staged evaluation beginning with a BASIC Exam for first-year residents, followed by 4 CORE Exam modules and a final APPLIED Exam following residency completion.
- When it comes to studying, there are more resources available than you will have time to explore fully. With so many options available, it is crucial to prioritize the ones that best match your learning style.
- A comprehensive study strategy begins during your first year of residency and appropriately intensifies in the months leading up to the exams. Make sure to cultivate test day strategies to help you stay calm, focused, and in the zone.
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
Serving those who serve has been one of the most meaningful parts of my career. A career in military medicine offers dermatologists not only a chance to practice within a unique and diverse patient population but also an opportunity to contribute to something larger than themselves. Whether working with active-duty service members and their families within the Military Health System (MHS) or caring for veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the experience can be both enriching and rewarding. This article will explore the various pathways available to dermatologists to serve military communities, whether they are at the start of their careers or are looking for a change of pace within their established practice.
Care Pathways for Military and Veterans
To care for uniformed service members, their families, and retired personnel, dermatologists typically serve within the MHS—a global, integrated network of military hospitals and clinics dedicated to delivering health care to this population.1 TRICARE is the health insurance program that covers those eligible for care within the system, including active-duty and retired service members.2 In this context, it is important to clarify what the term retired actually means, as it differs from the term veteran when it comes to accessing health care options, and these terms frequently are conflated. A retired service member is an individual who completed at least 20 years of active-duty service or who has been medically retired because of a condition or injury incurred while on active duty.3 In contrast, a veteran may not have completed 20 years of service but has separated honorably after serving at least 24 continuous months.4 Veterans typically receive care through the VA system.5
Serving on Active Duty
In general, there are 2 main pathways to serve as a dermatologist within the MHS. The first is to commission in the military and serve on active duty. Most often, this pathway begins with a premedical student applying to medical school. Those considering military service typically explore scholarship programs such as the Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP)(https://www.medicineandthemilitary.com/applying-and-what-to-expect/medical-school-programs/hpsp) or the Health Services Collegiate Program (HSCP), or they apply to the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU)(https://www.usuhs.edu/about). The HPSP and HSCP programs financially support medical students training at civilian medical schools, though in different ways—the HPSP covers tuition and fees, while the HSCP provides a salary during training but does not cover tuition.6 In contrast, students of USU attend the nation’s only military medical school, serving in uniform for 4 years while earning the pay and benefits of a junior officer in their respective service branch. Any premedical student considering the HPSP, HSCP or USU routes for service must meet the commissioning standards of their chosen branch—Army, Navy, or Air Force—and enter service as an officer before beginning medical school.
While direct commission prior to medical school is the most common route to active-duty service, board-certified dermatologists also can join a military branch later through what is called Direct Accession or Direct Commission; for example, the Navy offers a Residency to Direct Accession program, which commissions residents in their final year of training to join the Navy upon graduation. In some cases, commissioning at this stage includes a bonus of up to $600,000 in exchange for a 4-year active-duty commitment.7 The Army and Air Force offer similar direct commission programs, though specific incentives vary.8 Interested residents or practitioners can contact a local recruiting office within their branch of interest to learn more. Direct accession is open at many points in a dermatologist’s career—after residency, after fellowship, or even as an established civilian practitioner—and the initial commissioning rank and bonus generally reflect one’s level of experience.
Serving as a Civilian
Outside of uniformed service, dermatologists can find opportunities to provide care for active-duty service members, veterans, and military families through employment as General Schedule (GS) employees. The GS is a role classification and pay system that covers most federal employees in professional, administrative, and technical positions (eg, physicians). The GS system classifies most of these employees based on the complexity, responsibility, and qualifications required for their role.9 Such positions often are at the highest level of the GS pay scale, reflecting the expertise and years of education required to become a dermatologist, though pay varies by location and experience. In contrast, physicians employed through the VA system are classified as Title 38 federal employees, governed by a different pay structure and regulatory framework under the US Code of Federal Regulations.10 These regulations govern the hiring, retention, and firing guidelines for VA physicians, which differ from those of GS physicians. A full explanation is outside of the scope of this article, however.
Final Thoughts
In summary, uniformed or federal service as a dermatologist offers a meaningful and impactful way to give back to those who have served our country. Opportunities exist throughout the United States for dermatologists interested in serving within the MHS or VA. The most transparent and up-to-date resource for identifying open positions in both large metropolitan areas and smaller communities is USAJOBS.gov. While financial compensation may not always match that of private practice, the intangible benefits are considerable—stable employment, comprehensive benefits, malpractice coverage, and secure retirement, among others. There is something deeply fulfilling about using one’s medical skills in service of a larger mission. The relationships built with service members, the sense of shared purpose, and the opportunity to contribute to the readiness and well-being of those who serve all make this career path profoundly rewarding. For dermatologists seeking a practice that combines professional growth with purpose and patriotism, military medicine offers a truly special calling.
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
- Military Health System. Elements of the military health system. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.health.mil/About-MHS/MHS-Elements
- TRICARE. Plans and eligibility. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://tricare.mil/Plans/Eligibility
- Military Benefit. TRICARE for retirees. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.militarybenefit.org/get-educated/tricareforretirees/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Eligibility for VA health care. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA priority groups. Accessed October 11, 2025. https://www.va.gov/health-care/eligibility/priority-groups/
- Navy Medicine. Health Professions Scholarship Program (HPSP) and Financial Assistance Program (FAP). Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.med.navy.mil/Accessions/Health-Professions-Scholarship-Program-HPSP-and-Financial-Assistance-Program-FAP/
- US Navy. Navy Medicine R2DA program. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.navy.com/navy-medicine
- US Army Medical Department. Student programs. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://goamedd.com/student-programs
- US Office of Personnel Management. General Schedule. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.opm.gov/policy-data-oversight/pay-leave/pay-systems/general-schedule/
- Pines Federal Employment Attorneys. Title 38 employees: medical professionals. Accessed October 12, 2025. https://www.pinesfederal.com/va-federal-employees/title-38-employees-medical-professionals/
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
Dermatology on Duty: Pathways to a Career in Military Medicine
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatologists have diverse pathways to serve the military and veteran communities, either in uniform or as civilians.
- For those considering a military career, options include medical school scholarships or direct commission after residency.
- Those who prefer to remain civilians can find employment opportunities with the Military Heath System or the Department of Veterans Affairs that provide a way to care for this population without a service commitment.
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
I was accepted into my fellowship almost 1 year ago: major milestones on my curriculum vitae are now met, fellowship application materials are complete, and the stress of the match is long gone. At the start of my fellowship, I had 2 priorities: (1) to learn as much as I could about dermatologic surgery and (2) to be the best dad possible to my newborn son, Jay. However, most nights I still find myself up late editing a manuscript draft or chasing down references, long after the “need” to publish has passed. Recently, my wife asked me why—what’s left to prove?
I’ll be the first to admit it: early on, publishing felt almost purely transactional. Each project was little more than a line on an application or a way to stand out or meet a new mentor. I have reflected before on how easily that mindset can slip into a kind of research arms race, in which productivity overshadows purpose.1 This time, I wanted to explore the other side of that equation: the “why” behind it all.
I have learned that writing forces me to slow down and actually think about what I am seeing every day. It turns routine work into something I must understand well enough to explain. Even a small write-up can make me notice details I would otherwise skim past in clinic or surgery. These days, most of my projects start small: a case that taught me something, an observation that made me pause and think. Those seemingly small questions are what eventually grow into bigger ones. The clinical trial I am designing now did not begin as a grand plan—it started because I could not stop thinking about how we manage pain and analgesia after Mohs surgery. That curiosity, shaped by the experience of writing those earlier “smaller” papers, evolved into a study that might actually help improve patient care one day. Still, most of what I write will not revolutionize the field. It is not cutting-edge science or paradigm-shifting data; it is mostly modest analyses with a few interesting conclusions or surgical pearls that might cut down on a patient’s procedural time or save a dermatologist somewhere a few sutures. But it still feels worth doing.
While rotating with Dr. Anna Bar at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, I noticed a poster hanging on the wall titled, “Top 10 Reasons Why Our Faculty Are Dedicated to Academics and Teaching,” based on the wisdom of Dr. Jane M. Grant-Kels.2 My favorite line on the poster reads, “Residents make us better by asking questions.” I think this philosophy is the main reason why I still write. Even though I am not a resident anymore, I am still asking questions. But if I had to sum up my “why” into a neat list, here is what it might look like:
Because asking questions keeps your brain wired for curiosity. Even small projects train us to remain curious, and this curiosity can mean the difference between just doing your job and continuing to evolve within it. As Dr. Rodolfo Neirotti reminds us, “Questions are useful tools—they open communication, improve understanding, and drive scientific research. In medicine, doing things without knowing why is risky.”3
Because the small stuff builds the culture. Dermatology is a small world. Even short case series, pearls, or “how we do it” pieces can shape how we practice. They may not change paradigms, but they can refine them. Over time, those small practical contributions become part of the field’s collective muscle memory.
Because it preserves perspective. Residency, fellowship, and early practice can blur together. A tiny project can become a timestamp of what you were learning or caring about at that specific moment. Years later, you may remember the case through the paper.
Because the act of writing is the point. Writing forces clarity. You cannot hide behind saying, “That’s just how I do things,” when you have to explain it to others. The discipline of organizing your thoughts sharpens your clinical reasoning and keeps you honest about what you actually know.
Because sometimes it is simply about participating. Publishing, even small pieces, is a way of staying in touch with your field. It says, “I’m still here. I’m still paying attention.”
I think about how Dr. Frederic Mohs developed the technique that now bears his name while he was still a medical student.4 He could have said, “I already made it into medical school. That’s enough.” But he did not. I guess my point is not that we are all on the verge of inventing something revolutionary; it is that innovation happens only when curiosity keeps moving us forward. So no, I do not write to check boxes anymore. I write because it keeps me curious, and I have realized that curiosity is a habit I never want to outgrow.
Or maybe it’s because Jay keeps me up at night, and I have nothing better to do.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
- Jeha GM. A roadmap to research opportunities for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;114:E53-E56.
- Grant-Kels J. The gift that keeps on giving. UConn Health Dermatology. Accessed November 24, 2025. https://health.uconn.edu/dermatology/education/
- Neirotti RA. The importance of asking questions and doing things for a reason. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36:I-II.
- Trost LB, Bailin PL. History of Mohs surgery. Dermatol Clin. 2011;29:135-139, vii.
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
The Habit of Curiosity: How Writing Shapes Clinical Thinking in Medical Training
Practice Points
- Writing about everyday clinical experiences forces trainees to slow down, think more carefully, and better understand why they do what they do. Being able to write clearly about a clinical scenario reflects true understanding.
- The act of writing sharpens clinical judgment by requiring clarity, honesty, and reflection rather than relying on habit or routine.
- Writing fosters habits of curiosity that support continued professional growth and ongoing engagement with one’s field beyond formal training milestones.
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
The myths persist: You will lack colleagues. Your practice will be thin. You must sacrifice academic engagement. In reality, rural practice offers variety, leadership opportunities, and the chance to influence the health of entire communities in profound ways. In this article, we aim to unpack what rural dermatology actually looks like as a potential career path for residents, with a focus on private-academic hybrid and hospital-based practice models.
Definitions of the term rural vary. For the US Census Bureau, it is synonymous with nonurban, and for the Office of Management and Budget, the term nonmetropolitan is preferred. The US Department of Agriculture’s Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes recognize a continuum of classifications from micropolitan to remote. In practice, the term rural covers a wide spectrum: the rolling farmlands of the Midwest, the mountains of Montana, the bayous of the South, the Native American reservations in New Mexico, and everything in between. It is not one uniform reality—rural America is diverse, resilient, and deeply connected.
Daily clinic flow may look familiar: a full schedule, a mix of new and established patients, and frequent simple procedures such as biopsies and corticosteroid injections. But the scope of practice is wider. You become the dermatologist for hundreds of miles in every direction, managing most conditions locally while referring select cases to subspecialty centers.
Case variety is striking. Neglected tumors, unusual inflammatory presentations, pediatric conditions, and occupational dermatoses/injuries appear alongside the routine. Each day requires flexibility, judgment, confidence, and the ability to think outside the box. You must consider how a patient’s seasonal work, such as ranching or farming, and/or their total commute time impacts the risk-benefit discussion around treatment recommendations.
Matthew P. Shaffer, MD (Salina, Kansas), who has practiced rural dermatology for more than 20 years, explained that the breadth of dermatologic cases in which he served as the expert was both exciting and intimidating, but it became clear that this was the right professional path for him (email communication, September 5, 2025). In small communities, your role extends beyond the clinic walls. You will see patients at the grocery store, the library, and school events. That continuity fosters loyalty and accountability in ways that are hard to quantify.
Many practice structures exist: independent clinics, multispecialty groups, hospital employment, and increasingly, hybrid partnerships with academic centers.
Academic institutions have recognized the importance of rural exposure, and many now collaborate with rural dermatologists. For example, Heartland Dermatology in Salina, Kansas, where 2 of the authors (B.R.L. and T.G.) practice, partners with St. Louis University in Missouri to provide a residency track and rotations in rural clinics.
Rural-based hospital systems can create similar structures. Monument Health Dermatology in Spearfish, South Dakota, is integrated into the fabric of the community’s larger rural health care model. The physician (M.E.L.) collaborates daily with primary care providers, surgeons, and oncologists through a shared electronic health record (sometimes even through telephone speed-dial given the close collegiality of small-town providers). Patients come from across 4 states, some driving 6 hours each way. Patients who once doubted whether dermatology was worth the trip will consistently return for follow-up care once trust is earned. The stability of hospital employment supports volunteer faculty positions and a free satellite clinic in partnership with a local Lakota Tribal health center. There is never a dull day: the providers see urgent add-ons daily, which keeps them on their toes but in exchange brings immense reward. This includes a recent case from rural Wyoming: a complex mixed infantile hemangioma on the mid face just entering the rapid proliferation phase. Propranolol was started immediately, as opposed to months later when it was too late—a common complication for the majority of rural patients by the time to get to a dermatologist.
Complex cases can overwhelm rural practices, and this is when the hub-and-spoke model is invaluable. Dermatologists embed in local communities as spokes, while subspecialty services such as pediatric dermatology, dermatopathology, or Mohs micrographic surgery remain centralized at hubs. The hubs can be but do not have to be academic institutions; for Heartland Dermatology in Kansas, private practices fulfill both hub and spoke roles. With that said, 10 states do not have academic dermatology programs.1 Mohs surgeons and pediatric dermatologists still can establish robust and successful independent rural subspecialty practices outside academic hubs. Christopher Gasbarre, DO (Spearfish, South Dakota), a board-certified, fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon in rural practice, advises residents to be confident in their abilities and to trust their training, noting that they often will be asked to manage complicated cases because of patient travel and cost constraints; however, clinicians should recognize their own limitations and those of nearby specialists and develop a referral network for cases that require multidisciplinary care (text communication, September 14, 2025).
The hub-and-spoke models—whether they entail an academic center as the hub with private practices as the spokes, or a network of private practices that include rural subspecialists—allows rural dermatologists to remain trusted local experts while ensuring that patients can access advanced care via a more streamlined referral process/network. The challenge is triage: what can be managed locally and what must patients travel for? As Dr. Shaffer explained, decisions about whether care is managed locally or referred to a hub often depend on the experience and comfort level of both the physician and the patient (email communication, September 5, 2025). Ultimately, continuity and trust are central. Patients rely on their local dermatologist to guide these decisions, and that guidance makes the model effective.
The idea that rural practice means being stuck in a small solo clinic is outdated. Multiple pathways exist, each with strengths and challenges. Independent private practice offers maximum autonomy and deep community integration, though financial and staffing risks are yours to manage. Hospital employment with outreach clinics provides stability, benefits, and collegiality, but bureaucracy can limit innovation and efficiency. Private equity platforms supply resources and rapid growth, but alignment with mission and autonomy must be weighed carefully. Hybrid joint ventures with hospitals combine private control and institutional support, but contracts can be complex. Locum tenens–to-permanent arrangements let you try rural life with minimal commitment, but continuity with patients may be sacrificed. A self-screener can clarify your path: How much autonomy do I want? Do I prefer predictability or variety? How important are procedures, teaching, or community roles? Answer these questions honestly and pair that insight with mentor guidance.
Launching a rural dermatology clinic is equal parts vision and structure. A focused 90-day plan can make the difference between a smooth opening and early frustration. Think in 4 domains: site selection, employment and licensing, credentialing and contracting, and operations. Even in a compressed timeline, dozens of small but crucial tasks may surface. There are resources—such as the Medical Group Management Association’s practice start-up checklist—that can provide a roadmap, ensuring no detail is overlooked as you transform a vision into a functioning clinic.2
Site Selection—First, determine whether you are opening a new standalone clinic, extending an existing practice, or creating a part-time satellite. Referral mapping with local primary care providers is essential, as is a scan of payer mix and dermatologist density in the region to ensure sustainability.
Employment and Licensing—Confirm state licensure and Drug Enforcement Administration registration and initiate hospital privileges early. These processes can stretch across the entire 90-day window, so starting immediately is critical.
Credentialing and Contracting—Applications with commercial and federal payers, along with Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare updates, often consume weeks if not months. If you plan to perform office microscopy or establish a dermatopathology laboratory, begin the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments certification process in parallel.
Operations—Once the regulatory wheels are in motion, shift to building your practice infrastructure. Secure space, weigh lease vs purchase, and consider partnerships with local hospitals for shared clinic facilities. Recruit staff with dermatology-specific skills such as clinical photography and biopsy assistance. Implement an electronic health record, set up payroll and malpractice insurance, and establish supply chains for everything from liquid nitrogen to surgical trays. Decide whether revenue cycle management will be in-house or outsourced and finalize dermatopathology workflows including courier and transport agreements.
Compensation in rural dermatology mirrors that of other clinical settings: base salary with productivity bonuses, revenue pooling, or relative value unit structures. Financial planning is crucial. Develop a pro forma that models patient volume, expenses, and realistic growth. Risks exist, including payer mix, staffing, and competition, but the demand for care in underserved areas often offsets these, and communities may support practices with reduced overhead and strong loyalty. Hospital systems may add stipends for supervising advanced practitioners or outreach travel. Loan repayment programs, tax credits, and grants can further enhance packages. Consider checking with the state’s Office of Rural Health.
Career sustainability ultimately depends on more than finances. Geography, amenities, schedule flexibility, autonomy in medical decision-making, work-life balance, the value of being part of and serving a community, and other personal values will shape your “best-fit” practice model. Ask whether you can envision yourself thriving in the community you would be serving.
No one builds a rural dermatology practice alone. That is why one of the authors (M.E.L.) created the Rural Access to Dermatology Society (https://www.radsociety.org/), a nonprofit organization connecting dermatologists, residents, and medical students with a shared mission. The organization supports residents through scholarships, mentorship, and telementoring. Faculty can contribute through advocacy, residency track development, and outreach to uniquely underserved rural populations such as Native American reservations where access to dermatology care remains severely limited. Joining can be as simple as attending a webinar, finding a mentor, or volunteering at a free clinic. You do not need to launch your own clinic to get involved; you can begin by connecting with a network already laying the foundation.
Teledermatology and academic initiatives enhance rural care but do not replace in-person practice. Store-and-forward consultations extend reach but cannot match the continuity and trust of long-term patient relationships. Academic rural tracks prepare residents for unique challenges, but someone must staff the clinics. Private and hybrid models remain the backbone of rural access, where dermatologists take on the responsibility and the joy of being the local expert.
So here’s the invitation: bring one question to your mentor about rural practice and identify one rural site you could visit. The road less traveled in dermatology is closer than you think—and it might just be your path.
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
- Association of American Medical Colleges. ERAS Directory: Dermatology. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://systems.aamc.org/eras/erasstats/par/display.cfm?NAV_ROW=PAR&SPEC_CD=080
- Medical Group Management Association. Large group or organization practice startup checklist. Accessed December 11, 2025. https://www.mgma.com/member-tools/large-group-or-organization -practice-startup-checklist
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
The Road Less Traveled: Why Rural Dermatology Could Be Your Path After Residency
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
PRACTICE POINTS
- Direct care practices may be the new horizon of health care.
- Starting a direct care practice offers autonomy but demands entrepreneurial readiness.
- New dermatologists can enjoy control over scheduling, pricing, and patient care, but success requires business acumen, financial planning, and comfort with risk.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.
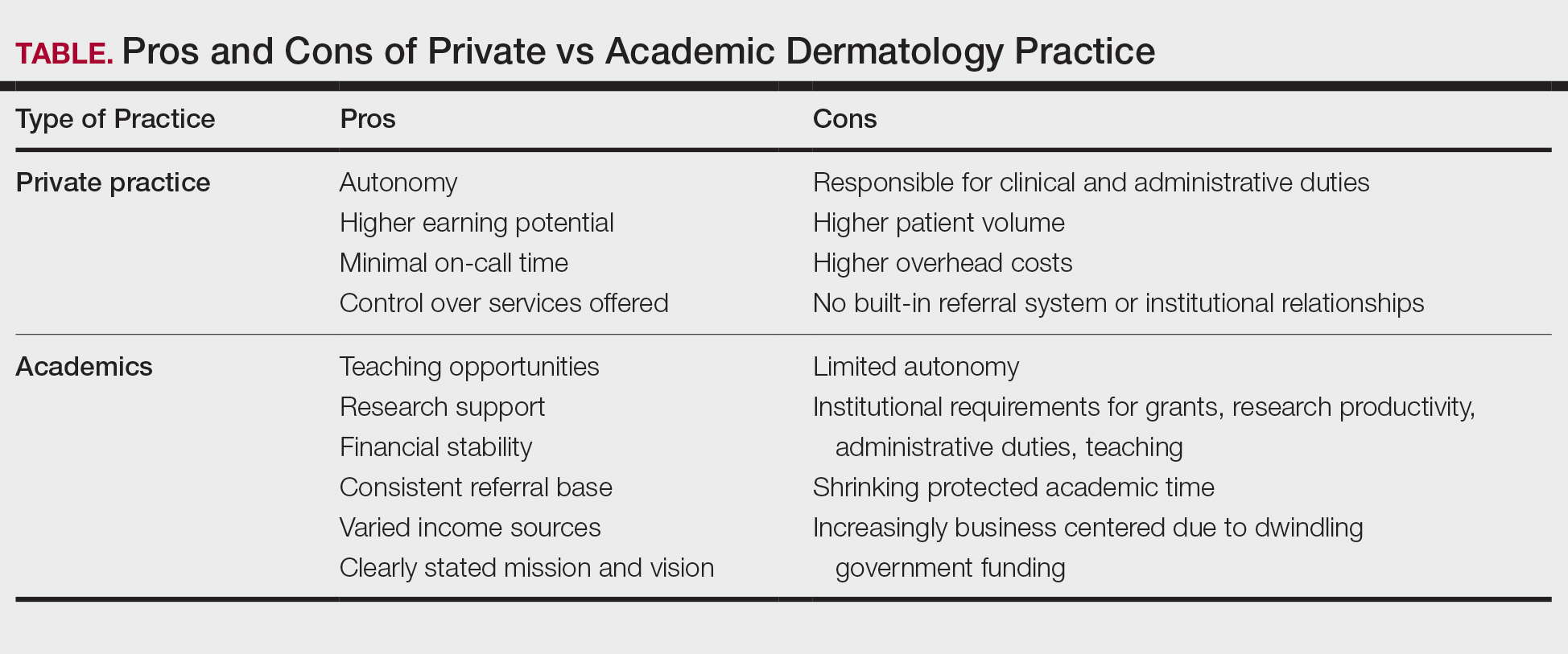
Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.

Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.

Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
PRACTICE POINTS
- In the field of dermatology, solo and small-group single-specialty private practices are shrinking while academic medicine is growing.
- Hybrid models reflect a desire among some dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment and sustainability associated with academic medicine and the professional autonomy of private practice.
Choosing a Job After Graduation: Advice for Residents From Scott Worswick, MD
Choosing a Job After Graduation: Advice for Residents From Scott Worswick, MD
What are the most important things to look at when considering joining a practice after residency?
DR. WORSWICK: When considering a private practice job, I think the most important things to determine might be how much control you will have over your day-to-day work experience (eg, will you be involved in the hiring/ firing of staff, how many rooms will you have in which to see patients, what flexibility exists for your daily schedule), who you will be working with, opportunities for growth and ownership, and the many extraneous things included in your contract (eg, medical insurance, time off, other benefits).
If you are considering joining an academic group, often times many of these things will be out of your control, but you will want to make sure you are finding a program where your teaching or research interests will be supported, that you are choosing a group with people and a mission statement similar to your own, and that you have mentorship available from faculty you want to emulate. There are many fun twists and turns that occur in careers in academic dermatology, so you want to be in a place that will foster your professional interests and allow you to grow and change.
What do academic dermatology programs look for when hiring new junior faculty members?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on time and place. At any given time, a program may need to find a specialist in a particular disease or niche (eg, a mycosis fungoides expert, a pediatric dermatologist, or someone doing hidradenitis suppurativa research). But in general, most academic places are looking to hire people who are excited to care for patients, will work well with the team and support the department’s mission, and enjoy teaching residents and students. For me, much of the fun of being in academics comes from mentorship (as a junior faculty member, this came from being a mentor to residents and students while also being mentored by more senior faculty), teaching, and the ability to care for patients with complicated problems that often require team-based care.
What are some red flags to watch for when considering joining a new practice?
DR. WORSWICK: I think the biggest red flags would be a practice that allows you no control over your schedule and no potential for growth of your compensation. We’ve had many residents choose to work for Kaiser lately, and I think in part that is because Kaiser is very clear regarding what salary, schedule, and expectations are. Fewer and fewer graduating residents are going into solo practice and even dermatologist-owned private practice, but I would encourage residents looking for jobs to consider these models rather than venture capital–funded practices that may not be patient care centered.
How many positions should graduating residents apply for?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on who you are, how specific your preferences are, and what part of the country/world you are looking to practice in. In general, there is a great need for dermatologists, and it shouldn’t be hard to find a job. If you’re in a more saturated urban area, you’re going to want to apply for multiple positions. But if you really know what you want, you may only apply to one practice. I generally advise our residents to consider at least 3 places, if only to compare them to give a better idea of best fit or to ensure that their “top choice” is indeed their top choice.
What are the most important things to look at when considering joining a practice after residency?
DR. WORSWICK: When considering a private practice job, I think the most important things to determine might be how much control you will have over your day-to-day work experience (eg, will you be involved in the hiring/ firing of staff, how many rooms will you have in which to see patients, what flexibility exists for your daily schedule), who you will be working with, opportunities for growth and ownership, and the many extraneous things included in your contract (eg, medical insurance, time off, other benefits).
If you are considering joining an academic group, often times many of these things will be out of your control, but you will want to make sure you are finding a program where your teaching or research interests will be supported, that you are choosing a group with people and a mission statement similar to your own, and that you have mentorship available from faculty you want to emulate. There are many fun twists and turns that occur in careers in academic dermatology, so you want to be in a place that will foster your professional interests and allow you to grow and change.
What do academic dermatology programs look for when hiring new junior faculty members?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on time and place. At any given time, a program may need to find a specialist in a particular disease or niche (eg, a mycosis fungoides expert, a pediatric dermatologist, or someone doing hidradenitis suppurativa research). But in general, most academic places are looking to hire people who are excited to care for patients, will work well with the team and support the department’s mission, and enjoy teaching residents and students. For me, much of the fun of being in academics comes from mentorship (as a junior faculty member, this came from being a mentor to residents and students while also being mentored by more senior faculty), teaching, and the ability to care for patients with complicated problems that often require team-based care.
What are some red flags to watch for when considering joining a new practice?
DR. WORSWICK: I think the biggest red flags would be a practice that allows you no control over your schedule and no potential for growth of your compensation. We’ve had many residents choose to work for Kaiser lately, and I think in part that is because Kaiser is very clear regarding what salary, schedule, and expectations are. Fewer and fewer graduating residents are going into solo practice and even dermatologist-owned private practice, but I would encourage residents looking for jobs to consider these models rather than venture capital–funded practices that may not be patient care centered.
How many positions should graduating residents apply for?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on who you are, how specific your preferences are, and what part of the country/world you are looking to practice in. In general, there is a great need for dermatologists, and it shouldn’t be hard to find a job. If you’re in a more saturated urban area, you’re going to want to apply for multiple positions. But if you really know what you want, you may only apply to one practice. I generally advise our residents to consider at least 3 places, if only to compare them to give a better idea of best fit or to ensure that their “top choice” is indeed their top choice.
What are the most important things to look at when considering joining a practice after residency?
DR. WORSWICK: When considering a private practice job, I think the most important things to determine might be how much control you will have over your day-to-day work experience (eg, will you be involved in the hiring/ firing of staff, how many rooms will you have in which to see patients, what flexibility exists for your daily schedule), who you will be working with, opportunities for growth and ownership, and the many extraneous things included in your contract (eg, medical insurance, time off, other benefits).
If you are considering joining an academic group, often times many of these things will be out of your control, but you will want to make sure you are finding a program where your teaching or research interests will be supported, that you are choosing a group with people and a mission statement similar to your own, and that you have mentorship available from faculty you want to emulate. There are many fun twists and turns that occur in careers in academic dermatology, so you want to be in a place that will foster your professional interests and allow you to grow and change.
What do academic dermatology programs look for when hiring new junior faculty members?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on time and place. At any given time, a program may need to find a specialist in a particular disease or niche (eg, a mycosis fungoides expert, a pediatric dermatologist, or someone doing hidradenitis suppurativa research). But in general, most academic places are looking to hire people who are excited to care for patients, will work well with the team and support the department’s mission, and enjoy teaching residents and students. For me, much of the fun of being in academics comes from mentorship (as a junior faculty member, this came from being a mentor to residents and students while also being mentored by more senior faculty), teaching, and the ability to care for patients with complicated problems that often require team-based care.
What are some red flags to watch for when considering joining a new practice?
DR. WORSWICK: I think the biggest red flags would be a practice that allows you no control over your schedule and no potential for growth of your compensation. We’ve had many residents choose to work for Kaiser lately, and I think in part that is because Kaiser is very clear regarding what salary, schedule, and expectations are. Fewer and fewer graduating residents are going into solo practice and even dermatologist-owned private practice, but I would encourage residents looking for jobs to consider these models rather than venture capital–funded practices that may not be patient care centered.
How many positions should graduating residents apply for?
DR. WORSWICK: I think this depends a lot on who you are, how specific your preferences are, and what part of the country/world you are looking to practice in. In general, there is a great need for dermatologists, and it shouldn’t be hard to find a job. If you’re in a more saturated urban area, you’re going to want to apply for multiple positions. But if you really know what you want, you may only apply to one practice. I generally advise our residents to consider at least 3 places, if only to compare them to give a better idea of best fit or to ensure that their “top choice” is indeed their top choice.
Choosing a Job After Graduation: Advice for Residents From Scott Worswick, MD
Choosing a Job After Graduation: Advice for Residents From Scott Worswick, MD
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
Residents and fellows in training have to navigate time management to balance reading, hands-on training, family responsibilities, exercise, diet, and sleep requirements. In addition, they grapple with the stress of financial commitments for food, housing, clothing, family members, transportation, and student loans. A brilliant friend of mine once said that she struggled throughout residency and her early career to find balance until it finally occurred to her that, while balance was aspirational, resilience was key. All that said, residents in training may find it appealing to earn a little extra money and gain additional clinical experience through moonlighting. This article discusses some key considerations when embarking on such a decision, including the effects of moonlighting on other commitments and some logistical factors to consider.
Will Moonlighting Adversely Affect My Other Commitments?
Residency and fellowship are precious opportunities to gain medical knowledge, hone your ability to make diagnoses through complex pattern recognition, and refine the necessary surgical and interpersonal skills to carry you through a successful career. Dermatology encompasses a vast array of conditions related only by their manifestation in skin. Dermatology residents and fellows may spend fewer sleepless hours on call, but the reading requirements are massive. Our treatment armamentarium has expanded rapidly with highly effective treatments for chronic conditions that have a dramatic impact on quality of life. With so many effective agents available, the choice often relates as much to comorbidities as to disease severity and location. There is so much to learn.
While making a full commitment to acquiring the skills of an expert clinician, it is important for residents to remain aware of those who depend on you—in particular, the fleeting time you have with your growing children. They grow up fast, and your interactions with them determine who they will grow up to be. In the past, salt, silk, gold, and jewels were the world’s greatest luxuries. Now, it’s time—time with family, time for self-care, time to reflect, and time to rest and renew. Be careful how you squander time in exchange for material possessions.
What Logistical Factors Should You Consider When Embarking on Moonlighting?
There are clearly stated policies from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education for when moonlighting can occur during training.1 It should not occur during typical residency or fellowship work hours, and the individual must be in good standing academically and progressing well on their journey to becoming a competent dermatologist. They must also have the appropriate skills to practice in the field of medicine chosen for moonlighting.
Moonlighting opportunities may exist in the form of emergency department or “quick clinic” coverage, especially for the evaluation and treatment of acute minor illnesses. Fellows who have completed a dermatology residency may supervise dermatology residents in afterhours or weekend clinics, offering enhanced opportunities for autonomy, additional clinical experience, and some welcome cash. To make such clinics viable, the office space must be available; the building must be open; and the costs of the space, scheduling, reception, and security services must be covered as well as nursing support (which should be voluntary and likely will require overtime pay scales). After all of these—as well as supplies—have been paid for, what is left is what is available to distribute as pay for service. Working through these factors provides valuable experience in resource management and helps prepare trainees for the economic realities of private practice. Large organizations may be able to provide the space and support, but all of that needs to be paid for through the proceeds that come from the patient care provided. No-show rates often are quite high for after-hours and weekend clinics, but the expenses for those unfilled appointment slots remain and must be paid in full. Be sure the demand exists and that you plan appropriately with strategic overbooking based on historical data on patient mix, procedural needs, and no-show rates.
My department has supported resident and fellow requests for moonlighting opportunities in the past. The most successful model was to have a limited number of early morning appointment slots prior to the start of morning didactics. Security typically already exists, rooms are available, and patients can be seen and still get to work or get their kids to school. No-show rates remained very low for morning appointments, and strategic overbooking was unnecessary.
In contrast, evening and weekend clinics start out strong with high patient satisfaction and deteriorate fairly quickly with accelerating no-show rates. People are busy at the end of the day, and unforeseen circumstances often affect their ability to keep an appointment. Weekends are precious; potential patients may be less schedule minded in the evenings and on weekends, and the residents and fellows themselves often find it stressful to commit to giving up a chunk of weekend time on a scheduled basis.
Before you commit to a moonlighting job, be sure to weigh all of the above factors and be sure the juice is worth the squeeze.
Final Thoughts
Moonlighting opportunities are a way to acquire both clinical and management skills and can provide a welcome extra bit of cash to ease financial burdens, but these benefits should be balanced with other time commitments and overall quality of life. Time is precious—choose wisely and be sure you spend it well.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Common Program Requirements (Residency). Updated September 17, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/cprresidency_2023v3.pdf
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
Navigating Moonlighting Opportunities During Dermatology Training
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatology training demands extensive study and hands-on skill development, which need to be balanced with family time, finances, and self-care.
- Before moonlighting, ensure it will not compromise your family’s quality of life or your core residency/fellowship commitments and that your program’s policies permit it.
- Carefully assess logistics to determine if an afterhours or weekend clinic can be a financially viable moonlighting opportunity.
Resident Participation Impact on Operative Time and Outcomes in Veterans Undergoing Total Laryngectomy
Resident Participation Impact on Operative Time and Outcomes in Veterans Undergoing Total Laryngectomy
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been integral in resident training. Resident surgical training requires a balance of supervision and autonomy, along with procedure repetition and appropriate feedback.1-3 Non-VA research has found that resident participation across various otolaryngology procedures, including thyroidectomy, neck dissection, and laryngectomy, does not increase patient morbidity.4-7 However, resident involvement in private and academic settings that included nonhead and neck procedures was linked to increased operative time and reduced productivity, as determined by work relative value units (wRVUs).7-13 This has also been identified in other specialties, including general surgery, orthopedics, and ophthalmology.14-16
Unlike the private sector, surgeon compensation at the VA is not as closely linked to operative productivity, offering a unique setting for resident training. While VA integration in otolaryngology residency programs increases resident case numbers, particularly in head and neck cases, the impact on VA patient outcomes and productivity is unknown.17 The use of larynxpreserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer has led to a decline in the number of total laryngectomies performed, which could potentially impact resident operative training for laryngectomies.18-20
This study sought to determine the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs, and patient outcomes in veterans who underwent a total laryngectomy. This study was reviewed and approved by the MedStar Georgetown University Hospital Institutional Review Board and Research and Development Committee (#1595672).
Methods
A retrospective cohort of veterans nationwide who underwent total laryngectomy between 2001 and 2021, with or without neck dissection, was identified from the Veterans Affairs Surgical Quality Improvement Program (VASQIP). Data were extracted via the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure and patients were included based on Current Procedural Terminology codes for total laryngectomy, with or without neck dissection (31320, 31360, 31365). Laryngopharyngectomies, partial laryngectomies, and minimally invasive laryngectomies were excluded. VASQIP nurse data managers reviewed patient data for operative data, postoperative outcomes (including 30- day morbidity and mortality), and preoperative risk factors (Appendix).21
The VASQIP data provide the highest resident or postgraduate year (PGY) per surgery. PGY 1, 2, and 3 were considered junior residents and PGY ≥4, surgical fellows, and individuals who took research years during residency were considered senior residents. Cases performed by attending physicians alone were compared with those involving junior or senior residents.
Patient demographic data included age, body mass index, smoking and alcohol use, weight loss, and functional status. Consumption of any tobacco products within 12 months of surgery was considered tobacco use. Drinking on average ≥2 alcoholic beverages daily was considered alcohol use. Weight loss was defined as a 10% reduction in body weight within the 6 months before surgery, excluding patients enrolled in a weight loss program. Functional status was categorized as independent, partially dependent, totally dependent, and unknown.
Primary outcomes included operative time, wRVUs generated, and wRVUs generated per hour of operative time. Postoperative complications were recorded both as a continuous variable and as a binary variable for presence or absence of a complication. Additional outcome variables included length of postoperative hospital stay, return to the operating room (OR), and death within 30 days of surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Data were summarized using frequency and percentage for categorical variables and median with IQR for continuous variables. Data were also summarized based on resident involvement in the surgery and the PGY level of the residents involved. The occurrence of total laryngectomy, rate of complications, and patient return to the OR were summarized by year.
Univariate associations between resident involvement and surgical outcomes were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and the ÷2 test for categorical variables. A Fisher exact test was used when the cell count in the contingency table was < 5. The univariate associations between surgical outcomes and demographic/preoperative variables were examined using 2-sided Wilcoxon ranksum tests or Kruskal-Wallis tests between continuous variables and categorical variables, X2 or Fisher exact test between 2 categorical variables, and 2-sided Spearman correlation test between 2 continuous variables. A false-discovery rate approach was used for simultaneous posthoc tests to determine the adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/operative time for attending physicians alone vs with junior residents and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents. Models were used to evaluate the effects of resident involvement on surgical outcomes, adjusting for variables that showed significant univariate associations. Linear regression models were used for operative time, wRVUs generated, wRVUs generated/operative time, and length of postoperative stay. A logistic regression model was used for death within 30 days. Models were not built for postoperative complications or patient return to the OR, as these were only statistically significantly associated with the patient’s preoperative functional status. A finding was considered significant if P < .05. All analyses were performed using statistical software RStudio Version 2023.03.0.
Results
Between 2001 and 2021, 1857 patients who underwent total laryngectomy were identified from the VASQIP database nationwide. Most of the total laryngectomies were staffed by an attending physician with a senior resident (n = 1190, 64%), 446 (24%) were conducted by the attending physician alone, and 221 (12%) by an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 1). The mean operating time for an attending physician alone was 378 minutes, 384 minutes for an attending physician with a senior resident, and 432 minutes for an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 2). There was a statistically significant increase in operating time for laryngectomies with resident participation compared to attending physicians operating alone (P < .001).
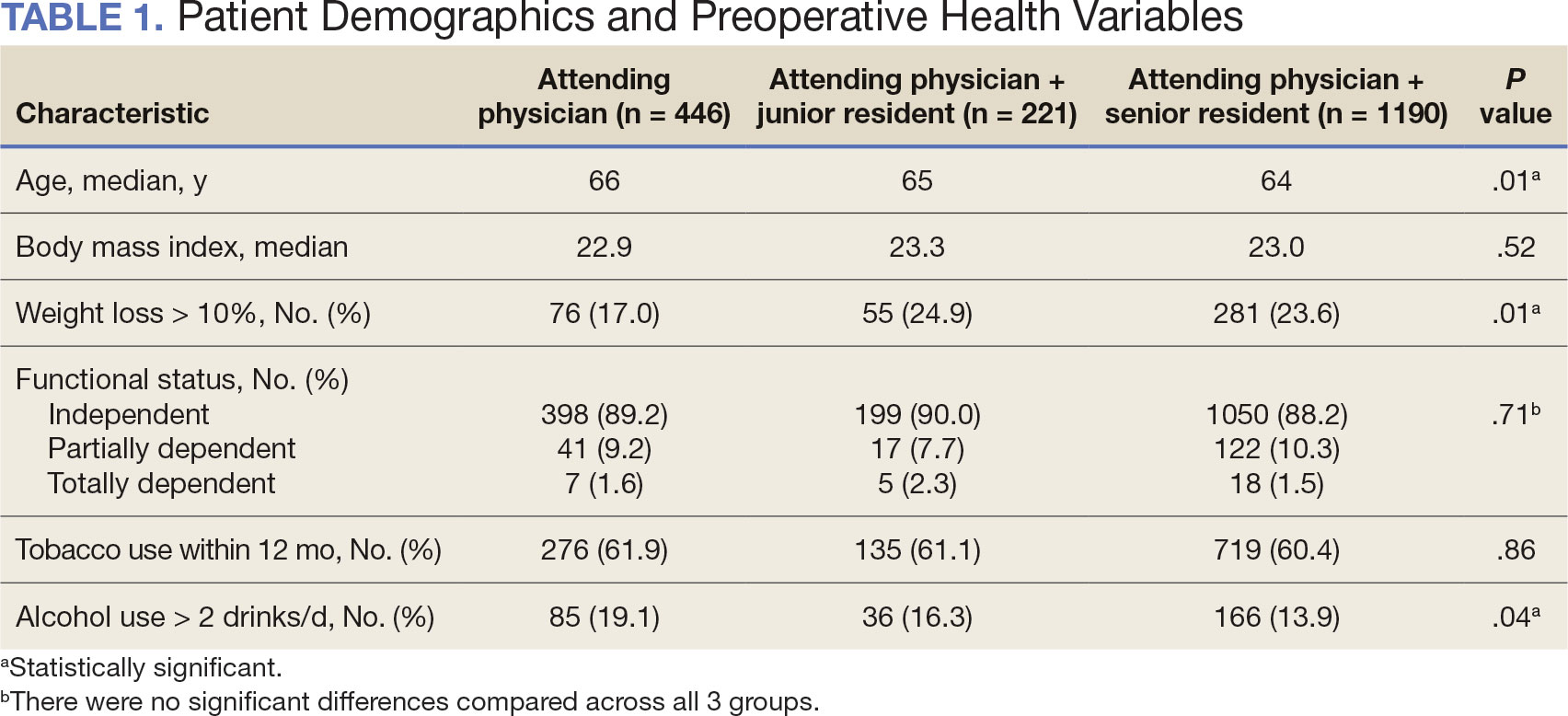
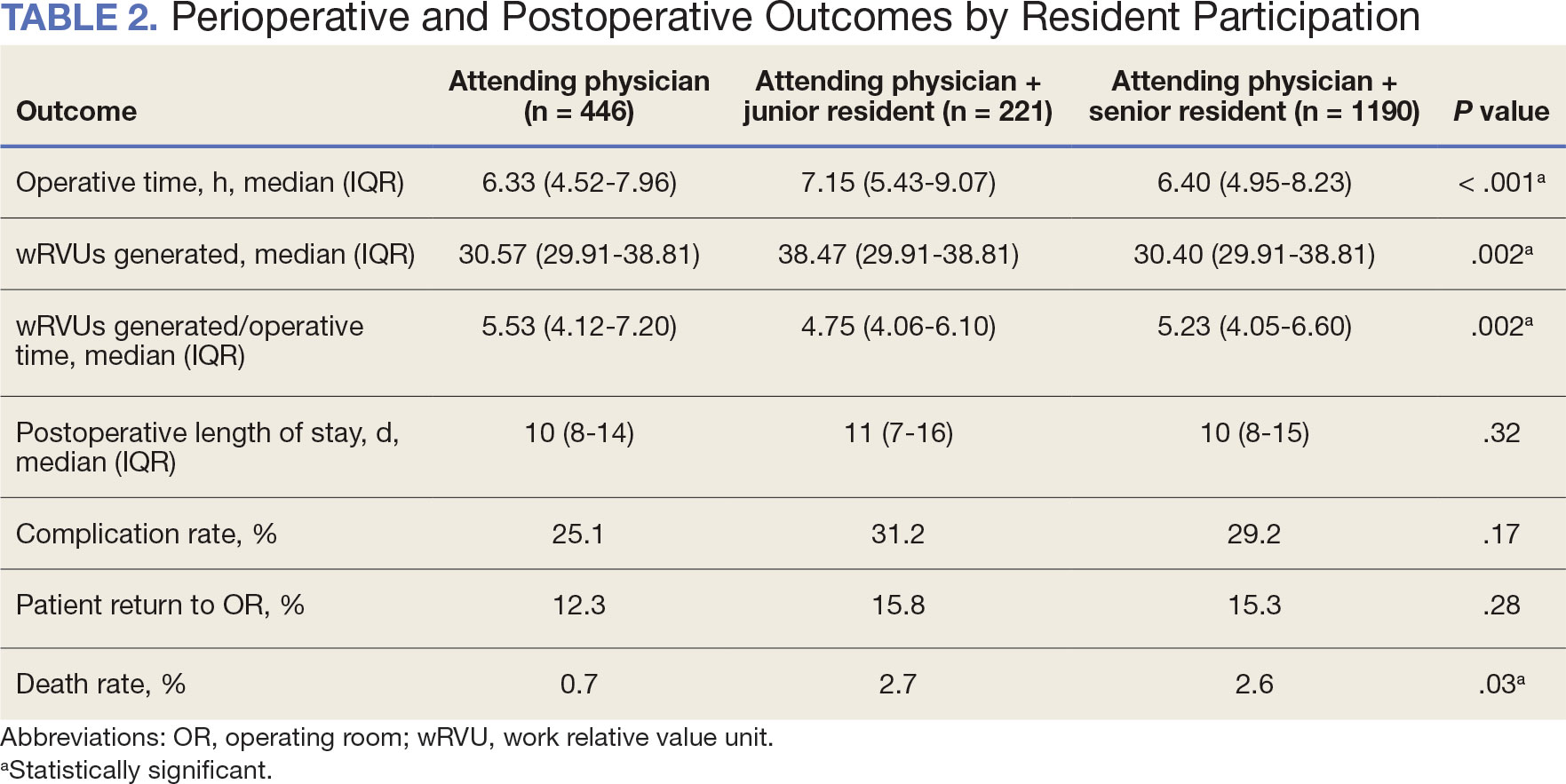
When the wRVUs generated/operative time was analyzed, there was a statistically significant difference between comparison groups. Total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone had the highest wRVUs generated/operative time (5.5), followed by laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with senior residents and laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with junior residents (5.2 and 4.8, respectively; P = .002). Table 3 describes adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/ operative time for total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone vs with junior residents (P = .003) and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents (P = .02). Resident participation in total laryngectomies did not significantly impact the development or number of postoperative complications or the rate of return to the OR.
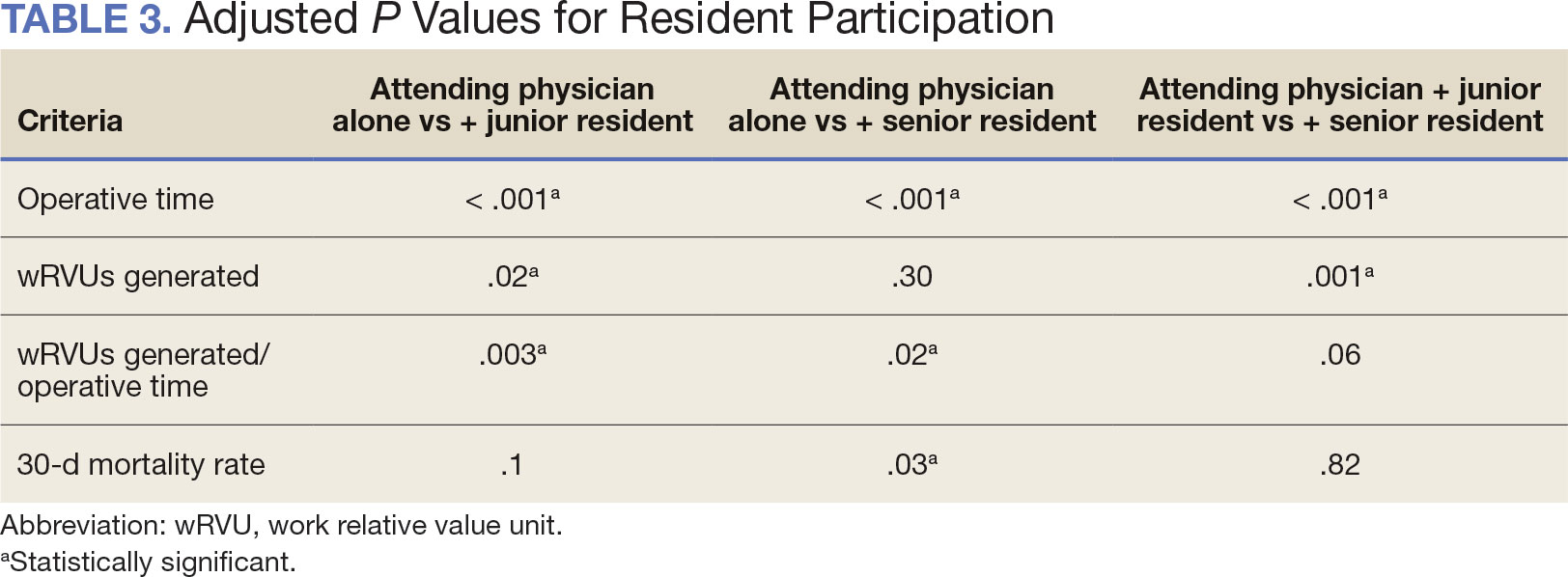
The number of laryngectomies performed in a single fiscal year peaked in 2010 at 170 cases (Figure 1). Between 2001 and 2021, the mean rates of postoperative complications (21.3%) and patient return to the OR (14.6%) did not significantly change. Resident participation in total laryngectomies also peaked in 2010 at 89.0% but has significantly declined, falling to a low of 43.6% in 2021 (Figure 2). From 2001 to 2011, the mean resident participation rate in total laryngectomies was 80.6%, compared with 68.3% from 2012 to 2021 (P < .001).
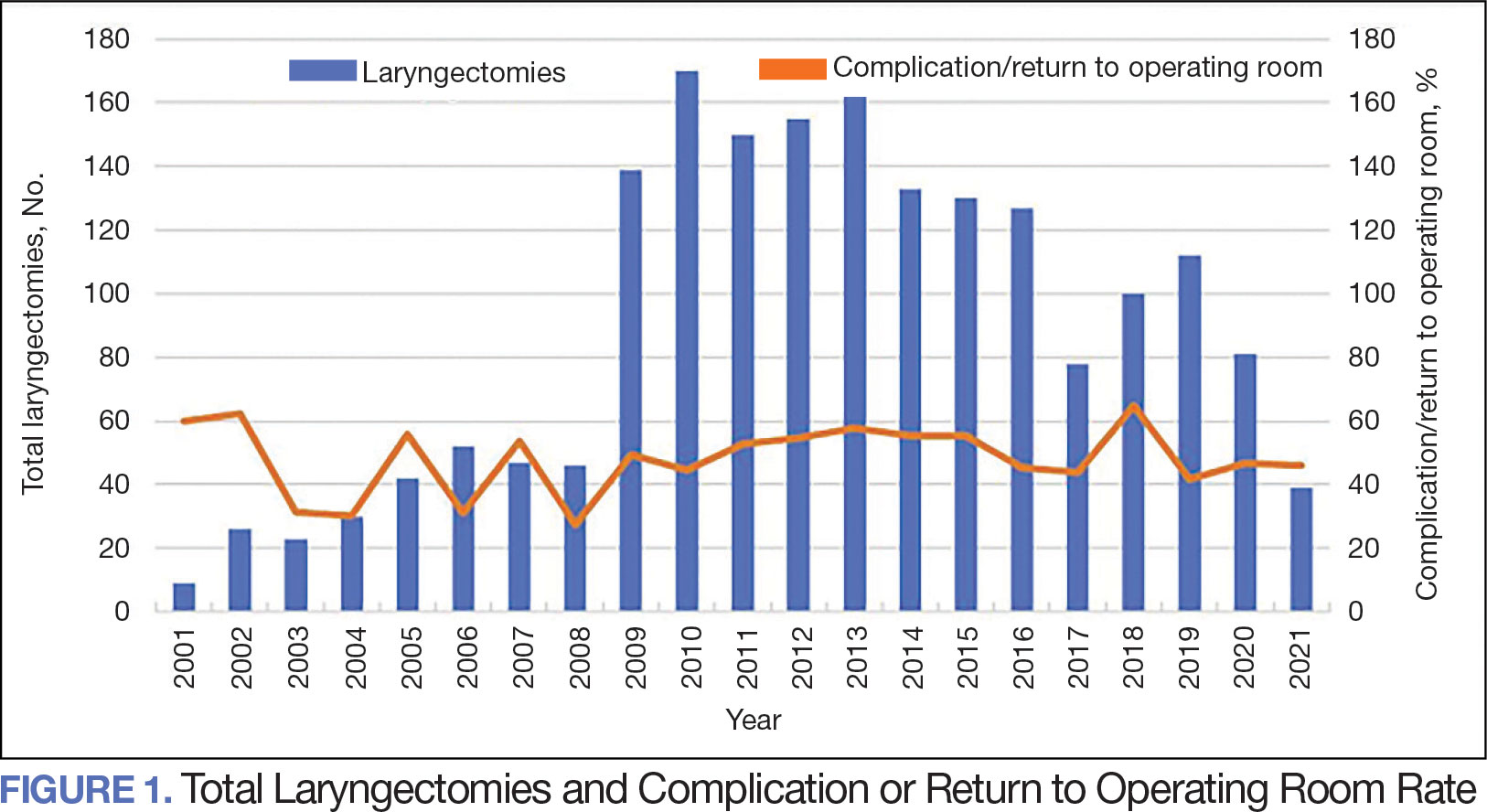
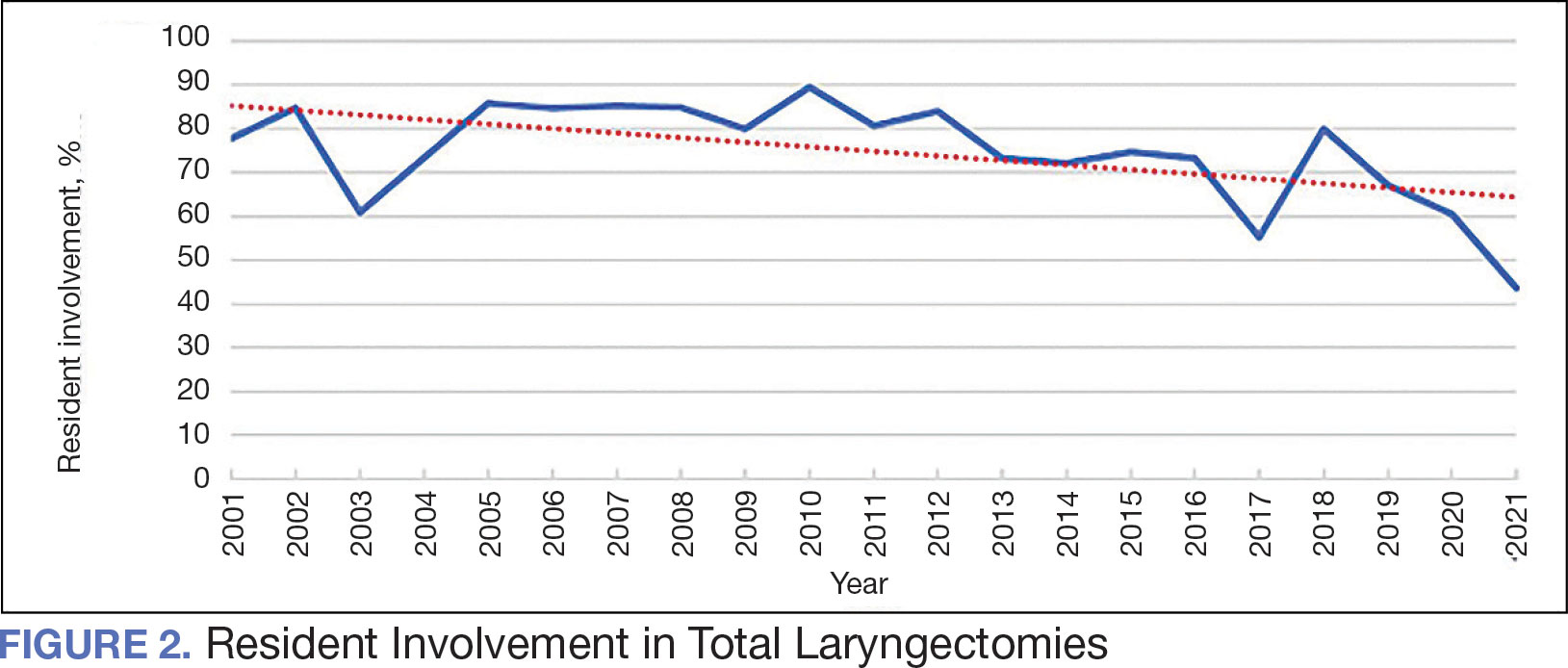
The effect of various demographic and preoperative characteristics on surgical outcomes was also analyzed. A linear regression model accounted for each variable significantly associated with operative time. On multivariable analysis, when all other variables were held constant, Table 4 shows the estimated change in operative time based on certain criteria. For instance, the operative time for attendings with junior residents surgeries was 40 minutes longer (95% CI, 16 to 64) than that of attending alone surgeries (P = .001). Furthermore, operative time decreased by 1.1 minutes (95% CI, 0.30 to 2.04) for each 1-year increase in patient age (P = .009).
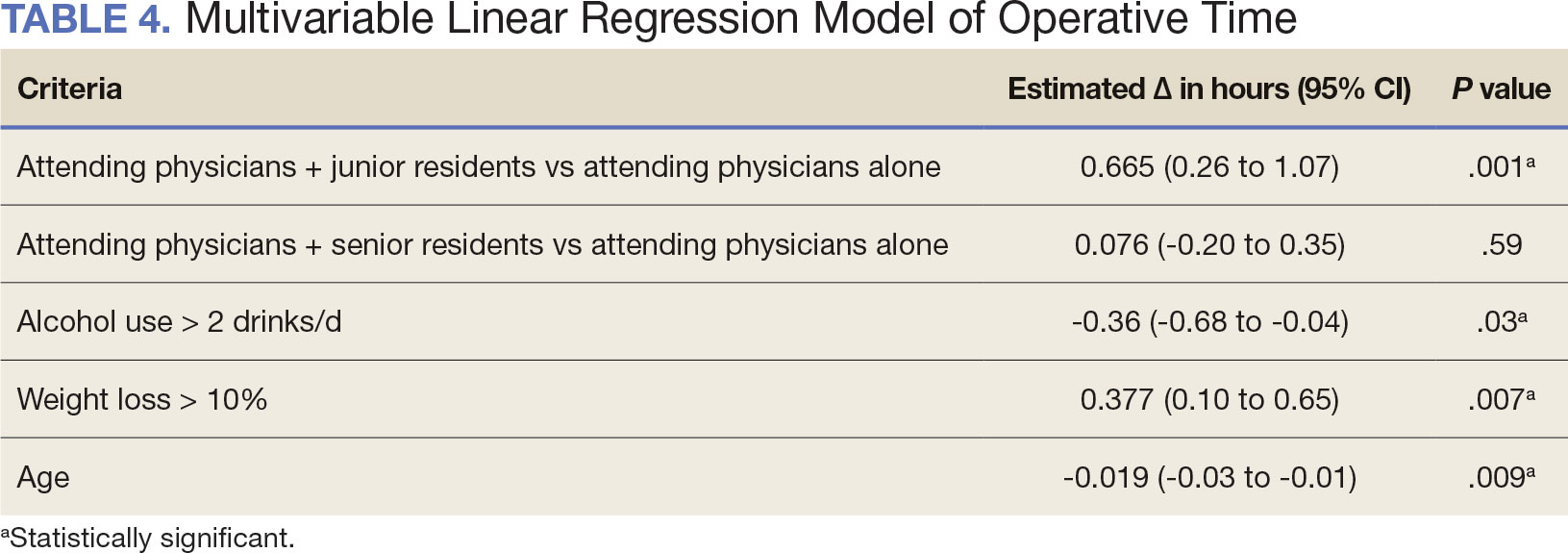
A multivariable logistic regression model evaluated the effect of resident involvement on 30-day mortality rates. Senior resident involvement (P = .02), partially dependent functional status (P = .01), totally dependent functional status (P < .001), and advanced age (P = .02) all were significantly associated with 30-day mortality (Table 5). When other variables remained constant, the odds of death for totally dependent patients were 10.4 times higher than that of patients with independent functional status. Thus, totally dependent functional status appeared to have a greater impact on this outcome than resident participation. The linear regression model for postoperative length of stay demonstrated that senior resident involvement (P = .04), functional status (partially dependent vs independent P < .001), and age (P = .03) were significantly associated with prolonged length of stay.
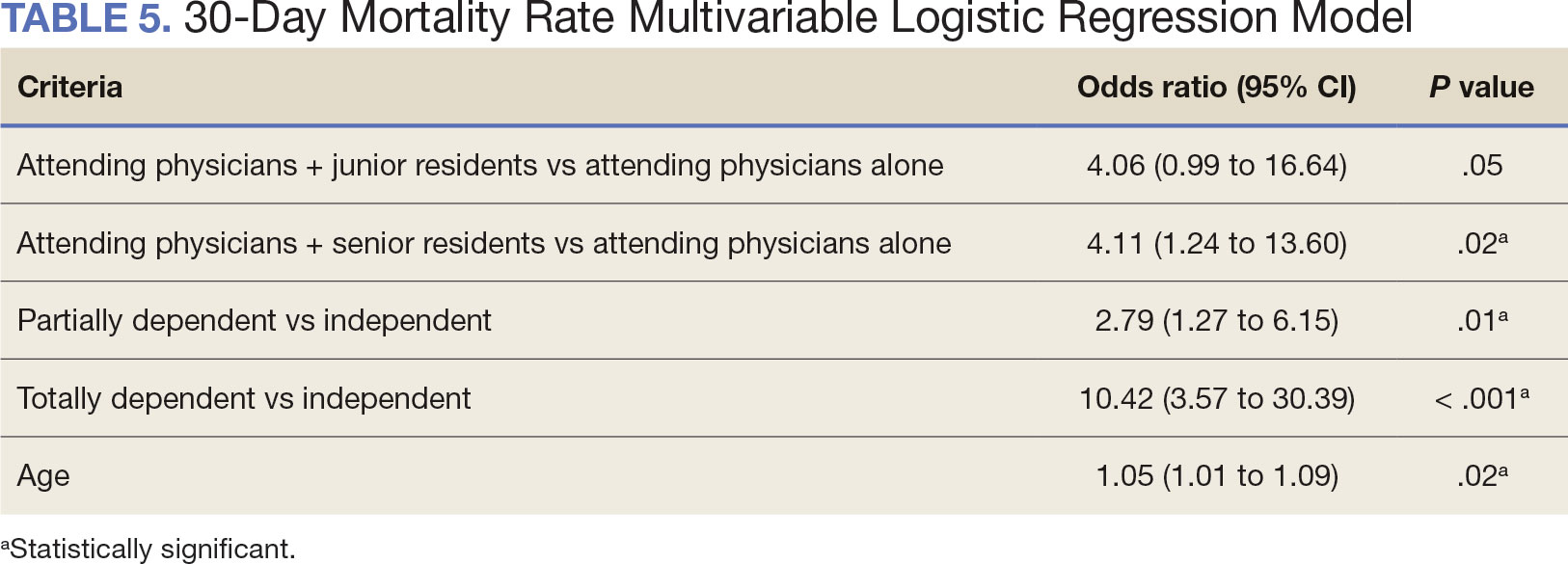
Discussion
Otolaryngology residency training is designed to educate future otolaryngologists through hands-on learning, adequate feedback, and supervision.1 Although this exposure is paramount for resident education, balancing appropriate supervision and autonomy while mitigating patient risk has been difficult. Numerous non-VA studies have reviewed the impact of resident participation on patient outcomes in various specialties, ranging from a single institution to the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP).4,5,7,22 This study is the first to describe the nationwide impact of resident participation on outcomes in veterans undergoing total laryngectomy.
This study found that resident participation increases operative time and decreases wRVUs generated/operative time without impacting complication rates or patient return to the OR. This reinforces the notion that under close supervision, resident participation does not negatively impact patient outcomes. Resident operative training requires time and dedication by the attending physician and surgical team, thereby increasing operative time. Because VA physician compensation is not linked with productivity as closely as it is in other private and academic settings, surgeons can dedicate more time to operative teaching. This study found that a total laryngectomy involving a junior resident took about 45 minutes longer than an attending physician working alone.
As expected, with longer operative times, the wRVUs generated/operative time ratio was lower in cases with resident participation. Even though resident participation leads to lower OR efficiency, their participation may not significantly impact ancillary costs.23 However, a recent study from NSQIP found an opportunity cost of $60.44 per hour for surgeons operating with a resident in head and neck cases.13
Postoperative complications and mortality are key measures of surgical outcomes in addition to operative time and efficiency. This study found that neither junior nor senior resident participation significantly increased complication rates or patient return to the OR. Despite declining resident involvement and the number of total laryngectomy surgeries in the VA, the complication rate has remained steady. The 30-day mortality rate was significantly higher in cases involving senior residents compared to cases with attending physicians alone. This could be a result of senior resident participation in more challenging cases, such as laryngectomies performed as salvage surgery following radiation. Residents are more often involved in cases with greater complexity at teaching institutions.24-26 Therefore, the higher mortality seen among laryngectomies with senior resident involvement is likely due to the higher complexity of those cases.
The proportion of resident involvement in laryngectomies at VA medical centers has been decreasing over time. Due to the single payer nature of the VA health care system and the number of complex and comorbid patients, the VA offers an invaluable space for resident education in the OR. The fact that less than half of laryngectomies in 2021 involved resident participation is noteworthy for residency training programs. As wRVU compensation models evolve, VA attending surgeons may face less pressure to move the case along, leading to a high potential for operative teaching. Therefore, complex cases, such as laryngectomies, are often ideal for resident participation in the VA.
The steady decline in total laryngectomies at the VA parallels the recent decrease seen in non-VA settings.20 This is due in part to the use of larynx-preserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer as well as decreases in the incidence of laryngeal cancer due to population level changes in smoking behaviors. 18,19 Although a laryngectomy is not a key indicator case as determined by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, it is important for otolaryngology residents to be exposed to these cases and have a thorough understanding of the operative technique.27 Total laryngectomy was selected for this study because it is a complex and time-consuming surgery with somewhat standardized surgical steps. Unlike microvascular surgery that is very rarely performed by an attending physician alone, laryngectomies can be performed by attending physicians alone or with a resident.28
Limitations
Since this was a retrospective study, it was susceptible to errors in data entry and data extraction from the VASQIP database. Another limitation is the lack of preoperative treatment data on tumor stage and prior nonoperative treatment. For example, a salvage laryngectomy after treatment with radiation and/or chemoradiation is a higher risk procedure than an upfront laryngectomy. Senior resident involvement may be more common in patients undergoing salvage laryngectomy due to the high risk of postoperative fistula and other complications. This may have contributed to the association identified between senior resident participation and 30-day mortality.
Since we could not account for residents who took research years or were fellows, a senior resident may have been mislabeled as a junior resident or vice versa. However, because most research years occur following the third year of residency. We are confident that PGY-1, PGY-2, and PGY-3 is likely to capture junior residents. Other factors, such as coattending surgeon cases, medical student assistance, and fellow involvement may have also impacted the results of this study.
Conclusions
This study is the first to investigate the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs generated, and complication rates in head and neck surgery at VA medical centers. It found that resident participation in total laryngectomies among veterans increased operative time and reduced wRVUs generated per hour but did not impact complication rate or patient return to the OR. The VA offers a unique and invaluable space for resident education and operative training, and the recent decline in resident participation among laryngectomies is important for residency programs to acknowledge and potentially address moving forward.
In contrast to oral cavity resections which can vary from partial glossectomies to composite resections, laryngectomy represents a homogenous procedure from which to draw meaningful conclusions about complication rates, operative time, and outcome. Future directions should include studying other types of head and neck surgery in the VA to determine whether the impact of resident participation mirrors the findings of this study.
- Chung RS. How much time do surgical residents need to learn operative surgery? Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):351-353. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.06.035
- S, Darzi A. Defining quality in surgical training: perceptions of the profession. Am J Surg. 2014;207(4):628-636. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.07.044
- Bhatti NI, Ahmed A, Choi SS. Identifying quality indicators of surgical of surgical training: a national survey. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(12):2685-2689. doi:10.1002/lary.25262
- Abt NB, Reh DD, Eisele DW, Francis HW, Gourin CG. Does resident participation influence otolaryngology-head and neck surgery morbidity and mortality? Laryngoscope. 2016;126(10):2263-2269. doi:10.1002/lary.25973
- Jubbal KT, Chang D, Izaddoost SA, Pederson W, Zavlin D, Echo A. Resident involvement in microsurgery: an American College of Surgeons national surgical quality improvement program analysis. J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):1124-1132. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2017.05.017
- Kshirsagar RS, Chandy Z, Mahboubi H, Verma SP. Does resident involvement in thyroid surgery lead to increased postoperative complications? Laryngoscope. 2017;127(5):1242-1246. doi:10.1002/lary.26176
- Vieira BL, Hernandez DJ, Qin C, Smith SS, Kim JY, Dutra JC. The impact of resident involvement on otolaryngology surgical outcomes. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(3):602-607. doi:10.1002/lary.25046
- Advani V, Ahad S, Gonczy C, Markwell S, Hassan I. Does resident involvement effect surgical times and complication rates during laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis? An analysis of 16,849 cases from the ACS-NSQIP. Am J Surg. 2012;203(3):347-352. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.08.015
- Quinn NA, Alt JA, Ashby S, Orlandi RR. Time, resident involvement, and supply drive cost variability in septoplasty with turbinate reduction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;159(2):310-314. doi:10.1177/0194599818765099
- Leader BA, Wiebracht ND, Meinzen-Derr J, Ishman SL. The impact of resident involvement on tonsillectomy outcomes and surgical time. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(10):2481-2486. doi:10.1002/lary.28427
- Muelleman T, Shew M, Muelleman RJ, et al. Impact of resident participation on operative time and outcomes in otologic surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158(1):151-154. doi:10.1177/0194599817737270
- Puram SV, Kozin ED, Sethi R, et al. Impact of resident surgeons on procedure length based on common pediatric otolaryngology cases. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(4):991 -997. doi:10.1002/lary.24912
- Chow MS, Gordon AJ, Talwar A, Lydiatt WM, Yueh B, Givi B. The RVU compensation model and head and neck surgical education. Laryngoscope. 2024;134(1):113-119. doi:10.1002/lary.30807
- Papandria D, Rhee D, Ortega G, et al. Assessing trainee impact on operative time for common general surgical procedures in ACS-NSQIP. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(2):149-155. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2011.08.003
- Pugely AJ, Gao Y, Martin CT, Callagh JJ, Weinstein SL, Marsh JL. The effect of resident participation on short-term outcomes after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2290-2300. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3567-0
- Hosler MR, Scott IU, Kunselman AR, Wolford KR, Oltra EZ, Murray WB. Impact of resident participation in cataract surgery on operative time and cost. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(1):95-98. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.06.026
- Lanigan A, Spaw M, Donaghe C, Brennan J. The impact of the Veteran’s Affairs medical system on an otolaryngology residency training program. Mil Med. 2018;183(11-12):e671-e675. doi:10.1093/milmed/usy041
- American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfister DG, Laurie SA, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline for the use of larynx-preservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(22):3693-3704. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.4559
- Forastiere AA, Ismaila N, Lewin JS, et al. Use of larynxpreservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(11):1143-1169. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.75.7385
- Verma SP, Mahboubi H. The changing landscape of total laryngectomy surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150(3):413-418. doi:10.1177/0194599813514515
- Habermann EB, Harris AHS, Giori NJ. Large surgical databases with direct data abstraction: VASQIP and ACSNSQIP. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(suppl 3):9-14. doi:10.2106/JBJS.22.00596
- Benito DA, Mamidi I, Pasick LJ, et al. Evaluating resident involvement and the ‘July effect’ in parotidectomy. J Laryngol Otol. 2021;135(5):452-457. doi:10.1017/S0022215121000578
- Hwang CS, Wichterman KA, Alfrey EJ. The cost of resident education. J Surg Res. 2010;163(1):18-23. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2010.03.013
- Saliba AN, Taher AT, Tamim H, et al. Impact of resident involvement in surgery (IRIS-NSQIP): looking at the bigger picture based on the American College of Surgeons- NSQIP database. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222(1):30-40. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.10.011
- Khuri SF, Najjar SF, Daley J, et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes between teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Ann Surg. 2001;234(3):370-383. doi:10.1097/00000658-200109000-00011
- Relles DM, Burkhart RA, Pucci MJ et al. Does resident experience affect outcomes in complex abdominal surgery? Pancreaticoduodenectomy as an example. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18(2):279-285. doi:10.1007/s11605-013-2372-5
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Required minimum number of key indicator procedures for graduating residents. June 2019. Accessed January 2, 2025. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programresources/280_core_case_log_minimums.pdf
- Brady JS, Crippen MM, Filimonov A, et al. The effect of training level on complications after free flap surgery of the head and neck. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017;38(5):560-564. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.06.001
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been integral in resident training. Resident surgical training requires a balance of supervision and autonomy, along with procedure repetition and appropriate feedback.1-3 Non-VA research has found that resident participation across various otolaryngology procedures, including thyroidectomy, neck dissection, and laryngectomy, does not increase patient morbidity.4-7 However, resident involvement in private and academic settings that included nonhead and neck procedures was linked to increased operative time and reduced productivity, as determined by work relative value units (wRVUs).7-13 This has also been identified in other specialties, including general surgery, orthopedics, and ophthalmology.14-16
Unlike the private sector, surgeon compensation at the VA is not as closely linked to operative productivity, offering a unique setting for resident training. While VA integration in otolaryngology residency programs increases resident case numbers, particularly in head and neck cases, the impact on VA patient outcomes and productivity is unknown.17 The use of larynxpreserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer has led to a decline in the number of total laryngectomies performed, which could potentially impact resident operative training for laryngectomies.18-20
This study sought to determine the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs, and patient outcomes in veterans who underwent a total laryngectomy. This study was reviewed and approved by the MedStar Georgetown University Hospital Institutional Review Board and Research and Development Committee (#1595672).
Methods
A retrospective cohort of veterans nationwide who underwent total laryngectomy between 2001 and 2021, with or without neck dissection, was identified from the Veterans Affairs Surgical Quality Improvement Program (VASQIP). Data were extracted via the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure and patients were included based on Current Procedural Terminology codes for total laryngectomy, with or without neck dissection (31320, 31360, 31365). Laryngopharyngectomies, partial laryngectomies, and minimally invasive laryngectomies were excluded. VASQIP nurse data managers reviewed patient data for operative data, postoperative outcomes (including 30- day morbidity and mortality), and preoperative risk factors (Appendix).21
The VASQIP data provide the highest resident or postgraduate year (PGY) per surgery. PGY 1, 2, and 3 were considered junior residents and PGY ≥4, surgical fellows, and individuals who took research years during residency were considered senior residents. Cases performed by attending physicians alone were compared with those involving junior or senior residents.
Patient demographic data included age, body mass index, smoking and alcohol use, weight loss, and functional status. Consumption of any tobacco products within 12 months of surgery was considered tobacco use. Drinking on average ≥2 alcoholic beverages daily was considered alcohol use. Weight loss was defined as a 10% reduction in body weight within the 6 months before surgery, excluding patients enrolled in a weight loss program. Functional status was categorized as independent, partially dependent, totally dependent, and unknown.
Primary outcomes included operative time, wRVUs generated, and wRVUs generated per hour of operative time. Postoperative complications were recorded both as a continuous variable and as a binary variable for presence or absence of a complication. Additional outcome variables included length of postoperative hospital stay, return to the operating room (OR), and death within 30 days of surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Data were summarized using frequency and percentage for categorical variables and median with IQR for continuous variables. Data were also summarized based on resident involvement in the surgery and the PGY level of the residents involved. The occurrence of total laryngectomy, rate of complications, and patient return to the OR were summarized by year.
Univariate associations between resident involvement and surgical outcomes were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and the ÷2 test for categorical variables. A Fisher exact test was used when the cell count in the contingency table was < 5. The univariate associations between surgical outcomes and demographic/preoperative variables were examined using 2-sided Wilcoxon ranksum tests or Kruskal-Wallis tests between continuous variables and categorical variables, X2 or Fisher exact test between 2 categorical variables, and 2-sided Spearman correlation test between 2 continuous variables. A false-discovery rate approach was used for simultaneous posthoc tests to determine the adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/operative time for attending physicians alone vs with junior residents and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents. Models were used to evaluate the effects of resident involvement on surgical outcomes, adjusting for variables that showed significant univariate associations. Linear regression models were used for operative time, wRVUs generated, wRVUs generated/operative time, and length of postoperative stay. A logistic regression model was used for death within 30 days. Models were not built for postoperative complications or patient return to the OR, as these were only statistically significantly associated with the patient’s preoperative functional status. A finding was considered significant if P < .05. All analyses were performed using statistical software RStudio Version 2023.03.0.
Results
Between 2001 and 2021, 1857 patients who underwent total laryngectomy were identified from the VASQIP database nationwide. Most of the total laryngectomies were staffed by an attending physician with a senior resident (n = 1190, 64%), 446 (24%) were conducted by the attending physician alone, and 221 (12%) by an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 1). The mean operating time for an attending physician alone was 378 minutes, 384 minutes for an attending physician with a senior resident, and 432 minutes for an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 2). There was a statistically significant increase in operating time for laryngectomies with resident participation compared to attending physicians operating alone (P < .001).


When the wRVUs generated/operative time was analyzed, there was a statistically significant difference between comparison groups. Total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone had the highest wRVUs generated/operative time (5.5), followed by laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with senior residents and laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with junior residents (5.2 and 4.8, respectively; P = .002). Table 3 describes adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/ operative time for total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone vs with junior residents (P = .003) and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents (P = .02). Resident participation in total laryngectomies did not significantly impact the development or number of postoperative complications or the rate of return to the OR.

The number of laryngectomies performed in a single fiscal year peaked in 2010 at 170 cases (Figure 1). Between 2001 and 2021, the mean rates of postoperative complications (21.3%) and patient return to the OR (14.6%) did not significantly change. Resident participation in total laryngectomies also peaked in 2010 at 89.0% but has significantly declined, falling to a low of 43.6% in 2021 (Figure 2). From 2001 to 2011, the mean resident participation rate in total laryngectomies was 80.6%, compared with 68.3% from 2012 to 2021 (P < .001).


The effect of various demographic and preoperative characteristics on surgical outcomes was also analyzed. A linear regression model accounted for each variable significantly associated with operative time. On multivariable analysis, when all other variables were held constant, Table 4 shows the estimated change in operative time based on certain criteria. For instance, the operative time for attendings with junior residents surgeries was 40 minutes longer (95% CI, 16 to 64) than that of attending alone surgeries (P = .001). Furthermore, operative time decreased by 1.1 minutes (95% CI, 0.30 to 2.04) for each 1-year increase in patient age (P = .009).

A multivariable logistic regression model evaluated the effect of resident involvement on 30-day mortality rates. Senior resident involvement (P = .02), partially dependent functional status (P = .01), totally dependent functional status (P < .001), and advanced age (P = .02) all were significantly associated with 30-day mortality (Table 5). When other variables remained constant, the odds of death for totally dependent patients were 10.4 times higher than that of patients with independent functional status. Thus, totally dependent functional status appeared to have a greater impact on this outcome than resident participation. The linear regression model for postoperative length of stay demonstrated that senior resident involvement (P = .04), functional status (partially dependent vs independent P < .001), and age (P = .03) were significantly associated with prolonged length of stay.

Discussion
Otolaryngology residency training is designed to educate future otolaryngologists through hands-on learning, adequate feedback, and supervision.1 Although this exposure is paramount for resident education, balancing appropriate supervision and autonomy while mitigating patient risk has been difficult. Numerous non-VA studies have reviewed the impact of resident participation on patient outcomes in various specialties, ranging from a single institution to the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP).4,5,7,22 This study is the first to describe the nationwide impact of resident participation on outcomes in veterans undergoing total laryngectomy.
This study found that resident participation increases operative time and decreases wRVUs generated/operative time without impacting complication rates or patient return to the OR. This reinforces the notion that under close supervision, resident participation does not negatively impact patient outcomes. Resident operative training requires time and dedication by the attending physician and surgical team, thereby increasing operative time. Because VA physician compensation is not linked with productivity as closely as it is in other private and academic settings, surgeons can dedicate more time to operative teaching. This study found that a total laryngectomy involving a junior resident took about 45 minutes longer than an attending physician working alone.
As expected, with longer operative times, the wRVUs generated/operative time ratio was lower in cases with resident participation. Even though resident participation leads to lower OR efficiency, their participation may not significantly impact ancillary costs.23 However, a recent study from NSQIP found an opportunity cost of $60.44 per hour for surgeons operating with a resident in head and neck cases.13
Postoperative complications and mortality are key measures of surgical outcomes in addition to operative time and efficiency. This study found that neither junior nor senior resident participation significantly increased complication rates or patient return to the OR. Despite declining resident involvement and the number of total laryngectomy surgeries in the VA, the complication rate has remained steady. The 30-day mortality rate was significantly higher in cases involving senior residents compared to cases with attending physicians alone. This could be a result of senior resident participation in more challenging cases, such as laryngectomies performed as salvage surgery following radiation. Residents are more often involved in cases with greater complexity at teaching institutions.24-26 Therefore, the higher mortality seen among laryngectomies with senior resident involvement is likely due to the higher complexity of those cases.
The proportion of resident involvement in laryngectomies at VA medical centers has been decreasing over time. Due to the single payer nature of the VA health care system and the number of complex and comorbid patients, the VA offers an invaluable space for resident education in the OR. The fact that less than half of laryngectomies in 2021 involved resident participation is noteworthy for residency training programs. As wRVU compensation models evolve, VA attending surgeons may face less pressure to move the case along, leading to a high potential for operative teaching. Therefore, complex cases, such as laryngectomies, are often ideal for resident participation in the VA.
The steady decline in total laryngectomies at the VA parallels the recent decrease seen in non-VA settings.20 This is due in part to the use of larynx-preserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer as well as decreases in the incidence of laryngeal cancer due to population level changes in smoking behaviors. 18,19 Although a laryngectomy is not a key indicator case as determined by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, it is important for otolaryngology residents to be exposed to these cases and have a thorough understanding of the operative technique.27 Total laryngectomy was selected for this study because it is a complex and time-consuming surgery with somewhat standardized surgical steps. Unlike microvascular surgery that is very rarely performed by an attending physician alone, laryngectomies can be performed by attending physicians alone or with a resident.28
Limitations
Since this was a retrospective study, it was susceptible to errors in data entry and data extraction from the VASQIP database. Another limitation is the lack of preoperative treatment data on tumor stage and prior nonoperative treatment. For example, a salvage laryngectomy after treatment with radiation and/or chemoradiation is a higher risk procedure than an upfront laryngectomy. Senior resident involvement may be more common in patients undergoing salvage laryngectomy due to the high risk of postoperative fistula and other complications. This may have contributed to the association identified between senior resident participation and 30-day mortality.
Since we could not account for residents who took research years or were fellows, a senior resident may have been mislabeled as a junior resident or vice versa. However, because most research years occur following the third year of residency. We are confident that PGY-1, PGY-2, and PGY-3 is likely to capture junior residents. Other factors, such as coattending surgeon cases, medical student assistance, and fellow involvement may have also impacted the results of this study.
Conclusions
This study is the first to investigate the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs generated, and complication rates in head and neck surgery at VA medical centers. It found that resident participation in total laryngectomies among veterans increased operative time and reduced wRVUs generated per hour but did not impact complication rate or patient return to the OR. The VA offers a unique and invaluable space for resident education and operative training, and the recent decline in resident participation among laryngectomies is important for residency programs to acknowledge and potentially address moving forward.
In contrast to oral cavity resections which can vary from partial glossectomies to composite resections, laryngectomy represents a homogenous procedure from which to draw meaningful conclusions about complication rates, operative time, and outcome. Future directions should include studying other types of head and neck surgery in the VA to determine whether the impact of resident participation mirrors the findings of this study.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has been integral in resident training. Resident surgical training requires a balance of supervision and autonomy, along with procedure repetition and appropriate feedback.1-3 Non-VA research has found that resident participation across various otolaryngology procedures, including thyroidectomy, neck dissection, and laryngectomy, does not increase patient morbidity.4-7 However, resident involvement in private and academic settings that included nonhead and neck procedures was linked to increased operative time and reduced productivity, as determined by work relative value units (wRVUs).7-13 This has also been identified in other specialties, including general surgery, orthopedics, and ophthalmology.14-16
Unlike the private sector, surgeon compensation at the VA is not as closely linked to operative productivity, offering a unique setting for resident training. While VA integration in otolaryngology residency programs increases resident case numbers, particularly in head and neck cases, the impact on VA patient outcomes and productivity is unknown.17 The use of larynxpreserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer has led to a decline in the number of total laryngectomies performed, which could potentially impact resident operative training for laryngectomies.18-20
This study sought to determine the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs, and patient outcomes in veterans who underwent a total laryngectomy. This study was reviewed and approved by the MedStar Georgetown University Hospital Institutional Review Board and Research and Development Committee (#1595672).
Methods
A retrospective cohort of veterans nationwide who underwent total laryngectomy between 2001 and 2021, with or without neck dissection, was identified from the Veterans Affairs Surgical Quality Improvement Program (VASQIP). Data were extracted via the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure and patients were included based on Current Procedural Terminology codes for total laryngectomy, with or without neck dissection (31320, 31360, 31365). Laryngopharyngectomies, partial laryngectomies, and minimally invasive laryngectomies were excluded. VASQIP nurse data managers reviewed patient data for operative data, postoperative outcomes (including 30- day morbidity and mortality), and preoperative risk factors (Appendix).21
The VASQIP data provide the highest resident or postgraduate year (PGY) per surgery. PGY 1, 2, and 3 were considered junior residents and PGY ≥4, surgical fellows, and individuals who took research years during residency were considered senior residents. Cases performed by attending physicians alone were compared with those involving junior or senior residents.
Patient demographic data included age, body mass index, smoking and alcohol use, weight loss, and functional status. Consumption of any tobacco products within 12 months of surgery was considered tobacco use. Drinking on average ≥2 alcoholic beverages daily was considered alcohol use. Weight loss was defined as a 10% reduction in body weight within the 6 months before surgery, excluding patients enrolled in a weight loss program. Functional status was categorized as independent, partially dependent, totally dependent, and unknown.
Primary outcomes included operative time, wRVUs generated, and wRVUs generated per hour of operative time. Postoperative complications were recorded both as a continuous variable and as a binary variable for presence or absence of a complication. Additional outcome variables included length of postoperative hospital stay, return to the operating room (OR), and death within 30 days of surgery.
Statistical Analysis
Data were summarized using frequency and percentage for categorical variables and median with IQR for continuous variables. Data were also summarized based on resident involvement in the surgery and the PGY level of the residents involved. The occurrence of total laryngectomy, rate of complications, and patient return to the OR were summarized by year.
Univariate associations between resident involvement and surgical outcomes were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and the ÷2 test for categorical variables. A Fisher exact test was used when the cell count in the contingency table was < 5. The univariate associations between surgical outcomes and demographic/preoperative variables were examined using 2-sided Wilcoxon ranksum tests or Kruskal-Wallis tests between continuous variables and categorical variables, X2 or Fisher exact test between 2 categorical variables, and 2-sided Spearman correlation test between 2 continuous variables. A false-discovery rate approach was used for simultaneous posthoc tests to determine the adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/operative time for attending physicians alone vs with junior residents and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents. Models were used to evaluate the effects of resident involvement on surgical outcomes, adjusting for variables that showed significant univariate associations. Linear regression models were used for operative time, wRVUs generated, wRVUs generated/operative time, and length of postoperative stay. A logistic regression model was used for death within 30 days. Models were not built for postoperative complications or patient return to the OR, as these were only statistically significantly associated with the patient’s preoperative functional status. A finding was considered significant if P < .05. All analyses were performed using statistical software RStudio Version 2023.03.0.
Results
Between 2001 and 2021, 1857 patients who underwent total laryngectomy were identified from the VASQIP database nationwide. Most of the total laryngectomies were staffed by an attending physician with a senior resident (n = 1190, 64%), 446 (24%) were conducted by the attending physician alone, and 221 (12%) by an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 1). The mean operating time for an attending physician alone was 378 minutes, 384 minutes for an attending physician with a senior resident, and 432 minutes for an attending physician with a junior resident (Table 2). There was a statistically significant increase in operating time for laryngectomies with resident participation compared to attending physicians operating alone (P < .001).


When the wRVUs generated/operative time was analyzed, there was a statistically significant difference between comparison groups. Total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone had the highest wRVUs generated/operative time (5.5), followed by laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with senior residents and laryngectomies performed by attending physicians with junior residents (5.2 and 4.8, respectively; P = .002). Table 3 describes adjusted P values for wRVUs generated/ operative time for total laryngectomies performed by attending physicians alone vs with junior residents (P = .003) and for attending physicians alone vs with senior residents (P = .02). Resident participation in total laryngectomies did not significantly impact the development or number of postoperative complications or the rate of return to the OR.

The number of laryngectomies performed in a single fiscal year peaked in 2010 at 170 cases (Figure 1). Between 2001 and 2021, the mean rates of postoperative complications (21.3%) and patient return to the OR (14.6%) did not significantly change. Resident participation in total laryngectomies also peaked in 2010 at 89.0% but has significantly declined, falling to a low of 43.6% in 2021 (Figure 2). From 2001 to 2011, the mean resident participation rate in total laryngectomies was 80.6%, compared with 68.3% from 2012 to 2021 (P < .001).


The effect of various demographic and preoperative characteristics on surgical outcomes was also analyzed. A linear regression model accounted for each variable significantly associated with operative time. On multivariable analysis, when all other variables were held constant, Table 4 shows the estimated change in operative time based on certain criteria. For instance, the operative time for attendings with junior residents surgeries was 40 minutes longer (95% CI, 16 to 64) than that of attending alone surgeries (P = .001). Furthermore, operative time decreased by 1.1 minutes (95% CI, 0.30 to 2.04) for each 1-year increase in patient age (P = .009).

A multivariable logistic regression model evaluated the effect of resident involvement on 30-day mortality rates. Senior resident involvement (P = .02), partially dependent functional status (P = .01), totally dependent functional status (P < .001), and advanced age (P = .02) all were significantly associated with 30-day mortality (Table 5). When other variables remained constant, the odds of death for totally dependent patients were 10.4 times higher than that of patients with independent functional status. Thus, totally dependent functional status appeared to have a greater impact on this outcome than resident participation. The linear regression model for postoperative length of stay demonstrated that senior resident involvement (P = .04), functional status (partially dependent vs independent P < .001), and age (P = .03) were significantly associated with prolonged length of stay.

Discussion
Otolaryngology residency training is designed to educate future otolaryngologists through hands-on learning, adequate feedback, and supervision.1 Although this exposure is paramount for resident education, balancing appropriate supervision and autonomy while mitigating patient risk has been difficult. Numerous non-VA studies have reviewed the impact of resident participation on patient outcomes in various specialties, ranging from a single institution to the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP).4,5,7,22 This study is the first to describe the nationwide impact of resident participation on outcomes in veterans undergoing total laryngectomy.
This study found that resident participation increases operative time and decreases wRVUs generated/operative time without impacting complication rates or patient return to the OR. This reinforces the notion that under close supervision, resident participation does not negatively impact patient outcomes. Resident operative training requires time and dedication by the attending physician and surgical team, thereby increasing operative time. Because VA physician compensation is not linked with productivity as closely as it is in other private and academic settings, surgeons can dedicate more time to operative teaching. This study found that a total laryngectomy involving a junior resident took about 45 minutes longer than an attending physician working alone.
As expected, with longer operative times, the wRVUs generated/operative time ratio was lower in cases with resident participation. Even though resident participation leads to lower OR efficiency, their participation may not significantly impact ancillary costs.23 However, a recent study from NSQIP found an opportunity cost of $60.44 per hour for surgeons operating with a resident in head and neck cases.13
Postoperative complications and mortality are key measures of surgical outcomes in addition to operative time and efficiency. This study found that neither junior nor senior resident participation significantly increased complication rates or patient return to the OR. Despite declining resident involvement and the number of total laryngectomy surgeries in the VA, the complication rate has remained steady. The 30-day mortality rate was significantly higher in cases involving senior residents compared to cases with attending physicians alone. This could be a result of senior resident participation in more challenging cases, such as laryngectomies performed as salvage surgery following radiation. Residents are more often involved in cases with greater complexity at teaching institutions.24-26 Therefore, the higher mortality seen among laryngectomies with senior resident involvement is likely due to the higher complexity of those cases.
The proportion of resident involvement in laryngectomies at VA medical centers has been decreasing over time. Due to the single payer nature of the VA health care system and the number of complex and comorbid patients, the VA offers an invaluable space for resident education in the OR. The fact that less than half of laryngectomies in 2021 involved resident participation is noteworthy for residency training programs. As wRVU compensation models evolve, VA attending surgeons may face less pressure to move the case along, leading to a high potential for operative teaching. Therefore, complex cases, such as laryngectomies, are often ideal for resident participation in the VA.
The steady decline in total laryngectomies at the VA parallels the recent decrease seen in non-VA settings.20 This is due in part to the use of larynx-preserving treatment modalities for laryngeal cancer as well as decreases in the incidence of laryngeal cancer due to population level changes in smoking behaviors. 18,19 Although a laryngectomy is not a key indicator case as determined by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, it is important for otolaryngology residents to be exposed to these cases and have a thorough understanding of the operative technique.27 Total laryngectomy was selected for this study because it is a complex and time-consuming surgery with somewhat standardized surgical steps. Unlike microvascular surgery that is very rarely performed by an attending physician alone, laryngectomies can be performed by attending physicians alone or with a resident.28
Limitations
Since this was a retrospective study, it was susceptible to errors in data entry and data extraction from the VASQIP database. Another limitation is the lack of preoperative treatment data on tumor stage and prior nonoperative treatment. For example, a salvage laryngectomy after treatment with radiation and/or chemoradiation is a higher risk procedure than an upfront laryngectomy. Senior resident involvement may be more common in patients undergoing salvage laryngectomy due to the high risk of postoperative fistula and other complications. This may have contributed to the association identified between senior resident participation and 30-day mortality.
Since we could not account for residents who took research years or were fellows, a senior resident may have been mislabeled as a junior resident or vice versa. However, because most research years occur following the third year of residency. We are confident that PGY-1, PGY-2, and PGY-3 is likely to capture junior residents. Other factors, such as coattending surgeon cases, medical student assistance, and fellow involvement may have also impacted the results of this study.
Conclusions
This study is the first to investigate the impact of resident participation on operative time, wRVUs generated, and complication rates in head and neck surgery at VA medical centers. It found that resident participation in total laryngectomies among veterans increased operative time and reduced wRVUs generated per hour but did not impact complication rate or patient return to the OR. The VA offers a unique and invaluable space for resident education and operative training, and the recent decline in resident participation among laryngectomies is important for residency programs to acknowledge and potentially address moving forward.
In contrast to oral cavity resections which can vary from partial glossectomies to composite resections, laryngectomy represents a homogenous procedure from which to draw meaningful conclusions about complication rates, operative time, and outcome. Future directions should include studying other types of head and neck surgery in the VA to determine whether the impact of resident participation mirrors the findings of this study.
- Chung RS. How much time do surgical residents need to learn operative surgery? Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):351-353. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.06.035
- S, Darzi A. Defining quality in surgical training: perceptions of the profession. Am J Surg. 2014;207(4):628-636. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.07.044
- Bhatti NI, Ahmed A, Choi SS. Identifying quality indicators of surgical of surgical training: a national survey. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(12):2685-2689. doi:10.1002/lary.25262
- Abt NB, Reh DD, Eisele DW, Francis HW, Gourin CG. Does resident participation influence otolaryngology-head and neck surgery morbidity and mortality? Laryngoscope. 2016;126(10):2263-2269. doi:10.1002/lary.25973
- Jubbal KT, Chang D, Izaddoost SA, Pederson W, Zavlin D, Echo A. Resident involvement in microsurgery: an American College of Surgeons national surgical quality improvement program analysis. J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):1124-1132. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2017.05.017
- Kshirsagar RS, Chandy Z, Mahboubi H, Verma SP. Does resident involvement in thyroid surgery lead to increased postoperative complications? Laryngoscope. 2017;127(5):1242-1246. doi:10.1002/lary.26176
- Vieira BL, Hernandez DJ, Qin C, Smith SS, Kim JY, Dutra JC. The impact of resident involvement on otolaryngology surgical outcomes. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(3):602-607. doi:10.1002/lary.25046
- Advani V, Ahad S, Gonczy C, Markwell S, Hassan I. Does resident involvement effect surgical times and complication rates during laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis? An analysis of 16,849 cases from the ACS-NSQIP. Am J Surg. 2012;203(3):347-352. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.08.015
- Quinn NA, Alt JA, Ashby S, Orlandi RR. Time, resident involvement, and supply drive cost variability in septoplasty with turbinate reduction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;159(2):310-314. doi:10.1177/0194599818765099
- Leader BA, Wiebracht ND, Meinzen-Derr J, Ishman SL. The impact of resident involvement on tonsillectomy outcomes and surgical time. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(10):2481-2486. doi:10.1002/lary.28427
- Muelleman T, Shew M, Muelleman RJ, et al. Impact of resident participation on operative time and outcomes in otologic surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158(1):151-154. doi:10.1177/0194599817737270
- Puram SV, Kozin ED, Sethi R, et al. Impact of resident surgeons on procedure length based on common pediatric otolaryngology cases. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(4):991 -997. doi:10.1002/lary.24912
- Chow MS, Gordon AJ, Talwar A, Lydiatt WM, Yueh B, Givi B. The RVU compensation model and head and neck surgical education. Laryngoscope. 2024;134(1):113-119. doi:10.1002/lary.30807
- Papandria D, Rhee D, Ortega G, et al. Assessing trainee impact on operative time for common general surgical procedures in ACS-NSQIP. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(2):149-155. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2011.08.003
- Pugely AJ, Gao Y, Martin CT, Callagh JJ, Weinstein SL, Marsh JL. The effect of resident participation on short-term outcomes after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2290-2300. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3567-0
- Hosler MR, Scott IU, Kunselman AR, Wolford KR, Oltra EZ, Murray WB. Impact of resident participation in cataract surgery on operative time and cost. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(1):95-98. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.06.026
- Lanigan A, Spaw M, Donaghe C, Brennan J. The impact of the Veteran’s Affairs medical system on an otolaryngology residency training program. Mil Med. 2018;183(11-12):e671-e675. doi:10.1093/milmed/usy041
- American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfister DG, Laurie SA, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline for the use of larynx-preservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(22):3693-3704. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.4559
- Forastiere AA, Ismaila N, Lewin JS, et al. Use of larynxpreservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(11):1143-1169. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.75.7385
- Verma SP, Mahboubi H. The changing landscape of total laryngectomy surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150(3):413-418. doi:10.1177/0194599813514515
- Habermann EB, Harris AHS, Giori NJ. Large surgical databases with direct data abstraction: VASQIP and ACSNSQIP. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(suppl 3):9-14. doi:10.2106/JBJS.22.00596
- Benito DA, Mamidi I, Pasick LJ, et al. Evaluating resident involvement and the ‘July effect’ in parotidectomy. J Laryngol Otol. 2021;135(5):452-457. doi:10.1017/S0022215121000578
- Hwang CS, Wichterman KA, Alfrey EJ. The cost of resident education. J Surg Res. 2010;163(1):18-23. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2010.03.013
- Saliba AN, Taher AT, Tamim H, et al. Impact of resident involvement in surgery (IRIS-NSQIP): looking at the bigger picture based on the American College of Surgeons- NSQIP database. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222(1):30-40. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.10.011
- Khuri SF, Najjar SF, Daley J, et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes between teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Ann Surg. 2001;234(3):370-383. doi:10.1097/00000658-200109000-00011
- Relles DM, Burkhart RA, Pucci MJ et al. Does resident experience affect outcomes in complex abdominal surgery? Pancreaticoduodenectomy as an example. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18(2):279-285. doi:10.1007/s11605-013-2372-5
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Required minimum number of key indicator procedures for graduating residents. June 2019. Accessed January 2, 2025. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programresources/280_core_case_log_minimums.pdf
- Brady JS, Crippen MM, Filimonov A, et al. The effect of training level on complications after free flap surgery of the head and neck. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017;38(5):560-564. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.06.001
- Chung RS. How much time do surgical residents need to learn operative surgery? Am J Surg. 2005;190(3):351-353. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.06.035
- S, Darzi A. Defining quality in surgical training: perceptions of the profession. Am J Surg. 2014;207(4):628-636. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2013.07.044
- Bhatti NI, Ahmed A, Choi SS. Identifying quality indicators of surgical of surgical training: a national survey. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(12):2685-2689. doi:10.1002/lary.25262
- Abt NB, Reh DD, Eisele DW, Francis HW, Gourin CG. Does resident participation influence otolaryngology-head and neck surgery morbidity and mortality? Laryngoscope. 2016;126(10):2263-2269. doi:10.1002/lary.25973
- Jubbal KT, Chang D, Izaddoost SA, Pederson W, Zavlin D, Echo A. Resident involvement in microsurgery: an American College of Surgeons national surgical quality improvement program analysis. J Surg Educ. 2017;74(6):1124-1132. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2017.05.017
- Kshirsagar RS, Chandy Z, Mahboubi H, Verma SP. Does resident involvement in thyroid surgery lead to increased postoperative complications? Laryngoscope. 2017;127(5):1242-1246. doi:10.1002/lary.26176
- Vieira BL, Hernandez DJ, Qin C, Smith SS, Kim JY, Dutra JC. The impact of resident involvement on otolaryngology surgical outcomes. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(3):602-607. doi:10.1002/lary.25046
- Advani V, Ahad S, Gonczy C, Markwell S, Hassan I. Does resident involvement effect surgical times and complication rates during laparoscopic appendectomy for uncomplicated appendicitis? An analysis of 16,849 cases from the ACS-NSQIP. Am J Surg. 2012;203(3):347-352. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.08.015
- Quinn NA, Alt JA, Ashby S, Orlandi RR. Time, resident involvement, and supply drive cost variability in septoplasty with turbinate reduction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;159(2):310-314. doi:10.1177/0194599818765099
- Leader BA, Wiebracht ND, Meinzen-Derr J, Ishman SL. The impact of resident involvement on tonsillectomy outcomes and surgical time. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(10):2481-2486. doi:10.1002/lary.28427
- Muelleman T, Shew M, Muelleman RJ, et al. Impact of resident participation on operative time and outcomes in otologic surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158(1):151-154. doi:10.1177/0194599817737270
- Puram SV, Kozin ED, Sethi R, et al. Impact of resident surgeons on procedure length based on common pediatric otolaryngology cases. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(4):991 -997. doi:10.1002/lary.24912
- Chow MS, Gordon AJ, Talwar A, Lydiatt WM, Yueh B, Givi B. The RVU compensation model and head and neck surgical education. Laryngoscope. 2024;134(1):113-119. doi:10.1002/lary.30807
- Papandria D, Rhee D, Ortega G, et al. Assessing trainee impact on operative time for common general surgical procedures in ACS-NSQIP. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(2):149-155. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2011.08.003
- Pugely AJ, Gao Y, Martin CT, Callagh JJ, Weinstein SL, Marsh JL. The effect of resident participation on short-term outcomes after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2290-2300. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3567-0
- Hosler MR, Scott IU, Kunselman AR, Wolford KR, Oltra EZ, Murray WB. Impact of resident participation in cataract surgery on operative time and cost. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(1):95-98. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.06.026
- Lanigan A, Spaw M, Donaghe C, Brennan J. The impact of the Veteran’s Affairs medical system on an otolaryngology residency training program. Mil Med. 2018;183(11-12):e671-e675. doi:10.1093/milmed/usy041
- American Society of Clinical Oncology, Pfister DG, Laurie SA, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline for the use of larynx-preservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(22):3693-3704. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.4559
- Forastiere AA, Ismaila N, Lewin JS, et al. Use of larynxpreservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(11):1143-1169. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.75.7385
- Verma SP, Mahboubi H. The changing landscape of total laryngectomy surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150(3):413-418. doi:10.1177/0194599813514515
- Habermann EB, Harris AHS, Giori NJ. Large surgical databases with direct data abstraction: VASQIP and ACSNSQIP. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(suppl 3):9-14. doi:10.2106/JBJS.22.00596
- Benito DA, Mamidi I, Pasick LJ, et al. Evaluating resident involvement and the ‘July effect’ in parotidectomy. J Laryngol Otol. 2021;135(5):452-457. doi:10.1017/S0022215121000578
- Hwang CS, Wichterman KA, Alfrey EJ. The cost of resident education. J Surg Res. 2010;163(1):18-23. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2010.03.013
- Saliba AN, Taher AT, Tamim H, et al. Impact of resident involvement in surgery (IRIS-NSQIP): looking at the bigger picture based on the American College of Surgeons- NSQIP database. J Am Coll Surg. 2016; 222(1):30-40. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.10.011
- Khuri SF, Najjar SF, Daley J, et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes between teaching and nonteaching hospitals in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Ann Surg. 2001;234(3):370-383. doi:10.1097/00000658-200109000-00011
- Relles DM, Burkhart RA, Pucci MJ et al. Does resident experience affect outcomes in complex abdominal surgery? Pancreaticoduodenectomy as an example. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18(2):279-285. doi:10.1007/s11605-013-2372-5
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Required minimum number of key indicator procedures for graduating residents. June 2019. Accessed January 2, 2025. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programresources/280_core_case_log_minimums.pdf
- Brady JS, Crippen MM, Filimonov A, et al. The effect of training level on complications after free flap surgery of the head and neck. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017;38(5):560-564. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.06.001
Resident Participation Impact on Operative Time and Outcomes in Veterans Undergoing Total Laryngectomy
Resident Participation Impact on Operative Time and Outcomes in Veterans Undergoing Total Laryngectomy