User login
Naltrexone cuts hospitalization, deaths in alcohol use disorder
Naltrexone reduces the risk for hospitalization for alcohol use disorder (AUD), regardless of whether it is used alone or in conjunction with disulfiram or acamprosate, research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 10-year data on more than 125,000 Swedish residents with AUD and found that naltrexone, used as monotherapy or combined with acamprosate or disulfiram, was associated with significantly lower risk for AUD hospitalization or all-cause hospitalization in comparison with patients who did not use AUD medication. The patients ranged in age from 16 to 64 years.
By contrast, benzodiazepines and acamprosate monotherapy were associated with increased risk for AUD hospitalization.
“The take-home message for practicing clinicians would be that especially naltrexone use is associated with favorable treatment outcomes and should be utilized as part of the treatment protocol for AUD,” study investigator Milja Heikkinen, MD, specialist in forensic psychiatry and addiction medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, told this news organization.
On the other hand, “benzodiazepines should be avoided and should not be administered other than for alcohol withdrawal symptoms,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 4 in Addiction.
Real-world data
Previous research has shown that disulfiram, acamprosate, naltrexone, and nalmefene are efficacious in treating AUD, but most studies have been randomized controlled trials or meta-analyses, the authors write.
“Very little is known about overall health outcomes (such as risks of hospitalization and mortality) associated with specific treatments in real-world circumstances,” they write.
“The study was motivated by the fact that, although AUD is a significant public health concern, very little is known, especially about the comparative effectiveness of medications indicated in AUD,” said Dr. Heikkinen.
who had been diagnosed with AUD (62.5% men; mean [standard deviation] age, 38.1 [15.9] years). They followed the cohort over a median of 4.6 years (interquartile range, 2.1-.2 years).
During the follow-up period, roughly one-fourth of patients (25.6) underwent treatment with one or more drugs.

The main outcome measure was AUD-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes were hospitalization for any cause and for alcohol-related somatic causes; all-cause mortality; and work disability.
Two types of analyses were conducted. The within-individual analyses, designed to eliminate selection bias, compared the use of a medication to periods during which the same individual was not using the medication.
Between-individual analyses (adjusted for sex, age, educational level, number of previous AUD-related hospitalizations, time since first AUD diagnosis, comorbidities, and use of other medications) utilized a “traditional” multivariate-adjusted Cox hazards regression model.
AUD pharmacotherapy ‘underutilized’
Close to one-fourth of patients (23.9%) experienced the main outcome event (AUD-related hospitalization) during the follow-up period.
The within-individual analysis showed that naltrexone – whether used as monotherapy or adjunctively with disulfiram or acamprosate – “was associated with a significantly lower risk of AUD-related hospitalization, compared to those time periods in which the same individual did not use any AUD medication,” the authors report.
By contrast, they state, acamprosate monotherapy and benzodiazepines were associated with a significantly higher risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
Similar results were obtained in the between-individual analysis. Longer duration of naltrexone use was associated with lower risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
The pattern was also found when the outcome was hospitalization for any cause. However, unlike the findings of the within-individual model, the second model found that acamprosate monotherapy was not associated with a higher risk for any-cause hospitalization.
Polytherapy, including combinations of the four AUD medications, as well as disulfiram monotherapy were similarly associated with lower risk for hospitalization for alcohol-related somatic causes.
Of the overall cohort, 6.2% died during the follow-up period. No association was found between disulfiram, acamprosate, nalmefene, and naltrexone use and all-cause mortality. By contrast, benzodiazepine use was associated with a significantly higher mortality rate (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.19).
“AUD drugs are underutilized, despite AUD being a significant public health concern,” Dr. Heikkinen noted. On the other hand, benzodiazepine use is “very common.”
‘Ravages’ of benzodiazepines
Commenting on the study in an interview, John Krystal, MD, professor and chair of psychiatry and director of the Center for the Translational Neuroscience of Alcoholism, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said, “The main message from the study for practicing clinicians is that treatment works.”
Dr. Krystal, who was not involved with the study, noted that “many practicing clinicians are discouraged by the course of their patients with AUD, and this study highlights that naltrexone, perhaps in combination with other medications, may be effective in preventing hospitalization and, presumably, other hospitalization-related complications of AUD.”
Also commenting on the study, Raymond Anton, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, suggested that the “clinical knowledge of the harm of benzodiazepines in those with AUD is reinforced by these findings.”
In fact, the harm of benzodiazepines might be the study’s “most important message ... [a message that was] recently highlighted by the Netflix series “The Queen’s Gambit”, which shows the ravages of using both together, or how one leads to potential addiction with the other,” said Dr. Anton, who was not involved with the study.
The other “big take-home message is that naltrexone should be used more frequently,” said Dr. Anton, distinguished professor of psychiatry at the university and scientific director of the Charleston Alcohol Research Center. He noted that there are “recent data suggesting some clinical and genetic indicators that predict responsiveness to these medications, improving efficacy.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health. Dr. Heikkinen reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Krystal consults for companies currently developing other treatments for AUDs and receives medications to test from AstraZeneca and Novartis for NIAAA-funded research programs. Dr. Anton has consulted for Alkermes, Lipha, and Lundbeck in the past. He is also chair of the Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which is a public-private partnership partially sponsored by several companies and has received grant funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to study pharmacotherapies, including naltrexone, nalmefene, and acamprosate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Naltrexone reduces the risk for hospitalization for alcohol use disorder (AUD), regardless of whether it is used alone or in conjunction with disulfiram or acamprosate, research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 10-year data on more than 125,000 Swedish residents with AUD and found that naltrexone, used as monotherapy or combined with acamprosate or disulfiram, was associated with significantly lower risk for AUD hospitalization or all-cause hospitalization in comparison with patients who did not use AUD medication. The patients ranged in age from 16 to 64 years.
By contrast, benzodiazepines and acamprosate monotherapy were associated with increased risk for AUD hospitalization.
“The take-home message for practicing clinicians would be that especially naltrexone use is associated with favorable treatment outcomes and should be utilized as part of the treatment protocol for AUD,” study investigator Milja Heikkinen, MD, specialist in forensic psychiatry and addiction medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, told this news organization.
On the other hand, “benzodiazepines should be avoided and should not be administered other than for alcohol withdrawal symptoms,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 4 in Addiction.
Real-world data
Previous research has shown that disulfiram, acamprosate, naltrexone, and nalmefene are efficacious in treating AUD, but most studies have been randomized controlled trials or meta-analyses, the authors write.
“Very little is known about overall health outcomes (such as risks of hospitalization and mortality) associated with specific treatments in real-world circumstances,” they write.
“The study was motivated by the fact that, although AUD is a significant public health concern, very little is known, especially about the comparative effectiveness of medications indicated in AUD,” said Dr. Heikkinen.
who had been diagnosed with AUD (62.5% men; mean [standard deviation] age, 38.1 [15.9] years). They followed the cohort over a median of 4.6 years (interquartile range, 2.1-.2 years).
During the follow-up period, roughly one-fourth of patients (25.6) underwent treatment with one or more drugs.

The main outcome measure was AUD-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes were hospitalization for any cause and for alcohol-related somatic causes; all-cause mortality; and work disability.
Two types of analyses were conducted. The within-individual analyses, designed to eliminate selection bias, compared the use of a medication to periods during which the same individual was not using the medication.
Between-individual analyses (adjusted for sex, age, educational level, number of previous AUD-related hospitalizations, time since first AUD diagnosis, comorbidities, and use of other medications) utilized a “traditional” multivariate-adjusted Cox hazards regression model.
AUD pharmacotherapy ‘underutilized’
Close to one-fourth of patients (23.9%) experienced the main outcome event (AUD-related hospitalization) during the follow-up period.
The within-individual analysis showed that naltrexone – whether used as monotherapy or adjunctively with disulfiram or acamprosate – “was associated with a significantly lower risk of AUD-related hospitalization, compared to those time periods in which the same individual did not use any AUD medication,” the authors report.
By contrast, they state, acamprosate monotherapy and benzodiazepines were associated with a significantly higher risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
Similar results were obtained in the between-individual analysis. Longer duration of naltrexone use was associated with lower risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
The pattern was also found when the outcome was hospitalization for any cause. However, unlike the findings of the within-individual model, the second model found that acamprosate monotherapy was not associated with a higher risk for any-cause hospitalization.
Polytherapy, including combinations of the four AUD medications, as well as disulfiram monotherapy were similarly associated with lower risk for hospitalization for alcohol-related somatic causes.
Of the overall cohort, 6.2% died during the follow-up period. No association was found between disulfiram, acamprosate, nalmefene, and naltrexone use and all-cause mortality. By contrast, benzodiazepine use was associated with a significantly higher mortality rate (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.19).
“AUD drugs are underutilized, despite AUD being a significant public health concern,” Dr. Heikkinen noted. On the other hand, benzodiazepine use is “very common.”
‘Ravages’ of benzodiazepines
Commenting on the study in an interview, John Krystal, MD, professor and chair of psychiatry and director of the Center for the Translational Neuroscience of Alcoholism, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said, “The main message from the study for practicing clinicians is that treatment works.”
Dr. Krystal, who was not involved with the study, noted that “many practicing clinicians are discouraged by the course of their patients with AUD, and this study highlights that naltrexone, perhaps in combination with other medications, may be effective in preventing hospitalization and, presumably, other hospitalization-related complications of AUD.”
Also commenting on the study, Raymond Anton, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, suggested that the “clinical knowledge of the harm of benzodiazepines in those with AUD is reinforced by these findings.”
In fact, the harm of benzodiazepines might be the study’s “most important message ... [a message that was] recently highlighted by the Netflix series “The Queen’s Gambit”, which shows the ravages of using both together, or how one leads to potential addiction with the other,” said Dr. Anton, who was not involved with the study.
The other “big take-home message is that naltrexone should be used more frequently,” said Dr. Anton, distinguished professor of psychiatry at the university and scientific director of the Charleston Alcohol Research Center. He noted that there are “recent data suggesting some clinical and genetic indicators that predict responsiveness to these medications, improving efficacy.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health. Dr. Heikkinen reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Krystal consults for companies currently developing other treatments for AUDs and receives medications to test from AstraZeneca and Novartis for NIAAA-funded research programs. Dr. Anton has consulted for Alkermes, Lipha, and Lundbeck in the past. He is also chair of the Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which is a public-private partnership partially sponsored by several companies and has received grant funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to study pharmacotherapies, including naltrexone, nalmefene, and acamprosate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Naltrexone reduces the risk for hospitalization for alcohol use disorder (AUD), regardless of whether it is used alone or in conjunction with disulfiram or acamprosate, research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 10-year data on more than 125,000 Swedish residents with AUD and found that naltrexone, used as monotherapy or combined with acamprosate or disulfiram, was associated with significantly lower risk for AUD hospitalization or all-cause hospitalization in comparison with patients who did not use AUD medication. The patients ranged in age from 16 to 64 years.
By contrast, benzodiazepines and acamprosate monotherapy were associated with increased risk for AUD hospitalization.
“The take-home message for practicing clinicians would be that especially naltrexone use is associated with favorable treatment outcomes and should be utilized as part of the treatment protocol for AUD,” study investigator Milja Heikkinen, MD, specialist in forensic psychiatry and addiction medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, told this news organization.
On the other hand, “benzodiazepines should be avoided and should not be administered other than for alcohol withdrawal symptoms,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 4 in Addiction.
Real-world data
Previous research has shown that disulfiram, acamprosate, naltrexone, and nalmefene are efficacious in treating AUD, but most studies have been randomized controlled trials or meta-analyses, the authors write.
“Very little is known about overall health outcomes (such as risks of hospitalization and mortality) associated with specific treatments in real-world circumstances,” they write.
“The study was motivated by the fact that, although AUD is a significant public health concern, very little is known, especially about the comparative effectiveness of medications indicated in AUD,” said Dr. Heikkinen.
who had been diagnosed with AUD (62.5% men; mean [standard deviation] age, 38.1 [15.9] years). They followed the cohort over a median of 4.6 years (interquartile range, 2.1-.2 years).
During the follow-up period, roughly one-fourth of patients (25.6) underwent treatment with one or more drugs.

The main outcome measure was AUD-related hospitalization. Secondary outcomes were hospitalization for any cause and for alcohol-related somatic causes; all-cause mortality; and work disability.
Two types of analyses were conducted. The within-individual analyses, designed to eliminate selection bias, compared the use of a medication to periods during which the same individual was not using the medication.
Between-individual analyses (adjusted for sex, age, educational level, number of previous AUD-related hospitalizations, time since first AUD diagnosis, comorbidities, and use of other medications) utilized a “traditional” multivariate-adjusted Cox hazards regression model.
AUD pharmacotherapy ‘underutilized’
Close to one-fourth of patients (23.9%) experienced the main outcome event (AUD-related hospitalization) during the follow-up period.
The within-individual analysis showed that naltrexone – whether used as monotherapy or adjunctively with disulfiram or acamprosate – “was associated with a significantly lower risk of AUD-related hospitalization, compared to those time periods in which the same individual did not use any AUD medication,” the authors report.
By contrast, they state, acamprosate monotherapy and benzodiazepines were associated with a significantly higher risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
Similar results were obtained in the between-individual analysis. Longer duration of naltrexone use was associated with lower risk for AUD-related hospitalization.
The pattern was also found when the outcome was hospitalization for any cause. However, unlike the findings of the within-individual model, the second model found that acamprosate monotherapy was not associated with a higher risk for any-cause hospitalization.
Polytherapy, including combinations of the four AUD medications, as well as disulfiram monotherapy were similarly associated with lower risk for hospitalization for alcohol-related somatic causes.
Of the overall cohort, 6.2% died during the follow-up period. No association was found between disulfiram, acamprosate, nalmefene, and naltrexone use and all-cause mortality. By contrast, benzodiazepine use was associated with a significantly higher mortality rate (hazard ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.19).
“AUD drugs are underutilized, despite AUD being a significant public health concern,” Dr. Heikkinen noted. On the other hand, benzodiazepine use is “very common.”
‘Ravages’ of benzodiazepines
Commenting on the study in an interview, John Krystal, MD, professor and chair of psychiatry and director of the Center for the Translational Neuroscience of Alcoholism, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said, “The main message from the study for practicing clinicians is that treatment works.”
Dr. Krystal, who was not involved with the study, noted that “many practicing clinicians are discouraged by the course of their patients with AUD, and this study highlights that naltrexone, perhaps in combination with other medications, may be effective in preventing hospitalization and, presumably, other hospitalization-related complications of AUD.”
Also commenting on the study, Raymond Anton, MD, professor, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, suggested that the “clinical knowledge of the harm of benzodiazepines in those with AUD is reinforced by these findings.”
In fact, the harm of benzodiazepines might be the study’s “most important message ... [a message that was] recently highlighted by the Netflix series “The Queen’s Gambit”, which shows the ravages of using both together, or how one leads to potential addiction with the other,” said Dr. Anton, who was not involved with the study.
The other “big take-home message is that naltrexone should be used more frequently,” said Dr. Anton, distinguished professor of psychiatry at the university and scientific director of the Charleston Alcohol Research Center. He noted that there are “recent data suggesting some clinical and genetic indicators that predict responsiveness to these medications, improving efficacy.”
The study was funded by the Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health. Dr. Heikkinen reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Krystal consults for companies currently developing other treatments for AUDs and receives medications to test from AstraZeneca and Novartis for NIAAA-funded research programs. Dr. Anton has consulted for Alkermes, Lipha, and Lundbeck in the past. He is also chair of the Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which is a public-private partnership partially sponsored by several companies and has received grant funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism to study pharmacotherapies, including naltrexone, nalmefene, and acamprosate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
National spike in methamphetamine overdose deaths
The national rate of methamphetamine overdose deaths shot up significantly between 2011 and 2018, particularly among non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native communities, new research shows.
Rates rose for both men and women but more so among men, the study found. The spike in these deaths underscores the need for culturally tailored prevention and treatment strategies, the study authors said.
“While much attention is focused on the opioid crisis, a methamphetamine crisis has been quietly, but actively, gaining steam – particularly among American Indians and Alaska Natives, who are disproportionately affected by a number of health conditions,” senior investigator Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a press release.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Highly toxic
Methamphetamine is highly toxic. Its use is associated with pulmonary and cardiovascular pathology and frequently co-occurs with other substance use and mental disorders.
In addition, there are currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications to reverse methamphetamine overdose or treat methamphetamine use disorder.
However, In addition, a recent clinical trial reported significant therapeutic benefits with the combination of naltrexone with bupropion in patients with methamphetamine use disorder.
For the study, the investigators used deidentified public health surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Vital Statistics System files for multiple causes of death.
The researchers used the psychostimulant category to estimate death rates from methamphetamine. The authors noted that up to 90% of psychostimulant-involved death certificates mentioned methamphetamine.
Researchers stratified age-adjusted overdose death rates during 2011-2018 by sex and race/ethnicity and limited the analysis to those aged 25-54 years. Approximately 80% of methamphetamine users are between the ages of 25 and 54 years.
During the study period, rates for methamphetamine-involved deaths increased from 1.8 to 10.1 per 100,000 among men (average annual percentage change, 29.1; 95% confidence interval, 25.5-32.8; P < .001) and from 0.8 to 4.5 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 28.1; 95% CI, 25.1-31.2; P < .001).
Need for tailored interventions
For both men and women, those in non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native communities had the highest rates. These increased from 5.6 to 26.4 per 100,000 among men and from 3.6 to 15.6 per 100,000 among women.
While American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experience sociostructural disadvantages, their cultural strengths “can be leveraged to improve addiction outcomes,” the investigators wrote.
Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest rates. These rose from 2.2 to 12.6 per 100,000 among men (AAPC, 29.8; 95% CI, 24.3-35.4; P < .001) and from 1.1 to 6.2 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 29.1; 95% CI, 25.2-33.2; P < .001).
Rates among Hispanic individuals increased from 1.4 to 6.6 per 100,000 for men and from 0.5 to 2.0 per 100,000 for women. Among non-Hispanic Asian individuals, rates increased to 3.4 per 100,000 for men and to 1.1 per 100,000 for women. Non-Hispanic Black individuals had low rates. Within each racial/ethnic group, rates were higher among men versus women.
Methamphetamine death rates may be underestimated because some overdose death certificates do not report specific drugs involved, the authors noted.
Identifying populations that have a higher rate of methamphetamine overdose is a crucial step toward curbing the underlying methamphetamine crisis,” study author Beth Han, MD, PhD, of NIDA, said in a press release.
“By focusing on the unique needs of individuals and developing culturally tailored interventions, we can begin to move away from one-size-fits-all approaches and toward more effective, tailored interventions,” she said.
The study was sponsored by NIDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The national rate of methamphetamine overdose deaths shot up significantly between 2011 and 2018, particularly among non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native communities, new research shows.
Rates rose for both men and women but more so among men, the study found. The spike in these deaths underscores the need for culturally tailored prevention and treatment strategies, the study authors said.
“While much attention is focused on the opioid crisis, a methamphetamine crisis has been quietly, but actively, gaining steam – particularly among American Indians and Alaska Natives, who are disproportionately affected by a number of health conditions,” senior investigator Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a press release.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Highly toxic
Methamphetamine is highly toxic. Its use is associated with pulmonary and cardiovascular pathology and frequently co-occurs with other substance use and mental disorders.
In addition, there are currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications to reverse methamphetamine overdose or treat methamphetamine use disorder.
However, In addition, a recent clinical trial reported significant therapeutic benefits with the combination of naltrexone with bupropion in patients with methamphetamine use disorder.
For the study, the investigators used deidentified public health surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Vital Statistics System files for multiple causes of death.
The researchers used the psychostimulant category to estimate death rates from methamphetamine. The authors noted that up to 90% of psychostimulant-involved death certificates mentioned methamphetamine.
Researchers stratified age-adjusted overdose death rates during 2011-2018 by sex and race/ethnicity and limited the analysis to those aged 25-54 years. Approximately 80% of methamphetamine users are between the ages of 25 and 54 years.
During the study period, rates for methamphetamine-involved deaths increased from 1.8 to 10.1 per 100,000 among men (average annual percentage change, 29.1; 95% confidence interval, 25.5-32.8; P < .001) and from 0.8 to 4.5 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 28.1; 95% CI, 25.1-31.2; P < .001).
Need for tailored interventions
For both men and women, those in non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native communities had the highest rates. These increased from 5.6 to 26.4 per 100,000 among men and from 3.6 to 15.6 per 100,000 among women.
While American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experience sociostructural disadvantages, their cultural strengths “can be leveraged to improve addiction outcomes,” the investigators wrote.
Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest rates. These rose from 2.2 to 12.6 per 100,000 among men (AAPC, 29.8; 95% CI, 24.3-35.4; P < .001) and from 1.1 to 6.2 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 29.1; 95% CI, 25.2-33.2; P < .001).
Rates among Hispanic individuals increased from 1.4 to 6.6 per 100,000 for men and from 0.5 to 2.0 per 100,000 for women. Among non-Hispanic Asian individuals, rates increased to 3.4 per 100,000 for men and to 1.1 per 100,000 for women. Non-Hispanic Black individuals had low rates. Within each racial/ethnic group, rates were higher among men versus women.
Methamphetamine death rates may be underestimated because some overdose death certificates do not report specific drugs involved, the authors noted.
Identifying populations that have a higher rate of methamphetamine overdose is a crucial step toward curbing the underlying methamphetamine crisis,” study author Beth Han, MD, PhD, of NIDA, said in a press release.
“By focusing on the unique needs of individuals and developing culturally tailored interventions, we can begin to move away from one-size-fits-all approaches and toward more effective, tailored interventions,” she said.
The study was sponsored by NIDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The national rate of methamphetamine overdose deaths shot up significantly between 2011 and 2018, particularly among non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native communities, new research shows.
Rates rose for both men and women but more so among men, the study found. The spike in these deaths underscores the need for culturally tailored prevention and treatment strategies, the study authors said.
“While much attention is focused on the opioid crisis, a methamphetamine crisis has been quietly, but actively, gaining steam – particularly among American Indians and Alaska Natives, who are disproportionately affected by a number of health conditions,” senior investigator Nora D. Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, said in a press release.
The study was published online Jan. 20 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Highly toxic
Methamphetamine is highly toxic. Its use is associated with pulmonary and cardiovascular pathology and frequently co-occurs with other substance use and mental disorders.
In addition, there are currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved medications to reverse methamphetamine overdose or treat methamphetamine use disorder.
However, In addition, a recent clinical trial reported significant therapeutic benefits with the combination of naltrexone with bupropion in patients with methamphetamine use disorder.
For the study, the investigators used deidentified public health surveillance data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Vital Statistics System files for multiple causes of death.
The researchers used the psychostimulant category to estimate death rates from methamphetamine. The authors noted that up to 90% of psychostimulant-involved death certificates mentioned methamphetamine.
Researchers stratified age-adjusted overdose death rates during 2011-2018 by sex and race/ethnicity and limited the analysis to those aged 25-54 years. Approximately 80% of methamphetamine users are between the ages of 25 and 54 years.
During the study period, rates for methamphetamine-involved deaths increased from 1.8 to 10.1 per 100,000 among men (average annual percentage change, 29.1; 95% confidence interval, 25.5-32.8; P < .001) and from 0.8 to 4.5 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 28.1; 95% CI, 25.1-31.2; P < .001).
Need for tailored interventions
For both men and women, those in non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native communities had the highest rates. These increased from 5.6 to 26.4 per 100,000 among men and from 3.6 to 15.6 per 100,000 among women.
While American Indian and Alaska Native individuals experience sociostructural disadvantages, their cultural strengths “can be leveraged to improve addiction outcomes,” the investigators wrote.
Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest rates. These rose from 2.2 to 12.6 per 100,000 among men (AAPC, 29.8; 95% CI, 24.3-35.4; P < .001) and from 1.1 to 6.2 per 100,000 among women (AAPC, 29.1; 95% CI, 25.2-33.2; P < .001).
Rates among Hispanic individuals increased from 1.4 to 6.6 per 100,000 for men and from 0.5 to 2.0 per 100,000 for women. Among non-Hispanic Asian individuals, rates increased to 3.4 per 100,000 for men and to 1.1 per 100,000 for women. Non-Hispanic Black individuals had low rates. Within each racial/ethnic group, rates were higher among men versus women.
Methamphetamine death rates may be underestimated because some overdose death certificates do not report specific drugs involved, the authors noted.
Identifying populations that have a higher rate of methamphetamine overdose is a crucial step toward curbing the underlying methamphetamine crisis,” study author Beth Han, MD, PhD, of NIDA, said in a press release.
“By focusing on the unique needs of individuals and developing culturally tailored interventions, we can begin to move away from one-size-fits-all approaches and toward more effective, tailored interventions,” she said.
The study was sponsored by NIDA.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Breaking the cycle of medication overuse headache
Medication overuse headache (MOH), a secondary headache diagnosis, is a prevalent phenomenon that complicates headache diagnosis and treatment, increases the cost of care, and reduces quality of life. Effective abortive medication is essential for the headache sufferer; when an abortive is used too frequently, however, headache frequency increases—potentially beginning a cycle in which the patient then takes more medication to abort the headache. Over time, the patient suffers from an ever-increasing number of headaches, takes even more abortive medication, and so on. In the presence of MOH, there is a reduction in pain response to preventive and abortive treatments; when medication overuse is eliminated, pain response improves.1
Although MOH is well recognized among headache specialists, the condition is often overlooked in primary care. Since headache is a top complaint in primary care, however, and prevention is a major goal in family medicine, the opportunity for you to recognize, treat, and prevent MOH is significant. In fact, a randomized controlled trial showed that brief patient education about headache care and MOH provided by a primary care physician can lead to a significant reduction in headache frequency among patients with MOH.2
This article reviews the recognition and diagnosis of MOH, based on historical features and current criteria; addresses risk factors for abortive medication overuse and how to withdraw an offending agent; and explores the value of bridging and preventive therapies to reduce the overall frequency of headache.

What defines MOH?
Typically, MOH is a chronification of a primary headache disorder. However, in patients with a history of migraine who are undergoing treatment for another chronic pain condition with an opioid or other analgesic, MOH can be induced.3 An increase in the frequency of headache raises the specter of a concomitant increase in the level of disability4; psychiatric comorbidity5; and more headache days, with time lost from school and work.
The Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire, a validated instrument that helps the provider (1) measure the impact that headache has on a patient’s life and (2) follow treatment progress, also provides information to employers and insurance companies on treatment coverage and the need for work modification. The MIDAS score is 3 times higher in patients with MOH than in patients with episodic migraine.6,7
The annual associated cost per person of MOH has been estimated at $4000, resulting in billions of dollars in associated costs8; most of these costs are related to absenteeism and disability. After detoxification for MOH, annual outpatient medication costs are reduced by approximately 24%.9
Efforts to solve a common problem create another
Headache affects nearly 50% of the general population worldwide,10 accounting for about 4% of primary care visits11 and approximately 20% of outpatient neurology consultations.12 Although inpatient stays for headache are approximately half the duration of the overall average hospital stay, headache accounts for 3% of admissions.13 According to the Global Burden of Disease study, tension-type headache, migraine, and MOH are the 3 most common headache disorders.10 Headache is the second leading cause of disability among people 15 to 49 years of age.10
Continue to: The prevalence of MOH...
The prevalence of MOH in the general population is 2%.7,14,15 A population-based study showed that the rate of progression from episodic headache (< 15 d/mo) to chronic headache (≥ 15 d/mo) in the general population is 2.5% per year16; however, progression to chronic headache is 14% per year in patients with medication overuse. One-third of the general population with chronic migraine overuses symptomatic medication; in US headache clinics, roughly one-half of patients with chronic headache overuse acute medication.6
Definitions and diagnosis
MOH is a secondary headache diagnosis in the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) (TABLE 1),17 which lists diagnostic criteria for recognized headache disorders.
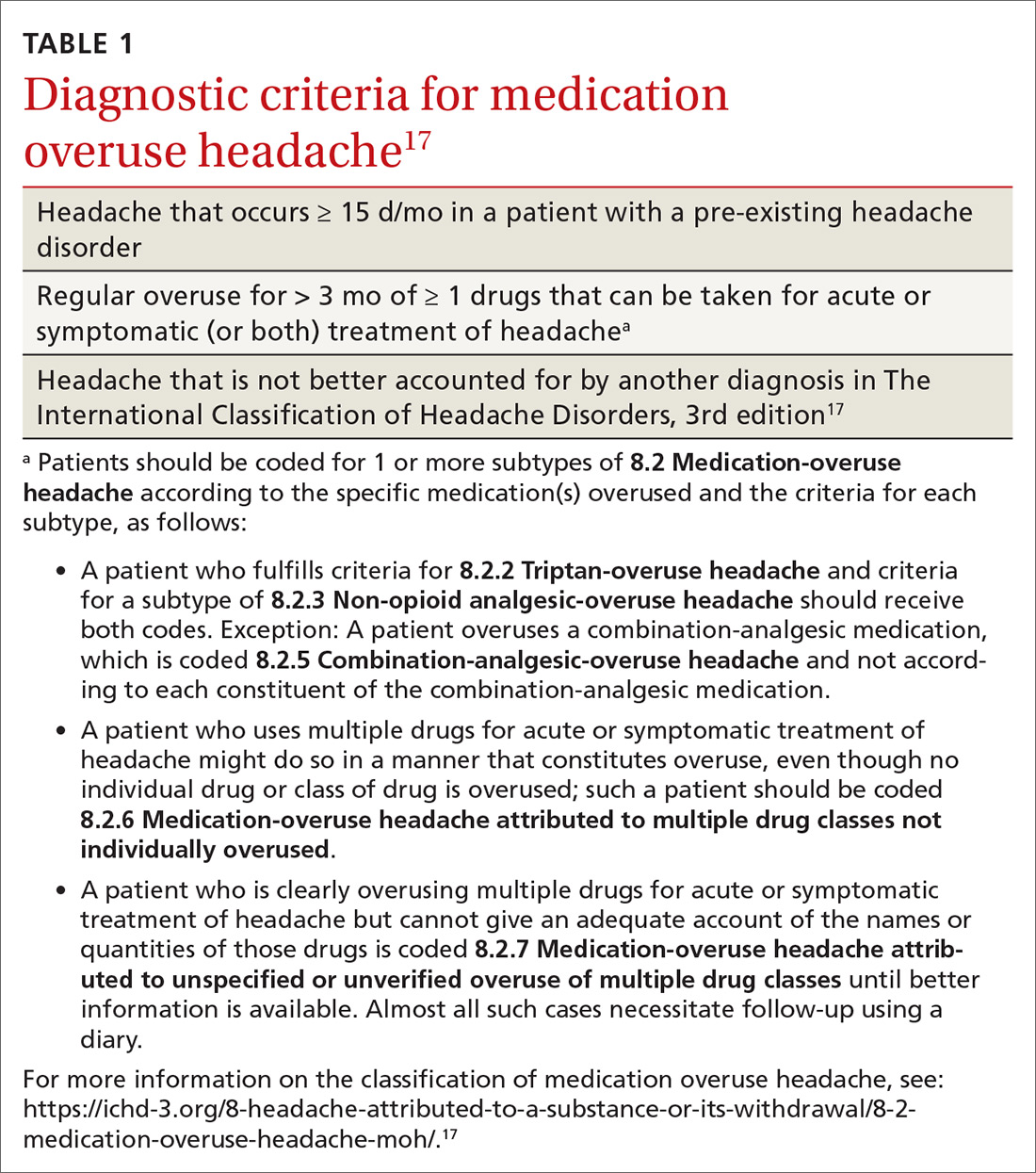
Terminology. MOH has also been called rebound headache, drug-induced headache, and transformed migraine, but these terms are outdated and are not formal diagnoses. Patients sometimes refer to substance-withdrawal headaches (not discussed in this article) as rebound headaches, so clarity is important when discussing headache with patients: namely, that MOH is an exacerbation of an existing headache condition caused by overuse of abortive headache medications, including analgesics, combination analgesics, triptans, barbiturates, and opioids.
MOH was recognized in the early 1950s and fully differentiated as a diagnosis in 2005 in the second edition of the ICHD. The disorder is subcategorized by offending abortive agent (TABLE 217) because the frequency of analgesic use required to develop MOH differs by agent.

Risk factors for MOH and chronification of a primary headache disorder. There are several risk factors for developing MOH, and others that contribute to increasing headache frequency in general (TABLE 35,14,18-23). Some risk factors are common to each. All are important to address because some are modifiable.
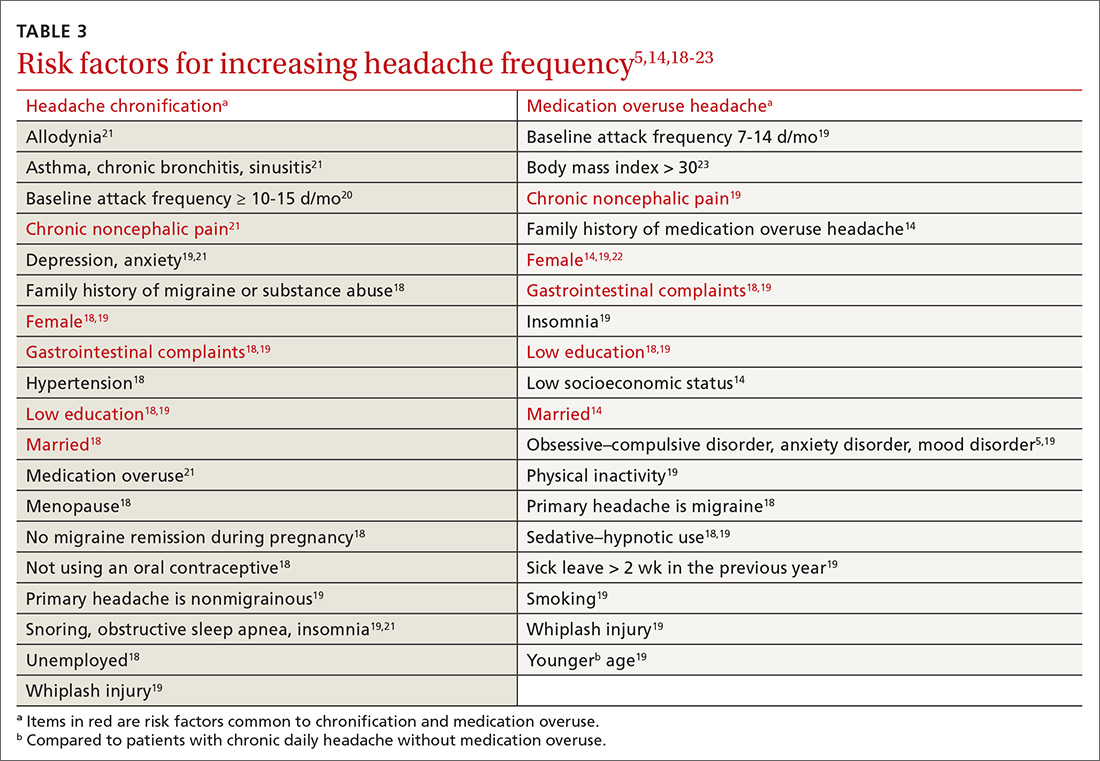
Continue to: Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology. The pathophysiology and psychology behind MOH are largely unknown. Physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes have been demonstrated in patients with MOH, both of which are reversible upon withdrawal of medication.23 Genetic factors and changes in hormone and neurotransmitter levels are found in MOH patients; this is not the case in patients who have an episodic headache pattern only.24
Presentation. Diagnostic criteria for MOH do not include clinical characteristics. Typically, the phenotype of MOH in a given patient is similar to the underlying primary headache25—although this principle can be complicated to tease out because these medications can suppress some symptoms. Diagnosis of a primary headache disorder should be documented along with the diagnosis of MOH.
Medication overuse can exist without MOH: Not every patient who frequently uses an abortive medication develops MOH.
Treatment is multifaceted—and can become complex
Mainstays of treatment of MOH are education about the disorder and detoxification from the overused agent, although specific treatments can differ depending on the agent involved, the frequency and duration of its use, and a patient’s behavioral patterns and psychiatric comorbidities. Often, a daily medication to prevent headache is considered upon, or after, withdrawal of the offending agent. The timing of introducing a preventive might impact its effectiveness. Some refractory cases require more intensive therapy, including hospitalization at a specialized tertiary center.
But before we look at detoxification from an overused agent, it’s important to review one of the best strategies of all in combatting MOH.
Continue to: First and best strategy
First and best strategy: Avoid onset of MOH
Select an appropriate abortive to reduce the risk of MOH. With regard to specific acute headache medications, some nuances other than type of headache should be considered. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are recommended as abortive therapy by the American Headache Society for their efficacy, favorable adverse effect profile, and low cost. NSAIDs are protective against development of MOH if a patient’s baseline headache frequency is < 10/mo; at a frequency of 10 to 14 d/mo, however, the risk of MOH increases when using an NSAID.6 A similar effect has been seen with triptans.16 Longer-acting NSAIDs, such as nabumetone and naproxen, have been proposed as less likely to cause MOH, and are even used as bridging therapy sometimes (as long as neither of these was the overused medication).26
The time it takes to develop MOH is shortest with triptans, followed by ergots, then analgesics.27
Prospective cohort studies6,16 have shown that barbiturates and opioids are more likely to induce MOH; for that reason, agents in these analgesic classes are almost universally avoided unless no other medically acceptable options exist. Using barbiturate-containing compounds or opioids > 4 d/mo exponentially increases the likelihood of MOH.
Promising preclinical data demonstrate that the gepant, or small-molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, class of medications used as abortive therapy does not induce medication overuse cutaneous allodynia.28
Provide education. Primary prevention of MOH involves (1) increasing patients’ awareness of how to take medications appropriately and (2) restricting intake of over-the-counter abortive medications. Often, the expert recommendation is to limit abortives to approximately 2 d/wk because more frequent use places patients at risk of further increased use and subsequent MOH.
Continue to: A randomized controlled trial in Norway...
A randomized controlled trial in Norway compared outcomes in 2 groups of patients with MOH: One group was given advice on the disorder by a physician; the other group was not provided with advice. In the “business-as-usual” group, there was no significant improvement; however, when general practitioners provided simple advice (lasting roughly 9 minutes) about reducing abortive medication use to a safe level and cautioned patients that they would be “feeling worse before feeling better,” headache days were reduced by approximately 8 per month and medication days, by 16 per month.2
A subsequent, long-term follow-up study29 of patients from the Norway trial2 who had been given advice and education showed a relapse rate (ie, into overuse of headache medication) of only 8% and sustained reduction of headache days and medication use at 16 months.
Offer support and other nondrug interventions. A recent review of 3 studies23 recommended that extra support for patients from a headache nurse, close follow-up, keeping an electronic diary that provides feedback, and undertaking a short course of psychotherapy can reduce medication overuse and prevent relapse.
If MOH develops, initiate withdrawal, introduce a preventive
Withdraw overused medication. Most current evidence suggests that withdrawal of the offending agent is the most effective factor in reducing headache days and improving quality of life. A randomized controlled trial compared the effects of (1) complete and immediate withdrawal of an abortive medication with (2) reducing its use (ie, limiting intake to 2 d/wk), on headache frequency, disability, and quality of life.30 There was a reduction of headache days in both groups; however, reduction was much greater at 2 months in the complete withdrawal group than in the restricted intake group (respectively, a 41% and a 26% reduction in headache days per month). This effect was sustained at 6 and 12 months in both groups. The study confirmed the results of earlier research2,15: Abrupt withdrawal leads to reversion to an episodic pattern at 2 to 6 months in approximately 40% to 60% of patients.
More studies are needed to determine the most appropriate treatment course for MOH; however, complete withdrawal of the causative drug is the most important intervention.
Continue to: Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment
Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment. Use of sodium valproate, in addition to medication overuse detoxification, led to a significant reduction in headache days and improvement in quality of life at 12 weeks but no difference after 24 weeks, compared with detoxification alone in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.31
A study of 61 patients showed a larger reduction (by 7.2 d/mo) in headache frequency with any preventive medication in addition to medication withdrawal, compared to withdrawal alone (by 4.1 d/mo) after 3 months; however, the relative benefit was gone at 6 months.32
A study of 98 patients compared immediate and delayed initiation of preventive medication upon withdrawal of overused abortive medication.33 Response was defined as a > 50% reduction in headache frequency and was similar in both groups; results showed a 28% response with immediate initiation of a preventive; a 23% response with delayed (ie, 2 months after withdrawal) initiation; and a 48% response in both groups at 12 months.
Collectively, these studies suggest that adding a preventive medication at the time of withdrawal has the potential to reduce headache frequency more quickly than withdrawal alone. However, after 3 to 6 months, the outcome of reduced headache frequency is the same whether or not a preventive medication is used—as long as the offending agent has been withdrawn.
Do preventives work without withdrawing overused medication? Patients with MOH often show little or no improvement with addition of a preventive medication only; their response to a preventive improves after withdrawal of the overused medication. Patients without previous headache improvement after addition of a preventive, who also did not improve 2 months after withdrawal, then demonstrated an overall reduction in headache by 26% when a preventive was reintroduced after withdrawal.2
Continue to: The research evidence for preventives
The research evidence for preventives. Medications for headache prevention have not been extensively evaluated specifically for treating MOH. Here is what’s known:
- Flunarizine, amitriptyline, and beta-blockers usually are ineffective for MOH.24
- Results for topiramate are mixed: A small, double-blind, placebo-controlled chronic migraine study in Europe showed that, in a subgroup of patients with MOH, topiramate led to a small but significant reduction (3.5 d/mo) in headache frequency, compared to placebo.27 A similar study done in the United States did not show a significant difference between the active-treatment and placebo groups.34
- Findings regarding onabotulinumtoxinA are intriguing: In a posthoc analysis of onabotulinumtoxinA to treat chronic migraine, patients with MOH who did not undergo detoxification had an 8 d/mo greater reduction in headache, compared to placebo.35 However, when compared to placebo in conjunction with detoxification, onabotulinumtoxinA demonstrated no benefit.36
- Newer CGRP antagonist and CGRP receptor antagonist monoclonal antibodies are successful preventive medications that have demonstrated a reduction in acute medication use days per month and headache days per month37; these compounds have not been compared to withdrawal alone.
Reducing the severity and duration of withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal from overused abortive headache medications can lead to worsening headache, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia, sleep disturbances, restlessness, anxiety, and nervousness. Symptoms usually last 2 to 10 days but can persist for as long as 4 weeks; duration of withdrawal symptoms varies with the medication that is being overused. In patients who have used a triptan, for example, mean duration of withdrawal is 4.1 days; ergotamine, 6.7 days; and NSAIDs, 9.5 days.23 Tapered withdrawal is sometimes recommended with opioids and barbiturates to reduce withdrawal symptoms. It is unclear whether starting a preventive medication during withdrawal assists in reducing withdrawal symptoms.38
Bridging therapy to reduce symptoms of withdrawal is often provided despite debatable utility. Available evidence does not favor one agent or method but suggests some strategies that could be helpful:
- A prednisone taper has a potential role during the first 6 days of withdrawal by reducing rebound headache and withdrawal symptoms39; however, oral prednisolone has been shown to have no benefit.40
- Alone, IV methylprednisolone seems not to be of benefit; however, in a retrospective study of 94 patients, IV methylprednisolone plus diazepam for 5 days led to a significant reduction in headache frequency and drug consumption that was sustained after 3 months.41
- Celecoxib was compared to prednisone over a 20-day course: a celecoxib dosage of 400 mg/d for the first 5 days, tapered by 100 mg every 5 days, and an oral prednisone dosage of 75 mg/d for the first 5 days, then tapered every 5 days. Patients taking celecoxib had lower headache intensity but there was no difference in headache frequency and acute medication intake between the groups.42
Other strategies. Using antiemetics and NSAIDs to reduce withdrawal symptoms is widely practiced, but no placebo-controlled trials have been conducted to support this strategy.
Patients in withdrawal might be more likely to benefit from inpatient care if they have a severe comorbidity, such as opioid or barbiturate use; failure to respond to, tolerate, or adhere to treatment; or relapse after withdrawal.38
Continue to: Cognitive behavioral therapy...
Cognitive behavioral therapy, exercise, a headache diary, and biofeedback should be considered in every patient’s treatment strategy because a multidisciplinary approach increases adherence and leads to improvement in headache frequency and a decrease in disability and medication use.43
Predictors of Tx success
A prospective cohort study determined that the rate of MOH relapse is 31% at 6 months, 41% at 1 year, and 45% at 4 years, with the highest risk of relapse during the first year.44 Looking at the correlation between type of medication overused and relapse rate, the research indicates that
- triptans have the lowest risk of relapse,44
- simple analgesics have a higher risk of relapse than triptans,22,44 and
- opioids have the highest risk of relapse.22
Where the data don’t agree. Data on combination analgesics and on ergots are conflicting.22 In addition, data on whether the primary type of headache predicts relapse rate conflict; however, migraine might predict a better outcome than tension-type headache.22
To recap and expand: Management pearls
The major goals of headache management generally are to rule out secondary headache, reach a correct diagnosis, reduce overall headache frequency, and provide effective abortive medication. A large component of reducing headache frequency is addressing and treating medication overuse.
Seek to understand the nature of the patient’s headache disorder. Components of the history are key in identifying the underlying headache diagnosis and ruling out other, more concerning secondary headache diagnoses. The ICHD-3 is an excellent resource for treating headache disorders because the classification lists specific diagnostic criteria for all recognized headache diagnoses.
Continue to: Medication withdrawal...
Medication withdrawal—with or without preventive medication—should reduce the frequency of MOH in 2 or 3 months. If headache does not become less frequent, however, the headache diagnosis might need to be reconsidered. Minimizing the use of abortive medication is generally recommended, but reduction or withdrawal of these medications does not guarantee that patients will revert to an episodic pattern of headache.
Treating withdrawal symptoms is a reasonable approach in some patients, but evidence does not support routinely providing bridging therapy.
Apply preventives carefully. Abortive medication withdrawal should generally be completed before initiating preventive medication; however, over the short term, starting preventive therapy while withdrawing the overused medication could assist in reducing headache frequency rapidly. This strategy can put patients at risk of medication adverse effects and using the medications longer than necessary, yet might be reasonable in certain patients, given their comorbidities, risk of relapse, and physician and patient preference. A preventive medication for an individual patient should generally be chosen in line with recommendations of the American Academy of Neurology45 and on the basis of the history and comorbidities.
Provide education, which is essential to lowering barriers to success. Patients with MOH must be counseled to understand that (1) a headache treatment that is supposed to be making them feel better is, in fact, making them feel worse and (2) they will get worse before they get better. Many patients are afraid to be without medication to use as needed. It is helpful to educate them on the different types of treatments (abortive, preventive); how MOH interferes with headache prophylaxis and medication efficacy; how MOH alters brain function (ie, aforementioned physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes23); and that such change is reversible when medication is withdrawn.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author thanks Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, for his support and editing assistance with the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Allison Crain, MD, 2927 N 7th Avenue, Phoenix, AZ 85013; [email protected].
1. Zeeberg P, Olesen J, Jensen R. Discontinuation of medication overuse in headache patients: recovery of therapeutic responsiveness. Cephalalgia. 2006;26:1192-1198.
2. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Vetvik KG, et al. Brief intervention for medication-overuse headache in primary care. The BIMOH study: a double-blind pragmatic cluster randomised parallel controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:505-512.
3. Bahra A, Walsh M, Menon S, et al. Does chronic daily headache arise de novo in association with regular use of analgesics? Headache. 2003;43:179-190.
4. Blumenfeld AM, Varon SF, Wilcox TK, et al. Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS) Cephalalgia. 2011;31:301-315.
5. Chu H-T, Liang C-S, Lee J-T, et al. Associations between depression/anxiety and headache frequency in migraineurs: a cross-sectional study. Headache. 2018;58:407-415.
6. Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Excessive acute migraine medication use and migraine progression. Neurology. 2008;71:1821-1828.
7. Colás R, Muñoz P, Temprano R, et al. Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse: epidemiology and impact on quality of life. Neurology. 2004;62:1338-1342.
8. Linde M, Gustavsson A, Stovner LJ, et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: the Eurolight project. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19:703-711.
9. Shah AM, Bendtsen L, Zeeberg P, et al. Reduction of medication costs after detoxification for medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2013;53:665-672.
10. . Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:954-976.
11. Kernick D, Stapley S, Goadsby PJ, et al. What happens to new-onset headache presenting to primary care? A case–cohort study using electronic primary care records. Cephalalgia. 2008;28:1188-1195.
12. Stone J, Carson A, Duncan R, et al. Who is referred to neurology clinics?—the diagnoses made in 3781 new patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:747-751.
13. Munoz-Ceron J, Marin-Careaga V, L, et al. Headache at the emergency room: etiologies, diagnostic usefulness of the ICHD 3 criteria, red and green flags. PloS One. 2019;14:e0208728.
14. Evers S, Marziniak M. Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment of medication-overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:391-401.
15. Tassorelli C, Jensen R, Allena M, et al; the . A consensus protocol for the management of medication-overuse headache: evaluation in a multicentric, multinational study. Cephalalgia. 2014;34:645-655.
16. Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, et al. Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study. Headache. 2008;48:1157-1168.
17. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:1-211.
18. Ferrari A, Leone S, Vergoni AV, et al. Similarities and differences between chronic migraine and episodic migraine. Headache. 2007;47:65-72.
19. Hagen K, Linde M, Steiner TJ, et al. Risk factors for medication-overuse headache: an 11-year follow-up study. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Studies. Pain. 2012;153:56-61.
20. Katsarava Z, Schneewiess S, Kurth T, et al. Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology. 2004;62:788-790.
21. Lipton RB, Fanning KM, Buse DC, et al. Migraine progression in subgroups of migraine based on comorbidities: results of the CaMEO study. Neurology. 2019;93:e2224-e2236.
22. Munksgaard SB, Madsen SK, Wienecke T. Treatment of medication overuse headache—a review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2019;139:405-414.
23. Ferraro S, Grazzi L, Mandelli M, et al. Pain processing in medication overuse headache: a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study. Pain Med. 2012;13:255-262.
24. Diener H-C, Holle D, Solbach K, et al. Medication-overuse headache: risk factors, pathophysiology and management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:575-583.
25. Limmroth V, Katsarava Z, Fritsche G, et al. Features of medication overuse headache following overuse of different acute headache drugs. Neurology. 2002;59:1011-1014.
26. Mauskop A, ed. Migraine and Headache. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2013.
27. Diener H-C, Bussone G, Van Oene JC, et al; . Topiramate reduces headache days in chronic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2007;27:814-823.
28. Navratilova E, Behravesh S, Oyarzo J, et al. Ubrogepant does not induce latent sensitization in a preclinical model of medication overuse headache Cephalalgia. 2020;40:892-902.
29. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Russell MB, et al. Lasting improvement of medication-overuse headache after brief intervention—a long-term follow-up in primary care. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:883-891.
30. Carlsen LN, Munksgaard SB, Jensen RH, et al. Complete detoxification is the most effective treatment of medication-overuse headache: a randomized controlled open-label trial. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:225-236.
31. Sarchielli P, Messina P, Cupini LM, et al; SAMOHA Study Group. Sodium valproate in migraine without aura and medication overuse headache: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;24:1289-1297.
32. Hagen K, Stovner LJ. A randomized controlled trial on medication-overuse headache: outcome after 1 and 4 years. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2011;124(suppl 191):38-43.
33. Munksgaard SB, Bendtsen L, Jensen RH. Detoxification of medication-overuse headache by a multidisciplinary treatment programme is highly effective: a comparison of two consecutive treatment methods in an open-label design. Cephalalgia. 2012;32:834-844.
34. Silberstein S, Lipton R, Dodick D, et al. Topiramate treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of quality of life and other efficacy measures. Headache. 2009;49:1153-1162.
35. Silberstein SD, Blumenfeld AM, Cady RK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: PREEMPT 24-week pooled subgroup analysis of patients who had acute headache medication overuse at baseline. J Neurol Sci. 2013;331:48-56.
36. Sandrini G, Perrotta A, Tassorelli C, et al. Botulinum toxin type-A in the prophylactic treatment of medication-overuse headache: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J Headache Pain. 2011;12:427-433.
37. Tepper SJ. CGRP and headache: a brief review. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(suppl 1):99-105.
38. Diener H-C, Dodick D, Evers S, et al. Pathophysiology, prevention and treatment of medication overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:891-902.
39. Krymchantowski AV, Barbosa JS. Prednisone as initial treatment of analgesic-induced daily headache. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:107-113.
40. Bøe MG, Mygland A, Salvesen R. Prednisolone does not reduce withdrawal headache: a randomized, double-blind study. Neurology. 2007;69:26-31.
41. Paolucci M, Altamura C, Brunelli N, et al. Methylprednisolone plus diazepam i.v. as bridge therapy for medication overuse headache. Neurol Sci. 2017;38:2025-2029.
42. Taghdiri F, Togha M, Razeghi Jahromi S, et al. Celecoxib vs prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Headache. 2015;55:128-135.
43. Ramsey RR, Ryan JL, Hershey AD, et al. Treatment adherence in patients with headache: a systematic review. Headache. 2014;54:795-816.
44. Katsarava Z, Muessig M, Dzagnidze A, et al. Medication overuse headache: rates and predictors for relapse in a 4-year prospective study. Cephalalgia. 2005;25:12-15.
45. Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, et al; . Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology. 2012; 78:1137-1145.
Medication overuse headache (MOH), a secondary headache diagnosis, is a prevalent phenomenon that complicates headache diagnosis and treatment, increases the cost of care, and reduces quality of life. Effective abortive medication is essential for the headache sufferer; when an abortive is used too frequently, however, headache frequency increases—potentially beginning a cycle in which the patient then takes more medication to abort the headache. Over time, the patient suffers from an ever-increasing number of headaches, takes even more abortive medication, and so on. In the presence of MOH, there is a reduction in pain response to preventive and abortive treatments; when medication overuse is eliminated, pain response improves.1
Although MOH is well recognized among headache specialists, the condition is often overlooked in primary care. Since headache is a top complaint in primary care, however, and prevention is a major goal in family medicine, the opportunity for you to recognize, treat, and prevent MOH is significant. In fact, a randomized controlled trial showed that brief patient education about headache care and MOH provided by a primary care physician can lead to a significant reduction in headache frequency among patients with MOH.2
This article reviews the recognition and diagnosis of MOH, based on historical features and current criteria; addresses risk factors for abortive medication overuse and how to withdraw an offending agent; and explores the value of bridging and preventive therapies to reduce the overall frequency of headache.

What defines MOH?
Typically, MOH is a chronification of a primary headache disorder. However, in patients with a history of migraine who are undergoing treatment for another chronic pain condition with an opioid or other analgesic, MOH can be induced.3 An increase in the frequency of headache raises the specter of a concomitant increase in the level of disability4; psychiatric comorbidity5; and more headache days, with time lost from school and work.
The Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire, a validated instrument that helps the provider (1) measure the impact that headache has on a patient’s life and (2) follow treatment progress, also provides information to employers and insurance companies on treatment coverage and the need for work modification. The MIDAS score is 3 times higher in patients with MOH than in patients with episodic migraine.6,7
The annual associated cost per person of MOH has been estimated at $4000, resulting in billions of dollars in associated costs8; most of these costs are related to absenteeism and disability. After detoxification for MOH, annual outpatient medication costs are reduced by approximately 24%.9
Efforts to solve a common problem create another
Headache affects nearly 50% of the general population worldwide,10 accounting for about 4% of primary care visits11 and approximately 20% of outpatient neurology consultations.12 Although inpatient stays for headache are approximately half the duration of the overall average hospital stay, headache accounts for 3% of admissions.13 According to the Global Burden of Disease study, tension-type headache, migraine, and MOH are the 3 most common headache disorders.10 Headache is the second leading cause of disability among people 15 to 49 years of age.10
Continue to: The prevalence of MOH...
The prevalence of MOH in the general population is 2%.7,14,15 A population-based study showed that the rate of progression from episodic headache (< 15 d/mo) to chronic headache (≥ 15 d/mo) in the general population is 2.5% per year16; however, progression to chronic headache is 14% per year in patients with medication overuse. One-third of the general population with chronic migraine overuses symptomatic medication; in US headache clinics, roughly one-half of patients with chronic headache overuse acute medication.6
Definitions and diagnosis
MOH is a secondary headache diagnosis in the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) (TABLE 1),17 which lists diagnostic criteria for recognized headache disorders.

Terminology. MOH has also been called rebound headache, drug-induced headache, and transformed migraine, but these terms are outdated and are not formal diagnoses. Patients sometimes refer to substance-withdrawal headaches (not discussed in this article) as rebound headaches, so clarity is important when discussing headache with patients: namely, that MOH is an exacerbation of an existing headache condition caused by overuse of abortive headache medications, including analgesics, combination analgesics, triptans, barbiturates, and opioids.
MOH was recognized in the early 1950s and fully differentiated as a diagnosis in 2005 in the second edition of the ICHD. The disorder is subcategorized by offending abortive agent (TABLE 217) because the frequency of analgesic use required to develop MOH differs by agent.

Risk factors for MOH and chronification of a primary headache disorder. There are several risk factors for developing MOH, and others that contribute to increasing headache frequency in general (TABLE 35,14,18-23). Some risk factors are common to each. All are important to address because some are modifiable.

Continue to: Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology. The pathophysiology and psychology behind MOH are largely unknown. Physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes have been demonstrated in patients with MOH, both of which are reversible upon withdrawal of medication.23 Genetic factors and changes in hormone and neurotransmitter levels are found in MOH patients; this is not the case in patients who have an episodic headache pattern only.24
Presentation. Diagnostic criteria for MOH do not include clinical characteristics. Typically, the phenotype of MOH in a given patient is similar to the underlying primary headache25—although this principle can be complicated to tease out because these medications can suppress some symptoms. Diagnosis of a primary headache disorder should be documented along with the diagnosis of MOH.
Medication overuse can exist without MOH: Not every patient who frequently uses an abortive medication develops MOH.
Treatment is multifaceted—and can become complex
Mainstays of treatment of MOH are education about the disorder and detoxification from the overused agent, although specific treatments can differ depending on the agent involved, the frequency and duration of its use, and a patient’s behavioral patterns and psychiatric comorbidities. Often, a daily medication to prevent headache is considered upon, or after, withdrawal of the offending agent. The timing of introducing a preventive might impact its effectiveness. Some refractory cases require more intensive therapy, including hospitalization at a specialized tertiary center.
But before we look at detoxification from an overused agent, it’s important to review one of the best strategies of all in combatting MOH.
Continue to: First and best strategy
First and best strategy: Avoid onset of MOH
Select an appropriate abortive to reduce the risk of MOH. With regard to specific acute headache medications, some nuances other than type of headache should be considered. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are recommended as abortive therapy by the American Headache Society for their efficacy, favorable adverse effect profile, and low cost. NSAIDs are protective against development of MOH if a patient’s baseline headache frequency is < 10/mo; at a frequency of 10 to 14 d/mo, however, the risk of MOH increases when using an NSAID.6 A similar effect has been seen with triptans.16 Longer-acting NSAIDs, such as nabumetone and naproxen, have been proposed as less likely to cause MOH, and are even used as bridging therapy sometimes (as long as neither of these was the overused medication).26
The time it takes to develop MOH is shortest with triptans, followed by ergots, then analgesics.27
Prospective cohort studies6,16 have shown that barbiturates and opioids are more likely to induce MOH; for that reason, agents in these analgesic classes are almost universally avoided unless no other medically acceptable options exist. Using barbiturate-containing compounds or opioids > 4 d/mo exponentially increases the likelihood of MOH.
Promising preclinical data demonstrate that the gepant, or small-molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, class of medications used as abortive therapy does not induce medication overuse cutaneous allodynia.28
Provide education. Primary prevention of MOH involves (1) increasing patients’ awareness of how to take medications appropriately and (2) restricting intake of over-the-counter abortive medications. Often, the expert recommendation is to limit abortives to approximately 2 d/wk because more frequent use places patients at risk of further increased use and subsequent MOH.
Continue to: A randomized controlled trial in Norway...
A randomized controlled trial in Norway compared outcomes in 2 groups of patients with MOH: One group was given advice on the disorder by a physician; the other group was not provided with advice. In the “business-as-usual” group, there was no significant improvement; however, when general practitioners provided simple advice (lasting roughly 9 minutes) about reducing abortive medication use to a safe level and cautioned patients that they would be “feeling worse before feeling better,” headache days were reduced by approximately 8 per month and medication days, by 16 per month.2
A subsequent, long-term follow-up study29 of patients from the Norway trial2 who had been given advice and education showed a relapse rate (ie, into overuse of headache medication) of only 8% and sustained reduction of headache days and medication use at 16 months.
Offer support and other nondrug interventions. A recent review of 3 studies23 recommended that extra support for patients from a headache nurse, close follow-up, keeping an electronic diary that provides feedback, and undertaking a short course of psychotherapy can reduce medication overuse and prevent relapse.
If MOH develops, initiate withdrawal, introduce a preventive
Withdraw overused medication. Most current evidence suggests that withdrawal of the offending agent is the most effective factor in reducing headache days and improving quality of life. A randomized controlled trial compared the effects of (1) complete and immediate withdrawal of an abortive medication with (2) reducing its use (ie, limiting intake to 2 d/wk), on headache frequency, disability, and quality of life.30 There was a reduction of headache days in both groups; however, reduction was much greater at 2 months in the complete withdrawal group than in the restricted intake group (respectively, a 41% and a 26% reduction in headache days per month). This effect was sustained at 6 and 12 months in both groups. The study confirmed the results of earlier research2,15: Abrupt withdrawal leads to reversion to an episodic pattern at 2 to 6 months in approximately 40% to 60% of patients.
More studies are needed to determine the most appropriate treatment course for MOH; however, complete withdrawal of the causative drug is the most important intervention.
Continue to: Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment
Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment. Use of sodium valproate, in addition to medication overuse detoxification, led to a significant reduction in headache days and improvement in quality of life at 12 weeks but no difference after 24 weeks, compared with detoxification alone in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.31
A study of 61 patients showed a larger reduction (by 7.2 d/mo) in headache frequency with any preventive medication in addition to medication withdrawal, compared to withdrawal alone (by 4.1 d/mo) after 3 months; however, the relative benefit was gone at 6 months.32
A study of 98 patients compared immediate and delayed initiation of preventive medication upon withdrawal of overused abortive medication.33 Response was defined as a > 50% reduction in headache frequency and was similar in both groups; results showed a 28% response with immediate initiation of a preventive; a 23% response with delayed (ie, 2 months after withdrawal) initiation; and a 48% response in both groups at 12 months.
Collectively, these studies suggest that adding a preventive medication at the time of withdrawal has the potential to reduce headache frequency more quickly than withdrawal alone. However, after 3 to 6 months, the outcome of reduced headache frequency is the same whether or not a preventive medication is used—as long as the offending agent has been withdrawn.
Do preventives work without withdrawing overused medication? Patients with MOH often show little or no improvement with addition of a preventive medication only; their response to a preventive improves after withdrawal of the overused medication. Patients without previous headache improvement after addition of a preventive, who also did not improve 2 months after withdrawal, then demonstrated an overall reduction in headache by 26% when a preventive was reintroduced after withdrawal.2
Continue to: The research evidence for preventives
The research evidence for preventives. Medications for headache prevention have not been extensively evaluated specifically for treating MOH. Here is what’s known:
- Flunarizine, amitriptyline, and beta-blockers usually are ineffective for MOH.24
- Results for topiramate are mixed: A small, double-blind, placebo-controlled chronic migraine study in Europe showed that, in a subgroup of patients with MOH, topiramate led to a small but significant reduction (3.5 d/mo) in headache frequency, compared to placebo.27 A similar study done in the United States did not show a significant difference between the active-treatment and placebo groups.34
- Findings regarding onabotulinumtoxinA are intriguing: In a posthoc analysis of onabotulinumtoxinA to treat chronic migraine, patients with MOH who did not undergo detoxification had an 8 d/mo greater reduction in headache, compared to placebo.35 However, when compared to placebo in conjunction with detoxification, onabotulinumtoxinA demonstrated no benefit.36
- Newer CGRP antagonist and CGRP receptor antagonist monoclonal antibodies are successful preventive medications that have demonstrated a reduction in acute medication use days per month and headache days per month37; these compounds have not been compared to withdrawal alone.
Reducing the severity and duration of withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal from overused abortive headache medications can lead to worsening headache, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia, sleep disturbances, restlessness, anxiety, and nervousness. Symptoms usually last 2 to 10 days but can persist for as long as 4 weeks; duration of withdrawal symptoms varies with the medication that is being overused. In patients who have used a triptan, for example, mean duration of withdrawal is 4.1 days; ergotamine, 6.7 days; and NSAIDs, 9.5 days.23 Tapered withdrawal is sometimes recommended with opioids and barbiturates to reduce withdrawal symptoms. It is unclear whether starting a preventive medication during withdrawal assists in reducing withdrawal symptoms.38
Bridging therapy to reduce symptoms of withdrawal is often provided despite debatable utility. Available evidence does not favor one agent or method but suggests some strategies that could be helpful:
- A prednisone taper has a potential role during the first 6 days of withdrawal by reducing rebound headache and withdrawal symptoms39; however, oral prednisolone has been shown to have no benefit.40
- Alone, IV methylprednisolone seems not to be of benefit; however, in a retrospective study of 94 patients, IV methylprednisolone plus diazepam for 5 days led to a significant reduction in headache frequency and drug consumption that was sustained after 3 months.41
- Celecoxib was compared to prednisone over a 20-day course: a celecoxib dosage of 400 mg/d for the first 5 days, tapered by 100 mg every 5 days, and an oral prednisone dosage of 75 mg/d for the first 5 days, then tapered every 5 days. Patients taking celecoxib had lower headache intensity but there was no difference in headache frequency and acute medication intake between the groups.42
Other strategies. Using antiemetics and NSAIDs to reduce withdrawal symptoms is widely practiced, but no placebo-controlled trials have been conducted to support this strategy.
Patients in withdrawal might be more likely to benefit from inpatient care if they have a severe comorbidity, such as opioid or barbiturate use; failure to respond to, tolerate, or adhere to treatment; or relapse after withdrawal.38
Continue to: Cognitive behavioral therapy...
Cognitive behavioral therapy, exercise, a headache diary, and biofeedback should be considered in every patient’s treatment strategy because a multidisciplinary approach increases adherence and leads to improvement in headache frequency and a decrease in disability and medication use.43
Predictors of Tx success
A prospective cohort study determined that the rate of MOH relapse is 31% at 6 months, 41% at 1 year, and 45% at 4 years, with the highest risk of relapse during the first year.44 Looking at the correlation between type of medication overused and relapse rate, the research indicates that
- triptans have the lowest risk of relapse,44
- simple analgesics have a higher risk of relapse than triptans,22,44 and
- opioids have the highest risk of relapse.22
Where the data don’t agree. Data on combination analgesics and on ergots are conflicting.22 In addition, data on whether the primary type of headache predicts relapse rate conflict; however, migraine might predict a better outcome than tension-type headache.22
To recap and expand: Management pearls
The major goals of headache management generally are to rule out secondary headache, reach a correct diagnosis, reduce overall headache frequency, and provide effective abortive medication. A large component of reducing headache frequency is addressing and treating medication overuse.
Seek to understand the nature of the patient’s headache disorder. Components of the history are key in identifying the underlying headache diagnosis and ruling out other, more concerning secondary headache diagnoses. The ICHD-3 is an excellent resource for treating headache disorders because the classification lists specific diagnostic criteria for all recognized headache diagnoses.
Continue to: Medication withdrawal...
Medication withdrawal—with or without preventive medication—should reduce the frequency of MOH in 2 or 3 months. If headache does not become less frequent, however, the headache diagnosis might need to be reconsidered. Minimizing the use of abortive medication is generally recommended, but reduction or withdrawal of these medications does not guarantee that patients will revert to an episodic pattern of headache.
Treating withdrawal symptoms is a reasonable approach in some patients, but evidence does not support routinely providing bridging therapy.
Apply preventives carefully. Abortive medication withdrawal should generally be completed before initiating preventive medication; however, over the short term, starting preventive therapy while withdrawing the overused medication could assist in reducing headache frequency rapidly. This strategy can put patients at risk of medication adverse effects and using the medications longer than necessary, yet might be reasonable in certain patients, given their comorbidities, risk of relapse, and physician and patient preference. A preventive medication for an individual patient should generally be chosen in line with recommendations of the American Academy of Neurology45 and on the basis of the history and comorbidities.
Provide education, which is essential to lowering barriers to success. Patients with MOH must be counseled to understand that (1) a headache treatment that is supposed to be making them feel better is, in fact, making them feel worse and (2) they will get worse before they get better. Many patients are afraid to be without medication to use as needed. It is helpful to educate them on the different types of treatments (abortive, preventive); how MOH interferes with headache prophylaxis and medication efficacy; how MOH alters brain function (ie, aforementioned physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes23); and that such change is reversible when medication is withdrawn.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author thanks Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, for his support and editing assistance with the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Allison Crain, MD, 2927 N 7th Avenue, Phoenix, AZ 85013; [email protected].
Medication overuse headache (MOH), a secondary headache diagnosis, is a prevalent phenomenon that complicates headache diagnosis and treatment, increases the cost of care, and reduces quality of life. Effective abortive medication is essential for the headache sufferer; when an abortive is used too frequently, however, headache frequency increases—potentially beginning a cycle in which the patient then takes more medication to abort the headache. Over time, the patient suffers from an ever-increasing number of headaches, takes even more abortive medication, and so on. In the presence of MOH, there is a reduction in pain response to preventive and abortive treatments; when medication overuse is eliminated, pain response improves.1
Although MOH is well recognized among headache specialists, the condition is often overlooked in primary care. Since headache is a top complaint in primary care, however, and prevention is a major goal in family medicine, the opportunity for you to recognize, treat, and prevent MOH is significant. In fact, a randomized controlled trial showed that brief patient education about headache care and MOH provided by a primary care physician can lead to a significant reduction in headache frequency among patients with MOH.2
This article reviews the recognition and diagnosis of MOH, based on historical features and current criteria; addresses risk factors for abortive medication overuse and how to withdraw an offending agent; and explores the value of bridging and preventive therapies to reduce the overall frequency of headache.

What defines MOH?
Typically, MOH is a chronification of a primary headache disorder. However, in patients with a history of migraine who are undergoing treatment for another chronic pain condition with an opioid or other analgesic, MOH can be induced.3 An increase in the frequency of headache raises the specter of a concomitant increase in the level of disability4; psychiatric comorbidity5; and more headache days, with time lost from school and work.
The Migraine Disability Assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire, a validated instrument that helps the provider (1) measure the impact that headache has on a patient’s life and (2) follow treatment progress, also provides information to employers and insurance companies on treatment coverage and the need for work modification. The MIDAS score is 3 times higher in patients with MOH than in patients with episodic migraine.6,7
The annual associated cost per person of MOH has been estimated at $4000, resulting in billions of dollars in associated costs8; most of these costs are related to absenteeism and disability. After detoxification for MOH, annual outpatient medication costs are reduced by approximately 24%.9
Efforts to solve a common problem create another
Headache affects nearly 50% of the general population worldwide,10 accounting for about 4% of primary care visits11 and approximately 20% of outpatient neurology consultations.12 Although inpatient stays for headache are approximately half the duration of the overall average hospital stay, headache accounts for 3% of admissions.13 According to the Global Burden of Disease study, tension-type headache, migraine, and MOH are the 3 most common headache disorders.10 Headache is the second leading cause of disability among people 15 to 49 years of age.10
Continue to: The prevalence of MOH...
The prevalence of MOH in the general population is 2%.7,14,15 A population-based study showed that the rate of progression from episodic headache (< 15 d/mo) to chronic headache (≥ 15 d/mo) in the general population is 2.5% per year16; however, progression to chronic headache is 14% per year in patients with medication overuse. One-third of the general population with chronic migraine overuses symptomatic medication; in US headache clinics, roughly one-half of patients with chronic headache overuse acute medication.6
Definitions and diagnosis
MOH is a secondary headache diagnosis in the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) (TABLE 1),17 which lists diagnostic criteria for recognized headache disorders.

Terminology. MOH has also been called rebound headache, drug-induced headache, and transformed migraine, but these terms are outdated and are not formal diagnoses. Patients sometimes refer to substance-withdrawal headaches (not discussed in this article) as rebound headaches, so clarity is important when discussing headache with patients: namely, that MOH is an exacerbation of an existing headache condition caused by overuse of abortive headache medications, including analgesics, combination analgesics, triptans, barbiturates, and opioids.
MOH was recognized in the early 1950s and fully differentiated as a diagnosis in 2005 in the second edition of the ICHD. The disorder is subcategorized by offending abortive agent (TABLE 217) because the frequency of analgesic use required to develop MOH differs by agent.

Risk factors for MOH and chronification of a primary headache disorder. There are several risk factors for developing MOH, and others that contribute to increasing headache frequency in general (TABLE 35,14,18-23). Some risk factors are common to each. All are important to address because some are modifiable.

Continue to: Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology. The pathophysiology and psychology behind MOH are largely unknown. Physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes have been demonstrated in patients with MOH, both of which are reversible upon withdrawal of medication.23 Genetic factors and changes in hormone and neurotransmitter levels are found in MOH patients; this is not the case in patients who have an episodic headache pattern only.24
Presentation. Diagnostic criteria for MOH do not include clinical characteristics. Typically, the phenotype of MOH in a given patient is similar to the underlying primary headache25—although this principle can be complicated to tease out because these medications can suppress some symptoms. Diagnosis of a primary headache disorder should be documented along with the diagnosis of MOH.
Medication overuse can exist without MOH: Not every patient who frequently uses an abortive medication develops MOH.
Treatment is multifaceted—and can become complex
Mainstays of treatment of MOH are education about the disorder and detoxification from the overused agent, although specific treatments can differ depending on the agent involved, the frequency and duration of its use, and a patient’s behavioral patterns and psychiatric comorbidities. Often, a daily medication to prevent headache is considered upon, or after, withdrawal of the offending agent. The timing of introducing a preventive might impact its effectiveness. Some refractory cases require more intensive therapy, including hospitalization at a specialized tertiary center.
But before we look at detoxification from an overused agent, it’s important to review one of the best strategies of all in combatting MOH.
Continue to: First and best strategy
First and best strategy: Avoid onset of MOH
Select an appropriate abortive to reduce the risk of MOH. With regard to specific acute headache medications, some nuances other than type of headache should be considered. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are recommended as abortive therapy by the American Headache Society for their efficacy, favorable adverse effect profile, and low cost. NSAIDs are protective against development of MOH if a patient’s baseline headache frequency is < 10/mo; at a frequency of 10 to 14 d/mo, however, the risk of MOH increases when using an NSAID.6 A similar effect has been seen with triptans.16 Longer-acting NSAIDs, such as nabumetone and naproxen, have been proposed as less likely to cause MOH, and are even used as bridging therapy sometimes (as long as neither of these was the overused medication).26
The time it takes to develop MOH is shortest with triptans, followed by ergots, then analgesics.27
Prospective cohort studies6,16 have shown that barbiturates and opioids are more likely to induce MOH; for that reason, agents in these analgesic classes are almost universally avoided unless no other medically acceptable options exist. Using barbiturate-containing compounds or opioids > 4 d/mo exponentially increases the likelihood of MOH.
Promising preclinical data demonstrate that the gepant, or small-molecule calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, class of medications used as abortive therapy does not induce medication overuse cutaneous allodynia.28
Provide education. Primary prevention of MOH involves (1) increasing patients’ awareness of how to take medications appropriately and (2) restricting intake of over-the-counter abortive medications. Often, the expert recommendation is to limit abortives to approximately 2 d/wk because more frequent use places patients at risk of further increased use and subsequent MOH.
Continue to: A randomized controlled trial in Norway...
A randomized controlled trial in Norway compared outcomes in 2 groups of patients with MOH: One group was given advice on the disorder by a physician; the other group was not provided with advice. In the “business-as-usual” group, there was no significant improvement; however, when general practitioners provided simple advice (lasting roughly 9 minutes) about reducing abortive medication use to a safe level and cautioned patients that they would be “feeling worse before feeling better,” headache days were reduced by approximately 8 per month and medication days, by 16 per month.2
A subsequent, long-term follow-up study29 of patients from the Norway trial2 who had been given advice and education showed a relapse rate (ie, into overuse of headache medication) of only 8% and sustained reduction of headache days and medication use at 16 months.
Offer support and other nondrug interventions. A recent review of 3 studies23 recommended that extra support for patients from a headache nurse, close follow-up, keeping an electronic diary that provides feedback, and undertaking a short course of psychotherapy can reduce medication overuse and prevent relapse.
If MOH develops, initiate withdrawal, introduce a preventive
Withdraw overused medication. Most current evidence suggests that withdrawal of the offending agent is the most effective factor in reducing headache days and improving quality of life. A randomized controlled trial compared the effects of (1) complete and immediate withdrawal of an abortive medication with (2) reducing its use (ie, limiting intake to 2 d/wk), on headache frequency, disability, and quality of life.30 There was a reduction of headache days in both groups; however, reduction was much greater at 2 months in the complete withdrawal group than in the restricted intake group (respectively, a 41% and a 26% reduction in headache days per month). This effect was sustained at 6 and 12 months in both groups. The study confirmed the results of earlier research2,15: Abrupt withdrawal leads to reversion to an episodic pattern at 2 to 6 months in approximately 40% to 60% of patients.
More studies are needed to determine the most appropriate treatment course for MOH; however, complete withdrawal of the causative drug is the most important intervention.
Continue to: Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment
Consider withdrawal plus preventive treatment. Use of sodium valproate, in addition to medication overuse detoxification, led to a significant reduction in headache days and improvement in quality of life at 12 weeks but no difference after 24 weeks, compared with detoxification alone in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.31
A study of 61 patients showed a larger reduction (by 7.2 d/mo) in headache frequency with any preventive medication in addition to medication withdrawal, compared to withdrawal alone (by 4.1 d/mo) after 3 months; however, the relative benefit was gone at 6 months.32
A study of 98 patients compared immediate and delayed initiation of preventive medication upon withdrawal of overused abortive medication.33 Response was defined as a > 50% reduction in headache frequency and was similar in both groups; results showed a 28% response with immediate initiation of a preventive; a 23% response with delayed (ie, 2 months after withdrawal) initiation; and a 48% response in both groups at 12 months.
Collectively, these studies suggest that adding a preventive medication at the time of withdrawal has the potential to reduce headache frequency more quickly than withdrawal alone. However, after 3 to 6 months, the outcome of reduced headache frequency is the same whether or not a preventive medication is used—as long as the offending agent has been withdrawn.
Do preventives work without withdrawing overused medication? Patients with MOH often show little or no improvement with addition of a preventive medication only; their response to a preventive improves after withdrawal of the overused medication. Patients without previous headache improvement after addition of a preventive, who also did not improve 2 months after withdrawal, then demonstrated an overall reduction in headache by 26% when a preventive was reintroduced after withdrawal.2
Continue to: The research evidence for preventives
The research evidence for preventives. Medications for headache prevention have not been extensively evaluated specifically for treating MOH. Here is what’s known:
- Flunarizine, amitriptyline, and beta-blockers usually are ineffective for MOH.24
- Results for topiramate are mixed: A small, double-blind, placebo-controlled chronic migraine study in Europe showed that, in a subgroup of patients with MOH, topiramate led to a small but significant reduction (3.5 d/mo) in headache frequency, compared to placebo.27 A similar study done in the United States did not show a significant difference between the active-treatment and placebo groups.34
- Findings regarding onabotulinumtoxinA are intriguing: In a posthoc analysis of onabotulinumtoxinA to treat chronic migraine, patients with MOH who did not undergo detoxification had an 8 d/mo greater reduction in headache, compared to placebo.35 However, when compared to placebo in conjunction with detoxification, onabotulinumtoxinA demonstrated no benefit.36
- Newer CGRP antagonist and CGRP receptor antagonist monoclonal antibodies are successful preventive medications that have demonstrated a reduction in acute medication use days per month and headache days per month37; these compounds have not been compared to withdrawal alone.
Reducing the severity and duration of withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal from overused abortive headache medications can lead to worsening headache, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia, sleep disturbances, restlessness, anxiety, and nervousness. Symptoms usually last 2 to 10 days but can persist for as long as 4 weeks; duration of withdrawal symptoms varies with the medication that is being overused. In patients who have used a triptan, for example, mean duration of withdrawal is 4.1 days; ergotamine, 6.7 days; and NSAIDs, 9.5 days.23 Tapered withdrawal is sometimes recommended with opioids and barbiturates to reduce withdrawal symptoms. It is unclear whether starting a preventive medication during withdrawal assists in reducing withdrawal symptoms.38
Bridging therapy to reduce symptoms of withdrawal is often provided despite debatable utility. Available evidence does not favor one agent or method but suggests some strategies that could be helpful:
- A prednisone taper has a potential role during the first 6 days of withdrawal by reducing rebound headache and withdrawal symptoms39; however, oral prednisolone has been shown to have no benefit.40
- Alone, IV methylprednisolone seems not to be of benefit; however, in a retrospective study of 94 patients, IV methylprednisolone plus diazepam for 5 days led to a significant reduction in headache frequency and drug consumption that was sustained after 3 months.41
- Celecoxib was compared to prednisone over a 20-day course: a celecoxib dosage of 400 mg/d for the first 5 days, tapered by 100 mg every 5 days, and an oral prednisone dosage of 75 mg/d for the first 5 days, then tapered every 5 days. Patients taking celecoxib had lower headache intensity but there was no difference in headache frequency and acute medication intake between the groups.42
Other strategies. Using antiemetics and NSAIDs to reduce withdrawal symptoms is widely practiced, but no placebo-controlled trials have been conducted to support this strategy.
Patients in withdrawal might be more likely to benefit from inpatient care if they have a severe comorbidity, such as opioid or barbiturate use; failure to respond to, tolerate, or adhere to treatment; or relapse after withdrawal.38
Continue to: Cognitive behavioral therapy...
Cognitive behavioral therapy, exercise, a headache diary, and biofeedback should be considered in every patient’s treatment strategy because a multidisciplinary approach increases adherence and leads to improvement in headache frequency and a decrease in disability and medication use.43
Predictors of Tx success
A prospective cohort study determined that the rate of MOH relapse is 31% at 6 months, 41% at 1 year, and 45% at 4 years, with the highest risk of relapse during the first year.44 Looking at the correlation between type of medication overused and relapse rate, the research indicates that
- triptans have the lowest risk of relapse,44
- simple analgesics have a higher risk of relapse than triptans,22,44 and
- opioids have the highest risk of relapse.22
Where the data don’t agree. Data on combination analgesics and on ergots are conflicting.22 In addition, data on whether the primary type of headache predicts relapse rate conflict; however, migraine might predict a better outcome than tension-type headache.22
To recap and expand: Management pearls
The major goals of headache management generally are to rule out secondary headache, reach a correct diagnosis, reduce overall headache frequency, and provide effective abortive medication. A large component of reducing headache frequency is addressing and treating medication overuse.
Seek to understand the nature of the patient’s headache disorder. Components of the history are key in identifying the underlying headache diagnosis and ruling out other, more concerning secondary headache diagnoses. The ICHD-3 is an excellent resource for treating headache disorders because the classification lists specific diagnostic criteria for all recognized headache diagnoses.
Continue to: Medication withdrawal...
Medication withdrawal—with or without preventive medication—should reduce the frequency of MOH in 2 or 3 months. If headache does not become less frequent, however, the headache diagnosis might need to be reconsidered. Minimizing the use of abortive medication is generally recommended, but reduction or withdrawal of these medications does not guarantee that patients will revert to an episodic pattern of headache.
Treating withdrawal symptoms is a reasonable approach in some patients, but evidence does not support routinely providing bridging therapy.
Apply preventives carefully. Abortive medication withdrawal should generally be completed before initiating preventive medication; however, over the short term, starting preventive therapy while withdrawing the overused medication could assist in reducing headache frequency rapidly. This strategy can put patients at risk of medication adverse effects and using the medications longer than necessary, yet might be reasonable in certain patients, given their comorbidities, risk of relapse, and physician and patient preference. A preventive medication for an individual patient should generally be chosen in line with recommendations of the American Academy of Neurology45 and on the basis of the history and comorbidities.
Provide education, which is essential to lowering barriers to success. Patients with MOH must be counseled to understand that (1) a headache treatment that is supposed to be making them feel better is, in fact, making them feel worse and (2) they will get worse before they get better. Many patients are afraid to be without medication to use as needed. It is helpful to educate them on the different types of treatments (abortive, preventive); how MOH interferes with headache prophylaxis and medication efficacy; how MOH alters brain function (ie, aforementioned physiologic changes in pain processing and functional imaging changes23); and that such change is reversible when medication is withdrawn.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author thanks Jeffrey Curtis, MD, MPH, for his support and editing assistance with the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Allison Crain, MD, 2927 N 7th Avenue, Phoenix, AZ 85013; [email protected].
1. Zeeberg P, Olesen J, Jensen R. Discontinuation of medication overuse in headache patients: recovery of therapeutic responsiveness. Cephalalgia. 2006;26:1192-1198.
2. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Vetvik KG, et al. Brief intervention for medication-overuse headache in primary care. The BIMOH study: a double-blind pragmatic cluster randomised parallel controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:505-512.
3. Bahra A, Walsh M, Menon S, et al. Does chronic daily headache arise de novo in association with regular use of analgesics? Headache. 2003;43:179-190.
4. Blumenfeld AM, Varon SF, Wilcox TK, et al. Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS) Cephalalgia. 2011;31:301-315.
5. Chu H-T, Liang C-S, Lee J-T, et al. Associations between depression/anxiety and headache frequency in migraineurs: a cross-sectional study. Headache. 2018;58:407-415.
6. Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Excessive acute migraine medication use and migraine progression. Neurology. 2008;71:1821-1828.
7. Colás R, Muñoz P, Temprano R, et al. Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse: epidemiology and impact on quality of life. Neurology. 2004;62:1338-1342.
8. Linde M, Gustavsson A, Stovner LJ, et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: the Eurolight project. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19:703-711.
9. Shah AM, Bendtsen L, Zeeberg P, et al. Reduction of medication costs after detoxification for medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2013;53:665-672.
10. . Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:954-976.
11. Kernick D, Stapley S, Goadsby PJ, et al. What happens to new-onset headache presenting to primary care? A case–cohort study using electronic primary care records. Cephalalgia. 2008;28:1188-1195.
12. Stone J, Carson A, Duncan R, et al. Who is referred to neurology clinics?—the diagnoses made in 3781 new patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:747-751.
13. Munoz-Ceron J, Marin-Careaga V, L, et al. Headache at the emergency room: etiologies, diagnostic usefulness of the ICHD 3 criteria, red and green flags. PloS One. 2019;14:e0208728.
14. Evers S, Marziniak M. Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment of medication-overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:391-401.
15. Tassorelli C, Jensen R, Allena M, et al; the . A consensus protocol for the management of medication-overuse headache: evaluation in a multicentric, multinational study. Cephalalgia. 2014;34:645-655.
16. Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, et al. Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study. Headache. 2008;48:1157-1168.
17. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:1-211.
18. Ferrari A, Leone S, Vergoni AV, et al. Similarities and differences between chronic migraine and episodic migraine. Headache. 2007;47:65-72.
19. Hagen K, Linde M, Steiner TJ, et al. Risk factors for medication-overuse headache: an 11-year follow-up study. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Studies. Pain. 2012;153:56-61.
20. Katsarava Z, Schneewiess S, Kurth T, et al. Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology. 2004;62:788-790.
21. Lipton RB, Fanning KM, Buse DC, et al. Migraine progression in subgroups of migraine based on comorbidities: results of the CaMEO study. Neurology. 2019;93:e2224-e2236.
22. Munksgaard SB, Madsen SK, Wienecke T. Treatment of medication overuse headache—a review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2019;139:405-414.
23. Ferraro S, Grazzi L, Mandelli M, et al. Pain processing in medication overuse headache: a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study. Pain Med. 2012;13:255-262.
24. Diener H-C, Holle D, Solbach K, et al. Medication-overuse headache: risk factors, pathophysiology and management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:575-583.
25. Limmroth V, Katsarava Z, Fritsche G, et al. Features of medication overuse headache following overuse of different acute headache drugs. Neurology. 2002;59:1011-1014.
26. Mauskop A, ed. Migraine and Headache. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2013.
27. Diener H-C, Bussone G, Van Oene JC, et al; . Topiramate reduces headache days in chronic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2007;27:814-823.
28. Navratilova E, Behravesh S, Oyarzo J, et al. Ubrogepant does not induce latent sensitization in a preclinical model of medication overuse headache Cephalalgia. 2020;40:892-902.
29. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Russell MB, et al. Lasting improvement of medication-overuse headache after brief intervention—a long-term follow-up in primary care. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:883-891.
30. Carlsen LN, Munksgaard SB, Jensen RH, et al. Complete detoxification is the most effective treatment of medication-overuse headache: a randomized controlled open-label trial. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:225-236.
31. Sarchielli P, Messina P, Cupini LM, et al; SAMOHA Study Group. Sodium valproate in migraine without aura and medication overuse headache: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;24:1289-1297.
32. Hagen K, Stovner LJ. A randomized controlled trial on medication-overuse headache: outcome after 1 and 4 years. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2011;124(suppl 191):38-43.
33. Munksgaard SB, Bendtsen L, Jensen RH. Detoxification of medication-overuse headache by a multidisciplinary treatment programme is highly effective: a comparison of two consecutive treatment methods in an open-label design. Cephalalgia. 2012;32:834-844.
34. Silberstein S, Lipton R, Dodick D, et al. Topiramate treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of quality of life and other efficacy measures. Headache. 2009;49:1153-1162.
35. Silberstein SD, Blumenfeld AM, Cady RK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: PREEMPT 24-week pooled subgroup analysis of patients who had acute headache medication overuse at baseline. J Neurol Sci. 2013;331:48-56.
36. Sandrini G, Perrotta A, Tassorelli C, et al. Botulinum toxin type-A in the prophylactic treatment of medication-overuse headache: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J Headache Pain. 2011;12:427-433.
37. Tepper SJ. CGRP and headache: a brief review. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(suppl 1):99-105.
38. Diener H-C, Dodick D, Evers S, et al. Pathophysiology, prevention and treatment of medication overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:891-902.
39. Krymchantowski AV, Barbosa JS. Prednisone as initial treatment of analgesic-induced daily headache. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:107-113.
40. Bøe MG, Mygland A, Salvesen R. Prednisolone does not reduce withdrawal headache: a randomized, double-blind study. Neurology. 2007;69:26-31.
41. Paolucci M, Altamura C, Brunelli N, et al. Methylprednisolone plus diazepam i.v. as bridge therapy for medication overuse headache. Neurol Sci. 2017;38:2025-2029.
42. Taghdiri F, Togha M, Razeghi Jahromi S, et al. Celecoxib vs prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Headache. 2015;55:128-135.
43. Ramsey RR, Ryan JL, Hershey AD, et al. Treatment adherence in patients with headache: a systematic review. Headache. 2014;54:795-816.
44. Katsarava Z, Muessig M, Dzagnidze A, et al. Medication overuse headache: rates and predictors for relapse in a 4-year prospective study. Cephalalgia. 2005;25:12-15.
45. Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, et al; . Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology. 2012; 78:1137-1145.
1. Zeeberg P, Olesen J, Jensen R. Discontinuation of medication overuse in headache patients: recovery of therapeutic responsiveness. Cephalalgia. 2006;26:1192-1198.
2. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Vetvik KG, et al. Brief intervention for medication-overuse headache in primary care. The BIMOH study: a double-blind pragmatic cluster randomised parallel controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2015;86:505-512.
3. Bahra A, Walsh M, Menon S, et al. Does chronic daily headache arise de novo in association with regular use of analgesics? Headache. 2003;43:179-190.
4. Blumenfeld AM, Varon SF, Wilcox TK, et al. Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS) Cephalalgia. 2011;31:301-315.
5. Chu H-T, Liang C-S, Lee J-T, et al. Associations between depression/anxiety and headache frequency in migraineurs: a cross-sectional study. Headache. 2018;58:407-415.
6. Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Excessive acute migraine medication use and migraine progression. Neurology. 2008;71:1821-1828.
7. Colás R, Muñoz P, Temprano R, et al. Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse: epidemiology and impact on quality of life. Neurology. 2004;62:1338-1342.
8. Linde M, Gustavsson A, Stovner LJ, et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: the Eurolight project. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19:703-711.
9. Shah AM, Bendtsen L, Zeeberg P, et al. Reduction of medication costs after detoxification for medication-overuse headache. Headache. 2013;53:665-672.
10. . Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:954-976.
11. Kernick D, Stapley S, Goadsby PJ, et al. What happens to new-onset headache presenting to primary care? A case–cohort study using electronic primary care records. Cephalalgia. 2008;28:1188-1195.
12. Stone J, Carson A, Duncan R, et al. Who is referred to neurology clinics?—the diagnoses made in 3781 new patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:747-751.
13. Munoz-Ceron J, Marin-Careaga V, L, et al. Headache at the emergency room: etiologies, diagnostic usefulness of the ICHD 3 criteria, red and green flags. PloS One. 2019;14:e0208728.
14. Evers S, Marziniak M. Clinical features, pathophysiology, and treatment of medication-overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:391-401.
15. Tassorelli C, Jensen R, Allena M, et al; the . A consensus protocol for the management of medication-overuse headache: evaluation in a multicentric, multinational study. Cephalalgia. 2014;34:645-655.
16. Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, et al. Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study. Headache. 2008;48:1157-1168.
17. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:1-211.
18. Ferrari A, Leone S, Vergoni AV, et al. Similarities and differences between chronic migraine and episodic migraine. Headache. 2007;47:65-72.
19. Hagen K, Linde M, Steiner TJ, et al. Risk factors for medication-overuse headache: an 11-year follow-up study. The Nord-Trøndelag Health Studies. Pain. 2012;153:56-61.
20. Katsarava Z, Schneewiess S, Kurth T, et al. Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology. 2004;62:788-790.
21. Lipton RB, Fanning KM, Buse DC, et al. Migraine progression in subgroups of migraine based on comorbidities: results of the CaMEO study. Neurology. 2019;93:e2224-e2236.
22. Munksgaard SB, Madsen SK, Wienecke T. Treatment of medication overuse headache—a review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2019;139:405-414.
23. Ferraro S, Grazzi L, Mandelli M, et al. Pain processing in medication overuse headache: a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study. Pain Med. 2012;13:255-262.
24. Diener H-C, Holle D, Solbach K, et al. Medication-overuse headache: risk factors, pathophysiology and management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:575-583.
25. Limmroth V, Katsarava Z, Fritsche G, et al. Features of medication overuse headache following overuse of different acute headache drugs. Neurology. 2002;59:1011-1014.
26. Mauskop A, ed. Migraine and Headache. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2013.
27. Diener H-C, Bussone G, Van Oene JC, et al; . Topiramate reduces headache days in chronic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2007;27:814-823.
28. Navratilova E, Behravesh S, Oyarzo J, et al. Ubrogepant does not induce latent sensitization in a preclinical model of medication overuse headache Cephalalgia. 2020;40:892-902.
29. Kristoffersen ES, Straand J, Russell MB, et al. Lasting improvement of medication-overuse headache after brief intervention—a long-term follow-up in primary care. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:883-891.
30. Carlsen LN, Munksgaard SB, Jensen RH, et al. Complete detoxification is the most effective treatment of medication-overuse headache: a randomized controlled open-label trial. Cephalalgia. 2018;38:225-236.
31. Sarchielli P, Messina P, Cupini LM, et al; SAMOHA Study Group. Sodium valproate in migraine without aura and medication overuse headache: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;24:1289-1297.
32. Hagen K, Stovner LJ. A randomized controlled trial on medication-overuse headache: outcome after 1 and 4 years. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2011;124(suppl 191):38-43.
33. Munksgaard SB, Bendtsen L, Jensen RH. Detoxification of medication-overuse headache by a multidisciplinary treatment programme is highly effective: a comparison of two consecutive treatment methods in an open-label design. Cephalalgia. 2012;32:834-844.
34. Silberstein S, Lipton R, Dodick D, et al. Topiramate treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of quality of life and other efficacy measures. Headache. 2009;49:1153-1162.
35. Silberstein SD, Blumenfeld AM, Cady RK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: PREEMPT 24-week pooled subgroup analysis of patients who had acute headache medication overuse at baseline. J Neurol Sci. 2013;331:48-56.
36. Sandrini G, Perrotta A, Tassorelli C, et al. Botulinum toxin type-A in the prophylactic treatment of medication-overuse headache: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J Headache Pain. 2011;12:427-433.
37. Tepper SJ. CGRP and headache: a brief review. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(suppl 1):99-105.
38. Diener H-C, Dodick D, Evers S, et al. Pathophysiology, prevention and treatment of medication overuse headache. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:891-902.
39. Krymchantowski AV, Barbosa JS. Prednisone as initial treatment of analgesic-induced daily headache. Cephalalgia. 2000;20:107-113.
40. Bøe MG, Mygland A, Salvesen R. Prednisolone does not reduce withdrawal headache: a randomized, double-blind study. Neurology. 2007;69:26-31.
41. Paolucci M, Altamura C, Brunelli N, et al. Methylprednisolone plus diazepam i.v. as bridge therapy for medication overuse headache. Neurol Sci. 2017;38:2025-2029.
42. Taghdiri F, Togha M, Razeghi Jahromi S, et al. Celecoxib vs prednisone for the treatment of withdrawal headache in patients with medication overuse headache: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Headache. 2015;55:128-135.
43. Ramsey RR, Ryan JL, Hershey AD, et al. Treatment adherence in patients with headache: a systematic review. Headache. 2014;54:795-816.
44. Katsarava Z, Muessig M, Dzagnidze A, et al. Medication overuse headache: rates and predictors for relapse in a 4-year prospective study. Cephalalgia. 2005;25:12-15.
45. Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, et al; . Evidence-based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology. 2012; 78:1137-1145.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Avoid prescribing barbiturates or opioids for a headache disorder. A
› Limit use of a headache-abortive medication to twice a week when starting a patient on the drug. C
› Consider providing bridging therapy during detoxification of the overused medication. C
› Do not provide a preventive medication without withdrawing the overused agent. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Unhealthy Alcohol Use May Increase in the Years After Bariatric Surgery
After bariatric surgery, patients have a “much higher” risk of unhealthy alcohol use—even if they had no documented unhealthy drinking at baseline, according to researchers from the Durham Veteran Affairs (VA) Medical Center in North Carolina.
Based on their findings, the researchers estimate that for every 21 patients who undergo laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), on average one from each group will develop unhealthy alcohol use.
The researchers collected electronic health record (EHR) data from 2,608 veterans who underwent LSG or RYGB at any bariatric center in the VA health system between 2008 and 2016, and compared that group with a nonsurgical control group.
Nearly all the patients screened negative for unhealthy alcohol use in the 2-year baseline period; however, their mean AUDIT-C scores and the probability of unhealthy alcohol use both increased significantly 3 to 8 years after surgery when compared with the control group. Eight years after an LSG, the probability was 3.4% higher (7.9% vs 4.5%). Eight years after an RYGB, the probability was 9.2% vs 4.4%, a difference of 4.8%.
The estimated prevalence of unhealthy alcohol use 8 years after bariatric surgery was higher for patients with unhealthy drinking at baseline (30 40%) than it was for those without baseline unhealthy drinking (5 - 10%). However, the probability was significantly higher for patients who had an RYGB than it was for nonsurgical control patients after 8 years, which might reflect alcohol pharmacokinetics changes, the researchers say.
Not drinking alcohol is the safest option after bariatric surgery, the researchers say, given that blood alcohol concentration peaks at higher levels after the operation. They advise monitoring patients long-term, using the three-item AUDIT-C scale. And, importantly, they advise cautioning patients undergoing bariatric surgery that drinking alcohol can escalate, even if they have had no history of drinking above recommended limits.
After bariatric surgery, patients have a “much higher” risk of unhealthy alcohol use—even if they had no documented unhealthy drinking at baseline, according to researchers from the Durham Veteran Affairs (VA) Medical Center in North Carolina.
Based on their findings, the researchers estimate that for every 21 patients who undergo laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), on average one from each group will develop unhealthy alcohol use.
The researchers collected electronic health record (EHR) data from 2,608 veterans who underwent LSG or RYGB at any bariatric center in the VA health system between 2008 and 2016, and compared that group with a nonsurgical control group.
Nearly all the patients screened negative for unhealthy alcohol use in the 2-year baseline period; however, their mean AUDIT-C scores and the probability of unhealthy alcohol use both increased significantly 3 to 8 years after surgery when compared with the control group. Eight years after an LSG, the probability was 3.4% higher (7.9% vs 4.5%). Eight years after an RYGB, the probability was 9.2% vs 4.4%, a difference of 4.8%.
The estimated prevalence of unhealthy alcohol use 8 years after bariatric surgery was higher for patients with unhealthy drinking at baseline (30 40%) than it was for those without baseline unhealthy drinking (5 - 10%). However, the probability was significantly higher for patients who had an RYGB than it was for nonsurgical control patients after 8 years, which might reflect alcohol pharmacokinetics changes, the researchers say.
Not drinking alcohol is the safest option after bariatric surgery, the researchers say, given that blood alcohol concentration peaks at higher levels after the operation. They advise monitoring patients long-term, using the three-item AUDIT-C scale. And, importantly, they advise cautioning patients undergoing bariatric surgery that drinking alcohol can escalate, even if they have had no history of drinking above recommended limits.
After bariatric surgery, patients have a “much higher” risk of unhealthy alcohol use—even if they had no documented unhealthy drinking at baseline, according to researchers from the Durham Veteran Affairs (VA) Medical Center in North Carolina.
Based on their findings, the researchers estimate that for every 21 patients who undergo laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), on average one from each group will develop unhealthy alcohol use.
The researchers collected electronic health record (EHR) data from 2,608 veterans who underwent LSG or RYGB at any bariatric center in the VA health system between 2008 and 2016, and compared that group with a nonsurgical control group.
Nearly all the patients screened negative for unhealthy alcohol use in the 2-year baseline period; however, their mean AUDIT-C scores and the probability of unhealthy alcohol use both increased significantly 3 to 8 years after surgery when compared with the control group. Eight years after an LSG, the probability was 3.4% higher (7.9% vs 4.5%). Eight years after an RYGB, the probability was 9.2% vs 4.4%, a difference of 4.8%.
The estimated prevalence of unhealthy alcohol use 8 years after bariatric surgery was higher for patients with unhealthy drinking at baseline (30 40%) than it was for those without baseline unhealthy drinking (5 - 10%). However, the probability was significantly higher for patients who had an RYGB than it was for nonsurgical control patients after 8 years, which might reflect alcohol pharmacokinetics changes, the researchers say.
Not drinking alcohol is the safest option after bariatric surgery, the researchers say, given that blood alcohol concentration peaks at higher levels after the operation. They advise monitoring patients long-term, using the three-item AUDIT-C scale. And, importantly, they advise cautioning patients undergoing bariatric surgery that drinking alcohol can escalate, even if they have had no history of drinking above recommended limits.
HHS will drop buprenorphine waiver rule for most physicians
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Federal officials on Thursday announced a plan to largely drop the so-called X-waiver requirement for buprenorphine prescriptions for physicians in a bid to remove an administrative procedure widely seen as a barrier to opioid use disorder (OUD) treatment.
The Department of Health & Human Services unveiled new practice guidelines that include an exemption from current certification requirements. The exemption applies to physicians already registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.
A restriction included in the new HHS policy is a limit of treating no more than 30 patients with buprenorphine for OUD at any one time. There is an exception to this limit for hospital-based physicians, such as those working in emergency departments, HHS said.
, such as buprenorphine, and does not apply to methadone. The new guidelines say the date on which they will take effect will be added after publication in the Federal Register. HHS did not immediately answer a request from this news organization for a more specific timeline.
Welcomed change
The change in prescribing rule was widely welcomed, with the American Medical Association issuing a statement endorsing the revision. The AMA and many prescribers and researchers had seen the X-waiver as a hurdle to address the nation’s opioid epidemic.
There were more than 83,000 deaths attributed to drug overdoses in the United States in the 12 months ending in June 2020. This is the highest number of overdose deaths ever recorded in a 12-month period, HHS said in a press release, which cited data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In a tweet about the new policy, Peter Grinspoon, MD, a Boston internist and author of the memoir “Free Refills: A Doctor Confronts His Addiction,” contrasted the relative ease with which clinicians can give medicines that carry a risk for abuse with the challenge that has existed in trying to provide patients with buprenorphine.
“Absolutely insane that we need a special waiver for buprenorphine to TREAT opioid addiction, but not to prescribe oxycodone, Vicodin, etc., which can get people in trouble in the first place!!” Dr. Grinspoon tweeted.
Patrice Harris, MD, chair of the AMA’s Opioid Task Force and the organization’s immediate past president, said removing the X-waiver requirement can help lessen the stigma associated with this OUD treatment. The AMA had urged HHS to change the regulation.
“With this change, office-based physicians and physician-led teams working with patients to manage their other medical conditions can also treat them for their opioid use disorder without being subjected to a separate and burdensome regulatory regime,” Dr. Harris said in the AMA statement.
Researchers have in recent years sought to highlight what they described as missed opportunities for OUD treatment because of the need for the X-waiver.
Buprenorphine is a cost-effective treatment for opioid use disorder, which reduces the risk of injection-related infections and mortality risk, notes a study published online last month in JAMA Network Open.
However, results showed that fewer than 2% of obstetrician-gynecologists who examined women enrolled in Medicaid were trained to prescribe buprenorphine. The study, which was based on data from 31, 211 ob.gyns. who accepted Medicaid insurance, was created to quantify how many were on the list of Drug Addiction Treatment Act buprenorphine-waived clinicians.
The Drug Addiction Treatment Act has required 8 hours of training for physicians and 24 hours for nurse practitioners and physician assistants for the X-waiver needed to prescribe buprenorphine, the investigators report.
‘X the X-waiver’
Only 10% of recent family residency graduates reported being adequately trained to prescribe buprenorphine and only 7% reported actually prescribing the drug, write Kevin Fiscella, MD, University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and colleagues in a 2018 Viewpoint article published in JAMA Psychiatry.
In the article, which was subtitled “X the X Waiver,” they called for deregulation of buprenorphine as a way of mainstreaming treatment for OUD.
“The DATA 2000 has failed – too few physicians have obtained X-waivers,” the authors write. “Regulations reinforce the stigma surrounding buprenorphine prescribers and patients who receive it while constraining access and discouraging patient engagement and retention in treatment.”
The change, announced Jan. 14, leaves in place restrictions on prescribing for clinicians other than physicians. On a call with reporters, Adm. Brett P. Giroir, MD, assistant secretary for health, suggested that federal officials should take further steps to remove hurdles to buprenorphine prescriptions.
“Many people will say this has gone too far,” Dr. Giroir said of the drive to end the X-waiver for clinicians. “But I believe more people will say this has not gone far enough.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood smoking and depression contribute to young adult opioid use
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Machine learning flags key risk factors for suicide attempts
A history of suicidal behaviors or ideation, functional impairment related to mental health disorders, and socioeconomic disadvantage are the three most important risk factors predicting subsequent suicide attempts, new research suggests.
Investigators applied a machine-learning model to data on over 34,500 adults drawn from a large national survey database. After analyzing more than 2,500 survey questions, key areas were identified that yielded the most accurate predictions of who might be at risk for later suicide attempt.
These predictors included experiencing previous suicidal behaviors and ideation or functional impairment because of emotional problems, being at a younger age, having a lower educational achievement, and experiencing a recent financial crisis.
“Our machine learning model confirmed well-known risk factors of suicide attempt, including previous suicidal behavior and depression; and we also identified functional impairment, such as doing activities less carefully or accomplishing less because of emotional problems, as a new important risk,” lead author Angel Garcia de la Garza, PhD candidate in the department of biostatistics, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“We hope our results provide a novel avenue for future suicide risk assessment,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The findings were published online Jan. 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Rich’ dataset
Previous research using machine learning approaches to study nonfatal suicide attempt prediction has focused on high-risk patients in clinical treatment. However, more than one-third of individuals making nonfatal suicide attempts do not receive mental health treatment, Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
To gain further insight into predictors of suicide risk in nonclinical populations, the researchers turned to the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC), a longitudinal survey of noninstitutionalized U.S. adults.
“We wanted to extend our understanding of suicide attempt risk factors beyond high-risk clinical populations to the general adult population; and the richness of the NESARC dataset provides a unique opportunity to do so,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The NESARC surveys were conducted in two waves: Wave 1 (2001-2002) and wave 2 (2004-2005), in which participants self-reported nonfatal suicide attempts in the preceding 3 years since wave 1.
Assessment of wave 1 participants was based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule DSM-IV.
“This survey’s extensive assessment instrument contained a detailed evaluation of substance use, psychiatric disorders, and symptoms not routinely available in electronic health records,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
The wave 1 survey contained 2,805 separate questions. From participants’ responses, the investigators derived 180 variables for three categories: past-year, prior-to-past-year, and lifetime mental disorders.
They then identified 2,978 factors associated with suicide attempts and used a statistical method called balanced random forest to classify suicide attempts at wave 2. Each variable was accorded an “importance score” using identified wave 1 features.
The outcome variable of attempted suicide at any point during the 3 years prior to the wave 2 interview was defined by combining responses to three wave 2 questions:
- In your entire life, did you ever attempt suicide?
- If yes, how old were you the first time?
- If the most recent event occurred within the last 3 years, how old were you during the most recent time?
Suicide risk severity was classified into four groups (low, medium, high, and very high) on the basis of the top-performing risk factors.
A statistical model combining survey design and nonresponse weights enabled estimates to be representative of the U.S. population, based on the 2000 census.
Out-of-fold model prediction assessed performance of the model, using area under receiver operator curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity.
Daily functioning
Of all participants, 70.2% (n = 34,653; almost 60% women) completed wave 2 interviews. The weighted mean ages at waves 1 and 2 were 45.1 and 48.2 years, respectively.
Of wave 2 respondents, 0.6% (n = 222) attempted suicide during the preceding 3 years.
Half of those who attempted suicide within the first year were classified as “very high risk,” while 33.2% of those who attempted suicide between the first and second year and 33.3% of those who attempted suicide between the second and third year were classified as “very high risk.”
Among participants who attempted suicide between the third year and follow-up, 16.48% were classified as “very high risk.”
The model accurately captured classification of participants, even across demographic characteristics, such as age, sex, race, and income.
Younger individuals (aged 18-36 years) were at higher risk, compared with older individuals. In addition, women were at higher risk than were men, White participants were at higher risk than were non-White participants, and individuals with lower income were at greater risk than were those with higher income.
The model found that 1.8% of the U.S. population had a 10% or greater risk of a suicide attempt.
The most important risk factors identified were the three questions about previous suicidal ideation or behavior; three items from the 12-Item Short Form Health Survey (feeling downhearted, doing activities less carefully, or accomplishing less because of emotional problems); younger age; lower educational achievement; and recent financial crisis.
“The clinical assessment of suicide risk typically focuses on acute suicidal symptoms, together with depression, anxiety, substance misuse, and recent stressful events,” coinvestigator Mark Olfson, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
Dr. Olfson said.
Extra vigilance
Commenting on the study in an interview, April C. Foreman, PhD, an executive board member of the American Association of Suicidology, noted that some of the findings were not surprising.
“When discharging a patient from inpatient care, or seeing them in primary care, bring up mental health concerns proactively and ask whether they have ever attempted suicide or harmed themselves – even a long time ago – just as you ask about a family history of heart disease or cancer, or other health issues,” said Dr. Foreman, chief medical officer of the Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
She noted that half of people who die by suicide have a primary care visit within the preceding month.
“Primary care is a great place to get a suicide history and follow the patient with extra vigilance, just as you would with any other risk factors,” Dr. Foreman said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and its Intramural Program. The study authors and Dr. Foreman have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A history of suicidal behaviors or ideation, functional impairment related to mental health disorders, and socioeconomic disadvantage are the three most important risk factors predicting subsequent suicide attempts, new research suggests.
Investigators applied a machine-learning model to data on over 34,500 adults drawn from a large national survey database. After analyzing more than 2,500 survey questions, key areas were identified that yielded the most accurate predictions of who might be at risk for later suicide attempt.
These predictors included experiencing previous suicidal behaviors and ideation or functional impairment because of emotional problems, being at a younger age, having a lower educational achievement, and experiencing a recent financial crisis.
“Our machine learning model confirmed well-known risk factors of suicide attempt, including previous suicidal behavior and depression; and we also identified functional impairment, such as doing activities less carefully or accomplishing less because of emotional problems, as a new important risk,” lead author Angel Garcia de la Garza, PhD candidate in the department of biostatistics, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“We hope our results provide a novel avenue for future suicide risk assessment,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The findings were published online Jan. 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Rich’ dataset
Previous research using machine learning approaches to study nonfatal suicide attempt prediction has focused on high-risk patients in clinical treatment. However, more than one-third of individuals making nonfatal suicide attempts do not receive mental health treatment, Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
To gain further insight into predictors of suicide risk in nonclinical populations, the researchers turned to the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC), a longitudinal survey of noninstitutionalized U.S. adults.
“We wanted to extend our understanding of suicide attempt risk factors beyond high-risk clinical populations to the general adult population; and the richness of the NESARC dataset provides a unique opportunity to do so,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The NESARC surveys were conducted in two waves: Wave 1 (2001-2002) and wave 2 (2004-2005), in which participants self-reported nonfatal suicide attempts in the preceding 3 years since wave 1.
Assessment of wave 1 participants was based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule DSM-IV.
“This survey’s extensive assessment instrument contained a detailed evaluation of substance use, psychiatric disorders, and symptoms not routinely available in electronic health records,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
The wave 1 survey contained 2,805 separate questions. From participants’ responses, the investigators derived 180 variables for three categories: past-year, prior-to-past-year, and lifetime mental disorders.
They then identified 2,978 factors associated with suicide attempts and used a statistical method called balanced random forest to classify suicide attempts at wave 2. Each variable was accorded an “importance score” using identified wave 1 features.
The outcome variable of attempted suicide at any point during the 3 years prior to the wave 2 interview was defined by combining responses to three wave 2 questions:
- In your entire life, did you ever attempt suicide?
- If yes, how old were you the first time?
- If the most recent event occurred within the last 3 years, how old were you during the most recent time?
Suicide risk severity was classified into four groups (low, medium, high, and very high) on the basis of the top-performing risk factors.
A statistical model combining survey design and nonresponse weights enabled estimates to be representative of the U.S. population, based on the 2000 census.
Out-of-fold model prediction assessed performance of the model, using area under receiver operator curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity.
Daily functioning
Of all participants, 70.2% (n = 34,653; almost 60% women) completed wave 2 interviews. The weighted mean ages at waves 1 and 2 were 45.1 and 48.2 years, respectively.
Of wave 2 respondents, 0.6% (n = 222) attempted suicide during the preceding 3 years.
Half of those who attempted suicide within the first year were classified as “very high risk,” while 33.2% of those who attempted suicide between the first and second year and 33.3% of those who attempted suicide between the second and third year were classified as “very high risk.”
Among participants who attempted suicide between the third year and follow-up, 16.48% were classified as “very high risk.”
The model accurately captured classification of participants, even across demographic characteristics, such as age, sex, race, and income.
Younger individuals (aged 18-36 years) were at higher risk, compared with older individuals. In addition, women were at higher risk than were men, White participants were at higher risk than were non-White participants, and individuals with lower income were at greater risk than were those with higher income.
The model found that 1.8% of the U.S. population had a 10% or greater risk of a suicide attempt.
The most important risk factors identified were the three questions about previous suicidal ideation or behavior; three items from the 12-Item Short Form Health Survey (feeling downhearted, doing activities less carefully, or accomplishing less because of emotional problems); younger age; lower educational achievement; and recent financial crisis.
“The clinical assessment of suicide risk typically focuses on acute suicidal symptoms, together with depression, anxiety, substance misuse, and recent stressful events,” coinvestigator Mark Olfson, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
Dr. Olfson said.
Extra vigilance
Commenting on the study in an interview, April C. Foreman, PhD, an executive board member of the American Association of Suicidology, noted that some of the findings were not surprising.
“When discharging a patient from inpatient care, or seeing them in primary care, bring up mental health concerns proactively and ask whether they have ever attempted suicide or harmed themselves – even a long time ago – just as you ask about a family history of heart disease or cancer, or other health issues,” said Dr. Foreman, chief medical officer of the Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
She noted that half of people who die by suicide have a primary care visit within the preceding month.
“Primary care is a great place to get a suicide history and follow the patient with extra vigilance, just as you would with any other risk factors,” Dr. Foreman said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and its Intramural Program. The study authors and Dr. Foreman have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A history of suicidal behaviors or ideation, functional impairment related to mental health disorders, and socioeconomic disadvantage are the three most important risk factors predicting subsequent suicide attempts, new research suggests.
Investigators applied a machine-learning model to data on over 34,500 adults drawn from a large national survey database. After analyzing more than 2,500 survey questions, key areas were identified that yielded the most accurate predictions of who might be at risk for later suicide attempt.
These predictors included experiencing previous suicidal behaviors and ideation or functional impairment because of emotional problems, being at a younger age, having a lower educational achievement, and experiencing a recent financial crisis.
“Our machine learning model confirmed well-known risk factors of suicide attempt, including previous suicidal behavior and depression; and we also identified functional impairment, such as doing activities less carefully or accomplishing less because of emotional problems, as a new important risk,” lead author Angel Garcia de la Garza, PhD candidate in the department of biostatistics, Columbia University, New York, said in an interview.
“We hope our results provide a novel avenue for future suicide risk assessment,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The findings were published online Jan. 6 in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Rich’ dataset
Previous research using machine learning approaches to study nonfatal suicide attempt prediction has focused on high-risk patients in clinical treatment. However, more than one-third of individuals making nonfatal suicide attempts do not receive mental health treatment, Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
To gain further insight into predictors of suicide risk in nonclinical populations, the researchers turned to the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC), a longitudinal survey of noninstitutionalized U.S. adults.
“We wanted to extend our understanding of suicide attempt risk factors beyond high-risk clinical populations to the general adult population; and the richness of the NESARC dataset provides a unique opportunity to do so,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza said.
The NESARC surveys were conducted in two waves: Wave 1 (2001-2002) and wave 2 (2004-2005), in which participants self-reported nonfatal suicide attempts in the preceding 3 years since wave 1.
Assessment of wave 1 participants was based on the Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule DSM-IV.
“This survey’s extensive assessment instrument contained a detailed evaluation of substance use, psychiatric disorders, and symptoms not routinely available in electronic health records,” Mr. Garcia de la Garza noted.
The wave 1 survey contained 2,805 separate questions. From participants’ responses, the investigators derived 180 variables for three categories: past-year, prior-to-past-year, and lifetime mental disorders.
They then identified 2,978 factors associated with suicide attempts and used a statistical method called balanced random forest to classify suicide attempts at wave 2. Each variable was accorded an “importance score” using identified wave 1 features.
The outcome variable of attempted suicide at any point during the 3 years prior to the wave 2 interview was defined by combining responses to three wave 2 questions:
- In your entire life, did you ever attempt suicide?
- If yes, how old were you the first time?
- If the most recent event occurred within the last 3 years, how old were you during the most recent time?
Suicide risk severity was classified into four groups (low, medium, high, and very high) on the basis of the top-performing risk factors.
A statistical model combining survey design and nonresponse weights enabled estimates to be representative of the U.S. population, based on the 2000 census.
Out-of-fold model prediction assessed performance of the model, using area under receiver operator curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity.
Daily functioning
Of all participants, 70.2% (n = 34,653; almost 60% women) completed wave 2 interviews. The weighted mean ages at waves 1 and 2 were 45.1 and 48.2 years, respectively.
Of wave 2 respondents, 0.6% (n = 222) attempted suicide during the preceding 3 years.
Half of those who attempted suicide within the first year were classified as “very high risk,” while 33.2% of those who attempted suicide between the first and second year and 33.3% of those who attempted suicide between the second and third year were classified as “very high risk.”
Among participants who attempted suicide between the third year and follow-up, 16.48% were classified as “very high risk.”
The model accurately captured classification of participants, even across demographic characteristics, such as age, sex, race, and income.
Younger individuals (aged 18-36 years) were at higher risk, compared with older individuals. In addition, women were at higher risk than were men, White participants were at higher risk than were non-White participants, and individuals with lower income were at greater risk than were those with higher income.
The model found that 1.8% of the U.S. population had a 10% or greater risk of a suicide attempt.
The most important risk factors identified were the three questions about previous suicidal ideation or behavior; three items from the 12-Item Short Form Health Survey (feeling downhearted, doing activities less carefully, or accomplishing less because of emotional problems); younger age; lower educational achievement; and recent financial crisis.
“The clinical assessment of suicide risk typically focuses on acute suicidal symptoms, together with depression, anxiety, substance misuse, and recent stressful events,” coinvestigator Mark Olfson, MD, PhD, professor of epidemiology, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
Dr. Olfson said.
Extra vigilance
Commenting on the study in an interview, April C. Foreman, PhD, an executive board member of the American Association of Suicidology, noted that some of the findings were not surprising.
“When discharging a patient from inpatient care, or seeing them in primary care, bring up mental health concerns proactively and ask whether they have ever attempted suicide or harmed themselves – even a long time ago – just as you ask about a family history of heart disease or cancer, or other health issues,” said Dr. Foreman, chief medical officer of the Kevin and Margaret Hines Foundation.
She noted that half of people who die by suicide have a primary care visit within the preceding month.
“Primary care is a great place to get a suicide history and follow the patient with extra vigilance, just as you would with any other risk factors,” Dr. Foreman said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and its Intramural Program. The study authors and Dr. Foreman have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Polydoctoring: The case against fragmented psychiatric care
How many providers does it take to depersonalize a patient? Nine? 1. A psychiatrist for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). 2. A psychiatrist for ketamine. 3. A psychiatrist who specializes in substance use disorder medication. 4. A psychiatrist for the rest of the psychotropic medication. 5. An alternative medicine provider who prescribes supplements. 6. A therapist for depression who uses cognitive-behavioral therapy. 7. A therapist for posttraumatic stress disorder who uses eye movement desensitization and reprocessing. 8. An addiction counselor. 9. An equine therapist.
This doesn’t include other providers and professionals who likely contribute to one’s mental well-being, including yoga instructors and personal trainers. In addition, any one of those psychiatrists may have one or more nurse practitioners who routinely step in to attend to appointments.
In our uncertain and lonely times, the value of human contact and interaction has become exponentially more precious. I long to see my patients in my private practice office. I am now much more aware of their grounding effect on my life, and I suspect I had a similar grounding effect on theirs. Few things provide me more comfort than sitting on my lounge chair with a curious gaze waiting for the patient to start the visit. I often wonder what makes a patient choose to go see a private practice physician. Yet a common reason offered is, “Wait! You do everything? Therapy and meds if I need them? You’ll see me every week?”
While I am realistic about the need and use of split-care, I have never been enamored with the concept. I think that few medical students choose psychiatry with the goal of referring all psychotherapeutic needs and intervention to “allied mental health providers” as my prior managed care organization liked to refer to psychologists, social workers, marriage and family therapists, and other counselors. I remember particularly as a chief resident being bombarded by complaints of therapists complaining about psychiatry residents. All of their patients’ symptoms allegedly required medication adjustment and residents were supposedly dismissing them. In return, residents would complain that the therapists did not address the psychological manifestations of the patient’s ailments. Herein lies my problem with split-care, it encourages psychotherapy to be about medication management, and medication management to be about psychotherapy.
However, this is not an article against split-treatment. Psychiatrists, for a variety of reasons, are not suited to perform psychotherapy in most management care models. The main reason being that psychiatrists’ time is too expensive to justify the expense, and psychiatrists are (for the most part), the only ones able to prescribe medications for which the wait-list is already long enough. This article is about the absurd levels at which we have fragmented care of certain patients. Split-treatment is relevant in that its negative side effects, we are almost all familiar with, exemplify the problem of the fragmentation of modern psychiatry. In many ways this fragmentation of care is similar to polypharmacy – the premise for each psychotropic intervention may be sound, but the end result is often incoherent.
My main concern with the fragmentation of modern psychiatry stems from my belief that the most important facet of our work is our relationship with our patients. It is the duty we owe them, the attention we give them, the unique nature of interactions. Who among the nine providers is responsible for writing a discharge summary? Who is responsible for calling an emergency contact in a critical situation? Who communicates with the new provider when someone is taken off an insurance panel? Who makes the patient feel cared for? I am often confronted by this situation when TMS or ketamine providers say, “I just give the procedure/medication that was ordered by the referring psychiatrist.” This response disturbs me in that I could not imagine myself being so hands off in the care of a patient. There is an implication of projected immunity and lack of responsibility that bothers me.
But my concerns are also practical. From my forensic experience, I am well aware that the larger the number of providers treating a patient, the larger the number of inconsistent diagnoses, the more likely medication reconciliations are not kept up to date or incorrect, and the more likely intervention recommendations are contrary to one another. A disengaged ketamine provider may not realize that the patient was more recently enrolled in a substance use disorder program, a potential contraindication for ketamine, if not well-abreast of the patient’s continued evolution. A substance use disorder psychiatric specialist may be at odds with a substance use disorder counselor who worries about the message of treating psychiatric symptoms with chemical substances if they don’t communicate.
As with polypharmacy, “polydoctoring” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to specialize, patients still desire and benefit from an intimate and close relationship with one provider who is warm, concerned, and hopeful. Those traits can theoretically be provided by anyone and there is not something inherently wrong with having more than one provider. However, psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, especially at a time when we all feel lonely, disconnected, and depersonalized.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
How many providers does it take to depersonalize a patient? Nine? 1. A psychiatrist for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). 2. A psychiatrist for ketamine. 3. A psychiatrist who specializes in substance use disorder medication. 4. A psychiatrist for the rest of the psychotropic medication. 5. An alternative medicine provider who prescribes supplements. 6. A therapist for depression who uses cognitive-behavioral therapy. 7. A therapist for posttraumatic stress disorder who uses eye movement desensitization and reprocessing. 8. An addiction counselor. 9. An equine therapist.
This doesn’t include other providers and professionals who likely contribute to one’s mental well-being, including yoga instructors and personal trainers. In addition, any one of those psychiatrists may have one or more nurse practitioners who routinely step in to attend to appointments.
In our uncertain and lonely times, the value of human contact and interaction has become exponentially more precious. I long to see my patients in my private practice office. I am now much more aware of their grounding effect on my life, and I suspect I had a similar grounding effect on theirs. Few things provide me more comfort than sitting on my lounge chair with a curious gaze waiting for the patient to start the visit. I often wonder what makes a patient choose to go see a private practice physician. Yet a common reason offered is, “Wait! You do everything? Therapy and meds if I need them? You’ll see me every week?”
While I am realistic about the need and use of split-care, I have never been enamored with the concept. I think that few medical students choose psychiatry with the goal of referring all psychotherapeutic needs and intervention to “allied mental health providers” as my prior managed care organization liked to refer to psychologists, social workers, marriage and family therapists, and other counselors. I remember particularly as a chief resident being bombarded by complaints of therapists complaining about psychiatry residents. All of their patients’ symptoms allegedly required medication adjustment and residents were supposedly dismissing them. In return, residents would complain that the therapists did not address the psychological manifestations of the patient’s ailments. Herein lies my problem with split-care, it encourages psychotherapy to be about medication management, and medication management to be about psychotherapy.
However, this is not an article against split-treatment. Psychiatrists, for a variety of reasons, are not suited to perform psychotherapy in most management care models. The main reason being that psychiatrists’ time is too expensive to justify the expense, and psychiatrists are (for the most part), the only ones able to prescribe medications for which the wait-list is already long enough. This article is about the absurd levels at which we have fragmented care of certain patients. Split-treatment is relevant in that its negative side effects, we are almost all familiar with, exemplify the problem of the fragmentation of modern psychiatry. In many ways this fragmentation of care is similar to polypharmacy – the premise for each psychotropic intervention may be sound, but the end result is often incoherent.
My main concern with the fragmentation of modern psychiatry stems from my belief that the most important facet of our work is our relationship with our patients. It is the duty we owe them, the attention we give them, the unique nature of interactions. Who among the nine providers is responsible for writing a discharge summary? Who is responsible for calling an emergency contact in a critical situation? Who communicates with the new provider when someone is taken off an insurance panel? Who makes the patient feel cared for? I am often confronted by this situation when TMS or ketamine providers say, “I just give the procedure/medication that was ordered by the referring psychiatrist.” This response disturbs me in that I could not imagine myself being so hands off in the care of a patient. There is an implication of projected immunity and lack of responsibility that bothers me.
But my concerns are also practical. From my forensic experience, I am well aware that the larger the number of providers treating a patient, the larger the number of inconsistent diagnoses, the more likely medication reconciliations are not kept up to date or incorrect, and the more likely intervention recommendations are contrary to one another. A disengaged ketamine provider may not realize that the patient was more recently enrolled in a substance use disorder program, a potential contraindication for ketamine, if not well-abreast of the patient’s continued evolution. A substance use disorder psychiatric specialist may be at odds with a substance use disorder counselor who worries about the message of treating psychiatric symptoms with chemical substances if they don’t communicate.
As with polypharmacy, “polydoctoring” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to specialize, patients still desire and benefit from an intimate and close relationship with one provider who is warm, concerned, and hopeful. Those traits can theoretically be provided by anyone and there is not something inherently wrong with having more than one provider. However, psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, especially at a time when we all feel lonely, disconnected, and depersonalized.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
How many providers does it take to depersonalize a patient? Nine? 1. A psychiatrist for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). 2. A psychiatrist for ketamine. 3. A psychiatrist who specializes in substance use disorder medication. 4. A psychiatrist for the rest of the psychotropic medication. 5. An alternative medicine provider who prescribes supplements. 6. A therapist for depression who uses cognitive-behavioral therapy. 7. A therapist for posttraumatic stress disorder who uses eye movement desensitization and reprocessing. 8. An addiction counselor. 9. An equine therapist.
This doesn’t include other providers and professionals who likely contribute to one’s mental well-being, including yoga instructors and personal trainers. In addition, any one of those psychiatrists may have one or more nurse practitioners who routinely step in to attend to appointments.
In our uncertain and lonely times, the value of human contact and interaction has become exponentially more precious. I long to see my patients in my private practice office. I am now much more aware of their grounding effect on my life, and I suspect I had a similar grounding effect on theirs. Few things provide me more comfort than sitting on my lounge chair with a curious gaze waiting for the patient to start the visit. I often wonder what makes a patient choose to go see a private practice physician. Yet a common reason offered is, “Wait! You do everything? Therapy and meds if I need them? You’ll see me every week?”
While I am realistic about the need and use of split-care, I have never been enamored with the concept. I think that few medical students choose psychiatry with the goal of referring all psychotherapeutic needs and intervention to “allied mental health providers” as my prior managed care organization liked to refer to psychologists, social workers, marriage and family therapists, and other counselors. I remember particularly as a chief resident being bombarded by complaints of therapists complaining about psychiatry residents. All of their patients’ symptoms allegedly required medication adjustment and residents were supposedly dismissing them. In return, residents would complain that the therapists did not address the psychological manifestations of the patient’s ailments. Herein lies my problem with split-care, it encourages psychotherapy to be about medication management, and medication management to be about psychotherapy.
However, this is not an article against split-treatment. Psychiatrists, for a variety of reasons, are not suited to perform psychotherapy in most management care models. The main reason being that psychiatrists’ time is too expensive to justify the expense, and psychiatrists are (for the most part), the only ones able to prescribe medications for which the wait-list is already long enough. This article is about the absurd levels at which we have fragmented care of certain patients. Split-treatment is relevant in that its negative side effects, we are almost all familiar with, exemplify the problem of the fragmentation of modern psychiatry. In many ways this fragmentation of care is similar to polypharmacy – the premise for each psychotropic intervention may be sound, but the end result is often incoherent.
My main concern with the fragmentation of modern psychiatry stems from my belief that the most important facet of our work is our relationship with our patients. It is the duty we owe them, the attention we give them, the unique nature of interactions. Who among the nine providers is responsible for writing a discharge summary? Who is responsible for calling an emergency contact in a critical situation? Who communicates with the new provider when someone is taken off an insurance panel? Who makes the patient feel cared for? I am often confronted by this situation when TMS or ketamine providers say, “I just give the procedure/medication that was ordered by the referring psychiatrist.” This response disturbs me in that I could not imagine myself being so hands off in the care of a patient. There is an implication of projected immunity and lack of responsibility that bothers me.
But my concerns are also practical. From my forensic experience, I am well aware that the larger the number of providers treating a patient, the larger the number of inconsistent diagnoses, the more likely medication reconciliations are not kept up to date or incorrect, and the more likely intervention recommendations are contrary to one another. A disengaged ketamine provider may not realize that the patient was more recently enrolled in a substance use disorder program, a potential contraindication for ketamine, if not well-abreast of the patient’s continued evolution. A substance use disorder psychiatric specialist may be at odds with a substance use disorder counselor who worries about the message of treating psychiatric symptoms with chemical substances if they don’t communicate.
As with polypharmacy, “polydoctoring” has negative effects. While the field of psychiatry’s advancing knowledge may encourage providers to specialize, patients still desire and benefit from an intimate and close relationship with one provider who is warm, concerned, and hopeful. Those traits can theoretically be provided by anyone and there is not something inherently wrong with having more than one provider. However, psychiatry would be wise to recognize this concerning trend, especially at a time when we all feel lonely, disconnected, and depersonalized.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
Heavy drinking by teens may affect white-matter integrity
Heavy alcohol use in adolescence is linked to disruptions in white-matter integrity, new research suggests.
In a case-control study of more than 400 participants, the association was more pronounced in younger adolescents and in the anterior and middle corpus callosum, which serve the interhemispheric integration of frontal networking and communication.
The results provide clinicians with yet another reason to ask adolescents about their alcohol use, said investigator Adolf Pfefferbaum, MD, Center for Health Sciences, SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif., and professor emeritus at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, when questioning adolescents about their alcohol use, “sometimes it’s better to ask: ‘How much alcohol do you drink?’ ” instead of just asking if they drink, Dr. Pfefferbaum said in an interview. That’s because they may be more willing to answer the first question honestly.
It’s also important for clinicians to nonjudgmentally tell teens there is evidence “that heavy drinking is bad for their brain,” he added.
The findings were published online Dec. 30, 2020, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Fractional anisotropy
Adolescence is a critical period of physiological and social maturation accompanied by significant structural, functional, and neurochemical brain changes, the investigators noted.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) produces a measure called fractional anisotropy (FA), which characterizes some of these brain changes by measuring molecular water diffusion in the brain.
“FA is a measure of the integrity of brain white matter; so, the part of the brain that connects neurons with each other,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. He added that FA decreases in diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), reflecting “some kind of pathology.”
Affected fiber systems include the corpus callosum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, internal and external capsule, brain stem, and cortical projection fibers. Disruption of these neural systems may degrade neural signal transmission and affect certain cognitive functions, possibly resulting in enhanced impulsivity, poor inhibitory control, and restricted working memory capacity, the researchers wrote.
FA follows an inverted U-shaped pattern. “The natural trajectory is to increase from infancy up to middle adolescence and then, as we get older, from about age 25 to 30 years, starts to go down. Our brains are starting to show signs of aging a bit by then,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum.
The current analysis assessed 451 adolescents (228 boys and 223 girls) from the NCANDA study, for whom researchers had four years of longitudinal DTI data. All were aged 12- 21 years at baseline.
The NCANDA cohort was recruited across five U.S. sites. Participants are assessed yearly on psychobiologic measures, including brain maturation. The cohort, which did not have any significant substance abuse upon entry, is balanced in terms of gender and ethnicity.
The investigators quantified the developmental change of white-matter (WM) integrity within each individual as the slope of FA over visits. They also examined altered developmental trajectories associated with drinking onset during adolescence and the differential alcohol associations by age with specific regional WM fiber tracts.
Researchers assessed drinking on a scale of 1-4, based on the youth-adjusted Cahalan score. The scale considers quantity and frequency to classify drinking levels based on past-year self-reported patterns.
Altered trajectory
Results showed that 291 participants (37.2%) remained at no to low drinking levels (youth-adjusted Cahalan score, 0) throughout the time points examined, and 160 (20.5%) were classified as heavy drinkers for at least two consecutive visits (youth-adjusted Cahalan score >1).
Among the no to low drinkers, 48.4% were boys with a mean age of 16.5 years and 51.2% were girls with a mean age of 16.5 years. About two thirds of the group (66%) were White.
Among heavy drinkers, 53.8% were boys with a mean age of 20.1 years and 46.3% were girls with a mean age of 20.5 years. In this group, 88.8% were White.
The investigators did not analyze moderate drinkers or those who initiated heavy drinking for only one visit.
The findings also showed that heavy drinkers exhibited significant reduction of whole-brain FA. The slopes of the 78 heavy drinkers were significantly more negative than the 78 matched no to low drinkers (mean, –0.0013 vs. 0.0001; P = .008).
“The concept of the slopes is really important here because it’s the trajectory that seems to be the most sensitive measure,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. “Probably what’s happening is the exposure to alcohol is interfering with the normal myelination and normal development of the adolescent’s white matter.”
The no to low drinkers had relatively stable FA measures across all visits.
A reduction in FA was significantly linked to heavy drinking. An analysis of 63 youth who transitioned from being a no to low drinker to a heavy drinker showed that before the transition, they had significantly increased FA over visits (95% CI of slope, 0.0011-0.0024; P < .001). In addition, their corresponding slopes were not different from other no to low drinkers of the same age range.
However, this group’s FA declined significantly after they reported heavy drinking, resulting in slopes significantly below zero (95% CI of slope, –0.0036 to –0.0014; P < .001) and that were lower than the no to low participants of the same age range.
and further illustrates that heavy drinking in adolescence affects WM integrity, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
Potential markers
None of the slope measures correlated with number of visits or use of tobacco or cannabis. The association of alcohol with the slope measures was more apparent in the younger cohort (<19 years).
“The effects were seen more readily in younger adolescents because they are the ones who are still progressing along this normal developmental trajectory,” Dr. Pfefferbaum noted. “In a sense, the younger you are when you’re exposed to alcohol, probably the more vulnerable you are.”
Previous studies have suggested that damage in WM tracts is associated with heightened neural reactivity to alcohol cues in adults with alcohol use disorder. Given this evidence, the greater WM degradation at younger versus older ages might help explain why adolescents who initiate early drinking are more likely to develop addiction later in life, the investigators wrote.
Of the five major fiber tracts, only the commissural fibers (corpus callosum) showed a significant association with alcohol. The researchers noted that WM volume shrinkage and callosal demyelination are two of the most prominent markers in adult alcoholism and are potential markers in adolescent alcohol abuse.
Upon further extending the analysis to the four subregions of the corpus callosum, the investigators found that only the anterior and middle callosal regions (genu and body) showed significant age-alcohol interactions.
This could be a result of the timing of fiber myelination in these regions of the brain, compared with others, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
He noted that these fibers connect the left and right part of the anterior regions of the brain, especially the frontal lobes, which are particularly vulnerable to the effects of alcohol. “It may well be that we have this interaction of the developmental time and the sensitivity of the frontal parts of the brain.”
Cognitive effects?
Although the researchers did not find any sex effects, Dr. Pfefferbaum stressed that this doesn’t mean they do not exist. “We just may not have the power to see them,” he said.
The study did not look specifically at binge drinkers, defined as consuming five drinks in 2 hours for men and four drinks in 2 hours for women. Dr. Pfefferbaum noted that it is difficult to get “good quantification” of binge drinking. “We don’t have a fine enough grain analysis to separate that out,” he said.
Asked whether the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers affects cognition, Dr. Pfefferbaum said “those studies are still in progress,” with results hopefully available within about a year.
Dr. Pfefferbaum said he and his colleagues are continuing to follow these adolescents and hope to see if the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers returns to normal, adding: “The real question now is: If they stop heavy drinking, will they get back on track?”
This study is believed to be the first to suggest in vivo differential vulnerability in WM microstructure with respect to age, the authors note.
In addition to asking teens about their alcohol use, the clinician’s role should be to “counsel and refer,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum. He also suggested accessing resources from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Important data, but several limitations
In an interview, Oscar G. Bukstein, MD, MPH, medical director of outpatient psychiatry service at Boston Children’s Hospital, and professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said the findings provide further evidence that alcohol affects the maturing brain.
This study, and others that have examined cannabis use, “show that you have a dynamically growing brain with certain sections, particularly in this case the anterior and middle corpus callosum, that mature later [and] that are more likely to be affected by early alcohol use,” said Dr. Bukstein, who was not involved with the research.
He stressed the importance of determining the mechanism involved and noted some study limitations. For example, the DTI technology used may “already be out of date,” he said.
Using older technology may have prevented finding an impact of heavy drinking on parts of the brain other than the anterior and middle corpus callosum, Dr. Bukstein noted.
Newer technology might provide “a finer-grain nonlinear voxel-wise analysis,” although using more updated scanning techniques may not have detected additional differences in study groups, he added.
Dr. Bukstein also noted that there were limitations: The study did not have “gradations,” but only looked at heavy drinking and no to low drinking. “You’d like to find out about kids who are somewhere in the middle.” It also didn’t determine a “cutoff” where deleterious effects of alcohol on the brain begin, Dr. Bukstein added.
Additionally, the study didn’t look at brain development outcomes in children with conditions such as depression and ADHD that are known to lead to substance use – something a larger study may have been able to do, he said.
Dr. Bukstein noted that a newer and much larger study, the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study, has begun assessing kids for risk factors such as substance use, starting at age 10 years.
The study was funded by grants from NIAAA and by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence–AWS Cloud Credits for Research. Dr. Pfefferbaum reported receiving an NIAAA grant during the conduct of the study. Dr. Bukstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heavy alcohol use in adolescence is linked to disruptions in white-matter integrity, new research suggests.
In a case-control study of more than 400 participants, the association was more pronounced in younger adolescents and in the anterior and middle corpus callosum, which serve the interhemispheric integration of frontal networking and communication.
The results provide clinicians with yet another reason to ask adolescents about their alcohol use, said investigator Adolf Pfefferbaum, MD, Center for Health Sciences, SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif., and professor emeritus at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, when questioning adolescents about their alcohol use, “sometimes it’s better to ask: ‘How much alcohol do you drink?’ ” instead of just asking if they drink, Dr. Pfefferbaum said in an interview. That’s because they may be more willing to answer the first question honestly.
It’s also important for clinicians to nonjudgmentally tell teens there is evidence “that heavy drinking is bad for their brain,” he added.
The findings were published online Dec. 30, 2020, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Fractional anisotropy
Adolescence is a critical period of physiological and social maturation accompanied by significant structural, functional, and neurochemical brain changes, the investigators noted.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) produces a measure called fractional anisotropy (FA), which characterizes some of these brain changes by measuring molecular water diffusion in the brain.
“FA is a measure of the integrity of brain white matter; so, the part of the brain that connects neurons with each other,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. He added that FA decreases in diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), reflecting “some kind of pathology.”
Affected fiber systems include the corpus callosum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, internal and external capsule, brain stem, and cortical projection fibers. Disruption of these neural systems may degrade neural signal transmission and affect certain cognitive functions, possibly resulting in enhanced impulsivity, poor inhibitory control, and restricted working memory capacity, the researchers wrote.
FA follows an inverted U-shaped pattern. “The natural trajectory is to increase from infancy up to middle adolescence and then, as we get older, from about age 25 to 30 years, starts to go down. Our brains are starting to show signs of aging a bit by then,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum.
The current analysis assessed 451 adolescents (228 boys and 223 girls) from the NCANDA study, for whom researchers had four years of longitudinal DTI data. All were aged 12- 21 years at baseline.
The NCANDA cohort was recruited across five U.S. sites. Participants are assessed yearly on psychobiologic measures, including brain maturation. The cohort, which did not have any significant substance abuse upon entry, is balanced in terms of gender and ethnicity.
The investigators quantified the developmental change of white-matter (WM) integrity within each individual as the slope of FA over visits. They also examined altered developmental trajectories associated with drinking onset during adolescence and the differential alcohol associations by age with specific regional WM fiber tracts.
Researchers assessed drinking on a scale of 1-4, based on the youth-adjusted Cahalan score. The scale considers quantity and frequency to classify drinking levels based on past-year self-reported patterns.
Altered trajectory
Results showed that 291 participants (37.2%) remained at no to low drinking levels (youth-adjusted Cahalan score, 0) throughout the time points examined, and 160 (20.5%) were classified as heavy drinkers for at least two consecutive visits (youth-adjusted Cahalan score >1).
Among the no to low drinkers, 48.4% were boys with a mean age of 16.5 years and 51.2% were girls with a mean age of 16.5 years. About two thirds of the group (66%) were White.
Among heavy drinkers, 53.8% were boys with a mean age of 20.1 years and 46.3% were girls with a mean age of 20.5 years. In this group, 88.8% were White.
The investigators did not analyze moderate drinkers or those who initiated heavy drinking for only one visit.
The findings also showed that heavy drinkers exhibited significant reduction of whole-brain FA. The slopes of the 78 heavy drinkers were significantly more negative than the 78 matched no to low drinkers (mean, –0.0013 vs. 0.0001; P = .008).
“The concept of the slopes is really important here because it’s the trajectory that seems to be the most sensitive measure,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. “Probably what’s happening is the exposure to alcohol is interfering with the normal myelination and normal development of the adolescent’s white matter.”
The no to low drinkers had relatively stable FA measures across all visits.
A reduction in FA was significantly linked to heavy drinking. An analysis of 63 youth who transitioned from being a no to low drinker to a heavy drinker showed that before the transition, they had significantly increased FA over visits (95% CI of slope, 0.0011-0.0024; P < .001). In addition, their corresponding slopes were not different from other no to low drinkers of the same age range.
However, this group’s FA declined significantly after they reported heavy drinking, resulting in slopes significantly below zero (95% CI of slope, –0.0036 to –0.0014; P < .001) and that were lower than the no to low participants of the same age range.
and further illustrates that heavy drinking in adolescence affects WM integrity, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
Potential markers
None of the slope measures correlated with number of visits or use of tobacco or cannabis. The association of alcohol with the slope measures was more apparent in the younger cohort (<19 years).
“The effects were seen more readily in younger adolescents because they are the ones who are still progressing along this normal developmental trajectory,” Dr. Pfefferbaum noted. “In a sense, the younger you are when you’re exposed to alcohol, probably the more vulnerable you are.”
Previous studies have suggested that damage in WM tracts is associated with heightened neural reactivity to alcohol cues in adults with alcohol use disorder. Given this evidence, the greater WM degradation at younger versus older ages might help explain why adolescents who initiate early drinking are more likely to develop addiction later in life, the investigators wrote.
Of the five major fiber tracts, only the commissural fibers (corpus callosum) showed a significant association with alcohol. The researchers noted that WM volume shrinkage and callosal demyelination are two of the most prominent markers in adult alcoholism and are potential markers in adolescent alcohol abuse.
Upon further extending the analysis to the four subregions of the corpus callosum, the investigators found that only the anterior and middle callosal regions (genu and body) showed significant age-alcohol interactions.
This could be a result of the timing of fiber myelination in these regions of the brain, compared with others, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
He noted that these fibers connect the left and right part of the anterior regions of the brain, especially the frontal lobes, which are particularly vulnerable to the effects of alcohol. “It may well be that we have this interaction of the developmental time and the sensitivity of the frontal parts of the brain.”
Cognitive effects?
Although the researchers did not find any sex effects, Dr. Pfefferbaum stressed that this doesn’t mean they do not exist. “We just may not have the power to see them,” he said.
The study did not look specifically at binge drinkers, defined as consuming five drinks in 2 hours for men and four drinks in 2 hours for women. Dr. Pfefferbaum noted that it is difficult to get “good quantification” of binge drinking. “We don’t have a fine enough grain analysis to separate that out,” he said.
Asked whether the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers affects cognition, Dr. Pfefferbaum said “those studies are still in progress,” with results hopefully available within about a year.
Dr. Pfefferbaum said he and his colleagues are continuing to follow these adolescents and hope to see if the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers returns to normal, adding: “The real question now is: If they stop heavy drinking, will they get back on track?”
This study is believed to be the first to suggest in vivo differential vulnerability in WM microstructure with respect to age, the authors note.
In addition to asking teens about their alcohol use, the clinician’s role should be to “counsel and refer,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum. He also suggested accessing resources from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Important data, but several limitations
In an interview, Oscar G. Bukstein, MD, MPH, medical director of outpatient psychiatry service at Boston Children’s Hospital, and professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said the findings provide further evidence that alcohol affects the maturing brain.
This study, and others that have examined cannabis use, “show that you have a dynamically growing brain with certain sections, particularly in this case the anterior and middle corpus callosum, that mature later [and] that are more likely to be affected by early alcohol use,” said Dr. Bukstein, who was not involved with the research.
He stressed the importance of determining the mechanism involved and noted some study limitations. For example, the DTI technology used may “already be out of date,” he said.
Using older technology may have prevented finding an impact of heavy drinking on parts of the brain other than the anterior and middle corpus callosum, Dr. Bukstein noted.
Newer technology might provide “a finer-grain nonlinear voxel-wise analysis,” although using more updated scanning techniques may not have detected additional differences in study groups, he added.
Dr. Bukstein also noted that there were limitations: The study did not have “gradations,” but only looked at heavy drinking and no to low drinking. “You’d like to find out about kids who are somewhere in the middle.” It also didn’t determine a “cutoff” where deleterious effects of alcohol on the brain begin, Dr. Bukstein added.
Additionally, the study didn’t look at brain development outcomes in children with conditions such as depression and ADHD that are known to lead to substance use – something a larger study may have been able to do, he said.
Dr. Bukstein noted that a newer and much larger study, the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study, has begun assessing kids for risk factors such as substance use, starting at age 10 years.
The study was funded by grants from NIAAA and by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence–AWS Cloud Credits for Research. Dr. Pfefferbaum reported receiving an NIAAA grant during the conduct of the study. Dr. Bukstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heavy alcohol use in adolescence is linked to disruptions in white-matter integrity, new research suggests.
In a case-control study of more than 400 participants, the association was more pronounced in younger adolescents and in the anterior and middle corpus callosum, which serve the interhemispheric integration of frontal networking and communication.
The results provide clinicians with yet another reason to ask adolescents about their alcohol use, said investigator Adolf Pfefferbaum, MD, Center for Health Sciences, SRI International, Menlo Park, Calif., and professor emeritus at Stanford (Calif.) University.
However, when questioning adolescents about their alcohol use, “sometimes it’s better to ask: ‘How much alcohol do you drink?’ ” instead of just asking if they drink, Dr. Pfefferbaum said in an interview. That’s because they may be more willing to answer the first question honestly.
It’s also important for clinicians to nonjudgmentally tell teens there is evidence “that heavy drinking is bad for their brain,” he added.
The findings were published online Dec. 30, 2020, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Fractional anisotropy
Adolescence is a critical period of physiological and social maturation accompanied by significant structural, functional, and neurochemical brain changes, the investigators noted.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) produces a measure called fractional anisotropy (FA), which characterizes some of these brain changes by measuring molecular water diffusion in the brain.
“FA is a measure of the integrity of brain white matter; so, the part of the brain that connects neurons with each other,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. He added that FA decreases in diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), reflecting “some kind of pathology.”
Affected fiber systems include the corpus callosum, superior longitudinal fasciculus, internal and external capsule, brain stem, and cortical projection fibers. Disruption of these neural systems may degrade neural signal transmission and affect certain cognitive functions, possibly resulting in enhanced impulsivity, poor inhibitory control, and restricted working memory capacity, the researchers wrote.
FA follows an inverted U-shaped pattern. “The natural trajectory is to increase from infancy up to middle adolescence and then, as we get older, from about age 25 to 30 years, starts to go down. Our brains are starting to show signs of aging a bit by then,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum.
The current analysis assessed 451 adolescents (228 boys and 223 girls) from the NCANDA study, for whom researchers had four years of longitudinal DTI data. All were aged 12- 21 years at baseline.
The NCANDA cohort was recruited across five U.S. sites. Participants are assessed yearly on psychobiologic measures, including brain maturation. The cohort, which did not have any significant substance abuse upon entry, is balanced in terms of gender and ethnicity.
The investigators quantified the developmental change of white-matter (WM) integrity within each individual as the slope of FA over visits. They also examined altered developmental trajectories associated with drinking onset during adolescence and the differential alcohol associations by age with specific regional WM fiber tracts.
Researchers assessed drinking on a scale of 1-4, based on the youth-adjusted Cahalan score. The scale considers quantity and frequency to classify drinking levels based on past-year self-reported patterns.
Altered trajectory
Results showed that 291 participants (37.2%) remained at no to low drinking levels (youth-adjusted Cahalan score, 0) throughout the time points examined, and 160 (20.5%) were classified as heavy drinkers for at least two consecutive visits (youth-adjusted Cahalan score >1).
Among the no to low drinkers, 48.4% were boys with a mean age of 16.5 years and 51.2% were girls with a mean age of 16.5 years. About two thirds of the group (66%) were White.
Among heavy drinkers, 53.8% were boys with a mean age of 20.1 years and 46.3% were girls with a mean age of 20.5 years. In this group, 88.8% were White.
The investigators did not analyze moderate drinkers or those who initiated heavy drinking for only one visit.
The findings also showed that heavy drinkers exhibited significant reduction of whole-brain FA. The slopes of the 78 heavy drinkers were significantly more negative than the 78 matched no to low drinkers (mean, –0.0013 vs. 0.0001; P = .008).
“The concept of the slopes is really important here because it’s the trajectory that seems to be the most sensitive measure,” Dr. Pfefferbaum said. “Probably what’s happening is the exposure to alcohol is interfering with the normal myelination and normal development of the adolescent’s white matter.”
The no to low drinkers had relatively stable FA measures across all visits.
A reduction in FA was significantly linked to heavy drinking. An analysis of 63 youth who transitioned from being a no to low drinker to a heavy drinker showed that before the transition, they had significantly increased FA over visits (95% CI of slope, 0.0011-0.0024; P < .001). In addition, their corresponding slopes were not different from other no to low drinkers of the same age range.
However, this group’s FA declined significantly after they reported heavy drinking, resulting in slopes significantly below zero (95% CI of slope, –0.0036 to –0.0014; P < .001) and that were lower than the no to low participants of the same age range.
and further illustrates that heavy drinking in adolescence affects WM integrity, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
Potential markers
None of the slope measures correlated with number of visits or use of tobacco or cannabis. The association of alcohol with the slope measures was more apparent in the younger cohort (<19 years).
“The effects were seen more readily in younger adolescents because they are the ones who are still progressing along this normal developmental trajectory,” Dr. Pfefferbaum noted. “In a sense, the younger you are when you’re exposed to alcohol, probably the more vulnerable you are.”
Previous studies have suggested that damage in WM tracts is associated with heightened neural reactivity to alcohol cues in adults with alcohol use disorder. Given this evidence, the greater WM degradation at younger versus older ages might help explain why adolescents who initiate early drinking are more likely to develop addiction later in life, the investigators wrote.
Of the five major fiber tracts, only the commissural fibers (corpus callosum) showed a significant association with alcohol. The researchers noted that WM volume shrinkage and callosal demyelination are two of the most prominent markers in adult alcoholism and are potential markers in adolescent alcohol abuse.
Upon further extending the analysis to the four subregions of the corpus callosum, the investigators found that only the anterior and middle callosal regions (genu and body) showed significant age-alcohol interactions.
This could be a result of the timing of fiber myelination in these regions of the brain, compared with others, Dr. Pfefferbaum said.
He noted that these fibers connect the left and right part of the anterior regions of the brain, especially the frontal lobes, which are particularly vulnerable to the effects of alcohol. “It may well be that we have this interaction of the developmental time and the sensitivity of the frontal parts of the brain.”
Cognitive effects?
Although the researchers did not find any sex effects, Dr. Pfefferbaum stressed that this doesn’t mean they do not exist. “We just may not have the power to see them,” he said.
The study did not look specifically at binge drinkers, defined as consuming five drinks in 2 hours for men and four drinks in 2 hours for women. Dr. Pfefferbaum noted that it is difficult to get “good quantification” of binge drinking. “We don’t have a fine enough grain analysis to separate that out,” he said.
Asked whether the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers affects cognition, Dr. Pfefferbaum said “those studies are still in progress,” with results hopefully available within about a year.
Dr. Pfefferbaum said he and his colleagues are continuing to follow these adolescents and hope to see if the altered FA trajectory in heavy drinkers returns to normal, adding: “The real question now is: If they stop heavy drinking, will they get back on track?”
This study is believed to be the first to suggest in vivo differential vulnerability in WM microstructure with respect to age, the authors note.
In addition to asking teens about their alcohol use, the clinician’s role should be to “counsel and refer,” said Dr. Pfefferbaum. He also suggested accessing resources from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Important data, but several limitations
In an interview, Oscar G. Bukstein, MD, MPH, medical director of outpatient psychiatry service at Boston Children’s Hospital, and professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, said the findings provide further evidence that alcohol affects the maturing brain.
This study, and others that have examined cannabis use, “show that you have a dynamically growing brain with certain sections, particularly in this case the anterior and middle corpus callosum, that mature later [and] that are more likely to be affected by early alcohol use,” said Dr. Bukstein, who was not involved with the research.
He stressed the importance of determining the mechanism involved and noted some study limitations. For example, the DTI technology used may “already be out of date,” he said.
Using older technology may have prevented finding an impact of heavy drinking on parts of the brain other than the anterior and middle corpus callosum, Dr. Bukstein noted.
Newer technology might provide “a finer-grain nonlinear voxel-wise analysis,” although using more updated scanning techniques may not have detected additional differences in study groups, he added.
Dr. Bukstein also noted that there were limitations: The study did not have “gradations,” but only looked at heavy drinking and no to low drinking. “You’d like to find out about kids who are somewhere in the middle.” It also didn’t determine a “cutoff” where deleterious effects of alcohol on the brain begin, Dr. Bukstein added.
Additionally, the study didn’t look at brain development outcomes in children with conditions such as depression and ADHD that are known to lead to substance use – something a larger study may have been able to do, he said.
Dr. Bukstein noted that a newer and much larger study, the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development study, has begun assessing kids for risk factors such as substance use, starting at age 10 years.
The study was funded by grants from NIAAA and by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence–AWS Cloud Credits for Research. Dr. Pfefferbaum reported receiving an NIAAA grant during the conduct of the study. Dr. Bukstein disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Retrospective Chart Review of Advanced Practice Pharmacist Prescribing of Controlled Substances for Pain Management at the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
In the midst of an opioid overdose public health crisis, the US Department of Health and Human Services developed a 5-point strategy to combat this problem. One aspect of this strategy is improved pain management.1 There is high demand for pain management services with a limited number of health care professionals appropriately trained to deliver care.2 Pharmacists are integral members of the interdisciplinary pain team and meet this demand.
Background
For almost 50 years, pharmacists at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) have been functioning as advanced practice providers (APP).3 Clinical pharmacy specialists (CPS) provide comprehensive medication management (CMM) and have a scope of practice (SOP). The SOP serves as the collaborating agreement and outlines the clinical duties permitted in delivering patient care. In addition, the SOP may indicate specific practice areas and are standardized across VA (Table 1).4,5 Pharmacists apply for a SOP and must prove their competency in the practice area and provide documentation of their education, training, experience, knowledge, and skills.5,6 Residency and/or board certification are not required though helpful. A pharmacist’s SOP is reviewed and approved by the facility executive committee.5 Pharmacists with a SOP undergo professional practice evaluation twice a year. Prescribing controlled substances is permissible in the SOP if approved by the facility and allowed by the state of licensure. According to the US Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as of February 10, 2020, 8 states (California, Washington, Idaho, Massachusetts, Montana, New Mexico, North Carolina, and Ohio) allow pharmacists to prescribe controlled substances.7
The VA developed the Pharmacists Achieve Results with Medications Documentation (PhARMD) tool that allows clinical pharmacists to document specific interventions made during clinical care and is included in their progress note. Data from fiscal year 2017 demonstrates that 136,041 pain management interventions were made by pharmacists across VA. The majority of these interventions were implemented by a CPS working autonomously as an APP.8
Several articles discuss the pharmacists role in the opioid crisis, although no outcomes data were provided. Chisholm-Burns and colleagues listed multiple potential ways that pharmacists can intervene, including managing pain in primary care clinic settings by using collaborative drug therapy agreements (CDTAs), using opioid exit plans and discharge planning in collaboration with other health care providers (HCPs), or making recommendations to the prescribers before writing prescriptions.9 Compton and colleagues similarly reviewed pharmacist roles in the opioid crisis. However, their focus was on dispensing pharmacists that provided education to patients about storage and disposal of opioids, identified opioid misuse, provided opioid overdose education and naloxone, and checked prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs).10 Missing from these articles was the role of the clinical pharmacist working as an APP delivering direct patient care and prescribing controlled substances.
Hammer and colleagues discussed the role of an oncology CPS with controlled substance prescriptive authority in pain management at an outpatient cancer center in Washington state.11 Under a CDTA, pharmacists could prescribe medications, including controlled substances if they obtain DEA registration. The pharmacist completed a comprehensive in-person assessment. The attending physician conducted a physical examination. Then the pharmacist presented the patient and proposed regimen to the interprofessional team to determine a final plan. Ultimately, the pharmacist wrote any controlled substance prescriptions. The patient followed up every 1 to 4 weeks by telephone with a nurse, and in-person assessments occurred at least every 6 months. No outcomes data were provided.11
Dole and colleagues reviewed the role of a pharmacist who had controlled substance prescriptive authority in a pain management clinic. The pharmacist provider saw up to 18 patients a day and then managed refill requests for 3 hours a day. The main outcome was change in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores. Findings showed that reductions in VAS pain scores were statistically significant (P < .01). The pharmacist processed about 150 refills with an unclear number of controlled substances requests a day based on a medication-refill protocol. This was felt to improve access to physicians for acute needs, improve consistency in refills, and capture patients in need of follow-up. Additionally, the clinic saved $455,238 after 1 year.12
Study Aims
A review of the literature indicated sparse data on the impact of a pharmacist on opioid tapering, opioid dose, and opioid risk mitigation when the pharmacist is prescribing controlled substances. The purpose of this retrospective review was to characterize the controlled substance prescribing practices by the pharmacy pain clinic. The aim was to examine the pharmacist impact on morphine milligram equivalent (MME) and compliance with opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Methods
This project was a retrospective, single-center, chart review. The project was reviewed and approved by the University of Missouri-Columbia Institutional Review Board used by the Harry S. Truman Memorial Veterans’ Hospital (HSTMVH) as a quality improvement project. The author applied for controlled substance registration through the DEA and was issued registration April 30, 2018. The State of Ohio Board of Pharmacy was contacted as required by Ohio Administrative Code. The author's updated SOP to allow controlled substance prescribing was approved July 23, 2018. The CPS functions as an APP within an interdisciplinary pain management team that includes physicians, occupational and physical therapists, complementary and integrative health, and a psychologist. The reason for Pharmacy Pain Consult is required and it is primarily submitted through the electronic health record. The consult is reviewed for appropriateness and once approved is scheduled by support staff. Once the patient is stabilized, the patient is discharged back to their primary care provider (PCP) or referring provider for continued care. Patients were considered stabilized when their patient-specific goals were met, which varied from use of the lowest effective opioid dose to taper to discontinuation of opioids with no further medication changes needed. The taper strategy for each patient was individualized. Patients were generally tapered on their existing opioid medication unless they were new to the VA and on nonformulary medications or experiencing a significant adverse reaction. Numerous references are available through VA to assist with opioid tapering.13,14 The CPS is able to refer patients to other services, including behavioral health for substance use disorder treatment and medication-assisted treatment if concerns were identified.
Initial data were collected from the Veterans Integrated Service Network (VISN) 15 Corporate Data Warehouse by the VISN pharmacy analytics program manager. The original report included patients prescribed a Schedule II to V controlled substance by the author from July 1, 2018 to January 31, 2020. Chart review was conducted on each patient to obtain additional data. At the time of consult and discharge the following data were collected: opioid medication; MME; use of opioid risk mitigation strategies, such as urine drug screens (UDS), informed consent, opioid overdose education and naloxone distribution program (OEND), risk assessment via stratification tool for opioid risk mitigation (STORM), PDMP checks; and nonopioid medication number and classes.
Patients were included in the review if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance between July 1, 2018 and January 31, 2020. Patient were excluded if they were prescribed an opioid Schedule II or III controlled substance primarily as coverage for another prescriber. Patients prescribed only pregabalin, tramadol, or a benzodiazepine also were excluded.
The primary endpoint was change in MME from baseline to discharge from clinic. Secondary endpoints included change in opioid risk mitigation strategies and change in opioid medications prescribed from baseline to discharge.
Descriptive statistics were used to analyze parts of the data. A 2-sided t test was used to compare baseline and discharge MME. The Fisher exact test was used to compare nominal data of opioid risk mitigation strategies.
Calculation of MME was performed using the conversion factors provided by the Centers Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for opioid guideline.15 For buprenorphine, tapentadol, and levorphanol conversion ratios were obtained from other sources. The conversion ratios used, included 75:1 for oral morphine to transdermal buprenorphine, 1:3.3 for oral morphine to oral tapentadol, and 1:7.5 for oral levorphanol to oral morphine.16,17 The Revised Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE 2.0) was used to write the manuscript.18
Results
Seventy-five patients were included in this review. The average age of patients was 66 years; and 12% were female (n = 9) (Table 2). The largest number of consults came from PCPs (44%, n = 33) and the pain clinic (43%, n = 32). Nearly half (48%) of the consultations were for opioid tapering (n = 36), followed by 37% for opioid optimization or monitoring (n = 28), and 19% for nonopioid optimization (n = 14). The most common primary diagnoses at consultation were for chronic low back pain (56%), chronic neck pain (20%), and osteoarthritis (16%).
The average MME at time of consult was 93 MME compared with 31 MME at discharge which was statisticially significant (P < .01) (Figure 1). The mean percent change in MME was 46%, including methadone and 42% excluding methadone. There was a 26% change in UDS, 28% change in informed consent, 85% change in PDMP, 194% change in naloxone, and 357% change in STORM reviews from baseline to discharge with all demonstrating statistical significance (P < .01) (Figure 2). At discharge, the most common opioid prescribed was morphine SA (short acting) (n = 10, 13%, 44 average MME) and oxycodone/acetaminophen (n = 10, 13%, 28 average MME) (Table 3).
The average number of days from consult to initial visit was 23 days (Table 4). Face-to-face was the primary means of initial visit with 92% (n = 69) of visits, but phone was the primary mode of follow-up with 73% of visits (n = 55). The average number of follow-up visits was 7, representing 176 average days of time in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Consultation to the behavioral health performance program was the most common referral (n = 13, 17%).
Five patients were new opioid starts in the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Two patients were on tramadol at time of consult. Of the 5 new opioid starts, 3 patients received oxycodone/acetaminophen, 1 received buprenorphine patch, and 1 received hydrocodone/acetaminophen. The new opioid start average was 25 MME. All 5 patients had a UDS for opioid risk mitigation, 4 used consent and STORM reviews, and 2 patients had PDMP checks and naloxone.
Discussion
There was a statistically significant decrease of the mean MME between the time of consult and the time of discharge. There also were statistically significant changes in use of opioid risk mitigation strategies. Since methadone has a high MME, the mean reduction of MME was calculated with methadone (46%) and without methadone (42%). These data are consistent with other published studies examining opioid tapers in the VA population. Harden and colleagues calculated a 46% mean reduction in MME over 12 months for 72 veterans from opioid tapers implemented by PCPs, pain service, or pharmacist-run clinics.19
There is controversy about equianalgesic doses and no established universal equianalgesic conversion calculator or dose. Numerous equianalgesic opioid dose calculators are available, but for this analysis the CDC MME conversion factors were used (available at: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/calculating_total_daily_dose-a.pdf). Previous literature compared existing calculators and found significant variances in calculated doses for methadone and fentanyl conversions.20 Additionally, there have been concerns expressed with the safety of the CDC opioid calculator specifically surrounding the conversions for methadone and tapentadol.21 In the end, I chose the CDC calculator because it is established, readily available, and consistent.
Pharmacists in pain management can address access issues.2,3,11,12 The average length of time from consult to initial visit was 23 days. Often patients may have seen a HCP who implemented a change at the time of consult and wanted the patient to be seen 1 month later. Many patients at the HSTMVH live far from the facility, making in-person visits difficult. A majority of the follow-up visits were conducted by telephone. Patients were offered all modalities available for follow-up, including telephone, in-person, or telemedicine, but patients most often picked telephone. Patients averaged 7 follow-up visits before discharge. This number of visits would have taken time from other health care team members who could have been addressing other veterans. Patients were seen in clinic for 176 days on average, which supports and follows recommendations for a slow, incremental taper.
The opioid medications prescribed changed over time in the clinic. Methadone prescriptions dropped from 20 to 6 at consult to discharge, and fentanyl prescriptions fell from 7 to 2, respectively. The CDC guideline suggests use of long-acting products with more predictable pharmacokinetics (eg, morphine SA or oxycodone SA) rather than fentanyl or methadone.15 Notably, the use of buprenorphine products with FDA approval for pain indications increased from consult to discharge. Many of the patients in this study had pulmonary comorbidities, placing them at higher risk for adverse outcomes. Buprenorphine is a partial μ-opioid receptor agonist with a ceiling on respiratory depression so is potentially less risky in those with pulmonary comorbidities.
The biggest changes in opioid risk mitigation occurred in PDMP, OEND program, and STORM reviews. An 85% increase in PDMP reviews occurred with referral to the clinic. Missouri is the only state without a state-run PDMP. However, the St. Louis County PDMP was developed based on city or county participation and encompasses 85% of the population of Missouri and 94% of HCPs in Missouri as of August 29, 2019.22 Because there is no state-level PDMP, a review of the St. Louis County PDMP was not required during the review period. Nevertheless, the Pharmacy Pain Clinic uses the St. Louis County PDMP at the initial visit and regularly during care. VA policy requires a specific note title be used to document each check of the PDMP.23
There was a 194% increase in patients receiving naloxone with consultation to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic. Due to low coprescribing of naloxone for patients prescribed chronic opioid therapy, The author led an interdisciplinary team analysis of health care failure mode effects during the study period. This led to a process change with coprescribing of naloxone at refill in the primary care clinic.
The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016 mandated that the VA review STORM on new start of opioids or patient identified as “very high-opioid prescription risk” category by an interdisciplinary opioid risk review team.24 Thus many of the patients referred to clinic didn’t require STORM reviews since they were not new opioid starts or identified as high risk. However, in the standard review of all new patients to the Pharmacy Pain Clinic, a STORM review is conducted and documented to assess the patient’s level of risk.
Only 5 patients were started on opioid medications during the study period. This is consistent with both CDC and the joint VA/US Department of Defense opioid prescribing guidelines that recommend against initiation of opioids for chronic nonmalignant pain.13,15 Two of the patients were prescribed tramadol for ineffective pain control at time of consult. Furthermore, 4 of the 5 patients were started on a short-acting opioid, which was supported by guidelines.13,15 One patient was initiated on buprenorphine patches due to comorbid chronic kidney disease. The VA does not limit the quantity of new opioid prescriptions, although some states and private insurance plans are implementing limitations. Guidelines also recommend against exceeding 90 MME due to risk. The average MME in this project at discharge was 25 MME. Use of opioid risk mitigation for the new opioid starts was reasonable. The reason for the missing PDMP report is unknown based on chart review and atypical according to clinic practice.
Recently, efforts to expand pharmacist training and positions in pain management at VA facilities have been undertaken. In 2016, there were just 11 American Society of Health-System Pharmacists-accredited pharmacy postgraduate year 2 pain and palliative care residency programs, which has expanded to 26 sites in 2020.2,3,25 In addition, the Clinical Pharmacy Practice Office and the VA Office of Rural Health have helped to hire 33 new pain management pharmacists.3
The role of pharmacists in prescribing controlled substances is limited mainly due to the small number of states that extend this authority.7 At the VA, a pharmacist can practice using any state of licensure. Therefore, a pharmacist working at a VA in a state that does not authorize controlled substance prescribing could obtain a license in a state that does permit it. However, the main barrier to obtaining other state licensures is the cost. At the time the author obtained controlled substance prescriptive authority, little direction was available on the process for advanced practice pharmacists at the VA. Since then, guidance has been developed to ease this process. Educational endeavors at VA have been implemented with the intent to increase the number of pharmacists with controlled substance prescriptive authority.
Barriers to pharmacists providing pain care extend beyond limited controlled substance prescriptive authority. Often pharmacists are still viewed in their traditional and operational role.9,10 Other health care team members and patients may not be aware or familiar with the training, knowledge, and skills of pharmacist's and their suitability as an APP.26,27 Most states permit pharmacists in establishing CDTA but not all. Additionally, some states recognize pharmacists as HCPs but many more do not. Furthermore, the Social Security Act does not include pharmacists as HCPs. This makes it challenging, though not impossible, for pharmacists to bill for their services.3
Strengths and Limitations
There were numerous strengths of the project. First, this addressed an unmet need in the literature with limited data discussing pharmacist prescribing controlled substances for pain management. There was 1 data reviewer who made the data collection process consistent. Since this retrospectively reviewed controlled substance prescribing in clinic, it captured real-world practice compared with that of experimental models. There were also several limitations in the project. The person collecting the data was also the person who conducted the clinic. The study was conducted retrospectively and based on documented information in the medical record. The population reviewed was primarily male and older, which fits the VA patient population but has less generalizability to other patient populations. This project was conducted at a single VA facility so may not be generalizable to other VA sites. It is unknown whether patients were again prescribed opioids if they left the VA for the community or another VA facility. The pain diagnoses or locations of pain were categorized to main groups and reliant on the referring provider. Another major weakness was the lack of comparison of pain scores or validated objective measure of function at baseline and at discharge. This consideration would be important for future work.
Conclusions
Pharmacists functioning as APP are key members of the pain management team. A review of a pharmacy-run pain clinic demonstrated statistically significant reduction in MME and improvement in opioid risk mitigation from consult to discharge. Patients enrolled in the pharmacy-managed clinic also had improvements in adherence to opioid risk mitigation strategies. Future attention should be focused on further expanding training and positions for pharmacists as APP in pain management.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Chris Sedgwick for his assistance with data capture.
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9
1. US Department of Health and Human Services. Help and resources: national opioid crisis. Updated August 30, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/about-the-epidemic/hhs-response/index.html
2. Atkinson TJ, Gulum AH, Forkum WG. The future of pain pharmacy: driven by need. Integr Pharm Res Pract. 2016;5:33-42. doi:10.2147/IPRP.S63824
3. Seckel E, Jorgenson T, McFarland S. Meeting the national need for expertise in pain management with clinical pharmacist advanced practice providers. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2019;45(5):387-392.doi:10.1016/j.jcjq.2019.01.002
4. McFarland MS, Groppi J, Ourth H, et al. Establishing a standardized clinical pharmacy practice model within the Veterans Health Administration: evolution of the credentialing and professional practice evaluation process. J Am Coll Clin Pharm. 2018;1(2):113-118. doi:10.1002/jac5.1022
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook. 1108.11. Clinical pharmacy services. Published July 1, 2015. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3120
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Handbook 1100.19. Credentialing and priveleging. Published October 15, 2012. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=2910
7. US Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Agency. Mid-level practitioners authorization by state. Updated February 10, 2020. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugreg/practioners/mlp_by_state.pdf
8. Groppi JA, Ourth H, Morreale AP, Hirsh JM, Wright S. Advancement of clinical pharmacy practice through intervention capture. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(12):886-892. doi:10.2146/ajhp170186
9. Chisholm-Burns MA, Spivey CA, Sherwin E, Wheeler J, Hohmeier K. The opioid crisis: origins, trends, policies, and the roles of pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(7):424-435. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxy089
10. Compton WM, Jones CM, Stein JB, Wargo EM. Promising roles for pharmacists in addressing the U.S. opioid crisis. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(8):910-916. doi:10.1016/j.sapharm.2017.12.009
11. Hammer KJ, Segal EM, Alwan L, et al. Collaborative practice model for management of pain in patients with cancer. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1434-1441. doi:10.2146/ajhp150770
12. Dole EJ, Murawski MM, Adolphe AB, Aragon FD, Hochstadt B. Provision of pain management by a pharmacist with prescribing authority. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007;64(1):85-89. doi:10.2146/ajhp060056
13. US Department of Defense, US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for Opioid Therapy for Chronic Pain. Updated 2017. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/Pain/cot/VADoDOTCPG022717.pdf
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA, VHA, VA Academic Detailing Service. Veterans Health Administration. Opioid taper decision tool. Updated October 2016. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.pbm.va.gov/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/Pain_Opioid_Taper_Tool_IB_10_939_P96820.pdf
15. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain - United States, 2016 [published correction appears in MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(11):295]. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(1):1-49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1
16. McPherson M. Demystifying opioid conversion calculations. Published 2009. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.ashp.org/-/media/store-files/p1985-frontmatter.ashx
17. Gudin J, Fudin J, Nalamachu S. Levorphanol use: past, present and future. Postgrad Med. 2016;128(1):46-53. doi:10.1080/00325481.2016.1128308
18. Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden P, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(12):986-992. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004411
19. Harden P, Ahmed S, Ang K, Wiedemer N. Clinical implications of tapering chronic opioids in a veteran population. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1975-1981. doi:10.1111/pme.12812
20. Shaw K, Fudin J. Evaluation and comparison of online equianalgesic opioid dose conversion calculators. Practical Pain Manag. 2013;13(7):61-66. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/opioids/evaluation-comparison-online-equianalgesic-opioid-dose-conversion
21. Fudin J, Raouf M, Wegrzyn EL, Schatman ME. Safety concerns with the Centers for Disease Control opioid calculator. J Pain Res. 2017;11:1-4. Published 2017 Dec 18. doi:10.2147/JPR.S155444
22. Saint Louis County Public Health. St. Louis County Prescription Drug Monitoring Program. Participating jurisdictions. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://pdmp-stlcogis.hub.arcgis.com
23. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. VHA Directive 1306: querying state prescription drug monitoring programs. Updated October 21, 2019. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=3283
24. Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016. 42 USC § 201 (2016).
25. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Residency directory. Accessed November 18, 2020. https://accreditation.ashp.org/directory/#/program/residency
26. Feehan M, Durante R, Ruble J, Munger MA. Qualitative interviews regarding pharmacist prescribing in the community setting. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1456-1461. doi:10.2146/ajhp150691
27. Giannitrapani KF, Glassman PA, Vang D, et al. Expanding the role of clinical pharmacists on interdisciplinary primary care teams for chronic pain and opioid management. BMC Fam Pract. 2018;19(1):107. doi:10.1186/s12875-018-0783-9