User login
Deep sleep may mitigate the impact of Alzheimer’s pathology
Investigators found that deep sleep, also known as non-REM (NREM) slow-wave sleep, can protect memory function in cognitively normal adults with a high beta-amyloid burden.
“Think of deep sleep almost like a life raft that keeps memory afloat, rather than memory getting dragged down by the weight of Alzheimer’s disease pathology,” senior investigator Matthew Walker, PhD, professor of neuroscience and psychology, University of California, Berkeley, said in a news release.
The study was published online in BMC Medicine.
Resilience factor
Studying resilience to existing brain pathology is “an exciting new research direction,” lead author Zsófia Zavecz, PhD, with the Center for Human Sleep Science at the University of California, Berkeley, said in an interview.
“That is, what factors explain the individual differences in cognitive function despite the same level of brain pathology, and how do some people with significant pathology have largely preserved memory?” she added.
The study included 62 cognitively normal older adults from the Berkeley Aging Cohort Study.
Sleep EEG recordings were obtained over 2 nights in a sleep lab and PET scans were used to quantify beta-amyloid. Half of the participants had high beta-amyloid burden and half were beta-amyloid negative.
After the sleep studies, all participants completed a memory task involving matching names to faces.
The results suggest that deep NREM slow-wave sleep significantly moderates the effect of beta-amyloid status on memory function.
Specifically, NREM slow-wave activity selectively supported superior memory function in adults with high beta-amyloid burden, who are most in need of cognitive reserve (B = 2.694, P = .019), the researchers report.
In contrast, adults without significant beta-amyloid pathological burden – and thus without the same need for cognitive reserve – did not similarly benefit from NREM slow-wave activity (B = –0.115, P = .876).
The findings remained significant after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, gray matter atrophy, and previously identified cognitive reserve factors, such as education and physical activity.
Dr. Zavecz said there are several potential reasons why deep sleep may support cognitive reserve.
One is that during deep sleep specifically, memories are replayed in the brain, and this results in a “neural reorganization” that helps stabilize the memory and make it more permanent.
“Other explanations include deep sleep’s role in maintaining homeostasis in the brain’s capacity to form new neural connections and providing an optimal brain state for the clearance of toxins interfering with healthy brain functioning,” she noted.
“The extent to which sleep could offer a protective buffer against severe cognitive impairment remains to be tested. However, this study is the first step in hopefully a series of new research that will investigate sleep as a cognitive reserve factor,” said Dr. Zavecz.
Encouraging data
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, said although the study sample is small, the results are “encouraging because sleep is a modifiable factor and can therefore be targeted.”
“More work is needed in a larger population before we can fully leverage this stage of sleep to reduce the risk of developing cognitive decline,” Dr. Griffin said.
Also weighing in on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said the study is “exciting on two fronts – we may have an additional marker for the development of Alzheimer’s disease to predict risk and track disease, but also targets for early intervention with sleep architecture–enhancing therapies, be they drug, device, or digital.”
“For the sake of our brain health, we all must get very familiar with the concept of cognitive or brain reserve,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
“Brain reserve refers to our ability to buttress against the threat of dementia and classically it’s been associated with ongoing brain stimulation (i.e., higher education, cognitively demanding job),” he noted.
“This line of research now opens the door that optimal sleep health – especially deep NREM slow wave sleep – correlates with greater brain reserve against Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Lakhan said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the University of California, Berkeley. Dr. Walker serves as an advisor to and has equity interest in Bryte, Shuni, Oura, and StimScience. Dr. Zavecz and Dr. Lakhan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that deep sleep, also known as non-REM (NREM) slow-wave sleep, can protect memory function in cognitively normal adults with a high beta-amyloid burden.
“Think of deep sleep almost like a life raft that keeps memory afloat, rather than memory getting dragged down by the weight of Alzheimer’s disease pathology,” senior investigator Matthew Walker, PhD, professor of neuroscience and psychology, University of California, Berkeley, said in a news release.
The study was published online in BMC Medicine.
Resilience factor
Studying resilience to existing brain pathology is “an exciting new research direction,” lead author Zsófia Zavecz, PhD, with the Center for Human Sleep Science at the University of California, Berkeley, said in an interview.
“That is, what factors explain the individual differences in cognitive function despite the same level of brain pathology, and how do some people with significant pathology have largely preserved memory?” she added.
The study included 62 cognitively normal older adults from the Berkeley Aging Cohort Study.
Sleep EEG recordings were obtained over 2 nights in a sleep lab and PET scans were used to quantify beta-amyloid. Half of the participants had high beta-amyloid burden and half were beta-amyloid negative.
After the sleep studies, all participants completed a memory task involving matching names to faces.
The results suggest that deep NREM slow-wave sleep significantly moderates the effect of beta-amyloid status on memory function.
Specifically, NREM slow-wave activity selectively supported superior memory function in adults with high beta-amyloid burden, who are most in need of cognitive reserve (B = 2.694, P = .019), the researchers report.
In contrast, adults without significant beta-amyloid pathological burden – and thus without the same need for cognitive reserve – did not similarly benefit from NREM slow-wave activity (B = –0.115, P = .876).
The findings remained significant after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, gray matter atrophy, and previously identified cognitive reserve factors, such as education and physical activity.
Dr. Zavecz said there are several potential reasons why deep sleep may support cognitive reserve.
One is that during deep sleep specifically, memories are replayed in the brain, and this results in a “neural reorganization” that helps stabilize the memory and make it more permanent.
“Other explanations include deep sleep’s role in maintaining homeostasis in the brain’s capacity to form new neural connections and providing an optimal brain state for the clearance of toxins interfering with healthy brain functioning,” she noted.
“The extent to which sleep could offer a protective buffer against severe cognitive impairment remains to be tested. However, this study is the first step in hopefully a series of new research that will investigate sleep as a cognitive reserve factor,” said Dr. Zavecz.
Encouraging data
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, said although the study sample is small, the results are “encouraging because sleep is a modifiable factor and can therefore be targeted.”
“More work is needed in a larger population before we can fully leverage this stage of sleep to reduce the risk of developing cognitive decline,” Dr. Griffin said.
Also weighing in on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said the study is “exciting on two fronts – we may have an additional marker for the development of Alzheimer’s disease to predict risk and track disease, but also targets for early intervention with sleep architecture–enhancing therapies, be they drug, device, or digital.”
“For the sake of our brain health, we all must get very familiar with the concept of cognitive or brain reserve,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
“Brain reserve refers to our ability to buttress against the threat of dementia and classically it’s been associated with ongoing brain stimulation (i.e., higher education, cognitively demanding job),” he noted.
“This line of research now opens the door that optimal sleep health – especially deep NREM slow wave sleep – correlates with greater brain reserve against Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Lakhan said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the University of California, Berkeley. Dr. Walker serves as an advisor to and has equity interest in Bryte, Shuni, Oura, and StimScience. Dr. Zavecz and Dr. Lakhan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators found that deep sleep, also known as non-REM (NREM) slow-wave sleep, can protect memory function in cognitively normal adults with a high beta-amyloid burden.
“Think of deep sleep almost like a life raft that keeps memory afloat, rather than memory getting dragged down by the weight of Alzheimer’s disease pathology,” senior investigator Matthew Walker, PhD, professor of neuroscience and psychology, University of California, Berkeley, said in a news release.
The study was published online in BMC Medicine.
Resilience factor
Studying resilience to existing brain pathology is “an exciting new research direction,” lead author Zsófia Zavecz, PhD, with the Center for Human Sleep Science at the University of California, Berkeley, said in an interview.
“That is, what factors explain the individual differences in cognitive function despite the same level of brain pathology, and how do some people with significant pathology have largely preserved memory?” she added.
The study included 62 cognitively normal older adults from the Berkeley Aging Cohort Study.
Sleep EEG recordings were obtained over 2 nights in a sleep lab and PET scans were used to quantify beta-amyloid. Half of the participants had high beta-amyloid burden and half were beta-amyloid negative.
After the sleep studies, all participants completed a memory task involving matching names to faces.
The results suggest that deep NREM slow-wave sleep significantly moderates the effect of beta-amyloid status on memory function.
Specifically, NREM slow-wave activity selectively supported superior memory function in adults with high beta-amyloid burden, who are most in need of cognitive reserve (B = 2.694, P = .019), the researchers report.
In contrast, adults without significant beta-amyloid pathological burden – and thus without the same need for cognitive reserve – did not similarly benefit from NREM slow-wave activity (B = –0.115, P = .876).
The findings remained significant after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, gray matter atrophy, and previously identified cognitive reserve factors, such as education and physical activity.
Dr. Zavecz said there are several potential reasons why deep sleep may support cognitive reserve.
One is that during deep sleep specifically, memories are replayed in the brain, and this results in a “neural reorganization” that helps stabilize the memory and make it more permanent.
“Other explanations include deep sleep’s role in maintaining homeostasis in the brain’s capacity to form new neural connections and providing an optimal brain state for the clearance of toxins interfering with healthy brain functioning,” she noted.
“The extent to which sleep could offer a protective buffer against severe cognitive impairment remains to be tested. However, this study is the first step in hopefully a series of new research that will investigate sleep as a cognitive reserve factor,” said Dr. Zavecz.
Encouraging data
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, said although the study sample is small, the results are “encouraging because sleep is a modifiable factor and can therefore be targeted.”
“More work is needed in a larger population before we can fully leverage this stage of sleep to reduce the risk of developing cognitive decline,” Dr. Griffin said.
Also weighing in on this research, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher in Boston, said the study is “exciting on two fronts – we may have an additional marker for the development of Alzheimer’s disease to predict risk and track disease, but also targets for early intervention with sleep architecture–enhancing therapies, be they drug, device, or digital.”
“For the sake of our brain health, we all must get very familiar with the concept of cognitive or brain reserve,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
“Brain reserve refers to our ability to buttress against the threat of dementia and classically it’s been associated with ongoing brain stimulation (i.e., higher education, cognitively demanding job),” he noted.
“This line of research now opens the door that optimal sleep health – especially deep NREM slow wave sleep – correlates with greater brain reserve against Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Lakhan said.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the University of California, Berkeley. Dr. Walker serves as an advisor to and has equity interest in Bryte, Shuni, Oura, and StimScience. Dr. Zavecz and Dr. Lakhan report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BMC MEDICINE
FDA approves first drug to treat Alzheimer’s agitation
(AD), making it the first FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“Agitation is one of the most common and challenging aspects of care among patients with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease,” Tiffany Farchione, MD, director of the division of psychiatry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
Agitation can include symptoms that range from pacing or restlessness to verbal and physical aggression. “These symptoms are leading causes of assisted living or nursing home placement and have been associated with accelerated disease progression,” Dr. Farchione said.
Brexpiprazole was approved by the FDA in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
Approval of the supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation associated with AD dementia was based on results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
In both studies, patients who received 2 mg or 3 mg of brexpiprazole showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in agitation symptoms, as shown by total Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) score, compared with patients who received placebo.
The recommended starting dosage for the treatment of agitation associated with AD dementia is 0.5 mg once daily on days 1-7; it was increased to 1 mg once daily on days 8-14 and then to the recommended target dose of 2 mg once daily.
The dosage can be increased to the maximum recommended daily dosage of 3 mg once daily after at least 14 days, depending on clinical response and tolerability.
The most common side effects of brexpiprazole in patients with agitation associated with AD dementia include headache, dizziness, urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and sleep disturbances.
The drug includes a boxed warning for medications in this class that elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death.
The supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation had fast-track designation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(AD), making it the first FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“Agitation is one of the most common and challenging aspects of care among patients with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease,” Tiffany Farchione, MD, director of the division of psychiatry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
Agitation can include symptoms that range from pacing or restlessness to verbal and physical aggression. “These symptoms are leading causes of assisted living or nursing home placement and have been associated with accelerated disease progression,” Dr. Farchione said.
Brexpiprazole was approved by the FDA in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
Approval of the supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation associated with AD dementia was based on results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
In both studies, patients who received 2 mg or 3 mg of brexpiprazole showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in agitation symptoms, as shown by total Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) score, compared with patients who received placebo.
The recommended starting dosage for the treatment of agitation associated with AD dementia is 0.5 mg once daily on days 1-7; it was increased to 1 mg once daily on days 8-14 and then to the recommended target dose of 2 mg once daily.
The dosage can be increased to the maximum recommended daily dosage of 3 mg once daily after at least 14 days, depending on clinical response and tolerability.
The most common side effects of brexpiprazole in patients with agitation associated with AD dementia include headache, dizziness, urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and sleep disturbances.
The drug includes a boxed warning for medications in this class that elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death.
The supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation had fast-track designation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(AD), making it the first FDA-approved drug for this indication.
“Agitation is one of the most common and challenging aspects of care among patients with dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease,” Tiffany Farchione, MD, director of the division of psychiatry in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release.
Agitation can include symptoms that range from pacing or restlessness to verbal and physical aggression. “These symptoms are leading causes of assisted living or nursing home placement and have been associated with accelerated disease progression,” Dr. Farchione said.
Brexpiprazole was approved by the FDA in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
Approval of the supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation associated with AD dementia was based on results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
In both studies, patients who received 2 mg or 3 mg of brexpiprazole showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in agitation symptoms, as shown by total Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) score, compared with patients who received placebo.
The recommended starting dosage for the treatment of agitation associated with AD dementia is 0.5 mg once daily on days 1-7; it was increased to 1 mg once daily on days 8-14 and then to the recommended target dose of 2 mg once daily.
The dosage can be increased to the maximum recommended daily dosage of 3 mg once daily after at least 14 days, depending on clinical response and tolerability.
The most common side effects of brexpiprazole in patients with agitation associated with AD dementia include headache, dizziness, urinary tract infection, nasopharyngitis, and sleep disturbances.
The drug includes a boxed warning for medications in this class that elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death.
The supplemental application for brexpiprazole for agitation had fast-track designation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hearing aids are a ‘powerful’ tool for reducing dementia risk
, new research confirms. A large observational study from the United Kingdom showed a 42% increased risk for dementia in people with hearing loss compared with their peers with no hearing trouble. In addition, there was no increased risk in those with hearing loss who used hearing aids.
“The evidence is building that hearing loss may be the most impactful modifiable risk factor for dementia in mid-life, but the effectiveness of hearing aid use on reducing the risk of dementia in the real world has remained unclear,” Dongshan Zhu, PhD, with Shandong University, Jinan, China, said in a news release.
“Our study provides the best evidence to date to suggest that hearing aids could be a minimally invasive, cost-effective treatment to mitigate the potential impact of hearing loss on dementia,” Dr. Zhu said.
The study, which was published online in Lancet Public Health, comes on the heels of the 2020 Lancet Commission report on dementia, which suggested hearing loss may be linked to approximately 8% of worldwide dementia cases.
‘Compelling’ evidence
For the study, investigators analyzed longitudinal data on 437,704 individuals, most of whom were White, from the UK Biobank (54% female; mean age at baseline, 56 years). Roughly three quarters of the cohort had no hearing loss and one quarter had some level of hearing loss, with 12% of these individuals using hearing aids.
After the researchers controlled for relevant cofactors, compared with people without hearing loss, those with hearing loss who were not using hearing aids had an increased risk for all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.29-1.56).
No increased risk was seen in people with hearing loss who were using hearing aids (HR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.98-1.10).
The positive association of hearing aid use was observed in all-cause dementia and cause-specific dementia subtypes, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and non–Alzheimer’s disease nonvascular dementia.
The data also suggest that the protection against dementia conferred by hearing aid use most likely stems from direct effects from hearing aids rather than indirect mediators, such as social isolation, loneliness, and low mood.
Dr. Zhu said the findings highlight the “urgent need” for the early use of hearing aids when an individual starts having trouble hearing.
“A group effort from across society is necessary, including raising awareness of hearing loss and the potential links with dementia; increasing accessibility to hearing aids by reducing cost; and more support for primary care workers to screen for hearing impairment, raise awareness, and deliver treatment such as fitting hearing aids,” Dr. Zhu said.
Writing in a linked comment, Gill Livingston, MD, and Sergi Costafreda, MD, PhD, with University College London, noted that with addition of this study, “the evidence that hearing aids are a powerful tool to reduce the risk of dementia in people with hearing loss, is as good as possible without randomized controlled trials, which might not be practically possible or ethical because people with hearing loss should not be stopped from using effective treatments.”
“The evidence is compelling that treating hearing loss is a promising way of reducing dementia risk. This is the time to increase awareness of and detection of hearing loss, as well as the acceptability and usability of hearing aids,” Dr. Livingston and Dr. Costafreda added.
High-quality evidence – with caveats
Several experts offered perspective on the analysis in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre, which was not involved with the conduct of this study. Charles Marshall, MRCP, PhD, with Queen Mary University of London, said that the study provides “high-quality evidence” that those with hearing loss who use hearing aids are at lower risk for dementia than are those with hearing loss who do not use hearing aids.
“This raises the possibility that a proportion of dementia cases could be prevented by using hearing aids to correct hearing loss. However, the observational nature of this study makes it difficult to be sure that hearing aids are actually causing the reduced risk of dementia,” Dr. Marshall added.
“Hearing aids produce slightly distorted sound, and the brain has to adapt to this in order for hearing aids to be helpful,” he said. “People who are at risk of developing dementia in the future may have early changes in their brain that impair this adaptation, and this may lead to them choosing to not use hearing aids. This would confound the association, creating the appearance that hearing aids were reducing dementia risk, when actually their use was just identifying people with relatively healthy brains,” Dr. Marshall added.
Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, with the University of Edinburgh, said this “well-conducted” study confirms previous similar studies showing an association between hearing loss and dementia risk.
Echoing Dr. Marshall, Dr. Spires-Jones noted that this type of study cannot prove conclusively that hearing loss causes dementia.
“For example,” she said, “it is possible that people who are already in the very early stages of disease are less likely to seek help for hearing loss. However, on balance, this study and the rest of the data in the field indicate that keeping your brain healthy and engaged reduces dementia risk.”
Dr. Spires-Jones said that she agrees with the investigators that it’s “important to help people with hearing loss to get effective hearing aids to help keep their brains engaged through allowing richer social interactions.”
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shandong Province, Taishan Scholars Project, China Medical Board, and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. Dr. Zhu, Dr. Livingston, Dr. Costafreda, Dr. Marshall, and Dr. Spires-Jones have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research confirms. A large observational study from the United Kingdom showed a 42% increased risk for dementia in people with hearing loss compared with their peers with no hearing trouble. In addition, there was no increased risk in those with hearing loss who used hearing aids.
“The evidence is building that hearing loss may be the most impactful modifiable risk factor for dementia in mid-life, but the effectiveness of hearing aid use on reducing the risk of dementia in the real world has remained unclear,” Dongshan Zhu, PhD, with Shandong University, Jinan, China, said in a news release.
“Our study provides the best evidence to date to suggest that hearing aids could be a minimally invasive, cost-effective treatment to mitigate the potential impact of hearing loss on dementia,” Dr. Zhu said.
The study, which was published online in Lancet Public Health, comes on the heels of the 2020 Lancet Commission report on dementia, which suggested hearing loss may be linked to approximately 8% of worldwide dementia cases.
‘Compelling’ evidence
For the study, investigators analyzed longitudinal data on 437,704 individuals, most of whom were White, from the UK Biobank (54% female; mean age at baseline, 56 years). Roughly three quarters of the cohort had no hearing loss and one quarter had some level of hearing loss, with 12% of these individuals using hearing aids.
After the researchers controlled for relevant cofactors, compared with people without hearing loss, those with hearing loss who were not using hearing aids had an increased risk for all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.29-1.56).
No increased risk was seen in people with hearing loss who were using hearing aids (HR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.98-1.10).
The positive association of hearing aid use was observed in all-cause dementia and cause-specific dementia subtypes, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and non–Alzheimer’s disease nonvascular dementia.
The data also suggest that the protection against dementia conferred by hearing aid use most likely stems from direct effects from hearing aids rather than indirect mediators, such as social isolation, loneliness, and low mood.
Dr. Zhu said the findings highlight the “urgent need” for the early use of hearing aids when an individual starts having trouble hearing.
“A group effort from across society is necessary, including raising awareness of hearing loss and the potential links with dementia; increasing accessibility to hearing aids by reducing cost; and more support for primary care workers to screen for hearing impairment, raise awareness, and deliver treatment such as fitting hearing aids,” Dr. Zhu said.
Writing in a linked comment, Gill Livingston, MD, and Sergi Costafreda, MD, PhD, with University College London, noted that with addition of this study, “the evidence that hearing aids are a powerful tool to reduce the risk of dementia in people with hearing loss, is as good as possible without randomized controlled trials, which might not be practically possible or ethical because people with hearing loss should not be stopped from using effective treatments.”
“The evidence is compelling that treating hearing loss is a promising way of reducing dementia risk. This is the time to increase awareness of and detection of hearing loss, as well as the acceptability and usability of hearing aids,” Dr. Livingston and Dr. Costafreda added.
High-quality evidence – with caveats
Several experts offered perspective on the analysis in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre, which was not involved with the conduct of this study. Charles Marshall, MRCP, PhD, with Queen Mary University of London, said that the study provides “high-quality evidence” that those with hearing loss who use hearing aids are at lower risk for dementia than are those with hearing loss who do not use hearing aids.
“This raises the possibility that a proportion of dementia cases could be prevented by using hearing aids to correct hearing loss. However, the observational nature of this study makes it difficult to be sure that hearing aids are actually causing the reduced risk of dementia,” Dr. Marshall added.
“Hearing aids produce slightly distorted sound, and the brain has to adapt to this in order for hearing aids to be helpful,” he said. “People who are at risk of developing dementia in the future may have early changes in their brain that impair this adaptation, and this may lead to them choosing to not use hearing aids. This would confound the association, creating the appearance that hearing aids were reducing dementia risk, when actually their use was just identifying people with relatively healthy brains,” Dr. Marshall added.
Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, with the University of Edinburgh, said this “well-conducted” study confirms previous similar studies showing an association between hearing loss and dementia risk.
Echoing Dr. Marshall, Dr. Spires-Jones noted that this type of study cannot prove conclusively that hearing loss causes dementia.
“For example,” she said, “it is possible that people who are already in the very early stages of disease are less likely to seek help for hearing loss. However, on balance, this study and the rest of the data in the field indicate that keeping your brain healthy and engaged reduces dementia risk.”
Dr. Spires-Jones said that she agrees with the investigators that it’s “important to help people with hearing loss to get effective hearing aids to help keep their brains engaged through allowing richer social interactions.”
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shandong Province, Taishan Scholars Project, China Medical Board, and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. Dr. Zhu, Dr. Livingston, Dr. Costafreda, Dr. Marshall, and Dr. Spires-Jones have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research confirms. A large observational study from the United Kingdom showed a 42% increased risk for dementia in people with hearing loss compared with their peers with no hearing trouble. In addition, there was no increased risk in those with hearing loss who used hearing aids.
“The evidence is building that hearing loss may be the most impactful modifiable risk factor for dementia in mid-life, but the effectiveness of hearing aid use on reducing the risk of dementia in the real world has remained unclear,” Dongshan Zhu, PhD, with Shandong University, Jinan, China, said in a news release.
“Our study provides the best evidence to date to suggest that hearing aids could be a minimally invasive, cost-effective treatment to mitigate the potential impact of hearing loss on dementia,” Dr. Zhu said.
The study, which was published online in Lancet Public Health, comes on the heels of the 2020 Lancet Commission report on dementia, which suggested hearing loss may be linked to approximately 8% of worldwide dementia cases.
‘Compelling’ evidence
For the study, investigators analyzed longitudinal data on 437,704 individuals, most of whom were White, from the UK Biobank (54% female; mean age at baseline, 56 years). Roughly three quarters of the cohort had no hearing loss and one quarter had some level of hearing loss, with 12% of these individuals using hearing aids.
After the researchers controlled for relevant cofactors, compared with people without hearing loss, those with hearing loss who were not using hearing aids had an increased risk for all-cause dementia (hazard ratio [HR], 1.42; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.29-1.56).
No increased risk was seen in people with hearing loss who were using hearing aids (HR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.98-1.10).
The positive association of hearing aid use was observed in all-cause dementia and cause-specific dementia subtypes, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and non–Alzheimer’s disease nonvascular dementia.
The data also suggest that the protection against dementia conferred by hearing aid use most likely stems from direct effects from hearing aids rather than indirect mediators, such as social isolation, loneliness, and low mood.
Dr. Zhu said the findings highlight the “urgent need” for the early use of hearing aids when an individual starts having trouble hearing.
“A group effort from across society is necessary, including raising awareness of hearing loss and the potential links with dementia; increasing accessibility to hearing aids by reducing cost; and more support for primary care workers to screen for hearing impairment, raise awareness, and deliver treatment such as fitting hearing aids,” Dr. Zhu said.
Writing in a linked comment, Gill Livingston, MD, and Sergi Costafreda, MD, PhD, with University College London, noted that with addition of this study, “the evidence that hearing aids are a powerful tool to reduce the risk of dementia in people with hearing loss, is as good as possible without randomized controlled trials, which might not be practically possible or ethical because people with hearing loss should not be stopped from using effective treatments.”
“The evidence is compelling that treating hearing loss is a promising way of reducing dementia risk. This is the time to increase awareness of and detection of hearing loss, as well as the acceptability and usability of hearing aids,” Dr. Livingston and Dr. Costafreda added.
High-quality evidence – with caveats
Several experts offered perspective on the analysis in a statement from the U.K.-based nonprofit Science Media Centre, which was not involved with the conduct of this study. Charles Marshall, MRCP, PhD, with Queen Mary University of London, said that the study provides “high-quality evidence” that those with hearing loss who use hearing aids are at lower risk for dementia than are those with hearing loss who do not use hearing aids.
“This raises the possibility that a proportion of dementia cases could be prevented by using hearing aids to correct hearing loss. However, the observational nature of this study makes it difficult to be sure that hearing aids are actually causing the reduced risk of dementia,” Dr. Marshall added.
“Hearing aids produce slightly distorted sound, and the brain has to adapt to this in order for hearing aids to be helpful,” he said. “People who are at risk of developing dementia in the future may have early changes in their brain that impair this adaptation, and this may lead to them choosing to not use hearing aids. This would confound the association, creating the appearance that hearing aids were reducing dementia risk, when actually their use was just identifying people with relatively healthy brains,” Dr. Marshall added.
Tara Spires-Jones, PhD, with the University of Edinburgh, said this “well-conducted” study confirms previous similar studies showing an association between hearing loss and dementia risk.
Echoing Dr. Marshall, Dr. Spires-Jones noted that this type of study cannot prove conclusively that hearing loss causes dementia.
“For example,” she said, “it is possible that people who are already in the very early stages of disease are less likely to seek help for hearing loss. However, on balance, this study and the rest of the data in the field indicate that keeping your brain healthy and engaged reduces dementia risk.”
Dr. Spires-Jones said that she agrees with the investigators that it’s “important to help people with hearing loss to get effective hearing aids to help keep their brains engaged through allowing richer social interactions.”
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shandong Province, Taishan Scholars Project, China Medical Board, and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation. Dr. Zhu, Dr. Livingston, Dr. Costafreda, Dr. Marshall, and Dr. Spires-Jones have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AHA backs screening for cognitive impairment after stroke
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Screening for cognitive impairment should be part of multidisciplinary care for stroke survivors, the American Heart Association says in a new scientific statement.
“Cognitive impairment after stroke is very common, is associated with other post-stroke outcomes, and often has significant impact on the quality of life,” Nada El Husseini, MD, MHSc, chair of the scientific statement writing group, told this news organization.
“It is important to screen stroke survivors for cognitive impairment as well as for associated comorbidities such as mood and sleep disorders,” said Dr. El Husseini, associate professor of neurology at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C.
The scientific statement was published online in Stroke. It’s the first to specifically focus on the cognitive impairment resulting from an overt stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic).
‘Actionable’ considerations for care
The writing group performed a “scoping” review of the literature on the prevalence, diagnosis, and management of poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) to provide a framework for “actionable considerations” for clinical practice as well as to highlight gaps needing additional studies, Dr. El Husseini explained.
PSCI, ranging from mild to severe, occurs in up to 60% of stroke survivors in the first year after stroke; yet, it is often underreported and underdiagnosed, the writing group notes.
Up to 20% of stroke survivors who experience mild cognitive impairment fully recover cognitive function, and cognitive recovery is most likely within the first 6 months after a stroke.
However, improvement in cognitive impairment without return to prestroke levels is more frequent than is complete recovery. As many as one in three stroke survivors may develop dementia within 5 years of stroke.
The writing group also notes that PSCI is often associated with other conditions, including physical disability, sleep disorders, behavioral and personality changes, depression, and other neuropsychological changes – each of which may contribute to lower quality of life.
Currently, there is no “gold standard” for cognitive screening following stroke, but several brief cognitive screening tests, including the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, are widely used to identify cognitive impairment after stroke.
The statement also highlights the importance of assessing cognitive changes over time after stroke. Stroke survivors who experience unexplained difficulties with cognitive-related activities of daily living, following care instructions, or providing a reliable health history may be candidates for additional cognitive screening.
Manage risk factors to prevent repeat stroke
“Anticipatory guidance regarding home and driving safety and, return to work (if applicable) along with interdisciplinary collaboration among different medical and ancillary specialists in the diagnosis and management of cognitive impairment is key for the holistic care of stroke survivors,” Dr. El Husseini told this news organization.
The multidisciplinary poststroke health care team could include neurologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, nurses, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, and primary care providers.
“Because recurrent stroke is strongly associated with the development of cognitive impairment and dementia, prevention of recurrent strokes should be sought to decrease that risk,” Dr. El Husseini said. This includes addressing stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and atrial fibrillation.
The writing group says research is needed in the future to determine how cognitive impairment develops after stroke and the impact of nonbrain factors, including infection, frailty, and social factors.
Further research is also needed to determine best practices for cognitive screening after stroke, including the development and use of screening instruments that consider demographic, cultural, and linguistic factors in determining “normal” function.
“Perhaps the most pressing need, however, is the development of effective and culturally relevant treatments for poststroke cognitive impairment,” Dr. El Husseini said in a news release.
“We hope to see big enough clinical trials that assess various techniques, medications, and lifestyle changes in diverse groups of patients that may help improve cognitive function,” she added.
This scientific statement was prepared by the volunteer writing group on behalf of the AHA Stroke Council, the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, the Council on Hypertension, and the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health.
Oral antiamyloid shows disease-modifying potential Phase 3 trial underway
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON – , represented by positive changes in plasma and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
Use of the drug, ALZ-801 (Alzheon), led to a significant reduction of plasma phosphorylated–tau 181 (p-tau181) , a marker of amyloid-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slowing of hippocampal atrophy and stabilization of cognition.
“The 12-month results of our phase 2 trial support the finding that ALZ-801 blocks misfolding of amyloid monomers and subsequent formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers, the key initial step in the amyloid aggregation cascade, which leads to a rapid and sustained reduction of brain neurodegeneration as measured by plasma p-tau181,” John Hey, PhD, Alzheon’s chief scientific officer, said in a statement.
“The severalfold greater reduction on the p-tau181 biomarker in plasma compared to plaque-clearing antiamyloid antibodies, combined with preservation of brain hippocampal volume and their positive correlations with cognitive benefits, further validate the disease-modifying effects of ALZ-801 in Alzheimer’s patients,” Dr. Hey added.
The results were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
ALZ-801 is an optimized prodrug of tramiprosate that has been shown to inhibit amyloid-beta 42 aggregation into toxic oligomers.
The ongoing phase 2 study is evaluating the effects of oral ALZ-801 (265 mg twice daily) on biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology for 84 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have either the APOE4/4 or APOE3/4 genotype. These genotypes represent the majority of patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
The mean age of the cohort was 69 years, and 51% are women; 70% had mild cognitive impairment, and 30% had mild Alzheimer’s disease. The mean Mini-Mental State Examination score for the cohort was 26.0. Roughly half were taking a cholinesterase inhibitor.
Significant plasma p-tau181 reduction was observed at 13 weeks. Levels were reduced by 41% by 52 weeks (P = .016). There was also a significant 5% reduction in plasma amyloid-beta 42 and 40 at 52 weeks (P = .002 and P = .005, respectively), Dr. Hey reported.
After 12 months of treatment, hippocampal atrophy was reduced by about 23%, and expansion of ventricular volume was reduced by about 15%, both in comparison with matched controls from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Composite cognitive z-score improved significantly at 13 and 26 weeks and remained above baseline at 52 weeks in comparison with matched ADNI controls. “These are very promising data,” Dr. Hey told conference attendees.
He noted that the safety profile of ALZ-801 remains favorable and consistent with prior safety data. Common adverse events were mild nausea and SARS-CoV-2 infection. There were no drug-related serious events or amyloid-related imaging abnormalities–edema (ARIA-E).
The phase 3 APOLLOE4 study of ALZ-801 is underway. This double-blind, randomized study is comparing oral ALZ-801 with placebo over 78 weeks for roughly 300 adults with early Alzheimer’s disease who have the APOE4/4 genotype. APOLLOE4 is expected to be completed in mid 2024.
The APOLLOE4 study is supported by a $47 million grant from the National Institute on Aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted ALZ-801 fast-track designation.
More accessible option?
Reached for comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific engagement, noted that the “biggest difference between this drug and others is that it is taken orally, rather than delivered through an infusion. This is important and valuable for reducing patient and caregiver burden and increasing ease of use and access.”
It’s also noteworthy that ALZ-801 was not associated with ARIA-E, “which has been reported in other antiamyloid trials and can occasionally be serious,” Dr. Griffin said.
Overall, he said the results are “encouraging, but more work is needed. If studies results continue to be positive, this treatment may provide a more accessible option for people who are at higher risk of ARIA,” Dr. Griffin said.
The study was funded by Alzheon. Dr. Hey is an employee of Alzheon and holds stock in the company. Dr. Griffin has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAN 2023
Donanemab bests aducanumab in head-to-head Alzheimer’s trial
BOSTON –
Nearly 40% of patients treated with donanemab had amyloid clearance at 6 months compared with less than 2% of those who received aducanumab, which was approved in 2021 amid a great deal of controversy.
Titration for donanemab progressed more quickly, with participants receiving a maximum dose twice as early as those on aducanumab, without any increase in rates of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) – the most common side effect of amyloid drugs.
Early results from the randomized phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 trial of donanemab come just 3 months after the Food and Drug Administration denied manufacturer Eli Lilly’s request for accelerated approval for the drug.
“This study shows that the drug with the quicker titration scheme, donanemab, produced more amyloid lowering and did it without having more ARIA,” said lead investigator Stephen P. Salloway, MD, director of the Memory and Aging Program at Butler Hospital in Providence, R.I., and a professor of neurology at Brown University.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Multicenter, head-to-head trial
Donanemab received breakthrough therapy designation in 2021. The drug works similarly to aducanumab and lecanemab, which was approved earlier this year. All three bind to different parts of the amyloid molecule and stimulate an immune response to help clear amyloid plaques, although they each have a distinctive binding component.
TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 was conducted at 31 sites across the United States, enrolling 140 patients aged 50-85 years with early and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Study participants received donanemab or aducanumab at escalating doses for 18 months.
Donanemab was titrated more quickly, with participants receiving 700 mg via IV infusion once a month for 3 months before reaching the maximum dose of 1,400 mg in the fourth month of the study.
Aducanumab titration was slower, beginning at 1 mg/kg via IV monthly for 2 months, then 3 mg/kg for another 2 months, and 6 mg/kg for 2 more months before reaching the maximum dose of 10 mg/kg in the seventh month.
After 6 months of treatment, PET scan analysis revealed that 37.9% of donanemab-treated patients achieved amyloid clearance compared with just 1.6% of those who received aducanumab (P < .001).
Among patients with intermediate tau levels (n = 27 for donanemab and n = 28 for aducanumab), 38.5% of those who received donanemab achieved amyloid clearance compared with 3.8% of patients in the aducanumab group (P = .008).
Amyloid levels were 65.2% lower in donanemab patients, while levels in those receiving aducanumab were reduced by 17.0% (P < .001). Among those with intermediate tau, amyloid levels decreased with donanemab by 63.9% and 25.4% with aducanumab (P ≤ .001).
Investigators also noted a greater reduction in plasma ptau217 with donanemab.
Adverse events were similar between groups, with 62.0% of the donanemab group and 66.7% of aducanumab-treated participants reporting an adverse event.
There were no serious adverse events due to ARIA with donanemab, but one participant in the aducanumab group had a serious adverse event linked to ARIA.
“Even though the amyloid lowering was greater with donanemab, the rate of ARIA was similar, which suggests that the speed and depth of amyloid removal is not driving ARIA,” Dr. Salloway said.
There are three other Trailblazer trials of donanemab. Unlike in similar trials, participants in all three of these studies who received the trial drug could discontinue treatment once criteria for amyloid clearance were met.
That’s precisely what happened with Trailblazer 2, the study on which Lilly based its request for accelerated approval. Ironically, that trial design also contributed to the FDA’s decision to reject that request.
The FDA required data from at least 100 patients who had received donanemab for a minimum of 1 year. While the trial included more than 100 patients, many patients discontinued treatment early after achieving the targeted amount of amyloid clearance.
“They had success, and they got punished for it, in my opinion,” Dr. Salloway said.
Final data from Trailblazer 2 is due in the next month, and if results are positive, Lilly is expected to file for full approval.
Questions remain
“This is an interesting study that suggests donanemab may remove amyloid faster in more people than aducanumab,” said Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings.
Howard Fillit, MD, cofounder and chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, also commented on the findings. He noted that faster amyloid clearance “means less time for requiring sometimes burdensome and expensive infusions.”
Both Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit noted that longer-term results are needed, along with studies of whether amyloid clearance offers a protective benefit against Alzheimer’s dementia. More results from Trailblazer 4 will be reported after 12 months and again at 18 months.
“There are obviously still a lot of questions about these drugs and whether reducing amyloid plaque will actually preserve cognitive function or at least slow decline,” Dr. Fillit said.
It will also be important to understand the timing of treatment, including when anti-amyloid therapies should be administered and for how long.
“It will be important to understand how these results translate to patient care and treatment plans, should this drug receive FDA approval,” Dr. Snyder said. “Patients should have the opportunity to make a decision, alongside their physician, on a treatment path that is right for them.”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Salloway has been a consultant for Biogen, EISAI, Lilly, Genentech, Novo Nordisk, Prothena, and others. Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON –
Nearly 40% of patients treated with donanemab had amyloid clearance at 6 months compared with less than 2% of those who received aducanumab, which was approved in 2021 amid a great deal of controversy.
Titration for donanemab progressed more quickly, with participants receiving a maximum dose twice as early as those on aducanumab, without any increase in rates of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) – the most common side effect of amyloid drugs.
Early results from the randomized phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 trial of donanemab come just 3 months after the Food and Drug Administration denied manufacturer Eli Lilly’s request for accelerated approval for the drug.
“This study shows that the drug with the quicker titration scheme, donanemab, produced more amyloid lowering and did it without having more ARIA,” said lead investigator Stephen P. Salloway, MD, director of the Memory and Aging Program at Butler Hospital in Providence, R.I., and a professor of neurology at Brown University.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Multicenter, head-to-head trial
Donanemab received breakthrough therapy designation in 2021. The drug works similarly to aducanumab and lecanemab, which was approved earlier this year. All three bind to different parts of the amyloid molecule and stimulate an immune response to help clear amyloid plaques, although they each have a distinctive binding component.
TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 was conducted at 31 sites across the United States, enrolling 140 patients aged 50-85 years with early and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Study participants received donanemab or aducanumab at escalating doses for 18 months.
Donanemab was titrated more quickly, with participants receiving 700 mg via IV infusion once a month for 3 months before reaching the maximum dose of 1,400 mg in the fourth month of the study.
Aducanumab titration was slower, beginning at 1 mg/kg via IV monthly for 2 months, then 3 mg/kg for another 2 months, and 6 mg/kg for 2 more months before reaching the maximum dose of 10 mg/kg in the seventh month.
After 6 months of treatment, PET scan analysis revealed that 37.9% of donanemab-treated patients achieved amyloid clearance compared with just 1.6% of those who received aducanumab (P < .001).
Among patients with intermediate tau levels (n = 27 for donanemab and n = 28 for aducanumab), 38.5% of those who received donanemab achieved amyloid clearance compared with 3.8% of patients in the aducanumab group (P = .008).
Amyloid levels were 65.2% lower in donanemab patients, while levels in those receiving aducanumab were reduced by 17.0% (P < .001). Among those with intermediate tau, amyloid levels decreased with donanemab by 63.9% and 25.4% with aducanumab (P ≤ .001).
Investigators also noted a greater reduction in plasma ptau217 with donanemab.
Adverse events were similar between groups, with 62.0% of the donanemab group and 66.7% of aducanumab-treated participants reporting an adverse event.
There were no serious adverse events due to ARIA with donanemab, but one participant in the aducanumab group had a serious adverse event linked to ARIA.
“Even though the amyloid lowering was greater with donanemab, the rate of ARIA was similar, which suggests that the speed and depth of amyloid removal is not driving ARIA,” Dr. Salloway said.
There are three other Trailblazer trials of donanemab. Unlike in similar trials, participants in all three of these studies who received the trial drug could discontinue treatment once criteria for amyloid clearance were met.
That’s precisely what happened with Trailblazer 2, the study on which Lilly based its request for accelerated approval. Ironically, that trial design also contributed to the FDA’s decision to reject that request.
The FDA required data from at least 100 patients who had received donanemab for a minimum of 1 year. While the trial included more than 100 patients, many patients discontinued treatment early after achieving the targeted amount of amyloid clearance.
“They had success, and they got punished for it, in my opinion,” Dr. Salloway said.
Final data from Trailblazer 2 is due in the next month, and if results are positive, Lilly is expected to file for full approval.
Questions remain
“This is an interesting study that suggests donanemab may remove amyloid faster in more people than aducanumab,” said Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings.
Howard Fillit, MD, cofounder and chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, also commented on the findings. He noted that faster amyloid clearance “means less time for requiring sometimes burdensome and expensive infusions.”
Both Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit noted that longer-term results are needed, along with studies of whether amyloid clearance offers a protective benefit against Alzheimer’s dementia. More results from Trailblazer 4 will be reported after 12 months and again at 18 months.
“There are obviously still a lot of questions about these drugs and whether reducing amyloid plaque will actually preserve cognitive function or at least slow decline,” Dr. Fillit said.
It will also be important to understand the timing of treatment, including when anti-amyloid therapies should be administered and for how long.
“It will be important to understand how these results translate to patient care and treatment plans, should this drug receive FDA approval,” Dr. Snyder said. “Patients should have the opportunity to make a decision, alongside their physician, on a treatment path that is right for them.”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Salloway has been a consultant for Biogen, EISAI, Lilly, Genentech, Novo Nordisk, Prothena, and others. Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
BOSTON –
Nearly 40% of patients treated with donanemab had amyloid clearance at 6 months compared with less than 2% of those who received aducanumab, which was approved in 2021 amid a great deal of controversy.
Titration for donanemab progressed more quickly, with participants receiving a maximum dose twice as early as those on aducanumab, without any increase in rates of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) – the most common side effect of amyloid drugs.
Early results from the randomized phase 3 TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 trial of donanemab come just 3 months after the Food and Drug Administration denied manufacturer Eli Lilly’s request for accelerated approval for the drug.
“This study shows that the drug with the quicker titration scheme, donanemab, produced more amyloid lowering and did it without having more ARIA,” said lead investigator Stephen P. Salloway, MD, director of the Memory and Aging Program at Butler Hospital in Providence, R.I., and a professor of neurology at Brown University.
The findings were presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology.
Multicenter, head-to-head trial
Donanemab received breakthrough therapy designation in 2021. The drug works similarly to aducanumab and lecanemab, which was approved earlier this year. All three bind to different parts of the amyloid molecule and stimulate an immune response to help clear amyloid plaques, although they each have a distinctive binding component.
TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 4 was conducted at 31 sites across the United States, enrolling 140 patients aged 50-85 years with early and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Study participants received donanemab or aducanumab at escalating doses for 18 months.
Donanemab was titrated more quickly, with participants receiving 700 mg via IV infusion once a month for 3 months before reaching the maximum dose of 1,400 mg in the fourth month of the study.
Aducanumab titration was slower, beginning at 1 mg/kg via IV monthly for 2 months, then 3 mg/kg for another 2 months, and 6 mg/kg for 2 more months before reaching the maximum dose of 10 mg/kg in the seventh month.
After 6 months of treatment, PET scan analysis revealed that 37.9% of donanemab-treated patients achieved amyloid clearance compared with just 1.6% of those who received aducanumab (P < .001).
Among patients with intermediate tau levels (n = 27 for donanemab and n = 28 for aducanumab), 38.5% of those who received donanemab achieved amyloid clearance compared with 3.8% of patients in the aducanumab group (P = .008).
Amyloid levels were 65.2% lower in donanemab patients, while levels in those receiving aducanumab were reduced by 17.0% (P < .001). Among those with intermediate tau, amyloid levels decreased with donanemab by 63.9% and 25.4% with aducanumab (P ≤ .001).
Investigators also noted a greater reduction in plasma ptau217 with donanemab.
Adverse events were similar between groups, with 62.0% of the donanemab group and 66.7% of aducanumab-treated participants reporting an adverse event.
There were no serious adverse events due to ARIA with donanemab, but one participant in the aducanumab group had a serious adverse event linked to ARIA.
“Even though the amyloid lowering was greater with donanemab, the rate of ARIA was similar, which suggests that the speed and depth of amyloid removal is not driving ARIA,” Dr. Salloway said.
There are three other Trailblazer trials of donanemab. Unlike in similar trials, participants in all three of these studies who received the trial drug could discontinue treatment once criteria for amyloid clearance were met.
That’s precisely what happened with Trailblazer 2, the study on which Lilly based its request for accelerated approval. Ironically, that trial design also contributed to the FDA’s decision to reject that request.
The FDA required data from at least 100 patients who had received donanemab for a minimum of 1 year. While the trial included more than 100 patients, many patients discontinued treatment early after achieving the targeted amount of amyloid clearance.
“They had success, and they got punished for it, in my opinion,” Dr. Salloway said.
Final data from Trailblazer 2 is due in the next month, and if results are positive, Lilly is expected to file for full approval.
Questions remain
“This is an interesting study that suggests donanemab may remove amyloid faster in more people than aducanumab,” said Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings.
Howard Fillit, MD, cofounder and chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, also commented on the findings. He noted that faster amyloid clearance “means less time for requiring sometimes burdensome and expensive infusions.”
Both Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit noted that longer-term results are needed, along with studies of whether amyloid clearance offers a protective benefit against Alzheimer’s dementia. More results from Trailblazer 4 will be reported after 12 months and again at 18 months.
“There are obviously still a lot of questions about these drugs and whether reducing amyloid plaque will actually preserve cognitive function or at least slow decline,” Dr. Fillit said.
It will also be important to understand the timing of treatment, including when anti-amyloid therapies should be administered and for how long.
“It will be important to understand how these results translate to patient care and treatment plans, should this drug receive FDA approval,” Dr. Snyder said. “Patients should have the opportunity to make a decision, alongside their physician, on a treatment path that is right for them.”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Salloway has been a consultant for Biogen, EISAI, Lilly, Genentech, Novo Nordisk, Prothena, and others. Dr. Snyder and Dr. Fillit have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAN 2023
Cautious optimism for new Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and treatments, expert says
SAN DIEGO – said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dementia prevalence is increasing as the proportion of the U.S. population older than 65 rises, said Zaldy Tan, MD, professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. AD deaths more than doubled between 2000 and 2018, he noted, while deaths from HIV infection, stroke, and heart disease decreased.
Most people in the United States who have AD are White, but studies suggest that, compared with Whites, the risk of AD is two times higher in Blacks and 1.5 times higher in Hispanics . “These data suggest that both genes and social determinants of health are at play,” Dr. Tan said.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease
The different types of dementia make it challenging for primary care physicians to identify the cause of cognitive impairment. “Even though AD is the most common type, clinicians should keep in mind that another type of dementia may be the cause of cognitive impairment,” Dr. Tan cautioned. Other dementia diagnoses include vascular, Lewy body, and frontotemporal.
Diagnostic criteria for AD include evidence of significant cognitive decline in at least one cognitive domain that interferes with independence in everyday activities, as well as the absence of another mental disorder or delirium that would explain the cognitive deficits.
“We see many patients with depressive symptoms and mild cognitive impairment, and it is not always easy to tell which of them have dementia because of the overlap in the symptoms of depression and AD,” said internist Roderick Kim, MD, of Grand Rapids, Mich., who attended the session.
It can be challenging to convince patients to undergo the appropriate diagnostic workup, Dr. Kim said. “This can delay treatment, so it is important to explain to patients that cognitive decline can progress quickly and that there are treatment options to slow it down.”
Why do we need biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease?
AD is characterized by a long preclinical phase with no specific symptoms other than the typical signs and symptoms of aging, Dr. Tan said. That means cognitive impairment progresses rapidly after diagnosis in most patients with AD.
“In most cases, an accurate history, physical and neurologic examinations, basic labs, and neuroimaging are sufficient for memory loss evaluation. However, as more disease-modifying therapies come to market, biomarkers will rise in importance in primary care,” he said.
This long asymptomatic phase of AD creates the need for diagnostic biomarkers for an earlier diagnosis, he said. Amyloid-beta and tau deposits in PET images and the levels of amyloid-beta seeds, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain in the cerebrospinal fluid can be used as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with suspected AD. Emerging blood biomarkers for earlier detection include the levels of amyloid-beta1–42, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain.
With biomarkers and other new tools for the diagnosis of dementia in primary care, Dr. Tan said: “The greatest challenge is cost, as blood-based biomarkers are not currently covered by insurance and still rather costly. In addition, blood-based biomarkers will need to receive [Food and Drug Administration] approval in order to have more widespread availability.”
New and emerging therapies for Alzheimer’s disease
There are two classes of FDA-approved medications to manage cognitive symptoms of dementia: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. The selections may be trial and error for each patient, Dr. Tan said.
“The approved medications can exert subtle benefits that are clinically observable. Thus, barring any contraindications or intolerance, most patients with AD would benefit from a trial of one or both of these medication classes,” said Dr. Tan. He added that it is equally important to wean off and discontinue these medications if there is intolerance or lack of a subjective or objective beneficial response.
Other medications are available for some of the most common behavioral problems associated with dementia, such as agitation, depression, and disorientation. Dr. Tan advised not to prescribe behavioral medications until nonpharmacologic interventions prove to be ineffective or impractical. Behavioral medications have many side effects, some of which are potentially serious, he said, so the risk-benefit ratio should be considered.
In his own practice, when nonpharmacologic strategies do not improve the behavioral symptoms of dementia, Dr. Tan said that, “in cases where a person is at risk of harm to themselves or others, a discussion with the patient and their caregivers about the pros and cons of medications to treat the behavior need to be had. Careful monitoring of the response and dose escalation or deprescribing when appropriate is important to keep in mind.”
Disease-modifying agents have recently provided new hope for AD treatment. Aducanumab and lecanemab, both monoclonal antibodies that target amyloids, are the first two drugs that received accelerated FDA approval for AD.
Although these monoclonal antibodies can help clear deposited amyloid plaques and show some benefit in slowing cognitive impairment in clinical trials, the real-world benefits were unclear enough for Medicare to limit coverage to people enrolled in approved studies to gather more data. Additionally, these agents can cause potentially amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, which may indicate edema, effusion, or microhemorrhage. Therefore, clinicians need to have a clear conversation of risks and benefits with patients and caregivers about these treatments.
Looking ahead
When asked about the most promising emerging technologies or techniques related to dementia diagnosis and management, Dr. Tan noted that multiple technology companies and start-ups are looking for new ways to detect dementia earlier or keep persons with dementia safe at home. Some devices deliver brain waves, computerized brain games or tests, automated pill dispensers, and fall monitors.
“Some of these are potentially helpful, but not every person with dementia will benefit. In addition, most of these technologies are out-of-pocket expenses for the patients and their families. It is important to know what is out there but also be cautious about outrageous claims,” he added.
Dr. Tan reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing health care products used by or on patients.
SAN DIEGO – said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dementia prevalence is increasing as the proportion of the U.S. population older than 65 rises, said Zaldy Tan, MD, professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. AD deaths more than doubled between 2000 and 2018, he noted, while deaths from HIV infection, stroke, and heart disease decreased.
Most people in the United States who have AD are White, but studies suggest that, compared with Whites, the risk of AD is two times higher in Blacks and 1.5 times higher in Hispanics . “These data suggest that both genes and social determinants of health are at play,” Dr. Tan said.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease
The different types of dementia make it challenging for primary care physicians to identify the cause of cognitive impairment. “Even though AD is the most common type, clinicians should keep in mind that another type of dementia may be the cause of cognitive impairment,” Dr. Tan cautioned. Other dementia diagnoses include vascular, Lewy body, and frontotemporal.
Diagnostic criteria for AD include evidence of significant cognitive decline in at least one cognitive domain that interferes with independence in everyday activities, as well as the absence of another mental disorder or delirium that would explain the cognitive deficits.
“We see many patients with depressive symptoms and mild cognitive impairment, and it is not always easy to tell which of them have dementia because of the overlap in the symptoms of depression and AD,” said internist Roderick Kim, MD, of Grand Rapids, Mich., who attended the session.
It can be challenging to convince patients to undergo the appropriate diagnostic workup, Dr. Kim said. “This can delay treatment, so it is important to explain to patients that cognitive decline can progress quickly and that there are treatment options to slow it down.”
Why do we need biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease?
AD is characterized by a long preclinical phase with no specific symptoms other than the typical signs and symptoms of aging, Dr. Tan said. That means cognitive impairment progresses rapidly after diagnosis in most patients with AD.
“In most cases, an accurate history, physical and neurologic examinations, basic labs, and neuroimaging are sufficient for memory loss evaluation. However, as more disease-modifying therapies come to market, biomarkers will rise in importance in primary care,” he said.
This long asymptomatic phase of AD creates the need for diagnostic biomarkers for an earlier diagnosis, he said. Amyloid-beta and tau deposits in PET images and the levels of amyloid-beta seeds, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain in the cerebrospinal fluid can be used as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with suspected AD. Emerging blood biomarkers for earlier detection include the levels of amyloid-beta1–42, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain.
With biomarkers and other new tools for the diagnosis of dementia in primary care, Dr. Tan said: “The greatest challenge is cost, as blood-based biomarkers are not currently covered by insurance and still rather costly. In addition, blood-based biomarkers will need to receive [Food and Drug Administration] approval in order to have more widespread availability.”
New and emerging therapies for Alzheimer’s disease
There are two classes of FDA-approved medications to manage cognitive symptoms of dementia: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. The selections may be trial and error for each patient, Dr. Tan said.
“The approved medications can exert subtle benefits that are clinically observable. Thus, barring any contraindications or intolerance, most patients with AD would benefit from a trial of one or both of these medication classes,” said Dr. Tan. He added that it is equally important to wean off and discontinue these medications if there is intolerance or lack of a subjective or objective beneficial response.
Other medications are available for some of the most common behavioral problems associated with dementia, such as agitation, depression, and disorientation. Dr. Tan advised not to prescribe behavioral medications until nonpharmacologic interventions prove to be ineffective or impractical. Behavioral medications have many side effects, some of which are potentially serious, he said, so the risk-benefit ratio should be considered.
In his own practice, when nonpharmacologic strategies do not improve the behavioral symptoms of dementia, Dr. Tan said that, “in cases where a person is at risk of harm to themselves or others, a discussion with the patient and their caregivers about the pros and cons of medications to treat the behavior need to be had. Careful monitoring of the response and dose escalation or deprescribing when appropriate is important to keep in mind.”
Disease-modifying agents have recently provided new hope for AD treatment. Aducanumab and lecanemab, both monoclonal antibodies that target amyloids, are the first two drugs that received accelerated FDA approval for AD.
Although these monoclonal antibodies can help clear deposited amyloid plaques and show some benefit in slowing cognitive impairment in clinical trials, the real-world benefits were unclear enough for Medicare to limit coverage to people enrolled in approved studies to gather more data. Additionally, these agents can cause potentially amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, which may indicate edema, effusion, or microhemorrhage. Therefore, clinicians need to have a clear conversation of risks and benefits with patients and caregivers about these treatments.
Looking ahead
When asked about the most promising emerging technologies or techniques related to dementia diagnosis and management, Dr. Tan noted that multiple technology companies and start-ups are looking for new ways to detect dementia earlier or keep persons with dementia safe at home. Some devices deliver brain waves, computerized brain games or tests, automated pill dispensers, and fall monitors.
“Some of these are potentially helpful, but not every person with dementia will benefit. In addition, most of these technologies are out-of-pocket expenses for the patients and their families. It is important to know what is out there but also be cautious about outrageous claims,” he added.
Dr. Tan reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing health care products used by or on patients.
SAN DIEGO – said a presenter at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians.
Dementia prevalence is increasing as the proportion of the U.S. population older than 65 rises, said Zaldy Tan, MD, professor of neurology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles. AD deaths more than doubled between 2000 and 2018, he noted, while deaths from HIV infection, stroke, and heart disease decreased.
Most people in the United States who have AD are White, but studies suggest that, compared with Whites, the risk of AD is two times higher in Blacks and 1.5 times higher in Hispanics . “These data suggest that both genes and social determinants of health are at play,” Dr. Tan said.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease
The different types of dementia make it challenging for primary care physicians to identify the cause of cognitive impairment. “Even though AD is the most common type, clinicians should keep in mind that another type of dementia may be the cause of cognitive impairment,” Dr. Tan cautioned. Other dementia diagnoses include vascular, Lewy body, and frontotemporal.
Diagnostic criteria for AD include evidence of significant cognitive decline in at least one cognitive domain that interferes with independence in everyday activities, as well as the absence of another mental disorder or delirium that would explain the cognitive deficits.
“We see many patients with depressive symptoms and mild cognitive impairment, and it is not always easy to tell which of them have dementia because of the overlap in the symptoms of depression and AD,” said internist Roderick Kim, MD, of Grand Rapids, Mich., who attended the session.
It can be challenging to convince patients to undergo the appropriate diagnostic workup, Dr. Kim said. “This can delay treatment, so it is important to explain to patients that cognitive decline can progress quickly and that there are treatment options to slow it down.”
Why do we need biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease?
AD is characterized by a long preclinical phase with no specific symptoms other than the typical signs and symptoms of aging, Dr. Tan said. That means cognitive impairment progresses rapidly after diagnosis in most patients with AD.
“In most cases, an accurate history, physical and neurologic examinations, basic labs, and neuroimaging are sufficient for memory loss evaluation. However, as more disease-modifying therapies come to market, biomarkers will rise in importance in primary care,” he said.
This long asymptomatic phase of AD creates the need for diagnostic biomarkers for an earlier diagnosis, he said. Amyloid-beta and tau deposits in PET images and the levels of amyloid-beta seeds, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain in the cerebrospinal fluid can be used as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with suspected AD. Emerging blood biomarkers for earlier detection include the levels of amyloid-beta1–42, phosphorylated tau, and neurofilament light chain.
With biomarkers and other new tools for the diagnosis of dementia in primary care, Dr. Tan said: “The greatest challenge is cost, as blood-based biomarkers are not currently covered by insurance and still rather costly. In addition, blood-based biomarkers will need to receive [Food and Drug Administration] approval in order to have more widespread availability.”
New and emerging therapies for Alzheimer’s disease
There are two classes of FDA-approved medications to manage cognitive symptoms of dementia: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists. The selections may be trial and error for each patient, Dr. Tan said.
“The approved medications can exert subtle benefits that are clinically observable. Thus, barring any contraindications or intolerance, most patients with AD would benefit from a trial of one or both of these medication classes,” said Dr. Tan. He added that it is equally important to wean off and discontinue these medications if there is intolerance or lack of a subjective or objective beneficial response.
Other medications are available for some of the most common behavioral problems associated with dementia, such as agitation, depression, and disorientation. Dr. Tan advised not to prescribe behavioral medications until nonpharmacologic interventions prove to be ineffective or impractical. Behavioral medications have many side effects, some of which are potentially serious, he said, so the risk-benefit ratio should be considered.
In his own practice, when nonpharmacologic strategies do not improve the behavioral symptoms of dementia, Dr. Tan said that, “in cases where a person is at risk of harm to themselves or others, a discussion with the patient and their caregivers about the pros and cons of medications to treat the behavior need to be had. Careful monitoring of the response and dose escalation or deprescribing when appropriate is important to keep in mind.”
Disease-modifying agents have recently provided new hope for AD treatment. Aducanumab and lecanemab, both monoclonal antibodies that target amyloids, are the first two drugs that received accelerated FDA approval for AD.
Although these monoclonal antibodies can help clear deposited amyloid plaques and show some benefit in slowing cognitive impairment in clinical trials, the real-world benefits were unclear enough for Medicare to limit coverage to people enrolled in approved studies to gather more data. Additionally, these agents can cause potentially amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, which may indicate edema, effusion, or microhemorrhage. Therefore, clinicians need to have a clear conversation of risks and benefits with patients and caregivers about these treatments.
Looking ahead
When asked about the most promising emerging technologies or techniques related to dementia diagnosis and management, Dr. Tan noted that multiple technology companies and start-ups are looking for new ways to detect dementia earlier or keep persons with dementia safe at home. Some devices deliver brain waves, computerized brain games or tests, automated pill dispensers, and fall monitors.
“Some of these are potentially helpful, but not every person with dementia will benefit. In addition, most of these technologies are out-of-pocket expenses for the patients and their families. It is important to know what is out there but also be cautious about outrageous claims,” he added.
Dr. Tan reported no relationships with entities whose primary business is producing, marketing, selling, reselling, or distributing health care products used by or on patients.
AT INTERNAL MEDICINE 2023
Interventional psychiatry (Part 1)
Advances in the understanding of neurobiological and neuropsychiatric pathophysiology have opened new avenues of treatment for psychiatric patients. Historically, with a few exceptions, most psychiatric medications have been administered orally. However, many of the newer treatments require some form of specialized administration because they cannot be taken orally due to their chemical property (such as aducanumab); because there is the need to produce stable blood levels of the medication (such as brexanolone); because oral administration greatly diminished efficacy (such as oral vs IV magnesium or scopolamine), or because the treatment is focused on specific brain structures. This need for specialized administration has created a subspecialty called interventional psychiatry.
Part 1 of this 2-part article provides an overview of 1 type of interventional psychiatry: parenterally administered medications, including those administered via IV. We also describe 3 other interventional approaches to treatment: stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin (BT) injections, and trigger point injections. In Part 2 we will review interventional approaches that involve neuromodulation.
Parenteral medications in psychiatry
In general, IV and IM medications can be more potent that oral medications due to their overall faster onset of action and higher blood concentrations. These more invasive forms of administration can have significant limitations, such as a risk of infection at the injection site, the need to be administered in a medical setting, additional time, and patient discomfort.
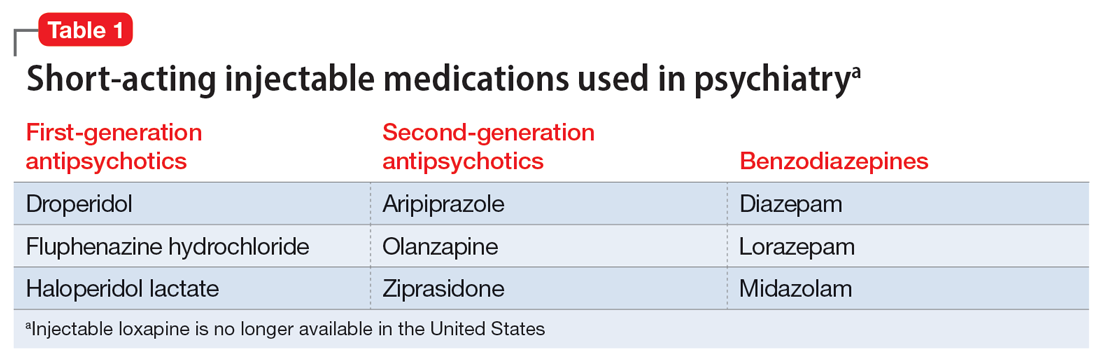
Table 1 lists short-acting injectable medications used in psychiatry, and Table 2 lists long-acting injectable medications. Parenteral administration of antipsychotics is performed to alleviate acute agitation or for chronic symptom control. These medications generally are not considered interventional treatments, but could be classified as such due to their invasive nature.1 Furthermore, inhalable loxapine—which is indicated for managing acute agitation—requires a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program consisting of 2 hours observation and monitoring of respiratory status.2,3 Other indications for parenteral treatments include IM naltrexone extended release4 and subcutaneous injections of buprenorphine extended release5 and risperidone.6
IV administration
Most IV treatments described in this article are not FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment. Despite this, many interventional psychiatric treatments are part of clinical practice. IV infusion of ketamine is the most widely known and most researched of these. Table 3 lists other IV treatments that could be used as psychiatric treatment.
Ketamine
Since the early 1960s, ketamine has been used as a surgical anesthetic for animals. In the United States, it was approved for human surgical anesthesia in 1970. It was widely used during the Vietnam War due to its lack of inhibition of respiratory drive; medical staff first noticed an improvement in depressive symptoms and the resolution of suicidal ideation in patients who received ketamine. This led to further research on ketamine, particularly to determine its application in treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and other conditions.7 IV ketamine administration is most widely researched, but IM injections, intranasal sprays, and lozenges are also available. The dissociative properties of ketamine have led to its recreational use.8
Hypotheses for the mechanism of action of ketamine as an antidepressant include direct synaptic or extrasynaptic (GluN2B-selective), N-methyl-
Continue to: Ketamine is a schedule...
Ketamine is a schedule III medication with addictive properties. Delirium, panic attacks, hallucinations, nightmares, dysphoria, and paranoia may occur during and after use.13 Premedication with benzodiazepines, most notably lorazepam, is occasionally used to minimize ketamine’s adverse effects, but this generally is not recommended because doing so reduces ketamine’s antidepressant effects.14 Driving and operating heavy machinery is contraindicated after IV infusion. The usual protocol involves an IV infusion of ketamine 0.4 mg/kg to 1 mg/kg dosing over 1 hour. Doses between 0.4 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg are most common. Ketamine has a therapeutic window; doses >0.5 mg/kg are progressively less effective.15 Unlike the recommendation after esketamine administration, after receiving ketamine, patients remain in the care of their treatment team for <2 hours.
Esketamine, the S enantiomer of ketamine, was FDA-approved for TRD as an intranasal formulation. Esketamine is more commonly used than IV ketamine because it is FDA-approved and typically covered by insurance, but it may not be as effective.16 An economic analysis by Brendle et al17 suggested insurance companies would lower costs if they covered ketamine infusions vs intranasal esketamine.
Aducanumab and lecanemab
The most recent FDA-approved interventional agents are aducanumab and lecanemab, which are indicated for treating Alzheimer disease.18,19 Both are human monoclonal antibodies that bind selectively and with high affinity to amyloid beta plaque aggregates and promote their removal by Fc receptor–mediated phagocytosis.20
FDA approval of aducanumab and lecanemab was controversial. Initially, aducanumab’s safety monitoring board performed a futility analysis that suggested aducanumab was unlikely to separate from placebo, and the research was stopped.21 The manufacturer petitioned the FDA to consider the medication for accelerated approval on the basis of biomarker data showing that amyloid beta plaque aggregates become smaller. Current FDA approval is temporary to allow patients access to this potentially beneficial agent, but the manufacturer must supply clinical evidence that the reduction of amyloid beta plaques is associated with desirable changes in the course of Alzheimer disease, or risk losing the approval.
Lecanemab is also a human monoclonal antibody intended to remove amyloid beta plaques that was FDA-approved under the accelerated approval pathway.22 Unlike aducanumab, lecanemab demonstrated a statistically significant (although clinically imperceptible) reduction in the rate of cognitive decline; it did not show cognitive improvement.23 Lecanemab also significantly reduced amyloid beta plaques.23
Continue to: Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally...
Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally not covered by insurance and typically cost >$26,000 annually. Both are administered by IV infusion once a month. More monoclonal antibody medications for treating early Alzheimer disease are in the late stages of development, most notably donanebab.24 Observations during clinical trials found that in the later stages of Alzheimer disease, forceful removal of plaques by the autoimmune process damages neurons, while in less dense deposits of early dementia such removal is not harmful to the cells and prevents amyloid buildup.
Brexanolone is an aqueous formulation of allopregnanolone, a major metabolite of progesterone and a positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors.25 Its levels are maximal at the end of the third trimester of pregnancy and fall rapidly following delivery. Research showed a 3-day infusion was rapidly and significantly effective for treating postpartum depression26 and brexanolone received FDA approval for this indication in March 2019.27 However, various administrative, economic, insurance, and other hurdles make it difficult for patients to access this treatment. Despite its rapid onset of action (usually 48 hours), brexanolone takes an average of 15 days to go through the prior authorization process.28 In addition to the need for prior authorization, the main impediment to the use of brexanolone is the 3-day infusion schedule, which greatly magnifies the cost but is partially circumvented by the availability of dedicated outpatient centers.
Magnesium
Magnesium is on the World Health Organization’s Model List of Essential Medicines.29 There has been extensive research on the use of magnesium sulfate for psychiatric indications, especially for depression.30 Magnesium functions similarly to calcium channel blockers by competitively blocking intracellular calcium channels, decreasing calcium availability, and inhibiting smooth muscle contractility.31 It also competes with calcium at the motor end plate, reducing excitation by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.32 This property is used for high-dose IV magnesium treatment of impending preterm labor in obstetrics. Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice in treating eclamptic seizures and preventing seizures in severe preeclampsia or gestational hypertension with severe features.33 It is also used to treat torsade de pointes, severe asthma exacerbations, constipation, and barium poisoning.34 Beneficial use in asthma treatment35 and the treatment of migraine36 have also been reported.
IV magnesium in myocardial infarction may be harmful,37 though outside of acute cardiac events, magnesium is found to be safe.38
Oral magnesium sulfate is a common over-the-counter anxiety remedy. As a general cell stabilizer (mediated by the reduction of intracellular calcium), magnesium is potentially beneficial outside of its muscle-relaxing properties, although muscle relaxing can benefit anxious patients. It is used to treat anxiety,39 alcohol withdrawal,40 and fear.41 Low magnesium blood levels are found in patients with depression, schizophrenia,42 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.43 However, it is important to note that the therapeutic effect of magnesium when treating anxiety and headache is independent of preinfusion magnesium blood levels.43
Continue to: The efficacy of oral magnesium...
The efficacy of oral magnesium is not robust. However, IV administration has a pronounced beneficial effect as an abortive and preventative treatment in many patients with anxiety.44
IV administration of magnesium can produce adverse effects, including flushing, sweating, hypotension, depressed reflexes, flaccid paralysis, hypothermia, circulatory collapse, and cardiac and CNS depression. These complications are very rare and dose-dependent.45 Magnesium is excreted by the kidneys, and dosing must be decreased in patients with kidney failure. The most common adverse effect is local burning along the vein upon infusion; small doses of IV lidocaine can remedy this. Hot flashes are also common.45
Various dosing strategies are available. In patients with anxiety, application dosing is based on the recommended preeclampsia IV dose of 4 g diluted in 250 mL of 5% dextrose. Much higher doses may be used in obstetrics. Unlike in obstetrics, for psychiatric indications, magnesium is administered over 60 to 90 minutes. Heart monitoring is recommended.
Scopolamine
Scopolamine is primarily used to relieve nausea, vomiting, and dizziness associated with motion sickness and recovery from anesthesia. It is also used in ophthalmology and in patients with excessive sweating. In off-label and experimental applications, scopolamine has been used in patients with TRD.46
Scopolamine is an anticholinergic medication. It is a nonselective antagonist at muscarinic receptors.47 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) possess strong anticholinergic function. Newer generations of antidepressants were designed specifically not to have this function because it was believed to be an unwanted and potentially dangerous adverse effect. However, data suggest that anticholinergic action is important in decreasing depressive symptoms. Several hypotheses of anticholinergic effects on depression have been published since the 1970s. They include the cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis,48 acetylcholine predominance relative to adrenergic action hypothesis,49 and insecticide poisoning observations.50 Centrally acting physostigmine (but not peripherally acting neostigmine) was reported to control mania.48,51 A genetic connection between the M2 acetylcholine receptor in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and alcohol use disorder is also suggestive.52
Continue to: Multiple animal studies show...
Multiple animal studies show direct improvement in mobility and a decrease in despair upon introducing anticholinergic substances.53-55 The cholinergic theory of depression has been studied in several controlled clinical human studies.56,57 Use of a short-acting anticholinergic glycopyrrolate during electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may contribute to the procedure’s efficacy.
Human research shows scopolamine has a higher efficacy as an antidepressant and anti-anxiety medication in women than in men,58 possibly because estrogen increases the activity of choline acetyltransferase and release of acetylcholine.59,60 M2 receptors mediate estrogen influence on the NMDAR, which may explain the anticholinergic effects of depression treatments in women.61
Another proposed mechanism of action of scopolamine is a potent inhibition of the NMDAR.62 Rapid treatments of depression may be based on this mechanism. Examples of such treatments include IV ketamine and sleep deprivation.63 IV scopolamine shows potency in treating MDD and bipolar depression. This treatment should be reserved for patients who do not respond to or are not candidates for other usual treatment modalities of MDD and for the most severe cases. Scopolamine is 30 times more potent than amitriptyline in anticholinergic effect and reportedly produces sustained improvement in MDD.64
Scopolamine has no black-box warnings. It has not been studied in pregnant women and is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Due to possible negative cardiovascular effects, a normal electrocardiogram is required before the start of treatment. Exercise caution in patients with glaucoma, benign prostatic enlargement, gastroparesis, unstable cardiovascular status, or severe renal impairment.
Treatment with scopolamine is not indicated for patients with myasthenia gravis, psychosis, or seizures. Patients must be off potassium for 3 days before beginning scopolamine treatment. Patients should consult with their cardiologist before having a scopolamine infusion. Adverse reactions may include psychosis, tachycardia, seizures, paralytic ileus, and glaucoma exacerbation. The most common adverse effects of scopolamine infusion treatment include drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, lightheadedness, and dizziness. Due to possible drowsiness, operating motor vehicles or heavy machinery must be avoided on the day of treatment.65 Overall, the adverse effects of scopolamine are preventable and manageable, and its antidepressant efficacy is noteworthy.66
Continue to: Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions...
Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions of 4 mcg/kg separated by 3 to 5 days.56 It is possible to have a longer treatment course if the patient experiences only partial improvement. Repeated courses or maintenance treatment (similar to ECT maintenance) are utilized in some patients if indicated. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Clomipramine
Clomipramine, a TCA, acts as a preferential inhibitor of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and has proven effective in managing depression, TRD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).67 Although this medication has reported treatment benefits for patients with phobia, panic disorder,15 chronic pain,68 Tourette syndrome,69 premature ejaculation, anorexia nervosa,70 cataplexy,49 and enuresis,71 it is FDA-approved only for the treatment of OCD.72 Clomipramine may also be beneficial for pain and headache, possibly because of its anti-inflammatory action.73 The anticholinergic effects of clomipramine may add to its efficacy in depression.
The pathophysiology of MDD is connected to hyperactivity of the HPA axis and elevated cortisol levels. Higher clomipramine plasma levels show a linear correlation with lower cortisol secretion and levels, possibly aiding in the treatment of MDD and anxiety.74 The higher the blood level, the more pronounced clomipramine’s therapeutic effect across multiple domains.75
IV infusion of clomipramine produces the highest concentration in the shortest time, but overall, research does not necessarily support increased efficacy of IV over oral administration. There is evidence suggesting that subgroups of patients with severe, treatment-refractory OCD may benefit from IV agents and research suggests a faster onset of action.76 Faster onset of symptom relief is the basis for IV clomipramine use. In patients with OCD, it can take several months for oral medications to produce therapeutic benefits; not all patients can tolerate this. In such scenarios, IV administration may be considered, though it is not appropriate for routine use until more research is available. Patients with treatment-resistant OCD who have exhausted other means of symptom relief may also be candidates for IV treatment.
The adverse effects of IV clomipramine are no different from oral use, though they may be more pronounced. A pretreatment cardiac exam is desirable because clomipramine, like other TCAs, may be cardiotoxic. The anticholinergic adverse effects of TCAs are well known to clinicians77 and partially explained in the scopolamine section of this article. It is not advisable to combine clomipramine with other TCAs or serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Clomipramine also should not be combined with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, though such a combination was reported in medical literature.78 Combination with antiarrhythmics such as lidocaine or opioids such as fentanyl or and tramadol is highly discouraged (fentanyl and tramadol also have serotonergic effects).79
Continue to: Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available...
Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available and must be sterilely compounded. The usual course of treatment is a series of 3 infusions: 150 mg on Day 1, 200 mg on Day 2 or Day 3, and 250 mg on Day 3, Day 4, or Day 5, depending on tolerability. A protocol with a 50 mg/d starting dose and titration up to a maximum dose of 225 mg/d over 5 to 7 days has been suggested for inpatient settings.67 Titration to 250 mg is more common.80
A longer series may be performed, but this increases the likelihood of adverse effects. Booster and maintenance treatments are also completed when required. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Vortioxetine and citalopram
IV treatment of depression with
Injections and blocks
Three interventional approaches to treatment that possess psychotherapeutic potential include stellate ganglion blocks (SGBs), glabellar BT injections, and trigger point injections (TPIs). None of these are FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment.
Stellate ganglion blocks
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in autonomic hyperarousal and is at the core of posttraumatic symptomatology.83 Insomnia, anxiety, irritability, hypervigilance, and other excitatory CNS events are connected to the sympathetic nervous system and amygdala activation is commonly observed in those exposed to extreme stress or traumatic events.84
Continue to: SGBs were first performed 100 years ago...
SGBs were first performed 100 years ago and reported to have beneficial psychiatric effects at the end of the 1940s. In 1998 in Finland, improvement of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms was observed accidentally via thoracic level spine blocks.85 In 2006, cervical level sympathetic blocks were shown to be effective for PTSD symptom control.86 By the end of 2010, Veterans Administration hospitals adopted SGBs to treat veterans with PTSD.87,88 The first multisite, randomized clinical trial of
Since the stellate ganglion is connected to the amygdala, SGB has also been assessed for treating anxiety and depression.89,90 Outside of PTSD, SGBs are used to treat complex regional pain syndrome,91 phantom limb pain, trigeminal neuralgia,92 intractable angina,93 and postherpetic neuralgia in the head, neck, upper chest, or arms.94 The procedure consists of an injection of a local anesthetic through a 25-gauge needle into the stellate sympathetic ganglion at the C6 or C7 vertebral levels. An injection into C6 is considered safer because of specific cervical spine anatomy. Ideally, fluoroscopic guidance or ultrasound is used to guide needle insertion.95
A severe drop in blood pressure may be associated with SGBs and is mitigated by IV hydration. Other adverse effects include red eyes, drooping of the eyelids, nasal congestion, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of a “lump” in the throat, and a sensation of warmth or tingling in the arm or hand. Bilateral SGB is contraindicated due to the danger of respiratory arrest.96
Glabellar BT injections
OnabotulinumtoxinA (BT) injection was first approved for therapeutic use in 1989 for eye muscle disorders such as strabismus97 and blepharospasm.98 It was later approved for several other indications, including cosmetic use, hyperhidrosis, migraine prevention, neurogenic bladder disorder, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and spasticity.99-104 BT is used off-label for achalasia and sialorrhea.105,106 Its mechanism of action is primarily attributed to muscle paralysis by blocking presynaptic acetylcholine release into neuromuscular junctions.107
Facial BT injections are usually administered for cosmetic purposes, but smoothing forehead wrinkles and frown lines (the glabellar region of the face) both have antidepressant effects.108 BT injections into the glabellar region also demonstrate antidepressant effects, particularly in patients with comorbid migraines and MDD.109 Early case observations supported the independent benefit of the toxin on MDD when the toxin was injected into the glabellar region.110,111 The most frequent protocol involves injections in the procerus and corrugator muscles.
Continue to: The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis...
The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis has dominated thinking about the mood-improving effects of BT. The theory is that blocking muscular expression of sadness (especially in the face) interrupts the experience of sadness; therefore, depression subsides.112,113 However, BT injections in the muscles involved in the smile and an expression of positive emotions (lateral part of the musculus orbicularis oculi) have been associated with increased MDD scores.114 Thus, the mechanism clearly involves more than the cosmetic effect, since facial muscle injections in rats also have antidepressant effects.115
The use of progressive muscle relaxation is well-established in psychiatric treatment. The investigated conditions of increased muscle tone, especially torticollis and blepharospasm, are associated with MDD, and it may be speculated that proprioceptive feedback from the affected muscles may be causally involved in this association.116-118 Activity of the corrugator muscle has been positively associated with increased amygdala activity.119 This suggests a potential similar mechanism to that hypothesized for SGB.
Alternatively, BT is commonly used to treat chronic conditions that may contribute to depression; its success in relieving the underlying problem may indirectly relieve MDD. Thus, in a postmarketing safety evaluation of BT, MDD was demonstrated 40% to 88% less often by patients treated with BT for 6 of the 8 conditions and injection sites, such as in spasms and spasticity of arms and legs, torticollis and neck pain, and axilla and palm injections for hyperhidrosis. In a parotid and submandibular glands BT injection subcohort, no patients experienced depressive symptoms.120
Medicinal BT is generally considered safe. The most common adverse effects are hypersensitivity, injection site reactions, and other adverse effects specific to the injection site.121 Additionally, the cosmetic effects are transient, given the nature of the medication.
Trigger point injections
TPIs in the neck and shoulders are frequently used to treat tension headaches and various referred pain locations in the face and arms. Tension and depression frequently overlap in clinical practice.122 Relieving muscle tension (with resulting trigger points) improves muscle function and mood.
Continue to: The higher the number of active...
The higher the number of active trigger points (TPs), the greater the physical burden of headache and the higher the anxiety level. Gender differences in TP prevalence and TPI efficacy have been described in the literature. For example, the number of active TPs seems directly associated with anxiety levels in women but not in men.123 Although TPs appear to be more closely associated with anxiety than depression,124 depression associated with muscle tension does improve with TPIs. European studies have demonstrated a decrease in scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale following TPI treatment.125 The effect may be indirect, as when a patient’s pain is relieved, sleep and other psychiatric symptoms improve.126
A randomized controlled trial by Castro Sánchez et al127 demonstrated that dry needling therapy in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) showed improvements in pain pressure thresholds, body pain, vitality, and social function, as well as total FMS symptoms, quality of sleep, anxiety, hospital anxiety and depression, general pain intensity, and fatigue.
Myofascial pain syndrome, catastrophizing, and muscle tension are common in patients with depression, anxiety, and somatization. Local TPI therapy aimed at inactivating pain generators is supported by moderate quality evidence. All manner of therapies have been described, including injection of saline, corticosteroids, local anesthetic agents, and dry needling. BT injections in chronic TPs are also practiced, though no specific injection therapy has been reliably shown to be more advantageous than another. The benefits of TPIs may be derived from the needle itself rather than from any specific substance injected. Stimulation of a local twitch response with direct needling of the TP appears of importance. There is no established consensus regarding the number of injection points, frequency of administration, and volume or type of injectate.128
Adverse effects of TPIs relate to the nature of the invasive therapy, with the risk of tissue damage and bleeding. Pneumothorax risk is present with needle insertion at the neck and thorax.129 Patients with diabetes may experience variations in blood sugar control if steroids are used.
Bottom Line
Interventional treatment modalities that may have a role in psychiatric treatment include IV administration of ketamine, aducanumab, lecanemab, brexanolone, magnesium, scopolamine, and clomipramine. Other interventional approaches include stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin injections, and trigger point injections.
Related Resources
- Dokucu ME, Janicak PG. Nontraditional therapies for treatment-resistant depression. Current Psychiatry. 2021; 20(9):38-43,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0166
- Kim J, Khoury R, Grossberg GT. Botulinum toxin: emerging psychiatric indications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):8-18.
Drug Brand Names
Aducanumab • Aduhelm
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Brexanolone • Zulresso
Buprenorphine • Sublocade
Citalopram • Celexa
Clomipramine • Anafranil
Diazepam • Valium
Droperidol • Inapsine
Esketamine • Spravato
Fentanyl • Actiq
Fluphenazine decanoate • Modecate
Fluphenazine hydrochloride • Prolixin
Haloperidol decanoate • Haldol decanoate
Haloperidol lactate • Haldol
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lecanemab • Leqembi
Lidocaine • Xylocaine
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Magnesium sulfate • Sulfamag
Midazolam • Versed
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
OnabotulinumtoxinA injection • Botox
Paliperidone • Invega Hafyera, Invega Sustenna, Invega Trinza
Rapamycin • Rapamune, Sirolimus
Risperidone • Perseris
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta, Rykindo
Scopolamine • Hyoscine
Tramadol • Conzip
Vortioxetine • Trintellix
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Vincent KM, Ryan M, Palmer E, et al. Interventional psychiatry. Postgrad Med. 2020;132(7):573-574.
2. Allen MH, Feifel D, Lesem MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of loxapine for inhalation in the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(10):1313-1321.
3. Kwentus J, Riesenberg RA, Marandi M, et al. Rapid acute treatment of agitation in patients with bipolar I disorder: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with inhaled loxapine. Bipolar Disord. 2012;14(1):31-40.
4. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790.
6. Andorn A, Graham J, Csernansky J, et al. Monthly extended-release risperidone (RBP-7000) in the treatment of schizophrenia: results from the phase 3 program. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;39(5):428-433.
7. Dundee TW. Twenty-five years of ketamine. A report of an international meeting. Anaesthesia. 1990;45(2):159. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1990.tb14287.x
8. White PF, Way WL, Trevor AJ. Ketamine--its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology. 1982;56(2):119-136. doi:10.1097/00000542-198202000-00007
9. Zanos P, Gould TD. Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(4):801-811.
10. Molero P, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Martin-Santos R, et al. Antidepressant efficacy and tolerability of ketamine and esketamine: a critical review. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(5):411-420. doi:10.1007/s40263-018-0519-3
11. Williams NR, Heifets BD, Blasey C, et al. Attenuation of antidepressant effects of ketamine by opioid receptor antagonism. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(12):1205-1215.
12. Witkin JM, Martin AE, Golani LK, et al. Rapid-acting antidepressants. Adv Pharmacol. 2019;86:47-96.
13. Strayer RJ, Nelson LS. Adverse events associated with ketamine for procedural sedation in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(9):985-1028. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.12.005
14. Frye MA, Blier P, Tye SJ. Concomitant benzodiazepine use attenuates ketamine response: implications for large scale study design and clinical development. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35(3):334-336.
15. Fava M, Freeman MP, Flynn M, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial of intravenous ketamine as adjunctive therapy in treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1592-1603.
16. Bahji A, Vazquez GH, Zarate CA Jr. Comparative efficacy of racemic ketamine and esketamine for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;278:542-555. Erratum in: J Affect Disord. 2021;281:1001.
17. Brendle M, Robison R, Malone DC. Cost-effectiveness of esketamine nasal spray compared to intravenous ketamine for patients with treatment-resistant depression in the US utilizing clinical trial efficacy and real-world effectiveness estimates. J Affect Disord. 2022;319:388-396.
18. Dhillon S. Aducanumab: first approval. Drugs. 2021;81(12):1437-1443. Erratum in: Drugs. 2021;81(14):1701.
19. van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(1):9-21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2212948
20. Sevigny J, Chiao P, Bussière T, et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2016;537(7618):50-56. Update in: Nature. 2017;546(7659):564.
21. Fillit H, Green A. Aducanumab and the FDA – where are we now? Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(3):129-130.
22. Reardon S. FDA approves Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab amid safety concerns. Nature. 2023;613(7943):227-228. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-00030-3
23. McDade E, Cummings JL, Dhadda S, et al. Lecanemab in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: detailed results on biomarker, cognitive, and clinical effects from the randomized and open-label extension of the phase 2 proof-of-concept study. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022;14(1):191. doi:10.1186/s13195-022-01124-2
24. Mintun MA, Lo AC, Evans CD, et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1691-1704.
25. Luisi S, Petraglia F, Benedetto C, et al. Serum allopregnanolone levels in pregnant women: changes during pregnancy, at delivery, and in hypertensive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(7):2429-2433.
26. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1058-1070.
27. Powell JG, Garland S, Preston K, et al. Brexanolone (Zulresso): finally, an FDA-approved treatment for postpartum depression. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54(2):157-163.
28. Patterson R, Krohn H, Richardson E, et al. A brexanolone treatment program at an academic medical center: patient selection, 90-day posttreatment outcomes, and lessons learned. J Acad Consult Liaison Psychiatry. 2022;63(1):14-22.
29. World Health Organization. WHO model list of essential medicines - 22nd list (2021). World Health Organization. September 30, 2021. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021.02
30. Eby GA, Eby KL, Mruk H. Magnesium and major depression. In: Vink R, Nechifor M, eds. Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. University of Adelaide Press; 2011.
31. Plant TM, Zeleznik AJ. Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction. 4th ed. Elsevier Inc.; 2015:2503-2550.
32. Sidebotham D, Le Grice IJ. Physiology and pathophysiology. In: Sidebotham D, McKee A, Gillham M, Levy J. Cardiothoracic Critical Care. Elsevier, Inc.; 2007:3-27.
33. Duley L, Gülmezoglu AM, Henderson-Smart DJ, et al. Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010(11):CD000025.
34. Emergency supply of medicines. In: British National Formulary. British Medical Association, Royal Pharmaceutical Society; 2015:6. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.academia.edu/35076015/british_national_formulary_2015_pdf
35. Kwofie K, Wolfson AB. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for acute asthma exacerbation in children and adults. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(4):245-246.
36. Patniyot IR, Gelfand AA. Acute treatment therapies for pediatric migraine: a qualitative systematic review. Headache. 2016;56(1):49-70.
37. Wang X, Du X, Yang H, et al. Use of intravenous magnesium sulfate among patients with acute myocardial infarction in China from 2001 to 2015: China PEACE-Retrospective AMI Study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(3):e033269.
38. Karhu E, Atlas SE, Jinrun G, et al. Intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate is not associated with cardiovascular, liver, kidney, and metabolic toxicity in adults. J Clin Transl Res. 2018;4(1):47-55.
39. Noah L, Pickering G, Mazur A, et al. Impact of magnesium supplementation, in combination with vitamin B6, on stress and magnesium status: secondary data from a randomized controlled trial. Magnes Res. 2020;33(3):45-57.
40. Erstad BL, Cotugno CL. Management of alcohol withdrawal. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1995;52(7):697-709.
41. Abumaria N, Luo L, Ahn M, et al. Magnesium supplement enhances spatial-context pattern separation and prevents fear overgeneralization. Behav Pharmacol. 2013;24(4):255-263.
42. Kirov GK, Tsachev KN. Magnesium, schizophrenia and manic-depressive disease. Neuropsychobiology. 1990;23(2):79-81.
43. Botturi A, Ciappolino V, Delvecchio G, et al. The role and the effect of magnesium in mental disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1661.
44. Kirkland AE, Sarlo GL, Holton KF. The role of magnesium in neurological disorders. Nutrients. 2018;10(6):730.
45. Magnesium sulfate intravenous side effects by likelihood and severity. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-149570/magnesium-sulfate-intravenous/details/list-sideeffects
46. Scopolamine base transdermal system – uses, side effects, and more. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-14032/scopolamine-transdermal/details
47. Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E. Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;260(2):576-580.
48. Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM, et al. A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet. 1972;2(7778):632-635.
49. Janowsky DS, Risch SC, Gillin JC. Adrenergic-cholinergic balance and the treatment of affective disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983;7(2-3):297-307.
50. Gershon S, Shaw FH. Psychiatric sequelae of chronic exposure to organophosphorous insecticides. Lancet. 1972;1(7191):1371-1374.
51. Davis KL, Berger PA, Hollister LE, et al. Physostigmine in mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978;35(1):119-122.
52. Wang JC, Hinrichs AL, Stock H, et al. Evidence of common and specific genetic effects: association of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene with alcohol dependence and major depressive syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(17):1903-1911.
53. Brown RG. Effects of antidepressants and anticholinergics in a mouse “behavioral despair” test. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979;58(3):331-334.
54. Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M. Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature. 1977;266(5604):730-732.
55. Ji CX, Zhang JJ. Effect of scopolamine on depression in mice. Abstract in English. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2011;46(4):400-405.
56. Furey ML, Drevets WC. Antidepressant efficacy of the antimuscarinic drug scopolamine: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(10):1121-1129.
57. Drevets WC, Furey ML. Replication of scopolamine’s antidepressant efficacy in major depressive disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(5):432-438.
58. Furey ML, Khanna A, Hoffman EM, et al. Scopolamine produces larger antidepressant and antianxiety effects in women than in men. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(12):2479-2488.
59. Gibbs RB, Gabor R, Cox T, et al. Effects of raloxifene and estradiol on hippocampal acetylcholine release and spatial learning in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2004;29(6):741-748.
60. Pongrac JL, Gibbs RB, Defranco DB. Estrogen-mediated regulation of cholinergic expression in basal forebrain neurons requires extracellular-signal-regulated kinase activity. Neuroscience. 2004;124(4):809-816.
61. Daniel JM, Dohanich GP. Acetylcholine mediates the estrogen-induced increase in NMDA receptor binding in CA1 of the hippocampus and the associated improvement in working memory. J Neurosci. 2001;21(17):6949-6956.
62. Gerhard DM, Wohleb ES, Duman RS. Emerging treatment mechanisms for depression: focus on glutamate and synaptic plasticity. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(3):454-464.
63. Voderholzer U. Sleep deprivation and antidepressant treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2003;5(4):366-369.
64. Hasselmann H. Scopolamine and depression: a role for muscarinic antagonism? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(4):673-683.
65. Transderm scopolamine [prescribing information]. Warren, NJ: GSK Consumer Healthcare; 2019.
66. Jaffe RJ, Novakovic V, Peselow ED. Scopolamine as an antidepressant: a systematic review. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2013;36(1):24-26.
67. Karameh WK, Khani M. Intravenous clomipramine for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;19(2):pyv084.
68. Andrews ET, Beattie RM, Tighe MP. Functional abdominal pain: what clinicians need to know. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105(10):938-944. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2020-318825
69. Aliane V, Pérez S, Bohren Y, et al. Key role of striatal cholinergic interneurons in processes leading to arrest of motor stereotypies. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 1):110-118. doi:10.1093/brain/awq285
70. Tzavara ET, Bymaster FP, Davis RJ, et al. M4 muscarinic receptors regulate the dynamics of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission: relevance to the pathophysiology and treatment of related CNS pathologies. FASEB J. 2004;18(12):1410-1412. doi:10.1096/fj.04-1575fje
71. Korczyn AD, Kish I. The mechanism of imipramine in enuresis nocturna. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979;6(1):31-35. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1979.tb00004.x
72. Trimble MR. Worldwide use of clomipramine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1990;51(Suppl):51-54; discussion 55-58.
73. Gong W, Zhang S, Zong Y, et al. Involvement of the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome in the anti-inflammatory effect of the antidepressant clomipramine. J Affect Disord. 2019;254:15-25.
74. Piwowarska J, Wrzosek M, Radziwon’-Zaleska M. Serum cortisol concentration in patients with major depression after treatment with clomipramine. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61(4):604-611.
75. Danish University Antidepressant Group (DUAG). Clomipramine dose-effect study in patients with depression: clinical end points and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999;66(2):152-165.
76. Moukaddam NJ, Hirschfeld RMA. Intravenous antidepressants: a review. Depress Anxiety. 2004;19(1):1-9.
77. Gerretsen P, Pollock BG. Rediscovering adverse anticholinergic effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(6):869-870. doi:10.4088/JCP.11ac07093
78. Thomas SJ, Shin M, McInnis MG, et al. Combination therapy with monoamine oxidase inhibitors and other antidepressants or stimulants: strategies for the management of treatment-resistant depression. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(4):433-449. doi:10.1002/phar.1576
79. Robles LA. Serotonin syndrome induced by fentanyl in a child: case report. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2015;38(5):206-208. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000100
80. Fallon BA, Liebowitz MR, Campeas R, et al. Intravenous clomipramine for obsessive-compulsive disorder refractory to oral clomipramine: a placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(10):918-924.
81. Vieta E, Florea I, Schmidt SN, et al. Intravenous vortioxetine to accelerate onset of effect in major depressive disorder: a 2-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(4):153-160.
82. Kasper S, Müller-Spahn F. Intravenous antidepressant treatment: focus on citalopram. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2002;252(3):105-109.
83. Togay B, El-Mallakh RS. Posttraumatic stress disorder: from pathophysiology to pharmacology. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):33-39.
84. Adhikari A, Lerner TN, Finkelstein J, et al. Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear. Nature. 2015;527(7577):179-185. doi:10.1038/nature15698
85. Lipov E. In search of an effective treatment for combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): can the stellate ganglion block be the answer? Pain Pract. 2010;10(4):265-266.
86. Lipov E, Ritchie EC. A review of the use of stellate ganglion block in the treatment of PTSD. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(8):599.
87. Olmsted KLR, Bartoszek M, McLean B, et al. Effect of stellate ganglion block treatment on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):130-138.
88. Lipov E, Candido K. The successful use of left-sided stellate ganglion block in patients that fail to respond to right-sided stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms: a retrospective analysis of 205 patients. Mil Med. 2021;186(11-12):319-320.
89. Li Y, Loshak H. Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety. Canadian J Health Technol. 2021;1(3):1-30.
90. Kerzner J, Liu H, Demchenko I, et al. Stellate ganglion block for psychiatric disorders: a systematic review of the clinical research landscape. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2021;5:24705470211055176.
91. Wie C, Gupta R, Maloney J, et al. Interventional modalities to treat complex regional pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021;25(2):10. doi:10.1007/s11916-020-00904-5
92. Chaturvedi A, Dash HH. Sympathetic blockade for the relief of chronic pain. J Indian Med Assoc. 2001;99(12):698-703.
93. Chester M, Hammond C. Leach A. Long-term benefits of stellate ganglion block in severe chronic refractory angina. Pain. 2000;87(1):103-105. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00270-0
94. Jeon Y. Therapeutic potential of stellate ganglion block in orofacial pain: a mini review. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2016;16(3):159-163. doi:10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.159
95. Shan HH, Chen HF, Ni Y, et al. Effects of stellate ganglion block through different approaches under guidance of ultrasound. Front Surg. 2022;8:797793. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2021.797793
96. Goel V, Patwardhan AM, Ibrahim M, et al. Complications associated with stellate ganglion nerve block: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019;rapm-2018-100127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2018-100127
97. Rowe FJ, Noonan CP. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;3(3):CD006499.
98. Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2006;113(3):303-312.
99. Heckmann M, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Plewig G; Hyperhidrosis Study Group. Botulinum toxin A for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). N Engl J Med. 2001;344(7):488-493.
100. Carruthers JA, Lowe NJ, Menter MA, et al. A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of glabellar lines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(6):840-849.
101. Schurch B, de Sèze M, Denys P, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6-month study. J Urol. 2005;174:196–200.
102. Aurora SK, Winner P, Freeman MC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled analyses of the 56-week PREEMPT clinical program. Headache. 2011;51(9):1358-1373.
103. Dashtipour K, Chen JJ, Walker HW, et al. Systematic literature review of abobotulinumtoxinA in clinical trials for adult upper limb spasticity. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(3):229-238.
104. Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Urol. 2017;197(2S):S216-S223.
105. Jongerius PH, van den Hoogen FJA, van Limbeek J, et al. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: a controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2004;114(3):620-627.
106. Zaninotto, G. Annese V, Costantini M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of botulinum toxin versus laparoscopic heller myotomy for esophageal achalasia. Ann Surg. 2004;239(3):364-370.
107. Dressler D, Adib Saberi F. Botulinum toxin: mechanisms of action. Eur Neurol. 2005;53:3-9.
108. Lewis MB, Bowler PJ. Botulinum toxin cosmetic therapy correlates with a more positive mood. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(1):24-26.
109. Affatato O, Moulin TC, Pisanu C, et al. High efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in patients with comorbid migraine and depression: a meta-analysis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):133.
110. Finzi E, Wasserman E. Treatment of depression with botulinum toxin A: a case series. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(5):645-649; discussion 649-650.
111. Schulze J, Neumann I, Magid M, et al. Botulinum toxin for the management of depression: an updated review of the evidence and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;135:332-340.
112. Finzi E, Rosenthal NE. Emotional proprioception: treatment of depression with afferent facial feedback. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;80:93-96.
113. Söderkvist S, Ohlén K, Dimberg U. How the experience of emotion is modulated by facial feedback. J Nonverbal Behav. 2018;42(1):129-151.
114. Lewis, MB. The interactions between botulinum-toxin-based facial treatments and embodied emotions. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14720.
115. Li Y, Liu J, Liu X, et al. Antidepressant-like action of single facial injection of botulinum neurotoxin A is associated with augmented 5-HT levels and BDNF/ERK/CREB pathways in mouse brain. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):661-672. Erratum in: Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):779-780.
116. Gündel H, Wolf A, Xidara V, et al. High psychiatric comorbidity in spasmodic torticollis: a controlled study. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(7):465-473.
117. Hall TA, McGwin G Jr, Searcey K, et al. Health-related quality of life and psychosocial characteristics of patients with benign essential blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006;124(1):116-119.
118. Ceylan D, Erer S, Zarifog˘lu M, et al. Evaluation of anxiety and depression scales and quality of life in cervical dystonia patients on botulinum toxin therapy and their relatives. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(4):725-731.
119. Heller AS, Lapate RC, Mayer KE, et al. The face of negative affect: trial-by-trial corrugator responses to negative pictures are positively associated with amygdala and negatively associated with ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(9):2102-2110.
120. Makunts T, Wollmer MA, Abagyan R. Postmarketing safety surveillance data reveals antidepressant effects of botulinum toxin across various indications and injection sites. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12851.
121. Ahsanuddin S, Roy S, Nasser W, et al. Adverse events associated with botox as reported in a Food and Drug Administration database. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45(3):1201-1209. doi:10.1007/s00266-020-02027-z
122. Kashif M, Tahir S, Ashfaq F, et al. Association of myofascial trigger points in neck and shoulder region with depression, anxiety, and stress among university students. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021;71(9):2139-2142.
123. Cigarán-Méndez M, Jiménez-Antona C, Parás-Bravo P, et al. Active trigger points are associated with anxiety and widespread pressure pain sensitivity in women, but not men, with tension type headache. Pain Pract. 2019;19(5):522-529.
124. Palacios-Ceña M, Castaldo M, Wang K, et al. Relationship of active trigger points with related disability and anxiety in people with tension-type headache. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(13):e6548.
125. Karadas Ö, Inan LE, Ulas Ü, et al. Efficacy of local lidocaine application on anxiety and depression and its curative effect on patients with chronic tension-type headache. Eur Neurol. 2013;70(1-2):95-101.
126. Gerwin RD. Classification, epidemiology and natural history of myofascial pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2001;5(5):412-420.
127. Castro Sánchez AM, García López H, Fernández Sánchez M, et al. Improvement in clinical outcomes after dry needling versus myofascial release on pain pressure thresholds, quality of life, fatigue, pain intensity, quality of sleep, anxiety, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41(19):2235-2246.
128. Healy GM, Finn DP, O’Gorman DA, et al. Pretreatment anxiety and pain acceptance are associated with response to trigger point injection therapy for chronic myofascial pain. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1955-1966.
129. Morjaria JB, Lakshminarayana UB, Liu-Shiu-Cheong P, et al. Pneumothorax: a tale of pain or spontaneity. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2014;5(6):269-273.
Advances in the understanding of neurobiological and neuropsychiatric pathophysiology have opened new avenues of treatment for psychiatric patients. Historically, with a few exceptions, most psychiatric medications have been administered orally. However, many of the newer treatments require some form of specialized administration because they cannot be taken orally due to their chemical property (such as aducanumab); because there is the need to produce stable blood levels of the medication (such as brexanolone); because oral administration greatly diminished efficacy (such as oral vs IV magnesium or scopolamine), or because the treatment is focused on specific brain structures. This need for specialized administration has created a subspecialty called interventional psychiatry.
Part 1 of this 2-part article provides an overview of 1 type of interventional psychiatry: parenterally administered medications, including those administered via IV. We also describe 3 other interventional approaches to treatment: stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin (BT) injections, and trigger point injections. In Part 2 we will review interventional approaches that involve neuromodulation.
Parenteral medications in psychiatry
In general, IV and IM medications can be more potent that oral medications due to their overall faster onset of action and higher blood concentrations. These more invasive forms of administration can have significant limitations, such as a risk of infection at the injection site, the need to be administered in a medical setting, additional time, and patient discomfort.

Table 1 lists short-acting injectable medications used in psychiatry, and Table 2 lists long-acting injectable medications. Parenteral administration of antipsychotics is performed to alleviate acute agitation or for chronic symptom control. These medications generally are not considered interventional treatments, but could be classified as such due to their invasive nature.1 Furthermore, inhalable loxapine—which is indicated for managing acute agitation—requires a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program consisting of 2 hours observation and monitoring of respiratory status.2,3 Other indications for parenteral treatments include IM naltrexone extended release4 and subcutaneous injections of buprenorphine extended release5 and risperidone.6
IV administration
Most IV treatments described in this article are not FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment. Despite this, many interventional psychiatric treatments are part of clinical practice. IV infusion of ketamine is the most widely known and most researched of these. Table 3 lists other IV treatments that could be used as psychiatric treatment.
Ketamine
Since the early 1960s, ketamine has been used as a surgical anesthetic for animals. In the United States, it was approved for human surgical anesthesia in 1970. It was widely used during the Vietnam War due to its lack of inhibition of respiratory drive; medical staff first noticed an improvement in depressive symptoms and the resolution of suicidal ideation in patients who received ketamine. This led to further research on ketamine, particularly to determine its application in treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and other conditions.7 IV ketamine administration is most widely researched, but IM injections, intranasal sprays, and lozenges are also available. The dissociative properties of ketamine have led to its recreational use.8
Hypotheses for the mechanism of action of ketamine as an antidepressant include direct synaptic or extrasynaptic (GluN2B-selective), N-methyl-
Continue to: Ketamine is a schedule...
Ketamine is a schedule III medication with addictive properties. Delirium, panic attacks, hallucinations, nightmares, dysphoria, and paranoia may occur during and after use.13 Premedication with benzodiazepines, most notably lorazepam, is occasionally used to minimize ketamine’s adverse effects, but this generally is not recommended because doing so reduces ketamine’s antidepressant effects.14 Driving and operating heavy machinery is contraindicated after IV infusion. The usual protocol involves an IV infusion of ketamine 0.4 mg/kg to 1 mg/kg dosing over 1 hour. Doses between 0.4 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg are most common. Ketamine has a therapeutic window; doses >0.5 mg/kg are progressively less effective.15 Unlike the recommendation after esketamine administration, after receiving ketamine, patients remain in the care of their treatment team for <2 hours.
Esketamine, the S enantiomer of ketamine, was FDA-approved for TRD as an intranasal formulation. Esketamine is more commonly used than IV ketamine because it is FDA-approved and typically covered by insurance, but it may not be as effective.16 An economic analysis by Brendle et al17 suggested insurance companies would lower costs if they covered ketamine infusions vs intranasal esketamine.
Aducanumab and lecanemab
The most recent FDA-approved interventional agents are aducanumab and lecanemab, which are indicated for treating Alzheimer disease.18,19 Both are human monoclonal antibodies that bind selectively and with high affinity to amyloid beta plaque aggregates and promote their removal by Fc receptor–mediated phagocytosis.20
FDA approval of aducanumab and lecanemab was controversial. Initially, aducanumab’s safety monitoring board performed a futility analysis that suggested aducanumab was unlikely to separate from placebo, and the research was stopped.21 The manufacturer petitioned the FDA to consider the medication for accelerated approval on the basis of biomarker data showing that amyloid beta plaque aggregates become smaller. Current FDA approval is temporary to allow patients access to this potentially beneficial agent, but the manufacturer must supply clinical evidence that the reduction of amyloid beta plaques is associated with desirable changes in the course of Alzheimer disease, or risk losing the approval.
Lecanemab is also a human monoclonal antibody intended to remove amyloid beta plaques that was FDA-approved under the accelerated approval pathway.22 Unlike aducanumab, lecanemab demonstrated a statistically significant (although clinically imperceptible) reduction in the rate of cognitive decline; it did not show cognitive improvement.23 Lecanemab also significantly reduced amyloid beta plaques.23
Continue to: Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally...
Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally not covered by insurance and typically cost >$26,000 annually. Both are administered by IV infusion once a month. More monoclonal antibody medications for treating early Alzheimer disease are in the late stages of development, most notably donanebab.24 Observations during clinical trials found that in the later stages of Alzheimer disease, forceful removal of plaques by the autoimmune process damages neurons, while in less dense deposits of early dementia such removal is not harmful to the cells and prevents amyloid buildup.
Brexanolone is an aqueous formulation of allopregnanolone, a major metabolite of progesterone and a positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors.25 Its levels are maximal at the end of the third trimester of pregnancy and fall rapidly following delivery. Research showed a 3-day infusion was rapidly and significantly effective for treating postpartum depression26 and brexanolone received FDA approval for this indication in March 2019.27 However, various administrative, economic, insurance, and other hurdles make it difficult for patients to access this treatment. Despite its rapid onset of action (usually 48 hours), brexanolone takes an average of 15 days to go through the prior authorization process.28 In addition to the need for prior authorization, the main impediment to the use of brexanolone is the 3-day infusion schedule, which greatly magnifies the cost but is partially circumvented by the availability of dedicated outpatient centers.
Magnesium
Magnesium is on the World Health Organization’s Model List of Essential Medicines.29 There has been extensive research on the use of magnesium sulfate for psychiatric indications, especially for depression.30 Magnesium functions similarly to calcium channel blockers by competitively blocking intracellular calcium channels, decreasing calcium availability, and inhibiting smooth muscle contractility.31 It also competes with calcium at the motor end plate, reducing excitation by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.32 This property is used for high-dose IV magnesium treatment of impending preterm labor in obstetrics. Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice in treating eclamptic seizures and preventing seizures in severe preeclampsia or gestational hypertension with severe features.33 It is also used to treat torsade de pointes, severe asthma exacerbations, constipation, and barium poisoning.34 Beneficial use in asthma treatment35 and the treatment of migraine36 have also been reported.
IV magnesium in myocardial infarction may be harmful,37 though outside of acute cardiac events, magnesium is found to be safe.38
Oral magnesium sulfate is a common over-the-counter anxiety remedy. As a general cell stabilizer (mediated by the reduction of intracellular calcium), magnesium is potentially beneficial outside of its muscle-relaxing properties, although muscle relaxing can benefit anxious patients. It is used to treat anxiety,39 alcohol withdrawal,40 and fear.41 Low magnesium blood levels are found in patients with depression, schizophrenia,42 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.43 However, it is important to note that the therapeutic effect of magnesium when treating anxiety and headache is independent of preinfusion magnesium blood levels.43
Continue to: The efficacy of oral magnesium...
The efficacy of oral magnesium is not robust. However, IV administration has a pronounced beneficial effect as an abortive and preventative treatment in many patients with anxiety.44
IV administration of magnesium can produce adverse effects, including flushing, sweating, hypotension, depressed reflexes, flaccid paralysis, hypothermia, circulatory collapse, and cardiac and CNS depression. These complications are very rare and dose-dependent.45 Magnesium is excreted by the kidneys, and dosing must be decreased in patients with kidney failure. The most common adverse effect is local burning along the vein upon infusion; small doses of IV lidocaine can remedy this. Hot flashes are also common.45
Various dosing strategies are available. In patients with anxiety, application dosing is based on the recommended preeclampsia IV dose of 4 g diluted in 250 mL of 5% dextrose. Much higher doses may be used in obstetrics. Unlike in obstetrics, for psychiatric indications, magnesium is administered over 60 to 90 minutes. Heart monitoring is recommended.
Scopolamine
Scopolamine is primarily used to relieve nausea, vomiting, and dizziness associated with motion sickness and recovery from anesthesia. It is also used in ophthalmology and in patients with excessive sweating. In off-label and experimental applications, scopolamine has been used in patients with TRD.46
Scopolamine is an anticholinergic medication. It is a nonselective antagonist at muscarinic receptors.47 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) possess strong anticholinergic function. Newer generations of antidepressants were designed specifically not to have this function because it was believed to be an unwanted and potentially dangerous adverse effect. However, data suggest that anticholinergic action is important in decreasing depressive symptoms. Several hypotheses of anticholinergic effects on depression have been published since the 1970s. They include the cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis,48 acetylcholine predominance relative to adrenergic action hypothesis,49 and insecticide poisoning observations.50 Centrally acting physostigmine (but not peripherally acting neostigmine) was reported to control mania.48,51 A genetic connection between the M2 acetylcholine receptor in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and alcohol use disorder is also suggestive.52
Continue to: Multiple animal studies show...
Multiple animal studies show direct improvement in mobility and a decrease in despair upon introducing anticholinergic substances.53-55 The cholinergic theory of depression has been studied in several controlled clinical human studies.56,57 Use of a short-acting anticholinergic glycopyrrolate during electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may contribute to the procedure’s efficacy.
Human research shows scopolamine has a higher efficacy as an antidepressant and anti-anxiety medication in women than in men,58 possibly because estrogen increases the activity of choline acetyltransferase and release of acetylcholine.59,60 M2 receptors mediate estrogen influence on the NMDAR, which may explain the anticholinergic effects of depression treatments in women.61
Another proposed mechanism of action of scopolamine is a potent inhibition of the NMDAR.62 Rapid treatments of depression may be based on this mechanism. Examples of such treatments include IV ketamine and sleep deprivation.63 IV scopolamine shows potency in treating MDD and bipolar depression. This treatment should be reserved for patients who do not respond to or are not candidates for other usual treatment modalities of MDD and for the most severe cases. Scopolamine is 30 times more potent than amitriptyline in anticholinergic effect and reportedly produces sustained improvement in MDD.64
Scopolamine has no black-box warnings. It has not been studied in pregnant women and is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Due to possible negative cardiovascular effects, a normal electrocardiogram is required before the start of treatment. Exercise caution in patients with glaucoma, benign prostatic enlargement, gastroparesis, unstable cardiovascular status, or severe renal impairment.
Treatment with scopolamine is not indicated for patients with myasthenia gravis, psychosis, or seizures. Patients must be off potassium for 3 days before beginning scopolamine treatment. Patients should consult with their cardiologist before having a scopolamine infusion. Adverse reactions may include psychosis, tachycardia, seizures, paralytic ileus, and glaucoma exacerbation. The most common adverse effects of scopolamine infusion treatment include drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, lightheadedness, and dizziness. Due to possible drowsiness, operating motor vehicles or heavy machinery must be avoided on the day of treatment.65 Overall, the adverse effects of scopolamine are preventable and manageable, and its antidepressant efficacy is noteworthy.66
Continue to: Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions...
Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions of 4 mcg/kg separated by 3 to 5 days.56 It is possible to have a longer treatment course if the patient experiences only partial improvement. Repeated courses or maintenance treatment (similar to ECT maintenance) are utilized in some patients if indicated. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Clomipramine
Clomipramine, a TCA, acts as a preferential inhibitor of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and has proven effective in managing depression, TRD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).67 Although this medication has reported treatment benefits for patients with phobia, panic disorder,15 chronic pain,68 Tourette syndrome,69 premature ejaculation, anorexia nervosa,70 cataplexy,49 and enuresis,71 it is FDA-approved only for the treatment of OCD.72 Clomipramine may also be beneficial for pain and headache, possibly because of its anti-inflammatory action.73 The anticholinergic effects of clomipramine may add to its efficacy in depression.
The pathophysiology of MDD is connected to hyperactivity of the HPA axis and elevated cortisol levels. Higher clomipramine plasma levels show a linear correlation with lower cortisol secretion and levels, possibly aiding in the treatment of MDD and anxiety.74 The higher the blood level, the more pronounced clomipramine’s therapeutic effect across multiple domains.75
IV infusion of clomipramine produces the highest concentration in the shortest time, but overall, research does not necessarily support increased efficacy of IV over oral administration. There is evidence suggesting that subgroups of patients with severe, treatment-refractory OCD may benefit from IV agents and research suggests a faster onset of action.76 Faster onset of symptom relief is the basis for IV clomipramine use. In patients with OCD, it can take several months for oral medications to produce therapeutic benefits; not all patients can tolerate this. In such scenarios, IV administration may be considered, though it is not appropriate for routine use until more research is available. Patients with treatment-resistant OCD who have exhausted other means of symptom relief may also be candidates for IV treatment.
The adverse effects of IV clomipramine are no different from oral use, though they may be more pronounced. A pretreatment cardiac exam is desirable because clomipramine, like other TCAs, may be cardiotoxic. The anticholinergic adverse effects of TCAs are well known to clinicians77 and partially explained in the scopolamine section of this article. It is not advisable to combine clomipramine with other TCAs or serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Clomipramine also should not be combined with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, though such a combination was reported in medical literature.78 Combination with antiarrhythmics such as lidocaine or opioids such as fentanyl or and tramadol is highly discouraged (fentanyl and tramadol also have serotonergic effects).79
Continue to: Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available...
Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available and must be sterilely compounded. The usual course of treatment is a series of 3 infusions: 150 mg on Day 1, 200 mg on Day 2 or Day 3, and 250 mg on Day 3, Day 4, or Day 5, depending on tolerability. A protocol with a 50 mg/d starting dose and titration up to a maximum dose of 225 mg/d over 5 to 7 days has been suggested for inpatient settings.67 Titration to 250 mg is more common.80
A longer series may be performed, but this increases the likelihood of adverse effects. Booster and maintenance treatments are also completed when required. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Vortioxetine and citalopram
IV treatment of depression with
Injections and blocks
Three interventional approaches to treatment that possess psychotherapeutic potential include stellate ganglion blocks (SGBs), glabellar BT injections, and trigger point injections (TPIs). None of these are FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment.
Stellate ganglion blocks
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in autonomic hyperarousal and is at the core of posttraumatic symptomatology.83 Insomnia, anxiety, irritability, hypervigilance, and other excitatory CNS events are connected to the sympathetic nervous system and amygdala activation is commonly observed in those exposed to extreme stress or traumatic events.84
Continue to: SGBs were first performed 100 years ago...
SGBs were first performed 100 years ago and reported to have beneficial psychiatric effects at the end of the 1940s. In 1998 in Finland, improvement of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms was observed accidentally via thoracic level spine blocks.85 In 2006, cervical level sympathetic blocks were shown to be effective for PTSD symptom control.86 By the end of 2010, Veterans Administration hospitals adopted SGBs to treat veterans with PTSD.87,88 The first multisite, randomized clinical trial of
Since the stellate ganglion is connected to the amygdala, SGB has also been assessed for treating anxiety and depression.89,90 Outside of PTSD, SGBs are used to treat complex regional pain syndrome,91 phantom limb pain, trigeminal neuralgia,92 intractable angina,93 and postherpetic neuralgia in the head, neck, upper chest, or arms.94 The procedure consists of an injection of a local anesthetic through a 25-gauge needle into the stellate sympathetic ganglion at the C6 or C7 vertebral levels. An injection into C6 is considered safer because of specific cervical spine anatomy. Ideally, fluoroscopic guidance or ultrasound is used to guide needle insertion.95
A severe drop in blood pressure may be associated with SGBs and is mitigated by IV hydration. Other adverse effects include red eyes, drooping of the eyelids, nasal congestion, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of a “lump” in the throat, and a sensation of warmth or tingling in the arm or hand. Bilateral SGB is contraindicated due to the danger of respiratory arrest.96
Glabellar BT injections
OnabotulinumtoxinA (BT) injection was first approved for therapeutic use in 1989 for eye muscle disorders such as strabismus97 and blepharospasm.98 It was later approved for several other indications, including cosmetic use, hyperhidrosis, migraine prevention, neurogenic bladder disorder, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and spasticity.99-104 BT is used off-label for achalasia and sialorrhea.105,106 Its mechanism of action is primarily attributed to muscle paralysis by blocking presynaptic acetylcholine release into neuromuscular junctions.107
Facial BT injections are usually administered for cosmetic purposes, but smoothing forehead wrinkles and frown lines (the glabellar region of the face) both have antidepressant effects.108 BT injections into the glabellar region also demonstrate antidepressant effects, particularly in patients with comorbid migraines and MDD.109 Early case observations supported the independent benefit of the toxin on MDD when the toxin was injected into the glabellar region.110,111 The most frequent protocol involves injections in the procerus and corrugator muscles.
Continue to: The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis...
The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis has dominated thinking about the mood-improving effects of BT. The theory is that blocking muscular expression of sadness (especially in the face) interrupts the experience of sadness; therefore, depression subsides.112,113 However, BT injections in the muscles involved in the smile and an expression of positive emotions (lateral part of the musculus orbicularis oculi) have been associated with increased MDD scores.114 Thus, the mechanism clearly involves more than the cosmetic effect, since facial muscle injections in rats also have antidepressant effects.115
The use of progressive muscle relaxation is well-established in psychiatric treatment. The investigated conditions of increased muscle tone, especially torticollis and blepharospasm, are associated with MDD, and it may be speculated that proprioceptive feedback from the affected muscles may be causally involved in this association.116-118 Activity of the corrugator muscle has been positively associated with increased amygdala activity.119 This suggests a potential similar mechanism to that hypothesized for SGB.
Alternatively, BT is commonly used to treat chronic conditions that may contribute to depression; its success in relieving the underlying problem may indirectly relieve MDD. Thus, in a postmarketing safety evaluation of BT, MDD was demonstrated 40% to 88% less often by patients treated with BT for 6 of the 8 conditions and injection sites, such as in spasms and spasticity of arms and legs, torticollis and neck pain, and axilla and palm injections for hyperhidrosis. In a parotid and submandibular glands BT injection subcohort, no patients experienced depressive symptoms.120
Medicinal BT is generally considered safe. The most common adverse effects are hypersensitivity, injection site reactions, and other adverse effects specific to the injection site.121 Additionally, the cosmetic effects are transient, given the nature of the medication.
Trigger point injections
TPIs in the neck and shoulders are frequently used to treat tension headaches and various referred pain locations in the face and arms. Tension and depression frequently overlap in clinical practice.122 Relieving muscle tension (with resulting trigger points) improves muscle function and mood.
Continue to: The higher the number of active...
The higher the number of active trigger points (TPs), the greater the physical burden of headache and the higher the anxiety level. Gender differences in TP prevalence and TPI efficacy have been described in the literature. For example, the number of active TPs seems directly associated with anxiety levels in women but not in men.123 Although TPs appear to be more closely associated with anxiety than depression,124 depression associated with muscle tension does improve with TPIs. European studies have demonstrated a decrease in scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale following TPI treatment.125 The effect may be indirect, as when a patient’s pain is relieved, sleep and other psychiatric symptoms improve.126
A randomized controlled trial by Castro Sánchez et al127 demonstrated that dry needling therapy in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) showed improvements in pain pressure thresholds, body pain, vitality, and social function, as well as total FMS symptoms, quality of sleep, anxiety, hospital anxiety and depression, general pain intensity, and fatigue.
Myofascial pain syndrome, catastrophizing, and muscle tension are common in patients with depression, anxiety, and somatization. Local TPI therapy aimed at inactivating pain generators is supported by moderate quality evidence. All manner of therapies have been described, including injection of saline, corticosteroids, local anesthetic agents, and dry needling. BT injections in chronic TPs are also practiced, though no specific injection therapy has been reliably shown to be more advantageous than another. The benefits of TPIs may be derived from the needle itself rather than from any specific substance injected. Stimulation of a local twitch response with direct needling of the TP appears of importance. There is no established consensus regarding the number of injection points, frequency of administration, and volume or type of injectate.128
Adverse effects of TPIs relate to the nature of the invasive therapy, with the risk of tissue damage and bleeding. Pneumothorax risk is present with needle insertion at the neck and thorax.129 Patients with diabetes may experience variations in blood sugar control if steroids are used.
Bottom Line
Interventional treatment modalities that may have a role in psychiatric treatment include IV administration of ketamine, aducanumab, lecanemab, brexanolone, magnesium, scopolamine, and clomipramine. Other interventional approaches include stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin injections, and trigger point injections.
Related Resources
- Dokucu ME, Janicak PG. Nontraditional therapies for treatment-resistant depression. Current Psychiatry. 2021; 20(9):38-43,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0166
- Kim J, Khoury R, Grossberg GT. Botulinum toxin: emerging psychiatric indications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):8-18.
Drug Brand Names
Aducanumab • Aduhelm
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Brexanolone • Zulresso
Buprenorphine • Sublocade
Citalopram • Celexa
Clomipramine • Anafranil
Diazepam • Valium
Droperidol • Inapsine
Esketamine • Spravato
Fentanyl • Actiq
Fluphenazine decanoate • Modecate
Fluphenazine hydrochloride • Prolixin
Haloperidol decanoate • Haldol decanoate
Haloperidol lactate • Haldol
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lecanemab • Leqembi
Lidocaine • Xylocaine
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Magnesium sulfate • Sulfamag
Midazolam • Versed
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
OnabotulinumtoxinA injection • Botox
Paliperidone • Invega Hafyera, Invega Sustenna, Invega Trinza
Rapamycin • Rapamune, Sirolimus
Risperidone • Perseris
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta, Rykindo
Scopolamine • Hyoscine
Tramadol • Conzip
Vortioxetine • Trintellix
Ziprasidone • Geodon
Advances in the understanding of neurobiological and neuropsychiatric pathophysiology have opened new avenues of treatment for psychiatric patients. Historically, with a few exceptions, most psychiatric medications have been administered orally. However, many of the newer treatments require some form of specialized administration because they cannot be taken orally due to their chemical property (such as aducanumab); because there is the need to produce stable blood levels of the medication (such as brexanolone); because oral administration greatly diminished efficacy (such as oral vs IV magnesium or scopolamine), or because the treatment is focused on specific brain structures. This need for specialized administration has created a subspecialty called interventional psychiatry.
Part 1 of this 2-part article provides an overview of 1 type of interventional psychiatry: parenterally administered medications, including those administered via IV. We also describe 3 other interventional approaches to treatment: stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin (BT) injections, and trigger point injections. In Part 2 we will review interventional approaches that involve neuromodulation.
Parenteral medications in psychiatry
In general, IV and IM medications can be more potent that oral medications due to their overall faster onset of action and higher blood concentrations. These more invasive forms of administration can have significant limitations, such as a risk of infection at the injection site, the need to be administered in a medical setting, additional time, and patient discomfort.

Table 1 lists short-acting injectable medications used in psychiatry, and Table 2 lists long-acting injectable medications. Parenteral administration of antipsychotics is performed to alleviate acute agitation or for chronic symptom control. These medications generally are not considered interventional treatments, but could be classified as such due to their invasive nature.1 Furthermore, inhalable loxapine—which is indicated for managing acute agitation—requires a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program consisting of 2 hours observation and monitoring of respiratory status.2,3 Other indications for parenteral treatments include IM naltrexone extended release4 and subcutaneous injections of buprenorphine extended release5 and risperidone.6
IV administration
Most IV treatments described in this article are not FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment. Despite this, many interventional psychiatric treatments are part of clinical practice. IV infusion of ketamine is the most widely known and most researched of these. Table 3 lists other IV treatments that could be used as psychiatric treatment.
Ketamine
Since the early 1960s, ketamine has been used as a surgical anesthetic for animals. In the United States, it was approved for human surgical anesthesia in 1970. It was widely used during the Vietnam War due to its lack of inhibition of respiratory drive; medical staff first noticed an improvement in depressive symptoms and the resolution of suicidal ideation in patients who received ketamine. This led to further research on ketamine, particularly to determine its application in treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and other conditions.7 IV ketamine administration is most widely researched, but IM injections, intranasal sprays, and lozenges are also available. The dissociative properties of ketamine have led to its recreational use.8
Hypotheses for the mechanism of action of ketamine as an antidepressant include direct synaptic or extrasynaptic (GluN2B-selective), N-methyl-
Continue to: Ketamine is a schedule...
Ketamine is a schedule III medication with addictive properties. Delirium, panic attacks, hallucinations, nightmares, dysphoria, and paranoia may occur during and after use.13 Premedication with benzodiazepines, most notably lorazepam, is occasionally used to minimize ketamine’s adverse effects, but this generally is not recommended because doing so reduces ketamine’s antidepressant effects.14 Driving and operating heavy machinery is contraindicated after IV infusion. The usual protocol involves an IV infusion of ketamine 0.4 mg/kg to 1 mg/kg dosing over 1 hour. Doses between 0.4 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg are most common. Ketamine has a therapeutic window; doses >0.5 mg/kg are progressively less effective.15 Unlike the recommendation after esketamine administration, after receiving ketamine, patients remain in the care of their treatment team for <2 hours.
Esketamine, the S enantiomer of ketamine, was FDA-approved for TRD as an intranasal formulation. Esketamine is more commonly used than IV ketamine because it is FDA-approved and typically covered by insurance, but it may not be as effective.16 An economic analysis by Brendle et al17 suggested insurance companies would lower costs if they covered ketamine infusions vs intranasal esketamine.
Aducanumab and lecanemab
The most recent FDA-approved interventional agents are aducanumab and lecanemab, which are indicated for treating Alzheimer disease.18,19 Both are human monoclonal antibodies that bind selectively and with high affinity to amyloid beta plaque aggregates and promote their removal by Fc receptor–mediated phagocytosis.20
FDA approval of aducanumab and lecanemab was controversial. Initially, aducanumab’s safety monitoring board performed a futility analysis that suggested aducanumab was unlikely to separate from placebo, and the research was stopped.21 The manufacturer petitioned the FDA to consider the medication for accelerated approval on the basis of biomarker data showing that amyloid beta plaque aggregates become smaller. Current FDA approval is temporary to allow patients access to this potentially beneficial agent, but the manufacturer must supply clinical evidence that the reduction of amyloid beta plaques is associated with desirable changes in the course of Alzheimer disease, or risk losing the approval.
Lecanemab is also a human monoclonal antibody intended to remove amyloid beta plaques that was FDA-approved under the accelerated approval pathway.22 Unlike aducanumab, lecanemab demonstrated a statistically significant (although clinically imperceptible) reduction in the rate of cognitive decline; it did not show cognitive improvement.23 Lecanemab also significantly reduced amyloid beta plaques.23
Continue to: Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally...
Aducanumab and lecanemab are generally not covered by insurance and typically cost >$26,000 annually. Both are administered by IV infusion once a month. More monoclonal antibody medications for treating early Alzheimer disease are in the late stages of development, most notably donanebab.24 Observations during clinical trials found that in the later stages of Alzheimer disease, forceful removal of plaques by the autoimmune process damages neurons, while in less dense deposits of early dementia such removal is not harmful to the cells and prevents amyloid buildup.
Brexanolone is an aqueous formulation of allopregnanolone, a major metabolite of progesterone and a positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors.25 Its levels are maximal at the end of the third trimester of pregnancy and fall rapidly following delivery. Research showed a 3-day infusion was rapidly and significantly effective for treating postpartum depression26 and brexanolone received FDA approval for this indication in March 2019.27 However, various administrative, economic, insurance, and other hurdles make it difficult for patients to access this treatment. Despite its rapid onset of action (usually 48 hours), brexanolone takes an average of 15 days to go through the prior authorization process.28 In addition to the need for prior authorization, the main impediment to the use of brexanolone is the 3-day infusion schedule, which greatly magnifies the cost but is partially circumvented by the availability of dedicated outpatient centers.
Magnesium
Magnesium is on the World Health Organization’s Model List of Essential Medicines.29 There has been extensive research on the use of magnesium sulfate for psychiatric indications, especially for depression.30 Magnesium functions similarly to calcium channel blockers by competitively blocking intracellular calcium channels, decreasing calcium availability, and inhibiting smooth muscle contractility.31 It also competes with calcium at the motor end plate, reducing excitation by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.32 This property is used for high-dose IV magnesium treatment of impending preterm labor in obstetrics. Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice in treating eclamptic seizures and preventing seizures in severe preeclampsia or gestational hypertension with severe features.33 It is also used to treat torsade de pointes, severe asthma exacerbations, constipation, and barium poisoning.34 Beneficial use in asthma treatment35 and the treatment of migraine36 have also been reported.
IV magnesium in myocardial infarction may be harmful,37 though outside of acute cardiac events, magnesium is found to be safe.38
Oral magnesium sulfate is a common over-the-counter anxiety remedy. As a general cell stabilizer (mediated by the reduction of intracellular calcium), magnesium is potentially beneficial outside of its muscle-relaxing properties, although muscle relaxing can benefit anxious patients. It is used to treat anxiety,39 alcohol withdrawal,40 and fear.41 Low magnesium blood levels are found in patients with depression, schizophrenia,42 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.43 However, it is important to note that the therapeutic effect of magnesium when treating anxiety and headache is independent of preinfusion magnesium blood levels.43
Continue to: The efficacy of oral magnesium...
The efficacy of oral magnesium is not robust. However, IV administration has a pronounced beneficial effect as an abortive and preventative treatment in many patients with anxiety.44
IV administration of magnesium can produce adverse effects, including flushing, sweating, hypotension, depressed reflexes, flaccid paralysis, hypothermia, circulatory collapse, and cardiac and CNS depression. These complications are very rare and dose-dependent.45 Magnesium is excreted by the kidneys, and dosing must be decreased in patients with kidney failure. The most common adverse effect is local burning along the vein upon infusion; small doses of IV lidocaine can remedy this. Hot flashes are also common.45
Various dosing strategies are available. In patients with anxiety, application dosing is based on the recommended preeclampsia IV dose of 4 g diluted in 250 mL of 5% dextrose. Much higher doses may be used in obstetrics. Unlike in obstetrics, for psychiatric indications, magnesium is administered over 60 to 90 minutes. Heart monitoring is recommended.
Scopolamine
Scopolamine is primarily used to relieve nausea, vomiting, and dizziness associated with motion sickness and recovery from anesthesia. It is also used in ophthalmology and in patients with excessive sweating. In off-label and experimental applications, scopolamine has been used in patients with TRD.46
Scopolamine is an anticholinergic medication. It is a nonselective antagonist at muscarinic receptors.47 Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) possess strong anticholinergic function. Newer generations of antidepressants were designed specifically not to have this function because it was believed to be an unwanted and potentially dangerous adverse effect. However, data suggest that anticholinergic action is important in decreasing depressive symptoms. Several hypotheses of anticholinergic effects on depression have been published since the 1970s. They include the cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis,48 acetylcholine predominance relative to adrenergic action hypothesis,49 and insecticide poisoning observations.50 Centrally acting physostigmine (but not peripherally acting neostigmine) was reported to control mania.48,51 A genetic connection between the M2 acetylcholine receptor in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and alcohol use disorder is also suggestive.52
Continue to: Multiple animal studies show...
Multiple animal studies show direct improvement in mobility and a decrease in despair upon introducing anticholinergic substances.53-55 The cholinergic theory of depression has been studied in several controlled clinical human studies.56,57 Use of a short-acting anticholinergic glycopyrrolate during electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may contribute to the procedure’s efficacy.
Human research shows scopolamine has a higher efficacy as an antidepressant and anti-anxiety medication in women than in men,58 possibly because estrogen increases the activity of choline acetyltransferase and release of acetylcholine.59,60 M2 receptors mediate estrogen influence on the NMDAR, which may explain the anticholinergic effects of depression treatments in women.61
Another proposed mechanism of action of scopolamine is a potent inhibition of the NMDAR.62 Rapid treatments of depression may be based on this mechanism. Examples of such treatments include IV ketamine and sleep deprivation.63 IV scopolamine shows potency in treating MDD and bipolar depression. This treatment should be reserved for patients who do not respond to or are not candidates for other usual treatment modalities of MDD and for the most severe cases. Scopolamine is 30 times more potent than amitriptyline in anticholinergic effect and reportedly produces sustained improvement in MDD.64
Scopolamine has no black-box warnings. It has not been studied in pregnant women and is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Due to possible negative cardiovascular effects, a normal electrocardiogram is required before the start of treatment. Exercise caution in patients with glaucoma, benign prostatic enlargement, gastroparesis, unstable cardiovascular status, or severe renal impairment.
Treatment with scopolamine is not indicated for patients with myasthenia gravis, psychosis, or seizures. Patients must be off potassium for 3 days before beginning scopolamine treatment. Patients should consult with their cardiologist before having a scopolamine infusion. Adverse reactions may include psychosis, tachycardia, seizures, paralytic ileus, and glaucoma exacerbation. The most common adverse effects of scopolamine infusion treatment include drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, lightheadedness, and dizziness. Due to possible drowsiness, operating motor vehicles or heavy machinery must be avoided on the day of treatment.65 Overall, the adverse effects of scopolamine are preventable and manageable, and its antidepressant efficacy is noteworthy.66
Continue to: Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions...
Treatment typically consists of 3 consecutive infusions of 4 mcg/kg separated by 3 to 5 days.56 It is possible to have a longer treatment course if the patient experiences only partial improvement. Repeated courses or maintenance treatment (similar to ECT maintenance) are utilized in some patients if indicated. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Clomipramine
Clomipramine, a TCA, acts as a preferential inhibitor of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and has proven effective in managing depression, TRD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).67 Although this medication has reported treatment benefits for patients with phobia, panic disorder,15 chronic pain,68 Tourette syndrome,69 premature ejaculation, anorexia nervosa,70 cataplexy,49 and enuresis,71 it is FDA-approved only for the treatment of OCD.72 Clomipramine may also be beneficial for pain and headache, possibly because of its anti-inflammatory action.73 The anticholinergic effects of clomipramine may add to its efficacy in depression.
The pathophysiology of MDD is connected to hyperactivity of the HPA axis and elevated cortisol levels. Higher clomipramine plasma levels show a linear correlation with lower cortisol secretion and levels, possibly aiding in the treatment of MDD and anxiety.74 The higher the blood level, the more pronounced clomipramine’s therapeutic effect across multiple domains.75
IV infusion of clomipramine produces the highest concentration in the shortest time, but overall, research does not necessarily support increased efficacy of IV over oral administration. There is evidence suggesting that subgroups of patients with severe, treatment-refractory OCD may benefit from IV agents and research suggests a faster onset of action.76 Faster onset of symptom relief is the basis for IV clomipramine use. In patients with OCD, it can take several months for oral medications to produce therapeutic benefits; not all patients can tolerate this. In such scenarios, IV administration may be considered, though it is not appropriate for routine use until more research is available. Patients with treatment-resistant OCD who have exhausted other means of symptom relief may also be candidates for IV treatment.
The adverse effects of IV clomipramine are no different from oral use, though they may be more pronounced. A pretreatment cardiac exam is desirable because clomipramine, like other TCAs, may be cardiotoxic. The anticholinergic adverse effects of TCAs are well known to clinicians77 and partially explained in the scopolamine section of this article. It is not advisable to combine clomipramine with other TCAs or serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Clomipramine also should not be combined with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, though such a combination was reported in medical literature.78 Combination with antiarrhythmics such as lidocaine or opioids such as fentanyl or and tramadol is highly discouraged (fentanyl and tramadol also have serotonergic effects).79
Continue to: Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available...
Clomipramine for IV use is not commercially available and must be sterilely compounded. The usual course of treatment is a series of 3 infusions: 150 mg on Day 1, 200 mg on Day 2 or Day 3, and 250 mg on Day 3, Day 4, or Day 5, depending on tolerability. A protocol with a 50 mg/d starting dose and titration up to a maximum dose of 225 mg/d over 5 to 7 days has been suggested for inpatient settings.67 Titration to 250 mg is more common.80
A longer series may be performed, but this increases the likelihood of adverse effects. Booster and maintenance treatments are also completed when required. Cardiac monitoring is mandatory.
Vortioxetine and citalopram
IV treatment of depression with
Injections and blocks
Three interventional approaches to treatment that possess psychotherapeutic potential include stellate ganglion blocks (SGBs), glabellar BT injections, and trigger point injections (TPIs). None of these are FDA-approved for psychiatric treatment.
Stellate ganglion blocks
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in autonomic hyperarousal and is at the core of posttraumatic symptomatology.83 Insomnia, anxiety, irritability, hypervigilance, and other excitatory CNS events are connected to the sympathetic nervous system and amygdala activation is commonly observed in those exposed to extreme stress or traumatic events.84
Continue to: SGBs were first performed 100 years ago...
SGBs were first performed 100 years ago and reported to have beneficial psychiatric effects at the end of the 1940s. In 1998 in Finland, improvement of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms was observed accidentally via thoracic level spine blocks.85 In 2006, cervical level sympathetic blocks were shown to be effective for PTSD symptom control.86 By the end of 2010, Veterans Administration hospitals adopted SGBs to treat veterans with PTSD.87,88 The first multisite, randomized clinical trial of
Since the stellate ganglion is connected to the amygdala, SGB has also been assessed for treating anxiety and depression.89,90 Outside of PTSD, SGBs are used to treat complex regional pain syndrome,91 phantom limb pain, trigeminal neuralgia,92 intractable angina,93 and postherpetic neuralgia in the head, neck, upper chest, or arms.94 The procedure consists of an injection of a local anesthetic through a 25-gauge needle into the stellate sympathetic ganglion at the C6 or C7 vertebral levels. An injection into C6 is considered safer because of specific cervical spine anatomy. Ideally, fluoroscopic guidance or ultrasound is used to guide needle insertion.95
A severe drop in blood pressure may be associated with SGBs and is mitigated by IV hydration. Other adverse effects include red eyes, drooping of the eyelids, nasal congestion, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, a sensation of a “lump” in the throat, and a sensation of warmth or tingling in the arm or hand. Bilateral SGB is contraindicated due to the danger of respiratory arrest.96
Glabellar BT injections
OnabotulinumtoxinA (BT) injection was first approved for therapeutic use in 1989 for eye muscle disorders such as strabismus97 and blepharospasm.98 It was later approved for several other indications, including cosmetic use, hyperhidrosis, migraine prevention, neurogenic bladder disorder, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and spasticity.99-104 BT is used off-label for achalasia and sialorrhea.105,106 Its mechanism of action is primarily attributed to muscle paralysis by blocking presynaptic acetylcholine release into neuromuscular junctions.107
Facial BT injections are usually administered for cosmetic purposes, but smoothing forehead wrinkles and frown lines (the glabellar region of the face) both have antidepressant effects.108 BT injections into the glabellar region also demonstrate antidepressant effects, particularly in patients with comorbid migraines and MDD.109 Early case observations supported the independent benefit of the toxin on MDD when the toxin was injected into the glabellar region.110,111 The most frequent protocol involves injections in the procerus and corrugator muscles.
Continue to: The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis...
The facial feedback/emotional proprioception hypothesis has dominated thinking about the mood-improving effects of BT. The theory is that blocking muscular expression of sadness (especially in the face) interrupts the experience of sadness; therefore, depression subsides.112,113 However, BT injections in the muscles involved in the smile and an expression of positive emotions (lateral part of the musculus orbicularis oculi) have been associated with increased MDD scores.114 Thus, the mechanism clearly involves more than the cosmetic effect, since facial muscle injections in rats also have antidepressant effects.115
The use of progressive muscle relaxation is well-established in psychiatric treatment. The investigated conditions of increased muscle tone, especially torticollis and blepharospasm, are associated with MDD, and it may be speculated that proprioceptive feedback from the affected muscles may be causally involved in this association.116-118 Activity of the corrugator muscle has been positively associated with increased amygdala activity.119 This suggests a potential similar mechanism to that hypothesized for SGB.
Alternatively, BT is commonly used to treat chronic conditions that may contribute to depression; its success in relieving the underlying problem may indirectly relieve MDD. Thus, in a postmarketing safety evaluation of BT, MDD was demonstrated 40% to 88% less often by patients treated with BT for 6 of the 8 conditions and injection sites, such as in spasms and spasticity of arms and legs, torticollis and neck pain, and axilla and palm injections for hyperhidrosis. In a parotid and submandibular glands BT injection subcohort, no patients experienced depressive symptoms.120
Medicinal BT is generally considered safe. The most common adverse effects are hypersensitivity, injection site reactions, and other adverse effects specific to the injection site.121 Additionally, the cosmetic effects are transient, given the nature of the medication.
Trigger point injections
TPIs in the neck and shoulders are frequently used to treat tension headaches and various referred pain locations in the face and arms. Tension and depression frequently overlap in clinical practice.122 Relieving muscle tension (with resulting trigger points) improves muscle function and mood.
Continue to: The higher the number of active...
The higher the number of active trigger points (TPs), the greater the physical burden of headache and the higher the anxiety level. Gender differences in TP prevalence and TPI efficacy have been described in the literature. For example, the number of active TPs seems directly associated with anxiety levels in women but not in men.123 Although TPs appear to be more closely associated with anxiety than depression,124 depression associated with muscle tension does improve with TPIs. European studies have demonstrated a decrease in scores on the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale following TPI treatment.125 The effect may be indirect, as when a patient’s pain is relieved, sleep and other psychiatric symptoms improve.126
A randomized controlled trial by Castro Sánchez et al127 demonstrated that dry needling therapy in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) showed improvements in pain pressure thresholds, body pain, vitality, and social function, as well as total FMS symptoms, quality of sleep, anxiety, hospital anxiety and depression, general pain intensity, and fatigue.
Myofascial pain syndrome, catastrophizing, and muscle tension are common in patients with depression, anxiety, and somatization. Local TPI therapy aimed at inactivating pain generators is supported by moderate quality evidence. All manner of therapies have been described, including injection of saline, corticosteroids, local anesthetic agents, and dry needling. BT injections in chronic TPs are also practiced, though no specific injection therapy has been reliably shown to be more advantageous than another. The benefits of TPIs may be derived from the needle itself rather than from any specific substance injected. Stimulation of a local twitch response with direct needling of the TP appears of importance. There is no established consensus regarding the number of injection points, frequency of administration, and volume or type of injectate.128
Adverse effects of TPIs relate to the nature of the invasive therapy, with the risk of tissue damage and bleeding. Pneumothorax risk is present with needle insertion at the neck and thorax.129 Patients with diabetes may experience variations in blood sugar control if steroids are used.
Bottom Line
Interventional treatment modalities that may have a role in psychiatric treatment include IV administration of ketamine, aducanumab, lecanemab, brexanolone, magnesium, scopolamine, and clomipramine. Other interventional approaches include stellate ganglion blocks, glabellar botulinum toxin injections, and trigger point injections.
Related Resources
- Dokucu ME, Janicak PG. Nontraditional therapies for treatment-resistant depression. Current Psychiatry. 2021; 20(9):38-43,49. doi:10.12788/cp.0166
- Kim J, Khoury R, Grossberg GT. Botulinum toxin: emerging psychiatric indications. Current Psychiatry. 2018;17(12):8-18.
Drug Brand Names
Aducanumab • Aduhelm
Aripiprazole • Abilify
Aripiprazole lauroxil • Aristada
Brexanolone • Zulresso
Buprenorphine • Sublocade
Citalopram • Celexa
Clomipramine • Anafranil
Diazepam • Valium
Droperidol • Inapsine
Esketamine • Spravato
Fentanyl • Actiq
Fluphenazine decanoate • Modecate
Fluphenazine hydrochloride • Prolixin
Haloperidol decanoate • Haldol decanoate
Haloperidol lactate • Haldol
Ketamine • Ketalar
Lecanemab • Leqembi
Lidocaine • Xylocaine
Lorazepam • Ativan
Loxapine inhaled • Adasuve
Naltrexone • Vivitrol
Magnesium sulfate • Sulfamag
Midazolam • Versed
Olanzapine • Zyprexa
OnabotulinumtoxinA injection • Botox
Paliperidone • Invega Hafyera, Invega Sustenna, Invega Trinza
Rapamycin • Rapamune, Sirolimus
Risperidone • Perseris
Risperidone microspheres • Risperdal Consta, Rykindo
Scopolamine • Hyoscine
Tramadol • Conzip
Vortioxetine • Trintellix
Ziprasidone • Geodon
1. Vincent KM, Ryan M, Palmer E, et al. Interventional psychiatry. Postgrad Med. 2020;132(7):573-574.
2. Allen MH, Feifel D, Lesem MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of loxapine for inhalation in the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(10):1313-1321.
3. Kwentus J, Riesenberg RA, Marandi M, et al. Rapid acute treatment of agitation in patients with bipolar I disorder: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with inhaled loxapine. Bipolar Disord. 2012;14(1):31-40.
4. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790.
6. Andorn A, Graham J, Csernansky J, et al. Monthly extended-release risperidone (RBP-7000) in the treatment of schizophrenia: results from the phase 3 program. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;39(5):428-433.
7. Dundee TW. Twenty-five years of ketamine. A report of an international meeting. Anaesthesia. 1990;45(2):159. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1990.tb14287.x
8. White PF, Way WL, Trevor AJ. Ketamine--its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology. 1982;56(2):119-136. doi:10.1097/00000542-198202000-00007
9. Zanos P, Gould TD. Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(4):801-811.
10. Molero P, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Martin-Santos R, et al. Antidepressant efficacy and tolerability of ketamine and esketamine: a critical review. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(5):411-420. doi:10.1007/s40263-018-0519-3
11. Williams NR, Heifets BD, Blasey C, et al. Attenuation of antidepressant effects of ketamine by opioid receptor antagonism. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(12):1205-1215.
12. Witkin JM, Martin AE, Golani LK, et al. Rapid-acting antidepressants. Adv Pharmacol. 2019;86:47-96.
13. Strayer RJ, Nelson LS. Adverse events associated with ketamine for procedural sedation in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(9):985-1028. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.12.005
14. Frye MA, Blier P, Tye SJ. Concomitant benzodiazepine use attenuates ketamine response: implications for large scale study design and clinical development. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35(3):334-336.
15. Fava M, Freeman MP, Flynn M, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial of intravenous ketamine as adjunctive therapy in treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1592-1603.
16. Bahji A, Vazquez GH, Zarate CA Jr. Comparative efficacy of racemic ketamine and esketamine for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;278:542-555. Erratum in: J Affect Disord. 2021;281:1001.
17. Brendle M, Robison R, Malone DC. Cost-effectiveness of esketamine nasal spray compared to intravenous ketamine for patients with treatment-resistant depression in the US utilizing clinical trial efficacy and real-world effectiveness estimates. J Affect Disord. 2022;319:388-396.
18. Dhillon S. Aducanumab: first approval. Drugs. 2021;81(12):1437-1443. Erratum in: Drugs. 2021;81(14):1701.
19. van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(1):9-21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2212948
20. Sevigny J, Chiao P, Bussière T, et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2016;537(7618):50-56. Update in: Nature. 2017;546(7659):564.
21. Fillit H, Green A. Aducanumab and the FDA – where are we now? Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(3):129-130.
22. Reardon S. FDA approves Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab amid safety concerns. Nature. 2023;613(7943):227-228. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-00030-3
23. McDade E, Cummings JL, Dhadda S, et al. Lecanemab in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: detailed results on biomarker, cognitive, and clinical effects from the randomized and open-label extension of the phase 2 proof-of-concept study. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022;14(1):191. doi:10.1186/s13195-022-01124-2
24. Mintun MA, Lo AC, Evans CD, et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1691-1704.
25. Luisi S, Petraglia F, Benedetto C, et al. Serum allopregnanolone levels in pregnant women: changes during pregnancy, at delivery, and in hypertensive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(7):2429-2433.
26. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1058-1070.
27. Powell JG, Garland S, Preston K, et al. Brexanolone (Zulresso): finally, an FDA-approved treatment for postpartum depression. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54(2):157-163.
28. Patterson R, Krohn H, Richardson E, et al. A brexanolone treatment program at an academic medical center: patient selection, 90-day posttreatment outcomes, and lessons learned. J Acad Consult Liaison Psychiatry. 2022;63(1):14-22.
29. World Health Organization. WHO model list of essential medicines - 22nd list (2021). World Health Organization. September 30, 2021. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021.02
30. Eby GA, Eby KL, Mruk H. Magnesium and major depression. In: Vink R, Nechifor M, eds. Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. University of Adelaide Press; 2011.
31. Plant TM, Zeleznik AJ. Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction. 4th ed. Elsevier Inc.; 2015:2503-2550.
32. Sidebotham D, Le Grice IJ. Physiology and pathophysiology. In: Sidebotham D, McKee A, Gillham M, Levy J. Cardiothoracic Critical Care. Elsevier, Inc.; 2007:3-27.
33. Duley L, Gülmezoglu AM, Henderson-Smart DJ, et al. Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010(11):CD000025.
34. Emergency supply of medicines. In: British National Formulary. British Medical Association, Royal Pharmaceutical Society; 2015:6. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.academia.edu/35076015/british_national_formulary_2015_pdf
35. Kwofie K, Wolfson AB. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for acute asthma exacerbation in children and adults. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(4):245-246.
36. Patniyot IR, Gelfand AA. Acute treatment therapies for pediatric migraine: a qualitative systematic review. Headache. 2016;56(1):49-70.
37. Wang X, Du X, Yang H, et al. Use of intravenous magnesium sulfate among patients with acute myocardial infarction in China from 2001 to 2015: China PEACE-Retrospective AMI Study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(3):e033269.
38. Karhu E, Atlas SE, Jinrun G, et al. Intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate is not associated with cardiovascular, liver, kidney, and metabolic toxicity in adults. J Clin Transl Res. 2018;4(1):47-55.
39. Noah L, Pickering G, Mazur A, et al. Impact of magnesium supplementation, in combination with vitamin B6, on stress and magnesium status: secondary data from a randomized controlled trial. Magnes Res. 2020;33(3):45-57.
40. Erstad BL, Cotugno CL. Management of alcohol withdrawal. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1995;52(7):697-709.
41. Abumaria N, Luo L, Ahn M, et al. Magnesium supplement enhances spatial-context pattern separation and prevents fear overgeneralization. Behav Pharmacol. 2013;24(4):255-263.
42. Kirov GK, Tsachev KN. Magnesium, schizophrenia and manic-depressive disease. Neuropsychobiology. 1990;23(2):79-81.
43. Botturi A, Ciappolino V, Delvecchio G, et al. The role and the effect of magnesium in mental disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1661.
44. Kirkland AE, Sarlo GL, Holton KF. The role of magnesium in neurological disorders. Nutrients. 2018;10(6):730.
45. Magnesium sulfate intravenous side effects by likelihood and severity. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-149570/magnesium-sulfate-intravenous/details/list-sideeffects
46. Scopolamine base transdermal system – uses, side effects, and more. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-14032/scopolamine-transdermal/details
47. Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E. Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;260(2):576-580.
48. Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM, et al. A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet. 1972;2(7778):632-635.
49. Janowsky DS, Risch SC, Gillin JC. Adrenergic-cholinergic balance and the treatment of affective disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983;7(2-3):297-307.
50. Gershon S, Shaw FH. Psychiatric sequelae of chronic exposure to organophosphorous insecticides. Lancet. 1972;1(7191):1371-1374.
51. Davis KL, Berger PA, Hollister LE, et al. Physostigmine in mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978;35(1):119-122.
52. Wang JC, Hinrichs AL, Stock H, et al. Evidence of common and specific genetic effects: association of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene with alcohol dependence and major depressive syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(17):1903-1911.
53. Brown RG. Effects of antidepressants and anticholinergics in a mouse “behavioral despair” test. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979;58(3):331-334.
54. Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M. Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature. 1977;266(5604):730-732.
55. Ji CX, Zhang JJ. Effect of scopolamine on depression in mice. Abstract in English. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2011;46(4):400-405.
56. Furey ML, Drevets WC. Antidepressant efficacy of the antimuscarinic drug scopolamine: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(10):1121-1129.
57. Drevets WC, Furey ML. Replication of scopolamine’s antidepressant efficacy in major depressive disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(5):432-438.
58. Furey ML, Khanna A, Hoffman EM, et al. Scopolamine produces larger antidepressant and antianxiety effects in women than in men. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(12):2479-2488.
59. Gibbs RB, Gabor R, Cox T, et al. Effects of raloxifene and estradiol on hippocampal acetylcholine release and spatial learning in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2004;29(6):741-748.
60. Pongrac JL, Gibbs RB, Defranco DB. Estrogen-mediated regulation of cholinergic expression in basal forebrain neurons requires extracellular-signal-regulated kinase activity. Neuroscience. 2004;124(4):809-816.
61. Daniel JM, Dohanich GP. Acetylcholine mediates the estrogen-induced increase in NMDA receptor binding in CA1 of the hippocampus and the associated improvement in working memory. J Neurosci. 2001;21(17):6949-6956.
62. Gerhard DM, Wohleb ES, Duman RS. Emerging treatment mechanisms for depression: focus on glutamate and synaptic plasticity. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(3):454-464.
63. Voderholzer U. Sleep deprivation and antidepressant treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2003;5(4):366-369.
64. Hasselmann H. Scopolamine and depression: a role for muscarinic antagonism? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(4):673-683.
65. Transderm scopolamine [prescribing information]. Warren, NJ: GSK Consumer Healthcare; 2019.
66. Jaffe RJ, Novakovic V, Peselow ED. Scopolamine as an antidepressant: a systematic review. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2013;36(1):24-26.
67. Karameh WK, Khani M. Intravenous clomipramine for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;19(2):pyv084.
68. Andrews ET, Beattie RM, Tighe MP. Functional abdominal pain: what clinicians need to know. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105(10):938-944. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2020-318825
69. Aliane V, Pérez S, Bohren Y, et al. Key role of striatal cholinergic interneurons in processes leading to arrest of motor stereotypies. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 1):110-118. doi:10.1093/brain/awq285
70. Tzavara ET, Bymaster FP, Davis RJ, et al. M4 muscarinic receptors regulate the dynamics of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission: relevance to the pathophysiology and treatment of related CNS pathologies. FASEB J. 2004;18(12):1410-1412. doi:10.1096/fj.04-1575fje
71. Korczyn AD, Kish I. The mechanism of imipramine in enuresis nocturna. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979;6(1):31-35. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1979.tb00004.x
72. Trimble MR. Worldwide use of clomipramine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1990;51(Suppl):51-54; discussion 55-58.
73. Gong W, Zhang S, Zong Y, et al. Involvement of the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome in the anti-inflammatory effect of the antidepressant clomipramine. J Affect Disord. 2019;254:15-25.
74. Piwowarska J, Wrzosek M, Radziwon’-Zaleska M. Serum cortisol concentration in patients with major depression after treatment with clomipramine. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61(4):604-611.
75. Danish University Antidepressant Group (DUAG). Clomipramine dose-effect study in patients with depression: clinical end points and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999;66(2):152-165.
76. Moukaddam NJ, Hirschfeld RMA. Intravenous antidepressants: a review. Depress Anxiety. 2004;19(1):1-9.
77. Gerretsen P, Pollock BG. Rediscovering adverse anticholinergic effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(6):869-870. doi:10.4088/JCP.11ac07093
78. Thomas SJ, Shin M, McInnis MG, et al. Combination therapy with monoamine oxidase inhibitors and other antidepressants or stimulants: strategies for the management of treatment-resistant depression. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(4):433-449. doi:10.1002/phar.1576
79. Robles LA. Serotonin syndrome induced by fentanyl in a child: case report. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2015;38(5):206-208. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000100
80. Fallon BA, Liebowitz MR, Campeas R, et al. Intravenous clomipramine for obsessive-compulsive disorder refractory to oral clomipramine: a placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(10):918-924.
81. Vieta E, Florea I, Schmidt SN, et al. Intravenous vortioxetine to accelerate onset of effect in major depressive disorder: a 2-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(4):153-160.
82. Kasper S, Müller-Spahn F. Intravenous antidepressant treatment: focus on citalopram. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2002;252(3):105-109.
83. Togay B, El-Mallakh RS. Posttraumatic stress disorder: from pathophysiology to pharmacology. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):33-39.
84. Adhikari A, Lerner TN, Finkelstein J, et al. Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear. Nature. 2015;527(7577):179-185. doi:10.1038/nature15698
85. Lipov E. In search of an effective treatment for combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): can the stellate ganglion block be the answer? Pain Pract. 2010;10(4):265-266.
86. Lipov E, Ritchie EC. A review of the use of stellate ganglion block in the treatment of PTSD. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(8):599.
87. Olmsted KLR, Bartoszek M, McLean B, et al. Effect of stellate ganglion block treatment on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):130-138.
88. Lipov E, Candido K. The successful use of left-sided stellate ganglion block in patients that fail to respond to right-sided stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms: a retrospective analysis of 205 patients. Mil Med. 2021;186(11-12):319-320.
89. Li Y, Loshak H. Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety. Canadian J Health Technol. 2021;1(3):1-30.
90. Kerzner J, Liu H, Demchenko I, et al. Stellate ganglion block for psychiatric disorders: a systematic review of the clinical research landscape. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2021;5:24705470211055176.
91. Wie C, Gupta R, Maloney J, et al. Interventional modalities to treat complex regional pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021;25(2):10. doi:10.1007/s11916-020-00904-5
92. Chaturvedi A, Dash HH. Sympathetic blockade for the relief of chronic pain. J Indian Med Assoc. 2001;99(12):698-703.
93. Chester M, Hammond C. Leach A. Long-term benefits of stellate ganglion block in severe chronic refractory angina. Pain. 2000;87(1):103-105. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00270-0
94. Jeon Y. Therapeutic potential of stellate ganglion block in orofacial pain: a mini review. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2016;16(3):159-163. doi:10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.159
95. Shan HH, Chen HF, Ni Y, et al. Effects of stellate ganglion block through different approaches under guidance of ultrasound. Front Surg. 2022;8:797793. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2021.797793
96. Goel V, Patwardhan AM, Ibrahim M, et al. Complications associated with stellate ganglion nerve block: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019;rapm-2018-100127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2018-100127
97. Rowe FJ, Noonan CP. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;3(3):CD006499.
98. Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2006;113(3):303-312.
99. Heckmann M, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Plewig G; Hyperhidrosis Study Group. Botulinum toxin A for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). N Engl J Med. 2001;344(7):488-493.
100. Carruthers JA, Lowe NJ, Menter MA, et al. A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of glabellar lines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(6):840-849.
101. Schurch B, de Sèze M, Denys P, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6-month study. J Urol. 2005;174:196–200.
102. Aurora SK, Winner P, Freeman MC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled analyses of the 56-week PREEMPT clinical program. Headache. 2011;51(9):1358-1373.
103. Dashtipour K, Chen JJ, Walker HW, et al. Systematic literature review of abobotulinumtoxinA in clinical trials for adult upper limb spasticity. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(3):229-238.
104. Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Urol. 2017;197(2S):S216-S223.
105. Jongerius PH, van den Hoogen FJA, van Limbeek J, et al. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: a controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2004;114(3):620-627.
106. Zaninotto, G. Annese V, Costantini M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of botulinum toxin versus laparoscopic heller myotomy for esophageal achalasia. Ann Surg. 2004;239(3):364-370.
107. Dressler D, Adib Saberi F. Botulinum toxin: mechanisms of action. Eur Neurol. 2005;53:3-9.
108. Lewis MB, Bowler PJ. Botulinum toxin cosmetic therapy correlates with a more positive mood. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(1):24-26.
109. Affatato O, Moulin TC, Pisanu C, et al. High efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in patients with comorbid migraine and depression: a meta-analysis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):133.
110. Finzi E, Wasserman E. Treatment of depression with botulinum toxin A: a case series. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(5):645-649; discussion 649-650.
111. Schulze J, Neumann I, Magid M, et al. Botulinum toxin for the management of depression: an updated review of the evidence and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;135:332-340.
112. Finzi E, Rosenthal NE. Emotional proprioception: treatment of depression with afferent facial feedback. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;80:93-96.
113. Söderkvist S, Ohlén K, Dimberg U. How the experience of emotion is modulated by facial feedback. J Nonverbal Behav. 2018;42(1):129-151.
114. Lewis, MB. The interactions between botulinum-toxin-based facial treatments and embodied emotions. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14720.
115. Li Y, Liu J, Liu X, et al. Antidepressant-like action of single facial injection of botulinum neurotoxin A is associated with augmented 5-HT levels and BDNF/ERK/CREB pathways in mouse brain. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):661-672. Erratum in: Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):779-780.
116. Gündel H, Wolf A, Xidara V, et al. High psychiatric comorbidity in spasmodic torticollis: a controlled study. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(7):465-473.
117. Hall TA, McGwin G Jr, Searcey K, et al. Health-related quality of life and psychosocial characteristics of patients with benign essential blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006;124(1):116-119.
118. Ceylan D, Erer S, Zarifog˘lu M, et al. Evaluation of anxiety and depression scales and quality of life in cervical dystonia patients on botulinum toxin therapy and their relatives. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(4):725-731.
119. Heller AS, Lapate RC, Mayer KE, et al. The face of negative affect: trial-by-trial corrugator responses to negative pictures are positively associated with amygdala and negatively associated with ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(9):2102-2110.
120. Makunts T, Wollmer MA, Abagyan R. Postmarketing safety surveillance data reveals antidepressant effects of botulinum toxin across various indications and injection sites. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12851.
121. Ahsanuddin S, Roy S, Nasser W, et al. Adverse events associated with botox as reported in a Food and Drug Administration database. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45(3):1201-1209. doi:10.1007/s00266-020-02027-z
122. Kashif M, Tahir S, Ashfaq F, et al. Association of myofascial trigger points in neck and shoulder region with depression, anxiety, and stress among university students. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021;71(9):2139-2142.
123. Cigarán-Méndez M, Jiménez-Antona C, Parás-Bravo P, et al. Active trigger points are associated with anxiety and widespread pressure pain sensitivity in women, but not men, with tension type headache. Pain Pract. 2019;19(5):522-529.
124. Palacios-Ceña M, Castaldo M, Wang K, et al. Relationship of active trigger points with related disability and anxiety in people with tension-type headache. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(13):e6548.
125. Karadas Ö, Inan LE, Ulas Ü, et al. Efficacy of local lidocaine application on anxiety and depression and its curative effect on patients with chronic tension-type headache. Eur Neurol. 2013;70(1-2):95-101.
126. Gerwin RD. Classification, epidemiology and natural history of myofascial pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2001;5(5):412-420.
127. Castro Sánchez AM, García López H, Fernández Sánchez M, et al. Improvement in clinical outcomes after dry needling versus myofascial release on pain pressure thresholds, quality of life, fatigue, pain intensity, quality of sleep, anxiety, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41(19):2235-2246.
128. Healy GM, Finn DP, O’Gorman DA, et al. Pretreatment anxiety and pain acceptance are associated with response to trigger point injection therapy for chronic myofascial pain. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1955-1966.
129. Morjaria JB, Lakshminarayana UB, Liu-Shiu-Cheong P, et al. Pneumothorax: a tale of pain or spontaneity. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2014;5(6):269-273.
1. Vincent KM, Ryan M, Palmer E, et al. Interventional psychiatry. Postgrad Med. 2020;132(7):573-574.
2. Allen MH, Feifel D, Lesem MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of loxapine for inhalation in the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(10):1313-1321.
3. Kwentus J, Riesenberg RA, Marandi M, et al. Rapid acute treatment of agitation in patients with bipolar I disorder: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with inhaled loxapine. Bipolar Disord. 2012;14(1):31-40.
4. Lee JD, Nunes EV Jr, Novo P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10118):309-318.
5. Haight BR, Learned SM, Laffont CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10173):778-790.
6. Andorn A, Graham J, Csernansky J, et al. Monthly extended-release risperidone (RBP-7000) in the treatment of schizophrenia: results from the phase 3 program. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;39(5):428-433.
7. Dundee TW. Twenty-five years of ketamine. A report of an international meeting. Anaesthesia. 1990;45(2):159. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.1990.tb14287.x
8. White PF, Way WL, Trevor AJ. Ketamine--its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology. 1982;56(2):119-136. doi:10.1097/00000542-198202000-00007
9. Zanos P, Gould TD. Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(4):801-811.
10. Molero P, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Martin-Santos R, et al. Antidepressant efficacy and tolerability of ketamine and esketamine: a critical review. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(5):411-420. doi:10.1007/s40263-018-0519-3
11. Williams NR, Heifets BD, Blasey C, et al. Attenuation of antidepressant effects of ketamine by opioid receptor antagonism. Am J Psychiatry. 2018;175(12):1205-1215.
12. Witkin JM, Martin AE, Golani LK, et al. Rapid-acting antidepressants. Adv Pharmacol. 2019;86:47-96.
13. Strayer RJ, Nelson LS. Adverse events associated with ketamine for procedural sedation in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(9):985-1028. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.12.005
14. Frye MA, Blier P, Tye SJ. Concomitant benzodiazepine use attenuates ketamine response: implications for large scale study design and clinical development. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2015;35(3):334-336.
15. Fava M, Freeman MP, Flynn M, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial of intravenous ketamine as adjunctive therapy in treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(7):1592-1603.
16. Bahji A, Vazquez GH, Zarate CA Jr. Comparative efficacy of racemic ketamine and esketamine for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;278:542-555. Erratum in: J Affect Disord. 2021;281:1001.
17. Brendle M, Robison R, Malone DC. Cost-effectiveness of esketamine nasal spray compared to intravenous ketamine for patients with treatment-resistant depression in the US utilizing clinical trial efficacy and real-world effectiveness estimates. J Affect Disord. 2022;319:388-396.
18. Dhillon S. Aducanumab: first approval. Drugs. 2021;81(12):1437-1443. Erratum in: Drugs. 2021;81(14):1701.
19. van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(1):9-21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2212948
20. Sevigny J, Chiao P, Bussière T, et al. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 2016;537(7618):50-56. Update in: Nature. 2017;546(7659):564.
21. Fillit H, Green A. Aducanumab and the FDA – where are we now? Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(3):129-130.
22. Reardon S. FDA approves Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab amid safety concerns. Nature. 2023;613(7943):227-228. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-00030-3
23. McDade E, Cummings JL, Dhadda S, et al. Lecanemab in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: detailed results on biomarker, cognitive, and clinical effects from the randomized and open-label extension of the phase 2 proof-of-concept study. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022;14(1):191. doi:10.1186/s13195-022-01124-2
24. Mintun MA, Lo AC, Evans CD, et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(18):1691-1704.
25. Luisi S, Petraglia F, Benedetto C, et al. Serum allopregnanolone levels in pregnant women: changes during pregnancy, at delivery, and in hypertensive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(7):2429-2433.
26. Meltzer-Brody S, Colquhoun H, Riesenberg R, et al. Brexanolone injection in post-partum depression: two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1058-1070.
27. Powell JG, Garland S, Preston K, et al. Brexanolone (Zulresso): finally, an FDA-approved treatment for postpartum depression. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54(2):157-163.
28. Patterson R, Krohn H, Richardson E, et al. A brexanolone treatment program at an academic medical center: patient selection, 90-day posttreatment outcomes, and lessons learned. J Acad Consult Liaison Psychiatry. 2022;63(1):14-22.
29. World Health Organization. WHO model list of essential medicines - 22nd list (2021). World Health Organization. September 30, 2021. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021.02
30. Eby GA, Eby KL, Mruk H. Magnesium and major depression. In: Vink R, Nechifor M, eds. Magnesium in the Central Nervous System. University of Adelaide Press; 2011.
31. Plant TM, Zeleznik AJ. Knobil and Neill’s Physiology of Reproduction. 4th ed. Elsevier Inc.; 2015:2503-2550.
32. Sidebotham D, Le Grice IJ. Physiology and pathophysiology. In: Sidebotham D, McKee A, Gillham M, Levy J. Cardiothoracic Critical Care. Elsevier, Inc.; 2007:3-27.
33. Duley L, Gülmezoglu AM, Henderson-Smart DJ, et al. Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010(11):CD000025.
34. Emergency supply of medicines. In: British National Formulary. British Medical Association, Royal Pharmaceutical Society; 2015:6. Accessed April 7, 2023. https://www.academia.edu/35076015/british_national_formulary_2015_pdf
35. Kwofie K, Wolfson AB. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for acute asthma exacerbation in children and adults. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(4):245-246.
36. Patniyot IR, Gelfand AA. Acute treatment therapies for pediatric migraine: a qualitative systematic review. Headache. 2016;56(1):49-70.
37. Wang X, Du X, Yang H, et al. Use of intravenous magnesium sulfate among patients with acute myocardial infarction in China from 2001 to 2015: China PEACE-Retrospective AMI Study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(3):e033269.
38. Karhu E, Atlas SE, Jinrun G, et al. Intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate is not associated with cardiovascular, liver, kidney, and metabolic toxicity in adults. J Clin Transl Res. 2018;4(1):47-55.
39. Noah L, Pickering G, Mazur A, et al. Impact of magnesium supplementation, in combination with vitamin B6, on stress and magnesium status: secondary data from a randomized controlled trial. Magnes Res. 2020;33(3):45-57.
40. Erstad BL, Cotugno CL. Management of alcohol withdrawal. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1995;52(7):697-709.
41. Abumaria N, Luo L, Ahn M, et al. Magnesium supplement enhances spatial-context pattern separation and prevents fear overgeneralization. Behav Pharmacol. 2013;24(4):255-263.
42. Kirov GK, Tsachev KN. Magnesium, schizophrenia and manic-depressive disease. Neuropsychobiology. 1990;23(2):79-81.
43. Botturi A, Ciappolino V, Delvecchio G, et al. The role and the effect of magnesium in mental disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1661.
44. Kirkland AE, Sarlo GL, Holton KF. The role of magnesium in neurological disorders. Nutrients. 2018;10(6):730.
45. Magnesium sulfate intravenous side effects by likelihood and severity. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-149570/magnesium-sulfate-intravenous/details/list-sideeffects
46. Scopolamine base transdermal system – uses, side effects, and more. WebMD. Accessed April 9, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-14032/scopolamine-transdermal/details
47. Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E. Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992;260(2):576-580.
48. Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM, et al. A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet. 1972;2(7778):632-635.
49. Janowsky DS, Risch SC, Gillin JC. Adrenergic-cholinergic balance and the treatment of affective disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1983;7(2-3):297-307.
50. Gershon S, Shaw FH. Psychiatric sequelae of chronic exposure to organophosphorous insecticides. Lancet. 1972;1(7191):1371-1374.
51. Davis KL, Berger PA, Hollister LE, et al. Physostigmine in mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978;35(1):119-122.
52. Wang JC, Hinrichs AL, Stock H, et al. Evidence of common and specific genetic effects: association of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene with alcohol dependence and major depressive syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13(17):1903-1911.
53. Brown RG. Effects of antidepressants and anticholinergics in a mouse “behavioral despair” test. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979;58(3):331-334.
54. Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M. Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature. 1977;266(5604):730-732.
55. Ji CX, Zhang JJ. Effect of scopolamine on depression in mice. Abstract in English. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2011;46(4):400-405.
56. Furey ML, Drevets WC. Antidepressant efficacy of the antimuscarinic drug scopolamine: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(10):1121-1129.
57. Drevets WC, Furey ML. Replication of scopolamine’s antidepressant efficacy in major depressive disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(5):432-438.
58. Furey ML, Khanna A, Hoffman EM, et al. Scopolamine produces larger antidepressant and antianxiety effects in women than in men. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(12):2479-2488.
59. Gibbs RB, Gabor R, Cox T, et al. Effects of raloxifene and estradiol on hippocampal acetylcholine release and spatial learning in the rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2004;29(6):741-748.
60. Pongrac JL, Gibbs RB, Defranco DB. Estrogen-mediated regulation of cholinergic expression in basal forebrain neurons requires extracellular-signal-regulated kinase activity. Neuroscience. 2004;124(4):809-816.
61. Daniel JM, Dohanich GP. Acetylcholine mediates the estrogen-induced increase in NMDA receptor binding in CA1 of the hippocampus and the associated improvement in working memory. J Neurosci. 2001;21(17):6949-6956.
62. Gerhard DM, Wohleb ES, Duman RS. Emerging treatment mechanisms for depression: focus on glutamate and synaptic plasticity. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(3):454-464.
63. Voderholzer U. Sleep deprivation and antidepressant treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2003;5(4):366-369.
64. Hasselmann H. Scopolamine and depression: a role for muscarinic antagonism? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014;13(4):673-683.
65. Transderm scopolamine [prescribing information]. Warren, NJ: GSK Consumer Healthcare; 2019.
66. Jaffe RJ, Novakovic V, Peselow ED. Scopolamine as an antidepressant: a systematic review. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2013;36(1):24-26.
67. Karameh WK, Khani M. Intravenous clomipramine for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;19(2):pyv084.
68. Andrews ET, Beattie RM, Tighe MP. Functional abdominal pain: what clinicians need to know. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105(10):938-944. doi:10.1136/archdischild-2020-318825
69. Aliane V, Pérez S, Bohren Y, et al. Key role of striatal cholinergic interneurons in processes leading to arrest of motor stereotypies. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 1):110-118. doi:10.1093/brain/awq285
70. Tzavara ET, Bymaster FP, Davis RJ, et al. M4 muscarinic receptors regulate the dynamics of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission: relevance to the pathophysiology and treatment of related CNS pathologies. FASEB J. 2004;18(12):1410-1412. doi:10.1096/fj.04-1575fje
71. Korczyn AD, Kish I. The mechanism of imipramine in enuresis nocturna. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979;6(1):31-35. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.1979.tb00004.x
72. Trimble MR. Worldwide use of clomipramine. J Clin Psychiatry. 1990;51(Suppl):51-54; discussion 55-58.
73. Gong W, Zhang S, Zong Y, et al. Involvement of the microglial NLRP3 inflammasome in the anti-inflammatory effect of the antidepressant clomipramine. J Affect Disord. 2019;254:15-25.
74. Piwowarska J, Wrzosek M, Radziwon’-Zaleska M. Serum cortisol concentration in patients with major depression after treatment with clomipramine. Pharmacol Rep. 2009;61(4):604-611.
75. Danish University Antidepressant Group (DUAG). Clomipramine dose-effect study in patients with depression: clinical end points and pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1999;66(2):152-165.
76. Moukaddam NJ, Hirschfeld RMA. Intravenous antidepressants: a review. Depress Anxiety. 2004;19(1):1-9.
77. Gerretsen P, Pollock BG. Rediscovering adverse anticholinergic effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(6):869-870. doi:10.4088/JCP.11ac07093
78. Thomas SJ, Shin M, McInnis MG, et al. Combination therapy with monoamine oxidase inhibitors and other antidepressants or stimulants: strategies for the management of treatment-resistant depression. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(4):433-449. doi:10.1002/phar.1576
79. Robles LA. Serotonin syndrome induced by fentanyl in a child: case report. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2015;38(5):206-208. doi:10.1097/WNF.0000000000000100
80. Fallon BA, Liebowitz MR, Campeas R, et al. Intravenous clomipramine for obsessive-compulsive disorder refractory to oral clomipramine: a placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55(10):918-924.
81. Vieta E, Florea I, Schmidt SN, et al. Intravenous vortioxetine to accelerate onset of effect in major depressive disorder: a 2-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2019;34(4):153-160.
82. Kasper S, Müller-Spahn F. Intravenous antidepressant treatment: focus on citalopram. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2002;252(3):105-109.
83. Togay B, El-Mallakh RS. Posttraumatic stress disorder: from pathophysiology to pharmacology. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(5):33-39.
84. Adhikari A, Lerner TN, Finkelstein J, et al. Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear. Nature. 2015;527(7577):179-185. doi:10.1038/nature15698
85. Lipov E. In search of an effective treatment for combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): can the stellate ganglion block be the answer? Pain Pract. 2010;10(4):265-266.
86. Lipov E, Ritchie EC. A review of the use of stellate ganglion block in the treatment of PTSD. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17(8):599.
87. Olmsted KLR, Bartoszek M, McLean B, et al. Effect of stellate ganglion block treatment on posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):130-138.
88. Lipov E, Candido K. The successful use of left-sided stellate ganglion block in patients that fail to respond to right-sided stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms: a retrospective analysis of 205 patients. Mil Med. 2021;186(11-12):319-320.
89. Li Y, Loshak H. Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety. Canadian J Health Technol. 2021;1(3):1-30.
90. Kerzner J, Liu H, Demchenko I, et al. Stellate ganglion block for psychiatric disorders: a systematic review of the clinical research landscape. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2021;5:24705470211055176.
91. Wie C, Gupta R, Maloney J, et al. Interventional modalities to treat complex regional pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021;25(2):10. doi:10.1007/s11916-020-00904-5
92. Chaturvedi A, Dash HH. Sympathetic blockade for the relief of chronic pain. J Indian Med Assoc. 2001;99(12):698-703.
93. Chester M, Hammond C. Leach A. Long-term benefits of stellate ganglion block in severe chronic refractory angina. Pain. 2000;87(1):103-105. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00270-0
94. Jeon Y. Therapeutic potential of stellate ganglion block in orofacial pain: a mini review. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2016;16(3):159-163. doi:10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.159
95. Shan HH, Chen HF, Ni Y, et al. Effects of stellate ganglion block through different approaches under guidance of ultrasound. Front Surg. 2022;8:797793. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2021.797793
96. Goel V, Patwardhan AM, Ibrahim M, et al. Complications associated with stellate ganglion nerve block: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019;rapm-2018-100127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2018-100127
97. Rowe FJ, Noonan CP. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of strabismus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;3(3):CD006499.
98. Roggenkämper P, Jost WH, Bihari K, et al. Efficacy and safety of a new botulinum toxin type A free of complexing proteins in the treatment of blepharospasm. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2006;113(3):303-312.
99. Heckmann M, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Plewig G; Hyperhidrosis Study Group. Botulinum toxin A for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). N Engl J Med. 2001;344(7):488-493.
100. Carruthers JA, Lowe NJ, Menter MA, et al. A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of glabellar lines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(6):840-849.
101. Schurch B, de Sèze M, Denys P, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment, randomized, placebo controlled 6-month study. J Urol. 2005;174:196–200.
102. Aurora SK, Winner P, Freeman MC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled analyses of the 56-week PREEMPT clinical program. Headache. 2011;51(9):1358-1373.
103. Dashtipour K, Chen JJ, Walker HW, et al. Systematic literature review of abobotulinumtoxinA in clinical trials for adult upper limb spasticity. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;94(3):229-238.
104. Nitti VW, Dmochowski R, Herschorn S, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder and urinary incontinence: results of a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Urol. 2017;197(2S):S216-S223.
105. Jongerius PH, van den Hoogen FJA, van Limbeek J, et al. Effect of botulinum toxin in the treatment of drooling: a controlled clinical trial. Pediatrics. 2004;114(3):620-627.
106. Zaninotto, G. Annese V, Costantini M, et al. Randomized controlled trial of botulinum toxin versus laparoscopic heller myotomy for esophageal achalasia. Ann Surg. 2004;239(3):364-370.
107. Dressler D, Adib Saberi F. Botulinum toxin: mechanisms of action. Eur Neurol. 2005;53:3-9.
108. Lewis MB, Bowler PJ. Botulinum toxin cosmetic therapy correlates with a more positive mood. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8(1):24-26.
109. Affatato O, Moulin TC, Pisanu C, et al. High efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA treatment in patients with comorbid migraine and depression: a meta-analysis. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):133.
110. Finzi E, Wasserman E. Treatment of depression with botulinum toxin A: a case series. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(5):645-649; discussion 649-650.
111. Schulze J, Neumann I, Magid M, et al. Botulinum toxin for the management of depression: an updated review of the evidence and meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;135:332-340.
112. Finzi E, Rosenthal NE. Emotional proprioception: treatment of depression with afferent facial feedback. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;80:93-96.
113. Söderkvist S, Ohlén K, Dimberg U. How the experience of emotion is modulated by facial feedback. J Nonverbal Behav. 2018;42(1):129-151.
114. Lewis, MB. The interactions between botulinum-toxin-based facial treatments and embodied emotions. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14720.
115. Li Y, Liu J, Liu X, et al. Antidepressant-like action of single facial injection of botulinum neurotoxin A is associated with augmented 5-HT levels and BDNF/ERK/CREB pathways in mouse brain. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):661-672. Erratum in: Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(4):779-780.
116. Gündel H, Wolf A, Xidara V, et al. High psychiatric comorbidity in spasmodic torticollis: a controlled study. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(7):465-473.
117. Hall TA, McGwin G Jr, Searcey K, et al. Health-related quality of life and psychosocial characteristics of patients with benign essential blepharospasm. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006;124(1):116-119.
118. Ceylan D, Erer S, Zarifog˘lu M, et al. Evaluation of anxiety and depression scales and quality of life in cervical dystonia patients on botulinum toxin therapy and their relatives. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(4):725-731.
119. Heller AS, Lapate RC, Mayer KE, et al. The face of negative affect: trial-by-trial corrugator responses to negative pictures are positively associated with amygdala and negatively associated with ventromedial prefrontal cortex activity. J Cogn Neurosci. 2014;26(9):2102-2110.
120. Makunts T, Wollmer MA, Abagyan R. Postmarketing safety surveillance data reveals antidepressant effects of botulinum toxin across various indications and injection sites. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12851.
121. Ahsanuddin S, Roy S, Nasser W, et al. Adverse events associated with botox as reported in a Food and Drug Administration database. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45(3):1201-1209. doi:10.1007/s00266-020-02027-z
122. Kashif M, Tahir S, Ashfaq F, et al. Association of myofascial trigger points in neck and shoulder region with depression, anxiety, and stress among university students. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021;71(9):2139-2142.
123. Cigarán-Méndez M, Jiménez-Antona C, Parás-Bravo P, et al. Active trigger points are associated with anxiety and widespread pressure pain sensitivity in women, but not men, with tension type headache. Pain Pract. 2019;19(5):522-529.
124. Palacios-Ceña M, Castaldo M, Wang K, et al. Relationship of active trigger points with related disability and anxiety in people with tension-type headache. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(13):e6548.
125. Karadas Ö, Inan LE, Ulas Ü, et al. Efficacy of local lidocaine application on anxiety and depression and its curative effect on patients with chronic tension-type headache. Eur Neurol. 2013;70(1-2):95-101.
126. Gerwin RD. Classification, epidemiology and natural history of myofascial pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2001;5(5):412-420.
127. Castro Sánchez AM, García López H, Fernández Sánchez M, et al. Improvement in clinical outcomes after dry needling versus myofascial release on pain pressure thresholds, quality of life, fatigue, pain intensity, quality of sleep, anxiety, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41(19):2235-2246.
128. Healy GM, Finn DP, O’Gorman DA, et al. Pretreatment anxiety and pain acceptance are associated with response to trigger point injection therapy for chronic myofascial pain. Pain Med. 2015;16(10):1955-1966.
129. Morjaria JB, Lakshminarayana UB, Liu-Shiu-Cheong P, et al. Pneumothorax: a tale of pain or spontaneity. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2014;5(6):269-273.
Depressed and cognitively impaired
CASE Depressed and anxious
Five years ago, Ms. X, age 60, was diagnosed with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) with anxiety. This diagnosis was established by a previous psychiatrist. She presents to a clinic for a second opinion.
Since her diagnosis, Ms. X has experienced sad mood, anhedonia, difficulty falling asleep, increased appetite and weight, and decreased concentration and attention. Her anxiety stems from her inability to work, which causes her to worry about her children. In the clinic, the treatment team conducts the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 item scale (GAD-7) with Ms. X. She scores 16 on the PHQ-9, indicating moderately severe depression, and scores 12 on the GAD-7, indicating moderate anxiety.
Ms. X’s current medication regimen consists of venlafaxine extended-release (XR) 225 mg/d, trazodone 100 mg/d at bedtime, and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. She reports no significant improvement of her symptoms from these medications. Additionally, Ms. X reports that in the past she had been prescribed fluoxetine, citalopram, and duloxetine, but she cannot recall the dosages.
Ms. X appears appropriately groomed, maintains appropriate eye contact, has clear speech, and does not show evidence of internal stimulation; however, she has difficulty following instructions. She makes negative comments about herself such as “I’m worthless” and “Nobody cares about me.” The treatment team decides to taper Ms. X off venlafaxine XR and initiates sertraline 50 mg/d, while continuing trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. The team refers her for cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address her cognitive distortions, sad mood, and anxiety. Ms. X is asked to follow up with Psychiatry in 1 week.
EVALUATION Unusual behavior
At her CBT intake, Ms. X endorses depression and anxiety. Her PHQ-9 score at this visit is 19 (moderately severe depression) and GAD-7 score is 16 (severe anxiety). The psychologist notes that Ms. X is able to complete activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living without assistance. Ms. X denies any use of illicit substances or alcohol. No gross memory impairment is noted during this appointment, though Ms. X exhibits unusual behavior, including exiting and re-entering the clinic multiple times to repeatedly ask about follow-up appointments. The psychologist concludes that Ms. X’s presentation and behavior can be explained by MDD and pseudodementia.
[polldaddy:12189562]
The authors’ observations
Pseudodementia gained recognition in clinical research >100 years ago.1 Officially coined by Kiloh in 1961, the term was used broadly to categorize psychiatric cases that present like dementia but are the result of reversible causes. More recently, it has been used to describe older adults who present with cognitive deficits in the context of depressive symptoms.2 The goal of evaluation is to determine if the primary issue is a cognitive disorder or a depressive episode. DSM-5-TR does not classify pseudodementia as a distinct diagnosis, but instead categorizes its symptoms as components under other major diagnostic categories. Patients can present with MDD and associated cognitive symptoms, or with a cognitive disorder with depressive symptoms, which would be diagnosed as a cognitive disorder with a major depressive-like episode.3
Pseudodementia is rare. Brodaty et al4 found the prevalence of pseudodementia in primary care settings was 0.6%. Older adults (age >65) who live alone are at increased risk of developing pseudodementia, which can be worsened by poor social support and acute psychosocial and environmental changes.5 A key characteristic of this disorder is that as the patient’s depressed mood improves, their memory and cognition also improve.6 Table 13,6 outlines overlapping features of MDD and pseudodementia.
Continue to: EVALUATION Worsening depression
EVALUATION Worsening depression
At her Psychiatry follow-up appointment, Ms. X reports that her mood is worse since she ended the relationship with her partner and she feels anxious because the partner was financially supporting her. Her PHQ-9 score is 24 (severe depression) and her GAD-7 score is 12 (moderate anxiety). Ms. X reports tolerating her transition from venlafaxine XR 225 mg/d to sertraline 50 mg/d well.
Additionally, Ms. X reports her children have called her “useless” since she continues to have difficulties following through on household tasks, even though she has no physical impairments that prevent her from completing them. The Psychiatry team observes that Ms. X has no problems walking or moving her arms or legs.
The Psychiatry team administers the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Ms. X scores 22, indicating mild impairment.
The team recommends a neuropsychological assessment to determine if this MoCA score is due to a cognitive disorder or is rooted in her mood symptoms. The team also recommends an MRI of the brain, complete blood count (CBC), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), and urinalysis (UA).
[polldaddy:12189567]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Neuropsychological assessments are important tools for exploring the behavioral manifestations of brain dysfunction (Table 2).7 These assessments factor in elements of neurology, psychiatry, and psychology to provide information about the diagnosis, prognosis, and functional status of patients with medical conditions, especially those with neurocognitive and psychiatric disorders. They combine information from the patient and collateral interviews, behavioral observations, a review of patient records, and objective tests of motor, emotional, and cognitive function.
Among other uses, neuropsychological assessments can help identify depression in patients with neurologic impairment, determine the diagnosis and plan of care for patients with concussions, determine the risk of a motor vehicle crash in patients with cognitive impairment, and distinguish Alzheimer disease from vascular dementia.8 Components of such assessments include the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) to assess anxiety, the Dementia Rating Scale-2 and Neuropsychological Assessment Battery-Screening Module to assess dementia, and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) to assess depression.9
EVALUATION Continued cognitive decline
A different psychologist performs the neuropsychological assessment, who conducts the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Update to determine if Ms. X is experiencing cognitive impairment. Her immediate memory, visuospatial/constructions, language, attention, and delayed memory are significantly impaired for someone her age. The psychologist also administers the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale IV and finds Ms. X’s general cognitive ability is within the low average range of intellectual functioning as measured by Full-Scale IQ. Ms. X scores 29 on the BDI-II, indicating significant depressive symptoms, and 13 on the BAI, indicating mild anxiety symptoms.
Ms. X is diagnosed with MDD and an unspecified neurocognitive disorder. The psychologist recommends she start CBT to address her mood and anxiety symptoms.
Upon reviewing the results with Ms. X, the treatment team again recommends a brain MRI, CBC, CMP, and UA to rule out organic causes of her cognitive decline. Ms. X decides against the MRI and laboratory workup and elects to continue her present medication regimen and CBT.
Several weeks later, Ms. X’s family brings her to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation of worsening mood, decreased personal hygiene, increased irritability, and further cognitive decline. They report she is having an increasingly difficult time remembering things such as where she parked her car. The ED team decides to discontinue clonazepam but continues sertraline and trazodone.
Continue to: CBC, CMP, and UA...
CBC, CMP, and UA are unremarkable. Ms. X undergoes a brain CT scan without contrast, which reveals hyperdense lesions in the inferior left tentorium, posterior fossa. A subsequent brain MRI with contrast reveals a dural-based enhancing mass, inferior to the left tentorium, in the left posterior fossa measuring 2.2 cm x 2.1 cm, suggestive of a meningioma. The team orders a Neurosurgery consult.
[polldaddy:12189571]
The authors’ observations
While most brain tumors are secondary to metastasis, meningiomas are the most common primary CNS tumor. Typically, they are asymptomatic; their diagnosis is often delayed until the patient presents with psychiatric symptoms without any focal neurologic findings. The frontal lobe is the most common location of meningioma. Data from 48 case reports of patients with meningiomas and psychiatric symptoms suggest symptoms do not always correlate with specific brain regions.10,11
Indications for neuroimaging in cases such as Ms. X include an abrupt change in behavior or personality, lack of response to psychiatric treatment, presence of focal neurologic signs, and an unusual psychiatric presentation and development of symptoms.11
TREATMENT Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery recommends and performs a suboccipital craniotomy for biopsy and resection. Ms. X tolerates the procedure well. A meningioma is found in the posterior fossa, near the cerebellar convexity. A biopsy finds no evidence of malignancies.
At her postoperative follow-up appointment several days after the procedure, Ms. X reports new-onset hearing loss and tinnitus.
[polldaddy:12189747]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Patients who require neurosurgery typically already carry a heavy psychiatric burden, which makes it challenging to determine the exact psychiatric consequences of neurosurgery.12-14 For example, research shows that temporal lobe resection and temporal lobectomy for treatment-resistant epilepsy can lead to an exacerbation of baseline psychiatric symptoms and the development of new symptoms (31% to 34%).15,16 However, Bommakanti et al13 found no new psychiatric symptoms after resection of meningiomas, and surgery seemed to play a role in ameliorating psychiatric symptoms in patients with intracranial tumors. Research attempting to document the psychiatric sequelae of neurosurgery has had mixed results, and it is difficult to determine what effects brain surgery has on mental health.
OUTCOME Minimal improvement
Several weeks after neurosurgery, Ms. X and her family report her mood is improved. Her PHQ-9 score improves to 15, but her GAD-7 score increases to 13, 1 point above her previous score.
The treatment team recommends Ms. X continue taking sertraline 50 mg/d and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. Ms. X’s family reports her cognition and memory have not improved; her MoCA score increases by 1 point to 23. The treatment team discusses with Ms. X and her family the possibility that her cognitive problems maybe better explained as a neurocognitive disorder rather than as a result of the meningioma, since her MoCA score has not significantly improved. Ms. X and her family decide to seek a second opinion from a neurologist.
Bottom Line
Pseudodementia is a term used to describe older adults who present with cognitive issues in the context of depressive symptoms. Even in the absence of focal findings, neuroimaging should be considered as part of the workup in patients who continue to experience a progressive decline in mood and cognitive function.
Related Resources
- Moller MD, Parmenter BA, Lane DW. Neuropsychological testing: a useful but underutilized resource. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(11):40-46,51.
- Pollak J. Psychological/neuropsychological testing: when to refer for reexamination. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(9):18- 19,30-31,37. doi:10.12788/cp.0157
Drug Brand Names
Citalopram • Celexa
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Venlafaxine extended- release • Effexor XR
1. Nussbaum PD. (1994). Pseudodementia: a slow death. Neuropsychol Rev. 1994;4(2):71-90. doi:10.1007/BF01874829
2. Kang H, Zhao F, You L, et al. (2014). Pseudo-dementia: a neuropsychological review. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 17(2):147-154. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.132613
3. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
4. Brodaty H, Connors MH. Pseudodementia, pseudo-pseudodementia, and pseudodepression. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020;12(1):e12027. doi:10.1002/dad2.12027
5. Sekhon S, Marwaha R. Depressive Cognitive Disorders. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559256/
6. Brown WA. Pseudodementia: issues in diagnosis. Psychiatric Times. April 9, 2005. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/pseudodementia-issues-diagnosis
7. Kulas JF, Naugle RI. (2003). Indications for neuropsychological assessment. Cleve Clin J Med. 2003;70(9):785-792.
8. Braun M, Tupper D, Kaufmann P, et al. Neuropsychological assessment: a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of neurological, neurodevelopmental, medical, and psychiatric disorders. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2011;24(3):107-114.
9. Michels TC, Tiu AY, Graver CJ. Neuropsychological evaluation in primary care. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82(5):495-502.
10. Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB. Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(3):307-314. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0386-3
11. Gyawali S, Sharma P, Mahapatra A. Meningioma and psychiatric symptoms: an individual patient data analysis. Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;42:94-103. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2019.03.029
12. McAllister TW. Neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury: evaluation and management. World Psychiatry. 2008;7(1):3-10. doi:10.1002/j.2051-5545.2008.tb00139.x
13. Bommakanti K, Gaddamanugu P, Alladi S, et al. Pre-operative and post-operative psychiatric manifestations in patients with supratentorial meningiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;147:24-29. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.05.018
14. Devinsky O, Barr WB, Vickrey BG, et al. Changes in depression and anxiety after resective surgery for epilepsy. Neurology. 2005;65(11):1744-1749. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187114.71524.c3
15. Blumer D, Wakhlu S, Davies K, et al. Psychiatric outcome of temporal lobectomy for epilepsy: incidence and treatment of psychiatric complications. Epilepsia. 1998;39(5):478-486. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01409.x
16. Glosser G, Zwil AS, Glosser DS, et al. Psychiatric aspects of temporal lobe epilepsy before and after anterior temporal lobectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;68(1):53-58. doi:10.1136/jnnp.68.1.53
CASE Depressed and anxious
Five years ago, Ms. X, age 60, was diagnosed with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) with anxiety. This diagnosis was established by a previous psychiatrist. She presents to a clinic for a second opinion.
Since her diagnosis, Ms. X has experienced sad mood, anhedonia, difficulty falling asleep, increased appetite and weight, and decreased concentration and attention. Her anxiety stems from her inability to work, which causes her to worry about her children. In the clinic, the treatment team conducts the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 item scale (GAD-7) with Ms. X. She scores 16 on the PHQ-9, indicating moderately severe depression, and scores 12 on the GAD-7, indicating moderate anxiety.
Ms. X’s current medication regimen consists of venlafaxine extended-release (XR) 225 mg/d, trazodone 100 mg/d at bedtime, and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. She reports no significant improvement of her symptoms from these medications. Additionally, Ms. X reports that in the past she had been prescribed fluoxetine, citalopram, and duloxetine, but she cannot recall the dosages.
Ms. X appears appropriately groomed, maintains appropriate eye contact, has clear speech, and does not show evidence of internal stimulation; however, she has difficulty following instructions. She makes negative comments about herself such as “I’m worthless” and “Nobody cares about me.” The treatment team decides to taper Ms. X off venlafaxine XR and initiates sertraline 50 mg/d, while continuing trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. The team refers her for cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address her cognitive distortions, sad mood, and anxiety. Ms. X is asked to follow up with Psychiatry in 1 week.
EVALUATION Unusual behavior
At her CBT intake, Ms. X endorses depression and anxiety. Her PHQ-9 score at this visit is 19 (moderately severe depression) and GAD-7 score is 16 (severe anxiety). The psychologist notes that Ms. X is able to complete activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living without assistance. Ms. X denies any use of illicit substances or alcohol. No gross memory impairment is noted during this appointment, though Ms. X exhibits unusual behavior, including exiting and re-entering the clinic multiple times to repeatedly ask about follow-up appointments. The psychologist concludes that Ms. X’s presentation and behavior can be explained by MDD and pseudodementia.
[polldaddy:12189562]
The authors’ observations
Pseudodementia gained recognition in clinical research >100 years ago.1 Officially coined by Kiloh in 1961, the term was used broadly to categorize psychiatric cases that present like dementia but are the result of reversible causes. More recently, it has been used to describe older adults who present with cognitive deficits in the context of depressive symptoms.2 The goal of evaluation is to determine if the primary issue is a cognitive disorder or a depressive episode. DSM-5-TR does not classify pseudodementia as a distinct diagnosis, but instead categorizes its symptoms as components under other major diagnostic categories. Patients can present with MDD and associated cognitive symptoms, or with a cognitive disorder with depressive symptoms, which would be diagnosed as a cognitive disorder with a major depressive-like episode.3
Pseudodementia is rare. Brodaty et al4 found the prevalence of pseudodementia in primary care settings was 0.6%. Older adults (age >65) who live alone are at increased risk of developing pseudodementia, which can be worsened by poor social support and acute psychosocial and environmental changes.5 A key characteristic of this disorder is that as the patient’s depressed mood improves, their memory and cognition also improve.6 Table 13,6 outlines overlapping features of MDD and pseudodementia.
Continue to: EVALUATION Worsening depression
EVALUATION Worsening depression
At her Psychiatry follow-up appointment, Ms. X reports that her mood is worse since she ended the relationship with her partner and she feels anxious because the partner was financially supporting her. Her PHQ-9 score is 24 (severe depression) and her GAD-7 score is 12 (moderate anxiety). Ms. X reports tolerating her transition from venlafaxine XR 225 mg/d to sertraline 50 mg/d well.
Additionally, Ms. X reports her children have called her “useless” since she continues to have difficulties following through on household tasks, even though she has no physical impairments that prevent her from completing them. The Psychiatry team observes that Ms. X has no problems walking or moving her arms or legs.
The Psychiatry team administers the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Ms. X scores 22, indicating mild impairment.
The team recommends a neuropsychological assessment to determine if this MoCA score is due to a cognitive disorder or is rooted in her mood symptoms. The team also recommends an MRI of the brain, complete blood count (CBC), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), and urinalysis (UA).
[polldaddy:12189567]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Neuropsychological assessments are important tools for exploring the behavioral manifestations of brain dysfunction (Table 2).7 These assessments factor in elements of neurology, psychiatry, and psychology to provide information about the diagnosis, prognosis, and functional status of patients with medical conditions, especially those with neurocognitive and psychiatric disorders. They combine information from the patient and collateral interviews, behavioral observations, a review of patient records, and objective tests of motor, emotional, and cognitive function.
Among other uses, neuropsychological assessments can help identify depression in patients with neurologic impairment, determine the diagnosis and plan of care for patients with concussions, determine the risk of a motor vehicle crash in patients with cognitive impairment, and distinguish Alzheimer disease from vascular dementia.8 Components of such assessments include the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) to assess anxiety, the Dementia Rating Scale-2 and Neuropsychological Assessment Battery-Screening Module to assess dementia, and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) to assess depression.9
EVALUATION Continued cognitive decline
A different psychologist performs the neuropsychological assessment, who conducts the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Update to determine if Ms. X is experiencing cognitive impairment. Her immediate memory, visuospatial/constructions, language, attention, and delayed memory are significantly impaired for someone her age. The psychologist also administers the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale IV and finds Ms. X’s general cognitive ability is within the low average range of intellectual functioning as measured by Full-Scale IQ. Ms. X scores 29 on the BDI-II, indicating significant depressive symptoms, and 13 on the BAI, indicating mild anxiety symptoms.
Ms. X is diagnosed with MDD and an unspecified neurocognitive disorder. The psychologist recommends she start CBT to address her mood and anxiety symptoms.
Upon reviewing the results with Ms. X, the treatment team again recommends a brain MRI, CBC, CMP, and UA to rule out organic causes of her cognitive decline. Ms. X decides against the MRI and laboratory workup and elects to continue her present medication regimen and CBT.
Several weeks later, Ms. X’s family brings her to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation of worsening mood, decreased personal hygiene, increased irritability, and further cognitive decline. They report she is having an increasingly difficult time remembering things such as where she parked her car. The ED team decides to discontinue clonazepam but continues sertraline and trazodone.
Continue to: CBC, CMP, and UA...
CBC, CMP, and UA are unremarkable. Ms. X undergoes a brain CT scan without contrast, which reveals hyperdense lesions in the inferior left tentorium, posterior fossa. A subsequent brain MRI with contrast reveals a dural-based enhancing mass, inferior to the left tentorium, in the left posterior fossa measuring 2.2 cm x 2.1 cm, suggestive of a meningioma. The team orders a Neurosurgery consult.
[polldaddy:12189571]
The authors’ observations
While most brain tumors are secondary to metastasis, meningiomas are the most common primary CNS tumor. Typically, they are asymptomatic; their diagnosis is often delayed until the patient presents with psychiatric symptoms without any focal neurologic findings. The frontal lobe is the most common location of meningioma. Data from 48 case reports of patients with meningiomas and psychiatric symptoms suggest symptoms do not always correlate with specific brain regions.10,11
Indications for neuroimaging in cases such as Ms. X include an abrupt change in behavior or personality, lack of response to psychiatric treatment, presence of focal neurologic signs, and an unusual psychiatric presentation and development of symptoms.11
TREATMENT Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery recommends and performs a suboccipital craniotomy for biopsy and resection. Ms. X tolerates the procedure well. A meningioma is found in the posterior fossa, near the cerebellar convexity. A biopsy finds no evidence of malignancies.
At her postoperative follow-up appointment several days after the procedure, Ms. X reports new-onset hearing loss and tinnitus.
[polldaddy:12189747]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Patients who require neurosurgery typically already carry a heavy psychiatric burden, which makes it challenging to determine the exact psychiatric consequences of neurosurgery.12-14 For example, research shows that temporal lobe resection and temporal lobectomy for treatment-resistant epilepsy can lead to an exacerbation of baseline psychiatric symptoms and the development of new symptoms (31% to 34%).15,16 However, Bommakanti et al13 found no new psychiatric symptoms after resection of meningiomas, and surgery seemed to play a role in ameliorating psychiatric symptoms in patients with intracranial tumors. Research attempting to document the psychiatric sequelae of neurosurgery has had mixed results, and it is difficult to determine what effects brain surgery has on mental health.
OUTCOME Minimal improvement
Several weeks after neurosurgery, Ms. X and her family report her mood is improved. Her PHQ-9 score improves to 15, but her GAD-7 score increases to 13, 1 point above her previous score.
The treatment team recommends Ms. X continue taking sertraline 50 mg/d and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. Ms. X’s family reports her cognition and memory have not improved; her MoCA score increases by 1 point to 23. The treatment team discusses with Ms. X and her family the possibility that her cognitive problems maybe better explained as a neurocognitive disorder rather than as a result of the meningioma, since her MoCA score has not significantly improved. Ms. X and her family decide to seek a second opinion from a neurologist.
Bottom Line
Pseudodementia is a term used to describe older adults who present with cognitive issues in the context of depressive symptoms. Even in the absence of focal findings, neuroimaging should be considered as part of the workup in patients who continue to experience a progressive decline in mood and cognitive function.
Related Resources
- Moller MD, Parmenter BA, Lane DW. Neuropsychological testing: a useful but underutilized resource. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(11):40-46,51.
- Pollak J. Psychological/neuropsychological testing: when to refer for reexamination. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(9):18- 19,30-31,37. doi:10.12788/cp.0157
Drug Brand Names
Citalopram • Celexa
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Venlafaxine extended- release • Effexor XR
CASE Depressed and anxious
Five years ago, Ms. X, age 60, was diagnosed with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) with anxiety. This diagnosis was established by a previous psychiatrist. She presents to a clinic for a second opinion.
Since her diagnosis, Ms. X has experienced sad mood, anhedonia, difficulty falling asleep, increased appetite and weight, and decreased concentration and attention. Her anxiety stems from her inability to work, which causes her to worry about her children. In the clinic, the treatment team conducts the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 item scale (GAD-7) with Ms. X. She scores 16 on the PHQ-9, indicating moderately severe depression, and scores 12 on the GAD-7, indicating moderate anxiety.
Ms. X’s current medication regimen consists of venlafaxine extended-release (XR) 225 mg/d, trazodone 100 mg/d at bedtime, and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. She reports no significant improvement of her symptoms from these medications. Additionally, Ms. X reports that in the past she had been prescribed fluoxetine, citalopram, and duloxetine, but she cannot recall the dosages.
Ms. X appears appropriately groomed, maintains appropriate eye contact, has clear speech, and does not show evidence of internal stimulation; however, she has difficulty following instructions. She makes negative comments about herself such as “I’m worthless” and “Nobody cares about me.” The treatment team decides to taper Ms. X off venlafaxine XR and initiates sertraline 50 mg/d, while continuing trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime and clonazepam 1 mg twice daily. The team refers her for cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to address her cognitive distortions, sad mood, and anxiety. Ms. X is asked to follow up with Psychiatry in 1 week.
EVALUATION Unusual behavior
At her CBT intake, Ms. X endorses depression and anxiety. Her PHQ-9 score at this visit is 19 (moderately severe depression) and GAD-7 score is 16 (severe anxiety). The psychologist notes that Ms. X is able to complete activities of daily living and instrumental activities of daily living without assistance. Ms. X denies any use of illicit substances or alcohol. No gross memory impairment is noted during this appointment, though Ms. X exhibits unusual behavior, including exiting and re-entering the clinic multiple times to repeatedly ask about follow-up appointments. The psychologist concludes that Ms. X’s presentation and behavior can be explained by MDD and pseudodementia.
[polldaddy:12189562]
The authors’ observations
Pseudodementia gained recognition in clinical research >100 years ago.1 Officially coined by Kiloh in 1961, the term was used broadly to categorize psychiatric cases that present like dementia but are the result of reversible causes. More recently, it has been used to describe older adults who present with cognitive deficits in the context of depressive symptoms.2 The goal of evaluation is to determine if the primary issue is a cognitive disorder or a depressive episode. DSM-5-TR does not classify pseudodementia as a distinct diagnosis, but instead categorizes its symptoms as components under other major diagnostic categories. Patients can present with MDD and associated cognitive symptoms, or with a cognitive disorder with depressive symptoms, which would be diagnosed as a cognitive disorder with a major depressive-like episode.3
Pseudodementia is rare. Brodaty et al4 found the prevalence of pseudodementia in primary care settings was 0.6%. Older adults (age >65) who live alone are at increased risk of developing pseudodementia, which can be worsened by poor social support and acute psychosocial and environmental changes.5 A key characteristic of this disorder is that as the patient’s depressed mood improves, their memory and cognition also improve.6 Table 13,6 outlines overlapping features of MDD and pseudodementia.
Continue to: EVALUATION Worsening depression
EVALUATION Worsening depression
At her Psychiatry follow-up appointment, Ms. X reports that her mood is worse since she ended the relationship with her partner and she feels anxious because the partner was financially supporting her. Her PHQ-9 score is 24 (severe depression) and her GAD-7 score is 12 (moderate anxiety). Ms. X reports tolerating her transition from venlafaxine XR 225 mg/d to sertraline 50 mg/d well.
Additionally, Ms. X reports her children have called her “useless” since she continues to have difficulties following through on household tasks, even though she has no physical impairments that prevent her from completing them. The Psychiatry team observes that Ms. X has no problems walking or moving her arms or legs.
The Psychiatry team administers the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). Ms. X scores 22, indicating mild impairment.
The team recommends a neuropsychological assessment to determine if this MoCA score is due to a cognitive disorder or is rooted in her mood symptoms. The team also recommends an MRI of the brain, complete blood count (CBC), comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), and urinalysis (UA).
[polldaddy:12189567]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Neuropsychological assessments are important tools for exploring the behavioral manifestations of brain dysfunction (Table 2).7 These assessments factor in elements of neurology, psychiatry, and psychology to provide information about the diagnosis, prognosis, and functional status of patients with medical conditions, especially those with neurocognitive and psychiatric disorders. They combine information from the patient and collateral interviews, behavioral observations, a review of patient records, and objective tests of motor, emotional, and cognitive function.
Among other uses, neuropsychological assessments can help identify depression in patients with neurologic impairment, determine the diagnosis and plan of care for patients with concussions, determine the risk of a motor vehicle crash in patients with cognitive impairment, and distinguish Alzheimer disease from vascular dementia.8 Components of such assessments include the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) to assess anxiety, the Dementia Rating Scale-2 and Neuropsychological Assessment Battery-Screening Module to assess dementia, and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) to assess depression.9
EVALUATION Continued cognitive decline
A different psychologist performs the neuropsychological assessment, who conducts the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Update to determine if Ms. X is experiencing cognitive impairment. Her immediate memory, visuospatial/constructions, language, attention, and delayed memory are significantly impaired for someone her age. The psychologist also administers the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale IV and finds Ms. X’s general cognitive ability is within the low average range of intellectual functioning as measured by Full-Scale IQ. Ms. X scores 29 on the BDI-II, indicating significant depressive symptoms, and 13 on the BAI, indicating mild anxiety symptoms.
Ms. X is diagnosed with MDD and an unspecified neurocognitive disorder. The psychologist recommends she start CBT to address her mood and anxiety symptoms.
Upon reviewing the results with Ms. X, the treatment team again recommends a brain MRI, CBC, CMP, and UA to rule out organic causes of her cognitive decline. Ms. X decides against the MRI and laboratory workup and elects to continue her present medication regimen and CBT.
Several weeks later, Ms. X’s family brings her to the emergency department (ED) for evaluation of worsening mood, decreased personal hygiene, increased irritability, and further cognitive decline. They report she is having an increasingly difficult time remembering things such as where she parked her car. The ED team decides to discontinue clonazepam but continues sertraline and trazodone.
Continue to: CBC, CMP, and UA...
CBC, CMP, and UA are unremarkable. Ms. X undergoes a brain CT scan without contrast, which reveals hyperdense lesions in the inferior left tentorium, posterior fossa. A subsequent brain MRI with contrast reveals a dural-based enhancing mass, inferior to the left tentorium, in the left posterior fossa measuring 2.2 cm x 2.1 cm, suggestive of a meningioma. The team orders a Neurosurgery consult.
[polldaddy:12189571]
The authors’ observations
While most brain tumors are secondary to metastasis, meningiomas are the most common primary CNS tumor. Typically, they are asymptomatic; their diagnosis is often delayed until the patient presents with psychiatric symptoms without any focal neurologic findings. The frontal lobe is the most common location of meningioma. Data from 48 case reports of patients with meningiomas and psychiatric symptoms suggest symptoms do not always correlate with specific brain regions.10,11
Indications for neuroimaging in cases such as Ms. X include an abrupt change in behavior or personality, lack of response to psychiatric treatment, presence of focal neurologic signs, and an unusual psychiatric presentation and development of symptoms.11
TREATMENT Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery recommends and performs a suboccipital craniotomy for biopsy and resection. Ms. X tolerates the procedure well. A meningioma is found in the posterior fossa, near the cerebellar convexity. A biopsy finds no evidence of malignancies.
At her postoperative follow-up appointment several days after the procedure, Ms. X reports new-onset hearing loss and tinnitus.
[polldaddy:12189747]
Continue to: The authors' observations
The authors’ observations
Patients who require neurosurgery typically already carry a heavy psychiatric burden, which makes it challenging to determine the exact psychiatric consequences of neurosurgery.12-14 For example, research shows that temporal lobe resection and temporal lobectomy for treatment-resistant epilepsy can lead to an exacerbation of baseline psychiatric symptoms and the development of new symptoms (31% to 34%).15,16 However, Bommakanti et al13 found no new psychiatric symptoms after resection of meningiomas, and surgery seemed to play a role in ameliorating psychiatric symptoms in patients with intracranial tumors. Research attempting to document the psychiatric sequelae of neurosurgery has had mixed results, and it is difficult to determine what effects brain surgery has on mental health.
OUTCOME Minimal improvement
Several weeks after neurosurgery, Ms. X and her family report her mood is improved. Her PHQ-9 score improves to 15, but her GAD-7 score increases to 13, 1 point above her previous score.
The treatment team recommends Ms. X continue taking sertraline 50 mg/d and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. Ms. X’s family reports her cognition and memory have not improved; her MoCA score increases by 1 point to 23. The treatment team discusses with Ms. X and her family the possibility that her cognitive problems maybe better explained as a neurocognitive disorder rather than as a result of the meningioma, since her MoCA score has not significantly improved. Ms. X and her family decide to seek a second opinion from a neurologist.
Bottom Line
Pseudodementia is a term used to describe older adults who present with cognitive issues in the context of depressive symptoms. Even in the absence of focal findings, neuroimaging should be considered as part of the workup in patients who continue to experience a progressive decline in mood and cognitive function.
Related Resources
- Moller MD, Parmenter BA, Lane DW. Neuropsychological testing: a useful but underutilized resource. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(11):40-46,51.
- Pollak J. Psychological/neuropsychological testing: when to refer for reexamination. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(9):18- 19,30-31,37. doi:10.12788/cp.0157
Drug Brand Names
Citalopram • Celexa
Clonazepam • Klonopin
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Oleptro
Venlafaxine extended- release • Effexor XR
1. Nussbaum PD. (1994). Pseudodementia: a slow death. Neuropsychol Rev. 1994;4(2):71-90. doi:10.1007/BF01874829
2. Kang H, Zhao F, You L, et al. (2014). Pseudo-dementia: a neuropsychological review. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 17(2):147-154. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.132613
3. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
4. Brodaty H, Connors MH. Pseudodementia, pseudo-pseudodementia, and pseudodepression. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020;12(1):e12027. doi:10.1002/dad2.12027
5. Sekhon S, Marwaha R. Depressive Cognitive Disorders. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559256/
6. Brown WA. Pseudodementia: issues in diagnosis. Psychiatric Times. April 9, 2005. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/pseudodementia-issues-diagnosis
7. Kulas JF, Naugle RI. (2003). Indications for neuropsychological assessment. Cleve Clin J Med. 2003;70(9):785-792.
8. Braun M, Tupper D, Kaufmann P, et al. Neuropsychological assessment: a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of neurological, neurodevelopmental, medical, and psychiatric disorders. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2011;24(3):107-114.
9. Michels TC, Tiu AY, Graver CJ. Neuropsychological evaluation in primary care. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82(5):495-502.
10. Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB. Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(3):307-314. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0386-3
11. Gyawali S, Sharma P, Mahapatra A. Meningioma and psychiatric symptoms: an individual patient data analysis. Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;42:94-103. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2019.03.029
12. McAllister TW. Neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury: evaluation and management. World Psychiatry. 2008;7(1):3-10. doi:10.1002/j.2051-5545.2008.tb00139.x
13. Bommakanti K, Gaddamanugu P, Alladi S, et al. Pre-operative and post-operative psychiatric manifestations in patients with supratentorial meningiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;147:24-29. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.05.018
14. Devinsky O, Barr WB, Vickrey BG, et al. Changes in depression and anxiety after resective surgery for epilepsy. Neurology. 2005;65(11):1744-1749. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187114.71524.c3
15. Blumer D, Wakhlu S, Davies K, et al. Psychiatric outcome of temporal lobectomy for epilepsy: incidence and treatment of psychiatric complications. Epilepsia. 1998;39(5):478-486. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01409.x
16. Glosser G, Zwil AS, Glosser DS, et al. Psychiatric aspects of temporal lobe epilepsy before and after anterior temporal lobectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;68(1):53-58. doi:10.1136/jnnp.68.1.53
1. Nussbaum PD. (1994). Pseudodementia: a slow death. Neuropsychol Rev. 1994;4(2):71-90. doi:10.1007/BF01874829
2. Kang H, Zhao F, You L, et al. (2014). Pseudo-dementia: a neuropsychological review. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 17(2):147-154. doi:10.4103/0972-2327.132613
3. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed, text revision. American Psychiatric Association; 2022.
4. Brodaty H, Connors MH. Pseudodementia, pseudo-pseudodementia, and pseudodepression. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020;12(1):e12027. doi:10.1002/dad2.12027
5. Sekhon S, Marwaha R. Depressive Cognitive Disorders. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559256/
6. Brown WA. Pseudodementia: issues in diagnosis. Psychiatric Times. April 9, 2005. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/pseudodementia-issues-diagnosis
7. Kulas JF, Naugle RI. (2003). Indications for neuropsychological assessment. Cleve Clin J Med. 2003;70(9):785-792.
8. Braun M, Tupper D, Kaufmann P, et al. Neuropsychological assessment: a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of neurological, neurodevelopmental, medical, and psychiatric disorders. Cogn Behav Neurol. 2011;24(3):107-114.
9. Michels TC, Tiu AY, Graver CJ. Neuropsychological evaluation in primary care. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82(5):495-502.
10. Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB. Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol. 2010;99(3):307-314. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0386-3
11. Gyawali S, Sharma P, Mahapatra A. Meningioma and psychiatric symptoms: an individual patient data analysis. Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;42:94-103. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2019.03.029
12. McAllister TW. Neurobehavioral sequelae of traumatic brain injury: evaluation and management. World Psychiatry. 2008;7(1):3-10. doi:10.1002/j.2051-5545.2008.tb00139.x
13. Bommakanti K, Gaddamanugu P, Alladi S, et al. Pre-operative and post-operative psychiatric manifestations in patients with supratentorial meningiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;147:24-29. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.05.018
14. Devinsky O, Barr WB, Vickrey BG, et al. Changes in depression and anxiety after resective surgery for epilepsy. Neurology. 2005;65(11):1744-1749. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187114.71524.c3
15. Blumer D, Wakhlu S, Davies K, et al. Psychiatric outcome of temporal lobectomy for epilepsy: incidence and treatment of psychiatric complications. Epilepsia. 1998;39(5):478-486. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01409.x
16. Glosser G, Zwil AS, Glosser DS, et al. Psychiatric aspects of temporal lobe epilepsy before and after anterior temporal lobectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;68(1):53-58. doi:10.1136/jnnp.68.1.53
Unawareness of memory slips could indicate risk for Alzheimer’s
Everyone’s memory fades to some extent as we age, but not everyone will develop Alzheimer’s disease. Screening the most likely people to develop Alzheimer’s remains an ongoing challenge, as some people present only unambiguous symptoms once their disease is advanced.
A new study in JAMA Network Open suggests that one early clue is found in people’s own self-perception of their memory skills. People who are more aware of their own declining memory capacity are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s, the study suggests.
“Some people are very aware of changes in their memory, but many people are unaware,” said study author Patrizia Vannini, PhD, a neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. There are gradations of unawareness of memory loss, Dr. Vannini said, from complete unawareness that anything is wrong, to a partial unawareness that memory is declining.
The study compared the records of 436 participants in the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, an Alzheimer’s research institute housed at the University of Southern California. More than 90% of the participants were White, and generally had a college education. Their average age was 75 years, and 53% of participants were women.
Dr. Vannini and colleagues tracked people whose cognitive function was normal at the beginning of the study, based on the Clinical Dementia Rating. Throughout the course of the study, which included data from 2010 to 2021, 91 of the 436 participants experienced a sustained decline in their Clinical Dementia Rating scores, indicating a risk for eventual Alzheimer’s, whereas the other participants held steady.
The people who declined in cognitive function were less aware of slips in their memory, as assessed by discrepancies between people’s self-reports of their own memory skills and the perceptions of someone in their lives. For this part of the study, Dr. Vannini and colleagues used the Everyday Cognition Questionnaire, which evaluates memory tasks such as shopping without a grocery list or recalling conversations from a few days ago. Both the participant and the study partner rated their performance on such tasks compared to 10 years earlier. Those who were less aware of their memory slips were more likely to experience declines in the Clinical Dementia Rating, compared with people with a heightened concern about memory loss (as measured by being more concerned about memory decline than their study partners).
“Partial or complete unawareness is often related to delayed diagnosis of Alzheimer’s, because the patient is unaware they are having problems,” Dr. Vannini said, adding that this is associated with a poorer prognosis as well.
Implications for clinicians
Soo Borson, MD, professor of clinical family medicine at the University of Southern California and coleader of a CDC-funded early dementia detection center at New York University, pointed out that sometimes people are genuinely unaware that their memory is declining, while at other times they know it all too well but say everything is fine when a doctor asks about their current memory status. That may be because people fear the label of “Alzheimer’s,” Dr. Borson suggested, or simply because they don’t want to start a protracted diagnostic pathway that could involve lots of tests and time.
Dr. Borson, who was not involved in the study, noted that the population was predominantly White and well-educated, and by definition included people who were concerned enough about potential memory loss to become part of an Alzheimer’s research network. This limits the generalizability of this study’s results to other populations, Dr. Borson said.
Despite that limitation, in Dr. Borson’s view the study points to the continued importance of clinicians (ideally a primary care doctor who knows the patient well) engaging with patients about their brain health once they reach midlife. A doctor could ask if patients have noticed a decline in their thinking or memory over the last year, for example, or a more open-ended question about any memory concerns.
Although some patients may choose to withhold concerns about their memory, Dr. Borson acknowledged, the overall thrust of these questions is to provide a safe space for patients to air their concerns if they so choose. In some cases it would be appropriate to do a simple memory test on the spot, and then proceed accordingly – either for further tests if something of concern emerges, or to reassure the patient if the test doesn’t yield anything of note. In the latter case some patients will still want further tests for additional reassurance, and Dr. Borson thinks doctors should facilitate that request even if in their own judgment nothing is wrong.
“This is not like testing for impaired kidney function by doing a serum creatinine test,” Dr. Borson said. While the orientation of the health care system is toward quick and easy answers for everything, detecting possible dementia eludes such an approach.
Dr. Vannini reports funding from the National Institutes of Health National Institute on Aging. Dr. Borson reported no disclosures.
Everyone’s memory fades to some extent as we age, but not everyone will develop Alzheimer’s disease. Screening the most likely people to develop Alzheimer’s remains an ongoing challenge, as some people present only unambiguous symptoms once their disease is advanced.
A new study in JAMA Network Open suggests that one early clue is found in people’s own self-perception of their memory skills. People who are more aware of their own declining memory capacity are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s, the study suggests.
“Some people are very aware of changes in their memory, but many people are unaware,” said study author Patrizia Vannini, PhD, a neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. There are gradations of unawareness of memory loss, Dr. Vannini said, from complete unawareness that anything is wrong, to a partial unawareness that memory is declining.
The study compared the records of 436 participants in the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, an Alzheimer’s research institute housed at the University of Southern California. More than 90% of the participants were White, and generally had a college education. Their average age was 75 years, and 53% of participants were women.
Dr. Vannini and colleagues tracked people whose cognitive function was normal at the beginning of the study, based on the Clinical Dementia Rating. Throughout the course of the study, which included data from 2010 to 2021, 91 of the 436 participants experienced a sustained decline in their Clinical Dementia Rating scores, indicating a risk for eventual Alzheimer’s, whereas the other participants held steady.
The people who declined in cognitive function were less aware of slips in their memory, as assessed by discrepancies between people’s self-reports of their own memory skills and the perceptions of someone in their lives. For this part of the study, Dr. Vannini and colleagues used the Everyday Cognition Questionnaire, which evaluates memory tasks such as shopping without a grocery list or recalling conversations from a few days ago. Both the participant and the study partner rated their performance on such tasks compared to 10 years earlier. Those who were less aware of their memory slips were more likely to experience declines in the Clinical Dementia Rating, compared with people with a heightened concern about memory loss (as measured by being more concerned about memory decline than their study partners).
“Partial or complete unawareness is often related to delayed diagnosis of Alzheimer’s, because the patient is unaware they are having problems,” Dr. Vannini said, adding that this is associated with a poorer prognosis as well.
Implications for clinicians
Soo Borson, MD, professor of clinical family medicine at the University of Southern California and coleader of a CDC-funded early dementia detection center at New York University, pointed out that sometimes people are genuinely unaware that their memory is declining, while at other times they know it all too well but say everything is fine when a doctor asks about their current memory status. That may be because people fear the label of “Alzheimer’s,” Dr. Borson suggested, or simply because they don’t want to start a protracted diagnostic pathway that could involve lots of tests and time.
Dr. Borson, who was not involved in the study, noted that the population was predominantly White and well-educated, and by definition included people who were concerned enough about potential memory loss to become part of an Alzheimer’s research network. This limits the generalizability of this study’s results to other populations, Dr. Borson said.
Despite that limitation, in Dr. Borson’s view the study points to the continued importance of clinicians (ideally a primary care doctor who knows the patient well) engaging with patients about their brain health once they reach midlife. A doctor could ask if patients have noticed a decline in their thinking or memory over the last year, for example, or a more open-ended question about any memory concerns.
Although some patients may choose to withhold concerns about their memory, Dr. Borson acknowledged, the overall thrust of these questions is to provide a safe space for patients to air their concerns if they so choose. In some cases it would be appropriate to do a simple memory test on the spot, and then proceed accordingly – either for further tests if something of concern emerges, or to reassure the patient if the test doesn’t yield anything of note. In the latter case some patients will still want further tests for additional reassurance, and Dr. Borson thinks doctors should facilitate that request even if in their own judgment nothing is wrong.
“This is not like testing for impaired kidney function by doing a serum creatinine test,” Dr. Borson said. While the orientation of the health care system is toward quick and easy answers for everything, detecting possible dementia eludes such an approach.
Dr. Vannini reports funding from the National Institutes of Health National Institute on Aging. Dr. Borson reported no disclosures.
Everyone’s memory fades to some extent as we age, but not everyone will develop Alzheimer’s disease. Screening the most likely people to develop Alzheimer’s remains an ongoing challenge, as some people present only unambiguous symptoms once their disease is advanced.
A new study in JAMA Network Open suggests that one early clue is found in people’s own self-perception of their memory skills. People who are more aware of their own declining memory capacity are less likely to develop Alzheimer’s, the study suggests.
“Some people are very aware of changes in their memory, but many people are unaware,” said study author Patrizia Vannini, PhD, a neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. There are gradations of unawareness of memory loss, Dr. Vannini said, from complete unawareness that anything is wrong, to a partial unawareness that memory is declining.
The study compared the records of 436 participants in the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, an Alzheimer’s research institute housed at the University of Southern California. More than 90% of the participants were White, and generally had a college education. Their average age was 75 years, and 53% of participants were women.
Dr. Vannini and colleagues tracked people whose cognitive function was normal at the beginning of the study, based on the Clinical Dementia Rating. Throughout the course of the study, which included data from 2010 to 2021, 91 of the 436 participants experienced a sustained decline in their Clinical Dementia Rating scores, indicating a risk for eventual Alzheimer’s, whereas the other participants held steady.
The people who declined in cognitive function were less aware of slips in their memory, as assessed by discrepancies between people’s self-reports of their own memory skills and the perceptions of someone in their lives. For this part of the study, Dr. Vannini and colleagues used the Everyday Cognition Questionnaire, which evaluates memory tasks such as shopping without a grocery list or recalling conversations from a few days ago. Both the participant and the study partner rated their performance on such tasks compared to 10 years earlier. Those who were less aware of their memory slips were more likely to experience declines in the Clinical Dementia Rating, compared with people with a heightened concern about memory loss (as measured by being more concerned about memory decline than their study partners).
“Partial or complete unawareness is often related to delayed diagnosis of Alzheimer’s, because the patient is unaware they are having problems,” Dr. Vannini said, adding that this is associated with a poorer prognosis as well.
Implications for clinicians
Soo Borson, MD, professor of clinical family medicine at the University of Southern California and coleader of a CDC-funded early dementia detection center at New York University, pointed out that sometimes people are genuinely unaware that their memory is declining, while at other times they know it all too well but say everything is fine when a doctor asks about their current memory status. That may be because people fear the label of “Alzheimer’s,” Dr. Borson suggested, or simply because they don’t want to start a protracted diagnostic pathway that could involve lots of tests and time.
Dr. Borson, who was not involved in the study, noted that the population was predominantly White and well-educated, and by definition included people who were concerned enough about potential memory loss to become part of an Alzheimer’s research network. This limits the generalizability of this study’s results to other populations, Dr. Borson said.
Despite that limitation, in Dr. Borson’s view the study points to the continued importance of clinicians (ideally a primary care doctor who knows the patient well) engaging with patients about their brain health once they reach midlife. A doctor could ask if patients have noticed a decline in their thinking or memory over the last year, for example, or a more open-ended question about any memory concerns.
Although some patients may choose to withhold concerns about their memory, Dr. Borson acknowledged, the overall thrust of these questions is to provide a safe space for patients to air their concerns if they so choose. In some cases it would be appropriate to do a simple memory test on the spot, and then proceed accordingly – either for further tests if something of concern emerges, or to reassure the patient if the test doesn’t yield anything of note. In the latter case some patients will still want further tests for additional reassurance, and Dr. Borson thinks doctors should facilitate that request even if in their own judgment nothing is wrong.
“This is not like testing for impaired kidney function by doing a serum creatinine test,” Dr. Borson said. While the orientation of the health care system is toward quick and easy answers for everything, detecting possible dementia eludes such an approach.
Dr. Vannini reports funding from the National Institutes of Health National Institute on Aging. Dr. Borson reported no disclosures.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN